Information Page. Desmos Graphing Calculator IXL Username: Password: gothunder
|
|
|
- Rebecca McKinney
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 i Information Page Class Website: Has PDFs of assignments. Additionally they can sometimes be found on Skyward. Desmos Graphing Calculator IXL Username: Password: gothunder Justin s Algebra II STEM Webpage This webpage catalogs a digital copy of the notebook, including many of the assignments as well (both homework and not). Kaden s Goats Group Chat Notes and other pages are posted on there sometimes, courtesy of yours truly.
3 iii Table of Contents Page Title 1 Modeling with Mathematics (Katy Pary) 2 Semester 1 Final Rational Functions 3 Fraction Rules and Parent Function 4 Laws of Exponents 5 Multiplying Fractions and Rational Expressions 6 Excluded Values 7 Dividing Rational Functions 8 Rational Operations Quiz 9 Graphing Rationals Notes 10 Graphing Rational Functions 11 Horizontal and Vertical Asymptotes (Part 1) 12 Horizontal and Vertical Asymptotes (Part 2) 13 Holes of Rational Functions 14 Oblique (Slant) Asymptote 15 X and Y Intercepts of Graphs 16 Graphing Complex Rational Functions 17 Steps for Graphing Rational Functions 18 Graphing Rational Functions Practice 19 Solving Rational Functions 20 Graphing Rational Functions Quiz 21 Rational Functions Quiz 22 Context and Rational Functions 23 Review/Test Rational Functions Radical Functions 24 Parent Function / Solving Radical Functions 25 Rational Exponents Worksheet 26 Solving / Simplifying Radical Functions 27 Graphing and Transformations of Radical Functions 28 Transformations of Radical Functions 29 Quiz / Simplifying Radicals 30 Words / Graphs Transformations 31 Review Sheets 32 Radicals Test Exponential Functions and Logarithmic Functions 33 Exploration of Exponential Functions 34 Exploring Exponential Functions (page 1 and 2) 35 Exploring Exponential Functions (page 3 and 4) 36 Transformations of Exponential Functions
4 iv Table of Contents Page Title 37 Growth Factors and Rates (S.10 and S.11 Notes) 38 Inverse Functions 39 Exploring Logarithmic Functions 40 Logarithmic Functions 41 Logarithmic Functions, Practice (Again!) 42 Common Logarithms vs. Natural Logarithms 43 Properties of Logarithms 44 Solving Logarithms 45 Compounding Interest 46 Exponential and Logarithmic Test Regression 47 Guessing Ages 48 Cases of Flu / Correlation Coefficient 49 Modeling with Technology Geometry and Circles 50 Right Triangles / Trig Functions 51 Final Review (Rationals) 52 Circles 53 Final Review (Radicals)
5 v Page Title Table of Contents
6
7 1, I
8 1, O
9 2, I Semester 1 Final
10 2, O
11 3, I Parent Function: f(x) = 1 x Rational Functions Fraction Rules: Adding and Subtracting: Make a common denominator (or LCD) and simplify. Multiplying Multiply top and bottom straight across = 5 8 Dividing Flip the denominator and multiply = =
12 3, O
13 4, I Zero Rule Laws of Exponents x 0 = 1 $1,000,000,000,000 0 = 1 Product Rule x 5 + x 2 = x 5+2 = x 7 You can t combine x 5 y 2 because they have a different base. Division Rule x 5 Negative Exponent Rule x 2 x 2 = x5 2 = x 3 x 5 = x2 5 = x 3 = 1 x 3 Additionally, the reverse becomes true. 1 x 4 = 1 1 x 4 = 1 1 x4 1 = x4
14 4, O Assignment. Simplifying exponents assignment, there are 8 problems.
15 5, I Multiplying Fractions: Rational Functions The rule for multiplying fractions is to simply multiply straight across = 9 20
16 5, O
17 6, I Excluded Values in Rational Functions Rational functions are fractions. Because of this, the denominator cannot be zero. Consider the following equation: x = 1 0 There is no way to get an answer for x. This affects the domain of the function. For example: x + 7 x + 7 The equation simplifies to one, but we cannot use a value of -7 in our equation because this puts a zero in the denominator. This example is a hole.
18 6, O
19 7, I Diving Rational Functions The rule to divide rational functions is to take the reciprocal of the denominator. For example: x x + 7 x 2 x + 7 x + 7 x 2 x x 2 x + 7 = x 2 1 The domain for this is x 7. = x 2
20 7, O
21 8, I Rational Expressions Quiz
22 8, O
23 9, I
24 9, O
25 10, I Rational Functions Extension
26 10, O
27 11, I Finding Asymptotes Vertical Asymptotes Simplify. Factor completely and cancel common factors. Solve the equation for the denominator. For example, for the rational function: (x + 3)(x 3)(x + 2) (x + 5)(x 3) The vertical asymptote would be at -5. Horizontal Asymptotes Degree(numerator) Degree(denominator) Asymptote Example Example Asymptote Less than 0 y = 0 f(x) = 1 x 2 y = Equal to 0 y = ratio of leading f(x) = 2x2 + 7 y = 2 3 coefficients Equal to 1 Divide the numerator by the denominator. 3x 2 + x + 12 f(x) = x2 + x + 1 y = x + 1 x More than 1 None f(x) = 2x4 None 3x 2 + 1
28 11, O Integrated Algebra 3 Rational Functions Asymptotes Exploration.
29 12, I Horizontal Asymptote page.
30 12, O
31 13, I Holes in Rational Functions Holes occur whenever the numerator and denominator have common factors. The hole is at x 3. (x + 3)(x 3) (x + 3) (x 3) 1 Another example perhaps? (x + 4)(x 5)(x + 6) (x + 7)(x + 4)(x + 6) x 5 x + 7 The vertical asymptote is at x 7, the horizontal asymptote at y 1 and there are two holes. They are at x 4, 6.
32 13, O Holes in Rational Functions
33 14, I Oblique Asymptotes Rule 3 If the degree of the numerator is greater than that of the denominator, there is no horizontal asymptote. However, if the numerator degree is greater by one, there exists an oblique asymptote. The expression 4x4 x2 has no horizontal asymptote, however, the expression 4x3 x2 has a oblique asymptote. Example f(x) = 3x3 4x x 2 2 The vertical asymptote is the solution to x 2 2, or ± 2. You can get the oblique asymptote through long division. The oblique asymptote is 3x 4.
34 14, O
35 15, I Finding Intercepts The y-intercept is (x, 0), or when y is equal to zero. To do that, solve the numerator substituting for 0. (You don t need to worry about the denominator, because 0 divided by anything is 0. Be sure to check for asymptotes or holes however.) The x-intercept is (0, y), or when x is equal to zero. To solve this, set the numerator equal to zero and solve.
36 15, O X-intercepts of Rational Functions
37 16, I Practice with Graphing Rational Functions
38 16, O Rational Functions matching (not the match game). This one has A-K on the graphs.
39 17, I Steps to Graphing Rational Functions 1) Simplify Factor Holes 2) Vertical Asymptotes (solve for denominator) 3) Horizontal/Oblique Asymptotes (see page 11) 4) x-intercept (set numerator equal to 0) 5) Y-intercept (set all x s to 0 and solve) 6) Input and output to find other points.
40 17, O Rational Asymptotes Worksheet
41 18, I Graphing Rational Functions
42 18, O Algebra 2 STEM Worksheet Rational Functions
43 19, I By the way, there was a volleyball game at 6:30 April 21 st in the main gym.
44 19, O
45 20, I
46 20, O
47 21, I Do Now! (Rational functions quiz on output side.) 1 x x + 3 = 4 x 2 + x 6 1(x 2)(x + 3) 3(x 2)(x + 3) 4(x 2)(x + 3) + = x 2 x + 3 x 2 + x 6 x (x 2) = 4 x x 6 = 4 4x 3 = 4 4x 4 = 7 4 x = 7 4
48 21, O Rational Functions Quiz (titled Unit 5 Quiz)
49 22, I STEMersion Anesthesiologist
50 22, O
51 23, I Rational Functions Test
52 23, O
53 24, I Graphing Radical Functions Exploration
54 24, O Solving Radical Equations
55 25, I Rational Exponents
56 25, O
57 26, I Simplify. Solving/Simplifying Radicals 3 64x 2 y 5 z 3 Our first step is to find things we can eliminate. To do so, (for this problem) we need to find er pairs of three. 64 does not have any pairs that fit the criteria, so we can create this branch to simplify. We re left with 6 2s ( = 6) or 2 6 z. We can now apply an exponent rule x y = x y z. For the purposes of our problem that leaves us with or 2 2 or 4. We can now put the 4 on the outside, giving us a new problem of: 3 4 x 2 y 5 z 3 We can get rid of one more thing: the z 3. This easily is removable into pairs of three. We ll put it on the outside as well, giving us a final answer of: 3 4z x 2 y 5 Solve. k 9 k = 1 First we need to isolate giving us a new equation of k 9 = k 1. Next we need to square both sides, resulting in a new equation of k 9 = ( k 1) 2. Foiling this right side gives you a new right side equation of: k 9 = k 2 k + 1 Only now can we manipulate the equation. Firstly, remove the k, and then subtract the one from the other side, giving an isolated equation. Rearranging the terms (for simplicity) gives: 2 k = 10 Divide the -2 out ( k = 5). Square both sides to get your answer. k = 25
58 26, O
59 27, I Radicals Transformations Worksheet
60 27, O Math Lab: Investigating Radical Functions
61 28, I Transformations of Radical Functions Quadratic y = x 2 y = a(x h) 2 + k Square Root y = x y = a x h + k A change in a is a dilation (if a > 1 it is steeper, if 0 < a < 1 it is shallower). a = reflection A change in h is a horizontal shift left or right (x h = 0) and a change in k is a vertical shift up or down. These are both translations.
62 28, O Graphing using Transformations
63 29, I Simplifying Radicals (Half-sheet)
64 29, O
65 30, I
66 30, O Writing Equations Using [sic] Transformations
67 31, I Can I Do This? (Radicals Edition)
68 31, O
69 32, I Radicals Unit Test
70 32, O
71 33, I Exponential Exploration
72 33, O Exponential Exploration
73 34, I Transformations of Exponential Functions Parent Function y = 2 x Answer the question: Where do you see transformations? y = a(b) x This isn t even my final form! If negative, it exponentially decays, instead of grows unless b is also negative. Moves the y-intercept. If negative, it reflects over the x-axis. This means you can have up to two reflections over the x- axis. When more than 0, but less than 1, a higher value means a shallower exponential decay. When more than 1, a higher value means a steeper exponential growth. When less than 0 but more than -1, a higher value means a shallower exponential decay with a reflection over the x-axis.
74 34, O Exploring Exponential Equations
75 35, I Exponential Explorations
76 35, O Exponential Explorations
77 36, I Transformations of Exponential Functions Parent Function y = 2 x Answer the question: Where do you see transformations? y = a(b) x This isn t even my final form! If negative, it exponentially decays, instead of grows unless b is also negative. Moves the y-intercept. If negative, it reflects over the x-axis. This means you can have up to two reflections over the x- axis. When more than 0, but less than 1, a higher value means a shallower exponential decay. When more than 1, a higher value means a steeper exponential growth. When less than 0 but more than -1, a higher value means a shallower exponential decay with a reflection over the x-axis.
78 36, O
79 37, I Exponential Functions and S.10/S.11 Notes Growth Factors and Growth Rates We know a linear function is linear because its growth rate is constant, or to put it another way y = 2x has a growth rate of 2. In exponential, we multiply by our rate of change, instead of adding like in linear. For example: EXPONENTIAL LINEAR y = 3 x y = 3x y = 0. 5 x y = 0. 5x We multiply by 3 each term. We multiply by 0.5 each term. We add by 3 each term. We add by 0.5 each term. What are the growth factors and growth rates? y = 5(4) x y = 100(0. 3) x This function is a growth function (it has a b value of more than 1). Growth Factor: 4 (400%) Growth Rate: 3 (300%) Because we start with 1 (100%), we have to subtract that from 4 (400%). 4 1 = 3 (400% 100% = 300%) The function is a decay function (it has a b value of less than 1 (but more than 0)). Growth Factor: 0.3 (30%) Growth Rate: 0.7 (70%) Because this is a decay function, we subtract our growth factor from 1, rather than the other way around. Exponential is about what you have left, not what they lose = 0.7 (100% 30% = 70%) Side note: we call it the growth factor and growth rate even in decay functions. Why? there isn t a reason.
80 37, O
81 38, I Inverse Functions Here s a function, and it s inverse. The inverse of a function is just swapping the inputs and outputs. See these two tables below. X Y X Y It can also be expressed as an equation. Here s a different function: y = x x = y Write the inverse of this function: 7x + 18 y = 2 The first thing to do is flip the variables. 7y + 18 x = 2 To re-write in y = mx + b form, solve for y (side note: also called algebraic stuff by Mr. Kaden). 2x = 7y x 18 = 7y 2x 18 y = 2 Write the inverse of this function: (Remember the inverse of the functions of x 2 is x, x 3 3 has an inverse of x, and so on and so forth. The inverse of exponential function y = b x is x = log b y. See the exploration for more details.) y = 2x x = 2y x 3 = 2y 3 x 3 = y y = x 3 2
82 38, O
83 39, I Introduction to Logarithms Logarithms are really exponents in disguise. The following examples will explain this idea: x y = log x , ,000 5 If you input each into your calculator, substituting x, you ll get each of these values. This is a good time to point out that like how y = x hides values so that the equation is actually y = 1x + 0, log x also hides something: in this case a 10. Our expanded function looks like: y = log 10 x Let s continue the example to see where we end up. x log x log 10 x 10 y = x The rule is log b x = y if and only if, b y = x Calculating Logarithms of Different Bases The calculator has a log key, but that calculates logarithms in base 10. If you want to calculate logartihms in different bases, use this in your calculator (the example here is calculating a base-2 logarithm, but it works for any base): log 2 32 = log log 10 2 Or you could just go into Math and click on LogBASE(, but you can t do that on the SBAC.
84 39, O
85 40, I Logarithmic Functions b y = x Inverse b x = y Inverse log b x = y log b y = x Rewrite the equation. log = x 11 2 = = 64 log 4 64 = 3 Evaluate. log 4 64 = 3 (4 3 = 64) log 2 16 = 4 (2 4 = 16) log 343 log = log 7 = 3 (73 = 343) IXL assignments are R.1 and R.3.
86 40, O
87 41, I
88 41, O
89 42, I Common Logs vs. Natural Logs The common logarithm is a logarithm that has a base of 10. log This is where that hiding comes in, the log 64 hides a 10 in the base. Expanded, it d look like this: log Remember, we were solving for the exponent. If written as an equation where we solve for x, it d look like this in the exponential form: 10 x = 64 Now, we are introduced to the uh number e. e 2.71 A natural logarithm is a logarithm that have a base of e. It is written like this: ln Written in exponential form, it looks like: And yeah, that s it. e = 7
90 42, O
91 43, I Properties of Logarithms Like exponents, logarithms have properties as well. Illustrated below are some of the properties. P of L: To illustrate the properties, some variables are defined here. Variable Defined Constraints m and n Real numbers greater than 0. b Real numbers greater than 1. p Any real number. If all of this is true, than the following properties hold: Property Condensed Form Expanded Form Product Property log b mn log b m + log b n Quotient Property m log log b m log b n b n Power Rule log b m p plog b m Property of Equality log b m = log b n m = n Remember, the bases have to be the same number.
92 43, O Solve the logarithm. Answer log 11 (x 6) + 7 = 9 log 11 (x 6) = = (x 6) 121 = x 6 x = 127 Solve the logarithm. log 7 4r = log 7 2r 4r = 2r 0 = 6r r = 0 Is r > 0? Because it is not, there is no solution.
93 44, I Solving Logarithms First things first Remember that you can t take a logarithm of zero or a negative number. For example, take this equation: log 7 4r = log 7 2r 4r = 2r 6r = 0 r = 0 Because when we substitute in 0 for r, we get 0, we cannot use this solution. There is no solution. Solve. Remember that the natural logarithm is just a logarithm to the base of e. ln(x + 5) 3 = 1 Our first step is to put this in solitary confinement (isolate). ln(x + 5) = 2 We know the definition of a logarithm is that the answer is the exponent and the base is the base. We can rewrite the equation to look like this: e 2 = x + 5 Evaluating e 2 ends up with an approximate answer of x + 5 We can move the 5 over giving us a final answer of: x Yay, we re done! Side note: If you want to use the precise answer (which you can do), you can skip the evaluation step. The process looks like this instead. ln(x + 5) 3 = 1 ln(x + 5) = 2 e 2 = x + 5 x = e 2 5
94 44, O
95 45, I Compounding Interest The Interest Compounding Equation A = P (1 + r n ) nt What are the variables? The variable A is our answer. The variable P is the principal value (the starting value). The variable r is the interest rate. The variable P is the amount of times we are compounding. For example, if it s yearly, it s 1, if it s monthly it s 12, weekly 52, daily 365, etc. The variable t is the time for which we are looking at interest. The Continuous Interest Compounding Equation A = Pe rt In this equation, e is the constant that is about 2.787, not a variable. Example Starting at a principal value of $341,000 (our starter home) at a market rate of 4.5%, what is the value of the home after 10 years? Starter home: $341,000 Time: 10 years Average market rate is 4.5% Using continuous interest A = $341,000 ( ) (1)(10) A = $341,000(1.045) 10 A = $529,600 A = $341000e (0.045)(10) A $341000(2.718) (0.045)(10) A $534,800
96 45, O Given a home that is $1,500,000, at an interest rate of 10% over 18 years, what is the value of the home? Compounded Quarterly Compound Continuously A = P (1 + r n ) nt A = $1,500,000 ( ) (4)(18) A $8,875, A = Pe rt A = $1,500,000e (0.10)(18) A $9,074, Buying a home There is another equation, one to find out how much you ll pay each month. For this example, we will be trying to buy a home for $950,000 with a 3.61% interest rate. We make $5000/month. Here are our equations: Let s plug our numbers in. 1 (1 + i) n P v = P ( ) i [APR] i = [Payments] (1 + P v = P ( 12 ) ) P v P( ) P v $950, P v $ We can also multiply this by the number of payments (360) to get how much it ll be if you paid interest on it for 30 years, which is about $1,556,
97 46, I
98 46, O
99 47, I
100 47, O
101 48, I
102 48, O
103 49, I Modeling with Technology The correlation coefficient (r) is a measure of how close to the data our regression matches. 1) What kind of function best models this data? Quadratic. (r ) 2) Equation of Best Fit: f(x) x x ) Predict if you study for 5 hours. f(5) ) How many hours did you study if your test score was 90? f(x) = 90 x = No Solution
104 49, O
105 50, I B Right Triangles and Trig Functions Consider the following Our right triangle is defined this way a c With a side length and an angle, we can figure out everything else of a right triangle. How? We can use the trigonometric functions. The important ones we will use are the sine, cosine, and tangent functions. C b A B Function Definition Inverse Function Sine (sin) Cosine (cos) Tangent (tan) Cotangent (cot) Secant (sec) sin θ = opposite hypotenuse sin 1 opposite hypotenuse = θ cos θ = adjacent hypotenuse cos 1 adjacent hypotenuse = θ tan θ = opposite adjacent tan 1 opposite adjacent = θ cot θ = adjacent opposite cot 1 adjacent opposite = θ sec θ = hypotenuse adjacent sec 1 hypotenuse adjacent = θ Cosecant (csc) csc θ = hypotenuse opposite csc 1 hypotenuse opposite = θ We can use algebra to figure out each side. For example, if we have an angle of 39.2 (for A), and a side of 2.1 (for b), we can figure out each side. Let s redraw and solve our triangle. a c First, let s solve for angle B. A triangle has 180, so we can remove the angles we already know from this to get angle B. ( = 50.8 ) Next, we can either solve for a or c (I m solving for a here). I m going to use A. Because of this, 2.1 is our adjacent and a the opposite. We need to use the tangent function Use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for c. tan 39.2 = a 2.1 (2.1) tan 39.2 = a a 1.7 c = c 2.7 Why multiply? Because the tangent of an angle is angle a divided by angle b. Or generally: tan θ = a b We know angle b, so we can use algebra to solve for angle a.
106 50, O
107 51, I Final Review Rational Functions Find all parts of the function below f(x) = x2 3x 4 2x 2 2x + 4 Vertical Asymptotes: x = 1, 2 = (x 4)(x + 1) 2(x + 2)(x 1) Horizontal Asymptotes: y = 1 2 Holes: None X-intercepts: x = 4, 1 Solve v + 2 4v v 3 = 1 v = 2 4v 3 ( v + 2 4v v 3 = 1) v = 4v 3 v + 3 = 4v = 3v 3 v = 2
108 51, O
109 52, I Circles Triangles and Circles on the Coordinate Grid A Right Triangle a 2 + b 2 = c 2 Distance Formula x 2 + y 2 = D 2 D = x 2 + y 2 With two points, it s like this D = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2 Example 1 Find the distance between (1,6) and (3, 5). Relate to a Circle D = (3 1) 2 + ( 5 3) 2 D = D = 125 D = 5 5 r = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2 Equation of a Circle x 2 + y 2 = r 2 The center of a circle is at (h, k). The radius is r. (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2
110 52, O Example 2 Write the equation of a circle with the center of (4, 2) and a radius 6. (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 (x 4) 2 + (y + 2) 2 = 36 Unit Circle The unit circle is a circle at the origin (0,0) with a radius of 1. (x 0) 2 + (y 0) 2 = 1 2 x 2 + y 2 = 1 Example 3 Find the x-intercepts of a circle with radius 6 centered at (2,4). (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 (x 2) 2 + (y 4) 2 = 36 x =? y = 0 (x 2) 2 + (0 4) 2 = 36 (x 2) = 36 (x 2) 2 = 20 x 2 = ± 20 x = 2 ± 20 x = 2 ± 2 5
111 53, I Final Review (Radicals) Simplify = (2) (2) ( 6 2 2) x 4 3 x 512x 3 8x x
Precalculus Review. Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions. Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties. Constants. Linear.
 Precalculus Review Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties Constants Linear Quadratic Cubic Generalizations for Polynomial Functions - The domain
Precalculus Review Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties Constants Linear Quadratic Cubic Generalizations for Polynomial Functions - The domain
Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers
 Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers CLASSIFICATIONS OF NUMBERS NATURAL NUMBERS = N = {1,2,3,4,...}
Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers CLASSIFICATIONS OF NUMBERS NATURAL NUMBERS = N = {1,2,3,4,...}
Hello Future Calculus Level One Student,
 Hello Future Calculus Level One Student, This assignment must be completed and handed in on the first day of class. This assignment will serve as the main review for a test on this material. The test will
Hello Future Calculus Level One Student, This assignment must be completed and handed in on the first day of class. This assignment will serve as the main review for a test on this material. The test will
DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus
 DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This packet contains background skills you need to know for your AP Calculus. My suggestion is, you read the information and
DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This packet contains background skills you need to know for your AP Calculus. My suggestion is, you read the information and
As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: Figure 1
 Trigonometry Basic Functions As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: sin θ = cos θ = opposite hypotenuse adjacent hypotenuse tan θ = opposite adjacent Where θ represents an
Trigonometry Basic Functions As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: sin θ = cos θ = opposite hypotenuse adjacent hypotenuse tan θ = opposite adjacent Where θ represents an
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC. Complex Fractions
 Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
Algebra 2 Khan Academy Video Correlations By SpringBoard Activity
 SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
Name: Math Analysis Chapter 3 Notes: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Name: Math Analysis Chapter 3 Notes: Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Day : Section 3-1 Eponential Functions 3-1: Eponential Functions After completing section 3-1 you should be able to do the following:
Name: Math Analysis Chapter 3 Notes: Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Day : Section 3-1 Eponential Functions 3-1: Eponential Functions After completing section 3-1 you should be able to do the following:
Algebra 2 Khan Academy Video Correlations By SpringBoard Activity
 SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
AP Calculus Summer Assignment Summer 2017 Expectations for Summer Assignment on the first day of the school year.
 Summer 07 Expectations for Summer Assignment This packet is to be submitted to your Calculus BC teacher on the first day of the school year. All work must be shown in the packet OR on separate paper attached
Summer 07 Expectations for Summer Assignment This packet is to be submitted to your Calculus BC teacher on the first day of the school year. All work must be shown in the packet OR on separate paper attached
Functions and their Graphs
 Chapter One Due Monday, December 12 Functions and their Graphs Functions Domain and Range Composition and Inverses Calculator Input and Output Transformations Quadratics Functions A function yields a specific
Chapter One Due Monday, December 12 Functions and their Graphs Functions Domain and Range Composition and Inverses Calculator Input and Output Transformations Quadratics Functions A function yields a specific
AP Calculus Summer Assignment Summer 2017 Expectations for Summer Assignment on the first day of the school year.
 Welcome to AP Calculus!!! For you to be successful in the fall when you come back to school you will need to complete this summer homework assignment. This will be worth grades when you get back to class
Welcome to AP Calculus!!! For you to be successful in the fall when you come back to school you will need to complete this summer homework assignment. This will be worth grades when you get back to class
2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with a graph. f(x) = 25 x 2
 29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
Summer Work for Students Entering Calculus
 For the problems sets which start on page 6 write out all solutions clearly on a separate sheet of paper. Show all steps and circle your answer. The following are examples of different types of problems.
For the problems sets which start on page 6 write out all solutions clearly on a separate sheet of paper. Show all steps and circle your answer. The following are examples of different types of problems.
PRE-CALCULUS General Specific Math Skills
 PRE-CALCULUS Welcome to Pre-Calculus! Pre-Calculus will be challenging but rewarding!! This full year course requires that everyone work hard and study for the entirety of the class. You will need a large
PRE-CALCULUS Welcome to Pre-Calculus! Pre-Calculus will be challenging but rewarding!! This full year course requires that everyone work hard and study for the entirety of the class. You will need a large
List of PreCalculus Algebra Mathematical Concept Practice Sheets (Updated Spring 2015)
 List of PreCalculus Algebra Mathematical Concept Practice Sheets (Updated Spring 2015) MAT 155P MAT 155 1 Absolute Value Equations P 7 P 3 2 Absolute Value Inequalities P 9 P 4 3 Algebraic Expressions:
List of PreCalculus Algebra Mathematical Concept Practice Sheets (Updated Spring 2015) MAT 155P MAT 155 1 Absolute Value Equations P 7 P 3 2 Absolute Value Inequalities P 9 P 4 3 Algebraic Expressions:
Polynomials and Rational Functions. Quadratic Equations and Inequalities. Remainder and Factor Theorems. Rational Root Theorem
 Pre-Calculus Pre-AP Scope and Sequence - Year at a Glance Pre-Calculus Pre-AP - First Semester Pre-calculus with Limits; Larson/Hostetler Three Weeks 1 st 3 weeks 2 nd 3 weeks 3 rd 3 weeks 4 th 3 weeks
Pre-Calculus Pre-AP Scope and Sequence - Year at a Glance Pre-Calculus Pre-AP - First Semester Pre-calculus with Limits; Larson/Hostetler Three Weeks 1 st 3 weeks 2 nd 3 weeks 3 rd 3 weeks 4 th 3 weeks
Section 6.2 Notes Page Trigonometric Functions; Unit Circle Approach
 Section Notes Page Trigonometric Functions; Unit Circle Approach A unit circle is a circle centered at the origin with a radius of Its equation is x y = as shown in the drawing below Here the letter t
Section Notes Page Trigonometric Functions; Unit Circle Approach A unit circle is a circle centered at the origin with a radius of Its equation is x y = as shown in the drawing below Here the letter t
Algebra/Trigonometry Review Notes
 Algebra/Trigonometry Review Notes MAC 41 Calculus for Life Sciences Instructor: Brooke Quinlan Hillsborough Community College ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR CALCULUS 1 TOPIC 1: POLYNOMIAL BASICS, POLYNOMIAL END BEHAVIOR,
Algebra/Trigonometry Review Notes MAC 41 Calculus for Life Sciences Instructor: Brooke Quinlan Hillsborough Community College ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR CALCULUS 1 TOPIC 1: POLYNOMIAL BASICS, POLYNOMIAL END BEHAVIOR,
Troy High School AP Calculus Summer Packet
 Troy High School AP Calculus Summer Packet As instructors of AP Calculus, we have etremely high epectations of students taking our courses. We epect a certain level of independence to be demonstrated by
Troy High School AP Calculus Summer Packet As instructors of AP Calculus, we have etremely high epectations of students taking our courses. We epect a certain level of independence to be demonstrated by
+ i sin. + i sin. = 2 cos
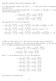 Math 11 Lesieutre); Exam review I; December 4, 017 1. a) Find all complex numbers z for which z = 8. Write your answers in rectangular non-polar) form. We are going to use de Moivre s theorem. For 1, r
Math 11 Lesieutre); Exam review I; December 4, 017 1. a) Find all complex numbers z for which z = 8. Write your answers in rectangular non-polar) form. We are going to use de Moivre s theorem. For 1, r
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities. Math 30-1 R 3. (Revisit, Review and Revive)
 SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
Welcome to AP Calculus!!!
 Welcome to AP Calculus!!! In preparation for next year, you need to complete this summer packet. This packet reviews & expands upon the concepts you studied in Algebra II and Pre-calculus. Make sure you
Welcome to AP Calculus!!! In preparation for next year, you need to complete this summer packet. This packet reviews & expands upon the concepts you studied in Algebra II and Pre-calculus. Make sure you
CK- 12 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1
 14.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine 1. A.,1 B. (, 1) C. 3,0 D. 11 1, 6 E. (, 1) F. G. H. 11, 4 7, 1 11, 3. 3. 5 9,,,,,,, 4 4 4 4 3 5 3, and, 3 3 CK- 1 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1 4.ans-1401-01 5.
14.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine 1. A.,1 B. (, 1) C. 3,0 D. 11 1, 6 E. (, 1) F. G. H. 11, 4 7, 1 11, 3. 3. 5 9,,,,,,, 4 4 4 4 3 5 3, and, 3 3 CK- 1 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1 4.ans-1401-01 5.
Summer 2017 Review For Students Entering AP Calculus AB/BC
 Summer 2017 Review For Students Entering AP Calculus AB/BC Holy Name High School AP Calculus Summer Homework 1 A.M.D.G. AP Calculus AB Summer Review Packet Holy Name High School Welcome to AP Calculus
Summer 2017 Review For Students Entering AP Calculus AB/BC Holy Name High School AP Calculus Summer Homework 1 A.M.D.G. AP Calculus AB Summer Review Packet Holy Name High School Welcome to AP Calculus
Precalculus Table of Contents Unit 1 : Algebra Review Lesson 1: (For worksheet #1) Factoring Review Factoring Using the Distributive Laws Factoring
 Unit 1 : Algebra Review Factoring Review Factoring Using the Distributive Laws Factoring Trinomials Factoring the Difference of Two Squares Factoring Perfect Square Trinomials Factoring the Sum and Difference
Unit 1 : Algebra Review Factoring Review Factoring Using the Distributive Laws Factoring Trinomials Factoring the Difference of Two Squares Factoring Perfect Square Trinomials Factoring the Sum and Difference
SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET
 SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET 017-018 Name: 1. This packet is to be handed in on Monday August 8, 017.. All work must be shown on separate paper attached to the packet. 3.
SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET 017-018 Name: 1. This packet is to be handed in on Monday August 8, 017.. All work must be shown on separate paper attached to the packet. 3.
Math 005A Prerequisite Material Answer Key
 Math 005A Prerequisite Material Answer Key 1. a) P = 4s (definition of perimeter and square) b) P = l + w (definition of perimeter and rectangle) c) P = a + b + c (definition of perimeter and triangle)
Math 005A Prerequisite Material Answer Key 1. a) P = 4s (definition of perimeter and square) b) P = l + w (definition of perimeter and rectangle) c) P = a + b + c (definition of perimeter and triangle)
1 Chapter 2 Perform arithmetic operations with polynomial expressions containing rational coefficients 2-2, 2-3, 2-4
 NYS Performance Indicators Chapter Learning Objectives Text Sections Days A.N. Perform arithmetic operations with polynomial expressions containing rational coefficients. -, -5 A.A. Solve absolute value
NYS Performance Indicators Chapter Learning Objectives Text Sections Days A.N. Perform arithmetic operations with polynomial expressions containing rational coefficients. -, -5 A.A. Solve absolute value
NYS Algebra II and Trigonometry Suggested Sequence of Units (P.I's within each unit are NOT in any suggested order)
 1 of 6 UNIT P.I. 1 - INTEGERS 1 A2.A.1 Solve absolute value equations and inequalities involving linear expressions in one variable 1 A2.A.4 * Solve quadratic inequalities in one and two variables, algebraically
1 of 6 UNIT P.I. 1 - INTEGERS 1 A2.A.1 Solve absolute value equations and inequalities involving linear expressions in one variable 1 A2.A.4 * Solve quadratic inequalities in one and two variables, algebraically
Math Academy I Fall Study Guide. CHAPTER ONE: FUNDAMENTALS Due Thursday, December 8
 Name: Math Academy I Fall Study Guide CHAPTER ONE: FUNDAMENTALS Due Thursday, December 8 1-A Terminology natural integer rational real complex irrational imaginary term expression argument monomial degree
Name: Math Academy I Fall Study Guide CHAPTER ONE: FUNDAMENTALS Due Thursday, December 8 1-A Terminology natural integer rational real complex irrational imaginary term expression argument monomial degree
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment
 Name: AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Due Date: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills
Name: AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Due Date: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills
A. Incorrect! For a point to lie on the unit circle, the sum of the squares of its coordinates must be equal to 1.
 Algebra - Problem Drill 19: Basic Trigonometry - Right Triangle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following points lies on the unit circle? (A) 1, 1 (B) 1, (C) (D) (E), 3, 3, For a point to lie on the unit circle,
Algebra - Problem Drill 19: Basic Trigonometry - Right Triangle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following points lies on the unit circle? (A) 1, 1 (B) 1, (C) (D) (E), 3, 3, For a point to lie on the unit circle,
AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet
 Name Date Section AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the summer. It is meant to help you practice mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus
Name Date Section AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the summer. It is meant to help you practice mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus
Summer Packet A Math Refresher For Students Entering IB Mathematics SL
 Summer Packet A Math Refresher For Students Entering IB Mathematics SL Name: PRECALCULUS SUMMER PACKET Directions: This packet is required if you are registered for Precalculus for the upcoming school
Summer Packet A Math Refresher For Students Entering IB Mathematics SL Name: PRECALCULUS SUMMER PACKET Directions: This packet is required if you are registered for Precalculus for the upcoming school
Partial Fractions. June 27, In this section, we will learn to integrate another class of functions: the rational functions.
 Partial Fractions June 7, 04 In this section, we will learn to integrate another class of functions: the rational functions. Definition. A rational function is a fraction of two polynomials. For example,
Partial Fractions June 7, 04 In this section, we will learn to integrate another class of functions: the rational functions. Definition. A rational function is a fraction of two polynomials. For example,
TRIGONOMETRY AND PRECALCULUS CURRICULUM Course 17008
 TRIGONOMETRY AND PRECALCULUS CURRICULUM Course 17008 Students taking this course will concentrate on algebraic concepts and applications. The use of graphing calculators and other technologies is emphasized
TRIGONOMETRY AND PRECALCULUS CURRICULUM Course 17008 Students taking this course will concentrate on algebraic concepts and applications. The use of graphing calculators and other technologies is emphasized
2017 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment
 07 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Mrs. Peck ( kapeck@spotsylvania.k.va.us) This assignment is designed to help prepare you to start Calculus on day and be successful. I recommend that you take off the
07 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Mrs. Peck ( kapeck@spotsylvania.k.va.us) This assignment is designed to help prepare you to start Calculus on day and be successful. I recommend that you take off the
STUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY
 STUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY 1) (LT 4A) Graph and indicate the Vertical Asymptote, Horizontal Asymptote, Domain, -intercepts, and y- intercepts of this rational function. 3 2 + 4 Vertical Asymptote: Set the
STUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY 1) (LT 4A) Graph and indicate the Vertical Asymptote, Horizontal Asymptote, Domain, -intercepts, and y- intercepts of this rational function. 3 2 + 4 Vertical Asymptote: Set the
ADVANCED ALGEBRA (and Honors)
 ADVANCED ALGEBRA (and Honors) Welcome to Advanced Algebra! Advanced Algebra will be challenging but rewarding!! This full year course requires that everyone work hard and study for the entirety of the
ADVANCED ALGEBRA (and Honors) Welcome to Advanced Algebra! Advanced Algebra will be challenging but rewarding!! This full year course requires that everyone work hard and study for the entirety of the
CARLISLE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT Carlisle, PA PRE-CALCULUS. GRADES 11 and 12
 CARLISLE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT Carlisle, PA 17013 PRE-CALCULUS GRADES 11 and 12 Date of Board Approval: April 17, 2014 CARLISLE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED INSTRUCTION COVER PAGE TITLE OF SUBJECT: Math
CARLISLE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT Carlisle, PA 17013 PRE-CALCULUS GRADES 11 and 12 Date of Board Approval: April 17, 2014 CARLISLE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED INSTRUCTION COVER PAGE TITLE OF SUBJECT: Math
MATH 1130 Exam 1 Review Sheet
 MATH 1130 Exam 1 Review Sheet The Cartesian Coordinate Plane The Cartesian Coordinate Plane is a visual representation of the collection of all ordered pairs (x, y) where x and y are real numbers. This
MATH 1130 Exam 1 Review Sheet The Cartesian Coordinate Plane The Cartesian Coordinate Plane is a visual representation of the collection of all ordered pairs (x, y) where x and y are real numbers. This
Journals Gr 12 - MHF Name: How Journals will be marked: NAME: Unit : Question chosen: Neat? Creative?
 Journals Gr 12 - MHF Name: How Journals will be marked: NAME: Unit : Question chosen: Neat? Creative? Definitions and/or diagrams? Colourful subheadings? Example? Can use HW question Numbered? Few pages
Journals Gr 12 - MHF Name: How Journals will be marked: NAME: Unit : Question chosen: Neat? Creative? Definitions and/or diagrams? Colourful subheadings? Example? Can use HW question Numbered? Few pages
2. Algebraic functions, power functions, exponential functions, trig functions
 Math, Prep: Familiar Functions (.,.,.5, Appendix D) Name: Names of collaborators: Main Points to Review:. Functions, models, graphs, tables, domain and range. Algebraic functions, power functions, exponential
Math, Prep: Familiar Functions (.,.,.5, Appendix D) Name: Names of collaborators: Main Points to Review:. Functions, models, graphs, tables, domain and range. Algebraic functions, power functions, exponential
Pre-Calculus Chapter 0. Solving Equations and Inequalities 0.1 Solving Equations with Absolute Value 0.2 Solving Quadratic Equations
 Pre-Calculus Chapter 0. Solving Equations and Inequalities 0.1 Solving Equations with Absolute Value 0.1.1 Solve Simple Equations Involving Absolute Value 0.2 Solving Quadratic Equations 0.2.1 Use the
Pre-Calculus Chapter 0. Solving Equations and Inequalities 0.1 Solving Equations with Absolute Value 0.1.1 Solve Simple Equations Involving Absolute Value 0.2 Solving Quadratic Equations 0.2.1 Use the
sin cos 1 1 tan sec 1 cot csc Pre-Calculus Mathematics Trigonometric Identities and Equations
 Pre-Calculus Mathematics 12 6.1 Trigonometric Identities and Equations Goal: 1. Identify the Fundamental Trigonometric Identities 2. Simplify a Trigonometric Expression 3. Determine the restrictions on
Pre-Calculus Mathematics 12 6.1 Trigonometric Identities and Equations Goal: 1. Identify the Fundamental Trigonometric Identities 2. Simplify a Trigonometric Expression 3. Determine the restrictions on
Objectives List. Important Students should expect test questions that require a synthesis of these objectives.
 MATH 1040 - of One Variable, Part I Textbook 1: : Algebra and Trigonometry for ET. 4 th edition by Brent, Muller Textbook 2:. Early Transcendentals, 3 rd edition by Briggs, Cochran, Gillett, Schulz s List
MATH 1040 - of One Variable, Part I Textbook 1: : Algebra and Trigonometry for ET. 4 th edition by Brent, Muller Textbook 2:. Early Transcendentals, 3 rd edition by Briggs, Cochran, Gillett, Schulz s List
Albertson AP Calculus AB AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school.
 Albertson AP Calculus AB Name AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET 2015 DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the
Albertson AP Calculus AB Name AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET 2015 DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the
HOW TO NOT LOSE POINTS...
 Math Analysis B Final Review GROUP MATERIALS INSTRUCTIONS 1) Ms. Lee picks a student randomly. 2) Selected student chooses a question. 3) Group discusses question and writes FINAL WORK & SOLUTION on whiteboard.
Math Analysis B Final Review GROUP MATERIALS INSTRUCTIONS 1) Ms. Lee picks a student randomly. 2) Selected student chooses a question. 3) Group discusses question and writes FINAL WORK & SOLUTION on whiteboard.
Trigonometry Trigonometry comes from the Greek word meaning measurement of triangles Angles are typically labeled with Greek letters
 Trigonometry Trigonometry comes from the Greek word meaning measurement of triangles Angles are typically labeled with Greek letters α( alpha), β ( beta), θ ( theta) as well as upper case letters A,B,
Trigonometry Trigonometry comes from the Greek word meaning measurement of triangles Angles are typically labeled with Greek letters α( alpha), β ( beta), θ ( theta) as well as upper case letters A,B,
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 2013/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 201/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 121 - Calculus 1, Fall 201/2014! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics
Introduction Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 201/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 121 - Calculus 1, Fall 201/2014! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics
ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 1 MATH00030 SEMESTER / Functions
 ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 1 MATH00030 SEMESTER 1 2017/2018 DR. ANTHONY BROWN 4. Functions 4.1. What is a Function: Domain, Codomain and Rule. In the course so far, we
ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 1 MATH00030 SEMESTER 1 2017/2018 DR. ANTHONY BROWN 4. Functions 4.1. What is a Function: Domain, Codomain and Rule. In the course so far, we
CHAPTERS 5-7 TRIG. FORMULAS PACKET
 CHAPTERS 5-7 TRIG. FORMULAS PACKET PRE-CALCULUS SECTION 5-2 IDENTITIES Reciprocal Identities sin x = ( 1 / csc x ) csc x = ( 1 / sin x ) cos x = ( 1 / sec x ) sec x = ( 1 / cos x ) tan x = ( 1 / cot x
CHAPTERS 5-7 TRIG. FORMULAS PACKET PRE-CALCULUS SECTION 5-2 IDENTITIES Reciprocal Identities sin x = ( 1 / csc x ) csc x = ( 1 / sin x ) cos x = ( 1 / sec x ) sec x = ( 1 / cos x ) tan x = ( 1 / cot x
Radicals: To simplify means that 1) no radicand has a perfect square factor and 2) there is no radical in the denominator (rationalize).
 Summer Review Packet for Students Entering Prealculus Radicals: To simplify means that 1) no radicand has a perfect square factor and ) there is no radical in the denominator (rationalize). Recall the
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering Prealculus Radicals: To simplify means that 1) no radicand has a perfect square factor and ) there is no radical in the denominator (rationalize). Recall the
AP CALCULUS SUMMER WORKSHEET
 AP CALCULUS SUMMER WORKSHEET DUE: First Day of School, 2011 Complete this assignment at your leisure during the summer. I strongly recommend you complete a little each week. It is designed to help you
AP CALCULUS SUMMER WORKSHEET DUE: First Day of School, 2011 Complete this assignment at your leisure during the summer. I strongly recommend you complete a little each week. It is designed to help you
Section 5.4 The Other Trigonometric Functions
 Section 5.4 The Other Trigonometric Functions Section 5.4 The Other Trigonometric Functions In the previous section, we defined the e and coe functions as ratios of the sides of a right triangle in a circle.
Section 5.4 The Other Trigonometric Functions Section 5.4 The Other Trigonometric Functions In the previous section, we defined the e and coe functions as ratios of the sides of a right triangle in a circle.
Topic Outline for Algebra 2 & and Trigonometry One Year Program
 Topic Outline for Algebra 2 & and Trigonometry One Year Program Algebra 2 & and Trigonometry - N - Semester 1 1. Rational Expressions 17 Days A. Factoring A2.A.7 B. Rationals A2.N.3 A2.A.17 A2.A.16 A2.A.23
Topic Outline for Algebra 2 & and Trigonometry One Year Program Algebra 2 & and Trigonometry - N - Semester 1 1. Rational Expressions 17 Days A. Factoring A2.A.7 B. Rationals A2.N.3 A2.A.17 A2.A.16 A2.A.23
Curriculum Mapper - Complete Curriculum Maps CONTENT. 1.2 Evaluate expressions (p.18 Activity 1.2).
 Page 1 of 9 Close Window Print Page Layout Show Standards View Paragraph Format View Course Description MATH 3 (MASTER MAP) School: Binghamton High School Teacher: Master Map Email: Course #: 203 Grade
Page 1 of 9 Close Window Print Page Layout Show Standards View Paragraph Format View Course Description MATH 3 (MASTER MAP) School: Binghamton High School Teacher: Master Map Email: Course #: 203 Grade
1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
 Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Winter 2012/2013 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Winter 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Winter 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from
Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Winter 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Winter 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment
 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, you will be epected to have attempted every problem. These skills are all different tools that you will pull out of your toolbo this
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, you will be epected to have attempted every problem. These skills are all different tools that you will pull out of your toolbo this
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 2012/2013 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Fall 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Fall 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from Algebra
Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Fall 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Fall 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from Algebra
Honors Algebra 2 Chapter 14 Page 1
 Section. (Introduction) Graphs of Trig Functions Objectives:. To graph basic trig functions using t-bar method. A. Sine and Cosecant. y = sinθ y y y y 0 --- --- 80 --- --- 30 0 0 300 5 35 5 35 60 50 0
Section. (Introduction) Graphs of Trig Functions Objectives:. To graph basic trig functions using t-bar method. A. Sine and Cosecant. y = sinθ y y y y 0 --- --- 80 --- --- 30 0 0 300 5 35 5 35 60 50 0
Exam Review 2 nd Semester 6-1 Operations on Functions
 NAME DATE PERIOD Exam Review 2 nd Semester 6-1 Operations on Functions Find (f + g)(x), (f g)(x), (f g)(x), and (x) for each f(x) and g(x). 1. f(x) = 8x 3; g(x) = 4x + 5 2. f(x) = + x 6; g(x) = x 2 If
NAME DATE PERIOD Exam Review 2 nd Semester 6-1 Operations on Functions Find (f + g)(x), (f g)(x), (f g)(x), and (x) for each f(x) and g(x). 1. f(x) = 8x 3; g(x) = 4x + 5 2. f(x) = + x 6; g(x) = x 2 If
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment 2016
 AP Calculus AB Name Dates: Start Finish AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment 016 Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This packet is a review of Advanced Algebra & Pre-Calculus topics that you will use continuously
AP Calculus AB Name Dates: Start Finish AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment 016 Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This packet is a review of Advanced Algebra & Pre-Calculus topics that you will use continuously
AP CALCULUS SUMMER WORKSHEET
 AP CALCULUS SUMMER WORKSHEET DUE: First Day of School Aug. 19, 2010 Complete this assignment at your leisure during the summer. It is designed to help you become more comfortable with your graphing calculator,
AP CALCULUS SUMMER WORKSHEET DUE: First Day of School Aug. 19, 2010 Complete this assignment at your leisure during the summer. It is designed to help you become more comfortable with your graphing calculator,
Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part)
 Fry Texas A&M University! Spring 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 8B-I! Page 79 Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part) Recall from geometry that if 2 corresponding triangles have 2 angles of
Fry Texas A&M University! Spring 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 8B-I! Page 79 Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part) Recall from geometry that if 2 corresponding triangles have 2 angles of
Pre-Calculus MATH 119 Fall Section 1.1. Section objectives. Section 1.3. Section objectives. Section A.10. Section objectives
 Pre-Calculus MATH 119 Fall 2013 Learning Objectives Section 1.1 1. Use the Distance Formula 2. Use the Midpoint Formula 4. Graph Equations Using a Graphing Utility 5. Use a Graphing Utility to Create Tables
Pre-Calculus MATH 119 Fall 2013 Learning Objectives Section 1.1 1. Use the Distance Formula 2. Use the Midpoint Formula 4. Graph Equations Using a Graphing Utility 5. Use a Graphing Utility to Create Tables
Mission 1 Simplify and Multiply Rational Expressions
 Algebra Honors Unit 6 Rational Functions Name Quest Review Questions Mission 1 Simplify and Multiply Rational Expressions 1) Compare the two functions represented below. Determine which of the following
Algebra Honors Unit 6 Rational Functions Name Quest Review Questions Mission 1 Simplify and Multiply Rational Expressions 1) Compare the two functions represented below. Determine which of the following
3 Inequalities Absolute Values Inequalities and Intervals... 18
 Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 1. Factoring Polynomials........................................ 1. Algebraic and Fractional
Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 1. Factoring Polynomials........................................ 1. Algebraic and Fractional
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Feedback D. Incorrect! Exponential functions are continuous everywhere. Look for features like square roots or denominators that could be made 0.
 Calculus Problem Solving Drill 07: Trigonometric Limits and Continuity No. of 0 Instruction: () Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully. () Do your work on a separate sheet of paper. (3)
Calculus Problem Solving Drill 07: Trigonometric Limits and Continuity No. of 0 Instruction: () Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully. () Do your work on a separate sheet of paper. (3)
Math 120: Precalculus Autumn 2017 A List of Topics for the Final
 Math 120: Precalculus Autumn 2017 A List of Topics for the Final Here s a fairly comprehensive list of things you should be comfortable doing for the final. Really Old Stuff 1. Unit conversion and rates
Math 120: Precalculus Autumn 2017 A List of Topics for the Final Here s a fairly comprehensive list of things you should be comfortable doing for the final. Really Old Stuff 1. Unit conversion and rates
NAME DATE PERIOD. Trigonometric Identities. Review Vocabulary Complete each identity. (Lesson 4-1) 1 csc θ = 1. 1 tan θ = cos θ sin θ = 1
 5-1 Trigonometric Identities What You ll Learn Scan the text under the Now heading. List two things that you will learn in the lesson. 1. 2. Lesson 5-1 Active Vocabulary Review Vocabulary Complete each
5-1 Trigonometric Identities What You ll Learn Scan the text under the Now heading. List two things that you will learn in the lesson. 1. 2. Lesson 5-1 Active Vocabulary Review Vocabulary Complete each
Step 1: Greatest Common Factor Step 2: Count the number of terms If there are: 2 Terms: Difference of 2 Perfect Squares ( + )( - )
 Review for Algebra 2 CC Radicals: r x p 1 r x p p r = x p r = x Imaginary Numbers: i = 1 Polynomials (to Solve) Try Factoring: i 2 = 1 Step 1: Greatest Common Factor Step 2: Count the number of terms If
Review for Algebra 2 CC Radicals: r x p 1 r x p p r = x p r = x Imaginary Numbers: i = 1 Polynomials (to Solve) Try Factoring: i 2 = 1 Step 1: Greatest Common Factor Step 2: Count the number of terms If
MATH 1040 Objectives List
 MATH 1040 Objectives List Textbook: Calculus, Early Transcendentals, 7th edition, James Stewart Students should expect test questions that require synthesis of these objectives. Unit 1 WebAssign problems
MATH 1040 Objectives List Textbook: Calculus, Early Transcendentals, 7th edition, James Stewart Students should expect test questions that require synthesis of these objectives. Unit 1 WebAssign problems
College Algebra with Trigonometry
 College Algebra with Trigonometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (556 topics + 614 additional
College Algebra with Trigonometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (556 topics + 614 additional
Unit 2 - The Trigonometric Functions - Classwork
 Unit 2 - The Trigonometric Functions - Classwork Given a right triangle with one of the angles named ", and the sides of the triangle relative to " named opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse (picture on
Unit 2 - The Trigonometric Functions - Classwork Given a right triangle with one of the angles named ", and the sides of the triangle relative to " named opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse (picture on
A Library of Functions
 LibraryofFunctions.nb 1 A Library of Functions Any study of calculus must start with the study of functions. Functions are fundamental to mathematics. In its everyday use the word function conveys to us
LibraryofFunctions.nb 1 A Library of Functions Any study of calculus must start with the study of functions. Functions are fundamental to mathematics. In its everyday use the word function conveys to us
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment
 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, it is my epectation that you will have this packet completed. You will be way behind at the beginning of the year if you haven t attempted
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, it is my epectation that you will have this packet completed. You will be way behind at the beginning of the year if you haven t attempted
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment
 AP Calculus AB 07-08 Summer Assignment Welcome to AP Calculus AB! You are epected to complete the attached homework assignment during the summer. This is because of class time constraints and the amount
AP Calculus AB 07-08 Summer Assignment Welcome to AP Calculus AB! You are epected to complete the attached homework assignment during the summer. This is because of class time constraints and the amount
TRIG REVIEW NOTES. Co-terminal Angles: Angles that end at the same spot. (sines, cosines, and tangents will equal)
 TRIG REVIEW NOTES Convert from radians to degrees: multiply by 0 180 Convert from degrees to radians: multiply by 0. 180 Co-terminal Angles: Angles that end at the same spot. (sines, cosines, and tangents
TRIG REVIEW NOTES Convert from radians to degrees: multiply by 0 180 Convert from degrees to radians: multiply by 0. 180 Co-terminal Angles: Angles that end at the same spot. (sines, cosines, and tangents
2014 Summer Review for Students Entering Algebra 2. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 1. Solving Linear Equations 2. Solving Linear Systems of Equations 3. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 4. Writing the Equation of a Line 5. Laws of Exponents and Scientific Notation 6. Solving
1. Solving Linear Equations 2. Solving Linear Systems of Equations 3. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 4. Writing the Equation of a Line 5. Laws of Exponents and Scientific Notation 6. Solving
a factors The exponential 0 is a special case. If b is any nonzero real number, then
 0.1 Exponents The expression x a is an exponential expression with base x and exponent a. If the exponent a is a positive integer, then the expression is simply notation that counts how many times the
0.1 Exponents The expression x a is an exponential expression with base x and exponent a. If the exponent a is a positive integer, then the expression is simply notation that counts how many times the
AP CALCULUS AB. Summer Assignment. Page 1
 AP CALCULUS AB Summer Assignment Page 1 Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This will be the toughest class yet in your mathematical careers but the benefit you will receive by having this experience in high school
AP CALCULUS AB Summer Assignment Page 1 Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This will be the toughest class yet in your mathematical careers but the benefit you will receive by having this experience in high school
REVIEW: MORE FUNCTIONS AP CALCULUS :: MR. VELAZQUEZ
 REVIEW: MORE FUNCTIONS AP CALCULUS :: MR. VELAZQUEZ INVERSE FUNCTIONS Two functions are inverses if they undo each other. In other words, composing one function in the other will result in simply x (the
REVIEW: MORE FUNCTIONS AP CALCULUS :: MR. VELAZQUEZ INVERSE FUNCTIONS Two functions are inverses if they undo each other. In other words, composing one function in the other will result in simply x (the
NAME: DATE: CLASS: AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER MATH 2018
 NAME: DATE: CLASS: AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER MATH 2018 A] Refer to your pre-calculus notebook, the internet, or the sheets/links provided for assistance. B] Do not wait until the last minute to complete this
NAME: DATE: CLASS: AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER MATH 2018 A] Refer to your pre-calculus notebook, the internet, or the sheets/links provided for assistance. B] Do not wait until the last minute to complete this
You should be comfortable with everything below (and if you aren t you d better brush up).
 Review You should be comfortable with everything below (and if you aren t you d better brush up).. Arithmetic You should know how to add, subtract, multiply, divide, and work with the integers Z = {...,,,
Review You should be comfortable with everything below (and if you aren t you d better brush up).. Arithmetic You should know how to add, subtract, multiply, divide, and work with the integers Z = {...,,,
We can see that f(2) is undefined. (Plugging x = 2 into the function results in a 0 in the denominator)
 In order to be successful in AP Calculus, you are expected to KNOW everything that came before. All topics from Algebra I, II, Geometry and of course Precalculus are expected to be mastered before you
In order to be successful in AP Calculus, you are expected to KNOW everything that came before. All topics from Algebra I, II, Geometry and of course Precalculus are expected to be mastered before you
MATH 32 FALL 2013 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS. 1 cos( 2. is in the first quadrant, so its sine is positive. Finally, csc( π 8 ) = 2 2.
 MATH FALL 01 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS (1) (1 points) Evalute the following (a) tan(0) Solution: tan(0) = 0. (b) csc( π 8 ) Solution: csc( π 8 ) = 1 sin( π 8 ) To find sin( π 8 ), we ll use the half angle formula:
MATH FALL 01 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS (1) (1 points) Evalute the following (a) tan(0) Solution: tan(0) = 0. (b) csc( π 8 ) Solution: csc( π 8 ) = 1 sin( π 8 ) To find sin( π 8 ), we ll use the half angle formula:
MTH 121 Fall 2007 Essex County College Division of Mathematics and Physics Worksheet #1 1
 MTH Fall 007 Essex County College Division of Mathematics and Physics Worksheet # Preamble It is extremely important that you complete the following two items as soon as possible. Please send an email
MTH Fall 007 Essex County College Division of Mathematics and Physics Worksheet # Preamble It is extremely important that you complete the following two items as soon as possible. Please send an email
Using the Definitions of the Trigonometric Functions
 1.4 Using the Definitions of the Trigonometric Functions Reciprocal Identities Signs and Ranges of Function Values Pythagorean Identities Quotient Identities February 1, 2013 Mrs. Poland Objectives Objective
1.4 Using the Definitions of the Trigonometric Functions Reciprocal Identities Signs and Ranges of Function Values Pythagorean Identities Quotient Identities February 1, 2013 Mrs. Poland Objectives Objective
Trigonometry and Analysis Mathematics
 Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 6 Week(s) 3 Week(s) 5 Week(s) 4 Week(s) 5 Week(s) Equations, Inequalties, Functions 1. Basic Equations (1.1) 2. Modeling with Equations (1.2) 3. Quadratic
Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 6 Week(s) 3 Week(s) 5 Week(s) 4 Week(s) 5 Week(s) Equations, Inequalties, Functions 1. Basic Equations (1.1) 2. Modeling with Equations (1.2) 3. Quadratic
Course Outline and Objectives. MA 1453 Precalculus with Graphing Calculators
 Effective Fall 2011 Course Outline and Objectives MA 1453 Precalculus with Graphing Calculators TEXT: Precalculus, 5 th Edition, by Faires and DeFranza ISBN 978-0-8400-6862-0 NOTE: A graphing calculator
Effective Fall 2011 Course Outline and Objectives MA 1453 Precalculus with Graphing Calculators TEXT: Precalculus, 5 th Edition, by Faires and DeFranza ISBN 978-0-8400-6862-0 NOTE: A graphing calculator
CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW
 CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS CHRISTOPHER NEWPORT UNIVERSITY 1. Introduction and Topics The purpose of these notes is to give an idea of what to expect on the Calculus Readiness
CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS CHRISTOPHER NEWPORT UNIVERSITY 1. Introduction and Topics The purpose of these notes is to give an idea of what to expect on the Calculus Readiness
Core A-level mathematics reproduced from the QCA s Subject criteria for Mathematics document
 Core A-level mathematics reproduced from the QCA s Subject criteria for Mathematics document Background knowledge: (a) The arithmetic of integers (including HCFs and LCMs), of fractions, and of real numbers.
Core A-level mathematics reproduced from the QCA s Subject criteria for Mathematics document Background knowledge: (a) The arithmetic of integers (including HCFs and LCMs), of fractions, and of real numbers.
Class Syllabus. Accessible Topic - Topics accessible to visually impaired students using a screen reader.
 Class Syllabus Class: MATH 1112 Spring 2019 Pilot - MWF 9:05 to 9:55 am Subject : College Algebra with Trigonometry Class Code: WQJQT-3GQW4 Inst ruct or: Ritter Class Dat es: 01/04/2019-05/10/2019 Class
Class Syllabus Class: MATH 1112 Spring 2019 Pilot - MWF 9:05 to 9:55 am Subject : College Algebra with Trigonometry Class Code: WQJQT-3GQW4 Inst ruct or: Ritter Class Dat es: 01/04/2019-05/10/2019 Class
SUMMER REVIEW PACKET. Name:
 Wylie East HIGH SCHOOL SUMMER REVIEW PACKET For students entering Regular PRECALCULUS Name: Welcome to Pre-Calculus. The following packet needs to be finished and ready to be turned the first week of the
Wylie East HIGH SCHOOL SUMMER REVIEW PACKET For students entering Regular PRECALCULUS Name: Welcome to Pre-Calculus. The following packet needs to be finished and ready to be turned the first week of the
Level 1 Advanced Mathematics Final Exam June 19, 2007
 Level Advanced Mathematics Final Exam June 9, 007 NAME: Instructions WRITE ANSWERS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED AND SHOW ALL WORK. Partial credit will not be given if work is not shown. Ask for extra paper if
Level Advanced Mathematics Final Exam June 9, 007 NAME: Instructions WRITE ANSWERS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED AND SHOW ALL WORK. Partial credit will not be given if work is not shown. Ask for extra paper if
Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry
 Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Overview: 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities 5.3 Solving Trig Equations 5.4 Sum and Difference Formulas 5.5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-sum
Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Overview: 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities 5.3 Solving Trig Equations 5.4 Sum and Difference Formulas 5.5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-sum
