Mutipy by r sin RT P to get sin R r r R + T sin (sin T )+ P P = (7) ffi So we hve P P ffi = m (8) choose m re so tht P is sinusoi. If we put this in b
|
|
|
- Lee Baker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topic 4: Lpce Eqution in Spheric Co-orintes n Mutipoe Expnsion Reing Assignment: Jckson Chpter Lpce Eqution in Spheric Coorintes Review of spheric por coorintes: x = r sin cos ffi y = r sin sin ffi z = r cos The three unit vectors er = (sin cos ffi; sin sin ffi; cos ) ; e = (cos cos ffi; sin sin ß; sin ) ; effi = ( sin ffi; cos ffi; )) form right hne coorinte system in the sense (r;;ffi). The unit of voume is where the eement of soi nge is the et function in spheric por coorintes is n Lpce's eqution is r ffi 3 (r r )= 3 x = r sin rffi=r r Ω Ω = (cos ) ffi () r sin ffi (r r ) ffi ( ) ffi (ffi ffi ) (3) + Φ + (4) r Cn the co-orintes be seprte? (not obvious) The nswer is yes, this is n importnt exmpe of seprbe coorinte system for the Lpcin. Let Φ=R(r)T()P(ffi) (5) so TP r r r R + RP sin r (sin T )+ RT r sin P = (6) ffi
2 Mutipy by r sin RT P to get sin R r r R + T sin (sin T )+ P P = (7) ffi So we hve P P ffi = m (8) choose m re so tht P is sinusoi. If we put this in bove n ivie by sin Choose R r r R + T sin (sin T ) m = (9) sin r R = const > () R r so tht R is not "wiggy" function. We cn imgine tht this is going to be ppicbe to spheric chrge istributions where the ri prt ies or grows with rius. As n nstz, tke so tht R r of c is given then + c =! r R = r R = r r R = r + r R = ( +)r r R = ( +)=const = c () = +p +4c = p +4c so + =. Thus we cou terntivey choose = s the constnt rther thn c n write the two soutions R = A r + B r () n r r R = A r + ( +)B r r r = A (+)r +(+)B r = (+)R=CR
3 So we finy hve the eqution for : or sin ( +)+ Tsin sin T (sin T ) m = (3) sin + ( +) m sin T = (4) The function T for the speci cse tht n m re integers (n speci initi conitions) is ce the ssocite Legenre function P m (cos ) : P m (x) stisfies x x x P m (x) + ( +) m P m (x)= (5) x This is the first time in the course tht we hve seen non-trivi exmpe of ifferenti eqution of the form x (p (x) f i)+q (i) f i = (6) where f i = f i (x), i cn be coection of inices, not necessriy integers, n both p (x) n q (i) (x) re given functions. If it is the cse tht p (x) n q (x) for rnge of x (or if both re negtive) then the soutions wi be oscitory in tht rnge since if f >, then x (pf ) < or pf is ecresing n since p>, f is ecresing. Eventuy f wi become negtive, f wi ecrese n pss through zero n its sign wi chnge, yieing the inverse of the bove rgument, so the gener behvior of f i when p> n q i >. The simpest exmpe is p = const; q = const so p> n q>wehve f k + k f k =!f k /e ±ikx (7) A cruciy importnt property of these oscitory functions is their orthogonity. We've seen this property for sines n cosines - now ook t it more genery. To fin the orthogonity conition, write for two ifferent i's syi; j Cross mutipy n subtrct to get But the first term is which is triviy integrbe Z b (pf i) + q (i) f i = pf j + q(j) f j = f j (pf i) f i pf j + q(i) q (j) fi f j = (8) x x x fj pf i f i pf jλ (9) Z b fj pf i f i pfjλ + q(i) q (j) fi f j x = () 3
4 Λ Λ Z b p (b) f j (b) f i (b) f i (b) f j (b) p () f j () f i () f i () f j () = q(j) q (i) fi f j x () If the points &b re chosen in such wy tht the eft hn sie of this eqution vnishes (e.g., in Legenre's eqution where p =x,choose = ;b= +) n if the right hn sie is proper integr, then we get Z b (q (j) q (i) )f i f j x = () Thus if q (j) q (i) 6=,wehve tht the functions f i n f j re orthogon with the weight function q (j) q (i) Strt with the m = cse which yies P (cos ) P (cos ) the Legenre function, or if is positive integer or zero, the Legenre poynomis. Then p =x ;q (i) =(+) (3) We therefore get the resut Z P P x = 6= (4) or Z P P x = ffi N () (5) More genery, ifm6=then q m = ( +) m x n so q m q m = ( +) ( +) (6) so Z where N m is normiztion ftor; P m (x) P m (x) x = ffi N ()m (7) N m = Z (P m ) x (8) n its vue is convention since the ifferenti eqution is iner n so ny mutipe of soution is soution. Note tht for sinusois in which p =;q = k > we cn rrnge the.h.s. to vnish by choosing &b suitby e.g. for k = integer= n we hve for exmpe Z ß sin nx sin mx x =if n 6= m (9) etc. In gener in soving the Sturm-Liouvie eqution, the points (if ny) t which p (x s )= re ce singur points since t them the n erivtive term vnishes from the eqution. If you were to ivie the eqution by p (x), i.e., write it s f i + P p f i + q (i) p f i = (3) 4
5 Then p = gives troube so x s where p (x s ) re the singur pointsof the eqution n except in speci cses, the soutions hve singurities t these points. Furthermore, if you mke series expnsion for to represent the function bout some point (tke Tyor series expnsion bout some point), the rius of convergence in the compex pne (exten the inepenent vribe x to the compex pne z = x + iy) is circe from the point of expnsion to the nerest singur point in the compex pne. For Legenre's eqution with m =,wehve x x P x + ( +)P = (3) One fins tht if is n integer tht the series soutions (for certin initi conitions) of this form re in fct simpe poynomis, ns so x = ± hve no probems. As usu, since this is n orer ifferentieqution, we nee two initi conitions; e.g. vue n sope t x =, to get prticur soution. As with sinusois we tke the "cosine-ike" function to hve c P (x =)= c P(x=)= (cosine-ike) (3) n s P (x =)= The bove nottion is by the wy not convention (more ter). To unerstn wht hppens, write Then if you pug this into x s P (x=)= (sine-ike) (33) P (x) = X n= n set ech coefficient ofpower of x to zero, you get n x n (34) x P + ( +)P = (35) m+ = m (m +)(+) m (36) (m+)(m+) For the cosine ike soution we hve o =; = n the eqution for the coefficients gives ; 4 ; 6 ::: 6=, ; 3 ; 5 ::: =. So c P (x) =+ (+) (+) 3(+) x + x 4 +::: (37) 3 4 Cery c P (x) = c P (x)n even function bout the origin n ifisneven number, the series termintes with the n = th term since the n =(+) th term vnishes n rger ones o so. So, if ) = even c P (x) is poynomi nit is usuy notte simpy by C P (x) 5
6 b) = o, c P (x) is n infinite series n it cn be shown to iverge ogrithmicy t x = ±. These functions re usuy ce D Q (x) (even function, o). For the sine-ike soutions we hve o =; = n the eqution gives ; 4 ; 6 ::: =, ; 3 ; 5 ::: 6=. So s P (x) =x+ (+) (+) 3 4(+) x 3 + x 5 +::: (38) Cery s P (x) = s P (x), n o function bout x = n if is n o number, the series termintes n we hve poynomi. So, if ) = o, s P (x) is poynomi n it is usuy simpy ce P (x) which is n o function when is o b) =even, s P (x) is n infinite series ivergent tx=±;usuy ce Q (x) (n o function where is even). Finy, ifis not n integer, the series re infinite n ivergent s x!±. So, in summry, with the convention normiztion constnts chosen to mke P (+) = P o (x) = P (x) = x P (x) = P 3 (x) = 3x3 5x3 3x R From the gener theory n the fct tht there re no ifficuties with the integr P P x we get Z P (x) P (x) = ()+ ffi (39) Jckson gives recursion retions n exmpes of expnsions. IMPORTANT FACT: The Legenre poynomis re the ony soutions owe in probems in which the points =n = ß re contine in the voume uner consiertion. For circumstnces which o not incue both these points, other soutions to Legenre's eqution show up we won't be concerne with these. 6
MAGIC058 & MATH64062: Partial Differential Equations 1
 MAGIC58 & MATH646: Prti Differenti Equtions 1 Section 4 Fourier series 4.1 Preiminry definitions Definition: Periodic function A function f( is sid to be periodic, with period p if, for, f( + p = f( where
MAGIC58 & MATH646: Prti Differenti Equtions 1 Section 4 Fourier series 4.1 Preiminry definitions Definition: Periodic function A function f( is sid to be periodic, with period p if, for, f( + p = f( where
Math 124B January 24, 2012
 Mth 24B Jnury 24, 22 Viktor Grigoryn 5 Convergence of Fourier series Strting from the method of seprtion of vribes for the homogeneous Dirichet nd Neumnn boundry vue probems, we studied the eigenvue probem
Mth 24B Jnury 24, 22 Viktor Grigoryn 5 Convergence of Fourier series Strting from the method of seprtion of vribes for the homogeneous Dirichet nd Neumnn boundry vue probems, we studied the eigenvue probem
1. The vibrating string problem revisited.
 Weeks 7 8: S eprtion of Vribes In the pst few weeks we hve expored the possibiity of soving first nd second order PDEs by trnsforming them into simper forms ( method of chrcteristics. Unfortuntey, this
Weeks 7 8: S eprtion of Vribes In the pst few weeks we hve expored the possibiity of soving first nd second order PDEs by trnsforming them into simper forms ( method of chrcteristics. Unfortuntey, this
Section 10.2 Angles and Triangles
 117 Ojective #1: Section 10.2 nges n Tringes Unerstning efinitions of ifferent types of nges. In the intersection of two ines, the nges tht re cttycorner fro ech other re vertic nges. Vertic nges wi hve
117 Ojective #1: Section 10.2 nges n Tringes Unerstning efinitions of ifferent types of nges. In the intersection of two ines, the nges tht re cttycorner fro ech other re vertic nges. Vertic nges wi hve
Fourier Series in Complex notation. cos(x) = eix + e ix 2. A n cos + B n sin l. i 2 B n. e inx=l + A n + ib n 2 8. ( 0 m 6= n. C n = 1 2l.
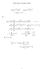 Fourier Series in Compex nottion sin(x) = eix e ix i = i eix e ix cos(x) = eix + e ix So So '(x) = A 1 0 + nx nx A n cos + B n sin = A 1 0 + e inx= + e inx= A n = A 0 + 1 = C n = C n 1 n= 1 A n ib n C
Fourier Series in Compex nottion sin(x) = eix e ix i = i eix e ix cos(x) = eix + e ix So So '(x) = A 1 0 + nx nx A n cos + B n sin = A 1 0 + e inx= + e inx= A n = A 0 + 1 = C n = C n 1 n= 1 A n ib n C
Lecture 6 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory I Dr. Christopher S. Baird University of Massachusetts Lowell
 Lecture 6 Notes, Eectrognetic Theory I Dr. Christopher S. Bird University of Msschusetts Lowe. Associted Legendre Poynois - We now return to soving the Lpce eqution in spheric coordintes when there is
Lecture 6 Notes, Eectrognetic Theory I Dr. Christopher S. Bird University of Msschusetts Lowe. Associted Legendre Poynois - We now return to soving the Lpce eqution in spheric coordintes when there is
Homework Assignment 5 Solution Set
 Homework Assignment 5 Solution Set PHYCS 44 3 Februry, 4 Problem Griffiths 3.8 The first imge chrge gurntees potentil of zero on the surfce. The secon imge chrge won t chnge the contribution to the potentil
Homework Assignment 5 Solution Set PHYCS 44 3 Februry, 4 Problem Griffiths 3.8 The first imge chrge gurntees potentil of zero on the surfce. The secon imge chrge won t chnge the contribution to the potentil
Statistical Physics. Solutions Sheet 5.
 Sttistic Physics. Soutions Sheet 5. Exercise. HS 04 Prof. Mnfred Sigrist Ide fermionic quntum gs in hrmonic trp In this exercise we study the fermionic spiness ide gs confined in three-dimension hrmonic
Sttistic Physics. Soutions Sheet 5. Exercise. HS 04 Prof. Mnfred Sigrist Ide fermionic quntum gs in hrmonic trp In this exercise we study the fermionic spiness ide gs confined in three-dimension hrmonic
Math 211A Homework. Edward Burkard. = tan (2x + z)
 Mth A Homework Ewr Burkr Eercises 5-C Eercise 8 Show tht the utonomous system: 5 Plne Autonomous Systems = e sin 3y + sin cos + e z, y = sin ( + 3y, z = tn ( + z hs n unstble criticl point t = y = z =
Mth A Homework Ewr Burkr Eercises 5-C Eercise 8 Show tht the utonomous system: 5 Plne Autonomous Systems = e sin 3y + sin cos + e z, y = sin ( + 3y, z = tn ( + z hs n unstble criticl point t = y = z =
LECTURE 3. Orthogonal Functions. n X. It should be noted, however, that the vectors f i need not be orthogonal nor need they have unit length for
 ECTURE 3 Orthogonl Functions 1. Orthogonl Bses The pproprite setting for our iscussion of orthogonl functions is tht of liner lgebr. So let me recll some relevnt fcts bout nite imensionl vector spces.
ECTURE 3 Orthogonl Functions 1. Orthogonl Bses The pproprite setting for our iscussion of orthogonl functions is tht of liner lgebr. So let me recll some relevnt fcts bout nite imensionl vector spces.
Chapter Five - Eigenvalues, Eigenfunctions, and All That
 Chpter Five - Eigenvlues, Eigenfunctions, n All Tht The prtil ifferentil eqution methos escrie in the previous chpter is specil cse of more generl setting in which we hve n eqution of the form L 1 xux,tl
Chpter Five - Eigenvlues, Eigenfunctions, n All Tht The prtil ifferentil eqution methos escrie in the previous chpter is specil cse of more generl setting in which we hve n eqution of the form L 1 xux,tl
Basic Derivative Properties
 Bsic Derivtive Properties Let s strt this section by remining ourselves tht the erivtive is the slope of function Wht is the slope of constnt function? c FACT 2 Let f () =c, where c is constnt Then f 0
Bsic Derivtive Properties Let s strt this section by remining ourselves tht the erivtive is the slope of function Wht is the slope of constnt function? c FACT 2 Let f () =c, where c is constnt Then f 0
5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 CHAPTER 5. THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL 35 5.3 The Funmentl Theorem of Clculus Emple. Let f(t) t +. () Fin the re of the region below f(t), bove the t-is, n between t n t. (You my wnt to look up the re formul
CHAPTER 5. THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL 35 5.3 The Funmentl Theorem of Clculus Emple. Let f(t) t +. () Fin the re of the region below f(t), bove the t-is, n between t n t. (You my wnt to look up the re formul
Suggested Solution to Assignment 5
 MATH 4 (5-6) prti diferenti equtions Suggested Soution to Assignment 5 Exercise 5.. () (b) A m = A m = = ( )m+ mπ x sin mπx dx = x mπ cos mπx + + 4( )m 4 m π. 4x cos mπx dx mπ x cos mπxdx = x mπ sin mπx
MATH 4 (5-6) prti diferenti equtions Suggested Soution to Assignment 5 Exercise 5.. () (b) A m = A m = = ( )m+ mπ x sin mπx dx = x mπ cos mπx + + 4( )m 4 m π. 4x cos mπx dx mπ x cos mπxdx = x mπ sin mπx
Summary: Method of Separation of Variables
 Physics 246 Electricity nd Mgnetism I, Fll 26, Lecture 22 1 Summry: Method of Seprtion of Vribles 1. Seprtion of Vribles in Crtesin Coordintes 2. Fourier Series Suggested Reding: Griffiths: Chpter 3, Section
Physics 246 Electricity nd Mgnetism I, Fll 26, Lecture 22 1 Summry: Method of Seprtion of Vribles 1. Seprtion of Vribles in Crtesin Coordintes 2. Fourier Series Suggested Reding: Griffiths: Chpter 3, Section
V. More General Eigenfunction Series. A. The Sturm-Liouville Family of Problems
 V. More Gener Eigenfunction Series c 214, Phiip D. Loewen A. The Sturm-Liouvie Fmiy of Probems Given n re interv, b], functions p(x), q(x), r(x), nd constnts c, c 1, d, d 1, consider (ODE) (p(x)y (x))
V. More Gener Eigenfunction Series c 214, Phiip D. Loewen A. The Sturm-Liouvie Fmiy of Probems Given n re interv, b], functions p(x), q(x), r(x), nd constnts c, c 1, d, d 1, consider (ODE) (p(x)y (x))
Notes on the Eigenfunction Method for solving differential equations
 Notes on the Eigenfunction Metho for solving ifferentil equtions Reminer: Wereconsieringtheinfinite-imensionlHilbertspceL 2 ([, b] of ll squre-integrble functions over the intervl [, b] (ie, b f(x 2
Notes on the Eigenfunction Metho for solving ifferentil equtions Reminer: Wereconsieringtheinfinite-imensionlHilbertspceL 2 ([, b] of ll squre-integrble functions over the intervl [, b] (ie, b f(x 2
f a L Most reasonable functions are continuous, as seen in the following theorem:
 Limits Suppose f : R R. To sy lim f(x) = L x mens tht s x gets closer n closer to, then f(x) gets closer n closer to L. This suggests tht the grph of f looks like one of the following three pictures: f
Limits Suppose f : R R. To sy lim f(x) = L x mens tht s x gets closer n closer to, then f(x) gets closer n closer to L. This suggests tht the grph of f looks like one of the following three pictures: f
A REVIEW OF CALCULUS CONCEPTS FOR JDEP 384H. Thomas Shores Department of Mathematics University of Nebraska Spring 2007
 A REVIEW OF CALCULUS CONCEPTS FOR JDEP 384H Thoms Shores Deprtment of Mthemtics University of Nebrsk Spring 2007 Contents Rtes of Chnge nd Derivtives 1 Dierentils 4 Are nd Integrls 5 Multivrite Clculus
A REVIEW OF CALCULUS CONCEPTS FOR JDEP 384H Thoms Shores Deprtment of Mthemtics University of Nebrsk Spring 2007 Contents Rtes of Chnge nd Derivtives 1 Dierentils 4 Are nd Integrls 5 Multivrite Clculus
x dx does exist, what does the answer look like? What does the answer to
 Review Guie or MAT Finl Em Prt II. Mony Decemer th 8:.m. 9:5.m. (or the 8:3.m. clss) :.m. :5.m. (or the :3.m. clss) Prt is worth 5% o your Finl Em gre. NO CALCULATORS re llowe on this portion o the Finl
Review Guie or MAT Finl Em Prt II. Mony Decemer th 8:.m. 9:5.m. (or the 8:3.m. clss) :.m. :5.m. (or the :3.m. clss) Prt is worth 5% o your Finl Em gre. NO CALCULATORS re llowe on this portion o the Finl
Homework Assignment #5 Solutions
 Physics 506 Winter 008 Textbook probems: Ch. 9: 9., 9., 9.4 Ch. 10: 10.1 Homework Assignment #5 Soutions 9. A spheric hoe of rdius in conducting medium cn serve s n eectromgnetic resonnt cvity. Assuming
Physics 506 Winter 008 Textbook probems: Ch. 9: 9., 9., 9.4 Ch. 10: 10.1 Homework Assignment #5 Soutions 9. A spheric hoe of rdius in conducting medium cn serve s n eectromgnetic resonnt cvity. Assuming
Fourier Series. with the period 2π, given that sin nx and cos nx are period functions with the period 2π. Then we.
 . Definition We c the trigonometric series the series of the form + cos x+ b sin x+ cos x+ b sin x+ or more briefy + ( ncos nx+ bnsin nx) () n The constnts, n nd b, n ( n,, ) re coefficients of the series
. Definition We c the trigonometric series the series of the form + cos x+ b sin x+ cos x+ b sin x+ or more briefy + ( ncos nx+ bnsin nx) () n The constnts, n nd b, n ( n,, ) re coefficients of the series
f(x) dx, If one of these two conditions is not met, we call the integral improper. Our usual definition for the value for the definite integral
 Improper Integrls Every time tht we hve evluted definite integrl such s f(x) dx, we hve mde two implicit ssumptions bout the integrl:. The intervl [, b] is finite, nd. f(x) is continuous on [, b]. If one
Improper Integrls Every time tht we hve evluted definite integrl such s f(x) dx, we hve mde two implicit ssumptions bout the integrl:. The intervl [, b] is finite, nd. f(x) is continuous on [, b]. If one
Improper Integrals. Type I Improper Integrals How do we evaluate an integral such as
 Improper Integrls Two different types of integrls cn qulify s improper. The first type of improper integrl (which we will refer to s Type I) involves evluting n integrl over n infinite region. In the grph
Improper Integrls Two different types of integrls cn qulify s improper. The first type of improper integrl (which we will refer to s Type I) involves evluting n integrl over n infinite region. In the grph
Before we can begin Ch. 3 on Radicals, we need to be familiar with perfect squares, cubes, etc. Try and do as many as you can without a calculator!!!
 Nme: Algebr II Honors Pre-Chpter Homework Before we cn begin Ch on Rdicls, we need to be fmilir with perfect squres, cubes, etc Try nd do s mny s you cn without clcultor!!! n The nth root of n n Be ble
Nme: Algebr II Honors Pre-Chpter Homework Before we cn begin Ch on Rdicls, we need to be fmilir with perfect squres, cubes, etc Try nd do s mny s you cn without clcultor!!! n The nth root of n n Be ble
Fluid Flow through a Tube
 . Theory through Tube In this experiment we wi determine how we physic retionship (so ced w ), nmey Poiseue s eqution, ppies. In the suppementry reding mteri this eqution ws derived s p Q 8 where Q is
. Theory through Tube In this experiment we wi determine how we physic retionship (so ced w ), nmey Poiseue s eqution, ppies. In the suppementry reding mteri this eqution ws derived s p Q 8 where Q is
Physics 116C Solution of inhomogeneous ordinary differential equations using Green s functions
 Physics 6C Solution of inhomogeneous ordinry differentil equtions using Green s functions Peter Young November 5, 29 Homogeneous Equtions We hve studied, especilly in long HW problem, second order liner
Physics 6C Solution of inhomogeneous ordinry differentil equtions using Green s functions Peter Young November 5, 29 Homogeneous Equtions We hve studied, especilly in long HW problem, second order liner
sec x over the interval (, ). x ) dx dx x 14. Use a graphing utility to generate some representative integral curves of the function Curve on 5
 Curve on Clcultor eperience Fin n ownlo (or type in) progrm on your clcultor tht will fin the re uner curve using given number of rectngles. Mke sure tht the progrm fins LRAM, RRAM, n MRAM. (You nee to
Curve on Clcultor eperience Fin n ownlo (or type in) progrm on your clcultor tht will fin the re uner curve using given number of rectngles. Mke sure tht the progrm fins LRAM, RRAM, n MRAM. (You nee to
Coordinate Geometry. Coordinate Geometry. Curriculum Ready ACMNA: 178, 214, 294.
 Coordinte Geometr Coordinte Geometr Curricuum Red ACMNA: 78, 4, 94 www.mthetics.com Coordinte COORDINATE Geometr GEOMETRY Shpes ou ve seen in geometr re put onto es nd nsed using gebr. Epect bit of both
Coordinte Geometr Coordinte Geometr Curricuum Red ACMNA: 78, 4, 94 www.mthetics.com Coordinte COORDINATE Geometr GEOMETRY Shpes ou ve seen in geometr re put onto es nd nsed using gebr. Epect bit of both
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 2, The Evaluation Part
 AP Clculus AB 6.4 Funmentl Theorem of Clculus The Funmentl Theorem of Clculus hs two prts. These two prts tie together the concept of integrtion n ifferentition n is regre by some to by the most importnt
AP Clculus AB 6.4 Funmentl Theorem of Clculus The Funmentl Theorem of Clculus hs two prts. These two prts tie together the concept of integrtion n ifferentition n is regre by some to by the most importnt
B Veitch. Calculus I Study Guide
 Clculus I Stuy Guie This stuy guie is in no wy exhustive. As stte in clss, ny type of question from clss, quizzes, exms, n homeworks re fir gme. There s no informtion here bout the wor problems. 1. Some
Clculus I Stuy Guie This stuy guie is in no wy exhustive. As stte in clss, ny type of question from clss, quizzes, exms, n homeworks re fir gme. There s no informtion here bout the wor problems. 1. Some
In this appendix, we evaluate the derivative of Eq. 9 in the main text, i.e., we need to calculate
 Supporting Tet Evoution of the Averge Synptic Updte Rue In this ppendi e evute the derivtive of Eq. 9 in the min tet i.e. e need to ccute Py ( ) Py ( Y ) og γ og. [] P( y Y ) P% ( y Y ) Before e strt et
Supporting Tet Evoution of the Averge Synptic Updte Rue In this ppendi e evute the derivtive of Eq. 9 in the min tet i.e. e need to ccute Py ( ) Py ( Y ) og γ og. [] P( y Y ) P% ( y Y ) Before e strt et
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 5 Jun 2015
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 5 Jun 2015 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 5 Jun 2015](/thumbs/78/77492077.jpg) First non-trivi upper bound on the circur chromtic number of the pne. Konstnty Junosz-Szniwski, Fcuty of Mthemtics nd Informtion Science, Wrsw University of Technoogy, Pond Abstrct rxiv:1506.01886v1 [mth.co]
First non-trivi upper bound on the circur chromtic number of the pne. Konstnty Junosz-Szniwski, Fcuty of Mthemtics nd Informtion Science, Wrsw University of Technoogy, Pond Abstrct rxiv:1506.01886v1 [mth.co]
Linear Systems COS 323
 Liner Systems COS 33 Soving Liner Systems of Equtions Define iner system Singurities in iner systems Gussin Eimintion: A gener purpose method Nïve Guss Guss with pivoting Asymptotic nysis Tringur systems
Liner Systems COS 33 Soving Liner Systems of Equtions Define iner system Singurities in iner systems Gussin Eimintion: A gener purpose method Nïve Guss Guss with pivoting Asymptotic nysis Tringur systems
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE
 SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
Infinite Geometric Series
 Infinite Geometric Series Finite Geometric Series ( finite SUM) Let 0 < r < 1, nd let n be positive integer. Consider the finite sum It turns out there is simple lgebric expression tht is equivlent to
Infinite Geometric Series Finite Geometric Series ( finite SUM) Let 0 < r < 1, nd let n be positive integer. Consider the finite sum It turns out there is simple lgebric expression tht is equivlent to
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON THE CONNECTION FORMULAE FOR THE SEMICLASSICAL APPROXIMATION
 Physics 8.06 Apr, 2008 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON THE CONNECTION FORMULAE FOR THE SEMICLASSICAL APPROXIMATION c R. L. Jffe 2002 The WKB connection formuls llow one to continue semiclssicl solutions from n
Physics 8.06 Apr, 2008 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON THE CONNECTION FORMULAE FOR THE SEMICLASSICAL APPROXIMATION c R. L. Jffe 2002 The WKB connection formuls llow one to continue semiclssicl solutions from n
Conservation Laws and Poynting
 Chpter 11 Conservtion Lws n Poynting Vector In electrosttics n mgnetosttics one ssocites n energy ensity to the presence of the fiels U = 1 2 E2 + 1 2 B2 = (electric n mgnetic energy)/volume (11.1) In
Chpter 11 Conservtion Lws n Poynting Vector In electrosttics n mgnetosttics one ssocites n energy ensity to the presence of the fiels U = 1 2 E2 + 1 2 B2 = (electric n mgnetic energy)/volume (11.1) In
Math 142: Final Exam Formulas to Know
 Mth 4: Finl Exm Formuls to Know This ocument tells you every formul/strtegy tht you shoul know in orer to o well on your finl. Stuy it well! The helpful rules/formuls from the vrious review sheets my be
Mth 4: Finl Exm Formuls to Know This ocument tells you every formul/strtegy tht you shoul know in orer to o well on your finl. Stuy it well! The helpful rules/formuls from the vrious review sheets my be
APPENDIX. Precalculus Review D.1. Real Numbers and the Real Number Line
 APPENDIX D Preclculus Review APPENDIX D.1 Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Orer n Inequlities Asolute Vlue n Distnce Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel numers cn e represente
APPENDIX D Preclculus Review APPENDIX D.1 Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Orer n Inequlities Asolute Vlue n Distnce Rel Numers n the Rel Numer Line Rel numers cn e represente
Improper Integrals, and Differential Equations
 Improper Integrls, nd Differentil Equtions October 22, 204 5.3 Improper Integrls Previously, we discussed how integrls correspond to res. More specificlly, we sid tht for function f(x), the region creted
Improper Integrls, nd Differentil Equtions October 22, 204 5.3 Improper Integrls Previously, we discussed how integrls correspond to res. More specificlly, we sid tht for function f(x), the region creted
Homework Problem Set 1 Solutions
 Chemistry 460 Dr. Jen M. Stnr Homework Problem Set 1 Solutions 1. Determine the outcomes of operting the following opertors on the functions liste. In these functions, is constnt..) opertor: / ; function:
Chemistry 460 Dr. Jen M. Stnr Homework Problem Set 1 Solutions 1. Determine the outcomes of operting the following opertors on the functions liste. In these functions, is constnt..) opertor: / ; function:
Sturm-Liouville Theory
 LECTURE 1 Sturm-Liouville Theory In the two preceing lectures I emonstrte the utility of Fourier series in solving PDE/BVPs. As we ll now see, Fourier series re just the tip of the iceerg of the theory
LECTURE 1 Sturm-Liouville Theory In the two preceing lectures I emonstrte the utility of Fourier series in solving PDE/BVPs. As we ll now see, Fourier series re just the tip of the iceerg of the theory
p(t) dt + i 1 re it ireit dt =
 Note: This mteril is contined in Kreyszig, Chpter 13. Complex integrtion We will define integrls of complex functions long curves in C. (This is bit similr to [relvlued] line integrls P dx + Q dy in R2.)
Note: This mteril is contined in Kreyszig, Chpter 13. Complex integrtion We will define integrls of complex functions long curves in C. (This is bit similr to [relvlued] line integrls P dx + Q dy in R2.)
x ) dx dx x sec x over the interval (, ).
 Curve on 6 For -, () Evlute the integrl, n (b) check your nswer by ifferentiting. ( ). ( ). ( ).. 6. sin cos 7. sec csccot 8. sec (sec tn ) 9. sin csc. Evlute the integrl sin by multiplying the numertor
Curve on 6 For -, () Evlute the integrl, n (b) check your nswer by ifferentiting. ( ). ( ). ( ).. 6. sin cos 7. sec csccot 8. sec (sec tn ) 9. sin csc. Evlute the integrl sin by multiplying the numertor
Lecture 13 - Linking E, ϕ, and ρ
 Lecture 13 - Linking E, ϕ, nd ρ A Puzzle... Inner-Surfce Chrge Density A positive point chrge q is locted off-center inside neutrl conducting sphericl shell. We know from Guss s lw tht the totl chrge on
Lecture 13 - Linking E, ϕ, nd ρ A Puzzle... Inner-Surfce Chrge Density A positive point chrge q is locted off-center inside neutrl conducting sphericl shell. We know from Guss s lw tht the totl chrge on
5.2 Exponent Properties Involving Quotients
 5. Eponent Properties Involving Quotients Lerning Objectives Use the quotient of powers property. Use the power of quotient property. Simplify epressions involving quotient properties of eponents. Use
5. Eponent Properties Involving Quotients Lerning Objectives Use the quotient of powers property. Use the power of quotient property. Simplify epressions involving quotient properties of eponents. Use
Problem Set 2 Solutions
 Chemistry 362 Dr. Jen M. Stnr Problem Set 2 Solutions 1. Determine the outcomes of operting the following opertors on the functions liste. In these functions, is constnt.).) opertor: /x ; function: x e
Chemistry 362 Dr. Jen M. Stnr Problem Set 2 Solutions 1. Determine the outcomes of operting the following opertors on the functions liste. In these functions, is constnt.).) opertor: /x ; function: x e
Chapter 0. What is the Lebesgue integral about?
 Chpter 0. Wht is the Lebesgue integrl bout? The pln is to hve tutoril sheet ech week, most often on Fridy, (to be done during the clss) where you will try to get used to the ides introduced in the previous
Chpter 0. Wht is the Lebesgue integrl bout? The pln is to hve tutoril sheet ech week, most often on Fridy, (to be done during the clss) where you will try to get used to the ides introduced in the previous
Orthogonal functions
 Orthogonl functions Given rel vrible over the intervl (, b nd set of rel or complex functions U n (ξ, n =, 2,..., which re squre integrble nd orthonorml b U n(ξu m (ξdξ = δ n,m ( if the set of of functions
Orthogonl functions Given rel vrible over the intervl (, b nd set of rel or complex functions U n (ξ, n =, 2,..., which re squre integrble nd orthonorml b U n(ξu m (ξdξ = δ n,m ( if the set of of functions
AQA Further Pure 1. Complex Numbers. Section 1: Introduction to Complex Numbers. The number system
 Complex Numbers Section 1: Introduction to Complex Numbers Notes nd Exmples These notes contin subsections on The number system Adding nd subtrcting complex numbers Multiplying complex numbers Complex
Complex Numbers Section 1: Introduction to Complex Numbers Notes nd Exmples These notes contin subsections on The number system Adding nd subtrcting complex numbers Multiplying complex numbers Complex
M 106 Integral Calculus and Applications
 M 6 Integrl Clculus n Applictions Contents The Inefinite Integrls.................................................... Antierivtives n Inefinite Integrls.. Antierivtives.............................................................
M 6 Integrl Clculus n Applictions Contents The Inefinite Integrls.................................................... Antierivtives n Inefinite Integrls.. Antierivtives.............................................................
Introduction to statically indeterminate structures
 Sttics of Buiding Structures I., EASUS Introduction to stticy indeterminte structures Deprtment of Structur echnics Fcuty of Civi Engineering, VŠB-Technic University of Ostrv Outine of Lecture Stticy indeterminte
Sttics of Buiding Structures I., EASUS Introduction to stticy indeterminte structures Deprtment of Structur echnics Fcuty of Civi Engineering, VŠB-Technic University of Ostrv Outine of Lecture Stticy indeterminte
Conservation Law. Chapter Goal. 6.2 Theory
 Chpter 6 Conservtion Lw 6.1 Gol Our long term gol is to unerstn how mthemticl moels re erive. Here, we will stuy how certin quntity chnges with time in given region (sptil omin). We then first erive the
Chpter 6 Conservtion Lw 6.1 Gol Our long term gol is to unerstn how mthemticl moels re erive. Here, we will stuy how certin quntity chnges with time in given region (sptil omin). We then first erive the
MA Lesson 21 Notes
 MA 000 Lesson 1 Notes ( 5) How would person solve n eqution with vrible in n eponent, such s 9? (We cnnot re-write this eqution esil with the sme bse.) A nottion ws developed so tht equtions such s this
MA 000 Lesson 1 Notes ( 5) How would person solve n eqution with vrible in n eponent, such s 9? (We cnnot re-write this eqution esil with the sme bse.) A nottion ws developed so tht equtions such s this
Riemann Sums and Riemann Integrals
 Riemnn Sums nd Riemnn Integrls Jmes K. Peterson Deprtment of Biologicl Sciences nd Deprtment of Mthemticl Sciences Clemson University August 26, 2013 Outline 1 Riemnn Sums 2 Riemnn Integrls 3 Properties
Riemnn Sums nd Riemnn Integrls Jmes K. Peterson Deprtment of Biologicl Sciences nd Deprtment of Mthemticl Sciences Clemson University August 26, 2013 Outline 1 Riemnn Sums 2 Riemnn Integrls 3 Properties
Chapter 28. Fourier Series An Eigenvalue Problem.
 Chpter 28 Fourier Series Every time I close my eyes The noise inside me mplifies I cn t escpe I relive every moment of the dy Every misstep I hve mde Finds wy it cn invde My every thought And this is why
Chpter 28 Fourier Series Every time I close my eyes The noise inside me mplifies I cn t escpe I relive every moment of the dy Every misstep I hve mde Finds wy it cn invde My every thought And this is why
lim P(t a,b) = Differentiate (1) and use the definition of the probability current, j = i (
 PHYS851 Quntum Mechnics I, Fll 2009 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 7 1. The continuity eqution: The probbility tht prticle of mss m lies on the intervl [,b] t time t is Pt,b b x ψx,t 2 1 Differentite 1 n use the
PHYS851 Quntum Mechnics I, Fll 2009 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 7 1. The continuity eqution: The probbility tht prticle of mss m lies on the intervl [,b] t time t is Pt,b b x ψx,t 2 1 Differentite 1 n use the
MATH34032: Green s Functions, Integral Equations and the Calculus of Variations 1
 MATH34032: Green s Functions, Integrl Equtions nd the Clculus of Vritions 1 Section 1 Function spces nd opertors Here we gives some brief detils nd definitions, prticulrly relting to opertors. For further
MATH34032: Green s Functions, Integrl Equtions nd the Clculus of Vritions 1 Section 1 Function spces nd opertors Here we gives some brief detils nd definitions, prticulrly relting to opertors. For further
20 MATHEMATICS POLYNOMIALS
 0 MATHEMATICS POLYNOMIALS.1 Introduction In Clss IX, you hve studied polynomils in one vrible nd their degrees. Recll tht if p(x) is polynomil in x, the highest power of x in p(x) is clled the degree of
0 MATHEMATICS POLYNOMIALS.1 Introduction In Clss IX, you hve studied polynomils in one vrible nd their degrees. Recll tht if p(x) is polynomil in x, the highest power of x in p(x) is clled the degree of
Bernoulli Numbers Jeff Morton
 Bernoulli Numbers Jeff Morton. We re interested in the opertor e t k d k t k, which is to sy k tk. Applying this to some function f E to get e t f d k k tk d k f f + d k k tk dk f, we note tht since f
Bernoulli Numbers Jeff Morton. We re interested in the opertor e t k d k t k, which is to sy k tk. Applying this to some function f E to get e t f d k k tk d k f f + d k k tk dk f, we note tht since f
Riemann Sums and Riemann Integrals
 Riemnn Sums nd Riemnn Integrls Jmes K. Peterson Deprtment of Biologicl Sciences nd Deprtment of Mthemticl Sciences Clemson University August 26, 203 Outline Riemnn Sums Riemnn Integrls Properties Abstrct
Riemnn Sums nd Riemnn Integrls Jmes K. Peterson Deprtment of Biologicl Sciences nd Deprtment of Mthemticl Sciences Clemson University August 26, 203 Outline Riemnn Sums Riemnn Integrls Properties Abstrct
c n φ n (x), 0 < x < L, (1) n=1
 SECTION : Fourier Series. MATH4. In section 4, we will study method clled Seprtion of Vribles for finding exct solutions to certin clss of prtil differentil equtions (PDEs. To do this, it will be necessry
SECTION : Fourier Series. MATH4. In section 4, we will study method clled Seprtion of Vribles for finding exct solutions to certin clss of prtil differentil equtions (PDEs. To do this, it will be necessry
MA 124 January 18, Derivatives are. Integrals are.
 MA 124 Jnury 18, 2018 Prof PB s one-minute introduction to clculus Derivtives re. Integrls re. In Clculus 1, we lern limits, derivtives, some pplictions of derivtives, indefinite integrls, definite integrls,
MA 124 Jnury 18, 2018 Prof PB s one-minute introduction to clculus Derivtives re. Integrls re. In Clculus 1, we lern limits, derivtives, some pplictions of derivtives, indefinite integrls, definite integrls,
Chapter 1 - Functions and Variables
 Business Clculus 1 Chpter 1 - Functions nd Vribles This Acdemic Review is brought to you free of chrge by preptests4u.com. Any sle or trde of this review is strictly prohibited. Business Clculus 1 Ch 1:
Business Clculus 1 Chpter 1 - Functions nd Vribles This Acdemic Review is brought to you free of chrge by preptests4u.com. Any sle or trde of this review is strictly prohibited. Business Clculus 1 Ch 1:
ENGI 9420 Lecture Notes 7 - Fourier Series Page 7.01
 ENGI 940 ecture Notes 7 - Fourier Series Pge 7.0 7. Fourier Series nd Fourier Trnsforms Fourier series hve multiple purposes, including the provision of series solutions to some liner prtil differentil
ENGI 940 ecture Notes 7 - Fourier Series Pge 7.0 7. Fourier Series nd Fourier Trnsforms Fourier series hve multiple purposes, including the provision of series solutions to some liner prtil differentil
Exam 2, Mathematics 4701, Section ETY6 6:05 pm 7:40 pm, March 31, 2016, IH-1105 Instructor: Attila Máté 1
 Exm, Mthemtics 471, Section ETY6 6:5 pm 7:4 pm, Mrch 1, 16, IH-115 Instructor: Attil Máté 1 17 copies 1. ) Stte the usul sufficient condition for the fixed-point itertion to converge when solving the eqution
Exm, Mthemtics 471, Section ETY6 6:5 pm 7:4 pm, Mrch 1, 16, IH-115 Instructor: Attil Máté 1 17 copies 1. ) Stte the usul sufficient condition for the fixed-point itertion to converge when solving the eqution
How do we solve these things, especially when they get complicated? How do we know when a system has a solution, and when is it unique?
 XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk bout solving systems of liner equtions. These re problems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6 2 3 7 4
XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk bout solving systems of liner equtions. These re problems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6 2 3 7 4
ax bx c (2) x a x a x a 1! 2!! gives a useful way of approximating a function near to some specific point x a, giving a power-series expansion in x
 Elementr mthemticl epressions Qurtic equtions b b b The solutions to the generl qurtic eqution re (1) b c () b b 4c (3) Tlor n Mclurin series (power-series epnsion) The Tlor series n n f f f n 1!! n! f
Elementr mthemticl epressions Qurtic equtions b b b The solutions to the generl qurtic eqution re (1) b c () b b 4c (3) Tlor n Mclurin series (power-series epnsion) The Tlor series n n f f f n 1!! n! f
CHAPTER 9 BASIC CONCEPTS OF DIFFERENTIAL AND INTEGRAL CALCULUS
 CHAPTER 9 BASIC CONCEPTS OF DIFFERENTIAL AND INTEGRAL CALCULUS BASIC CONCEPTS OF DIFFERENTIAL AND INTEGRAL CALCULUS LEARNING OBJECTIVES After stuying this chpter, you will be ble to: Unerstn the bsics
CHAPTER 9 BASIC CONCEPTS OF DIFFERENTIAL AND INTEGRAL CALCULUS BASIC CONCEPTS OF DIFFERENTIAL AND INTEGRAL CALCULUS LEARNING OBJECTIVES After stuying this chpter, you will be ble to: Unerstn the bsics
If we have a function f(x) which is well-defined for some a x b, its integral over those two values is defined as
 Y. D. Chong (26) MH28: Complex Methos for the Sciences 2. Integrls If we hve function f(x) which is well-efine for some x, its integrl over those two vlues is efine s N ( ) f(x) = lim x f(x n ) where x
Y. D. Chong (26) MH28: Complex Methos for the Sciences 2. Integrls If we hve function f(x) which is well-efine for some x, its integrl over those two vlues is efine s N ( ) f(x) = lim x f(x n ) where x
Theoretical foundations of Gaussian quadrature
 Theoreticl foundtions of Gussin qudrture 1 Inner product vector spce Definition 1. A vector spce (or liner spce) is set V = {u, v, w,...} in which the following two opertions re defined: (A) Addition of
Theoreticl foundtions of Gussin qudrture 1 Inner product vector spce Definition 1. A vector spce (or liner spce) is set V = {u, v, w,...} in which the following two opertions re defined: (A) Addition of
Exponentials - Grade 10 [CAPS] *
![Exponentials - Grade 10 [CAPS] * Exponentials - Grade 10 [CAPS] *](/thumbs/88/115984632.jpg) OpenStx-CNX module: m859 Exponentils - Grde 0 [CAPS] * Free High School Science Texts Project Bsed on Exponentils by Rory Adms Free High School Science Texts Project Mrk Horner Hether Willims This work
OpenStx-CNX module: m859 Exponentils - Grde 0 [CAPS] * Free High School Science Texts Project Bsed on Exponentils by Rory Adms Free High School Science Texts Project Mrk Horner Hether Willims This work
EXPONENT. Section 2.1. Do you see a pattern? Do you see a pattern? Try a) ( ) b) ( ) c) ( ) d)
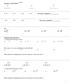 Section. EXPONENT RULES Do ou see pttern? Do ou see pttern? Tr ) ( ) b) ( ) c) ( ) d) Eponent rules strt here:. Epnd the following s bove. ) b) 7 c) d) How n 's re ou ultipling in ech proble? ) b) c) d)
Section. EXPONENT RULES Do ou see pttern? Do ou see pttern? Tr ) ( ) b) ( ) c) ( ) d) Eponent rules strt here:. Epnd the following s bove. ) b) 7 c) d) How n 's re ou ultipling in ech proble? ) b) c) d)
Main topics for the First Midterm
 Min topics for the First Midterm The Midterm will cover Section 1.8, Chpters 2-3, Sections 4.1-4.8, nd Sections 5.1-5.3 (essentilly ll of the mteril covered in clss). Be sure to know the results of the
Min topics for the First Midterm The Midterm will cover Section 1.8, Chpters 2-3, Sections 4.1-4.8, nd Sections 5.1-5.3 (essentilly ll of the mteril covered in clss). Be sure to know the results of the
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 M Dynmics - Dmped nd forced hrmonic motion. A P α B A ight estic spring hs ntur ength nd moduus of esticity mg. One end of the spring is ttched to point A on pne tht is incined to the horizont t n nge
M Dynmics - Dmped nd forced hrmonic motion. A P α B A ight estic spring hs ntur ength nd moduus of esticity mg. One end of the spring is ttched to point A on pne tht is incined to the horizont t n nge
Year 11 Matrices. A row of seats goes across an auditorium So Rows are horizontal. The columns of the Parthenon stand upright and Columns are vertical
 Yer 11 Mtrices Terminology: A single MATRIX (singulr) or Mny MATRICES (plurl) Chpter 3A Intro to Mtrices A mtrix is escribe s n orgnise rry of t. We escribe the ORDER of Mtrix (it's size) by noting how
Yer 11 Mtrices Terminology: A single MATRIX (singulr) or Mny MATRICES (plurl) Chpter 3A Intro to Mtrices A mtrix is escribe s n orgnise rry of t. We escribe the ORDER of Mtrix (it's size) by noting how
Linear Inequalities. Work Sheet 1
 Work Sheet 1 Liner Inequlities Rent--Hep, cr rentl compny,chrges $ 15 per week plus $ 0.0 per mile to rent one of their crs. Suppose you re limited y how much money you cn spend for the week : You cn spend
Work Sheet 1 Liner Inequlities Rent--Hep, cr rentl compny,chrges $ 15 per week plus $ 0.0 per mile to rent one of their crs. Suppose you re limited y how much money you cn spend for the week : You cn spend
Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration
 MA Techniques of Integrtion Asst.Prof.Dr.Suprnee Liswdi Chpter 6 Techniques of Integrtion Recll: Some importnt integrls tht we hve lernt so fr. Tle of Integrls n+ n d = + C n + e d = e + C ( n ) d = ln
MA Techniques of Integrtion Asst.Prof.Dr.Suprnee Liswdi Chpter 6 Techniques of Integrtion Recll: Some importnt integrls tht we hve lernt so fr. Tle of Integrls n+ n d = + C n + e d = e + C ( n ) d = ln
(4.1) D r v(t) ω(t, v(t))
 1.4. Differentil inequlities. Let D r denote the right hnd derivtive of function. If ω(t, u) is sclr function of the sclrs t, u in some open connected set Ω, we sy tht function v(t), t < b, is solution
1.4. Differentil inequlities. Let D r denote the right hnd derivtive of function. If ω(t, u) is sclr function of the sclrs t, u in some open connected set Ω, we sy tht function v(t), t < b, is solution
Abstract inner product spaces
 WEEK 4 Abstrct inner product spces Definition An inner product spce is vector spce V over the rel field R equipped with rule for multiplying vectors, such tht the product of two vectors is sclr, nd the
WEEK 4 Abstrct inner product spces Definition An inner product spce is vector spce V over the rel field R equipped with rule for multiplying vectors, such tht the product of two vectors is sclr, nd the
Physics 2135 Exam 1 September 23, 2014
 Exm Totl Physics 2135 Exm 1 September 23, 2014 Key Printe Nme: 200 / 200 N/A Rec. Sec. Letter: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points ech. Choose the best or most nerly correct nswer. B 1. Object A hs
Exm Totl Physics 2135 Exm 1 September 23, 2014 Key Printe Nme: 200 / 200 N/A Rec. Sec. Letter: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points ech. Choose the best or most nerly correct nswer. B 1. Object A hs
Best Approximation. Chapter The General Case
 Chpter 4 Best Approximtion 4.1 The Generl Cse In the previous chpter, we hve seen how n interpolting polynomil cn be used s n pproximtion to given function. We now wnt to find the best pproximtion to given
Chpter 4 Best Approximtion 4.1 The Generl Cse In the previous chpter, we hve seen how n interpolting polynomil cn be used s n pproximtion to given function. We now wnt to find the best pproximtion to given
A sequence is a list of numbers in a specific order. A series is a sum of the terms of a sequence.
 Core Module Revision Sheet The C exm is hour 30 minutes long nd is in two sections. Section A (36 mrks) 8 0 short questions worth no more thn 5 mrks ech. Section B (36 mrks) 3 questions worth mrks ech.
Core Module Revision Sheet The C exm is hour 30 minutes long nd is in two sections. Section A (36 mrks) 8 0 short questions worth no more thn 5 mrks ech. Section B (36 mrks) 3 questions worth mrks ech.
8 Laplace s Method and Local Limit Theorems
 8 Lplce s Method nd Locl Limit Theorems 8. Fourier Anlysis in Higher DImensions Most of the theorems of Fourier nlysis tht we hve proved hve nturl generliztions to higher dimensions, nd these cn be proved
8 Lplce s Method nd Locl Limit Theorems 8. Fourier Anlysis in Higher DImensions Most of the theorems of Fourier nlysis tht we hve proved hve nturl generliztions to higher dimensions, nd these cn be proved
The Regulated and Riemann Integrals
 Chpter 1 The Regulted nd Riemnn Integrls 1.1 Introduction We will consider severl different pproches to defining the definite integrl f(x) dx of function f(x). These definitions will ll ssign the sme vlue
Chpter 1 The Regulted nd Riemnn Integrls 1.1 Introduction We will consider severl different pproches to defining the definite integrl f(x) dx of function f(x). These definitions will ll ssign the sme vlue
Introduction and Review
 Chpter 6A Notes Pge of Introuction n Review Derivtives y = f(x) y x = f (x) Evlute erivtive t x = : y = x x= f f(+h) f() () = lim h h Geometric Interprettion: see figure slope of the line tngent to f t
Chpter 6A Notes Pge of Introuction n Review Derivtives y = f(x) y x = f (x) Evlute erivtive t x = : y = x x= f f(+h) f() () = lim h h Geometric Interprettion: see figure slope of the line tngent to f t
Integration. 148 Chapter 7 Integration
 48 Chpter 7 Integrtion 7 Integrtion t ech, by supposing tht during ech tenth of second the object is going t constnt speed Since the object initilly hs speed, we gin suppose it mintins this speed, but
48 Chpter 7 Integrtion 7 Integrtion t ech, by supposing tht during ech tenth of second the object is going t constnt speed Since the object initilly hs speed, we gin suppose it mintins this speed, but
Chapter 3 Polynomials
 Dr M DRAIEF As described in the introduction of Chpter 1, pplictions of solving liner equtions rise in number of different settings In prticulr, we will in this chpter focus on the problem of modelling
Dr M DRAIEF As described in the introduction of Chpter 1, pplictions of solving liner equtions rise in number of different settings In prticulr, we will in this chpter focus on the problem of modelling
New Expansion and Infinite Series
 Interntionl Mthemticl Forum, Vol. 9, 204, no. 22, 06-073 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikri.com http://dx.doi.org/0.2988/imf.204.4502 New Expnsion nd Infinite Series Diyun Zhng College of Computer Nnjing University
Interntionl Mthemticl Forum, Vol. 9, 204, no. 22, 06-073 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikri.com http://dx.doi.org/0.2988/imf.204.4502 New Expnsion nd Infinite Series Diyun Zhng College of Computer Nnjing University
Name Solutions to Test 3 November 8, 2017
 Nme Solutions to Test 3 November 8, 07 This test consists of three prts. Plese note tht in prts II nd III, you cn skip one question of those offered. Some possibly useful formuls cn be found below. Brrier
Nme Solutions to Test 3 November 8, 07 This test consists of three prts. Plese note tht in prts II nd III, you cn skip one question of those offered. Some possibly useful formuls cn be found below. Brrier
The area under the graph of f and above the x-axis between a and b is denoted by. f(x) dx. π O
 1 Section 5. The Definite Integrl Suppose tht function f is continuous nd positive over n intervl [, ]. y = f(x) x The re under the grph of f nd ove the x-xis etween nd is denoted y f(x) dx nd clled the
1 Section 5. The Definite Integrl Suppose tht function f is continuous nd positive over n intervl [, ]. y = f(x) x The re under the grph of f nd ove the x-xis etween nd is denoted y f(x) dx nd clled the
(0.0)(0.1)+(0.3)(0.1)+(0.6)(0.1)+ +(2.7)(0.1) = 1.35
 7 Integrtion º½ ÌÛÓ Ü ÑÔÐ Up to now we hve been concerned with extrcting informtion bout how function chnges from the function itself. Given knowledge bout n object s position, for exmple, we wnt to know
7 Integrtion º½ ÌÛÓ Ü ÑÔÐ Up to now we hve been concerned with extrcting informtion bout how function chnges from the function itself. Given knowledge bout n object s position, for exmple, we wnt to know
Math 1431 Section M TH 4:00 PM 6:00 PM Susan Wheeler Office Hours: Wed 6:00 7:00 PM Online ***NOTE LABS ARE MON AND WED
 Mth 43 Section 4839 M TH 4: PM 6: PM Susn Wheeler swheeler@mth.uh.edu Office Hours: Wed 6: 7: PM Online ***NOTE LABS ARE MON AND WED t :3 PM to 3: pm ONLINE Approimting the re under curve given the type
Mth 43 Section 4839 M TH 4: PM 6: PM Susn Wheeler swheeler@mth.uh.edu Office Hours: Wed 6: 7: PM Online ***NOTE LABS ARE MON AND WED t :3 PM to 3: pm ONLINE Approimting the re under curve given the type
ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS. The real numbers have the following properties: a b c ab ac
 REVIEW OF ALGEBRA Here we review the bsic rules nd procedures of lgebr tht you need to know in order to be successful in clculus. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS The rel numbers hve the following properties: b b
REVIEW OF ALGEBRA Here we review the bsic rules nd procedures of lgebr tht you need to know in order to be successful in clculus. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS The rel numbers hve the following properties: b b
Calculus of Variations
 Clculus of Vritions Com S 477/577 Notes) Yn-Bin Ji Dec 4, 2017 1 Introduction A functionl ssigns rel number to ech function or curve) in some clss. One might sy tht functionl is function of nother function
Clculus of Vritions Com S 477/577 Notes) Yn-Bin Ji Dec 4, 2017 1 Introduction A functionl ssigns rel number to ech function or curve) in some clss. One might sy tht functionl is function of nother function
UNIFORM CONVERGENCE. Contents 1. Uniform Convergence 1 2. Properties of uniform convergence 3
 UNIFORM CONVERGENCE Contents 1. Uniform Convergence 1 2. Properties of uniform convergence 3 Suppose f n : Ω R or f n : Ω C is sequence of rel or complex functions, nd f n f s n in some sense. Furthermore,
UNIFORM CONVERGENCE Contents 1. Uniform Convergence 1 2. Properties of uniform convergence 3 Suppose f n : Ω R or f n : Ω C is sequence of rel or complex functions, nd f n f s n in some sense. Furthermore,
ODE: Existence and Uniqueness of a Solution
 Mth 22 Fll 213 Jerry Kzdn ODE: Existence nd Uniqueness of Solution The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus tells us how to solve the ordinry differentil eqution (ODE) du = f(t) dt with initil condition u() =
Mth 22 Fll 213 Jerry Kzdn ODE: Existence nd Uniqueness of Solution The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus tells us how to solve the ordinry differentil eqution (ODE) du = f(t) dt with initil condition u() =
Jackson 2.7 Homework Problem Solution Dr. Christopher S. Baird University of Massachusetts Lowell
 Jckson.7 Homework Problem Solution Dr. Christopher S. Bird University of Msschusetts Lowell PROBLEM: Consider potentil problem in the hlf-spce defined by, with Dirichlet boundry conditions on the plne
Jckson.7 Homework Problem Solution Dr. Christopher S. Bird University of Msschusetts Lowell PROBLEM: Consider potentil problem in the hlf-spce defined by, with Dirichlet boundry conditions on the plne
The Dirac distribution
 A DIRAC DISTRIBUTION A The Dirc distribution A Definition of the Dirc distribution The Dirc distribution δx cn be introduced by three equivlent wys Dirc [] defined it by reltions δx dx, δx if x The distribution
A DIRAC DISTRIBUTION A The Dirc distribution A Definition of the Dirc distribution The Dirc distribution δx cn be introduced by three equivlent wys Dirc [] defined it by reltions δx dx, δx if x The distribution
