11. What is the change in the units of capacitance if we increase the units of I and V 200 times? A. Zero$ B. 200 times C. 400 times D.
|
|
|
- Marian White
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AE Electrical 1. Consider two coils having self inductance of 20 mh and 15 mh. If the effective inductance is 50 mh when connected in series aiding, what is the equivalent inductance when they are connected in series opposing? A. 20 mh$ B. 15mH C. 10mH 2. Which of the following is the reason for not using a Wheatstone bridge for precision measurement? A. Errors are introduced because of thermo-electric emfs B. Errors are introduced because of resistance of connecting leads C. Both A and B$ 3. Which of the following strategies can be used to increase the sensitivity of a potentiometer? A. Reducing the length of potentiometer wire B. Decreasing the current in the potentiometer wire$ C. Both A and B 4. what is the current through a DC voltmeter when it measures half full scale in the range of 100V, given that the voltmeter has a sensitivity of 1000 Ω/V A. 50 ma$ B. 100 ma C. 500 ma 5. Capacitive transducers are normally used for which of the following? A. Intermediate measurements B. Static measurements C. Dynamic measurement$ 6. Which of the following is true with thermocouples? A. They are a widely used as temperature sensor for measurement and control B. They can convert a temperature gradient into electricity C. Both A and B$ 7. Which of the following give the right order of their sensitivity (from highest to lowest) among the three types of temperature transducers? A. Thermistors, thermocouples, RTDs B. RTDs, Thermistors, thermocouples C. Thermistors, RTDs, thermocouples$ D. None of the above
2 8. What is the primary purpose of using bifilar winding in some of the wire-wound resisters? A. To reduce inductance of winding$ B. To increase inductance of winding C. To increase thermal stability 9. What is the change in the resistance of a metal strain gauge when it is exposed to a strain of 10-5? Assume that it has a strain factor of 2.5 and a nominal resistance of 150 ohms. A. 3.75x10-3 ohms$ B. 3.75x10-5 ohms C. 2.5 x 10-3 ohms 10. Which of the following differentiate thermistors from from resistance temperature detectors (RTDs)? A. Thermistors are generally made of ceramic or polymer, while RTDs use pure metals B. RTDs are useful over larger temperature ranges, while thermistors typically achieve a higher precision within a limited temperature range C. Both A and B$ 11. What is the change in the units of capacitance if we increase the units of I and V 200 times? A. Zero$ B. 200 times C. 400 times 12. A particular single phase energy meter operating 230 V, 50 Hz supply made 2760 revolutions in 3 hours with a load of 20 A. What is the meter constant? A. 100 B. 150 C. 200$ 13. The traditional analog wattmeter which consists of a pair of fixed coils, known as current coils, and a movable coil known as the potential coil belongs to which of the following types? A. Electrolytic instruments B. Electrodynamic instruments$ C. Potentiometer 14. What is the current required to deflect the meter movement to full scale if the sensitivity of the meter is Ω/V A. 40 µa$ B. 25 µa C. 400 µa
3 15. Which of the following is not an energy source? A. Potentiometer$ B. Solar Cell C. Generator D. Leclanché cell 16. What is the resistance of a 2000 Ω/V meter which is used to measure the resistance on 200 V scale? A. 20 ohms B. 10 ohms$ C. 0.1 ohms 17. Consider a single phase wattmeter operating on 230 V and 5 A and 400 as the constant in revolutions. If it made 2000 revolutions in 5 hours, what is the power factor of the load (rounding off to two decimal places)? A. 0.87$ B C What is Hysteresis in an instrument? A. A typical mark of hysteresis is that the output does not change even if a given input alternately increases and decreases B. A typical mark of hysteresis is that the output forms a loop, if a given input alternately increases and decreases$ C. A typical mark of hysteresis is that the output changes based on the changes in temperature, even if a given input does not change 19. Consider a resistance strain gauge fastened to a steel member which is subjected to a stress of 150 N/mm 2. Given that the modulus of elasticity of steel is 2x10 5 N/mm 2 and the gauge factor of the strain gauge is 4, what is the percentage change in resistance? A. 0.2 B. 0.3$ C What is the sensitivity of a voltmeter using 0 to 10 ma meter movement? A. 100 ohm/v$ B. 200 ohm/v C. 10 ohm/v 21. Which of the following is measured by an ammeter? A. Power B. Voltage C. Current$
4 22. Which of the following is measured by a ohmmeter? A. Power B. Current C. Voltage D. Resistance$ 23. What is the degree equivalent of π/2 rad? A $ B C D What is the secondary current in a loaded transformer where the secondary voltage is one-third of the primary voltage? A. One third the primary current B. Nine times the primary current C. Three time the primary current$ 25. What is the turns ratio required to step up 120 V ac to 600 V ac? A. 4 B. 5$ C Which of the following statements is true? A. In step down transformer the number of turns in secondary winding (Ns) will be less than the number of turns in primary (Np). B. In step up transformer the number of turns in secondary winding (Ns) will be more than the number of turns in primary (Np). C. Both A and B$ 27. What is a center tap of a transformer? A. It is a direct connection between the primary coil and the secondary coil located at the center of the transformer B. It is a contact made to a point halfway along a secondary winding of a transformer $ C. It is a point where current is tapped from the primary and fed into the secondary 28. What is the unit of measurement of frequency? A. Freq B. Hertz$ C. Heinz
5 29. Consider a circuit with 3 resistors. What happens to the total resistance if two more resisters are added to then circuit? A. The total resistance increases$ B. The total resistance is reduced by 50% C. The total resistance will remain as earlier 30. What is the total resistance of a circuit consisting of three resistors with values of 160Ω, 230 Ω, and 370 Ω? A. 760 Ω$ B. 370 Ω C. 1/760 Ω 31. Consider a circuit which has 6 equal value resisters connected in series. What is the dissipation of each of them if the total power is 24 W? A. 2 W B. 3 W C. 4 W$ 32. A circuit consists of a 3.2 kω and a 6.4 kω resisters in series. What is the voltage across 6.4 kω resister if the voltage drop across 3.2 kω resister is 10 V? A. 10 V B. 20 V$ C. 5 V 33. What is the efficiency if a power supply uses 0.96 W input to produce 0.72 W output? A % B % C %$ 34. If the utility bill for a time-share apartment for 7 days is 17 kwh, what is the average daily power? A. 10 kwh B kwh$ C kwh D kwh 35. What is the the power for 18 V 50 ma? A. 900 mw B. 0.9 W C. 900,000 µw D. All the above$
6 36. What is the current when a 4.5 kω resistor dissipates 0.65 W? A ma$ B ma C µa D A 37. What is the power when the current through a 16 kω resistor is 14 ma? A mw B mw$ C mw D mw 38. Which of the following is true? A. Energy equals power divided by time B. Energy equals power multiplied by time$ C. Energy equals sum of power and time D. Energy equals time divided by power 39. What is the output voltage of the power supply when a 81Ω load uses 4 W of power? A. 36 V B. 9 V C V D. 18 V$ 40. How much energy is used in 4 minutes when a 15 V source is connected across a 20Ω resistor? A Wh$ B. 7.5 Wh C Wh 41. What is the total resistance when three 1.6 kω resistors are in series and this series combination is connected in parallel with a 5.2 kω resistor? A kω B. 10,000 Ω C. 2,496 Ω$ 42. Consider a circuit with two 10 kω resistors connected in series and a 20 kω resistor connected in parallel across one of these 10 kω resistors. What is the total current in the circuit if the voltage source is 24 V? A µa$ B A C ma
7 43. What is permeability? A. It is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself$ B. It is the measure of the ability of a material to oppose the formation of a magnetic field within itself C. It is the measure of the ability of a material to support conductance of electric current through itself 44. What is the power dissipated by a 54 Ω resistor connected across the terminals of a 6 V battery? A mw B mw C. 900 mw$ 45. What is the total capacitance when six 0.20 µf capacitors are in parallel? A µf B µf$ C. 3.6 µf 46. Which of the following is equal to 0.03 µf? A. 3,000 pf B. 30,000 pf$ C. 300 pf 47. What is the total capacitance if 3 capacitors of 2 µf, 5 µf, and 10 µf respectively are connected in series? A. 17 µf B µf C µf$ 48. Which of the following is true with a Y configuration? A. This configuration of voltage sources is characterized by a separate connection for each source B. This configuration of voltage sources is characterized by a common connection between two sources and a separate connection with the third source C. This configuration of voltage sources is characterized by a common connection point joining one side of each source$ 49. What is the amount of power in each phase in a balanced three-phase load? A. One-ninth of the total power B. Two thirds of the total power C. Half of the total power D. One-third of the total power$
8 50. Which of the following is the correct statement? A. In a three-phase system, the phases are separated from each other by one-third of the period$ B. In a three-phase system, each phase carries a sinusoidal alternating current whose phase exactly coincides with the other two neighbors C. Both A and B 51. An uniform conversion of electrical to mechanical energy implies A. Variable load power B. Constant load power$ C. Load power varying between 0.1X and 0.9X where X is a given constant 52. Which of the following statements is true? A. A simple three-phase generator consists of three conductive loops separated by 120. B. A balanced load is one in which all the impedances are equal. C. Both A and B$ 53. What is the amount of current that flows through a 3.3 MΩ resistor across a 30 V source? A. 1.1 µa B µa C µa$ 54. What is the current when 18 V are applied across a 72 Ω resistor? A. 816 ma B. 250 ma$ C. 90 ma 55. If a light bulb is drawing 18 ma from a 24 volt source, what is the filament resistance of the light bulb? A. 750 Ω$ B. 750 kω C. 750 mω 56. How much voltage is produced by a source when six amperes of current are measured through a 22Ω resistor? A. 132 V$ B V C. 28 V 57. What should the increase in the voltage from the present 24 V, the amount of current in a resistor is to be increased from 150 ma to 200 ma? A. 32 V B. 8 V$ C. 40 V
9 58. Which of the following is the unit for measuring reluctance? A. At/Wb$ B. H/Wb C. Columb/Wb 59. Which of the following describes Gauss's law for magnetism? states that the total magnetic flux through a closed surface is equal to zero. (A "closed surface" is a surface that completely encloses a volume(s) with no holes.) A. The total magnetic flux through a closed surface is equal to zero$ B. The total magnetic flux through any surface is equal to zero C. The total magnetic flux through a closed surface is equal 2 times the area of the surface 60. Which of the following is the units for magnetic flux density? having the unit of (tesla), A. Wb/m 2 B. Tesla C. Bothe A and B$ 61. What is the magneto-motive force in a 125-turn coil of wire when there is 6 A of current through it? A. 125 At B. 375 At C. 750 At$ 62. When the South poles of two bar magnets are brought close to each other, they A. Repel each other$ B. Attract each other C. Lose their magnetic property D. Increase their magnetic property 63. What is retentivity? A. The ability of a material to lose magnetism when of the magnetizing force is removed B. The ability of a material to remain magnetized after removal of the magnetizing force$ C. The ability of a material to remove magnetism from any material that comes closer to it 64. What is the amount of current induced when the voltage induced across a coil is 220 mv with a 88 Ω resistor connected to its terminals? A ma B. 2.5 ma$ C A
10 65. Which of the following is true when a loop in a basic dc generator is made rotate at a faster? A. The induced voltage does not change B. The induced voltage will increase$ C. The induced voltage will decrease 66. Which of the following statements describes Lenz s law? A. If an induced current flows, its direction is always such that it will oppose the change which produced it$ B. If an induced current flows, its direction is always be same as that of the change which produced it C. If an induced current flows, its direction is independent of the direction of the change which produced it 67. Which of the following constitute a magnetic field? A. Magnetic flux lines$ B. Increasing electrical resistance C. Decreasing voltage D. Conducting material 68. What is a solenoid? A. It is a type of electromagnet which produces a magnetic field in the presence of solar energy B. It is a type of electromagnet which produces a magnetic field due to increase in temperature C. It is a type of electromagnet which produces a uniform magnetic field in a volume of space$ 69. Which of the following are possible uses of a solenoid? A. Pneumatic valves B. Hydraulic valves C. Automobile starter D. All the above$ 70. When a current carrying conductor is brought into magnetic field, the force that moves the Conductor depends upon which of the following? A. Length of the conductor B. Amount of current$ C. Thickness of conductor D. Gravitational force exerted on the conductor
11 PART II A ELECTRICAL 1. What is permeance? A. In general, it is the degree to which any material admits a flow of matter or energy B. In electromagnetism, it is a measure of the quantity of flux for a number of current-turns in magnetic circuit C. Both A and B$ 2. The SI unit of magnetic permeance? A. Webers per ampere-turn$ B. Webers per mm 2 C. Webers 3. Which of the following is used to measure Dielectric reluctance? A. Wb -1 B. F -1 $ C. H What is resistive heating? A. It is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a non-conductor releases heat B. It is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor releases heat$ C. It is the process by which the passage of an magnetic retentivity through a conductor releases heat 5. Which of the following happens when a magnet is heated? A. It generates electric current B. It gains magnetism C. Both A and B $ 6. Which of the following is the main reason for preferring HVDC transmission? A. Low cost of DC conversion equipment B. It can be used for bulk power transmission over very long distances with low transmission losses$ C. Both A and B 7. Which of the following statements is true with respect to HVDC? A. HVDC allows power transmission between unsynchronized AC transmission systems B. HVDC can stabilize a network against disturbances due to rapid changes in power C. HVDC allows transfer of power between grid systems running at different frequencies D. All the above$
12 8. What is synchronization is the process of matching the speed and frequency of a generator or other source to a running network A. It is the process of matching the production capacities of different generators connected to a particular network B. It is the process of matching the speed and frequency of a generator or other source to a running network C. It is the process of matching the speed and frequency of a generator or other source to a running network$ D. none of these 9. What is the output power to the load if 12.2 W are lost to the winding resistance, given that the input power to the primary in a transformer is 150 W? A W B. 150 W C W $ 10. What is the reflective load on the source when a 100Ω load is connected across the secondary winding of a transformer with a turns ratio of 2? A. 50 Ω B. 25 Ω$ C. 100 Ω 11. What is the required turns ratio if you want to step up 220 V ac up to 1100 V ac? A. 0.2 B. 5.0$ C Which of the following is true with respect to a single-phase induction motor? A. It requires separate starting circuitry B. normal running windings within a single-phase motor can cause the rotor to turn in either direction C. the starting circuit determines the operating direction D. All the above$ 13. Fleming's left-hand rule (for motors) helps to figure out the direction of motion of which of the following? A. mechanical force B. magnetic field C. electric current D. all the above$ 14. An armature can be used A. Only as a stator B. Only as a rotor C. Either as a rotor or a stator$
13 15. Which of the following is true with respect to a dynamo? A. The magnetic field can be provided by either or permanent magnets B. electromagnets mounted on either the rotor or the stator C. Both A and B$ 16. Which of the following is the advantage of two-phase electrical power over a single-phase one? A. The two-phase system are simple, self-starting electric motors B. The revolving magnetic field produced with a two-phase system allowed electric motors to provide torque from zero motor speed C. Both A and B$ 17. What is the phase separation in a two-phase electrical system? A B $ C What is a squirrel cage? A. It is a single phase AC generator B. It is a two phase AC generator C. It is a three phase AC generator$ 19. What is a delta-wye transformer? A. It employs delta-connected windings on its primary B. It is a three phase system C. It employs wye/star connected windings on its secondary D. All the above$ 20. What is the phase separation in a three-phase electrical system? A B C $ 21. What is advantage of high voltage transmission lines? A. Increasing the voltage reduces the current in transmission and distribution lines reducing the distribution losses$ B. Increasing voltage leads to higher current which in turn leads to bulk carriage of power over long distances C. Increasing voltage is not an advantage at all because it involves expensive equipment to step up voltage initially and then step down later
14 22. Which of the following can be used to increase the capacitance? A. Increase the plate area$ B. Increase the width of dielectric thereby increasing the separation C. Both A and B 23. An electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field is called A. A super conductor B. A dielectric$ C. Compressed conductors 24. Which of the following capacitors has the highest capacitance to volume ratio? much higher than to and A. Ceramic capacitors B. Film capacitors C. Electrolytic capacitors$ D. All have the same ratio 25. Faraday s law is the the fundamental operating principle for which of the following? A. Solenoids B. Inductors C. Electric motors D. All the above$ 26. What is a magnetic flow meter? A. Magnetic flow meters are used for measuring the flow of electrically conductive liquids and slurries using the principle of electromagnetic induction$ B. Magnetic flow meters are used for measuring the resistance to electrical conductivity of insulators using the principle of electromagnetic induction C. Magnetic flow meters are used for measuring the magnetic retentivity of electro magnetic materials using the principle of electromagnetic induction 27. What is the current flow in the coil with a winding resistance of 156 Ω, connected to a 16 V power supply? A ma B ma$ C ma 28. Two resistors are connected in parallel and the total resistance of the circuit is 1,875Ω. If one of the resistors is 3 kω, what is the value of the other resistor? A. 3 kω B. 4 kω C. 5 kω$
15 29. Three resistors are connected in series with a source supplying 12 V. What happens to the current in the circuit if one of the resisters is removed? A. The current will increase B. The current will decrease$ C. The current will increase by 12 A D. The current will remain the same 30. How much continuous current can be drawn from a 75 Ah battery for 15 h? A. 4 A B. 4.5 A C. 5 A$
16 1. How many neutrons does a Silicon-30 has? A. 14 B. 15 C. 16$ Part II B Electronics 2. What is the impact of increase in temperature on the conductivity of semiconductors? A. Conductivity increases$ B. Conductivity decreases C. Conductivity remains the same D. The change in conductivity depends on the atmospheric pressure 3. What is recombination A. It is a process by by which electrons are created B. It is a process by by which electrons and electron holes are created and eliminated$ C. It is a process by by which electron holes are created 4. Which of the following is a photoconductive material? A. Selenium B. Lead sulphide C. Polyvinylcarbazole D. All the above$ 5. Fleming s right hand rule is applicable to which of the following? A. Generators$ B. Motors C. Capacitors 6. What is the binary equivalent of decimal number 11? A B. 1011$ C Which of the following is an important characteristic of CMOS? A. high noise immunity B. low static power consumption C. both A and B$ D. none of these 8. Which of the following is true with the octal system? A. It has 7 digits (1 to 7) B. It has 8 digits (0 to 7)$ C. It has 8 digits (1 to 8)
17 9. What is the hexadecimal equivalent of decimal number 123? A. 7B$ B. 70 C. 7F 10. Which of the following is an example of bistable multivibrator circuit? A. Relaxation oscillator B. Flip flop$ C. Both A and B 11. Which of the following is true with a half-adder? A. It adds two single binary digits and has two outputs$ B. It adds two single binary digits and has one output C. It adds half a binary digits and has half binary output 12. What are Hamming codes? A. They are a class of binary non-linear codes used for carry over decision B. They are a compendium of multivariate linear codes used for carry over decision C. They are a class of binary linear codes used for error detection$ 13. Consider a binary number What is its equivalent hexadecimal number? A. E9$ B. E9 C. F0 14. How many memory locations can be accessed by 8 address bits? A. 2 8 $ B. (2 8 ) 1 C Which of the following is a property of CE amplifier? A. The base terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the collector is the output, and the emitter is common to both$ B. The base terminal of the transistor serves as the output, the collector is the input, and the emitter is common to both C. the emitter serves as input as well as output D. none of these 16. what is the name given to a unidirectional voltage that rapidly rises to a peak and then drops to zero very rapidly? A. Impulse voltage B. Pulse voltage C. Both A and B$ 17. Which of the following has the most volatile memory?
18 A. CD Rom B. RAM$ C. Hard disk D. Pen drive 18. Which of the following, usually, will not allow modification data? A. ROM$ B. RAM C. Hard disk D. Floppy disk 19. Which of the following send data as a serial stream? A. USB B. Ethernet C. Fire wire D. All the above$ 20. Which of the following can be used as a software for financial accounting? A. Microsoft Word B. Microsoft Excel$ C. Photoshop D. Microsoft Project 21. Frequency multiplexing can be used for which of the following? This allows a single transmission medium such as the, a cable or to be shared by multiple separate signals A. radio spectrum B. optical fiber C. both A and B$ D. none of these 22. which of the following bands in the electromagnetic spectrum are used by communication satellites? A. Ku band B. Ka band C. VHF D. Both A and B$ 23. Which of the following statements describes Shannon Hartley theorem? A. It tells the maximum rate at which information can be transmitted over a communications channel of a specified bandwidth in the presence of noise$ B. It tells the minimum rate at which information can be transmitted over a communications channel of a specified bandwidth in the presence of noise C. It tells the maximum rate at which information can be transmitted over a communications channel of a specified bandwidth in the absence of noise D. It tells the minimum rate at which information can be transmitted over a communications channel of a specified bandwidth in the absence of noise 24. What should be the distance of the satellite from the surface of the earth in order to be geosynchronous? A. About 36,000 km$ B. About 10,000 km C. About 36,000 miles D. About 56,000 km 25. What is a chopper? A. It is an electronic instrument used to the signal strength B. It is an electronic resistance that is used to eliminate signals emanating from another switch
19 C. It is an electronic switch that is used to interrupt one signal under the control of another$ 26. What is the value of β of a particular bipolar junction transistor with α = 0.95? A. 20 B C. 19$ 27. Which of the following is true with respect to a reverse conducting thyristor? A. It has an integrated reverse diode B. It is not capable of reverse blocking C. It is often used in frequency changer and inverter D. All the above$ 28. What is the unit of electrical charge? A. Coulomb$ B. Henry C. Faraday 29. What are valances? A. Electrons in the inner orbits B. Electrons in the outer orbit$ C. Neutrons in the nucleus 30. Which of the following are the majority carriers in a p-type? A. Holes$ B. Electrons C. Both holes and electrons
Module 3 Electrical Fundamentals
 3.1 Electron Theory Structure and distribution of electrical charges within: atoms, molecules, ions, compounds; Molecular structure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators. 3.2 Static Electricity
3.1 Electron Theory Structure and distribution of electrical charges within: atoms, molecules, ions, compounds; Molecular structure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators. 3.2 Static Electricity
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3. OUTCOME 3 - MAGNETISM and INDUCTION
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 3 - MAGNETISM and INDUCTION 3 Understand the principles and properties of magnetism Magnetic field:
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 3 - MAGNETISM and INDUCTION 3 Understand the principles and properties of magnetism Magnetic field:
1. An isolated stationary point charge produces around it. a) An electric field only. b) A magnetic field only. c) Electric as well magnetic fields.
 1. An isolated stationary point charge produces around it. a) An electric field only. b) A magnetic field only. c) Electric as well magnetic fields. 2. An isolated moving point charge produces around it.
1. An isolated stationary point charge produces around it. a) An electric field only. b) A magnetic field only. c) Electric as well magnetic fields. 2. An isolated moving point charge produces around it.
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies
 Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies Induced emf - Faraday s Experiment When a magnet moves toward a loop of wire, the ammeter shows the presence of a current When
Ch. 23 Electromagnetic Induction, AC Circuits, And Electrical Technologies Induced emf - Faraday s Experiment When a magnet moves toward a loop of wire, the ammeter shows the presence of a current When
5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS
 5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS TOPIC OUTLINE Section Recommended Time Giancoli Section 5.1 Potential Difference, Current, Resistance 5.2 Electric Circuits 3h 19.1, 19.2 6.2 Electric Field and Force 6.3 Magnetic
5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS TOPIC OUTLINE Section Recommended Time Giancoli Section 5.1 Potential Difference, Current, Resistance 5.2 Electric Circuits 3h 19.1, 19.2 6.2 Electric Field and Force 6.3 Magnetic
1 Written and composed by: Prof. Muhammad Ali Malik (M. Phil. Physics), Govt. Degree College, Naushera
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Q # 1. What do you know about electric current? Ans. Electric Current The amount of electric charge that flows through a cross section of a conductor per unit time is known as electric
CURRENT ELECTRICITY Q # 1. What do you know about electric current? Ans. Electric Current The amount of electric charge that flows through a cross section of a conductor per unit time is known as electric
fusion production of elements in stars, 345
 I N D E X AC circuits capacitive reactance, 278 circuit frequency, 267 from wall socket, 269 fundamentals of, 267 impedance in general, 283 peak to peak voltage, 268 phase shift in RC circuit, 280-281
I N D E X AC circuits capacitive reactance, 278 circuit frequency, 267 from wall socket, 269 fundamentals of, 267 impedance in general, 283 peak to peak voltage, 268 phase shift in RC circuit, 280-281
coil of the circuit. [8+8]
![coil of the circuit. [8+8] coil of the circuit. [8+8]](/thumbs/80/81218867.jpg) Code No: R05310202 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS (Electrical & Electronic Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: R05310202 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS (Electrical & Electronic Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Curriculum Interpretation Electricity and Magnetism. Lee Wai Kit
 Curriculum Interpretation Electricity and Magnetism Lee Wai Kit Electricity and Magnetism 4.1 Electrostatics 4.2 Circuits and domestic electricity 4.3 Electromagnetism 4.1 Electrostatics electric charges
Curriculum Interpretation Electricity and Magnetism Lee Wai Kit Electricity and Magnetism 4.1 Electrostatics 4.2 Circuits and domestic electricity 4.3 Electromagnetism 4.1 Electrostatics electric charges
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY. 1. Understands the physical construction and characteristics of basic components.
 SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
Solved Problems. Electric Circuits & Components. 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown.
 Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Electron Theory. Elements of an Atom
 Electron Theory Elements of an Atom All matter is composed of molecules which are made up of a combination of atoms. Atoms have a nucleus with electrons orbiting around it. The nucleus is composed of protons
Electron Theory Elements of an Atom All matter is composed of molecules which are made up of a combination of atoms. Atoms have a nucleus with electrons orbiting around it. The nucleus is composed of protons
Revision Guide for Chapter 15
 Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents Revision Checklist Revision otes Transformer...4 Electromagnetic induction...4 Lenz's law...5 Generator...6 Electric motor...7 Magnetic field...9 Magnetic flux...
Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents Revision Checklist Revision otes Transformer...4 Electromagnetic induction...4 Lenz's law...5 Generator...6 Electric motor...7 Magnetic field...9 Magnetic flux...
Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]
![Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark] Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]](/thumbs/88/115570773.jpg) Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
CHAPTER 5. BRIDGES AND THEIR APPLICATION Resistance Measurements. Dr. Wael Salah
 CHAPTER 5 BRIDGES AND THEIR APPLICATION Resistance Measurements 1 RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS Conventional Ways of Measuring Resistance:- 1) Using a Ohmmeter Convenient but inaccurate, requires calibration
CHAPTER 5 BRIDGES AND THEIR APPLICATION Resistance Measurements 1 RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS Conventional Ways of Measuring Resistance:- 1) Using a Ohmmeter Convenient but inaccurate, requires calibration
ENGR 2405 Chapter 6. Capacitors And Inductors
 ENGR 2405 Chapter 6 Capacitors And Inductors Overview This chapter will introduce two new linear circuit elements: The capacitor The inductor Unlike resistors, these elements do not dissipate energy They
ENGR 2405 Chapter 6 Capacitors And Inductors Overview This chapter will introduce two new linear circuit elements: The capacitor The inductor Unlike resistors, these elements do not dissipate energy They
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 Electricity May 02 1. The graphs show the variation with potential difference V of the current I for three circuit elements. PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com When the four lamps are connected as shown in diagram
Electricity May 02 1. The graphs show the variation with potential difference V of the current I for three circuit elements. PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com When the four lamps are connected as shown in diagram
Basic Electrical Engineering SYLLABUS. Total No. of Lecture Hrs. : 50 Exam Marks : 80
 SYLLABUS Subject Code: /25 No. of Lecture Hrs./ Week : 04 IA Marks : 20 Exam Hours : 03 Total No. of Lecture Hrs. : 50 Exam Marks : 80 Course objectives: Impart a basic knowledge of electrical quantities
SYLLABUS Subject Code: /25 No. of Lecture Hrs./ Week : 04 IA Marks : 20 Exam Hours : 03 Total No. of Lecture Hrs. : 50 Exam Marks : 80 Course objectives: Impart a basic knowledge of electrical quantities
Physics Department. CfE Higher Unit 3: Electricity. Problem Booklet
 Physics Department CfE Higher Unit 3: Electricity Problem Booklet Name Class 1 Contents Exercise 1: Monitoring and measuring a.c. Exercise 2: Current, voltage, power and resistance Exercise 3: Electrical
Physics Department CfE Higher Unit 3: Electricity Problem Booklet Name Class 1 Contents Exercise 1: Monitoring and measuring a.c. Exercise 2: Current, voltage, power and resistance Exercise 3: Electrical
EXEMPLAR NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 ( ) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00
 NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 2008 (12041002) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 EXEMPLAR This question paper consists of 7 pages. EXEMPLAR -2- NC(V) TIME: 3 HOURS
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 2008 (12041002) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 EXEMPLAR This question paper consists of 7 pages. EXEMPLAR -2- NC(V) TIME: 3 HOURS
Revision Guide for Chapter 15
 Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents tudent s Checklist Revision otes Transformer... 4 Electromagnetic induction... 4 Generator... 5 Electric motor... 6 Magnetic field... 8 Magnetic flux... 9 Force on
Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents tudent s Checklist Revision otes Transformer... 4 Electromagnetic induction... 4 Generator... 5 Electric motor... 6 Magnetic field... 8 Magnetic flux... 9 Force on
EE Branch GATE Paper 2010
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Electron Theory of Charge. Electricity. 1. Matter is made of atoms. Refers to the generation of or the possession of electric charge.
 Electricity Refers to the generation of or the possession of electric charge. There are two kinds of electricity: 1. Static Electricity the electric charges are "still" or static 2. Current Electricity
Electricity Refers to the generation of or the possession of electric charge. There are two kinds of electricity: 1. Static Electricity the electric charges are "still" or static 2. Current Electricity
RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS
 RAE-Lessons by 4S7VJ 1 CHAPTER- 2 RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS By 4S7VJ 2.1 Sine-wave If a magnet rotates near a coil, an alternating e.m.f. (a.c.) generates in the coil. This e.m.f. gradually increase
RAE-Lessons by 4S7VJ 1 CHAPTER- 2 RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS By 4S7VJ 2.1 Sine-wave If a magnet rotates near a coil, an alternating e.m.f. (a.c.) generates in the coil. This e.m.f. gradually increase
PHYSICS (Theory) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70
 Sample Paper (CBSE) Series PHY/SP/1D Code No. SP/1-D PHYSICS (Theory) Time Allowed: hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) All questions are compulsory. This question paper
Sample Paper (CBSE) Series PHY/SP/1D Code No. SP/1-D PHYSICS (Theory) Time Allowed: hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) All questions are compulsory. This question paper
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS
 UNIT 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS MODULE 1: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand
UNIT 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS MODULE 1: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194
 MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194 Question 1 (a) List three sources of heat in soldering (b) state the functions of flux in soldering (c) briefly describe with aid of diagram
MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194 Question 1 (a) List three sources of heat in soldering (b) state the functions of flux in soldering (c) briefly describe with aid of diagram
Lecture 24. April 5 th, Magnetic Circuits & Inductance
 Lecture 24 April 5 th, 2005 Magnetic Circuits & Inductance Reading: Boylestad s Circuit Analysis, 3 rd Canadian Edition Chapter 11.1-11.5, Pages 331-338 Chapter 12.1-12.4, Pages 341-349 Chapter 12.7-12.9,
Lecture 24 April 5 th, 2005 Magnetic Circuits & Inductance Reading: Boylestad s Circuit Analysis, 3 rd Canadian Edition Chapter 11.1-11.5, Pages 331-338 Chapter 12.1-12.4, Pages 341-349 Chapter 12.7-12.9,
The principles of conservation of energy and charge apply to electrical circuits. Properties of magnetic fields apply in nature and technology.
 UIT E UMMARY KEY COCEPT CHAPTER UMMARY 11 The principles of conservation of energy and charge apply to electrical circuits. Electrical circuits Conventional current and electron flow Current, electrical
UIT E UMMARY KEY COCEPT CHAPTER UMMARY 11 The principles of conservation of energy and charge apply to electrical circuits. Electrical circuits Conventional current and electron flow Current, electrical
Renewable Energy Systems
 Renewable Energy Systems 2 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd Chapter Outline Electrical Fundamentals 2 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd 2-1 ENERGY, CHARGE, AND VOLTAGE 2-2 ELECTRICAL CURRENT 2-3 RESISTANCE AND OHM'S LAW 2-4
Renewable Energy Systems 2 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd Chapter Outline Electrical Fundamentals 2 Buchla, Kissell, Floyd 2-1 ENERGY, CHARGE, AND VOLTAGE 2-2 ELECTRICAL CURRENT 2-3 RESISTANCE AND OHM'S LAW 2-4
Resistivity and Temperature Coefficients (at 20 C)
 Homework # 4 Resistivity and Temperature Coefficients (at 0 C) Substance Resistivity, Temperature ( m) Coefficient, (C ) - Conductors Silver.59 x 0-0.006 Copper.6 x 0-0.006 Aluminum.65 x 0-0.0049 Tungsten
Homework # 4 Resistivity and Temperature Coefficients (at 0 C) Substance Resistivity, Temperature ( m) Coefficient, (C ) - Conductors Silver.59 x 0-0.006 Copper.6 x 0-0.006 Aluminum.65 x 0-0.0049 Tungsten
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives
 AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION
 ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 1) A Circular coil is placed near a current carrying conductor. The induced current is anti clock wise when the coil is, 1. Stationary 2. Moved away from the conductor 3. Moved
ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 1) A Circular coil is placed near a current carrying conductor. The induced current is anti clock wise when the coil is, 1. Stationary 2. Moved away from the conductor 3. Moved
Part 4: Electromagnetism. 4.1: Induction. A. Faraday's Law. The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is
 1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
1 Part 4: Electromagnetism 4.1: Induction A. Faraday's Law The magnetic flux through a loop of wire is Φ = BA cos θ B A B = magnetic field penetrating loop [T] A = area of loop [m 2 ] = angle between field
 Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
Transducers. EEE355 Industrial Electronics
 Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
Summary Notes ALTERNATING CURRENT AND VOLTAGE
 HIGHER CIRCUIT THEORY Wheatstone Bridge Circuit Any method of measuring resistance using an ammeter or voltmeter necessarily involves some error unless the resistances of the meters themselves are taken
HIGHER CIRCUIT THEORY Wheatstone Bridge Circuit Any method of measuring resistance using an ammeter or voltmeter necessarily involves some error unless the resistances of the meters themselves are taken
Farr High School HIGHER PHYSICS. Unit 3 Electricity. Question Booklet
 Farr High School HIGHER PHYSICS Unit 3 Electricity Question Booklet 1 MONITORING ND MESURING.C. 1. What is the peak voltage of the 230 V mains supply? The frequency of the mains supply is 50 Hz. How many
Farr High School HIGHER PHYSICS Unit 3 Electricity Question Booklet 1 MONITORING ND MESURING.C. 1. What is the peak voltage of the 230 V mains supply? The frequency of the mains supply is 50 Hz. How many
Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors
 Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors 1 Revision of Electromagnetic Induction and Inductors (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Magnetic Field
Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors 1 Revision of Electromagnetic Induction and Inductors (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Magnetic Field
REVISED HIGHER PHYSICS REVISION BOOKLET ELECTRONS AND ENERGY
 REVSED HGHER PHYSCS REVSON BOOKLET ELECTRONS AND ENERGY Kinross High School Monitoring and measuring a.c. Alternating current: Mains supply a.c.; batteries/cells supply d.c. Electrons moving back and forth,
REVSED HGHER PHYSCS REVSON BOOKLET ELECTRONS AND ENERGY Kinross High School Monitoring and measuring a.c. Alternating current: Mains supply a.c.; batteries/cells supply d.c. Electrons moving back and forth,
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE
 I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Pretest ELEA1831 Module 11 Units 1& 2 Inductance & Capacitance
 Pretest ELEA1831 Module 11 Units 1& 2 Inductance & Capacitance 1. What is Faraday s Law? Magnitude of voltage induced in a turn of wire is proportional to the rate of change of flux passing through that
Pretest ELEA1831 Module 11 Units 1& 2 Inductance & Capacitance 1. What is Faraday s Law? Magnitude of voltage induced in a turn of wire is proportional to the rate of change of flux passing through that
Calculus Relationships in AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism
 C: Electricity This chapter focuses on some of the quantitative skills that are important in your C: Mechanics course. These are not all of the skills that you will learn, practice, and apply during the
C: Electricity This chapter focuses on some of the quantitative skills that are important in your C: Mechanics course. These are not all of the skills that you will learn, practice, and apply during the
Part 2. Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour)
 Part 2 Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour) At the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the definition of sensor and transducer Determine the specification of control
Part 2 Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour) At the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the definition of sensor and transducer Determine the specification of control
Physics 55 Final Exam Fall 2012 Dr. Alward Page 1
 Physics 55 Final Exam Fall 2012 Dr. Alward Page 1 1. The specific heat of lead is 0.030 cal/g C. 300 g of lead shot at 100 C is mixed with 100 g of water at 70 C in an insulated container. The final temperature
Physics 55 Final Exam Fall 2012 Dr. Alward Page 1 1. The specific heat of lead is 0.030 cal/g C. 300 g of lead shot at 100 C is mixed with 100 g of water at 70 C in an insulated container. The final temperature
Transducer. A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity. Transducer. (Input) Sensor.
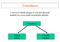 Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law of Induction
 Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law of Induction 1 Overview of Chapter 23 Induced Electromotive Force Magnetic Flux Faraday s Law of Induction Lenz s Law Mechanical Work and Electrical Energy Generators
Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law of Induction 1 Overview of Chapter 23 Induced Electromotive Force Magnetic Flux Faraday s Law of Induction Lenz s Law Mechanical Work and Electrical Energy Generators
PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION STD : XII MARKS : 150
 PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION STD : XII MARKS : 150 SUB : PHYSICS TIME : 3.00 Hrs I.Choose the correct answer: 30x1=30 1.Which of the following quantities not a scalar? a)electric flux b) electric potential c)
PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION STD : XII MARKS : 150 SUB : PHYSICS TIME : 3.00 Hrs I.Choose the correct answer: 30x1=30 1.Which of the following quantities not a scalar? a)electric flux b) electric potential c)
3. (a) Figure 3(a) shows a Bridge T network used in control systems. The element values are clearly marked in the figure.
 I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
18 - ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENTS ( Answers at the end of all questions ) Page 1
 ( Answers at the end of all questions ) Page ) The self inductance of the motor of an electric fan is 0 H. In order to impart maximum power at 50 Hz, it should be connected to a capacitance of 8 µ F (
( Answers at the end of all questions ) Page ) The self inductance of the motor of an electric fan is 0 H. In order to impart maximum power at 50 Hz, it should be connected to a capacitance of 8 µ F (
Chapter 7. Chapter 7. Electric Circuits Fundamentals - Floyd. Copyright 2007 Prentice-Hall
 Chapter 7 Magnetic Quantities Magnetic fields are described by drawing flux lines that represent the magnetic field. Where lines are close together, the flux density is higher. Where lines are further
Chapter 7 Magnetic Quantities Magnetic fields are described by drawing flux lines that represent the magnetic field. Where lines are close together, the flux density is higher. Where lines are further
Most matter is electrically neutral; its atoms and molecules have the same number of electrons as protons.
 Magnetism Electricity Magnetism Magnetic fields are produced by the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. -> permanent magnets Magnetic
Magnetism Electricity Magnetism Magnetic fields are produced by the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. -> permanent magnets Magnetic
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011
 ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: PHYSICS 2 CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 29 TIME: 1:00 DURATION: 2 HOUR INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This paper consists
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: PHYSICS 2 CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 29 TIME: 1:00 DURATION: 2 HOUR INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This paper consists
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
Introduction. Upon completion of Basics of Electricity you will be able to: Explain the difference between conductors and insulators
 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Electron Theory...4 Conductors, Insulators and Semiconductors...5 Electric Charges...7 Current...9 Voltage...11 Resistance...13 Simple Electric Circuit...15 Ohm s Law...16
Table of Contents Introduction...2 Electron Theory...4 Conductors, Insulators and Semiconductors...5 Electric Charges...7 Current...9 Voltage...11 Resistance...13 Simple Electric Circuit...15 Ohm s Law...16
Section 1 Electric Charge and Force
 CHAPTER OUTLINE Section 1 Electric Charge and Force Key Idea questions > What are the different kinds of electric charge? > How do materials become charged when rubbed together? > What force is responsible
CHAPTER OUTLINE Section 1 Electric Charge and Force Key Idea questions > What are the different kinds of electric charge? > How do materials become charged when rubbed together? > What force is responsible
PHYSICS Course Structure Units Topics Marks Electrostatics Current Electricity III Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism
 PHYSICS Course Structure Units Topics Marks I Chapter 1 Chapter 2 II Chapter 3 III Chapter 4 Chapter 5 IV Chapter 6 Chapter 7 V Chapter 8 VI Chapter 9 Electrostatics Electric Charges and Fields Electrostatic
PHYSICS Course Structure Units Topics Marks I Chapter 1 Chapter 2 II Chapter 3 III Chapter 4 Chapter 5 IV Chapter 6 Chapter 7 V Chapter 8 VI Chapter 9 Electrostatics Electric Charges and Fields Electrostatic
Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation.
 Use the following to answer question 1. Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation. 1. Which combination of charges would yield
Use the following to answer question 1. Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation. 1. Which combination of charges would yield
Dept. of Electrical Engineering Final Exam, Summer Semester: 2014/2015
 de Form No. T611 Philadelphia University Faculty of Engineering Dept. of Electrical Engineering Final Exam, Summer Semester: 2014/2015 Student Name: Student Number: Course Title: nstrumentation and Measurement
de Form No. T611 Philadelphia University Faculty of Engineering Dept. of Electrical Engineering Final Exam, Summer Semester: 2014/2015 Student Name: Student Number: Course Title: nstrumentation and Measurement
Chapter 30. Induction and Inductance
 Chapter 30 Induction and Inductance 30.2: First Experiment: 1. A current appears only if there is relative motion between the loop and the magnet (one must move relative to the other); the current disappears
Chapter 30 Induction and Inductance 30.2: First Experiment: 1. A current appears only if there is relative motion between the loop and the magnet (one must move relative to the other); the current disappears
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester. Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE
 INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
ELECTRICAL FUNDAMENTALS
 Part 66 Cat. B1 / B2 Module 3 ELECTRICAL FUNDAMENTALS Vilnius-2017 Issue 1. Effective date 2017-02-28 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY Page 1 of 280 If we look at electronic configuration of a carbon C atom,
Part 66 Cat. B1 / B2 Module 3 ELECTRICAL FUNDAMENTALS Vilnius-2017 Issue 1. Effective date 2017-02-28 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY Page 1 of 280 If we look at electronic configuration of a carbon C atom,
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
 1. A square loop of wire moves with a constant speed v from a field-free region into a region of uniform B field, as shown. Which of the five graphs correctly shows the induced current i in the loop as
1. A square loop of wire moves with a constant speed v from a field-free region into a region of uniform B field, as shown. Which of the five graphs correctly shows the induced current i in the loop as
Objective Type Questions Instrumentation System & Devices (IDS)
 1. A balance beam scale uses which of the following units? a. grams b.pounds c. ounces d. kilograms 2. Which of the following would be about the height of the average doorway? a. 2 meters b. 2 centimeters
1. A balance beam scale uses which of the following units? a. grams b.pounds c. ounces d. kilograms 2. Which of the following would be about the height of the average doorway? a. 2 meters b. 2 centimeters
Basic Electricity. Unit 2 Basic Instrumentation
 Basic Electricity Unit 2 Basic Instrumentation Outlines Terms related to basic electricity-definitions of EMF, Current, Potential Difference, Power, Energy and Efficiency Definition: Resistance, resistivity
Basic Electricity Unit 2 Basic Instrumentation Outlines Terms related to basic electricity-definitions of EMF, Current, Potential Difference, Power, Energy and Efficiency Definition: Resistance, resistivity
Mutual Inductance. The field lines flow from a + charge to a - change
 Capacitors Mutual Inductance Since electrical charges do exist, electric field lines have a starting point and an ending point. For example, if you have a + and a - change, the field lines would look something
Capacitors Mutual Inductance Since electrical charges do exist, electric field lines have a starting point and an ending point. For example, if you have a + and a - change, the field lines would look something
An Introduction to Electrical Machines. P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy
 An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le2
 Le1 Le3 Le4 Le6 Le8 IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le2 Ex1 Ex2 Ex4 Ex5 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, serial and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulse sensors, Menu program Kirchhoffs laws
Le1 Le3 Le4 Le6 Le8 IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le2 Ex1 Ex2 Ex4 Ex5 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, serial and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulse sensors, Menu program Kirchhoffs laws
UNIT II CURRENT ELECTRICITY
 UNIT II CUENT ELECTICITY Weightage : 07 Marks Electric current; flow of electric charges in a metllic conductor, drift velocity, mobility and their relation with electric current. Ohm s law electrical
UNIT II CUENT ELECTICITY Weightage : 07 Marks Electric current; flow of electric charges in a metllic conductor, drift velocity, mobility and their relation with electric current. Ohm s law electrical
3 Electric current, resistance, energy and power
 3 3.1 Introduction Having looked at static charges, we will now look at moving charges in the form of electric current. We will examine how current passes through conductors and the nature of resistance
3 3.1 Introduction Having looked at static charges, we will now look at moving charges in the form of electric current. We will examine how current passes through conductors and the nature of resistance
PHYSICS. Chapter 30 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 30 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 30 Electromagnetic Induction IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn what electromagnetic induction is
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 30 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 30 Electromagnetic Induction IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn what electromagnetic induction is
IE1206 Embedded Electronics
 IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le1 Le3 Le4 Le2 Ex1 Ex2 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, series and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs
IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le1 Le3 Le4 Le2 Ex1 Ex2 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, series and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs
4.7.1 Permanent and induced magnetism, magnetic forces and fields. Content Key opportunities for skills development
 4.7 Magnetism and electromagnetism Electromagnetic effects are used in a wide variety of devices. Engineers make use of the fact that a magnet moving in a coil can produce electric current and also that
4.7 Magnetism and electromagnetism Electromagnetic effects are used in a wide variety of devices. Engineers make use of the fact that a magnet moving in a coil can produce electric current and also that
PHYS 241 EXAM #2 November 9, 2006
 1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
Control Engineering BDA30703
 Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT. Physics. Electricity. Questions and Solutions. James Page Arthur Baillie [HIGHER]
![NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT. Physics. Electricity. Questions and Solutions. James Page Arthur Baillie [HIGHER] NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT. Physics. Electricity. Questions and Solutions. James Page Arthur Baillie [HIGHER]](/thumbs/86/93982339.jpg) NTIONL QULIFICTIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT Physics Electricity Questions and Solutions James Page rthur Baillie [HIGHER] The Scottish Qualifications uthority regularly reviews the arrangements for National
NTIONL QULIFICTIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT Physics Electricity Questions and Solutions James Page rthur Baillie [HIGHER] The Scottish Qualifications uthority regularly reviews the arrangements for National
Chapter 21 Magnetic Induction Lecture 12
 Chapter 21 Magnetic Induction Lecture 12 21.1 Why is it called Electromagnetism? 21.2 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law 21.3 Lenz s Law and Work-Energy Principles 21.4 Inductance 21.5 RL Circuits 21.6 Energy
Chapter 21 Magnetic Induction Lecture 12 21.1 Why is it called Electromagnetism? 21.2 Magnetic Flux and Faraday s Law 21.3 Lenz s Law and Work-Energy Principles 21.4 Inductance 21.5 RL Circuits 21.6 Energy
The object experiencing the field is called the TEST OBJECT
 A field is an invisible area of influence around an object If you place another object in the field it will experience a force 1 object is said to be causing the field The object experiencing the field
A field is an invisible area of influence around an object If you place another object in the field it will experience a force 1 object is said to be causing the field The object experiencing the field
Outline of College Physics OpenStax Book
 Outline of College Physics OpenStax Book Taken from the online version of the book Dec. 27, 2017 18. Electric Charge and Electric Field 18.1. Static Electricity and Charge: Conservation of Charge Define
Outline of College Physics OpenStax Book Taken from the online version of the book Dec. 27, 2017 18. Electric Charge and Electric Field 18.1. Static Electricity and Charge: Conservation of Charge Define
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION
 MARKING GUIDELINE NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 This marking guideline consists of 8 pages. MARKING GUIDELINE -2- NC770(E)(F19)V SECTION A QUESTION 1: COMPONENTS
MARKING GUIDELINE NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 This marking guideline consists of 8 pages. MARKING GUIDELINE -2- NC770(E)(F19)V SECTION A QUESTION 1: COMPONENTS
RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS
 RAE-Lessons by 4S7VJ 1 RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS CHAPTER- 1 BASIC ELECTRICITY By 4S7VJ 1.1 ELECTRIC CHARGE Everything physical is built up of atoms, or particles. They are so small that they cannot
RAE-Lessons by 4S7VJ 1 RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS CHAPTER- 1 BASIC ELECTRICITY By 4S7VJ 1.1 ELECTRIC CHARGE Everything physical is built up of atoms, or particles. They are so small that they cannot
AP Physics C. Magnetism - Term 4
 AP Physics C Magnetism - Term 4 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the world
AP Physics C Magnetism - Term 4 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the world
Some Important Electrical Units
 Some Important Electrical Units Quantity Unit Symbol Current Charge Voltage Resistance Power Ampere Coulomb Volt Ohm Watt A C V W W These derived units are based on fundamental units from the meterkilogram-second
Some Important Electrical Units Quantity Unit Symbol Current Charge Voltage Resistance Power Ampere Coulomb Volt Ohm Watt A C V W W These derived units are based on fundamental units from the meterkilogram-second
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors)
 Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
NEW HORIZON PRE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LESSON PLAN FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR Department of PHYSICS (II PUC)
 NEW HORIZON PRE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LESSON PLAN FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2017 2018 Department of PHYSICS (II PUC) Week Month: June 4 Electric charges and properties Coulomb s law superposition principle Electric
NEW HORIZON PRE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LESSON PLAN FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2017 2018 Department of PHYSICS (II PUC) Week Month: June 4 Electric charges and properties Coulomb s law superposition principle Electric
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION 1. Magnetic Flux 2. Faraday s Experiments 3. Faraday s Laws of Electromagnetic Induction 4. Lenz s Law and Law of Conservation of Energy 5. Expression for Induced emf based on
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION 1. Magnetic Flux 2. Faraday s Experiments 3. Faraday s Laws of Electromagnetic Induction 4. Lenz s Law and Law of Conservation of Energy 5. Expression for Induced emf based on
Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance
 Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance First Six-Weeks Second Six-Weeks Third Six-Weeks Lab safety Lab practices and ethical practices Math and Calculus
Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance First Six-Weeks Second Six-Weeks Third Six-Weeks Lab safety Lab practices and ethical practices Math and Calculus
Electromagnetic Induction
 362 Mechanical Engineering Technician UNIT 7 Electromagnetic Induction Structure 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Faraday s laws of Electromagnetic Induction 7.3. Lenz s law 7.4. Fleming s right and rule 7.5. Self
362 Mechanical Engineering Technician UNIT 7 Electromagnetic Induction Structure 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Faraday s laws of Electromagnetic Induction 7.3. Lenz s law 7.4. Fleming s right and rule 7.5. Self
ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME
 ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME CONTENTS 1 [ 5 marks ]...4 2...5 a. [ 2 marks ]...5 b. [ 2 marks ]...5 c. [ 5 marks ]...5 d. [ 2 marks ]...5 3...6 a. [ 3 marks ]...6 b. [ 3 marks ]...6 4 [ 7 marks ]...7 5...8
ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME CONTENTS 1 [ 5 marks ]...4 2...5 a. [ 2 marks ]...5 b. [ 2 marks ]...5 c. [ 5 marks ]...5 d. [ 2 marks ]...5 3...6 a. [ 3 marks ]...6 b. [ 3 marks ]...6 4 [ 7 marks ]...7 5...8
Conventional Paper I-2010
 Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips. any 3
 (a) Ammeter deflects in one direction The magnetic flux through the coil and then in the opposite direction. increases and in one direction, and then decreases, as the -pole passes through. This process
(a) Ammeter deflects in one direction The magnetic flux through the coil and then in the opposite direction. increases and in one direction, and then decreases, as the -pole passes through. This process
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL
 MARKING GUIDELINES NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL 2 NOVEMBER 2009 This marking guideline consists of 8 pages. (MARKING GUIDELINES) -2- NC770(E)(O30)V SECTION A QUESTION 1: COMPONENTS AND CIRCUIT
MARKING GUIDELINES NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL 2 NOVEMBER 2009 This marking guideline consists of 8 pages. (MARKING GUIDELINES) -2- NC770(E)(O30)V SECTION A QUESTION 1: COMPONENTS AND CIRCUIT
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I)
 Basics of Network Theory (Part-I) 1. One coulomb charge is equal to the charge on (a) 6.24 x 10 18 electrons (b) 6.24 x 10 24 electrons (c) 6.24 x 10 18 atoms (d) none of the above 2. The correct relation
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I) 1. One coulomb charge is equal to the charge on (a) 6.24 x 10 18 electrons (b) 6.24 x 10 24 electrons (c) 6.24 x 10 18 atoms (d) none of the above 2. The correct relation
Read Chapter 7; pages:
 Forces Read Chapter 7; pages: 191-221 Objectives: - Describe how electrical charges exert forces on each other; Compare the strengths of electric and gravitational forces; Distinguish between conductors
Forces Read Chapter 7; pages: 191-221 Objectives: - Describe how electrical charges exert forces on each other; Compare the strengths of electric and gravitational forces; Distinguish between conductors
1. Mark the correct statement(s)
 1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 1. "Electrical Eng Science"
 ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 1 COURSE NAME: "Electrical Eng Science" CODE: GROUP: "[ADET 2]" DATE: December 2010 TIME: DURATION: 9:00 am "Two hours" INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 1 COURSE NAME: "Electrical Eng Science" CODE: GROUP: "[ADET 2]" DATE: December 2010 TIME: DURATION: 9:00 am "Two hours" INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This
