Part I Week 7 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes
|
|
|
- Agnes Nash
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Part I Week 7 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting December 2, / 1 2 / 1 Neural networks Artificial Neural networks: Networks single layer (ANN) Neural network Another classifier (or regression technique) for 2-class problems. Like logistic regression, it tries to predict labels y from x. Tries to find f = argmin f C (Y i f (X i )) 2 where C = { neural net functions }. 3 / 1 4 / 1
2 Neural networks Neural networks: double layer Single layer neural nets With p inputs, there are p + 1 weights ( ) f (x 1,..., x p ) = S α + x T β Here, S is a sigmoid function like the logistic curve. S(η) = eη 1 + e η. The algorithm must estimate (α, β) from data. Classifier would assign +1 to anything with S( α + x T β) > t for some threshold like / 1 6 / 1 Neural networks Neural networks Single layer neural nets In the previous figure, there are 15 weights and 3 intercept terms (α s) for input hidden layer. There are 3 weights and one intercept term for hidden output layer. The outputs from the hidden layer have the form ( ) 5 S α j + w ij x i 1 j 3. Single layer neural nets Fitting this model is done via nonlinear least squares. Computationally difficult due to the highly nonlinear form of the regression function. So, the final output is of the form ( 3 S α 0 + v j S α j + j=1 5 w ij x i ). 7 / 1 8 / 1
3 Support vector machines Support Support Vector vector machine Machines Support vector machine Another classifier (or regression technique) for 2-class problems. Like logistic regression, it tries to predict labels y from x using a linear function. A linear function with an intercept α determines an affine function f α,β (x) = x T β + α and a hyperplane { } H α,β = x : x T β + α = 0. A good classifier will separate the classes into the sides where f α,β (x) > 0, f α,β (x) < 0. It seeks to find the hyperplane that separates the classes the most. Support Support Vector vector machine Machines 9 / 1 Support Vector Machines Support vector machine! Find a linear hyperplane (decision boundary) that will separate the da Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to 4/18/ / 1 11 / 1 12 / 1
4 Support Support Vector vector machine Machines Support Vector Machines Support vector machine Support! Other possible Support Vector solutions vector machine Machines 13 / 1! Which one is better? B1 or B2?! How do you define better? Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to 4/18/2004 Tan,Steinbach, 62 Kumar Introduction to 4/18/ Support vector machines Support vector machine The reciprocal maximum margin can be written as subject to y i (x T i β + α) 1. inf β,α β 2 Therefore, the support vector machine problem is subject to y i (x T i β + α) 1. minimize β,α β 2 14 / 1 15 / 1 16 / 1
5 Support vector machine! What if the problem is not linearly separable? Support vector machines Non-separable problems If we cannot completely separate the classes it is common to modify the problem to minimize β,α,ξ β 2 subject to y i (x T i β + α) 1 ξ i, ξ i 0, n ξ i C Or the Lagrange version minimize β,α,ξ β γ subject to y i (x T i β + α) 1 ξ i, ξ i 0. ξ i 17 / 1 18 / 1 Support vector machines Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to 4/18/ Logistic vs. SVM Non-separable problems The ξ i s can be removed from this problem, yielding Logistic SVM minimize β,α β γ (1 y i f α,β (x i )) + where (z) + = max(z, 0) is the positive part function. Or, minimize β,α (1 y i f α,β (x i )) + + λ β / 1 20 / 1
6 Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width / 1 22 / 1 Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width Support vector machines Kernel trick The term β 2 2 can be thought of as a complexity penalty on the function f α,β so we could write minimize fβ,α (1 y i (α + f β (x i )) + + λ f β 2 2 We could also add such a complexity penalty to logistic regression minimize f β,α DEV(α + f β (x i ), y i ) + λ f β / 1 So, in both SVM and penalized logistic, we are looking for the best linear function where best is determined by either logistic loss (deviance) or the hinge loss (SVM). 24 / 1
7 Support vector machines Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width Kernel trick If the decision boundary is nonlinear, one might look for functions other than linear. 5.0 There are classes of functions called Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces (RKHS) for which it is theoretically (and computationally) possible to solve minimize f H (1 y i (α + f (x i ))) + + λ f 2 H or minimize f H DEV(α + f (x i ), y i ) + λ f 2 H The svm function in R allows some such kernels for SVM. 25 / 1 26 / 1 Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width 27 / 1 28 / 1
8 Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width / 1 30 / 1 Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width General EnsembleIdea methods 31 / 1 32 / 1
9 Why use ensemble methods? Basic idea: weak learners / classifiers are noisy learners. Aggregating over a large number of weak learners should improve the output. Assumes some independence across weak learners, otherwise aggregation does nothing. That is, if every learner is the same, then any sensible agrregation technique should return this classifier. Bagging In this method, one takes several bootstrap samples (samples with replacement) of the data. For each bootstrap sample S b, 1 b B, fit a model, retaining the classifier f,b. After all models have been fit, use majority vote These are often some of the best classifiers in terms of performance. f (x) = majority vote of (f,b (x)) 1 i B. Downside: they have lost interpretability in the aggregation stage. 33 / 1 34 / 1 Bagging Approximately 1/3 of data is not selected in each bootstrap sample (recall rule). Using this observation, we can define the Out-of-bag (OOB) estimate of accuracy based on OOB prediction f OOB (x i ) = majority vote of (f b (x x i )) 1 b B(i) where B(i) = {all trees not built with x i }. Total OOB error is Random forests: bagging trees If the weak learners are trees, this method is called a Random Forest. Some variations on random forests inject more randomness than just bagging. For example: Taking a random subset of features. Random linear combinations of features. OOB = 1 n ( f OOB (x i ) y i ) 35 / 1 36 / 1
10 Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width using randomforest Boosting Unlike bagging, boosting does not insert randomizaton into the algorithm. Boosting works by iteratively reweighting each observation and refitting a given classifier. To begin, suppose we have a classification algorithm that accepts case weights w = (w 1,..., w n ) f w = argmin f w i L(y i, f (x i )). and returns labels of {+1, 1}. 37 / 1 38 / 1 Boosting algorithm (AdaBoost.M1) Step 0 Initiailize weights w (0) i = 1 n, 1 i n. Step 1 For 1 t T, fit a classifier with weights w (t 1) yielding ĝ (t) = f w (t 1) = argmin f Step 2 Compute the total error rate w (t 1) i L(y i, f (x i )). Boosting algorithm (AdaBoost.M1) Step 3 Produce new weights w (t) i = w (t 1) i exp(α (t) (y i ĝ (t) (x i )) Step 4 Repeat steps 1-3 until termination. Step 5 Output the classifier ( T ) n err (t) = w (t 1) i (y i ĝ (t) (x i )) n w (t 1) i ( ) α (t) 1 err (t) = log err (t) 39 / 1 f (x) = sign t=1 α (t) ĝ (t) (x) 40 / 1
11 Illustrating AdaBoost Illustrating AdaBoost Initial weights for each data point Data points for training Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to 4/18/ / 1 Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to 4/18/ / 1 Boosting as gradient descent It turns out that boosting can be thought of as something like gradient descent. Above, we assumed we were solving Boosting as gradient descent Call the space of all possible classifiers above F 0, and all linear combinations of such classifiers F = α j f j, f j F 0 j argmin f w (t 1) i L(y i, f (x i )) but we didn t say what type of f we considered. In some sense, the boosting algorithm is a steepest descent algorithm to find argmin f F L(y i, f (x i )). 43 / 1 For more details, see ESL, but we will discuss some of these ideas. In R, this idea is implemented in the gbm package. 44 / 1
12 Boosting as gradient descent Consider the problem minimize f F = L(y i, f (x i )) = L(f ) This can be solved by gradient descent where the gradient L(f ) is in F 0 and is the direction of steepest descent for some stepsize α Boosting as gradient descent We might also optimize the stepsize argmin g F0,αL(f + α g) argmin g F0 L(f + α g) 45 / 1 Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width, 1000 trees 46 / 1 Boosting as gradient descent In this context, the forward stagewise algorithm for steepest descent is: 1 Initialize: f (0) (x) = 0; 2 For i = 1,..., T : solve α (t), ĝ (t) = argmin α,g F 0 L(f (t 1) + α g) and update f (t) = f (t 1) + α (t) ĝ (t). 3 Return the final classifier f (T ) When L(y, f (x)) = e y f (x) this corresponds to AdaBoost.M1 Changing the loss function yields new gradient boosting algorithms. 47 / 1 48 / 1
13 Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width, 5000 trees Iris data: sepal.length, sepal.width, trees {Versicolor} vs. {Setosa, Virginica} 49 / 1 {Versicolor} vs. {Setosa, Virginica} 50 / 1 Boosting fits an additive model (by default) Boosting fits an additive model (by default) 51 / 1 52 / 1
14 Out-of-bag error improvement 53 / 1
Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes. December 2, 2012
 Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 2, 2012 1 / 1 Neural networks Neural network Another classifier (or regression technique)
Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 2, 2012 1 / 1 Neural networks Neural network Another classifier (or regression technique)
Part I. Linear regression & LASSO. Linear Regression. Linear Regression. Week 10 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes
 Week 10 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Part I Linear regression & December 5, 2012 1 / 1 2 / 1 We ve talked mostly about classification, where the outcome categorical. If
Week 10 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Part I Linear regression & December 5, 2012 1 / 1 2 / 1 We ve talked mostly about classification, where the outcome categorical. If
Big Data Analytics. Special Topics for Computer Science CSE CSE Feb 24
 Big Data Analytics Special Topics for Computer Science CSE 4095-001 CSE 5095-005 Feb 24 Fei Wang Associate Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering fei_wang@uconn.edu Prediction III Goal
Big Data Analytics Special Topics for Computer Science CSE 4095-001 CSE 5095-005 Feb 24 Fei Wang Associate Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering fei_wang@uconn.edu Prediction III Goal
Recitation 9. Gradient Boosting. Brett Bernstein. March 30, CDS at NYU. Brett Bernstein (CDS at NYU) Recitation 9 March 30, / 14
 Brett Bernstein CDS at NYU March 30, 2017 Brett Bernstein (CDS at NYU) Recitation 9 March 30, 2017 1 / 14 Initial Question Intro Question Question Suppose 10 different meteorologists have produced functions
Brett Bernstein CDS at NYU March 30, 2017 Brett Bernstein (CDS at NYU) Recitation 9 March 30, 2017 1 / 14 Initial Question Intro Question Question Suppose 10 different meteorologists have produced functions
Boosting. Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: / April Optional reading: ISL 8.2, ESL , 10.7, 10.13
 Boosting Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: 36-462/36-662 April 25 2013 Optional reading: ISL 8.2, ESL 10.1 10.4, 10.7, 10.13 1 Reminder: classification trees Suppose that we are given training data (x i, y
Boosting Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: 36-462/36-662 April 25 2013 Optional reading: ISL 8.2, ESL 10.1 10.4, 10.7, 10.13 1 Reminder: classification trees Suppose that we are given training data (x i, y
VBM683 Machine Learning
 VBM683 Machine Learning Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Dhruv Batra Bias is the algorithm's tendency to consistently learn the wrong thing by not taking into account all the information in the data
VBM683 Machine Learning Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Dhruv Batra Bias is the algorithm's tendency to consistently learn the wrong thing by not taking into account all the information in the data
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning
 ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions. f(x) = c m 1(x R m )
 CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions with R 1,..., R m R p disjoint. f(x) = M c m 1(x R m ) m=1 The CART algorithm is a heuristic, adaptive
CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions with R 1,..., R m R p disjoint. f(x) = M c m 1(x R m ) m=1 The CART algorithm is a heuristic, adaptive
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Final Review. Henry Chai 12/4/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions
 CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions f (x) = M c m 1(x R m ) m=1 with R 1,..., R m R p disjoint. The CART algorithm is a heuristic, adaptive
CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions f (x) = M c m 1(x R m ) m=1 with R 1,..., R m R p disjoint. The CART algorithm is a heuristic, adaptive
Part I. Linear Discriminant Analysis. Discriminant analysis. Discriminant analysis
 Week 5 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Part I Linear Discriminant Analysis October 29, 2012 1 / 1 2 / 1 Nearest centroid rule Suppose we break down our data matrix as by the
Week 5 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Part I Linear Discriminant Analysis October 29, 2012 1 / 1 2 / 1 Nearest centroid rule Suppose we break down our data matrix as by the
6.036 midterm review. Wednesday, March 18, 15
 6.036 midterm review 1 Topics covered supervised learning labels available unsupervised learning no labels available semi-supervised learning some labels available - what algorithms have you learned that
6.036 midterm review 1 Topics covered supervised learning labels available unsupervised learning no labels available semi-supervised learning some labels available - what algorithms have you learned that
Lecture 13: Ensemble Methods
 Lecture 13: Ensemble Methods Applied Multivariate Analysis Math 570, Fall 2014 Xingye Qiao Department of Mathematical Sciences Binghamton University E-mail: qiao@math.binghamton.edu 1 / 71 Outline 1 Bootstrap
Lecture 13: Ensemble Methods Applied Multivariate Analysis Math 570, Fall 2014 Xingye Qiao Department of Mathematical Sciences Binghamton University E-mail: qiao@math.binghamton.edu 1 / 71 Outline 1 Bootstrap
ECE 5984: Introduction to Machine Learning
 ECE 5984: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting Readings: Murphy 16.4; Hastie 16 Dhruv Batra Virginia Tech Administrativia HW3 Due: April 14, 11:55pm You will implement
ECE 5984: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting Readings: Murphy 16.4; Hastie 16 Dhruv Batra Virginia Tech Administrativia HW3 Due: April 14, 11:55pm You will implement
Indirect Rule Learning: Support Vector Machines. Donglin Zeng, Department of Biostatistics, University of North Carolina
 Indirect Rule Learning: Support Vector Machines Indirect learning: loss optimization It doesn t estimate the prediction rule f (x) directly, since most loss functions do not have explicit optimizers. Indirection
Indirect Rule Learning: Support Vector Machines Indirect learning: loss optimization It doesn t estimate the prediction rule f (x) directly, since most loss functions do not have explicit optimizers. Indirection
Neural Networks and Ensemble Methods for Classification
 Neural Networks and Ensemble Methods for Classification NEURAL NETWORKS 2 Neural Networks A neural network is a set of connected input/output units (neurons) where each connection has a weight associated
Neural Networks and Ensemble Methods for Classification NEURAL NETWORKS 2 Neural Networks A neural network is a set of connected input/output units (neurons) where each connection has a weight associated
Linear Discriminant Analysis Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes. November 9, Statistics 202: Data Mining
 Linear Discriminant Analysis Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes November 9, 2012 1 / 1 Nearest centroid rule Suppose we break down our data matrix as by the labels yielding (X
Linear Discriminant Analysis Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes November 9, 2012 1 / 1 Nearest centroid rule Suppose we break down our data matrix as by the labels yielding (X
CS7267 MACHINE LEARNING
 CS7267 MACHINE LEARNING ENSEMBLE LEARNING Ref: Dr. Ricardo Gutierrez-Osuna at TAMU, and Aarti Singh at CMU Mingon Kang, Ph.D. Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Definition of Ensemble Learning
CS7267 MACHINE LEARNING ENSEMBLE LEARNING Ref: Dr. Ricardo Gutierrez-Osuna at TAMU, and Aarti Singh at CMU Mingon Kang, Ph.D. Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Definition of Ensemble Learning
Gradient Boosting (Continued)
 Gradient Boosting (Continued) David Rosenberg New York University April 4, 2016 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 April 4, 2016 1 / 31 Boosting Fits an Additive Model Boosting Fits an Additive
Gradient Boosting (Continued) David Rosenberg New York University April 4, 2016 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 April 4, 2016 1 / 31 Boosting Fits an Additive Model Boosting Fits an Additive
Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function.
 Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick
 SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University February 26 th, 2007 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 1 SVMs reminder 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 2 Today
SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University February 26 th, 2007 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 1 SVMs reminder 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 2 Today
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
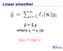 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2014 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2014 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Data Mining und Maschinelles Lernen
 Data Mining und Maschinelles Lernen Ensemble Methods Bias-Variance Trade-off Basic Idea of Ensembles Bagging Basic Algorithm Bagging with Costs Randomization Random Forests Boosting Stacking Error-Correcting
Data Mining und Maschinelles Lernen Ensemble Methods Bias-Variance Trade-off Basic Idea of Ensembles Bagging Basic Algorithm Bagging with Costs Randomization Random Forests Boosting Stacking Error-Correcting
Learning with multiple models. Boosting.
 CS 2750 Machine Learning Lecture 21 Learning with multiple models. Boosting. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Learning with multiple models: Approach 2 Approach 2: use multiple models
CS 2750 Machine Learning Lecture 21 Learning with multiple models. Boosting. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Learning with multiple models: Approach 2 Approach 2: use multiple models
TDT4173 Machine Learning
 TDT4173 Machine Learning Lecture 9 Learning Classifiers: Bagging & Boosting Norwegian University of Science and Technology Helge Langseth IT-VEST 310 helgel@idi.ntnu.no 1 TDT4173 Machine Learning Outline
TDT4173 Machine Learning Lecture 9 Learning Classifiers: Bagging & Boosting Norwegian University of Science and Technology Helge Langseth IT-VEST 310 helgel@idi.ntnu.no 1 TDT4173 Machine Learning Outline
Nonlinear Classification
 Nonlinear Classification INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder October 5-10, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Linear Classification Most classifiers we ve seen use linear functions
Nonlinear Classification INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder October 5-10, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Linear Classification Most classifiers we ve seen use linear functions
Stochastic Gradient Descent
 Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 9, 2013 1 Logistic Regression Logistic function (or Sigmoid): Learn P(Y X) directly Assume a particular
Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 9, 2013 1 Logistic Regression Logistic function (or Sigmoid): Learn P(Y X) directly Assume a particular
Numerical Learning Algorithms
 Numerical Learning Algorithms Example SVM for Separable Examples.......................... Example SVM for Nonseparable Examples....................... 4 Example Gaussian Kernel SVM...............................
Numerical Learning Algorithms Example SVM for Separable Examples.......................... Example SVM for Nonseparable Examples....................... 4 Example Gaussian Kernel SVM...............................
Artificial Neural Networks" and Nonparametric Methods" CMPSCI 383 Nov 17, 2011!
 Artificial Neural Networks" and Nonparametric Methods" CMPSCI 383 Nov 17, 2011! 1 Todayʼs lecture" How the brain works (!)! Artificial neural networks! Perceptrons! Multilayer feed-forward networks! Error
Artificial Neural Networks" and Nonparametric Methods" CMPSCI 383 Nov 17, 2011! 1 Todayʼs lecture" How the brain works (!)! Artificial neural networks! Perceptrons! Multilayer feed-forward networks! Error
Ensemble Methods. Charles Sutton Data Mining and Exploration Spring Friday, 27 January 12
 Ensemble Methods Charles Sutton Data Mining and Exploration Spring 2012 Bias and Variance Consider a regression problem Y = f(x)+ N(0, 2 ) With an estimate regression function ˆf, e.g., ˆf(x) =w > x Suppose
Ensemble Methods Charles Sutton Data Mining and Exploration Spring 2012 Bias and Variance Consider a regression problem Y = f(x)+ N(0, 2 ) With an estimate regression function ˆf, e.g., ˆf(x) =w > x Suppose
Support Vector Machines. Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar
 Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Announcements - Homework
 Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Chapter 6. Ensemble Methods
 Chapter 6. Ensemble Methods Wei Pan Division of Biostatistics, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455 Email: weip@biostat.umn.edu PubH 7475/8475 c Wei Pan Introduction
Chapter 6. Ensemble Methods Wei Pan Division of Biostatistics, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455 Email: weip@biostat.umn.edu PubH 7475/8475 c Wei Pan Introduction
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2015 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2015 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
18.9 SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES
 744 Chapter 8. Learning from Examples is the fact that each regression problem will be easier to solve, because it involves only the examples with nonzero weight the examples whose kernels overlap the
744 Chapter 8. Learning from Examples is the fact that each regression problem will be easier to solve, because it involves only the examples with nonzero weight the examples whose kernels overlap the
Chapter 9. Support Vector Machine. Yongdai Kim Seoul National University
 Chapter 9. Support Vector Machine Yongdai Kim Seoul National University 1. Introduction Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a classification method developed by Vapnik (1996). It is thought that SVM improved
Chapter 9. Support Vector Machine Yongdai Kim Seoul National University 1. Introduction Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a classification method developed by Vapnik (1996). It is thought that SVM improved
Support Vector Machine (continued)
 Support Vector Machine continued) Overlapping class distribution: In practice the class-conditional distributions may overlap, so that the training data points are no longer linearly separable. We need
Support Vector Machine continued) Overlapping class distribution: In practice the class-conditional distributions may overlap, so that the training data points are no longer linearly separable. We need
Learning Ensembles. 293S T. Yang. UCSB, 2017.
 Learning Ensembles 293S T. Yang. UCSB, 2017. Outlines Learning Assembles Random Forest Adaboost Training data: Restaurant example Examples described by attribute values (Boolean, discrete, continuous)
Learning Ensembles 293S T. Yang. UCSB, 2017. Outlines Learning Assembles Random Forest Adaboost Training data: Restaurant example Examples described by attribute values (Boolean, discrete, continuous)
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Hypothesis Space variable size deterministic continuous parameters Learning Algorithm linear and quadratic programming eager batch SVMs combine three important ideas Apply optimization
Support Vector Machines Hypothesis Space variable size deterministic continuous parameters Learning Algorithm linear and quadratic programming eager batch SVMs combine three important ideas Apply optimization
Support Vector Machines
 Two SVM tutorials linked in class website (please, read both): High-level presentation with applications (Hearst 1998) Detailed tutorial (Burges 1998) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning 10701/15781
Two SVM tutorials linked in class website (please, read both): High-level presentation with applications (Hearst 1998) Detailed tutorial (Burges 1998) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning 10701/15781
Statistical Pattern Recognition
 Statistical Pattern Recognition Support Vector Machine (SVM) Hamid R. Rabiee Hadi Asheri, Jafar Muhammadi, Nima Pourdamghani Spring 2013 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/91-92/2/ce725-1/ Agenda Introduction
Statistical Pattern Recognition Support Vector Machine (SVM) Hamid R. Rabiee Hadi Asheri, Jafar Muhammadi, Nima Pourdamghani Spring 2013 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/91-92/2/ce725-1/ Agenda Introduction
Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2012
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Linear classifier Which classifier? x 2 x 1 2 Linear classifier Margin concept x 2
Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Linear classifier Which classifier? x 2 x 1 2 Linear classifier Margin concept x 2
Logistic Regression and Boosting for Labeled Bags of Instances
 Logistic Regression and Boosting for Labeled Bags of Instances Xin Xu and Eibe Frank Department of Computer Science University of Waikato Hamilton, New Zealand {xx5, eibe}@cs.waikato.ac.nz Abstract. In
Logistic Regression and Boosting for Labeled Bags of Instances Xin Xu and Eibe Frank Department of Computer Science University of Waikato Hamilton, New Zealand {xx5, eibe}@cs.waikato.ac.nz Abstract. In
Support Vector Machines for Classification: A Statistical Portrait
 Support Vector Machines for Classification: A Statistical Portrait Yoonkyung Lee Department of Statistics The Ohio State University May 27, 2011 The Spring Conference of Korean Statistical Society KAIST,
Support Vector Machines for Classification: A Statistical Portrait Yoonkyung Lee Department of Statistics The Ohio State University May 27, 2011 The Spring Conference of Korean Statistical Society KAIST,
A Brief Introduction to Adaboost
 A Brief Introduction to Adaboost Hongbo Deng 6 Feb, 2007 Some of the slides are borrowed from Derek Hoiem & Jan ˇSochman. 1 Outline Background Adaboost Algorithm Theory/Interpretations 2 What s So Good
A Brief Introduction to Adaboost Hongbo Deng 6 Feb, 2007 Some of the slides are borrowed from Derek Hoiem & Jan ˇSochman. 1 Outline Background Adaboost Algorithm Theory/Interpretations 2 What s So Good
Logistic Regression. Machine Learning Fall 2018
 Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
Learning theory. Ensemble methods. Boosting. Boosting: history
 Learning theory Probability distribution P over X {0, 1}; let (X, Y ) P. We get S := {(x i, y i )} n i=1, an iid sample from P. Ensemble methods Goal: Fix ɛ, δ (0, 1). With probability at least 1 δ (over
Learning theory Probability distribution P over X {0, 1}; let (X, Y ) P. We get S := {(x i, y i )} n i=1, an iid sample from P. Ensemble methods Goal: Fix ɛ, δ (0, 1). With probability at least 1 δ (over
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
Delta Boosting Machine and its application in Actuarial Modeling Simon CK Lee, Sheldon XS Lin KU Leuven, University of Toronto
 Delta Boosting Machine and its application in Actuarial Modeling Simon CK Lee, Sheldon XS Lin KU Leuven, University of Toronto This presentation has been prepared for the Actuaries Institute 2015 ASTIN
Delta Boosting Machine and its application in Actuarial Modeling Simon CK Lee, Sheldon XS Lin KU Leuven, University of Toronto This presentation has been prepared for the Actuaries Institute 2015 ASTIN
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
CSC242: Intro to AI. Lecture 21
 CSC242: Intro to AI Lecture 21 Administrivia Project 4 (homeworks 18 & 19) due Mon Apr 16 11:59PM Posters Apr 24 and 26 You need an idea! You need to present it nicely on 2-wide by 4-high landscape pages
CSC242: Intro to AI Lecture 21 Administrivia Project 4 (homeworks 18 & 19) due Mon Apr 16 11:59PM Posters Apr 24 and 26 You need an idea! You need to present it nicely on 2-wide by 4-high landscape pages
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine
 CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
10-701/ Machine Learning - Midterm Exam, Fall 2010
 10-701/15-781 Machine Learning - Midterm Exam, Fall 2010 Aarti Singh Carnegie Mellon University 1. Personal info: Name: Andrew account: E-mail address: 2. There should be 15 numbered pages in this exam
10-701/15-781 Machine Learning - Midterm Exam, Fall 2010 Aarti Singh Carnegie Mellon University 1. Personal info: Name: Andrew account: E-mail address: 2. There should be 15 numbered pages in this exam
Article from. Predictive Analytics and Futurism. July 2016 Issue 13
 Article from Predictive Analytics and Futurism July 2016 Issue 13 Regression and Classification: A Deeper Look By Jeff Heaton Classification and regression are the two most common forms of models fitted
Article from Predictive Analytics and Futurism July 2016 Issue 13 Regression and Classification: A Deeper Look By Jeff Heaton Classification and regression are the two most common forms of models fitted
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2016 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2016 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
What makes good ensemble? CS789: Machine Learning and Neural Network. Introduction. More on diversity
 What makes good ensemble? CS789: Machine Learning and Neural Network Ensemble methods Jakramate Bootkrajang Department of Computer Science Chiang Mai University 1. A member of the ensemble is accurate.
What makes good ensemble? CS789: Machine Learning and Neural Network Ensemble methods Jakramate Bootkrajang Department of Computer Science Chiang Mai University 1. A member of the ensemble is accurate.
CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019)
 CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019) Prof. Victor Adamchik U of Southern California Mar. 19, 2019 March 19, 2019 1 / 43 Administration March 19, 2019 2 / 43 Administration TA3 is due this week March
CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019) Prof. Victor Adamchik U of Southern California Mar. 19, 2019 March 19, 2019 1 / 43 Administration March 19, 2019 2 / 43 Administration TA3 is due this week March
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Here we approach the two-class classification problem in a direct way: We try and find a plane that separates the classes in feature space. If we cannot, we get creative in two
Support Vector Machines Here we approach the two-class classification problem in a direct way: We try and find a plane that separates the classes in feature space. If we cannot, we get creative in two
Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron
 CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
A Magiv CV Theory for Large-Margin Classifiers
 A Magiv CV Theory for Large-Margin Classifiers Hui Zou School of Statistics, University of Minnesota June 30, 2018 Joint work with Boxiang Wang Outline 1 Background 2 Magic CV formula 3 Magic support vector
A Magiv CV Theory for Large-Margin Classifiers Hui Zou School of Statistics, University of Minnesota June 30, 2018 Joint work with Boxiang Wang Outline 1 Background 2 Magic CV formula 3 Magic support vector
Dimension Reduction Using Rule Ensemble Machine Learning Methods: A Numerical Study of Three Ensemble Methods
 Dimension Reduction Using Rule Ensemble Machine Learning Methods: A Numerical Study of Three Ensemble Methods Orianna DeMasi, Juan Meza, David H. Bailey Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory 1 Cyclotron
Dimension Reduction Using Rule Ensemble Machine Learning Methods: A Numerical Study of Three Ensemble Methods Orianna DeMasi, Juan Meza, David H. Bailey Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory 1 Cyclotron
Neural Networks biological neuron artificial neuron 1
 Neural Networks biological neuron artificial neuron 1 A two-layer neural network Output layer (activation represents classification) Weighted connections Hidden layer ( internal representation ) Input
Neural Networks biological neuron artificial neuron 1 A two-layer neural network Output layer (activation represents classification) Weighted connections Hidden layer ( internal representation ) Input
Bagging and Other Ensemble Methods
 Bagging and Other Ensemble Methods Sargur N. Srihari srihari@buffalo.edu 1 Regularization Strategies 1. Parameter Norm Penalties 2. Norm Penalties as Constrained Optimization 3. Regularization and Underconstrained
Bagging and Other Ensemble Methods Sargur N. Srihari srihari@buffalo.edu 1 Regularization Strategies 1. Parameter Norm Penalties 2. Norm Penalties as Constrained Optimization 3. Regularization and Underconstrained
Stat 502X Exam 2 Spring 2014
 Stat 502X Exam 2 Spring 2014 I have neither given nor received unauthorized assistance on this exam. Name Signed Date Name Printed This exam consists of 12 parts. I'll score it at 10 points per problem/part
Stat 502X Exam 2 Spring 2014 I have neither given nor received unauthorized assistance on this exam. Name Signed Date Name Printed This exam consists of 12 parts. I'll score it at 10 points per problem/part
Data Mining Classification: Alternative Techniques. Lecture Notes for Chapter 5. Introduction to Data Mining
 Data Mining Classification: Alternative Techniques Lecture Notes for Chapter 5 Introduction to Data Mining by Tan, Steinbach, Kumar Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to Data Mining 4/18/2004 1 Neural networks
Data Mining Classification: Alternative Techniques Lecture Notes for Chapter 5 Introduction to Data Mining by Tan, Steinbach, Kumar Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to Data Mining 4/18/2004 1 Neural networks
Support Vector Machine I
 Support Vector Machine I Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative Please use piazza. No emails. HW 0 grades are back. Re-grade request for one week. HW 1 due soon. HW
Support Vector Machine I Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative Please use piazza. No emails. HW 0 grades are back. Re-grade request for one week. HW 1 due soon. HW
Machine Learning Ensemble Learning I Hamid R. Rabiee Jafar Muhammadi, Alireza Ghasemi Spring /
 Machine Learning Ensemble Learning I Hamid R. Rabiee Jafar Muhammadi, Alireza Ghasemi Spring 2015 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/93-94/2/ce717-1 / Agenda Combining Classifiers Empirical view Theoretical
Machine Learning Ensemble Learning I Hamid R. Rabiee Jafar Muhammadi, Alireza Ghasemi Spring 2015 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/93-94/2/ce717-1 / Agenda Combining Classifiers Empirical view Theoretical
Pattern Recognition 2018 Support Vector Machines
 Pattern Recognition 2018 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recognition 1 / 48 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht
Pattern Recognition 2018 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recognition 1 / 48 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht
Midterm exam CS 189/289, Fall 2015
 Midterm exam CS 189/289, Fall 2015 You have 80 minutes for the exam. Total 100 points: 1. True/False: 36 points (18 questions, 2 points each). 2. Multiple-choice questions: 24 points (8 questions, 3 points
Midterm exam CS 189/289, Fall 2015 You have 80 minutes for the exam. Total 100 points: 1. True/False: 36 points (18 questions, 2 points each). 2. Multiple-choice questions: 24 points (8 questions, 3 points
Machine Learning Lecture 7
 Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 7 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Statistical Learning Theory 23.05.2016 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear Discriminant
Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 7 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Statistical Learning Theory 23.05.2016 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear Discriminant
Evaluation. Andrea Passerini Machine Learning. Evaluation
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Basic concepts requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Basic concepts requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain
> DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE GRAVIS 2016 BASEL. Logistic Regression. Pattern Recognition 2016 Sandro Schönborn University of Basel
 Logistic Regression Pattern Recognition 2016 Sandro Schönborn University of Basel Two Worlds: Probabilistic & Algorithmic We have seen two conceptual approaches to classification: data class density estimation
Logistic Regression Pattern Recognition 2016 Sandro Schönborn University of Basel Two Worlds: Probabilistic & Algorithmic We have seen two conceptual approaches to classification: data class density estimation
Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning. Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas
 Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning Reinforcement Learning Parametric Y Continuous Non-parametric
Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning Reinforcement Learning Parametric Y Continuous Non-parametric
Boosted Lasso and Reverse Boosting
 Boosted Lasso and Reverse Boosting Peng Zhao University of California, Berkeley, USA. Bin Yu University of California, Berkeley, USA. Summary. This paper introduces the concept of backward step in contrast
Boosted Lasso and Reverse Boosting Peng Zhao University of California, Berkeley, USA. Bin Yu University of California, Berkeley, USA. Summary. This paper introduces the concept of backward step in contrast
Ensemble Methods: Jay Hyer
 Ensemble Methods: committee-based learning Jay Hyer linkedin.com/in/jayhyer @adatahead Overview Why Ensemble Learning? What is learning? How is ensemble learning different? Boosting Weak and Strong Learners
Ensemble Methods: committee-based learning Jay Hyer linkedin.com/in/jayhyer @adatahead Overview Why Ensemble Learning? What is learning? How is ensemble learning different? Boosting Weak and Strong Learners
Final Overview. Introduction to ML. Marek Petrik 4/25/2017
 Final Overview Introduction to ML Marek Petrik 4/25/2017 This Course: Introduction to Machine Learning Build a foundation for practice and research in ML Basic machine learning concepts: max likelihood,
Final Overview Introduction to ML Marek Petrik 4/25/2017 This Course: Introduction to Machine Learning Build a foundation for practice and research in ML Basic machine learning concepts: max likelihood,
Evaluation requires to define performance measures to be optimized
 Evaluation Basic concepts Evaluation requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain (generalization error) approximation
Evaluation Basic concepts Evaluation requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain (generalization error) approximation
SVMs: Non-Separable Data, Convex Surrogate Loss, Multi-Class Classification, Kernels
 SVMs: Non-Separable Data, Convex Surrogate Loss, Multi-Class Classification, Kernels Karl Stratos June 21, 2018 1 / 33 Tangent: Some Loose Ends in Logistic Regression Polynomial feature expansion in logistic
SVMs: Non-Separable Data, Convex Surrogate Loss, Multi-Class Classification, Kernels Karl Stratos June 21, 2018 1 / 33 Tangent: Some Loose Ends in Logistic Regression Polynomial feature expansion in logistic
COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning. Nakul Verma
 COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning Nakul Verma Announcements HW1 due next lecture Project details are available decide on the group and topic by Thursday Last time Generative vs. Discriminative
COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning Nakul Verma Announcements HW1 due next lecture Project details are available decide on the group and topic by Thursday Last time Generative vs. Discriminative
Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons
 Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons Cognitive Systems II - Machine Learning SS 2005 Part I: Basic Approaches of Concept Learning Perceptrons, Artificial Neuronal Networks Lecture 4: Perceptrons
Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons Cognitive Systems II - Machine Learning SS 2005 Part I: Basic Approaches of Concept Learning Perceptrons, Artificial Neuronal Networks Lecture 4: Perceptrons
The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page (two sides) or two-page (one side) crib sheet.
 CS 189 Spring 013 Introduction to Machine Learning Final You have 3 hours for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page (two sides) or two-page (one side) crib sheet. Please
CS 189 Spring 013 Introduction to Machine Learning Final You have 3 hours for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page (two sides) or two-page (one side) crib sheet. Please
Linear Classifiers: Expressiveness
 Linear Classifiers: Expressiveness Machine Learning Spring 2018 The slides are mainly from Vivek Srikumar 1 Lecture outline Linear classifiers: Introduction What functions do linear classifiers express?
Linear Classifiers: Expressiveness Machine Learning Spring 2018 The slides are mainly from Vivek Srikumar 1 Lecture outline Linear classifiers: Introduction What functions do linear classifiers express?
Statistical Methods for Data Mining
 Statistical Methods for Data Mining Kuangnan Fang Xiamen University Email: xmufkn@xmu.edu.cn Support Vector Machines Here we approach the two-class classification problem in a direct way: We try and find
Statistical Methods for Data Mining Kuangnan Fang Xiamen University Email: xmufkn@xmu.edu.cn Support Vector Machines Here we approach the two-class classification problem in a direct way: We try and find
Machine Learning. Ensemble Methods. Manfred Huber
 Machine Learning Ensemble Methods Manfred Huber 2015 1 Bias, Variance, Noise Classification errors have different sources Choice of hypothesis space and algorithm Training set Noise in the data The expected
Machine Learning Ensemble Methods Manfred Huber 2015 1 Bias, Variance, Noise Classification errors have different sources Choice of hypothesis space and algorithm Training set Noise in the data The expected
Name (NetID): (1 Point)
 CS446: Machine Learning (D) Spring 2017 March 16 th, 2017 This is a closed book exam. Everything you need in order to solve the problems is supplied in the body of this exam. This exam booklet contains
CS446: Machine Learning (D) Spring 2017 March 16 th, 2017 This is a closed book exam. Everything you need in order to solve the problems is supplied in the body of this exam. This exam booklet contains
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines
 Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
CS 484 Data Mining. Classification 7. Some slides are from Professor Padhraic Smyth at UC Irvine
 CS 484 Data Mining Classification 7 Some slides are from Professor Padhraic Smyth at UC Irvine Bayesian Belief networks Conditional independence assumption of Naïve Bayes classifier is too strong. Allows
CS 484 Data Mining Classification 7 Some slides are from Professor Padhraic Smyth at UC Irvine Bayesian Belief networks Conditional independence assumption of Naïve Bayes classifier is too strong. Allows
Announcements Kevin Jamieson
 Announcements My office hours TODAY 3:30 pm - 4:30 pm CSE 666 Poster Session - Pick one First poster session TODAY 4:30 pm - 7:30 pm CSE Atrium Second poster session December 12 4:30 pm - 7:30 pm CSE Atrium
Announcements My office hours TODAY 3:30 pm - 4:30 pm CSE 666 Poster Session - Pick one First poster session TODAY 4:30 pm - 7:30 pm CSE Atrium Second poster session December 12 4:30 pm - 7:30 pm CSE Atrium
Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11. Mehryar Mohri Courant Institute and Google Research
 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11 Mehryar Mohri Courant Institute and Google Research mohri@cims.nyu.edu Boosting Mehryar Mohri - Introduction to Machine Learning page 2 Boosting Ideas Main idea:
Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11 Mehryar Mohri Courant Institute and Google Research mohri@cims.nyu.edu Boosting Mehryar Mohri - Introduction to Machine Learning page 2 Boosting Ideas Main idea:
Discriminative Models
 No.5 Discriminative Models Hui Jiang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Lassonde School of Engineering York University, Toronto, Canada Outline Generative vs. Discriminative models
No.5 Discriminative Models Hui Jiang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Lassonde School of Engineering York University, Toronto, Canada Outline Generative vs. Discriminative models
Voting (Ensemble Methods)
 1 2 Voting (Ensemble Methods) Instead of learning a single classifier, learn many weak classifiers that are good at different parts of the data Output class: (Weighted) vote of each classifier Classifiers
1 2 Voting (Ensemble Methods) Instead of learning a single classifier, learn many weak classifiers that are good at different parts of the data Output class: (Weighted) vote of each classifier Classifiers
Neural Networks DWML, /25
 DWML, 2007 /25 Neural networks: Biological and artificial Consider humans: Neuron switching time 0.00 second Number of neurons 0 0 Connections per neuron 0 4-0 5 Scene recognition time 0. sec 00 inference
DWML, 2007 /25 Neural networks: Biological and artificial Consider humans: Neuron switching time 0.00 second Number of neurons 0 0 Connections per neuron 0 4-0 5 Scene recognition time 0. sec 00 inference
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2018
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression
Neural Networks and Deep Learning
 Neural Networks and Deep Learning Professor Ameet Talwalkar November 12, 2015 Professor Ameet Talwalkar Neural Networks and Deep Learning November 12, 2015 1 / 16 Outline 1 Review of last lecture AdaBoost
Neural Networks and Deep Learning Professor Ameet Talwalkar November 12, 2015 Professor Ameet Talwalkar Neural Networks and Deep Learning November 12, 2015 1 / 16 Outline 1 Review of last lecture AdaBoost
10/05/2016. Computational Methods for Data Analysis. Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES. Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers
 Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions
 CS281B/Stat241B (Spring 2008) Statistical Learning Theory Lecture: 3 Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions Lecturer: Peter Bartlett Scribe: Hao Zhang 1 Review We assume that there is a probability
CS281B/Stat241B (Spring 2008) Statistical Learning Theory Lecture: 3 Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions Lecturer: Peter Bartlett Scribe: Hao Zhang 1 Review We assume that there is a probability
Regularization Paths
 December 2005 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Regularization Paths Trevor Hastie Stanford University drawing on collaborations with Brad Efron, Saharon Rosset, Ji Zhu, Hui Zhou, Rob Tibshirani and
December 2005 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Regularization Paths Trevor Hastie Stanford University drawing on collaborations with Brad Efron, Saharon Rosset, Ji Zhu, Hui Zhou, Rob Tibshirani and
Infinite Ensemble Learning with Support Vector Machinery
 Infinite Ensemble Learning with Support Vector Machinery Hsuan-Tien Lin and Ling Li Learning Systems Group, California Institute of Technology ECML/PKDD, October 4, 2005 H.-T. Lin and L. Li (Learning Systems
Infinite Ensemble Learning with Support Vector Machinery Hsuan-Tien Lin and Ling Li Learning Systems Group, California Institute of Technology ECML/PKDD, October 4, 2005 H.-T. Lin and L. Li (Learning Systems
