Adversarial Examples
|
|
|
- Colleen Walton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adversarial Examples presentation by Ian Goodfellow Deep Learning Summer School Montreal August 9, 2015
2 In this presentation. - Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks. Szegedy et al., ICLR Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples. Goodfellow et al., ICLR Distributional Smoothing by Virtual Adversarial Examples. Miyato et al ArXiv 2015.
3 Universal engineering machine (model-based optimization) Make new inventions by finding input that maximizes model s predicted performance Training data Extrapolation
4 Deep neural networks are as good as humans at......recognizing objects and faces. (Szegedy et al, 2014) (Taigmen et al, 2013)...solving CAPTCHAS and reading addresses... (Goodfellow et al, 2013) (Goodfellow et al, 2013) and other tasks...
5 Do neural networks understand these tasks? - John Searle s Chinese Room thought experiment 你好嗎? -> 我很好, 你呢? - What happens for a sentence not in the instruction book? 您貴姓 大名? ->
6 Turning objects into airplanes
7 Attacking a linear model
8 Clever Hans ( Clever Hans, Clever Algorithms, Bob Sturm)
9 Adversarial examples from overfitting O O O x x x x O O
10 Adversarial examples from underfitting O O x x x O x O O
11 Different kinds of low capacity Linear model: overconfident when extrapolating RBF: no opinion in most places
12 Modern deep nets are very (piecewise) linear Rectified linear unit Maxout Carefully tuned sigmoid LSTM
13 A thin manifold of accuracy Argument to softmax
14 Not every class change is a mistake Clean example Perturbation Corrupted example Perturbation changes the true class Random perturbation does not change the class Perturbation changes the input to rubbish class All three perturbations have L2 norm 3.96 This is actually small. We typically use 7!
15 Guaranteeing that class changes are mistakes Clean example Perturbation Corrupted example Each pixel has some precision below which changes can t be measured. -> Max norm constraint blocks previous attempt at changing the class constrain the max norm and we can guarantee that we do not change the class. To make adversarial examples for other kinds of data, we need to define different invariant constraint regions. Random perturbations still do not change the class Max norm constraint blocks change to rubbish class All three perturbations have L2 norm 3.96, same as on prev slide. They now have max norm This is accomplished by taking * sign(perturbation) and choosing the sign randomly for pixels that were not perturbed before.
16 The Fast Gradient Sign Method
17 Linear Adversarial examples
18 High-dimensional linear models Weights Clean examples Adversarial examples Signs of weights
19 Higher-dimensional linear models (Andrej Karpathy, Breaking Linear Classifiers on ImageNet )
20 RBFs behave more intuitively far from the data
21 Easy to optimize = easy to perturb Do we need to move past gradient-based optimization to overcome adversarial examples?
22 Ubiquitous hallucinations
23 Methods based on expensive search, strong hand-designed priors (Nguyen et al 2015) (Olah 2015)
24 Cross-model, cross-dataset generalization
25 Cross-model, cross-dataset generalization Neural net -> nearest neighbor: 25.3% error rate Smoothed nearest neighbor -> nearest neighbor: 47.2% error rate (a non-differentiable model doesn t provide much protection, it just requires the attacker to work indirectly) Adversarially trained neural net -> nearest neighbor: 22.15% error rate (Adversarially trained neural net -> self: 18% error rate) Maxout net -> relu net: 99.4% error rate agree on wrong class 85% of the time Maxout net -> tanh net: 99.3% error rate Maxout net -> softmax regression: 88.9% error rate agree on wrong class 67% of the time Maxout net -> shallow RBF: 36.8% error rate agree on class 43% of the time
26 Adversarial examples in the human visual system (Circles are concentric but appear intertwining) (Pinna and Gregory, 2002)
27 Failed defenses - Defenses that fail due to cross-model transfer: - Ensembles - Voting after multiple saccades - Other failed defenses: - Noise resistance - Generative modeling / unsupervised pretraining - Denoise the input with an autoencoder (Gu and Rigazio, 2014) - Defenses that solve the adversarial task only if they break the clean task performance: - Weight decay (L1 or L2) - Jacobian regularization (like double backprop) - Deep RBF network
28 Limiting total variation (weight constraints) Usually underfits before it solves the adversarial example problem. Limiting sensitivity to infinitesimal perturbation (double backprop, CAE) -Very hard to make the derivative close to 0 -Only provides constraint very near training examples, so does not solve adversarial examples. Limiting sensitivity to finite perturbation (adversarial training) -Easy to fit because slope is not constrained -Constrains function over a wide area
29 Generative modeling cannot solve the problem Both these two class mixture models implement the same marginal over x, with totally different posteriors over the classes. The likelihood criterion can t prefer one to the other, and in many cases will prefer the bad one.
30 Security implications - Must consider existence of adversarial examples when deciding whether to use machine learning - Attackers can shut down a system that detects and refuses to process adversarial examples - Attackers can control the output of a naive system - Attacks can resemble regular data, or can appear to be unstructured noise, or can be structured but unusual - Attacker does not need access to your model, parameters, or training set
31 Universal approximator theorem Neural nets can represent either function: Maximum Maximum likelihood likelihood doesn t doesn t cause cause them them to to learn the right function. But we can fix that...
32 Training on adversarial examples % error on MNIST
33 Weaknesses persist
34 More weaknesses
35 Pertubation s effect on class distributions
36 Pertubation s effect after adversarial training
37 Virtual adversarial training - Penalize full KL divergence between predictions on clean and adversarial point - Does not need y - Semi-supervised learning - MNIST results: 0.64% test error (statistically tied with state of the art) 100 examples: VAE -> 3.33% error Virtual Adversarial -> 2.12% Ladder network -> 1.13%
38 Clearing up common misconceptions - Inputs that the model processes incorrectly are ubiquitous, not rare, and occur most often in half-spaces rather than pockets - Adversarial examples are not specific to deep learning - Deep learning is uniquely able to overcome adversarial examples, due to the universal approximator theorem - An attacker does not need access to a model or its training set - Common off-the-shelf regularization techniques like model averaging and unsupervised learning do not automatically solve the problem
39 Please use evidence, not speculation - It s common to say that obviously some technique will fix adversarial examples, and then just assume it will work without testing it - It s common to say in the introduction to some new paper on regularizing neural nets that this regularization research is justifie because of adversarial examples - Usually this is wrong - Please actually test your method on adversarial examples and report the results - Consider doing this even if you re not primarily concerned with adversarial examples
40 Recommended adversarial example benchmark - Fix epsilon - Compute the error rate on test data perturbed by the fast gradi sign method - Report the error rate, epsilon, and the version of the model use for both forward and back-prop - Alternative variant: design your own fixed-size perturbation scheme and report the error rate and size. For example, rotatio by some angle.
41 Alternative adversarial example benchmark - Use L-BFGS or other optimizer - Search for minimum size misclassified perturbation - Report average size - Report exhaustive detail to make the optimizer reproducible - Downsides: computation cost, difficulty of reproducing, hard to guarantee the perturbations will really be mistakes
42 Recommended fooling image / rubbish class benchmark - Fix epsilon - Fit a Gaussian to the training inputs - Draw samples from the Gaussian - Perturb them toward a specific positive class with the fast grad sign method - Report the rate at which you achieved this positive class - Report the rate at which the model believed any specific nonrubbish class was present (probability of that class being prese exceeds 0.5) - Report epsilon
43 Conclusion - Many modern ML algorithms - get the right answer for the wrong reason on naturally occurring inputs - get very wrong answers on almost all inputs - Adversarial training can expand the very narrow manifold of accuracy - Deep learning is on course to overcome adversarial examples, but maybe only by expanding our instruction book - Measure your model s error rate on fast gradient sign method adversarial examples and report it!
Notes on Adversarial Examples
 Notes on Adversarial Examples David Meyer dmm@{1-4-5.net,uoregon.edu,...} March 14, 2017 1 Introduction The surprising discovery of adversarial examples by Szegedy et al. [6] has led to new ways of thinking
Notes on Adversarial Examples David Meyer dmm@{1-4-5.net,uoregon.edu,...} March 14, 2017 1 Introduction The surprising discovery of adversarial examples by Szegedy et al. [6] has led to new ways of thinking
Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, Spis treści
 Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, 2017 Spis treści Website Acknowledgments Notation xiii xv xix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Who Should Read This Book?
Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, 2017 Spis treści Website Acknowledgments Notation xiii xv xix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Who Should Read This Book?
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron. Can only model linear functions. Kernel Machines. Non-linearity provided by kernels
 Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Deep Generative Models. (Unsupervised Learning)
 Deep Generative Models (Unsupervised Learning) CEng 783 Deep Learning Fall 2017 Emre Akbaş Reminders Next week: project progress demos in class Describe your problem/goal What you have done so far What
Deep Generative Models (Unsupervised Learning) CEng 783 Deep Learning Fall 2017 Emre Akbaş Reminders Next week: project progress demos in class Describe your problem/goal What you have done so far What
Neural networks and optimization
 Neural networks and optimization Nicolas Le Roux Criteo 18/05/15 Nicolas Le Roux (Criteo) Neural networks and optimization 18/05/15 1 / 85 1 Introduction 2 Deep networks 3 Optimization 4 Convolutional
Neural networks and optimization Nicolas Le Roux Criteo 18/05/15 Nicolas Le Roux (Criteo) Neural networks and optimization 18/05/15 1 / 85 1 Introduction 2 Deep networks 3 Optimization 4 Convolutional
Learning Deep Architectures for AI. Part II - Vijay Chakilam
 Learning Deep Architectures for AI - Yoshua Bengio Part II - Vijay Chakilam Limitations of Perceptron x1 W, b 0,1 1,1 y x2 weight plane output =1 output =0 There is no value for W and b such that the model
Learning Deep Architectures for AI - Yoshua Bengio Part II - Vijay Chakilam Limitations of Perceptron x1 W, b 0,1 1,1 y x2 weight plane output =1 output =0 There is no value for W and b such that the model
Lecture 3 Feedforward Networks and Backpropagation
 Lecture 3 Feedforward Networks and Backpropagation CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago April 3, 2017 Things we will look at today Recap of Logistic Regression
Lecture 3 Feedforward Networks and Backpropagation CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago April 3, 2017 Things we will look at today Recap of Logistic Regression
CS60010: Deep Learning
 CS60010: Deep Learning Sudeshna Sarkar Spring 2018 16 Jan 2018 FFN Goal: Approximate some unknown ideal function f : X! Y Ideal classifier: y = f*(x) with x and category y Feedforward Network: Define parametric
CS60010: Deep Learning Sudeshna Sarkar Spring 2018 16 Jan 2018 FFN Goal: Approximate some unknown ideal function f : X! Y Ideal classifier: y = f*(x) with x and category y Feedforward Network: Define parametric
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron. Can only model linear functions. Kernel Machines. Non-linearity provided by kernels
 Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Understanding How ConvNets See
 Understanding How ConvNets See Slides from Andrej Karpathy Springerberg et al, Striving for Simplicity: The All Convolutional Net (ICLR 2015 workshops) CSC321: Intro to Machine Learning and Neural Networks,
Understanding How ConvNets See Slides from Andrej Karpathy Springerberg et al, Striving for Simplicity: The All Convolutional Net (ICLR 2015 workshops) CSC321: Intro to Machine Learning and Neural Networks,
Lecture 14: Deep Generative Learning
 Generative Modeling CSED703R: Deep Learning for Visual Recognition (2017F) Lecture 14: Deep Generative Learning Density estimation Reconstructing probability density function using samples Bohyung Han
Generative Modeling CSED703R: Deep Learning for Visual Recognition (2017F) Lecture 14: Deep Generative Learning Density estimation Reconstructing probability density function using samples Bohyung Han
Deep Feedforward Networks
 Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1
 Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1 Stephane Lathuiliere & Pablo Mesejo 2 June 2016 1/31 Contents Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks to understand, and to be able to efficiently use, the popular
Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1 Stephane Lathuiliere & Pablo Mesejo 2 June 2016 1/31 Contents Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks to understand, and to be able to efficiently use, the popular
Deep Learning: Self-Taught Learning and Deep vs. Shallow Architectures. Lecture 04
 Deep Learning: Self-Taught Learning and Deep vs. Shallow Architectures Lecture 04 Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Self-Taught Learning 1. Learn
Deep Learning: Self-Taught Learning and Deep vs. Shallow Architectures Lecture 04 Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Self-Taught Learning 1. Learn
CS 179: LECTURE 16 MODEL COMPLEXITY, REGULARIZATION, AND CONVOLUTIONAL NETS
 CS 179: LECTURE 16 MODEL COMPLEXITY, REGULARIZATION, AND CONVOLUTIONAL NETS LAST TIME Intro to cudnn Deep neural nets using cublas and cudnn TODAY Building a better model for image classification Overfitting
CS 179: LECTURE 16 MODEL COMPLEXITY, REGULARIZATION, AND CONVOLUTIONAL NETS LAST TIME Intro to cudnn Deep neural nets using cublas and cudnn TODAY Building a better model for image classification Overfitting
How to do backpropagation in a brain
 How to do backpropagation in a brain Geoffrey Hinton Canadian Institute for Advanced Research & University of Toronto & Google Inc. Prelude I will start with three slides explaining a popular type of deep
How to do backpropagation in a brain Geoffrey Hinton Canadian Institute for Advanced Research & University of Toronto & Google Inc. Prelude I will start with three slides explaining a popular type of deep
Fundamentals of Machine Learning
 Fundamentals of Machine Learning Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan AIP (RIKEN), Tokyo http://icapeople.epfl.ch/mekhan/ emtiyaz@gmail.com Jan 2, 27 Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan 27 Goals Understand (some) fundamentals of Machine
Fundamentals of Machine Learning Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan AIP (RIKEN), Tokyo http://icapeople.epfl.ch/mekhan/ emtiyaz@gmail.com Jan 2, 27 Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan 27 Goals Understand (some) fundamentals of Machine
Deep Feedforward Networks. Lecture slides for Chapter 6 of Deep Learning Ian Goodfellow Last updated
 Deep Feedforward Networks Lecture slides for Chapter 6 of Deep Learning www.deeplearningbook.org Ian Goodfellow Last updated 2016-10-04 Roadmap Example: Learning XOR Gradient-Based Learning Hidden Units
Deep Feedforward Networks Lecture slides for Chapter 6 of Deep Learning www.deeplearningbook.org Ian Goodfellow Last updated 2016-10-04 Roadmap Example: Learning XOR Gradient-Based Learning Hidden Units
Lecture 3 Feedforward Networks and Backpropagation
 Lecture 3 Feedforward Networks and Backpropagation CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago April 3, 2017 Things we will look at today Recap of Logistic Regression
Lecture 3 Feedforward Networks and Backpropagation CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago April 3, 2017 Things we will look at today Recap of Logistic Regression
Tutorial on: Optimization I. (from a deep learning perspective) Jimmy Ba
 Tutorial on: Optimization I (from a deep learning perspective) Jimmy Ba Outline Random search v.s. gradient descent Finding better search directions Design white-box optimization methods to improve computation
Tutorial on: Optimization I (from a deep learning perspective) Jimmy Ba Outline Random search v.s. gradient descent Finding better search directions Design white-box optimization methods to improve computation
A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs)
 BOLTZMANN MACHINES Generative Models Graphical Models A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs) In a probabilistic graphical model, each node represents a random variable,
BOLTZMANN MACHINES Generative Models Graphical Models A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs) In a probabilistic graphical model, each node represents a random variable,
Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning. Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas
 Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning Reinforcement Learning Parametric Y Continuous Non-parametric
Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning Reinforcement Learning Parametric Y Continuous Non-parametric
CSC321 Lecture 20: Autoencoders
 CSC321 Lecture 20: Autoencoders Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 20: Autoencoders 1 / 16 Overview Latent variable models so far: mixture models Boltzmann machines Both of these involve discrete
CSC321 Lecture 20: Autoencoders Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 20: Autoencoders 1 / 16 Overview Latent variable models so far: mixture models Boltzmann machines Both of these involve discrete
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning CS4731 Dr. Mihail Fall 2017 Slide content based on books by Bishop and Barber. https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/people/cmbishop/ http://web4.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/d.barber/pmwiki/pmwiki.php?n=brml.homepage
Introduction to Machine Learning CS4731 Dr. Mihail Fall 2017 Slide content based on books by Bishop and Barber. https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/people/cmbishop/ http://web4.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/d.barber/pmwiki/pmwiki.php?n=brml.homepage
STA 414/2104: Lecture 8
 STA 414/2104: Lecture 8 6-7 March 2017: Continuous Latent Variable Models, Neural networks With thanks to Russ Salakhutdinov, Jimmy Ba and others Outline Continuous latent variable models Background PCA
STA 414/2104: Lecture 8 6-7 March 2017: Continuous Latent Variable Models, Neural networks With thanks to Russ Salakhutdinov, Jimmy Ba and others Outline Continuous latent variable models Background PCA
CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019)
 CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019) Prof. Victor Adamchik U of Southern California Mar. 19, 2019 March 19, 2019 1 / 43 Administration March 19, 2019 2 / 43 Administration TA3 is due this week March
CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019) Prof. Victor Adamchik U of Southern California Mar. 19, 2019 March 19, 2019 1 / 43 Administration March 19, 2019 2 / 43 Administration TA3 is due this week March
Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning CS224N/Ling284
 Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning CS224N/Ling284 Lecture 4: Word Window Classification and Neural Networks Richard Socher Organization Main midterm: Feb 13 Alternative midterm: Friday Feb
Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning CS224N/Ling284 Lecture 4: Word Window Classification and Neural Networks Richard Socher Organization Main midterm: Feb 13 Alternative midterm: Friday Feb
Online Videos FERPA. Sign waiver or sit on the sides or in the back. Off camera question time before and after lecture. Questions?
 Online Videos FERPA Sign waiver or sit on the sides or in the back Off camera question time before and after lecture Questions? Lecture 1, Slide 1 CS224d Deep NLP Lecture 4: Word Window Classification
Online Videos FERPA Sign waiver or sit on the sides or in the back Off camera question time before and after lecture Questions? Lecture 1, Slide 1 CS224d Deep NLP Lecture 4: Word Window Classification
Generative adversarial networks
 14-1: Generative adversarial networks Prof. J.C. Kao, UCLA Generative adversarial networks Why GANs? GAN intuition GAN equilibrium GAN implementation Practical considerations Much of these notes are based
14-1: Generative adversarial networks Prof. J.C. Kao, UCLA Generative adversarial networks Why GANs? GAN intuition GAN equilibrium GAN implementation Practical considerations Much of these notes are based
Deep Learning Lab Course 2017 (Deep Learning Practical)
 Deep Learning Lab Course 207 (Deep Learning Practical) Labs: (Computer Vision) Thomas Brox, (Robotics) Wolfram Burgard, (Machine Learning) Frank Hutter, (Neurorobotics) Joschka Boedecker University of
Deep Learning Lab Course 207 (Deep Learning Practical) Labs: (Computer Vision) Thomas Brox, (Robotics) Wolfram Burgard, (Machine Learning) Frank Hutter, (Neurorobotics) Joschka Boedecker University of
Bagging and Other Ensemble Methods
 Bagging and Other Ensemble Methods Sargur N. Srihari srihari@buffalo.edu 1 Regularization Strategies 1. Parameter Norm Penalties 2. Norm Penalties as Constrained Optimization 3. Regularization and Underconstrained
Bagging and Other Ensemble Methods Sargur N. Srihari srihari@buffalo.edu 1 Regularization Strategies 1. Parameter Norm Penalties 2. Norm Penalties as Constrained Optimization 3. Regularization and Underconstrained
Ch.6 Deep Feedforward Networks (2/3)
 Ch.6 Deep Feedforward Networks (2/3) 16. 10. 17. (Mon.) System Software Lab., Dept. of Mechanical & Information Eng. Woonggy Kim 1 Contents 6.3. Hidden Units 6.3.1. Rectified Linear Units and Their Generalizations
Ch.6 Deep Feedforward Networks (2/3) 16. 10. 17. (Mon.) System Software Lab., Dept. of Mechanical & Information Eng. Woonggy Kim 1 Contents 6.3. Hidden Units 6.3.1. Rectified Linear Units and Their Generalizations
CSC321 Lecture 9: Generalization
 CSC321 Lecture 9: Generalization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 9: Generalization 1 / 27 Overview We ve focused so far on how to optimize neural nets how to get them to make good predictions
CSC321 Lecture 9: Generalization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 9: Generalization 1 / 27 Overview We ve focused so far on how to optimize neural nets how to get them to make good predictions
Deep Neural Networks (3) Computational Graphs, Learning Algorithms, Initialisation
 Deep Neural Networks (3) Computational Graphs, Learning Algorithms, Initialisation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 5 16 October 2018 MLP Lecture 5 / 16 October 2018 Deep Neural Networks
Deep Neural Networks (3) Computational Graphs, Learning Algorithms, Initialisation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 5 16 October 2018 MLP Lecture 5 / 16 October 2018 Deep Neural Networks
Regularization in Neural Networks
 Regularization in Neural Networks Sargur Srihari 1 Topics in Neural Network Regularization What is regularization? Methods 1. Determining optimal number of hidden units 2. Use of regularizer in error function
Regularization in Neural Networks Sargur Srihari 1 Topics in Neural Network Regularization What is regularization? Methods 1. Determining optimal number of hidden units 2. Use of regularizer in error function
Backpropagation Introduction to Machine Learning. Matt Gormley Lecture 12 Feb 23, 2018
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Backpropagation Matt Gormley Lecture 12 Feb 23, 2018 1 Neural Networks Outline
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Backpropagation Matt Gormley Lecture 12 Feb 23, 2018 1 Neural Networks Outline
Article from. Predictive Analytics and Futurism. July 2016 Issue 13
 Article from Predictive Analytics and Futurism July 2016 Issue 13 Regression and Classification: A Deeper Look By Jeff Heaton Classification and regression are the two most common forms of models fitted
Article from Predictive Analytics and Futurism July 2016 Issue 13 Regression and Classification: A Deeper Look By Jeff Heaton Classification and regression are the two most common forms of models fitted
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
STA 414/2104: Lecture 8
 STA 414/2104: Lecture 8 6-7 March 2017: Continuous Latent Variable Models, Neural networks Delivered by Mark Ebden With thanks to Russ Salakhutdinov, Jimmy Ba and others Outline Continuous latent variable
STA 414/2104: Lecture 8 6-7 March 2017: Continuous Latent Variable Models, Neural networks Delivered by Mark Ebden With thanks to Russ Salakhutdinov, Jimmy Ba and others Outline Continuous latent variable
ECE 595: Machine Learning I Adversarial Attack 1
 ECE 595: Machine Learning I Adversarial Attack 1 Spring 2019 Stanley Chan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University 1 / 32 Outline Examples of Adversarial Attack Basic Terminology
ECE 595: Machine Learning I Adversarial Attack 1 Spring 2019 Stanley Chan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University 1 / 32 Outline Examples of Adversarial Attack Basic Terminology
Distillation as a Defense to Adversarial Perturbations against Deep Neural Networks
 Accepted to the 37th IEEE Symposium on Security & Privacy, IEEE 2016. San Jose, CA. Distillation as a Defense to Adversarial Perturbations against Deep Neural Networks 1 Nicolas Papernot, Patrick McDaniel,
Accepted to the 37th IEEE Symposium on Security & Privacy, IEEE 2016. San Jose, CA. Distillation as a Defense to Adversarial Perturbations against Deep Neural Networks 1 Nicolas Papernot, Patrick McDaniel,
Day 3 Lecture 3. Optimizing deep networks
 Day 3 Lecture 3 Optimizing deep networks Convex optimization A function is convex if for all α [0,1]: f(x) Tangent line Examples Quadratics 2-norms Properties Local minimum is global minimum x Gradient
Day 3 Lecture 3 Optimizing deep networks Convex optimization A function is convex if for all α [0,1]: f(x) Tangent line Examples Quadratics 2-norms Properties Local minimum is global minimum x Gradient
Machine Learning Lecture 14
 Machine Learning Lecture 14 Tricks of the Trade 07.12.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory Probability
Machine Learning Lecture 14 Tricks of the Trade 07.12.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory Probability
Tips for Deep Learning
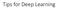 Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Maxout Networks. Hien Quoc Dang
 Maxout Networks Hien Quoc Dang Outline Introduction Maxout Networks Description A Universal Approximator & Proof Experiments with Maxout Why does Maxout work? Conclusion 10/12/13 Hien Quoc Dang Machine
Maxout Networks Hien Quoc Dang Outline Introduction Maxout Networks Description A Universal Approximator & Proof Experiments with Maxout Why does Maxout work? Conclusion 10/12/13 Hien Quoc Dang Machine
Tips for Deep Learning
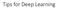 Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Neural Networks with Applications to Vision and Language. Feedforward Networks. Marco Kuhlmann
 Neural Networks with Applications to Vision and Language Feedforward Networks Marco Kuhlmann Feedforward networks Linear separability x 2 x 2 0 1 0 1 0 0 x 1 1 0 x 1 linearly separable not linearly separable
Neural Networks with Applications to Vision and Language Feedforward Networks Marco Kuhlmann Feedforward networks Linear separability x 2 x 2 0 1 0 1 0 0 x 1 1 0 x 1 linearly separable not linearly separable
ECE 595: Machine Learning I Adversarial Attack 1
 ECE 595: Machine Learning I Adversarial Attack 1 Spring 2019 Stanley Chan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University 1 / 32 Outline Examples of Adversarial Attack Basic Terminology
ECE 595: Machine Learning I Adversarial Attack 1 Spring 2019 Stanley Chan School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University 1 / 32 Outline Examples of Adversarial Attack Basic Terminology
Introduction to Neural Networks
 CUONG TUAN NGUYEN SEIJI HOTTA MASAKI NAKAGAWA Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Copyright by Nguyen, Hotta and Nakagawa 1 Pattern classification Which category of an input? Example: Character
CUONG TUAN NGUYEN SEIJI HOTTA MASAKI NAKAGAWA Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Copyright by Nguyen, Hotta and Nakagawa 1 Pattern classification Which category of an input? Example: Character
Midterm Exam, Spring 2005
 10-701 Midterm Exam, Spring 2005 1. Write your name and your email address below. Name: Email address: 2. There should be 15 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet). 3. Write your name
10-701 Midterm Exam, Spring 2005 1. Write your name and your email address below. Name: Email address: 2. There should be 15 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet). 3. Write your name
AE = q < H(p < ) + (1 q < )H(p > ) H(p) = p lg(p) (1 p) lg(1 p)
 1 Decision Trees (13 pts) Data points are: Negative: (-1, 0) (2, 1) (2, -2) Positive: (0, 0) (1, 0) Construct a decision tree using the algorithm described in the notes for the data above. 1. Show the
1 Decision Trees (13 pts) Data points are: Negative: (-1, 0) (2, 1) (2, -2) Positive: (0, 0) (1, 0) Construct a decision tree using the algorithm described in the notes for the data above. 1. Show the
Comments. Assignment 3 code released. Thought questions 3 due this week. Mini-project: hopefully you have started. implement classification algorithms
 Neural networks Comments Assignment 3 code released implement classification algorithms use kernels for census dataset Thought questions 3 due this week Mini-project: hopefully you have started 2 Example:
Neural networks Comments Assignment 3 code released implement classification algorithms use kernels for census dataset Thought questions 3 due this week Mini-project: hopefully you have started 2 Example:
CSC321 Lecture 9: Generalization
 CSC321 Lecture 9: Generalization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 9: Generalization 1 / 26 Overview We ve focused so far on how to optimize neural nets how to get them to make good predictions
CSC321 Lecture 9: Generalization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 9: Generalization 1 / 26 Overview We ve focused so far on how to optimize neural nets how to get them to make good predictions
Deep Feedforward Networks
 Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
CSC321 Lecture 16: ResNets and Attention
 CSC321 Lecture 16: ResNets and Attention Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 16: ResNets and Attention 1 / 24 Overview Two topics for today: Topic 1: Deep Residual Networks (ResNets) This is the state-of-the
CSC321 Lecture 16: ResNets and Attention Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 16: ResNets and Attention 1 / 24 Overview Two topics for today: Topic 1: Deep Residual Networks (ResNets) This is the state-of-the
Neural networks and support vector machines
 Neural netorks and support vector machines Perceptron Input x 1 Weights 1 x 2 x 3... x D 2 3 D Output: sgn( x + b) Can incorporate bias as component of the eight vector by alays including a feature ith
Neural netorks and support vector machines Perceptron Input x 1 Weights 1 x 2 x 3... x D 2 3 D Output: sgn( x + b) Can incorporate bias as component of the eight vector by alays including a feature ith
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2012
 Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
The connection of dropout and Bayesian statistics
 The connection of dropout and Bayesian statistics Interpretation of dropout as approximate Bayesian modelling of NN http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/yarin/thesis/thesis.pdf Dropout Geoffrey Hinton Google, University
The connection of dropout and Bayesian statistics Interpretation of dropout as approximate Bayesian modelling of NN http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/yarin/thesis/thesis.pdf Dropout Geoffrey Hinton Google, University
Deep unsupervised learning
 Deep unsupervised learning Advanced data-mining Yongdai Kim Department of Statistics, Seoul National University, South Korea Unsupervised learning In machine learning, there are 3 kinds of learning paradigm.
Deep unsupervised learning Advanced data-mining Yongdai Kim Department of Statistics, Seoul National University, South Korea Unsupervised learning In machine learning, there are 3 kinds of learning paradigm.
Today. Calculus. Linear Regression. Lagrange Multipliers
 Today Calculus Lagrange Multipliers Linear Regression 1 Optimization with constraints What if I want to constrain the parameters of the model. The mean is less than 10 Find the best likelihood, subject
Today Calculus Lagrange Multipliers Linear Regression 1 Optimization with constraints What if I want to constrain the parameters of the model. The mean is less than 10 Find the best likelihood, subject
Final Exam, Fall 2002
 15-781 Final Exam, Fall 22 1. Write your name and your andrew email address below. Name: Andrew ID: 2. There should be 17 pages in this exam (excluding this cover sheet). 3. If you need more room to work
15-781 Final Exam, Fall 22 1. Write your name and your andrew email address below. Name: Andrew ID: 2. There should be 17 pages in this exam (excluding this cover sheet). 3. If you need more room to work
Linear Models for Regression
 Linear Models for Regression CSE 4309 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 The Regression Problem Training data: A set of input-output
Linear Models for Regression CSE 4309 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 The Regression Problem Training data: A set of input-output
Midterm Review CS 7301: Advanced Machine Learning. Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas
 Midterm Review CS 7301: Advanced Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Supervised Learning Issues in supervised learning What makes learning hard Point Estimation: MLE vs Bayesian
Midterm Review CS 7301: Advanced Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Supervised Learning Issues in supervised learning What makes learning hard Point Estimation: MLE vs Bayesian
SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning
 SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia, May 2016 www.cs.ubc.ca/~schmidtm/svan16 Some images from this lecture are
SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia, May 2016 www.cs.ubc.ca/~schmidtm/svan16 Some images from this lecture are
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
From perceptrons to word embeddings. Simon Šuster University of Groningen
 From perceptrons to word embeddings Simon Šuster University of Groningen Outline A basic computational unit Weighting some input to produce an output: classification Perceptron Classify tweets Written
From perceptrons to word embeddings Simon Šuster University of Groningen Outline A basic computational unit Weighting some input to produce an output: classification Perceptron Classify tweets Written
Towards ML You Can Rely On. Aleksander Mądry
 Towards ML You Can Rely On Aleksander Mądry @aleks_madry madry-lab.ml Machine Learning: The Success Story? Image classification Reinforcement Learning Machine translation Machine Learning: The Success
Towards ML You Can Rely On Aleksander Mądry @aleks_madry madry-lab.ml Machine Learning: The Success Story? Image classification Reinforcement Learning Machine translation Machine Learning: The Success
Midterm Exam Solutions, Spring 2007
 1-71 Midterm Exam Solutions, Spring 7 1. Personal info: Name: Andrew account: E-mail address:. There should be 16 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet). 3. You can use any material you
1-71 Midterm Exam Solutions, Spring 7 1. Personal info: Name: Andrew account: E-mail address:. There should be 16 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet). 3. You can use any material you
Unsupervised Learning
 CS 3750 Advanced Machine Learning hkc6@pitt.edu Unsupervised Learning Data: Just data, no labels Goal: Learn some underlying hidden structure of the data P(, ) P( ) Principle Component Analysis (Dimensionality
CS 3750 Advanced Machine Learning hkc6@pitt.edu Unsupervised Learning Data: Just data, no labels Goal: Learn some underlying hidden structure of the data P(, ) P( ) Principle Component Analysis (Dimensionality
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017
 ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
Logistic Regression & Neural Networks
 Logistic Regression & Neural Networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 Marine Carpuat Slides credit: Graham Neubig, Jacob Eisenstein Logistic Regression Perceptron & Probabilities What if we want a probability
Logistic Regression & Neural Networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 Marine Carpuat Slides credit: Graham Neubig, Jacob Eisenstein Logistic Regression Perceptron & Probabilities What if we want a probability
text classification 3: neural networks
 text classification 3: neural networks CS 585, Fall 2018 Introduction to Natural Language Processing http://people.cs.umass.edu/~miyyer/cs585/ Mohit Iyyer College of Information and Computer Sciences University
text classification 3: neural networks CS 585, Fall 2018 Introduction to Natural Language Processing http://people.cs.umass.edu/~miyyer/cs585/ Mohit Iyyer College of Information and Computer Sciences University
arxiv: v3 [stat.ml] 20 Mar 2015
![arxiv: v3 [stat.ml] 20 Mar 2015 arxiv: v3 [stat.ml] 20 Mar 2015](/thumbs/72/67737405.jpg) EXPLAINING AND HARNESSING ADVERSARIAL EXAMPLES Ian J. Goodfellow, Jonathon Shlens & Christian Szegedy Google Inc., Mountain View, CA {goodfellow,shlens,szegedy}@google.com arxiv:1412.6572v3 [stat.ml] 20
EXPLAINING AND HARNESSING ADVERSARIAL EXAMPLES Ian J. Goodfellow, Jonathon Shlens & Christian Szegedy Google Inc., Mountain View, CA {goodfellow,shlens,szegedy}@google.com arxiv:1412.6572v3 [stat.ml] 20
Neural Networks. Single-layer neural network. CSE 446: Machine Learning Emily Fox University of Washington March 10, /9/17
 3/9/7 Neural Networks Emily Fox University of Washington March 0, 207 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi (via Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer) Single-layer neural network 3/9/7 Perceptron as a neural
3/9/7 Neural Networks Emily Fox University of Washington March 0, 207 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi (via Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer) Single-layer neural network 3/9/7 Perceptron as a neural
Lecture : Probabilistic Machine Learning
 Lecture : Probabilistic Machine Learning Riashat Islam Reasoning and Learning Lab McGill University September 11, 2018 ML : Many Methods with Many Links Modelling Views of Machine Learning Machine Learning
Lecture : Probabilistic Machine Learning Riashat Islam Reasoning and Learning Lab McGill University September 11, 2018 ML : Many Methods with Many Links Modelling Views of Machine Learning Machine Learning
Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function.
 Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Training Neural Networks Practical Issues
 Training Neural Networks Practical Issues M. Soleymani Sharif University of Technology Fall 2017 Most slides have been adapted from Fei Fei Li and colleagues lectures, cs231n, Stanford 2017, and some from
Training Neural Networks Practical Issues M. Soleymani Sharif University of Technology Fall 2017 Most slides have been adapted from Fei Fei Li and colleagues lectures, cs231n, Stanford 2017, and some from
Neural Networks in Structured Prediction. November 17, 2015
 Neural Networks in Structured Prediction November 17, 2015 HWs and Paper Last homework is going to be posted soon Neural net NER tagging model This is a new structured model Paper - Thursday after Thanksgiving
Neural Networks in Structured Prediction November 17, 2015 HWs and Paper Last homework is going to be posted soon Neural net NER tagging model This is a new structured model Paper - Thursday after Thanksgiving
WHY ARE DEEP NETS REVERSIBLE: A SIMPLE THEORY,
 WHY ARE DEEP NETS REVERSIBLE: A SIMPLE THEORY, WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR TRAINING Sanjeev Arora, Yingyu Liang & Tengyu Ma Department of Computer Science Princeton University Princeton, NJ 08540, USA {arora,yingyul,tengyu}@cs.princeton.edu
WHY ARE DEEP NETS REVERSIBLE: A SIMPLE THEORY, WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR TRAINING Sanjeev Arora, Yingyu Liang & Tengyu Ma Department of Computer Science Princeton University Princeton, NJ 08540, USA {arora,yingyul,tengyu}@cs.princeton.edu
Learning with multiple models. Boosting.
 CS 2750 Machine Learning Lecture 21 Learning with multiple models. Boosting. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Learning with multiple models: Approach 2 Approach 2: use multiple models
CS 2750 Machine Learning Lecture 21 Learning with multiple models. Boosting. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Learning with multiple models: Approach 2 Approach 2: use multiple models
Universal Adversarial Networks
 1 Universal Adversarial Networks Jamie Hayes University College London j.hayes@cs.ucl.ac.uk Abstract Neural networks are known to be vulnerable to adversarial examples, inputs that have been intentionally
1 Universal Adversarial Networks Jamie Hayes University College London j.hayes@cs.ucl.ac.uk Abstract Neural networks are known to be vulnerable to adversarial examples, inputs that have been intentionally
arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 15 Nov 2017 ABSTRACT
![arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 15 Nov 2017 ABSTRACT arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 15 Nov 2017 ABSTRACT](/thumbs/90/101619255.jpg) THE BEST DEFENSE IS A GOOD OFFENSE: COUNTERING BLACK BOX ATTACKS BY PREDICTING SLIGHTLY WRONG LABELS Yannic Kilcher Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich yannic.kilcher@inf.ethz.ch Thomas Hofmann Department
THE BEST DEFENSE IS A GOOD OFFENSE: COUNTERING BLACK BOX ATTACKS BY PREDICTING SLIGHTLY WRONG LABELS Yannic Kilcher Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich yannic.kilcher@inf.ethz.ch Thomas Hofmann Department
Machine Learning Techniques
 Machine Learning Techniques ( 機器學習技法 ) Lecture 13: Deep Learning Hsuan-Tien Lin ( 林軒田 ) htlin@csie.ntu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan University ( 國立台灣大學資訊工程系
Machine Learning Techniques ( 機器學習技法 ) Lecture 13: Deep Learning Hsuan-Tien Lin ( 林軒田 ) htlin@csie.ntu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan University ( 國立台灣大學資訊工程系
CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients
 CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients 1 / 23 Overview Yesterday, we saw how to compute the gradient descent
CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients 1 / 23 Overview Yesterday, we saw how to compute the gradient descent
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
FINAL: CS 6375 (Machine Learning) Fall 2014
 FINAL: CS 6375 (Machine Learning) Fall 2014 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for
FINAL: CS 6375 (Machine Learning) Fall 2014 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for
Adversarially Robust Optimization and Generalization
 Adversarially Robust Optimization and Generalization Ludwig Schmidt MIT UC Berkeley Based on joint works with Logan ngstrom (MIT), Aleksander Madry (MIT), Aleksandar Makelov (MIT), Dimitris Tsipras (MIT),
Adversarially Robust Optimization and Generalization Ludwig Schmidt MIT UC Berkeley Based on joint works with Logan ngstrom (MIT), Aleksander Madry (MIT), Aleksandar Makelov (MIT), Dimitris Tsipras (MIT),
Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE 151 University of California, San Diego Fall Midterm Examination
 Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE 151 University of California, San Diego Fall 2008 Your name: Midterm Examination Tuesday October 28, 9:30am to 10:50am Instructions: Look through the
Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE 151 University of California, San Diego Fall 2008 Your name: Midterm Examination Tuesday October 28, 9:30am to 10:50am Instructions: Look through the
CS 6501: Deep Learning for Computer Graphics. Basics of Neural Networks. Connelly Barnes
 CS 6501: Deep Learning for Computer Graphics Basics of Neural Networks Connelly Barnes Overview Simple neural networks Perceptron Feedforward neural networks Multilayer perceptron and properties Autoencoders
CS 6501: Deep Learning for Computer Graphics Basics of Neural Networks Connelly Barnes Overview Simple neural networks Perceptron Feedforward neural networks Multilayer perceptron and properties Autoencoders
Topics in AI (CPSC 532L): Multimodal Learning with Vision, Language and Sound. Lecture 3: Introduction to Deep Learning (continued)
 Topics in AI (CPSC 532L): Multimodal Learning with Vision, Language and Sound Lecture 3: Introduction to Deep Learning (continued) Course Logistics - Update on course registrations - 6 seats left now -
Topics in AI (CPSC 532L): Multimodal Learning with Vision, Language and Sound Lecture 3: Introduction to Deep Learning (continued) Course Logistics - Update on course registrations - 6 seats left now -
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 10-708 Probabilistic Graphical Models Homework 3 (v1.1.0) Due Apr 14, 7:00 PM Rules: 1. Homework is due on the due date at 7:00 PM. The homework should be submitted via Gradescope. Solution to each problem
10-708 Probabilistic Graphical Models Homework 3 (v1.1.0) Due Apr 14, 7:00 PM Rules: 1. Homework is due on the due date at 7:00 PM. The homework should be submitted via Gradescope. Solution to each problem
Fundamentals of Machine Learning (Part I)
 Fundamentals of Machine Learning (Part I) Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan AIP (RIKEN), Tokyo http://emtiyaz.github.io emtiyaz.khan@riken.jp April 12, 2018 Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan 2018 1 Goals Understand (some) fundamentals
Fundamentals of Machine Learning (Part I) Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan AIP (RIKEN), Tokyo http://emtiyaz.github.io emtiyaz.khan@riken.jp April 12, 2018 Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan 2018 1 Goals Understand (some) fundamentals
CSE 190 Fall 2015 Midterm DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO START!!!!
 CSE 190 Fall 2015 Midterm DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO START!!!! November 18, 2015 THE EXAM IS CLOSED BOOK. Once the exam has started, SORRY, NO TALKING!!! No, you can t even say see ya
CSE 190 Fall 2015 Midterm DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO START!!!! November 18, 2015 THE EXAM IS CLOSED BOOK. Once the exam has started, SORRY, NO TALKING!!! No, you can t even say see ya
Data Mining und Maschinelles Lernen
 Data Mining und Maschinelles Lernen Ensemble Methods Bias-Variance Trade-off Basic Idea of Ensembles Bagging Basic Algorithm Bagging with Costs Randomization Random Forests Boosting Stacking Error-Correcting
Data Mining und Maschinelles Lernen Ensemble Methods Bias-Variance Trade-off Basic Idea of Ensembles Bagging Basic Algorithm Bagging with Costs Randomization Random Forests Boosting Stacking Error-Correcting
Machine Learning, Midterm Exam: Spring 2008 SOLUTIONS. Q Topic Max. Score Score. 1 Short answer questions 20.
 10-601 Machine Learning, Midterm Exam: Spring 2008 Please put your name on this cover sheet If you need more room to work out your answer to a question, use the back of the page and clearly mark on the
10-601 Machine Learning, Midterm Exam: Spring 2008 Please put your name on this cover sheet If you need more room to work out your answer to a question, use the back of the page and clearly mark on the
OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING
 Tutorial outline OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING Based on Deep Learning, chapter 8 by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Presented By Nadav Bhonker Optimization vs Learning Surrogate
Tutorial outline OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING Based on Deep Learning, chapter 8 by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Presented By Nadav Bhonker Optimization vs Learning Surrogate
what can deep learning learn from linear regression? Benjamin Recht University of California, Berkeley
 what can deep learning learn from linear regression? Benjamin Recht University of California, Berkeley Collaborators Joint work with Samy Bengio, Moritz Hardt, Michael Jordan, Jason Lee, Max Simchowitz,
what can deep learning learn from linear regression? Benjamin Recht University of California, Berkeley Collaborators Joint work with Samy Bengio, Moritz Hardt, Michael Jordan, Jason Lee, Max Simchowitz,
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Final Review. Henry Chai 12/4/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
Deep Learning for NLP
 Deep Learning for NLP CS224N Christopher Manning (Many slides borrowed from ACL 2012/NAACL 2013 Tutorials by me, Richard Socher and Yoshua Bengio) Machine Learning and NLP NER WordNet Usually machine learning
Deep Learning for NLP CS224N Christopher Manning (Many slides borrowed from ACL 2012/NAACL 2013 Tutorials by me, Richard Socher and Yoshua Bengio) Machine Learning and NLP NER WordNet Usually machine learning
Qualifying Exam in Machine Learning
 Qualifying Exam in Machine Learning October 20, 2009 Instructions: Answer two out of the three questions in Part 1. In addition, answer two out of three questions in two additional parts (choose two parts
Qualifying Exam in Machine Learning October 20, 2009 Instructions: Answer two out of the three questions in Part 1. In addition, answer two out of three questions in two additional parts (choose two parts
