Vibrations and Properties of Inertia Continuously Variable Transmissions
|
|
|
- Abner Burns
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science 017 Vol II WCECS 017, October 5-7, 017, San Francisco, USA Vibrations and Properties of Inertia Continuously Variable Transmissions S. Aliukov, A. Keller, and A. Alyukov Abstract The inertial continuously variable transmission is a mechanical transmission which is based on the principle of inertia. This transmission has a lot of advantages, namely: compactness, minimum friction losses and high efficiency as a result of the relatively small number of rotating components, a wide range of transformation of the torque. It does not need any conventional friction clutches. This transmission protects the engine from overload when the output shaft is braked. This drive guarantees optimum conditions of work for the engine regardless of the changing of load, and smoothly changes output speed according to the load. Mostly, design of this transmission consists of a pulsed mechanism with unbalanced inertial units and two overrunning clutches. The objects of the investigation are structural dynamic analysis of the continuously variable transmission. The physical and mathematical models of this transmission are developed. Dynamics of the transmissions is described by systems of substantial nonlinear differential equations. In general, precise methods of solution for such equations do not exist. Therefore, in practice, approximate analytical and numerical methods must be employed. Each approach has its advantages and disadvantages. Besides, the nonlinear differential equations were solved on the basis of Runge-Kutta numerical method. In this paper, a new design of the inertial transmission with only one overrunning clutch is suggested. This transmission provides a high level of the load ability. Besides, the periodic solutions of the equations were also received by means of the numerical methods. Optimal working modes of the transmission were found using these periodical solutions. Index Terms Inertia transmission, dynamics, vibrations, external characteristics T I. INTRODUCTION HE inertial continuously variable transmission is a mechanical transmission which is based on the principle of inertia [1]. This transmission has a lot of advantages: compactness, minimum friction losses, high efficiency, and wide range of the torque transformation. It does not need any conventional friction clutches. This transmission protects the engine from overload when output shaft is stopped. This drive guarantees optimum Manuscript received July 3, 017. The work was supported by Act 11 Government of the Russian Federation, contract 0.A03.1. S. V. Aliukov is with the South Ural State University, 76 Prospekt Lenina, Chelyabinsk, , Russian Federation (corresponding author, home phone: ; sell phone: ; alysergey@gmail.com). A. V. Keller is with the South Ural State University, 76 Prospekt Lenina, Chelyabinsk, , Russian Federation ( andreikeller@rambler.ru). A. S. Alyukov is with the South Ural State University, 76 Prospekt Lenina, Chelyabinsk, , Russian Federation, sell phone: ; alyukovalexandr@gmail.com). ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) conditions of work for the engine regardless of the changing of load, and smoothly changes output speed with change the load. However, despite of these advantages, the inertial continuously variable transmissions are not widely used in the automotive industry. The main reason for this is that in the design of the transmissions there are two overrunning clutches which are characterized by low reliability under severe operating conditions: high dynamic loads and high on and off power frequency. The purpose of the paper is the increase the load ability of the continuously variable transmission by reducing the number of the overrunning clutches. II. THE PHYSICAL MODEL OF THE CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION In general, the inertial continuously variable transmission contains the pulsed mechanism with unbalanced inertial elements, for example, planetary gear with unbalanced satellites, and two overrunning clutches. The main purpose of the pulsed mechanism is to create alternative-sign impulses of the torque. One of the overrunning clutches (the output overrunning clutch) transmits direct impulses of the torque to the output shaft, the other one (the body overrunning clutch) transmits the reverse impulse of the torque on the body of the transmission. The presence of two overrunning clutches determines the possible way for increasing of the reliability of the transmission by reducing the number of the overrunning clutches. For example, the well-known Hobbs inertial transmission [1] has only the body overrunning clutch. In this transmission design, there is no the output overrunning clutch and the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism is directly connected with the driven shaft of the transmission. This design is characterized by a high level of irregular rotation of the driven shaft, because the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism rigidly connected with the driven shaft of the transmission. It leads to irregular rotation of the driven shaft of the transmission. In this paper, the design of the inertial continuously variable transmission without the body overrunning clutch is suggested. In the design solution, the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism is connected with the body of transmission, not through the overrunning clutch, but through an elastic element in the circumferential direction. A spring or a torsion shaft can be used as elastic element. The scheme of such a transmission is shown in Figure 1. Here, 1 is the drive shaft of the transmission, are unbalanced loading elements, 3 is the output shaft (the reactor) of the pulsed mechanism, 4 is the elastic element, 5 is the output overrunning clutch, and 6 is the output shaft WCECS 017
2 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science 017 Vol II WCECS 017, October 5-7, 017, San Francisco, USA of the transmission. The elastic link is shown schematically and this link determines the connection of the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism with the body of the transmission, not in the radial direction, but in circumferential one. π М В (1 sin x) dx πb, ср 0 where, A and B are coefficients depending on the parameters of the pulsed mechanism. Matching the average values, we obtain B A/π. It is easy to determine that the maximum value of the torque acting on the driven shaft of the transmission in the second case decreases in π / times. Fig. 1. Kinematic scheme of the inertial continuously variable transmission with high load ability The principle of operation of the proposed transmission is as follows. While the driving shaft 1 is rotating, the unbalanced loading elements provide alternative-sign impulses of the torque acting on the output shaft 3 of the pulsed mechanism. Because the output shaft 3 is connected with the body of the transmission by means of the elastic link 4, the shaft performs alternating vibration. The elastic link accumulates the potential energy during the reverse impulse of the torque and transfers the energy during direct rotation of the shaft 3 on the output shaft 6. Such kind of the design of the inertial transmission allows using only one overrunning clutch, such as in Hobbs transmission. In contrast to Hobbs transmission, the suggested design provides high equability of the rotation of the driven shaft 6. In this case, the output shaft 3 of the pulsed mechanism is not rigid connected with the driven shaft 6 of the transmission. Transfer of the motion is occurred through the output overrunning clutch. The driven shaft 6 of the transmission has the ability for independent rotation. Figure illustrates the pulsed mechanism. It is important to note, the replacement of the body overrunning clutch by means of the elastic link not only reduces the number of overrunning clutches but also reduces the peak load on the output overrunning clutch. The reduction of the load is due to the accumulation of the potential energy in the elastic link 4 during the reverse impulse of the torque. For example, let consider the mode of the operation of the transmission when the driven shaft 6 of the transmission is stopped. This mode is the most loaded mode of the operation of the transmission. Average values of the torque acting on the driven shaft in the usual rigid design of the inertial transmission and the suggested transmission with the elastic link are defined by the expressions, respectively π M A sin xdx A; ср 0 Fig.. Pulsed mechanism The above example is illustrated by Figure 3. Here, the thick line shows the graph of the torque acting on the driven shaft in the usual rigid design of the inertial transmission; the thin line is for the suggested transmission. Fig. 3. Graphs of torques acting on the driven shaft Moreover, if there are two pulsed mechanisms in the suggested design of the inertial transmission, we can have the reduction of the maximum value of the torque in π times. In this case, the value of the torque acting on the driven shaft of the transmission is constant. A similar ability to stabilize the torque in the pulsed continuously variable drive is described in []. ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) WCECS 017
3 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science 017 Vol II WCECS 017, October 5-7, 017, San Francisco, USA III. THE MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF THE CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION The mathematical model of the inertial continuously variable transmission is based on Lagrange equations of the second kind. Note, that the inertial transmission is a system of variable structure. The values of some of its physical parameters vary abruptly during the transmission s operating cycle and are described by piecewise linear functions. Therefore, in formulating the mathematical model, the differential equations of motion of the transmission are constructed in sections (intervals). For the transmission we consider the following sections: 1) the section of the separated motion of the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism and the driven shaft of the transmission; ) the section of their joint motion. In each section the motion of the transmission is described by means of its own systems of differential equations. Besides, while we construct the differential equations, the dynamic characteristic of the drive engine [3] is taken into account. As the generalized coordinates, we take the angle of rotation of the driving shaft 1, the angle of rotation of the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism, and the angle of the driven shaft 6. In the section of the separated motion of the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism and the driven shaft of the transmission, the system of differential equations takes the form where, A1 A A4 ( ) A6 M D, A A3 A5 ( ) A6 с 0, J4 MC, 1 M D М Т М Д ( ), Х b A3 J nmb q nj k a A4 nmah qqsin, k b А5 nmbh q q sin, k A nmkhqsin, a a A1 J1 nma q nj3 nmah qcos, k k a b ab A nmab q qnj3 nmh b aq cos, k k k 6 q( ), 3 b nmbh qcos, k k a b, J 1, J, J 4 are the moments of inertia of the driving shaft, the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism, and the driven shaft of the transmission, respectively, (1) nj is the total moment of inertia of the unbalanced 3 elements relative to the geometric center, nm is the total mass of the unbalanced elements, h is the distance between the geometric center and the center of mass of the unbalanced elements, a, b, q are parameters of the pulsed mechanism, с is the angular stiffness of the elastic link, М is the drag torque acting on the driven shaft of the С transmission, M is the engine torque acting on the drive shaft, D M is the rated torque of the engine, Х, are the angular ideal idling and nominal velocities, respectively, Т is the electromagnetic constant of time of the engine, is the slope coefficient of the static characteristic. In the section of the joint motion of the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism and the driven shaft of the transmission, the system of differential equations takes the form A1 A A4 ( ) A6 M D, A ( A3 J4) A5 ( ) A6 с MC, (), 1 M D М Т М Д ( ). Х We assume that the speed of the driving shaft is constant const [4]. This is acceptable because the moment of inertia of the driving component is usually much greater than the moments of inertia of the inertial transmission s other components. The driving component acts as a flywheel stabilizing its speed. Assuming constant speed of the driving shaft, we may simplify the mathematical model of the transmission and reduce the order of the systems of differential equations. The equations will take the forms (3) and (4), respectively. A3 A5 ( ) A6 с 0, J. 4 MC ( A3 J4) A5 ( ) A6 с M C,. Using Heaviside function, we can write the systems (3) and (4) in the form of one system [5], as follows ( A3 J4 (1 Ф( )) A5 ( ) A6 с M C (1 Ф( )), J4 MC Ф( ) J4(1 Ф( )). (3) (4) (5) ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) WCECS 017
4 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science 017 Vol II WCECS 017, October 5-7, 017, San Francisco, USA IV. SOLUTION OF THE MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF THE CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION As it was mentioned above, the inertial transmission is a system of variable structure [6-9]. A study of the dynamics of such systems is usually difficult [10-1]. The study assumes the consideration of the sections separately with further "matching" solutions for these sections. The representation of the mathematical model in the form of only one system (5) allows not caring about tracking movement from one section to another one. It is need only specification of the initial conditions. In this case, the procedure of the study of the dynamics of the transmission is greatly simplified. In addition, the Heaviside function can be approximated by analytic functions [6]. The mathematical model of the transmission in the form of the single system (5) can be used in a study of periodic solutions and their stability on the basis of analytical methods [13-16]. The numerical solution of the system (5) was received by using the Runge-Kutta method in MathCAD software. The transmission parameters were taken as follows: Fig. 5. The trajectory of the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism in phase space Similarly, we can get the periodical solutions for other modes (Figure 6). J кг м, J 0,5 кг м, nj 0,5 кг м, J 4 кг м, nm 5 кг, a 0,0 м, b 0,08 м, k 0,1 м, h 0,083 м, q 4/3, M 60 H м, 150 рад/с, с 500 м. C The plots of the velocity of the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism (thin line) and the driven shaft (thickened line) depending on time are shown in Figure 4. As we can see, the driven shaft of the transmission quickly goes to the steady state of the motion from the initial conditions with a little ripple of the rotation. It confirms the advantages of the suggested transmission in compare with Hobbes transmission. Fig. 4. Graphs of the velocities of the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism and the driven shaft of the transmission depending on the time Figure 5 depicts a trajectory of the motion of the output shaft of the pulsed mechanism to the steady state in the periodic solution. One of the advantages of the traditional inertial continuously variable transmission is that it can work in the mode of a dynamic clutch. The suggested transmission also can work in this mode. For this purpose, it is sufficient to provide a constructive controlled connection of the elastic links to the body of the transmission. ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) Fig. 6. Graphs of the angular velocities of the driven and the output shafts depending on time in the area of high values of the drag torque In the Figure 7 there is the external characteristic of the inertial continuously variable transmission. As we can see from the graph shown in the Figure 7, the external characteristic of the inertial transmission almost meets the WCECS 017
5 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science 017 Vol II WCECS 017, October 5-7, 017, San Francisco, USA ideal characteristic, which once again underlines the prospects of using of the inertial transmission in machinery for various purposes. Fig. 7. Graph of the external characteristic of the inertial transmission V. CONCLUSION The suggested transmission is more reliable and has high load ability in compare with the known designs of inertial continuously variable transmissions. It reduces number of overrunning clutches, which are limiting the reliability of the transmission. The elastic links which are setting into the design of the transmission instead of the body overrunning clutch does not limit the reliability of the transmission. The numerous examples of the successful use of elastic connections prove it. In the suggested design of the inertial transmission, the peak load on the output overrunning clutch is significantly reduced due to the accumulation of potential energy in the elastic elements. The reduction of the load can be more than 3 times. The conventional mathematical models for rigid and elastic inertial torque transformers consist of a set of significantly nonlinear systems of differential equations, which must be solved in separate sections. The results must be stitched together at the boundaries between the sections. Analysis of these systems is difficult since the boundary conditions between sections must constantly be monitored. Suggested approach proposes reduction of the mathematical models of the transmission to a single system of differential equations, in which the initial conditions need only be specified at the beginning of the solution. The mathematical model is considerably simplified. In this paper, the physical and mathematical models of the suggested transmission are developed, and the mathematical model is reduced to only one system of nonlinear differential equations. The received solutions of the mathematical model confirmed the validity of the theoretical proposals. It is shown that the resulting external characteristic is close to an ideal one. This result indicates the potential for widespread usage of the inertial transmission in drives of different engineering systems for various applications. [] Blagonravov, A.A., "Stelpess Mechanical Transmission of Impulse Type," Automobile Industry, #5, 007, pp [3] Veytz, V.A., "Dynamics of Machine Units," Leningrad: Mashinostroenie, [4] Poletskii, A.T. and Vasin, G.G., "Integrating the Equations of an Inertial Torque Transformer," Machine Dynamics, Moscow: Mashinostroenie, 1969, pp [5] Alyukov, S.V., "Improved Models of Inertial Torque Transformers," Russian Engineering Research, 010, vol. 30, #6, pp [6] Alyukov, S.V., "Approximation of step functions in problems of mathematical modeling," Mathematical Models and Computer Simulations, vol. 3, Issue 5, 1 October 011, pp [7] Keller, A., Murog, I., and Aliukov, S., "Comparative Analysis of Methods of Power Distribution in Mechanical Transmissions and Evaluation of their Effectiveness," SAE Technical Paper , 015, doi:10.471/ [8] Aliukov, S. and Gorshenin, V., "On the Question of External Characteristic of the Inertial Continuously Variable Transmission," SAE Technical Paper , 014, doi:10.471/ [9] Keller, A. and Aliukov, S., "Rational Criteria for Power Distribution in All-wheel-drive Trucks," SAE Technical Paper , 015, doi:10.471/ [10] Keller, A. and Aliukov, S., "Analysis of possible ways of power distribution in an all-wheel drive vehicle," Lecture Notes in Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 18, 015, pp [11] Aliukov, S., Keller, A., and Alyukov, A., "Dynamics of Overrunning Clutches of Relay Type," SAE Technical Paper , 015, doi:10.471/ [1] Aliukov, S., Keller, A., and Alyukov, A., "Method of Calculating of Relay Type Free-Wheel Mechanism," SAE Technical Paper , 015, doi:10.471/ [13] Keller, A. and Aliukov, S., "Methodology of System Analysis of Power Distribution among Drive Wheels of an All-wheel drive Truck," SAE Technical Paper , 015, doi:10.471/ [14] Alyukov, S., Gladyshev, S., Dynamics of an Inertial Continuously Variable Transmission with High Load Ability, SAE Technical Paper , 013, doi:10.471/ [15] Alyukov, S.V., "Characteristic of an improved continuous inertial transmission," Russian Engineering Research, vol. 34, Issue 7, 1 July 014, pp, [16] Alyukov, S.V., "Improved models of inertial torque transformers," Russian Engineering Research, vol. 30, Issue 6, 010, pp, REFERENCES [1] Leonov, A.I., "Inertial Automatic Torque Transformers," Moscow: Mashinostroenie, ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) WCECS 017
METHOD OF DETERMINATION OF VIBRATING SCREENS' OSCILLATION'S AMPLITUDE IN A CHARACTERISTIC POINT FOR PLANE MOTION
 VOL 11 NO 20 OCTOBER 2016 ISSN 1819-6608 METHOD OF DETERMINATION OF VIBRATING SCREENS' OSCILLATION'S AMPLITUDE IN A CHARACTERISTIC POINT FOR PLANE MOTION Michail Dmitrievish Gerasimov 1 Oleg Vitalievish
VOL 11 NO 20 OCTOBER 2016 ISSN 1819-6608 METHOD OF DETERMINATION OF VIBRATING SCREENS' OSCILLATION'S AMPLITUDE IN A CHARACTERISTIC POINT FOR PLANE MOTION Michail Dmitrievish Gerasimov 1 Oleg Vitalievish
1820. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation
 8. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation Tomasz Matyja, Bogusław Łazarz Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport, Gliwice, Poland Corresponding author
8. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation Tomasz Matyja, Bogusław Łazarz Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport, Gliwice, Poland Corresponding author
Dynamics of Planar Five-Link Hinged RRRRT Type Mechanism with Two Degrees of Freedom
 International ournal of Mechanical Engineering and Applications 2017; 5(2): 87-94 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmea doi: 10.11648/j.ijmea.20170502.13 ISSN: 2330-023X (Print); ISSN: 2330-0248
International ournal of Mechanical Engineering and Applications 2017; 5(2): 87-94 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmea doi: 10.11648/j.ijmea.20170502.13 ISSN: 2330-023X (Print); ISSN: 2330-0248
Advanced Mechanical Principles
 Unit 36: Unit code Advanced Mechanical Principles R/615/1504 Unit level 5 Credit value 15 Introduction A mechanical engineer is required to have an advanced knowledge of most of the machinery used within
Unit 36: Unit code Advanced Mechanical Principles R/615/1504 Unit level 5 Credit value 15 Introduction A mechanical engineer is required to have an advanced knowledge of most of the machinery used within
Experimental analysis and modeling of transmission torsional vibrations
 Experimental analysis and modeling of transmission torsional vibrations ENRICO GALVAGNO *, GUIDO RICARDO GUERCIONI, MAURO VELARDOCCHIA Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (DIMEAS) Politecnico
Experimental analysis and modeling of transmission torsional vibrations ENRICO GALVAGNO *, GUIDO RICARDO GUERCIONI, MAURO VELARDOCCHIA Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (DIMEAS) Politecnico
Finite-Element Analysis of Parts Stress State of Tight Joint Assembled by Press Fitting
 Modern Mechanical Engineering, 04, 4, 98-06 Published Online November 04 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/mme http://dx.doi.org/0.46/mme.04.4409 Finite-Element Analysis of Parts Stress State of
Modern Mechanical Engineering, 04, 4, 98-06 Published Online November 04 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/mme http://dx.doi.org/0.46/mme.04.4409 Finite-Element Analysis of Parts Stress State of
Jamil Sami Haddad 1, Waleed Momani 2
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 11, Issue 4 Ver. VIII (Jul- Aug. 014), PP 46-5 A comparison of two theoretical methods of the materials
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 11, Issue 4 Ver. VIII (Jul- Aug. 014), PP 46-5 A comparison of two theoretical methods of the materials
METHOD FOR ANALYZING EPICYCLIC GEARBOXES
 International Journal of Automotive Technology Vol. No. pp. 67 7 () DOI.7/s39 4 Copyright KSAE 9 938//5 4 METHOD FOR ANALYZING EPICYCLIC GEARBOXES T. CIOBOTARU )* D. FRUNZETI ) and L. JÄNTSCHI ) ) Military
International Journal of Automotive Technology Vol. No. pp. 67 7 () DOI.7/s39 4 Copyright KSAE 9 938//5 4 METHOD FOR ANALYZING EPICYCLIC GEARBOXES T. CIOBOTARU )* D. FRUNZETI ) and L. JÄNTSCHI ) ) Military
Structural Dynamics Lecture 2. Outline of Lecture 2. Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.)
 Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Dynamics of assembled structures of rotor systems of aviation gas turbine engines of type two-rotor
 Dynamics of assembled structures of rotor systems of aviation gas turbine engines of type two-rotor Anatoly А. Pykhalov 1, Mikhail А. Dudaev 2, Mikhail Ye. Kolotnikov 3, Paul V. Makarov 4 1 Irkutsk State
Dynamics of assembled structures of rotor systems of aviation gas turbine engines of type two-rotor Anatoly А. Pykhalov 1, Mikhail А. Dudaev 2, Mikhail Ye. Kolotnikov 3, Paul V. Makarov 4 1 Irkutsk State
Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing Considering the Effect of a Rotating or Stationary Herringbone Groove
 G. H. Jang e-mail: ghjang@hanyang.ac.kr J. W. Yoon PREM, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, 133-791, Korea Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing Considering
G. H. Jang e-mail: ghjang@hanyang.ac.kr J. W. Yoon PREM, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, 133-791, Korea Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing Considering
A METHOD FOR EVALUATION OF THE CHAIN DRIVE EFFICIENCY
 Original Scientific Paper doi:10.5937/jaes13-9170 Paper number: 13(2015)4, 341, 277-282 A METHOD FOR EVALUATION OF THE CHAIN DRIVE EFFICIENCY Aleksey Egorov* Volga State University of Technology, Yoshkar-Ola,
Original Scientific Paper doi:10.5937/jaes13-9170 Paper number: 13(2015)4, 341, 277-282 A METHOD FOR EVALUATION OF THE CHAIN DRIVE EFFICIENCY Aleksey Egorov* Volga State University of Technology, Yoshkar-Ola,
Graph-theoretic Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of an Automotive Torque Converter
 Graph-theoretic Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of an Automotive Torque Converter Joydeep M. Banerjee and John J. McPhee Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario
Graph-theoretic Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of an Automotive Torque Converter Joydeep M. Banerjee and John J. McPhee Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario
Practical and controlled laboratory vibration experiments that demonstrate the impulsive response of multi-staged clutch dampers
 Practical and controlled laboratory vibration experiments that demonstrate the impulsive response of multi-staged clutch dampers Michael D. Krak a Rajendra Singh b coustics and Dynamics Laboratory, NSF
Practical and controlled laboratory vibration experiments that demonstrate the impulsive response of multi-staged clutch dampers Michael D. Krak a Rajendra Singh b coustics and Dynamics Laboratory, NSF
CAE DEVELOPMENT OF PRECESSIONAL DRIVES USING AUTODESK INVENTOR PLATFORM
 CAE DEVELOPMENT OF PRECESSIONAL DRIVES USING AUTODESK INVENTOR PLATFORM Dr.Sc., PhD, acad. Ion BOSTAN, Technical University of Moldova, bostan@adm.utm.md, Dr.Sc., PhD, Valeriu DULGHERU, Technical University
CAE DEVELOPMENT OF PRECESSIONAL DRIVES USING AUTODESK INVENTOR PLATFORM Dr.Sc., PhD, acad. Ion BOSTAN, Technical University of Moldova, bostan@adm.utm.md, Dr.Sc., PhD, Valeriu DULGHERU, Technical University
Influence of the gap and the friction on trajectory reproduction accuracy in a multiaxis machine with CNC
 Influence of the gap and the friction on trajectory reproduction accuracy in a multiaxis machine with CNC O. V. Pas 1, N. A. Serkov 2 Blagonravov Institute of Engineering Science, Russian Academy of Sciences,
Influence of the gap and the friction on trajectory reproduction accuracy in a multiaxis machine with CNC O. V. Pas 1, N. A. Serkov 2 Blagonravov Institute of Engineering Science, Russian Academy of Sciences,
Cork Institute of Technology. Summer 2007 Mechanics of Machines (Time: 3 Hours)
 Cork Institute of Technology Bachelor of Engineering (Honours) in Mechanical Engineering- Award Instructions Answer FOUR questions. All questions carry equal marks. (NFQ Level 8) Summer 2007 Mechanics
Cork Institute of Technology Bachelor of Engineering (Honours) in Mechanical Engineering- Award Instructions Answer FOUR questions. All questions carry equal marks. (NFQ Level 8) Summer 2007 Mechanics
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads
 Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Cardan s Coupling Shaft as a Dynamic Evolutionary System
 American Journal of Modern Physics and Application 2017; 4(2): 6-11 http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/ajmpa Cardan s Coupling Shaft as a Dynamic Evolutionary System Petr Hrubý 1, Zdeněk Hlaváč 2,
American Journal of Modern Physics and Application 2017; 4(2): 6-11 http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/ajmpa Cardan s Coupling Shaft as a Dynamic Evolutionary System Petr Hrubý 1, Zdeněk Hlaváč 2,
41514 Dynamics of Machinery
 41514 Dynamics of Machinery Theory, Experiment, Phenomenology and Industrial Applications Ilmar Ferreira Santos 1. Recapitulation Mathematical Modeling & Steps 2. Example System of Particle 3. Example
41514 Dynamics of Machinery Theory, Experiment, Phenomenology and Industrial Applications Ilmar Ferreira Santos 1. Recapitulation Mathematical Modeling & Steps 2. Example System of Particle 3. Example
The Simplest Automatic Transfer Box
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol II WCE June - July London U The Simplest utomatic Transfer ox S Ivanov bstract It is proved: kinematic chain with two degrees of freedom containing
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol II WCE June - July London U The Simplest utomatic Transfer ox S Ivanov bstract It is proved: kinematic chain with two degrees of freedom containing
EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING TRANSIENT REGIME OF KINEMATIC CHAINS INCLUDING PLANETARY TRANSMISSIONS USED IN INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
 International Journal of Modern Manufacturing Technologies ISSN 2067 3604, Vol. VIII, No. 1 / 2016 EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING TRANSIENT REGIME OF KINEMATIC CHAINS INCLUDING PLANETARY TRANSMISSIONS
International Journal of Modern Manufacturing Technologies ISSN 2067 3604, Vol. VIII, No. 1 / 2016 EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING TRANSIENT REGIME OF KINEMATIC CHAINS INCLUDING PLANETARY TRANSMISSIONS
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
USE OF MECHANICAL RESONANCE IN MACHINES DRIVE SYSTEMS
 USE OF MECHANICAL RESONANCE IN MACHINES DRIVE SYSTEMS Wieslaw Fiebig, Jakub Wrobel Wroclaw University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Lukasiewicza 7/9, 51-370 Wroclaw, Poland
USE OF MECHANICAL RESONANCE IN MACHINES DRIVE SYSTEMS Wieslaw Fiebig, Jakub Wrobel Wroclaw University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Lukasiewicza 7/9, 51-370 Wroclaw, Poland
Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (007) 603-61 Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power L. Pst Institute of Thermomechanics, Academy of Sciences of CR, Dolejškova 5,18 00
Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (007) 603-61 Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power L. Pst Institute of Thermomechanics, Academy of Sciences of CR, Dolejškova 5,18 00
IMPACT OF ROAD SURFACE ROUGHNESS AND ENGINE TORQUE ON THE LOAD OF AUTOMOTIVE TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
 International Journal of echanical Engineering and Technology (IJET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 1752 1761, Article ID: IJET_10_02_181 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijet&vtype=10&itype=2
International Journal of echanical Engineering and Technology (IJET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 1752 1761, Article ID: IJET_10_02_181 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijet&vtype=10&itype=2
Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations
 Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations Bogumil Chiliński 1, Maciej Zawisza 2 Warsaw University of Technology, Institute of Machine Design Fundamentals,
Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations Bogumil Chiliński 1, Maciej Zawisza 2 Warsaw University of Technology, Institute of Machine Design Fundamentals,
Modeling and simulation of multi-disk auto-balancing rotor
 IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues, Volume, Issue 6, November 6 ISSN (Print): 69-8 ISSN (Online): 69-78 www.ijcsi.org https://doi.org/.9/66.8897 88 Modeling and simulation of multi-disk
IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues, Volume, Issue 6, November 6 ISSN (Print): 69-8 ISSN (Online): 69-78 www.ijcsi.org https://doi.org/.9/66.8897 88 Modeling and simulation of multi-disk
Improving Energy Efficiency of Smart Household Appliances and Devices
 Journal of Power and Energy Engineering, 14,, 58-6 Published Online April 14 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jpee http://dx.doi.org/1.436/jpee.14.49 Improving Energy Efficiency of Smart Household
Journal of Power and Energy Engineering, 14,, 58-6 Published Online April 14 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jpee http://dx.doi.org/1.436/jpee.14.49 Improving Energy Efficiency of Smart Household
Torsional vibrations in truck powertrains with dual mass flywheel having piecewise linear stiffness
 Torsional vibrations in truck powertrains with dual mass flywheel having piecewise lineatiffness Lina Wramner Dement of Mechanics and Maritime Sciences at Chalmers University of Technology and Volvo Group
Torsional vibrations in truck powertrains with dual mass flywheel having piecewise lineatiffness Lina Wramner Dement of Mechanics and Maritime Sciences at Chalmers University of Technology and Volvo Group
Experimental Analysis of the Relative Motion of a Gear Pair under Rattle Conditions Induced by Multi-harmonic Excitation
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering 5 Vol II WCE 5, July -, 5, London, U.K. Experimental Analysis of the Relative Motion of a Gear Pair under Rattle Conditions Induced by Multi-harmonic Excitation
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering 5 Vol II WCE 5, July -, 5, London, U.K. Experimental Analysis of the Relative Motion of a Gear Pair under Rattle Conditions Induced by Multi-harmonic Excitation
Contact problems in rotor systems
 Contact problems in rotor systems Liudmila Banakh Mechanical Engineering Research Institute of RAS, Moscow, Russia E-mail: banl@inbox.ru (Received 18 July 2016; accepted 24 August 2016) Abstract. We consider
Contact problems in rotor systems Liudmila Banakh Mechanical Engineering Research Institute of RAS, Moscow, Russia E-mail: banl@inbox.ru (Received 18 July 2016; accepted 24 August 2016) Abstract. We consider
Appendix A Prototypes Models
 Appendix A Prototypes Models This appendix describes the model of the prototypes used in Chap. 3. These mathematical models can also be found in the Student Handout by Quanser. A.1 The QUANSER SRV-02 Setup
Appendix A Prototypes Models This appendix describes the model of the prototypes used in Chap. 3. These mathematical models can also be found in the Student Handout by Quanser. A.1 The QUANSER SRV-02 Setup
Road Vehicle Dynamics
 Road Vehicle Dynamics Table of Contents: Foreword Preface Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 General 1.2 Vehicle System Classification 1.3 Dynamic System 1.4 Classification of Dynamic System Models 1.5 Constraints,
Road Vehicle Dynamics Table of Contents: Foreword Preface Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 General 1.2 Vehicle System Classification 1.3 Dynamic System 1.4 Classification of Dynamic System Models 1.5 Constraints,
[7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21
![[7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21](/thumbs/88/115835122.jpg) [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion [7.1] Torsion [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion [7] Torsion Page 2 of 21 [7.1] Torsion SHEAR STRAIN DUE TO TORSION 1) A shaft with a circular cross section is
[7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion [7.1] Torsion [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion [7] Torsion Page 2 of 21 [7.1] Torsion SHEAR STRAIN DUE TO TORSION 1) A shaft with a circular cross section is
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF OVERLOAD ABSORBING GEAR COUPLINGS
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 12, December 2018, pp. 1240 1255, Article ID: IJMET_09_12_126 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 12, December 2018, pp. 1240 1255, Article ID: IJMET_09_12_126 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=
Stabilization of Motion of the Segway 1
 Stabilization of Motion of the Segway 1 Houtman P. Siregar, 2 Yuri G. Martynenko 1 Department of Mechatronics Engineering, Indonesia Institute of Technology, Jl. Raya Puspiptek-Serpong, Indonesia 15320,
Stabilization of Motion of the Segway 1 Houtman P. Siregar, 2 Yuri G. Martynenko 1 Department of Mechatronics Engineering, Indonesia Institute of Technology, Jl. Raya Puspiptek-Serpong, Indonesia 15320,
SERBIATRIB th International Conference on Tribology. Belgrade, Serbia, May 2015
 Serbian Tribology Society SERBIATRIB 15 14 th International Conference on Tribology Belgrade, Serbia, 13 15 May 2015 University of Belgrade, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering MODELLING OF NONLINEAR DYNAMIC
Serbian Tribology Society SERBIATRIB 15 14 th International Conference on Tribology Belgrade, Serbia, 13 15 May 2015 University of Belgrade, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering MODELLING OF NONLINEAR DYNAMIC
Planar Multi-body Dynamics of a Tracked Vehicle using Imaginary Wheel Model for Tracks
 Defence Science Journal, Vol. 67, No. 4, July 2017, pp. 460-464, DOI : 10.14429/dsj.67.11548 2017, DESIDOC Planar Multi-body Dynamics of a Tracked Vehicle using Imaginary Wheel Model for Tracks Ilango
Defence Science Journal, Vol. 67, No. 4, July 2017, pp. 460-464, DOI : 10.14429/dsj.67.11548 2017, DESIDOC Planar Multi-body Dynamics of a Tracked Vehicle using Imaginary Wheel Model for Tracks Ilango
HADDONFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS Curriculum Map for AP Physics, Mechanics C
 Curriculum Map for AP Physics, Mechanics C September Enduring Understandings (The big ideas): Chapter 2 -- Motion Along a Straight Line Essential Questions: How do objects move? 1. Displacement, time,
Curriculum Map for AP Physics, Mechanics C September Enduring Understandings (The big ideas): Chapter 2 -- Motion Along a Straight Line Essential Questions: How do objects move? 1. Displacement, time,
OPTIMAL DESIGN OF CLUTCH PLATE BASED ON HEAT AND STRUCTURAL PARAMETERS USING CFD AND FEA
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 5, May 2018, pp. 717 724, Article ID: IJMET_09_05_079 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=9&itype=5
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 5, May 2018, pp. 717 724, Article ID: IJMET_09_05_079 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=9&itype=5
ANALYTICAL MODELING OF PLANETARY GEAR AND SENSITIVITY OF NATURAL FREQUENCIES
 ANALYTICAL MODELING OF PLANETARY GEAR AND SENSITIVITY OF NATURAL FREQUENCIES MAJID MEHRABI 1, DR. V.P.SINGH 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of Mechanical Engg. Department-PEC University of Technology
ANALYTICAL MODELING OF PLANETARY GEAR AND SENSITIVITY OF NATURAL FREQUENCIES MAJID MEHRABI 1, DR. V.P.SINGH 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of Mechanical Engg. Department-PEC University of Technology
A STUDY ON THE BASIC CONTROL OF SPEED RATIO OF THE CVT SYSTEM USED FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES
 A STUDY ON THE BASIC CONTROL OF SPEED RATIO OF THE CVT SYSTEM USED FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES A. Yildiz, O. Kopmaz Uludag University, Engineering Faculty, Mechanical Engineering Department, 1659 Gorukle Campus,
A STUDY ON THE BASIC CONTROL OF SPEED RATIO OF THE CVT SYSTEM USED FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES A. Yildiz, O. Kopmaz Uludag University, Engineering Faculty, Mechanical Engineering Department, 1659 Gorukle Campus,
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus
 , July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus G. Di Massa Member IAENG, S. Pagano, M. Ramondini Abstract Ring shear apparatus are used to determine the ultimate shear strength of
, July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus G. Di Massa Member IAENG, S. Pagano, M. Ramondini Abstract Ring shear apparatus are used to determine the ultimate shear strength of
Tutorial 1 - Drive fundamentals and DC motor characteristics
 University of New South Wales School of Electrical Engineering & elecommunications ELEC4613 ELECRIC DRIVE SYSEMS utorial 1 - Drive fundamentals and DC motor characteristics 1. In the hoist drive system
University of New South Wales School of Electrical Engineering & elecommunications ELEC4613 ELECRIC DRIVE SYSEMS utorial 1 - Drive fundamentals and DC motor characteristics 1. In the hoist drive system
A Study on the Tube of Integral Propeller Shaft for the Rear-wheel Drive Automobile Using Carbon Composite Fiber
 A Study on the Tube of Integral Propeller Shaft for the Rear-wheel Drive Automobile Using Carbon Composite Fiber Kibong Han Mechatronics Department, Jungwon University, 85 Munmu-ro, Goesan-gun, South Korea.
A Study on the Tube of Integral Propeller Shaft for the Rear-wheel Drive Automobile Using Carbon Composite Fiber Kibong Han Mechatronics Department, Jungwon University, 85 Munmu-ro, Goesan-gun, South Korea.
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF LIGHT WEIGHT MOTOR VEHICLE FLYWHEEL M.LAVAKUMAR #1, R.PRASANNA SRINIVAS* 2
 International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology (IJCTT) volume 4 Issue 7 July 013 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF LIGHT WEIGHT MOTOR VEHICLE FLYWHEEL M.LAVAKUMAR #1, R.PRASANNA SRINIVAS* 1 Assistant Professor
International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology (IJCTT) volume 4 Issue 7 July 013 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF LIGHT WEIGHT MOTOR VEHICLE FLYWHEEL M.LAVAKUMAR #1, R.PRASANNA SRINIVAS* 1 Assistant Professor
Theory of gear adaptive transmission
 American Journal of echanics and Applications 04; (6-): - Published online December 6, 04 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajma) doi: 0.648/j.ajma.s.040060. Theory of gear adaptive transmission
American Journal of echanics and Applications 04; (6-): - Published online December 6, 04 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajma) doi: 0.648/j.ajma.s.040060. Theory of gear adaptive transmission
Mechanical Principles
 Unit 4: Mechanical Principles Unit code: F/601/1450 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learners understanding of an extended range of mechanical principles that underpin the design
Unit 4: Mechanical Principles Unit code: F/601/1450 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learners understanding of an extended range of mechanical principles that underpin the design
Mechatronics. MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1
 Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
Contents. Dynamics and control of mechanical systems. Focus on
 Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (01/08) Day 2 (03/08) Day 3 (05/08) Day 4 (07/08) Day 5 (09/08) Day 6 (11/08) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid bodies
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (01/08) Day 2 (03/08) Day 3 (05/08) Day 4 (07/08) Day 5 (09/08) Day 6 (11/08) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid bodies
Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly
 Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly Mariyam Sattar 1, Cheng Wei 2, Awais Jalali 3 1, 2 Beihang University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly Mariyam Sattar 1, Cheng Wei 2, Awais Jalali 3 1, 2 Beihang University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
The impact of rotor elastic suspension settings on the acceleration of the automatic balancer compensating mass
 The impact of rotor elastic suspension settings on the acceleration of the automatic balancer compensating mass Guntis Strautmanis 1, Mareks Mezitis 2, Valentina Strautmane 3 1, 2 Riga Technical University,
The impact of rotor elastic suspension settings on the acceleration of the automatic balancer compensating mass Guntis Strautmanis 1, Mareks Mezitis 2, Valentina Strautmane 3 1, 2 Riga Technical University,
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
Methodology for modeling, parameter estimation, and validation of powertrain torsional vibration
 Methodology for modeling, parameter estimation, and validation of powertrain torsional vibration Abstract Neda Nickmehr, Lars Eriksson, and Jan Åslund Dep. of Electrical Engineering, Linköping University,
Methodology for modeling, parameter estimation, and validation of powertrain torsional vibration Abstract Neda Nickmehr, Lars Eriksson, and Jan Åslund Dep. of Electrical Engineering, Linköping University,
MECTROL CORPORATION 9 NORTHWESTERN DRIVE, SALEM, NH PHONE FAX TIMING BELT THEORY
 MECTRO CORPORATION 9 NORTHWESTERN DRIVE, SAEM, NH 03079 PHONE 603-890-55 FAX 603-890-66 TIMING BET THEORY Copyright 997, 999, 00 Mectrol Corporation. All rights reserved. April 00 Timing Belt Theory Introduction
MECTRO CORPORATION 9 NORTHWESTERN DRIVE, SAEM, NH 03079 PHONE 603-890-55 FAX 603-890-66 TIMING BET THEORY Copyright 997, 999, 00 Mectrol Corporation. All rights reserved. April 00 Timing Belt Theory Introduction
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 7 Instability in rotor systems Lecture - 4 Steam Whirl and
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 7 Instability in rotor systems Lecture - 4 Steam Whirl and
Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session. Dr. David Herrin March 27, 2012
 Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session Dr. David Herrin March 7, 0 Example A 0 g ball is released vertically from a height of 0 m. The ball strikes a horizontal surface and bounces back.
Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session Dr. David Herrin March 7, 0 Example A 0 g ball is released vertically from a height of 0 m. The ball strikes a horizontal surface and bounces back.
Modeling of Electromechanical Systems
 Page 1 of 54 Modeling of Electromechanical Systems Werner Haas, Kurt Schlacher and Reinhard Gahleitner Johannes Kepler University Linz, Department of Automatic Control, Altenbergerstr.69, A 4040 Linz,
Page 1 of 54 Modeling of Electromechanical Systems Werner Haas, Kurt Schlacher and Reinhard Gahleitner Johannes Kepler University Linz, Department of Automatic Control, Altenbergerstr.69, A 4040 Linz,
Impact. m k. Natural Period of Vibration τ. Static load Gray area Impact load t > 3 τ. Absorbing energy. Carrying loads
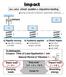 Impact also called shock, sudden or impulsive loading driving a nail with a hammer, automobile collisions. dashpot a) Rapidly moving vehicles crossing a bridge To distinguish: b) Suddenly applied c) Direct
Impact also called shock, sudden or impulsive loading driving a nail with a hammer, automobile collisions. dashpot a) Rapidly moving vehicles crossing a bridge To distinguish: b) Suddenly applied c) Direct
Finite Element Analysis Lecture 1. Dr./ Ahmed Nagib
 Finite Element Analysis Lecture 1 Dr./ Ahmed Nagib April 30, 2016 Research and Development Mathematical Model Mathematical Model Mathematical Model Finite Element Analysis The linear equation of motion
Finite Element Analysis Lecture 1 Dr./ Ahmed Nagib April 30, 2016 Research and Development Mathematical Model Mathematical Model Mathematical Model Finite Element Analysis The linear equation of motion
D DAVID PUBLISHING. Design of Torque Balancing Mechanisms. 1. Introduction. Bruno Zappa, Vittorio Lorenzi, Paolo Righettini and Roberto Strada
 Journal of Mechanics Engineering and Automation 7 (207) 32-320 doi: 0.7265/259-5275/207.06.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Bruno Zappa, Vittorio Lorenzi, Paolo Righettini and Roberto Strada Department of Engineering
Journal of Mechanics Engineering and Automation 7 (207) 32-320 doi: 0.7265/259-5275/207.06.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Bruno Zappa, Vittorio Lorenzi, Paolo Righettini and Roberto Strada Department of Engineering
FORCE ANALYSIS OF MACHINERY. School of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, AAiT
 1 FORCE ANALYSIS OF MACHINERY School of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, AAiT INTRODUCTION 2 A machine is a device that performs work and, as such, transmits energy by means mechanical force from a
1 FORCE ANALYSIS OF MACHINERY School of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, AAiT INTRODUCTION 2 A machine is a device that performs work and, as such, transmits energy by means mechanical force from a
Engineering Science OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Selection of Servomotors and Reducer Units for a 2 DoF PKM
 Selection of Servomotors and Reducer Units for a 2 DoF PKM Hermes GIBERTI, Simone CINQUEMANI Mechanical Engineering Department, Politecnico di Milano, Campus Bovisa Sud, via La Masa 34, 20156, Milano,
Selection of Servomotors and Reducer Units for a 2 DoF PKM Hermes GIBERTI, Simone CINQUEMANI Mechanical Engineering Department, Politecnico di Milano, Campus Bovisa Sud, via La Masa 34, 20156, Milano,
Study Guide Solutions
 Study Guide Solutions Table of Contents Chapter 1 A Physics Toolkit... 3 Vocabulary Review... 3 Section 1.1: Mathematics and Physics... 3 Section 1.2: Measurement... 3 Section 1.3: Graphing Data... 4 Chapter
Study Guide Solutions Table of Contents Chapter 1 A Physics Toolkit... 3 Vocabulary Review... 3 Section 1.1: Mathematics and Physics... 3 Section 1.2: Measurement... 3 Section 1.3: Graphing Data... 4 Chapter
Name: Fall 2014 CLOSED BOOK
 Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machines. Prof. Amitabha Ghosh. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Module No.
 Dynamics of Machines Prof. Amitabha Ghosh Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module No. # 07 Lecture No. # 01 In our previous lectures, you have noticed that we
Dynamics of Machines Prof. Amitabha Ghosh Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module No. # 07 Lecture No. # 01 In our previous lectures, you have noticed that we
Lecture 9: Harmonic Loads (Con t)
 Lecture 9: Harmonic Loads (Con t) Reading materials: Sections 3.4, 3.5, 3.6 and 3.7 1. Resonance The dynamic load magnification factor (DLF) The peak dynamic magnification occurs near r=1 for small damping
Lecture 9: Harmonic Loads (Con t) Reading materials: Sections 3.4, 3.5, 3.6 and 3.7 1. Resonance The dynamic load magnification factor (DLF) The peak dynamic magnification occurs near r=1 for small damping
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems
 Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
Analysis of flow along smooth side of disc impeller in a pump
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow along smooth side of disc impeller in a pump To cite this article: E M Kraeva 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow along smooth side of disc impeller in a pump To cite this article: E M Kraeva 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
THE RUNNING SIMULATION OF A HYBRID CAR
 UNIVERSITY OF PITESTI SCIENTIFIC BULLETIN FACULTY OF MECHANICS AND TECHNOLOGY AUTOMOTIVE series, year XVII, no. ( ) THE RUNNING SIMULATION OF A HYBRID CAR Dinel POPA *, University of Piteşti, Romania e-mail:
UNIVERSITY OF PITESTI SCIENTIFIC BULLETIN FACULTY OF MECHANICS AND TECHNOLOGY AUTOMOTIVE series, year XVII, no. ( ) THE RUNNING SIMULATION OF A HYBRID CAR Dinel POPA *, University of Piteşti, Romania e-mail:
Abstract. Solomon I. Khmelnik Unsupported Motion Without Violating the Laws of Physics
 Solomon I. Khmelnik Unsupported Motion Without iolating the Laws of Physics Abstract We are considering some speculative experiments with charges and currents, which demonstrate a breach of Newton's third
Solomon I. Khmelnik Unsupported Motion Without iolating the Laws of Physics Abstract We are considering some speculative experiments with charges and currents, which demonstrate a breach of Newton's third
Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground To cite this article: Jozef Vlek and Veronika
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground To cite this article: Jozef Vlek and Veronika
The theoretical model for determinig critical rotation speed flexible coupling type SEGE
 Volume XXI 018 ISSUE no.1 MBNA Publishing House Constanta 018 SBNA PAPER OPEN ACCESS The theoretical model for determinig critical rotation speed flexible coupling type SEGE To cite this article: E Ivanova,
Volume XXI 018 ISSUE no.1 MBNA Publishing House Constanta 018 SBNA PAPER OPEN ACCESS The theoretical model for determinig critical rotation speed flexible coupling type SEGE To cite this article: E Ivanova,
2108. Free vibration properties of rotate vector reducer
 2108. Free vibration properties of rotate vector reducer Chuan Chen 1, Yuhu Yang 2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072, P. R. China 1 Corresponding author E-mail: 1 chenchuan1985728@126.com,
2108. Free vibration properties of rotate vector reducer Chuan Chen 1, Yuhu Yang 2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072, P. R. China 1 Corresponding author E-mail: 1 chenchuan1985728@126.com,
Dynamic Model of a Badminton Stroke
 ISEA 28 CONFERENCE Dynamic Model of a Badminton Stroke M. Kwan* and J. Rasmussen Department of Mechanical Engineering, Aalborg University, 922 Aalborg East, Denmark Phone: +45 994 9317 / Fax: +45 9815
ISEA 28 CONFERENCE Dynamic Model of a Badminton Stroke M. Kwan* and J. Rasmussen Department of Mechanical Engineering, Aalborg University, 922 Aalborg East, Denmark Phone: +45 994 9317 / Fax: +45 9815
UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS)
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEACH AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME2302 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY III YEAR/ V SEMESTER UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS) PART-A (2 marks)
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEACH AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME2302 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY III YEAR/ V SEMESTER UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS) PART-A (2 marks)
Control of Vibrations in a Micromechanical Gyroscope Using Inertia Properties of Standing Elastic Waves
 Preprints of the 9th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Cape Town, South Africa August 4-9, 04 Control of Vibrations in a Micromechanical Gyroscope Using Inertia Properties
Preprints of the 9th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Cape Town, South Africa August 4-9, 04 Control of Vibrations in a Micromechanical Gyroscope Using Inertia Properties
CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS
 CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J Vector Representation Statics Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics Control
CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J Vector Representation Statics Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics Control
Keywords: Principle Of Escapement Mechanism, Tower Escape Apparatus, Mechanism Design.
 Key Engineering Materials Online: 2013-07-15 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vol. 561, pp 568-571 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.561.568 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Design and Research on tower escape
Key Engineering Materials Online: 2013-07-15 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vol. 561, pp 568-571 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.561.568 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Design and Research on tower escape
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV
 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
Mathematical model of electromechanical system with variable dissipativity
 Mathematical model of electromechanical system with variable dissipativity Alexsandr Baykov, Boris Gordeev 2 Nizhny Novgorod State Technical University n. a. R. E. Alexeev, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia 2 Institute
Mathematical model of electromechanical system with variable dissipativity Alexsandr Baykov, Boris Gordeev 2 Nizhny Novgorod State Technical University n. a. R. E. Alexeev, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia 2 Institute
Integration simulation method concerning speed control of ultrasonic motor
 Integration simulation method concerning speed control of ultrasonic motor R Miyauchi 1, B Yue 2, N Matsunaga 1 and S Ishizuka 1 1 Cybernet Systems Co., Ltd. 3 Kanda-neribeicho,Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo,101-0022,Japan
Integration simulation method concerning speed control of ultrasonic motor R Miyauchi 1, B Yue 2, N Matsunaga 1 and S Ishizuka 1 1 Cybernet Systems Co., Ltd. 3 Kanda-neribeicho,Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo,101-0022,Japan
Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT
 Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT Product overview Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive Actuators with ball monorail
Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT Product overview Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive Actuators with ball monorail
Research Article Robust Switching Control Strategy for a Transmission System with Unknown Backlash
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 24, Article ID 79384, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/79384 Research Article Robust Switching Control Strategy for a Transmission System with Unknown Backlash
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 24, Article ID 79384, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/79384 Research Article Robust Switching Control Strategy for a Transmission System with Unknown Backlash
Simulating Two-Dimensional Stick-Slip Motion of a Rigid Body using a New Friction Model
 Proceedings of the 2 nd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'16) Budapest, Hungary August 22 23, 2016 Paper No. ICMIE 116 DOI: 10.11159/icmie16.116 Simulating Two-Dimensional
Proceedings of the 2 nd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'16) Budapest, Hungary August 22 23, 2016 Paper No. ICMIE 116 DOI: 10.11159/icmie16.116 Simulating Two-Dimensional
1 2 Models, Theories, and Laws 1.5 Distinguish between models, theories, and laws 2.1 State the origin of significant figures in measurement
 Textbook Correlation Textbook Correlation Physics 1115/2015 Chapter 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating 1.1 Describe thoughts of Aristotle vs. Galileo in describing motion 1 1 Nature of Science 1.2
Textbook Correlation Textbook Correlation Physics 1115/2015 Chapter 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating 1.1 Describe thoughts of Aristotle vs. Galileo in describing motion 1 1 Nature of Science 1.2
Research on transmission stability of rotation roller screw for rail transit vehicles door
 vailable online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 014, 6(4):94-933 Research rticle ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(US) : JCPRC5 Research on transmission stability of rotation roller
vailable online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 014, 6(4):94-933 Research rticle ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(US) : JCPRC5 Research on transmission stability of rotation roller
WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery
 WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2011 Mechanical Vibrations, Singiresu S. Rao, 2010 Mechanical Vibrations: Theory and
WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2011 Mechanical Vibrations, Singiresu S. Rao, 2010 Mechanical Vibrations: Theory and
T20WN. Data Sheet. Torque transducers. Special features. Installation example with bellows couplings. B en
 T20WN Torque transducers Data Sheet Special features - Nominal (rated) torques 0.1 N m, 0.2 N m, 0. N m, 1 N m, 2 N m, N m, 10 N m, 20 N m, 0 N m, 100 N m, 200 N m - Accuracy class: 0.2 - Contactless transmission
T20WN Torque transducers Data Sheet Special features - Nominal (rated) torques 0.1 N m, 0.2 N m, 0. N m, 1 N m, 2 N m, N m, 10 N m, 20 N m, 0 N m, 100 N m, 200 N m - Accuracy class: 0.2 - Contactless transmission
Parameter Prediction and Modelling Methods for Traction Motor of Hybrid Electric Vehicle
 Page 359 World Electric Vehicle Journal Vol. 3 - ISSN 232-6653 - 29 AVERE Parameter Prediction and Modelling Methods for Traction Motor of Hybrid Electric Vehicle Tao Sun, Soon-O Kwon, Geun-Ho Lee, Jung-Pyo
Page 359 World Electric Vehicle Journal Vol. 3 - ISSN 232-6653 - 29 AVERE Parameter Prediction and Modelling Methods for Traction Motor of Hybrid Electric Vehicle Tao Sun, Soon-O Kwon, Geun-Ho Lee, Jung-Pyo
Coupling Heat Structure Analysis of the Clutch Pressure Plate in Vehicle Overloaded Start Procession
 Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Coupling Heat Structure Analysis of the Clutch Pressure Plate in Vehicle Overloaded Start Procession Qi-Tang WANG, Mao-Tao
Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Coupling Heat Structure Analysis of the Clutch Pressure Plate in Vehicle Overloaded Start Procession Qi-Tang WANG, Mao-Tao
The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval.
 Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Course Name: AP Physics. Team Names: Jon Collins. Velocity Acceleration Displacement
 Course Name: AP Physics Team Names: Jon Collins 1 st 9 weeks Objectives Vocabulary 1. NEWTONIAN MECHANICS and lab skills: Kinematics (including vectors, vector algebra, components of vectors, coordinate
Course Name: AP Physics Team Names: Jon Collins 1 st 9 weeks Objectives Vocabulary 1. NEWTONIAN MECHANICS and lab skills: Kinematics (including vectors, vector algebra, components of vectors, coordinate
Improvement in the Design & Manufacturing of Twin Worm Self Locking Technique and applications
 Improvement in the Design & Manufacturing of Twin Worm Self Locking Technique and applications Prof. P.B. Kadam 1, Prof. M.R. Todkar 2 1 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering Department, T.K.I.E.T.Warananagar,
Improvement in the Design & Manufacturing of Twin Worm Self Locking Technique and applications Prof. P.B. Kadam 1, Prof. M.R. Todkar 2 1 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering Department, T.K.I.E.T.Warananagar,
Stepping Motors. Chapter 11 L E L F L D
 Chapter 11 Stepping Motors In the synchronous motor, the combination of sinusoidally distributed windings and sinusoidally time varying current produces a smoothly rotating magnetic field. We can eliminate
Chapter 11 Stepping Motors In the synchronous motor, the combination of sinusoidally distributed windings and sinusoidally time varying current produces a smoothly rotating magnetic field. We can eliminate
String tyre model for evaluating steering agility performance using tyre cornering force and lateral static characteristics
 Vehicle System Dynamics International Journal of Vehicle Mechanics and Mobility ISSN: 0042-3114 (Print) 1744-5159 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/nvsd20 String tyre model for
Vehicle System Dynamics International Journal of Vehicle Mechanics and Mobility ISSN: 0042-3114 (Print) 1744-5159 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/nvsd20 String tyre model for
