NEUTRON MODERATION. LIST three desirable characteristics of a moderator.
|
|
|
- Mitchell Quinn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reactor Theory (eutron Characteristics) DOE-HDBK-1019/1-93 EUTRO MODERATIO EUTRO MODERATIO In thermal reactors, the neutrons that cause fission are at a much lower energy than the energy level at which they were born from fission. In this type of reactor, specific materials must be included in the reactor design to reduce the energy level of the neutrons in an efficient manner. EO.1 DEFIE the following concepts: a. Thermalization d. Average logarithmic energy decrement b. Moderator e. Macroscopic slowing down power c. Moderating ratio EO.13 EO.14 LIST three desirable characteristics of a moderator. Given an average fractional energy loss per collision, CALCULATE the energy loss after a specified number of collisions. eutron Slowing Down and Thermalization Fission neutrons are produced at an average energy level of MeV and immediately begin to slow down as the result of numerous scattering reactions with a variety of target nuclei. After a number of collisions with nuclei, the speed of a neutron is reduced to such an extent that it has approximately the same average kinetic energy as the atoms (or molecules) of the medium in which the neutron is undergoing elastic scattering. This energy, which is only a small fraction of an electron volt at ordinary temperatures (0.05 ev at 0(C), is frequently referred to as the thermal energy, since it depends upon the temperature. eutrons whose energies have been reduced to values in this region (< 1 ev) are designated thermal neutrons. The process of reducing the energy of a neutron to the thermal region by elastic scattering is referred to as thermalization, slowing down, or moderation. The material used for the purpose of thermalizing neutrons is called a moderator. A good moderator reduces the speed of neutrons in a small number of collisions, but does not absorb them to any great extent. Slowing the neutrons in as few collisions as possible is desirable in order to reduce the amount of neutron leakage from the core and also to reduce the number of resonance absorptions in non-fuel materials. eutron leakage and resonance absorption will be discussed in the next module. Rev. 0 Page 3 P-0
2 EUTRO MODERATIO DOE-HDBK-1019/1-93 Reactor Theory (eutron Characteristics) The ideal moderating material (moderator) should have the following nuclear properties. large scattering cross section small absorption cross section large energy loss per collision A convenient measure of energy loss per collision is the logarithmic energy decrement. The average logarithmic energy decrement is the average decrease per collision in the logarithm of the neutron energy. This quantity is represented by the symbol (Greek letter xi). E i E f E i E f (-8) where: = average logarithmic energy decrement E i = average initial neutron energy E f = average final neutron energy The symbol is commonly called the average logarithmic energy decrement because of the fact that a neutron loses, on the average, a fixed fraction of its energy per scattering collision. Since the fraction of energy retained by a neutron in a single elastic collision is a constant for a given material, is also a constant. Because it is a constant for each type of material and does not depend upon the initial neutron energy, is a convenient quantity for assessing the moderating ability of a material. The values for the lighter nuclei are tabulated in a variety of sources. The following commonly used approximation may be used when a tabulated value is not available. A 3 This approximation is relatively accurate for mass numbers (A) greater than 10, but for some low values of A it may be in error by over three percent. P-0 Page 4 Rev. 0
3 Reactor Theory (eutron Characteristics) DOE-HDBK-1019/1-93 EUTRO MODERATIO Since represents the average logarithmic energy loss per collision, the total number of collisions necessary for a neutron to lose a given amount of energy may be determined by dividing into the difference of the natural logarithms of the energy range in question. The number of collisions () to travel from any energy, E high, to any lower energy, E low, can be calculated as shown below. E high E low E high E low Example: Solution: How many collisions are required to slow a neutron from an energy of MeV to a thermal energy of 0.05 ev, using water as the moderator? Water has a value of for. E high E low x 10 6 ev 0.05 ev collisions Sometimes it is convenient, based upon information known, to work with an average fractional energy loss per collision as opposed to an average logarithmic fraction. If the initial neutron energy level and the average fractional energy loss per collision are known, the final energy level for a given number of collisions may be computed using the following formula. Rev. 0 Page 5 P-0
4 EUTRO MODERATIO DOE-HDBK-1019/1-93 Reactor Theory (eutron Characteristics) (-9) where: E E x o = initial neutron energy = neutron energy after collisions = average fractional energy loss per collision = number of collisions Example: Solution: If the average fractional energy loss per collision in hydrogen is 0.63, what will be the energy of a MeV neutron after (a) 5 collisions? (b) 10 collisions? a) b) Macroscopic Slowing Down Power Although the logarithmic energy decrement is a convenient measure of the ability of a material to slow neutrons, it does not measure all necessary properties of a moderator. A better measure of the capabilities of a material is the macroscopic slowing down power. The macroscopic slowing down power (MSDP) is the product of the logarithmic energy decrement and the macroscopic cross section for scattering in the material. Equation (-10) illustrates how to calculate the macroscopic slowing down power.!( (-10) P-0 Page 6 Rev. 0
5 Reactor Theory (eutron Characteristics) DOE-HDBK-1019/1-93 EUTRO MODERATIO Moderating Ratio Macroscopic slowing down power indicates how rapidly a neutron will slow down in the material in question, but it still does not fully explain the effectiveness of the material as a moderator. An element such as boron has a high logarithmic energy decrement and a good slowing down power, but it is a poor moderator because of its high probability of absorbing neutrons. The most complete measure of the effectiveness of a moderator is the moderating ratio. The moderating ratio is the ratio of the macroscopic slowing down power to the macroscopic cross section for absorption. The higher the moderating ratio, the more effectively the material performs as a moderator. Equation (-11) shows how to calculate the moderating ratio of a material. MR a s (-11) Moderating properties of different materials are compared in Table. TABLE Moderating Properties of Materials umber of Macroscopic Material Collisions to Slowing Down Thermalize Power Moderating Ratio H O D O Helium x Beryllium Boron Carbon Rev. 0 Page 7 P-0
6 EUTRO MODERATIO DOE-HDBK-1019/1-93 Reactor Theory (eutron Characteristics) Summary The important information in this chapter is summarized below. eutron Moderation Summary Thermalization is the process of reducing the energy level of a neutron from the energy level at which it is produced to an energy level in the thermal range. The moderator is the reactor material that is present for the purpose of thermalizing neutrons. Moderating ratio is the ratio of the macroscopic slowing down power to the macroscopic cross section for absorption. The average logarithmic energy decrement (!) is the average change in the logarithm of neutron energy per collision. Macroscopic slowing down power is the product of the average logarithmic energy decrement and the macroscopic cross section for scattering. There are three desirable characteristics of a moderator. 1. large scattering cross section. small absorption cross section 3. large energy loss per collision The energy loss after a specified number of collisions can be calculated using the equation below. E = E (1 - x) o P-0 Page 8 Rev. 0
Elastic scattering. Elastic scattering
 Elastic scattering Now we have worked out how much energy is lost when a neutron is scattered through an angle, θ We would like to know how much energy, on average, is lost per collision In order to do
Elastic scattering Now we have worked out how much energy is lost when a neutron is scattered through an angle, θ We would like to know how much energy, on average, is lost per collision In order to do
VI. Chain Reaction. Two basic requirements must be filled in order to produce power in a reactor:
 VI. Chain Reaction VI.1. Basic of Chain Reaction Two basic requirements must be filled in order to produce power in a reactor: The fission rate should be high. This rate must be continuously maintained.
VI. Chain Reaction VI.1. Basic of Chain Reaction Two basic requirements must be filled in order to produce power in a reactor: The fission rate should be high. This rate must be continuously maintained.
turbine (a) (i) Which part of the power station provides thermal (heat) energy from a chain reaction?
 Nuclear fission and radiation 1 The diagram shows parts of a nuclear power station. control rods boiler steam generator electricity out turbine condenser nuclear reactor (a) (i) Which part of the power
Nuclear fission and radiation 1 The diagram shows parts of a nuclear power station. control rods boiler steam generator electricity out turbine condenser nuclear reactor (a) (i) Which part of the power
Nuclear Physics 2. D. atomic energy levels. (1) D. scattered back along the original direction. (1)
 Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 2. Which of the following gives the correct number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of B? 5 Number of protons Number of neutrons A. 5 6 B. 5 C. 6 5 D. 5 2. The
Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 2. Which of the following gives the correct number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of B? 5 Number of protons Number of neutrons A. 5 6 B. 5 C. 6 5 D. 5 2. The
Lectures on Applied Reactor Technology and Nuclear Power Safety. Lecture No 1. Title: Neutron Life Cycle
 Lectures on Nuclear Power Safety Lecture No 1 Title: Neutron Life Cycle Department of Energy Technology KTH Spring 2005 Slide No 1 Outline of the Lecture Infinite Multiplication Factor, k Four Factor Formula
Lectures on Nuclear Power Safety Lecture No 1 Title: Neutron Life Cycle Department of Energy Technology KTH Spring 2005 Slide No 1 Outline of the Lecture Infinite Multiplication Factor, k Four Factor Formula
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter
 Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
VIII. Neutron Moderation and the Six Factors
 Introduction VIII. Neutron Moderation and the Six Factors 130 We continue our quest to calculate the multiplication factor (keff) and the neutron distribution (in position and energy) in nuclear reactors.
Introduction VIII. Neutron Moderation and the Six Factors 130 We continue our quest to calculate the multiplication factor (keff) and the neutron distribution (in position and energy) in nuclear reactors.
Slowing down the neutrons
 Slowing down the neutrons Clearly, an obvious way to make a reactor work, and to make use of this characteristic of the 3 U(n,f) cross-section, is to slow down the fast, fission neutrons. This can be accomplished,
Slowing down the neutrons Clearly, an obvious way to make a reactor work, and to make use of this characteristic of the 3 U(n,f) cross-section, is to slow down the fast, fission neutrons. This can be accomplished,
6 Neutrons and Neutron Interactions
 6 Neutrons and Neutron Interactions A nuclear reactor will not operate without neutrons. Neutrons induce the fission reaction, which produces the heat in CANDU reactors, and fission creates more neutrons.
6 Neutrons and Neutron Interactions A nuclear reactor will not operate without neutrons. Neutrons induce the fission reaction, which produces the heat in CANDU reactors, and fission creates more neutrons.
17 Neutron Life Cycle
 17 Neutron Life Cycle A typical neutron, from birth as a prompt fission neutron to absorption in the fuel, survives for about 0.001 s (the neutron lifetime) in a CANDU. During this short lifetime, it travels
17 Neutron Life Cycle A typical neutron, from birth as a prompt fission neutron to absorption in the fuel, survives for about 0.001 s (the neutron lifetime) in a CANDU. During this short lifetime, it travels
Lecture 20 Reactor Theory-V
 Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following We will discuss the criticality condition and then introduce the concept of k eff.. We then will introduce the four factor formula and two group
Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following We will discuss the criticality condition and then introduce the concept of k eff.. We then will introduce the four factor formula and two group
Lewis 2.1, 2.2 and 2.3
 Chapter 2(and 3) Cross-Sections TA Lewis 2.1, 2.2 and 2.3 Learning Objectives Understand different types of nuclear reactions Understand cross section behavior for different reactions Understand d resonance
Chapter 2(and 3) Cross-Sections TA Lewis 2.1, 2.2 and 2.3 Learning Objectives Understand different types of nuclear reactions Understand cross section behavior for different reactions Understand d resonance
2. The neutron may just bounce off (elastic scattering), and this can happen at all neutron energies.
 Nuclear Theory - Course 227 NEUTRON CROSS SECTONS, NEUTRON DENSTY AND NEUTRON FLUX Neutron Cross Sections Let us have a look at the various reactions a neutron can undergo with a U-235 nucleus: As mentioned
Nuclear Theory - Course 227 NEUTRON CROSS SECTONS, NEUTRON DENSTY AND NEUTRON FLUX Neutron Cross Sections Let us have a look at the various reactions a neutron can undergo with a U-235 nucleus: As mentioned
Cross-Sections for Neutron Reactions
 22.05 Reactor Physics Part Four Cross-Sections for Neutron Reactions 1. Interactions: Cross-sections deal with the measurement of interactions between moving particles and the material through which they
22.05 Reactor Physics Part Four Cross-Sections for Neutron Reactions 1. Interactions: Cross-sections deal with the measurement of interactions between moving particles and the material through which they
Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions.
 Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions. I first need to acknowledge that these two lectures were based on lectures presented previously in Med Phys I by Dr Howell. 1 Before
Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions. I first need to acknowledge that these two lectures were based on lectures presented previously in Med Phys I by Dr Howell. 1 Before
NUCLEAR SCIENCE ACAD BASIC CURRICULUM CHAPTER 5 NEUTRON LIFE CYCLE STUDENT TEXT REV 2. L th. L f U-235 FUEL MODERATOR START CYCLE HERE THERMAL NEUTRON
 ACAD BASIC CURRICULUM NUCLEAR SCIENCE CHAPTER 5 NEUTRON LIFE CYCLE 346 RESONANCE LOSSES p 038 THERMAL NEUTRON 2 THERMAL NEUTRON LEAKAGE 52 THERMAL ABSORBED BY NON-FUEL ATOMS L th 07 THERMAL f 965 THERMAL
ACAD BASIC CURRICULUM NUCLEAR SCIENCE CHAPTER 5 NEUTRON LIFE CYCLE 346 RESONANCE LOSSES p 038 THERMAL NEUTRON 2 THERMAL NEUTRON LEAKAGE 52 THERMAL ABSORBED BY NON-FUEL ATOMS L th 07 THERMAL f 965 THERMAL
Lesson 8: Slowing Down Spectra, p, Fermi Age
 Lesson 8: Slowing Down Spectra, p, Fermi Age Slowing Down Spectra in Infinite Homogeneous Media Resonance Escape Probability ( p ) Resonance Integral ( I, I eff ) p, for a Reactor Lattice Semi-empirical
Lesson 8: Slowing Down Spectra, p, Fermi Age Slowing Down Spectra in Infinite Homogeneous Media Resonance Escape Probability ( p ) Resonance Integral ( I, I eff ) p, for a Reactor Lattice Semi-empirical
State the main interaction when an alpha particle is scattered by a gold nucleus
 Q1.(a) Scattering experiments are used to investigate the nuclei of gold atoms. In one experiment, alpha particles, all of the same energy (monoenergetic), are incident on a foil made from a single isotope
Q1.(a) Scattering experiments are used to investigate the nuclei of gold atoms. In one experiment, alpha particles, all of the same energy (monoenergetic), are incident on a foil made from a single isotope
X. Assembling the Pieces
 X. Assembling the Pieces 179 Introduction Our goal all along has been to gain an understanding of nuclear reactors. As we ve noted many times, this requires knowledge of how neutrons are produced and lost.
X. Assembling the Pieces 179 Introduction Our goal all along has been to gain an understanding of nuclear reactors. As we ve noted many times, this requires knowledge of how neutrons are produced and lost.
Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter)
 Al-Mustansiriyah University College of Science Physics Department Fourth Grade Nuclear Physics Dr. Ali A. Ridha Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter) Different types of radiation interact
Al-Mustansiriyah University College of Science Physics Department Fourth Grade Nuclear Physics Dr. Ali A. Ridha Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter) Different types of radiation interact
Energy Dependence of Neutron Flux
 Energy Dependence of Neutron Flux B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Contents We start the discussion of the energy
Energy Dependence of Neutron Flux B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Contents We start the discussion of the energy
Nuclear Theory - Course 127 NEUTRON BALANCE AND THE FOUR FACTOR FORMULA
 ' Nuclear Theory - Course 127 NEUTRON BALANCE AND THE FOUR FACTOR FORMULA When a reactor is operating at steady power, the chain reaction is just being maintained. One neutro~ only is available from each
' Nuclear Theory - Course 127 NEUTRON BALANCE AND THE FOUR FACTOR FORMULA When a reactor is operating at steady power, the chain reaction is just being maintained. One neutro~ only is available from each
Energy. on this world and elsewhere. Instructor: Gordon D. Cates Office: Physics 106a, Phone: (434)
 Energy on this world and elsewhere Instructor: Gordon D. Cates Office: Physics 106a, Phone: (434) 924-4792 email: cates@virginia.edu Course web site available at www.phys.virginia.edu, click on classes
Energy on this world and elsewhere Instructor: Gordon D. Cates Office: Physics 106a, Phone: (434) 924-4792 email: cates@virginia.edu Course web site available at www.phys.virginia.edu, click on classes
Write down the nuclear equation that represents the decay of neptunium 239 into plutonium 239.
 Q1.A rod made from uranium 238 ( U) is placed in the core of a nuclear reactor where it absorbs free neutrons. When a nucleus of uranium 238 absorbs a neutron it becomes unstable and decays to neptunium
Q1.A rod made from uranium 238 ( U) is placed in the core of a nuclear reactor where it absorbs free neutrons. When a nucleus of uranium 238 absorbs a neutron it becomes unstable and decays to neptunium
(b) The type of matter is irrelevant since the energy is directly proportional to mass only
 Exercise J.3.1. Answers 1. m = 800kg v = 70kmh -1 = 70 103 = 60 60 19.4ms-1 KK. EE = 1 2 mmvv2 = 800 19.42 2 = 150544JJ Using E= mc 2 and the kinetic energy of the car we obtain mm = EE cc 2 = 151235 (3
Exercise J.3.1. Answers 1. m = 800kg v = 70kmh -1 = 70 103 = 60 60 19.4ms-1 KK. EE = 1 2 mmvv2 = 800 19.42 2 = 150544JJ Using E= mc 2 and the kinetic energy of the car we obtain mm = EE cc 2 = 151235 (3
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Describe briefly one scattering experiment to investigate the size of the nucleus of the atom. Include a description of the properties of the incident radiation which makes
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Describe briefly one scattering experiment to investigate the size of the nucleus of the atom. Include a description of the properties of the incident radiation which makes
Nuclear Reactions. Fission Fusion
 Nuclear Reactions Fission Fusion Nuclear Reactions and the Transmutation of Elements A nuclear reaction takes place when a nucleus is struck by another nucleus or particle. Compare with chemical reactions!
Nuclear Reactions Fission Fusion Nuclear Reactions and the Transmutation of Elements A nuclear reaction takes place when a nucleus is struck by another nucleus or particle. Compare with chemical reactions!
Chemistry 132 NT. Nuclear Chemistry. Review. You can t escape death and taxes. But, at least, death doesn t get worse. Will Rogers
 Chemistry 3 NT You can t escape death and taxes. But, at least, death doesn t get worse. Will Rogers Chem 3 NT Nuclear Chemistry Module 3 Energy and Nuclear Reactions The core of a nuclear reactor used
Chemistry 3 NT You can t escape death and taxes. But, at least, death doesn t get worse. Will Rogers Chem 3 NT Nuclear Chemistry Module 3 Energy and Nuclear Reactions The core of a nuclear reactor used
MCRT L8: Neutron Transport
 MCRT L8: Neutron Transport Recap fission, absorption, scattering, cross sections Fission products and secondary neutrons Slow and fast neutrons Energy spectrum of fission neutrons Nuclear reactor safety
MCRT L8: Neutron Transport Recap fission, absorption, scattering, cross sections Fission products and secondary neutrons Slow and fast neutrons Energy spectrum of fission neutrons Nuclear reactor safety
The Attenuation of Neutrons in Barite Concrete
 Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 4 The Attenuation of Neutrons in Barite Concrete Wunna Ko Abstract The aim of this research is to study the neutron attenuation in barite concrete as a result
Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 4 The Attenuation of Neutrons in Barite Concrete Wunna Ko Abstract The aim of this research is to study the neutron attenuation in barite concrete as a result
[2] State in what form the energy is released in such a reaction.... [1]
![[2] State in what form the energy is released in such a reaction.... [1] [2] State in what form the energy is released in such a reaction.... [1]](/thumbs/87/96058923.jpg) (a) The following nuclear reaction occurs when a slow-moving neutron is absorbed by an isotope of uranium-35. 0n + 35 9 U 4 56 Ba + 9 36Kr + 3 0 n Explain how this reaction is able to produce energy....
(a) The following nuclear reaction occurs when a slow-moving neutron is absorbed by an isotope of uranium-35. 0n + 35 9 U 4 56 Ba + 9 36Kr + 3 0 n Explain how this reaction is able to produce energy....
Nuclear Theory - Course 227 THERMAL REACTORS (BASIC DESIGN)
 Nuclear Theory - Course 227 THERMAL REACTORS (BASC DESGN) When a U-235 nucleus fissions an average of 2.5 neutrons are released in addition to the energy. This suggests that these neutrons could be used
Nuclear Theory - Course 227 THERMAL REACTORS (BASC DESGN) When a U-235 nucleus fissions an average of 2.5 neutrons are released in addition to the energy. This suggests that these neutrons could be used
Introduction to Nuclear Physics Physics 124 Solution Set 6
 Introduction to Nuclear Physics Physics 124 Solution Set 6 J.T. Burke January 18, 2000 1 Problem 22 In order to thermalize a neutron it must undergo multiple elastic collisions. Upon each interaction it
Introduction to Nuclear Physics Physics 124 Solution Set 6 J.T. Burke January 18, 2000 1 Problem 22 In order to thermalize a neutron it must undergo multiple elastic collisions. Upon each interaction it
Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) The neutrons interact with other uranium (nuclei) / the neutrons cause further (fission) reactions
 Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) The neutrons interact with other uranium (nuclei) / the neutrons cause further (fission) reactions Not: neutrons interact with uranium atoms / molecules / particles
Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) The neutrons interact with other uranium (nuclei) / the neutrons cause further (fission) reactions Not: neutrons interact with uranium atoms / molecules / particles
Reactors and Fuels. Allen G. Croff Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ret.) NNSA/DOE Nevada Support Facility 232 Energy Way Las Vegas, NV
 Reactors and Fuels Allen G. Croff Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ret.) NNSA/DOE Nevada Support Facility 232 Energy Way Las Vegas, NV July 19-21, 2011 This course is partially based on work supported by
Reactors and Fuels Allen G. Croff Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ret.) NNSA/DOE Nevada Support Facility 232 Energy Way Las Vegas, NV July 19-21, 2011 This course is partially based on work supported by
Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface
 Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface 2005 2006 Time: 60 minutes Total Value: 33 Marks Formulae and Constants v = f λ E = hf h f = E k + W 0 E = m c 2 p = h λ 1 A= A T 0 2 t 1 2 E k = ½ mv 2
Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface 2005 2006 Time: 60 minutes Total Value: 33 Marks Formulae and Constants v = f λ E = hf h f = E k + W 0 E = m c 2 p = h λ 1 A= A T 0 2 t 1 2 E k = ½ mv 2
Lecture 14, 8/9/2017. Nuclear Reactions and the Transmutation of Elements Nuclear Fission; Nuclear Reactors Nuclear Fusion
 Lecture 14, 8/9/2017 Nuclear Reactions and the Transmutation of Elements Nuclear Fission; Nuclear Reactors Nuclear Fusion Nuclear Reactions and the Transmutation of Elements A nuclear reaction takes place
Lecture 14, 8/9/2017 Nuclear Reactions and the Transmutation of Elements Nuclear Fission; Nuclear Reactors Nuclear Fusion Nuclear Reactions and the Transmutation of Elements A nuclear reaction takes place
Simple Experimental Design for Calculation of Neutron Removal Cross Sections K. Groves 1 1) McMaster University, 1280 Main St. W, Hamilton, Canada.
 Simple Experimental Design for Calculation of Neutron Removal Cross Sections K. Groves 1 1) McMaster University, 1280 Main St. W, Hamilton, Canada. (Dated: 5 August 2017) This article proposes an experimental
Simple Experimental Design for Calculation of Neutron Removal Cross Sections K. Groves 1 1) McMaster University, 1280 Main St. W, Hamilton, Canada. (Dated: 5 August 2017) This article proposes an experimental
Efficient Energy Conversion of the 14MeV Neutrons in DT Inertial Confinement Fusion. By F. Winterberg University of Nevada, Reno
 Efficient Energy Conversion of the 14MeV Neutrons in DT Inertial Confinement Fusion By F. Winterberg University of Nevada, Reno Abstract In DT fusion 80% of the energy released goes into 14MeV neutrons,
Efficient Energy Conversion of the 14MeV Neutrons in DT Inertial Confinement Fusion By F. Winterberg University of Nevada, Reno Abstract In DT fusion 80% of the energy released goes into 14MeV neutrons,
Reactivity Balance & Reactor Control System
 Reactivity Balance & Reactor Control System K.S. Rajan Professor, School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 6 Table of Contents 1 MULTIPLICATION
Reactivity Balance & Reactor Control System K.S. Rajan Professor, School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 6 Table of Contents 1 MULTIPLICATION
Energy. on this world and elsewhere. Instructor: Gordon D. Cates Office: Physics 106a, Phone: (434)
 Energy on this world and elsewhere Instructor: Gordon D. Cates Office: Physics 106a, Phone: (434) 924-4792 email: cates@virginia.edu Course web site available at www.phys.virginia.edu, click on classes
Energy on this world and elsewhere Instructor: Gordon D. Cates Office: Physics 106a, Phone: (434) 924-4792 email: cates@virginia.edu Course web site available at www.phys.virginia.edu, click on classes
1 v. L18.pdf Spring 2010, P627, YK February 22, 2012
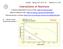 L18.pdf Spring 2010, P627, YK February 22, 2012 18 T2 Nuclear Information Service at LANL: http://t2.lanl.gov/data/ ENDF/B VI Neutron Data : http://t2.lanl.gov/cgi bin/nuclides/endind Thermal neutron x
L18.pdf Spring 2010, P627, YK February 22, 2012 18 T2 Nuclear Information Service at LANL: http://t2.lanl.gov/data/ ENDF/B VI Neutron Data : http://t2.lanl.gov/cgi bin/nuclides/endind Thermal neutron x
Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactions
 Slide 1 / 33 Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactions The Nucleus Slide 2 / 33 Proton: The charge on a proton is +1.6x10-19 C. The mass of a proton is 1.6726x10-27 kg. Neutron: The neutron is neutral. The
Slide 1 / 33 Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactions The Nucleus Slide 2 / 33 Proton: The charge on a proton is +1.6x10-19 C. The mass of a proton is 1.6726x10-27 kg. Neutron: The neutron is neutral. The
NUCLEAR ENERGY MATERIALS AND REACTORS Vol. I - Nuclear Interactions - R.A. Chaplin
 NUCLEAR INTERACTIONS R.A. Chaplin University of New Brunswick, Canada Keywords: Nuclear Interactions, Nuclear Cross Sections, Neutron Energies, Fission and Fusion Contents 1. Neutron Interactions 1.1.
NUCLEAR INTERACTIONS R.A. Chaplin University of New Brunswick, Canada Keywords: Nuclear Interactions, Nuclear Cross Sections, Neutron Energies, Fission and Fusion Contents 1. Neutron Interactions 1.1.
Interaction of Ionizing Radiation with Matter
 Type of radiation charged particles photonen neutronen Uncharged particles Charged particles electrons (β - ) He 2+ (α), H + (p) D + (d) Recoil nuclides Fission fragments Interaction of ionizing radiation
Type of radiation charged particles photonen neutronen Uncharged particles Charged particles electrons (β - ) He 2+ (α), H + (p) D + (d) Recoil nuclides Fission fragments Interaction of ionizing radiation
 http://imgs.xkcd.com/comics/cell_phones.png Announcements: Thursday: Group A to Hayes 105 for hands-on experience Group B comes here to work on worksheet Both groups: bring your calculator! Next Tuesday
http://imgs.xkcd.com/comics/cell_phones.png Announcements: Thursday: Group A to Hayes 105 for hands-on experience Group B comes here to work on worksheet Both groups: bring your calculator! Next Tuesday
Neutron reproduction. factor ε. k eff = Neutron Life Cycle. x η
 Neutron reproduction factor k eff = 1.000 What is: Migration length? Critical size? How does the geometry affect the reproduction factor? x 0.9 Thermal utilization factor f x 0.9 Resonance escape probability
Neutron reproduction factor k eff = 1.000 What is: Migration length? Critical size? How does the geometry affect the reproduction factor? x 0.9 Thermal utilization factor f x 0.9 Resonance escape probability
Term 3 Week 2 Nuclear Fusion & Nuclear Fission
 Term 3 Week 2 Nuclear Fusion & Nuclear Fission Tuesday, November 04, 2014 Nuclear Fusion To understand nuclear fusion & fission Nuclear Fusion Why do stars shine? Stars release energy as a result of fusing
Term 3 Week 2 Nuclear Fusion & Nuclear Fission Tuesday, November 04, 2014 Nuclear Fusion To understand nuclear fusion & fission Nuclear Fusion Why do stars shine? Stars release energy as a result of fusing
The moderator temperature coefficient MTC is defined as the change in reactivity per degree change in moderator temperature.
 Moderator Temperature Coefficient MTC 1 Moderator Temperature Coefficient The moderator temperature coefficient MTC is defined as the change in reactivity per degree change in moderator temperature. α
Moderator Temperature Coefficient MTC 1 Moderator Temperature Coefficient The moderator temperature coefficient MTC is defined as the change in reactivity per degree change in moderator temperature. α
Neutron Interactions with Matter
 Radioactivity - Radionuclides - Radiation 8 th Multi-Media Training Course with Nuclides.net (Institute Josžef Stefan, Ljubljana, 13th - 15th September 2006) Thursday, 14 th September 2006 Neutron Interactions
Radioactivity - Radionuclides - Radiation 8 th Multi-Media Training Course with Nuclides.net (Institute Josžef Stefan, Ljubljana, 13th - 15th September 2006) Thursday, 14 th September 2006 Neutron Interactions
Unit 2 Exam - Atomic Structure and Nuclear
 1. The atomic number of an atom is always equal to the total number of. neutrons in the nucleus. protons in the nucleus 5. The mass number of an atom is equal to the number of. neutrons, only. protons,
1. The atomic number of an atom is always equal to the total number of. neutrons in the nucleus. protons in the nucleus 5. The mass number of an atom is equal to the number of. neutrons, only. protons,
Nuclear Theory - Course 227
 Lesson 227.00-2 NEUTRON BALANCE Nuclear Theory - Course 227 DURNG STEADY REACTOR OPERATON We have seen, in the previous lesson, what type of neutrons are produced and how they are produced in a reactor.
Lesson 227.00-2 NEUTRON BALANCE Nuclear Theory - Course 227 DURNG STEADY REACTOR OPERATON We have seen, in the previous lesson, what type of neutrons are produced and how they are produced in a reactor.
Introduction to Radiological Sciences Neutron Detectors. Theory of operation. Types of detectors Source calibration Survey for Dose
 Introduction to Radiological Sciences Neutron Detectors Neutron counting Theory of operation Slow neutrons Fast neutrons Types of detectors Source calibration Survey for Dose 2 Neutrons, what are they?
Introduction to Radiological Sciences Neutron Detectors Neutron counting Theory of operation Slow neutrons Fast neutrons Types of detectors Source calibration Survey for Dose 2 Neutrons, what are they?
Energy Changes in Chemical and Nuclear Reactions
 Energy Changes in Chemical and Nuclear Reactions What happens when matter undergoes change? Clearly, new substances or states are produced, but energy changes also occur. If chemistry is the study of matter
Energy Changes in Chemical and Nuclear Reactions What happens when matter undergoes change? Clearly, new substances or states are produced, but energy changes also occur. If chemistry is the study of matter
Reactor Operation Without Feedback Effects
 22.05 Reactor Physics - Part Twenty-Six Reactor Operation Without Feedback Effects 1. Reference Material: See pp. 363-368 of the article, Light Water Reactor Control Systems, in Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical
22.05 Reactor Physics - Part Twenty-Six Reactor Operation Without Feedback Effects 1. Reference Material: See pp. 363-368 of the article, Light Water Reactor Control Systems, in Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical
M10/4/PHYSI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ Physics Standard level Paper 1. Monday 10 May 2010 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M1/4/PHYSI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ 221651 Physics Standard level Paper 1 Monday 1 May 21 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all
M1/4/PHYSI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ 221651 Physics Standard level Paper 1 Monday 1 May 21 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all
Chapter 12: Nuclear Reaction
 Chapter 12: Nuclear Reaction A nuclear reaction occurs when a nucleus is unstable or is being bombarded by a nuclear particle. The product of a nuclear reaction is a new nuclide with an emission of a nuclear
Chapter 12: Nuclear Reaction A nuclear reaction occurs when a nucleus is unstable or is being bombarded by a nuclear particle. The product of a nuclear reaction is a new nuclide with an emission of a nuclear
Step 2: Calculate the total amount of U-238 present at time=0. Step 4: Calculate the rate constant for the decay process.
 LP#9. A meteor contains 0.556 g of Pb-206 to every 1.00g U-238. Determine the age of the meteor. Step 1: Calculate the moles of each nuclide present. 0.566g Pb-206 x 1.00g U-238 x Step 2: Calculate the
LP#9. A meteor contains 0.556 g of Pb-206 to every 1.00g U-238. Determine the age of the meteor. Step 1: Calculate the moles of each nuclide present. 0.566g Pb-206 x 1.00g U-238 x Step 2: Calculate the
Nuclear Energy; Effects and Uses of Radiation
 Nuclear Energy; Effects and Uses of Radiation Nuclear Reactions and the Transmutation of Elements A nuclear reaction takes place when a nucleus is struck by another nucleus or particle. Compare with chemical
Nuclear Energy; Effects and Uses of Radiation Nuclear Reactions and the Transmutation of Elements A nuclear reaction takes place when a nucleus is struck by another nucleus or particle. Compare with chemical
Quiz, Physics & Chemistry
 Eight Sessions 1. Pressurized Water Reactor 2. Quiz, Thermodynamics & HTFF 3. Quiz, Physics & Chemistry 4. Exam #1, Electrical Concepts & Systems 5. Quiz, Materials Science 6. Quiz, Strength of Materials
Eight Sessions 1. Pressurized Water Reactor 2. Quiz, Thermodynamics & HTFF 3. Quiz, Physics & Chemistry 4. Exam #1, Electrical Concepts & Systems 5. Quiz, Materials Science 6. Quiz, Strength of Materials
UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN. EEE4101F / EEE4103F: Basic Nuclear Physics Problem Set 04. Due 12:00 (!) Wednesday 8 April 2015
 UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN EEE4101F / EEE4103F: Basic Nuclear Physics Problem Set 04 Due 12:00 (!) Wednesday 8 April 2015 1) Explain the concept of a cross-section, using language that a high-school teacher
UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN EEE4101F / EEE4103F: Basic Nuclear Physics Problem Set 04 Due 12:00 (!) Wednesday 8 April 2015 1) Explain the concept of a cross-section, using language that a high-school teacher
Interaction of Particles and Matter
 MORE CHAPTER 11, #7 Interaction of Particles and Matter In this More section we will discuss briefly the main interactions of charged particles, neutrons, and photons with matter. Understanding these interactions
MORE CHAPTER 11, #7 Interaction of Particles and Matter In this More section we will discuss briefly the main interactions of charged particles, neutrons, and photons with matter. Understanding these interactions
Reactivity Coefficients
 Reactivity Coefficients B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Reactivity Changes In studying kinetics, we have seen
Reactivity Coefficients B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Reactivity Changes In studying kinetics, we have seen
1897 J.J. Thompson discovers the electron
 CHAPTER 1 BASIC CONCEPTS OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS 1.1 Historical survey: The origin of nuclear physics and the progress after can be understand from the historical review as follow: 1895 The discovery of X-Ray
CHAPTER 1 BASIC CONCEPTS OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS 1.1 Historical survey: The origin of nuclear physics and the progress after can be understand from the historical review as follow: 1895 The discovery of X-Ray
Chapter 7.1. Q4 (a) In 1 s the energy is 500 MJ or (i) 5.0! 10 J, (ii) 5.0! 10 kw! hr " 140 kwh or (iii) MWh. (b) In one year the energy is
 Chapter 7.1 Q1 The thermal energy discarded must be returned to a reservoir that has a lower temperature from where the energy was extracted. In this case the temperatures are the same and so this will
Chapter 7.1 Q1 The thermal energy discarded must be returned to a reservoir that has a lower temperature from where the energy was extracted. In this case the temperatures are the same and so this will
Nuclear Reactions A Z. Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q > 0. Exothermic Endothermic
 Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
Lecture 5 Nuclear Reactions
 Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following We shall understand the concept of kinetic energy from the perspective of particle physics. We shall conclude that for all practical purposes, mass
Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following We shall understand the concept of kinetic energy from the perspective of particle physics. We shall conclude that for all practical purposes, mass
B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec.
 2: Fission and Other Neutron Reactions B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Contents Concepts: Fission and other
2: Fission and Other Neutron Reactions B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Contents Concepts: Fission and other
Control of the fission chain reaction
 Control of the fission chain reaction Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 April 8, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 30) April 8, 2011 1 / 29 Outline 1 Fission chain reaction
Control of the fission chain reaction Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 April 8, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 30) April 8, 2011 1 / 29 Outline 1 Fission chain reaction
Nuclear Chemistry. Chapter 24
 Nuclear Chemistry Chapter 24 Radioactivity Radioisotopes are isotopes that have an unstable nucleus. They emit radiation to attain more stable atomic configurations in a process called radioactive decay.
Nuclear Chemistry Chapter 24 Radioactivity Radioisotopes are isotopes that have an unstable nucleus. They emit radiation to attain more stable atomic configurations in a process called radioactive decay.
Episode 528: Controlling fission
 Episode 528: Controlling fission In this episode, you can look at the different features of the core of a nuclear reactor, and explain its operation using your students knowledge of nuclear physics. Summary
Episode 528: Controlling fission In this episode, you can look at the different features of the core of a nuclear reactor, and explain its operation using your students knowledge of nuclear physics. Summary
Delayed neutrons in nuclear fission chain reaction
 Delayed neutrons in nuclear fission chain reaction 1 Critical state Temporal flow Loss by leakage Loss by Absorption If the number of neutrons (the number of fission reactions) is practically constant
Delayed neutrons in nuclear fission chain reaction 1 Critical state Temporal flow Loss by leakage Loss by Absorption If the number of neutrons (the number of fission reactions) is practically constant
The number of protons in the nucleus is known as the atomic number Z, and determines the chemical properties of the element.
 I. NUCLEAR PHYSICS I.1 Atomic Nucleus Very briefly, an atom is formed by a nucleus made up of nucleons (neutrons and protons) and electrons in external orbits. The number of electrons and protons is equal
I. NUCLEAR PHYSICS I.1 Atomic Nucleus Very briefly, an atom is formed by a nucleus made up of nucleons (neutrons and protons) and electrons in external orbits. The number of electrons and protons is equal
1. Explain the significance of negative energy of electron in an orbit. askiitians
 Class: 12 Subject: Physics Topic: Atoms and Nuclei No. of Questions: 30 1. Explain the significance of negative energy of electron in an orbit. The energy of an electron in the orbits of an atom is negative.
Class: 12 Subject: Physics Topic: Atoms and Nuclei No. of Questions: 30 1. Explain the significance of negative energy of electron in an orbit. The energy of an electron in the orbits of an atom is negative.
9 Nuclear decay Answers to exam practice questions
 Pages 173 178 Exam practice questions 1 X-rays are quanta of energy emitted when electrons fall to a lower energy level, and so do not emanate from the nucleus Answer D. 2 Alpha particles, being the most
Pages 173 178 Exam practice questions 1 X-rays are quanta of energy emitted when electrons fall to a lower energy level, and so do not emanate from the nucleus Answer D. 2 Alpha particles, being the most
GCSE 247/02 SCIENCE PHYSICS HIGHER TIER PHYSICS 3. A.M. FRIDAY, 27 May minutes. Candidate Name. Candidate Number.
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number GCSE 247/2 SCIENCE PHYSICS HIGHER TIER PHYSICS 3 A.M. FRIDAY, 27 May 211 45 minutes Question 1. For s use Maximum Mark 6 Mark awarded 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 4 9
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number GCSE 247/2 SCIENCE PHYSICS HIGHER TIER PHYSICS 3 A.M. FRIDAY, 27 May 211 45 minutes Question 1. For s use Maximum Mark 6 Mark awarded 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 4 9
Neutron interactions and dosimetry. Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland
 Neutron interactions and dosimetry Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland Topics 1. Neutron interactions 1. Scattering 2. Absorption 2. Neutron dosimetry 3. Applications The neutron Uncharged particle, mass close
Neutron interactions and dosimetry Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland Topics 1. Neutron interactions 1. Scattering 2. Absorption 2. Neutron dosimetry 3. Applications The neutron Uncharged particle, mass close
SHAWNEE ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES, INC Identify the definitions of the following terms: a. Nucleon b. Nuclide c. Isotope
 Course Title: Radiological Control Technician Module Title: uclear Physics Module umber: 1.04 Objectives: 1.04.01 Identify the definitions of the following terms: a. ucleon b. uclide c. Isotope 1.04.02
Course Title: Radiological Control Technician Module Title: uclear Physics Module umber: 1.04 Objectives: 1.04.01 Identify the definitions of the following terms: a. ucleon b. uclide c. Isotope 1.04.02
EEE4101F / EEE4103F Radiation Interactions & Detection
 EEE4101F / EEE4103F Radiation Interactions & Detection 1. Interaction of Radiation with Matter Dr. Steve Peterson 5.14 RW James Department of Physics University of Cape Town steve.peterson@uct.ac.za March
EEE4101F / EEE4103F Radiation Interactions & Detection 1. Interaction of Radiation with Matter Dr. Steve Peterson 5.14 RW James Department of Physics University of Cape Town steve.peterson@uct.ac.za March
Lecture 27 Reactor Kinetics-III
 Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following In this lecture we will understand some general concepts on control. We will learn about reactivity coefficients and their general nature. Finally,
Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following In this lecture we will understand some general concepts on control. We will learn about reactivity coefficients and their general nature. Finally,
At the conclusion of this lesson the trainee will be able to: a) Write a typical equation for the production of each type of radiation.
 RADIOACTIVITY - SPONTANEOUS NUCLEAR PROCESSES OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this lesson the trainee will be able to: 1. For~, p and 7 decays a) Write a typical equation for the production of each type
RADIOACTIVITY - SPONTANEOUS NUCLEAR PROCESSES OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this lesson the trainee will be able to: 1. For~, p and 7 decays a) Write a typical equation for the production of each type
Chapter NP-4. Nuclear Physics. Particle Behavior/ Gamma Interactions TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 IONIZATION
 Chapter NP-4 Nuclear Physics Particle Behavior/ Gamma Interactions TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 IONIZATION 2.0 ALPHA PARTICLE INTERACTIONS 3.0 BETA INTERACTIONS 4.0 GAMMA INTERACTIONS
Chapter NP-4 Nuclear Physics Particle Behavior/ Gamma Interactions TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 IONIZATION 2.0 ALPHA PARTICLE INTERACTIONS 3.0 BETA INTERACTIONS 4.0 GAMMA INTERACTIONS
3. State each of the four types of inelastic collisions, giving an example of each (zaa type example is acceptable)
 Nuclear Theory - Course 227 OBJECTIVES to: At the conclusion of this course the trainee will be able 227.00-1 Nuclear Structure 1. Explain and use the ZXA notation. 2. Explain the concept of binding energy.
Nuclear Theory - Course 227 OBJECTIVES to: At the conclusion of this course the trainee will be able 227.00-1 Nuclear Structure 1. Explain and use the ZXA notation. 2. Explain the concept of binding energy.
NUCLEAR ENGINEERING. 6. Amongst the following, the fissionable materials are (a) U233andPu239 (b) U23iandPu233 (c) U235andPu235 (d) U238andPu239
 NUCLEAR ENGINEERING 1. The efficiency of a nuclear power plant in comparsion to a conventional thermal power plant is (a) same (b) more (c) less (d) may be less or mote depending on size (e) unpredictable.
NUCLEAR ENGINEERING 1. The efficiency of a nuclear power plant in comparsion to a conventional thermal power plant is (a) same (b) more (c) less (d) may be less or mote depending on size (e) unpredictable.
Nuclear Fission. 1/v Fast neutrons. U thermal cross sections σ fission 584 b. σ scattering 9 b. σ radiative capture 97 b.
 Nuclear Fission 1/v Fast neutrons should be moderated. 235 U thermal cross sections σ fission 584 b. σ scattering 9 b. σ radiative capture 97 b. Fission Barriers 1 Nuclear Fission Q for 235 U + n 236 U
Nuclear Fission 1/v Fast neutrons should be moderated. 235 U thermal cross sections σ fission 584 b. σ scattering 9 b. σ radiative capture 97 b. Fission Barriers 1 Nuclear Fission Q for 235 U + n 236 U
u d Fig. 6.1 (i) Identify the anti-proton from the table of particles shown in Fig [1]
![u d Fig. 6.1 (i) Identify the anti-proton from the table of particles shown in Fig [1] u d Fig. 6.1 (i) Identify the anti-proton from the table of particles shown in Fig [1]](/thumbs/79/80122691.jpg) 1 (a) Fig. 6.1 shows the quark composition of some particles. proton neutron A B u u d u d d u d u u u u d Fig. 6.1 (i) Identify the anti-proton from the table of particles shown in Fig. 6.1. (ii) State
1 (a) Fig. 6.1 shows the quark composition of some particles. proton neutron A B u u d u d d u d u u u u d Fig. 6.1 (i) Identify the anti-proton from the table of particles shown in Fig. 6.1. (ii) State
i. Explain how heat is produced by nuclear flssion Describe what is meant by sub-critical, critical, and supercritical
 Introduction to CANDU Processes Module 2 - The Reactor Side of the Station ENABLING OBJECTIVES: 2.i 2.2 2.3 2.4 Explain how heat is produced by nuclear flssion. Describe what is meant by sub-critical,
Introduction to CANDU Processes Module 2 - The Reactor Side of the Station ENABLING OBJECTIVES: 2.i 2.2 2.3 2.4 Explain how heat is produced by nuclear flssion. Describe what is meant by sub-critical,
NJCTL.org 2015 AP Physics 2 Nuclear Physics
 AP Physics 2 Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
AP Physics 2 Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
E LEWIS Fundamentals of Nuclear Reactor Physics (Academic Press, 2008) Chapter 2 - Neutron Interactions
 E LEWIS Fundamentals of Nuclear Reactor Physics (Academic Press, 2008) Chapter 2 - Neutron Interactions . CHAPTER 2 Neutron Interactions 2.1 Introduction The behavior of the neutrons emitted from fission
E LEWIS Fundamentals of Nuclear Reactor Physics (Academic Press, 2008) Chapter 2 - Neutron Interactions . CHAPTER 2 Neutron Interactions 2.1 Introduction The behavior of the neutrons emitted from fission
Subcritical Multiplication and Reactor Startup
 22.05 Reactor Physics - Part Twenty-Five Subcritical Multiplication and Reactor Startup 1. Reference Material See pp. 357-363 of the article, Light Water Reactor Control Systems, in Wiley Encyclopedia
22.05 Reactor Physics - Part Twenty-Five Subcritical Multiplication and Reactor Startup 1. Reference Material See pp. 357-363 of the article, Light Water Reactor Control Systems, in Wiley Encyclopedia
Nuclear Chemistry. Decay Reactions The most common form of nuclear decay reactions are the following:
 Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear reactions are transmutation of the one element into another. We can describe nuclear reactions in a similar manner as regular chemical reactions using ideas of stoichiometry,
Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear reactions are transmutation of the one element into another. We can describe nuclear reactions in a similar manner as regular chemical reactions using ideas of stoichiometry,
Lectures on Applied Reactor Technology and Nuclear Power Safety. Lecture No 5. Title: Reactor Kinetics and Reactor Operation
 Lectures on Nuclear Power Safety Lecture No 5 Title: Reactor Kinetics and Reactor Operation Department of Energy Technology KTH Spring 2005 Slide No 1 Outline of the Lecture (1) Reactor Kinetics Reactor
Lectures on Nuclear Power Safety Lecture No 5 Title: Reactor Kinetics and Reactor Operation Department of Energy Technology KTH Spring 2005 Slide No 1 Outline of the Lecture (1) Reactor Kinetics Reactor
Theoretical Task 3 (T-3) : Solutions 1 of 9
 Theoretical Task 3 (T-3) : Solutions of 9 The Design of a Nuclear Reactor Uranium occurs in nature as UO with only 0.70% of the uranium atoms being 35 U. Neutron induced fission occurs readily in 35 U
Theoretical Task 3 (T-3) : Solutions of 9 The Design of a Nuclear Reactor Uranium occurs in nature as UO with only 0.70% of the uranium atoms being 35 U. Neutron induced fission occurs readily in 35 U
Chapter 3C. 3-4C. Ionization
 Chapter 3C The excitation ratio N B /N A increases as the excitation potential get smaller. Also, as T increases, the higher energy levels become more populated. One should see that as T goes to infinity,
Chapter 3C The excitation ratio N B /N A increases as the excitation potential get smaller. Also, as T increases, the higher energy levels become more populated. One should see that as T goes to infinity,
Fission and Fusion Book pg cgrahamphysics.com 2016
 Fission and Fusion Book pg 286-287 cgrahamphysics.com 2016 Review BE is the energy that holds a nucleus together. This is equal to the mass defect of the nucleus. Also called separation energy. The energy
Fission and Fusion Book pg 286-287 cgrahamphysics.com 2016 Review BE is the energy that holds a nucleus together. This is equal to the mass defect of the nucleus. Also called separation energy. The energy
= : K A
 Atoms and Nuclei. State two limitations of JJ Thomson s model of atom. 2. Write the SI unit for activity of a radioactive substance. 3. What observations led JJ Thomson to conclusion that all atoms have
Atoms and Nuclei. State two limitations of JJ Thomson s model of atom. 2. Write the SI unit for activity of a radioactive substance. 3. What observations led JJ Thomson to conclusion that all atoms have
Emphasis on what happens to emitted particle (if no nuclear reaction and MEDIUM (i.e., atomic effects)
 LECTURE 5: INTERACTION OF RADIATION WITH MATTER All radiation is detected through its interaction with matter! INTRODUCTION: What happens when radiation passes through matter? Emphasis on what happens
LECTURE 5: INTERACTION OF RADIATION WITH MATTER All radiation is detected through its interaction with matter! INTRODUCTION: What happens when radiation passes through matter? Emphasis on what happens
Operational Reactor Safety
 Operational Reactor Safety 22.091/22.903 Professor Andrew C. Kadak Professor of the Practice Lecture 3 Reactor Kinetics and Control Page 1 Topics to Be Covered Time Dependent Diffusion Equation Prompt
Operational Reactor Safety 22.091/22.903 Professor Andrew C. Kadak Professor of the Practice Lecture 3 Reactor Kinetics and Control Page 1 Topics to Be Covered Time Dependent Diffusion Equation Prompt
Fundamentals of Nuclear Reactor Physics
 Fundamentals of Nuclear Reactor Physics E. E. Lewis Professor of Mechanical Engineering McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science Northwestern University AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW
Fundamentals of Nuclear Reactor Physics E. E. Lewis Professor of Mechanical Engineering McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science Northwestern University AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW
The Physics of Nuclear Reactors. Heather King Physics 420
 The Physics of Nuclear Reactors Heather King Physics 420 Nuclear Reactions A nuclear reaction is a reaction that involves atomic nuclei, or nuclear particles (protons, neutrons), producing products different
The Physics of Nuclear Reactors Heather King Physics 420 Nuclear Reactions A nuclear reaction is a reaction that involves atomic nuclei, or nuclear particles (protons, neutrons), producing products different
