KEY. Math 334 Midterm III Fall 2008 sections 001 and 003 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
|
|
|
- Milton Jacobs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Fall 28 secions and 3 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering paper. Wrie your name, course, and secion number on he blue book, or on your own pile of papers. Again, do no wrie his or any oher ype of informaion on his exam. Good Pracice: A differenial equaion has he propery ha one can check wheher a given funcion saisfies i. So check your soluions! If one doesn work, ry again, or a leas noe ha your proposed soluion doesn work. You will ge much more parial credi if you know wheher or no you answer is correc.
2 a. Compue he Laplace ransform L f ( s) of f ( ) e cosdirecly from he definiion. For which values of s does your formula hold? Assume here ha a is a real number. 2 poins By definiion of he Laplace ransform, and by using inegraion by pars, and provided s a, we ge L s a cos sa sa e e d cos s a sa sa e sin d sin de sa sa sa sa sa sine e sa sa dsin sa cose d f ( s). sa sa L sa sa s a s s a f () s e f () d e e cosd e cosd cosde Noe ha s ais also necessary for he inegral o converge. Solving he las equaion algebraically for L f ( s) we ge () s a s a s a L f s. (.2) 2 s a 2 sasa s a s a (.)
3 2 2. Solve he following IVP. Using he Laplace ransform and knowing how o deal wih piecewise defined funcions in his ransform should make hings easier. Wha is he value of y ()? Do no express his value in erms of an absrac formula, bu raher as a concree number. To compue his value concreely, you will need o know ha he funcion sin( ) is 2 periodic.,, y 4 y f( ), y() y(). 2, 2, 2 (.3) 25 poins Taking he Laplace ransform of (.3) we ge 2 2 L L L s 2 y ( s) y 4 y ( s) f ( s) L, (.4) y () s f (). s 2 2 s 2 L To compue L f ( s) we rewrie f in (.3) as: 2 u() 2 2 u2() 2 u2() f() u () u () 2 u () u () u () 2 u () 2 u (). 2 4 (.5) So, according o he relevan heorem, and given 2 per he able provided you), hen L g () s when g () u() (as s s 2s L f () s L g () s 2 e L g () s e L g () s s 2s s 2s Lg( s) 2e e 2 2 e e. s (.6) Thus, explicily, (.4) is L s 2s y() s 2 2 f () s e e. s 2 L s 2 s (.7)
4 3 and we already know hen ha he soluion is of he form y() h() u () 2 h( ) u () h( 2 ) u (), (.8) 2 where hen we need only find h ( ), whose Laplace ransform is L s 2 s s s s 2 s 2 h() s (.9) Thus, according o he able, or memorized formulae, we have ha he soluion is given by (.8) and by h () sin(2). 4 2 (.) Noe ha for any 2, including, we have y () hu () () 2 h ( ) u () h ( 2 ) u (), 2 h () 2 h ( ) h ( 2 ) sin(2 ) 2 sin 2 2 sin sin(2 ) 2 sin 2 2 sin (.) 3. Solve he following iniial value problem in erms of he convoluion inegral: D D y g( ), y() y(). (.2) Here I expec you o wrie he soluion y y ( ) of (.2) as y() y g () y( ) g( ) d, (.3) so ha he problem is effecively only o deermine he funcion y ( ) in (.3). 2 2 Recall DDy D y y y, bu realize he represenaion in (.2) may be a leas as useful as wriing y y on he lef-hand side. (Hin: Use
5 4 9 poins he Laplace ransform and he convoluion heorem. Noe he poin value his is sraighforward if you recall he relevan heory.) By he Laplace Transform we have from (.2) ha L L L s s y () s D D y() s g () s Ly() s Lg() s Lg() s (.4) ss s s L e e () s g() s sinh() s g() s 2 L L L L sinhg so ha evidenly in (.3) we have y () sinh(). (.5) 4. Suppose ha boh x sin ( ) and 2( ) sin x (.6) solve he sysem and ha solves he sysem an sec x sec an x (.7) cos x p () cos (.8) x an sec sec an x. (.9) Then wha is he soluion of he IVP
6 5 x an sec, ()? sec an x x (.2) This problem ess your general undersanding of he srucure of soluions of linear sysems wihou requiring you o regurgiae a heorem (wih all of he inricacies of is ariculaion). Noe he poin value his problem is sraighforward if you recall he heory. 2 poins According o he informaion given, he general soluion of (.2) can be expressed as x sin cos x () sin c cos, (.2) Choosing and using he iniial daa in(.2), (.2) becomes () x c c c. (.22) So (.2) becomes x sin cos sin cos sin cos x (). sin cos cos cos (.23) 5. Find he fundamenal marix of soluions ( ) o he sysem he one ha has he propery ha() I. 2 poins x 2 x, (.24)
7 6 Firs we find a represenaion of he general soluion of he sysem(.24). This can be expressed as xx() cξ e c ξ e, (.25) 2 provided he ξ s are independen eigenvecors associaed wih he eigenvalues and of he marix in (.24). To deermine his we noe 2 ξ ξ unless de 2 2 i i, i :, (.26) So i i. 2 i 2 i i ξ ξ ξ (.27) Thus, explicily, (.25) is x i i x () c e c2 e. i i (.28) As per he usual heory, we can find a real-valued represenaion by finding he real and imaginary pars of eiher of he above complex-valued soluions: x i cos sin (): e cosisin i, i i cossin cossin (.29) whence a real-valued represenaion of he general soluion is x cos sin () c c 2. cossin cossin (.3)
8 7 A fundamenal marix of soluions ( ), one no necessarily having he desired propery, can be found from he above general soluion (.3) as in cos sin () cossin cossin. (.3) The desired fundamenal marix ( ) can be obained from ( ) via cos sin () () () cos sin cos sin cos sin cos sin cos sin cos sin sin. 2sin cossin (.32) 6. Solve he iniial value problem given by he sysem of problem 5 and he iniial daa 6 poins Using he fundamenal marix of problem 5 we have x (). (.33) cossin sin cos sin sin x() () x() 2sin cos sin 2sin cos sin (.34) cos. cos sin 7. Calculae 6 poins 2 e. (.35)
9 8 We have, from problem 5 and he general heory, 2 cos sin sin e ( ). 2sin cos sin (.36) 8. Find a represenaion of he general soluion of he sysem 2 poins x x. (.37) The marix in (.37) has a repeaed eigenvalue wih only one eigenvecor. Hence he general soluion is of he form 2 x x() cξe c ξη e (.38) where is he sole eigenvalue,ξ is one of is eigenvecors, and ηis an associaed pseudo eigenvecor: Firs ξ ξ unless 2 2 de,. (.39) So, ξξ and. ηξ η η (.4) Thus, explicily, (.38) is
10 9 xx() c e c e 2 c c 2. (.4) 9. Find he fundamenal marix of soluions () for he sysem of problem 8 ha saisfies () I. 5 poins From (.4) we have a fundamenal marix of soluions whence he one desired is (), (.42) () () () (). (.43). Solve he iniial value problem obained from combining he differenial equaion of problem 8 wih he iniial daa 2 x (). (.44) 2
11 6 poins From problem 9 we have 2 x() () x() (). x 2 (.45)
KEY. Math 334 Midterm III Winter 2008 section 002 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Winer 008 secion 00 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Winer 008 secion 00 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
KEY. Math 334 Midterm I Fall 2008 sections 001 and 003 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
Math Final Exam Solutions
 Mah 246 - Final Exam Soluions Friday, July h, 204 () Find explici soluions and give he inerval of definiion o he following iniial value problems (a) ( + 2 )y + 2y = e, y(0) = 0 Soluion: In normal form,
Mah 246 - Final Exam Soluions Friday, July h, 204 () Find explici soluions and give he inerval of definiion o he following iniial value problems (a) ( + 2 )y + 2y = e, y(0) = 0 Soluion: In normal form,
t is a basis for the solution space to this system, then the matrix having these solutions as columns, t x 1 t, x 2 t,... x n t x 2 t...
 Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
Section 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equations; Method of Undetermined Coefficients
 Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
23.2. Representing Periodic Functions by Fourier Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Concourse Math Spring 2012 Worked Examples: Matrix Methods for Solving Systems of 1st Order Linear Differential Equations
 Concourse Mah 80 Spring 0 Worked Examples: Marix Mehods for Solving Sysems of s Order Linear Differenial Equaions The Main Idea: Given a sysem of s order linear differenial equaions d x d Ax wih iniial
Concourse Mah 80 Spring 0 Worked Examples: Marix Mehods for Solving Sysems of s Order Linear Differenial Equaions The Main Idea: Given a sysem of s order linear differenial equaions d x d Ax wih iniial
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Solutions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Math 246, Spring 2011, Professor David Levermore
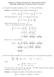 Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Math 334 Fall 2011 Homework 11 Solutions
 Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
dt = C exp (3 ln t 4 ). t 4 W = C exp ( ln(4 t) 3) = C(4 t) 3.
 Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
ODEs II, Lecture 1: Homogeneous Linear Systems - I. Mike Raugh 1. March 8, 2004
 ODEs II, Lecure : Homogeneous Linear Sysems - I Mike Raugh March 8, 4 Inroducion. In he firs lecure we discussed a sysem of linear ODEs for modeling he excreion of lead from he human body, saw how o ransform
ODEs II, Lecure : Homogeneous Linear Sysems - I Mike Raugh March 8, 4 Inroducion. In he firs lecure we discussed a sysem of linear ODEs for modeling he excreion of lead from he human body, saw how o ransform
Hamilton- J acobi Equation: Weak S olution We continue the study of the Hamilton-Jacobi equation:
 M ah 5 7 Fall 9 L ecure O c. 4, 9 ) Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Weak S oluion We coninue he sudy of he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: We have shown ha u + H D u) = R n, ) ; u = g R n { = }. ). In general we canno
M ah 5 7 Fall 9 L ecure O c. 4, 9 ) Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Weak S oluion We coninue he sudy of he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: We have shown ha u + H D u) = R n, ) ; u = g R n { = }. ). In general we canno
Math 334 Test 1 KEY Spring 2010 Section: 001. Instructor: Scott Glasgow Dates: May 10 and 11.
 1 Mah 334 Tes 1 KEY Spring 21 Secion: 1 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Daes: Ma 1 and 11. Do NOT wrie on his problem saemen bookle, excep for our indicaion of following he honor code jus below. No credi will be
1 Mah 334 Tes 1 KEY Spring 21 Secion: 1 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Daes: Ma 1 and 11. Do NOT wrie on his problem saemen bookle, excep for our indicaion of following he honor code jus below. No credi will be
Mon Apr 9 EP 7.6 Convolutions and Laplace transforms. Announcements: Warm-up Exercise:
 Mah 225-4 Week 3 April 9-3 EP 7.6 - convoluions; 6.-6.2 - eigenvalues, eigenvecors and diagonalizabiliy; 7. - sysems of differenial equaions. Mon Apr 9 EP 7.6 Convoluions and Laplace ransforms. Announcemens:
Mah 225-4 Week 3 April 9-3 EP 7.6 - convoluions; 6.-6.2 - eigenvalues, eigenvecors and diagonalizabiliy; 7. - sysems of differenial equaions. Mon Apr 9 EP 7.6 Convoluions and Laplace ransforms. Announcemens:
Two Coupled Oscillators / Normal Modes
 Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Differential Equations
 Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Math 2142 Exam 1 Review Problems. x 2 + f (0) 3! for the 3rd Taylor polynomial at x = 0. To calculate the various quantities:
 Mah 4 Eam Review Problems Problem. Calculae he 3rd Taylor polynomial for arcsin a =. Soluion. Le f() = arcsin. For his problem, we use he formula f() + f () + f ()! + f () 3! for he 3rd Taylor polynomial
Mah 4 Eam Review Problems Problem. Calculae he 3rd Taylor polynomial for arcsin a =. Soluion. Le f() = arcsin. For his problem, we use he formula f() + f () + f ()! + f () 3! for he 3rd Taylor polynomial
ENGI 9420 Engineering Analysis Assignment 2 Solutions
 ENGI 940 Engineering Analysis Assignmen Soluions 0 Fall [Second order ODEs, Laplace ransforms; Secions.0-.09]. Use Laplace ransforms o solve he iniial value problem [0] dy y, y( 0) 4 d + [This was Quesion
ENGI 940 Engineering Analysis Assignmen Soluions 0 Fall [Second order ODEs, Laplace ransforms; Secions.0-.09]. Use Laplace ransforms o solve he iniial value problem [0] dy y, y( 0) 4 d + [This was Quesion
MATH 128A, SUMMER 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION
 MATH 28A, SUMME 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION BENJAMIN JOHNSON () (8 poins) [Lagrange Inerpolaion] (a) (4 poins) Le f be a funcion defined a some real numbers x 0,..., x n. Give a defining equaion for he Lagrange
MATH 28A, SUMME 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION BENJAMIN JOHNSON () (8 poins) [Lagrange Inerpolaion] (a) (4 poins) Le f be a funcion defined a some real numbers x 0,..., x n. Give a defining equaion for he Lagrange
dy dx = xey (a) y(0) = 2 (b) y(1) = 2.5 SOLUTION: See next page
 Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
t + t sin t t cos t sin t. t cos t sin t dt t 2 = exp 2 log t log(t cos t sin t) = Multiplying by this factor and then integrating, we conclude that
 ODEs, Homework #4 Soluions. Check ha y ( = is a soluion of he second-order ODE ( cos sin y + y sin y sin = 0 and hen use his fac o find all soluions of he ODE. When y =, we have y = and also y = 0, so
ODEs, Homework #4 Soluions. Check ha y ( = is a soluion of he second-order ODE ( cos sin y + y sin y sin = 0 and hen use his fac o find all soluions of he ODE. When y =, we have y = and also y = 0, so
System of Linear Differential Equations
 Sysem of Linear Differenial Equaions In "Ordinary Differenial Equaions" we've learned how o solve a differenial equaion for a variable, such as: y'k5$e K2$x =0 solve DE yx = K 5 2 ek2 x C_C1 2$y''C7$y
Sysem of Linear Differenial Equaions In "Ordinary Differenial Equaions" we've learned how o solve a differenial equaion for a variable, such as: y'k5$e K2$x =0 solve DE yx = K 5 2 ek2 x C_C1 2$y''C7$y
f t te e = possesses a Laplace transform. Exercises for Module-III (Transform Calculus)
 Exercises for Module-III (Transform Calculus) ) Discuss he piecewise coninuiy of he following funcions: =,, +, > c) e,, = d) sin,, = ) Show ha he funcion ( ) sin ( ) f e e = possesses a Laplace ransform.
Exercises for Module-III (Transform Calculus) ) Discuss he piecewise coninuiy of he following funcions: =,, +, > c) e,, = d) sin,, = ) Show ha he funcion ( ) sin ( ) f e e = possesses a Laplace ransform.
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 31 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #1 C-T Sysems: Convoluion Represenaion Reading Assignmen: Secion 2.6 of Kamen and Heck 1/11 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual flow beween
EECE 31 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #1 C-T Sysems: Convoluion Represenaion Reading Assignmen: Secion 2.6 of Kamen and Heck 1/11 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual flow beween
Chapter 6. Systems of First Order Linear Differential Equations
 Chaper 6 Sysems of Firs Order Linear Differenial Equaions We will only discuss firs order sysems However higher order sysems may be made ino firs order sysems by a rick shown below We will have a sligh
Chaper 6 Sysems of Firs Order Linear Differenial Equaions We will only discuss firs order sysems However higher order sysems may be made ino firs order sysems by a rick shown below We will have a sligh
Solutions to Assignment 1
 MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
Math 23 Spring Differential Equations. Final Exam Due Date: Tuesday, June 6, 5pm
 Mah Spring 6 Differenial Equaions Final Exam Due Dae: Tuesday, June 6, 5pm Your name (please prin): Insrucions: This is an open book, open noes exam. You are free o use a calculaor or compuer o check your
Mah Spring 6 Differenial Equaions Final Exam Due Dae: Tuesday, June 6, 5pm Your name (please prin): Insrucions: This is an open book, open noes exam. You are free o use a calculaor or compuer o check your
23.5. Half-Range Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
Predator - Prey Model Trajectories and the nonlinear conservation law
 Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Echocardiography Project and Finite Fourier Series
 Echocardiography Projec and Finie Fourier Series 1 U M An echocardiagram is a plo of how a porion of he hear moves as he funcion of ime over he one or more hearbea cycles If he hearbea repeas iself every
Echocardiography Projec and Finie Fourier Series 1 U M An echocardiagram is a plo of how a porion of he hear moves as he funcion of ime over he one or more hearbea cycles If he hearbea repeas iself every
LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION
 CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
6.2 Transforms of Derivatives and Integrals.
 SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
Q1) [20 points] answer for the following questions (ON THIS SHEET):
![Q1) [20 points] answer for the following questions (ON THIS SHEET): Q1) [20 points] answer for the following questions (ON THIS SHEET):](/thumbs/87/96063197.jpg) Dr. Anas Al Tarabsheh The Hashemie Universiy Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Deparmen (Makeup Exam) Signals and Sysems Firs Semeser 011/01 Final Exam Dae: 1/06/01 Exam Duraion: hours Noe: means convoluion
Dr. Anas Al Tarabsheh The Hashemie Universiy Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Deparmen (Makeup Exam) Signals and Sysems Firs Semeser 011/01 Final Exam Dae: 1/06/01 Exam Duraion: hours Noe: means convoluion
Laplace Transforms. Examples. Is this equation differential? y 2 2y + 1 = 0, y 2 2y + 1 = 0, (y ) 2 2y + 1 = cos x,
 Laplace Transforms Definiion. An ordinary differenial equaion is an equaion ha conains one or several derivaives of an unknown funcion which we call y and which we wan o deermine from he equaion. The equaion
Laplace Transforms Definiion. An ordinary differenial equaion is an equaion ha conains one or several derivaives of an unknown funcion which we call y and which we wan o deermine from he equaion. The equaion
Math 334 Midterm III KEY Fall 2006 sections 001 and 004 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 Math 334 Midterm III KEY Fall 6 sections 1 and 4 Instructor: Scott Glasgow Please do NO write on this exam No credit will be given for such work Rather write in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably
Math 334 Midterm III KEY Fall 6 sections 1 and 4 Instructor: Scott Glasgow Please do NO write on this exam No credit will be given for such work Rather write in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
Announcements: Warm-up Exercise:
 Fri Apr 13 7.1 Sysems of differenial equaions - o model muli-componen sysems via comparmenal analysis hp//en.wikipedia.org/wiki/muli-comparmen_model Announcemens Warm-up Exercise Here's a relaively simple
Fri Apr 13 7.1 Sysems of differenial equaions - o model muli-componen sysems via comparmenal analysis hp//en.wikipedia.org/wiki/muli-comparmen_model Announcemens Warm-up Exercise Here's a relaively simple
MATH 4330/5330, Fourier Analysis Section 6, Proof of Fourier s Theorem for Pointwise Convergence
 MATH 433/533, Fourier Analysis Secion 6, Proof of Fourier s Theorem for Poinwise Convergence Firs, some commens abou inegraing periodic funcions. If g is a periodic funcion, g(x + ) g(x) for all real x,
MATH 433/533, Fourier Analysis Secion 6, Proof of Fourier s Theorem for Poinwise Convergence Firs, some commens abou inegraing periodic funcions. If g is a periodic funcion, g(x + ) g(x) for all real x,
6.003 Homework #9 Solutions
 6.00 Homework #9 Soluions Problems. Fourier varieies a. Deermine he Fourier series coefficiens of he following signal, which is periodic in 0. x () 0 0 a 0 5 a k sin πk 5 sin πk 5 πk for k 0 a k 0 πk j
6.00 Homework #9 Soluions Problems. Fourier varieies a. Deermine he Fourier series coefficiens of he following signal, which is periodic in 0. x () 0 0 a 0 5 a k sin πk 5 sin πk 5 πk for k 0 a k 0 πk j
Math Week 14 April 16-20: sections first order systems of linear differential equations; 7.4 mass-spring systems.
 Mah 2250-004 Week 4 April 6-20 secions 7.-7.3 firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions; 7.4 mass-spring sysems. Mon Apr 6 7.-7.2 Sysems of differenial equaions (7.), and he vecor Calculus we need
Mah 2250-004 Week 4 April 6-20 secions 7.-7.3 firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions; 7.4 mass-spring sysems. Mon Apr 6 7.-7.2 Sysems of differenial equaions (7.), and he vecor Calculus we need
6.003 Homework #9 Solutions
 6.003 Homework #9 Soluions Problems. Fourier varieies a. Deermine he Fourier series coefficiens of he following signal, which is periodic in 0. x () 0 3 0 a 0 5 a k a k 0 πk j3 e 0 e j πk 0 jπk πk e 0
6.003 Homework #9 Soluions Problems. Fourier varieies a. Deermine he Fourier series coefficiens of he following signal, which is periodic in 0. x () 0 3 0 a 0 5 a k a k 0 πk j3 e 0 e j πk 0 jπk πk e 0
MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du.
![MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du. MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du.](/thumbs/86/93221008.jpg) MATH 3B: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Inegraion by Pars. Evaluae 3 e. Soluion: Firs make he subsiuion u =. Then =, hence 3 e = e = ue u Now inegrae by pars o ge ue u = ue u e u + C and subsiue he definiion
MATH 3B: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Inegraion by Pars. Evaluae 3 e. Soluion: Firs make he subsiuion u =. Then =, hence 3 e = e = ue u Now inegrae by pars o ge ue u = ue u e u + C and subsiue he definiion
Math 10B: Mock Mid II. April 13, 2016
 Name: Soluions Mah 10B: Mock Mid II April 13, 016 1. ( poins) Sae, wih jusificaion, wheher he following saemens are rue or false. (a) If a 3 3 marix A saisfies A 3 A = 0, hen i canno be inverible. True.
Name: Soluions Mah 10B: Mock Mid II April 13, 016 1. ( poins) Sae, wih jusificaion, wheher he following saemens are rue or false. (a) If a 3 3 marix A saisfies A 3 A = 0, hen i canno be inverible. True.
Solutions from Chapter 9.1 and 9.2
 Soluions from Chaper 9 and 92 Secion 9 Problem # This basically boils down o an exercise in he chain rule from calculus We are looking for soluions of he form: u( x) = f( k x c) where k x R 3 and k is
Soluions from Chaper 9 and 92 Secion 9 Problem # This basically boils down o an exercise in he chain rule from calculus We are looking for soluions of he form: u( x) = f( k x c) where k x R 3 and k is
The Eigenvalue Problems - 8.8
 The Eigenvalue Problems - 8.8. Definiion of Eigenvalues and Eigenvecors: Le A be an n! n marix. A scalar s said o be an eigenvalue of A if he linear sysem Av!v has a nonzero soluion vecor v. The soluion
The Eigenvalue Problems - 8.8. Definiion of Eigenvalues and Eigenvecors: Le A be an n! n marix. A scalar s said o be an eigenvalue of A if he linear sysem Av!v has a nonzero soluion vecor v. The soluion
Final Spring 2007
 .615 Final Spring 7 Overview The purpose of he final exam is o calculae he MHD β limi in a high-bea oroidal okamak agains he dangerous n = 1 exernal ballooning-kink mode. Effecively, his corresponds o
.615 Final Spring 7 Overview The purpose of he final exam is o calculae he MHD β limi in a high-bea oroidal okamak agains he dangerous n = 1 exernal ballooning-kink mode. Effecively, his corresponds o
Chapter 7: Solving Trig Equations
 Haberman MTH Secion I: The Trigonomeric Funcions Chaper 7: Solving Trig Equaions Le s sar by solving a couple of equaions ha involve he sine funcion EXAMPLE a: Solve he equaion sin( ) The inverse funcions
Haberman MTH Secion I: The Trigonomeric Funcions Chaper 7: Solving Trig Equaions Le s sar by solving a couple of equaions ha involve he sine funcion EXAMPLE a: Solve he equaion sin( ) The inverse funcions
Ordinary Differential Equations
 Ordinary Differenial Equaions 5. Examples of linear differenial equaions and heir applicaions We consider some examples of sysems of linear differenial equaions wih consan coefficiens y = a y +... + a
Ordinary Differenial Equaions 5. Examples of linear differenial equaions and heir applicaions We consider some examples of sysems of linear differenial equaions wih consan coefficiens y = a y +... + a
THE 2-BODY PROBLEM. FIGURE 1. A pair of ellipses sharing a common focus. (c,b) c+a ROBERT J. VANDERBEI
 THE 2-BODY PROBLEM ROBERT J. VANDERBEI ABSTRACT. In his shor noe, we show ha a pair of ellipses wih a common focus is a soluion o he 2-body problem. INTRODUCTION. Solving he 2-body problem from scrach
THE 2-BODY PROBLEM ROBERT J. VANDERBEI ABSTRACT. In his shor noe, we show ha a pair of ellipses wih a common focus is a soluion o he 2-body problem. INTRODUCTION. Solving he 2-body problem from scrach
e 2t u(t) e 2t u(t) =?
 EE : Signals, Sysems, and Transforms Fall 7. Skech he convoluion of he following wo signals. Tes No noes, closed book. f() Show your work. Simplify your answers. g(). Using he convoluion inegral, find
EE : Signals, Sysems, and Transforms Fall 7. Skech he convoluion of he following wo signals. Tes No noes, closed book. f() Show your work. Simplify your answers. g(). Using he convoluion inegral, find
Y 0.4Y 0.45Y Y to a proper ARMA specification.
 HG Jan 04 ECON 50 Exercises II - 0 Feb 04 (wih answers Exercise. Read secion 8 in lecure noes 3 (LN3 on he common facor problem in ARMA-processes. Consider he following process Y 0.4Y 0.45Y 0.5 ( where
HG Jan 04 ECON 50 Exercises II - 0 Feb 04 (wih answers Exercise. Read secion 8 in lecure noes 3 (LN3 on he common facor problem in ARMA-processes. Consider he following process Y 0.4Y 0.45Y 0.5 ( where
Finish reading Chapter 2 of Spivak, rereading earlier sections as necessary. handout and fill in some missing details!
 MAT 257, Handou 6: Ocober 7-2, 20. I. Assignmen. Finish reading Chaper 2 of Spiva, rereading earlier secions as necessary. handou and fill in some missing deails! II. Higher derivaives. Also, read his
MAT 257, Handou 6: Ocober 7-2, 20. I. Assignmen. Finish reading Chaper 2 of Spiva, rereading earlier secions as necessary. handou and fill in some missing deails! II. Higher derivaives. Also, read his
MA 214 Calculus IV (Spring 2016) Section 2. Homework Assignment 1 Solutions
 MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
Hamilton- J acobi Equation: Explicit Formulas In this lecture we try to apply the method of characteristics to the Hamilton-Jacobi equation: u t
 M ah 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecure 1 0 O c. 7, 2 0 0 9 Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Explici Formulas In his lecure we ry o apply he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u + H D u, x = 0 in R n
M ah 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecure 1 0 O c. 7, 2 0 0 9 Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Explici Formulas In his lecure we ry o apply he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u + H D u, x = 0 in R n
After the completion of this section the student. Theory of Linear Systems of ODEs. Autonomous Systems. Review Questions and Exercises
 Chaper V ODE V.5 Sysems of Ordinary Differenial Equaions 45 V.5 SYSTEMS OF FIRST ORDER LINEAR ODEs Objecives: Afer he compleion of his secion he suden - should recall he definiion of a sysem of linear
Chaper V ODE V.5 Sysems of Ordinary Differenial Equaions 45 V.5 SYSTEMS OF FIRST ORDER LINEAR ODEs Objecives: Afer he compleion of his secion he suden - should recall he definiion of a sysem of linear
Hamilton Jacobi equations
 Hamilon Jacobi equaions Inoducion o PDE The rigorous suff from Evans, mosly. We discuss firs u + H( u = 0, (1 where H(p is convex, and superlinear a infiniy, H(p lim p p = + This by comes by inegraion
Hamilon Jacobi equaions Inoducion o PDE The rigorous suff from Evans, mosly. We discuss firs u + H( u = 0, (1 where H(p is convex, and superlinear a infiniy, H(p lim p p = + This by comes by inegraion
Math 116 Second Midterm March 21, 2016
 Mah 6 Second Miderm March, 06 UMID: EXAM SOLUTIONS Iniials: Insrucor: Secion:. Do no open his exam unil you are old o do so.. Do no wrie your name anywhere on his exam. 3. This exam has pages including
Mah 6 Second Miderm March, 06 UMID: EXAM SOLUTIONS Iniials: Insrucor: Secion:. Do no open his exam unil you are old o do so.. Do no wrie your name anywhere on his exam. 3. This exam has pages including
Problem Set 11(Practice Problems) Spring 2014
 Issued: Wednesday April, ECE Signals and Sysems I Problem Se (Pracice Problems) Spring Due: For pracice only. No due. Reading in Oppenheim/Willsky/Nawab /9/ Secions 6.-6. // Secions 6.-6. See revised schedule
Issued: Wednesday April, ECE Signals and Sysems I Problem Se (Pracice Problems) Spring Due: For pracice only. No due. Reading in Oppenheim/Willsky/Nawab /9/ Secions 6.-6. // Secions 6.-6. See revised schedule
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics. Fokker-Planck Equation. Time Evolution
 Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx.
![1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx. 1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx.](/thumbs/71/65799522.jpg) . Use Simpson s rule wih n 4 o esimae an () +. Soluion: Since we are using 4 seps, 4 Thus we have [ ( ) f() + 4f + f() + 4f 3 [ + 4 4 6 5 + + 4 4 3 + ] 5 [ + 6 6 5 + + 6 3 + ]. 5. Our funcion is f() +.
. Use Simpson s rule wih n 4 o esimae an () +. Soluion: Since we are using 4 seps, 4 Thus we have [ ( ) f() + 4f + f() + 4f 3 [ + 4 4 6 5 + + 4 4 3 + ] 5 [ + 6 6 5 + + 6 3 + ]. 5. Our funcion is f() +.
Challenge Problems. DIS 203 and 210. March 6, (e 2) k. k(k + 2). k=1. f(x) = k(k + 2) = 1 x k
 Challenge Problems DIS 03 and 0 March 6, 05 Choose one of he following problems, and work on i in your group. Your goal is o convince me ha your answer is correc. Even if your answer isn compleely correc,
Challenge Problems DIS 03 and 0 March 6, 05 Choose one of he following problems, and work on i in your group. Your goal is o convince me ha your answer is correc. Even if your answer isn compleely correc,
ON THE DEGREES OF RATIONAL KNOTS
 ON THE DEGREES OF RATIONAL KNOTS DONOVAN MCFERON, ALEXANDRA ZUSER Absrac. In his paper, we explore he issue of minimizing he degrees on raional knos. We se a bound on hese degrees using Bézou s heorem,
ON THE DEGREES OF RATIONAL KNOTS DONOVAN MCFERON, ALEXANDRA ZUSER Absrac. In his paper, we explore he issue of minimizing he degrees on raional knos. We se a bound on hese degrees using Bézou s heorem,
SOLUTIONS TO ECE 3084
 SOLUTIONS TO ECE 384 PROBLEM 2.. For each sysem below, specify wheher or no i is: (i) memoryless; (ii) causal; (iii) inverible; (iv) linear; (v) ime invarian; Explain your reasoning. If he propery is no
SOLUTIONS TO ECE 384 PROBLEM 2.. For each sysem below, specify wheher or no i is: (i) memoryless; (ii) causal; (iii) inverible; (iv) linear; (v) ime invarian; Explain your reasoning. If he propery is no
Review - Quiz # 1. 1 g(y) dy = f(x) dx. y x. = u, so that y = xu and dy. dx (Sometimes you may want to use the substitution x y
 Review - Quiz # 1 (1) Solving Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Separable Equaions (SE). d = f() g() Mehod of Soluion : 1 g() d = f() (The soluions ma be given implicil b he above formula. Remember,
Review - Quiz # 1 (1) Solving Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Separable Equaions (SE). d = f() g() Mehod of Soluion : 1 g() d = f() (The soluions ma be given implicil b he above formula. Remember,
Maple Tools for Differential Equations A. J. Meir
 Maple Tools for Differenial Equaions A. J. Meir Copyrigh (C) A. J. Meir. All righs reserved. This workshee is for educaional use only. No par of his publicaion may be reproduced or ransmied for profi in
Maple Tools for Differenial Equaions A. J. Meir Copyrigh (C) A. J. Meir. All righs reserved. This workshee is for educaional use only. No par of his publicaion may be reproduced or ransmied for profi in
Hint: There's a table of particular solutions at the end of today's notes.
 Mah 8- Fri Apr 4, Finish Wednesday's noes firs Then 94 Forced oscillaion problems via Fourier Series Today we will revisi he forced oscillaion problems of las Friday, where we prediced wheher or no resonance
Mah 8- Fri Apr 4, Finish Wednesday's noes firs Then 94 Forced oscillaion problems via Fourier Series Today we will revisi he forced oscillaion problems of las Friday, where we prediced wheher or no resonance
Linear Response Theory: The connection between QFT and experiments
 Phys540.nb 39 3 Linear Response Theory: The connecion beween QFT and experimens 3.1. Basic conceps and ideas Q: How do we measure he conduciviy of a meal? A: we firs inroduce a weak elecric field E, and
Phys540.nb 39 3 Linear Response Theory: The connecion beween QFT and experimens 3.1. Basic conceps and ideas Q: How do we measure he conduciviy of a meal? A: we firs inroduce a weak elecric field E, and
14 Autoregressive Moving Average Models
 14 Auoregressive Moving Average Models In his chaper an imporan parameric family of saionary ime series is inroduced, he family of he auoregressive moving average, or ARMA, processes. For a large class
14 Auoregressive Moving Average Models In his chaper an imporan parameric family of saionary ime series is inroduced, he family of he auoregressive moving average, or ARMA, processes. For a large class
Linear Dynamic Models
 Linear Dnamic Models and Forecasing Reference aricle: Ineracions beween he muliplier analsis and he principle of acceleraion Ouline. The sae space ssem as an approach o working wih ssems of difference
Linear Dnamic Models and Forecasing Reference aricle: Ineracions beween he muliplier analsis and he principle of acceleraion Ouline. The sae space ssem as an approach o working wih ssems of difference
Exercises: Similarity Transformation
 Exercises: Similariy Transformaion Problem. Diagonalize he following marix: A [ 2 4 Soluion. Marix A has wo eigenvalues λ 3 and λ 2 2. Since (i) A is a 2 2 marix and (ii) i has 2 disinc eigenvalues, we
Exercises: Similariy Transformaion Problem. Diagonalize he following marix: A [ 2 4 Soluion. Marix A has wo eigenvalues λ 3 and λ 2 2. Since (i) A is a 2 2 marix and (ii) i has 2 disinc eigenvalues, we
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #2 Wha are Coninuous-Time Signals??? Reading Assignmen: Secion. of Kamen and Heck /22 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual flow beween ideas.
EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #2 Wha are Coninuous-Time Signals??? Reading Assignmen: Secion. of Kamen and Heck /22 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual flow beween ideas.
Representation of Stochastic Process by Means of Stochastic Integrals
 Inernaional Journal of Mahemaics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 5, Number 4 (2013), pp. 385-397 Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Represenaion of Sochasic Process by Means of
Inernaional Journal of Mahemaics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 5, Number 4 (2013), pp. 385-397 Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Represenaion of Sochasic Process by Means of
Solution to Review Problems for Midterm II
 Soluion o Review Problems for Miderm II MATH 3860 001 Correcion: (i) should be y () ( + )y () + ( + )y() = e (1 + ). Given ha () = e is a soluion of y () ( + )y () + ( + )y() = 0. You should do problems
Soluion o Review Problems for Miderm II MATH 3860 001 Correcion: (i) should be y () ( + )y () + ( + )y() = e (1 + ). Given ha () = e is a soluion of y () ( + )y () + ( + )y() = 0. You should do problems
Section 4.4 Logarithmic Properties
 Secion. Logarihmic Properies 59 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Secion. Logarihmic Properies 59 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Simulation-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010
 Simulaion-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010 Week Descripion Reading Maerial 2 Compuer Simulaion of Dynamic Models Finie Difference, coninuous saes, discree ime Simple Mehods Euler Trapezoid
Simulaion-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010 Week Descripion Reading Maerial 2 Compuer Simulaion of Dynamic Models Finie Difference, coninuous saes, discree ime Simple Mehods Euler Trapezoid
ME 391 Mechanical Engineering Analysis
 Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Class Meeting # 10: Introduction to the Wave Equation
 MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
Sections 2.2 & 2.3 Limit of a Function and Limit Laws
 Mah 80 www.imeodare.com Secions. &. Limi of a Funcion and Limi Laws In secion. we saw how is arise when we wan o find he angen o a curve or he velociy of an objec. Now we urn our aenion o is in general
Mah 80 www.imeodare.com Secions. &. Limi of a Funcion and Limi Laws In secion. we saw how is arise when we wan o find he angen o a curve or he velociy of an objec. Now we urn our aenion o is in general
INDEX. Transient analysis 1 Initial Conditions 1
 INDEX Secion Page Transien analysis 1 Iniial Condiions 1 Please inform me of your opinion of he relaive emphasis of he review maerial by simply making commens on his page and sending i o me a: Frank Mera
INDEX Secion Page Transien analysis 1 Iniial Condiions 1 Please inform me of your opinion of he relaive emphasis of he review maerial by simply making commens on his page and sending i o me a: Frank Mera
δ (τ )dτ denotes the unit step function, and
 ECE-202 Homework Problems (Se 1) Spring 18 TO THE STUDENT: ALWAYS CHECK THE ERRATA on he web. ANCIENT ASIAN/AFRICAN/NATIVE AMERICAN/SOUTH AMERICAN ETC. PROVERB: If you give someone a fish, you give hem
ECE-202 Homework Problems (Se 1) Spring 18 TO THE STUDENT: ALWAYS CHECK THE ERRATA on he web. ANCIENT ASIAN/AFRICAN/NATIVE AMERICAN/SOUTH AMERICAN ETC. PROVERB: If you give someone a fish, you give hem
MA 366 Review - Test # 1
 MA 366 Review - Tes # 1 Fall 5 () Resuls from Calculus: differeniaion formulas, implici differeniaion, Chain Rule; inegraion formulas, inegraion b pars, parial fracions, oher inegraion echniques. (1) Order
MA 366 Review - Tes # 1 Fall 5 () Resuls from Calculus: differeniaion formulas, implici differeniaion, Chain Rule; inegraion formulas, inegraion b pars, parial fracions, oher inegraion echniques. (1) Order
A New Perturbative Approach in Nonlinear Singularity Analysis
 Journal of Mahemaics and Saisics 7 (: 49-54, ISSN 549-644 Science Publicaions A New Perurbaive Approach in Nonlinear Singulariy Analysis Ta-Leung Yee Deparmen of Mahemaics and Informaion Technology, The
Journal of Mahemaics and Saisics 7 (: 49-54, ISSN 549-644 Science Publicaions A New Perurbaive Approach in Nonlinear Singulariy Analysis Ta-Leung Yee Deparmen of Mahemaics and Informaion Technology, The
4.6 One Dimensional Kinematics and Integration
 4.6 One Dimensional Kinemaics and Inegraion When he acceleraion a( of an objec is a non-consan funcion of ime, we would like o deermine he ime dependence of he posiion funcion x( and he x -componen of
4.6 One Dimensional Kinemaics and Inegraion When he acceleraion a( of an objec is a non-consan funcion of ime, we would like o deermine he ime dependence of he posiion funcion x( and he x -componen of
Math Linear Differential Equations
 Mah 65 - Linear Differenial Equaions A. J. Meir Copyrigh (C) A. J. Meir. All righs reserved. This workshee is for educaional use only. No par of his publicaion may be reproduced or ransmied for profi in
Mah 65 - Linear Differenial Equaions A. J. Meir Copyrigh (C) A. J. Meir. All righs reserved. This workshee is for educaional use only. No par of his publicaion may be reproduced or ransmied for profi in
2.7. Some common engineering functions. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Some common engineering funcions 2.7 Inroducion This secion provides a caalogue of some common funcions ofen used in Science and Engineering. These include polynomials, raional funcions, he modulus funcion
Some common engineering funcions 2.7 Inroducion This secion provides a caalogue of some common funcions ofen used in Science and Engineering. These include polynomials, raional funcions, he modulus funcion
Undetermined coefficients for local fractional differential equations
 Available online a www.isr-publicaions.com/jmcs J. Mah. Compuer Sci. 16 (2016), 140 146 Research Aricle Undeermined coefficiens for local fracional differenial equaions Roshdi Khalil a,, Mohammed Al Horani
Available online a www.isr-publicaions.com/jmcs J. Mah. Compuer Sci. 16 (2016), 140 146 Research Aricle Undeermined coefficiens for local fracional differenial equaions Roshdi Khalil a,, Mohammed Al Horani
Solutions for homework 12
 y Soluions for homework Secion Nonlinear sysems: The linearizaion of a nonlinear sysem Consider he sysem y y y y y (i) Skech he nullclines Use a disincive marking for each nullcline so hey can be disinguished
y Soluions for homework Secion Nonlinear sysems: The linearizaion of a nonlinear sysem Consider he sysem y y y y y (i) Skech he nullclines Use a disincive marking for each nullcline so hey can be disinguished
Second quantization and gauge invariance.
 1 Second quanizaion and gauge invariance. Dan Solomon Rauland-Borg Corporaion Moun Prospec, IL Email: dsolom@uic.edu June, 1. Absrac. I is well known ha he single paricle Dirac equaion is gauge invarian.
1 Second quanizaion and gauge invariance. Dan Solomon Rauland-Borg Corporaion Moun Prospec, IL Email: dsolom@uic.edu June, 1. Absrac. I is well known ha he single paricle Dirac equaion is gauge invarian.
Chapter #1 EEE8013 EEE3001. Linear Controller Design and State Space Analysis
 Chaper EEE83 EEE3 Chaper # EEE83 EEE3 Linear Conroller Design and Sae Space Analysis Ordinary Differenial Equaions.... Inroducion.... Firs Order ODEs... 3. Second Order ODEs... 7 3. General Maerial...
Chaper EEE83 EEE3 Chaper # EEE83 EEE3 Linear Conroller Design and Sae Space Analysis Ordinary Differenial Equaions.... Inroducion.... Firs Order ODEs... 3. Second Order ODEs... 7 3. General Maerial...
Properties Of Solutions To A Generalized Liénard Equation With Forcing Term
 Applied Mahemaics E-Noes, 8(28), 4-44 c ISSN 67-25 Available free a mirror sies of hp://www.mah.nhu.edu.w/ amen/ Properies Of Soluions To A Generalized Liénard Equaion Wih Forcing Term Allan Kroopnick
Applied Mahemaics E-Noes, 8(28), 4-44 c ISSN 67-25 Available free a mirror sies of hp://www.mah.nhu.edu.w/ amen/ Properies Of Soluions To A Generalized Liénard Equaion Wih Forcing Term Allan Kroopnick
ME 452 Fourier Series and Fourier Transform
 ME 452 Fourier Series and Fourier ransform Fourier series From Joseph Fourier in 87 as a resul of his sudy on he flow of hea. If f() is almos any periodic funcion i can be wrien as an infinie sum of sines
ME 452 Fourier Series and Fourier ransform Fourier series From Joseph Fourier in 87 as a resul of his sudy on he flow of hea. If f() is almos any periodic funcion i can be wrien as an infinie sum of sines
The following report makes use of the process from Chapter 2 in Dr. Cumming s thesis.
 Zaleski 1 Joseph Zaleski Mah 451H Final Repor Conformal Mapping Mehods and ZST Hele Shaw Flow Inroducion The Hele Shaw problem has been sudied using linear sabiliy analysis and numerical mehods, bu a novel
Zaleski 1 Joseph Zaleski Mah 451H Final Repor Conformal Mapping Mehods and ZST Hele Shaw Flow Inroducion The Hele Shaw problem has been sudied using linear sabiliy analysis and numerical mehods, bu a novel
SMT 2014 Calculus Test Solutions February 15, 2014 = 3 5 = 15.
 SMT Calculus Tes Soluions February 5,. Le f() = and le g() =. Compue f ()g (). Answer: 5 Soluion: We noe ha f () = and g () = 6. Then f ()g () =. Plugging in = we ge f ()g () = 6 = 3 5 = 5.. There is a
SMT Calculus Tes Soluions February 5,. Le f() = and le g() =. Compue f ()g (). Answer: 5 Soluion: We noe ha f () = and g () = 6. Then f ()g () =. Plugging in = we ge f ()g () = 6 = 3 5 = 5.. There is a
Solution of Integro-Differential Equations by Using ELzaki Transform
 Global Journal of Mahemaical Sciences: Theory and Pracical. Volume, Number (), pp. - Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Soluion of Inegro-Differenial Equaions by Using ELzaki Transform
Global Journal of Mahemaical Sciences: Theory and Pracical. Volume, Number (), pp. - Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Soluion of Inegro-Differenial Equaions by Using ELzaki Transform
Exam 1 Solutions. 1 Question 1. February 10, Part (A) 1.2 Part (B) To find equilibrium solutions, set P (t) = C = dp
 Exam Soluions Februar 0, 05 Quesion. Par (A) To find equilibrium soluions, se P () = C = = 0. This implies: = P ( P ) P = P P P = P P = P ( + P ) = 0 The equilibrium soluion are hus P () = 0 and P () =..
Exam Soluions Februar 0, 05 Quesion. Par (A) To find equilibrium soluions, se P () = C = = 0. This implies: = P ( P ) P = P P P = P P = P ( + P ) = 0 The equilibrium soluion are hus P () = 0 and P () =..
The complex Fourier series has an important limiting form when the period approaches infinity, i.e., T 0. 0 since it is proportional to 1/L, but
 Fourier Transforms The complex Fourier series has an imporan limiing form when he period approaches infiniy, i.e., T or L. Suppose ha in his limi () k = nπ L remains large (ranging from o ) and (2) c n
Fourier Transforms The complex Fourier series has an imporan limiing form when he period approaches infiniy, i.e., T or L. Suppose ha in his limi () k = nπ L remains large (ranging from o ) and (2) c n
Math 315: Linear Algebra Solutions to Assignment 6
 Mah 35: Linear Algebra s o Assignmen 6 # Which of he following ses of vecors are bases for R 2? {2,, 3, }, {4,, 7, 8}, {,,, 3}, {3, 9, 4, 2}. Explain your answer. To generae he whole R 2, wo linearly independen
Mah 35: Linear Algebra s o Assignmen 6 # Which of he following ses of vecors are bases for R 2? {2,, 3, }, {4,, 7, 8}, {,,, 3}, {3, 9, 4, 2}. Explain your answer. To generae he whole R 2, wo linearly independen
Week 1 Lecture 2 Problems 2, 5. What if something oscillates with no obvious spring? What is ω? (problem set problem)
 Week 1 Lecure Problems, 5 Wha if somehing oscillaes wih no obvious spring? Wha is ω? (problem se problem) Sar wih Try and ge o SHM form E. Full beer can in lake, oscillaing F = m & = ge rearrange: F =
Week 1 Lecure Problems, 5 Wha if somehing oscillaes wih no obvious spring? Wha is ω? (problem se problem) Sar wih Try and ge o SHM form E. Full beer can in lake, oscillaing F = m & = ge rearrange: F =
