PROBLEM SET 6. E [w] = 1 2 D. is the smallest for w = u, where u is the solution of the Neumann problem. u = 0 in D u = h (x) on D,
|
|
|
- Jasmine Fleming
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROBLEM SET 6 UE ATE: - APR 25 Chap 7, 9. Questions are either directl from the text or a small variation of a problem in the text. Collaboration is oka, but final submission must be written individuall. Mention all collaborators on our submission. The terms in the bracket indicate the problem number from the text. Section 7. Prob 5, Pg 84 Prove irichlet s Principle for Neumann boundar condition. It asserts that among all real-valued functions w x on, the quantit E [w = w 2, dx hw ds, 2 is the smallest for w = u, where u is the solution of the Neumann problem where h satisfies the constraint u = in = h x on, h x ds =. Note that there are no restrictions on w as opposed to the irichlet principle for irichlet boundar conditions, the function h x appears in the energ and the energ does not change if ou add a constant to w. Comment on the last bit in context of solutions to the Neumann problem for Laplace s equation. Let w be the minimizer of the energ above, then given an function v C 2, consider f v ɛ = E [w + ɛv = 2 Since w is a minimizer, f =. Using our standard calculation f ɛ = v w dx + ɛ f = On using integration b parts for the first term, we get = f = The above identit holds for all functions v and hence we must have w + ɛv 2 dx h w + ɛv v 2 hv ds v w dx hv ds v w dx v h w w = w = h x x Now suppose u satisfies the above Neumnn boundar value problem. Then
2 PROBLEM SET 6 2 E [u = E [w + u w = E [w + E [u w + w u w dx = E [w + u w 2 dx u w h ds + 2 = E [w + u w 2 dx + u w w dx 2 = E [w + u w 2 dx. 2 w u w dx Thus, E [u E [w. The fact that the energ does not change b adding constants is consistent with the fact that we can onl compute solutions of the Neumann equation up to a constant. Section Prob, Pg 87 erive the representation formula for hamronic functions in two dimensions u x = [ u x log x x log x x ds Without loss of generalit, let x =. Let v x = log x and appl Green s second identit to the domain \ B ɛ. Then = \B ɛ u v v u dx = \B ɛ u v v The boundar again separates into two parts, and B ɛ where the normal to B ɛ is inward facing. \B ɛ u v v ds = B ɛ u x log x + log x ds+ u x log x + log x On B ɛ, n = r and x = ɛr, and ds = ɛdθ where r is the unit vector in the outward radial direction. u x log x ds = B ɛ = lim u x log x ds = u, ɛ B ɛ where the last equalit follows from the continuit of u. Similarl, u x u ɛ, θ dθ x n x 2 ɛdθ
3 PROBLEM SET 6 3 log x ds = log x ɛdθ B ɛ lim ɛ B ɛ B ɛ = log ɛ ɛdθ log x ds = log ɛ ɛdθ log ɛ ɛ log x ds = Taking the limit ɛ in Equation, we get u x log x + log x ds + u =, which proves the result. Section Prob, Pg 9 Show that the Green s function is unique. Hint: Take the difference of two of them Let G x, = 4π x + H x, and G 2 x, = 4π x + H 2 x, be two Green s functions. Then, their difference G G 2 = H x, H 2 x, is a harmonic in the x variable for ever and moreover, for a fixed, H H 2 = on the boundar since G = G 2 = on the boundar as a function of x. Thus, for a fixed, the difference of two Green s functions is a harmonic function in x and on the boundar. B uniqueness of the interior irichlet problem, we conclude that the difference must be identicall zero in the interior. Section Prob 7,8 Pg 96 a If u x, = f x is a harmonic function, solve the OE satisfied b f. b Show that r u, where r = x c Suppose v x, is an { > } such that r v. Show that v x, is a function of the quotient x. d Find the boundar values lim u x, = h x e Find the harmonic function in the half plane { > } with boundar data h x = for x > and h x = for x <. f Find the harmonic function in the half plane { > } with boundar data h x = for x > a and h x = for x < a. a b x = r cos θ, = r sin θ c r u = d dx f f s = A arctan s + B = f x = x x r + d x r f x d f x r v x, = x r xv + r v = r x 2 r Use method of characteristics to conclude that d v = f x. h x = { 2 πa + B x > 2 πa + B x <
4 PROBLEM SET 6 4 e f u x, = 2 + π arctan x u x, = 2 + x a π arctan 5 Prob 7, Pg 97 a Find the Green s function for the quadrant b Use the answer in part a to solve the irichlet problem Q = {x, : x >, > }. u = in Q u, = g > u x, = h x x >. Use method of images to place appropriate charges in each quadrant. a b G x, x = x log x log u x, = x x log x log + x x + x [ xg η η 2 + x 2 + η 2 + x 2 [ h ξ x ξ x + ξ Prob 2, Pg 98 The Neumann function N x, for a domain is defined exactl like the Green s function with the following conditions: N x, = + H x, 4π x where H x, is a harmonic function of x for each fixed, and = c x for a suitable constant c. a Show that c = A where A is the area of the boundar. b State and prove the analog of Theorem 7.3., expressing the solution of the Neumann problem in terms of the Neumann function. a Without loss of generalit, we ma assume that =. = N x, dv = ds \B ɛ = \B ɛ = ca. ds + B ɛ Thus, c = A. b u x = N x, ds + u A 7 Prob 22: Pg 98 Solve the Neumann problem in the half plane: u = in { > }, x, = h x dη π + dξ π. ds
5 PROBLEM SET 6 5 and u x, is bounded at. u x, = C + h x ξ log 2 + ξ 2 dξ, boundedness follows from the fact that h x ξ dξ =. Section 9. 8 Prob, Pg 233 Find all three-dimensional plane waves: i.e., all the solutions of the wave equation of the form u x, t = f k x ct where k is a fixed vector and f is a function of one variable Either k = and an arbitar f works or 9 Prob 8, Pg 234 Consider the equation where m >, known as the Klein-Gordon equation. a What is the energ? Show that it is a constant. b Prove the causalit principle for this equation. a E t = 2 u = a + b k x ct tt u c 2 u + m 2 u =, R 2 u t 2 + c 2 u 2 + m 2 u 2 dx d dt E t = ut u tt + c 2 u u t + m 2 uu t dx R 2 = ut u tt c 2 u t u + m 2 uu t dx integration b parts R 2 = b Proof of causalit follows in exactl the same fashion, since t 2 u t c2 u m2 u 2 c 2 u t u = u tt c 2 u + m 2 u u t
u xx + u yy = 0. (5.1)
 Chapter 5 Laplace Equation The following equation is called Laplace equation in two independent variables x, y: The non-homogeneous problem u xx + u yy =. (5.1) u xx + u yy = F, (5.) where F is a function
Chapter 5 Laplace Equation The following equation is called Laplace equation in two independent variables x, y: The non-homogeneous problem u xx + u yy =. (5.1) u xx + u yy = F, (5.) where F is a function
GREEN S IDENTITIES AND GREEN S FUNCTIONS
 GREEN S IENTITIES AN GREEN S FUNCTIONS Green s first identity First, recall the following theorem. Theorem: (ivergence Theorem) Let be a bounded solid region with a piecewise C 1 boundary surface. Let
GREEN S IENTITIES AN GREEN S FUNCTIONS Green s first identity First, recall the following theorem. Theorem: (ivergence Theorem) Let be a bounded solid region with a piecewise C 1 boundary surface. Let
Suggested Solution to Assignment 7
 MATH 422 (25-6) partial diferential equations Suggested Solution to Assignment 7 Exercise 7.. Suppose there exists one non-constant harmonic function u in, which attains its maximum M at x. Then by the
MATH 422 (25-6) partial diferential equations Suggested Solution to Assignment 7 Exercise 7.. Suppose there exists one non-constant harmonic function u in, which attains its maximum M at x. Then by the
Elliptic Equations. Chapter Definitions. Contents. 4.2 Properties of Laplace s and Poisson s Equations
 5 4. Properties of Laplace s and Poisson s Equations Chapter 4 Elliptic Equations Contents. Neumann conditions the normal derivative, / = n u is prescribed on the boundar second BP. In this case we have
5 4. Properties of Laplace s and Poisson s Equations Chapter 4 Elliptic Equations Contents. Neumann conditions the normal derivative, / = n u is prescribed on the boundar second BP. In this case we have
Math 4263 Homework Set 1
 Homework Set 1 1. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2u t + 3u x = 0 u (x, 0) = sin (x) u x + e x u y = 0 u (0, y) = y 2 3. (a) Find the curves γ : t (x (t), y (t)) such that that
Homework Set 1 1. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2u t + 3u x = 0 u (x, 0) = sin (x) u x + e x u y = 0 u (0, y) = y 2 3. (a) Find the curves γ : t (x (t), y (t)) such that that
MATH 124B Solution Key HW 05
 7.1 GREEN S FIRST IENTITY MATH 14B Solution Key HW 05 7.1 GREEN S FIRST IENTITY 1. erive the 3-dimensional maximum principle from the mean value property. SOLUTION. We aim to prove that if u is harmonic
7.1 GREEN S FIRST IENTITY MATH 14B Solution Key HW 05 7.1 GREEN S FIRST IENTITY 1. erive the 3-dimensional maximum principle from the mean value property. SOLUTION. We aim to prove that if u is harmonic
Summer 2017 MATH Solution to Exercise 5
 Summer 07 MATH00 Solution to Exercise 5. Find the partial derivatives of the following functions: (a (xy 5z/( + x, (b x/ x + y, (c arctan y/x, (d log((t + 3 + ts, (e sin(xy z 3, (f x α, x = (x,, x n. (a
Summer 07 MATH00 Solution to Exercise 5. Find the partial derivatives of the following functions: (a (xy 5z/( + x, (b x/ x + y, (c arctan y/x, (d log((t + 3 + ts, (e sin(xy z 3, (f x α, x = (x,, x n. (a
MATH 131P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER 12, 2012
 MATH 3P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER, This is a closed ook, closed notes, no calculators/computers exam. There are 6 prolems. Write your solutions to Prolems -3 in lue ook #, and your solutions to
MATH 3P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER, This is a closed ook, closed notes, no calculators/computers exam. There are 6 prolems. Write your solutions to Prolems -3 in lue ook #, and your solutions to
MA8502 Numerical solution of partial differential equations. The Poisson problem: Mixed Dirichlet/Neumann boundary conditions along curved boundaries
 MA85 Numerical solution of partial differential equations The Poisson problem: Mied Dirichlet/Neumann boundar conditions along curved boundaries Fall c Einar M. Rønquist Department of Mathematical Sciences
MA85 Numerical solution of partial differential equations The Poisson problem: Mied Dirichlet/Neumann boundar conditions along curved boundaries Fall c Einar M. Rønquist Department of Mathematical Sciences
16.3. Conservative Vector Fields
 16.3 onservative Vector Fields Review: Work F d r = FT ds = Fr '( t ) dt Mdx Nd Pdz if F Mi Nj Pk F d r is also called circulation if F represents a velocit vector field. Outward flux across a simple closed
16.3 onservative Vector Fields Review: Work F d r = FT ds = Fr '( t ) dt Mdx Nd Pdz if F Mi Nj Pk F d r is also called circulation if F represents a velocit vector field. Outward flux across a simple closed
Green s Theorem Jeremy Orloff
 Green s Theorem Jerem Orloff Line integrals and Green s theorem. Vector Fields Vector notation. In 8.4 we will mostl use the notation (v) = (a, b) for vectors. The other common notation (v) = ai + bj runs
Green s Theorem Jerem Orloff Line integrals and Green s theorem. Vector Fields Vector notation. In 8.4 we will mostl use the notation (v) = (a, b) for vectors. The other common notation (v) = ai + bj runs
Math 342 Partial Differential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan
 Math 342 Partial ifferential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan 3 Green s first identity Having studied Laplace s equation in regions with simple geometry, we now start developing some tools, which will lead
Math 342 Partial ifferential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan 3 Green s first identity Having studied Laplace s equation in regions with simple geometry, we now start developing some tools, which will lead
Approximation of Continuous Functions
 Approximation of Continuous Functions Francis J. Narcowich October 2014 1 Modulus of Continuit Recall that ever function continuous on a closed interval < a x b < is uniforml continuous: For ever ɛ > 0,
Approximation of Continuous Functions Francis J. Narcowich October 2014 1 Modulus of Continuit Recall that ever function continuous on a closed interval < a x b < is uniforml continuous: For ever ɛ > 0,
is the two-dimensional curl of the vector field F = P, Q. Suppose D is described by a x b and f(x) y g(x) (aka a type I region).
 Math 55 - Vector alculus II Notes 4.4 Green s Theorem We begin with Green s Theorem: Let be a positivel oriented (parameterized counterclockwise) piecewise smooth closed simple curve in R and be the region
Math 55 - Vector alculus II Notes 4.4 Green s Theorem We begin with Green s Theorem: Let be a positivel oriented (parameterized counterclockwise) piecewise smooth closed simple curve in R and be the region
Applications of the Maximum Principle
 Jim Lambers MAT 606 Spring Semester 2015-16 Lecture 26 Notes These notes correspond to Sections 7.4-7.6 in the text. Applications of the Maximum Principle The maximum principle for Laplace s equation is
Jim Lambers MAT 606 Spring Semester 2015-16 Lecture 26 Notes These notes correspond to Sections 7.4-7.6 in the text. Applications of the Maximum Principle The maximum principle for Laplace s equation is
. Then Φ is a diffeomorphism from (0, ) onto (0, 1)
 1 + 5..0: uv i Set F s, t s α 1 t β 1 e s+t and Φu, v. Then Φ is a u1 v diffeomorphism from 0, 0, 1 onto 0,, and JΦu, v u. Hence, ΓαΓβ F s, t dsdt F Φu, vjφu, v dudv 0, 0, 0,1 u α+β 1 e u v α 1 1 v β 1
1 + 5..0: uv i Set F s, t s α 1 t β 1 e s+t and Φu, v. Then Φ is a u1 v diffeomorphism from 0, 0, 1 onto 0,, and JΦu, v u. Hence, ΓαΓβ F s, t dsdt F Φu, vjφu, v dudv 0, 0, 0,1 u α+β 1 e u v α 1 1 v β 1
Math 53 Homework 4 Solutions
 Math 5 Homework 4 Solutions Problem 1. (a) z = is a paraboloid with its highest point at (0,0,) and intersecting the -plane at the circle + = of radius. (or: rotate the parabola z = in the z-plane about
Math 5 Homework 4 Solutions Problem 1. (a) z = is a paraboloid with its highest point at (0,0,) and intersecting the -plane at the circle + = of radius. (or: rotate the parabola z = in the z-plane about
3.2 Differentiability; Tangent planes; differentials
 4 Chapter 3 Draft October 23, 2009 3.2 Differentiabilit; Tangent planes; differentials Overview: In this section, differentiabilit is defined in terms of linear approximation. A function is differentiable
4 Chapter 3 Draft October 23, 2009 3.2 Differentiabilit; Tangent planes; differentials Overview: In this section, differentiabilit is defined in terms of linear approximation. A function is differentiable
Mat 267 Engineering Calculus III Updated on 9/19/2010
 Chapter 11 Partial Derivatives Section 11.1 Functions o Several Variables Deinition: A unction o two variables is a rule that assigns to each ordered pair o real numbers (, ) in a set D a unique real number
Chapter 11 Partial Derivatives Section 11.1 Functions o Several Variables Deinition: A unction o two variables is a rule that assigns to each ordered pair o real numbers (, ) in a set D a unique real number
Heat Conduction in semi-infinite Slab
 1 Module : Diffusive heat and mass transfer Lecture 11: Heat Conduction in semi-infinite Slab with Constant wall Temperature Semi-infinite Solid Semi-infinite solids can be visualized as ver thick walls
1 Module : Diffusive heat and mass transfer Lecture 11: Heat Conduction in semi-infinite Slab with Constant wall Temperature Semi-infinite Solid Semi-infinite solids can be visualized as ver thick walls
MATH 6337: Homework 8 Solutions
 6.1. MATH 6337: Homework 8 Solutions (a) Let be a measurable subset of 2 such that for almost every x, {y : (x, y) } has -measure zero. Show that has measure zero and that for almost every y, {x : (x,
6.1. MATH 6337: Homework 8 Solutions (a) Let be a measurable subset of 2 such that for almost every x, {y : (x, y) } has -measure zero. Show that has measure zero and that for almost every y, {x : (x,
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping
 Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
Differential Equations: Homework 2
 Differential Equations: Homework Alvin Lin January 08 - May 08 Section.3 Exercise The direction field for provided x 0. dx = 4x y is shown. Verify that the straight lines y = ±x are solution curves, y
Differential Equations: Homework Alvin Lin January 08 - May 08 Section.3 Exercise The direction field for provided x 0. dx = 4x y is shown. Verify that the straight lines y = ±x are solution curves, y
MATH MIDTERM 4 - SOME REVIEW PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS Calculus, Fall 2017 Professor: Jared Speck. Problem 1. Approximate the integral
 MATH 8. - MIDTERM 4 - SOME REVIEW PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS 8. Calculus, Fall 7 Professor: Jared Speck Problem. Approimate the integral 4 d using first Simpson s rule with two equal intervals and then the
MATH 8. - MIDTERM 4 - SOME REVIEW PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS 8. Calculus, Fall 7 Professor: Jared Speck Problem. Approimate the integral 4 d using first Simpson s rule with two equal intervals and then the
Math 102 Spring 2008: Solutions: HW #3 Instructor: Fei Xu
 Math Spring 8: Solutions: HW #3 Instructor: Fei Xu. section 7., #8 Evaluate + 3 d. + We ll solve using partial fractions. If we assume 3 A + B + C, clearing denominators gives us A A + B B + C +. Then
Math Spring 8: Solutions: HW #3 Instructor: Fei Xu. section 7., #8 Evaluate + 3 d. + We ll solve using partial fractions. If we assume 3 A + B + C, clearing denominators gives us A A + B B + C +. Then
Directional derivatives and gradient vectors (Sect. 14.5). Directional derivative of functions of two variables.
 Directional derivatives and gradient vectors (Sect. 14.5). Directional derivative of functions of two variables. Partial derivatives and directional derivatives. Directional derivative of functions of
Directional derivatives and gradient vectors (Sect. 14.5). Directional derivative of functions of two variables. Partial derivatives and directional derivatives. Directional derivative of functions of
MATH 271 Test #4T Solutions
 MATH 7 Test #4T Solutions You do not need to evaluate the integrals in problems () (5); just set them up. () ( points) Consider the curve which is represented b the parametric equations x = + t + t, =
MATH 7 Test #4T Solutions You do not need to evaluate the integrals in problems () (5); just set them up. () ( points) Consider the curve which is represented b the parametric equations x = + t + t, =
Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential Functions
 Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential Functions Ranga Rodrigo June 23, 2010 Lecture notes are fully based on Balanis [?]. Some diagrams and text are directly from the books. Contents 1 The Vector
Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential Functions Ranga Rodrigo June 23, 2010 Lecture notes are fully based on Balanis [?]. Some diagrams and text are directly from the books. Contents 1 The Vector
Part A: From (14.19) in your text (see notes Stability1 ), we have
 Prob14.4 14.4 Consider a round-rotor generator delivering a steady-state power P G =.5 to an infinite bus through a transmission line with reactance X L =.4. Assume that E a =1.8, V =1/_, H=5sec, and X
Prob14.4 14.4 Consider a round-rotor generator delivering a steady-state power P G =.5 to an infinite bus through a transmission line with reactance X L =.4. Assume that E a =1.8, V =1/_, H=5sec, and X
Conservation of Linear Momentum
 Conservation of Linear Momentum Once we have determined the continuit equation in di erential form we proceed to derive the momentum equation in di erential form. We start b writing the integral form of
Conservation of Linear Momentum Once we have determined the continuit equation in di erential form we proceed to derive the momentum equation in di erential form. We start b writing the integral form of
Physics/Astronomy 226, Problem set 4, Due 2/10 Solutions. Solution: Our vectors consist of components and basis vectors:
 Physics/Astronomy 226, Problem set 4, Due 2/10 Solutions Reading: Carroll, Ch. 3 1. Derive the explicit expression for the components of the commutator (a.k.a. Lie bracket): [X, Y ] u = X λ λ Y µ Y λ λ
Physics/Astronomy 226, Problem set 4, Due 2/10 Solutions Reading: Carroll, Ch. 3 1. Derive the explicit expression for the components of the commutator (a.k.a. Lie bracket): [X, Y ] u = X λ λ Y µ Y λ λ
3.6 Applications of Poisson s equation
 William J. Parnell: MT3432. Section 3: Green s functions in 2 and 3D 69 3.6 Applications of Poisson s equation The beaut of Green s functions is that the are useful! Let us consider an example here where
William J. Parnell: MT3432. Section 3: Green s functions in 2 and 3D 69 3.6 Applications of Poisson s equation The beaut of Green s functions is that the are useful! Let us consider an example here where
Math 372 Syllabus and Lecture Schedule. Gautam Iyer, Spring 2012
 Math 37 Syllabus and ecture Schedule. Gautam Iyer, Spring ecture, Mon /6: Introduction and motivation. (Sec..) Introduction. A PE is a differential equation involving derivatives with respect to more than
Math 37 Syllabus and ecture Schedule. Gautam Iyer, Spring ecture, Mon /6: Introduction and motivation. (Sec..) Introduction. A PE is a differential equation involving derivatives with respect to more than
Math 162: Calculus IIA
 Math 62: Calculus IIA Final Exam ANSWERS December 9, 26 Part A. (5 points) Evaluate the integral x 4 x 2 dx Substitute x 2 cos θ: x 8 cos dx θ ( 2 sin θ) dθ 4 x 2 2 sin θ 8 cos θ dθ 8 cos 2 θ cos θ dθ
Math 62: Calculus IIA Final Exam ANSWERS December 9, 26 Part A. (5 points) Evaluate the integral x 4 x 2 dx Substitute x 2 cos θ: x 8 cos dx θ ( 2 sin θ) dθ 4 x 2 2 sin θ 8 cos θ dθ 8 cos 2 θ cos θ dθ
MATHEMATICS 317 April 2017 Final Exam Solutions
 MATHEMATI 7 April 7 Final Eam olutions. Let r be the vector field r = îı + ĵj + z ˆk and let r be the function r = r. Let a be the constant vector a = a îı + a ĵj + a ˆk. ompute and simplif the following
MATHEMATI 7 April 7 Final Eam olutions. Let r be the vector field r = îı + ĵj + z ˆk and let r be the function r = r. Let a be the constant vector a = a îı + a ĵj + a ˆk. ompute and simplif the following
2.2 The derivative as a Function
 2.2 The derivative as a Function Recall: The derivative of a function f at a fixed number a: f a f a+h f(a) = lim h 0 h Definition (Derivative of f) For any number x, the derivative of f is f x f x+h f(x)
2.2 The derivative as a Function Recall: The derivative of a function f at a fixed number a: f a f a+h f(a) = lim h 0 h Definition (Derivative of f) For any number x, the derivative of f is f x f x+h f(x)
Dr. Allen Back. Dec. 3, 2014
 Dr. Allen Back Dec. 3, 2014 forms are sums of wedge products of the basis 1-forms dx, dy, and dz. They are kinds of tensors generalizing ordinary scalar functions and vector fields. They have a skew-symmetry
Dr. Allen Back Dec. 3, 2014 forms are sums of wedge products of the basis 1-forms dx, dy, and dz. They are kinds of tensors generalizing ordinary scalar functions and vector fields. They have a skew-symmetry
Harmonic functions, Poisson kernels
 June 17, 16 Harmonic functions, Poisson kernels Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ [This document is http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/m/complex/notes 14-15/8c harmonic.pdf]
June 17, 16 Harmonic functions, Poisson kernels Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ [This document is http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/m/complex/notes 14-15/8c harmonic.pdf]
(0,2) L 1 L 2 R (-1,0) (2,0) MA4006: Exercise Sheet 3: Solutions. 1. Evaluate the integral R
 MA6: Eercise Sheet 3: Solutions 1. Evaluate the integral d d over the triangle with vertices ( 1, ), (, 2) and (2, ). Solution. See Figure 1. Let be the inner variable and the outer variable. we need the
MA6: Eercise Sheet 3: Solutions 1. Evaluate the integral d d over the triangle with vertices ( 1, ), (, 2) and (2, ). Solution. See Figure 1. Let be the inner variable and the outer variable. we need the
Preliminary Exam 2018 Solutions to Morning Exam
 Preliminary Exam 28 Solutions to Morning Exam Part I. Solve four of the following five problems. Problem. Consider the series n 2 (n log n) and n 2 (n(log n)2 ). Show that one converges and one diverges
Preliminary Exam 28 Solutions to Morning Exam Part I. Solve four of the following five problems. Problem. Consider the series n 2 (n log n) and n 2 (n(log n)2 ). Show that one converges and one diverges
Vector Calculus. Vector Fields. Reading Trim Vector Fields. Assignment web page assignment #9. Chapter 14 will examine a vector field.
 Vector alculus Vector Fields Reading Trim 14.1 Vector Fields Assignment web page assignment #9 hapter 14 will eamine a vector field. For eample, if we eamine the temperature conditions in a room, for ever
Vector alculus Vector Fields Reading Trim 14.1 Vector Fields Assignment web page assignment #9 hapter 14 will eamine a vector field. For eample, if we eamine the temperature conditions in a room, for ever
and ( x, y) in a domain D R a unique real number denoted x y and b) = x y = {(, ) + 36} that is all points inside and on
 Mat 7 Calculus III Updated on 10/4/07 Dr. Firoz Chapter 14 Partial Derivatives Section 14.1 Functions o Several Variables Deinition: A unction o two variables is a rule that assigns to each ordered pair
Mat 7 Calculus III Updated on 10/4/07 Dr. Firoz Chapter 14 Partial Derivatives Section 14.1 Functions o Several Variables Deinition: A unction o two variables is a rule that assigns to each ordered pair
Math 1B Final Exam, Solution. Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring (6 points) Use substitution and integration by parts to find:
 Math B Final Eam, Solution Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring 20 The eam is closed book, apart from a sheet of notes 8. Calculators are not allowed. It is your responsibility to write your answers clearly..
Math B Final Eam, Solution Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring 20 The eam is closed book, apart from a sheet of notes 8. Calculators are not allowed. It is your responsibility to write your answers clearly..
Partial Differential Equations
 M3M3 Partial Differential Equations Solutions to problem sheet 3/4 1* (i) Show that the second order linear differential operators L and M, defined in some domain Ω R n, and given by Mφ = Lφ = j=1 j=1
M3M3 Partial Differential Equations Solutions to problem sheet 3/4 1* (i) Show that the second order linear differential operators L and M, defined in some domain Ω R n, and given by Mφ = Lφ = j=1 j=1
Pattern formation and Turing instability
 Pattern formation and Turing instability. Gurarie Topics: - Pattern formation through symmetry breaing and loss of stability - Activator-inhibitor systems with diffusion Turing proposed a mechanism for
Pattern formation and Turing instability. Gurarie Topics: - Pattern formation through symmetry breaing and loss of stability - Activator-inhibitor systems with diffusion Turing proposed a mechanism for
SOLUTION OF THE DIRICHLET PROBLEM WITH A VARIATIONAL METHOD. 1. Dirichlet integral
 SOLUTION OF THE DIRICHLET PROBLEM WITH A VARIATIONAL METHOD CRISTIAN E. GUTIÉRREZ FEBRUARY 3, 29. Dirichlet integral Let f C( ) with open and bounded. Let H = {u C ( ) : u = f on } and D(u) = Du(x) 2 dx.
SOLUTION OF THE DIRICHLET PROBLEM WITH A VARIATIONAL METHOD CRISTIAN E. GUTIÉRREZ FEBRUARY 3, 29. Dirichlet integral Let f C( ) with open and bounded. Let H = {u C ( ) : u = f on } and D(u) = Du(x) 2 dx.
AP Calculus 2004 AB FRQ Solutions
 AP Calculus 4 AB FRQ Solutions Louis A. Talman, Ph. D. Emeritus Professor of Mathematics Metropolitan State University of Denver July, 7 Problem. Part a The function F (t) = 8 + 4 sin(t/) gives the rate,
AP Calculus 4 AB FRQ Solutions Louis A. Talman, Ph. D. Emeritus Professor of Mathematics Metropolitan State University of Denver July, 7 Problem. Part a The function F (t) = 8 + 4 sin(t/) gives the rate,
M545 Homework 8. Mark Blumstein. December 9, [f (x)] 2 dx = 1. Find such a function if you can. If it cannot be found, explain why not.
![M545 Homework 8. Mark Blumstein. December 9, [f (x)] 2 dx = 1. Find such a function if you can. If it cannot be found, explain why not. M545 Homework 8. Mark Blumstein. December 9, [f (x)] 2 dx = 1. Find such a function if you can. If it cannot be found, explain why not.](/thumbs/93/114057829.jpg) M545 Homework 8 Mark Blumstein ecember 9, 5..) Let fx) be a function such that f) f3), 3 [fx)] dx, and 3 [f x)] dx. Find such a function if you can. If it cannot be found, explain why not. Proof. We will
M545 Homework 8 Mark Blumstein ecember 9, 5..) Let fx) be a function such that f) f3), 3 [fx)] dx, and 3 [f x)] dx. Find such a function if you can. If it cannot be found, explain why not. Proof. We will
Math 20C Homework 2 Partial Solutions
 Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Math 181/281. Rumbos Spring 2011 Page 1. Solutions to Assignment #5. Hence, the dynamical system, θ(t, p, q), for (t, p, q) R 3 corresponding = F.
 Math 181/281. Rumbos Spring 2011 Page 1 Solutions to Assignment #5 1. For real numbers a and b with a 2 + b 2 = 0, let F : R 2 R 2 be given b ( ) ( ) ( ) x ax b x F =, for all R 2. (1) bx + a (a) Explain
Math 181/281. Rumbos Spring 2011 Page 1 Solutions to Assignment #5 1. For real numbers a and b with a 2 + b 2 = 0, let F : R 2 R 2 be given b ( ) ( ) ( ) x ax b x F =, for all R 2. (1) bx + a (a) Explain
21 Laplace s Equation and Harmonic Functions
 2 Laplace s Equation and Harmonic Functions 2. Introductory Remarks on the Laplacian operator Given a domain Ω R d, then 2 u = div(grad u) = in Ω () is Laplace s equation defined in Ω. If d = 2, in cartesian
2 Laplace s Equation and Harmonic Functions 2. Introductory Remarks on the Laplacian operator Given a domain Ω R d, then 2 u = div(grad u) = in Ω () is Laplace s equation defined in Ω. If d = 2, in cartesian
Part D. Complex Analysis
 Part D. Comple Analsis Chapter 3. Comple Numbers and Functions. Man engineering problems ma be treated and solved b using comple numbers and comple functions. First, comple numbers and the comple plane
Part D. Comple Analsis Chapter 3. Comple Numbers and Functions. Man engineering problems ma be treated and solved b using comple numbers and comple functions. First, comple numbers and the comple plane
Math 261 Solutions to Sample Final Exam Problems
 Math 61 Solutions to Sample Final Eam Problems 1 Math 61 Solutions to Sample Final Eam Problems 1. Let F i + ( + ) j, and let G ( + ) i + ( ) j, where C 1 is the curve consisting of the circle of radius,
Math 61 Solutions to Sample Final Eam Problems 1 Math 61 Solutions to Sample Final Eam Problems 1. Let F i + ( + ) j, and let G ( + ) i + ( ) j, where C 1 is the curve consisting of the circle of radius,
Antibound State for Klein-Gordon Equation
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 8, 2014, no. 59, 2945-2949 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2014.411374 Antibound State for Klein-Gordon Equation Ana-Magnolia
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 8, 2014, no. 59, 2945-2949 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2014.411374 Antibound State for Klein-Gordon Equation Ana-Magnolia
y=1/4 x x=4y y=x 3 x=y 1/3 Example: 3.1 (1/2, 1/8) (1/2, 1/8) Find the area in the positive quadrant bounded by y = 1 x and y = x3
 Eample: 3.1 Find the area in the positive quadrant bounded b 1 and 3 4 First find the points of intersection of the two curves: clearl the curves intersect at (, ) and at 1 4 3 1, 1 8 Select a strip at
Eample: 3.1 Find the area in the positive quadrant bounded b 1 and 3 4 First find the points of intersection of the two curves: clearl the curves intersect at (, ) and at 1 4 3 1, 1 8 Select a strip at
dzdydx. [Hint: switch dzdydx into dxdydz.] z(2 z) dzdydx. z(2 z) 2 )dz z(2 z) 2 sin(πz)dz = 1 x = u + 3v (2 points) y = v (2 points) (u, v) = 1 2
![dzdydx. [Hint: switch dzdydx into dxdydz.] z(2 z) dzdydx. z(2 z) 2 )dz z(2 z) 2 sin(πz)dz = 1 x = u + 3v (2 points) y = v (2 points) (u, v) = 1 2 dzdydx. [Hint: switch dzdydx into dxdydz.] z(2 z) dzdydx. z(2 z) 2 )dz z(2 z) 2 sin(πz)dz = 1 x = u + 3v (2 points) y = v (2 points) (u, v) = 1 2](/thumbs/83/88911949.jpg) Page of 6. (%) Evaluate x z( z) 微甲 8- 班期末考解答和評分標準 dzddx. [Hint: switch dzddx into dxddz.] We need to compute x z( z) dzddx. The region of integration is bounded b [, ] [, ] [, ] {(x,, z) 3 x +, z }. (4%
Page of 6. (%) Evaluate x z( z) 微甲 8- 班期末考解答和評分標準 dzddx. [Hint: switch dzddx into dxddz.] We need to compute x z( z) dzddx. The region of integration is bounded b [, ] [, ] [, ] {(x,, z) 3 x +, z }. (4%
UNIVERSIDAD CARLOS III DE MADRID MATHEMATICS II EXERCISES (SOLUTIONS )
 UNIVERSIDAD CARLOS III DE MADRID MATHEMATICS II EXERCISES (SOLUTIONS ) CHAPTER : Limits and continuit of functions in R n. -. Sketch the following subsets of R. Sketch their boundar and the interior. Stud
UNIVERSIDAD CARLOS III DE MADRID MATHEMATICS II EXERCISES (SOLUTIONS ) CHAPTER : Limits and continuit of functions in R n. -. Sketch the following subsets of R. Sketch their boundar and the interior. Stud
Engineering Mathematics I
 Engineering Mathematics I_ 017 Engineering Mathematics I 1. Introduction to Differential Equations Dr. Rami Zakaria Terminolog Differential Equation Ordinar Differential Equations Partial Differential
Engineering Mathematics I_ 017 Engineering Mathematics I 1. Introduction to Differential Equations Dr. Rami Zakaria Terminolog Differential Equation Ordinar Differential Equations Partial Differential
67. (a) Use a computer algebra system to find the partial fraction CAS. 68. (a) Find the partial fraction decomposition of the function CAS
 SECTION 7.5 STRATEGY FOR INTEGRATION 483 6. 2 sin 2 2 cos CAS 67. (a) Use a computer algebra sstem to find the partial fraction decomposition of the function 62 63 Find the area of the region under the
SECTION 7.5 STRATEGY FOR INTEGRATION 483 6. 2 sin 2 2 cos CAS 67. (a) Use a computer algebra sstem to find the partial fraction decomposition of the function 62 63 Find the area of the region under the
HW6. 1. Book problems 8.5, 8.6, 8.9, 8.23, 8.31
 HW6 1. Book problems 8.5, 8.6, 8.9, 8.3, 8.31. Add an equal strength sink and a source separated by a small distance, dx, and take the limit of dx approaching zero to obtain the following equations for
HW6 1. Book problems 8.5, 8.6, 8.9, 8.3, 8.31. Add an equal strength sink and a source separated by a small distance, dx, and take the limit of dx approaching zero to obtain the following equations for
y = ± x 2 + c. ln y = 2 ln x + 2C sin(x) dx
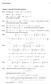 Worked Solutions Chapter 4: Separable First-Order Equations 43 a Factoring out 2, we get 3 sinx)) 2, which is f x)g), ds with f x) 3 sinx) and g) 2 So the equation is separable 43 c x x )2 x )2 f x)g)
Worked Solutions Chapter 4: Separable First-Order Equations 43 a Factoring out 2, we get 3 sinx)) 2, which is f x)g), ds with f x) 3 sinx) and g) 2 So the equation is separable 43 c x x )2 x )2 f x)g)
Brownian survival and Lifshitz tail in perturbed lattice disorder
 Brownian survival and Lifshitz tail in perturbed lattice disorder Ryoki Fukushima Kyoto niversity Random Processes and Systems February 16, 2009 6 B T 1. Model ) ({B t t 0, P x : standard Brownian motion
Brownian survival and Lifshitz tail in perturbed lattice disorder Ryoki Fukushima Kyoto niversity Random Processes and Systems February 16, 2009 6 B T 1. Model ) ({B t t 0, P x : standard Brownian motion
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Figure 25:Differentials of surface.
 2.5. Change of variables and Jacobians In the previous example we saw that, once we have identified the type of coordinates which is best to use for solving a particular problem, the next step is to do
2.5. Change of variables and Jacobians In the previous example we saw that, once we have identified the type of coordinates which is best to use for solving a particular problem, the next step is to do
Practice Final Solutions
 Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
MATH 0350 PRACTICE FINAL FALL 2017 SAMUEL S. WATSON. a c. b c.
 MATH 35 PRACTICE FINAL FALL 17 SAMUEL S. WATSON Problem 1 Verify that if a and b are nonzero vectors, the vector c = a b + b a bisects the angle between a and b. The cosine of the angle between a and c
MATH 35 PRACTICE FINAL FALL 17 SAMUEL S. WATSON Problem 1 Verify that if a and b are nonzero vectors, the vector c = a b + b a bisects the angle between a and b. The cosine of the angle between a and c
Jim Lambers MAT 280 Summer Semester Practice Final Exam Solution. dy + xz dz = x(t)y(t) dt. t 3 (4t 3 ) + e t2 (2t) + t 7 (3t 2 ) dt
 Jim Lambers MAT 28 ummer emester 212-1 Practice Final Exam olution 1. Evaluate the line integral xy dx + e y dy + xz dz, where is given by r(t) t 4, t 2, t, t 1. olution From r (t) 4t, 2t, t 2, we obtain
Jim Lambers MAT 28 ummer emester 212-1 Practice Final Exam olution 1. Evaluate the line integral xy dx + e y dy + xz dz, where is given by r(t) t 4, t 2, t, t 1. olution From r (t) 4t, 2t, t 2, we obtain
Chapter 4 Analytic Trigonometry
 Analtic Trigonometr Chapter Analtic Trigonometr Inverse Trigonometric Functions The trigonometric functions act as an operator on the variable (angle, resulting in an output value Suppose this process
Analtic Trigonometr Chapter Analtic Trigonometr Inverse Trigonometric Functions The trigonometric functions act as an operator on the variable (angle, resulting in an output value Suppose this process
Topic 3 Notes Jeremy Orloff
 Topic 3 Notes Jerem Orloff 3 Line integrals and auch s theorem 3.1 Introduction The basic theme here is that comple line integrals will mirror much of what we ve seen for multivariable calculus line integrals.
Topic 3 Notes Jerem Orloff 3 Line integrals and auch s theorem 3.1 Introduction The basic theme here is that comple line integrals will mirror much of what we ve seen for multivariable calculus line integrals.
12.11 Laplace s Equation in Cylindrical and
 SEC. 2. Laplace s Equation in Cylinrical an Spherical Coorinates. Potential 593 2. Laplace s Equation in Cylinrical an Spherical Coorinates. Potential One of the most important PDEs in physics an engineering
SEC. 2. Laplace s Equation in Cylinrical an Spherical Coorinates. Potential 593 2. Laplace s Equation in Cylinrical an Spherical Coorinates. Potential One of the most important PDEs in physics an engineering
Practice Problems for Exam 3 (Solutions) 1. Let F(x, y) = xyi+(y 3x)j, and let C be the curve r(t) = ti+(3t t 2 )j for 0 t 2. Compute F dr.
 1. Let F(x, y) xyi+(y 3x)j, and let be the curve r(t) ti+(3t t 2 )j for t 2. ompute F dr. Solution. F dr b a 2 2 F(r(t)) r (t) dt t(3t t 2 ), 3t t 2 3t 1, 3 2t dt t 3 dt 1 2 4 t4 4. 2. Evaluate the line
1. Let F(x, y) xyi+(y 3x)j, and let be the curve r(t) ti+(3t t 2 )j for t 2. ompute F dr. Solution. F dr b a 2 2 F(r(t)) r (t) dt t(3t t 2 ), 3t t 2 3t 1, 3 2t dt t 3 dt 1 2 4 t4 4. 2. Evaluate the line
INSTRUCTOR S SOLUTIONS MANUAL SECTION 17.1 (PAGE 902)
 INSTRUCTOR S SOLUTIONS MANUAL SECTION 7 PAGE 90 CHAPTER 7 ORDINARY DIFFEREN- TIAL EQUATIONS Section 7 Classifing Differential Equations page 90 = 5: st order, linear, homogeneous d d + = : nd order, linear,
INSTRUCTOR S SOLUTIONS MANUAL SECTION 7 PAGE 90 CHAPTER 7 ORDINARY DIFFEREN- TIAL EQUATIONS Section 7 Classifing Differential Equations page 90 = 5: st order, linear, homogeneous d d + = : nd order, linear,
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 10 (Second moments of an arc) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 13.1 INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 1 (Second moments of an arc) by A.J.Hobson 13.1.1 Introduction 13.1. The second moment of an arc about the y-axis 13.1.3 The second moment of an
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 13.1 INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 1 (Second moments of an arc) by A.J.Hobson 13.1.1 Introduction 13.1. The second moment of an arc about the y-axis 13.1.3 The second moment of an
Complex Homework Summer 2014
 omplex Homework Summer 24 Based on Brown hurchill 7th Edition June 2, 24 ontents hw, omplex Arithmetic, onjugates, Polar Form 2 2 hw2 nth roots, Domains, Functions 2 3 hw3 Images, Transformations 3 4 hw4
omplex Homework Summer 24 Based on Brown hurchill 7th Edition June 2, 24 ontents hw, omplex Arithmetic, onjugates, Polar Form 2 2 hw2 nth roots, Domains, Functions 2 3 hw3 Images, Transformations 3 4 hw4
MATH 52 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MAH 5 FINAL EXAM OLUION. (a) ketch the region R of integration in the following double integral. x xe y5 dy dx R = {(x, y) x, x y }. (b) Express the region R as an x-simple region. R = {(x, y) y, x y }
MAH 5 FINAL EXAM OLUION. (a) ketch the region R of integration in the following double integral. x xe y5 dy dx R = {(x, y) x, x y }. (b) Express the region R as an x-simple region. R = {(x, y) y, x y }
Math 342 Partial Differential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan
 Math 342 Partial Differential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan 15 Heat with a source So far we considered homogeneous wave and heat equations and the associated initial value problems on the whole line, as
Math 342 Partial Differential Equations «Viktor Grigoryan 15 Heat with a source So far we considered homogeneous wave and heat equations and the associated initial value problems on the whole line, as
Physics 1501 Lecture 28
 Phsics 1501 Lecture 28 Phsics 1501: Lecture 28 Toda s Agenda Homework #10 (due Frida No. 11) Midterm 2: No. 16 Topics 1-D traeling waes Waes on a string Superposition Power Phsics 1501: Lecture 28, Pg
Phsics 1501 Lecture 28 Phsics 1501: Lecture 28 Toda s Agenda Homework #10 (due Frida No. 11) Midterm 2: No. 16 Topics 1-D traeling waes Waes on a string Superposition Power Phsics 1501: Lecture 28, Pg
First Order Equations
 10 1 Linear and Semilinear Equations Chapter First Order Equations Contents 1 Linear and Semilinear Equations 9 Quasilinear Equations 19 3 Wave Equation 6 4 Sstems of Equations 31 1 Linear and Semilinear
10 1 Linear and Semilinear Equations Chapter First Order Equations Contents 1 Linear and Semilinear Equations 9 Quasilinear Equations 19 3 Wave Equation 6 4 Sstems of Equations 31 1 Linear and Semilinear
Final Examination Linear Partial Differential Equations. Matthew J. Hancock. Feb. 3, 2006
 Final Examination 8.303 Linear Partial ifferential Equations Matthew J. Hancock Feb. 3, 006 Total points: 00 Rules [requires student signature!]. I will use only pencils, pens, erasers, and straight edges
Final Examination 8.303 Linear Partial ifferential Equations Matthew J. Hancock Feb. 3, 006 Total points: 00 Rules [requires student signature!]. I will use only pencils, pens, erasers, and straight edges
MATH 126 FINAL EXAM. Name:
 MATH 126 FINAL EXAM Name: Exam policies: Closed book, closed notes, no external resources, individual work. Please write your name on the exam and on each page you detach. Unless stated otherwise, you
MATH 126 FINAL EXAM Name: Exam policies: Closed book, closed notes, no external resources, individual work. Please write your name on the exam and on each page you detach. Unless stated otherwise, you
Functions of Several Variables
 Chapter 1 Functions of Several Variables 1.1 Introduction A real valued function of n variables is a function f : R, where the domain is a subset of R n. So: for each ( 1,,..., n ) in, the value of f is
Chapter 1 Functions of Several Variables 1.1 Introduction A real valued function of n variables is a function f : R, where the domain is a subset of R n. So: for each ( 1,,..., n ) in, the value of f is
MATH 425, FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MATH 425, FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Each exercise is worth 50 points. Exercise. a The operator L is defined on smooth functions of (x, y by: Is the operator L linear? Prove your answer. L (u := arctan(xy u
MATH 425, FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Each exercise is worth 50 points. Exercise. a The operator L is defined on smooth functions of (x, y by: Is the operator L linear? Prove your answer. L (u := arctan(xy u
f(p i )Area(T i ) F ( r(u, w) ) (r u r w ) da
 MAH 55 Flux integrals Fall 16 1. Review 1.1. Surface integrals. Let be a surface in R. Let f : R be a function defined on. efine f ds = f(p i Area( i lim mesh(p as a limit of Riemann sums over sampled-partitions.
MAH 55 Flux integrals Fall 16 1. Review 1.1. Surface integrals. Let be a surface in R. Let f : R be a function defined on. efine f ds = f(p i Area( i lim mesh(p as a limit of Riemann sums over sampled-partitions.
We denote the space of distributions on Ω by D ( Ω) 2.
 Sep. 1 0, 008 Distributions Distributions are generalized functions. Some familiarity with the theory of distributions helps understanding of various function spaces which play important roles in the study
Sep. 1 0, 008 Distributions Distributions are generalized functions. Some familiarity with the theory of distributions helps understanding of various function spaces which play important roles in the study
Math 113 Fall 2005 key Departmental Final Exam
 Math 3 Fall 5 key Departmental Final Exam Part I: Short Answer and Multiple Choice Questions Do not show your work for problems in this part.. Fill in the blanks with the correct answer. (a) The integral
Math 3 Fall 5 key Departmental Final Exam Part I: Short Answer and Multiple Choice Questions Do not show your work for problems in this part.. Fill in the blanks with the correct answer. (a) The integral
The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and engineering.
 Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions
 Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions Jim Agler 26. (# pg. 73 Conway). Prove the assertion made in Proposition 2. (pg. 68) that g is continuous. Solution. We wish to show that if g : [a, b] [c, d] C is a continuous
Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions Jim Agler 26. (# pg. 73 Conway). Prove the assertion made in Proposition 2. (pg. 68) that g is continuous. Solution. We wish to show that if g : [a, b] [c, d] C is a continuous
Leaving Cert Differentiation
 Leaving Cert Differentiation Types of Differentiation 1. From First Principles 2. Using the Rules From First Principles You will be told when to use this, the question will say differentiate with respect
Leaving Cert Differentiation Types of Differentiation 1. From First Principles 2. Using the Rules From First Principles You will be told when to use this, the question will say differentiate with respect
Partial Differential Equations
 Part II Partial Differential Equations Year 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2015 Paper 4, Section II 29E Partial Differential Equations 72 (a) Show that the Cauchy problem for u(x,
Part II Partial Differential Equations Year 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2015 Paper 4, Section II 29E Partial Differential Equations 72 (a) Show that the Cauchy problem for u(x,
A Space-Time Boundary Element Method for the Wave Equation
 W I S S E N T E C H N I K L E I D E N S C H A F T A Space-Time Boundary Element Method for the Wave Equation Marco Zank and Olaf Steinbach Institut für Numerische Mathematik Space-Time Methods for PDEs,
W I S S E N T E C H N I K L E I D E N S C H A F T A Space-Time Boundary Element Method for the Wave Equation Marco Zank and Olaf Steinbach Institut für Numerische Mathematik Space-Time Methods for PDEs,
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi The Fourier Transform
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 4 The Fourier Transform Yung-Hsiang Huang 2017.11.05 1 Exercises 1. Suppose f L 1 (), and f 0. Show that f 0. emark 1. This proof is observed by Newmann (published
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 4 The Fourier Transform Yung-Hsiang Huang 2017.11.05 1 Exercises 1. Suppose f L 1 (), and f 0. Show that f 0. emark 1. This proof is observed by Newmann (published
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part I
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Comple Analsis II Lecture Notes Part I Chapter 1 Preliminar results/review of Comple Analsis I These are more detailed notes for the results
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Comple Analsis II Lecture Notes Part I Chapter 1 Preliminar results/review of Comple Analsis I These are more detailed notes for the results
Strauss PDEs 2e: Section Exercise 1 Page 1 of 6
 Strauss PDEs 2e: Section 3 - Exercise Page of 6 Exercise Carefully derive the equation of a string in a medium in which the resistance is proportional to the velocity Solution There are two ways (among
Strauss PDEs 2e: Section 3 - Exercise Page of 6 Exercise Carefully derive the equation of a string in a medium in which the resistance is proportional to the velocity Solution There are two ways (among
18 Green s function for the Poisson equation
 8 Green s function for the Poisson equation Now we have some experience working with Green s functions in dimension, therefore, we are ready to see how Green s functions can be obtained in dimensions 2
8 Green s function for the Poisson equation Now we have some experience working with Green s functions in dimension, therefore, we are ready to see how Green s functions can be obtained in dimensions 2
14.5 The Chain Rule. dx dt
 SECTION 14.5 THE CHAIN RULE 931 27. w lns 2 2 z 2 28. w e z 37. If R is the total resistance of three resistors, connected in parallel, with resistances,,, then R 1 R 2 R 3 29. If z 5 2 2 and, changes
SECTION 14.5 THE CHAIN RULE 931 27. w lns 2 2 z 2 28. w e z 37. If R is the total resistance of three resistors, connected in parallel, with resistances,,, then R 1 R 2 R 3 29. If z 5 2 2 and, changes
Evolution equations with spectral methods: the case of the wave equation
 Evolution equations with spectral methods: the case of the wave equation Jerome.Novak@obspm.fr Laboratoire de l Univers et de ses Théories (LUTH) CNRS / Observatoire de Paris, France in collaboration with
Evolution equations with spectral methods: the case of the wave equation Jerome.Novak@obspm.fr Laboratoire de l Univers et de ses Théories (LUTH) CNRS / Observatoire de Paris, France in collaboration with
x 2 y = 1 2. Problem 2. Compute the Taylor series (at the base point 0) for the function 1 (1 x) 3.
 MATH 8.0 - FINAL EXAM - SOME REVIEW PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS 8.0 Calculus, Fall 207 Professor: Jared Speck Problem. Consider the following curve in the plane: x 2 y = 2. Let a be a number. The portion of
MATH 8.0 - FINAL EXAM - SOME REVIEW PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS 8.0 Calculus, Fall 207 Professor: Jared Speck Problem. Consider the following curve in the plane: x 2 y = 2. Let a be a number. The portion of
Applied Mathematics Masters Examination Fall 2016, August 18, 1 4 pm.
 Applied Mathematics Masters Examination Fall 16, August 18, 1 4 pm. Each of the fifteen numbered questions is worth points. All questions will be graded, but your score for the examination will be the
Applied Mathematics Masters Examination Fall 16, August 18, 1 4 pm. Each of the fifteen numbered questions is worth points. All questions will be graded, but your score for the examination will be the
MATH 32A: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. sin 2 u du z(t) = sin 2 t + cos 2 2
 MATH 3A: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES 1. Curvature 1. Consider the curve r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t), where x(t) = t Find the curvature κ(t). 0 cos(u) sin(u) du y(t) = Solution: The formula for curvature is t
MATH 3A: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES 1. Curvature 1. Consider the curve r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t), where x(t) = t Find the curvature κ(t). 0 cos(u) sin(u) du y(t) = Solution: The formula for curvature is t
Quantifying Intermittent Transport in Cell Cytoplasm
 Quantifying Intermittent Transport in Cell Cytoplasm Ecole Normale Supérieure, Mathematics and Biology Department. Paris, France. May 19 th 2009 Cellular Transport Introduction Cellular Transport Intermittent
Quantifying Intermittent Transport in Cell Cytoplasm Ecole Normale Supérieure, Mathematics and Biology Department. Paris, France. May 19 th 2009 Cellular Transport Introduction Cellular Transport Intermittent
