Simple thermodynamic derivation of the electrocapillary equations
|
|
|
- Amanda Hutchinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This document is downloaded from the Digital Open Access Repository of VTT Title Simple thermodynamic derivation of the electrocapillary equations Author(s) Makkonen, Lasse Citation Surface Science. Elsevier. Vol. 635 (2015),Pages Date 2014 URL Rights Post-print version of the article. This article may be downloaded for personal use only. VTT P.O. box 1000 FI VTT Finland By using VTT Digital Open Access Repository you are bound by the following Terms & Conditions. I have read and I understand the following statement: This document is protected by copyright and other intellectual property rights, and duplication or sale of all or part of any of this document is not permitted, except duplication for research use or educational purposes in electronic or print form. You must obtain permission for any other use. Electronic or print copies may not be offered for sale.
2 Submitted to Surface Science (accepted) Simple thermodynamic derivation of the electrocapillary equations Lasse Makkonen VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Espoo, VTT, Finland Abstract Debate on the equations for surface excess stress and charge density on a solid continues in the literature. The various points of views are supported by complex mathematical argumentations. This hampers forming a unified understanding on the issue. To alleviate the situation, a concise but rigorous thermodynamic analysis is presented here. It shows that the Shuttleworth equation is invalid and the second Gokhshtein equation is incompatible with the thermodynamic formalism. The validity of the Lippman equation and the first Gokhshtein equation depends on the independent variable of the system. Keywords: Thermodynamics; Electrochemistry; Surface tension; Capillary phenomena; Residual stresses
3 1. Introduction Understanding on surface excess stress and surface excess charge density is fundamental in surface thermodynamics and electrochemistry. The so called Shuttleworth equation and the Gokhshtein equations are widely used for them. However, the validity of these relations has been frequently questioned and a very lively discussion on them is continuing, e.g. [1-5]. The points of views presented have been supported by extensive verbal and mathematical argumentation, making it difficult to comprehend the key aspects of the issue. The crucial aspects of the problem are, however, quite simple and need not be imbedded into an extensively complex presentation. The main problem related to derivations of the basic electrocapillary equations has been the wide-spread use of variables that are defined by dividing a total surface excess quantity by the surface area A. These include excess surface energy density defined by s = G/A, where G is the surface excess Gibbs energy, and surface excess charge density q s = Q/A, where Q is the surface excess charge. Numerous publications, starting from 1950, include inserting variables defined this way into the fundamental thermodynamic relations or the Maxwell relations. However, these definitions are incompatible with the mathematical structure of thermodynamics [6,7]. In the thermodynamic theory, an intensive property must be defined as a derivative of a state function with respect to an extensive property. Thus the variables used in connection with thermodynamic equations must be of the form = G/ A and q = dq/da. The erroneous nature of using variables defined as s and q s in a thermodynamic analysis of surfaces has been thoroughly discussed in the literature [7-12] but, nevertheless, many recent discussions still include this basic error. Simple calculus shows that X/Y equals dx/dy only when d(x/y) = 0. For the thermodynamic variables of a surface this means that (other extensive variables being constant) s /da= 0 and dq s /da= 0. These are serious
4 restrictions of the system. In particular, the former restriction, that the excess surface energy density is independent of surface area upon straining, requires that the material in question is a liquid. Here, the issue is clarified by deriving the relevant equations in a rigorous way by using only such definitions that comply with the mathematical theory of thermodynamics. 2. The thermodynamic relations When straining a liquid, molecules are lifted onto the surface causing an increase in the surface Gibbs energy. When straining of a solid, molecules are not lifted onto the surface in the same manner. Rather, distances between the molecules increase in the lateral direction, which causes an elastic stress, i.e. storing elastic energy. Therefore, in addition to the specific surface energy of creating new surface area, c = ( G A c e ) A, we need to define a specific surface elastic energy e = ( G A e ) Ns for the process where the surface area changes in such a way that the number of particles at the surface N s remains constant. Accordingly, here da e is the change in the surface area by elastic straining alone. The starting point of constructing a fundamental thermodynamic equation for a strained surface is the change in the surface Gibbs energy. For simplicity, we assume throughout this analysis that a one-species system and no changes in temperature or pressure, and no phase transitions. In the general case of straining, without a surface charge, the fundamental thermodynamic equation for the surface is dg = ( G A e ) Ns da + ( G N s ) A e dn s (1)
5 With the substitution of the definitions of the specific surface energy of creating new surface c and the surface chemical potential µ s, this is transformed into dg = e da e + µ s dn s (2) or dg = dg e + dg c (3) On the right hand side of eqs. (2) and (3), the first term represents the elastic energy stored in the moving the particles laterally further apart from each other, and the second term the excess energy brought by new particles moving perpendicularly onto the surface. The change in area due to increasing the number of particles at the surface is da c = (µ s / c )dn s, so that eq. (3) can also be written as dg = e da e + c da c (4) One can indeed postulate that there is a way to strain reversibly a soft solid in such a manner that the particles move both laterally and perpendicularly. In such a general case, eq. (4) would apply. However, such a complex situation is outside the scope of the ongoing dispute on the electrocapillary relations, and will not be discussed here. Accordingly, the cases of a liquid and a solid are considered below separately. Upon straining a liquid, dg e = 0 and dn s /da = c /µ s 0, Thus, for a liquid system, eq. (4) reads dg = c da (5) Hence, on a liquid, the work spent in creating new surface equals the mechanical work of straining.
6 Upon straining a solid, dg e = e da e 0 and dn s /da= 0. Thus, on a solid system, the mechanical work of straining arises solely from the elastic deformation and eq. (4) becomes dg = e da (6) The considerations above demonstrate that the independent variable upon straining a liquid is c, while upon straining a solid it is N s. This difference must be taken into account when considering the fundamental thermodynamic relations, as outlined above. The two cases represented by eqs. (5) and (6), are fundamentally different physical processes, where the operating force vectors are of different magnitude as well as direction. 3. The electrocapillary relations Next, we consider a solid surface with an electric charge. Due to the similar form of equations (5) and (6) we use, for simplicity, a common notation so that for an electrocapillary system involving a liquid = c, and for a solid electrode = e. As was demonstrated above, we need to know, prior to writing up the fundamental thermodynamic equation, which is the independent variable in the process. Thus, the process or experiment that is supposed to be described by the theory must determine the terms involved. The fundamental thermodynamic equation for a surface of a solid with a total excess surface charge Q and electric potential E includes an additional term related to the electric surface potential energy. In analogy with eq. (1), we may now consider what follows from taking either E or Q as the independent variable, i.e. the extensive variable of the thermodynamic equation.
7 If one follows [1,13] and takes the total excess surface charge Q as the independent variable, then the fundamental thermodynamic relation reads dg = da + EdQ (7) In writing up the thermodynamic relation (8), one assumes that q = ( Q A) = 0. The corresponding Maxwell relation is ( / Q) A = ( E/ A) Q (8) which is the first Gokhshtein equation. Considering that Q is the independent variable here, equation (8) may be valid e.g. for an experiment where an electrode is charged from an external circuit and disconnected, resulting in elastic elongation [1]. If one instead follows [3,14,15] and considers a system where E is the independent variable, then the corresponding fundamental thermodynamic relation must be written as dg = da - QdE (9) Note that eq. (9) is not a transform of eq. (7), but a fundamental thermodynamic relation for another system. In this system, E is the independent variable instead of Q. The Maxwell relation for eq. (9) is ( / E) A = - ( Q/ A) E (10) that equals ( / E) A = - q (11) which is the Lippman equation. Considering that E is independent variable here, equation (11) is valid e.g. for an experiment where elastic deformation is achieved by applying a
8 voltage to an ideally polarizable electrode, in which case only the cell voltage can be varied [3,16]. It should be stressed again that in case of a solid electrode, the variable in eqs. (8) and (11) equals e. In other words, regardless of the independent variable, the change in the surface energy of a solid electrode is due to an elastic deformation. 4. Discussion and conclusions The analysis above relies only on the definitions that are compatible with the mathematical structure of thermodynamics and specific to the system in question. No other useful fundamental surface electrocapillary equations can be deduced by a correct thermodynamic treatment. This outlines that the very extensive and complex attempts over more than six decades to derive such equations have unnecessarily complicated the issue. The problems in many of these developments have been confusing the modes of deformation on a liquid and on a solid, as well as including in the analysis variables that are incompatible with the thermodynamic theory. An example of such problems is that for a system (an unstrained solid) for which da e and dn s in eq. (1) are zero, a relation has been obtained by inserting G = G c = s A into a definition of surface stress = dg/da. This procedure formally results in the Shuttleworth equation = s + A( s /da), but includes three errors: 1) A definition of s = G/A that is incompatible with the thermodynamic theory, is used in a thermodynamic equation, 2) s is interpreted as c instead of e, i.e. liquid and solid systems are confused, and 3) A misleading illusion of a physical surface stress due to capillarity is created by separating the zero-term
9 = dg c /da = 0 into two non-zero terms. Detailed analysis of such terms [2] is irrelevant as long as their sum equals zero, i.e. the physical variable being analysed does not exist. The following conclusion can be made based on the analysis in this paper. The thermodynamic theory, eq. (6), shows no connection, on a solid, between the surface excess stress and specific surface energy of creating new surface c. Thus, the interpretation that the Shuttleworth equation provides such a relationship is invalid. Since the fundamental thermodynamic relation, eq. (7) requires that there is no dependence of the specific surface energy of a solid on the electric potential E, the second Gokhstein equation cannot be deduced from it. On the other hand, eq. (10) can be transformed into the second Gokhsthein equation only by introducing the variable q s which is incompatible with the mathematical theory of thermodynamics. The derivations leading to eqs. (8) and (11) show that the when the electric potential is an independent variable, the Lippman equation is valid. It follows that the first Gokhstein equation is valid only when the system is such that the total charge is an independent variable. Whether such systems exist is an issue of present dispute [1,3,16]. Acknowledgements This work was supported in part by the Academy of Finland grant no
10 References 1) A.Y. Gokhstein, On the simple check of electrocapillarity, J. Solid State Electrochem. 16 (2012) ) S. Fletcher, J., Surface thermodynamics reconsidered. Derivation of the Gokhstein relations from the Gibbs potential and a new approach to surface stress, J. Solid State Electrochem. (2014) DOI /s ) E.M. Gutman, Theoretical problems in solid electrocapillarity. J. Solid State Electrochem. (2014) DOI /s ) V.A. Marichev, A new view on the surface energy surface tension problem, Protect. Metals Phys. Chem. Surf. 48 (2012) ) V.A. Marichev, Surface energy and surface tension of condensed matter and the principle of minimum potential energy of systems, J. Solid State Electrochem. 16 (2012) ) R. Hermann, Geometry, Physics and Systems. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, ) D.J. Bottomley, L. Makkonen, K. Kolari, Incompatibility of the Shuttleworth equation with Hermann s mathematical structure of thermodynamics, Surf. Sci. 604 (2010) ) G. Láng, K.E. Heusler, J., Can the internal energy function of solid interfaces be of nonhomogeneous nature?, Electroanal. Chem. 472 (1999) ) E.M. Gutman, On the thermodynamic definition of surface stress, Phys. Cond. Matter 7 (1995) L ) D.J. Bottomley, L. Makkonen, K. Kolari, Reply to: Comment by P. Hecquet on: Incompatibility of the Shuttleworth equation with Hermann s mathematical structure of thermodynamics, Surf. Sci. 604 (2010)
11 11) L. Makkonen, Misinterpretation of the Shuttleworth equation, Scripta Mater. 66 (2012) ) L. Makkonen, Misconceptions of the relation between surface energy surface tension on a solid, Langmuir 30 (2014) ) A.Y. Gokhstein, Surface tension of solids and adsorption, Nauka, Moscow (in Russian), ) J. Proost, Thermodynamic issues associated with combined cyclic voltammetry and wafer curvature measurements in electrolytes, J Solid State Electrochem. 9 (2005) ) A.N. Frumkin, B.B. Damaskin, A.A. Survila, Congruence of the adsorption isotherm with respect to the electrode potential or charge and the choice of an independent electric variable J. Electroanal. Chem. 16 (1968) ) E.M. Gutman, Comments on On the simple check of electrocapillarity by A.Y. Gokhstein J. Solid State Electrochem. (2014) DOI /s z.
Surface thermodynamics reconsidered. Derivation of the Gokhshtein relations from the Gibbs potential and a new approach to surface stress
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Surface thermodynamics reconsidered. Derivation of the Gokhshtein relations from the Gibbs potential and a new approach to surface stress This item was
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Surface thermodynamics reconsidered. Derivation of the Gokhshtein relations from the Gibbs potential and a new approach to surface stress This item was
Counterintuitive results from Bayesian belief network software reliability model
 This document is downloaded from the Digital Open Access Repository of VTT Title Counterintuitive results from Bayesian belief network software reliability model Author(s) Tyrväinen, Tero Citation Research
This document is downloaded from the Digital Open Access Repository of VTT Title Counterintuitive results from Bayesian belief network software reliability model Author(s) Tyrväinen, Tero Citation Research
Electrocapillarity Behavior of Au(111) in SO 4 2- and F -
 Langmuir 2004, 20, 6639-6643 6639 Electrocapillarity Behavior of Au(111) in SO 4 2- and F - N. Vasiljevic, T. Trimble, N. Dimitrov, and K. Sieradzki* The Ira A. Fulton School of Engineering, Arizona State
Langmuir 2004, 20, 6639-6643 6639 Electrocapillarity Behavior of Au(111) in SO 4 2- and F - N. Vasiljevic, T. Trimble, N. Dimitrov, and K. Sieradzki* The Ira A. Fulton School of Engineering, Arizona State
Adsorption of tert-butanol at the electrode from concentrated NaClO 4
 Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 11(1) 213 8693 DOI: 1.2478/s11532121378 Central European Journal of Chemistry Adsorption of tertbutanol at the electrode from concentrated NaClO 4 Research Article Jolanta Nieszporek
Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 11(1) 213 8693 DOI: 1.2478/s11532121378 Central European Journal of Chemistry Adsorption of tertbutanol at the electrode from concentrated NaClO 4 Research Article Jolanta Nieszporek
This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail.
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Dunaevskiy, M. S.; Alekseev, P. A.;
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Dunaevskiy, M. S.; Alekseev, P. A.;
The thermodynamics of solid-solid interfaces in systems of fixed mass
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository The thermodynamics of solid-solid interfaces in systems of fixed mass This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an
Loughborough University Institutional Repository The thermodynamics of solid-solid interfaces in systems of fixed mass This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an
Comprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry
 Comprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry Volume 1: The Double Layer Edited by J. O'M. Bockris Texas A&M University College Station, Texas Brian E. Conway University of Ottawa Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
Comprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry Volume 1: The Double Layer Edited by J. O'M. Bockris Texas A&M University College Station, Texas Brian E. Conway University of Ottawa Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
Niiranen, Jarkko; Khakalo, Sergei; Balobanov, Viacheslav Strain gradient elasticity theories in lattice structure modelling
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Niiranen, Jarkko; Khakalo, Sergei;
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Niiranen, Jarkko; Khakalo, Sergei;
Direct Oil Recovery from Saturated Carbon Nanotube Sponges
 Supporting Information Direct Oil Recovery from Saturated Carbon Nanotube Sponges Xiying Li 1, Yahui Xue 1, Mingchu Zou 2, Dongxiao Zhang 3, Anyuan Cao 2,* 1, 4,*, and Huiling Duan 1 State Key Laboratory
Supporting Information Direct Oil Recovery from Saturated Carbon Nanotube Sponges Xiying Li 1, Yahui Xue 1, Mingchu Zou 2, Dongxiao Zhang 3, Anyuan Cao 2,* 1, 4,*, and Huiling Duan 1 State Key Laboratory
Thermally more durable electromechanical films by POSS nanomodification. Paajanen, Mika; Karttunen, Mikko; Kortet, Satu; Orko, Inka
 This document is downloaded from the Digital Open Access Repository of VTT Title Author(s) Thermally more durable electromechanical films by POSS nanomodification Paajanen, Mika; Karttunen, Mikko; Kortet,
This document is downloaded from the Digital Open Access Repository of VTT Title Author(s) Thermally more durable electromechanical films by POSS nanomodification Paajanen, Mika; Karttunen, Mikko; Kortet,
This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail.
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Singh, Deepak; Mökkönen, Kati; Poutala,
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Singh, Deepak; Mökkönen, Kati; Poutala,
Harju, A.; Sverdlov, V.A.; Nieminen, Risto; Halonen, V. Many-body wave function for a quantum dot in a weak magnetic field
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Harju, A.; Sverdlov, V.A.; Nieminen,
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Harju, A.; Sverdlov, V.A.; Nieminen,
Goals. The laboratory instructor has already purged the solutions of dissolved. Purging the from these solutions prevents spurious
 Goals 41 Cyclic Voltammetry XXGoals The goals of this experiment are to: Learn how to set up a screen-printed electrode Learn how to operate the Gamry potentiostat Determine the redox potential of potassium
Goals 41 Cyclic Voltammetry XXGoals The goals of this experiment are to: Learn how to set up a screen-printed electrode Learn how to operate the Gamry potentiostat Determine the redox potential of potassium
University of Huddersfield Repository
 University of Huddersfield Repository Leeungculsatien, Teerachai, Lucas, Gary and Zhao, Xin A numerical approach to determine the magnetic field distribution of an electromagnetic flow meter. Original
University of Huddersfield Repository Leeungculsatien, Teerachai, Lucas, Gary and Zhao, Xin A numerical approach to determine the magnetic field distribution of an electromagnetic flow meter. Original
Thermodynamics of Surfaces and Capillary Systems
 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING SERIES CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS SET Volume 7 Thermodynamics of Surfaces and Capillary Systems Michel Soustelle Thermodynamics of Surfaces and Capillary Systems Chemical Thermodynamics
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING SERIES CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS SET Volume 7 Thermodynamics of Surfaces and Capillary Systems Michel Soustelle Thermodynamics of Surfaces and Capillary Systems Chemical Thermodynamics
Gustafsson, Tom; Stenberg, Rolf; Videman, Juha A posteriori analysis of classical plate elements
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Gustafsson, Tom; Stenberg, Rolf;
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Gustafsson, Tom; Stenberg, Rolf;
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS ABSTRACT : P Mata1, AH Barbat1, S Oller1, R Boroschek2 1 Technical University of Catalonia, Civil Engineering
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS ABSTRACT : P Mata1, AH Barbat1, S Oller1, R Boroschek2 1 Technical University of Catalonia, Civil Engineering
Geometry explains the large difference in the elastic properties of fcc and hcp crystals of hard spheres Sushko, N.; van der Schoot, P.P.A.M.
 Geometry explains the large difference in the elastic properties of fcc and hcp crystals of hard spheres Sushko, N.; van der Schoot, P.P.A.M. Published in: Physical Review E DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.067104
Geometry explains the large difference in the elastic properties of fcc and hcp crystals of hard spheres Sushko, N.; van der Schoot, P.P.A.M. Published in: Physical Review E DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.067104
Chapter 2 Gibbs and Helmholtz Energies
 Chapter 2 Gibbs and Helmholtz Energies Abstract Some properties of the Gibbs and Helmholtz energies, two thermodynamic functions of utmost importance in chemistry especially for the study of the notion
Chapter 2 Gibbs and Helmholtz Energies Abstract Some properties of the Gibbs and Helmholtz energies, two thermodynamic functions of utmost importance in chemistry especially for the study of the notion
Solution Purging. Goals. 1. Purge both solutions with an inert gas (preferably N 2
 Goals 43 Cyclic Voltammetry XXGoals The goals of this experiment are to: Learn how to set up a screen-printed electrode Learn how to operate the Gamry potentiostat Determine the redox potential of potassium
Goals 43 Cyclic Voltammetry XXGoals The goals of this experiment are to: Learn how to set up a screen-printed electrode Learn how to operate the Gamry potentiostat Determine the redox potential of potassium
The Chemical Potential
 CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Fall 2017 The Chemical Potential Here we complete our pivot towards chemical thermodynamics with the introduction of the Chemical Potential ( ). This concept was first introduced
CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Fall 2017 The Chemical Potential Here we complete our pivot towards chemical thermodynamics with the introduction of the Chemical Potential ( ). This concept was first introduced
Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces
 Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
Tutorial on rate constants and reorganization energies
 www.elsevier.nl/locate/jelechem Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 483 (2000) 2 6 Tutorial on rate constants reorganization energies R.A. Marcus * Noyes Laboratory of Chemical Physics, MC 127-72, California
www.elsevier.nl/locate/jelechem Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 483 (2000) 2 6 Tutorial on rate constants reorganization energies R.A. Marcus * Noyes Laboratory of Chemical Physics, MC 127-72, California
Chapter 5. Chemical potential and Gibbs distribution
 Chapter 5 Chemical potential and Gibbs distribution 1 Chemical potential So far we have only considered systems in contact that are allowed to exchange heat, ie systems in thermal contact with one another
Chapter 5 Chemical potential and Gibbs distribution 1 Chemical potential So far we have only considered systems in contact that are allowed to exchange heat, ie systems in thermal contact with one another
Chemistry. Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations. NC State University
 Chemistry Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations NC State University Thermodynamic state functions expressed in differential form We have seen that the internal energy is conserved and depends on mechanical (dw)
Chemistry Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations NC State University Thermodynamic state functions expressed in differential form We have seen that the internal energy is conserved and depends on mechanical (dw)
ELECTROCHEMICAL SYSTEMS
 ELECTROCHEMICAL SYSTEMS Third Edition JOHN NEWMAN and KAREN E. THOMAS-ALYEA University of California, Berkeley ELECTROCHEMICAL SOCIETY SERIES WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC PUBLICATION PREFACE
ELECTROCHEMICAL SYSTEMS Third Edition JOHN NEWMAN and KAREN E. THOMAS-ALYEA University of California, Berkeley ELECTROCHEMICAL SOCIETY SERIES WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC PUBLICATION PREFACE
Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem
 CHAPTER 3 Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem 3.1 Introduction In the mathematical theory of elasticity, the principles of minimum potential energy and minimum complimentary energy are
CHAPTER 3 Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem 3.1 Introduction In the mathematical theory of elasticity, the principles of minimum potential energy and minimum complimentary energy are
Principles of Electrochemistry Second Edition
 Principles of Electrochemistry Second Edition Jiri Koryta Institute of Physiology, Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences, Prague HKJin Dvorak Department of Physical Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Charles University,
Principles of Electrochemistry Second Edition Jiri Koryta Institute of Physiology, Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences, Prague HKJin Dvorak Department of Physical Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Charles University,
1044 Lecture #14 of 18
 Lecture #14 of 18 1044 1045 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 13 main concepts: Section 1.2.3: Diffuse double layer structure Sections 13.1 & 13.2: Gibbs adsorption isotherm; Electrocapillary
Lecture #14 of 18 1044 1045 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 13 main concepts: Section 1.2.3: Diffuse double layer structure Sections 13.1 & 13.2: Gibbs adsorption isotherm; Electrocapillary
Courtesy of Marc De Graef. Used with permission.
 Courtesy of Marc De Graef. Used with permission. 3.01 PS 5 3.01 Issued: 10.31.04 Fall 005 Due: 10..04 1. Electrochemistry. a. What voltage is measured across the electrodes of a Zn/Cu Daniell galvanic
Courtesy of Marc De Graef. Used with permission. 3.01 PS 5 3.01 Issued: 10.31.04 Fall 005 Due: 10..04 1. Electrochemistry. a. What voltage is measured across the electrodes of a Zn/Cu Daniell galvanic
A MIXED ELECTRIC DOUBLE LAYER MODEL AT THE SOLID (LIQUID) / ELECTROLYTE INTERFACE
 A MIXED ELECTRIC DOUBLE LAYER MODEL AT THE SOLID (LIQUID) / ELECTROLYTE INTERFACE Gh. Semenescu*, C. Cioacă **, Gh. Potcovaru *** abstract. The tension surface defined by Gibbs in treating the interface
A MIXED ELECTRIC DOUBLE LAYER MODEL AT THE SOLID (LIQUID) / ELECTROLYTE INTERFACE Gh. Semenescu*, C. Cioacă **, Gh. Potcovaru *** abstract. The tension surface defined by Gibbs in treating the interface
Chapter 2 The Structure of the Metal-Solution Interface 2.1 Introduction: Spatial Separation of Electric Charge
 Chapter 2 The Structure of the Metal-Solution Interface 2.1 Introduction: Spatial Separation of Electric Charge The electrodeposition of metals or alloys occurs within a spatial region of finite thickness
Chapter 2 The Structure of the Metal-Solution Interface 2.1 Introduction: Spatial Separation of Electric Charge The electrodeposition of metals or alloys occurs within a spatial region of finite thickness
STEAMEST: A Software Tool for Estimation of Physical Properties of Water and Steam
 226 JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE, VOL. 4, NO. 3, MAY 2009 STEAMEST: A Software Tool for Estimation of Physical Properties of Water and Steam Muhammad Faheem Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Engineering
226 JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE, VOL. 4, NO. 3, MAY 2009 STEAMEST: A Software Tool for Estimation of Physical Properties of Water and Steam Muhammad Faheem Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Engineering
The fast dropping oil water electrode
 Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 464 (1999) 128 132 Short Communication The fast dropping oil water electrode Antonie Baars 1, Koichi Aoki *, Jun Watanabe Department of Applied Physics, Fukui Uni
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 464 (1999) 128 132 Short Communication The fast dropping oil water electrode Antonie Baars 1, Koichi Aoki *, Jun Watanabe Department of Applied Physics, Fukui Uni
This document is downloaded from the Digital Open Access Repository of VTT. P.O. box 1000 FI VTT Finland VTT
 This document is downloaded from the Digital Open Access Repository of VTT Title Determination of Temperature and Fuel Utilization Distributions in SOFC Stacks with EIS Author(s) Tallgren, Johan; Boigues
This document is downloaded from the Digital Open Access Repository of VTT Title Determination of Temperature and Fuel Utilization Distributions in SOFC Stacks with EIS Author(s) Tallgren, Johan; Boigues
On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer
 1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
18.13 Review & Summary
 5/2/10 10:04 PM Print this page 18.13 Review & Summary Temperature; Thermometers Temperature is an SI base quantity related to our sense of hot and cold. It is measured with a thermometer, which contains
5/2/10 10:04 PM Print this page 18.13 Review & Summary Temperature; Thermometers Temperature is an SI base quantity related to our sense of hot and cold. It is measured with a thermometer, which contains
The Liquid Vapor Interface
 Howard University Digital Howard @ Howard University Faculty Reprints 4-1-1932 The Liquid Vapor Interface Leon J. Shereshefsky Follow this and additional works at: http://dh.howard.edu/reprints Part of
Howard University Digital Howard @ Howard University Faculty Reprints 4-1-1932 The Liquid Vapor Interface Leon J. Shereshefsky Follow this and additional works at: http://dh.howard.edu/reprints Part of
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa.
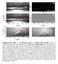 Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail.
 This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Goncharov, S.A.; Demyanova, A.S.; Gloukhov, Yu.A.; Danilov,
This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Goncharov, S.A.; Demyanova, A.S.; Gloukhov, Yu.A.; Danilov,
Physical Chemistry (A)
 S/N: 10421100-10421110 Classification: Specialized basic course Applicable to: Chemical Engineering and Technics Materials Science and Engineering Pharmaceutical Engineering Total Hours: 102 Credit Points:
S/N: 10421100-10421110 Classification: Specialized basic course Applicable to: Chemical Engineering and Technics Materials Science and Engineering Pharmaceutical Engineering Total Hours: 102 Credit Points:
BASICS OF ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIA
 BASICS OF ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIA BASICS OF ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIA BRIAN M. TISSUE Virginia Tech Department of Chemistry Blacksburg, VA Cover Design: Wiley Cover
BASICS OF ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIA BASICS OF ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIA BRIAN M. TISSUE Virginia Tech Department of Chemistry Blacksburg, VA Cover Design: Wiley Cover
The Free Energy of an Electrical Double Layer
 The Free Energy of an Electrical Double Layer DEREK Y. C. CHAN AND D. JOHN MITCHELL Department of Applied Mathematics, Research School of Physical Sciences, Australian National University, Canberra ACT
The Free Energy of an Electrical Double Layer DEREK Y. C. CHAN AND D. JOHN MITCHELL Department of Applied Mathematics, Research School of Physical Sciences, Australian National University, Canberra ACT
Generalized Wenzel equation for contact angle of droplets on spherical rough solid substrates
 Science Front Publishers Journal for Foundations and Applications of Physics, 3 (2), (2016) (sciencefront.org) ISSN 2394-3688 Generalized Wenzel equation for contact angle of droplets on spherical rough
Science Front Publishers Journal for Foundations and Applications of Physics, 3 (2), (2016) (sciencefront.org) ISSN 2394-3688 Generalized Wenzel equation for contact angle of droplets on spherical rough
On Relationship between PVT and Rheological Measurements of Polymer Melts
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 3, 2005 On Relationship between PVT and Rheological Measurements of Polymer Melts Tomas Sedlacek, Peter Filip 2, Peter Saha Polymer Centre, Faculty
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 3, 2005 On Relationship between PVT and Rheological Measurements of Polymer Melts Tomas Sedlacek, Peter Filip 2, Peter Saha Polymer Centre, Faculty
A NEW AND A SIMPLE MODEL FOR SURFACE TENSION PREDICTION OF WATER AND ORGANIC LIQUID MIXTURES * R. TAHERY AND H. MODARRESS **
 Iranian Journal of Science & Technology, Transaction B, Engineering, Vol. 29, No. B5 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 25 Shiraz University NE ND SIMPLE MODEL FOR SURFCE TENSION PREDICTION OF TER
Iranian Journal of Science & Technology, Transaction B, Engineering, Vol. 29, No. B5 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 25 Shiraz University NE ND SIMPLE MODEL FOR SURFCE TENSION PREDICTION OF TER
Harju, A.; Siljamäki, S.; Nieminen, Risto Wave function for quantum-dot ground states beyond the maximum-density droplet
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Harju, A.; Siljamäki, S.; ieminen,
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Harju, A.; Siljamäki, S.; ieminen,
Logical Kronecker delta deconstruction of the absolute value function and the treatment of absolute deviations
 Logical Kronecker delta deconstruction of the absolute value function and the treatment of absolute deviations Journal of Mathematical Chemistry ISSN 0259-9791 Volume 49 Number 3 J Math Chem (2010) 49:619-624
Logical Kronecker delta deconstruction of the absolute value function and the treatment of absolute deviations Journal of Mathematical Chemistry ISSN 0259-9791 Volume 49 Number 3 J Math Chem (2010) 49:619-624
Electrochemistry. in situ in situ. in situ. Key Words. electrochemical surface science. flame annealing and quenching method.
 in situ in situ in situ Key Words electrochemical surface science flame annealing and quenching method in situ in situ in situ not only but also in situ Q Q Q in situ δ q r in situ in situ et al in situ
in situ in situ in situ Key Words electrochemical surface science flame annealing and quenching method in situ in situ in situ not only but also in situ Q Q Q in situ δ q r in situ in situ et al in situ
1. Introduction. Jinyoung Chun and Jang H. Chun*,
 Korean Chem. Eng. Res., 54(6), 734-745 (2016) http://dx.doi.org/10.9713/kcer.2016.54.6.734 PISSN 0304-128X, EISSN 2233-9558 총설 Review on the Determination of Frumkin, Langmuir, and Temkin Adsorption Isotherms
Korean Chem. Eng. Res., 54(6), 734-745 (2016) http://dx.doi.org/10.9713/kcer.2016.54.6.734 PISSN 0304-128X, EISSN 2233-9558 총설 Review on the Determination of Frumkin, Langmuir, and Temkin Adsorption Isotherms
Physical Chemistry of Surfaces
 Physical Chemistry of Surfaces Fifth Edition ARTHUR W. ADAMSON Department of Chemistry, University of Southern California Los Angeles, California >) A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION John Wiley &. Sons,
Physical Chemistry of Surfaces Fifth Edition ARTHUR W. ADAMSON Department of Chemistry, University of Southern California Los Angeles, California >) A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION John Wiley &. Sons,
957 Lecture #13 of 18
 Lecture #13 of 18 957 958 Q: What was in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 2 main concepts: Section 2.1 : Section 2.3: Salt; Activity; Underpotential deposition Transference numbers; Liquid junction
Lecture #13 of 18 957 958 Q: What was in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 2 main concepts: Section 2.1 : Section 2.3: Salt; Activity; Underpotential deposition Transference numbers; Liquid junction
Reference Electrode Storage and Master Reference Electrodes
 Document #: DRP10031 (REV001 NOV 2016) Reference Electrode Storage and Master Reference Electrodes A Guide Detailing the Advantages and Setup of Master Reference Electrodes Pine Research Instrumentation
Document #: DRP10031 (REV001 NOV 2016) Reference Electrode Storage and Master Reference Electrodes A Guide Detailing the Advantages and Setup of Master Reference Electrodes Pine Research Instrumentation
CHEM Introduction to Thermodynamics Fall Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 CHEM2011.03 Introduction to Thermodynamics Fall 2003 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Introduction It is a matter of everyday observation that things tend to change in a certain direction.
CHEM2011.03 Introduction to Thermodynamics Fall 2003 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Introduction It is a matter of everyday observation that things tend to change in a certain direction.
Wave-Digital Polarity and Current Inverters and Their Application to Virtual Analog Audio Processing
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): D'Angelo, Stefano Title:
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): D'Angelo, Stefano Title:
V. Electrostatics. MIT Student
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
A New Linear Equation Relating Interfacial Tension of Mercury and. Isotension Potentials Describing Asymmetry in Electrocapillary Curves
 1 A New Linear Equation Relating Interfacial Tension of Mercury and Isotension Potentials Describing Asymmetry in Electrocapillary Curves - Dedicated to the polarographer, Prof. J. Heyrovsky* (Dec. 20,
1 A New Linear Equation Relating Interfacial Tension of Mercury and Isotension Potentials Describing Asymmetry in Electrocapillary Curves - Dedicated to the polarographer, Prof. J. Heyrovsky* (Dec. 20,
A Note on Powers in Finite Fields
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 11, 2018 A Note on Powers in Finite Fields Aabrandt, Andreas; Hansen, Vagn Lundsgaard Published in: International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jul 11, 2018 A Note on Powers in Finite Fields Aabrandt, Andreas; Hansen, Vagn Lundsgaard Published in: International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology
74HC General description. 2. Features. 3-to-8 line decoder, demultiplexer with address latches; inverting
 3-to-8 line decoder, demultiplexer with address latches; inverting Rev. 03 11 November 2004 Product data sheet 1. General description 2. Features The is a high-speed Si-gate CMOS device and is pin compatible
3-to-8 line decoder, demultiplexer with address latches; inverting Rev. 03 11 November 2004 Product data sheet 1. General description 2. Features The is a high-speed Si-gate CMOS device and is pin compatible
Decomposition of the point-dipole field into homogeneous and evanescent parts
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Setälä, Tero & Kaivola,
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Setälä, Tero & Kaivola,
Course Specification
 Al-Azhar University (Girls branch) Faculty of Science Department of Chemistry )فرع البنات( جامعة األزهر كلية العلوم قسم الكيمياء Course Specification Course title: Physical chemistry Code: chem. 468 Program(s)
Al-Azhar University (Girls branch) Faculty of Science Department of Chemistry )فرع البنات( جامعة األزهر كلية العلوم قسم الكيمياء Course Specification Course title: Physical chemistry Code: chem. 468 Program(s)
CHEM 235 Physical Chemistry II NJIT Spring Semester, 2016
 CHEM 235 Physical Chemistry II NJIT Spring Semester, 2016 Prerequisites: Textbook: Chem 231 or equivalent, Math 211 or 213, Phys 111 P. W. Atkins and J. de Paula Physical Chemistry 10th Edition, Freeman
CHEM 235 Physical Chemistry II NJIT Spring Semester, 2016 Prerequisites: Textbook: Chem 231 or equivalent, Math 211 or 213, Phys 111 P. W. Atkins and J. de Paula Physical Chemistry 10th Edition, Freeman
HS AP Chemistry Science
 Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 3 Week(s) 5 Week(s) 3 Week(s) Course Description AP Chemistry should meet the objectives of a good general chemistry course. Students should attain
Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 3 Week(s) 5 Week(s) 3 Week(s) Course Description AP Chemistry should meet the objectives of a good general chemistry course. Students should attain
HOMOGENEOUS CLOSED SYSTEM
 CHAE II A closed system is one that does not exchange matter with its surroundings, although it may exchange energy. W n in = 0 HOMOGENEOUS CLOSED SYSEM System n out = 0 Q dn i = 0 (2.1) i = 1, 2, 3,...
CHAE II A closed system is one that does not exchange matter with its surroundings, although it may exchange energy. W n in = 0 HOMOGENEOUS CLOSED SYSEM System n out = 0 Q dn i = 0 (2.1) i = 1, 2, 3,...
 Studies on the Coalescence o f Liqu Title Influence of the Polarizing Potenti Phases in Aqueous Solutions (Commem to Professor Rempei Gotoh On the Oc Author(s) Matsumoto, Mutsuo Citation Bulletin of the
Studies on the Coalescence o f Liqu Title Influence of the Polarizing Potenti Phases in Aqueous Solutions (Commem to Professor Rempei Gotoh On the Oc Author(s) Matsumoto, Mutsuo Citation Bulletin of the
 Title Super- and subcritical hydration of Thermodynamics of hydration Author(s) Matubayasi, N; Nakahara, M Citation JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS (2000), 8109 Issue Date 2000-05-08 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/50350
Title Super- and subcritical hydration of Thermodynamics of hydration Author(s) Matubayasi, N; Nakahara, M Citation JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS (2000), 8109 Issue Date 2000-05-08 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/50350
Wheatstone Bridge Nonlinearity
 Index: Nonlinearity Wheatstone Bridge Nonlinearity Introduction General Considerations The "Unbalanced" Circuit The Unbalanced Circuit Table of Contents Output & Nonlinearity with Various Bridge/Strain
Index: Nonlinearity Wheatstone Bridge Nonlinearity Introduction General Considerations The "Unbalanced" Circuit The Unbalanced Circuit Table of Contents Output & Nonlinearity with Various Bridge/Strain
Comment on Conjectures on exact solution of three-dimensional (3D) simple orthorhombic Ising lattices
 arxiv:0811.1802v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Nov 2008 Comment on Conectures on exact solution of three-dimensional (3D) simple orthorhombic Ising lattices Jacques H.H. Perk 145 Physical Sciences, Oklahoma
arxiv:0811.1802v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Nov 2008 Comment on Conectures on exact solution of three-dimensional (3D) simple orthorhombic Ising lattices Jacques H.H. Perk 145 Physical Sciences, Oklahoma
Electrochemical Properties of Materials for Electrical Energy Storage Applications
 Electrochemical Properties of Materials for Electrical Energy Storage Applications Lecture Note 3 October 11, 2013 Kwang Kim Yonsei Univ., KOREA kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 Y 88.91 8 O 16.00 7 N 14.01 34 Se
Electrochemical Properties of Materials for Electrical Energy Storage Applications Lecture Note 3 October 11, 2013 Kwang Kim Yonsei Univ., KOREA kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 Y 88.91 8 O 16.00 7 N 14.01 34 Se
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 102,
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 102, 014904 2007 Generation mechanism of residual direct current voltage in a liquid crystal display and its evaluation parameters related to liquid crystal and alignment layer
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 102, 014904 2007 Generation mechanism of residual direct current voltage in a liquid crystal display and its evaluation parameters related to liquid crystal and alignment layer
Theory of Charge Transport in Mixed Conductors: Description of Interfacial Contributions Compatible with the Gibbs Thermodynamics
 Theory of Charge Transport in Mixed Conductors: Description of Interfacial Contributions Compatible with the Gibbs Thermodynamics Mikhail A. Vorotyntsev LSEO-UMR 5188 CNRS, Université de Bourgogne, Dijon,
Theory of Charge Transport in Mixed Conductors: Description of Interfacial Contributions Compatible with the Gibbs Thermodynamics Mikhail A. Vorotyntsev LSEO-UMR 5188 CNRS, Université de Bourgogne, Dijon,
Elasticité de surface. P. Muller and A. Saul Surf. Sci Rep. 54, 157 (2004).
 Elasticité de surface P. Muller and A. Saul Surf. Sci Rep. 54, 157 (2004). The concept I Physical origin Definition Applications Surface stress and crystallographic parameter of small crystals Surface
Elasticité de surface P. Muller and A. Saul Surf. Sci Rep. 54, 157 (2004). The concept I Physical origin Definition Applications Surface stress and crystallographic parameter of small crystals Surface
Charles Cao. Growth. Properties. Bio-analytical Applications. Assembly. 226 Leigh hall. 20 nm
 Charles Cao (cao@chem.ufl.edu), 226 Leigh hall. 20 nm Growth Properties Assembly Bio-analytical Applications CHM 6154 (Spring, 2015) Chemical Separations Instructor: Charles Cao (cao@chem.ufl.edu), 226
Charles Cao (cao@chem.ufl.edu), 226 Leigh hall. 20 nm Growth Properties Assembly Bio-analytical Applications CHM 6154 (Spring, 2015) Chemical Separations Instructor: Charles Cao (cao@chem.ufl.edu), 226
Line adsorption in a mean-field density functional model
 Chemistry Physical & Theoretical Chemistry fields Okayama University Year 2006 Line adsorption in a mean-field density functional model Kenichiro Koga Benjamin Widom Okayama University, koga@cc.okayama-u.ac.jp
Chemistry Physical & Theoretical Chemistry fields Okayama University Year 2006 Line adsorption in a mean-field density functional model Kenichiro Koga Benjamin Widom Okayama University, koga@cc.okayama-u.ac.jp
Grading System Text Book
 CHEM 240 Who am I? Thermodynamic studies Course for Engineering Students Dr. Mohamed Abdel Salam Assistant Professor of Physical Chemistry King Abdul Aziz University Jeddah KSA PhD in Nano Chemistry, Canada
CHEM 240 Who am I? Thermodynamic studies Course for Engineering Students Dr. Mohamed Abdel Salam Assistant Professor of Physical Chemistry King Abdul Aziz University Jeddah KSA PhD in Nano Chemistry, Canada
CSCE 155N Fall Homework Assignment 2: Stress-Strain Curve. Assigned: September 11, 2012 Due: October 02, 2012
 CSCE 155N Fall 2012 Homework Assignment 2: Stress-Strain Curve Assigned: September 11, 2012 Due: October 02, 2012 Note: This assignment is to be completed individually - collaboration is strictly prohibited.
CSCE 155N Fall 2012 Homework Assignment 2: Stress-Strain Curve Assigned: September 11, 2012 Due: October 02, 2012 Note: This assignment is to be completed individually - collaboration is strictly prohibited.
Theory of Interfacial Tension of Partially Miscible Liquids
 Theory of Interfacial Tension of Partially Miscible Liquids M.-E. BOUDH-HIR and G.A. MANSOORI * University of Illinois at Chicago (M/C 063) Chicago, Illinois USA 60607-7052 Abstract The aim of this work
Theory of Interfacial Tension of Partially Miscible Liquids M.-E. BOUDH-HIR and G.A. MANSOORI * University of Illinois at Chicago (M/C 063) Chicago, Illinois USA 60607-7052 Abstract The aim of this work
 This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
CHAPTER 3 LECTURE NOTES 3.1. The Carnot Cycle Consider the following reversible cyclic process involving one mole of an ideal gas:
 CHATER 3 LECTURE NOTES 3.1. The Carnot Cycle Consider the following reversible cyclic process involving one mole of an ideal gas: Fig. 3. (a) Isothermal expansion from ( 1, 1,T h ) to (,,T h ), (b) Adiabatic
CHATER 3 LECTURE NOTES 3.1. The Carnot Cycle Consider the following reversible cyclic process involving one mole of an ideal gas: Fig. 3. (a) Isothermal expansion from ( 1, 1,T h ) to (,,T h ), (b) Adiabatic
Carbon nanotubes and conducting polymer composites
 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 4 Carbon nanotubes and conducting polymer composites May Tahhan University of Wollongong
University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 4 Carbon nanotubes and conducting polymer composites May Tahhan University of Wollongong
Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation
 Experiment Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation The CCLI Initiative Computers in Chemistry Laboratory Instruction The objectives of this experiment are to... LEARNING OBJECTIVES construct galvanic
Experiment Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation The CCLI Initiative Computers in Chemistry Laboratory Instruction The objectives of this experiment are to... LEARNING OBJECTIVES construct galvanic
3.5. Kinetic Approach for Isotherms
 We have arrived isotherm equations which describe adsorption from the two dimensional equation of state via the Gibbs equation (with a saturation limit usually associated with monolayer coverage). The
We have arrived isotherm equations which describe adsorption from the two dimensional equation of state via the Gibbs equation (with a saturation limit usually associated with monolayer coverage). The
Kettunen, Henrik & Wallén, Henrik & Sihvola, Ari Polarizability of a dielectric hemisphere
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Title: Kettunen, Henrik
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Title: Kettunen, Henrik
Polymer Physics MSE 458 / CHEM 482 Spring 2018
 Polymer Physics MSE 458 / CHEM 482 Spring 2018 Instructor: Prof. A.L. Ferguson 204 MSEB (217) 300-2354 alf@illinois.edu Grader: Class: Location: 4101 MSEB Time: 2:00 3:20 pm Days: T, Th Sections: A3 (CRN-38260)
Polymer Physics MSE 458 / CHEM 482 Spring 2018 Instructor: Prof. A.L. Ferguson 204 MSEB (217) 300-2354 alf@illinois.edu Grader: Class: Location: 4101 MSEB Time: 2:00 3:20 pm Days: T, Th Sections: A3 (CRN-38260)
CHEM465/865 Electrochemistry
 CHEM465/865 Electrochemistry Instructor: Dr. Michael Eikerling Office: C9034 Phone: 604-291-4463 e-mail: meikerl@sfu.ca Office hours (room C9034) : Friday: 1 2 pm Monday, Wednesday: 10:30 11:30 am Tutorials
CHEM465/865 Electrochemistry Instructor: Dr. Michael Eikerling Office: C9034 Phone: 604-291-4463 e-mail: meikerl@sfu.ca Office hours (room C9034) : Friday: 1 2 pm Monday, Wednesday: 10:30 11:30 am Tutorials
where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = atm L mol R = atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit)
 Ideal Gas Law PV = nrt where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = 0.0821 atm L mol 1 K 1 R = 0.0821 atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = 8.314 J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit) Standard molar volume = 22.4 L mol 1 at 0 C and
Ideal Gas Law PV = nrt where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = 0.0821 atm L mol 1 K 1 R = 0.0821 atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = 8.314 J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit) Standard molar volume = 22.4 L mol 1 at 0 C and
Contact, Adhesion and Rupture of Elastic Solids
 D. Maugis Contact, Adhesion and Rupture of Elastic Solids With 186 Figures Springer Contents г 1. Elements of Surface Physics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 3 1.2.1 The
D. Maugis Contact, Adhesion and Rupture of Elastic Solids With 186 Figures Springer Contents г 1. Elements of Surface Physics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 3 1.2.1 The
Apeiron, Vol. 8, No. 2, April
 Apeiron, Vol. 8, No. 2, April 2001 74 Is the Theory of Relativity Self-consistent? Reply by the author to the comment by Vladimir Onoochin on the paper Remarks about Correspondence of Relativity and Causality
Apeiron, Vol. 8, No. 2, April 2001 74 Is the Theory of Relativity Self-consistent? Reply by the author to the comment by Vladimir Onoochin on the paper Remarks about Correspondence of Relativity and Causality
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer The ns and nd Rydberg states of O-2 described by Hund's case (e) Citation for published version: Lefebvre-Brion, H & Ridley, T 2005, 'The ns and nd Rydberg states of O-2 described
Edinburgh Research Explorer The ns and nd Rydberg states of O-2 described by Hund's case (e) Citation for published version: Lefebvre-Brion, H & Ridley, T 2005, 'The ns and nd Rydberg states of O-2 described
CONDUCTOMETRIC TITRATIONS. Reading: 1. Skoog, Holler and Nieman: Chapter 22 A. INTRODUCTION. A.1 Classification of Electroanalytical Methods
 Reading: 1. Skoog, Holler and Nieman: Chapter 22 A. INTRODUCTION A.1 Classification of Electroanalytical Methods Electroanalytical methods are methods of analysis which rely on electrical properties of
Reading: 1. Skoog, Holler and Nieman: Chapter 22 A. INTRODUCTION A.1 Classification of Electroanalytical Methods Electroanalytical methods are methods of analysis which rely on electrical properties of
6 Adsorption on metal electrodes: principles
 6 Adsorption on metal electrodes: principles 6.1 Adsorption phenomena Whenever the concentration of a species at the interface is greater than can be accounted for by electrostatic interactions, we speak
6 Adsorption on metal electrodes: principles 6.1 Adsorption phenomena Whenever the concentration of a species at the interface is greater than can be accounted for by electrostatic interactions, we speak
2002 HSC Notes from the Marking Centre Geography
 2002 HSC Notes from the Marking Centre Geography 2003 Copyright Board of Studies NSW for and on behalf of the Crown in right of the State of New South Wales. This document contains Material prepared by
2002 HSC Notes from the Marking Centre Geography 2003 Copyright Board of Studies NSW for and on behalf of the Crown in right of the State of New South Wales. This document contains Material prepared by
Potentiodynamic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for solid state chemistry. G. A. Ragoisha and A. S. Bondarenko
 Preprint from Solid State Phenomena V.90-91(2003) (Proceedings of Solid State Chemistry 2002) Potentiodynamic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for solid state chemistry G. A. Ragoisha and A. S. Bondarenko
Preprint from Solid State Phenomena V.90-91(2003) (Proceedings of Solid State Chemistry 2002) Potentiodynamic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for solid state chemistry G. A. Ragoisha and A. S. Bondarenko
Thermodynamic expansion of nucleation free-energy barrier and size of critical nucleus near the vapor-liquid coexistence
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 110, NUMBER 7 15 FEBRUARY 1999 hermodynamic expansion of nucleation free-energy barrier and size of critical nucleus near the vapor-liquid coexistence Kenichiro Koga
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 110, NUMBER 7 15 FEBRUARY 1999 hermodynamic expansion of nucleation free-energy barrier and size of critical nucleus near the vapor-liquid coexistence Kenichiro Koga
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
 CHEM465/865, 24-3, Lecture 26-28, 19 th Nov., 24 Please, note the following error in the notes lecture19+2 (Hydrodynamic electrodes and Microelectrodes: on page two, 3 rd line, the correct expression for
CHEM465/865, 24-3, Lecture 26-28, 19 th Nov., 24 Please, note the following error in the notes lecture19+2 (Hydrodynamic electrodes and Microelectrodes: on page two, 3 rd line, the correct expression for
Observable Electric Potential and Electrostatic Potential in Electrochemical Systems
 658 J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 658-662 Observable Electric Potential and Electrostatic Potential in Electrochemical Systems Javier Garrido* and José A. Manzanares Departamento de Termodinámica, UniVersitat
658 J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 658-662 Observable Electric Potential and Electrostatic Potential in Electrochemical Systems Javier Garrido* and José A. Manzanares Departamento de Termodinámica, UniVersitat
Mind Association. Oxford University Press and Mind Association are collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Mind.
 Mind Association Response to Colyvan Author(s): Joseph Melia Source: Mind, New Series, Vol. 111, No. 441 (Jan., 2002), pp. 75-79 Published by: Oxford University Press on behalf of the Mind Association
Mind Association Response to Colyvan Author(s): Joseph Melia Source: Mind, New Series, Vol. 111, No. 441 (Jan., 2002), pp. 75-79 Published by: Oxford University Press on behalf of the Mind Association
Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation
 Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation LEARNING OBJECTIVES The objectives of this experiment are to... construct galvanic cells and develop an electrochemical series based on potential differences between
Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation LEARNING OBJECTIVES The objectives of this experiment are to... construct galvanic cells and develop an electrochemical series based on potential differences between
Vacuum Structure and Potential
 Vacuum Structure and Potential arxiv:0704.0131v1 [physics.gen-ph] 2 Apr 2007 J X Zheng-Johansson Institute of Fundamental Physics Research, 611 93 Nyköping, Sweden. March, 2007 Abstract Based on overall
Vacuum Structure and Potential arxiv:0704.0131v1 [physics.gen-ph] 2 Apr 2007 J X Zheng-Johansson Institute of Fundamental Physics Research, 611 93 Nyköping, Sweden. March, 2007 Abstract Based on overall
