Write and Apply Exponential and Power Functions
|
|
|
- Brianne Potter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TEKS 7.7 a., 2A..B, 2A..F Write and Apply Exponential and Power Functions Before You wrote linear, quadratic, and other polynomial functions. Now You will write exponential and power functions. Why? So you can model biology problems, as in Example 5. Key Vocabulary power function, In Chapter 2, you learned that two points determine a line. Similarly, two points determine an exponential curve. p. 428 exponential function, p. 478 E XAMPLE Write an exponential function Write an exponential function y 5 ab x whose graph passes through (, 2) and (, 08). STEP Substitute the coordinates of the two given points into y 5 ab x. 2 5 ab Substitute 2 for y and for x ab Substitute 08 for y and for x. STEP 2 Solve for a in the first equation to obtain a 5 2 } b, and substitute this expression for a in the second equation } b 2 b Substitute 2 } b for a in second equation b 2 Simplify. 95 b 2 Divide each side by 2. 5 b Take the positive square root because b > 0. STEP Determine that a 5 2 } b 5 2 } 5 4. So, y 5 4 p x. TRANSFORMING EXPONENTIAL DATA A set of more than two points (x, y) fits an exponential pattern if and only if the set of transformed points (x, ln y) fits a linear pattern. Graph of points (x, y) Graph of points (x, ln y) y 5 2 x s22, 4d s2, 2d 2 y (0, ) (, 2) x ln y 5 x(ln 2) ln y (0, 0) (, 0.69) (2, 20.69) x (22, 2.9) The graph is an exponential curve. The graph is a line. 7.7 Write and Apply Exponential and Power Functions 529
2 E XAMPLE 2 Find an exponential model SCOOTERS A store sells motor scooters. The table shows the number y of scooters sold during the xth year that the store has been open. Year, x Number of scooters sold, y Draw a scatter plot of the data pairs (x, ln y). Is an exponential model a good fit for the original data pairs (x, y)? Find an exponential model for the original data. STEP Use a calculator to create a table of data pairs (x, ln y). x ln y STEP 2 Plot the new points as shown. The points lie close to a line, so an exponential model should be a good fit for the original data. ln y (7, 4.56) USE POINT-SLOPE FORM Because the axes are x and ln y, the point-slope form is rewritten as ln y 2 y 5 m(x 2 x ). The slope of the line through (, 2.48) and (7, 4.56) is: } ø STEP Find an exponential model y 5 ab x by choosing two points on the line, such as (, 2.48) and (7, 4.56). Use these points to write an equation of the line. Then solve for y. ln y (x 2 ) ln y 5 0.5x 2. Equation of line Simplify. y5 e 0.5x 2. Exponentiate each side using base e. y5 e 2. (e 0.5 ) x Use properties of exponents. (, 2.48) x y5 8.4(.42) x Exponential model EXPONENTIAL REGRESSION A graphing calculator that performs exponential regression uses all of the original data to find the best-fitting model. E XAMPLE Use exponential regression SCOOTERS Use a graphing calculator to find an exponential model for the data in Example 2. Predict the number of scooters sold in the eighth year. Enter the original data into a graphing calculator and perform an exponential regression. The model is y (.42) x. Substituting x 5 8 (for year 8) into the model gives y (.42) 8 ø 40 scooters sold. ExpReg y=a*b^x a= b= Chapter 7 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
3 GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples, 2, and Write an exponential function y 5 ab x whose graph passes through the given points.. (, 6), (, 24) 2. (2, 8), (, 2). (, 8), (6, 64) 4. WHAT IF? In Examples 2 and, how would the exponential models change if the scooter sales were as shown in the table below? Year, x Number of scooters sold, y WRITING POWER FUNCTIONS Recall from Lesson 6. that a power function has the form y 5 ax b. Because there are only two constants (a and b), only two points are needed to determine a power curve through the points. E XAMPLE 4 Write a power function Write a power function y 5 ax b whose graph passes through (, 2) and (6, 9). STEP Substitute the coordinates of the two given points into y 5 ax b. 2 5 a p b Substitute 2 for y and for x. 9 5 a p 6 b Substitute 9 for y and 6 for x. STEP 2 Solve for a in the first equation to obtain a 5 } 2, and substitute this b expression for a in the second equation } b 2 6 b Substitute 2 } b p 2 b Simplify b Divide each side by 2. for a in second equation. log b Take log 2 of each side. log 4.5 } log 2 5 b Change-of-base formula 2.7 ø b Use a calculator. STEP Determine that a 5 2 } 2.7 ø So, y x2.7. GUIDED PRACTICE for Example 4 Write a power function y 5 ax b whose graph passes through the given points. 5. (2, ), (7, 6) 6. (, 4), (6, 5) 7. (5, 8), (0, 4) 8. REASONING Try using the method of Example 4 to find a power function whose graph passes through (, 5) and (, 7). What can you conclude? 7.7 Write and Apply Exponential and Power Functions 5
4 TRANSFORMING POWER DATA A set of more than two points (x, y) fits a power pattern if and only if the set of transformed points (ln x, ln y) fits a linear pattern. Graph of points (x, y) Graph of points (ln x, ln y) y y 5 x /2 (,.7) (6, 2.45) (4, 2) ln y ln y 5 ln x 2 (.9, 0.69) (, ) x (.79, 0.9) (., 0.55) (0, 0) 2 ln x The graph is a power curve. The graph is a line. E XAMPLE 5 Find a power model BIOLOGY The table at the right shows the typical wingspans x (in feet) and the typical weights y (in pounds) for several types of birds. Draw a scatter plot of the data pairs (ln x, ln y). Is a power model a good fit for the original data pairs (x, y)? Find a power model for the original data. STEP Use a calculator to create a table of data pairs (ln x, ln y). ln x ln y USE POINT-SLOPE FORM The slope of the line is } ø STEP 2 STEP Plot the new points as shown. The points lie close to a line, so a power model should be a good fit for the original data. Find a power model y 5 ax b by choosing two points on the line, such as (.227, 0.525) and (2.28, 2.774). Use these points to write an equation of the line. Then solve for y. ln y 2 y 5 m(ln x 2 x ) ln y (ln x ) ln y ln x ln y 5 ln x y5 e ln x y5 e ln x2.5 p e Product y x 2.5 Equation when axes are ln x and ln y Substitute. Simplify. Power property of logarithms Exponentiate each side using base e. of powers property Simplify. ln y (.227, 0.525) (2.28, 2.774) ln x 52 Chapter 7 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
5 POWER REGRESSION A graphing calculator that performs power regression uses all of the original data to find the best-fitting model. E XAMPLE 6 Use power regression BIOLOGY Use a graphing calculator to find a power model for the data in Example 5. Estimate the weight of a bird with a wingspan of 4.5 feet. Enter the original data into a graphing calculator and perform a power regression. The model is y x Substituting x into the model gives y (4.5) 2.87 ø. pounds. PwrReg y=a*x^b a= b= GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 5 and 6 9. The table below shows the atomic number x and the melting point y (in degrees Celsius) for the alkali metals. Find a power model for the data. Alkali metal Lithium Sodium Potassium Rubidium Cesium Atomic number, x Melting point, y EXERCISES SKILL PRACTICE HOMEWORK KEY 5 WORKED-OUT SOLUTIONS on p. WS for Exs., 2, and 5 TAKS PRACTICE AND REASONING Exs. 27,, 5, 7, and 8. VOCABULARY Copy and complete: Given a set of more than two data pairs (x, y), you can decide whether a(n)? function fits the data well by making a scatter plot of the points (x, ln y). 2. WRITING Explain how you can determine whether a power function is a good model for a set of data pairs (x, y). EXAMPLE on p. 529 for Exs. 0 EXAMPLE 2 on p. 50 for Exs. 4 WRITING EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS Write an exponential function y 5 ab x whose graph passes through the given points.. (, ), (2, 2) 4. (2, 24), (, 44) 5. (, ), (5, 4) 6. (, 27), (5, 24) 7. (, 2), (, 50) 8. (, 40), (, 640) 9. (2, 0), (4, 0.) 0. (2, 6.4), (5, 409.6) FINDING EXPONENTIAL MODELS Use the points (x, y) to draw a scatter plot of the points (x, ln y). Then find an exponential model for the data.. (, 8), (2, 6), (, 72), (4, 44), (5, 288) 2. (,.), (2, 0.), (, 0.6), (4, 92.7), (5, 280.9). (, 9.8), (2, 2.2), (, 5.2), (4, 9), (5, 2.8) 4. (,.4), (2, 6.7), (, 2.9), (4. 6.4), (5, 790.9) 7.7 Write and Apply Exponential and Power Functions 5
6 EXAMPLE 4 on p. 5 for Exs WRITING POWER FUNCTIONS Write a power function y 5 ax b whose graph passes through the given points. 5. (4, ), (8, 5) 6. (5, 9), (8, 4) 7. (2, ), (6, 2) 8. (, 4), (9, 44) 9. (4, 8), (8, 0) 20. (5, 0), (2, 8) 2. (4, 6.2), (7, 2) 22. (., 5), (6.8, 9.7) EXAMPLE 5 on p. 52 for Exs FINDING POWER MODELS Use the given points (x, y) to draw a scatter plot of the points (ln x, ln y). Then find a power model for the data. 2. (, 0.6), (2, 4.), (, 2.4), (4, 27), (5, 49.5) 24. (,.5), (2, 4.8), (, 9.5), (4, 5.4), (5, 22.) 25. (, 2.5), (2,.7), (, 4.7), (4, 5.5), (5, 6.2) 26. (, 0.8), (2, 0.99), (,.), (4,.2), (5,.29) 27. MULTIPLE TAKS REASONING CHOICE Which equation is equivalent to log y 5 2x? A y 5 0(00) x B y 5 0 x C y 5 e 2x D y 5 e 2 ERROR ANALYSIS Describe and correct the error in writing y as a function of x. 28. ln y 5 2x y 5 e 2x 29. ln y 5 ln x 2 2 ln y 5 ln x 2 2 ln x 2 2 y 5 e y 5 e 2x e y 5 (e 2 ) x e y 5 e ln x p e 22 y x 2.72 y 5 (x)(0.5) x 0. CHALLENGE Take the natural logarithm of both sides of the equations y 5 ab x and y 5 ax b. What are the slope and y-intercept of the line relating x and ln y for y 5 ab x? of the line relating ln x and ln y for y 5 ax b? PROBLEM SOLVING GRAPHING CALCULATOR You may wish to use a graphing calculator to complete the following Problem Solving exercises. EXAMPLES 2,, 5, and 6 on pp for Exs. 5. BIOLOGY Scientists use the circumference of an animal s femur to estimate the animal s weight. The table shows the femur circumference C (in millimeters) and the weight W (in kilograms) for several animals. Animal Giraffe Polar bear Lion Squirrel Otter C (mm) W (kg) a. Draw a scatter plot of the data pairs (ln C, ln W). b. Find a power model for the original data. c. Predict the weight of a cheetah if the circumference of its femur is 68.7 millimeters. 5 WORKED-OUT SOLUTIONS 54 Chapter 7 Exponential p. WS and Logarithmic Functions 5 TAKS PRACTICE AND REASONING
7 2. ASTRONOMY The table shows the mean distance x from the sun (in astronomical units) and the period y (in years) of six planets. Draw a scatter plot of the data pairs (ln x, ln y). Find a power model for the original data. Planet Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn x y SHORT TAKS REASONING RESPONSE The table shows the numbers of business and nonbusiness users of instant messaging for the years Years since Business users (in millions) Non-business users (in millions) a. Find an exponential model for the number of business users over time. b. Explain how to tell whether a linear, exponential, or power function best models the number of non-business users over time. Then find the bestfitting model. 4. MULTI-STEP PROBLEM The boiling point of water increases with atmospheric pressure. At sea level, where the atmospheric pressure is about 760 millimeters of mercury, water boils at 008C. The table shows the boiling point T of water (in degrees Celsius) for several different values of atmospheric pressure P (in millimeters of mercury). a. Graph Draw a scatter plot of the data pairs (ln P, ln T). b. Model Find a power model for the original data. c. Predict When the atmospheric pressure is 620 millimeters of mercury, at what temperature does water boil? P T EXTENDED TAKS REASONING RESPONSE Your visual near point is the closest point at which your eyes can see an object distinctly. Your near point moves farther away from you as you grow older. The diagram shows the near point y (in centimeters) at age x (in years). a. Graph Draw a scatter plot of the data pairs (x, ln y). b. Graph Draw a scatter plot of the data pairs (ln x, ln y). c. Interpret Based on your scatter plots, does an exponential function or a power function best fit the original data? Explain your reasoning. d. Model Based on your answer for part (c), write a model for the original data. Use your model to predict the near point for an 80-year-old person. 7.7 Write and Apply Exponential and Power Functions 55
8 6. CHALLENGE A doctor measures an astronaut s pulse rate y (in beats per minute) at various times x (in minutes) after the astronaut has finished exercising. The results are shown in the table. The astronaut s resting pulse rate is 70 beats per minute. Write an exponential model for the data. x y MIXED REVIEW FOR TAKS TAKS PRACTICE at classzone.com REVIEW Lesson 4.; TAKS Workbook 7. TAKS PRACTICE A poster is 8 inches taller than it is wide. The area of the poster is 84 square inches. Which equation can be used to find the width of the poster? TAKS Obj. 0 A x B x(x 8) 5 84 C x 2 (x 8) D x (x 8) 5 84 x x 8 REVIEW Lesson 2.; TAKS Workbook 8. TAKS PRACTICE Use the graph of y 52} x to solve the 4 equation for x when y 522. TAKS Obj. 4 F x 5 G x 5 4 H x 5 8 J x x y QUIZ for Lessons Solve the equation. Check for extraneous solutions. (p. 55). 2 x 5 6 x 2 2. e 2x x x log 4 (4x 7) 5 log 4 x 6. ln (x 2 2) 5 ln 6x 7. log x ln x log 2 (x 4) 5 5 Write an exponential function y 5 ab x whose graph passes through the given points. (p. 529) 0. (, 5), (2, 0). (, 4), (2, 2) 2. (2, 5), (, 45) Write a power function y 5 ax b whose graph passes through the given points. (p. 529). (4, 8), (9, 2) 4. (, 2), (0, 6) 5. (5, 4), (, 5) 6. BIOLOGY The average weight y (in kilograms) of an Atlantic cod from the Gulf of Maine can be modeled by y 5 0.5(.46) x where x is the age of the cod (in years). Estimate the age of a cod that weighs 5 kilograms. (p. 55) 56 Chapter 7 EXTRA Exponential PRACTICE and Logarithmic for Lesson Functions 7.7, p. 06 ONLINE QUIZ at classzone.com
Model Direct Variation. You wrote and graphed linear equations. You will write and graph direct variation equations.
 2.5 Model Direct Variation a.3, 2A.1.B, TEKS 2A.10.G Before Now You wrote and graphed linear equations. You will write and graph direct variation equations. Why? So you can model animal migration, as in
2.5 Model Direct Variation a.3, 2A.1.B, TEKS 2A.10.G Before Now You wrote and graphed linear equations. You will write and graph direct variation equations. Why? So you can model animal migration, as in
Modeling with Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 6.7. Essential Question How can you recognize polynomial, exponential, and logarithmic models?
 .7 Modeling with Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Essential Question How can ou recognize polnomial, eponential, and logarithmic models? Recognizing Different Tpes of Models Work with a partner. Match
.7 Modeling with Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Essential Question How can ou recognize polnomial, eponential, and logarithmic models? Recognizing Different Tpes of Models Work with a partner. Match
Solve Radical Equations
 6.6 Solve Radical Equations TEKS 2A.9.B, 2A.9.C, 2A.9.D, 2A.9.F Before Now You solved polynomial equations. You will solve radical equations. Why? So you can calculate hang time, as in Ex. 60. Key Vocabulary
6.6 Solve Radical Equations TEKS 2A.9.B, 2A.9.C, 2A.9.D, 2A.9.F Before Now You solved polynomial equations. You will solve radical equations. Why? So you can calculate hang time, as in Ex. 60. Key Vocabulary
Apply Properties of 1.1 Real Numbers
 TEKS Apply Properties of 1.1 Real Numbers a.1, a.6 Before Now You performed operations with real numbers. You will study properties of real numbers. Why? So you can order elevations, as in Ex. 58. Key
TEKS Apply Properties of 1.1 Real Numbers a.1, a.6 Before Now You performed operations with real numbers. You will study properties of real numbers. Why? So you can order elevations, as in Ex. 58. Key
Solve Exponential and Logarithmic Equations. You studied exponential and logarithmic functions. You will solve exponential and logarithmic equations.
 TEKS 7.6 Solve Exponential and Logarithmic Equations 2A..A, 2A..C, 2A..D, 2A..F Before Now You studied exponential and logarithmic functions. You will solve exponential and logarithmic equations. Why?
TEKS 7.6 Solve Exponential and Logarithmic Equations 2A..A, 2A..C, 2A..D, 2A..F Before Now You studied exponential and logarithmic functions. You will solve exponential and logarithmic equations. Why?
Graph Square Root and Cube Root Functions
 TEKS 6.5 2A.4.B, 2A.9.A, 2A.9.B, 2A.9.F Graph Square Root and Cube Root Functions Before You graphed polnomial functions. Now You will graph square root and cube root functions. Wh? So ou can graph the
TEKS 6.5 2A.4.B, 2A.9.A, 2A.9.B, 2A.9.F Graph Square Root and Cube Root Functions Before You graphed polnomial functions. Now You will graph square root and cube root functions. Wh? So ou can graph the
Solve Radical Equations
 6.6 Solve Radical Equations Before You solved polynomial equations. Now You will solve radical equations. Why? So you can calculate hang time, as in Ex. 60. Key Vocabulary radical equation extraneous solution,
6.6 Solve Radical Equations Before You solved polynomial equations. Now You will solve radical equations. Why? So you can calculate hang time, as in Ex. 60. Key Vocabulary radical equation extraneous solution,
Write Quadratic Functions and Models
 4.0 A..B, A.6.B, A.6.C, A.8.A TEKS Write Quadratic Functions and Models Before You wrote linear functions and models. Now You will write quadratic functions and models. Wh? So ou can model the cross section
4.0 A..B, A.6.B, A.6.C, A.8.A TEKS Write Quadratic Functions and Models Before You wrote linear functions and models. Now You will write quadratic functions and models. Wh? So ou can model the cross section
Evaluate and Simplify Algebraic Expressions
 TEKS 1.2 a.1, a.2, 2A.2.A, A.4.B Evaluate and Simplify Algebraic Expressions Before You studied properties of real numbers. Now You will evaluate and simplify expressions involving real numbers. Why? So
TEKS 1.2 a.1, a.2, 2A.2.A, A.4.B Evaluate and Simplify Algebraic Expressions Before You studied properties of real numbers. Now You will evaluate and simplify expressions involving real numbers. Why? So
You studied exponential growth and decay functions.
 TEKS 7. 2A.4.B, 2A..B, 2A..C, 2A..F Before Use Functions Involving e You studied eponential growth and deca functions. Now You will stud functions involving the natural base e. Wh? So ou can model visibilit
TEKS 7. 2A.4.B, 2A..B, 2A..C, 2A..F Before Use Functions Involving e You studied eponential growth and deca functions. Now You will stud functions involving the natural base e. Wh? So ou can model visibilit
68% 95% 99.7% x x 1 σ. x 1 2σ. x 1 3σ. Find a normal probability
 11.3 a.1, 2A.1.B TEKS Use Normal Distributions Before You interpreted probability distributions. Now You will study normal distributions. Why? So you can model animal populations, as in Example 3. Key
11.3 a.1, 2A.1.B TEKS Use Normal Distributions Before You interpreted probability distributions. Now You will study normal distributions. Why? So you can model animal populations, as in Example 3. Key
Add, Subtract, and Multiply Polynomials
 TEKS 5.3 a.2, 2A.2.A; P.3.A, P.3.B Add, Subtract, and Multiply Polynomials Before You evaluated and graphed polynomial functions. Now You will add, subtract, and multiply polynomials. Why? So you can model
TEKS 5.3 a.2, 2A.2.A; P.3.A, P.3.B Add, Subtract, and Multiply Polynomials Before You evaluated and graphed polynomial functions. Now You will add, subtract, and multiply polynomials. Why? So you can model
Use Scientific Notation
 8.4 Use Scientific Notation Before You used properties of exponents. Now You will read and write numbers in scientific notation. Why? So you can compare lengths of insects, as in Ex. 51. Key Vocabulary
8.4 Use Scientific Notation Before You used properties of exponents. Now You will read and write numbers in scientific notation. Why? So you can compare lengths of insects, as in Ex. 51. Key Vocabulary
Find Sums of Infinite Geometric Series
 a, AA; PB, PD TEKS Find Sums of Infinite Geometric Series Before You found the sums of finite geometric series Now You will find the sums of infinite geometric series Why? So you can analyze a fractal,
a, AA; PB, PD TEKS Find Sums of Infinite Geometric Series Before You found the sums of finite geometric series Now You will find the sums of infinite geometric series Why? So you can analyze a fractal,
Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions
 TEKS 7.4 2A.4.C, 2A..A, 2A..B, 2A..C Before Now Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions You evaluated and graphed eponential functions. You will evaluate logarithms and graph logarithmic functions.
TEKS 7.4 2A.4.C, 2A..A, 2A..B, 2A..C Before Now Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions You evaluated and graphed eponential functions. You will evaluate logarithms and graph logarithmic functions.
Solve Linear Systems Algebraically
 TEKS 3.2 a.5, 2A.3.A, 2A.3.B, 2A.3.C Solve Linear Systems Algebraically Before You solved linear systems graphically. Now You will solve linear systems algebraically. Why? So you can model guitar sales,
TEKS 3.2 a.5, 2A.3.A, 2A.3.B, 2A.3.C Solve Linear Systems Algebraically Before You solved linear systems graphically. Now You will solve linear systems algebraically. Why? So you can model guitar sales,
Solve Trigonometric Equations. Solve a trigonometric equation
 14.4 a.5, a.6, A..A; P.3.D TEKS Before Now Solve Trigonometric Equations You verified trigonometric identities. You will solve trigonometric equations. Why? So you can solve surface area problems, as in
14.4 a.5, a.6, A..A; P.3.D TEKS Before Now Solve Trigonometric Equations You verified trigonometric identities. You will solve trigonometric equations. Why? So you can solve surface area problems, as in
Analyze Geometric Sequences and Series
 23 a4, 2A2A; P4A, P4B TEKS Analyze Geometric Sequences and Series Before You studied arithmetic sequences and series Now You will study geometric sequences and series Why? So you can solve problems about
23 a4, 2A2A; P4A, P4B TEKS Analyze Geometric Sequences and Series Before You studied arithmetic sequences and series Now You will study geometric sequences and series Why? So you can solve problems about
Apply Properties of Logarithms. Let b, m, and n be positive numbers such that b Þ 1. m 1 log b. mn 5 log b. m }n 5 log b. log b.
 TEKS 7.5 a.2, 2A.2.A, 2A.11.C Apply Properties of Logarithms Before You evaluated logarithms. Now You will rewrite logarithmic epressions. Why? So you can model the loudness of sounds, as in E. 63. Key
TEKS 7.5 a.2, 2A.2.A, 2A.11.C Apply Properties of Logarithms Before You evaluated logarithms. Now You will rewrite logarithmic epressions. Why? So you can model the loudness of sounds, as in E. 63. Key
Solve Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
 TEKS 1.7 a.1, a.2, a.5, 2A.2.A Solve Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities Before You solved linear equations and inequalities. Now You will solve absolute value equations and inequalities. Why? So
TEKS 1.7 a.1, a.2, a.5, 2A.2.A Solve Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities Before You solved linear equations and inequalities. Now You will solve absolute value equations and inequalities. Why? So
You evaluated powers. You will simplify expressions involving powers. Consider what happens when you multiply two powers that have the same base:
 TEKS.1 a.1, 2A.2.A Before Now Use Properties of Eponents You evaluated powers. You will simplify epressions involving powers. Why? So you can compare the volumes of two stars, as in Eample. Key Vocabulary
TEKS.1 a.1, 2A.2.A Before Now Use Properties of Eponents You evaluated powers. You will simplify epressions involving powers. Why? So you can compare the volumes of two stars, as in Eample. Key Vocabulary
Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas
 TEKS 9.2 a.5, 2A.5.B, 2A.5.C Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas that open up or down. Now You will graph and write equations of parabolas that open
TEKS 9.2 a.5, 2A.5.B, 2A.5.C Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas that open up or down. Now You will graph and write equations of parabolas that open
Represent Relations and Functions
 TEKS. a., a., a.5, A..A Represent Relations and Functions Before You solved linear equations. Now You will represent relations and graph linear functions. Wh? So ou can model changes in elevation, as in
TEKS. a., a., a.5, A..A Represent Relations and Functions Before You solved linear equations. Now You will represent relations and graph linear functions. Wh? So ou can model changes in elevation, as in
Perform Basic Matrix Operations
 TEKS 3.5 a.1, a. Perform Basic Matrix Operations Before You performed operations with real numbers. Now You will perform operations with matrices. Why? So you can organize sports data, as in Ex. 34. Key
TEKS 3.5 a.1, a. Perform Basic Matrix Operations Before You performed operations with real numbers. Now You will perform operations with matrices. Why? So you can organize sports data, as in Ex. 34. Key
Define General Angles and Use Radian Measure
 1.2 a.1, a.4, a.5; P..E TEKS Define General Angles and Use Radian Measure Before You used acute angles measured in degrees. Now You will use general angles that ma be measured in radians. Wh? So ou can
1.2 a.1, a.4, a.5; P..E TEKS Define General Angles and Use Radian Measure Before You used acute angles measured in degrees. Now You will use general angles that ma be measured in radians. Wh? So ou can
Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
 TEKS 4. 2A.4.A, 2A.4.B, 2A.6.B, 2A.8.A Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Before You graphed linear functions. Now You will graph quadratic functions. Wh? So ou can model sports revenue, as in
TEKS 4. 2A.4.A, 2A.4.B, 2A.6.B, 2A.8.A Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Before You graphed linear functions. Now You will graph quadratic functions. Wh? So ou can model sports revenue, as in
A linear inequality in one variable can be written in one of the following forms, where a and b are real numbers and a Þ 0:
 TEKS.6 a.2, a.5, A.7.A, A.7.B Solve Linear Inequalities Before You solved linear equations. Now You will solve linear inequalities. Why? So you can describe temperature ranges, as in Ex. 54. Key Vocabulary
TEKS.6 a.2, a.5, A.7.A, A.7.B Solve Linear Inequalities Before You solved linear equations. Now You will solve linear inequalities. Why? So you can describe temperature ranges, as in Ex. 54. Key Vocabulary
UNIT 14 Exponents. Scientific Notation
 Unit 14 CCM6+/7+ Page 1 UNIT 14 Exponents and Scientific Notation CCM6+/7+ Name Math Teacher Projected Test Date Main Ideas Page(s) Unit 14 Vocabulary 2 Exponent Basics, Zero & Negative Exponents 3 6 Multiplying,
Unit 14 CCM6+/7+ Page 1 UNIT 14 Exponents and Scientific Notation CCM6+/7+ Name Math Teacher Projected Test Date Main Ideas Page(s) Unit 14 Vocabulary 2 Exponent Basics, Zero & Negative Exponents 3 6 Multiplying,
Solve Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
 10.5 Solve Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square Before You solved quadratic equations by finding square roots. Now You will solve quadratic equations by completing the square. Why? So you can solve
10.5 Solve Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square Before You solved quadratic equations by finding square roots. Now You will solve quadratic equations by completing the square. Why? So you can solve
Factor and Solve Polynomial Equations. In Chapter 4, you learned how to factor the following types of quadratic expressions.
 TEKS 5.4 2A.1.A, 2A.2.A; P..A, P..B Factor and Solve Polynomial Equations Before You factored and solved quadratic equations. Now You will factor and solve other polynomial equations. Why? So you can find
TEKS 5.4 2A.1.A, 2A.2.A; P..A, P..B Factor and Solve Polynomial Equations Before You factored and solved quadratic equations. Now You will factor and solve other polynomial equations. Why? So you can find
Graph and Write Equations of Circles
 TEKS 9.3 a.5, A.5.B Graph and Write Equations of Circles Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas. Now You will graph and write equations of circles. Wh? So ou can model transmission ranges,
TEKS 9.3 a.5, A.5.B Graph and Write Equations of Circles Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas. Now You will graph and write equations of circles. Wh? So ou can model transmission ranges,
Graph Simple Rational Functions. is a rational function. The graph of this function when a 5 1 is shown below.
 TEKS 8.2 2A.0.A, 2A.0.B, 2A.0.C, 2A.0.F Graph Simple Rational Functions Before You graphed polnomial functions. Now You will graph rational functions. Wh? So ou can find average monthl costs, as in E.
TEKS 8.2 2A.0.A, 2A.0.B, 2A.0.C, 2A.0.F Graph Simple Rational Functions Before You graphed polnomial functions. Now You will graph rational functions. Wh? So ou can find average monthl costs, as in E.
Properties of the Graph of a Quadratic Function. has a vertex with an x-coordinate of 2 b } 2a
 0.2 Graph 5 a 2 b c Before You graphed simple quadratic functions. Now You will graph general quadratic functions. Wh? So ou can investigate a cable s height, as in Eample 4. Ke Vocabular minimum value
0.2 Graph 5 a 2 b c Before You graphed simple quadratic functions. Now You will graph general quadratic functions. Wh? So ou can investigate a cable s height, as in Eample 4. Ke Vocabular minimum value
Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses. You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses.
 TEKS 9.4 a.5, A.5.B, A.5.C Before Now Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses. Wh? So ou can model
TEKS 9.4 a.5, A.5.B, A.5.C Before Now Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses. Wh? So ou can model
Words Algebra Graph. 5 rise } run. } x2 2 x 1. m 5 y 2 2 y 1. slope. Find slope in real life
 TEKS 2.2 a.1, a.4, a.5 Find Slope and Rate of Change Before You graphed linear functions. Now You will find slopes of lines and rates of change. Wh? So ou can model growth rates, as in E. 46. Ke Vocabular
TEKS 2.2 a.1, a.4, a.5 Find Slope and Rate of Change Before You graphed linear functions. Now You will find slopes of lines and rates of change. Wh? So ou can model growth rates, as in E. 46. Ke Vocabular
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Polynomial and Rational Functions Figure 1 5-mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largely obsolete by digital photography. (credit film : modification of work by
Polynomial and Rational Functions Figure 1 5-mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largely obsolete by digital photography. (credit film : modification of work by
Graph Linear Inequalities in Two Variables. You solved linear inequalities in one variable. You will graph linear inequalities in two variables.
 TEKS.8 a.5 Before Now Graph Linear Inequalities in Two Variables You solved linear inequalities in one variable. You will graph linear inequalities in two variables. Wh? So ou can model data encoding,
TEKS.8 a.5 Before Now Graph Linear Inequalities in Two Variables You solved linear inequalities in one variable. You will graph linear inequalities in two variables. Wh? So ou can model data encoding,
Activity Overview. Background. Concepts. Kepler s Third Law
 By Michele Impedovo Grade level: secondary (Years 10-12) Subject: mathematics Time required: 2 hours Activity Overview Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) is remembered for laying firm mathematical foundations
By Michele Impedovo Grade level: secondary (Years 10-12) Subject: mathematics Time required: 2 hours Activity Overview Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) is remembered for laying firm mathematical foundations
10.7. Interpret the Discriminant. For Your Notebook. x5 2b 6 Ï} b 2 2 4ac E XAMPLE 1. Use the discriminant KEY CONCEPT
 10.7 Interpret the Discriminant Before You used the quadratic formula. Now You will use the value of the discriminant. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about gmnastics, as in E. 49. Ke Vocabular discriminant
10.7 Interpret the Discriminant Before You used the quadratic formula. Now You will use the value of the discriminant. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about gmnastics, as in E. 49. Ke Vocabular discriminant
Modeling with Polynomial Functions. Writing a Cubic Function. Write the cubic function whose graph is shown at the right.
 Page 1 of 7 E X P L O R I N G D ATA A N D S TAT I S T I C S 6.9 What you should learn GOAL 1 Use finite differences to determine the degree of a polynomial function that will fit a set of data. GOAL 2
Page 1 of 7 E X P L O R I N G D ATA A N D S TAT I S T I C S 6.9 What you should learn GOAL 1 Use finite differences to determine the degree of a polynomial function that will fit a set of data. GOAL 2
proportion, p. 163 cross product, p. 168 scale drawing, p. 170
 REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY classzone.com Multi-Language Glossary Vocabulary practice inverse operations, p. 14 equivalent equations, p. 14 identity, p. 156 ratio, p. 162 proportion, p. 16 cross product, p.
REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY classzone.com Multi-Language Glossary Vocabulary practice inverse operations, p. 14 equivalent equations, p. 14 identity, p. 156 ratio, p. 162 proportion, p. 16 cross product, p.
Use slope and y-intercept to write an equation. Write an equation of the line with a slope of 1 } 2. Write slope-intercept form.
 5.1 Study Guide For use with pages 282 291 GOAL Write equations of lines. EXAMPLE 1 Use slope and y-intercept to write an equation Write an equation of the line with a slope of 1 } 2 and a y-intercept
5.1 Study Guide For use with pages 282 291 GOAL Write equations of lines. EXAMPLE 1 Use slope and y-intercept to write an equation Write an equation of the line with a slope of 1 } 2 and a y-intercept
Solve Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables
 TEKS 3.4 a.5, 2A.3.A, 2A.3.B, 2A.3.C Solve Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables Before You solved systems of equations in two variables. Now You will solve systems of equations in three variables.
TEKS 3.4 a.5, 2A.3.A, 2A.3.B, 2A.3.C Solve Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables Before You solved systems of equations in two variables. Now You will solve systems of equations in three variables.
Solving Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities. The distance between. 0 and itself is 0, so 0 0.
 1.7 Solving Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities What you should learn GOAL 1 Solve absolute value equations and inequalities. GOAL 2 Use absolute value equations and inequalities to solve real-life
1.7 Solving Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities What you should learn GOAL 1 Solve absolute value equations and inequalities. GOAL 2 Use absolute value equations and inequalities to solve real-life
Ms. Campos Math 8 Unit 11 Scientific Notation
 Ms. Campos Math 8 Unit 11 Scientific Notation 2017-2018 Date Lesson Topic Homework T 3 3/15 1 Introduction to Scientific Notation Lesson 1 Page 4 F 4 3/16 2 Converting Scientific Notation Lesson 2 Page
Ms. Campos Math 8 Unit 11 Scientific Notation 2017-2018 Date Lesson Topic Homework T 3 3/15 1 Introduction to Scientific Notation Lesson 1 Page 4 F 4 3/16 2 Converting Scientific Notation Lesson 2 Page
LESSON 13.1 NONLINEAR EQUATIONS
 LESSON. NONLINEAR EQUATIONS LESSON. NONLINEAR EQUATIONS 58 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Solving Equations a. Solving polynomial equations by factoring b. Solving quadratic type equations
LESSON. NONLINEAR EQUATIONS LESSON. NONLINEAR EQUATIONS 58 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Solving Equations a. Solving polynomial equations by factoring b. Solving quadratic type equations
Writing Scientific Notation ACTIVITY: Finding ph Levels. How can you write a number in. scientific notation?
 10.6 Writing Scientific Notation scientific notation? How can you write a number in 1 ACTIVITY: Finding ph Levels Work with a partner. In chemistry, ph is a measure of the activity of dissolved hydrogen
10.6 Writing Scientific Notation scientific notation? How can you write a number in 1 ACTIVITY: Finding ph Levels Work with a partner. In chemistry, ph is a measure of the activity of dissolved hydrogen
Lesson 4 Linear Functions and Applications
 In this lesson, we take a close look at Linear Functions and how real world situations can be modeled using Linear Functions. We study the relationship between Average Rate of Change and Slope and how
In this lesson, we take a close look at Linear Functions and how real world situations can be modeled using Linear Functions. We study the relationship between Average Rate of Change and Slope and how
date: math analysis 2 chapter 18: curve fitting and models
 name: period: date: math analysis 2 mr. mellina chapter 18: curve fitting and models Sections: 18.1 Introduction to Curve Fitting; the Least-Squares Line 18.2 Fitting Exponential Curves 18.3 Fitting Power
name: period: date: math analysis 2 mr. mellina chapter 18: curve fitting and models Sections: 18.1 Introduction to Curve Fitting; the Least-Squares Line 18.2 Fitting Exponential Curves 18.3 Fitting Power
2275 Speedway, Mail Code C9000 Austin, TX (512) Planet Fun
 Lesson Plan for Grades: Middle School Length of Lesson: 70 min Authored by: UT Environmental Science Institute Date created: 12/03/2016 Subject area/course: Mathematics, Astronomy, and Space Materials:
Lesson Plan for Grades: Middle School Length of Lesson: 70 min Authored by: UT Environmental Science Institute Date created: 12/03/2016 Subject area/course: Mathematics, Astronomy, and Space Materials:
MOTITHANG HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL THIMPHU THROMDE Every child is inspired to learn and empowered with wisdom to excel in life MIDTERM EXAMINATION-2018
 MOTITHANG HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL THIMPHU THROMDE Every child is inspired to learn and empowered with wisdom to excel in life MIDTERM EXAMINATION-2018 Mathematics Reading Time: 15 mins Class: IX Writing
MOTITHANG HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL THIMPHU THROMDE Every child is inspired to learn and empowered with wisdom to excel in life MIDTERM EXAMINATION-2018 Mathematics Reading Time: 15 mins Class: IX Writing
Classroom Assessments Based on Standards Integrated College Prep I Unit 3 CP 103A
 Classroom Assessments Based on Standards Integrated College Prep I Unit 3 CP 103A Name: ID Number: Teacher Name: Score: Proficient: yes no How Tall Can He Be? The table below shows the average height in
Classroom Assessments Based on Standards Integrated College Prep I Unit 3 CP 103A Name: ID Number: Teacher Name: Score: Proficient: yes no How Tall Can He Be? The table below shows the average height in
You analyzed parent functions and their families of graphs. (Lesson 1-5)
 You analyzed parent functions and their families of graphs. (Lesson 1-5) Graph and analyze power functions. Graph and analyze radical functions, and solve radical equations. power function monomial function
You analyzed parent functions and their families of graphs. (Lesson 1-5) Graph and analyze power functions. Graph and analyze radical functions, and solve radical equations. power function monomial function
You identified, graphed, and described several parent functions. (Lesson 1-5)
 You identified, graphed, and described several parent functions. (Lesson 1-5) Evaluate, analyze, and graph exponential functions. Solve problems involving exponential growth and decay. algebraic function
You identified, graphed, and described several parent functions. (Lesson 1-5) Evaluate, analyze, and graph exponential functions. Solve problems involving exponential growth and decay. algebraic function
Exponential Growth and Decay Functions (Exponent of t) Read 6.1 Examples 1-3
 CC Algebra II HW #42 Name Period Row Date Section 6.1 1. Vocabulary In the eponential growth model Eponential Growth and Decay Functions (Eponent of t) Read 6.1 Eamples 1-3 y = 2.4(1.5), identify the initial
CC Algebra II HW #42 Name Period Row Date Section 6.1 1. Vocabulary In the eponential growth model Eponential Growth and Decay Functions (Eponent of t) Read 6.1 Eamples 1-3 y = 2.4(1.5), identify the initial
2.5 Justify a Number Trick
 Investigating g Geometry ACTIVITY Use before Lesson 2.5 2.5 Justify a Number Trick MATERIALS paper pencil QUESTION How can you use algebra to justify a number trick? Number tricks can allow you to guess
Investigating g Geometry ACTIVITY Use before Lesson 2.5 2.5 Justify a Number Trick MATERIALS paper pencil QUESTION How can you use algebra to justify a number trick? Number tricks can allow you to guess
Analyzing Lines of Fit
 4.5 Analyzing Lines of Fit Essential Question How can you analytically find a line of best fit for a scatter plot? Finding a Line of Best Fit Work with a partner. The scatter plot shows the median ages
4.5 Analyzing Lines of Fit Essential Question How can you analytically find a line of best fit for a scatter plot? Finding a Line of Best Fit Work with a partner. The scatter plot shows the median ages
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt McDougal Algebra 2
 4-5 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Solve. 1. log 16 x = 3 2 64 2. log x 1.331 = 3 1.1 3. log10,000 = x 4 Objectives Solve exponential and logarithmic equations and equalities.
4-5 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Solve. 1. log 16 x = 3 2 64 2. log x 1.331 = 3 1.1 3. log10,000 = x 4 Objectives Solve exponential and logarithmic equations and equalities.
a factors The exponential 0 is a special case. If b is any nonzero real number, then
 0.1 Exponents The expression x a is an exponential expression with base x and exponent a. If the exponent a is a positive integer, then the expression is simply notation that counts how many times the
0.1 Exponents The expression x a is an exponential expression with base x and exponent a. If the exponent a is a positive integer, then the expression is simply notation that counts how many times the
3.4. Properties of Logarithmic Functions
 310 CHAPTER 3 Eponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic Functions What you ll learn about Properties of Logarithms Change of Base Graphs of Logarithmic Functions with
310 CHAPTER 3 Eponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic Functions What you ll learn about Properties of Logarithms Change of Base Graphs of Logarithmic Functions with
The activities below cover LO1: Be able to apply the principles of good laboratory practice. Associated files:
 Unit R074 How scientists use analytical techniques to collect data Interpreting evidence and suggesting conclusions Instructions and answers for teachers The activities below cover LO1: Be able to apply
Unit R074 How scientists use analytical techniques to collect data Interpreting evidence and suggesting conclusions Instructions and answers for teachers The activities below cover LO1: Be able to apply
Warm-up: 1) A craft shop sells canvasses in a variety of sizes. The table below shows the area and price of each canvas type.
 Name Date: Lesson 10-3: Correlation Coefficient & Making Predictions Learning Goals: #3: How do we use the line of best fit to make predictions about our data? What does it mean to extrapolate? Warm-up:
Name Date: Lesson 10-3: Correlation Coefficient & Making Predictions Learning Goals: #3: How do we use the line of best fit to make predictions about our data? What does it mean to extrapolate? Warm-up:
Unit 5. Linear equations and inequalities OUTLINE. Topic 13: Solving linear equations. Topic 14: Problem solving with slope triangles
 Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Solving and Graphing Linear Inequalities 66.1 Solve Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction
 Solving and Graphing Linear Inequalities 66.1 Solve Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction 6.2 Solve Inequalities Using Multiplication and Division 6.3 Solve Multi-Step Inequalities 6.4 Solve Compound
Solving and Graphing Linear Inequalities 66.1 Solve Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction 6.2 Solve Inequalities Using Multiplication and Division 6.3 Solve Multi-Step Inequalities 6.4 Solve Compound
3.1 Notes for Lines and Linear Growth: What does a constant rate mean?
 3.1 Notes for Lines and Linear Growth: What does a constant rate mean? Key concept: A function is called _Linear_ if it has a _Constant growth rate You take notes and put in your own words. What is positive
3.1 Notes for Lines and Linear Growth: What does a constant rate mean? Key concept: A function is called _Linear_ if it has a _Constant growth rate You take notes and put in your own words. What is positive
3.4 Properties of Logarithmic Functions
 SECTION 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic Functions 283 What you ll learn about Properties of Logarithms Change of Base Graphs of Logarithmic Functions with Base b Re-expressing Data... and why The applications
SECTION 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic Functions 283 What you ll learn about Properties of Logarithms Change of Base Graphs of Logarithmic Functions with Base b Re-expressing Data... and why The applications
Chapter 3. Graphing Linear Equations and Functions
 Chapter 3 Graphing Linear Equations and Functions 3.1 Plot Points in a Coordinate Plane Coordinate Plane- Two intersecting at a angle. x-axis the axis y-axis the axis The coordinate plane is divided into.
Chapter 3 Graphing Linear Equations and Functions 3.1 Plot Points in a Coordinate Plane Coordinate Plane- Two intersecting at a angle. x-axis the axis y-axis the axis The coordinate plane is divided into.
What You ll Learn. or irrational. New Vocabulary perfect square, square root, irrational numbers, real numbers. Why Learn This?
 -. Plan - Exploring Square Roots and Irrational Numbers Objective To find and estimate square roots and to classify numbers as rational or irrational Examples Finding Square Roots of Perfect Squares Estimating
-. Plan - Exploring Square Roots and Irrational Numbers Objective To find and estimate square roots and to classify numbers as rational or irrational Examples Finding Square Roots of Perfect Squares Estimating
Lesson 2: Introduction to Variables
 In this lesson we begin our study of algebra by introducing the concept of a variable as an unknown or varying quantity in an algebraic expression. We then take a closer look at algebraic expressions to
In this lesson we begin our study of algebra by introducing the concept of a variable as an unknown or varying quantity in an algebraic expression. We then take a closer look at algebraic expressions to
Modeling Data with Functions
 Chapter 11 Modeling Data with Functions 11.1 Data Modeling Concepts 1 11.1.1 Conceptual Explanations: Modeling Data with Functions In school, you generally start with a function and work from there to
Chapter 11 Modeling Data with Functions 11.1 Data Modeling Concepts 1 11.1.1 Conceptual Explanations: Modeling Data with Functions In school, you generally start with a function and work from there to
Chapter 2.1 Relations and Functions
 Analyze and graph relations. Find functional values. Chapter 2.1 Relations and Functions We are familiar with a number line. A number line enables us to locate points, denoted by numbers, and find distances
Analyze and graph relations. Find functional values. Chapter 2.1 Relations and Functions We are familiar with a number line. A number line enables us to locate points, denoted by numbers, and find distances
Solve Quadratic Equations by Graphing
 0.3 Solve Quadratic Equations b Graphing Before You solved quadratic equations b factoring. Now You will solve quadratic equations b graphing. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about sports, as in Eample 6.
0.3 Solve Quadratic Equations b Graphing Before You solved quadratic equations b factoring. Now You will solve quadratic equations b graphing. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about sports, as in Eample 6.
Evaluate and Graph Polynomial Functions
 5.2 Evaluate and Graph Polynomial Functions Before You evaluated and graphed linear and quadratic functions. Now You will evaluate and graph other polynomial functions. Why? So you can model skateboarding
5.2 Evaluate and Graph Polynomial Functions Before You evaluated and graphed linear and quadratic functions. Now You will evaluate and graph other polynomial functions. Why? So you can model skateboarding
6-6. Fitting a Quadratic Model to Data. Vocabulary. Lesson. Mental Math
 Chapter 6 Lesson 6-6 Fitting a Quadratic odel to Data Vocabulary quadratic regression BG DEA Quadratic regression is like linear regression in that it fi nds the model with the least sum of squares of
Chapter 6 Lesson 6-6 Fitting a Quadratic odel to Data Vocabulary quadratic regression BG DEA Quadratic regression is like linear regression in that it fi nds the model with the least sum of squares of
Final Exam Study Aid
 Math 112 Final Exam Study Aid 1 of 33 Final Exam Study Aid Note: This study aid is intended to help you review for the final exam. It covers the primary concepts in the course, with a large emphasis on
Math 112 Final Exam Study Aid 1 of 33 Final Exam Study Aid Note: This study aid is intended to help you review for the final exam. It covers the primary concepts in the course, with a large emphasis on
Unit 5. Linear equations and inequalities OUTLINE. Topic 13: Solving linear equations. Topic 14: Problem solving with slope triangles
 Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Chapter 3: Linear Functions & Their Algebra
 Chapter 3: Linear Functions & Their Algebra Lesson 1: Direct Variation Lesson 2: Average Rate of Change Lesson 3: Forms of a Line Lesson 4: Linear Modeling Lesson 5: Inverse of Linear Functions Lesson
Chapter 3: Linear Functions & Their Algebra Lesson 1: Direct Variation Lesson 2: Average Rate of Change Lesson 3: Forms of a Line Lesson 4: Linear Modeling Lesson 5: Inverse of Linear Functions Lesson
Large and Small Numbers
 Astronomy Basics Large and Small Numbers Astronomers work with very large and very small numbers. For example: The radius of the sun is 70,000,000,000 centimeters The mass of the sun is 20,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
Astronomy Basics Large and Small Numbers Astronomers work with very large and very small numbers. For example: The radius of the sun is 70,000,000,000 centimeters The mass of the sun is 20,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
Lesson 12: Choice of Unit
 Student Outcomes Students understand how choice of unit determines how easy or difficult it is to understand an expression of measurement. Students determine appropriate units for various measurements
Student Outcomes Students understand how choice of unit determines how easy or difficult it is to understand an expression of measurement. Students determine appropriate units for various measurements
Algebra 3-4 Unit 1 Absolute Value Functions and Equations
 Name Period Algebra 3-4 Unit 1 Absolute Value Functions and Equations 1.1 I can write domain and range in interval notation when given a graph or an equation. 1.1 I can write a function given a real world
Name Period Algebra 3-4 Unit 1 Absolute Value Functions and Equations 1.1 I can write domain and range in interval notation when given a graph or an equation. 1.1 I can write a function given a real world
Solve by equating exponents
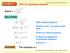 EXAMPLE 1 x Solve 4 = 1 Solve by equating exponents x 3 SOLUTION x 1 4 = x x 3 1 ( ) = ( ) x x + 3 = x = x + 3 x = 1 x 3 Write original equation. Rewrite 4 and base. 1 as powers with Power of a power property
EXAMPLE 1 x Solve 4 = 1 Solve by equating exponents x 3 SOLUTION x 1 4 = x x 3 1 ( ) = ( ) x x + 3 = x = x + 3 x = 1 x 3 Write original equation. Rewrite 4 and base. 1 as powers with Power of a power property
Experimental Uncertainty (Error) and Data Analysis
 Experimental Uncertainty (Error) and Data Analysis Advance Study Assignment Please contact Dr. Reuven at yreuven@mhrd.org if you have any questions Read the Theory part of the experiment (pages 2-14) and
Experimental Uncertainty (Error) and Data Analysis Advance Study Assignment Please contact Dr. Reuven at yreuven@mhrd.org if you have any questions Read the Theory part of the experiment (pages 2-14) and
Outline. Lesson 3: Linear Functions. Objectives:
 Lesson 3: Linear Functions Objectives: Outline I can determine the dependent and independent variables in a linear function. I can read and interpret characteristics of linear functions including x- and
Lesson 3: Linear Functions Objectives: Outline I can determine the dependent and independent variables in a linear function. I can read and interpret characteristics of linear functions including x- and
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt Algebra 2 2
 6-5 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 2 Warm Up Factor completely. 1. 2y 3 + 4y 2 30y 2y(y 3)(y + 5) 2. 3x 4 6x 2 24 Solve each equation. 3(x 2)(x + 2)(x 2 + 2) 3. x 2 9 = 0 x = 3, 3 4. x 3 + 3x
6-5 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 2 Warm Up Factor completely. 1. 2y 3 + 4y 2 30y 2y(y 3)(y + 5) 2. 3x 4 6x 2 24 Solve each equation. 3(x 2)(x + 2)(x 2 + 2) 3. x 2 9 = 0 x = 3, 3 4. x 3 + 3x
Multiplying Polynomials. The rectangle shown at the right has a width of (x + 2) and a height of (2x + 1).
 Page 1 of 6 10.2 Multiplying Polynomials What you should learn GOAL 1 Multiply two polynomials. GOAL 2 Use polynomial multiplication in real-life situations, such as calculating the area of a window in
Page 1 of 6 10.2 Multiplying Polynomials What you should learn GOAL 1 Multiply two polynomials. GOAL 2 Use polynomial multiplication in real-life situations, such as calculating the area of a window in
8 th Grade Intensive Math
 8 th Grade Intensive Math Ready Florida MAFS Student Edition August-September 2014 Lesson 1 Part 1: Introduction Properties of Integer Exponents Develop Skills and Strategies MAFS 8.EE.1.1 In the past,
8 th Grade Intensive Math Ready Florida MAFS Student Edition August-September 2014 Lesson 1 Part 1: Introduction Properties of Integer Exponents Develop Skills and Strategies MAFS 8.EE.1.1 In the past,
Appendix. Using Your Calculator. Squares, Square Roots, Reciprocals, and Logs. Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division
 370770_app.qxd 1/9/03 7:2 PM Page A1 mac114 Mac 114:2nd shift:4_rst: Using Your Calculator In this section we will review how to use your calculator to perform common mathematical operations. This discussion
370770_app.qxd 1/9/03 7:2 PM Page A1 mac114 Mac 114:2nd shift:4_rst: Using Your Calculator In this section we will review how to use your calculator to perform common mathematical operations. This discussion
TEACHER NOTES MATH NSPIRED
 Math Objectives Students will understand how various data transformations can be used to achieve a linear relationship and, consequently, how to use the methods of linear regression to obtain a line of
Math Objectives Students will understand how various data transformations can be used to achieve a linear relationship and, consequently, how to use the methods of linear regression to obtain a line of
Exponents and Polynomials
 Exponents and Polynomials 7A Exponents 7-1 Integer Exponents 7- Powers of 10 and Scientific Notation Lab Explore Properties of Exponents 7-3 Multiplication Properties of Exponents 7-4 Division Properties
Exponents and Polynomials 7A Exponents 7-1 Integer Exponents 7- Powers of 10 and Scientific Notation Lab Explore Properties of Exponents 7-3 Multiplication Properties of Exponents 7-4 Division Properties
Answers to the problems will be posted on the school website, go to Academics tab, then select Mathematics and select Summer Packets.
 Name Geometry SUMMER PACKET This packet contains Algebra I topics that you have learned before and should be familiar with coming into Geometry. We will use these concepts on a regular basis throughout
Name Geometry SUMMER PACKET This packet contains Algebra I topics that you have learned before and should be familiar with coming into Geometry. We will use these concepts on a regular basis throughout
Solving an Equation with One Radical
 Page 1 of 8 7.6 Solving Radical Equations What you should learn GOAL 1 Solve equations that contain radicals or rational exponents. GOAL 2 Use radical equations to solve real-life problems, such as determining
Page 1 of 8 7.6 Solving Radical Equations What you should learn GOAL 1 Solve equations that contain radicals or rational exponents. GOAL 2 Use radical equations to solve real-life problems, such as determining
1Factor binomials that. 2Use the difference. Then. Why? Now. New Vocabulary dif ference of two squares
 Then You factored trinomials into two binomials. (Lesson 8-3, 8-) New Vocabulary dif ference of two squares Now Quadratic Equations: Differences of Squares 1Factor binomials that are the difference of
Then You factored trinomials into two binomials. (Lesson 8-3, 8-) New Vocabulary dif ference of two squares Now Quadratic Equations: Differences of Squares 1Factor binomials that are the difference of
EXPONENTIAL, LOGARITHMIC, AND TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 Calculus for the Life Sciences nd Edition Greenwell SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/calculus-for-the-life-sciences-nd-editiongreenwell-solutions-manual-/ Calculus for
Calculus for the Life Sciences nd Edition Greenwell SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/calculus-for-the-life-sciences-nd-editiongreenwell-solutions-manual-/ Calculus for
Unit 4 Linear Functions
 Algebra I: Unit 4 Revised 10/16 Unit 4 Linear Functions Name: 1 P a g e CONTENTS 3.4 Direct Variation 3.5 Arithmetic Sequences 2.3 Consecutive Numbers Unit 4 Assessment #1 (3.4, 3.5, 2.3) 4.1 Graphing
Algebra I: Unit 4 Revised 10/16 Unit 4 Linear Functions Name: 1 P a g e CONTENTS 3.4 Direct Variation 3.5 Arithmetic Sequences 2.3 Consecutive Numbers Unit 4 Assessment #1 (3.4, 3.5, 2.3) 4.1 Graphing
Rational Numbers. Integers. Irrational Numbers
 EOC Review: Pre-Algebra Unit Rational Numbers Integers Irrational Numbers Ex: Matrices: Ex 1: Ex 2: Ex 3: Unit 1 Equations Equations To solve an equation, use your calculator. STEPS: 1. Menu 2. Algebra
EOC Review: Pre-Algebra Unit Rational Numbers Integers Irrational Numbers Ex: Matrices: Ex 1: Ex 2: Ex 3: Unit 1 Equations Equations To solve an equation, use your calculator. STEPS: 1. Menu 2. Algebra
Lesson 2: Introduction to Variables
 In this lesson we begin our study of algebra by introducing the concept of a variable as an unknown or varying quantity in an algebraic expression. We then take a closer look at algebraic expressions to
In this lesson we begin our study of algebra by introducing the concept of a variable as an unknown or varying quantity in an algebraic expression. We then take a closer look at algebraic expressions to
What is Crater Number Density?
 Ronald Wilhelm & Jennifer Wilhelm, University of Kentucky 2008 What is Crater Number Density? REAL Curriculum Crater Number Density Today we will learn some math that is necessary in order to learn important
Ronald Wilhelm & Jennifer Wilhelm, University of Kentucky 2008 What is Crater Number Density? REAL Curriculum Crater Number Density Today we will learn some math that is necessary in order to learn important
Unit 7: It s in the System
 Unit 7: It s in the System Investigation 1: Linear Equations with Two Variables I can convert between standard and slope intercept forms, and graph systems of equations. Solving equations is one of the
Unit 7: It s in the System Investigation 1: Linear Equations with Two Variables I can convert between standard and slope intercept forms, and graph systems of equations. Solving equations is one of the
2.2 Power Functions with Modeling
 174 CHAPTER 2 Polynomial, Power, and Rational Functions 2.2 Power Functions with Modeling TEKS 1.F, 2.F, 2.G, 2.J, 2.L, 2.N What you ll learn about Power Functions and Variation Monomial Functions and
174 CHAPTER 2 Polynomial, Power, and Rational Functions 2.2 Power Functions with Modeling TEKS 1.F, 2.F, 2.G, 2.J, 2.L, 2.N What you ll learn about Power Functions and Variation Monomial Functions and
1.2 Inductive Reasoning
 1.2 Inductive Reasoning Goal Use inductive reasoning to make conjectures. Key Words conjecture inductive reasoning counterexample Scientists and mathematicians look for patterns and try to draw conclusions
1.2 Inductive Reasoning Goal Use inductive reasoning to make conjectures. Key Words conjecture inductive reasoning counterexample Scientists and mathematicians look for patterns and try to draw conclusions
