7.4. Characteristics of Logarithmic Functions with Base 10 and Base e. INVESTIGATE the Math
|
|
|
- Avice Nichols
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 7. Characteristics of Logarithmic Functions with Base 1 and Base e YOU WILL NEED graphing technolog EXPLORE Use benchmarks to estimate the solution to this equation: logarithmic function A function of the form 5 a log b where b., b 1, and a, and a and b are real numbers. GOAL Investigate the characteristics of logarithmic functions with base 1 and base e from graphs and equations. INVESTIGATE the Math Rand came across a new tpe of function in his chemistr class. He learned that the ph of a solution is determined b a logarithmic function. He wondered how the characteristics of these functions differ from the characteristics of polnomial and eponential functions. Rand noticed that he had a log button on his calculator, so he looked in his user manual and discovered that this was a base 1 logarithm. Using this button, he created a table of values and a graph for each of the functions shown below to investigate the similarities and differences. f1 5 log 1 g1 5 log 1 h1 5 5 log 1 1 undefined 1 undefined 1 undefined undefined undefined undefined f() log 1 g() log h() 5 log 1 7 Chapter 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions NEL
2 ? What are the characteristics of logarithmic functions of the form 5 a log b, where b 5 1 or b 5 e, and a is a real number? A. Use a graphing calculator to graph the logarithmic function 5 log 1. On the same aes, graph 5 1. How are these two graphs related? B. Rand choose three functions of the form 5 a log 1, where a.. On a new screen, graph Rand s functions, shown on the previous page. C. Eamine the graph of each function, and state the following characteristics: the number of -intercepts the -intercept the end behaviour the domain the range D. Eamine the graphs ou created in part B. As ou move from left to right along the -ais, do the -values of each function increase or decrease? Then eamine the table of values for each function on our graphing calculator. What happens to the -values as the -values increase? Tip Communication The epression log 1 is known as the common logarithm or a logarithm with a base of 1. The epression is often written without the 1, so the two functions 5 log 1 and 5 log are equivalent. Tip Communication The function 5 log 1 is equivalent to 5 1, so a logarithm is an eponent. The meaning of log 1 is the eponent that must be applied to base 1 to get the value of. For eample, log E. Choose three new functions of the form 5 a log 1, where a,. Repeat parts C and D for these new functions. F. On a new screen, graph the natural logarithmic function 5 ln. On the same aes, graph 5 e. How are these two graphs related? G. On a new screen, graph the function 5 ln and two other functions of the form 5 a ln, where a.. Eamine the graph of each function, and state the following characteristics: the number of -intercepts the -intercept the end behaviour the domain the range Tip Communication A logarithm with base e is called the natural logarithm and is written as ln. The functions 5 log e, 5 ln, and 5 e are equivalent. H. Eamine the graphs ou created in part G. As ou move from left to right along the -ais, do the -values of each function increase or decrease? Then eamine the table of values for each function on our graphing calculator. What happens to the -values as the -values increase? I. Choose three new functions of the form 5 a ln, where a,. Repeat parts G and H for these new functions. NEL 7. Characteristics of Logarithmic Functions with Base 1 and Base e 75
3 Reflecting J. Based on our observations, which characteristics of the graphs of logarithmic functions are similar to the characteristics of graphs of eponential functions ou have studied? K. Based on our observations, which characteristics of the graphs of logarithmic functions differ from the characteristics of graphs of eponential functions ou have studied? L. Can ou predict the end behaviour of functions of the form 5 a log or 5 a ln based on the parameter a? Eplain. M. In logarithmic functions of the form 5 a log b, did changing the base from b 5 1 to b 5 e cause an of the characteristics to change? Eplain. APPLY the Math eample 1 Connecting the characteristics of an increasing logarithmic function to its equation and graph Predict the -intercept, the number of -intercepts, the end behaviour, the domain, and the range of the following function: 5 15 log Use the equation of the function to make our predictions. Verif our predictions using graphing technolog. Sid s Solution The function 5 15 log is a logarithmic function of the form 5 a log b, with a 5 15 and b 5 1. Common Characteristics -intercept: 1 Number of -intercepts: Domain: 5., [ R Range: 5 [ R I knew that this is a common logarithmic function since the base is not written. Its base is 1. I determined the values of the parameters a and b. I predicted the characteristics of the function from its equation. I started with the common characteristics I knew for all logarithmic functions of the form 5 a log b, where b Chapter 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions NEL
4 Unique Characteristics End behaviour: The curve etends from quadrant IV to quadrant 1. Since the parameter a is greater than, I knew that the function increases as ou move from left to right along the -ais. I used a graphing calculator to create a table of values and a graph to verif m predictions. M predictions were correct. Your Turn Predict the -intercept, the number of -intercepts, the end behaviour, the domain, and the range of this function: 5 5 log Use the equation of the function to make our predictions. Verif our predictions using graphing technolog. eample Connecting the characteristics of a decreasing natural logarithmic function to its equation and graph Predict the -intercept, the number of -intercepts, the end behaviour, the domain, and the range of the following function: 5 ln Use the equation of the function to make our predictions. Verif our predictions using graphing technolog. NEL 7. Characteristics of Logarithmic Functions with Base 1 and Base e 77
5 Anne s Solution The function 5 ln is a logarithmic function of the form 5 a log b with a base of e. In this function, a 5 and b 5 e. Common Characteristics -intercept: 1 Number of -intercepts: Domain: 5., [ R Range: 5 [ R Unique Characteristics End behaviour: The curve etends from quadrant I to quadrant IV. I knew that 5 ln is the natural logarithmic function, which is equivalent to 5 log e, so I knew the base of the logarithmic function is.71. I determined the values of the parameters a and b. I predicted the characteristics of the function from its equation. I started with the common characteristics I knew for all logarithmic functions of the form 5 a log b, where b 5 e. Since the paameter a is less than, I knew that the function decreases as ou move from left to right along the -ais. I used a graphing calculator to create a table of values and a graph. M predictions were correct. Your Turn Predict the -intercept, the number of -intercepts, the end behaviour, the domain, and the range of this function: 5 1 ln Use the equation of the function to make our predictions. Verif our predictions using graphing technolog. 7 Chapter 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions NEL
6 eample 3 Matching equations of eponential and logarithmic functions with their graphs Which function matches each graph below? Provide our reasoning. i) 5 51 ii) iii) 5 log iv) 5 ln a) c) b) d) Errn s Solution Eponential functions: I know that graphs b) and d) are eponential functions of the form 5 a1b, where a., b., and b 1, since both etend from quadrant II to quadrant I. I also know that functions i) and ii) are eponential, since the eponent in each equation is a variable. 5() Since b. in the function 5 51, I knew that this function matches the graph of the increasing function. NEL 7. Characteristics of Logarithmic Functions with Base 1 and Base e 79
7 (.1) Since b, in the function 5 1.1, I knew that this function matches the graph of the decreasing function intercept: intercept: Function i) matches graph b) and function ii) matches graph d). Logarithmic functions: I know that graphs a) and c) are logarithmic, since the etend from quadrant I to quadrant IV and from quadrant IV to quadrant I, respectivel. I also know that functions iii) and iv) are logarithmic. log I knew that I was right since the -intercepts for the equations match the -intercepts on the graphs. Since a. in the function 5 log, I knew that this function matches the graph of the increasing function. ln Since a, in the function 5 ln, I knew that this function matches the graph of the decreasing function. Function iii) matches graph c) and function iv) matches graph a). Your Turn Jordan claims that she can tell which graphs are eponential and which graphs are logarithmic b eamining the domain of each function. Do ou agree or disagree? Eplain. Chapter 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions NEL
8 In Summar Ke Ideas A logarithmic function has the form f1 5 a log b, where b., b 1, and a, and a and b are real numbers. All logarithmic functions of the form f1 5 a log and f1 5 a ln have these characteristics: -Intercept 1 Number of -Intercepts End Behaviour Domain Range The curve etends from quadrant IV to quadrant I or quadrant I to quadrant IV. 5., [ R 5 [ R All logarithmic functions of the form f1 5 a log and f1 5 a ln have these unique characteristics: - If a., the function increases. - If a,, the function decreases. Need to Know The graph of a logarithmic function of the form f1 5 a log or f1 5 a ln will look like one of the following cases: Case 1: an increasing function, where a. Case : a decreasing function, where a, The graph of 5 log is a reflection of the graph of 5 1 about the line 5. - log - 1 The graph of 5 ln is a reflection of the graph of 5 e about the line 5. - ln - e NEL 7. Characteristics of Logarithmic Functions with Base 1 and Base e 1
9 1 log check Your Understanding 1. State the -intercept, the number of -intercepts, the end behaviour, the domain, and the range of the function shown on the left.. Identif which of these graphs are logarithmic functions. Eplain how ou know. a) d) b) e) c) f ) Chapter 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions NEL
10 3. For the functions in question that are logarithmic, state the -intercept, the number of -intercepts, the end behaviour, the domain, and the range. Also state whether the parameter a in the equation of the function is greater than zero or less than zero, and eplain how ou know. PRACTISING. Use graphing technolog to graph the functions 5 log and 5 log. Compare the graphs of the functions. Consider the -intercept, the number of -intercepts, the end behaviour, the domain, the range, and whether the are increasing or decreasing. 5. Predict the -intercept, the number of -intercepts, the end behaviour, the domain, the range, and whether each logarithmic function is increasing or decreasing, based on its equation. Verif our predictions using graphing technolog. a) f log b) f log c) f ln d) f ln e) f 1 5. log f) f ln. State three reasons wh ou know that the following graph represents a logarithmic function of the form 5 a log NEL 7. Characteristics of Logarithmic Functions with Base 1 and Base e 3
11 7. Sketch the graph of the logarithmic function with each set of characteristics. a) -intercept: 1 Number of -intercepts: End behaviour: The curve etends from quadrant IV to quadrant I. Domain: 5., [ R Range: 5 [ R b) -intercept: 1 Number of -intercepts: End behaviour: The curve etends from quadrant I to quadrant IV. Domain: 5., [ R Range: 5 [ R. Match each function with its corresponding graph. Provide our reasoning. i) 5. log ii) 5 3 log iii) 5 iv) a) - - c) - - b) d) Chapter 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions NEL
12 9. Holl claims that she can distinguish between the graph of an eponential function of the form 5 a1b, where a., b., and b 1, and the graph of a logarithmic function of the form 5 a log, where a, based entirel on the number of -intercepts shown. Do ou agree or disagree? Eplain. 1. The ph of a solution, p(), can be determined using the function p1 5 log where represents the concentration of hdrogen ions in the solution, in moles per litre. Use the equation of the function to predict what happens to the ph of a solution as the concentration of hdrogen ions increases. Verif our prediction using graphing technolog. 11. Sound intensit is measured on the decibel scale. A decibel is 1 1 of a bel, named after Aleander Graham Bell. The intensit of a sound (number of decibels) can be determined using the function D1 5 1 log 11 1 # where represents the energ of the sound in watts per square centimetre (watts/cm ). Use the equation of the function to predict what happens to the number of decibels, D(), as the energ of the sound,, increases. Verif our prediction using graphing technolog. A recording of speech. Like other sounds, speech can be measured b pitch (top graph) and b intensit (bottom graph). NEL 7. Characteristics of Logarithmic Functions with Base 1 and Base e 5
13 Time (ears) t Radioactive Deca of Cesium-137 P Percent of original cesium Cesium-137 is created in nuclear reactors. It decas naturall over time. The approimate time for cesium-137 to deca is given b the function t 5 1. log P where t represents the time in ears and P represents the percent of the original amount of cesium-137, as a decimal, that remains. The function is graphed at the left. a) State the following characteristics of the graph: the intercepts the domain and range within the contet of this problem whether the function is increasing or decreasing the value of the function at P 5 1 b) A sample of cesium-137 is taken from a reactor. Estimate the time when 5% of the sample will remain. c) Estimate the time when 5% of the sample will remain. Closing 13. Consider the following functions: 5 a log and 5 a ln a) For what values of a is each function decreasing? b) Do these functions have an unrestricted domain? Eplain. c) Do these functions have an unrestricted range? Eplain. Etending 1. The largest known earthquake in Saskatchewan occurred in 199. Based on recorded observations, the earthquake is believed to have measured approimatel 5.5 on the Richter scale. The magnitude, M, of an earthquake that is T times more intense than an earthquake registering 5.5 on the Richter scale is given b the following function: M 5 log T For ever 1 unit increase on the Richter scale, the intensit of an earthquake increases b a factor of 1. a) Use technolog to graph the function, and state the following characteristics of the graph: the intercepts the domain and range within the contet of this problem whether the function is increasing or decreasing the value of the function at T 5 1 b) Determine the magnitude of an earthquake that is 5 times more intense than the Saskatchewan earthquake. c) In 11, an earthquake that measured 9. on the Richter scale occurred off the coast of Japan, creating a devastating tsunami. About how man times more intense was this earthquake than the Saskatchewan earthquake? Use our graph to estimate. Chapter 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions NEL
14 15. Christie has $3 invested in a savings account that earns %/a. The approimate time for her investment to reach a given future value is modelled b the function t log A.1 where t is the time in ears and A is the future value. The function is graphed below. Value of Savings t Time, t (ears) Future value, A ($) A a) State the following characteristics of this function: the intercepts the domain and range within the contet of this problem whether the function is increasing or decreasing b) How long, in ears, will it take for Christie s investment to reach $1? c) How long, in ears, will it take for Christie s investment to double? NEL 7. Characteristics of Logarithmic Functions with Base 1 and Base e 7
2. Tell whether the equation or graph represents an exponential growth or exponential decay function.
 Name: Date: Period: ID: 1 Unit 9 Review Eponents & Logarithms NO GRAPHING CALCULATOR 1. Under each function, write es if it is an eponential function. If the answer is no, write an eplanation wh not. a)
Name: Date: Period: ID: 1 Unit 9 Review Eponents & Logarithms NO GRAPHING CALCULATOR 1. Under each function, write es if it is an eponential function. If the answer is no, write an eplanation wh not. a)
7 Chapter Review. FREQUENTLY ASKED Questions. Aid
 7 Chapter Review FREQUENTLY ASKED Questions Stud Aid See Lesson 7.. 3 1-1 -3 Stud 1 Aid ln log 3 See Lesson 7., Eamples 1 and. Tr Chapter Review Question 9. Q: How are the functions 5 log and 5 ln similar
7 Chapter Review FREQUENTLY ASKED Questions Stud Aid See Lesson 7.. 3 1-1 -3 Stud 1 Aid ln log 3 See Lesson 7., Eamples 1 and. Tr Chapter Review Question 9. Q: How are the functions 5 log and 5 ln similar
) approaches e
 COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSF-IF.C.7e HSF-LE.B.5. USING TOOLS STRATEGICALLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use technological tools to eplore and deepen our understanding of concepts. The Natural
COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSF-IF.C.7e HSF-LE.B.5. USING TOOLS STRATEGICALLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use technological tools to eplore and deepen our understanding of concepts. The Natural
7-1. Exploring Exponential Models. Vocabulary. Review. Vocabulary Builder. Use Your Vocabulary. 1. Cross out the expressions that are NOT powers.
 7-1 Eploring Eponential Models Vocabular Review 1. Cross out the epressions that are NOT powers. 16 6a 1 7. Circle the eponents in the epressions below. 5 6 5a z Vocabular Builder eponential deca (noun)
7-1 Eploring Eponential Models Vocabular Review 1. Cross out the epressions that are NOT powers. 16 6a 1 7. Circle the eponents in the epressions below. 5 6 5a z Vocabular Builder eponential deca (noun)
Practice A ( 1, 3 ( 0, 1. Match the function with its graph. 3 x. Explain how the graph of g can be obtained from the graph of f. 5 x.
 8. Practice A For use with pages 65 7 Match the function with its graph.. f. f.. f 5. f 6. f f Lesson 8. A. B. C. (, 6) (0, ) (, ) (0, ) ( 0, ) (, ) D. E. F. (0, ) (, 6) ( 0, ) (, ) (, ) (0, ) Eplain how
8. Practice A For use with pages 65 7 Match the function with its graph.. f. f.. f 5. f 6. f f Lesson 8. A. B. C. (, 6) (0, ) (, ) (0, ) ( 0, ) (, ) D. E. F. (0, ) (, 6) ( 0, ) (, ) (, ) (0, ) Eplain how
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions, Applications, and Models
 86 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions, Applications, and Models Eponential Functions In this section we introduce two new tpes of functions The first of these is the eponential function Eponential Function
86 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions, Applications, and Models Eponential Functions In this section we introduce two new tpes of functions The first of these is the eponential function Eponential Function
Honors Algebra 2: Semester 1 Review
 Name Block Date Honors Algebra : Semester 1 Review NON-CALCULATOR 6-5 1. Given the functions f ( ) 5 11 1, g( ) 6 ( f h)( ) b) ( g f )( ), and h ( ) 4, find each function. g c) (g h)( ) d) ( ) f -1, 4-7,
Name Block Date Honors Algebra : Semester 1 Review NON-CALCULATOR 6-5 1. Given the functions f ( ) 5 11 1, g( ) 6 ( f h)( ) b) ( g f )( ), and h ( ) 4, find each function. g c) (g h)( ) d) ( ) f -1, 4-7,
3.2 LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS
 Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 7. LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Ariel Skelle/Corbis What ou should learn Recognize and evaluate logarithmic functions with base a. Graph logarithmic
Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 7. LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Ariel Skelle/Corbis What ou should learn Recognize and evaluate logarithmic functions with base a. Graph logarithmic
LESSON 12.2 LOGS AND THEIR PROPERTIES
 LESSON. LOGS AND THEIR PROPERTIES LESSON. LOGS AND THEIR PROPERTIES 5 OVERVIEW Here's what ou'll learn in this lesson: The Logarithm Function a. Converting from eponents to logarithms and from logarithms
LESSON. LOGS AND THEIR PROPERTIES LESSON. LOGS AND THEIR PROPERTIES 5 OVERVIEW Here's what ou'll learn in this lesson: The Logarithm Function a. Converting from eponents to logarithms and from logarithms
Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions
 CHAPTER 3 Eponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions 3.1 Eponential and Logistic Functions 3.2 Eponential and Logistic Modeling 3.3 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic
CHAPTER 3 Eponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions 3.1 Eponential and Logistic Functions 3.2 Eponential and Logistic Modeling 3.3 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic
7-1 Practice. Graphing Exponential Functions. Graph each function. State the domain and range. 1. y = 1.5(2) x 2. y = 4(3) x 3. y = 3(0.
 7-1 Practice Graphing Eponential Functions Graph each function. State the domain and range. 1. = 1.5(2) 2. = 4(3) 3. = 3(0.5) 4. = 5 ( 1 2) - 8 5. = - 2 ( 1 4) - 3 6. = 1 2 (3) + 4-5 7. BILGY The initial
7-1 Practice Graphing Eponential Functions Graph each function. State the domain and range. 1. = 1.5(2) 2. = 4(3) 3. = 3(0.5) 4. = 5 ( 1 2) - 8 5. = - 2 ( 1 4) - 3 6. = 1 2 (3) + 4-5 7. BILGY The initial
3.3 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs
 274 CHAPTER 3 Eponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions What ou ll learn about Inverses of Eponential Functions Common Logarithms Base 0 Natural Logarithms Base e Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
274 CHAPTER 3 Eponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions What ou ll learn about Inverses of Eponential Functions Common Logarithms Base 0 Natural Logarithms Base e Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
Lesson 5.1 Exponential Functions
 Lesson.1 Eponential Functions 1. Evaluate each function at the given value. Round to four decimal places if necessar. a. r (t) 2(1 0.0) t, t 8 b. j() 9.(1 0.09), 10 2. Record the net three terms for each
Lesson.1 Eponential Functions 1. Evaluate each function at the given value. Round to four decimal places if necessar. a. r (t) 2(1 0.0) t, t 8 b. j() 9.(1 0.09), 10 2. Record the net three terms for each
Power Functions. A polynomial expression is an expression of the form a n. x n 2... a 3. ,..., a n. , a 1. A polynomial function has the form f(x) a n
 1.1 Power Functions A rock that is tossed into the water of a calm lake creates ripples that move outward in a circular pattern. The area, A, spanned b the ripples can be modelled b the function A(r) πr,
1.1 Power Functions A rock that is tossed into the water of a calm lake creates ripples that move outward in a circular pattern. The area, A, spanned b the ripples can be modelled b the function A(r) πr,
1. For each of the following, state the domain and range and whether the given relation defines a function. b)
 Eam Review Unit 0:. For each of the following, state the domain and range and whether the given relation defines a function. (,),(,),(,),(5,) a) { }. For each of the following, sketch the relation and
Eam Review Unit 0:. For each of the following, state the domain and range and whether the given relation defines a function. (,),(,),(,),(5,) a) { }. For each of the following, sketch the relation and
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions.1 Eponential Growth and Deca Functions. The Natural Base e.3 Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions. Transformations of Eponential and Logarithmic Functions.5 Properties
Eponential and Logarithmic Functions.1 Eponential Growth and Deca Functions. The Natural Base e.3 Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions. Transformations of Eponential and Logarithmic Functions.5 Properties
Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8
 Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8 Name Period Section 8-: Eploring Eponential Models Section 8-2: Properties of Eponential Functions In Chapter 7, we used properties of eponents to determine roots and some of
Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8 Name Period Section 8-: Eploring Eponential Models Section 8-2: Properties of Eponential Functions In Chapter 7, we used properties of eponents to determine roots and some of
Math 121. Practice Problems from Chapter 4 Fall 2016
 Math 11. Practice Problems from Chapter Fall 01 1 Inverse Functions 1. The graph of a function f is given below. On same graph sketch the inverse function of f; notice that f goes through the points (0,
Math 11. Practice Problems from Chapter Fall 01 1 Inverse Functions 1. The graph of a function f is given below. On same graph sketch the inverse function of f; notice that f goes through the points (0,
13.2 Exponential Growth Functions
 Name Class Date. Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > related to the graph of f () = b? A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the
Name Class Date. Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > related to the graph of f () = b? A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the
Math 3201 UNIT 5: Polynomial Functions NOTES. Characteristics of Graphs and Equations of Polynomials Functions
 1 Math 301 UNIT 5: Polnomial Functions NOTES Section 5.1 and 5.: Characteristics of Graphs and Equations of Polnomials Functions What is a polnomial function? Polnomial Function: - A function that contains
1 Math 301 UNIT 5: Polnomial Functions NOTES Section 5.1 and 5.: Characteristics of Graphs and Equations of Polnomials Functions What is a polnomial function? Polnomial Function: - A function that contains
Math 121. Practice Problems from Chapter 4 Fall 2016
 Math 11. Practice Problems from Chapter Fall 01 Section 1. Inverse Functions 1. Graph an inverse function using the graph of the original function. For practice see Eercises 1,.. Use information about
Math 11. Practice Problems from Chapter Fall 01 Section 1. Inverse Functions 1. Graph an inverse function using the graph of the original function. For practice see Eercises 1,.. Use information about
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions 7.1 Eponential Growth and Deca Functions 7. The Natural Base e 7.3 Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions 7. Transformations of Eponential and Logarithmic Functions
7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions 7.1 Eponential Growth and Deca Functions 7. The Natural Base e 7.3 Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions 7. Transformations of Eponential and Logarithmic Functions
13.1 Exponential Growth Functions
 Name Class Date 1.1 Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f
Name Class Date 1.1 Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f
MATH 181, Class Work 5, Professor Susan Sun Nunamaker
 MATH 8, Class Work 5, Professor Susan Sun Nunamaker Due Date: April 5, 006 Student's Name:. Graph these functions using graphing calculator. Then record your result. What pattern/conclusion/generalization
MATH 8, Class Work 5, Professor Susan Sun Nunamaker Due Date: April 5, 006 Student's Name:. Graph these functions using graphing calculator. Then record your result. What pattern/conclusion/generalization
8-1 Exploring Exponential Models
 8- Eploring Eponential Models Eponential Function A function with the general form, where is a real number, a 0, b > 0 and b. Eample: y = 4() Growth Factor When b >, b is the growth factor Eample: y =
8- Eploring Eponential Models Eponential Function A function with the general form, where is a real number, a 0, b > 0 and b. Eample: y = 4() Growth Factor When b >, b is the growth factor Eample: y =
Sec 5.1 Exponential & Logarithmic Functions (Exponential Models)
 Sec 5.1 Eponential & Logarithmic Functions (Eponential Models) 1. The population of the cit Suwanee, GA has consistentl grown b 4% for the last several ears. In the ear 000, the population was 9,500 people.
Sec 5.1 Eponential & Logarithmic Functions (Eponential Models) 1. The population of the cit Suwanee, GA has consistentl grown b 4% for the last several ears. In the ear 000, the population was 9,500 people.
Intermediate Algebra Section 9.3 Logarithmic Functions
 Intermediate Algebra Section 9.3 Logarithmic Functions We have studied inverse functions, learning when they eist and how to find them. If we look at the graph of the eponential function, f ( ) = a, where
Intermediate Algebra Section 9.3 Logarithmic Functions We have studied inverse functions, learning when they eist and how to find them. If we look at the graph of the eponential function, f ( ) = a, where
Name Class Date. Finding Real Roots of Polynomial Equations Extension: Graphing Factorable Polynomial Functions
 Name Class Date -1 Finding Real Roots of Polnomial Equations Etension: Graphing Factorable Polnomial Functions Essential question: How do ou use zeros to graph polnomial functions? Video Tutor prep for
Name Class Date -1 Finding Real Roots of Polnomial Equations Etension: Graphing Factorable Polnomial Functions Essential question: How do ou use zeros to graph polnomial functions? Video Tutor prep for
Functions. Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of an exponential function? ) x e. f (x) = ( 1 3 ) x f.
 7. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A..A Eponential Growth and Deca Functions Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of an eponential function? You can use a graphing
7. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A..A Eponential Growth and Deca Functions Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of an eponential function? You can use a graphing
6.4 graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
 SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Exponential Functions, Growth, and Decay
 7A Find these vocabular words in Lesson 7-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Eponential Functions, Growth, and Deca eponential growth eponential deca asmptote
7A Find these vocabular words in Lesson 7-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Eponential Functions, Growth, and Deca eponential growth eponential deca asmptote
Math Chapter 5 - More Practice MUST SHOW WORK IN ALL PROBLEMS - Also, review all handouts from the chapter, and homework from the book.
 Math 101 - Chapter - More Practice Name MUST SHOW WORK IN ALL PROBLEMS - Also, review all handouts from the chapter, and homework from the book. Write the equation in eponential form. 1) log 2 1 4 = -2
Math 101 - Chapter - More Practice Name MUST SHOW WORK IN ALL PROBLEMS - Also, review all handouts from the chapter, and homework from the book. Write the equation in eponential form. 1) log 2 1 4 = -2
2. Jan 2010 qu June 2009 qu.8
 C3 Functions. June 200 qu.9 The functions f and g are defined for all real values of b f() = 4 2 2 and g() = a + b, where a and b are non-zero constants. (i) Find the range of f. [3] Eplain wh the function
C3 Functions. June 200 qu.9 The functions f and g are defined for all real values of b f() = 4 2 2 and g() = a + b, where a and b are non-zero constants. (i) Find the range of f. [3] Eplain wh the function
1. Graph these functions using graphing calculator. Then record your result. What pattern/conclusion/generalization can you make from these functions.
 MAC1105, Class Work (Eponential & Logarithmic Functions), Susan Sun Nunamaker Student's Name: 1. Graph these functions using graphing calculator. Then record your result. What pattern/conclusion/generalization
MAC1105, Class Work (Eponential & Logarithmic Functions), Susan Sun Nunamaker Student's Name: 1. Graph these functions using graphing calculator. Then record your result. What pattern/conclusion/generalization
decreases as x increases.
 Chapter Review FREQUENTLY ASKED Questions Q: How can ou identif an eponential function from its equation? its graph? a table of values? A: The eponential function has the form f () 5 b, where the variable
Chapter Review FREQUENTLY ASKED Questions Q: How can ou identif an eponential function from its equation? its graph? a table of values? A: The eponential function has the form f () 5 b, where the variable
Math125 Exam 5 Review Name. Do the following as indicated.
 Math Eam Review Name Do the following as indicated. For the given functions f and g, find the requested function. ) f() = - 6; g() = 9 Find (f - g)(). ) ) f() = 33 + ; g() = - Find (f g)(). 3) f() = ;
Math Eam Review Name Do the following as indicated. For the given functions f and g, find the requested function. ) f() = - 6; g() = 9 Find (f - g)(). ) ) f() = 33 + ; g() = - Find (f g)(). 3) f() = ;
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge
 Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Math 3201 Sample Exam. PART I Total Value: 50% 1. Given the Venn diagram below, what is the number of elements in both A and B, n(aub)?
 Math 0 Sample Eam PART I Total : 50%. Given the Venn diagram below, what is the number of elements in both A and B, n(aub)? 6 8 A green white black blue red ellow B purple orange. Given the Venn diagram
Math 0 Sample Eam PART I Total : 50%. Given the Venn diagram below, what is the number of elements in both A and B, n(aub)? 6 8 A green white black blue red ellow B purple orange. Given the Venn diagram
INVESTIGATE the Math
 . Graphs of Reciprocal Functions YOU WILL NEED graph paper coloured pencils or pens graphing calculator or graphing software f() = GOAL Sketch the graphs of reciprocals of linear and quadratic functions.
. Graphs of Reciprocal Functions YOU WILL NEED graph paper coloured pencils or pens graphing calculator or graphing software f() = GOAL Sketch the graphs of reciprocals of linear and quadratic functions.
a. The cubic function with zeros 1, -2, -5 and y-intercept 10. b. The quartic function with zeros 2, -1, 3 (order 2) and passing through (4,-10)
 MHFU Final Eam Review Polynomial Functions Determine the zeros of the function f ( ) ( )( + + ) The remainder when + C is divided by + is 8 Determine the equation of: a The cubic function with zeros, -,
MHFU Final Eam Review Polynomial Functions Determine the zeros of the function f ( ) ( )( + + ) The remainder when + C is divided by + is 8 Determine the equation of: a The cubic function with zeros, -,
5.4 Logarithmic Functions
 SECTION 5.4 Logarithmic Functions 8 Problems and provide definitions for two other transcendental functions.. The hperbolic sine function, designated b sinh, is defined as sinh = e - e - (a) Show that
SECTION 5.4 Logarithmic Functions 8 Problems and provide definitions for two other transcendental functions.. The hperbolic sine function, designated b sinh, is defined as sinh = e - e - (a) Show that
Chapter 4 Page 1 of 16. Lecture Guide. Math College Algebra Chapter 4. to accompany. College Algebra by Julie Miller
 Chapter 4 Page 1 of 16 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 4 to accompan College Algebra b Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared b Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
Chapter 4 Page 1 of 16 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 4 to accompan College Algebra b Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared b Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
Chapter 8 Prerequisite Skills
 Chapter 8 Prerequisite Skills BLM 8. How are 9 and 7 the same? How are they different?. Between which two consecutive whole numbers does the value of each root fall? Which number is it closer to? a) 8
Chapter 8 Prerequisite Skills BLM 8. How are 9 and 7 the same? How are they different?. Between which two consecutive whole numbers does the value of each root fall? Which number is it closer to? a) 8
Functions. Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of a logarithmic function?
 5. Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions Essential Question What are some o the characteristics o the graph o a logarithmic unction? Ever eponential unction o the orm () = b, where b is a positive real
5. Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions Essential Question What are some o the characteristics o the graph o a logarithmic unction? Ever eponential unction o the orm () = b, where b is a positive real
Logarithms. Bacteria like Staph aureus are very common.
 UNIT 10 Eponentials and Logarithms Bacteria like Staph aureus are ver common. Copright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material ma not be reproduced in whole or in part, including illustrations,
UNIT 10 Eponentials and Logarithms Bacteria like Staph aureus are ver common. Copright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material ma not be reproduced in whole or in part, including illustrations,
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs. Properties of Logarithms. Eponential and Logarithmic Equations.5 Eponential and Logarithmic
Eponential and Logarithmic Functions. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs. Properties of Logarithms. Eponential and Logarithmic Equations.5 Eponential and Logarithmic
3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs
 .1 Eponential Functions and Their Graphs Sllabus Objective: 9.1 The student will sketch the graph of a eponential, logistic, or logarithmic function. 9. The student will evaluate eponential or logarithmic
.1 Eponential Functions and Their Graphs Sllabus Objective: 9.1 The student will sketch the graph of a eponential, logistic, or logarithmic function. 9. The student will evaluate eponential or logarithmic
Ch. 4 Review College Algebra Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Ch. Review College Algebra Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the functions are inverses of each other. 3 5 +
Ch. Review College Algebra Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the functions are inverses of each other. 3 5 +
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions In this chapter ou will stud two tpes of nonalgebraic functions eponential functions and logarithmic functions. Eponential and logarithmic functions are widel used
7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions In this chapter ou will stud two tpes of nonalgebraic functions eponential functions and logarithmic functions. Eponential and logarithmic functions are widel used
Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions
 TEKS 7.4 2A.4.C, 2A..A, 2A..B, 2A..C Before Now Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions You evaluated and graphed eponential functions. You will evaluate logarithms and graph logarithmic functions.
TEKS 7.4 2A.4.C, 2A..A, 2A..B, 2A..C Before Now Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions You evaluated and graphed eponential functions. You will evaluate logarithms and graph logarithmic functions.
2.0 % annual 3.0 % Quiz. CD Specials
 6.1 6. Quiz Tell whether the function represents eponential growth or eponential deca. Eplain our reasoning. (Sections 6.1 and 6.) 1. f () = (.5). = ( 3 8) Simplif the epression. (Sections 6. and 6.3)
6.1 6. Quiz Tell whether the function represents eponential growth or eponential deca. Eplain our reasoning. (Sections 6.1 and 6.) 1. f () = (.5). = ( 3 8) Simplif the epression. (Sections 6. and 6.3)
is on the graph of y = f 1 (x).
 Objective 2 Inverse Functions Illustrate the idea of inverse functions. f() = 2 + f() = Two one-to-one functions are inverses of each other if (f g)() = of g, and (g f)() = for all in the domain of f.
Objective 2 Inverse Functions Illustrate the idea of inverse functions. f() = 2 + f() = Two one-to-one functions are inverses of each other if (f g)() = of g, and (g f)() = for all in the domain of f.
every hour 8760 A every minute 525,000 A continuously n A
 In the previous lesson we introduced Eponential Functions and their graphs, and covered an application of Eponential Functions (Compound Interest). We saw that when interest is compounded n times per year
In the previous lesson we introduced Eponential Functions and their graphs, and covered an application of Eponential Functions (Compound Interest). We saw that when interest is compounded n times per year
The Natural Base e. ( 1, e 1 ) 220 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Example 6 Evaluating the Natural Exponential Function.
 0 Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Functions (, e) f() = e (, e ) (0, ) (, e ) FIGURE.9 The Natural Base e In man applications, the most convenient choice for a base is the irrational number e.78888....
0 Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Functions (, e) f() = e (, e ) (0, ) (, e ) FIGURE.9 The Natural Base e In man applications, the most convenient choice for a base is the irrational number e.78888....
Math098 Practice Final Test
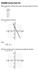 Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
Logarithmic Functions. 4. f(f -1 (x)) = x and f -1 (f(x)) = x. 5. The graph of f -1 is the reflection of the graph of f about the line y = x.
 SECTION. Logarithmic Functions 83 SECTION. Logarithmic Functions Objectives Change from logarithmic to eponential form. Change from eponential to logarithmic form. 3 Evaluate logarithms. 4 Use basic logarithmic
SECTION. Logarithmic Functions 83 SECTION. Logarithmic Functions Objectives Change from logarithmic to eponential form. Change from eponential to logarithmic form. 3 Evaluate logarithms. 4 Use basic logarithmic
Math 111 Final Exam Review
 Math 111 Final Eam Review With the eception of rounding irrational logarithmic epressions and problems that specif that a calculator should be used, ou should be prepared to do the entire problem without
Math 111 Final Eam Review With the eception of rounding irrational logarithmic epressions and problems that specif that a calculator should be used, ou should be prepared to do the entire problem without
Section 0.4 Inverse functions and logarithms
 Section 0.4 Inverse functions and logarithms (5/3/07) Overview: Some applications require not onl a function that converts a numer into a numer, ut also its inverse, which converts ack into. In this section
Section 0.4 Inverse functions and logarithms (5/3/07) Overview: Some applications require not onl a function that converts a numer into a numer, ut also its inverse, which converts ack into. In this section
Sections 4.1 & 4.2 Exponential Growth and Exponential Decay
 8 Sections 4. & 4.2 Eponential Growth and Eponential Deca What You Will Learn:. How to graph eponential growth functions. 2. How to graph eponential deca functions. Eponential Growth This is demonstrated
8 Sections 4. & 4.2 Eponential Growth and Eponential Deca What You Will Learn:. How to graph eponential growth functions. 2. How to graph eponential deca functions. Eponential Growth This is demonstrated
is on the graph of y = f 1 (x).
 Objective 2 Inverse Functions Illustrate the idea of inverse functions. f() = 2 + f() = Two one-to-one functions are inverses of each other if (f g)() = of g, and (g f)() = for all in the domain of f.
Objective 2 Inverse Functions Illustrate the idea of inverse functions. f() = 2 + f() = Two one-to-one functions are inverses of each other if (f g)() = of g, and (g f)() = for all in the domain of f.
Math 111 Final Exam Review KEY
 Math Final Eam Review KEY. Use the graph of = f in Figure to answer the following. Approimate where necessar. a Evaluate f. f = 0 b Evaluate f0. f0 = 6 c Solve f = 0. =, =, =,or = 3 d Solve f = 7..5, 0.5,
Math Final Eam Review KEY. Use the graph of = f in Figure to answer the following. Approimate where necessar. a Evaluate f. f = 0 b Evaluate f0. f0 = 6 c Solve f = 0. =, =, =,or = 3 d Solve f = 7..5, 0.5,
( 3x. Chapter Review. Review Key Vocabulary. Review Examples and Exercises 6.1 Properties of Square Roots (pp )
 6 Chapter Review Review Ke Vocabular closed, p. 266 nth root, p. 278 eponential function, p. 286 eponential growth, p. 296 eponential growth function, p. 296 compound interest, p. 297 Vocabular Help eponential
6 Chapter Review Review Ke Vocabular closed, p. 266 nth root, p. 278 eponential function, p. 286 eponential growth, p. 296 eponential growth function, p. 296 compound interest, p. 297 Vocabular Help eponential
3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs
 96 Chapter 3 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Logarithmic Functions In Section.6, you studied the concept of an inverse function. There, you learned that
96 Chapter 3 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Logarithmic Functions In Section.6, you studied the concept of an inverse function. There, you learned that
4Logarithmic ONLINE PAGE PROOFS. functions. 4.1 Kick off with CAS
 4. Kick off with CAS 4Logarithmic functions 4. Logarithm laws and equations 4.3 Logarithmic scales 4.4 Indicial equations 4.5 Logarithmic graphs 4.6 Applications 4.7 Review 4. Kick off with CAS Eponentials
4. Kick off with CAS 4Logarithmic functions 4. Logarithm laws and equations 4.3 Logarithmic scales 4.4 Indicial equations 4.5 Logarithmic graphs 4.6 Applications 4.7 Review 4. Kick off with CAS Eponentials
Summary, Review, and Test
 45 Chapter Equations and Inequalities Chapter Summar Summar, Review, and Test DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS EXAMPLES. Eponential Functions a. The eponential function with base b is defined b f = b, where b
45 Chapter Equations and Inequalities Chapter Summar Summar, Review, and Test DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS EXAMPLES. Eponential Functions a. The eponential function with base b is defined b f = b, where b
Math 111 Final Exam Review KEY
 Math 111 Final Eam Review KEY 1. Use the graph of = f in Figure 1 to answer the following. Approimate where necessar. a b Evaluate f 1. f 1 = 0 Evaluate f0. f0 = 6 c Solve f = 0. =, = 1, =, or = 3 Solution
Math 111 Final Eam Review KEY 1. Use the graph of = f in Figure 1 to answer the following. Approimate where necessar. a b Evaluate f 1. f 1 = 0 Evaluate f0. f0 = 6 c Solve f = 0. =, = 1, =, or = 3 Solution
MAC 1105 Review for Exam 4. Name
 MAC 1105 Review for Eam Name For the given functions f and g, find the requested composite function. 1) f() = +, g() = 8-7; Find (f g)(). 1) Find the domain of the composite function f g. 9 ) f() = + 9;
MAC 1105 Review for Eam Name For the given functions f and g, find the requested composite function. 1) f() = +, g() = 8-7; Find (f g)(). 1) Find the domain of the composite function f g. 9 ) f() = + 9;
Lesson Goals. Unit 5 Exponential/Logarithmic Functions Exponential Functions (Unit 5.1) Exponential Functions. Exponential Growth: f (x) = ab x, b > 1
 Unit 5 Eponential/Logarithmic Functions Eponential Functions Unit 5.1) William Bill) Finch Mathematics Department Denton High School Lesson Goals When ou have completed this lesson ou will: Recognize and
Unit 5 Eponential/Logarithmic Functions Eponential Functions Unit 5.1) William Bill) Finch Mathematics Department Denton High School Lesson Goals When ou have completed this lesson ou will: Recognize and
7Exponential and. Logarithmic Functions
 7Eponential and Logarithmic Functions A band of green light occasionall appears above the rising or setting sun. This phenomenon is known as a green flash because it lasts for a ver brief period of time.
7Eponential and Logarithmic Functions A band of green light occasionall appears above the rising or setting sun. This phenomenon is known as a green flash because it lasts for a ver brief period of time.
1. Radium has a half-life of 1600 years. How much radium will be left from a 1000-gram sample after 1600 years?
 The Radioactive Deca Eperiment ACTIVITY 7 Learning Targets: Given a verbal description of a function, make a table and a graph of the function. Graph a function and identif and interpret ke features of
The Radioactive Deca Eperiment ACTIVITY 7 Learning Targets: Given a verbal description of a function, make a table and a graph of the function. Graph a function and identif and interpret ke features of
You studied exponential growth and decay functions.
 TEKS 7. 2A.4.B, 2A..B, 2A..C, 2A..F Before Use Functions Involving e You studied eponential growth and deca functions. Now You will stud functions involving the natural base e. Wh? So ou can model visibilit
TEKS 7. 2A.4.B, 2A..B, 2A..C, 2A..F Before Use Functions Involving e You studied eponential growth and deca functions. Now You will stud functions involving the natural base e. Wh? So ou can model visibilit
f 0 ab a b: base f
 Precalculus Notes: Unit Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Sllabus Objective: 9. The student will sketch the graph of a eponential, logistic, or logarithmic function. 9. The student will evaluate eponential
Precalculus Notes: Unit Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Sllabus Objective: 9. The student will sketch the graph of a eponential, logistic, or logarithmic function. 9. The student will evaluate eponential
6. The braking distance (in feet) for a car traveling 50 miles per hour on a wet uphill road is given by
 MATH 34 - College Algebra Review for Test 3 Section 4.6. Let f ( ) = 3 5 + 4. (a) What is the domain? (b) Give the -intercept(s), if an. (c) Give the -intercept(s), if an. (d) Give the equation(s) of the
MATH 34 - College Algebra Review for Test 3 Section 4.6. Let f ( ) = 3 5 + 4. (a) What is the domain? (b) Give the -intercept(s), if an. (c) Give the -intercept(s), if an. (d) Give the equation(s) of the
Chapters 8 & 9 Review for Final
 Math 203 - Intermediate Algebra Professor Valdez Chapters 8 & 9 Review for Final SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the formula for
Math 203 - Intermediate Algebra Professor Valdez Chapters 8 & 9 Review for Final SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the formula for
EAST LOS ANGELES COLLEGE
 EAST LOS ANGELES COLLEGE NAME: MATHEMATICS FINAL EXAM SAMPLE INSTRUCTOR: ANNE SISWANTO; TIME: 10 MINUTES --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EAST LOS ANGELES COLLEGE NAME: MATHEMATICS FINAL EXAM SAMPLE INSTRUCTOR: ANNE SISWANTO; TIME: 10 MINUTES --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZETA MATHS. Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist
 ZETA MATHS Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Epressions & Functions Page Logarithmic & Eponential Functions Addition Formulae. 3 Wave Function.... 4 Graphs of Functions. 5 Sets of Functions
ZETA MATHS Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Epressions & Functions Page Logarithmic & Eponential Functions Addition Formulae. 3 Wave Function.... 4 Graphs of Functions. 5 Sets of Functions
Modeling with Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 6.7. Essential Question How can you recognize polynomial, exponential, and logarithmic models?
 .7 Modeling with Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Essential Question How can ou recognize polnomial, eponential, and logarithmic models? Recognizing Different Tpes of Models Work with a partner. Match
.7 Modeling with Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Essential Question How can ou recognize polnomial, eponential, and logarithmic models? Recognizing Different Tpes of Models Work with a partner. Match
Exponential Growth. b.) What will the population be in 3 years?
 0 Eponential Growth y = a b a b Suppose your school has 4512 students this year. The student population is growing 2.5% each year. a.) Write an equation to model the student population. b.) What will the
0 Eponential Growth y = a b a b Suppose your school has 4512 students this year. The student population is growing 2.5% each year. a.) Write an equation to model the student population. b.) What will the
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs. Properties of Logarithms. Eponential and Logarithmic Equations.5 Eponential and Logarithmic
Eponential and Logarithmic Functions. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs. Properties of Logarithms. Eponential and Logarithmic Equations.5 Eponential and Logarithmic
5A Exponential functions
 Chapter 5 5 Eponential and logarithmic functions bjectives To graph eponential and logarithmic functions and transformations of these functions. To introduce Euler s number e. To revise the inde and logarithm
Chapter 5 5 Eponential and logarithmic functions bjectives To graph eponential and logarithmic functions and transformations of these functions. To introduce Euler s number e. To revise the inde and logarithm
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Unit 3 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Eponential and logarithmic functions can be used to describe and solve a wide range of problems. Some of the questions that can be answered using these two tpes
Unit 3 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Eponential and logarithmic functions can be used to describe and solve a wide range of problems. Some of the questions that can be answered using these two tpes
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Practice for the Final Eam MAC 1 Sullivan Version 1 (2007) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(p1, P2) between the points
Practice for the Final Eam MAC 1 Sullivan Version 1 (2007) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(p1, P2) between the points
KEY IDEAS. Chapter 1 Function Transformations. 1.1 Horizontal and Vertical Translations Pre-Calculus 12 Student Workbook MHR 1
 Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations A translation can move the graph of a function up or down (vertical translation) and right or left (horizontal translation). A translation
Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations A translation can move the graph of a function up or down (vertical translation) and right or left (horizontal translation). A translation
Math 0210 Common Final Review Questions (2 5 i)(2 5 i )
 Math 0 Common Final Review Questions In problems 1 6, perform the indicated operations and simplif if necessar. 1. ( 8)(4) ( )(9) 4 7 4 6( ). 18 6 8. ( i) ( 1 4 i ) 4. (8 i ). ( 9 i)( 7 i) 6. ( i)( i )
Math 0 Common Final Review Questions In problems 1 6, perform the indicated operations and simplif if necessar. 1. ( 8)(4) ( )(9) 4 7 4 6( ). 18 6 8. ( i) ( 1 4 i ) 4. (8 i ). ( 9 i)( 7 i) 6. ( i)( i )
8 Logarithmic. Functions CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 8 Logarithmic Functions Logarithms were developed over 00 ears ago, and the still have numerous applications in the modern world. Logarithms allow ou to solve an eponential equation. Logarithmic
CHAPTER 8 Logarithmic Functions Logarithms were developed over 00 ears ago, and the still have numerous applications in the modern world. Logarithms allow ou to solve an eponential equation. Logarithmic
Graphing Exponential Functions
 MHF UI Unit Da Graphing Eponential Functions. Using a table of values (no decimals), graph the function.. For the function, state: a) domain b) range c) equation of the asmptote d) -intercept e) -intercept
MHF UI Unit Da Graphing Eponential Functions. Using a table of values (no decimals), graph the function.. For the function, state: a) domain b) range c) equation of the asmptote d) -intercept e) -intercept
 Test #4 33 QUESTIONS MATH1314 09281700 COLLEGE ALGEBRA Name atfm1314bli28 www.alvarezmathhelp.com website SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
Test #4 33 QUESTIONS MATH1314 09281700 COLLEGE ALGEBRA Name atfm1314bli28 www.alvarezmathhelp.com website SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
Explore 1 Graphing and Analyzing f(x) = e x. The following table represents the function ƒ (x) = (1 + 1 x) x for several values of x.
 1_ 8 6 8 Locker LESSON 13. The Base e Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes of the graphs of ƒ () = b and ƒ () = log b () where b is, 1, and e
1_ 8 6 8 Locker LESSON 13. The Base e Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes of the graphs of ƒ () = b and ƒ () = log b () where b is, 1, and e
 Test # 33 QUESTIONS MATH131 091700 COLLEGE ALGEBRA Name atfm131bli www.alvarezmathhelp.com website MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Test # 33 QUESTIONS MATH131 091700 COLLEGE ALGEBRA Name atfm131bli www.alvarezmathhelp.com website MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
( ) ( ) x. The exponential function f(x) with base b is denoted by x
 Page of 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Eponential Functions and Their Graphs: Section Objectives: Students will know how to recognize, graph, and evaluate eponential functions. The eponential function
Page of 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Eponential Functions and Their Graphs: Section Objectives: Students will know how to recognize, graph, and evaluate eponential functions. The eponential function
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 2
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 2 Unit 2 FUNCTIONS MATH 1202 FUNCTIONS INTRODUCTION 3 1. LINEAR FUNCTIONS 5 GRAPHS OF LINEAR FUNCTIONS 5 EQUATIONS OF LINEAR FUNCTIONS 10 SELF TEST 1: LINEAR FUNCTIONS
MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 2 Unit 2 FUNCTIONS MATH 1202 FUNCTIONS INTRODUCTION 3 1. LINEAR FUNCTIONS 5 GRAPHS OF LINEAR FUNCTIONS 5 EQUATIONS OF LINEAR FUNCTIONS 10 SELF TEST 1: LINEAR FUNCTIONS
Name Date. Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions For use with Exploration 3.3
 3.3 Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions For use with Eploration 3.3 Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of a logarithmic function? Every eponential function of the form
3.3 Logarithms and Logarithmic Functions For use with Eploration 3.3 Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of a logarithmic function? Every eponential function of the form
Math Review Packet #5 Algebra II (Part 2) Notes
 SCIE 0, Spring 0 Miller Math Review Packet #5 Algebra II (Part ) Notes Quadratic Functions (cont.) So far, we have onl looked at quadratic functions in which the term is squared. A more general form of
SCIE 0, Spring 0 Miller Math Review Packet #5 Algebra II (Part ) Notes Quadratic Functions (cont.) So far, we have onl looked at quadratic functions in which the term is squared. A more general form of
3.2. Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Relations. LEARN ABOUT the Math. Reasoning from a table of values and a graph of a quadratic model
 3. Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Relations YOU WILL NEED grid paper ruler graphing calculator GOAL Describe the ke features of the graphs of quadratic relations, and use the graphs to solve problems.
3. Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Relations YOU WILL NEED grid paper ruler graphing calculator GOAL Describe the ke features of the graphs of quadratic relations, and use the graphs to solve problems.
UNIT TWO EXPONENTS AND LOGARITHMS MATH 621B 20 HOURS
 UNIT TWO EXPONENTS AND LOGARITHMS MATH 61B 0 HOURS Revised Apr 9, 0 9 SCO: By the end of grade 1, students will be epected to: B30 understand and use zero, negative and fractional eponents Elaborations
UNIT TWO EXPONENTS AND LOGARITHMS MATH 61B 0 HOURS Revised Apr 9, 0 9 SCO: By the end of grade 1, students will be epected to: B30 understand and use zero, negative and fractional eponents Elaborations
4.5 Practice B. 4.5 Practice A. Name Date. Possible zeros: Possible zeros: 5. Justify. your answer. your answer. In Exercises 1 6, solve the equation.
 Practice A Practice B In Eercises, solve the equation.. q q 0q 0. k + k + 9k 0.. p p. 8u u n + n 9n 8 0 In Eercises 7 0, find the zeros of the function. Then sketch a graph of the function. 7. f + 8. g
Practice A Practice B In Eercises, solve the equation.. q q 0q 0. k + k + 9k 0.. p p. 8u u n + n 9n 8 0 In Eercises 7 0, find the zeros of the function. Then sketch a graph of the function. 7. f + 8. g
Properties of Elementary Functions
 2 Properties of Elementar Functions If a mother mouse is twice as long as her offspring, then the mother s weight is about eight times the bab s weight. But the mother mouse s skin area is onl about four
2 Properties of Elementar Functions If a mother mouse is twice as long as her offspring, then the mother s weight is about eight times the bab s weight. But the mother mouse s skin area is onl about four
Unit 10 - Graphing Quadratic Functions
 Unit - Graphing Quadratic Functions PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multipl polnomials students should be able to factor polnomials students should be able to identif
Unit - Graphing Quadratic Functions PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multipl polnomials students should be able to factor polnomials students should be able to identif
LESSON #24 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1. What is the domain and range of the function? 2. Any asymptotes?
 Section 8.1 Eponential Functions Goals: 1. To simplify epressions and solve eponential equations involving real eponents. I. Definition of Eponential Function An function is in the form, where and. II.
Section 8.1 Eponential Functions Goals: 1. To simplify epressions and solve eponential equations involving real eponents. I. Definition of Eponential Function An function is in the form, where and. II.
