1.5. The Tools of the Trade!
|
|
|
- Ronald Gray
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1.5. The Tools of the Trade! Two things are required for material analysis: excitation mechanism for originating characteristic signature (radiation) radiation detection and identification system (spectroscopy) For dating techniques you need either: measurement of activity A(t) counting of radioactive atoms N(t)
2 Accelerators for Excitation Processes Required energy transfer for atomic processes: E 1 kev-5 MeV Required energy transfer for nuclear processes: E 1 MeV-15 MeV Two kind of accelerators are in use: cyclotron Van de Graaff
3 Technical Principle of the Cyclotron Ion Source Period T for particle with mass m and charge q in magnetic field B: T = 2 π m q B Energy of particle in cyclotron of radius R: ΔV Acceleration across Voltage gap ΔV between the Dees: ΔE=q ΔV E 1 2 q B R = m v = 2 2 m E < 20 MeV (relativistic effects) sufficient for material analysis.
4 Technical Principle of the Van de Graaff potential: U = Q with Q = charge and C = capacity C Energy: E = mv = qu ; with 7 U up to V: E q 10 ev = 10 q MeV Sufficient energy for necessary excitation mechanisms!
5 The single-ended Van de Graaff 1. charging system 2. Belt 3. Terminal charge pick-up 4. High pressure N 2 /CO 2 gas vessel 5. Ion source 6. Acceleration tube 7. Vacuum tube 8. Generating voltmeter 9. Analyzing magnet 10. Target system
6 Advantage of ion-source at ground The Tandem Accelerator Terminal potential V term Ion-source Total energy: E=(1+q)V term
7 The smallest and the largest Zürich tandem for 14 C analysis Holifield tandem (ORNL) for 36 Cl analysis
8 Typical Accelerator Laboratory for Material Analysis and Dating beamproduction Mass analysis or dating Material analysis
9 Ion Beam Production by Sputter Source Sputtering & charge exchange Extraction and focusing E ion 100 kev
10 Signatures through reaction processes A(a,b)B A(a,γ)C A(a,a)A A(a,a )A* (in-) elastic scattering characteristic particle energy characteristic X-ray radiation characteristic γ-ray radiation nuclear reaction processes characteristic g-radiation characteristic particle break-up
11 Reaction Probability Cross Section The probability for a reaction to occur is the cross-section σ! R probability for incoming beam to hit a target nucleus with radius R: σ πr 2 Typical radius of nucleus m cross section area, unit barn: 1 barn = cm 2
12 Interaction processes between projectile and target material atomic excitation processes X-ray-visible light (Coulomb Interaction between projectile and atomic electrons): σ i [kbarn] elastic scattering processes char. particle energies (mechanical momentum without energy transfer): inelastic scattering processes char. g-radiation (mechanical momentum and energy transfer): σ i [barn] σ i [barn] radiative capture reactions char. g-radiation (Coulomb Interaction between projectile and atomic nucleus): σ i [mbarn] nuclear reaction processes char. particle radiation (Strong Interaction between projectile and atomic nucleus): σ i [mbarn]
13 Total probability for reaction Yield If target has thickness d, and target material has # nuclei/volume: n 0 [part./cm 3 ] Y=σ n 0 d The yield gives the intensity of the characteristic signal from the reaction process per incoming particle with the cross section σ! It also gives the number of reaction products per incoming particle!
14 Example: The cosmic ray bombardment of air produces the radioisotope 14 C by the 14 N(n,p) 14 C reaction. Calculate the number of produced 14 C assuming an average 14 N density of part/cm 3 along the cosmic ray path length of 1.0 km, a reaction cross section of σ=0.1barn and a cosmic ray induced neutron flux of /cm 2 s Y( C) = σ n( N) d = 01. [ barn] 5 10 [ part/ cm ] 1[ km] Y( C) = 1 10 [ cm ] 5 10 [ part / cm ] 10 [ cm] = 05. / neutron a cosmic ray flux of [ neutrons / cm s] 14 2 [ C/ cm s] 12 2 for entire surface area of earth: S = [ cm ] C 3 2 yields a total production rate of: production of: [ C s] = [ Cy] = 102. [ g/ y]
15 Another Example Estimate the number of 14 C atoms produced in the mummy of Ramses II by 3290 years of cosmic ray bombardment! Cosmic ray flux at ground level of ~ particles/m 2 s. The mummy contains N particles & C particles. Adopt a cross section of σ = 0.1 barn for 14 N(n,p) 14 C.
16 Estimate of 14 C production & 14 C content Production: use standard production equation! Y( C) = σ [ barn] N( N) Icosmic[ particles m s] t Y( C) = [ cm ] [ particles m s] 3290[ y] Y( C) = [ cm ] [ particles cm s] [ s] Y( C) = particles are produced in the mummy. Content: use standard decay equation! N N N are ( t ) = (3290 (3290 N 0 y ) y ) contained e = = λ t in the e 15 ln mummy! 3290 y C y particles
17 Radiation Detectors Radiation detectors are based on material which shows a high probability (cross section) for interacting with a particular kind of radiation (in a particular energy range)! The interaction process initiates an excitation or ionisation event in the material (e.g. atomic excitation, or solid state excitation) which results in light or particle emission which in turn can be used for generating an electrical pulse for analyzing and interpreting the event in the data acquisition electronics. There are three kind of detector materials: Scintillator Solid State Detector Ionisation Chamber X-ray, γ-ray, and neutron radiation particle- and γ-ray radiation particle radiation
18 Example: NaI scintillator Photons in the visible light range are created by excitation of NaI material with radiation photons are absorbed on photo cathode and generate free electrons by photo-effect electrons are multiplied in photo multiplier and converted to an electrical signal
19 Ionization chamber and semiconductor detectors Detectors are based on the principle of ionization along the track of energetic charged particle, production of ion-electron pairs, which are accelerated by attached electrical fields to anode or cathode pole of detector, charge pulse is converted in electrical pulse, pulse height corresponds to energy loss of initial energetic particle.
20 Summary Tools are needed to instigate the characteristic excitation processes by energy transfer Tools are needed to analyze the characteristic light or radiation signatures
1.4 The Tools of the Trade!
 1.4 The Tools of the Trade! Two things are required for material analysis: excitation mechanism for originating characteristic signature (radiation) radiation detection and identification system (spectroscopy)
1.4 The Tools of the Trade! Two things are required for material analysis: excitation mechanism for originating characteristic signature (radiation) radiation detection and identification system (spectroscopy)
Total probability for reaction Yield
 Total probability for reaction Yield If target has thickness d, and target material has # nuclei/volume: n 0 [part./cm 3 ] Y=σ n 0 d The yield gives the intensity of the characteristic signal from the
Total probability for reaction Yield If target has thickness d, and target material has # nuclei/volume: n 0 [part./cm 3 ] Y=σ n 0 d The yield gives the intensity of the characteristic signal from the
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics
 Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-30 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 4 - Detectors Binding Energy Nuclear mass MN less than sum of nucleon masses Shows nucleus is a bound (lower energy) state for this configuration
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-30 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 4 - Detectors Binding Energy Nuclear mass MN less than sum of nucleon masses Shows nucleus is a bound (lower energy) state for this configuration
The interaction of radiation with matter
 Basic Detection Techniques 2009-2010 http://www.astro.rug.nl/~peletier/detectiontechniques.html Detection of energetic particles and gamma rays The interaction of radiation with matter Peter Dendooven
Basic Detection Techniques 2009-2010 http://www.astro.rug.nl/~peletier/detectiontechniques.html Detection of energetic particles and gamma rays The interaction of radiation with matter Peter Dendooven
EEE4106Z Radiation Interactions & Detection
 EEE4106Z Radiation Interactions & Detection 2. Radiation Detection Dr. Steve Peterson 5.14 RW James Department of Physics University of Cape Town steve.peterson@uct.ac.za May 06, 2015 EEE4106Z :: Radiation
EEE4106Z Radiation Interactions & Detection 2. Radiation Detection Dr. Steve Peterson 5.14 RW James Department of Physics University of Cape Town steve.peterson@uct.ac.za May 06, 2015 EEE4106Z :: Radiation
3.5. Accelerator Mass Spectroscopy -AMS -
 3.5. Accelerator Mass Spectroscopy -AMS - AMS is a method which counts radioactive particles ( 14 C) rather than measuring the characteristic decay activity. Comparison Traditional 14 C dating and AMS
3.5. Accelerator Mass Spectroscopy -AMS - AMS is a method which counts radioactive particles ( 14 C) rather than measuring the characteristic decay activity. Comparison Traditional 14 C dating and AMS
Appendix A2. Particle Accelerators and Detectors The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Geneva, Switzerland on the Border of France.
 Appendix A. Particle Accelerators and Detectors The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Geneva, Switzerland on the Border of France. Prepared by: Arash Akbari-Sharbaf Why Build Accelerators? Probe deeper From
Appendix A. Particle Accelerators and Detectors The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Geneva, Switzerland on the Border of France. Prepared by: Arash Akbari-Sharbaf Why Build Accelerators? Probe deeper From
RDCH 702 Lecture 8: Accelerators and Isotope Production
 RDCH 702 Lecture 8: Accelerators and Isotope Production Particle generation Accelerator Direct Voltage Linear Cyclotrons Synchrotrons Photons * XAFS * Photonuclear Heavy Ions Neutrons sources Fission products
RDCH 702 Lecture 8: Accelerators and Isotope Production Particle generation Accelerator Direct Voltage Linear Cyclotrons Synchrotrons Photons * XAFS * Photonuclear Heavy Ions Neutrons sources Fission products
hν' Φ e - Gamma spectroscopy - Prelab questions 1. What characteristics distinguish x-rays from gamma rays? Is either more intrinsically dangerous?
 Gamma spectroscopy - Prelab questions 1. What characteristics distinguish x-rays from gamma rays? Is either more intrinsically dangerous? 2. Briefly discuss dead time in a detector. What factors are important
Gamma spectroscopy - Prelab questions 1. What characteristics distinguish x-rays from gamma rays? Is either more intrinsically dangerous? 2. Briefly discuss dead time in a detector. What factors are important
APPLIED RADIATION PHYSICS
 A PRIMER IN APPLIED RADIATION PHYSICS F A SMITH Queen Mary & Westfield College, London fe World Scientific m Singapore * New Jersey London Hong Kong CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 : SOURCES of RADIATION 1.1 Introduction
A PRIMER IN APPLIED RADIATION PHYSICS F A SMITH Queen Mary & Westfield College, London fe World Scientific m Singapore * New Jersey London Hong Kong CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 : SOURCES of RADIATION 1.1 Introduction
Radiation (Particle) Detection and Measurement
 Radiation (Particle) Detection and Measurement Radiation detection implies that the radiation interacts (e.g. leaves at least part of its energy) in the material. A specific material is chosen, because
Radiation (Particle) Detection and Measurement Radiation detection implies that the radiation interacts (e.g. leaves at least part of its energy) in the material. A specific material is chosen, because
Copyright 2008, University of Chicago, Department of Physics. Experiment VI. Gamma Ray Spectroscopy
 Experiment VI Gamma Ray Spectroscopy 1. GAMMA RAY INTERACTIONS WITH MATTER In order for gammas to be detected, they must lose energy in the detector. Since gammas are electromagnetic radiation, we must
Experiment VI Gamma Ray Spectroscopy 1. GAMMA RAY INTERACTIONS WITH MATTER In order for gammas to be detected, they must lose energy in the detector. Since gammas are electromagnetic radiation, we must
Radiation Quantities and Units
 Radiation Quantities and Units George Starkschall, Ph.D. Lecture Objectives Define and identify units for the following: Exposure Kerma Absorbed dose Dose equivalent Relative biological effectiveness Activity
Radiation Quantities and Units George Starkschall, Ph.D. Lecture Objectives Define and identify units for the following: Exposure Kerma Absorbed dose Dose equivalent Relative biological effectiveness Activity
Scintillation Detector
 Scintillation Detector Introduction The detection of ionizing radiation by the scintillation light produced in certain materials is one of the oldest techniques on record. In Geiger and Marsden s famous
Scintillation Detector Introduction The detection of ionizing radiation by the scintillation light produced in certain materials is one of the oldest techniques on record. In Geiger and Marsden s famous
Radioactivity. Lecture 6 Detectors and Instrumentation
 Radioactivity Lecture 6 Detectors and Instrumentation The human organs Neither humans nor animals have an organ for detecting radiation from radioactive decay! We can not hear it, smell it, feel it or
Radioactivity Lecture 6 Detectors and Instrumentation The human organs Neither humans nor animals have an organ for detecting radiation from radioactive decay! We can not hear it, smell it, feel it or
Lecture 32 April
 Lecture 32 April 08. 2016. Hydrogen Discharge Tube and Emission of Discrete Wavelengths Description of the discrete Hydrogen Emission Spectrum by the Balmer (1884) Rydberg Ritz formula (1908) Cathode Ray
Lecture 32 April 08. 2016. Hydrogen Discharge Tube and Emission of Discrete Wavelengths Description of the discrete Hydrogen Emission Spectrum by the Balmer (1884) Rydberg Ritz formula (1908) Cathode Ray
Non-radioactive radiation sources. Lesson FYSKJM4710 Eirik Malinen
 Non-radioactive radiation sources Lesson FYSKJM4710 Eirik Malinen X-ray tube Electrons are released from the cathode (negative electrode) by thermionic emission accelerated in an evacuated tube hit the
Non-radioactive radiation sources Lesson FYSKJM4710 Eirik Malinen X-ray tube Electrons are released from the cathode (negative electrode) by thermionic emission accelerated in an evacuated tube hit the
Introduction to Radiological Sciences Neutron Detectors. Theory of operation. Types of detectors Source calibration Survey for Dose
 Introduction to Radiological Sciences Neutron Detectors Neutron counting Theory of operation Slow neutrons Fast neutrons Types of detectors Source calibration Survey for Dose 2 Neutrons, what are they?
Introduction to Radiological Sciences Neutron Detectors Neutron counting Theory of operation Slow neutrons Fast neutrons Types of detectors Source calibration Survey for Dose 2 Neutrons, what are they?
PARTICLE ACCELERATORS
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE PARTICLE ACCELERATORS Particle accelerators are used to accelerate elementary particles to very high energies for: Production of radioisotopes Probing the structure of matter There
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE PARTICLE ACCELERATORS Particle accelerators are used to accelerate elementary particles to very high energies for: Production of radioisotopes Probing the structure of matter There
Accelerators and radiation spectra
 X-ray tube Accelerators and radiation spectra Electrons are released from the cathode (negative electrode) by thermionic emission accelerated in an evacuated tube hit the anode (target, positive electrode)
X-ray tube Accelerators and radiation spectra Electrons are released from the cathode (negative electrode) by thermionic emission accelerated in an evacuated tube hit the anode (target, positive electrode)
Particle Energy Loss in Matter
 Particle Energy Loss in Matter Charged particles loose energy when passing through material via atomic excitation and ionization These are protons, pions, muons, The energy loss can be described for moderately
Particle Energy Loss in Matter Charged particles loose energy when passing through material via atomic excitation and ionization These are protons, pions, muons, The energy loss can be described for moderately
Quality Assurance. Purity control. Polycrystalline Ingots
 Quality Assurance Purity control Polycrystalline Ingots 1 Gamma Spectrometry Nuclide Identification Detection of Impurity Traces 1.1 Nuclides Notation: Atomic Mass Atomic Number Element Neutron Atomic
Quality Assurance Purity control Polycrystalline Ingots 1 Gamma Spectrometry Nuclide Identification Detection of Impurity Traces 1.1 Nuclides Notation: Atomic Mass Atomic Number Element Neutron Atomic
Physics 736. Experimental Methods in Nuclear-, Particle-, and Astrophysics. Lecture 3
 Physics 736 Experimental Methods in Nuclear-, Particle-, and Astrophysics Lecture 3 Karsten Heeger heeger@wisc.edu Review of Last Lecture a colleague shows you this data... what type of reaction is this?
Physics 736 Experimental Methods in Nuclear-, Particle-, and Astrophysics Lecture 3 Karsten Heeger heeger@wisc.edu Review of Last Lecture a colleague shows you this data... what type of reaction is this?
Interaction of Ionizing Radiation with Matter
 Type of radiation charged particles photonen neutronen Uncharged particles Charged particles electrons (β - ) He 2+ (α), H + (p) D + (d) Recoil nuclides Fission fragments Interaction of ionizing radiation
Type of radiation charged particles photonen neutronen Uncharged particles Charged particles electrons (β - ) He 2+ (α), H + (p) D + (d) Recoil nuclides Fission fragments Interaction of ionizing radiation
22.54 Neutron Interactions and Applications (Spring 2004) Chapter 1 (2/3/04) Overview -- Interactions, Distributions, Cross Sections, Applications
 .54 Neutron Interactions and Applications (Spring 004) Chapter 1 (/3/04) Overview -- Interactions, Distributions, Cross Sections, Applications There are many references in the vast literature on nuclear
.54 Neutron Interactions and Applications (Spring 004) Chapter 1 (/3/04) Overview -- Interactions, Distributions, Cross Sections, Applications There are many references in the vast literature on nuclear
Neutron Interactions Part I. Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics Y2.5321
 Neutron Interactions Part I Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics rhowell@mdanderson.org Y2.5321 Why do we as Medical Physicists care about neutrons? Neutrons in Radiation Therapy Neutron Therapy
Neutron Interactions Part I Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics rhowell@mdanderson.org Y2.5321 Why do we as Medical Physicists care about neutrons? Neutrons in Radiation Therapy Neutron Therapy
Emphasis on what happens to emitted particle (if no nuclear reaction and MEDIUM (i.e., atomic effects)
 LECTURE 5: INTERACTION OF RADIATION WITH MATTER All radiation is detected through its interaction with matter! INTRODUCTION: What happens when radiation passes through matter? Emphasis on what happens
LECTURE 5: INTERACTION OF RADIATION WITH MATTER All radiation is detected through its interaction with matter! INTRODUCTION: What happens when radiation passes through matter? Emphasis on what happens
Direct-Current Accelerator
 Nuclear Science A Teacher s Guide to the Nuclear Science Wall Chart 1998 Contemporary Physics Education Project (CPEP) Chapter 11 Accelerators One of the most important tools of nuclear science is the
Nuclear Science A Teacher s Guide to the Nuclear Science Wall Chart 1998 Contemporary Physics Education Project (CPEP) Chapter 11 Accelerators One of the most important tools of nuclear science is the
Summary of lecture 1 and 2: Main ingredients in LHC success
 Summary of lecture 1 and 2: Main ingredients in LHC success LHC LHC Tevatron Tevatron s=1.8tev Energy 10 times higher cross section than Tevatron and integrated luminosity already ½ at end of 2011! 1 Lectures
Summary of lecture 1 and 2: Main ingredients in LHC success LHC LHC Tevatron Tevatron s=1.8tev Energy 10 times higher cross section than Tevatron and integrated luminosity already ½ at end of 2011! 1 Lectures
Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 21 (11/29/06) Detection of Nuclear Radiation: Pulse Height Spectra
 22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 21 (11/29/06) Detection of Nuclear Radiation: Pulse Height Spectra References: W. E. Meyerhof, Elements of Nuclear Physics (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1967),
22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 21 (11/29/06) Detection of Nuclear Radiation: Pulse Height Spectra References: W. E. Meyerhof, Elements of Nuclear Physics (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1967),
Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis
 Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis 3.1. Neutron Activation Techniques 3.2. Neutron Activation of Paintings 3.3. From Qumran to Napoleon 3.4. Neutron Activation with Accelerators 3.5. Isotope
Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis 3.1. Neutron Activation Techniques 3.2. Neutron Activation of Paintings 3.3. From Qumran to Napoleon 3.4. Neutron Activation with Accelerators 3.5. Isotope
CHAPTER 12 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 76 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 12 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 76 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 12 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
Detekce a spektrometrie neutronů. neutron detection and spectroscopy
 Detekce a spektrometrie neutronů neutron detection and spectroscopy 1. Slow neutrons 2. Fast neutrons 1 1. Slow neutrons neutron kinetic energy E a) charged particles are produced, protons, α particle,
Detekce a spektrometrie neutronů neutron detection and spectroscopy 1. Slow neutrons 2. Fast neutrons 1 1. Slow neutrons neutron kinetic energy E a) charged particles are produced, protons, α particle,
Radioactivity and Ionizing Radiation
 Radioactivity and Ionizing Radiation QuarkNet summer workshop June 24-28, 2013 1 Recent History Most natural phenomena can be explained by a small number of simple rules. You can determine what these rules
Radioactivity and Ionizing Radiation QuarkNet summer workshop June 24-28, 2013 1 Recent History Most natural phenomena can be explained by a small number of simple rules. You can determine what these rules
Homework 2: Forces on Charged Particles
 Homework 2: Forces on Charged Particles 1. In the arrangement shown below, 2 C of positive charge is moved from plate S, which is at a potential of 250 V, to plate T, which is at a potential of 750 V.
Homework 2: Forces on Charged Particles 1. In the arrangement shown below, 2 C of positive charge is moved from plate S, which is at a potential of 250 V, to plate T, which is at a potential of 750 V.
Modern Physics Laboratory (Physics 6180/7180)
 Alpha Particle Spectroscopy Week of Jan. 18, 2010 Modern Physics Laboratory (Physics 6180/7180) The University of Toledo Instructor: Randy Ellingson Alpha Particle Spectroscopy Alpha particle source alpha
Alpha Particle Spectroscopy Week of Jan. 18, 2010 Modern Physics Laboratory (Physics 6180/7180) The University of Toledo Instructor: Randy Ellingson Alpha Particle Spectroscopy Alpha particle source alpha
Particle Acceleration
 Nuclear and Particle Physics Junior Honours: Particle Physics Lecture 4: Accelerators and Detectors February 19th 2007 Particle Beams and Accelerators Particle Physics Labs Accelerators Synchrotron Radiation
Nuclear and Particle Physics Junior Honours: Particle Physics Lecture 4: Accelerators and Detectors February 19th 2007 Particle Beams and Accelerators Particle Physics Labs Accelerators Synchrotron Radiation
Activation Analysis. Characteristic decay mechanisms, α, β, γ Activity A reveals the abundance N:
 2.5. Isotope analysis and neutron activation techniques The previously discussed techniques of material analysis are mainly based on the characteristic atomic structure of the elements and the associated
2.5. Isotope analysis and neutron activation techniques The previously discussed techniques of material analysis are mainly based on the characteristic atomic structure of the elements and the associated
Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry
 Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry EMSE-515 Fall 2005 F. Ernst 1 Bohr s Model of an Atom existence of central core established by single collision, large-angle scattering of alpha particles ( 4 He
Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry EMSE-515 Fall 2005 F. Ernst 1 Bohr s Model of an Atom existence of central core established by single collision, large-angle scattering of alpha particles ( 4 He
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter
 Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
Particle Nature of Matter. Chapter 4
 Particle Nature of Matter Chapter 4 Modern physics When my grandfather was born, atoms were just an idea. That year, 1897, was marked by the discovery of the electron by J.J. Thomson. The nuclear model
Particle Nature of Matter Chapter 4 Modern physics When my grandfather was born, atoms were just an idea. That year, 1897, was marked by the discovery of the electron by J.J. Thomson. The nuclear model
3/29/2010. Structure of the Atom. Knowledge of atoms in 1900 CHAPTER 6. Evidence in 1900 indicated that the atom was not a fundamental unit:
 3/9/010 CHAPTER 6 Rutherford Scattering 6.1 The Atomic Models of Thomson and Rutherford 6. Definition of Cross Section 6. Rutherford Scattering 6.3 Structure of the Nucleus The opposite of a correct statement
3/9/010 CHAPTER 6 Rutherford Scattering 6.1 The Atomic Models of Thomson and Rutherford 6. Definition of Cross Section 6. Rutherford Scattering 6.3 Structure of the Nucleus The opposite of a correct statement
Angular Correlation Experiments
 Angular Correlation Experiments John M. LoSecco April 2, 2007 Angular Correlation Experiments J. LoSecco Notre Dame du Lac Nuclear Spin In atoms one can use the Zeeman Effect to determine the spin state.
Angular Correlation Experiments John M. LoSecco April 2, 2007 Angular Correlation Experiments J. LoSecco Notre Dame du Lac Nuclear Spin In atoms one can use the Zeeman Effect to determine the spin state.
Absorber Alpha emission Alpha particle Atom. Atomic line spectra Atomic mass unit Atomic number Atomic structure. Background radiation
 Material that prevent radioactive emission from passing through it Release of alpha particle from unstable nucleus(a 2+ helium ion or a helium nucleus) The nucleus of a helium atom (two protons and two
Material that prevent radioactive emission from passing through it Release of alpha particle from unstable nucleus(a 2+ helium ion or a helium nucleus) The nucleus of a helium atom (two protons and two
Principles of neutron TOF cross section measurements
 Principles of neutron TOF cross section measurements J. Heyse, C. Paradela, P. Schillebeeckx EC JRC IRMM Standards for Nuclear Safety, Security and Safeguards (SN3S) H.I. Kim Korea Atomic Energy Research
Principles of neutron TOF cross section measurements J. Heyse, C. Paradela, P. Schillebeeckx EC JRC IRMM Standards for Nuclear Safety, Security and Safeguards (SN3S) H.I. Kim Korea Atomic Energy Research
1. Nuclear Size. A typical atom radius is a few!10 "10 m (Angstroms). The nuclear radius is a few!10 "15 m (Fermi).
 1. Nuclear Size We have known since Rutherford s! " scattering work at Manchester in 1907, that almost all the mass of the atom is contained in a very small volume with high electric charge. Nucleus with
1. Nuclear Size We have known since Rutherford s! " scattering work at Manchester in 1907, that almost all the mass of the atom is contained in a very small volume with high electric charge. Nucleus with
Neutron Detection. n interactions with matter n detection High/low energy n detectors
 Neutron Detection Example of n detection: Well logging Reservoir/Formation Evaluation Brief introduction to neutron generation Continuous sources Large accelerators Pulsed neutron generators n interactions
Neutron Detection Example of n detection: Well logging Reservoir/Formation Evaluation Brief introduction to neutron generation Continuous sources Large accelerators Pulsed neutron generators n interactions
Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions.
 Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions. I first need to acknowledge that these two lectures were based on lectures presented previously in Med Phys I by Dr Howell. 1 Before
Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions. I first need to acknowledge that these two lectures were based on lectures presented previously in Med Phys I by Dr Howell. 1 Before
Particle Energy Loss in Matter
 Particle Energy Loss in Matter Charged particles, except electrons, loose energy when passing through material via atomic excitation and ionization These are protons, pions, muons, The energy loss can
Particle Energy Loss in Matter Charged particles, except electrons, loose energy when passing through material via atomic excitation and ionization These are protons, pions, muons, The energy loss can
CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS
 CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS Background Charged Particles Heavy charged particles Charged particles with Mass > m e α, proton, deuteron, heavy ion (e.g., C +, Fe + ), fission fragment, muon, etc. α is
CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS Background Charged Particles Heavy charged particles Charged particles with Mass > m e α, proton, deuteron, heavy ion (e.g., C +, Fe + ), fission fragment, muon, etc. α is
Accelerator Physics, BAU, First Semester, (Saed Dababneh).
 Accelerator Physics 501503746 Course web http://nuclear.bau.edu.jo/accelerators/ edu or http://nuclear.dababneh.com/accelerators/ com/accelerators/ 1 Grading Mid-term Exam 25% Projects 25% Final Exam 50%
Accelerator Physics 501503746 Course web http://nuclear.bau.edu.jo/accelerators/ edu or http://nuclear.dababneh.com/accelerators/ com/accelerators/ 1 Grading Mid-term Exam 25% Projects 25% Final Exam 50%
University of Oslo. Department of Physics. Interaction Between Ionizing Radiation And Matter, Part 2 Charged-Particles.
 Interaction Between Ionizing Radiation And Matter, Part Charged-Particles Audun Sanderud Excitation / ionization Incoming charged particle interact with atom/molecule: Ionization Excitation Ion pair created
Interaction Between Ionizing Radiation And Matter, Part Charged-Particles Audun Sanderud Excitation / ionization Incoming charged particle interact with atom/molecule: Ionization Excitation Ion pair created
Neutron induced reaction and neutron sources
 Neutron induced reaction and neutron sources Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 April 6, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 29) April 6, 2011 1 / 29 Outline 1 Neutron-induced
Neutron induced reaction and neutron sources Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 April 6, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 29) April 6, 2011 1 / 29 Outline 1 Neutron-induced
APEX CARE INSTITUTE FOR PG - TRB, SLET AND NET IN PHYSICS
 Page 1 1. Within the nucleus, the charge distribution A) Is constant, but falls to zero sharply at the nuclear radius B) Increases linearly from the centre, but falls off exponentially at the surface C)
Page 1 1. Within the nucleus, the charge distribution A) Is constant, but falls to zero sharply at the nuclear radius B) Increases linearly from the centre, but falls off exponentially at the surface C)
Nuclear Physics. (PHY-231) Dr C. M. Cormack. Nuclear Physics This Lecture
 Nuclear Physics (PHY-31) Dr C. M. Cormack 11 Nuclear Physics This Lecture This Lecture We will discuss an important effect in nuclear spectroscopy The Mössbauer Effect and its applications in technology
Nuclear Physics (PHY-31) Dr C. M. Cormack 11 Nuclear Physics This Lecture This Lecture We will discuss an important effect in nuclear spectroscopy The Mössbauer Effect and its applications in technology
O WILEY- MODERN NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY. WALTER D. LOVELAND Oregon State University. DAVID J. MORRISSEY Michigan State University
 MODERN NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY WALTER D. LOVELAND Oregon State University DAVID J. MORRISSEY Michigan State University GLENN T. SEABORG University of California, Berkeley O WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY &
MODERN NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY WALTER D. LOVELAND Oregon State University DAVID J. MORRISSEY Michigan State University GLENN T. SEABORG University of California, Berkeley O WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY &
X-RAY PRODUCTION. Prepared by:- EN KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH
 X-RAY PRODUCTION Prepared by:- EN KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH OBJECTIVES Discuss the process of x-ray being produced (conditions) Explain the principles of energy conversion in x-ray production (how energy
X-RAY PRODUCTION Prepared by:- EN KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH OBJECTIVES Discuss the process of x-ray being produced (conditions) Explain the principles of energy conversion in x-ray production (how energy
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 19 Chapter 12. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 19 Chapter 12 There are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry X-ray Techniques include:
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 19 Chapter 12 There are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry X-ray Techniques include:
Particle Detectors. How to See the Invisible
 Particle Detectors How to See the Invisible Which Subatomic Particles are Seen? Which particles live long enough to be visible in a detector? 2 Which Subatomic Particles are Seen? Protons Which particles
Particle Detectors How to See the Invisible Which Subatomic Particles are Seen? Which particles live long enough to be visible in a detector? 2 Which Subatomic Particles are Seen? Protons Which particles
GAMMA RAY SPECTROSCOPY
 GAMMA RAY SPECTROSCOPY Gamma Ray Spectroscopy 1 In this experiment you will use a sodium iodide (NaI) detector along with a multichannel analyzer (MCA) to measure gamma ray energies from energy level transitions
GAMMA RAY SPECTROSCOPY Gamma Ray Spectroscopy 1 In this experiment you will use a sodium iodide (NaI) detector along with a multichannel analyzer (MCA) to measure gamma ray energies from energy level transitions
PHYS 3446 Lecture #12
 PHYS 3446 Lecture #12 Wednesday, Oct. 18, 2006 Dr. 1. Particle Detection Ionization Detectors MWPC Scintillation Counters Time of Flight 1 Announcements Next LPCC Workshop Preparation work Each group to
PHYS 3446 Lecture #12 Wednesday, Oct. 18, 2006 Dr. 1. Particle Detection Ionization Detectors MWPC Scintillation Counters Time of Flight 1 Announcements Next LPCC Workshop Preparation work Each group to
Nuclear Reactions A Z. Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q > 0. Exothermic Endothermic
 Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
Rb, which had been compressed to a density of 1013
 Modern Physics Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Departmental Exam December 3, 2017 1. An electron is initially at rest in a uniform electric field E in the negative y direction and a uniform magnetic
Modern Physics Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Departmental Exam December 3, 2017 1. An electron is initially at rest in a uniform electric field E in the negative y direction and a uniform magnetic
Physics 100 PIXE F06
 Introduction: Ion Target Interaction Elastic Atomic Collisions Very low energies, typically below a few kev Surface composition and structure Ion Scattering spectrometry (ISS) Inelastic Atomic Collisions
Introduction: Ion Target Interaction Elastic Atomic Collisions Very low energies, typically below a few kev Surface composition and structure Ion Scattering spectrometry (ISS) Inelastic Atomic Collisions
Nuclear Physics Laboratory. Gamma spectroscopy with scintillation detectors. M. Makek Faculty of Science Department of Physics
 Nuclear Physics Laboratory Gamma spectroscopy with scintillation detectors M. Makek Faculty of Science Department of Physics Zagreb, 2015 1 1 Introduction The goal of this excercise is to familiarize with
Nuclear Physics Laboratory Gamma spectroscopy with scintillation detectors M. Makek Faculty of Science Department of Physics Zagreb, 2015 1 1 Introduction The goal of this excercise is to familiarize with
Introduction to Accelerator Physics Part 1
 Introduction to Accelerator Physics Part 1 Pedro Castro / Accelerator Physics Group (MPY) Introduction to Accelerator Physics DESY, 28th July 2014 Pedro Castro / MPY Accelerator Physics 28 th July 2014
Introduction to Accelerator Physics Part 1 Pedro Castro / Accelerator Physics Group (MPY) Introduction to Accelerator Physics DESY, 28th July 2014 Pedro Castro / MPY Accelerator Physics 28 th July 2014
Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon
 Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon Mohammad QH 1* and Maghdid HA 2 1 Department of Physics, College of Science, Raparin University, Sulaimanyah, Iraqi Kurdistan, Iraq 2 Department of Physics,
Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon Mohammad QH 1* and Maghdid HA 2 1 Department of Physics, College of Science, Raparin University, Sulaimanyah, Iraqi Kurdistan, Iraq 2 Department of Physics,
Contents. Charged Particles. Coulomb Interactions Elastic Scattering. Coulomb Interactions - Inelastic Scattering. Bremsstrahlung
 Contents Marcel MiGLiERiNi Nuclear Medicine, Radiology and Their Metrological Aspects. Radiation in Medicine. Dosimetry 4. Diagnostics & Therapy 5. Accelerators in Medicine 6. Therapy Planning 7. Nuclear
Contents Marcel MiGLiERiNi Nuclear Medicine, Radiology and Their Metrological Aspects. Radiation in Medicine. Dosimetry 4. Diagnostics & Therapy 5. Accelerators in Medicine 6. Therapy Planning 7. Nuclear
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 19 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions Medical Applications Radiation Detectors Chapter 29 http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm 1 Lightning
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 19 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions Medical Applications Radiation Detectors Chapter 29 http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm 1 Lightning
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lightning Review Lecture 19 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions Medical Applications Radiation Detectors Chapter 29 http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lightning Review Lecture 19 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions Medical Applications Radiation Detectors Chapter 29 http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm
The Compton Effect. Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA (Dated: November 26, 2002)
 The Compton Effect Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA 02139 marthab@mit.edu (Dated: November 26, 2002) We measured the angular dependence of the energies of 661.6 kev photons scattered
The Compton Effect Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA 02139 marthab@mit.edu (Dated: November 26, 2002) We measured the angular dependence of the energies of 661.6 kev photons scattered
Radionuclide Imaging MII Detection of Nuclear Emission
 Radionuclide Imaging MII 3073 Detection of Nuclear Emission Nuclear radiation detectors Detectors that are commonly used in nuclear medicine: 1. Gas-filled detectors 2. Scintillation detectors 3. Semiconductor
Radionuclide Imaging MII 3073 Detection of Nuclear Emission Nuclear radiation detectors Detectors that are commonly used in nuclear medicine: 1. Gas-filled detectors 2. Scintillation detectors 3. Semiconductor
Outline. Chapter 6 The Basic Interactions between Photons and Charged Particles with Matter. Photon interactions. Photoelectric effect
 Chapter 6 The Basic Interactions between Photons and Charged Particles with Matter Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther
Chapter 6 The Basic Interactions between Photons and Charged Particles with Matter Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther
Photons: Interactions
 Photons: Interactions Photons appear in detector systems as primary photons, created in Bremsstrahlung and de-excitations Photons are also used for medical applications, both imaging and radiation treatment.
Photons: Interactions Photons appear in detector systems as primary photons, created in Bremsstrahlung and de-excitations Photons are also used for medical applications, both imaging and radiation treatment.
Chapter 2 Radiation-Matter Interactions
 Chapter 2 Radiation-Matter Interactions The behavior of radiation and matter as a function of energy governs the degradation of astrophysical information along the path and the characteristics of the detectors.
Chapter 2 Radiation-Matter Interactions The behavior of radiation and matter as a function of energy governs the degradation of astrophysical information along the path and the characteristics of the detectors.
L-35 Modern Physics-3 Nuclear Physics 29:006 FINAL EXAM. Structure of the nucleus. The atom and the nucleus. Nuclear Terminology
 9:006 FINAL EXAM L-5 Modern Physics- Nuclear Physics The final exam is on Monday MAY 7:0 AM - 9:0 AM in W90 CB The FE is not cumulative, and will cover lectures through 6. (50 questions) The last regular
9:006 FINAL EXAM L-5 Modern Physics- Nuclear Physics The final exam is on Monday MAY 7:0 AM - 9:0 AM in W90 CB The FE is not cumulative, and will cover lectures through 6. (50 questions) The last regular
Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na. Ellen Simmons
 Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na Ellen Simmons 1 Contents Introduction Review of the Types of Radiation Charged Particle Radiation Detection Review of Semiconductor
Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na Ellen Simmons 1 Contents Introduction Review of the Types of Radiation Charged Particle Radiation Detection Review of Semiconductor
This paper should be understood as an extended version of a talk given at the
 This paper should be understood as an extended version of a talk given at the Abstract: 1 st JINA workshop at Gull Lake, 2002. Recent experimental developments at LANL (Los Alamos, NM, USA) and CERN (Geneva,
This paper should be understood as an extended version of a talk given at the Abstract: 1 st JINA workshop at Gull Lake, 2002. Recent experimental developments at LANL (Los Alamos, NM, USA) and CERN (Geneva,
Science of Nuclear Energy and Radiation a Comprehensive Course for Science Teachers June 22-25, 1998 McMaster University
 Science of Nuclear Energy and Radiation a Comprehensive Course for Science Teachers June 22-25, 1998 McMaster University Notes to accompany Lab demonstrations by Barry Diacon, Technician, Department of
Science of Nuclear Energy and Radiation a Comprehensive Course for Science Teachers June 22-25, 1998 McMaster University Notes to accompany Lab demonstrations by Barry Diacon, Technician, Department of
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ MeV, 4 T 8 MeV
 Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
CHAPTER 3 Prelude to Quantum Theory. Observation of X Rays. Thomson s Cathode-Ray Experiment. Röntgen s X-Ray Tube
 CHAPTER Prelude to Quantum Theory.1 Discovery of the X Ray and the Electron. Determination of Electron Charge. Line Spectra.4 Quantization.5 Blackbody Radiation.6 Photoelectric Effect.7 X-Ray Production.8
CHAPTER Prelude to Quantum Theory.1 Discovery of the X Ray and the Electron. Determination of Electron Charge. Line Spectra.4 Quantization.5 Blackbody Radiation.6 Photoelectric Effect.7 X-Ray Production.8
energy loss Ionization + excitation of atomic energy levels Mean energy loss rate de /dx proportional to (electric charge) 2 of incident particle
 Lecture 4 Particle physics processes - particles are small, light, energetic à processes described by quantum mechanics and relativity à processes are probabilistic, i.e., we cannot know the outcome of
Lecture 4 Particle physics processes - particles are small, light, energetic à processes described by quantum mechanics and relativity à processes are probabilistic, i.e., we cannot know the outcome of
Chemistry 311: Instrumentation Analysis Topic 2: Atomic Spectroscopy. Chemistry 311: Instrumentation Analysis Topic 2: Atomic Spectroscopy
 Topic 2b: X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry Text: Chapter 12 Rouessac (1 week) 4.0 X-ray Fluorescence Download, read and understand EPA method 6010C ICP-OES Winter 2009 Page 1 Atomic X-ray Spectrometry Fundamental
Topic 2b: X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry Text: Chapter 12 Rouessac (1 week) 4.0 X-ray Fluorescence Download, read and understand EPA method 6010C ICP-OES Winter 2009 Page 1 Atomic X-ray Spectrometry Fundamental
ATOMIC WORLD P.1. ejected photoelectrons. current amplifier. photomultiplier tube (PMT)
 ATOMIC WORLD P. HKAL PAPER I 0 8 The metal Caesium has a work function of.08 ev. Given: Planck constant h = 6.63 0 34 J s, charge of an electron e =.60 0 9 C (a) (i) Calculate the longest wavelength of
ATOMIC WORLD P. HKAL PAPER I 0 8 The metal Caesium has a work function of.08 ev. Given: Planck constant h = 6.63 0 34 J s, charge of an electron e =.60 0 9 C (a) (i) Calculate the longest wavelength of
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions
 Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap
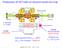 Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
PHY492: Nuclear & Particle Physics. Lecture 25. Particle Detectors
 PHY492: Nuclear & Particle Physics Lecture 25 Particle Detectors http://pdg.lbl.gov/2006/reviews/contents_sports.html S(T ) = dt dx nz = ρa 0 Units for energy loss Minimum ionization in thin solids Z/A
PHY492: Nuclear & Particle Physics Lecture 25 Particle Detectors http://pdg.lbl.gov/2006/reviews/contents_sports.html S(T ) = dt dx nz = ρa 0 Units for energy loss Minimum ionization in thin solids Z/A
Lecture 4. Detectors for Ionizing Particles
 Lecture 4 Detectors for Ionizing Particles Introduction Overview of detector systems Sources of radiation Radioactive decay Cosmic Radiation Accelerators Content Interaction of Radiation with Matter General
Lecture 4 Detectors for Ionizing Particles Introduction Overview of detector systems Sources of radiation Radioactive decay Cosmic Radiation Accelerators Content Interaction of Radiation with Matter General
V. 3. Development of an Accelerator Beam Loss Monitor Using an Optical Fiber
 CYRIC Annual Report 2001 V. 3. Development of an Accelerator Beam Loss Monitor Using an Optical Fiber Kawata N. Baba M. Kato M.*, Miura T.**, and Yamadera A.***, Cyclotron and Radioisotope Center, Tohoku
CYRIC Annual Report 2001 V. 3. Development of an Accelerator Beam Loss Monitor Using an Optical Fiber Kawata N. Baba M. Kato M.*, Miura T.**, and Yamadera A.***, Cyclotron and Radioisotope Center, Tohoku
Fundamental Forces. Range Carrier Observed? Strength. Gravity Infinite Graviton No. Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983)
 Fundamental Forces Force Relative Strength Range Carrier Observed? Gravity 10-39 Infinite Graviton No Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983) Electromagnetic 10-2 Infinite Photon Yes (1923) Strong 1 Nuclear
Fundamental Forces Force Relative Strength Range Carrier Observed? Gravity 10-39 Infinite Graviton No Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983) Electromagnetic 10-2 Infinite Photon Yes (1923) Strong 1 Nuclear
Neutron interactions and dosimetry. Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland
 Neutron interactions and dosimetry Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland Topics 1. Neutron interactions 1. Scattering 2. Absorption 2. Neutron dosimetry 3. Applications The neutron Uncharged particle, mass close
Neutron interactions and dosimetry Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland Topics 1. Neutron interactions 1. Scattering 2. Absorption 2. Neutron dosimetry 3. Applications The neutron Uncharged particle, mass close
(Total for Question = 5 marks) PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 1 Rutherford designed an experiment to see what happened when alpha particles were directed at a piece of gold foil. Summarise the observations and state the conclusions Rutherford reached about the structure
1 Rutherford designed an experiment to see what happened when alpha particles were directed at a piece of gold foil. Summarise the observations and state the conclusions Rutherford reached about the structure
DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
 Chapter Eleven DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER MCQ I 111 A particle is dropped from a height H The de Broglie wavelength of the particle as a function of height is proportional to (a) H (b) H 1/2 (c)
Chapter Eleven DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER MCQ I 111 A particle is dropped from a height H The de Broglie wavelength of the particle as a function of height is proportional to (a) H (b) H 1/2 (c)
Radiation Detection. 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program.
 Radiation Detection 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org GM Detectors 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org 1 A closer look 15 th Annual OSC Readiness
Radiation Detection 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org GM Detectors 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org 1 A closer look 15 th Annual OSC Readiness
Decays and Scattering. Decay Rates Cross Sections Calculating Decays Scattering Lifetime of Particles
 Decays and Scattering Decay Rates Cross Sections Calculating Decays Scattering Lifetime of Particles 1 Decay Rates There are THREE experimental probes of Elementary Particle Interactions - bound states
Decays and Scattering Decay Rates Cross Sections Calculating Decays Scattering Lifetime of Particles 1 Decay Rates There are THREE experimental probes of Elementary Particle Interactions - bound states
Elastic scattering. Elastic scattering
 Elastic scattering Now we have worked out how much energy is lost when a neutron is scattered through an angle, θ We would like to know how much energy, on average, is lost per collision In order to do
Elastic scattering Now we have worked out how much energy is lost when a neutron is scattered through an angle, θ We would like to know how much energy, on average, is lost per collision In order to do
Accelerators Ideal Case
 Accelerators Ideal Case Goal of an accelerator: increase energy of CHARGED par:cles Increase energy ΔE = r 2 F dr = q ( E + v B)d r The par:cle trajectory direc:on dr parallel to v ΔE = increase of energy
Accelerators Ideal Case Goal of an accelerator: increase energy of CHARGED par:cles Increase energy ΔE = r 2 F dr = q ( E + v B)d r The par:cle trajectory direc:on dr parallel to v ΔE = increase of energy
Physics 102: Lecture 26. X-rays. Make sure your grade book entries are correct. Physics 102: Lecture 26, Slide 1
 Physics 102: Lecture 26 X-rays Make sure your grade book entries are correct. Physics 102: Lecture 26, Slide 1 X-Rays Photons with energy in approx range 100eV to 100,000eV. This large energy means they
Physics 102: Lecture 26 X-rays Make sure your grade book entries are correct. Physics 102: Lecture 26, Slide 1 X-Rays Photons with energy in approx range 100eV to 100,000eV. This large energy means they
Radioactivity. (b) Fig shows two samples of the same radioactive substance. The substance emits β-particles. Fig. 12.1
 112 (a) What is meant by radioactive decay? Radioactivity [2] (b) Fig. 12.1 shows two samples of the same radioactive substance. The substance emits β-particles. Fig. 12.1 Put a tick alongside any of the
112 (a) What is meant by radioactive decay? Radioactivity [2] (b) Fig. 12.1 shows two samples of the same radioactive substance. The substance emits β-particles. Fig. 12.1 Put a tick alongside any of the
Chapter 29. Nuclear Physics
 Chapter 29 Nuclear Physics Ernest Rutherford 1871 1937 Discovery that atoms could be broken apart Studied radioactivity Nobel prize in 1908 Some Properties of Nuclei All nuclei are composed of protons
Chapter 29 Nuclear Physics Ernest Rutherford 1871 1937 Discovery that atoms could be broken apart Studied radioactivity Nobel prize in 1908 Some Properties of Nuclei All nuclei are composed of protons
