Cumpleaños de Carlos, HA&PDE
|
|
|
- Ethelbert Waters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Shell interactions for Dirac operators: selfadjointeness, point spectrum, and confinement (with N. Arrizabalaga and A. Mas) Cumpleaños de Carlos, HA&PDE Luis VEGA, BCAM-UPV/EHU CHICAGO, September 21st, 2014
2
3 Free Dirac operator in R 3 Definition. H : Cc 1 (R 3 ) 4!Cc 1 (R 3 ) 4 free Dirac operator in R 3, 0 m 0 i@ 2 i@ 1 H = i r+m = B 0 2 i@ 1 i@ i@ 2 i@ 1 m 2 i@ 1 i@ 3 0 m 1 C A. Remarks. 1st order symmetric di erential operator. Local version of p +m 2 : H 2 =( +m 2 )I 4. Dirac (1928)
4 Previous results on + for Lipschitz surfaces. Subcritical/Critical. Coupling with a singular potential First Question. R 3 bounded regular domain, =@, surface measure on, V potential L 2 ( ) 4 -valued. To find D L 2 (R 3 ) 4 such that H + V defined on D is self-adjoint. Motivation. Quantum Physics requires self-adjointness. x critical (scaling) for H, < 1 (Dolbeault, Esteban, Sere, 00; Hardy Inequality, Uncertainty Principle). H+ x =1 (and other critical V s on S 2 ) (Dittrich,Exner& Seba 89; Spherical Harmonics. Albeverio, Gesztesy, Hoegh- Krohn & Holden 88-05).
5 Initial Approach First Question. To find D L 2 (R 3 ) 4 such that H + V defined on D is self-adjoint. Our Approach. Take ' 2 D, V potential L 2 ( ) 4 -valued =) V (') = g for some g 2 L 2 ( ) 4. (H+V )(') 2 L 2 (R 3 ) 4 =) (H+V )(') =G for some G 2 L 2 (R 3 ) 4. H(') =G + g in the sense of distributions. Therefore ' = (G + g) and (H + V )(') =G, V (') = g, where is the fundamental solution of H = i r+ m, (x) = e m x 4 x m +(1+m x ) i x x 2 for x 2 R 3 \{0}.
6 Self-adjointness of H + V Property. If G 2 L 2 (R 3 ) 4,then ( G) 2 L 2 ( ) 4. G 2 W 1,2 (R 3 ) 4 and Theorem (Self-adjointness). Given : L 2 ( ) 4! L 2 ( ) 4 bounded, self-adjoint and with closed range, define D = (G + g) : ( G) = (g) L 2 (R 3 ) 4. If V (G + g) = g, thenh + V defined on D is essentially self-adjoint. Remarks. Under more assumptions on, H + V is self-adjoint. Posilicano Other di erential operators and measures are considered. Other relations between ( G) and g are considered.
7 Resolvent of H Resolvent. Given a 2 ( m, m), let a be the fundamental solution of H a = i r+ m a, a (x) = e p m 2 4 x a 2 x a + m + 1+ p m 2 a 2 x i x x 2. Our Setting. + R 3 bounded regular domain, = R 3 \ +, =@ ±, surface measure on, N normal vector on w.r.t. +. Properties. If g 2 L 2 ( ) 4,then(H x 2, set a)( a g) =0in c. For Then, C a ±g(x) = lim ( a g)(y), C a g(x) =p.v. ( a g)(x). ± 3y!x nt C a ± = i 2 ( N)+Ca (Plemelj-Sokhotski jump formulae), C a ( N) 2 = 1 4.
8 Point spectrum and confinement for H + V Our Setting. Set D = ' = (G + g) : ( G) = (g) and H + V : D L 2 (R 3 ) 4! L 2 (R 3 ) 4 defined by V (') = g and (H + V )(') =G for ' 2 D. Our Theorem (Point Spectrum). Given a 2 ( m, m), Ker (H + V a) 6= ; i Ker ( + C C a ) 6= ;.
9 Point spectrum and confinement for H + V Definition. V generates confinement w.r.t. H and i supp e it(h+v ) (f) ± for all f 2 L 2 ( ± ) 4 and all t 2 R. This is equivalent to require that ± ' 2 D for all ' 2 D. Theorem (Confinement). Assume that H + V is self-adjoint on D. Then, V generates confinement w.r.t. H and if {C ( N), ( N)} = ( ( N)) 2.
10 Some applications. Electrostatic shell potentials Theorem. Let 2 R \{0} and a 2 ( m, m). Take = (1/ + C ), D = ' = (G + g) : ( G) = (g), and V (') = 2 (' + + ' ) (' ± n.t. boundary values of ' on ). H + V defined on D is self-adjoint for all 6= ±2. Ker (H + V a) 6= ; i Ker (1/ + C a ) 6= ;. H +V and H +V 4/ have the same eigenvalues in ( m, m). If 62 [1/kC a k, 4kC a k], then Ker (H + V a) =;. If 62 [1/C, 4C], where C =sup a2( m,m) kc a k < 1, then H + V has no eigenvalues in ( m, m). Theorem. Let H + V be as above. If is connected, then H + V has no eigenvalues in R \ [ m, m].
11 Some applications. Electrostatic plus Lorentz scalar shell potentials Theorem. Let e, s 2 R be such that 2 e 2 s 6=0, 4. Take = s e 2 2 e s C, D = ' = (G + g) : ( G) = (g), and V es (') = 1 2 ( e + s )(' + + ' ) (' ± n.t. boundary values of '). H + V es defined on D is self-adjoint. V es generates confinement w.r.t H and i 2 e 2 s = 4.
12 Some applications. Electrostatic plus Lorentz scalar shell potentials Remarks. That V es generates confinement means that the particles modelized by the t + i(h + V es ) never cross over time, i.e., becomes impenetrable. The impenetrability condition s = 4 was known for ={x 2 R 3 : x = R}, R>0 (Dittrich-Exner-Seba). 2 e 2
13 Uncertainty Principle on the sphere S 2 We focus on H + V for = S 2 = {x 2 R 3 : x =1} Definition. Let e =( 1, 2, 3) be the family of Pauli matrices. Given a 2 ( m, m), define k a (x) = e p m 2 4 x w a (x) = e p m 2 4 x 3 a 2 x a 2 x I 2 and 1+ p m 2 a 2 x i e x. For f 2 L 2 ( ) 2 and x 2 S 2,set K a f(x) =(k a f)(x) and W a (f) =p.v.(w a f)(x).
14 Uncertainty Principle on the sphere S 2 Remarks. K a and W a are bounded operators in L 2 ( ) 2. K a is a positive operator.
15 Uncertainty Principle on the sphere S 2 Theorem. Let >0 and a 2 ( m, m). The operator is invertible in L 2 ( ) 2. 1/ +(m + a)k a Furthermore, for any f 2 L 2 ( ) 2 and any >0, Z f 2 d apple 1 Z (1/ +(m + a)k a ) 1 (W a (f)) W S 2M a (f) d 2 S 2 + 2M ZS 2 (1/ +(m + a)k a )((e N)f) (e N)f d, where M is a constant depending only on m and a. Moreover, M 1 2 e p m 2 a 2p 2 e 2p m 2 a 2. (1) For suitable attained. s, the inequality (1) is sharp and the equality can be
16 Uncertainty Principle on the sphere S 2. Consequences Definition (2-dimensional Riesz transform). Given a finite Borel measure in R 3, h 2 L 2 ( ) and x 2 R 3, one defines the 2-dimensional Riesz transform of h as Z x y R (h)(x) =lim h(y) d (y), &0 x y 3 x y > whenever the limit makes sense.
17 Uncertainty Principle on the sphere S 2. Consequences Corollary. 2 khk L 2 ( ) applekr (h)k L 2 ( ) 3 for all real-valued h 2 L 2 ( ), and the inequality is sharp. Hofmann, Marmolejo-Olea, Mitrea, Pérez-Esteva, & Michael Taylor 09 For suitable elections of, a, and, the minimizers of (1) give rise to eigenfunctions of H + V with eigenvalue a. The set of s for which H +V has a non-trivial eigenfunction contains an interval.
18 THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION
SELF-ADJOINTNESS OF DIRAC OPERATORS VIA HARDY-DIRAC INEQUALITIES
 SELF-ADJOINTNESS OF DIRAC OPERATORS VIA HARDY-DIRAC INEQUALITIES MARIA J. ESTEBAN 1 AND MICHAEL LOSS Abstract. Distinguished selfadjoint extension of Dirac operators are constructed for a class of potentials
SELF-ADJOINTNESS OF DIRAC OPERATORS VIA HARDY-DIRAC INEQUALITIES MARIA J. ESTEBAN 1 AND MICHAEL LOSS Abstract. Distinguished selfadjoint extension of Dirac operators are constructed for a class of potentials
SOME REMARKS ABOUT THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE
 SOME REMARKS ABOUT THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE Luis VEGA (a mathematician) Rubio de Francia Lecture UAM, 5-06-015 1 Summary Uncertainty Principle (Heisenberg). Examples: Schrödinger stationary equation (Heisenberg,
SOME REMARKS ABOUT THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE Luis VEGA (a mathematician) Rubio de Francia Lecture UAM, 5-06-015 1 Summary Uncertainty Principle (Heisenberg). Examples: Schrödinger stationary equation (Heisenberg,
10.1. The spectrum of an operator. Lemma If A < 1 then I A is invertible with bounded inverse
 10. Spectral theory For operators on finite dimensional vectors spaces, we can often find a basis of eigenvectors (which we use to diagonalize the matrix). If the operator is symmetric, this is always
10. Spectral theory For operators on finite dimensional vectors spaces, we can often find a basis of eigenvectors (which we use to diagonalize the matrix). If the operator is symmetric, this is always
11. Spectral theory For operators on finite dimensional vectors spaces, we can often find a basis of eigenvectors (which we use to diagonalize the
 11. Spectral theory For operators on finite dimensional vectors spaces, we can often find a basis of eigenvectors (which we use to diagonalize the matrix). If the operator is symmetric, this is always
11. Spectral theory For operators on finite dimensional vectors spaces, we can often find a basis of eigenvectors (which we use to diagonalize the matrix). If the operator is symmetric, this is always
arxiv:math-ph/ v2 2 Nov 1999
 Delta Interactions and Electrodynamics of Point Particles arxiv:math-ph/9907009 v Nov 999 Diego Noja and Andrea Posilicano Abstract. We report on some recent work of the authors showing the relations between
Delta Interactions and Electrodynamics of Point Particles arxiv:math-ph/9907009 v Nov 999 Diego Noja and Andrea Posilicano Abstract. We report on some recent work of the authors showing the relations between
A Spectral Characterization of Closed Range Operators 1
 A Spectral Characterization of Closed Range Operators 1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (IIT Madras) 1 Closed Range Operators Operator equations of the form T x = y, where T : X Y is a linear operator between normed linear
A Spectral Characterization of Closed Range Operators 1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (IIT Madras) 1 Closed Range Operators Operator equations of the form T x = y, where T : X Y is a linear operator between normed linear
Hilbert Space Problems
 Hilbert Space Problems Prescribed books for problems. ) Hilbert Spaces, Wavelets, Generalized Functions and Modern Quantum Mechanics by Willi-Hans Steeb Kluwer Academic Publishers, 998 ISBN -7923-523-9
Hilbert Space Problems Prescribed books for problems. ) Hilbert Spaces, Wavelets, Generalized Functions and Modern Quantum Mechanics by Willi-Hans Steeb Kluwer Academic Publishers, 998 ISBN -7923-523-9
Functional Analysis Review
 Functional Analysis Review Lorenzo Rosasco slides courtesy of Andre Wibisono 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications September 9, 2013 1 2 3 4 Vector Space A vector space is a set V with binary
Functional Analysis Review Lorenzo Rosasco slides courtesy of Andre Wibisono 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications September 9, 2013 1 2 3 4 Vector Space A vector space is a set V with binary
Lecture notes: Applied linear algebra Part 1. Version 2
 Lecture notes: Applied linear algebra Part 1. Version 2 Michael Karow Berlin University of Technology karow@math.tu-berlin.de October 2, 2008 1 Notation, basic notions and facts 1.1 Subspaces, range and
Lecture notes: Applied linear algebra Part 1. Version 2 Michael Karow Berlin University of Technology karow@math.tu-berlin.de October 2, 2008 1 Notation, basic notions and facts 1.1 Subspaces, range and
Entanglement of boundary conditions giving rise to spontaneous symmetry breaking in quantum mechanics
 arxiv:1902.05836v1 [math-ph] 15 Feb 2019 Entanglement of boundary conditions giving rise to spontaneous symmetry breaking in quantum mechanics A. Restuccia 1,2, A. Sotomayor 3 and V. Strauss 4 February
arxiv:1902.05836v1 [math-ph] 15 Feb 2019 Entanglement of boundary conditions giving rise to spontaneous symmetry breaking in quantum mechanics A. Restuccia 1,2, A. Sotomayor 3 and V. Strauss 4 February
The oblique derivative problem for general elliptic systems in Lipschitz domains
 M. MITREA The oblique derivative problem for general elliptic systems in Lipschitz domains Let M be a smooth, oriented, connected, compact, boundaryless manifold of real dimension m, and let T M and T
M. MITREA The oblique derivative problem for general elliptic systems in Lipschitz domains Let M be a smooth, oriented, connected, compact, boundaryless manifold of real dimension m, and let T M and T
The Finite Spectrum of Sturm-Liouville Operator With δ-interactions
 Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 93-9466 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) Vol. 3, Issue (June 08), pp. 496 507 The Finite Spectrum of Sturm-Liouville
Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 93-9466 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) Vol. 3, Issue (June 08), pp. 496 507 The Finite Spectrum of Sturm-Liouville
1 Distributions (due January 22, 2009)
 Distributions (due January 22, 29). The distribution derivative of the locally integrable function ln( x ) is the principal value distribution /x. We know that, φ = lim φ(x) dx. x ɛ x Show that x, φ =
Distributions (due January 22, 29). The distribution derivative of the locally integrable function ln( x ) is the principal value distribution /x. We know that, φ = lim φ(x) dx. x ɛ x Show that x, φ =
Vector Spaces and SubSpaces
 Vector Spaces and SubSpaces Linear Algebra MATH 2076 Linear Algebra Vector Spaces & SubSpaces Chapter 4, Section 1b 1 / 10 What is a Vector Space? A vector space is a bunch of objects that we call vectors
Vector Spaces and SubSpaces Linear Algebra MATH 2076 Linear Algebra Vector Spaces & SubSpaces Chapter 4, Section 1b 1 / 10 What is a Vector Space? A vector space is a bunch of objects that we call vectors
4. We accept without proofs that the following functions are differentiable: (e x ) = e x, sin x = cos x, cos x = sin x, log (x) = 1 sin x
 4 We accept without proofs that the following functions are differentiable: (e x ) = e x, sin x = cos x, cos x = sin x, log (x) = 1 sin x x, x > 0 Since tan x = cos x, from the quotient rule, tan x = sin
4 We accept without proofs that the following functions are differentiable: (e x ) = e x, sin x = cos x, cos x = sin x, log (x) = 1 sin x x, x > 0 Since tan x = cos x, from the quotient rule, tan x = sin
APPENDIX A. Background Mathematics. A.1 Linear Algebra. Vector algebra. Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components x 1 x 2.
 APPENDIX A Background Mathematics A. Linear Algebra A.. Vector algebra Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components 0 x x 2 B C @. A x n Definition 6 (scalar product). The scalar product
APPENDIX A Background Mathematics A. Linear Algebra A.. Vector algebra Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components 0 x x 2 B C @. A x n Definition 6 (scalar product). The scalar product
Function spaces and stochastic processes on fractals I. Takashi Kumagai. (RIMS, Kyoto University, Japan)
 Function spaces and stochastic processes on fractals I Takashi Kumagai (RIMS, Kyoto University, Japan) http://www.kurims.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~kumagai/ International workshop on Fractal Analysis September 11-17,
Function spaces and stochastic processes on fractals I Takashi Kumagai (RIMS, Kyoto University, Japan) http://www.kurims.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~kumagai/ International workshop on Fractal Analysis September 11-17,
Second Order ODEs. CSCC51H- Numerical Approx, Int and ODEs p.130/177
 Second Order ODEs Often physical or biological systems are best described by second or higher-order ODEs. That is, second or higher order derivatives appear in the mathematical model of the system. For
Second Order ODEs Often physical or biological systems are best described by second or higher-order ODEs. That is, second or higher order derivatives appear in the mathematical model of the system. For
MATH 409 Advanced Calculus I Lecture 10: Continuity. Properties of continuous functions.
 MATH 409 Advanced Calculus I Lecture 10: Continuity. Properties of continuous functions. Continuity Definition. Given a set E R, a function f : E R, and a point c E, the function f is continuous at c if
MATH 409 Advanced Calculus I Lecture 10: Continuity. Properties of continuous functions. Continuity Definition. Given a set E R, a function f : E R, and a point c E, the function f is continuous at c if
Nonlinear Programming Algorithms Handout
 Nonlinear Programming Algorithms Handout Michael C. Ferris Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 5376 September 9 1 Eigenvalues The eigenvalues of a matrix A C n n are
Nonlinear Programming Algorithms Handout Michael C. Ferris Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 5376 September 9 1 Eigenvalues The eigenvalues of a matrix A C n n are
f(x) f(z) c x z > 0 1
 INVERSE AND IMPLICIT FUNCTION THEOREMS I use df x for the linear transformation that is the differential of f at x.. INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM Definition. Suppose S R n is open, a S, and f : S R n is a
INVERSE AND IMPLICIT FUNCTION THEOREMS I use df x for the linear transformation that is the differential of f at x.. INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM Definition. Suppose S R n is open, a S, and f : S R n is a
Rough metrics, the Kato square root problem, and the continuity of a flow tangent to the Ricci flow
 Rough metrics, the Kato square root problem, and the continuity of a flow tangent to the Ricci flow Lashi Bandara Mathematical Sciences Chalmers University of Technology and University of Gothenburg 22
Rough metrics, the Kato square root problem, and the continuity of a flow tangent to the Ricci flow Lashi Bandara Mathematical Sciences Chalmers University of Technology and University of Gothenburg 22
ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING FROM PERTURBED SURFACES. Katharine Ott Advisor: Irina Mitrea Department of Mathematics University of Virginia
 ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING FROM PERTURBED SURFACES Katharine Ott Advisor: Irina Mitrea Department of Mathematics University of Virginia Abstract This paper is concerned with the study of scattering of
ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING FROM PERTURBED SURFACES Katharine Ott Advisor: Irina Mitrea Department of Mathematics University of Virginia Abstract This paper is concerned with the study of scattering of
NORMS ON SPACE OF MATRICES
 NORMS ON SPACE OF MATRICES. Operator Norms on Space of linear maps Let A be an n n real matrix and x 0 be a vector in R n. We would like to use the Picard iteration method to solve for the following system
NORMS ON SPACE OF MATRICES. Operator Norms on Space of linear maps Let A be an n n real matrix and x 0 be a vector in R n. We would like to use the Picard iteration method to solve for the following system
Critical magnetic fields for the magnetic Dirac-Coulomb operator. Maria J. ESTEBAN. C.N.R.S. and University Paris-Dauphine
 Critical magnetic fields for the magnetic Dirac-Coulomb operator Maria J. ESTEBAN C.N.R.S. and University Paris-Dauphine In collaboration with : Jean Dolbeault and Michael Loss http://www.ceremade.dauphine.fr/
Critical magnetic fields for the magnetic Dirac-Coulomb operator Maria J. ESTEBAN C.N.R.S. and University Paris-Dauphine In collaboration with : Jean Dolbeault and Michael Loss http://www.ceremade.dauphine.fr/
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 5
 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 5 DUE 1 MARCH, 2016 1) Let f(x) = 1 if x is rational and f(x) = 0 if x is irrational. Show that f is not continuous at any real number. Solution Fix any x R. We will show that f is
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 5 DUE 1 MARCH, 2016 1) Let f(x) = 1 if x is rational and f(x) = 0 if x is irrational. Show that f is not continuous at any real number. Solution Fix any x R. We will show that f is
Course 212: Academic Year Section 1: Metric Spaces
 Course 212: Academic Year 1991-2 Section 1: Metric Spaces D. R. Wilkins Contents 1 Metric Spaces 3 1.1 Distance Functions and Metric Spaces............. 3 1.2 Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces.........
Course 212: Academic Year 1991-2 Section 1: Metric Spaces D. R. Wilkins Contents 1 Metric Spaces 3 1.1 Distance Functions and Metric Spaces............. 3 1.2 Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces.........
LECTURE 5 APPLICATIONS OF BDIE METHOD: ACOUSTIC SCATTERING BY INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC OBSTACLES DAVID NATROSHVILI
 LECTURE 5 APPLICATIONS OF BDIE METHOD: ACOUSTIC SCATTERING BY INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC OBSTACLES DAVID NATROSHVILI Georgian Technical University Tbilisi, GEORGIA 0-0 1. Formulation of the corresponding
LECTURE 5 APPLICATIONS OF BDIE METHOD: ACOUSTIC SCATTERING BY INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC OBSTACLES DAVID NATROSHVILI Georgian Technical University Tbilisi, GEORGIA 0-0 1. Formulation of the corresponding
Self-adjoint extensions of symmetric operators
 Self-adjoint extensions of symmetric operators Simon Wozny Proseminar on Linear Algebra WS216/217 Universität Konstanz Abstract In this handout we will first look at some basics about unbounded operators.
Self-adjoint extensions of symmetric operators Simon Wozny Proseminar on Linear Algebra WS216/217 Universität Konstanz Abstract In this handout we will first look at some basics about unbounded operators.
76 Griesemer, Lewis, Siedentop the Dirac operator in the gap with the number of negative eigenvalues of a corresponding Schrodinger operator (see [5])
![76 Griesemer, Lewis, Siedentop the Dirac operator in the gap with the number of negative eigenvalues of a corresponding Schrodinger operator (see [5]) 76 Griesemer, Lewis, Siedentop the Dirac operator in the gap with the number of negative eigenvalues of a corresponding Schrodinger operator (see [5])](/thumbs/74/70997672.jpg) Doc. Math. J. DMV 75 A Minimax Principle for Eigenvalues in Spectral Gaps: Dirac Operators with Coulomb Potentials Marcel Griesemer, Roger T. Lewis, Heinz Siedentop Received: March 9, 999 Communicated
Doc. Math. J. DMV 75 A Minimax Principle for Eigenvalues in Spectral Gaps: Dirac Operators with Coulomb Potentials Marcel Griesemer, Roger T. Lewis, Heinz Siedentop Received: March 9, 999 Communicated
EIGENFUNCTIONS OF DIRAC OPERATORS AT THE THRESHOLD ENERGIES
 EIGENFUNCTIONS OF DIRAC OPERATORS AT THE THRESHOLD ENERGIES TOMIO UMEDA Abstract. We show that the eigenspaces of the Dirac operator H = α (D A(x)) + mβ at the threshold energies ±m are coincide with the
EIGENFUNCTIONS OF DIRAC OPERATORS AT THE THRESHOLD ENERGIES TOMIO UMEDA Abstract. We show that the eigenspaces of the Dirac operator H = α (D A(x)) + mβ at the threshold energies ±m are coincide with the
Math 421, Homework #9 Solutions
 Math 41, Homework #9 Solutions (1) (a) A set E R n is said to be path connected if for any pair of points x E and y E there exists a continuous function γ : [0, 1] R n satisfying γ(0) = x, γ(1) = y, and
Math 41, Homework #9 Solutions (1) (a) A set E R n is said to be path connected if for any pair of points x E and y E there exists a continuous function γ : [0, 1] R n satisfying γ(0) = x, γ(1) = y, and
MA2AA1 (ODE s): The inverse and implicit function theorem
 MA2AA1 (ODE s): The inverse and implicit function theorem Sebastian van Strien (Imperial College) February 3, 2013 Differential Equations MA2AA1 Sebastian van Strien (Imperial College) 0 Some of you did
MA2AA1 (ODE s): The inverse and implicit function theorem Sebastian van Strien (Imperial College) February 3, 2013 Differential Equations MA2AA1 Sebastian van Strien (Imperial College) 0 Some of you did
Hardy-Stein identity and Square functions
 Hardy-Stein identity and Square functions Daesung Kim (joint work with Rodrigo Bañuelos) Department of Mathematics Purdue University March 28, 217 Daesung Kim (Purdue) Hardy-Stein identity UIUC 217 1 /
Hardy-Stein identity and Square functions Daesung Kim (joint work with Rodrigo Bañuelos) Department of Mathematics Purdue University March 28, 217 Daesung Kim (Purdue) Hardy-Stein identity UIUC 217 1 /
UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLES FOR THE FOCK SPACE
 UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLES FOR THE FOCK SPACE KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. We prove several versions of the uncertainty principle for the Fock space F 2 in the complex plane. In particular, for any unit vector f in
UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLES FOR THE FOCK SPACE KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. We prove several versions of the uncertainty principle for the Fock space F 2 in the complex plane. In particular, for any unit vector f in
THE POINT SPECTRUM OF FROBENIUS-PERRON AND KOOPMAN OPERATORS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE MERICN MTHEMTICL SOCIETY Volume 126, Number 5, May 1998, Pages 1355 1361 S 0002-9939(98)04188-4 THE POINT SPECTRUM OF FROBENIUS-PERRON ND KOOPMN OPERTORS J. DING (Communicated by Palle
PROCEEDINGS OF THE MERICN MTHEMTICL SOCIETY Volume 126, Number 5, May 1998, Pages 1355 1361 S 0002-9939(98)04188-4 THE POINT SPECTRUM OF FROBENIUS-PERRON ND KOOPMN OPERTORS J. DING (Communicated by Palle
EXAM MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF PHYSICS. TRACK ANALYSIS (Chapters I-V). Thursday, June 7th,
 EXAM MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF PHYSICS TRACK ANALYSIS (Chapters I-V) Thursday, June 7th, 1-13 Students who are entitled to a lighter version of the exam may skip problems 1, 8-11 and 16 Consider the differential
EXAM MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF PHYSICS TRACK ANALYSIS (Chapters I-V) Thursday, June 7th, 1-13 Students who are entitled to a lighter version of the exam may skip problems 1, 8-11 and 16 Consider the differential
From Haar to Lebesgue via Domain Theory
 From Haar to Lebesgue via Domain Theory Michael Mislove Tulane University Topology Seminar CUNY Queensboro Thursday, October 15, 2015 Joint work with Will Brian Work Supported by US NSF & US AFOSR Lebesgue
From Haar to Lebesgue via Domain Theory Michael Mislove Tulane University Topology Seminar CUNY Queensboro Thursday, October 15, 2015 Joint work with Will Brian Work Supported by US NSF & US AFOSR Lebesgue
A dual form of the sharp Nash inequality and its weighted generalization
 A dual form of the sharp Nash inequality and its weighted generalization Elliott Lieb Princeton University Joint work with Eric Carlen, arxiv: 1704.08720 Kato conference, University of Tokyo September
A dual form of the sharp Nash inequality and its weighted generalization Elliott Lieb Princeton University Joint work with Eric Carlen, arxiv: 1704.08720 Kato conference, University of Tokyo September
8 Periodic Linear Di erential Equations - Floquet Theory
 8 Periodic Linear Di erential Equations - Floquet Theory The general theory of time varying linear di erential equations _x(t) = A(t)x(t) is still amazingly incomplete. Only for certain classes of functions
8 Periodic Linear Di erential Equations - Floquet Theory The general theory of time varying linear di erential equations _x(t) = A(t)x(t) is still amazingly incomplete. Only for certain classes of functions
FIXED POINT ITERATIONS
 FIXED POINT ITERATIONS MARKUS GRASMAIR 1. Fixed Point Iteration for Non-linear Equations Our goal is the solution of an equation (1) F (x) = 0, where F : R n R n is a continuous vector valued mapping in
FIXED POINT ITERATIONS MARKUS GRASMAIR 1. Fixed Point Iteration for Non-linear Equations Our goal is the solution of an equation (1) F (x) = 0, where F : R n R n is a continuous vector valued mapping in
Boundary triples for Schrödinger operators with singular interactions on hypersurfaces
 NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2012, 0 0, P. 1 13 Boundary triples for Schrödinger operators with singular interactions on hypersurfaces Jussi Behrndt Institut für Numerische Mathematik,
NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2012, 0 0, P. 1 13 Boundary triples for Schrödinger operators with singular interactions on hypersurfaces Jussi Behrndt Institut für Numerische Mathematik,
KREIN S RESOLVENT FORMULA AND PERTURBATION THEORY
 J. OPERATOR THEORY 52004), 32 334 c Copyright by Theta, 2004 KREIN S RESOLVENT FORMULA AND PERTURBATION THEORY P. KURASOV and S.T. KURODA Communicated by Florian-Horia Vasilescu Abstract. The difference
J. OPERATOR THEORY 52004), 32 334 c Copyright by Theta, 2004 KREIN S RESOLVENT FORMULA AND PERTURBATION THEORY P. KURASOV and S.T. KURODA Communicated by Florian-Horia Vasilescu Abstract. The difference
Linear and Nonlinear Dirac Equation: advances and open problems. Programme & Abstracts
 Linear and Nonlinear Dirac Equation: advances and open problems February 8 13, 2017, Como (Italy) Dipartimento di Scienza e Alta Tecnologia Università degli Studi dell Insubria Programme & Abstracts Wednesday
Linear and Nonlinear Dirac Equation: advances and open problems February 8 13, 2017, Como (Italy) Dipartimento di Scienza e Alta Tecnologia Università degli Studi dell Insubria Programme & Abstracts Wednesday
Convex Geometry. Otto-von-Guericke Universität Magdeburg. Applications of the Brascamp-Lieb and Barthe inequalities. Exercise 12.
 Applications of the Brascamp-Lieb and Barthe inequalities Exercise 12.1 Show that if m Ker M i {0} then both BL-I) and B-I) hold trivially. Exercise 12.2 Let λ 0, 1) and let f, g, h : R 0 R 0 be measurable
Applications of the Brascamp-Lieb and Barthe inequalities Exercise 12.1 Show that if m Ker M i {0} then both BL-I) and B-I) hold trivially. Exercise 12.2 Let λ 0, 1) and let f, g, h : R 0 R 0 be measurable
Linear Algebra Massoud Malek
 CSUEB Linear Algebra Massoud Malek Inner Product and Normed Space In all that follows, the n n identity matrix is denoted by I n, the n n zero matrix by Z n, and the zero vector by θ n An inner product
CSUEB Linear Algebra Massoud Malek Inner Product and Normed Space In all that follows, the n n identity matrix is denoted by I n, the n n zero matrix by Z n, and the zero vector by θ n An inner product
LINEAR OPERATORS IN HILBERT SPACES
 Chapter 24 LINEAR OPERATORS IN HILBERT SPACES 24.1 Linear Functionals Definition 24.1.1. The space of continuous linear functionals L (H, C) is H, the dual space of H. Theorem 24.1.2 (Riesz s lemma). For
Chapter 24 LINEAR OPERATORS IN HILBERT SPACES 24.1 Linear Functionals Definition 24.1.1. The space of continuous linear functionals L (H, C) is H, the dual space of H. Theorem 24.1.2 (Riesz s lemma). For
CHAPTER 6. Differentiation
 CHPTER 6 Differentiation The generalization from elementary calculus of differentiation in measure theory is less obvious than that of integration, and the methods of treating it are somewhat involved.
CHPTER 6 Differentiation The generalization from elementary calculus of differentiation in measure theory is less obvious than that of integration, and the methods of treating it are somewhat involved.
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics PVK - Solutions. Nicolas Lanzetti
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics PVK - Solutions Nicolas Lanzetti lnicolas@student.ethz.ch 1 Contents 1 The Wave Function and the Schrödinger Equation 3 1.1 Quick Checks......................................
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics PVK - Solutions Nicolas Lanzetti lnicolas@student.ethz.ch 1 Contents 1 The Wave Function and the Schrödinger Equation 3 1.1 Quick Checks......................................
Twisting versus bending in quantum waveguides
 Twisting versus bending in quantum waveguides David KREJČIŘÍK Nuclear Physics Institute, Academy of Sciences, Řež, Czech Republic http://gemma.ujf.cas.cz/ david/ Based on: [Chenaud, Duclos, Freitas, D.K.]
Twisting versus bending in quantum waveguides David KREJČIŘÍK Nuclear Physics Institute, Academy of Sciences, Řež, Czech Republic http://gemma.ujf.cas.cz/ david/ Based on: [Chenaud, Duclos, Freitas, D.K.]
Weighted norm inequalities for singular integral operators
 Weighted norm inequalities for singular integral operators C. Pérez Journal of the London mathematical society 49 (994), 296 308. Departmento de Matemáticas Universidad Autónoma de Madrid 28049 Madrid,
Weighted norm inequalities for singular integral operators C. Pérez Journal of the London mathematical society 49 (994), 296 308. Departmento de Matemáticas Universidad Autónoma de Madrid 28049 Madrid,
Math 104: Homework 7 solutions
 Math 04: Homework 7 solutions. (a) The derivative of f () = is f () = 2 which is unbounded as 0. Since f () is continuous on [0, ], it is uniformly continous on this interval by Theorem 9.2. Hence for
Math 04: Homework 7 solutions. (a) The derivative of f () = is f () = 2 which is unbounded as 0. Since f () is continuous on [0, ], it is uniformly continous on this interval by Theorem 9.2. Hence for
Math 127C, Spring 2006 Final Exam Solutions. x 2 ), g(y 1, y 2 ) = ( y 1 y 2, y1 2 + y2) 2. (g f) (0) = g (f(0))f (0).
 Math 27C, Spring 26 Final Exam Solutions. Define f : R 2 R 2 and g : R 2 R 2 by f(x, x 2 (sin x 2 x, e x x 2, g(y, y 2 ( y y 2, y 2 + y2 2. Use the chain rule to compute the matrix of (g f (,. By the chain
Math 27C, Spring 26 Final Exam Solutions. Define f : R 2 R 2 and g : R 2 R 2 by f(x, x 2 (sin x 2 x, e x x 2, g(y, y 2 ( y y 2, y 2 + y2 2. Use the chain rule to compute the matrix of (g f (,. By the chain
4 Power Series Solutions: Frobenius Method
 4 Power Series Solutions: Frobenius Method Now the ODE adventure takes us to series solutions for ODEs, a technique A & W, that is often viable, valuable and informative. These can be readily applied Sec.
4 Power Series Solutions: Frobenius Method Now the ODE adventure takes us to series solutions for ODEs, a technique A & W, that is often viable, valuable and informative. These can be readily applied Sec.
Hilbert Spaces. Hilbert space is a vector space with some extra structure. We start with formal (axiomatic) definition of a vector space.
 Hilbert Spaces Hilbert space is a vector space with some extra structure. We start with formal (axiomatic) definition of a vector space. Vector Space. Vector space, ν, over the field of complex numbers,
Hilbert Spaces Hilbert space is a vector space with some extra structure. We start with formal (axiomatic) definition of a vector space. Vector Space. Vector space, ν, over the field of complex numbers,
Mathematics I. Exercises with solutions. 1 Linear Algebra. Vectors and Matrices Let , C = , B = A = Determine the following matrices:
 Mathematics I Exercises with solutions Linear Algebra Vectors and Matrices.. Let A = 5, B = Determine the following matrices: 4 5, C = a) A + B; b) A B; c) AB; d) BA; e) (AB)C; f) A(BC) Solution: 4 5 a)
Mathematics I Exercises with solutions Linear Algebra Vectors and Matrices.. Let A = 5, B = Determine the following matrices: 4 5, C = a) A + B; b) A B; c) AB; d) BA; e) (AB)C; f) A(BC) Solution: 4 5 a)
Introduction to Mathematical Physics
 Introduction to Mathematical Physics Methods and Concepts Second Edition Chun Wa Wong Department of Physics and Astronomy University of California Los Angeles OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Vectors
Introduction to Mathematical Physics Methods and Concepts Second Edition Chun Wa Wong Department of Physics and Astronomy University of California Los Angeles OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Vectors
Resolvent differences and their spectral estimates
 Resolvent differences and their spectral estimates Gerd Grubb Copenhagen University M.Z. Solomyak 80 years, Imperial College September 2011 Plan 1. Spectral upper estimates 1. Spectral upper estimates
Resolvent differences and their spectral estimates Gerd Grubb Copenhagen University M.Z. Solomyak 80 years, Imperial College September 2011 Plan 1. Spectral upper estimates 1. Spectral upper estimates
Introduction to Modern Quantum Field Theory
 Department of Mathematics University of Texas at Arlington Arlington, TX USA Febuary, 2016 Recall Einstein s famous equation, E 2 = (Mc 2 ) 2 + (c p) 2, where c is the speed of light, M is the classical
Department of Mathematics University of Texas at Arlington Arlington, TX USA Febuary, 2016 Recall Einstein s famous equation, E 2 = (Mc 2 ) 2 + (c p) 2, where c is the speed of light, M is the classical
Lecture notes on Quantum Computing. Chapter 1 Mathematical Background
 Lecture notes on Quantum Computing Chapter 1 Mathematical Background Vector states of a quantum system with n physical states are represented by unique vectors in C n, the set of n 1 column vectors 1 For
Lecture notes on Quantum Computing Chapter 1 Mathematical Background Vector states of a quantum system with n physical states are represented by unique vectors in C n, the set of n 1 column vectors 1 For
UNIVERSITY OF SURREY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS. BSc and MPhys Undergraduate Programmes in Physics LEVEL HE2
 Phys/Level /1/9/Semester, 009-10 (1 handout) UNIVERSITY OF SURREY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS BSc and MPhys Undergraduate Programmes in Physics LEVEL HE PAPER 1 MATHEMATICAL,
Phys/Level /1/9/Semester, 009-10 (1 handout) UNIVERSITY OF SURREY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS BSc and MPhys Undergraduate Programmes in Physics LEVEL HE PAPER 1 MATHEMATICAL,
COMPLETE METRIC SPACES AND THE CONTRACTION MAPPING THEOREM
 COMPLETE METRIC SPACES AND THE CONTRACTION MAPPING THEOREM A metric space (M, d) is a set M with a metric d(x, y), x, y M that has the properties d(x, y) = d(y, x), x, y M d(x, y) d(x, z) + d(z, y), x,
COMPLETE METRIC SPACES AND THE CONTRACTION MAPPING THEOREM A metric space (M, d) is a set M with a metric d(x, y), x, y M that has the properties d(x, y) = d(y, x), x, y M d(x, y) d(x, z) + d(z, y), x,
Lebesgue Integration: A non-rigorous introduction. What is wrong with Riemann integration?
 Lebesgue Integration: A non-rigorous introduction What is wrong with Riemann integration? xample. Let f(x) = { 0 for x Q 1 for x / Q. The upper integral is 1, while the lower integral is 0. Yet, the function
Lebesgue Integration: A non-rigorous introduction What is wrong with Riemann integration? xample. Let f(x) = { 0 for x Q 1 for x / Q. The upper integral is 1, while the lower integral is 0. Yet, the function
Heisenberg s inequality
 Heisenberg s inequality Michael Walter 1 Introduction 1 Definition. Let P be a probability measure on R. Then its mean or expectation is defined as E(P) := x dp(x) Its variance is the expected square deviation
Heisenberg s inequality Michael Walter 1 Introduction 1 Definition. Let P be a probability measure on R. Then its mean or expectation is defined as E(P) := x dp(x) Its variance is the expected square deviation
What is an RKHS? Dino Sejdinovic, Arthur Gretton. March 11, 2014
 What is an RKHS? Dino Sejdinovic, Arthur Gretton March 11, 2014 1 Outline Normed and inner product spaces Cauchy sequences and completeness Banach and Hilbert spaces Linearity, continuity and boundedness
What is an RKHS? Dino Sejdinovic, Arthur Gretton March 11, 2014 1 Outline Normed and inner product spaces Cauchy sequences and completeness Banach and Hilbert spaces Linearity, continuity and boundedness
The following definition is fundamental.
 1. Some Basics from Linear Algebra With these notes, I will try and clarify certain topics that I only quickly mention in class. First and foremost, I will assume that you are familiar with many basic
1. Some Basics from Linear Algebra With these notes, I will try and clarify certain topics that I only quickly mention in class. First and foremost, I will assume that you are familiar with many basic
(, ) : R n R n R. 1. It is bilinear, meaning it s linear in each argument: that is
 17 Inner products Up until now, we have only examined the properties of vectors and matrices in R n. But normally, when we think of R n, we re really thinking of n-dimensional Euclidean space - that is,
17 Inner products Up until now, we have only examined the properties of vectors and matrices in R n. But normally, when we think of R n, we re really thinking of n-dimensional Euclidean space - that is,
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 6
 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 6 DUE 15 MARCH, 2016 1) Suppose f, g : A R are uniformly continuous on A. Show that f + g is uniformly continuous on A. Solution First we note: In order to show that f + g is uniformly
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 6 DUE 15 MARCH, 2016 1) Suppose f, g : A R are uniformly continuous on A. Show that f + g is uniformly continuous on A. Solution First we note: In order to show that f + g is uniformly
Reversible Markov chains
 Reversible Markov chains Variational representations and ordering Chris Sherlock Abstract This pedagogical document explains three variational representations that are useful when comparing the efficiencies
Reversible Markov chains Variational representations and ordering Chris Sherlock Abstract This pedagogical document explains three variational representations that are useful when comparing the efficiencies
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 21 Jun 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 21 Jun 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 21 Jun 2016](/thumbs/88/117506527.jpg) B. N. Khabibullin, N. R. Tamindarova SUBHARMONIC TEST FUNCTIONS AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF ZERO SETS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS arxiv:1606.06714v1 [math.cv] 21 Jun 2016 Abstract. Let m, n 1 are integers and
B. N. Khabibullin, N. R. Tamindarova SUBHARMONIC TEST FUNCTIONS AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF ZERO SETS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS arxiv:1606.06714v1 [math.cv] 21 Jun 2016 Abstract. Let m, n 1 are integers and
Lecture #1. Review. Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1
 L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
4 Linear operators and linear functionals
 4 Linear operators and linear functionals The next section is devoted to studying linear operators between normed spaces. Definition 4.1. Let V and W be normed spaces over a field F. We say that T : V
4 Linear operators and linear functionals The next section is devoted to studying linear operators between normed spaces. Definition 4.1. Let V and W be normed spaces over a field F. We say that T : V
The Gauss-Green Formula (And Elliptic Boundary Problems On Rough Domains) Joint Work with Steve Hofmann and Marius Mitrea
 The Gauss-Green Formula And Elliptic Boundary Problems On Rough Domains) Joint Work with Steve Hofmann and Marius Mitrea Dirichlet Problem on open in a compact Riemannian manifold M), dimension n: ) Lu
The Gauss-Green Formula And Elliptic Boundary Problems On Rough Domains) Joint Work with Steve Hofmann and Marius Mitrea Dirichlet Problem on open in a compact Riemannian manifold M), dimension n: ) Lu
Calculus Example Exam Solutions
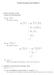 Calculus Example Exam Solutions. Limits (8 points, 6 each) Evaluate the following limits: p x 2 (a) lim x 4 We compute as follows: lim p x 2 x 4 p p x 2 x +2 x 4 p x +2 x 4 (x 4)( p x + 2) p x +2 = p 4+2
Calculus Example Exam Solutions. Limits (8 points, 6 each) Evaluate the following limits: p x 2 (a) lim x 4 We compute as follows: lim p x 2 x 4 p p x 2 x +2 x 4 p x +2 x 4 (x 4)( p x + 2) p x +2 = p 4+2
The uniform uncertainty principle and compressed sensing Harmonic analysis and related topics, Seville December 5, 2008
 The uniform uncertainty principle and compressed sensing Harmonic analysis and related topics, Seville December 5, 2008 Emmanuel Candés (Caltech), Terence Tao (UCLA) 1 Uncertainty principles A basic principle
The uniform uncertainty principle and compressed sensing Harmonic analysis and related topics, Seville December 5, 2008 Emmanuel Candés (Caltech), Terence Tao (UCLA) 1 Uncertainty principles A basic principle
Course 224: Geometry - Continuity and Differentiability
 Course 224: Geometry - Continuity and Differentiability Lecture Notes by Prof. David Simms L A TEXed by Chris Blair 1 Continuity Consider M, N finite dimensional real or complex vector spaces. What does
Course 224: Geometry - Continuity and Differentiability Lecture Notes by Prof. David Simms L A TEXed by Chris Blair 1 Continuity Consider M, N finite dimensional real or complex vector spaces. What does
MATH34032 Mid-term Test 10.00am 10.50am, 26th March 2010 Answer all six question [20% of the total mark for this course]
![MATH34032 Mid-term Test 10.00am 10.50am, 26th March 2010 Answer all six question [20% of the total mark for this course] MATH34032 Mid-term Test 10.00am 10.50am, 26th March 2010 Answer all six question [20% of the total mark for this course]](/thumbs/78/76857283.jpg) MATH3432: Green s Functions, Integral Equations and the Calculus of Variations 1 MATH3432 Mid-term Test 1.am 1.5am, 26th March 21 Answer all six question [2% of the total mark for this course] Qu.1 (a)
MATH3432: Green s Functions, Integral Equations and the Calculus of Variations 1 MATH3432 Mid-term Test 1.am 1.5am, 26th March 21 Answer all six question [2% of the total mark for this course] Qu.1 (a)
Trace Class Operators and Lidskii s Theorem
 Trace Class Operators and Lidskii s Theorem Tom Phelan Semester 2 2009 1 Introduction The purpose of this paper is to provide the reader with a self-contained derivation of the celebrated Lidskii Trace
Trace Class Operators and Lidskii s Theorem Tom Phelan Semester 2 2009 1 Introduction The purpose of this paper is to provide the reader with a self-contained derivation of the celebrated Lidskii Trace
Advanced Calculus Math 127B, Winter 2005 Solutions: Final. nx2 1 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x
 . Define f n, g n : [, ] R by f n (x) = Advanced Calculus Math 27B, Winter 25 Solutions: Final nx2 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x 2 + n 2 x. 2 Show that the sequences (f n ), (g n ) converge pointwise on [, ],
. Define f n, g n : [, ] R by f n (x) = Advanced Calculus Math 27B, Winter 25 Solutions: Final nx2 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x 2 + n 2 x. 2 Show that the sequences (f n ), (g n ) converge pointwise on [, ],
HARMONIC ANALYSIS. Date:
 HARMONIC ANALYSIS Contents. Introduction 2. Hardy-Littlewood maximal function 3. Approximation by convolution 4. Muckenhaupt weights 4.. Calderón-Zygmund decomposition 5. Fourier transform 6. BMO (bounded
HARMONIC ANALYSIS Contents. Introduction 2. Hardy-Littlewood maximal function 3. Approximation by convolution 4. Muckenhaupt weights 4.. Calderón-Zygmund decomposition 5. Fourier transform 6. BMO (bounded
The goal of this chapter is to study linear systems of ordinary differential equations: dt,..., dx ) T
 1 1 Linear Systems The goal of this chapter is to study linear systems of ordinary differential equations: ẋ = Ax, x(0) = x 0, (1) where x R n, A is an n n matrix and ẋ = dx ( dt = dx1 dt,..., dx ) T n.
1 1 Linear Systems The goal of this chapter is to study linear systems of ordinary differential equations: ẋ = Ax, x(0) = x 0, (1) where x R n, A is an n n matrix and ẋ = dx ( dt = dx1 dt,..., dx ) T n.
r( = f 2 L 2 (1.2) iku)! 0 as r!1: (1.3) It was shown in book [7] that if f is assumed to be the restriction of a function in C
![r( = f 2 L 2 (1.2) iku)! 0 as r!1: (1.3) It was shown in book [7] that if f is assumed to be the restriction of a function in C r( = f 2 L 2 (1.2) iku)! 0 as r!1: (1.3) It was shown in book [7] that if f is assumed to be the restriction of a function in C](/thumbs/87/97098106.jpg) Inverse Obstacle Problem: Local Uniqueness for Rougher Obstacles and the Identication of A Ball Changmei Liu Department of Mathematics University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC 27599 December, 1995
Inverse Obstacle Problem: Local Uniqueness for Rougher Obstacles and the Identication of A Ball Changmei Liu Department of Mathematics University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC 27599 December, 1995
Math 110: Worksheet 1 Solutions
 Math 110: Worksheet 1 Solutions August 30 Thursday Aug. 4 1. Determine whether or not the following sets form vector spaces over the given fields. (a) The set V of all matrices of the form where a, b R,
Math 110: Worksheet 1 Solutions August 30 Thursday Aug. 4 1. Determine whether or not the following sets form vector spaces over the given fields. (a) The set V of all matrices of the form where a, b R,
Inequalities in Hilbert Spaces
 Inequalities in Hilbert Spaces Jan Wigestrand Master of Science in Mathematics Submission date: March 8 Supervisor: Eugenia Malinnikova, MATH Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of
Inequalities in Hilbert Spaces Jan Wigestrand Master of Science in Mathematics Submission date: March 8 Supervisor: Eugenia Malinnikova, MATH Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of
A review: The Laplacian and the d Alembertian. j=1
 Chapter One A review: The Laplacian and the d Alembertian 1.1 THE LAPLACIAN One of the main goals of this course is to understand well the solution of wave equation both in Euclidean space and on manifolds
Chapter One A review: The Laplacian and the d Alembertian 1.1 THE LAPLACIAN One of the main goals of this course is to understand well the solution of wave equation both in Euclidean space and on manifolds
Math 320: Real Analysis MWF 1pm, Campion Hall 302 Homework 7 Solutions Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible.
 Math 320: Real Analysis MWF 1pm, Campion Hall 302 Homework 7 Solutions Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible. Do the following problems from the book: 4.2.1, 4.2.3, 4.2.6, 4.2.8,
Math 320: Real Analysis MWF 1pm, Campion Hall 302 Homework 7 Solutions Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible. Do the following problems from the book: 4.2.1, 4.2.3, 4.2.6, 4.2.8,
Mathematical Analysis Outline. William G. Faris
 Mathematical Analysis Outline William G. Faris January 8, 2007 2 Chapter 1 Metric spaces and continuous maps 1.1 Metric spaces A metric space is a set X together with a real distance function (x, x ) d(x,
Mathematical Analysis Outline William G. Faris January 8, 2007 2 Chapter 1 Metric spaces and continuous maps 1.1 Metric spaces A metric space is a set X together with a real distance function (x, x ) d(x,
LINEAR ALGEBRA BOOT CAMP WEEK 4: THE SPECTRAL THEOREM
 LINEAR ALGEBRA BOOT CAMP WEEK 4: THE SPECTRAL THEOREM Unless otherwise stated, all vector spaces in this worksheet are finite dimensional and the scalar field F is R or C. Definition 1. A linear operator
LINEAR ALGEBRA BOOT CAMP WEEK 4: THE SPECTRAL THEOREM Unless otherwise stated, all vector spaces in this worksheet are finite dimensional and the scalar field F is R or C. Definition 1. A linear operator
Math 141: Section 4.1 Extreme Values of Functions - Notes
 Math 141: Section 4.1 Extreme Values of Functions - Notes Definition: Let f be a function with domain D. Thenf has an absolute (global) maximum value on D at a point c if f(x) apple f(c) for all x in D
Math 141: Section 4.1 Extreme Values of Functions - Notes Definition: Let f be a function with domain D. Thenf has an absolute (global) maximum value on D at a point c if f(x) apple f(c) for all x in D
5 Compact linear operators
 5 Compact linear operators One of the most important results of Linear Algebra is that for every selfadjoint linear map A on a finite-dimensional space, there exists a basis consisting of eigenvectors.
5 Compact linear operators One of the most important results of Linear Algebra is that for every selfadjoint linear map A on a finite-dimensional space, there exists a basis consisting of eigenvectors.
1.2 Functions and Their Properties Name:
 1.2 Functions and Their Properties Name: Objectives: Students will be able to represent functions numerically, algebraically, and graphically, determine the domain and range for functions, and analyze
1.2 Functions and Their Properties Name: Objectives: Students will be able to represent functions numerically, algebraically, and graphically, determine the domain and range for functions, and analyze
TEST CODE: PMB SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: PMB SYLLABUS Convergence and divergence of sequence and series; Cauchy sequence and completeness; Bolzano-Weierstrass theorem; continuity, uniform continuity, differentiability; directional
TEST CODE: PMB SYLLABUS Convergence and divergence of sequence and series; Cauchy sequence and completeness; Bolzano-Weierstrass theorem; continuity, uniform continuity, differentiability; directional
Analysis of the anomalous localized resonance
 Hyundae Lee(Inha University, Korea) Joint work with Habib Ammari, Giulio Ciraolo, Hyeonbae Kang, Graeme Milton. UCI, June 22, 2012 A conference on inverse problems in honor of Gunther Uhlmann Outline Introduction
Hyundae Lee(Inha University, Korea) Joint work with Habib Ammari, Giulio Ciraolo, Hyeonbae Kang, Graeme Milton. UCI, June 22, 2012 A conference on inverse problems in honor of Gunther Uhlmann Outline Introduction
Functional Analysis Review
 Outline 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 3 4 Vector Space Outline A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V V such that for all
Outline 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 3 4 Vector Space Outline A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V V such that for all
Potential Analysis meets Geometric Measure Theory
 Potential Analysis meets Geometric Measure Theory T. Toro Abstract A central question in Potential Theory is the extend to which the geometry of a domain influences the boundary regularity of the solution
Potential Analysis meets Geometric Measure Theory T. Toro Abstract A central question in Potential Theory is the extend to which the geometry of a domain influences the boundary regularity of the solution
Asymptotic behaviour of the heat equation in twisted waveguides
 Asymptotic behaviour of the heat equation in twisted waveguides Gabriela Malenová Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, CTU, Prague Nuclear Physics Institute, AS ČR, Řež Graphs and Spectra,
Asymptotic behaviour of the heat equation in twisted waveguides Gabriela Malenová Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, CTU, Prague Nuclear Physics Institute, AS ČR, Řež Graphs and Spectra,
1.1 Limits and Continuity. Precise definition of a limit and limit laws. Squeeze Theorem. Intermediate Value Theorem. Extreme Value Theorem.
 STATE EXAM MATHEMATICS Variant A ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 1 1.1 Limits and Continuity. Precise definition of a limit and limit laws. Squeeze Theorem. Intermediate Value Theorem. Extreme Value Theorem. Definition
STATE EXAM MATHEMATICS Variant A ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 1 1.1 Limits and Continuity. Precise definition of a limit and limit laws. Squeeze Theorem. Intermediate Value Theorem. Extreme Value Theorem. Definition
One-Dimensional Diffusion Operators
 One-Dimensional Diffusion Operators Stanley Sawyer Washington University Vs. July 7, 28 1. Basic Assumptions. Let sx be a continuous, strictly-increasing function sx on I, 1 and let mdx be a Borel measure
One-Dimensional Diffusion Operators Stanley Sawyer Washington University Vs. July 7, 28 1. Basic Assumptions. Let sx be a continuous, strictly-increasing function sx on I, 1 and let mdx be a Borel measure
A Brief Introduction to Functional Analysis
 A Brief Introduction to Functional Analysis Sungwook Lee Department of Mathematics University of Southern Mississippi sunglee@usm.edu July 5, 2007 Definition 1. An algebra A is a vector space over C with
A Brief Introduction to Functional Analysis Sungwook Lee Department of Mathematics University of Southern Mississippi sunglee@usm.edu July 5, 2007 Definition 1. An algebra A is a vector space over C with
Total Angular Momentum for Hydrogen
 Physics 4 Lecture 7 Total Angular Momentum for Hydrogen Lecture 7 Physics 4 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, April th, 008 We have the Hydrogen Hamiltonian for central potential φ(r), we can write: H r = p
Physics 4 Lecture 7 Total Angular Momentum for Hydrogen Lecture 7 Physics 4 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, April th, 008 We have the Hydrogen Hamiltonian for central potential φ(r), we can write: H r = p
