Stochastic Gradient Descent. CS 584: Big Data Analytics
|
|
|
- Joseph Cole
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stochastic Gradient Descent CS 584: Big Data Analytics
2 Gradient Descent Recap Simplest and extremely popular Main Idea: take a step proportional to the negative of the gradient Easy to implement Each iteration is relatively cheap Can be slow to converge
3 Example: Linear Regression Optimization problem: min w Xw y 2 Closed form solution: w =(X > X) 1 X > y Gradient update: w + 1 = w m X (x > i w y i )x i i Requires an entire pass through the data!
4 Tackling Compute Problems: Scaling to Large n Streaming implementation Parallelize your batch algorithm Aggressively subsample the data Change algorithm or training method Optimization is a surrogate for learning Trade-off weaker optimization with more data
5 Tradeoffs of Large Scale Learning True (generalization) error is a function of approximation error, estimation error, and optimization error subject to number of training examples and computational time Solution will depend on which budget constraint is active Bottom and Bousquet (2011). The Tradeoffs of Large-Scale Learning. In Optimization for Machine Learning (pp ).
6 Minimizing Generalization Error If n!1, then " est! 0 For fixed generalization error, as number of samples increases, we can increase optimization tolerance Talk by Aditya Menon, UCSD
7 Expected Risk vs Empirical Risk Minimization Expected Risk Assume we know the ground truth distribution P(x,y) Expected risk associated with classification function Z E(f w )= L(f w (x),y)dp (x, y) Empirical Risk Real world, ground truth distribution is not known Only empirical risk can be calculated for function E n (f w )= 1 n X L(f w (x i ),y i ) i = E[L(f w (x),y)]
8 Gradient Descent Reformulated w + = w 1 n X i r w L(f w (x i ),y i ) learning rate or gain re n (f w ) True gradient descent is a batch algorithm, slow but sure Under sufficient regularity assumptions, initial estimate is close to the optimal and gain is sufficiently small, there is linear convergence
9 Stochastic Optimization Motivation Information is redundant amongst samples Sufficient samples means we can afford more frequent, noisy updates Never-ending stream means we should not wait for all data Tracking non-stationary data means that the target is moving
10 Stochastic Optimization Idea: Estimate function and gradient from a small, current subsample of your data and with enough iterations and data, you will converge to the true minimum Pro: Better for large datasets and often faster convergence Con: Hard to reach high accuracy Con: Best classical methods can t handle stochastic approximation Con: Theoretical definitions for convergence not as welldefined
11 Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) Randomized gradient estimate to minimize the function using a single randomly picked example Instead of rf,use rf,where E[ rf] =rf The resulting update is of the form: w + = w r w L(f w (x i,y i )) Although random noise is introduced, it behaves like gradient descent in its expectation
12 SGD Algorithm Randomly initialize parameter w and learning rate while Not Converged do Randomly shu e examples in training set for i =1,,N do w + = w r w L(f w (x i,y i )) end end
13 The Benefits of SGD Gradient is easy to calculate ( instantaneous ) Less prone to local minima Small memory footprint Get to a reasonable solution quickly Works for non-stationary environments as well as online settings Can be used for more complex models and error surfaces
14 Importance of Learning Rate Learning rate has a large impact on convergence Too small > too slow Too large > oscillatory and may even diverge Should learning rate be fixed or adaptive? Is convergence necessary? Non-stationary: convergence may not be required or desired Stationary: learning rate should decrease with time Robbins-Monroe sequence is adequate t = 1 t
15 Mini-batch Stochastic Gradient Descent Rather than using a single point, use a random subset where the size is less than the original data size w + 1 X = w r w L(f w (x i,y i )), where S k [n] S k i2s k Like the single random sample, the full gradient is approximated via an unbiased noisy estimate Random subset reduces the variance by a factor of 1/ Sk, but is also Sk times more expensive
16 Example: Regularized Logistic Regression Optimization problem: min 1 n X Gradient computation: i y i x > i + log(1 + e x> i ) rf( )= X i (y i p i ( ))x i + Update costs: Batch: O(nd) Stochastic: O(d) Batch is doable if n is moderate but not when n is huge Mini-batch: O( S k d)
17 Example: n=10,000, d=20 Iterations make better progress as mini-batch size is larger but also takes more computation time
18 SGD Updates for Various Systems Bottou, L. (2012). Stochastic Gradient Descent Tricks. Neural Networks Tricks of the Trade.
19 Asymptotic Analysis of GD and SGD Bottou, L. (2012). Stochastic Gradient Descent Tricks. Neural Networks Tricks of the Trade.
20 SGD Recommendations Randomly shuffle training examples Although theory says you should randomly pick examples, it is easier to make a pass through your training set sequentially Shuffling before each iteration eliminates the effect of order Monitor both training cost and validation error Set aside samples for a decent validation set Compute the objective on the training set and validation set (expensive but better than overfitting or wasting computation) Bottou, L. (2012). Stochastic Gradient Descent Tricks. Neural Networks Tricks of the Trade.
21 SGD Recommendations (2) Check gradient using finite differences If computation is slightly incorrect can yield erratic and slow algorithm Verify your code by slightly perturbing the parameter and inspecting differences between the two gradients Experiment with the learning rates using small sample of training set SGD convergence rates are independent from sample size Use traditional optimization algorithms as a reference point
22 SGD Recommendations (3) Leverage sparsity of the training examples For very high-dimensional vectors with few non zero coefficients, you only need to update the weight coefficients corresponding to nonzero pattern in x Use learning rates of the form t = 0 (1 + 0 t) 1 Allows you to start from reasonable learning rates determined by testing on a small sample Works well in most situations if the initial point is slightly smaller than best value observed in training sample
23 Some Resources for SGD Francis Bach s talk in 2012: bach2012.pdf Stochastic Gradient Methods Workshop: yaroslavvb.blogspot.com/2014/03/stochastic-gradientmethods-2014.html Python implementation in scikit-learn: stable/modules/sgd.html ipython notebook for implementing GD and SGD in Python: stochastic_gradient_descent.ipynb
Optimization in the Big Data Regime 2: SVRG & Tradeoffs in Large Scale Learning. Sham M. Kakade
 Optimization in the Big Data Regime 2: SVRG & Tradeoffs in Large Scale Learning. Sham M. Kakade Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548 University of Washington S. M. Kakade (UW) Optimization for
Optimization in the Big Data Regime 2: SVRG & Tradeoffs in Large Scale Learning. Sham M. Kakade Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548 University of Washington S. M. Kakade (UW) Optimization for
ECS171: Machine Learning
 ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 4: Optimization (LFD 3.3, SGD) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 22, 2018 Gradient descent Optimization Goal: find the minimizer of a function min f (w) w For now we assume f
ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 4: Optimization (LFD 3.3, SGD) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 22, 2018 Gradient descent Optimization Goal: find the minimizer of a function min f (w) w For now we assume f
Linear classifiers: Overfitting and regularization
 Linear classifiers: Overfitting and regularization Emily Fox University of Washington January 25, 2017 Logistic regression recap 1 . Thus far, we focused on decision boundaries Score(x i ) = w 0 h 0 (x
Linear classifiers: Overfitting and regularization Emily Fox University of Washington January 25, 2017 Logistic regression recap 1 . Thus far, we focused on decision boundaries Score(x i ) = w 0 h 0 (x
Comparison of Modern Stochastic Optimization Algorithms
 Comparison of Modern Stochastic Optimization Algorithms George Papamakarios December 214 Abstract Gradient-based optimization methods are popular in machine learning applications. In large-scale problems,
Comparison of Modern Stochastic Optimization Algorithms George Papamakarios December 214 Abstract Gradient-based optimization methods are popular in machine learning applications. In large-scale problems,
CS260: Machine Learning Algorithms
 CS260: Machine Learning Algorithms Lecture 4: Stochastic Gradient Descent Cho-Jui Hsieh UCLA Jan 16, 2019 Large-scale Problems Machine learning: usually minimizing the training loss min w { 1 N min w {
CS260: Machine Learning Algorithms Lecture 4: Stochastic Gradient Descent Cho-Jui Hsieh UCLA Jan 16, 2019 Large-scale Problems Machine learning: usually minimizing the training loss min w { 1 N min w {
Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron
 CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
Why should you care about the solution strategies?
 Optimization Why should you care about the solution strategies? Understanding the optimization approaches behind the algorithms makes you more effectively choose which algorithm to run Understanding the
Optimization Why should you care about the solution strategies? Understanding the optimization approaches behind the algorithms makes you more effectively choose which algorithm to run Understanding the
Simple Techniques for Improving SGD. CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017
 Simple Techniques for Improving SGD CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017 Step Sizes and Convergence Where we left off Stochastic gradient descent x t+1 = x t rf(x t ; yĩt ) Much faster per iteration than gradient
Simple Techniques for Improving SGD CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017 Step Sizes and Convergence Where we left off Stochastic gradient descent x t+1 = x t rf(x t ; yĩt ) Much faster per iteration than gradient
Contents. 1 Introduction. 1.1 History of Optimization ALG-ML SEMINAR LISSA: LINEAR TIME SECOND-ORDER STOCHASTIC ALGORITHM FEBRUARY 23, 2016
 ALG-ML SEMINAR LISSA: LINEAR TIME SECOND-ORDER STOCHASTIC ALGORITHM FEBRUARY 23, 2016 LECTURERS: NAMAN AGARWAL AND BRIAN BULLINS SCRIBE: KIRAN VODRAHALLI Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 History of Optimization.....................................
ALG-ML SEMINAR LISSA: LINEAR TIME SECOND-ORDER STOCHASTIC ALGORITHM FEBRUARY 23, 2016 LECTURERS: NAMAN AGARWAL AND BRIAN BULLINS SCRIBE: KIRAN VODRAHALLI Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 History of Optimization.....................................
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining. Stochastic Gradient Fall 2017
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Stochastic Gradient Fall 2017 Assignment 3: Admin Check update thread on Piazza for correct definition of trainndx. This could make your cross-validation code
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Stochastic Gradient Fall 2017 Assignment 3: Admin Check update thread on Piazza for correct definition of trainndx. This could make your cross-validation code
Term Paper: How and Why to Use Stochastic Gradient Descent?
 000 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 010 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 019 020 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 029 030 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 039 040 041 042 043 044 045 046 047 048 049 050
000 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 010 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 019 020 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 029 030 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 039 040 041 042 043 044 045 046 047 048 049 050
Large-scale Stochastic Optimization
 Large-scale Stochastic Optimization 11-741/641/441 (Spring 2016) Hanxiao Liu hanxiaol@cs.cmu.edu March 24, 2016 1 / 22 Outline 1. Gradient Descent (GD) 2. Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) Formulation
Large-scale Stochastic Optimization 11-741/641/441 (Spring 2016) Hanxiao Liu hanxiaol@cs.cmu.edu March 24, 2016 1 / 22 Outline 1. Gradient Descent (GD) 2. Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) Formulation
Logistic Regression. Stochastic Gradient Descent
 Tutorial 8 CPSC 340 Logistic Regression Stochastic Gradient Descent Logistic Regression Model A discriminative probabilistic model for classification e.g. spam filtering Let x R d be input and y { 1, 1}
Tutorial 8 CPSC 340 Logistic Regression Stochastic Gradient Descent Logistic Regression Model A discriminative probabilistic model for classification e.g. spam filtering Let x R d be input and y { 1, 1}
Stochastic Gradient Descent
 Stochastic Gradient Descent Weihang Chen, Xingchen Chen, Jinxiu Liang, Cheng Xu, Zehao Chen and Donglin He March 26, 2017 Outline What is Stochastic Gradient Descent Comparison between BGD and SGD Analysis
Stochastic Gradient Descent Weihang Chen, Xingchen Chen, Jinxiu Liang, Cheng Xu, Zehao Chen and Donglin He March 26, 2017 Outline What is Stochastic Gradient Descent Comparison between BGD and SGD Analysis
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
 STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 8: Optimization Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis May 9, 2017 Optimization Numerical Optimization Numerical Optimization: min X f (X ) Can be applied
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 8: Optimization Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis May 9, 2017 Optimization Numerical Optimization Numerical Optimization: min X f (X ) Can be applied
Beyond stochastic gradient descent for large-scale machine learning
 Beyond stochastic gradient descent for large-scale machine learning Francis Bach INRIA - Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, France Joint work with Eric Moulines, Nicolas Le Roux and Mark Schmidt - CAP, July
Beyond stochastic gradient descent for large-scale machine learning Francis Bach INRIA - Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, France Joint work with Eric Moulines, Nicolas Le Roux and Mark Schmidt - CAP, July
Linear Regression (continued)
 Linear Regression (continued) Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 6, 2017 1 / 39 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Linear regression
Linear Regression (continued) Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 6, 2017 1 / 39 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Linear regression
ECE521 lecture 4: 19 January Optimization, MLE, regularization
 ECE521 lecture 4: 19 January 2017 Optimization, MLE, regularization First four lectures Lectures 1 and 2: Intro to ML Probability review Types of loss functions and algorithms Lecture 3: KNN Convexity
ECE521 lecture 4: 19 January 2017 Optimization, MLE, regularization First four lectures Lectures 1 and 2: Intro to ML Probability review Types of loss functions and algorithms Lecture 3: KNN Convexity
Fast Stochastic Optimization Algorithms for ML
 Fast Stochastic Optimization Algorithms for ML Aaditya Ramdas April 20, 205 This lecture is about efficient algorithms for minimizing finite sums min w R d n i= f i (w) or min w R d n f i (w) + λ 2 w 2
Fast Stochastic Optimization Algorithms for ML Aaditya Ramdas April 20, 205 This lecture is about efficient algorithms for minimizing finite sums min w R d n i= f i (w) or min w R d n f i (w) + λ 2 w 2
More Optimization. Optimization Methods. Methods
 More More Optimization Optimization Methods Methods Yann YannLeCun LeCun Courant CourantInstitute Institute http://yann.lecun.com http://yann.lecun.com (almost) (almost) everything everything you've you've
More More Optimization Optimization Methods Methods Yann YannLeCun LeCun Courant CourantInstitute Institute http://yann.lecun.com http://yann.lecun.com (almost) (almost) everything everything you've you've
Sub-Sampled Newton Methods for Machine Learning. Jorge Nocedal
 Sub-Sampled Newton Methods for Machine Learning Jorge Nocedal Northwestern University Goldman Lecture, Sept 2016 1 Collaborators Raghu Bollapragada Northwestern University Richard Byrd University of Colorado
Sub-Sampled Newton Methods for Machine Learning Jorge Nocedal Northwestern University Goldman Lecture, Sept 2016 1 Collaborators Raghu Bollapragada Northwestern University Richard Byrd University of Colorado
Stochastic optimization in Hilbert spaces
 Stochastic optimization in Hilbert spaces Aymeric Dieuleveut Aymeric Dieuleveut Stochastic optimization Hilbert spaces 1 / 48 Outline Learning vs Statistics Aymeric Dieuleveut Stochastic optimization Hilbert
Stochastic optimization in Hilbert spaces Aymeric Dieuleveut Aymeric Dieuleveut Stochastic optimization Hilbert spaces 1 / 48 Outline Learning vs Statistics Aymeric Dieuleveut Stochastic optimization Hilbert
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE (INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE LEARNING) SS16
 COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE (INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE LEARNING) SS6 Lecture 3: Classification with Logistic Regression Advanced optimization techniques Underfitting & Overfitting Model selection (Training-
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE (INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE LEARNING) SS6 Lecture 3: Classification with Logistic Regression Advanced optimization techniques Underfitting & Overfitting Model selection (Training-
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning First-Order Methods, L1-Regularization, Coordinate Descent Winter 2016 Some images from this lecture are taken from Google Image Search. Admin Room: We ll count final numbers
CPSC 540: Machine Learning First-Order Methods, L1-Regularization, Coordinate Descent Winter 2016 Some images from this lecture are taken from Google Image Search. Admin Room: We ll count final numbers
Beyond stochastic gradient descent for large-scale machine learning
 Beyond stochastic gradient descent for large-scale machine learning Francis Bach INRIA - Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, France Joint work with Eric Moulines - October 2014 Big data revolution? A new
Beyond stochastic gradient descent for large-scale machine learning Francis Bach INRIA - Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, France Joint work with Eric Moulines - October 2014 Big data revolution? A new
Convex Optimization Lecture 16
 Convex Optimization Lecture 16 Today: Projected Gradient Descent Conditional Gradient Descent Stochastic Gradient Descent Random Coordinate Descent Recall: Gradient Descent (Steepest Descent w.r.t Euclidean
Convex Optimization Lecture 16 Today: Projected Gradient Descent Conditional Gradient Descent Stochastic Gradient Descent Random Coordinate Descent Recall: Gradient Descent (Steepest Descent w.r.t Euclidean
Stochastic Gradient Descent
 Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 9, 2013 1 Logistic Regression Logistic function (or Sigmoid): Learn P(Y X) directly Assume a particular
Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 9, 2013 1 Logistic Regression Logistic function (or Sigmoid): Learn P(Y X) directly Assume a particular
Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function.
 Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization
 CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization 1 / 25 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization 1 / 25 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
CS60021: Scalable Data Mining. Large Scale Machine Learning
 J. Leskovec, A. Rajaraman, J. Ullman: Mining of Massive Datasets, http://www.mmds.org 1 CS60021: Scalable Data Mining Large Scale Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Example: Spam filtering Instance
J. Leskovec, A. Rajaraman, J. Ullman: Mining of Massive Datasets, http://www.mmds.org 1 CS60021: Scalable Data Mining Large Scale Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Example: Spam filtering Instance
CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization
 CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization 1 / 26 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization 1 / 26 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
Support Vector Machines: Training with Stochastic Gradient Descent. Machine Learning Fall 2017
 Support Vector Machines: Training with Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Support vector machines Training by maximizing margin The SVM objective Solving the SVM optimization problem
Support Vector Machines: Training with Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Support vector machines Training by maximizing margin The SVM objective Solving the SVM optimization problem
Stochastic Gradient Descent. Ryan Tibshirani Convex Optimization
 Stochastic Gradient Descent Ryan Tibshirani Convex Optimization 10-725 Last time: proximal gradient descent Consider the problem min x g(x) + h(x) with g, h convex, g differentiable, and h simple in so
Stochastic Gradient Descent Ryan Tibshirani Convex Optimization 10-725 Last time: proximal gradient descent Consider the problem min x g(x) + h(x) with g, h convex, g differentiable, and h simple in so
Logistic Regression. COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala
 Logistic Regression COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala Binary Classification Given an instance x we must classify it to either positive (1) or negative (0) class We can use {1,-1} instead of {1,0} but we will
Logistic Regression COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala Binary Classification Given an instance x we must classify it to either positive (1) or negative (0) class We can use {1,-1} instead of {1,0} but we will
Stochastic gradient descent and robustness to ill-conditioning
 Stochastic gradient descent and robustness to ill-conditioning Francis Bach INRIA - Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, France ÉCOLE NORMALE SUPÉRIEURE Joint work with Aymeric Dieuleveut, Nicolas Flammarion,
Stochastic gradient descent and robustness to ill-conditioning Francis Bach INRIA - Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, France ÉCOLE NORMALE SUPÉRIEURE Joint work with Aymeric Dieuleveut, Nicolas Flammarion,
Least Mean Squares Regression. Machine Learning Fall 2018
 Least Mean Squares Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are we? Least Squares Method for regression Examples The LMS objective Gradient descent Incremental/stochastic gradient descent Exercises
Least Mean Squares Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are we? Least Squares Method for regression Examples The LMS objective Gradient descent Incremental/stochastic gradient descent Exercises
Least Mean Squares Regression
 Least Mean Squares Regression Machine Learning Spring 2018 The slides are mainly from Vivek Srikumar 1 Lecture Overview Linear classifiers What functions do linear classifiers express? Least Squares Method
Least Mean Squares Regression Machine Learning Spring 2018 The slides are mainly from Vivek Srikumar 1 Lecture Overview Linear classifiers What functions do linear classifiers express? Least Squares Method
Stochastic Optimization Algorithms Beyond SG
 Stochastic Optimization Algorithms Beyond SG Frank E. Curtis 1, Lehigh University involving joint work with Léon Bottou, Facebook AI Research Jorge Nocedal, Northwestern University Optimization Methods
Stochastic Optimization Algorithms Beyond SG Frank E. Curtis 1, Lehigh University involving joint work with Léon Bottou, Facebook AI Research Jorge Nocedal, Northwestern University Optimization Methods
Nonlinear Optimization Methods for Machine Learning
 Nonlinear Optimization Methods for Machine Learning Jorge Nocedal Northwestern University University of California, Davis, Sept 2018 1 Introduction We don t really know, do we? a) Deep neural networks
Nonlinear Optimization Methods for Machine Learning Jorge Nocedal Northwestern University University of California, Davis, Sept 2018 1 Introduction We don t really know, do we? a) Deep neural networks
Big Data Analytics. Lucas Rego Drumond
 Big Data Analytics Lucas Rego Drumond Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Institute of Computer Science University of Hildesheim, Germany Predictive Models Predictive Models 1 / 34 Outline
Big Data Analytics Lucas Rego Drumond Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Institute of Computer Science University of Hildesheim, Germany Predictive Models Predictive Models 1 / 34 Outline
Lecture 1: Supervised Learning
 Lecture 1: Supervised Learning Tuo Zhao Schools of ISYE and CSE, Georgia Tech ISYE6740/CSE6740/CS7641: Computational Data Analysis/Machine from Portland, Learning Oregon: pervised learning (Supervised)
Lecture 1: Supervised Learning Tuo Zhao Schools of ISYE and CSE, Georgia Tech ISYE6740/CSE6740/CS7641: Computational Data Analysis/Machine from Portland, Learning Oregon: pervised learning (Supervised)
CSC2515 Winter 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning. Lecture 2: Linear regression
 CSC2515 Winter 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 2: Linear regression All lecture slides will be available as.pdf on the course website: http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~urtasun/courses/csc2515/csc2515_winter15.html
CSC2515 Winter 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 2: Linear regression All lecture slides will be available as.pdf on the course website: http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~urtasun/courses/csc2515/csc2515_winter15.html
Non-Convex Optimization. CS6787 Lecture 7 Fall 2017
 Non-Convex Optimization CS6787 Lecture 7 Fall 2017 First some words about grading I sent out a bunch of grades on the course management system Everyone should have all their grades in Not including paper
Non-Convex Optimization CS6787 Lecture 7 Fall 2017 First some words about grading I sent out a bunch of grades on the course management system Everyone should have all their grades in Not including paper
Machine Learning & Data Mining CMS/CS/CNS/EE 155. Lecture 2: Perceptron & Gradient Descent
 Machine Learning & Data Mining CMS/CS/CNS/EE 155 Lecture 2: Perceptron & Gradient Descent Announcements Homework 1 is out Due Tuesday Jan 12 th at 2pm Via Moodle Sign up for Moodle & Piazza if you haven
Machine Learning & Data Mining CMS/CS/CNS/EE 155 Lecture 2: Perceptron & Gradient Descent Announcements Homework 1 is out Due Tuesday Jan 12 th at 2pm Via Moodle Sign up for Moodle & Piazza if you haven
Machine Learning Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University. September 20, 2012
 Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University September 20, 2012 Today: Logistic regression Generative/Discriminative classifiers Readings: (see class website)
Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University September 20, 2012 Today: Logistic regression Generative/Discriminative classifiers Readings: (see class website)
Stochastic Variance Reduction for Nonconvex Optimization. Barnabás Póczos
 1 Stochastic Variance Reduction for Nonconvex Optimization Barnabás Póczos Contents 2 Stochastic Variance Reduction for Nonconvex Optimization Joint work with Sashank Reddi, Ahmed Hefny, Suvrit Sra, and
1 Stochastic Variance Reduction for Nonconvex Optimization Barnabás Póczos Contents 2 Stochastic Variance Reduction for Nonconvex Optimization Joint work with Sashank Reddi, Ahmed Hefny, Suvrit Sra, and
A Parallel SGD method with Strong Convergence
 A Parallel SGD method with Strong Convergence Dhruv Mahajan Microsoft Research India dhrumaha@microsoft.com S. Sundararajan Microsoft Research India ssrajan@microsoft.com S. Sathiya Keerthi Microsoft Corporation,
A Parallel SGD method with Strong Convergence Dhruv Mahajan Microsoft Research India dhrumaha@microsoft.com S. Sundararajan Microsoft Research India ssrajan@microsoft.com S. Sathiya Keerthi Microsoft Corporation,
Day 3 Lecture 3. Optimizing deep networks
 Day 3 Lecture 3 Optimizing deep networks Convex optimization A function is convex if for all α [0,1]: f(x) Tangent line Examples Quadratics 2-norms Properties Local minimum is global minimum x Gradient
Day 3 Lecture 3 Optimizing deep networks Convex optimization A function is convex if for all α [0,1]: f(x) Tangent line Examples Quadratics 2-norms Properties Local minimum is global minimum x Gradient
CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 12: Variants of Gradient Descent
 CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 12: Variants of Gradient Descent April 27, 2018 1 / 32 Outline 1) Moment and Nesterov s accelerated gradient descent 2) AdaGrad and RMSProp 4) Adam 5) Stochastic
CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 12: Variants of Gradient Descent April 27, 2018 1 / 32 Outline 1) Moment and Nesterov s accelerated gradient descent 2) AdaGrad and RMSProp 4) Adam 5) Stochastic
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Lecture 11: Review. Henry Chai 10/02/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
Overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms. HYUNG IL KOO Based on
 Overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms HYUNG IL KOO Based on http://sebastianruder.com/optimizing-gradient-descent/ Problem Statement Machine Learning Optimization Problem Training samples:
Overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms HYUNG IL KOO Based on http://sebastianruder.com/optimizing-gradient-descent/ Problem Statement Machine Learning Optimization Problem Training samples:
ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning
 ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Sept 29, 2016 Outline Convex vs Nonconvex Functions Coordinate Descent Gradient Descent Newton s method Stochastic Gradient Descent Numerical Optimization
ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Sept 29, 2016 Outline Convex vs Nonconvex Functions Coordinate Descent Gradient Descent Newton s method Stochastic Gradient Descent Numerical Optimization
Optimization Methods for Machine Learning
 Optimization Methods for Machine Learning Sathiya Keerthi Microsoft Talks given at UC Santa Cruz February 21-23, 2017 The slides for the talks will be made available at: http://www.keerthis.com/ Introduction
Optimization Methods for Machine Learning Sathiya Keerthi Microsoft Talks given at UC Santa Cruz February 21-23, 2017 The slides for the talks will be made available at: http://www.keerthis.com/ Introduction
Dan Roth 461C, 3401 Walnut
 CIS 519/419 Applied Machine Learning www.seas.upenn.edu/~cis519 Dan Roth danroth@seas.upenn.edu http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~danroth/ 461C, 3401 Walnut Slides were created by Dan Roth (for CIS519/419 at Penn
CIS 519/419 Applied Machine Learning www.seas.upenn.edu/~cis519 Dan Roth danroth@seas.upenn.edu http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~danroth/ 461C, 3401 Walnut Slides were created by Dan Roth (for CIS519/419 at Penn
Deep Learning Lab Course 2017 (Deep Learning Practical)
 Deep Learning Lab Course 207 (Deep Learning Practical) Labs: (Computer Vision) Thomas Brox, (Robotics) Wolfram Burgard, (Machine Learning) Frank Hutter, (Neurorobotics) Joschka Boedecker University of
Deep Learning Lab Course 207 (Deep Learning Practical) Labs: (Computer Vision) Thomas Brox, (Robotics) Wolfram Burgard, (Machine Learning) Frank Hutter, (Neurorobotics) Joschka Boedecker University of
Large Scale Machine Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent
 Large Scale Machine Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent Léon Bottou leon@bottou.org Microsoft (since June) Summary i. Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent. ii. The Tradeoffs of Large Scale Learning.
Large Scale Machine Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent Léon Bottou leon@bottou.org Microsoft (since June) Summary i. Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent. ii. The Tradeoffs of Large Scale Learning.
Sample questions for Fundamentals of Machine Learning 2018
 Sample questions for Fundamentals of Machine Learning 2018 Teacher: Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan A few important informations: In the final exam, no electronic devices are allowed except a calculator. Make sure
Sample questions for Fundamentals of Machine Learning 2018 Teacher: Mohammad Emtiyaz Khan A few important informations: In the final exam, no electronic devices are allowed except a calculator. Make sure
Overfitting, Bias / Variance Analysis
 Overfitting, Bias / Variance Analysis Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 8, 207 / 40 Outline Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Basic
Overfitting, Bias / Variance Analysis Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 8, 207 / 40 Outline Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Basic
Large-scale machine learning Stochastic gradient descent
 Stochastic gradient descent IRKM Lab April 22, 2010 Introduction Very large amounts of data being generated quicker than we know what do with it ( 08 stats): NYSE generates 1 terabyte/day of new trade
Stochastic gradient descent IRKM Lab April 22, 2010 Introduction Very large amounts of data being generated quicker than we know what do with it ( 08 stats): NYSE generates 1 terabyte/day of new trade
Optimization for Machine Learning
 Optimization for Machine Learning Elman Mansimov 1 September 24, 2015 1 Modified based on Shenlong Wang s and Jake Snell s tutorials, with additional contents borrowed from Kevin Swersky and Jasper Snoek
Optimization for Machine Learning Elman Mansimov 1 September 24, 2015 1 Modified based on Shenlong Wang s and Jake Snell s tutorials, with additional contents borrowed from Kevin Swersky and Jasper Snoek
Topics we covered. Machine Learning. Statistics. Optimization. Systems! Basics of probability Tail bounds Density Estimation Exponential Families
 Midterm Review Topics we covered Machine Learning Optimization Basics of optimization Convexity Unconstrained: GD, SGD Constrained: Lagrange, KKT Duality Linear Methods Perceptrons Support Vector Machines
Midterm Review Topics we covered Machine Learning Optimization Basics of optimization Convexity Unconstrained: GD, SGD Constrained: Lagrange, KKT Duality Linear Methods Perceptrons Support Vector Machines
An Evolving Gradient Resampling Method for Machine Learning. Jorge Nocedal
 An Evolving Gradient Resampling Method for Machine Learning Jorge Nocedal Northwestern University NIPS, Montreal 2015 1 Collaborators Figen Oztoprak Stefan Solntsev Richard Byrd 2 Outline 1. How to improve
An Evolving Gradient Resampling Method for Machine Learning Jorge Nocedal Northwestern University NIPS, Montreal 2015 1 Collaborators Figen Oztoprak Stefan Solntsev Richard Byrd 2 Outline 1. How to improve
Comments. Assignment 3 code released. Thought questions 3 due this week. Mini-project: hopefully you have started. implement classification algorithms
 Neural networks Comments Assignment 3 code released implement classification algorithms use kernels for census dataset Thought questions 3 due this week Mini-project: hopefully you have started 2 Example:
Neural networks Comments Assignment 3 code released implement classification algorithms use kernels for census dataset Thought questions 3 due this week Mini-project: hopefully you have started 2 Example:
Logistic Regression Logistic
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities L2 Regularization for Logistic Regression Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Carlos Guestrin January 10 th,
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities L2 Regularization for Logistic Regression Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Carlos Guestrin January 10 th,
Gradient Descent. Sargur Srihari
 Gradient Descent Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics Simple Gradient Descent/Ascent Difficulties with Simple Gradient Descent Line Search Brent s Method Conjugate Gradient Descent Weight vectors
Gradient Descent Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics Simple Gradient Descent/Ascent Difficulties with Simple Gradient Descent Line Search Brent s Method Conjugate Gradient Descent Weight vectors
J. Sadeghi E. Patelli M. de Angelis
 J. Sadeghi E. Patelli Institute for Risk and, Department of Engineering, University of Liverpool, United Kingdom 8th International Workshop on Reliable Computing, Computing with Confidence University of
J. Sadeghi E. Patelli Institute for Risk and, Department of Engineering, University of Liverpool, United Kingdom 8th International Workshop on Reliable Computing, Computing with Confidence University of
Introduction to Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine
 Introduction to Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine guest lecturer: Ming-Wei Chang CS 446 Fall, 2009 () / 25 Fall, 2009 / 25 Before we start () 2 / 25 Fall, 2009 2 / 25 Before we start Feel
Introduction to Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine guest lecturer: Ming-Wei Chang CS 446 Fall, 2009 () / 25 Fall, 2009 / 25 Before we start () 2 / 25 Fall, 2009 2 / 25 Before we start Feel
Machine Learning. Lecture 2: Linear regression. Feng Li. https://funglee.github.io
 Machine Learning Lecture 2: Linear regression Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 2017 Supervised Learning Regression: Predict
Machine Learning Lecture 2: Linear regression Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 2017 Supervised Learning Regression: Predict
Machine Learning
 Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University February 2, 2015 Today: Logistic regression Generative/Discriminative classifiers Readings: (see class website)
Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University February 2, 2015 Today: Logistic regression Generative/Discriminative classifiers Readings: (see class website)
Machine Learning Basics Lecture 4: SVM I. Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang
 Machine Learning Basics Lecture 4: SVM I Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Review: machine learning basics Math formulation Given training data x i, y i : 1 i n i.i.d. from distribution
Machine Learning Basics Lecture 4: SVM I Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Review: machine learning basics Math formulation Given training data x i, y i : 1 i n i.i.d. from distribution
Advanced computational methods X Selected Topics: SGD
 Advanced computational methods X071521-Selected Topics: SGD. In this lecture, we look at the stochastic gradient descent (SGD) method 1 An illustrating example The MNIST is a simple dataset of variety
Advanced computational methods X071521-Selected Topics: SGD. In this lecture, we look at the stochastic gradient descent (SGD) method 1 An illustrating example The MNIST is a simple dataset of variety
Motivation Subgradient Method Stochastic Subgradient Method. Convex Optimization. Lecture 15 - Gradient Descent in Machine Learning
 Convex Optimization Lecture 15 - Gradient Descent in Machine Learning Instructor: Yuanzhang Xiao University of Hawaii at Manoa Fall 2017 1 / 21 Today s Lecture 1 Motivation 2 Subgradient Method 3 Stochastic
Convex Optimization Lecture 15 - Gradient Descent in Machine Learning Instructor: Yuanzhang Xiao University of Hawaii at Manoa Fall 2017 1 / 21 Today s Lecture 1 Motivation 2 Subgradient Method 3 Stochastic
Data Mining & Machine Learning
 Data Mining & Machine Learning CS57300 Purdue University March 1, 2018 1 Recap of Last Class (Model Search) Forward and Backward passes 2 Feedforward Neural Networks Neural Networks: Architectures 2-layer
Data Mining & Machine Learning CS57300 Purdue University March 1, 2018 1 Recap of Last Class (Model Search) Forward and Backward passes 2 Feedforward Neural Networks Neural Networks: Architectures 2-layer
Gradient Boosting (Continued)
 Gradient Boosting (Continued) David Rosenberg New York University April 4, 2016 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 April 4, 2016 1 / 31 Boosting Fits an Additive Model Boosting Fits an Additive
Gradient Boosting (Continued) David Rosenberg New York University April 4, 2016 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 April 4, 2016 1 / 31 Boosting Fits an Additive Model Boosting Fits an Additive
Selected Topics in Optimization. Some slides borrowed from
 Selected Topics in Optimization Some slides borrowed from http://www.stat.cmu.edu/~ryantibs/convexopt/ Overview Optimization problems are almost everywhere in statistics and machine learning. Input Model
Selected Topics in Optimization Some slides borrowed from http://www.stat.cmu.edu/~ryantibs/convexopt/ Overview Optimization problems are almost everywhere in statistics and machine learning. Input Model
Computational and Statistical Learning Theory
 Computational and Statistical Learning Theory TTIC 31120 Prof. Nati Srebro Lecture 17: Stochastic Optimization Part II: Realizable vs Agnostic Rates Part III: Nearest Neighbor Classification Stochastic
Computational and Statistical Learning Theory TTIC 31120 Prof. Nati Srebro Lecture 17: Stochastic Optimization Part II: Realizable vs Agnostic Rates Part III: Nearest Neighbor Classification Stochastic
CSC321 Lecture 2: Linear Regression
 CSC32 Lecture 2: Linear Regression Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC32 Lecture 2: Linear Regression / 26 Overview First learning algorithm of the course: linear regression Task: predict scalar-valued targets,
CSC32 Lecture 2: Linear Regression Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC32 Lecture 2: Linear Regression / 26 Overview First learning algorithm of the course: linear regression Task: predict scalar-valued targets,
Linear Models for Regression
 Linear Models for Regression CSE 4309 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 The Regression Problem Training data: A set of input-output
Linear Models for Regression CSE 4309 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 The Regression Problem Training data: A set of input-output
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines
 Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Linear discriminant functions
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Importance Sampling for Minibatches
 Importance Sampling for Minibatches Dominik Csiba School of Mathematics University of Edinburgh 07.09.2016, Birmingham Dominik Csiba (University of Edinburgh) Importance Sampling for Minibatches 07.09.2016,
Importance Sampling for Minibatches Dominik Csiba School of Mathematics University of Edinburgh 07.09.2016, Birmingham Dominik Csiba (University of Edinburgh) Importance Sampling for Minibatches 07.09.2016,
Accelerating Stochastic Optimization
 Accelerating Stochastic Optimization Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of CS and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Mobileye Master Class at Tel-Aviv, Tel-Aviv University, November 2014 Shalev-Shwartz
Accelerating Stochastic Optimization Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of CS and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Mobileye Master Class at Tel-Aviv, Tel-Aviv University, November 2014 Shalev-Shwartz
HOMEWORK #4: LOGISTIC REGRESSION
 HOMEWORK #4: LOGISTIC REGRESSION Probabilistic Learning: Theory and Algorithms CS 274A, Winter 2018 Due: Friday, February 23rd, 2018, 11:55 PM Submit code and report via EEE Dropbox You should submit a
HOMEWORK #4: LOGISTIC REGRESSION Probabilistic Learning: Theory and Algorithms CS 274A, Winter 2018 Due: Friday, February 23rd, 2018, 11:55 PM Submit code and report via EEE Dropbox You should submit a
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
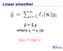 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Logistic Regression Review Fall 2012 Recitation. September 25, 2012 TA: Selen Uguroglu
 Logistic Regression Review 10-601 Fall 2012 Recitation September 25, 2012 TA: Selen Uguroglu!1 Outline Decision Theory Logistic regression Goal Loss function Inference Gradient Descent!2 Training Data
Logistic Regression Review 10-601 Fall 2012 Recitation September 25, 2012 TA: Selen Uguroglu!1 Outline Decision Theory Logistic regression Goal Loss function Inference Gradient Descent!2 Training Data
Optimization for Machine Learning
 Optimization for Machine Learning (Lecture 3-A - Convex) SUVRIT SRA Massachusetts Institute of Technology Special thanks: Francis Bach (INRIA, ENS) (for sharing this material, and permitting its use) MPI-IS
Optimization for Machine Learning (Lecture 3-A - Convex) SUVRIT SRA Massachusetts Institute of Technology Special thanks: Francis Bach (INRIA, ENS) (for sharing this material, and permitting its use) MPI-IS
Algorithmic Stability and Generalization Christoph Lampert
 Algorithmic Stability and Generalization Christoph Lampert November 28, 2018 1 / 32 IST Austria (Institute of Science and Technology Austria) institute for basic research opened in 2009 located in outskirts
Algorithmic Stability and Generalization Christoph Lampert November 28, 2018 1 / 32 IST Austria (Institute of Science and Technology Austria) institute for basic research opened in 2009 located in outskirts
Linear Regression. Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington. Oct 5, Kevin Jamieson 1
 Linear Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington Oct 5, 2017 1 The regression problem Given past sales data on zillow.com, predict: y = House sale price from x = {# sq.
Linear Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington Oct 5, 2017 1 The regression problem Given past sales data on zillow.com, predict: y = House sale price from x = {# sq.
Minimizing Finite Sums with the Stochastic Average Gradient Algorithm
 Minimizing Finite Sums with the Stochastic Average Gradient Algorithm Joint work with Nicolas Le Roux and Francis Bach University of British Columbia Context: Machine Learning for Big Data Large-scale
Minimizing Finite Sums with the Stochastic Average Gradient Algorithm Joint work with Nicolas Le Roux and Francis Bach University of British Columbia Context: Machine Learning for Big Data Large-scale
Stochastic gradient descent on Riemannian manifolds
 Stochastic gradient descent on Riemannian manifolds Silvère Bonnabel 1 Centre de Robotique - Mathématiques et systèmes Mines ParisTech SMILE Seminar Mines ParisTech Novembre 14th, 2013 1 silvere.bonnabel@mines-paristech
Stochastic gradient descent on Riemannian manifolds Silvère Bonnabel 1 Centre de Robotique - Mathématiques et systèmes Mines ParisTech SMILE Seminar Mines ParisTech Novembre 14th, 2013 1 silvere.bonnabel@mines-paristech
An interior-point stochastic approximation method and an L1-regularized delta rule
 Photograph from National Geographic, Sept 2008 An interior-point stochastic approximation method and an L1-regularized delta rule Peter Carbonetto, Mark Schmidt and Nando de Freitas University of British
Photograph from National Geographic, Sept 2008 An interior-point stochastic approximation method and an L1-regularized delta rule Peter Carbonetto, Mark Schmidt and Nando de Freitas University of British
Machine Learning Basics
 Security and Fairness of Deep Learning Machine Learning Basics Anupam Datta CMU Spring 2019 Image Classification Image Classification Image classification pipeline Input: A training set of N images, each
Security and Fairness of Deep Learning Machine Learning Basics Anupam Datta CMU Spring 2019 Image Classification Image Classification Image classification pipeline Input: A training set of N images, each
Stochastic Gradient Methods for Large-Scale Machine Learning
 Stochastic Gradient Methods for Large-Scale Machine Learning Leon Bottou Facebook A Research Frank E. Curtis Lehigh University Jorge Nocedal Northwestern University 1 Our Goal 1. This is a tutorial about
Stochastic Gradient Methods for Large-Scale Machine Learning Leon Bottou Facebook A Research Frank E. Curtis Lehigh University Jorge Nocedal Northwestern University 1 Our Goal 1. This is a tutorial about
Linear Regression. CSL603 - Fall 2017 Narayanan C Krishnan
 Linear Regression CSL603 - Fall 2017 Narayanan C Krishnan ckn@iitrpr.ac.in Outline Univariate regression Multivariate regression Probabilistic view of regression Loss functions Bias-Variance analysis Regularization
Linear Regression CSL603 - Fall 2017 Narayanan C Krishnan ckn@iitrpr.ac.in Outline Univariate regression Multivariate regression Probabilistic view of regression Loss functions Bias-Variance analysis Regularization
Lecture 10. Neural networks and optimization. Machine Learning and Data Mining November Nando de Freitas UBC. Nonlinear Supervised Learning
 Lecture 0 Neural networks and optimization Machine Learning and Data Mining November 2009 UBC Gradient Searching for a good solution can be interpreted as looking for a minimum of some error (loss) function
Lecture 0 Neural networks and optimization Machine Learning and Data Mining November 2009 UBC Gradient Searching for a good solution can be interpreted as looking for a minimum of some error (loss) function
Introduction to Logistic Regression
 Introduction to Logistic Regression Guy Lebanon Binary Classification Binary classification is the most basic task in machine learning, and yet the most frequent. Binary classifiers often serve as the
Introduction to Logistic Regression Guy Lebanon Binary Classification Binary classification is the most basic task in machine learning, and yet the most frequent. Binary classifiers often serve as the
Linear Regression. CSL465/603 - Fall 2016 Narayanan C Krishnan
 Linear Regression CSL465/603 - Fall 2016 Narayanan C Krishnan ckn@iitrpr.ac.in Outline Univariate regression Multivariate regression Probabilistic view of regression Loss functions Bias-Variance analysis
Linear Regression CSL465/603 - Fall 2016 Narayanan C Krishnan ckn@iitrpr.ac.in Outline Univariate regression Multivariate regression Probabilistic view of regression Loss functions Bias-Variance analysis
Modern Optimization Techniques
 Modern Optimization Techniques 2. Unconstrained Optimization / 2.2. Stochastic Gradient Descent Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Institute of Computer Science University
Modern Optimization Techniques 2. Unconstrained Optimization / 2.2. Stochastic Gradient Descent Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Institute of Computer Science University
OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING
 Tutorial outline OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING Based on Deep Learning, chapter 8 by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Presented By Nadav Bhonker Optimization vs Learning Surrogate
Tutorial outline OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING Based on Deep Learning, chapter 8 by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Presented By Nadav Bhonker Optimization vs Learning Surrogate
IFT Lecture 6 Nesterov s Accelerated Gradient, Stochastic Gradient Descent
 IFT 6085 - Lecture 6 Nesterov s Accelerated Gradient, Stochastic Gradient Descent This version of the notes has not yet been thoroughly checked. Please report any bugs to the scribes or instructor. Scribe(s):
IFT 6085 - Lecture 6 Nesterov s Accelerated Gradient, Stochastic Gradient Descent This version of the notes has not yet been thoroughly checked. Please report any bugs to the scribes or instructor. Scribe(s):
