Hydrogen atom energies. Friday Honors lecture. Quantum Particle in a box. Classical vs Quantum. Quantum version
|
|
|
- Emery Dawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Friday onors lecture Prof. Clint Sprott takes us on a tour of fractals. ydrogen atom energies Quantized energy levels: Each corresponds to different Orbit radius Velocity Particle wavefunction Energy Each described by a quantum number n E n = " 13.6 n 2 ev n=4 Zero energy E 3 = " ev E 2 = " ev E 1 = " ev Energy Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture 25 2 Quantum Particle in a box Particle confined to a fixed region of space e.g. ball in a tube- ball moves only along length Classical vs Quantum Classical: particle bounces back and forth. Sometimes velocity is to left, sometimes to right Classically, ball bounces back and forth in tube. This is a classical state of the ball. Identify each state by speed, =(mass)x(speed), or kinetic energy. Classical: any, energy is possible. Quantum: momenta, energy are quantized Quantum mechanics: Particle represented by wave: p = mv = h / λ Different motions: waves traveling left and right Quantum wave function: superposition of both at same time Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture 25 3 Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture 25 4 Quantum version Quantum state is both velocities at the same time " = 2 One halfwavelength Ground state is a standing wave, made equally of Wave traveling right ( p = +h/λ ) Wave traveling left ( p = - h/λ ) Determined by standing wave condition =n(λ/2) : p = h " = h 2 Different quantum states p = mv = h / λ Different speeds correspond to different λ subject to standing wave condition integer number of half-wavelengths fit in the tube. " = 2 One halfwavelength "( x) = 2 sin % ' 2# & $ x ( Wavefunction: * ) p = h " = h 2 # p o "( x) = 2 sin % ' 2# & $ x ( * ) Quantum wave function: superposition of both motions. " = Two halfwavelengths p = h " = h = 2p o Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture 25 5 Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture
2 Particle in box question Particle in box energy levels A particle in a box has a mass m. Its energy is all kinetic = p 2 /2m. Just saw that in state n is np o. It s energy levels A. are equally spaced everywhere B. get farther apart at higher energy C. get closer together at higher energy. Quantized p = h " = n h 2 = np o Energy = kinetic ( ) 2 E = p2 2m = np o 2m Or Quantized Energy = n 2 E o Energy n=5 n=4 E n = n 2 E o n=quantum number Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture 25 7 Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture 25 8 Question A particle is in a particular quantum state in a box of length. The box is now squeezed to a shorter length, /2. The particle remains in the same quantum state. The energy of the particle is now A. 2 times bigger B. 2 times smaller C. 4 times bigger D. 4 times smaller E. unchanged Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture 25 9 Quantum dot: particle in 3D box Decreasing particle size Energy level spacing increases as particle size decreases. i.e E n +1 " E n = ( n +1)2 h 2 " n 2 h 2 8m 2 8m 2 CdSe quantum dots dispersed in hexane (Bawendi group, MIT) Color from photon absorption Determined by energylevel spacing Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Interpreting the wavefunction igher energy wave functions Probabilistic interpretation The square magnitude of the wavefunction Ψ 2 gives the probability of finding the particle at a particular spatial location n p E 3 h h 2 8m 2 Wavefunction Probability Wavefunction Probability = (Wavefunction) 2 2 h h 2 8m 2 h 2 h 2 8m 2 Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture
3 Probability of finding electron Quantum Corral Classically, equally likely to find particle anywhere QM - true on average for high n Zeroes in the probability! Purely quantum, interference effect Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Iron atoms assembled into a circular ring. The ripples inside the ring reflect the electron quantum states of a circular ring (interference effects). Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Tip Particle in a box, again Wavefunction Probability = (Wavefunction) 2 Particle contained entirely within closed tube. Sample Over the last 20 yrs, technology developed to controllably position tip and sample 1-2 nm apart. Is a very useful microscope! Open top: particle can escape if we shake hard enough. But at low energies, particle stays entirely within box. ike an electron in metal (remember photoelectric effect) Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Quantum mechanics says something different! ow energy Classical state ow energy Quantum state Quantum Mechanics: some probability of the particle penetrating walls of box! Two neighboring boxes When another box is brought nearby, the electron may disappear from one well, and appear in the other! The reverse then happens, and the electron oscillates back an forth, without traversing the intervening distance. Nonzero probability of being outside the box. Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture
4 Question Suppose separation between boxes increases by a factor of two. The tunneling probability A. Increases by 2 B. Decreases by 2 C. Decreases by <2 D. Decreases by >2 E. Stays same high probability Example: Ammonia molecule Ammonia molecule: N 3 Nitrogen (N) has two equivalent stable positions. Quantum-mechanically tunnels 2.4x10 11 times per second (24 Gz) N Known as inversion line Basis of first atomic clock (1949) low probability Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Atomic clock question Suppose we changed the ammonia molecule so that the distance between the two stable positions of the nitrogen atom INCREASED. The clock would Tunneling between conductors Make one well deeper: particle tunnels, then stays in other well. Well made deeper by applying electric field. This is the principle of scanning tunneling microscope. A. slow down. B. speed up. C. stay the same. N Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Tip Tip, sample are quantum boxes Potential difference induces tunneling Tunneling extremely sensitive to tip-sample spacing Surface steps on Si Sample Over the last 20 yrs, technology developed to controllably position tip and sample 1-2 nm apart. Is a very useful microscope! Images courtesy M. agally, Univ. Wisconsin Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture
5 Manipulation of atoms Take advantage of tip-atom interactions to physically move atoms around on the surface Quantum Corral This shows the assembly of a circular corral by moving individual Iron atoms on the surface of Copper (111). The (111) orientation supports an electron surface state which can be trapped in the corral Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Iron atoms assembled into a circular ring. The ripples inside the ring reflect the electron quantum states of a circular ring (interference effects). Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture The Stadium Corral Some fun! Again Iron on copper. This was assembled to investigate quantum chaos. The electron wavefunction leaked out beyond the stadium too much to to observe expected effects. Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture Kanji for atom (lit. original child) Iron on copper (111) Carbon Monoxide man Carbon Monoxide on Pt (111) Thu. Nov Physics 208, ecture
Particle in a box. From Last Time. Classical vs quantum. Wavefunction of pendulum. Wavefunctions in two dimensions. Probability density of oscillator
 No office hours Tuesday Guest lecturer Wed: Entanglement & Quantum Computing From ast Time Particle can exist in different quantum states, having Different energy Different momentum Different wavelength
No office hours Tuesday Guest lecturer Wed: Entanglement & Quantum Computing From ast Time Particle can exist in different quantum states, having Different energy Different momentum Different wavelength
From Last time. Exam 3 results. Probability. The wavefunction. Example wavefunction. Discrete vs continuous. De Broglie wavelength
 From ast time Eam 3 results De Broglie wavelength Uncertainty principle Eam average ~ 70% Scores posted on learn@uw D C BC B AB A Wavefunction of a particle Course evaluations: Tuesday, Dec. 9 Tue. Dec.
From ast time Eam 3 results De Broglie wavelength Uncertainty principle Eam average ~ 70% Scores posted on learn@uw D C BC B AB A Wavefunction of a particle Course evaluations: Tuesday, Dec. 9 Tue. Dec.
Hydrogen atom energies. From Last Time. Today. Another question. Hydrogen atom question. Compton scattering and Photoelectric effect
 From ast Time Observation of atoms indicated quantized energy states. Atom only emitted certain wavelengths of light Structure of the allowed wavelengths indicated the what the energy structure was Quantum
From ast Time Observation of atoms indicated quantized energy states. Atom only emitted certain wavelengths of light Structure of the allowed wavelengths indicated the what the energy structure was Quantum
Back to the particle in a box. From Last Time. Where is the particle? How fast is it moving? Quantum momentum. Uncertainty in Quantum Mechanics
 From ast Time Back to the particle in a box Particle can exist in different quantum states, having Different energy Different momentum Different wavelength Wavefunction Probability = (Wavefunction) 2 The
From ast Time Back to the particle in a box Particle can exist in different quantum states, having Different energy Different momentum Different wavelength Wavefunction Probability = (Wavefunction) 2 The
The wavefunction and quantum jumps
 ydrogen atom in 3D Today From ast Time Electron has a particle and wave nature and is spread out over space Wave nature must interfere constructively to exist Satisfies 3 conditions for constructive interference
ydrogen atom in 3D Today From ast Time Electron has a particle and wave nature and is spread out over space Wave nature must interfere constructively to exist Satisfies 3 conditions for constructive interference
From Last Time. Mon. Nov 8 Phy107 Lecture 26
 From Last Time Particle can exist in different quantum states, having Different energy Different momentum Different wavelength The quantum wavefunction describes wave nature of particle. Square of the
From Last Time Particle can exist in different quantum states, having Different energy Different momentum Different wavelength The quantum wavefunction describes wave nature of particle. Square of the
Energy levels. From Last Time. Emitting and absorbing light. Hydrogen atom. Energy conservation for Bohr atom. Summary of Hydrogen atom
 From Last Time Hydrogen atom: One electron orbiting around one proton (nucleus) Electron can be in different quantum states Quantum states labeled by integer,2,3,4, In each different quantum state, electron
From Last Time Hydrogen atom: One electron orbiting around one proton (nucleus) Electron can be in different quantum states Quantum states labeled by integer,2,3,4, In each different quantum state, electron
Chapter 28 Quantum Theory Lecture 24
 Chapter 28 Quantum Theory Lecture 24 28.1 Particles, Waves, and Particles-Waves 28.2 Photons 28.3 Wavelike Properties Classical Particles 28.4 Electron Spin 28.5 Meaning of the Wave Function 28.6 Tunneling
Chapter 28 Quantum Theory Lecture 24 28.1 Particles, Waves, and Particles-Waves 28.2 Photons 28.3 Wavelike Properties Classical Particles 28.4 Electron Spin 28.5 Meaning of the Wave Function 28.6 Tunneling
Hour Exam 3 Review. Quantum Mechanics. Photoelectric effect summary. Photoelectric effect question. Compton scattering. Compton scattering question
 Hour Exam 3 Review Hour Exam 3: Wednesday, Apr. 19 In-class (2241 Chamberlin Hall) Twenty multiple-choice questions Will cover: Basic Quantum Mechanics Uses of Quantum Mechanics Addl. Lecture Material
Hour Exam 3 Review Hour Exam 3: Wednesday, Apr. 19 In-class (2241 Chamberlin Hall) Twenty multiple-choice questions Will cover: Basic Quantum Mechanics Uses of Quantum Mechanics Addl. Lecture Material
There is light at the end of the tunnel. -- proverb. The light at the end of the tunnel is just the light of an oncoming train. --R.
 A vast time bubble has been projected into the future to the precise moment of the end of the universe. This is, of course, impossible. --D. Adams, The Hitchhiker s Guide to the Galaxy There is light at
A vast time bubble has been projected into the future to the precise moment of the end of the universe. This is, of course, impossible. --D. Adams, The Hitchhiker s Guide to the Galaxy There is light at
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214
 Not all chemicals are bad. Without chemicals such as hydrogen and oxygen, for example, there would be no way to make water, a vital ingredient in beer. -Dave Barry David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton
Not all chemicals are bad. Without chemicals such as hydrogen and oxygen, for example, there would be no way to make water, a vital ingredient in beer. -Dave Barry David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton
QUANTUM MECHANICS Intro to Basic Features
 PCES 4.21 QUANTUM MECHANICS Intro to Basic Features 1. QUANTUM INTERFERENCE & QUANTUM PATHS Rather than explain the rules of quantum mechanics as they were devised, we first look at a more modern formulation
PCES 4.21 QUANTUM MECHANICS Intro to Basic Features 1. QUANTUM INTERFERENCE & QUANTUM PATHS Rather than explain the rules of quantum mechanics as they were devised, we first look at a more modern formulation
Lecture 15: Time-Dependent QM & Tunneling Review and Examples, Ammonia Maser
 ecture 15: Time-Dependent QM & Tunneling Review and Examples, Ammonia Maser ψ(x,t=0) 2 U(x) 0 x ψ(x,t 0 ) 2 x U 0 0 E x 0 x ecture 15, p.1 Special (Optional) ecture Quantum Information One of the most
ecture 15: Time-Dependent QM & Tunneling Review and Examples, Ammonia Maser ψ(x,t=0) 2 U(x) 0 x ψ(x,t 0 ) 2 x U 0 0 E x 0 x ecture 15, p.1 Special (Optional) ecture Quantum Information One of the most
Lecture 10: The Schrödinger Equation. Lecture 10, p 2
 Quantum mechanics is the description of the behavior of matter and light in all its details and, in particular, of the happenings on an atomic scale. Things on a very small scale behave like nothing that
Quantum mechanics is the description of the behavior of matter and light in all its details and, in particular, of the happenings on an atomic scale. Things on a very small scale behave like nothing that
CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II
 CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II 6.1 The Schrödinger Wave Equation 6.2 Expectation Values 6.3 Infinite Square-Well Potential 6.4 Finite Square-Well Potential 6.5 Three-Dimensional Infinite-Potential Well
CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II 6.1 The Schrödinger Wave Equation 6.2 Expectation Values 6.3 Infinite Square-Well Potential 6.4 Finite Square-Well Potential 6.5 Three-Dimensional Infinite-Potential Well
Lecture 10: The Schrödinger Equation. Lecture 10, p 2
 Quantum mechanics is the description of the behavior of matter and light in all its details and, in particular, of the happenings on an atomic scale. Things on a very small scale behave like nothing that
Quantum mechanics is the description of the behavior of matter and light in all its details and, in particular, of the happenings on an atomic scale. Things on a very small scale behave like nothing that
LECTURE # 17 Modern Optics Matter Waves
 PHYS 270-SPRING 2011 LECTURE # 17 Modern Optics Matter Waves April 5, 2011 1 Spectroscopy: Unlocking the Structure of Atoms There are two types of spectra, continuous spectra and discrete spectra: Hot,
PHYS 270-SPRING 2011 LECTURE # 17 Modern Optics Matter Waves April 5, 2011 1 Spectroscopy: Unlocking the Structure of Atoms There are two types of spectra, continuous spectra and discrete spectra: Hot,
Notes on wavefunctions IV: the Schrödinger equation in a potential and energy eigenstates.
 Notes on wavefunctions IV: the Schrödinger equation in a potential and energy eigenstates. We have now seen that the wavefunction for a free electron changes with time according to the Schrödinger Equation
Notes on wavefunctions IV: the Schrödinger equation in a potential and energy eigenstates. We have now seen that the wavefunction for a free electron changes with time according to the Schrödinger Equation
Lecture 10: The Schrödinger Equation Lecture 10, p 1
 Lecture 10: The Schrödinger Equation Lecture 10, p 1 Overview Probability distributions Schrödinger s Equation Particle in a Bo Matter waves in an infinite square well Quantized energy levels y() U= n=1
Lecture 10: The Schrödinger Equation Lecture 10, p 1 Overview Probability distributions Schrödinger s Equation Particle in a Bo Matter waves in an infinite square well Quantized energy levels y() U= n=1
Particle in a 3 Dimensional Box just extending our model from 1D to 3D
 CHEM 2060 Lecture 20: Particle in a 3D Box; H atom L20-1 Particle in a 3 Dimensional Box just extending our model from 1D to 3D A 3D model is a step closer to reality than a 1D model. Let s increase the
CHEM 2060 Lecture 20: Particle in a 3D Box; H atom L20-1 Particle in a 3 Dimensional Box just extending our model from 1D to 3D A 3D model is a step closer to reality than a 1D model. Let s increase the
From Last Time. Electron diffraction. Making a particle out of waves. Planetary model of atom. Using quantum mechanics ev 1/ 2 nm E kinetic
 From Last Time All objects show both wave-like properties and particle-like properties. Electromagnetic radiation (e.g. light) shows interference effects (wave-like properties), but also comes in discrete
From Last Time All objects show both wave-like properties and particle-like properties. Electromagnetic radiation (e.g. light) shows interference effects (wave-like properties), but also comes in discrete
INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM MECHANICS
 4 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM MECHANICS 4.1 Preliminaries: Wave Motion and Light 4.2 Evidence for Energy Quantization in Atoms 4.3 The Bohr Model: Predicting Discrete Energy Levels in Atoms 4.4 Evidence
4 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM MECHANICS 4.1 Preliminaries: Wave Motion and Light 4.2 Evidence for Energy Quantization in Atoms 4.3 The Bohr Model: Predicting Discrete Energy Levels in Atoms 4.4 Evidence
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
Electron in a Box. A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time.
 Electron in a Box A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time. Last Time: Light Wave model: Interference pattern is in terms of wave intensity Photon model: Interference in
Electron in a Box A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time. Last Time: Light Wave model: Interference pattern is in terms of wave intensity Photon model: Interference in
Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling
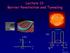 Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling nucleus x U(x) U(x) U 0 E A B C B A 0 L x 0 x Lecture 13, p 1 Today Tunneling of quantum particles Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) Nuclear Decay Solar
Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling nucleus x U(x) U(x) U 0 E A B C B A 0 L x 0 x Lecture 13, p 1 Today Tunneling of quantum particles Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) Nuclear Decay Solar
Modern physics. 4. Barriers and wells. Lectures in Physics, summer
 Modern physics 4. Barriers and wells Lectures in Physics, summer 016 1 Outline 4.1. Particle motion in the presence of a potential barrier 4.. Wave functions in the presence of a potential barrier 4.3.
Modern physics 4. Barriers and wells Lectures in Physics, summer 016 1 Outline 4.1. Particle motion in the presence of a potential barrier 4.. Wave functions in the presence of a potential barrier 4.3.
* = 2 = Probability distribution function. probability of finding a particle near a given point x,y,z at a time t
 Quantum Mechanics Wave functions and the Schrodinger equation Particles behave like waves, so they can be described with a wave function (x,y,z,t) A stationary state has a definite energy, and can be written
Quantum Mechanics Wave functions and the Schrodinger equation Particles behave like waves, so they can be described with a wave function (x,y,z,t) A stationary state has a definite energy, and can be written
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 1-1B: THE INTERACTION OF MATTER WITH RADIATION Introductory Video Quantum Mechanics Essential Idea: The microscopic quantum world offers
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 1-1B: THE INTERACTION OF MATTER WITH RADIATION Introductory Video Quantum Mechanics Essential Idea: The microscopic quantum world offers
Quantum Mechanics (made fun and easy)
 Lecture 7 Quantum Mechanics (made fun and easy) Why the world needs quantum mechanics Why the world needs quantum mechanics Why the world needs quantum mechanics Why the world needs quantum mechanics Why
Lecture 7 Quantum Mechanics (made fun and easy) Why the world needs quantum mechanics Why the world needs quantum mechanics Why the world needs quantum mechanics Why the world needs quantum mechanics Why
PHYS 172: Modern Mechanics Fall 2009
 PHYS 172: Modern Mechanics Fall 2009 Lecture 14 Energy Quantization Read 7.1 7.9 Reading Question: Ch. 7, Secs 1-5 A simple model for the hydrogen atom treats the electron as a particle in circular orbit
PHYS 172: Modern Mechanics Fall 2009 Lecture 14 Energy Quantization Read 7.1 7.9 Reading Question: Ch. 7, Secs 1-5 A simple model for the hydrogen atom treats the electron as a particle in circular orbit
Complementi di Fisica Lectures 10-11
 Complementi di Fisica - Lectures 1-11 15/16-1-1 Complementi di Fisica Lectures 1-11 Livio Lanceri Università di Trieste Trieste, 15/16-1-1 Course Outline - Reminder Quantum Mechanics: an introduction Reminder
Complementi di Fisica - Lectures 1-11 15/16-1-1 Complementi di Fisica Lectures 1-11 Livio Lanceri Università di Trieste Trieste, 15/16-1-1 Course Outline - Reminder Quantum Mechanics: an introduction Reminder
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Planck s Quantum Hypothesis; Blackbody Radiation Photon Theory of Light and the Photoelectric Effect Energy, Mass, and Momentum of a Photon Compton
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Planck s Quantum Hypothesis; Blackbody Radiation Photon Theory of Light and the Photoelectric Effect Energy, Mass, and Momentum of a Photon Compton
Final Exam: Tuesday, May 8, 2012 Starting at 8:30 a.m., Hoyt Hall.
 Final Exam: Tuesday, May 8, 2012 Starting at 8:30 a.m., Hoyt Hall. Chapter 38 Quantum Mechanics Units of Chapter 38 38-1 Quantum Mechanics A New Theory 37-2 The Wave Function and Its Interpretation; the
Final Exam: Tuesday, May 8, 2012 Starting at 8:30 a.m., Hoyt Hall. Chapter 38 Quantum Mechanics Units of Chapter 38 38-1 Quantum Mechanics A New Theory 37-2 The Wave Function and Its Interpretation; the
Today: Finite box wavefunctions
 Toay: Finite bo wavefunctions 1.Think outsie the bo!.solving the S.E. 3.Unerstaning the results. HWK1 ue We. 1AM. Reaing for Monay.: TZ&D Chap. 8 Reaing Quiz Classically forbien regions are where A. a
Toay: Finite bo wavefunctions 1.Think outsie the bo!.solving the S.E. 3.Unerstaning the results. HWK1 ue We. 1AM. Reaing for Monay.: TZ&D Chap. 8 Reaing Quiz Classically forbien regions are where A. a
STM spectroscopy (STS)
 STM spectroscopy (STS) di dv 4 e ( E ev, r) ( E ) M S F T F Basic concepts of STS. With the feedback circuit open the variation of the tunneling current due to the application of a small oscillating voltage
STM spectroscopy (STS) di dv 4 e ( E ev, r) ( E ) M S F T F Basic concepts of STS. With the feedback circuit open the variation of the tunneling current due to the application of a small oscillating voltage
Explanations of quantum animations Sohrab Ismail-Beigi April 22, 2009
 Explanations of quantum animations Sohrab Ismail-Beigi April 22, 2009 I ve produced a set of animations showing the time evolution of various wave functions in various potentials according to the Schrödinger
Explanations of quantum animations Sohrab Ismail-Beigi April 22, 2009 I ve produced a set of animations showing the time evolution of various wave functions in various potentials according to the Schrödinger
Title / paragraph example Topic: Quantum Computers. Course essay. Photoelectric effect summary. From Last Time. Photon interference?
 Course essay Friday, Nov 3: Due in class essay topic(review article, operating experiment, noble prize) short description - one paragraph http://www.hep.wisc.edu/~herndon/107-0609/essay.htm Friday, Nov
Course essay Friday, Nov 3: Due in class essay topic(review article, operating experiment, noble prize) short description - one paragraph http://www.hep.wisc.edu/~herndon/107-0609/essay.htm Friday, Nov
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
 Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Units of Chapter 37 37-7 Wave Nature of Matter 37-8 Electron Microscopes 37-9 Early Models of the Atom 37-10 Atomic Spectra: Key to the Structure
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Units of Chapter 37 37-7 Wave Nature of Matter 37-8 Electron Microscopes 37-9 Early Models of the Atom 37-10 Atomic Spectra: Key to the Structure
ECE 487 Lecture 5 : Foundations of Quantum Mechanics IV Class Outline:
 ECE 487 Lecture 5 : Foundations of Quantum Mechanics IV Class Outline: Linearly Varying Potential Triangular Potential Well Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation Things you should know when you leave Key
ECE 487 Lecture 5 : Foundations of Quantum Mechanics IV Class Outline: Linearly Varying Potential Triangular Potential Well Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation Things you should know when you leave Key
From Atoms to Solids. Outline. - Atomic and Molecular Wavefunctions - Molecular Hydrogen - Benzene
 From Atoms to Solids Outline - Atomic and Molecular Wavefunctions - Molecular Hydrogen - Benzene 1 A Simple Approximation for an Atom Let s represent the atom in space by its Coulomb potential centered
From Atoms to Solids Outline - Atomic and Molecular Wavefunctions - Molecular Hydrogen - Benzene 1 A Simple Approximation for an Atom Let s represent the atom in space by its Coulomb potential centered
Probability and Normalization
 Probability and Normalization Although we don t know exactly where the particle might be inside the box, we know that it has to be in the box. This means that, ψ ( x) dx = 1 (normalization condition) L
Probability and Normalization Although we don t know exactly where the particle might be inside the box, we know that it has to be in the box. This means that, ψ ( x) dx = 1 (normalization condition) L
Modern Physics notes Paul Fendley Lecture 6
 Modern Physics notes Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 6 Size of the atom A digression on hand-waving arguments Spectral lines Feynman, 2.4-5 Fowler, Spectra, The Bohr atom The size of the atom
Modern Physics notes Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 6 Size of the atom A digression on hand-waving arguments Spectral lines Feynman, 2.4-5 Fowler, Spectra, The Bohr atom The size of the atom
atoms and light. Chapter Goal: To understand the structure and properties of atoms.
 Quantum mechanics provides us with an understanding of atomic structure and atomic properties. Lasers are one of the most important applications of the quantummechanical properties of atoms and light.
Quantum mechanics provides us with an understanding of atomic structure and atomic properties. Lasers are one of the most important applications of the quantummechanical properties of atoms and light.
Modern Physics Part 3: Bohr Model & Matter Waves
 Modern Physics Part 3: Bohr Model & Matter Waves Last modified: 28/08/2018 Links Atomic Spectra Introduction Atomic Emission Spectra Atomic Absorption Spectra Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom Emission Spectrum
Modern Physics Part 3: Bohr Model & Matter Waves Last modified: 28/08/2018 Links Atomic Spectra Introduction Atomic Emission Spectra Atomic Absorption Spectra Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom Emission Spectrum
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 27 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 27 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 27 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture 21: Lasers, Schrödinger s Cat, Atoms, Molecules, Solids, etc. Review and Examples. Lecture 21, p 1
 Lecture 21: Lasers, Schrödinger s Cat, Atoms, Molecules, Solids, etc. Review and Examples Lecture 21, p 1 Act 1 The Pauli exclusion principle applies to all fermions in all situations (not just to electrons
Lecture 21: Lasers, Schrödinger s Cat, Atoms, Molecules, Solids, etc. Review and Examples Lecture 21, p 1 Act 1 The Pauli exclusion principle applies to all fermions in all situations (not just to electrons
Lecture 12: Particle in 1D boxes & Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Lecture 12: Particle in 1D boxes & Simple Harmonic Oscillator U(x) E Dx y(x) x Dx Lecture 12, p 1 Properties of Bound States Several trends exhibited by the particle-in-box states are generic to bound
Lecture 12: Particle in 1D boxes & Simple Harmonic Oscillator U(x) E Dx y(x) x Dx Lecture 12, p 1 Properties of Bound States Several trends exhibited by the particle-in-box states are generic to bound
When I hear of Schrödinger s cat, I reach for my gun. --Stephen W. Hawking. Lecture 21, p 1
 When I hear of Schrödinger s cat, I reach for my gun. --Stephen W. Hawking Lecture 21, p 1 Lecture 21: Lasers, Schrödinger s Cat, Atoms, Molecules, Solids, etc. Review and Examples Lecture 21, p 2 Act
When I hear of Schrödinger s cat, I reach for my gun. --Stephen W. Hawking Lecture 21, p 1 Lecture 21: Lasers, Schrödinger s Cat, Atoms, Molecules, Solids, etc. Review and Examples Lecture 21, p 2 Act
Chapter 37. Lasers, a Model Atom and Zero Point Energy
 Chapter 37 Lasers, a Model Atom and Zero Point Energy CHAPTER 37 LASERS, A MOEL ATOM AN ZERO POINT ENERGY Once at the end of a colloquium I heard ebye saying something like: Schrödinger, you are not working
Chapter 37 Lasers, a Model Atom and Zero Point Energy CHAPTER 37 LASERS, A MOEL ATOM AN ZERO POINT ENERGY Once at the end of a colloquium I heard ebye saying something like: Schrödinger, you are not working
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214
 All the fifty years of conscious brooding have brought me no closer to answer the question, What are light quanta? Of course today every rascal thinks he knows the answer, but he is deluding himself. -Albert
All the fifty years of conscious brooding have brought me no closer to answer the question, What are light quanta? Of course today every rascal thinks he knows the answer, but he is deluding himself. -Albert
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I
 CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5.2 De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Uncertainty Principle 5.7 Probability,
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5.2 De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Uncertainty Principle 5.7 Probability,
PHYS 3313 Section 001 Lecture #16
 PHYS 3313 Section 001 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 24, 2014 De Broglie Waves Bohr s Quantization Conditions Electron Scattering Wave Packets and Packet Envelops Superposition of Waves Electron Double Slit
PHYS 3313 Section 001 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 24, 2014 De Broglie Waves Bohr s Quantization Conditions Electron Scattering Wave Packets and Packet Envelops Superposition of Waves Electron Double Slit
5.111 Lecture Summary #4 Wednesday, September 10, 2014
 5.111 Lecture Summary #4 Wednesday, September 10, 2014 Reading for today: Section 1.5 and Section 1.6. (Same sections in 5 th and 4 th editions) Read for Lecture #5: Section 1.3 Atomic Spectra, Section
5.111 Lecture Summary #4 Wednesday, September 10, 2014 Reading for today: Section 1.5 and Section 1.6. (Same sections in 5 th and 4 th editions) Read for Lecture #5: Section 1.3 Atomic Spectra, Section
Chapter 8 Chapter 8 Quantum Theory: Techniques and Applications (Part II)
 Chapter 8 Chapter 8 Quantum Theory: Techniques and Applications (Part II) The Particle in the Box and the Real World, Phys. Chem. nd Ed. T. Engel, P. Reid (Ch.16) Objectives Importance of the concept for
Chapter 8 Chapter 8 Quantum Theory: Techniques and Applications (Part II) The Particle in the Box and the Real World, Phys. Chem. nd Ed. T. Engel, P. Reid (Ch.16) Objectives Importance of the concept for
Chapter 28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms
 Chapter 28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms 28.1 Quantum Mechanics The Theory Quantum mechanics incorporates wave-particle duality, and successfully explains energy states in complex atoms and molecules, the
Chapter 28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms 28.1 Quantum Mechanics The Theory Quantum mechanics incorporates wave-particle duality, and successfully explains energy states in complex atoms and molecules, the
Lecture 9: Introduction to QM: Review and Examples
 Lecture 9: Introduction to QM: Review and Examples S 1 S 2 Lecture 9, p 1 Photoelectric Effect V stop (v) KE e V hf F max stop Binding energy F The work function: F is the minimum energy needed to strip
Lecture 9: Introduction to QM: Review and Examples S 1 S 2 Lecture 9, p 1 Photoelectric Effect V stop (v) KE e V hf F max stop Binding energy F The work function: F is the minimum energy needed to strip
LECTURE # 19 Dennis Papadopoulos End of Classical Physics Quantization Bohr Atom Chapters 38 39
 PHYS 270-SPRING 2011 LECTURE # 19 Dennis Papadopoulos End of Classical Physics Quantization Bohr Atom Chapters 38 39 April 14, 2011 1 HOW TO MEASURE SPECTRA Spectroscopy: Unlocking the Structure of Atoms
PHYS 270-SPRING 2011 LECTURE # 19 Dennis Papadopoulos End of Classical Physics Quantization Bohr Atom Chapters 38 39 April 14, 2011 1 HOW TO MEASURE SPECTRA Spectroscopy: Unlocking the Structure of Atoms
Dept. of Physics, MIT Manipal 1
 Chapter 1: Optics 1. In the phenomenon of interference, there is A Annihilation of light energy B Addition of energy C Redistribution energy D Creation of energy 2. Interference fringes are obtained using
Chapter 1: Optics 1. In the phenomenon of interference, there is A Annihilation of light energy B Addition of energy C Redistribution energy D Creation of energy 2. Interference fringes are obtained using
Lecture 16 Quantum Physics Chapter 28
 Lecture 16 Quantum Physics Chapter 28 Particles vs. Waves Physics of particles p = mv K = ½ mv2 Particles collide and do not pass through each other Conservation of: Momentum Energy Electric Charge Physics
Lecture 16 Quantum Physics Chapter 28 Particles vs. Waves Physics of particles p = mv K = ½ mv2 Particles collide and do not pass through each other Conservation of: Momentum Energy Electric Charge Physics
The Schrödinger Equation in One Dimension
 The Schrödinger Equation in One Dimension Introduction We have defined a comple wave function Ψ(, t) for a particle and interpreted it such that Ψ ( r, t d gives the probability that the particle is at
The Schrödinger Equation in One Dimension Introduction We have defined a comple wave function Ψ(, t) for a particle and interpreted it such that Ψ ( r, t d gives the probability that the particle is at
RED. BLUE Light. Light-Matter
 1 Light-Matter This experiment demonstrated that light behaves as a wave. Essentially Thomas Young passed a light of a single frequency ( colour) through a pair of closely spaced narrow slits and on the
1 Light-Matter This experiment demonstrated that light behaves as a wave. Essentially Thomas Young passed a light of a single frequency ( colour) through a pair of closely spaced narrow slits and on the
Physics 1C Lecture 29A. Finish off Ch. 28 Start Ch. 29
 Physics 1C Lecture 29A Finish off Ch. 28 Start Ch. 29 Particle in a Box Let s consider a particle confined to a one-dimensional region in space. Following the quantum mechanics approach, we need to find
Physics 1C Lecture 29A Finish off Ch. 28 Start Ch. 29 Particle in a Box Let s consider a particle confined to a one-dimensional region in space. Following the quantum mechanics approach, we need to find
Quantum Mechanics. Exam 3. Photon(or electron) interference? Photoelectric effect summary. Using Quantum Mechanics. Wavelengths of massive objects
 Exam 3 Hour Exam 3: Wednesday, November 29th In-class, Quantum Physics and Nuclear Physics Twenty multiple-choice questions Will cover:chapters 13, 14, 15 and 16 Lecture material You should bring 1 page
Exam 3 Hour Exam 3: Wednesday, November 29th In-class, Quantum Physics and Nuclear Physics Twenty multiple-choice questions Will cover:chapters 13, 14, 15 and 16 Lecture material You should bring 1 page
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
 Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules +e r n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 +e +e r ψ even Lecture 19, p 1 Today Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Using RF photons to drive transitions between nuclear spin orientations in
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules +e r n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 +e +e r ψ even Lecture 19, p 1 Today Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Using RF photons to drive transitions between nuclear spin orientations in
Atomic Spectra. if you pass white light through a gas dark narrow lines on a bright continuum "Absorption spectrum"
 By the end of the 1800 s, classical physics had many successes. One prominent physicist even had suggested that all that remained was to further increase the significant digits for measurements. However,
By the end of the 1800 s, classical physics had many successes. One prominent physicist even had suggested that all that remained was to further increase the significant digits for measurements. However,
ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline:
 ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline: Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation Solutions to thetime-dependent Schrödinger Equation Expansion of Energy Eigenstates Things you
ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline: Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation Solutions to thetime-dependent Schrödinger Equation Expansion of Energy Eigenstates Things you
CHAPTER 2: POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS
 CHAPTER 2: POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS Basics of Quantum Mechanics - Why Quantum Physics? - Classical mechanics (Newton's mechanics) and Maxwell's equations (electromagnetics theory) can explain MACROSCOPIC
CHAPTER 2: POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS Basics of Quantum Mechanics - Why Quantum Physics? - Classical mechanics (Newton's mechanics) and Maxwell's equations (electromagnetics theory) can explain MACROSCOPIC
Larbert High School. Quanta and Waves. Homework Exercises ADVANCED HIGHER PHYSICS
 Larbert High School ADVANCED HIGHER PHYSICS Quanta and Waves Homework Exercises 3.1 3.6 3.1 Intro to Quantum Theory HW 1. (a) Explain what is meant by term black body. (1) (b) State two observations that
Larbert High School ADVANCED HIGHER PHYSICS Quanta and Waves Homework Exercises 3.1 3.6 3.1 Intro to Quantum Theory HW 1. (a) Explain what is meant by term black body. (1) (b) State two observations that
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 15
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 15 Modern Physics Chapter 27 1. Quantum Physics The Compton Effect Photons and EM Waves Wave Properties of Particles Wave Functions The Uncertainty Principle http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 15 Modern Physics Chapter 27 1. Quantum Physics The Compton Effect Photons and EM Waves Wave Properties of Particles Wave Functions The Uncertainty Principle http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm
Single Slit Diffraction and Resolving Power. Quantum Mechanics: Blackbody Radiation & Photoelectric Effect. Physics 102: Lecture 22
 Physics 102: Lecture 22 Single Slit Diffraction and Resolving Power Quantum Mechanics: Blackbody Radiation & Photoelectric Effect Physics 102: Lecture 22, Slide 1 Diffraction/Huygens principle Huygens:
Physics 102: Lecture 22 Single Slit Diffraction and Resolving Power Quantum Mechanics: Blackbody Radiation & Photoelectric Effect Physics 102: Lecture 22, Slide 1 Diffraction/Huygens principle Huygens:
Physics 1C. Lecture 28D
 Physics 1C Lecture 28D "I ask you to look both ways. For the road to a knowledge of the stars leads through the atom; and important knowledge of the atom has been reached through the stars." --Sir Arthur
Physics 1C Lecture 28D "I ask you to look both ways. For the road to a knowledge of the stars leads through the atom; and important knowledge of the atom has been reached through the stars." --Sir Arthur
Lecture 12: Particle in 1D boxes, Simple Harmonic Oscillators
 Lecture 1: Particle in 1D boes, Simple Harmonic Oscillators U U() ψ() U n= n=0 n=1 n=3 Lecture 1, p 1 This week and last week are critical for the course: Week 3, Lectures 7-9: Week 4, Lectures 10-1: Light
Lecture 1: Particle in 1D boes, Simple Harmonic Oscillators U U() ψ() U n= n=0 n=1 n=3 Lecture 1, p 1 This week and last week are critical for the course: Week 3, Lectures 7-9: Week 4, Lectures 10-1: Light
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
 Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules +e r n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 +e +e r y even Lecture 19, p 1 Today Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Using RF photons to drive transitions between nuclear spin orientations in
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules +e r n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 +e +e r y even Lecture 19, p 1 Today Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Using RF photons to drive transitions between nuclear spin orientations in
28-2 Models of the Atom
 Answer to Essential Question 28.1: (a) In general, four energy levels give six photon energies. One way to count these is to start with the highest level, 12 ev. An electron starting in the 12 ev level
Answer to Essential Question 28.1: (a) In general, four energy levels give six photon energies. One way to count these is to start with the highest level, 12 ev. An electron starting in the 12 ev level
Quantum Mechanics. The Schrödinger equation. Erwin Schrödinger
 Quantum Mechanics The Schrödinger equation Erwin Schrödinger The Nobel Prize in Physics 1933 "for the discovery of new productive forms of atomic theory" The Schrödinger Equation in One Dimension Time-Independent
Quantum Mechanics The Schrödinger equation Erwin Schrödinger The Nobel Prize in Physics 1933 "for the discovery of new productive forms of atomic theory" The Schrödinger Equation in One Dimension Time-Independent
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Discovery and Properties of the electron
 Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom 27-1 Discovery and Properties of the electron Measure charge to mass ratio e/m (J. J. Thomson, 1897) When apply magnetic field only, the rays are
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom 27-1 Discovery and Properties of the electron Measure charge to mass ratio e/m (J. J. Thomson, 1897) When apply magnetic field only, the rays are
Wave nature of particles
 Wave nature of particles We have thus far developed a model of atomic structure based on the particle nature of matter: Atoms have a dense nucleus of positive charge with electrons orbiting the nucleus
Wave nature of particles We have thus far developed a model of atomic structure based on the particle nature of matter: Atoms have a dense nucleus of positive charge with electrons orbiting the nucleus
Quantum Mechanics & Atomic Structure (Chapter 11)
 Quantum Mechanics & Atomic Structure (Chapter 11) Quantum mechanics: Microscopic theory of light & matter at molecular scale and smaller. Atoms and radiation (light) have both wave-like and particlelike
Quantum Mechanics & Atomic Structure (Chapter 11) Quantum mechanics: Microscopic theory of light & matter at molecular scale and smaller. Atoms and radiation (light) have both wave-like and particlelike
The Schrodinger Equation
 The Schrodinger quation Dae Yong JONG Inha University nd week Review lectron device (electrical energy traducing) Understand the electron properties energy point of view To know the energy of electron
The Schrodinger quation Dae Yong JONG Inha University nd week Review lectron device (electrical energy traducing) Understand the electron properties energy point of view To know the energy of electron
Revision Guide. Chapter 7 Quantum Behaviour
 Revision Guide Chapter 7 Quantum Behaviour Contents CONTENTS... 2 REVISION CHECKLIST... 3 REVISION NOTES... 4 QUANTUM BEHAVIOUR... 4 Random arrival of photons... 4 Photoelectric effect... 5 PHASE AN PHASORS...
Revision Guide Chapter 7 Quantum Behaviour Contents CONTENTS... 2 REVISION CHECKLIST... 3 REVISION NOTES... 4 QUANTUM BEHAVIOUR... 4 Random arrival of photons... 4 Photoelectric effect... 5 PHASE AN PHASORS...
Quantum Mechanical Tunneling
 The square barrier: Quantum Mechanical Tunneling Behaviour of a classical ball rolling towards a hill (potential barrier): If the ball has energy E less than the potential energy barrier (U=mgy), then
The square barrier: Quantum Mechanical Tunneling Behaviour of a classical ball rolling towards a hill (potential barrier): If the ball has energy E less than the potential energy barrier (U=mgy), then
Barrier Penetration, Radioactivity, and the Scanning Tunneling Microscope
 Physics 5K Lecture Friday April 20, 2012 Barrier Penetration, Radioactivity, and the Scanning Tunneling Microscope Joel Primack Physics Department UCSC Topics to be covered in Physics 5K include the following:
Physics 5K Lecture Friday April 20, 2012 Barrier Penetration, Radioactivity, and the Scanning Tunneling Microscope Joel Primack Physics Department UCSC Topics to be covered in Physics 5K include the following:
( ) # velocity. Wavelengths of massive objects. From Last Time. Wavelength of electron. Wavelength of 1 ev electron. A little complicated ( ) " = h mv
 From Last Time Wavelengths of massive objects Light shows both particle and wavelike properties Matter shows both particle and wavelike properties. How can we make sense of this? debroglie wavelength =
From Last Time Wavelengths of massive objects Light shows both particle and wavelike properties Matter shows both particle and wavelike properties. How can we make sense of this? debroglie wavelength =
Lecture Outline Chapter 30. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 30 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 30 Quantum Physics Units of Chapter 30 Blackbody Radiation and Planck s Hypothesis of Quantized Energy Photons and the Photoelectric
Lecture Outline Chapter 30 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 30 Quantum Physics Units of Chapter 30 Blackbody Radiation and Planck s Hypothesis of Quantized Energy Photons and the Photoelectric
Quantum and Atomic Physics - Multiple Choice
 PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. The Cathode Ray Tube experiment is associated with: (A) J. J. Thomson (B) J. S. Townsend (C) M. Plank (D) A. H. Compton 2. The electron charge was measured the first time in: (A)
PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. The Cathode Ray Tube experiment is associated with: (A) J. J. Thomson (B) J. S. Townsend (C) M. Plank (D) A. H. Compton 2. The electron charge was measured the first time in: (A)
Title / paragraph example Topic: Quantum Computers. Course Essay. Photoelectric effect summary. From Last Time. Compton scattering
 Course Essay 500-750 word typed essay due Wed. Apr. 26 First deadline: Fri. this week (Mar. 24) turn in Topic and Paragraph Description Topic ideas: Nobel prize winner: work & importance Big science project:
Course Essay 500-750 word typed essay due Wed. Apr. 26 First deadline: Fri. this week (Mar. 24) turn in Topic and Paragraph Description Topic ideas: Nobel prize winner: work & importance Big science project:
Explanations of animations
 Explanations of animations This directory has a number of animations in MPEG4 format showing the time evolutions of various starting wave functions for the particle-in-a-box, the free particle, and the
Explanations of animations This directory has a number of animations in MPEG4 format showing the time evolutions of various starting wave functions for the particle-in-a-box, the free particle, and the
In chapter 3, when we discussed metallic bonding, the primary attribute was that electrons are delocalized.
 Lecture 15: free electron gas Up to this point we have not discussed electrons explicitly, but electrons are the first offenders for most useful phenomena in materials. When we distinguish between metals,
Lecture 15: free electron gas Up to this point we have not discussed electrons explicitly, but electrons are the first offenders for most useful phenomena in materials. When we distinguish between metals,
LECTURE 6 QUANTUM PHYSICS II. Instructor: Shih-Chieh Hsu
 LECTURE 6 QUANTUM PHYSICS II Instructor: Shih-Chieh Hsu Development of Quantum Mechanics 2 In 1862, Kirchhoff coined black body radiation or known as cavity radiation The experiments raised the question
LECTURE 6 QUANTUM PHYSICS II Instructor: Shih-Chieh Hsu Development of Quantum Mechanics 2 In 1862, Kirchhoff coined black body radiation or known as cavity radiation The experiments raised the question
A fluorescent tube is filled with mercury vapour at low pressure. After mercury atoms have been excited they emit photons.
 Q1.(a) A fluorescent tube is filled with mercury vapour at low pressure. After mercury atoms have been excited they emit photons. In which part of the electromagnetic spectrum are these photons? What is
Q1.(a) A fluorescent tube is filled with mercury vapour at low pressure. After mercury atoms have been excited they emit photons. In which part of the electromagnetic spectrum are these photons? What is
Chap. 3. Elementary Quantum Physics
 Chap. 3. Elementary Quantum Physics 3.1 Photons - Light: e.m "waves" - interference, diffraction, refraction, reflection with y E y Velocity = c Direction of Propagation z B z Fig. 3.1: The classical view
Chap. 3. Elementary Quantum Physics 3.1 Photons - Light: e.m "waves" - interference, diffraction, refraction, reflection with y E y Velocity = c Direction of Propagation z B z Fig. 3.1: The classical view
If electrons moved in simple orbits, p and x could be determined, but this violates the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle.
 CHEM 2060 Lecture 18: Particle in a Box L18-1 Atomic Orbitals If electrons moved in simple orbits, p and x could be determined, but this violates the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. We can only talk
CHEM 2060 Lecture 18: Particle in a Box L18-1 Atomic Orbitals If electrons moved in simple orbits, p and x could be determined, but this violates the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. We can only talk
CLASSICAL OR QUANTUM?
 3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lecture 1 CLASSICAL OR QUANTUM? Reading Material (Bonding) Textbook: Engel and Reid, Physical Chemistry, Pearson (2006) Further readings for the first half of the course
3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lecture 1 CLASSICAL OR QUANTUM? Reading Material (Bonding) Textbook: Engel and Reid, Physical Chemistry, Pearson (2006) Further readings for the first half of the course
It illustrates quantum mechanical principals. It illustrates the use of differential eqns. & boundary conditions to solve for ψ
 MODEL SYSTEM: PARTICLE IN A BOX Important because: It illustrates quantum mechanical principals It illustrates the use of differential eqns. & boundary conditions to solve for ψ It shows how discrete energy
MODEL SYSTEM: PARTICLE IN A BOX Important because: It illustrates quantum mechanical principals It illustrates the use of differential eqns. & boundary conditions to solve for ψ It shows how discrete energy
2) Atom manipulation. Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment:
 2) Atom manipulation D. Eigler & E. Schweizer, Nature 344, 524 (1990) Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment: G.Meyer, et al. Applied Physics A 68, 125 (1999) First the tip is approached close to the adsorbate
2) Atom manipulation D. Eigler & E. Schweizer, Nature 344, 524 (1990) Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment: G.Meyer, et al. Applied Physics A 68, 125 (1999) First the tip is approached close to the adsorbate
Complementi di Fisica Lectures 5, 6
 Complementi di Fisica - Lectures 5, 6 9/3-9-15 Complementi di Fisica Lectures 5, 6 Livio Lanceri Università di Trieste Trieste, 9/3-9-15 Course Outline - Reminder Quantum Mechanics: an introduction Reminder
Complementi di Fisica - Lectures 5, 6 9/3-9-15 Complementi di Fisica Lectures 5, 6 Livio Lanceri Università di Trieste Trieste, 9/3-9-15 Course Outline - Reminder Quantum Mechanics: an introduction Reminder
Lecture 21 Matter acts like waves!
 Particles Act Like Waves! De Broglie s Matter Waves λ = h / p Schrodinger s Equation Announcements Schedule: Today: de Broglie and matter waves, Schrodinger s Equation March Ch. 16, Lightman Ch. 4 Net
Particles Act Like Waves! De Broglie s Matter Waves λ = h / p Schrodinger s Equation Announcements Schedule: Today: de Broglie and matter waves, Schrodinger s Equation March Ch. 16, Lightman Ch. 4 Net
Atoms and Spectroscopy
 Atoms and Spectroscopy Lecture 3 1 ONE SMALL STEP FOR MAN ONE GIANT LEAP FOR MANKIND 2 FROM ATOMS TO STARS AND GALAXIES HOW DO WE KNOW? Observations The Scientific Method Hypothesis Verifications LAW 3
Atoms and Spectroscopy Lecture 3 1 ONE SMALL STEP FOR MAN ONE GIANT LEAP FOR MANKIND 2 FROM ATOMS TO STARS AND GALAXIES HOW DO WE KNOW? Observations The Scientific Method Hypothesis Verifications LAW 3
Chapter 4 (Lecture 6-7) Schrodinger equation for some simple systems Table: List of various one dimensional potentials System Physical correspondence
 V, E, Chapter (Lecture 6-7) Schrodinger equation for some simple systems Table: List of various one dimensional potentials System Physical correspondence Potential Total Energies and Probability density
V, E, Chapter (Lecture 6-7) Schrodinger equation for some simple systems Table: List of various one dimensional potentials System Physical correspondence Potential Total Energies and Probability density
Lecture 3 Review of Quantum Physics & Basic AMO Physics
 Lecture 3 Review of Quantum Physics & Basic AMO Physics How to do quantum mechanics QO tries to understand it (partly) Purdue University Spring 2016 Prof. Yong P. Chen (yongchen@purdue.edu) Lecture 3 (1/19/2016)
Lecture 3 Review of Quantum Physics & Basic AMO Physics How to do quantum mechanics QO tries to understand it (partly) Purdue University Spring 2016 Prof. Yong P. Chen (yongchen@purdue.edu) Lecture 3 (1/19/2016)
