The Effect of Clouds and Rain on the Aquarius Salinity Retrieval
|
|
|
- Justin Webster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Effect of Clouds and ain on the Aquarius Salinity etrieval Frank J. Wentz 1. adiative Transfer Equations At 1.4 GHz, the radiative transfer model for cloud and rain is considerably simpler than that required at higher frequencies. The radiation wavelength (21 cm) is much larger than the raindrop diameter ( mm), and the ayleigh scattering approximation is valid for specifying the absorption coefficient liq for liquid water. a (1) liq ray liq where liq is the combined density of cloud water and rain water (volume of total water per unit volume of air) and a ray is the ayleigh coefficient given by a ray 6 1 Im 2 where is the radiation wavelength, is the complex dielectric constant of water, and Im( ) denotes taking the imaginary part of the argument. At a frequency of 1.4 GHz and a temperature 5C, a ray = mm -1. The ayleigh coefficient has a significant inverse dependence on temperature. Going from 15C to 0C, a ray increases by 50%. The upwelling brightness temperature measured at the top of the atmosphere is given by 1 1 T T ET E T T E T B Bup S Bdown Bspace Bdown where T Bup and T Bdown are the upwelling and downwelling brightness temperature contributions just due to the atmosphere, is the total atmospheric transmission, E is the sea-surface emissivity, T S is the sea-surface temperature, and T Bspace is the brightness of space (cosmic background plus galactic). The term accounts for downwelling radiation that is scattered upward, rather than specularly reflected, into the viewing direction. It is a small term relative to the other terms. The atmospheric quantities T Bup, T Bdown, and are computed by integrating through the atmosphere [Wentz, 1997]. The integrals involve the vertical profiles of temperature, pressure, water vapor density, and liquid water density liq. Due to the fact that the absorption coefficient liq is extremely small at 1.4 GHz (as compared to unity), it can be shown that an excellent approximation for the increase in T B due to the presence of clouds and rain is the following: H T 2 1 E sec dht h ( h) (4) B, liq i liq liq 0 where the integral goes vertically up from the surface (h = 0) to the top of the rain cloud (h = H ). The term T liq (h) is the temperature of the liquid water. The angle i is the Earth incidence angle, and the term sec i accounts for the fact that the viewing path is longer than the vertical distance H. Doing the integration and setting the temperature and absorption coefficients to effective values gives (2) (3) 1
2 TB, liq 2 1 E TliqarayLseci (5) where L is the total columnar content of liquid water found by vertically integrating the liquid water content for the surface to the top of the rain cloud. H L dh liq (6) 0 The terms Tliq is the averaged temperature of the rain cloud and a ray = a ray ( T liq ). Equation (5) shows that the increase in brightness temperature due to cloud and rain is simply proportional to the total content of liquid water in the field of view. 2. Calculation of Liquid Water Content from AMS-E This section is based on the cloud/rain retrieval algorithm described by Wentz and Spencer [1998]. This algorithm provides an estimate of both cloud water L C (mm) and rain rate (mm/h). Assuming a Marshall and Palmer drop size distribution and a uniform terminal velocity, the liquid water content for the rain L (mm) is given by: L H (7) where H (km) is the rain column height. The rain-rate retrieval is parameterized in terms a columnar rain rate C defined as C H (8) This parameterization is based on the fact that C is more directly related to the brightness temperature observation than is. In the Wentz and Spencer algorithm, C is the actual retrieved parameter, and (8) is used to convert it to a surface rain rate. Combining (7) and (8) shows that the calculation of L is only weakly dependent on the specification of H C L 0.078H (9) The rain cloud height is assumed to be a simple function of sea-surface temperature. H 1 T 0 H T T T H The total liquid water is then S S 0 S T 28 C S S (10) L L L (11) Figure 1 shows a daily map of L for January 1, 2004 as derived from AMS-E. Only the ascending orbit segments are shows. As can be seen, L reaches maximum values of 2 mm or greater in areas of heavy rain. 2
3 Figure 1. Total atmospheric liquid water (both cloud and rain) as derived by AMS-E on January 1, Only the results for the ascending orbits are shown. Liquid water has first been averaged into 1 latitude-longitude bins before displaying. As mentioned above, the columnar rain rate C is the more basic observable for microwave radiometers as compared to surface rain rate. In fact, it can be shown that the rain retrieval algorithm can be parameterized directly in terms of L rather than or C. The retrieval of L is more robust than that for because it is less dependent on assumptions regarding the rain column height and the partitioning of cloud water and rain water. Therefore, an accurate estimation of L does not require that rain rate be retrieved. However, since surface rain rate is a familiar parameter, it is informative in a qualitative sense to show how the 1.4 GHz brightness temperature increases with. Figure 2 shows this relationship. The particular shape to the curve is due to the details of the cloud and rain relationships given in Wentz and Spencer [1998]. 3
4 H-pol V-pol Figure 2. The increase in the 1.4 GHz brightness temperature versus rain rate assuming an incidence angle of i = Simulation of Aquarius Errors esulting from Liquid Water The liquid water retrievals from AMS-E are converted into a brightness temperature increase at 1.4 GHz using equation (5). In addition to L, the T B,liq calculation requires the specification of the sea-surface emissivity E and the average temperature of the liquid water T liq. The emissivity E is found by assuming a specular emissivity with the dielectric constant given by the Meissner and Wentz [2004] model (which is similar to the Klein-Swift model). Surface roughness has a completely negligible effect on the calculation oft B,liq. The specular emissivity is a function of surface temperature T S and sea-surface salinity S. T S is found from the eynolds weekly SST product that is interpolated in time and space to the location of the AMS-E observation. The salinity is set to a constant value of 35 psu. The liquid water temperature is specified by assuming a mean cloud height of 2 km above the sea surface and a typical atmospheric lapse rate. This allows us to specify a Tliq versus T S relationship. Once T B,liq is computed for both v-pol and h-pol, an equivalent salinity retrieval error can be found from our basic salinity retrieval algorithm:,,,, Sˆ a T a T T a T T a T Wˆ (12) 0 S i 1 S i BV 2 S i BH 3 S i 4
5 where the coefficients a i are known functions of T S and incidence angle i, and ˆ W is our best estimate of wind speed. The salinity error due to liquid water is then Sˆ a T, T a T, T (13) liq 1 S i BV, liq 2 S i BH, liq The quantities T BV,liq, T BH,liq, and Sˆliq are found for the month of January Table 1 provides the mean and standard deviation for each error. The error has a small dependence on incidence angle. The longer path through the atmosphere that occurs at the higher incidence angles causes the error to increase. The value of i for horns 1, 2, and 3 are 29.2, 37.9, and 45.5, respectively. Table 1. Statistics on Errors esulting from Liquid Water in the Atmosphere. Num. Obs. T BV,liq Mean (K) T BV,liq Std. Dev. (K) T BH,liq Mean (K) T BH,liq Std. Dev. (K) Sˆliq Mean (psu) Sˆliq Std. Dev. (psu) Inner Horn Middle Horn Outer Horn The errors are further characterized by showing their normalized histogram and their cumulative distribution function in Figures 3 and 4. (The histograms are normalized by their maximum value.) The results shown in these figures are for Aquarius outer horn. Similar statistics are done for July 2004, and the results are about the same as for January
6 Figure 3. The normalized histogram and cumulative distribution function for the increase in the v-pol brightness temperature (top 2 plots) and the h-pol brightness temperature (bottom 2 plots). 6
7 Figure 4. The normalized histogram and cumulative distribution function for the error in the salinity retrieval. The above statistics tend to understate the potential problem of atmospheric liquid water. The problem can be more clearly seen in Figures 5, 6 and 7 that show the AMS-E results for one day: January 1, These figures is very similar to the liquid water map shown in Figure 1 except that L has been mapped into the brightness temperature increase at 1.4 GHz (T BV,liq, T BH,liq ) and salinity retrieval error ( Sˆliq ). Salinity errors exceeding 0.1 psu are common within rain systems. The cumulative distribution function in Figure 4 shows that the salinity error exceeds 0.1 psu for 11% of the observations. 7
8 Figure 5. The simulated increase in the 1.4 GHz v-pol brightness temperatures due to atmospheric liquid water derived from the AMS-E observations for January 1, Only the results for the ascending orbits are shown. The observations are at a 1-latitude by 1-longitude spatial resolution. 8
9 Figure 6. Same as Figure 5 except that the h-pol brightness temperature is shown. 9
10 Figure 7. Same as Figure 5 except that the salinity error is shown. 10
11 4. Discussion The overall error in salinity retrievals due to atmosphere liquid water is about 0.07 to 0.08 psu. Although this average global error is relatively small, its real impact is that it is spatially correlated with rain systems and can become quite large in areas of intense rain. About 11% of the Aquarius observations will have a salinity error greater than 0.1 psu if no flagging or correction procedure is implemented. With respect to flagging and correcting areas having large liquid water contents, there are three options: 1. Aquarius will have a 23/37 GHz radiometer onboard that is collocated with the 1.4 GHz salinity observations. If this radiometer operates successfully, it will provide an ideal tool for flagging and correcting observations that are affect by large L values. For this application, the requirements on the 23/37 GHz radiometer calibration are not very stringent. The radiometer only needs to be stable over time scales of 10-minutes to measure the contrast between rain and no-rain scenes. Furthermore, this T B contrast only needs to be measured to an accuracy of a few Kelvin. These requirements are well within the design goals of the 23/37 GHz radiometer. 2. The Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) will be flying the operational SSM/IS microwave radiometer in an orbit similar to Aquarius. The SSM/IS is capable of making very accurate measurements of the total liquid water. We are currently obtaining information on the planned DMSP ascending node times so that we can access the collocation geometry between SSM/IS and Aquarius. 3. The Global Precipitation Mission (GPM) will be producing daily maps of global precipitation from multiple satellites. These daily maps could be used to flag and correct areas of moderateto-heavy rain. We have done some preliminary investigations on the possibility of correcting the salinity retrievals in areas of high L rather than just flagging them. Due to the fact that at L-band the radiative transfer equations simply depend on L (rather than factors like drop-size distribution, radiative scattering, and rain cloud height), a liquid water correction is certainly feasible. The primary requirement is to obtain an accurate estimate of L at spatial scales near 100 km. Collocation issues not withstanding, we expect that L can be estimated to an accuracy of about 25% from satellite microwave radiometers operating in the GHz band. This 25% accuracy is based on results coming from the GPM community from which accuracies of 25% to 40% are being reported for microwave rain rate retrievals. The estimation of L at a 100-km resolution is considerably easier than surface rain rate at 25-km resolution, so a 25% error on L seems reasonable. However, to achieve this will require a detailed investigation using satellite data at multiple frequencies. For example, we have completed a very preliminary study based on AMS-E. The AMS-E observations at GHz are used to estimate L as described herein, and then this estimate of L is used to predict the increase in the 6.9 and 10.7 GHz brightness temperatures. The predicted T B increase is compared to the observed increase in areas of moderate to heavy rain, and the agreement suggests the accuracy of L is better than 25%. If the Aquarius 23/37 GHz radiometer operates marginally well and/or if the DMSP SSM/IS flies in an orbit overlapping Aquarius, then accurate collocation will be achievable. Given good collocation and a 25% accuracy on the estimate L, a correction will be possible that reduces the impact of L by a factor of 4, at least for liquid water contents up to about 2 mm (about 6 mm/h 11
12 rain rate). For higher rain rates, our ability to estimate L will degrade and flagging may be the better option. At a spatial resolution of 100 km, the AMS-E data show that observations for which L > 2 mm occur only 0.2% of the time. The salinity error for the remaining 99.8% of the observations after correcting for L is about 0.02 psu. A map of the salinity error for this scenario is shown in Figure 8. Figure 8. The salinity retrieval error assuming that L can be estimated to an accuracy of 25%. Observations for which L > 2 mm are discarded. The area of high salinity errors in the South Atlantic could be removed by decreasing the L cutoff from 2 mm to 1 mm. The 2-mm cutoff removes 0.2% of the observations, whereas a 1-mm cutoff would remove 0.9% of the observations. 12
13 5. eferences Wentz, F.J., A well calibrated ocean algorithm for special sensor microwave / imager, Journal of Geophysical esearch, 102 (C4), , Wentz, F.J., and.w. Spencer, SSM/I rain retrievals within a unified all-weather ocean algorithm, Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 55 (9), , Meissner, T. and F.J. Wentz, The Complex Dielectric Constant of Pure and Sea Water from Microwave Satellite Observations, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and emote Sensing, 42(9), ,
14 Appendix: Math Notes (for internal use) Derivation of Equation (5) : 2 TB TX r r r r r AL Lsec e T T e T A L T A L 2 AL Lsec B X X L sec 2 X L sec 2 1 E T a Lsec liq ray i 14
URSI-F Microwave Signatures Meeting 2010, Florence, Italy, October 4 8, Thomas Meissner Lucrezia Ricciardulli Frank Wentz
 URSI-F Microwave Signatures Meeting 2010, Florence, Italy, October 4 8, 2010 Wind Measurements from Active and Passive Microwave Sensors High Winds and Winds in Rain Thomas Meissner Lucrezia Ricciardulli
URSI-F Microwave Signatures Meeting 2010, Florence, Italy, October 4 8, 2010 Wind Measurements from Active and Passive Microwave Sensors High Winds and Winds in Rain Thomas Meissner Lucrezia Ricciardulli
RAIN RATE RETRIEVAL ALGORITHM FOR AQUARIUS/SAC-D MICROWAVE RADIOMETER. ROSA ANA MENZEROTOLO B.S. University of Central Florida, 2005
 RAIN RATE RETRIEVAL ALGORITHM FOR AQUARIUS/SAC-D MICROWAVE RADIOMETER by ROSA ANA MENZEROTOLO B.S. University of Central Florida, 2005 A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
RAIN RATE RETRIEVAL ALGORITHM FOR AQUARIUS/SAC-D MICROWAVE RADIOMETER by ROSA ANA MENZEROTOLO B.S. University of Central Florida, 2005 A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
MWR Rain Rate Retrieval Algorithm. Rosa Menzerotolo MSEE Thesis defense Aug. 29, 2010
 MWR Rain Rate Retrieval Algorithm Rosa Menzerotolo MSEE Thesis defense Aug. 29, 2010 1 Outline Objective Theoretical Basis Algorithm Approach Geophysical Retrieval Results Conclusion Future Work 2 Thesis
MWR Rain Rate Retrieval Algorithm Rosa Menzerotolo MSEE Thesis defense Aug. 29, 2010 1 Outline Objective Theoretical Basis Algorithm Approach Geophysical Retrieval Results Conclusion Future Work 2 Thesis
VALIDATION OF WIDEBAND OCEAN EMISSIVITY RADIATIVE TRANSFER MODEL. SONYA CROFTON B.S. University of Florida, 2005
 VALIDATION OF WIDEBAND OCEAN EMISSIVITY RADIATIVE TRANSFER MODEL by SONYA CROFTON B.S. University of Florida, 2005 A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master
VALIDATION OF WIDEBAND OCEAN EMISSIVITY RADIATIVE TRANSFER MODEL by SONYA CROFTON B.S. University of Florida, 2005 A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master
Microwave Satellite Observations
 The Complex Dielectric Constant of Pure and Sea Water from Microwave Satellite Observations Thomas Meissner and Frank Wentz Abstract We provide a new fit for the microwave complex dielectric constant of
The Complex Dielectric Constant of Pure and Sea Water from Microwave Satellite Observations Thomas Meissner and Frank Wentz Abstract We provide a new fit for the microwave complex dielectric constant of
SSM/I Rain Retrievals Within an Unified All-Weather Ocean Algorithm
 SSM/I Rain Retrievals Within an Unified All-Weather Ocean Algorithm Frank J. Wentz* Remote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, California Roy W. Spencer NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, Global Hydrology and
SSM/I Rain Retrievals Within an Unified All-Weather Ocean Algorithm Frank J. Wentz* Remote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, California Roy W. Spencer NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, Global Hydrology and
SSM/I Rain Retrievals within a Unified All-Weather Ocean Algorithm
 1613 SSM/I Rain Retrievals within a Unified All-Weather Ocean Algorithm FRANK J. WENTZ Remote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, California ROY W. SPENCER Global Hydrology and Climate Center, NASA/Marshall Space
1613 SSM/I Rain Retrievals within a Unified All-Weather Ocean Algorithm FRANK J. WENTZ Remote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, California ROY W. SPENCER Global Hydrology and Climate Center, NASA/Marshall Space
THE first space-based fully polarimetric microwave radiometer,
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 44, NO. 3, MARCH 2006 597 A Nonlinear Optimization Algorithm for WindSat Wind Vector Retrievals Michael H. Bettenhausen, Member, IEEE, Craig K.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 44, NO. 3, MARCH 2006 597 A Nonlinear Optimization Algorithm for WindSat Wind Vector Retrievals Michael H. Bettenhausen, Member, IEEE, Craig K.
A radiative transfer model function for 85.5 GHz Special Sensor Microwave Imager ocean brightness temperatures
 RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 38, NO. 4, 8066, doi:10.1029/2002rs002655, 2003 A radiative transfer model function for 85.5 GHz Special Sensor Microwave Imager ocean brightness temperatures Thomas Meissner and Frank
RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 38, NO. 4, 8066, doi:10.1029/2002rs002655, 2003 A radiative transfer model function for 85.5 GHz Special Sensor Microwave Imager ocean brightness temperatures Thomas Meissner and Frank
A Time-varying Radiometric Bias Correction for the TRMM Microwave Imager. Kaushik Gopalan Thesis defense : Oct 29, 2008
 A Time-varying Radiometric Bias Correction for the TRMM Microwave Imager Kaushik Gopalan Thesis defense : Oct 29, 2008 Outline Dissertation Objective Initial research Introduction to GPM and ICWG Inter-satellite
A Time-varying Radiometric Bias Correction for the TRMM Microwave Imager Kaushik Gopalan Thesis defense : Oct 29, 2008 Outline Dissertation Objective Initial research Introduction to GPM and ICWG Inter-satellite
Ocean Vector Winds in Storms from the SMAP L-Band Radiometer
 International Workshop on Measuring High Wind Speeds over the Ocean 15 17 November 2016 UK Met Office, Exeter Ocean Vector Winds in Storms from the SMAP L-Band Radiometer Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli,
International Workshop on Measuring High Wind Speeds over the Ocean 15 17 November 2016 UK Met Office, Exeter Ocean Vector Winds in Storms from the SMAP L-Band Radiometer Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli,
For those 5 x5 boxes that are primarily land, AE_RnGd is simply an average of AE_Rain_L2B; the ensuing discussion pertains entirely to oceanic boxes.
 AMSR-E Monthly Level-3 Rainfall Accumulations Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Thomas T. Wilheit Department of Atmospheric Science Texas A&M University 2007 For those 5 x5 boxes that are primarily
AMSR-E Monthly Level-3 Rainfall Accumulations Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Thomas T. Wilheit Department of Atmospheric Science Texas A&M University 2007 For those 5 x5 boxes that are primarily
A two-season impact study of the Navy s WindSat surface wind retrievals in the NCEP global data assimilation system
 A two-season impact study of the Navy s WindSat surface wind retrievals in the NCEP global data assimilation system Li Bi James Jung John Le Marshall 16 April 2008 Outline WindSat overview and working
A two-season impact study of the Navy s WindSat surface wind retrievals in the NCEP global data assimilation system Li Bi James Jung John Le Marshall 16 April 2008 Outline WindSat overview and working
Version 1: Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Aquarius Salinity Retrieval Algorithm
 Version 1: Algorithm heoretical Basis Document Aquarius Salinity Retrieval Algorithm Frank J. Wentz and David M. Le Vine 1 Introduction... he Forward Model....1 he Antenna emperature Equation.... Radiation
Version 1: Algorithm heoretical Basis Document Aquarius Salinity Retrieval Algorithm Frank J. Wentz and David M. Le Vine 1 Introduction... he Forward Model....1 he Antenna emperature Equation.... Radiation
Aquarius L2 Algorithm: Geophysical Model Func;ons
 Aquarius L2 Algorithm: Geophysical Model Func;ons Thomas Meissner and Frank J. Wentz, Remote Sensing Systems Presented at Aquarius Cal/Val Web- Workshop January 29 30, 2013 Outline 1. Aquarius Wind Speed
Aquarius L2 Algorithm: Geophysical Model Func;ons Thomas Meissner and Frank J. Wentz, Remote Sensing Systems Presented at Aquarius Cal/Val Web- Workshop January 29 30, 2013 Outline 1. Aquarius Wind Speed
SSS retrieval from space Comparison study using Aquarius and SMOS data
 44 th International Liège Colloquium on Ocean Dynamics 7-11 May 2012 SSS retrieval from space Comparison study using Aquarius and SMOS data Physical Oceanography Department Institute of Marine Sciences
44 th International Liège Colloquium on Ocean Dynamics 7-11 May 2012 SSS retrieval from space Comparison study using Aquarius and SMOS data Physical Oceanography Department Institute of Marine Sciences
Sea water dielectric constant, temperature and remote sensing of Sea Surface Salinity
 Sea water dielectric constant, temperature and remote sensing of Sea Surface Salinity E. P. Dinnat 1,2, D. M. Le Vine 1, J. Boutin 3, X. Yin 3, 1 Cryospheric Sciences Lab., NASA GSFC, Greenbelt, MD, U.S.A
Sea water dielectric constant, temperature and remote sensing of Sea Surface Salinity E. P. Dinnat 1,2, D. M. Le Vine 1, J. Boutin 3, X. Yin 3, 1 Cryospheric Sciences Lab., NASA GSFC, Greenbelt, MD, U.S.A
WindSat Ocean Surface Emissivity Dependence on Wind Speed in Tropical Cyclones. Amanda Mims University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
 WindSat Ocean Surface Emissivity Dependence on Wind Speed in Tropical Cyclones Amanda Mims University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Abstract Radiometers are adept at retrieving near surface ocean wind vectors.
WindSat Ocean Surface Emissivity Dependence on Wind Speed in Tropical Cyclones Amanda Mims University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Abstract Radiometers are adept at retrieving near surface ocean wind vectors.
Decadal Trends and Variability in Special Sensor Microwave / Imager (SSM/I) Brightness Temperatures and Earth Incidence Angle
 Decadal Trends and Variability in Special Sensor Microwave / Imager (SSM/I) rightness Temperatures and Earth Incidence Angle Hilburn, K. A. (*) and C.-L. Shie (+) (*) Remote Sensing Systems (+) UMC/JCET,
Decadal Trends and Variability in Special Sensor Microwave / Imager (SSM/I) rightness Temperatures and Earth Incidence Angle Hilburn, K. A. (*) and C.-L. Shie (+) (*) Remote Sensing Systems (+) UMC/JCET,
Remote Sensing of Precipitation
 Lecture Notes Prepared by Prof. J. Francis Spring 2003 Remote Sensing of Precipitation Primary reference: Chapter 9 of KVH I. Motivation -- why do we need to measure precipitation with remote sensing instruments?
Lecture Notes Prepared by Prof. J. Francis Spring 2003 Remote Sensing of Precipitation Primary reference: Chapter 9 of KVH I. Motivation -- why do we need to measure precipitation with remote sensing instruments?
P7.5 STUDIES OF SEA SURFACE NORMALIZED RADAR CROSS SECTIONS OBSERVED BY CLOUDSAT
 P7.5 STUDIES OF SEA SURFACE NORMALIZED RADAR CROSS SECTIONS OBSERVED BY CLOUDSAT Ninoslav Majurec 1, Joel T. Johnson 1, and Simone Tanelli 1 ElectroScience Laboratory, The Ohio State University, Columbus,
P7.5 STUDIES OF SEA SURFACE NORMALIZED RADAR CROSS SECTIONS OBSERVED BY CLOUDSAT Ninoslav Majurec 1, Joel T. Johnson 1, and Simone Tanelli 1 ElectroScience Laboratory, The Ohio State University, Columbus,
A New Satellite Wind Climatology from QuikSCAT, WindSat, AMSR-E and SSM/I
 A New Satellite Wind Climatology from QuikSCAT, WindSat, AMSR-E and SSM/I Frank J. Wentz (presenting), Lucrezia Ricciardulli, Thomas Meissner, and Deborah Smith Remote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, CA Supported
A New Satellite Wind Climatology from QuikSCAT, WindSat, AMSR-E and SSM/I Frank J. Wentz (presenting), Lucrezia Ricciardulli, Thomas Meissner, and Deborah Smith Remote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, CA Supported
Christian Sutton. Microwave Water Radiometer measurements of tropospheric moisture. ATOC 5235 Remote Sensing Spring 2003
 Christian Sutton Microwave Water Radiometer measurements of tropospheric moisture ATOC 5235 Remote Sensing Spring 23 ABSTRACT The Microwave Water Radiometer (MWR) is a two channel microwave receiver used
Christian Sutton Microwave Water Radiometer measurements of tropospheric moisture ATOC 5235 Remote Sensing Spring 23 ABSTRACT The Microwave Water Radiometer (MWR) is a two channel microwave receiver used
F O U N D A T I O N A L C O U R S E
 F O U N D A T I O N A L C O U R S E December 6, 2018 Satellite Foundational Course for JPSS (SatFC-J) F O U N D A T I O N A L C O U R S E Introduction to Microwave Remote Sensing (with a focus on passive
F O U N D A T I O N A L C O U R S E December 6, 2018 Satellite Foundational Course for JPSS (SatFC-J) F O U N D A T I O N A L C O U R S E Introduction to Microwave Remote Sensing (with a focus on passive
Lecture 19: Operational Remote Sensing in Visible, IR, and Microwave Channels
 MET 4994 Remote Sensing: Radar and Satellite Meteorology MET 5994 Remote Sensing in Meteorology Lecture 19: Operational Remote Sensing in Visible, IR, and Microwave Channels Before you use data from any
MET 4994 Remote Sensing: Radar and Satellite Meteorology MET 5994 Remote Sensing in Meteorology Lecture 19: Operational Remote Sensing in Visible, IR, and Microwave Channels Before you use data from any
Radiometric Calibration of RapidScat Using the GPM Microwave Imager
 Proceedings Radiometric Calibration of RapidScat Using the GPM Microwave Imager Ali Al-Sabbagh *, Ruaa Alsabah and Josko Zec Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Florida Institute of Technology,
Proceedings Radiometric Calibration of RapidScat Using the GPM Microwave Imager Ali Al-Sabbagh *, Ruaa Alsabah and Josko Zec Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Florida Institute of Technology,
3D.6 ESTIMATES OF HURRICANE WIND SPEED MEASUREMENT ACCURACY USING THE AIRBORNE HURRICANE IMAGING RADIOMETER
 3D.6 ESTIMATES OF HURRICANE WIND SPEED MEASUREMENT ACCURACY USING THE AIRBORNE HURRICANE IMAGING RADIOMETER Ruba A. Amarin *, Linwood Jones 1, James Johnson 1, Christopher Ruf 2, Timothy Miller 3 and Shuyi
3D.6 ESTIMATES OF HURRICANE WIND SPEED MEASUREMENT ACCURACY USING THE AIRBORNE HURRICANE IMAGING RADIOMETER Ruba A. Amarin *, Linwood Jones 1, James Johnson 1, Christopher Ruf 2, Timothy Miller 3 and Shuyi
Rain Effects on Scatterometer Systems A summary of what is known to date
 Rain Effects on Scatterometer Systems A summary of what is known to date Kyle Hilburn, Deborah K Smith, *Frank J. Wentz Remote Sensing Systems NASA Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting May 18-20, 2009
Rain Effects on Scatterometer Systems A summary of what is known to date Kyle Hilburn, Deborah K Smith, *Frank J. Wentz Remote Sensing Systems NASA Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting May 18-20, 2009
Results of intercalibration between AMSR2 and TMI/AMSR-E (AMSR2 Version 1.1)
 Results of intercalibration between AMSR2 and TMI/AMSR-E (AMSR2 Version 1.1) Earth Observation Research Center Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency May 8, 2014 Correction of erroneous intercalibration slopes/offsets
Results of intercalibration between AMSR2 and TMI/AMSR-E (AMSR2 Version 1.1) Earth Observation Research Center Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency May 8, 2014 Correction of erroneous intercalibration slopes/offsets
T. Meissner and F. Wentz Remote Sensing Systems
 T. Meissner and F. Wentz Remote Sensing Systems meissner@remss.com 2014 Aquarius / SAC- D Science Team Mee8ng November 11-14, 2014 Sea?le. Washington, USA Outline 1. Current Status: Observed Biases Post-
T. Meissner and F. Wentz Remote Sensing Systems meissner@remss.com 2014 Aquarius / SAC- D Science Team Mee8ng November 11-14, 2014 Sea?le. Washington, USA Outline 1. Current Status: Observed Biases Post-
RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 38, NO. 4, 8065, doi: /2002rs002659, 2003
 RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 38, NO. 4, 8065, doi:10.1029/2002rs002659, 2003 Retrieval of atmospheric and ocean surface parameters from ADEOS-II Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR) data: Comparison of
RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 38, NO. 4, 8065, doi:10.1029/2002rs002659, 2003 Retrieval of atmospheric and ocean surface parameters from ADEOS-II Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR) data: Comparison of
COMPARISON OF SATELLITE DERIVED OCEAN SURFACE WIND SPEEDS AND THEIR ERROR DUE TO PRECIPITATION
 COMPARISON OF SATELLITE DERIVED OCEAN SURFACE WIND SPEEDS AND THEIR ERROR DUE TO PRECIPITATION A.-M. Blechschmidt and H. Graßl Meteorological Institute, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany ABSTRACT
COMPARISON OF SATELLITE DERIVED OCEAN SURFACE WIND SPEEDS AND THEIR ERROR DUE TO PRECIPITATION A.-M. Blechschmidt and H. Graßl Meteorological Institute, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany ABSTRACT
Version 7 SST from AMSR-E & WindSAT
 Version 7 SST from AMSR-E & WindSAT Chelle L. Gentemann, Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli & Frank Wentz www.remss.com Retrieval algorithm Validation results RFI THE 44th International Liege Colloquium
Version 7 SST from AMSR-E & WindSAT Chelle L. Gentemann, Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli & Frank Wentz www.remss.com Retrieval algorithm Validation results RFI THE 44th International Liege Colloquium
P1.23 HISTOGRAM MATCHING OF ASMR-E AND TMI BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURES
 P1.23 HISTOGRAM MATCHING OF ASMR-E AND TMI BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURES Thomas A. Jones* and Daniel J. Cecil Department of Atmospheric Science University of Alabama in Huntsville Huntsville, AL 1. Introduction
P1.23 HISTOGRAM MATCHING OF ASMR-E AND TMI BRIGHTNESS TEMPERATURES Thomas A. Jones* and Daniel J. Cecil Department of Atmospheric Science University of Alabama in Huntsville Huntsville, AL 1. Introduction
Meteorological Satellite Image Interpretations, Part III. Acknowledgement: Dr. S. Kidder at Colorado State Univ.
 Meteorological Satellite Image Interpretations, Part III Acknowledgement: Dr. S. Kidder at Colorado State Univ. Dates EAS417 Topics Jan 30 Introduction & Matlab tutorial Feb 1 Satellite orbits & navigation
Meteorological Satellite Image Interpretations, Part III Acknowledgement: Dr. S. Kidder at Colorado State Univ. Dates EAS417 Topics Jan 30 Introduction & Matlab tutorial Feb 1 Satellite orbits & navigation
A NEW METHOD OF RETRIEVAL OF WIND VELOCITY OVER THE SEA SURFACE IN TROPICAL CYCLONES OVER THE DATA OF MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS. A.F.
 A NEW METHOD OF RETRIEVAL OF WIND VELOCITY OVER THE SEA SURFACE IN TROPICAL CYCLONES OVER THE DATA OF MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS A.F. Nerushev Institute of Experimental Meteorology. 82 Lenin Ave., Obninsk,
A NEW METHOD OF RETRIEVAL OF WIND VELOCITY OVER THE SEA SURFACE IN TROPICAL CYCLONES OVER THE DATA OF MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS A.F. Nerushev Institute of Experimental Meteorology. 82 Lenin Ave., Obninsk,
Post-Launch Calibration of the TRMM Microwave Imager
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 39, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2001 415 Post-Launch Calibration of the TRMM Microwave Imager Frank J. Wentz, Peter Ashcroft, and Chelle Gentemann Abstract
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 39, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2001 415 Post-Launch Calibration of the TRMM Microwave Imager Frank J. Wentz, Peter Ashcroft, and Chelle Gentemann Abstract
OCEAN VECTOR WINDS IN STORMS FROM THE SMAP L-BAND RADIOMETER
 Proceedings for the 2016 EUMETSAT Meteorological Satellite Conference, 26-30 September 2016, Darmstadt, Germany OCEAN VECTOR WINDS IN STORMS FROM THE SMAP L-BAND RADIOMETER Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli,
Proceedings for the 2016 EUMETSAT Meteorological Satellite Conference, 26-30 September 2016, Darmstadt, Germany OCEAN VECTOR WINDS IN STORMS FROM THE SMAP L-BAND RADIOMETER Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia Ricciardulli,
Post-Launch Calibration of the TRMM Microwave
 Post-Launch Calibration of the TRMM Microwave Imager Frank Wentz, Peter Ashcroft, Chelle Gentemann Abstract: --- Three post-launch calibration methods are used to examine the TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI)
Post-Launch Calibration of the TRMM Microwave Imager Frank Wentz, Peter Ashcroft, Chelle Gentemann Abstract: --- Three post-launch calibration methods are used to examine the TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI)
Bringing Consistency into High Wind Measurements with Spaceborne Microwave Radiometers and Scatterometers
 International Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting May 2-4, 2017, Scripps Bringing Consistency into High Wind Measurements with Spaceborne Microwave Radiometers and Scatterometers Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia
International Ocean Vector Wind Science Team Meeting May 2-4, 2017, Scripps Bringing Consistency into High Wind Measurements with Spaceborne Microwave Radiometers and Scatterometers Thomas Meissner, Lucrezia
MARCH 2010 VOLUME 48 NUMBER 3 IGRSD2 (ISSN )
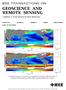 MARCH 2010 VOLUME 48 NUMBER 3 IGRSD2 (ISSN 0196-2892) PART I OF TWO PARTS Uncertainty of SST retrievals at 7 and 11 GHz shown by the standard deviation of (top) 7-GHz AMSR-E Reynolds SSTs and (bottom)
MARCH 2010 VOLUME 48 NUMBER 3 IGRSD2 (ISSN 0196-2892) PART I OF TWO PARTS Uncertainty of SST retrievals at 7 and 11 GHz shown by the standard deviation of (top) 7-GHz AMSR-E Reynolds SSTs and (bottom)
Direct assimilation of all-sky microwave radiances at ECMWF
 Direct assimilation of all-sky microwave radiances at ECMWF Peter Bauer, Alan Geer, Philippe Lopez, Deborah Salmond European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Reading, Berkshire, UK Slide 1 17
Direct assimilation of all-sky microwave radiances at ECMWF Peter Bauer, Alan Geer, Philippe Lopez, Deborah Salmond European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Reading, Berkshire, UK Slide 1 17
Hyperspectral Microwave Atmospheric Sounding
 Hyperspectral Microwave Atmospheric Sounding W. J. Blackwell, L. J. Bickmeier, R. V. Leslie, M. L. Pieper, J. E. Samra, and C. Surussavadee 1 April 14, 2010 ITSC-17 This work is sponsored by the Department
Hyperspectral Microwave Atmospheric Sounding W. J. Blackwell, L. J. Bickmeier, R. V. Leslie, M. L. Pieper, J. E. Samra, and C. Surussavadee 1 April 14, 2010 ITSC-17 This work is sponsored by the Department
The construction and application of the AMSR-E global microwave emissivity database
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS The construction and application of the AMSR-E global microwave emissivity database To cite this article: Shi Lijuan et al 014 IOP Conf.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS The construction and application of the AMSR-E global microwave emissivity database To cite this article: Shi Lijuan et al 014 IOP Conf.
Parameterization of the surface emissivity at microwaves to submillimeter waves
 Parameterization of the surface emissivity at microwaves to submillimeter waves Catherine Prigent, Filipe Aires, Observatoire de Paris and Estellus Lise Kilic, Die Wang, Observatoire de Paris with contributions
Parameterization of the surface emissivity at microwaves to submillimeter waves Catherine Prigent, Filipe Aires, Observatoire de Paris and Estellus Lise Kilic, Die Wang, Observatoire de Paris with contributions
Aquarius Cal/Val: Salinity Retrieval Algorithm V1.3. Thomas Meissner Frank Wentz
 Aquarius Cal/Val: Salinity Retrieval Algorithm V1.3 Thomas Meissner Frank Wentz L2 Algorithm: Overview Aquarius Radiometer Counts Earth + Calibration View Radiometer Calibration Algorithm RFI flagging
Aquarius Cal/Val: Salinity Retrieval Algorithm V1.3 Thomas Meissner Frank Wentz L2 Algorithm: Overview Aquarius Radiometer Counts Earth + Calibration View Radiometer Calibration Algorithm RFI flagging
Use of FY-3C/GNOS Data for Assessing the on-orbit Performance of Microwave Sounding Instruments
 Use of FY-3C/GNOS Data for Assessing the on-orbit Performance of Microwave Sounding Instruments Xiuqing Hu 1 Xueyan Hou 2, and Mi Liao 1 1 National Satellite Meteorological Center (NSMC), CMA 2 Chinese
Use of FY-3C/GNOS Data for Assessing the on-orbit Performance of Microwave Sounding Instruments Xiuqing Hu 1 Xueyan Hou 2, and Mi Liao 1 1 National Satellite Meteorological Center (NSMC), CMA 2 Chinese
THE SPECIAL Sensor Microwave/Imager (SSM/I) [1] is a
![THE SPECIAL Sensor Microwave/Imager (SSM/I) [1] is a THE SPECIAL Sensor Microwave/Imager (SSM/I) [1] is a](/thumbs/86/94893011.jpg) 1492 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 51, NO. 3, MARCH 2013 Toward an Intercalibrated Fundamental Climate Data Record of the SSM/I Sensors Mathew R. P. Sapiano, Wesley K. Berg,
1492 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 51, NO. 3, MARCH 2013 Toward an Intercalibrated Fundamental Climate Data Record of the SSM/I Sensors Mathew R. P. Sapiano, Wesley K. Berg,
+SOI Neutral SOI -SOI. Melt+ Melt- Melt+ Melt- Melt+ Melt- +SAM 1 (0.76) 6 (3.02) 1 (1.13) 5 (4.92) 1 (2.27) 0 (1.89) 14
 Supplementary Table 1. Contingency table tallying the respective counts of positive and negative surface melt index anomalies in the Ross sector as a function of the signs of the Southern Annular Mode
Supplementary Table 1. Contingency table tallying the respective counts of positive and negative surface melt index anomalies in the Ross sector as a function of the signs of the Southern Annular Mode
GCOM-W1 now on the A-Train
 GCOM-W1 now on the A-Train GCOM-W1 Global Change Observation Mission-Water Taikan Oki, K. Imaoka, and M. Kachi JAXA/EORC (& IIS/The University of Tokyo) Mini-Workshop on A-Train Science, March 8 th, 2013
GCOM-W1 now on the A-Train GCOM-W1 Global Change Observation Mission-Water Taikan Oki, K. Imaoka, and M. Kachi JAXA/EORC (& IIS/The University of Tokyo) Mini-Workshop on A-Train Science, March 8 th, 2013
Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Ice
 Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Ice What is Sea Ice? Passive Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Ice Basics Sea Ice Concentration Active Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Ice Basics Sea Ice Type Sea Ice Motion
Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Ice What is Sea Ice? Passive Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Ice Basics Sea Ice Concentration Active Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Ice Basics Sea Ice Type Sea Ice Motion
Retrieval of sea surface wind vectors from simulated satellite microwave polarimetric measurements
 RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 38, NO. 4, 8078, doi:10.1029/2002rs002729, 2003 Retrieval of sea surface wind vectors from simulated satellite microwave polarimetric measurements Quanhua Liu 1 Cooperative Institute
RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 38, NO. 4, 8078, doi:10.1029/2002rs002729, 2003 Retrieval of sea surface wind vectors from simulated satellite microwave polarimetric measurements Quanhua Liu 1 Cooperative Institute
New Technique for Retrieving Liquid Water Path over Land using Satellite Microwave Observations
 New Technique for Retrieving Liquid Water Path over Land using Satellite Microwave Observations M.N. Deeter and J. Vivekanandan Research Applications Library National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder,
New Technique for Retrieving Liquid Water Path over Land using Satellite Microwave Observations M.N. Deeter and J. Vivekanandan Research Applications Library National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder,
Evaluation of Regressive Analysis Based Sea Surface Temperature Estimation Accuracy with NCEP/GDAS Data
 Evaluation of Regressive Analysis Based Sea Surface Temperature Estimation Accuracy with NCEP/GDAS Data Kohei Arai 1 Graduate School of Science and Engineering Saga University Saga City, Japan Abstract
Evaluation of Regressive Analysis Based Sea Surface Temperature Estimation Accuracy with NCEP/GDAS Data Kohei Arai 1 Graduate School of Science and Engineering Saga University Saga City, Japan Abstract
RSS SMAP Salinity. Version 2.0 Validated Release. Thomas Meissner + Frank Wentz, RSS Tony Lee, JPL
 RSS SMAP Salinity Version 2.0 Validated Release Thomas Meissner + Frank Wentz, RSS Tony Lee, JPL hap://www.remss.com/missions/smap/salinity 1. Level 2C 2. Level 3 8-day running averages 3. Level 3 monthly
RSS SMAP Salinity Version 2.0 Validated Release Thomas Meissner + Frank Wentz, RSS Tony Lee, JPL hap://www.remss.com/missions/smap/salinity 1. Level 2C 2. Level 3 8-day running averages 3. Level 3 monthly
Aquarius Pioneering the L- band Passive and Ac6ve Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Surface Salinity and Wind
 Aquarius Pioneering the L- band Passive and Ac6ve Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Surface Salinity and Wind SIMON YUEH, WENQING TANG, ALEXANDER FORE, AKIKO HAYASHI Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California
Aquarius Pioneering the L- band Passive and Ac6ve Microwave Remote Sensing of Sea Surface Salinity and Wind SIMON YUEH, WENQING TANG, ALEXANDER FORE, AKIKO HAYASHI Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California
Level 2 Processing of HUT-2D Data: Preliminary Results
 Level Processing of HU-D Data: Preliminary Results SMOS-BEC Level eam. SMOS Barcelona Expert Centre Pg. Marítim de la Barceloneta 37-49, Barcelona SPAIN E-mail: talone@icm.csic.es URL: www.smos-bec.icm.csic.es
Level Processing of HU-D Data: Preliminary Results SMOS-BEC Level eam. SMOS Barcelona Expert Centre Pg. Marítim de la Barceloneta 37-49, Barcelona SPAIN E-mail: talone@icm.csic.es URL: www.smos-bec.icm.csic.es
Status of the GeoKompsat-2A AMI rainfall rate algorithm
 Status of the GeoKompsat-2A AMI rainfall rate algorithm Dong-Bin Shin, Damwon So, Hyo-Jin Park Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Yonsei University Algorithm Strategy Well-known assumption in IR-based
Status of the GeoKompsat-2A AMI rainfall rate algorithm Dong-Bin Shin, Damwon So, Hyo-Jin Park Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Yonsei University Algorithm Strategy Well-known assumption in IR-based
EVALUATION OF WINDSAT SURFACE WIND DATA AND ITS IMPACT ON OCEAN SURFACE WIND ANALYSES AND NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION
 5.8 EVALUATION OF WINDSAT SURFACE WIND DATA AND ITS IMPACT ON OCEAN SURFACE WIND ANALYSES AND NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION Robert Atlas* NOAA/Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, Miami,
5.8 EVALUATION OF WINDSAT SURFACE WIND DATA AND ITS IMPACT ON OCEAN SURFACE WIND ANALYSES AND NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION Robert Atlas* NOAA/Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, Miami,
The assimilation of AMSU and SSM/I brightness temperatures in clear skies at the Meteorological Service of Canada
 The assimilation of AMSU and SSM/I brightness temperatures in clear skies at the Meteorological Service of Canada Abstract David Anselmo and Godelieve Deblonde Meteorological Service of Canada, Dorval,
The assimilation of AMSU and SSM/I brightness temperatures in clear skies at the Meteorological Service of Canada Abstract David Anselmo and Godelieve Deblonde Meteorological Service of Canada, Dorval,
Description of Precipitation Retrieval Algorithm For ADEOS II AMSR
 Description of Precipitation Retrieval Algorithm For ADEOS II Guosheng Liu Florida State University 1. Basic Concepts of the Algorithm This algorithm is based on Liu and Curry (1992, 1996), in which the
Description of Precipitation Retrieval Algorithm For ADEOS II Guosheng Liu Florida State University 1. Basic Concepts of the Algorithm This algorithm is based on Liu and Curry (1992, 1996), in which the
Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements
 Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements Ching-Yuang Huang 1,2, Wen-Hsin Teng 1, Shu-Peng Ho 3, Ying-Hwa Kuo 3, and Xin-Jia Zhou 3 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements Ching-Yuang Huang 1,2, Wen-Hsin Teng 1, Shu-Peng Ho 3, Ying-Hwa Kuo 3, and Xin-Jia Zhou 3 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
ASSIMILATION EXPERIMENTS WITH DATA FROM THREE CONICALLY SCANNING MICROWAVE INSTRUMENTS (SSMIS, AMSR-E, TMI) IN THE ECMWF SYSTEM
 ASSIMILATION EXPERIMENTS WITH DATA FROM THREE CONICALLY SCANNING MICROWAVE INSTRUMENTS (SSMIS, AMSR-E, TMI) IN THE ECMWF SYSTEM Niels Bormann 1, Graeme Kelly 1, Peter Bauer 1, and Bill Bell 2 1 ECMWF,
ASSIMILATION EXPERIMENTS WITH DATA FROM THREE CONICALLY SCANNING MICROWAVE INSTRUMENTS (SSMIS, AMSR-E, TMI) IN THE ECMWF SYSTEM Niels Bormann 1, Graeme Kelly 1, Peter Bauer 1, and Bill Bell 2 1 ECMWF,
Summary The present report describes one possible way to correct radiometric measurements of the SSM/I (Special Sensor Microwave Imager) at 85.5 GHz f
 Compensating for atmospheric eects on passive radiometry at 85.5 GHz using a radiative transfer model and NWP model data Stefan Kern Institute of Environmental Physics University of Bremen, 28334 Bremen,
Compensating for atmospheric eects on passive radiometry at 85.5 GHz using a radiative transfer model and NWP model data Stefan Kern Institute of Environmental Physics University of Bremen, 28334 Bremen,
Determination of an Amazon Hot Reference Target for the On-Orbit Calibration of Microwave Radiometers
 1340 J O U R N A L O F A T M O S P H E R I C A N D O C E A N I C T E C H N O L O G Y VOLUME 22 Determination of an Amazon Hot Reference Target for the On-Orbit Calibration of Microwave Radiometers SHANNON
1340 J O U R N A L O F A T M O S P H E R I C A N D O C E A N I C T E C H N O L O G Y VOLUME 22 Determination of an Amazon Hot Reference Target for the On-Orbit Calibration of Microwave Radiometers SHANNON
Future Opportunities of Using Microwave Data from Small Satellites for Monitoring and Predicting Severe Storms
 Future Opportunities of Using Microwave Data from Small Satellites for Monitoring and Predicting Severe Storms Fuzhong Weng Environmental Model and Data Optima Inc., Laurel, MD 21 st International TOV
Future Opportunities of Using Microwave Data from Small Satellites for Monitoring and Predicting Severe Storms Fuzhong Weng Environmental Model and Data Optima Inc., Laurel, MD 21 st International TOV
Snowfall Detection and Rate Retrieval from ATMS
 Snowfall Detection and Rate Retrieval from ATMS Jun Dong 1, Huan Meng 2, Cezar Kongoli 1, Ralph Ferraro 2, Banghua Yan 2, Nai-Yu Wang 1, Bradley Zavodsky 3 1 University of Maryland/ESSIC/Cooperative Institute
Snowfall Detection and Rate Retrieval from ATMS Jun Dong 1, Huan Meng 2, Cezar Kongoli 1, Ralph Ferraro 2, Banghua Yan 2, Nai-Yu Wang 1, Bradley Zavodsky 3 1 University of Maryland/ESSIC/Cooperative Institute
Microwave-TC intensity estimation. Ryo Oyama Meteorological Research Institute Japan Meteorological Agency
 Microwave-TC intensity estimation Ryo Oyama Meteorological Research Institute Japan Meteorological Agency Contents 1. Introduction 2. Estimation of TC Maximum Sustained Wind (MSW) using TRMM Microwave
Microwave-TC intensity estimation Ryo Oyama Meteorological Research Institute Japan Meteorological Agency Contents 1. Introduction 2. Estimation of TC Maximum Sustained Wind (MSW) using TRMM Microwave
NWP SAF. Quantitative precipitation estimation from satellite data. Satellite Application Facility for Numerical Weather Prediction
 NWP SAF Satellite Application Facility for Numerical Weather Prediction Document NWPSAF-MO-VS-011 Version 1.0 15 April 2006 Quantitative precipitation estimation from satellite data Sante Laviola University
NWP SAF Satellite Application Facility for Numerical Weather Prediction Document NWPSAF-MO-VS-011 Version 1.0 15 April 2006 Quantitative precipitation estimation from satellite data Sante Laviola University
From L1 to L2 for sea ice concentration. Rasmus Tonboe Danish Meteorological Institute EUMETSAT OSISAF
 From L1 to L2 for sea ice concentration Rasmus Tonboe Danish Meteorological Institute EUMETSAT OSISAF Sea-ice concentration = sea-ice surface fraction Water Ice e.g. Kern et al. 2016, The Cryosphere
From L1 to L2 for sea ice concentration Rasmus Tonboe Danish Meteorological Institute EUMETSAT OSISAF Sea-ice concentration = sea-ice surface fraction Water Ice e.g. Kern et al. 2016, The Cryosphere
Creating a Consistent Oceanic Multi-decadal Intercalibrated TMI-GMI Constellation Data Record
 University of Central Florida Electronic Theses and Dissertations Doctoral Dissertation (Open Access) Creating a Consistent Oceanic Multi-decadal Intercalibrated TMI-GMI Constellation Data Record 2018
University of Central Florida Electronic Theses and Dissertations Doctoral Dissertation (Open Access) Creating a Consistent Oceanic Multi-decadal Intercalibrated TMI-GMI Constellation Data Record 2018
Towards a better use of AMSU over land at ECMWF
 Towards a better use of AMSU over land at ECMWF Blazej Krzeminski 1), Niels Bormann 1), Fatima Karbou 2) and Peter Bauer 1) 1) European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), Shinfield Park,
Towards a better use of AMSU over land at ECMWF Blazej Krzeminski 1), Niels Bormann 1), Fatima Karbou 2) and Peter Bauer 1) 1) European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), Shinfield Park,
Active rain-gauge concept for liquid clouds using W-band and S-band Doppler radars
 Active rain-gauge concept for liquid clouds using W-band and S-band Doppler radars Leyda León-Colón *a, Sandra L. Cruz-Pol *a, Stephen M. Sekelsky **b a Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Univ.
Active rain-gauge concept for liquid clouds using W-band and S-band Doppler radars Leyda León-Colón *a, Sandra L. Cruz-Pol *a, Stephen M. Sekelsky **b a Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Univ.
Annual Validation Report: Rain
 Annual Validation Report: Rain Remote Sensing Systems 2013 Lead Author: Kyle Hilburn RAIN ANNUAL VALIDATION REPORT Authors: Hilburn, Smith, and Mears Finalized: January 30, 2014 INTRODUCTION The purpose
Annual Validation Report: Rain Remote Sensing Systems 2013 Lead Author: Kyle Hilburn RAIN ANNUAL VALIDATION REPORT Authors: Hilburn, Smith, and Mears Finalized: January 30, 2014 INTRODUCTION The purpose
New retrieval algorithm for the wet tropospheric correction of altimetry missions
 New retrieval algorithm for the wet tropospheric correction of altimetry missions A. Rahmani, E. Obligis and L. Eymard CLS/LOCEAN MicroRad Conference March 2008 Page n 1/13 Introduction Altimeters are
New retrieval algorithm for the wet tropospheric correction of altimetry missions A. Rahmani, E. Obligis and L. Eymard CLS/LOCEAN MicroRad Conference March 2008 Page n 1/13 Introduction Altimeters are
Quality Control and Wind Retrieval for SeaWinds
 Quality Control and Wind Retrieval for SeaWinds by M. Portabella and A. Stoffelen Final report of the EUMETSAT QuikSCAT fellowship February 2002 Contents PREFACE... 3 1 INTRODUCTION... 5 2 PRODUCT VALIDATION...
Quality Control and Wind Retrieval for SeaWinds by M. Portabella and A. Stoffelen Final report of the EUMETSAT QuikSCAT fellowship February 2002 Contents PREFACE... 3 1 INTRODUCTION... 5 2 PRODUCT VALIDATION...
"Cloud and Rainfall Observations using Microwave Radiometer Data and A-priori Constraints" Christian Kummerow and Fang Wang Colorado State University
 "Cloud and Rainfall Observations using Microwave Radiometer Data and A-priori Constraints" Christian Kummerow and Fang Wang Colorado State University ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop Reading, England June 16-18, 2010
"Cloud and Rainfall Observations using Microwave Radiometer Data and A-priori Constraints" Christian Kummerow and Fang Wang Colorado State University ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop Reading, England June 16-18, 2010
Assessment of Precipitation Characters between Ocean and Coast area during Winter Monsoon in Taiwan
 Assessment of Precipitation Characters between Ocean and Coast area during Winter Monsoon in Taiwan Peter K.H. Wang Central Weather Bureau Abstract SSM/I has been applied in derivation of liquid water
Assessment of Precipitation Characters between Ocean and Coast area during Winter Monsoon in Taiwan Peter K.H. Wang Central Weather Bureau Abstract SSM/I has been applied in derivation of liquid water
Sea surface salinity from space: Science goals and measurement approach
 RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 38, NO. 4, 8064, doi:10.1029/2001rs002584, 2003 Sea surface salinity from space: Science goals and measurement approach C. J. Koblinsky, P. Hildebrand, D. LeVine, and F. Pellerano NASA
RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 38, NO. 4, 8064, doi:10.1029/2001rs002584, 2003 Sea surface salinity from space: Science goals and measurement approach C. J. Koblinsky, P. Hildebrand, D. LeVine, and F. Pellerano NASA
Assimilating AMSU-A over Sea Ice in HIRLAM 3D-Var
 Abstract Assimilating AMSU-A over Sea Ice in HIRLAM 3D-Var Vibeke W. Thyness 1, Leif Toudal Pedersen 2, Harald Schyberg 1, Frank T. Tveter 1 1 Norwegian Meteorological Institute (met.no) Box 43 Blindern,
Abstract Assimilating AMSU-A over Sea Ice in HIRLAM 3D-Var Vibeke W. Thyness 1, Leif Toudal Pedersen 2, Harald Schyberg 1, Frank T. Tveter 1 1 Norwegian Meteorological Institute (met.no) Box 43 Blindern,
AN IMPROVED MICROWAVE RADIATIVE TRANSFER MODEL FOR OCEAN EMISSIVITY AT HURRICANE FORCE SURFACE WIND SPEED
 AN IMPROVED MICROWAVE RADIATIVE TRANSFER MODEL FOR OCEAN EMISSIVITY AT HURRICANE FORCE SURFACE WIND SPEED by SALEM FAWWAZ EL-NIMRI B.S. Princess Sumaya University for Technology, 2004 A thesis submitted
AN IMPROVED MICROWAVE RADIATIVE TRANSFER MODEL FOR OCEAN EMISSIVITY AT HURRICANE FORCE SURFACE WIND SPEED by SALEM FAWWAZ EL-NIMRI B.S. Princess Sumaya University for Technology, 2004 A thesis submitted
Foreword. March Dr. Akira Shibata AMSR lead scientist
 Foreword The Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR) is a multi-frequency, dual-polarized microwave radiometer that detects microwave emissions from the Earth's surface and atmosphere. Various geophysical
Foreword The Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR) is a multi-frequency, dual-polarized microwave radiometer that detects microwave emissions from the Earth's surface and atmosphere. Various geophysical
THE FEASIBILITY OF EXTRACTING LOWLEVEL WIND BY TRACING LOW LEVEL MOISTURE OBSERVED IN IR IMAGERY OVER CLOUD FREE OCEAN AREA IN THE TROPICS
 THE FEASIBILITY OF EXTRACTING LOWLEVEL WIND BY TRACING LOW LEVEL MOISTURE OBSERVED IN IR IMAGERY OVER CLOUD FREE OCEAN AREA IN THE TROPICS Toshiro Ihoue and Tetsuo Nakazawa Meteorological Research Institute
THE FEASIBILITY OF EXTRACTING LOWLEVEL WIND BY TRACING LOW LEVEL MOISTURE OBSERVED IN IR IMAGERY OVER CLOUD FREE OCEAN AREA IN THE TROPICS Toshiro Ihoue and Tetsuo Nakazawa Meteorological Research Institute
APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1
 APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1 1. Introduction Precipitation is one of most important environmental parameters.
APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1 1. Introduction Precipitation is one of most important environmental parameters.
HURRICANE WIND SPEED AND RAIN RATE RETRIEVAL ALGORITHM FOR THE STEPPED FREQUENCY MICROWAVE RADIOMETER
 HURRICANE WIND SPEED AND RAIN RATE RETRIEVAL ALGORITHM FOR THE STEPPED FREQUENCY MICROWAVE RADIOMETER by RUBA AKRAM AMARIN B.S. Princess Sumaya University for Technology, 2004 A thesis submitted in partial
HURRICANE WIND SPEED AND RAIN RATE RETRIEVAL ALGORITHM FOR THE STEPPED FREQUENCY MICROWAVE RADIOMETER by RUBA AKRAM AMARIN B.S. Princess Sumaya University for Technology, 2004 A thesis submitted in partial
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture
 Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Integrating Multiple Scatterometer Observations into a Climate Data Record of Ocean Vector Winds
 Integrating Multiple Scatterometer Observations into a Climate Data Record of Ocean Vector Winds Lucrezia Ricciardulli and Frank Wentz Remote Sensing Systems, CA, USA E-mail: Ricciardulli@remss.com presented
Integrating Multiple Scatterometer Observations into a Climate Data Record of Ocean Vector Winds Lucrezia Ricciardulli and Frank Wentz Remote Sensing Systems, CA, USA E-mail: Ricciardulli@remss.com presented
Combining Satellite & Model Information for Snowfall Retrieval
 Combining Satellite & Model Information for Snowfall Retrieval Yoo-Jeong Noh Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere Colorado State University CIRA/Colorado State University 5th Annual CoRP
Combining Satellite & Model Information for Snowfall Retrieval Yoo-Jeong Noh Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere Colorado State University CIRA/Colorado State University 5th Annual CoRP
Improving Sea Surface Microwave Emissivity Model for Radiance Assimilation
 Improving Sea Surface Microwave Emissivity Model for Radiance Assimilation Quanhua (Mark) Liu 1, Steve English 2, Fuzhong Weng 3 1 Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation, Maryland, U.S.A 2 Met. Office,
Improving Sea Surface Microwave Emissivity Model for Radiance Assimilation Quanhua (Mark) Liu 1, Steve English 2, Fuzhong Weng 3 1 Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation, Maryland, U.S.A 2 Met. Office,
Addendum III to ATBD
 Addendum III to ATD T. Meissner, F. Wentz, D. LeVine and J. Scott June 04, 014 This addendum documents change made to the ATD between V.0 and V3.0 of the Aquarius L salinity retrieval algorithm which was
Addendum III to ATD T. Meissner, F. Wentz, D. LeVine and J. Scott June 04, 014 This addendum documents change made to the ATD between V.0 and V3.0 of the Aquarius L salinity retrieval algorithm which was
Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency
 Development of an all-sky assimilation of microwave imager and sounder radiances for the Japan Meteorological Agency global numerical weather prediction system Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical
Development of an all-sky assimilation of microwave imager and sounder radiances for the Japan Meteorological Agency global numerical weather prediction system Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical
/JAMC-D American Meteorological Society. Version of Record
 Revealing the Winds under the Rain. Part I: Passive Microwave Rain Retrievals Using a New Observation-Based Parameterization of Subsatellite Rain Variability and Intensity Algorithm Description Hristova-Veleva,
Revealing the Winds under the Rain. Part I: Passive Microwave Rain Retrievals Using a New Observation-Based Parameterization of Subsatellite Rain Variability and Intensity Algorithm Description Hristova-Veleva,
Effects of Possible Scan Geometries on the Accuracy of Satellite Measurements of Water Vapor
 1710 JOURNAL OF ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC TECHNOLOGY VOLUME 16 Effects of Possible Scan Geometries on the Accuracy of Satellite Measurements of Water Vapor LARRY M. MCMILLIN National Environmental Satellite,
1710 JOURNAL OF ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC TECHNOLOGY VOLUME 16 Effects of Possible Scan Geometries on the Accuracy of Satellite Measurements of Water Vapor LARRY M. MCMILLIN National Environmental Satellite,
THREE-WAY ERROR ANALYSIS BETWEEN AATSR, AMSR-E AND IN SITU SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURE OBSERVATIONS.
 THREE-WAY ERROR ANALYSIS BETWEEN AATSR, AMSR-E AND IN SITU SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURE OBSERVATIONS. Anne O Carroll (1), John Eyre (1), and Roger Saunders (1) (1) Met Office, Satellite Applications, Fitzroy
THREE-WAY ERROR ANALYSIS BETWEEN AATSR, AMSR-E AND IN SITU SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURE OBSERVATIONS. Anne O Carroll (1), John Eyre (1), and Roger Saunders (1) (1) Met Office, Satellite Applications, Fitzroy
Lambertian surface scattering at AMSU-B frequencies:
 Lambertian surface scattering at AMSU-B frequencies: An analysis of airborne microwave data measured over snowcovered surfaces Chawn Harlow, 2nd Workshop on Remote Sensing and Modeling of Land Surface
Lambertian surface scattering at AMSU-B frequencies: An analysis of airborne microwave data measured over snowcovered surfaces Chawn Harlow, 2nd Workshop on Remote Sensing and Modeling of Land Surface
A New Microwave Snow Emissivity Model
 A New Microwave Snow Emissivity Model Fuzhong Weng 1,2 1. Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation 2. NOAA/NESDIS/Office of Research and Applications Banghua Yan DSTI. Inc The 13 th International TOVS
A New Microwave Snow Emissivity Model Fuzhong Weng 1,2 1. Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation 2. NOAA/NESDIS/Office of Research and Applications Banghua Yan DSTI. Inc The 13 th International TOVS
CALIBRATING THE QUIKSCAT/SEAWINDS RADAR FOR MEASURING RAINRATE OVER THE OCEANS
 CALIBRATING THE QUIKSCAT/SEAWINDS RADAR FOR MEASURING RAINRATE OVER THE OCEANS David E. Weissman Hofstra University, Hempstead, New York 11549 Mark A. Bourassa COAPS/The Florida State University, Tallahassee,
CALIBRATING THE QUIKSCAT/SEAWINDS RADAR FOR MEASURING RAINRATE OVER THE OCEANS David E. Weissman Hofstra University, Hempstead, New York 11549 Mark A. Bourassa COAPS/The Florida State University, Tallahassee,
A study of the NOAA 16 AMSU-A brightness temperatures observed over Libyan Desert
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. D14, 4226, 10.1029/2001JD001158, 2002 A study of the NOAA 16 AMSU-A brightness temperatures observed over Libyan Desert Tsan Mo Office of Research and Applications,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. D14, 4226, 10.1029/2001JD001158, 2002 A study of the NOAA 16 AMSU-A brightness temperatures observed over Libyan Desert Tsan Mo Office of Research and Applications,
APPLICATIONS WITH METEOROLOGICAL SATELLITES. W. Paul Menzel. Office of Research and Applications NOAA/NESDIS University of Wisconsin Madison, WI
 APPLICATIONS WITH METEOROLOGICAL SATELLITES by W. Paul Menzel Office of Research and Applications NOAA/NESDIS University of Wisconsin Madison, WI July 2004 Unpublished Work Copyright Pending TABLE OF CONTENTS
APPLICATIONS WITH METEOROLOGICAL SATELLITES by W. Paul Menzel Office of Research and Applications NOAA/NESDIS University of Wisconsin Madison, WI July 2004 Unpublished Work Copyright Pending TABLE OF CONTENTS
Assimilation of precipitation-related observations into global NWP models
 Assimilation of precipitation-related observations into global NWP models Alan Geer, Katrin Lonitz, Philippe Lopez, Fabrizio Baordo, Niels Bormann, Peter Lean, Stephen English Slide 1 H-SAF workshop 4
Assimilation of precipitation-related observations into global NWP models Alan Geer, Katrin Lonitz, Philippe Lopez, Fabrizio Baordo, Niels Bormann, Peter Lean, Stephen English Slide 1 H-SAF workshop 4
