Lecture 6. 1 Normalization and time evolution 1. 2 The Wavefunction as a Probability Amplitude 3. 3 The Probability Current 5
|
|
|
- Jade Boyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 6 B. Zwiebach February 23, 2016 Contents 1 Normalization and time evolution 1 2 The Wavefunction as a Probability Amplitude 3 3 The Probability Current 5 4 Probability current in 3D and current conservation 7 1 Normalization and time evolution The wavefunction Ψ(x, t) that describes the quantum mechanics of a particle of mass m moving in a potential V(x, t) satisfies the Schrödinger equation 2 Ψ(x, t) ( 2 ) i = +V(x,t) Ψ(x,t), (1.1) t 2m x2 or more briefly Ψ(x, t) i = HΨ(x,t). ˆ (1.2) t The interpretation of the wavefunction arises by declaring that dp, defined by dp = Ψ(x,t) 2 dx, (1.3) is the probability to find the particle in the interval dx centered on x at time t. It follows that the probabilities of finding the particle at all possible points must add up to one: Ψ (x,t)ψ(x,t)dx = 1. (1.4) We will try to understand how this equation is compatible with the time evolution prescribed by the Schrödinger equation. But before that let us examine what kind of conditions are required from wavefunctions in order to satisfy (1.4). Suppose the wavefunction has well-defined limits as x ±. If those limits are different from zero, the integral around infinity would produce an infinite result, which is inconsistent with the claim that the total integral is one. Therefore the limits should be zero: lim Ψ(x,t) = 0. (1.5) x ± 1
2 It is in principle possible to have a wavefunction that has no well-defined limit at infinity but is still is square integrable. But such cases do not seem to appear in practice so we will assume that (1.5) holds. It would also be natural to assume that the spatial derivative of Ψ vanishes as x ± but, as we will see soon, it suffices to assume that the limit of the spatial derivative of Ψ is bounded Ψ(x, t) lim <. (1.6) x ± x We have emphasized before that the overall numerical factor multiplying the wavefunction is not physical. But equation (1.4) seems to be in conflict with this: if a given Ψ satisfies it, the presumed equivalent 2Ψ will not! To make precise sense of probabilities it is convenient to work with normalized wavefunctions, but it is not necessary, as we show now. Since time plays no role in the argument, so assume in all that follows that the equations refer to some time t 0 arbitrary but fixed. Suppose you have a wavefunction such that dx Ψ 2 = N = 1. (1.7) Then I claim that the probability dp to find the particle in the interval dx about x is given by This is consistent because dp = 1 dp = Ψ 2 dx. (1.8) N 1 1 dx Ψ 2 = N = 1. (1.9) N N Note that dp is not changed when Ψ is multiplied by any number. Thus, this picture makes it clear that the overall scale of Ψ contains no physics. As long as the integral Ψ 2 dx < the wavefunction is said to be normalizable, or square-integrable. By adjusting the overall coefficient of Ψ we can then make it normalized. Indeed, again assuming (1.7) the new wavefunction Ψ defined by Ψ 1 = Ψ, (1.10) N is properly normalized. Indeed dx Ψ 2 1 = Ψ 2 dx = 1. (1.11) N We sometimes work with wavefunctions for which the integral (1.4) is infinite. Such wavefunctions can be very useful. In fact, the de Broglie plane wave Ψ = exp(ikx iωt) for a free particle is a good example: since Ψ 2 = 1 the integral is in fact infinite. What this means is that exp(ikx iωt) does not truly represent a single particle. To construct a square-integrable wavefunction we can use a superposition of plane waves. It is indeed a pleasant surprise that the superposition of infinitely many non-square integrable waves is square integrable! 2
3 2 The Wavefunction as a Probability Amplitude Let s begin with a normalized wavefunction at initial time t 0 Ψ (x,t 0 )Ψ(x,t 0 )dx = 1. (2.1) Since Ψ(x,t 0 ) and the Schrödinger equation determine Ψ for all times, do we then have Ψ (x,t)ψ(x,t)dx = 1? (2.2) Define the probability density ρ(x, t) ρ(x,t) Ψ (x,t)ψ(x,t) = Ψ(x,t) 2. (2.3) Define also N(t) as the integral of the probability density throughout space: N(t) ρ(x, t)dx. (2.4) The statement in (2.1) that the wavefunction begins well normalized is N(t 0 ) = 1, (2.5) and the condition that it remain normalized for all later times is N(t) = 1. This would be guaranteed if we showed that for all times dn(t) = 0. (2.6) dt We call this conservation of probability. Let s check if the Schrödinger equation ensures this condition will hold: dn(t) ρ(x,t) = dx dt t ( ) (2.7) Ψ Ψ(x,t)+Ψ Ψ(x,t) = (x, t) dx. t t From the Schrödinger equation, and its complex conjugate Ψ Ψ i i = HΨ ˆ = = ĤΨ, (2.8) t t Ψ Ψ i i = (Hˆ Ψ) = = (HΨ) ˆ. (2.9) t t In complex conjugating the Schrödinger equation we used that the complex conjugate of the time derivative of Ψ is simply the time derivative of the complex conjugate of Ψ. To conjugate 3
4 the right hand side we simply added the star to the whole of HΨ. ˆ We now use (2.8) and (2.9) in (2.7) to find ( dn(t) ) i i = (HΨ) ˆ Ψ Ψ (HΨ) ˆ dx dt i ( ) (2.10) = (HΨ) ˆ Ψdx Ψ ( ĤΨ)dx. To show that the time derivative of N(t) vanishes, it suffices to show that (HΨ) ˆ Ψ = Ψ ˆ (HΨ). (2.11) Equation (2.11) is the condition on the Hamiltonian operator Hˆ for conservation of probability. In fact, if Hˆ is a Hermitian operator the condition will be satisfied. The operator Hˆ is a Hermitian operator if it satisfies Hˆ Hermitian operator: ( Ψ 1 ) Ψ 2 = Ψ 1 ( ĤΨ 2 ). (2.12) Here we have two wavefunctions that are arbitrary, but satisfy the conditions (1.5) and (1.6). As you can see, a Hermitian operator can be switched from acting on the first function to acting on the second function. When the two functions are the same, we recover condition (2.11). It is worth closing this circle of ideas by defining the Hermitian conjugate T of the linear operator T. This is done as follows: Ψ 1(TΨ 2) = (T Ψ 1) Ψ 2. (2.13) The operator T, which is also linear, is calculated by starting from the left-hand side and trying to recast the expression with no operator acting on the second function. An operator T is said to be Hermitian if it is equal to its Hermitian conjugate: T is Hermitian if T = T. (2.14) Hermitian operators are very important in Quantum Mechanics. They have real eigenvalues and one can always find a basis of the state space in terms of orthonormal eigenstates. It turns out that observables in Quantum Mechanics are represented by Hermitian operators, and the possible measured values of those observables are given by their eigenvalues. Our quest to show that normalization is preserved under time evolution in Quantum Mechanics has come down to showing that the Hamiltonian operator is Hermitian. 4
5 3 The Probability Current Let s take a closer look at the integrand of equation (2.10). Using the explicit expression for the Hamiltonian we have ρ t i = ((HΨ) ˆ Ψ Ψ (HΨ)) ˆ [ ( i 2 2 Ψ 2 Ψ = 2m x Ψ )+V(x,t)Ψ Ψ Ψ Ψ V(x,t)Ψ 2 x 2 ] (3.1). The contributions from the potential cancel and we then get ( ) i 2 2 Ψ ((ĤΨ) Ψ ˆ Ψ Ψ (HΨ)) = Ψ Ψ. (3.2) 2im x 2 x 2 The only chance to get to show that the integral of the right-hand side is zero is to show that it is a total derivative. Indeed, it is! [ ( i ((HΨ) ˆ Ψ Ψ ˆ Ψ (HΨ)) = Ψ Ψ Ψ )] x 2im x x [ ( )] = Ψ Ψ Ψ Ψ x 2im x x (3.3) [ ( = 2iIm Ψ Ψ )] x 2im x [ ( )] Ψ = Im Ψ, x m x where we used that z z = 2iIm(z). Recall that the left-hand side we have evaluated is actually ρ and therefore the result obtained so far is t [ ( ρ + Im Ψ Ψ)] = 0. (3.4) t x m x This equation encodes charge conservation and is of the type ρ J + = 0, (3.5) t x where J(x, t) is the current associated with the charge density ρ. We have therefore identified a probability current ( J(x,t) Im Ψ Ψ ). (3.6) m x There is just one component for this current since the particle moves in one dimension. The units of J are one over time, or probability per unit time, as we now verify. 5
6 For one spatial dimension, [Ψ] = L 1/2, which is easily seen from the requirement that dx Ψ 2 is unit free. (When working with d spatial dimensions the wavefunction will have units of L d/2 ). We then have [Ψ Ψ] [ ] 1 ML 2 L 2 =, [] =, x L2 T m =, (3.7) T 1 = [J] = = probability per unit time (3.8) T We can now show that the time derivative of N is zero. Indeed, using (3.5) we have dn ρ J = dx = dx = (J(,t) J(,t)). (3.9) dt t x The derivative vanishes if the probability current vanishes at infinity. Recalling that ( Ψ J = Ψ Ψ ) Ψ, (3.10) 2im x x we see that the current indeed vanishes because we restrict ourselves to wavefunctions for which Ψ limx ± Ψ = 0 and limx ± remains bounded. We therefore have x as we wanted to show. dn = 0, (3.11) dt To illustrate how probability conservation works more generally in one dimension, focus on a segment x [a,b]. Then the probability P ab to find the particle in the segment [a,b], is given by b P ab = ρ(x,t)dx. (3.12) a If we now take the time derivative of this and, as before, use current conservation we get dp ab = dt b J(x,t) dt = J(b,t)+J(a,t). (3.13) x a This is the expected result. If the amount of probability in the region [a,b] changes in time, it must be due to probability current flowing in or out at the edges of the interval. Assuming the currents at x = b and at x = a are positive, we note that probability is flowing out at x = b and is coming in at x = a. The signs in the above right-hand side correctly reflect the effect of these flows on the rate of change of the total probability inside the segment. 6
7 4 Probability current in 3D and current conservation The determination of the probability current J for a particle moving in three dimensions follows the route taken before, but we use the 3D version of the Schrödinger equation. After some work (homework) the probability density and the current are determined to be and satisfy the conservation equation ρ(x,t) = Ψ(x,t) 2, J(x,t) = Im(Ψ Ψ), (4.1) m ρ + J = 0. (4.2) t In three spatial dimensions, [Ψ] = L 3 2 and the units of J are quickly determined [ ] 1 L 2 [Ψ Ψ] = 4, = (4.3) L m T 1 = [J] = = probability per unit time per unit area (4.4) TL2 The conservation equation (4.2) is particularly clear in integral language. Consider a fixed region V of space and the probability Q V (t) to find the particle inside the region: Q V (t) = ρ(x,t)d 3 x. (4.5) V The time derivative of the probability is then calculated using the conservation equation dq V ρ = d 3 x = Jd 3 x. (4.6) dt V t V Finally, using Gauss law we find dq V = dt S J da, (4.7) where S is the boundary of the volume V. The interpretation here is clear. The probability that the particle is inside V may change in time if there is flux of the probability current across the boundary of the region. When the volume extends throughout space, the boundary is at infinity, and the conditions on the wavefunction (which we have not discussed in the 3D case) imply that the flux across the boundary at infinity vanishes. Our probability density, probability current, and current conservation are in perfect analogy to electromagnetic charge density, current density, and current conservation. In electromagnetism charges flow, in quantum mechanics probability flows. The terms of the correspondence are summarized by the table. 7
8 Electromagnetism Quantum Mechanics ρ charge density probability density Q V charge in a volume V probability to find particle in V J current density probability current density Sarah Geller transcribed Zwiebach s handwritten notes to create the first LaTeX version of this document. 8
9 MIT OpenCourseWare Quantum Physics I Spring 2016 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
Lecture 10: Solving the Time-Independent Schrödinger Equation. 1 Stationary States 1. 2 Solving for Energy Eigenstates 3
 Contents Lecture 1: Solving the Time-Independent Schrödinger Equation B. Zwiebach March 14, 16 1 Stationary States 1 Solving for Energy Eigenstates 3 3 Free particle on a circle. 6 1 Stationary States
Contents Lecture 1: Solving the Time-Independent Schrödinger Equation B. Zwiebach March 14, 16 1 Stationary States 1 Solving for Energy Eigenstates 3 3 Free particle on a circle. 6 1 Stationary States
Lecture 8. 1 Uncovering momentum space 1. 2 Expectation Values of Operators 4. 3 Time dependence of expectation values 6
 Lecture 8 B. Zwiebach February 29, 206 Contents Uncovering momentum space 2 Expectation Values of Operators 4 Time dependence of expectation values 6 Uncovering momentum space We now begin a series of
Lecture 8 B. Zwiebach February 29, 206 Contents Uncovering momentum space 2 Expectation Values of Operators 4 Time dependence of expectation values 6 Uncovering momentum space We now begin a series of
Lecture 4. 1 de Broglie wavelength and Galilean transformations 1. 2 Phase and Group Velocities 4. 3 Choosing the wavefunction for a free particle 6
 Lecture 4 B. Zwiebach February 18, 2016 Contents 1 de Broglie wavelength and Galilean transformations 1 2 Phase and Group Velocities 4 3 Choosing the wavefunction for a free particle 6 1 de Broglie wavelength
Lecture 4 B. Zwiebach February 18, 2016 Contents 1 de Broglie wavelength and Galilean transformations 1 2 Phase and Group Velocities 4 3 Choosing the wavefunction for a free particle 6 1 de Broglie wavelength
The Particle in a Box
 Page 324 Lecture 17: Relation of Particle in a Box Eigenstates to Position and Momentum Eigenstates General Considerations on Bound States and Quantization Continuity Equation for Probability Date Given:
Page 324 Lecture 17: Relation of Particle in a Box Eigenstates to Position and Momentum Eigenstates General Considerations on Bound States and Quantization Continuity Equation for Probability Date Given:
Lectures 21 and 22: Hydrogen Atom. 1 The Hydrogen Atom 1. 2 Hydrogen atom spectrum 4
 Lectures and : Hydrogen Atom B. Zwiebach May 4, 06 Contents The Hydrogen Atom Hydrogen atom spectrum 4 The Hydrogen Atom Our goal here is to show that the two-body quantum mechanical problem of the hydrogen
Lectures and : Hydrogen Atom B. Zwiebach May 4, 06 Contents The Hydrogen Atom Hydrogen atom spectrum 4 The Hydrogen Atom Our goal here is to show that the two-body quantum mechanical problem of the hydrogen
Lecture 7. 1 Wavepackets and Uncertainty 1. 2 Wavepacket Shape Changes 4. 3 Time evolution of a free wave packet 6. 1 Φ(k)e ikx dk. (1.
 Lecture 7 B. Zwiebach February 8, 06 Contents Wavepackets and Uncertainty Wavepacket Shape Changes 4 3 Time evolution of a free wave packet 6 Wavepackets and Uncertainty A wavepacket is a superposition
Lecture 7 B. Zwiebach February 8, 06 Contents Wavepackets and Uncertainty Wavepacket Shape Changes 4 3 Time evolution of a free wave packet 6 Wavepackets and Uncertainty A wavepacket is a superposition
Chapter 17: Resonant transmission and Ramsauer Townsend. 1 Resonant transmission in a square well 1. 2 The Ramsauer Townsend Effect 3
 Contents Chapter 17: Resonant transmission and Ramsauer Townsend B. Zwiebach April 6, 016 1 Resonant transmission in a square well 1 The Ramsauer Townsend Effect 3 1 Resonant transmission in a square well
Contents Chapter 17: Resonant transmission and Ramsauer Townsend B. Zwiebach April 6, 016 1 Resonant transmission in a square well 1 The Ramsauer Townsend Effect 3 1 Resonant transmission in a square well
Lecture 5 (Sep. 20, 2017)
 Lecture 5 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 22 Lecture 5 (Sep. 20, 2017) 5.1 The Position Operator In the last class, we talked about operators with a continuous spectrum. A prime eample is the position
Lecture 5 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 22 Lecture 5 (Sep. 20, 2017) 5.1 The Position Operator In the last class, we talked about operators with a continuous spectrum. A prime eample is the position
Lecture 4 (Sep. 18, 2017)
 Lecture 4 8.3 Quantum Theory I, Fall 07 Lecture 4 (Sep. 8, 07) 4. Measurement 4.. Spin- Systems Last time, we said that a general state in a spin- system can be written as ψ = c + + + c, (4.) where +,
Lecture 4 8.3 Quantum Theory I, Fall 07 Lecture 4 (Sep. 8, 07) 4. Measurement 4.. Spin- Systems Last time, we said that a general state in a spin- system can be written as ψ = c + + + c, (4.) where +,
Chapter 18: Scattering in one dimension. 1 Scattering in One Dimension Time Delay An Example... 5
 Chapter 18: Scattering in one dimension B. Zwiebach April 26, 2016 Contents 1 Scattering in One Dimension 1 1.1 Time Delay.......................................... 4 1.2 An Example..........................................
Chapter 18: Scattering in one dimension B. Zwiebach April 26, 2016 Contents 1 Scattering in One Dimension 1 1.1 Time Delay.......................................... 4 1.2 An Example..........................................
Lecture #5: Begin Quantum Mechanics: Free Particle and Particle in a 1D Box
 561 Fall 017 Lecture #5 page 1 Last time: Lecture #5: Begin Quantum Mechanics: Free Particle and Particle in a 1D Box 1-D Wave equation u x = 1 u v t * u(x,t): displacements as function of x,t * nd -order:
561 Fall 017 Lecture #5 page 1 Last time: Lecture #5: Begin Quantum Mechanics: Free Particle and Particle in a 1D Box 1-D Wave equation u x = 1 u v t * u(x,t): displacements as function of x,t * nd -order:
PY 351 Modern Physics - Lecture notes, 3
 PY 351 Modern Physics - Lecture notes, 3 Copyright by Claudio Rebbi, Boston University, October 2016. These notes cannot be duplicated and distributed without explicit permission of the author. Time dependence
PY 351 Modern Physics - Lecture notes, 3 Copyright by Claudio Rebbi, Boston University, October 2016. These notes cannot be duplicated and distributed without explicit permission of the author. Time dependence
1 Mach-Zehder Interferometer 1. 2 Elitzur-Vaidman Bombs 6
 Chapter : Experiments with photons B. Zwiebach February 9, 6 Contents Mach-Zehder Interferometer Elitzur-Vaidman Bombs 6 Mach-Zehder Interferometer We have discussed before the Mach-Zehnder interferometer,
Chapter : Experiments with photons B. Zwiebach February 9, 6 Contents Mach-Zehder Interferometer Elitzur-Vaidman Bombs 6 Mach-Zehder Interferometer We have discussed before the Mach-Zehnder interferometer,
8.04 Spring 2013 March 12, 2013 Problem 1. (10 points) The Probability Current
 Prolem Set 5 Solutions 8.04 Spring 03 March, 03 Prolem. (0 points) The Proaility Current We wish to prove that dp a = J(a, t) J(, t). () dt Since P a (t) is the proaility of finding the particle in the
Prolem Set 5 Solutions 8.04 Spring 03 March, 03 Prolem. (0 points) The Proaility Current We wish to prove that dp a = J(a, t) J(, t). () dt Since P a (t) is the proaility of finding the particle in the
Statistical Interpretation
 Physics 342 Lecture 15 Statistical Interpretation Lecture 15 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, February 29th, 2008 Quantum mechanics is a theory of probability densities given that we now have an
Physics 342 Lecture 15 Statistical Interpretation Lecture 15 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, February 29th, 2008 Quantum mechanics is a theory of probability densities given that we now have an
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case:
 The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
Quantum Physics I (8.04) Spring 2016 Assignment 6
 Quantum Physics I (8.04) Spring 016 Assignment 6 MIT Physics Department Due Friday April 1, 016 March 17, 016 1:00 noon Reading: Griffiths section.6. For the following week sections.5 and.3. Problem Set
Quantum Physics I (8.04) Spring 016 Assignment 6 MIT Physics Department Due Friday April 1, 016 March 17, 016 1:00 noon Reading: Griffiths section.6. For the following week sections.5 and.3. Problem Set
Lecture 6 Quantum Mechanical Systems and Measurements
 Lecture 6 Quantum Mechanical Systems and Measurements Today s Program: 1. Simple Harmonic Oscillator (SHO). Principle of spectral decomposition. 3. Predicting the results of measurements, fourth postulate
Lecture 6 Quantum Mechanical Systems and Measurements Today s Program: 1. Simple Harmonic Oscillator (SHO). Principle of spectral decomposition. 3. Predicting the results of measurements, fourth postulate
8.05 Quantum Physics II, Fall 2011 FINAL EXAM Thursday December 22, 9:00 am -12:00 You have 3 hours.
 8.05 Quantum Physics II, Fall 0 FINAL EXAM Thursday December, 9:00 am -:00 You have 3 hours. Answer all problems in the white books provided. Write YOUR NAME and YOUR SECTION on your white books. There
8.05 Quantum Physics II, Fall 0 FINAL EXAM Thursday December, 9:00 am -:00 You have 3 hours. Answer all problems in the white books provided. Write YOUR NAME and YOUR SECTION on your white books. There
Harmonic Oscillator I
 Physics 34 Lecture 7 Harmonic Oscillator I Lecture 7 Physics 34 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, February th, 008 We can manipulate operators, to a certain extent, as we would algebraic expressions. By considering
Physics 34 Lecture 7 Harmonic Oscillator I Lecture 7 Physics 34 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, February th, 008 We can manipulate operators, to a certain extent, as we would algebraic expressions. By considering
Lecture 19 (Nov. 15, 2017)
 Lecture 19 8.31 Quantum Theory I, Fall 017 8 Lecture 19 Nov. 15, 017) 19.1 Rotations Recall that rotations are transformations of the form x i R ij x j using Einstein summation notation), where R is an
Lecture 19 8.31 Quantum Theory I, Fall 017 8 Lecture 19 Nov. 15, 017) 19.1 Rotations Recall that rotations are transformations of the form x i R ij x j using Einstein summation notation), where R is an
The quantum state as a vector
 The quantum state as a vector February 6, 27 Wave mechanics In our review of the development of wave mechanics, we have established several basic properties of the quantum description of nature:. A particle
The quantum state as a vector February 6, 27 Wave mechanics In our review of the development of wave mechanics, we have established several basic properties of the quantum description of nature:. A particle
E = hν light = hc λ = ( J s)( m/s) m = ev J = ev
 Problem The ionization potential tells us how much energy we need to use to remove an electron, so we know that any energy left afterwards will be the kinetic energy of the ejected electron. So first we
Problem The ionization potential tells us how much energy we need to use to remove an electron, so we know that any energy left afterwards will be the kinetic energy of the ejected electron. So first we
Chemistry 3502/4502. Exam I Key. September 19, ) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer.
 D Chemistry 350/450 Exam I Key September 19, 003 1) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer. ) There is one correct answer to every problem. There is no partial credit. 3) A table of
D Chemistry 350/450 Exam I Key September 19, 003 1) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer. ) There is one correct answer to every problem. There is no partial credit. 3) A table of
Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017)
 Lecture 1 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 1 Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017) 1.1 Simultaneous Diagonalization In the last lecture, we discussed the situations in which two operators can be simultaneously
Lecture 1 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 1 Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017) 1.1 Simultaneous Diagonalization In the last lecture, we discussed the situations in which two operators can be simultaneously
Wave Mechanics Relevant sections in text: , 2.1
 Wave Mechanics Relevant sections in text: 1.1 1.6, 2.1 The wave function We will now create a model for the system that we call a particle in one dimension. To do this we should define states and observables.
Wave Mechanics Relevant sections in text: 1.1 1.6, 2.1 The wave function We will now create a model for the system that we call a particle in one dimension. To do this we should define states and observables.
Lecture 16: Scattering States and the Step Potential. 1 The Step Potential 1. 4 Wavepackets in the step potential 6
 Lecture 16: Scattering States and the Step Potential B. Zwiebach April 19, 2016 Contents 1 The Step Potential 1 2 Step Potential with E>V 0 2 3 Step Potential with E
Lecture 16: Scattering States and the Step Potential B. Zwiebach April 19, 2016 Contents 1 The Step Potential 1 2 Step Potential with E>V 0 2 3 Step Potential with E
The Schrodinger Wave Equation (Engel 2.4) In QM, the behavior of a particle is described by its wave function Ψ(x,t) which we get by solving:
 When do we use Quantum Mechanics? (Engel 2.1) Basically, when λ is close in magnitude to the dimensions of the problem, and to the degree that the system has a discrete energy spectrum The Schrodinger
When do we use Quantum Mechanics? (Engel 2.1) Basically, when λ is close in magnitude to the dimensions of the problem, and to the degree that the system has a discrete energy spectrum The Schrodinger
Chemistry 3502/4502. Exam I. September 19, ) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer.
 D Chemistry 350/450 Exam I September 9, 003 ) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer. ) There is one correct answer to every problem. There is no partial credit. 3) A table of useful
D Chemistry 350/450 Exam I September 9, 003 ) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer. ) There is one correct answer to every problem. There is no partial credit. 3) A table of useful
E = φ 1 A The dynamics of a particle with mass m and charge q is determined by the Hamiltonian
 Lecture 9 Relevant sections in text: 2.6 Charged particle in an electromagnetic field We now turn to another extremely important example of quantum dynamics. Let us describe a non-relativistic particle
Lecture 9 Relevant sections in text: 2.6 Charged particle in an electromagnetic field We now turn to another extremely important example of quantum dynamics. Let us describe a non-relativistic particle
Physics 342 Lecture 17. Midterm I Recap. Lecture 17. Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I
 Physics 342 Lecture 17 Midterm I Recap Lecture 17 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1th, 28 17.1 Introduction In the context of the first midterm, there are a few points I d like to make about
Physics 342 Lecture 17 Midterm I Recap Lecture 17 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1th, 28 17.1 Introduction In the context of the first midterm, there are a few points I d like to make about
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Friday May 24, Final Exam
 8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Friday May 24, 2012 Final Exam Last Name: First Name: Check Recitation Instructor Time R01 Barton Zwiebach 10:00 R02
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Friday May 24, 2012 Final Exam Last Name: First Name: Check Recitation Instructor Time R01 Barton Zwiebach 10:00 R02
Lecture 6. Four postulates of quantum mechanics. The eigenvalue equation. Momentum and energy operators. Dirac delta function. Expectation values
 Lecture 6 Four postulates of quantum mechanics The eigenvalue equation Momentum and energy operators Dirac delta function Expectation values Objectives Learn about eigenvalue equations and operators. Learn
Lecture 6 Four postulates of quantum mechanics The eigenvalue equation Momentum and energy operators Dirac delta function Expectation values Objectives Learn about eigenvalue equations and operators. Learn
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 7, February 1, 2006
 Chem 350/450 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 006 Christopher J. Cramer ecture 7, February 1, 006 Solved Homework We are given that A is a Hermitian operator such that
Chem 350/450 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 006 Christopher J. Cramer ecture 7, February 1, 006 Solved Homework We are given that A is a Hermitian operator such that
8.05, Quantum Physics II, Fall 2013 TEST Wednesday October 23, 12:30-2:00pm You have 90 minutes.
 8.05, Quantum Physics II, Fall 03 TEST Wednesday October 3, :30-:00pm You have 90 minutes. Answer all problems in the white books provided. Write YOUR NAME and YOUR SECTION on your white books). There
8.05, Quantum Physics II, Fall 03 TEST Wednesday October 3, :30-:00pm You have 90 minutes. Answer all problems in the white books provided. Write YOUR NAME and YOUR SECTION on your white books). There
df(x) = h(x) dx Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 2009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation
 Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation Linearity of differential equation Partial vs. Ordinary Differential Equations
Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation Linearity of differential equation Partial vs. Ordinary Differential Equations
If electrons moved in simple orbits, p and x could be determined, but this violates the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle.
 CHEM 2060 Lecture 18: Particle in a Box L18-1 Atomic Orbitals If electrons moved in simple orbits, p and x could be determined, but this violates the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. We can only talk
CHEM 2060 Lecture 18: Particle in a Box L18-1 Atomic Orbitals If electrons moved in simple orbits, p and x could be determined, but this violates the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. We can only talk
Physics-I. Dr. Anurag Srivastava. Web address: Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus
 Physics-I Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus Syllabus Electrodynamics: Maxwell s equations: differential
Physics-I Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus Syllabus Electrodynamics: Maxwell s equations: differential
Quantum Mechanics: Postulates
 Quantum Mechanics: Postulates 25th March 2008 I. Physical meaning of the Wavefunction Postulate 1: The wavefunction attempts to describe a quantum mechanical entity (photon, electron, x-ray, etc.) through
Quantum Mechanics: Postulates 25th March 2008 I. Physical meaning of the Wavefunction Postulate 1: The wavefunction attempts to describe a quantum mechanical entity (photon, electron, x-ray, etc.) through
Physics 200 Lecture 4. Integration. Lecture 4. Physics 200 Laboratory
 Physics 2 Lecture 4 Integration Lecture 4 Physics 2 Laboratory Monday, February 21st, 211 Integration is the flip-side of differentiation in fact, it is often possible to write a differential equation
Physics 2 Lecture 4 Integration Lecture 4 Physics 2 Laboratory Monday, February 21st, 211 Integration is the flip-side of differentiation in fact, it is often possible to write a differential equation
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 5, January 27, 2006
 Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 5, January 27, 2006 Solved Homework (Homework for grading is also due today) We are told
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 5, January 27, 2006 Solved Homework (Homework for grading is also due today) We are told
Waves and the Schroedinger Equation
 Waves and the Schroedinger Equation 5 april 010 1 The Wave Equation We have seen from previous discussions that the wave-particle duality of matter requires we describe entities through some wave-form
Waves and the Schroedinger Equation 5 april 010 1 The Wave Equation We have seen from previous discussions that the wave-particle duality of matter requires we describe entities through some wave-form
Q U A N T U M M E C H A N I C S : L E C T U R E 5
 Q U A N T U M M E C H A N I C S : L E C T U R E 5 salwa al saleh Abstract This lecture discusses the formal solution of Schrödinger s equation for a free particle. Including the separation of variables
Q U A N T U M M E C H A N I C S : L E C T U R E 5 salwa al saleh Abstract This lecture discusses the formal solution of Schrödinger s equation for a free particle. Including the separation of variables
The Sommerfeld Polynomial Method: Harmonic Oscillator Example
 Chemistry 460 Fall 2017 Dr. Jean M. Standard October 2, 2017 The Sommerfeld Polynomial Method: Harmonic Oscillator Example Scaling the Harmonic Oscillator Equation Recall the basic definitions of the harmonic
Chemistry 460 Fall 2017 Dr. Jean M. Standard October 2, 2017 The Sommerfeld Polynomial Method: Harmonic Oscillator Example Scaling the Harmonic Oscillator Equation Recall the basic definitions of the harmonic
1 Mathematical preliminaries
 1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
Page 684. Lecture 40: Coordinate Transformations: Time Transformations Date Revised: 2009/02/02 Date Given: 2009/02/02
 Page 684 Lecture 40: Coordinate Transformations: Time Transformations Date Revised: 2009/02/02 Date Given: 2009/02/02 Time Transformations Section 12.5 Symmetries: Time Transformations Page 685 Time Translation
Page 684 Lecture 40: Coordinate Transformations: Time Transformations Date Revised: 2009/02/02 Date Given: 2009/02/02 Time Transformations Section 12.5 Symmetries: Time Transformations Page 685 Time Translation
Section 9 Variational Method. Page 492
 Section 9 Variational Method Page 492 Page 493 Lecture 27: The Variational Method Date Given: 2008/12/03 Date Revised: 2008/12/03 Derivation Section 9.1 Variational Method: Derivation Page 494 Motivation
Section 9 Variational Method Page 492 Page 493 Lecture 27: The Variational Method Date Given: 2008/12/03 Date Revised: 2008/12/03 Derivation Section 9.1 Variational Method: Derivation Page 494 Motivation
t [Ψ (x, t)ψ(x, t)]dx = 0 Ψ (x, t) Ψ(x, t) + Ψ Ψ(x, t) (x, t) = 0 t Ψ(HΨ) dx = Ψ (HΨ)dx
![t [Ψ (x, t)ψ(x, t)]dx = 0 Ψ (x, t) Ψ(x, t) + Ψ Ψ(x, t) (x, t) = 0 t Ψ(HΨ) dx = Ψ (HΨ)dx t [Ψ (x, t)ψ(x, t)]dx = 0 Ψ (x, t) Ψ(x, t) + Ψ Ψ(x, t) (x, t) = 0 t Ψ(HΨ) dx = Ψ (HΨ)dx](/thumbs/84/90601446.jpg) .6 Reality check... The next few sections take a bodyswerve into more formal language. But they make some very important points, so its worth while to do them! One thing that might worry us is whether
.6 Reality check... The next few sections take a bodyswerve into more formal language. But they make some very important points, so its worth while to do them! One thing that might worry us is whether
Quantum Dynamics. March 10, 2017
 Quantum Dynamics March 0, 07 As in classical mechanics, time is a parameter in quantum mechanics. It is distinct from space in the sense that, while we have Hermitian operators, X, for position and therefore
Quantum Dynamics March 0, 07 As in classical mechanics, time is a parameter in quantum mechanics. It is distinct from space in the sense that, while we have Hermitian operators, X, for position and therefore
Attempts at relativistic QM
 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics should incorporate both quantum mechanics and special relativity. However historically combining quantum mechanics and
Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics should incorporate both quantum mechanics and special relativity. However historically combining quantum mechanics and
Quantum Theory and Group Representations
 Quantum Theory and Group Representations Peter Woit Columbia University LaGuardia Community College, November 1, 2017 Queensborough Community College, November 15, 2017 Peter Woit (Columbia University)
Quantum Theory and Group Representations Peter Woit Columbia University LaGuardia Community College, November 1, 2017 Queensborough Community College, November 15, 2017 Peter Woit (Columbia University)
Lecture-XXVI. Time-Independent Schrodinger Equation
 Lecture-XXVI Time-Independent Schrodinger Equation Time Independent Schrodinger Equation: The time-dependent Schrodinger equation: Assume that V is independent of time t. In that case the Schrodinger equation
Lecture-XXVI Time-Independent Schrodinger Equation Time Independent Schrodinger Equation: The time-dependent Schrodinger equation: Assume that V is independent of time t. In that case the Schrodinger equation
04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics
 04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics () States are represented by vectors of length. A physical system is represented by a linear vector space (the space of all its possible states). () Properties
04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics () States are represented by vectors of length. A physical system is represented by a linear vector space (the space of all its possible states). () Properties
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701
 Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/23//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Outline 1 General Formulation of Quantum Mechanics 2 Measurement of physical quantities and observables 3 Representations
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/23//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Outline 1 General Formulation of Quantum Mechanics 2 Measurement of physical quantities and observables 3 Representations
Under evolution for a small time δt the area A(t) = q p evolves into an area
 Physics 106a, Caltech 6 November, 2018 Lecture 11: Hamiltonian Mechanics II Towards statistical mechanics Phase space volumes are conserved by Hamiltonian dynamics We can use many nearby initial conditions
Physics 106a, Caltech 6 November, 2018 Lecture 11: Hamiltonian Mechanics II Towards statistical mechanics Phase space volumes are conserved by Hamiltonian dynamics We can use many nearby initial conditions
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS
 MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
= X = X ( ~) } ( ) ( ) On the other hand, when the Hamiltonian acts on ( ) one finds that
 6. A general normalized solution to Schrödinger s equation of motion for a particle moving in a time-independent potential is of the form ( ) = P } where the and () are, respectively, eigenvalues and normalized
6. A general normalized solution to Schrödinger s equation of motion for a particle moving in a time-independent potential is of the form ( ) = P } where the and () are, respectively, eigenvalues and normalized
Bound and Scattering Solutions for a Delta Potential
 Physics 342 Lecture 11 Bound and Scattering Solutions for a Delta Potential Lecture 11 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, February 20th, 2008 We understand that free particle solutions are meant
Physics 342 Lecture 11 Bound and Scattering Solutions for a Delta Potential Lecture 11 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, February 20th, 2008 We understand that free particle solutions are meant
Chemistry 3502/4502. Exam I. February 6, ) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems.
 D Chemistry 3502/4502 Exam I February 6, 2006 1) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems. 2) There is one correct answer to every multiple-choice problem. There is no partial credit. On the
D Chemistry 3502/4502 Exam I February 6, 2006 1) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems. 2) There is one correct answer to every multiple-choice problem. There is no partial credit. On the
So far we have limited the discussion to state spaces of finite dimensions, but it turns out that, in
 Chapter 0 State Spaces of Infinite Dimension So far we have limited the discussion to state spaces of finite dimensions, but it turns out that, in practice, state spaces of infinite dimension are fundamental
Chapter 0 State Spaces of Infinite Dimension So far we have limited the discussion to state spaces of finite dimensions, but it turns out that, in practice, state spaces of infinite dimension are fundamental
This is the important completeness relation,
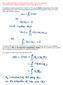 Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space
 Physics 342 Lecture 16 Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space Lecture 16 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1st, 2010 We have seen the importance of the plane wave solutions to the potentialfree Schrödinger
Physics 342 Lecture 16 Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space Lecture 16 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1st, 2010 We have seen the importance of the plane wave solutions to the potentialfree Schrödinger
Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics
 Chapter 3 Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 3. Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics We have introduced two concepts: (i the state of a particle or a quantum mechanical system is described by a wave
Chapter 3 Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 3. Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics We have introduced two concepts: (i the state of a particle or a quantum mechanical system is described by a wave
Chapter 10 Operators of the scalar Klein Gordon field. from my book: Understanding Relativistic Quantum Field Theory.
 Chapter 10 Operators of the scalar Klein Gordon field from my book: Understanding Relativistic Quantum Field Theory Hans de Vries November 11, 2008 2 Chapter Contents 10 Operators of the scalar Klein Gordon
Chapter 10 Operators of the scalar Klein Gordon field from my book: Understanding Relativistic Quantum Field Theory Hans de Vries November 11, 2008 2 Chapter Contents 10 Operators of the scalar Klein Gordon
Chemistry 3502/4502. Exam I. February 6, ) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems.
 A Chemistry 3502/4502 Exam I February 6, 2006 1) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems. 2) There is one correct answer to every multiple-choice problem. There is no partial credit. On the
A Chemistry 3502/4502 Exam I February 6, 2006 1) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems. 2) There is one correct answer to every multiple-choice problem. There is no partial credit. On the
C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/02/08 Fall 2008 Lecture 11
 C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/0/08 Fall 008 Lecture 11 Last time we saw that the time dependent Schr. eqn. can be decomposed into two equations, one in time (t) and one in space (x): space
C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/0/08 Fall 008 Lecture 11 Last time we saw that the time dependent Schr. eqn. can be decomposed into two equations, one in time (t) and one in space (x): space
1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation
 1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation A. M. Steane, Exeter College, Oxford University 1.1 Introduction These pages are intended to help you get a feel for the mathematics behind Quantum Mechanics. The
1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation A. M. Steane, Exeter College, Oxford University 1.1 Introduction These pages are intended to help you get a feel for the mathematics behind Quantum Mechanics. The
Quantum Mechanics Basics II
 Quantum Mechanics Basics II VBS/MRC Quantum Mechanics Basics II 0 Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 1. State of a Particle Wave Functions 2. Physical Observables Hermitian Operators 3. Outcome of Experiment
Quantum Mechanics Basics II VBS/MRC Quantum Mechanics Basics II 0 Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 1. State of a Particle Wave Functions 2. Physical Observables Hermitian Operators 3. Outcome of Experiment
Chapter 2 The Group U(1) and its Representations
 Chapter 2 The Group U(1) and its Representations The simplest example of a Lie group is the group of rotations of the plane, with elements parametrized by a single number, the angle of rotation θ. It is
Chapter 2 The Group U(1) and its Representations The simplest example of a Lie group is the group of rotations of the plane, with elements parametrized by a single number, the angle of rotation θ. It is
4. Supplementary Notes on Time and Space Evolution of a Neutrino Beam
 Lecture Notes for Quantum Physics II & III 8.05 & 8.059 Academic Year 1996/1997 4. Supplementary Notes on Time and Space Evolution of a Neutrino Beam c D. Stelitano 1996 As an example of a two-state system
Lecture Notes for Quantum Physics II & III 8.05 & 8.059 Academic Year 1996/1997 4. Supplementary Notes on Time and Space Evolution of a Neutrino Beam c D. Stelitano 1996 As an example of a two-state system
Physics 486 Discussion 5 Piecewise Potentials
 Physics 486 Discussion 5 Piecewise Potentials Problem 1 : Infinite Potential Well Checkpoints 1 Consider the infinite well potential V(x) = 0 for 0 < x < 1 elsewhere. (a) First, think classically. Potential
Physics 486 Discussion 5 Piecewise Potentials Problem 1 : Infinite Potential Well Checkpoints 1 Consider the infinite well potential V(x) = 0 for 0 < x < 1 elsewhere. (a) First, think classically. Potential
2. As we shall see, we choose to write in terms of σ x because ( X ) 2 = σ 2 x.
 Section 5.1 Simple One-Dimensional Problems: The Free Particle Page 9 The Free Particle Gaussian Wave Packets The Gaussian wave packet initial state is one of the few states for which both the { x } and
Section 5.1 Simple One-Dimensional Problems: The Free Particle Page 9 The Free Particle Gaussian Wave Packets The Gaussian wave packet initial state is one of the few states for which both the { x } and
3.024 Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials Spring 2012 Recitation 3 Notes
 3.024 Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials Spring 2012 Outline 1. Schr dinger: Eigenfunction Problems & Operator Properties 2. Piecewise Function/Continuity Review -Scattering from
3.024 Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials Spring 2012 Outline 1. Schr dinger: Eigenfunction Problems & Operator Properties 2. Piecewise Function/Continuity Review -Scattering from
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams. Problem Set 7. Due Tuesday April 9 at 11.00AM
 8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Thursday April 4 Problem Set 7 Due Tuesday April 9 at 11.00AM Assigned Reading: E&R 6 all Li. 7 1 9, 8 1 Ga. 4 all, 6
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Thursday April 4 Problem Set 7 Due Tuesday April 9 at 11.00AM Assigned Reading: E&R 6 all Li. 7 1 9, 8 1 Ga. 4 all, 6
Math 115 Spring 11 Written Homework 10 Solutions
 Math 5 Spring Written Homework 0 Solutions. For following its, state what indeterminate form the its are in and evaluate the its. (a) 3x 4x 4 x x 8 Solution: This is in indeterminate form 0. Algebraically,
Math 5 Spring Written Homework 0 Solutions. For following its, state what indeterminate form the its are in and evaluate the its. (a) 3x 4x 4 x x 8 Solution: This is in indeterminate form 0. Algebraically,
1 Planck-Einstein Relation E = hν
 C/CS/Phys C191 Representations and Wavefunctions 09/30/08 Fall 2008 Lecture 8 1 Planck-Einstein Relation E = hν This is the equation relating energy to frequency. It was the earliest equation of quantum
C/CS/Phys C191 Representations and Wavefunctions 09/30/08 Fall 2008 Lecture 8 1 Planck-Einstein Relation E = hν This is the equation relating energy to frequency. It was the earliest equation of quantum
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations
 Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
5.61 FIRST HOUR EXAM ANSWERS Fall, 2013
 5.61 FIRST HOUR EXAM ANSWERS Fall, 013 I. A. Sketch ψ 5(x)ψ 5 (x) vs. x, where ψ 5 (x) is the n = 5 wavefunction of a particle in a box. Describe, in a few words, each of the essential qualitative features
5.61 FIRST HOUR EXAM ANSWERS Fall, 013 I. A. Sketch ψ 5(x)ψ 5 (x) vs. x, where ψ 5 (x) is the n = 5 wavefunction of a particle in a box. Describe, in a few words, each of the essential qualitative features
Topic 2: The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thin
 The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
Quantum Physics III (8.06) Spring 2016 Assignment 3
 Quantum Physics III (8.6) Spring 6 Assignment 3 Readings Griffiths Chapter 9 on time-dependent perturbation theory Shankar Chapter 8 Cohen-Tannoudji, Chapter XIII. Problem Set 3. Semi-classical approximation
Quantum Physics III (8.6) Spring 6 Assignment 3 Readings Griffiths Chapter 9 on time-dependent perturbation theory Shankar Chapter 8 Cohen-Tannoudji, Chapter XIII. Problem Set 3. Semi-classical approximation
Problem 1: A 3-D Spherical Well(10 Points)
 Problem : A 3-D Spherical Well( Points) For this problem, consider a particle of mass m in a three-dimensional spherical potential well, V (r), given as, V = r a/2 V = W r > a/2. with W >. All of the following
Problem : A 3-D Spherical Well( Points) For this problem, consider a particle of mass m in a three-dimensional spherical potential well, V (r), given as, V = r a/2 V = W r > a/2. with W >. All of the following
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Quantum Optical Communication
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.453 Quantum Optical Communication Date: Tuesday, September 13, 216 Dirac-notation Quantum Mechanics. Introduction
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.453 Quantum Optical Communication Date: Tuesday, September 13, 216 Dirac-notation Quantum Mechanics. Introduction
We start with some important background material in classical and quantum mechanics.
 Chapter Basics We start with some important background material in classical and quantum mechanics.. Classical mechanics Lagrangian mechanics Compared to Newtonian mechanics, Lagrangian mechanics has the
Chapter Basics We start with some important background material in classical and quantum mechanics.. Classical mechanics Lagrangian mechanics Compared to Newtonian mechanics, Lagrangian mechanics has the
Derivation of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation. from First Principles. Theodore Bodurov
 Annales de la Fondation Louis de Broglie, Volume 30, no 3-4, 2005 343 Derivation of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation from First Principles Theodore Bodurov Eugene, Oregon, USA, email: bodt@efn.org ABSTRACT.
Annales de la Fondation Louis de Broglie, Volume 30, no 3-4, 2005 343 Derivation of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation from First Principles Theodore Bodurov Eugene, Oregon, USA, email: bodt@efn.org ABSTRACT.
1 Position Representation of Quantum State Function
 C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell II 10/09/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 13 1 Position Representation of Quantum State Function We will motivate this using the framework of measurements. Consider first
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell II 10/09/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 13 1 Position Representation of Quantum State Function We will motivate this using the framework of measurements. Consider first
Announcement Second HW will be due on Monday Sept 19! The text book is on reserve in SERC reading room
 Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics Lecture 4: Schodinger s Equation: Part II http://www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/361 Prof. Sean Oh Announcement Second HW will be due on Monday Sept 19! The text book
Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics Lecture 4: Schodinger s Equation: Part II http://www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/361 Prof. Sean Oh Announcement Second HW will be due on Monday Sept 19! The text book
harmonic oscillator in quantum mechanics
 Physics 400 Spring 016 harmonic oscillator in quantum mechanics lecture notes, spring semester 017 http://www.phys.uconn.edu/ rozman/ourses/p400_17s/ Last modified: May 19, 017 Dimensionless Schrödinger
Physics 400 Spring 016 harmonic oscillator in quantum mechanics lecture notes, spring semester 017 http://www.phys.uconn.edu/ rozman/ourses/p400_17s/ Last modified: May 19, 017 Dimensionless Schrödinger
8.04 Spring 2013 April 09, 2013 Problem 1. (15 points) Mathematical Preliminaries: Facts about Unitary Operators. Uφ u = uφ u
 Problem Set 7 Solutions 8.4 Spring 13 April 9, 13 Problem 1. (15 points) Mathematical Preliminaries: Facts about Unitary Operators (a) (3 points) Suppose φ u is an eigenfunction of U with eigenvalue u,
Problem Set 7 Solutions 8.4 Spring 13 April 9, 13 Problem 1. (15 points) Mathematical Preliminaries: Facts about Unitary Operators (a) (3 points) Suppose φ u is an eigenfunction of U with eigenvalue u,
Lecture 3 Dynamics 29
 Lecture 3 Dynamics 29 30 LECTURE 3. DYNAMICS 3.1 Introduction Having described the states and the observables of a quantum system, we shall now introduce the rules that determine their time evolution.
Lecture 3 Dynamics 29 30 LECTURE 3. DYNAMICS 3.1 Introduction Having described the states and the observables of a quantum system, we shall now introduce the rules that determine their time evolution.
Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors,
 chmy564-19 Fri 18jan19 Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors, 3. Theorems vs. Postulates Scalar (inner) prod.
chmy564-19 Fri 18jan19 Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors, 3. Theorems vs. Postulates Scalar (inner) prod.
Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam 2 Solutions
 Chemistry 46 Fall 7 Dr. Jean M. Standard Name SAMPE EXAM Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam Solutions.) ( points) Answer the following questions by selecting the correct answer from the choices provided. a.)
Chemistry 46 Fall 7 Dr. Jean M. Standard Name SAMPE EXAM Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam Solutions.) ( points) Answer the following questions by selecting the correct answer from the choices provided. a.)
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Wednesday April Exam 2
 8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Wednesday April 18 2012 Exam 2 Last Name: First Name: Check Recitation Instructor Time R01 Barton Zwiebach 10:00 R02
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Wednesday April 18 2012 Exam 2 Last Name: First Name: Check Recitation Instructor Time R01 Barton Zwiebach 10:00 R02
CHM 532 Notes on Wavefunctions and the Schrödinger Equation
 CHM 532 Notes on Wavefunctions and the Schrödinger Equation In class we have discussed a thought experiment 1 that contrasts the behavior of classical particles, classical waves and quantum particles.
CHM 532 Notes on Wavefunctions and the Schrödinger Equation In class we have discussed a thought experiment 1 that contrasts the behavior of classical particles, classical waves and quantum particles.
Quantum Mechanics Solutions. λ i λ j v j v j v i v i.
 Quantum Mechanics Solutions 1. (a) If H has an orthonormal basis consisting of the eigenvectors { v i } of A with eigenvalues λ i C, then A can be written in terms of its spectral decomposition as A =
Quantum Mechanics Solutions 1. (a) If H has an orthonormal basis consisting of the eigenvectors { v i } of A with eigenvalues λ i C, then A can be written in terms of its spectral decomposition as A =
1 The postulates of quantum mechanics
 1 The postulates of quantum mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics were derived after a long process of trial and error. These postulates provide a connection between the physical world and the
1 The postulates of quantum mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics were derived after a long process of trial and error. These postulates provide a connection between the physical world and the
Quantum Mechanics. L. Del Debbio, University of Edinburgh Version 0.9
 Quantum Mechanics L. Del Debbio, University of Edinburgh Version 0.9 November 26, 2010 Contents 1 Quantum states 1 1.1 Introduction..................................... 2 1.1.1 Experiment with classical
Quantum Mechanics L. Del Debbio, University of Edinburgh Version 0.9 November 26, 2010 Contents 1 Quantum states 1 1.1 Introduction..................................... 2 1.1.1 Experiment with classical
Physics 216 Spring The Optical Theorem
 Physics 6 Spring 0 The Optical Theorem. The probability currents In the quantum theory of scattering, the optical theorem is a consequence of the conservation of probability. As usual, we define ρ(x,t)
Physics 6 Spring 0 The Optical Theorem. The probability currents In the quantum theory of scattering, the optical theorem is a consequence of the conservation of probability. As usual, we define ρ(x,t)
1. For the case of the harmonic oscillator, the potential energy is quadratic and hence the total Hamiltonian looks like: d 2 H = h2
 15 Harmonic Oscillator 1. For the case of the harmonic oscillator, the potential energy is quadratic and hence the total Hamiltonian looks like: d 2 H = h2 2mdx + 1 2 2 kx2 (15.1) where k is the force
15 Harmonic Oscillator 1. For the case of the harmonic oscillator, the potential energy is quadratic and hence the total Hamiltonian looks like: d 2 H = h2 2mdx + 1 2 2 kx2 (15.1) where k is the force
Physics 351 Wednesday, April 22, 2015
 Physics 351 Wednesday, April 22, 2015 HW13 due Friday. The last one! You read Taylor s Chapter 16 this week (waves, stress, strain, fluids), most of which is Phys 230 review. Next weekend, you ll read
Physics 351 Wednesday, April 22, 2015 HW13 due Friday. The last one! You read Taylor s Chapter 16 this week (waves, stress, strain, fluids), most of which is Phys 230 review. Next weekend, you ll read
Generators for Continuous Coordinate Transformations
 Page 636 Lecture 37: Coordinate Transformations: Continuous Passive Coordinate Transformations Active Coordinate Transformations Date Revised: 2009/01/28 Date Given: 2009/01/26 Generators for Continuous
Page 636 Lecture 37: Coordinate Transformations: Continuous Passive Coordinate Transformations Active Coordinate Transformations Date Revised: 2009/01/28 Date Given: 2009/01/26 Generators for Continuous
