1. The Polar Decomposition
|
|
|
- Gilbert Black
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A PERSONAL INTERVIEW WITH THE SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSITION MATAN GAVISH Part. Theory. The Polar Decomposition In what follows, F denotes either R or C. The vector space F n is an inner product space with the standard inner product,,. Let us denote by M n m (F) the set of matrices over F with n rows and m columns. Vectors will denote columns, that is, we will write F n v = v. The following fact is known as the (Left) Polar Decomposition: Let m n. Any matrix A M n m (F) may be factorized as A = U P where U M n m (F) has a orthonormal columns and P M m m (F) is positive semi-denite. Remark. When F = R and n = m, the polar decomposition makes precise the statement, that every linear transformation T : R n R n is a composition of a dilation and a rotation/reection. The proof will imply that in this case there is an orthonormal base (the eigenvectors of the matrix A A) on which A acts as a rotation/reection (U) composed with a dilation (P ). The polar decomposition follows directly from a remarkable connection between the (general) matrix A and the positive semi-denite matrix P = A A. Date: June 30, 200.
2 A PERSONAL INTERVIEW WITH THE SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSITION 2.. The Matrix A A. We rst note that the matrix A A M m m (F) is self-adjoint and positive semi-denite, since for any v F m we have 0 Av 2 = Av, Av = v, A Av = v A Av. There are several equivalent ways to dene the matrix A A. To name one, note that A A can be diagonalized over F, A A = W DW, where W is unitary and D is diagonal. In fact, since A A is positive semi-denite, all its eigenvalues are real and non-negative, and we can denote D = λ 2 λ 2 m, for some numbers 0 λ,..., R, called the Singular Values of A. We dene λ A A = W W. This notation is justied since positive semi-denite. ( A ) 2 A = A A. Note that A A is also self-adjoint and Why is the matrix A A is interesting? one reason is that for all v F m, Av 2 = Av, Av = v, A Av = v, A A A Av = A Av, A Av = A Av 2, that is, (.) Av = A Av. Besides the geometrical interpretation that A and A A have the same eect on a vector's length, this has the useful consequence, ker A = ker A A. As m = dim ker A + ranka = dim ker A A + rank A A, it also follows that We denote their common value by l. rank A A = ranka.
3 A PERSONAL INTERVIEW WITH THE SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSITION 3.2. Proof of the (Right) Polar Decomposition. Since A A is self-adjoint, there exists an orthonormal basis ψ,..., ψ m of F m whose elements are eigenvectors of A A. Using our previous notation for the eigenvalues of A A, suppose that A A ψ i = λ i ψ i for i =,..., m. For simplicity, let us assume that λ... > 0 (where m l = ranka) or in other words, that ψ l+,..., ψ m are basis vectors for ker A = ker A A (in case A has a non-trivial kernel). To factor A = U P, let P = A A and dene U M n m (F) as follows. Consider the vectors λ Aψ,..., Aψ l. This set is orthonormal: for i, j l, we have Aψ i, Aψ j = Aψ i, Aψ j = ψ i, A Aψ j = ψi, λ 2 λ j λ i λ j λ i λ j λ i λ j λ i λ jψ j = ψ i, ψ j = δ i,j j λ i (recall that λ,... are reals). Remark. In fact, we discovered that ψ l+,..., ψ m λ Aψ,..., Aψ l is an orthonormal basis for ImA. is an orthonormal basis for ker A, and We now use the assumption m n. that If l < m, take an orthonormal completion ϕ l+,..., ϕ m such that λ Aψ,..., Aψ l, ϕ l+,..., ϕ m constitutes an orthonormal set of vectors in F n. This is possible since m n. Finally, dene U = λ Aψ Aψ l ϕ l+ ϕ m ψ ψ2 M. n m (F). ψm Let us check that the matrix U has the desired properties. First, U has orthonormal columns: the left-hand matrix in the above product is unitary and hence has orthonormal columns, as does the right-hand matrix. It is simple to verify that generally, a product of matrices with orthonormal columns again has orthonormal columns. Next, Since 0 ψ. ψ2 0. ψ i = i, ψm 0. 0
4 A PERSONAL INTERVIEW WITH THE SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSITION 4 we nd that λ Uψ i = i Aψ i ϕ i i l l < i m so that λ i Uψ i i l UP ψ i = 0 Uψ i l < i m Aψ i i l = 0 ϕ i l < i m = Aψ i where we have used the fact that Aψ i = 0 for i = l +,..., m (these vector actually span ker A). Since the identity A = UP holds on the basis vectors, ψ,..., ψ m, we are done. Remark. If A is inverible, ker A = ker A A implies that A A is invertible. In this case, U is uniquely determined since U = A P. Remark. If A M n m (F) and m n, we can perform a right polar decomposition for A M m n (F). We obtain a matrix U M m n (F) with orthonormal columns such that A = U AA, or equivalently, A = AA U. Here AA is again positive semi-denite, but now U has orthonormal rows. This is the Left Polar Decomposition. If n = m, that is, if our matrix A is square, both decompositions are possible: there exist unitary matrices U, U M n n (F) such that A = U A A = AA U. It is interesting to note that t, in this case U = U holds if and only if A is normal (AA = A A). 2. The Singular Value Decomposition 2.. Roughly Speaking. At least two dierent decompositions go by the name of Singular Value Decomposition (SVD): () Any matrix A M n m (F) may be factorized as A = V D W, where V M n p (F) and W M m p (F) have orthonormal columns for p = min {m, n}, and D M p p (F) is diagonal with non-negative entries.
5 A PERSONAL INTERVIEW WITH THE SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSITION 5 (2) Any matrix A M n m (F) may be factorized as A = V D W, where V M n n (F) and W M m m (F) are unitary matrices, and D M n m (F) has non-negative entries on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere. (The main diagonal of a matrix D M n m (F) is (D,..., D nn ).) We will work out SVD using the rst denition. Suppose that such a decompisition does exist, and denote V = v v p ; W = w w p ; D = d 0 0 d p. Since W W = V V = I p, for each i p, we have (2.) A A w i = W DV V DW w i = W D 2 W w i = W D 2 w. w p w i = d2 i w i and similarly (2.2) AA v i = V DW W DV v i = V D 2 V v i = V D 2 v. v p v i = d2 i v i. Should such a decomposition exist, then, the column w i of W must be an eigenvector of A A with eigenvalue d 2 i. Using notation from the previous section, if m n (so p = m) we must have simply W = ψ ψ m ; D = λ 0 0. Matlab, for example, uses the second one
6 A PERSONAL INTERVIEW WITH THE SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSITION SVD from the Polar Decomposition. Formally, the SVD is an easy consequence of the polar decomposition. Assume that m n (so p = m) and A M n m (F). We use the notations dened above, and employ the right polar decomposition: A = U A A = UW λ W = = = λ Aψ Aψ l ϕ l+ ϕ m λ Aψ Aψ l ϕ l+ ϕ m } {{ } V W W λ λ } {{ } D W = ψ. ; } ψm {{ } W Dene, then D = λ V = W = λ Aψ Aψ l ϕ l+ ϕ m ψ ψ m and we have, by denition, an SVD decomposition of A. Manifestly, (2.) holds. Let us convince ourselves that (2.2) also holds, namely, that the column v i of V is an eigenvectors of AA, which corresponds to the eigenvalue λ 2 i. Indeed, for i l we have AA v i = AA Aψ i = A (A Aψ i ) = A ( ( ) λ 2 ) i ψ i = λ 2 λ i λ i λ i Aψ i. i λ i
7 A PERSONAL INTERVIEW WITH THE SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSITION 7 For the case where l + i m, recall that by our construction ϕ l+,..., ϕ m (ImA). We always have (ImA) ker AA : indeed, x v (ImA), then for any u F n, 0 = AA u, v = u, AA v - which implies AA v = 0. Now, if l + i m then λ i = 0 and v i = ϕ i ker AA, so that AA v i = 0 = 0 ϕ i = λ 2 i ϕ i. Thus, in either case, the column v i of V is an eigenvectors of AA that corresponds to the eigenvalue λ 2 i.
linearly indepedent eigenvectors as the multiplicity of the root, but in general there may be no more than one. For further discussion, assume matrice
 3. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, Spectral Representation 3.. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors A vector ' is eigenvector of a matrix K, if K' is parallel to ' and ' 6, i.e., K' k' k is the eigenvalue. If is
3. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, Spectral Representation 3.. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors A vector ' is eigenvector of a matrix K, if K' is parallel to ' and ' 6, i.e., K' k' k is the eigenvalue. If is
Linear Algebra Review. Vectors
 Linear Algebra Review 9/4/7 Linear Algebra Review By Tim K. Marks UCSD Borrows heavily from: Jana Kosecka http://cs.gmu.edu/~kosecka/cs682.html Virginia de Sa (UCSD) Cogsci 8F Linear Algebra review Vectors
Linear Algebra Review 9/4/7 Linear Algebra Review By Tim K. Marks UCSD Borrows heavily from: Jana Kosecka http://cs.gmu.edu/~kosecka/cs682.html Virginia de Sa (UCSD) Cogsci 8F Linear Algebra review Vectors
The Singular Value Decomposition
 The Singular Value Decomposition Philippe B. Laval KSU Fall 2015 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) SVD Fall 2015 1 / 13 Review of Key Concepts We review some key definitions and results about matrices that will
The Singular Value Decomposition Philippe B. Laval KSU Fall 2015 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) SVD Fall 2015 1 / 13 Review of Key Concepts We review some key definitions and results about matrices that will
Review problems for MA 54, Fall 2004.
 Review problems for MA 54, Fall 2004. Below are the review problems for the final. They are mostly homework problems, or very similar. If you are comfortable doing these problems, you should be fine on
Review problems for MA 54, Fall 2004. Below are the review problems for the final. They are mostly homework problems, or very similar. If you are comfortable doing these problems, you should be fine on
Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Polar Form
 Chapter 2 Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Polar Form 2.1 Polar Form In this chapter, we assume that we are dealing with a real Euclidean space E. Let f: E E be any linear map. In general, it may
Chapter 2 Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Polar Form 2.1 Polar Form In this chapter, we assume that we are dealing with a real Euclidean space E. Let f: E E be any linear map. In general, it may
Notes on singular value decomposition for Math 54. Recall that if A is a symmetric n n matrix, then A has real eigenvalues A = P DP 1 A = P DP T.
 Notes on singular value decomposition for Math 54 Recall that if A is a symmetric n n matrix, then A has real eigenvalues λ 1,, λ n (possibly repeated), and R n has an orthonormal basis v 1,, v n, where
Notes on singular value decomposition for Math 54 Recall that if A is a symmetric n n matrix, then A has real eigenvalues λ 1,, λ n (possibly repeated), and R n has an orthonormal basis v 1,, v n, where
The Singular Value Decomposition and Least Squares Problems
 The Singular Value Decomposition and Least Squares Problems Tom Lyche Centre of Mathematics for Applications, Department of Informatics, University of Oslo September 27, 2009 Applications of SVD solving
The Singular Value Decomposition and Least Squares Problems Tom Lyche Centre of Mathematics for Applications, Department of Informatics, University of Oslo September 27, 2009 Applications of SVD solving
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2018
 Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2018 1 Vectors k, M, N are scalars A one-dimensional array c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, ( ) c1 c = c 2 c i is the i-th component of c c T = (c 1, c
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2018 1 Vectors k, M, N are scalars A one-dimensional array c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, ( ) c1 c = c 2 c i is the i-th component of c c T = (c 1, c
(a) If A is a 3 by 4 matrix, what does this tell us about its nullspace? Solution: dim N(A) 1, since rank(a) 3. Ax =
 . (5 points) (a) If A is a 3 by 4 matrix, what does this tell us about its nullspace? dim N(A), since rank(a) 3. (b) If we also know that Ax = has no solution, what do we know about the rank of A? C(A)
. (5 points) (a) If A is a 3 by 4 matrix, what does this tell us about its nullspace? dim N(A), since rank(a) 3. (b) If we also know that Ax = has no solution, what do we know about the rank of A? C(A)
Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 3
 Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 3 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University February 1, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 3 February 1, 2017 1 / 16
Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 3 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University February 1, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 3 February 1, 2017 1 / 16
Throughout these notes we assume V, W are finite dimensional inner product spaces over C.
 Math 342 - Linear Algebra II Notes Throughout these notes we assume V, W are finite dimensional inner product spaces over C 1 Upper Triangular Representation Proposition: Let T L(V ) There exists an orthonormal
Math 342 - Linear Algebra II Notes Throughout these notes we assume V, W are finite dimensional inner product spaces over C 1 Upper Triangular Representation Proposition: Let T L(V ) There exists an orthonormal
Polar Decomposition of a Matrix
 Polar Decomposition of a Matrix Garrett Buffington May 4, 2014 Table of Contents 1 The Polar Decomposition What is it? Square Root Matrix The Theorem Table of Contents 1 The Polar Decomposition What is
Polar Decomposition of a Matrix Garrett Buffington May 4, 2014 Table of Contents 1 The Polar Decomposition What is it? Square Root Matrix The Theorem Table of Contents 1 The Polar Decomposition What is
Basic Calculus Review
 Basic Calculus Review Lorenzo Rosasco ISML Mod. 2 - Machine Learning Vector Spaces Functionals and Operators (Matrices) Vector Space A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V
Basic Calculus Review Lorenzo Rosasco ISML Mod. 2 - Machine Learning Vector Spaces Functionals and Operators (Matrices) Vector Space A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V
Problem # Max points possible Actual score Total 120
 FINAL EXAMINATION - MATH 2121, FALL 2017. Name: ID#: Email: Lecture & Tutorial: Problem # Max points possible Actual score 1 15 2 15 3 10 4 15 5 15 6 15 7 10 8 10 9 15 Total 120 You have 180 minutes to
FINAL EXAMINATION - MATH 2121, FALL 2017. Name: ID#: Email: Lecture & Tutorial: Problem # Max points possible Actual score 1 15 2 15 3 10 4 15 5 15 6 15 7 10 8 10 9 15 Total 120 You have 180 minutes to
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2017
 Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2017 1 Vectors k is a scalar (a number) c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, c = ( c1 c 2 ) (Advanced: More precisely, a vector is defined in a vector space.
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2017 1 Vectors k is a scalar (a number) c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, c = ( c1 c 2 ) (Advanced: More precisely, a vector is defined in a vector space.
Properties of Matrices and Operations on Matrices
 Properties of Matrices and Operations on Matrices A common data structure for statistical analysis is a rectangular array or matris. Rows represent individual observational units, or just observations,
Properties of Matrices and Operations on Matrices A common data structure for statistical analysis is a rectangular array or matris. Rows represent individual observational units, or just observations,
Lecture notes on Quantum Computing. Chapter 1 Mathematical Background
 Lecture notes on Quantum Computing Chapter 1 Mathematical Background Vector states of a quantum system with n physical states are represented by unique vectors in C n, the set of n 1 column vectors 1 For
Lecture notes on Quantum Computing Chapter 1 Mathematical Background Vector states of a quantum system with n physical states are represented by unique vectors in C n, the set of n 1 column vectors 1 For
Summary of Week 9 B = then A A =
 Summary of Week 9 Finding the square root of a positive operator Last time we saw that positive operators have a unique positive square root We now briefly look at how one would go about calculating the
Summary of Week 9 Finding the square root of a positive operator Last time we saw that positive operators have a unique positive square root We now briefly look at how one would go about calculating the
Fall TMA4145 Linear Methods. Exercise set Given the matrix 1 2
 Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematical Sciences TMA445 Linear Methods Fall 07 Exercise set Please justify your answers! The most important part is how you arrive at an
Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematical Sciences TMA445 Linear Methods Fall 07 Exercise set Please justify your answers! The most important part is how you arrive at an
Linear Algebra Review. Fei-Fei Li
 Linear Algebra Review Fei-Fei Li 1 / 37 Vectors Vectors and matrices are just collections of ordered numbers that represent something: movements in space, scaling factors, pixel brightnesses, etc. A vector
Linear Algebra Review Fei-Fei Li 1 / 37 Vectors Vectors and matrices are just collections of ordered numbers that represent something: movements in space, scaling factors, pixel brightnesses, etc. A vector
MATH 583A REVIEW SESSION #1
 MATH 583A REVIEW SESSION #1 BOJAN DURICKOVIC 1. Vector Spaces Very quick review of the basic linear algebra concepts (see any linear algebra textbook): (finite dimensional) vector space (or linear space),
MATH 583A REVIEW SESSION #1 BOJAN DURICKOVIC 1. Vector Spaces Very quick review of the basic linear algebra concepts (see any linear algebra textbook): (finite dimensional) vector space (or linear space),
1. Linear systems of equations. Chapters 7-8: Linear Algebra. Solution(s) of a linear system of equations (continued)
 1 A linear system of equations of the form Sections 75, 78 & 81 a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 + + a 2n x n = b 2 a m1 x 1 + a m2 x 2 + + a mn x n = b m can be written in matrix
1 A linear system of equations of the form Sections 75, 78 & 81 a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 + + a 2n x n = b 2 a m1 x 1 + a m2 x 2 + + a mn x n = b m can be written in matrix
Math 408 Advanced Linear Algebra
 Math 408 Advanced Linear Algebra Chi-Kwong Li Chapter 4 Hermitian and symmetric matrices Basic properties Theorem Let A M n. The following are equivalent. Remark (a) A is Hermitian, i.e., A = A. (b) x
Math 408 Advanced Linear Algebra Chi-Kwong Li Chapter 4 Hermitian and symmetric matrices Basic properties Theorem Let A M n. The following are equivalent. Remark (a) A is Hermitian, i.e., A = A. (b) x
Lecture 7: Positive Semidefinite Matrices
 Lecture 7: Positive Semidefinite Matrices Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The main aim of this lecture note is to prepare your background for semidefinite programming. We have already seen some linear algebra.
Lecture 7: Positive Semidefinite Matrices Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The main aim of this lecture note is to prepare your background for semidefinite programming. We have already seen some linear algebra.
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators.
 MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators. Adjoint operator and adjoint matrix Given a linear operator L on an inner product space V, the adjoint of L is a transformation
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators. Adjoint operator and adjoint matrix Given a linear operator L on an inner product space V, the adjoint of L is a transformation
MATH 240 Spring, Chapter 1: Linear Equations and Matrices
 MATH 240 Spring, 2006 Chapter Summaries for Kolman / Hill, Elementary Linear Algebra, 8th Ed. Sections 1.1 1.6, 2.1 2.2, 3.2 3.8, 4.3 4.5, 5.1 5.3, 5.5, 6.1 6.5, 7.1 7.2, 7.4 DEFINITIONS Chapter 1: Linear
MATH 240 Spring, 2006 Chapter Summaries for Kolman / Hill, Elementary Linear Algebra, 8th Ed. Sections 1.1 1.6, 2.1 2.2, 3.2 3.8, 4.3 4.5, 5.1 5.3, 5.5, 6.1 6.5, 7.1 7.2, 7.4 DEFINITIONS Chapter 1: Linear
Singular Value Decomposition
 Singular Value Decomposition Motivatation The diagonalization theorem play a part in many interesting applications. Unfortunately not all matrices can be factored as A = PDP However a factorization A =
Singular Value Decomposition Motivatation The diagonalization theorem play a part in many interesting applications. Unfortunately not all matrices can be factored as A = PDP However a factorization A =
1 Linearity and Linear Systems
 Mathematical Tools for Neuroscience (NEU 34) Princeton University, Spring 26 Jonathan Pillow Lecture 7-8 notes: Linear systems & SVD Linearity and Linear Systems Linear system is a kind of mapping f( x)
Mathematical Tools for Neuroscience (NEU 34) Princeton University, Spring 26 Jonathan Pillow Lecture 7-8 notes: Linear systems & SVD Linearity and Linear Systems Linear system is a kind of mapping f( x)
Chapter 7: Symmetric Matrices and Quadratic Forms
 Chapter 7: Symmetric Matrices and Quadratic Forms (Last Updated: December, 06) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved
Chapter 7: Symmetric Matrices and Quadratic Forms (Last Updated: December, 06) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved
Dimensionality Reduction: PCA. Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas
 Dimensionality Reduction: PCA Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Eigenvalues λ is an eigenvalue of a matrix A R n n if the linear system Ax = λx has at least one non-zero solution If Ax = λx
Dimensionality Reduction: PCA Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Eigenvalues λ is an eigenvalue of a matrix A R n n if the linear system Ax = λx has at least one non-zero solution If Ax = λx
UNIT 6: The singular value decomposition.
 UNIT 6: The singular value decomposition. María Barbero Liñán Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Bachelor in Statistics and Business Mathematical methods II 2011-2012 A square matrix is symmetric if A T
UNIT 6: The singular value decomposition. María Barbero Liñán Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Bachelor in Statistics and Business Mathematical methods II 2011-2012 A square matrix is symmetric if A T
(VII.E) The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
 (VII.E) The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) In this section we describe a generalization of the Spectral Theorem to non-normal operators, and even to transformations between different vector spaces.
(VII.E) The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) In this section we describe a generalization of the Spectral Theorem to non-normal operators, and even to transformations between different vector spaces.
Review of some mathematical tools
 MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS OF SIGNAL PROCESSING Fall 2016 Benjamín Béjar Haro, Mihailo Kolundžija, Reza Parhizkar, Adam Scholefield Teaching assistants: Golnoosh Elhami, Hanjie Pan Review of some mathematical
MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS OF SIGNAL PROCESSING Fall 2016 Benjamín Béjar Haro, Mihailo Kolundžija, Reza Parhizkar, Adam Scholefield Teaching assistants: Golnoosh Elhami, Hanjie Pan Review of some mathematical
Multivariate Statistical Analysis
 Multivariate Statistical Analysis Fall 2011 C. L. Williams, Ph.D. Lecture 4 for Applied Multivariate Analysis Outline 1 Eigen values and eigen vectors Characteristic equation Some properties of eigendecompositions
Multivariate Statistical Analysis Fall 2011 C. L. Williams, Ph.D. Lecture 4 for Applied Multivariate Analysis Outline 1 Eigen values and eigen vectors Characteristic equation Some properties of eigendecompositions
1 Inner Product and Orthogonality
 CSCI 4/Fall 6/Vora/GWU/Orthogonality and Norms Inner Product and Orthogonality Definition : The inner product of two vectors x and y, x x x =.., y =. x n y y... y n is denoted x, y : Note that n x, y =
CSCI 4/Fall 6/Vora/GWU/Orthogonality and Norms Inner Product and Orthogonality Definition : The inner product of two vectors x and y, x x x =.., y =. x n y y... y n is denoted x, y : Note that n x, y =
The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
 Chapter 5 The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA) 5.1 Basics of SVD 5.1.1 Review of Key Concepts We review some key definitions and results about matrices that will
Chapter 5 The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA) 5.1 Basics of SVD 5.1.1 Review of Key Concepts We review some key definitions and results about matrices that will
Functional Analysis Review
 Outline 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 3 4 Vector Space Outline A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V V such that for all
Outline 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 3 4 Vector Space Outline A vector space is a set V with binary operations +: V V V and : R V V such that for all
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Answer any eight)
 Name of the student : Roll No : CS65: Linear Algebra and Random Processes Exam - Course Instructor : Prashanth L.A. Date : Sep-24, 27 Duration : 5 minutes INSTRUCTIONS: The test will be evaluated ONLY
Name of the student : Roll No : CS65: Linear Algebra and Random Processes Exam - Course Instructor : Prashanth L.A. Date : Sep-24, 27 Duration : 5 minutes INSTRUCTIONS: The test will be evaluated ONLY
The University of Texas at Austin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EE381V: Large Scale Learning Spring 2013.
 The University of Texas at Austin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE381V: Large Scale Learning Spring 2013 Assignment Two Caramanis/Sanghavi Due: Tuesday, Feb. 19, 2013. Computational
The University of Texas at Austin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE381V: Large Scale Learning Spring 2013 Assignment Two Caramanis/Sanghavi Due: Tuesday, Feb. 19, 2013. Computational
Glossary of Linear Algebra Terms. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Glossary of Linear Algebra Terms Basis (for a subspace) A linearly independent set of vectors that spans the space Basic Variable A variable in a linear system that corresponds to a pivot column in the
Glossary of Linear Algebra Terms Basis (for a subspace) A linearly independent set of vectors that spans the space Basic Variable A variable in a linear system that corresponds to a pivot column in the
MATHEMATICS 217 NOTES
 MATHEMATICS 27 NOTES PART I THE JORDAN CANONICAL FORM The characteristic polynomial of an n n matrix A is the polynomial χ A (λ) = det(λi A), a monic polynomial of degree n; a monic polynomial in the variable
MATHEMATICS 27 NOTES PART I THE JORDAN CANONICAL FORM The characteristic polynomial of an n n matrix A is the polynomial χ A (λ) = det(λi A), a monic polynomial of degree n; a monic polynomial in the variable
1. What is the determinant of the following matrix? a 1 a 2 4a 3 2a 2 b 1 b 2 4b 3 2b c 1. = 4, then det
 What is the determinant of the following matrix? 3 4 3 4 3 4 4 3 A 0 B 8 C 55 D 0 E 60 If det a a a 3 b b b 3 c c c 3 = 4, then det a a 4a 3 a b b 4b 3 b c c c 3 c = A 8 B 6 C 4 D E 3 Let A be an n n matrix
What is the determinant of the following matrix? 3 4 3 4 3 4 4 3 A 0 B 8 C 55 D 0 E 60 If det a a a 3 b b b 3 c c c 3 = 4, then det a a 4a 3 a b b 4b 3 b c c c 3 c = A 8 B 6 C 4 D E 3 Let A be an n n matrix
Background Mathematics (2/2) 1. David Barber
 Background Mathematics (2/2) 1 David Barber University College London Modified by Samson Cheung (sccheung@ieee.org) 1 These slides accompany the book Bayesian Reasoning and Machine Learning. The book and
Background Mathematics (2/2) 1 David Barber University College London Modified by Samson Cheung (sccheung@ieee.org) 1 These slides accompany the book Bayesian Reasoning and Machine Learning. The book and
COMP 558 lecture 18 Nov. 15, 2010
 Least squares We have seen several least squares problems thus far, and we will see more in the upcoming lectures. For this reason it is good to have a more general picture of these problems and how to
Least squares We have seen several least squares problems thus far, and we will see more in the upcoming lectures. For this reason it is good to have a more general picture of these problems and how to
Math 102, Winter Final Exam Review. Chapter 1. Matrices and Gaussian Elimination
 Math 0, Winter 07 Final Exam Review Chapter. Matrices and Gaussian Elimination { x + x =,. Different forms of a system of linear equations. Example: The x + 4x = 4. [ ] [ ] [ ] vector form (or the column
Math 0, Winter 07 Final Exam Review Chapter. Matrices and Gaussian Elimination { x + x =,. Different forms of a system of linear equations. Example: The x + 4x = 4. [ ] [ ] [ ] vector form (or the column
Matrices and Vectors. Definition of Matrix. An MxN matrix A is a two-dimensional array of numbers A =
 30 MATHEMATICS REVIEW G A.1.1 Matrices and Vectors Definition of Matrix. An MxN matrix A is a two-dimensional array of numbers A = a 11 a 12... a 1N a 21 a 22... a 2N...... a M1 a M2... a MN A matrix can
30 MATHEMATICS REVIEW G A.1.1 Matrices and Vectors Definition of Matrix. An MxN matrix A is a two-dimensional array of numbers A = a 11 a 12... a 1N a 21 a 22... a 2N...... a M1 a M2... a MN A matrix can
Positive Definite Matrix
 1/29 Chia-Ping Chen Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Linear Algebra Positive Definite, Negative Definite, Indefinite 2/29 Pure Quadratic Function
1/29 Chia-Ping Chen Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Linear Algebra Positive Definite, Negative Definite, Indefinite 2/29 Pure Quadratic Function
Notes on the matrix exponential
 Notes on the matrix exponential Erik Wahlén erik.wahlen@math.lu.se February 14, 212 1 Introduction The purpose of these notes is to describe how one can compute the matrix exponential e A when A is not
Notes on the matrix exponential Erik Wahlén erik.wahlen@math.lu.se February 14, 212 1 Introduction The purpose of these notes is to describe how one can compute the matrix exponential e A when A is not
Solutions to Final Practice Problems Written by Victoria Kala Last updated 12/5/2015
 Solutions to Final Practice Problems Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu Last updated /5/05 Answers This page contains answers only. See the following pages for detailed solutions. (. (a x. See
Solutions to Final Practice Problems Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu Last updated /5/05 Answers This page contains answers only. See the following pages for detailed solutions. (. (a x. See
Final Exam, Linear Algebra, Fall, 2003, W. Stephen Wilson
 Final Exam, Linear Algebra, Fall, 2003, W. Stephen Wilson Name: TA Name and section: NO CALCULATORS, SHOW ALL WORK, NO OTHER PAPERS ON DESK. There is very little actual work to be done on this exam if
Final Exam, Linear Algebra, Fall, 2003, W. Stephen Wilson Name: TA Name and section: NO CALCULATORS, SHOW ALL WORK, NO OTHER PAPERS ON DESK. There is very little actual work to be done on this exam if
Computational math: Assignment 1
 Computational math: Assignment 1 Thanks Ting Gao for her Latex file 11 Let B be a 4 4 matrix to which we apply the following operations: 1double column 1, halve row 3, 3add row 3 to row 1, 4interchange
Computational math: Assignment 1 Thanks Ting Gao for her Latex file 11 Let B be a 4 4 matrix to which we apply the following operations: 1double column 1, halve row 3, 3add row 3 to row 1, 4interchange
3D Computer Vision - WT 2004
 3D Computer Vision - WT 2004 Singular Value Decomposition Darko Zikic CAMP - Chair for Computer Aided Medical Procedures November 4, 2004 1 2 3 4 5 Properties For any given matrix A R m n there exists
3D Computer Vision - WT 2004 Singular Value Decomposition Darko Zikic CAMP - Chair for Computer Aided Medical Procedures November 4, 2004 1 2 3 4 5 Properties For any given matrix A R m n there exists
Math Final December 2006 C. Robinson
 Math 285-1 Final December 2006 C. Robinson 2 5 8 5 1 2 0-1 0 1. (21 Points) The matrix A = 1 2 2 3 1 8 3 2 6 has the reduced echelon form U = 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 1. 2 6 1 0 0 0 0 0 a. Find a basis for the
Math 285-1 Final December 2006 C. Robinson 2 5 8 5 1 2 0-1 0 1. (21 Points) The matrix A = 1 2 2 3 1 8 3 2 6 has the reduced echelon form U = 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 1. 2 6 1 0 0 0 0 0 a. Find a basis for the
Quantum Computing Lecture 2. Review of Linear Algebra
 Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
Lecture 2: Linear operators
 Lecture 2: Linear operators Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The mathematical formulation of Quantum computing requires vector spaces and linear operators So, we need to be comfortable with linear algebra to study
Lecture 2: Linear operators Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The mathematical formulation of Quantum computing requires vector spaces and linear operators So, we need to be comfortable with linear algebra to study
Symmetric and self-adjoint matrices
 Symmetric and self-adjoint matrices A matrix A in M n (F) is called symmetric if A T = A, ie A ij = A ji for each i, j; and self-adjoint if A = A, ie A ij = A ji or each i, j Note for A in M n (R) that
Symmetric and self-adjoint matrices A matrix A in M n (F) is called symmetric if A T = A, ie A ij = A ji for each i, j; and self-adjoint if A = A, ie A ij = A ji or each i, j Note for A in M n (R) that
Linear Least Squares. Using SVD Decomposition.
 Linear Least Squares. Using SVD Decomposition. Dmitriy Leykekhman Spring 2011 Goals SVD-decomposition. Solving LLS with SVD-decomposition. D. Leykekhman Linear Least Squares 1 SVD Decomposition. For any
Linear Least Squares. Using SVD Decomposition. Dmitriy Leykekhman Spring 2011 Goals SVD-decomposition. Solving LLS with SVD-decomposition. D. Leykekhman Linear Least Squares 1 SVD Decomposition. For any
Ir O D = D = ( ) Section 2.6 Example 1. (Bottom of page 119) dim(v ) = dim(l(v, W )) = dim(v ) dim(f ) = dim(v )
 Section 3.2 Theorem 3.6. Let A be an m n matrix of rank r. Then r m, r n, and, by means of a finite number of elementary row and column operations, A can be transformed into the matrix ( ) Ir O D = 1 O
Section 3.2 Theorem 3.6. Let A be an m n matrix of rank r. Then r m, r n, and, by means of a finite number of elementary row and column operations, A can be transformed into the matrix ( ) Ir O D = 1 O
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA WITH APPLICATIONS. 1. Linear Equations and Matrices
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA WITH APPLICATIONS KOLMAN & HILL NOTES BY OTTO MUTZBAUER 11 Systems of Linear Equations 1 Linear Equations and Matrices Numbers in our context are either real numbers or complex
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA WITH APPLICATIONS KOLMAN & HILL NOTES BY OTTO MUTZBAUER 11 Systems of Linear Equations 1 Linear Equations and Matrices Numbers in our context are either real numbers or complex
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 23: Diagonalization. Review for Test 2.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 23: Diagonalization. Review for Test 2. Diagonalization Let L be a linear operator on a finite-dimensional vector space V. Then the following conditions are equivalent:
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 23: Diagonalization. Review for Test 2. Diagonalization Let L be a linear operator on a finite-dimensional vector space V. Then the following conditions are equivalent:
Linear Algebra Review. Fei-Fei Li
 Linear Algebra Review Fei-Fei Li 1 / 51 Vectors Vectors and matrices are just collections of ordered numbers that represent something: movements in space, scaling factors, pixel brightnesses, etc. A vector
Linear Algebra Review Fei-Fei Li 1 / 51 Vectors Vectors and matrices are just collections of ordered numbers that represent something: movements in space, scaling factors, pixel brightnesses, etc. A vector
2. Linear algebra. matrices and vectors. linear equations. range and nullspace of matrices. function of vectors, gradient and Hessian
 FE661 - Statistical Methods for Financial Engineering 2. Linear algebra Jitkomut Songsiri matrices and vectors linear equations range and nullspace of matrices function of vectors, gradient and Hessian
FE661 - Statistical Methods for Financial Engineering 2. Linear algebra Jitkomut Songsiri matrices and vectors linear equations range and nullspace of matrices function of vectors, gradient and Hessian
Linear Algebra, part 3 QR and SVD
 Linear Algebra, part 3 QR and SVD Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2012 Going back to least squares (Section 1.4 from Strang, now also see section 5.2). We
Linear Algebra, part 3 QR and SVD Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2012 Going back to least squares (Section 1.4 from Strang, now also see section 5.2). We
Review of similarity transformation and Singular Value Decomposition
 Review of similarity transformation and Singular Value Decomposition Nasser M Abbasi Applied Mathematics Department, California State University, Fullerton July 8 7 page compiled on June 9, 5 at 9:5pm
Review of similarity transformation and Singular Value Decomposition Nasser M Abbasi Applied Mathematics Department, California State University, Fullerton July 8 7 page compiled on June 9, 5 at 9:5pm
Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2
 Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University February 6, 2018 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 February 6, 2018
Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University February 6, 2018 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra using Dirac Notation: Pt. 2 February 6, 2018
PRACTICE FINAL EXAM. why. If they are dependent, exhibit a linear dependence relation among them.
 Prof A Suciu MTH U37 LINEAR ALGEBRA Spring 2005 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Are the following vectors independent or dependent? If they are independent, say why If they are dependent, exhibit a linear dependence
Prof A Suciu MTH U37 LINEAR ALGEBRA Spring 2005 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Are the following vectors independent or dependent? If they are independent, say why If they are dependent, exhibit a linear dependence
The Singular Value Decomposition
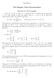 CHAPTER 6 The Singular Value Decomposition Exercise 67: SVD examples (a) For A =[, 4] T we find a matrixa T A =5,whichhastheeigenvalue =5 Thisprovidesuswiththesingularvalue =+ p =5forA Hence the matrix
CHAPTER 6 The Singular Value Decomposition Exercise 67: SVD examples (a) For A =[, 4] T we find a matrixa T A =5,whichhastheeigenvalue =5 Thisprovidesuswiththesingularvalue =+ p =5forA Hence the matrix
Linear Algebra, part 3. Going back to least squares. Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation = 0. a T 1 e. a T n e. Anna-Karin Tornberg
 Linear Algebra, part 3 Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2010 Going back to least squares (Sections 1.7 and 2.3 from Strang). We know from before: The vector
Linear Algebra, part 3 Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2010 Going back to least squares (Sections 1.7 and 2.3 from Strang). We know from before: The vector
Review of Some Concepts from Linear Algebra: Part 2
 Review of Some Concepts from Linear Algebra: Part 2 Department of Mathematics Boise State University January 16, 2019 Math 566 Linear Algebra Review: Part 2 January 16, 2019 1 / 22 Vector spaces A set
Review of Some Concepts from Linear Algebra: Part 2 Department of Mathematics Boise State University January 16, 2019 Math 566 Linear Algebra Review: Part 2 January 16, 2019 1 / 22 Vector spaces A set
Lecture notes: Applied linear algebra Part 1. Version 2
 Lecture notes: Applied linear algebra Part 1. Version 2 Michael Karow Berlin University of Technology karow@math.tu-berlin.de October 2, 2008 1 Notation, basic notions and facts 1.1 Subspaces, range and
Lecture notes: Applied linear algebra Part 1. Version 2 Michael Karow Berlin University of Technology karow@math.tu-berlin.de October 2, 2008 1 Notation, basic notions and facts 1.1 Subspaces, range and
Foundations of Matrix Analysis
 1 Foundations of Matrix Analysis In this chapter we recall the basic elements of linear algebra which will be employed in the remainder of the text For most of the proofs as well as for the details, the
1 Foundations of Matrix Analysis In this chapter we recall the basic elements of linear algebra which will be employed in the remainder of the text For most of the proofs as well as for the details, the
Applied Mathematics 205. Unit V: Eigenvalue Problems. Lecturer: Dr. David Knezevic
 Applied Mathematics 205 Unit V: Eigenvalue Problems Lecturer: Dr. David Knezevic Unit V: Eigenvalue Problems Chapter V.2: Fundamentals 2 / 31 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Eigenvalues and eigenvectors of
Applied Mathematics 205 Unit V: Eigenvalue Problems Lecturer: Dr. David Knezevic Unit V: Eigenvalue Problems Chapter V.2: Fundamentals 2 / 31 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Eigenvalues and eigenvectors of
Pseudoinverse & Moore-Penrose Conditions
 ECE 275AB Lecture 7 Fall 2008 V1.0 c K. Kreutz-Delgado, UC San Diego p. 1/1 Lecture 7 ECE 275A Pseudoinverse & Moore-Penrose Conditions ECE 275AB Lecture 7 Fall 2008 V1.0 c K. Kreutz-Delgado, UC San Diego
ECE 275AB Lecture 7 Fall 2008 V1.0 c K. Kreutz-Delgado, UC San Diego p. 1/1 Lecture 7 ECE 275A Pseudoinverse & Moore-Penrose Conditions ECE 275AB Lecture 7 Fall 2008 V1.0 c K. Kreutz-Delgado, UC San Diego
ALGEBRA QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEMS LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ALGEBRA QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEMS LINEAR ALGEBRA Kent State University Department of Mathematical Sciences Compiled and Maintained by Donald L. White Version: August 29, 2017 CONTENTS LINEAR ALGEBRA AND
ALGEBRA QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEMS LINEAR ALGEBRA Kent State University Department of Mathematical Sciences Compiled and Maintained by Donald L. White Version: August 29, 2017 CONTENTS LINEAR ALGEBRA AND
MODULE 8 Topics: Null space, range, column space, row space and rank of a matrix
 MODULE 8 Topics: Null space, range, column space, row space and rank of a matrix Definition: Let L : V 1 V 2 be a linear operator. The null space N (L) of L is the subspace of V 1 defined by N (L) = {x
MODULE 8 Topics: Null space, range, column space, row space and rank of a matrix Definition: Let L : V 1 V 2 be a linear operator. The null space N (L) of L is the subspace of V 1 defined by N (L) = {x
Math 4A Notes. Written by Victoria Kala Last updated June 11, 2017
 Math 4A Notes Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu Last updated June 11, 2017 Systems of Linear Equations A linear equation is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 +...
Math 4A Notes Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu Last updated June 11, 2017 Systems of Linear Equations A linear equation is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 +...
j=1 u 1jv 1j. 1/ 2 Lemma 1. An orthogonal set of vectors must be linearly independent.
 Lecture Notes: Orthogonal and Symmetric Matrices Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong taoyf@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Orthogonal Matrix Definition. Let u = [u
Lecture Notes: Orthogonal and Symmetric Matrices Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong taoyf@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Orthogonal Matrix Definition. Let u = [u
Singular Value Decomposition
 Singular Value Decomposition CS 205A: Mathematical Methods for Robotics, Vision, and Graphics Doug James (and Justin Solomon) CS 205A: Mathematical Methods Singular Value Decomposition 1 / 35 Understanding
Singular Value Decomposition CS 205A: Mathematical Methods for Robotics, Vision, and Graphics Doug James (and Justin Solomon) CS 205A: Mathematical Methods Singular Value Decomposition 1 / 35 Understanding
The Singular Value Decomposition
 The Singular Value Decomposition An Important topic in NLA Radu Tiberiu Trîmbiţaş Babeş-Bolyai University February 23, 2009 Radu Tiberiu Trîmbiţaş ( Babeş-Bolyai University)The Singular Value Decomposition
The Singular Value Decomposition An Important topic in NLA Radu Tiberiu Trîmbiţaş Babeş-Bolyai University February 23, 2009 Radu Tiberiu Trîmbiţaş ( Babeş-Bolyai University)The Singular Value Decomposition
14 Singular Value Decomposition
 14 Singular Value Decomposition For any high-dimensional data analysis, one s first thought should often be: can I use an SVD? The singular value decomposition is an invaluable analysis tool for dealing
14 Singular Value Decomposition For any high-dimensional data analysis, one s first thought should often be: can I use an SVD? The singular value decomposition is an invaluable analysis tool for dealing
Control Systems. Linear Algebra topics. L. Lanari
 Control Systems Linear Algebra topics L Lanari outline basic facts about matrices eigenvalues - eigenvectors - characteristic polynomial - algebraic multiplicity eigenvalues invariance under similarity
Control Systems Linear Algebra topics L Lanari outline basic facts about matrices eigenvalues - eigenvectors - characteristic polynomial - algebraic multiplicity eigenvalues invariance under similarity
Singular Value Decomposition and Polar Form
 Chapter 12 Singular Value Decomposition and Polar Form 12.1 Singular Value Decomposition for Square Matrices Let f : E! E be any linear map, where E is a Euclidean space. In general, it may not be possible
Chapter 12 Singular Value Decomposition and Polar Form 12.1 Singular Value Decomposition for Square Matrices Let f : E! E be any linear map, where E is a Euclidean space. In general, it may not be possible
Linear Algebra Formulas. Ben Lee
 Linear Algebra Formulas Ben Lee January 27, 2016 Definitions and Terms Diagonal: Diagonal of matrix A is a collection of entries A ij where i = j. Diagonal Matrix: A matrix (usually square), where entries
Linear Algebra Formulas Ben Lee January 27, 2016 Definitions and Terms Diagonal: Diagonal of matrix A is a collection of entries A ij where i = j. Diagonal Matrix: A matrix (usually square), where entries
Math Linear Algebra II. 1. Inner Products and Norms
 Math 342 - Linear Algebra II Notes 1. Inner Products and Norms One knows from a basic introduction to vectors in R n Math 254 at OSU) that the length of a vector x = x 1 x 2... x n ) T R n, denoted x,
Math 342 - Linear Algebra II Notes 1. Inner Products and Norms One knows from a basic introduction to vectors in R n Math 254 at OSU) that the length of a vector x = x 1 x 2... x n ) T R n, denoted x,
Jordan Normal Form and Singular Decomposition
 University of Debrecen Diagonalization and eigenvalues Diagonalization We have seen that if A is an n n square matrix, then A is diagonalizable if and only if for all λ eigenvalues of A we have dim(u λ
University of Debrecen Diagonalization and eigenvalues Diagonalization We have seen that if A is an n n square matrix, then A is diagonalizable if and only if for all λ eigenvalues of A we have dim(u λ
LinGloss. A glossary of linear algebra
 LinGloss A glossary of linear algebra Contents: Decompositions Types of Matrices Theorems Other objects? Quasi-triangular A matrix A is quasi-triangular iff it is a triangular matrix except its diagonal
LinGloss A glossary of linear algebra Contents: Decompositions Types of Matrices Theorems Other objects? Quasi-triangular A matrix A is quasi-triangular iff it is a triangular matrix except its diagonal
STAT 309: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 2017 LECTURE 5
 STAT 39: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 17 LECTURE 5 1 existence of svd Theorem 1 (Existence of SVD) Every matrix has a singular value decomposition (condensed version) Proof Let A C m n and for simplicity
STAT 39: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 17 LECTURE 5 1 existence of svd Theorem 1 (Existence of SVD) Every matrix has a singular value decomposition (condensed version) Proof Let A C m n and for simplicity
Elementary linear algebra
 Chapter 1 Elementary linear algebra 1.1 Vector spaces Vector spaces owe their importance to the fact that so many models arising in the solutions of specific problems turn out to be vector spaces. The
Chapter 1 Elementary linear algebra 1.1 Vector spaces Vector spaces owe their importance to the fact that so many models arising in the solutions of specific problems turn out to be vector spaces. The
Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering
 Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering Lectures 13 15, Tuesday 8 th and Friday 11 th November 016 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE
Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering Lectures 13 15, Tuesday 8 th and Friday 11 th November 016 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE
Assignment #10: Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices, Quadratic Forms, Optimization, Singular Value Decomposition. Name:
 Assignment #10: Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices, Quadratic Forms, Optimization, Singular Value Decomposition Due date: Friday, May 4, 2018 (1:35pm) Name: Section Number Assignment #10: Diagonalization
Assignment #10: Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices, Quadratic Forms, Optimization, Singular Value Decomposition Due date: Friday, May 4, 2018 (1:35pm) Name: Section Number Assignment #10: Diagonalization
Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB
 Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional Plots Programming in
Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional Plots Programming in
Jordan normal form notes (version date: 11/21/07)
 Jordan normal form notes (version date: /2/7) If A has an eigenbasis {u,, u n }, ie a basis made up of eigenvectors, so that Au j = λ j u j, then A is diagonal with respect to that basis To see this, let
Jordan normal form notes (version date: /2/7) If A has an eigenbasis {u,, u n }, ie a basis made up of eigenvectors, so that Au j = λ j u j, then A is diagonal with respect to that basis To see this, let
Frame Diagonalization of Matrices
 Frame Diagonalization of Matrices Fumiko Futamura Mathematics and Computer Science Department Southwestern University 00 E University Ave Georgetown, Texas 78626 U.S.A. Phone: + (52) 863-98 Fax: + (52)
Frame Diagonalization of Matrices Fumiko Futamura Mathematics and Computer Science Department Southwestern University 00 E University Ave Georgetown, Texas 78626 U.S.A. Phone: + (52) 863-98 Fax: + (52)
Lecture 2: Linear Algebra Review
 EE 227A: Convex Optimization and Applications January 19 Lecture 2: Linear Algebra Review Lecturer: Mert Pilanci Reading assignment: Appendix C of BV. Sections 2-6 of the web textbook 1 2.1 Vectors 2.1.1
EE 227A: Convex Optimization and Applications January 19 Lecture 2: Linear Algebra Review Lecturer: Mert Pilanci Reading assignment: Appendix C of BV. Sections 2-6 of the web textbook 1 2.1 Vectors 2.1.1
CS 143 Linear Algebra Review
 CS 143 Linear Algebra Review Stefan Roth September 29, 2003 Introductory Remarks This review does not aim at mathematical rigor very much, but instead at ease of understanding and conciseness. Please see
CS 143 Linear Algebra Review Stefan Roth September 29, 2003 Introductory Remarks This review does not aim at mathematical rigor very much, but instead at ease of understanding and conciseness. Please see
Large Scale Data Analysis Using Deep Learning
 Large Scale Data Analysis Using Deep Learning Linear Algebra U Kang Seoul National University U Kang 1 In This Lecture Overview of linear algebra (but, not a comprehensive survey) Focused on the subset
Large Scale Data Analysis Using Deep Learning Linear Algebra U Kang Seoul National University U Kang 1 In This Lecture Overview of linear algebra (but, not a comprehensive survey) Focused on the subset
Linear Algebra- Final Exam Review
 Linear Algebra- Final Exam Review. Let A be invertible. Show that, if v, v, v 3 are linearly independent vectors, so are Av, Av, Av 3. NOTE: It should be clear from your answer that you know the definition.
Linear Algebra- Final Exam Review. Let A be invertible. Show that, if v, v, v 3 are linearly independent vectors, so are Av, Av, Av 3. NOTE: It should be clear from your answer that you know the definition.
Lecture 2: Linear Algebra
 Lecture 2: Linear Algebra Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur We will start with the basics of linear algebra that will be needed throughout this course That means, we will learn about vector spaces, linear independence,
Lecture 2: Linear Algebra Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur We will start with the basics of linear algebra that will be needed throughout this course That means, we will learn about vector spaces, linear independence,
 MTH50 Spring 07 HW Assignment 7 {From [FIS0]}: Sec 44 #4a h 6; Sec 5 #ad ac 4ae 4 7 The due date for this assignment is 04/05/7 Sec 44 #4a h Evaluate the erminant of the following matrices by any legitimate
MTH50 Spring 07 HW Assignment 7 {From [FIS0]}: Sec 44 #4a h 6; Sec 5 #ad ac 4ae 4 7 The due date for this assignment is 04/05/7 Sec 44 #4a h Evaluate the erminant of the following matrices by any legitimate
Image Registration Lecture 2: Vectors and Matrices
 Image Registration Lecture 2: Vectors and Matrices Prof. Charlene Tsai Lecture Overview Vectors Matrices Basics Orthogonal matrices Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) 2 1 Preliminary Comments Some of this
Image Registration Lecture 2: Vectors and Matrices Prof. Charlene Tsai Lecture Overview Vectors Matrices Basics Orthogonal matrices Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) 2 1 Preliminary Comments Some of this
