09a. Collapse. Recall: There are two ways a quantum state can change: 1. In absence of measurement, states change via Schrödinger dynamics:
|
|
|
- Adelia Horton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 09a. Collapse Recall: There are two ways a quantum state can change:. In absence of measurement, states change via Schrödinger dynamics: ψ(t )!!! ψ(t 2 ) Schrödinger evolution 2. In presence of measurement, states change via the Projection Postulate: When a measurement of property B is made on a state ψ = a b a N b N expanded in the eigenvector basis of B with result b i, then ψ collapses to b i : ψ!!! b i collapse Problems:! What is a measurement?! When is the Projection Postulate supposed to take over from the Schrödinger dynamics?
2 Possible Responses:. When a conscious observer looks at a measuring device. Consequence: Dualism -- 2 fundamentally different types of physical system.! Purely physical systems: Always evolve via Schrödinger dynamics.! Conscious systems: Interact with physical systems in certain situations to cause collapse via Projection Postulate. Eugene Wigner 2. When a macroscopic system interacts with a microscopic system. Consequence: Dualism again -- 2 fundamentally different types of physical system.! Microscopic systems: Always evolve via Schrödinger dynamics.! Macroscopic systems: Interact with microscopic systems in certain situations to cause collapse via Projection Postulate.
3 Can experiments determine when a collapse occurs? black electron ready "hard" "soft" In principle, Yes! But in practice, No! initial state at t 0 ( ) What is final state at t > t 0?! 2 ready m hard e + ready m soft e Theory : Collapse occurs at t. Prediction : At t, state will be: either "hard" m hard e or "soft" m soft e, each with prob = /2." Theory 2: Collapse occurs after t. Prediction 2: At t, state will be: "hard" 2 ( hard + "soft" soft m e m e ). Suppose the m-e entangled state of Theory 2 has a measureable "2-particle" property that neither of the m-e separable states of Theory have. This would let us distinguish between Theory and Theory 2.
4 Task: Find a "2-particle" property of the entangled m-e state of Prediction that is not possessed by the separable m-e states of Prediction 2. We have Hardness H e and Color C e operators that act on states of e: H e hard e = + hard e H e soft e = soft e C e black e = + black e C e white e = white e Now define properties and states for m.! Let "Hardness" operator H m represent the property of m of pointing to either ready, "hard", or "soft".! Let ready m, "hard" m, "soft" m be states of m that are eigenvectors of H m.! Let "Color" operator C m represent property of m of pointing to either ready, "black", or "soft".! Let ready m, "black" m, "white" m be states of m that are eigenvectors of C m.
5 Represent the states of m by column vectors: ready m = "hard " m = 0 0 "soft " m = 0 0 "black " m = "white " m = Then: ( ) ( ) "hard " m = 2 "black " m + "white " "soft " m = 2 "black " m "white " ( ) ( ) "black " m = 2 "hard " m + "soft " "white " m = 2 "hard " m "soft " Represent the "Hardness" and "Color" operators by: H m = C m = Then: H m ready m = 0 ready m C m ready m = 0 ready m H m "hard" m = + "hard" m C m "black" m = + "black" m H m "soft" m = "soft" m C m "white" m = "white" m
6 The 2-particle operator C m I e represents m's "Color" in the 2-particle system. The 2-particle operator I m C e represents e's Color in the 2-particle system. And: The 2-particle operator (C m I e ) (I m C e ) represents another 2- particle property, call it ("Color" Color). Recall: The final states of predicted by Theories and 2 are given by T = T2 = "hard" m hard e (prob = /2) "soft" m soft e (prob = /2) "hard " 2 ( hard + "soft " soft m e m e ). Claim: T2 is an eigenstate of (C m I e ) (I m C e ) with eigenvalue 0, but T in either form is not! So: At time t we can (in principle) measure the property ("Color" Color).! If Theory 2 is correct, the value should always be 0.! If Theory is correct, measurements should yield values other than 0.
7 But: What happens if there is a single air molecule in the measuring device? black electron ready "hard" "soft" System is now a "3- particle" system m-e-a. Let center a represent state of air molecule located underneath "hard" pointer-reading. Let right a represent state of air molecule located underneath "soft" pointer-reading. Theory : Collapse occurs at t. Prediction : At t, state will be: either "hard" m hard e center a or "soft" m soft e right a, each with prob = /2. Theory 2: Collapse occurs after t. Prediction 2: At t, state will be: "hard " hard center + 2 m e a "soft " soft right. 2 m e a These predictions are not eigenstates of ("Color" Color)! To tell them apart, need a more complicated, 3-particle property of the m-e-a system. If there are other microscopic systems in m, need even more complicated multi-particle properties.
8 09b. GRW Collapse Theory Ghirardi, Rimini, Weber (986) Motivation: Most (all?) properties can be correlated with the position of a pointer in an appropriate measuring device. We can maintain Option A if we stipulate that (for whatever reason) superpositions of position eigenstates collapse with high probability. GRW Dynamical Law During any time interval, there is a non-zero probability that the state of an elementary particle will collapse to a position eigenstate. Suppose ψ represents the state of an elementary particle. Expand ψ in a basis of eigenvectors of position: ψ = a x a N x N. The GRW Collapse Theory says:! ψ generally evolves via the Schrödinger dynamics.! But there is a non-zero chance that ψ will collapse to a position eigenstate.! If this occurs, the probability of it ending up in the specific position eigenstate x i is given by the Born Rule: Pr(particle is located at position x i in state ψ ) = ψ x i 2 = ψ(x i ) 2
9 Why this helps: Consider the entangled composite state of pointer particles and electron: x x x... 2 ( 2 3 ) hard e + x 2 ( x x ) soft e Position states of pointer particles when pointer is located at the position, call it x, that registers "hard". Position states of pointer particles when pointer is located at the position, call it x 2, that registers "soft". Particle is in a superposition of being located at x and x 2, particle 2 is is a superposition of being located at x and x 2, etc. If just one of all of these (trillions of) pointer particles has a definite location, then according to the Projection Postulate, the composite state will collapse to the term containing that position eigenstate. So: Even if the probability of collapse in the GRW Law is extremely small, since any measuring device has trillions of particles, any superposition containing them will have an extremely likely chance of collapsing. Upshot: By modifying the Schrödinger dynamics with the GRW Law we guarantee that pointers in measuring devices will always have well-defined post-measurement positions.
10 The GRW Law in terms of Wavefunctions: Let ψ = a x a N x N represent the state of an elementary particle expanded in a basis of eigenvectors of position. The corresponding position wavefunction is defined by ψ(x) = ψ x. ψ(x) encodes all the values of the expansion coefficients. Ex: ψ(x i ) = a i. Now: Represent state vector collapse: ψ!!! x i collapse as wavefunction collapse: ψ(x)!!! ψ(x i ) collapse general form of wavefunction for all position eigenstates specific form of wavefunction for state x i Mathematically, wavefunction collapse is accomplished by multiplying the general wavefunction ψ(x) by a Dirac delta function δ(x x i ): "ψ(x i ) = δ(x x i )ψ(x)"
11 The Dirac Delta Function Think of δ(x x i ) as a position eigenfunction. It is an infinite spike exactly at x i, and zero everywhere else: δ(x x i ) δ(x x') is "defined" by the following: () δ(x x') = 0, when x x'. (2) δ(x x') =, when x = x'. Initial Problem: x i x (3) (4) δ(x x')dx' =. δ(x x')f(x)dx' If our state is represented by an eigenvector of position, then according to the EE Rule, this means that it has a definite value of position (namely, x i ). So, more precisely, ψ(x i ) = = f(x'), for any f(x). δ(x x i )ψ(x)dx. So: Properties incompatible with position will be maximally indeterminate. Uncertainty in position = 0 Uncertainty in momentum =! When a GRW collapse occurs (and we get an exact value of position), we could potentially have violations of conservation of momentum and energy!
12 Technical Solution For GRW collapses, instead of multiplying the wavefunction by a Dirac delta function δ(x x i ), use a Gaussian (i.e., Bell-shaped) function g L (x x i ) spread out a finite width L about x i. L x i g L (x x ) = e (x x )/L2 πl 2 x The Gaussian function is a legitimate function. Centered at x'. Width = L. Maximum height = Unit area. πl 2. lim g L 0 L (x x ) = δ(x x i ). Can choose L so that the uncertainty in momentum is effectively cut-off. The price: We've had to smear the position about x i.
13 Essential Characteristics of GRW Collapse Theory:. Modifies Schrödinger dynamics with GRW Law. 2. Keeps Projection Postulate. 3. Introduces two new constants of nature: (a) Probability per time per particle of collapse. (b) Width L of Gaussian position eigenfunctions.
14 Problems. Wavefunction Tails We just saw that GRW needs Gaussian position functions g L (x x i ) in order to avoid violations of energy/momentum conservation. But: g L (x x i ) is never zero: It has non-vanishing tails. g L (x x i ) The tails asymptotically approach the x-axis, but never reach it, no matter how far away from x i you get. g L (x x i ) 0 for all finite values of x. x i x So: Even after a GRW collapse, an elementary particle is still in a superposition of position eigenvectors (there is still a non-zero probability of finding it at some location x x i ). Thus: According to the EE Rule, it still has no definite value of position! (When GRW agreed to use Gaussians instead of Dirac delta functions, they gave up exact position collapses.)
15 2. Positionless Measurements GRW assume that the position property is fundamental, in-so-far as all other properties must be correlated with the positions of pointers in measuring devices in order to measure them. Is this correct? Ex: Measuring a particle's Hardness by means of a fluorescent screen.! To measure Hardness of P, insert it into Hardness box.! If it's hard, it will exit at h and impact screen at A.! If it's soft, it will exit at s and impact screen at B. A h P Hardness s Human Observer B fluorescent screen
16 Claim: At no point in this process is the Hardness of the particle correlated with the position of a pointer (or any sort of measuring device). The impact of P at A or B correlates its Hardness with the energies (and not positions) of the electrons in the atoms of the fluorescent screen. Suppose: P is initially black. Then: Just after impact, its state can be represented by: energy states of excited screen electrons in the vicinity of A energy states of unexcited screen electrons in the vicinity of B 2 hard,x = A P ex e... ex en unex en +... unex e2n + 2 soft,x = B P unex e... unex en ex en +... ex e2n energy states of unexcited screen electrons in the vicinity of A energy states of excited screen electrons in the vicinity of B A GRW collapse of any of the energy states of the electrons onto a position eigenstate will not cause the state of P to collapse into one or the other of these terms.
17 What about the photons that the electrons emit? Don't they experience GRW collapses? No!! The GRW Collapse Law doesn't apply to relativistic objects (like photons).! Moreover: There can be just a few photons released on impact to record the Hardness measurement (the human eye can discern photons at very low intensities).! The GRW Collapse Law only guarantees that one of a large number (trillions!) of elementary particles will collapse for real times. So: To address this problem, GRW advocates will have to push back the process of measurement, perhaps to brain states in the human observer, to a point at which they can say the positions of something (brain neuron states?) get correlated with the Hardness property of P.
18 3. Microscopic Measurements Due to the randomness of the GRW collapse, collapses will only occur in real times for macrosopic measuring devices (that have trillions of elementary particles). But: What about the possibility of microsopic measuring devices? These would not be expected to have GRW collapses in real times. If they could be correlated with macroscopic measuring devices, we would have the measurement problem all over again!
04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics
 04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics () States are represented by vectors of length. A physical system is represented by a linear vector space (the space of all its possible states). () Properties
04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics () States are represented by vectors of length. A physical system is represented by a linear vector space (the space of all its possible states). () Properties
2. As we shall see, we choose to write in terms of σ x because ( X ) 2 = σ 2 x.
 Section 5.1 Simple One-Dimensional Problems: The Free Particle Page 9 The Free Particle Gaussian Wave Packets The Gaussian wave packet initial state is one of the few states for which both the { x } and
Section 5.1 Simple One-Dimensional Problems: The Free Particle Page 9 The Free Particle Gaussian Wave Packets The Gaussian wave packet initial state is one of the few states for which both the { x } and
05. Multiparticle Systems
 05. Multiparticle Systems I. -Particle Product Spaces Suppose: Particle and particle are represented by vector spaces V and W. Then: The composite -particle system is represented by a product vector space
05. Multiparticle Systems I. -Particle Product Spaces Suppose: Particle and particle are represented by vector spaces V and W. Then: The composite -particle system is represented by a product vector space
Lecture 6. Four postulates of quantum mechanics. The eigenvalue equation. Momentum and energy operators. Dirac delta function. Expectation values
 Lecture 6 Four postulates of quantum mechanics The eigenvalue equation Momentum and energy operators Dirac delta function Expectation values Objectives Learn about eigenvalue equations and operators. Learn
Lecture 6 Four postulates of quantum mechanics The eigenvalue equation Momentum and energy operators Dirac delta function Expectation values Objectives Learn about eigenvalue equations and operators. Learn
BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS. Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5
 BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5 Interesting things happen when electrons are confined to small regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an
BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5 Interesting things happen when electrons are confined to small regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an
The Colla pse of the Wave Function
 .. 5... The Colla pse of the Wave Function The Idea of the Collapse The measurement problem was first put in its sharpest possible form in the 1930s, by John von Neumann, in an extraordinary book called
.. 5... The Colla pse of the Wave Function The Idea of the Collapse The measurement problem was first put in its sharpest possible form in the 1930s, by John von Neumann, in an extraordinary book called
HSSP Philosophy of Quantum Mechanics 08/07/11 Lecture Notes
 HSSP Philosophy of Quantum Mechanics 08/07/11 Lecture Notes Outline: 1. Homework 4 (discuss reading assignment) 2. The Measurement Problem 3. GRW theory Handouts: None Homework: Yes Vocabulary/Equations:
HSSP Philosophy of Quantum Mechanics 08/07/11 Lecture Notes Outline: 1. Homework 4 (discuss reading assignment) 2. The Measurement Problem 3. GRW theory Handouts: None Homework: Yes Vocabulary/Equations:
Topic 2: The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thin
 The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations
 PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations 1 Τhe continuous spectrum-a n So far we have seen problems where the involved operators have a discrete spectrum of eigenfunctions and eigenvalues.! n
PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations 1 Τhe continuous spectrum-a n So far we have seen problems where the involved operators have a discrete spectrum of eigenfunctions and eigenvalues.! n
1 Mathematical preliminaries
 1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
Why quantum field theory?
 Why quantum field theory? It is often said that quantum field theory is the natural marriage of Einstein s special theory of relativity and the quantum theory. The point of this section will be to motivate
Why quantum field theory? It is often said that quantum field theory is the natural marriage of Einstein s special theory of relativity and the quantum theory. The point of this section will be to motivate
Quantum Mechanics: Interpretation and Philosophy
 Quantum Mechanics: Interpretation and Philosophy Significant content from: Quantum Mechanics and Experience by David Z. Albert, Harvard University Press (1992). Main Concepts: -- complementarity -- the
Quantum Mechanics: Interpretation and Philosophy Significant content from: Quantum Mechanics and Experience by David Z. Albert, Harvard University Press (1992). Main Concepts: -- complementarity -- the
The Foundations of Quantum Mechanics and The Limitations of Human Being
 The Foundations of Quantum Mechanics and The Limitations of Human Beings Department of Mathematics 21 February 2011 Supported by NSF Quantum mechanics is very successful in computing quantities than can
The Foundations of Quantum Mechanics and The Limitations of Human Beings Department of Mathematics 21 February 2011 Supported by NSF Quantum mechanics is very successful in computing quantities than can
10. Physics from Quantum Information. I. The Clifton-Bub-Halvorson (CBH) Theorem.
 10. Physics from Quantum Information. I. The Clifton-Bub-Halvorson (CBH) Theorem. Clifton, Bub, Halvorson (2003) Motivation: Can quantum physics be reduced to information-theoretic principles? CBH Theorem:
10. Physics from Quantum Information. I. The Clifton-Bub-Halvorson (CBH) Theorem. Clifton, Bub, Halvorson (2003) Motivation: Can quantum physics be reduced to information-theoretic principles? CBH Theorem:
Topic 10: Bohm s Theory
 http://philosophy.ucsd.edu/faculty/wuthrich/ 146 Philosophy of Physics: Quantum Mechanics David Bohm (1917-1992) Berkeley PhD 1943 Princeton, U of Sao Paolo, Technion Haifa, U Bristol, Birkbeck College
http://philosophy.ucsd.edu/faculty/wuthrich/ 146 Philosophy of Physics: Quantum Mechanics David Bohm (1917-1992) Berkeley PhD 1943 Princeton, U of Sao Paolo, Technion Haifa, U Bristol, Birkbeck College
So far we have limited the discussion to state spaces of finite dimensions, but it turns out that, in
 Chapter 0 State Spaces of Infinite Dimension So far we have limited the discussion to state spaces of finite dimensions, but it turns out that, in practice, state spaces of infinite dimension are fundamental
Chapter 0 State Spaces of Infinite Dimension So far we have limited the discussion to state spaces of finite dimensions, but it turns out that, in practice, state spaces of infinite dimension are fundamental
Master Projects (EPFL) Philosophical perspectives on the exact sciences and their history
 Master Projects (EPFL) Philosophical perspectives on the exact sciences and their history Some remarks on the measurement problem in quantum theory (Davide Romano) 1. An introduction to the quantum formalism
Master Projects (EPFL) Philosophical perspectives on the exact sciences and their history Some remarks on the measurement problem in quantum theory (Davide Romano) 1. An introduction to the quantum formalism
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case:
 The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline:
 ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline: Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation Solutions to thetime-dependent Schrödinger Equation Expansion of Energy Eigenstates Things you
ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline: Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation Solutions to thetime-dependent Schrödinger Equation Expansion of Energy Eigenstates Things you
Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space
 Physics 342 Lecture 16 Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space Lecture 16 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1st, 2010 We have seen the importance of the plane wave solutions to the potentialfree Schrödinger
Physics 342 Lecture 16 Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space Lecture 16 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1st, 2010 We have seen the importance of the plane wave solutions to the potentialfree Schrödinger
The Philosophy of Quantum Mechanics (Handout Eight) between the microphysical and the macrophysical. The macrophysical world could be understood
 The Philosophy of Quantum Mechanics (Handout Eight) 1. The Copenhagen Interpretation Bohr interpreted quantum theory as showing that there is a fundamental partition in nature, between the microphysical
The Philosophy of Quantum Mechanics (Handout Eight) 1. The Copenhagen Interpretation Bohr interpreted quantum theory as showing that there is a fundamental partition in nature, between the microphysical
Honors 225 Physics Study Guide/Chapter Summaries for Final Exam; Roots Chapters 15-18
 Honors 225 Physics Study Guide/Chapter Summaries for Final Exam; Roots Chapters 15-18 Chapter 15 Collapsing the Wave If a particle is in a quantum superposition state (that is, a superposition of eigenfunctions
Honors 225 Physics Study Guide/Chapter Summaries for Final Exam; Roots Chapters 15-18 Chapter 15 Collapsing the Wave If a particle is in a quantum superposition state (that is, a superposition of eigenfunctions
Harmonic Oscillator I
 Physics 34 Lecture 7 Harmonic Oscillator I Lecture 7 Physics 34 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, February th, 008 We can manipulate operators, to a certain extent, as we would algebraic expressions. By considering
Physics 34 Lecture 7 Harmonic Oscillator I Lecture 7 Physics 34 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, February th, 008 We can manipulate operators, to a certain extent, as we would algebraic expressions. By considering
Beginning Modern Quantum
 Beginning Modern Quantum Born s probability interpretation The indeterminacy ( uncertainty ) principle The Schroedinger equation The Copenhagen interpretation 419 Term Paper Abstract due today Homework
Beginning Modern Quantum Born s probability interpretation The indeterminacy ( uncertainty ) principle The Schroedinger equation The Copenhagen interpretation 419 Term Paper Abstract due today Homework
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case
 The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about the
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about the
The Preferred Basis Problem and the Quantum Mechanics of Everything
 The Preferred Basis Problem and the Quantum Mechanics of Everything Jeffrey A. Barrett 11 January 2004 Abstract Jereon Vink (1993) argued that there are two options for what he called a realistic solution
The Preferred Basis Problem and the Quantum Mechanics of Everything Jeffrey A. Barrett 11 January 2004 Abstract Jereon Vink (1993) argued that there are two options for what he called a realistic solution
What is it like to be a quantum observer? And what does it imply about the nature of consciousness?
 What is it like to be a quantum observer? And what does it imply about the nature of consciousness? Shan Gao Research Center for Philosophy of Science and Technology, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006,
What is it like to be a quantum observer? And what does it imply about the nature of consciousness? Shan Gao Research Center for Philosophy of Science and Technology, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006,
1. For the case of the harmonic oscillator, the potential energy is quadratic and hence the total Hamiltonian looks like: d 2 H = h2
 15 Harmonic Oscillator 1. For the case of the harmonic oscillator, the potential energy is quadratic and hence the total Hamiltonian looks like: d 2 H = h2 2mdx + 1 2 2 kx2 (15.1) where k is the force
15 Harmonic Oscillator 1. For the case of the harmonic oscillator, the potential energy is quadratic and hence the total Hamiltonian looks like: d 2 H = h2 2mdx + 1 2 2 kx2 (15.1) where k is the force
The Particle in a Box
 Page 324 Lecture 17: Relation of Particle in a Box Eigenstates to Position and Momentum Eigenstates General Considerations on Bound States and Quantization Continuity Equation for Probability Date Given:
Page 324 Lecture 17: Relation of Particle in a Box Eigenstates to Position and Momentum Eigenstates General Considerations on Bound States and Quantization Continuity Equation for Probability Date Given:
Quantum Mechanics: Particles in Potentials
 Quantum Mechanics: Particles in Potentials 3 april 2010 I. Applications of the Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Now that some of the machinery of quantum mechanics has been assembled, one can begin to apply
Quantum Mechanics: Particles in Potentials 3 april 2010 I. Applications of the Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Now that some of the machinery of quantum mechanics has been assembled, one can begin to apply
The Measurement Problem
 The Measurement Problem Johannes Kofler Quantum Foundations Seminar Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics Munich, December 12 th 2011 The measurement problem Different aspects: How does the wavefunction
The Measurement Problem Johannes Kofler Quantum Foundations Seminar Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics Munich, December 12 th 2011 The measurement problem Different aspects: How does the wavefunction
228 My God - He Plays Dice! Schrödinger s Cat. Chapter 28. This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/scrodingerscat
 228 My God - He Plays Dice! Schrödinger s Cat This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/scrodingerscat Schrödinger s Cat Schrödinger s Cat Erwin Schrödinger s goal for his infamous cat-killing
228 My God - He Plays Dice! Schrödinger s Cat This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/scrodingerscat Schrödinger s Cat Schrödinger s Cat Erwin Schrödinger s goal for his infamous cat-killing
GRW Theory (Ghirardi, Rimini, Weber Model of Quantum Mechanics)
 266 GRW Theory (Ghirardi, Rimini, Weber Model of Quantum Mechanics) Roman Frigg: GRW Theory, in: Daniel Greenberger, Brigitte Secondary Falkenburg, Roman Frigg: Literature Klaus GRW Hentschel Theory, and
266 GRW Theory (Ghirardi, Rimini, Weber Model of Quantum Mechanics) Roman Frigg: GRW Theory, in: Daniel Greenberger, Brigitte Secondary Falkenburg, Roman Frigg: Literature Klaus GRW Hentschel Theory, and
Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics
 Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics are often stated in textbooks. There are two main properties of physics upon which these postulates are based: 1)the probability
Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics are often stated in textbooks. There are two main properties of physics upon which these postulates are based: 1)the probability
The Measurement Problem of Quantum Mechanics Click to edit Master title style. Wells Wulsin SASS 24 September 2008
 The Measurement Problem of Quantum Mechanics Click to edit Master title style Wells Wulsin SASS 24 September 2008 Outline Invitation Stern-Gerlach experiment What is the measurement problem? Decoherence
The Measurement Problem of Quantum Mechanics Click to edit Master title style Wells Wulsin SASS 24 September 2008 Outline Invitation Stern-Gerlach experiment What is the measurement problem? Decoherence
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations
 Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
1 Planck-Einstein Relation E = hν
 C/CS/Phys C191 Representations and Wavefunctions 09/30/08 Fall 2008 Lecture 8 1 Planck-Einstein Relation E = hν This is the equation relating energy to frequency. It was the earliest equation of quantum
C/CS/Phys C191 Representations and Wavefunctions 09/30/08 Fall 2008 Lecture 8 1 Planck-Einstein Relation E = hν This is the equation relating energy to frequency. It was the earliest equation of quantum
Tails of Schroedinger's Cat. In his famous thought experiment Schroedinger (1935) imagined a cat that measures the
 1 Published in Perspectives on Quantum Reality ed Rob Clifton When bodies are borne downwards sheer through void by their own weights, at quite uncertain times and uncertain spots they push themselves
1 Published in Perspectives on Quantum Reality ed Rob Clifton When bodies are borne downwards sheer through void by their own weights, at quite uncertain times and uncertain spots they push themselves
Quantum Entanglement. Chapter Introduction. 8.2 Entangled Two-Particle States
 Chapter 8 Quantum Entanglement 8.1 Introduction In our final chapter on quantum mechanics we introduce the concept of entanglement. This is a feature of two-particle states (or multi-particle states) in
Chapter 8 Quantum Entanglement 8.1 Introduction In our final chapter on quantum mechanics we introduce the concept of entanglement. This is a feature of two-particle states (or multi-particle states) in
Week 11: April 9, The Enigma of Measurement: Detecting the Quantum World
 Week 11: April 9, 2018 Quantum Measurement The Enigma of Measurement: Detecting the Quantum World Two examples: (2) Measuring the state of electron in H-atom Electron can be in n = 1, 2, 3... state. In
Week 11: April 9, 2018 Quantum Measurement The Enigma of Measurement: Detecting the Quantum World Two examples: (2) Measuring the state of electron in H-atom Electron can be in n = 1, 2, 3... state. In
Quantum Measurements: some technical background
 Quantum Measurements: some technical background [From the projection postulate to density matrices & (introduction to) von Neumann measurements] (AKA: the boring lecture) First: One more example I wanted
Quantum Measurements: some technical background [From the projection postulate to density matrices & (introduction to) von Neumann measurements] (AKA: the boring lecture) First: One more example I wanted
QFT. Unit 1: Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
 QFT Unit 1: Relativistic Quantum Mechanics What s QFT? Relativity deals with things that are fast Quantum mechanics deals with things that are small QFT deals with things that are both small and fast What
QFT Unit 1: Relativistic Quantum Mechanics What s QFT? Relativity deals with things that are fast Quantum mechanics deals with things that are small QFT deals with things that are both small and fast What
Lecture 4 (Sep. 18, 2017)
 Lecture 4 8.3 Quantum Theory I, Fall 07 Lecture 4 (Sep. 8, 07) 4. Measurement 4.. Spin- Systems Last time, we said that a general state in a spin- system can be written as ψ = c + + + c, (4.) where +,
Lecture 4 8.3 Quantum Theory I, Fall 07 Lecture 4 (Sep. 8, 07) 4. Measurement 4.. Spin- Systems Last time, we said that a general state in a spin- system can be written as ψ = c + + + c, (4.) where +,
PHY 407 QUANTUM MECHANICS Fall 05 Problem set 1 Due Sep
 Problem set 1 Due Sep 15 2005 1. Let V be the set of all complex valued functions of a real variable θ, that are periodic with period 2π. That is u(θ + 2π) = u(θ), for all u V. (1) (i) Show that this V
Problem set 1 Due Sep 15 2005 1. Let V be the set of all complex valued functions of a real variable θ, that are periodic with period 2π. That is u(θ + 2π) = u(θ), for all u V. (1) (i) Show that this V
Some remarks on the mentalistic reformulation of the measurement problem. A reply to S. Gao
 Some remarks on the mentalistic reformulation of the measurement problem. A reply to S. Gao Andrea Oldofredi January 16, 2019 Abstract Gao (2017) presents a new mentalistic reformulation of the well-known
Some remarks on the mentalistic reformulation of the measurement problem. A reply to S. Gao Andrea Oldofredi January 16, 2019 Abstract Gao (2017) presents a new mentalistic reformulation of the well-known
1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box
 1 OF 5 1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box Consider a particle of mass m confined to an infinite one-dimensional well of width L. The potential is given by V (x) = V 0 x L/2, V (x) =
1 OF 5 1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box Consider a particle of mass m confined to an infinite one-dimensional well of width L. The potential is given by V (x) = V 0 x L/2, V (x) =
Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra. Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 2014
 Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 24 Linear Algebra Cheat Sheet Column vector quantum state: v = v v 2. Row vector dual state: w = w w 2... Inner product:
Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 24 Linear Algebra Cheat Sheet Column vector quantum state: v = v v 2. Row vector dual state: w = w w 2... Inner product:
Physics 342 Lecture 17. Midterm I Recap. Lecture 17. Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I
 Physics 342 Lecture 17 Midterm I Recap Lecture 17 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1th, 28 17.1 Introduction In the context of the first midterm, there are a few points I d like to make about
Physics 342 Lecture 17 Midterm I Recap Lecture 17 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1th, 28 17.1 Introduction In the context of the first midterm, there are a few points I d like to make about
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules
 The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules The postulates of quantum mechanics Dr Grant Ritchie The postulates.. 1. Associated with any particle moving in a conservative field of force is a wave function,
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules The postulates of quantum mechanics Dr Grant Ritchie The postulates.. 1. Associated with any particle moving in a conservative field of force is a wave function,
C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/02/08 Fall 2008 Lecture 11
 C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/0/08 Fall 008 Lecture 11 Last time we saw that the time dependent Schr. eqn. can be decomposed into two equations, one in time (t) and one in space (x): space
C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/0/08 Fall 008 Lecture 11 Last time we saw that the time dependent Schr. eqn. can be decomposed into two equations, one in time (t) and one in space (x): space
Mathematical Tripos Part IB Michaelmas Term Example Sheet 1. Values of some physical constants are given on the supplementary sheet
 Mathematical Tripos Part IB Michaelmas Term 2015 Quantum Mechanics Dr. J.M. Evans Example Sheet 1 Values of some physical constants are given on the supplementary sheet 1. Whenasampleofpotassiumisilluminatedwithlightofwavelength3
Mathematical Tripos Part IB Michaelmas Term 2015 Quantum Mechanics Dr. J.M. Evans Example Sheet 1 Values of some physical constants are given on the supplementary sheet 1. Whenasampleofpotassiumisilluminatedwithlightofwavelength3
Quantum Mechanics Solutions
 Quantum Mechanics Solutions (a (i f A and B are Hermitian, since (AB = B A = BA, operator AB is Hermitian if and only if A and B commute So, we know that [A,B] = 0, which means that the Hilbert space H
Quantum Mechanics Solutions (a (i f A and B are Hermitian, since (AB = B A = BA, operator AB is Hermitian if and only if A and B commute So, we know that [A,B] = 0, which means that the Hilbert space H
Advanced Quantum Mechanics, Notes based on online course given by Leonard Susskind - Lecture 8
 Advanced Quantum Mechanics, Notes based on online course given by Leonard Susskind - Lecture 8 If neutrinos have different masses how do you mix and conserve energy Mass is energy. The eigenstates of energy
Advanced Quantum Mechanics, Notes based on online course given by Leonard Susskind - Lecture 8 If neutrinos have different masses how do you mix and conserve energy Mass is energy. The eigenstates of energy
Electron in a Box. A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time.
 Electron in a Box A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time. Last Time: Light Wave model: Interference pattern is in terms of wave intensity Photon model: Interference in
Electron in a Box A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time. Last Time: Light Wave model: Interference pattern is in terms of wave intensity Photon model: Interference in
Where is quantum theory headed?
 Where is quantum theory headed? Stephen L. Adler January 5, 2014 arxiv Abstract Public talk at the EmQM13 conference opening event on The Future of Quantum Mechanics The organizers have asked me to state
Where is quantum theory headed? Stephen L. Adler January 5, 2014 arxiv Abstract Public talk at the EmQM13 conference opening event on The Future of Quantum Mechanics The organizers have asked me to state
Quantum Decoherence and the Measurement Problem
 Quantum Decoherence and the Measurement Problem Dan Stahle PHYS652 Introduction Quantum mechanics has been one of the most useful and successful theories in the history of physics it has been able to describe
Quantum Decoherence and the Measurement Problem Dan Stahle PHYS652 Introduction Quantum mechanics has been one of the most useful and successful theories in the history of physics it has been able to describe
Page 404. Lecture 22: Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 2008/11/19 Date Revised: 2008/11/19
 Page 404 Lecture : Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 008/11/19 Date Revised: 008/11/19 Coordinate Basis Section 6. The One-Dimensional Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Coordinate Basis Page
Page 404 Lecture : Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 008/11/19 Date Revised: 008/11/19 Coordinate Basis Section 6. The One-Dimensional Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Coordinate Basis Page
INTRODUCTORY NOTES ON QUANTUM COMPUTATION
 INTRODUCTORY NOTES ON QUANTUM COMPUTATION Keith Hannabuss Balliol College, Oxford Hilary Term 2009 Notation. In these notes we shall often use the physicists bra-ket notation, writing ψ for a vector ψ
INTRODUCTORY NOTES ON QUANTUM COMPUTATION Keith Hannabuss Balliol College, Oxford Hilary Term 2009 Notation. In these notes we shall often use the physicists bra-ket notation, writing ψ for a vector ψ
E = hν light = hc λ = ( J s)( m/s) m = ev J = ev
 Problem The ionization potential tells us how much energy we need to use to remove an electron, so we know that any energy left afterwards will be the kinetic energy of the ejected electron. So first we
Problem The ionization potential tells us how much energy we need to use to remove an electron, so we know that any energy left afterwards will be the kinetic energy of the ejected electron. So first we
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Tuesday March 19. Problem Set 6. Due Wednesday April 3 at 10.
 8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Tuesday March 19 Problem Set 6 Due Wednesday April 3 at 10.00AM Assigned Reading: E&R 6 all, G, H Li. 7 1 9, 8 1 Ga.
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Tuesday March 19 Problem Set 6 Due Wednesday April 3 at 10.00AM Assigned Reading: E&R 6 all, G, H Li. 7 1 9, 8 1 Ga.
8.04 Spring 2013 March 12, 2013 Problem 1. (10 points) The Probability Current
 Prolem Set 5 Solutions 8.04 Spring 03 March, 03 Prolem. (0 points) The Proaility Current We wish to prove that dp a = J(a, t) J(, t). () dt Since P a (t) is the proaility of finding the particle in the
Prolem Set 5 Solutions 8.04 Spring 03 March, 03 Prolem. (0 points) The Proaility Current We wish to prove that dp a = J(a, t) J(, t). () dt Since P a (t) is the proaility of finding the particle in the
This is the important completeness relation,
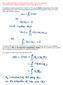 Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Is quantum linear superposition exact on all energy scales? A unique case study with flavour oscillating systems
 Is quantum linear superposition exact on all energy scales? A unique case study with flavour oscillating systems Supervisor: Dr. Beatrix C. Hiesmayr Universität Wien, Fakultät für Physik March 17, 2015
Is quantum linear superposition exact on all energy scales? A unique case study with flavour oscillating systems Supervisor: Dr. Beatrix C. Hiesmayr Universität Wien, Fakultät für Physik March 17, 2015
CHMY 564 Homework #3 2Feb17 Due Friday, 10Feb17
 564-17 Lec 11 Mon 6feb17 CHMY 564 Homework #3 2Feb17 Due Friday, 10Feb17 1. (a) Find the eigenfunctions and eigenvalues of the x component of linear momentum. (b) Why can a momentum eigenfunction never
564-17 Lec 11 Mon 6feb17 CHMY 564 Homework #3 2Feb17 Due Friday, 10Feb17 1. (a) Find the eigenfunctions and eigenvalues of the x component of linear momentum. (b) Why can a momentum eigenfunction never
1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box
 1 OF 5 NOTE: This problem set is to be handed in to my mail slot (SMITH) located in the Clarendon Laboratory by 5:00 PM (noon) Tuesday, 24 May. 1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box Consider
1 OF 5 NOTE: This problem set is to be handed in to my mail slot (SMITH) located in the Clarendon Laboratory by 5:00 PM (noon) Tuesday, 24 May. 1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box Consider
Notes on wavefunctions IV: the Schrödinger equation in a potential and energy eigenstates.
 Notes on wavefunctions IV: the Schrödinger equation in a potential and energy eigenstates. We have now seen that the wavefunction for a free electron changes with time according to the Schrödinger Equation
Notes on wavefunctions IV: the Schrödinger equation in a potential and energy eigenstates. We have now seen that the wavefunction for a free electron changes with time according to the Schrödinger Equation
= X = X ( ~) } ( ) ( ) On the other hand, when the Hamiltonian acts on ( ) one finds that
 6. A general normalized solution to Schrödinger s equation of motion for a particle moving in a time-independent potential is of the form ( ) = P } where the and () are, respectively, eigenvalues and normalized
6. A general normalized solution to Schrödinger s equation of motion for a particle moving in a time-independent potential is of the form ( ) = P } where the and () are, respectively, eigenvalues and normalized
If quantum mechanics hasn t profoundly shocked you, you haven t understood it.
 Quantum Mechanics If quantum mechanics hasn t profoundly shocked you, you haven t understood it. Niels Bohr Today, I will tell you more about quantum mechanics what weird thing it is and why it is so weird.
Quantum Mechanics If quantum mechanics hasn t profoundly shocked you, you haven t understood it. Niels Bohr Today, I will tell you more about quantum mechanics what weird thing it is and why it is so weird.
Pure Quantum States Are Fundamental, Mixtures (Composite States) Are Mathematical Constructions: An Argument Using Algorithmic Information Theory
 Pure Quantum States Are Fundamental, Mixtures (Composite States) Are Mathematical Constructions: An Argument Using Algorithmic Information Theory Vladik Kreinovich and Luc Longpré Department of Computer
Pure Quantum States Are Fundamental, Mixtures (Composite States) Are Mathematical Constructions: An Argument Using Algorithmic Information Theory Vladik Kreinovich and Luc Longpré Department of Computer
8.04 Quantum Physics Lecture IV. ψ(x) = dkφ (k)e ikx 2π
 Last time Heisenberg uncertainty ΔxΔp x h as diffraction phenomenon Fourier decomposition ψ(x) = dkφ (k)e ikx π ipx/ h = dpφ(p)e (4-) πh φ(p) = φ (k) (4-) h Today how to calculate φ(k) interpretation of
Last time Heisenberg uncertainty ΔxΔp x h as diffraction phenomenon Fourier decomposition ψ(x) = dkφ (k)e ikx π ipx/ h = dpφ(p)e (4-) πh φ(p) = φ (k) (4-) h Today how to calculate φ(k) interpretation of
Lecture #1. Review. Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1
 L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
Physics 202 Laboratory 5. Linear Algebra 1. Laboratory 5. Physics 202 Laboratory
 Physics 202 Laboratory 5 Linear Algebra Laboratory 5 Physics 202 Laboratory We close our whirlwind tour of numerical methods by advertising some elements of (numerical) linear algebra. There are three
Physics 202 Laboratory 5 Linear Algebra Laboratory 5 Physics 202 Laboratory We close our whirlwind tour of numerical methods by advertising some elements of (numerical) linear algebra. There are three
PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send to
 Teoretisk Fysik KTH Advanced QM (SI2380), Lecture 2 (Summary of concepts) 1 PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send email to langmann@kth.se) The laws of QM 1. I now discuss the laws of QM and their
Teoretisk Fysik KTH Advanced QM (SI2380), Lecture 2 (Summary of concepts) 1 PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send email to langmann@kth.se) The laws of QM 1. I now discuss the laws of QM and their
1 The postulates of quantum mechanics
 1 The postulates of quantum mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics were derived after a long process of trial and error. These postulates provide a connection between the physical world and the
1 The postulates of quantum mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics were derived after a long process of trial and error. These postulates provide a connection between the physical world and the
Physics 137A Quantum Mechanics Fall 2012 Midterm II - Solutions
 Physics 37A Quantum Mechanics Fall 0 Midterm II - Solutions These are the solutions to the exam given to Lecture Problem [5 points] Consider a particle with mass m charge q in a simple harmonic oscillator
Physics 37A Quantum Mechanics Fall 0 Midterm II - Solutions These are the solutions to the exam given to Lecture Problem [5 points] Consider a particle with mass m charge q in a simple harmonic oscillator
Quantum Chemistry Exam 2 Solutions
 Chemistry 46 Fall 17 Dr. Jean M. Standard November 8, 17 Name KEY Quantum Chemistry Exam Solutions 1.) ( points) Answer the following questions by selecting the correct answer from the choices provided.
Chemistry 46 Fall 17 Dr. Jean M. Standard November 8, 17 Name KEY Quantum Chemistry Exam Solutions 1.) ( points) Answer the following questions by selecting the correct answer from the choices provided.
Time-Independent Perturbation Theory
 4 Phys46.nb Time-Independent Perturbation Theory.. Overview... General question Assuming that we have a Hamiltonian, H = H + λ H (.) where λ is a very small real number. The eigenstates of the Hamiltonian
4 Phys46.nb Time-Independent Perturbation Theory.. Overview... General question Assuming that we have a Hamiltonian, H = H + λ H (.) where λ is a very small real number. The eigenstates of the Hamiltonian
The Birth of Quantum Mechanics. New Wave Rock Stars
 The Birth of Quantum Mechanics Louis de Broglie 1892-1987 Erwin Schrödinger 1887-1961 Paul Dirac 1902-1984 Werner Heisenberg 1901-1976 New Wave Rock Stars Blackbody radiation: Light energy is quantized.
The Birth of Quantum Mechanics Louis de Broglie 1892-1987 Erwin Schrödinger 1887-1961 Paul Dirac 1902-1984 Werner Heisenberg 1901-1976 New Wave Rock Stars Blackbody radiation: Light energy is quantized.
Wave function collapse
 Wave function collapse I.-O. Stamatescu November 15, 2007 Under collapse of the wave function (or state vector reduction ) one understands the sudden change of the system s state in a measurement. This
Wave function collapse I.-O. Stamatescu November 15, 2007 Under collapse of the wave function (or state vector reduction ) one understands the sudden change of the system s state in a measurement. This
Quantum measurement theory
 1 Quantum measurement theory 1.1 Classical measurement theory 1.1.1 Basic concepts Although this chapter, and indeed this book, is concerned with quantum measurements, we begin with a discussion of some
1 Quantum measurement theory 1.1 Classical measurement theory 1.1.1 Basic concepts Although this chapter, and indeed this book, is concerned with quantum measurements, we begin with a discussion of some
What does Quantum Mechanics Tell us about Time?
 What does Quantum Mechanics Tell us about Time? Valia Allori Department of Philosophy Northern Illinois University May 12-14 2014 Gargnano Philosophy of Time Conference 1 Outline Quantum Mechanics: Orthodox
What does Quantum Mechanics Tell us about Time? Valia Allori Department of Philosophy Northern Illinois University May 12-14 2014 Gargnano Philosophy of Time Conference 1 Outline Quantum Mechanics: Orthodox
0.1 Schrödinger Equation in 2-dimensional system
 0.1 Schrödinger Equation in -dimensional system In HW problem set 5, we introduced a simpleminded system describing the ammonia (NH 3 ) molecule, consisting of a plane spanned by the 3 hydrogen atoms and
0.1 Schrödinger Equation in -dimensional system In HW problem set 5, we introduced a simpleminded system describing the ammonia (NH 3 ) molecule, consisting of a plane spanned by the 3 hydrogen atoms and
COPENHAGEN INTERPRETATION:
 QUANTUM PHILOSOPHY PCES 4.41 Perhaps the most difficult things to understand about QM are (i) how to reconcile our common sense ideas about physical reality with phenomena such as entanglement, & (ii)
QUANTUM PHILOSOPHY PCES 4.41 Perhaps the most difficult things to understand about QM are (i) how to reconcile our common sense ideas about physical reality with phenomena such as entanglement, & (ii)
df(x) = h(x) dx Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 2009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation
 Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation Linearity of differential equation Partial vs. Ordinary Differential Equations
Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation Linearity of differential equation Partial vs. Ordinary Differential Equations
General Physical Chemistry II
 General Physical Chemistry II Lecture 3 Aleksey Kocherzhenko September 2, 2014" Last time " The time-independent Schrödinger equation" Erwin Schrödinger " ~ 2 2m d 2 (x) dx 2 The wavefunction:" (x) The
General Physical Chemistry II Lecture 3 Aleksey Kocherzhenko September 2, 2014" Last time " The time-independent Schrödinger equation" Erwin Schrödinger " ~ 2 2m d 2 (x) dx 2 The wavefunction:" (x) The
Bound and Scattering Solutions for a Delta Potential
 Physics 342 Lecture 11 Bound and Scattering Solutions for a Delta Potential Lecture 11 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, February 20th, 2008 We understand that free particle solutions are meant
Physics 342 Lecture 11 Bound and Scattering Solutions for a Delta Potential Lecture 11 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, February 20th, 2008 We understand that free particle solutions are meant
Physics-I. Dr. Anurag Srivastava. Web address: Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus
 Physics-I Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus Syllabus Electrodynamics: Maxwell s equations: differential
Physics-I Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus Syllabus Electrodynamics: Maxwell s equations: differential
PHY413 Quantum Mechanics B Duration: 2 hours 30 minutes
 BSc/MSci Examination by Course Unit Thursday nd May 4 : - :3 PHY43 Quantum Mechanics B Duration: hours 3 minutes YOU ARE NOT PERMITTED TO READ THE CONTENTS OF THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO
BSc/MSci Examination by Course Unit Thursday nd May 4 : - :3 PHY43 Quantum Mechanics B Duration: hours 3 minutes YOU ARE NOT PERMITTED TO READ THE CONTENTS OF THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO
Quantum Mechanics - I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 7 The Uncertainty Principle
 Quantum Mechanics - I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 7 The Uncertainty Principle (Refer Slide Time: 00:07) In the last lecture, I had spoken
Quantum Mechanics - I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 7 The Uncertainty Principle (Refer Slide Time: 00:07) In the last lecture, I had spoken
Chapter 10. The Measurement Problem I: The Orthodox View, Spontaneous Localization, and. Worlds and Minds
 Formatted Chapter 10 The Measurement Problem I: The Orthodox View, Spontaneous Localization, and Worlds and Minds In this chapter, we begin the consideration of some of the proposed solutions to Deleted:
Formatted Chapter 10 The Measurement Problem I: The Orthodox View, Spontaneous Localization, and Worlds and Minds In this chapter, we begin the consideration of some of the proposed solutions to Deleted:
Collapse and the Tritium Endpoint Pileup
 Collapse and the Tritium Endpoint Pileup arxiv:nucl-th/9901092v2 4 Feb 1999 Richard Shurtleff January 23, 1999 Abstract The beta-decay of a tritium nucleus produces an entangled quantum system, a beta
Collapse and the Tritium Endpoint Pileup arxiv:nucl-th/9901092v2 4 Feb 1999 Richard Shurtleff January 23, 1999 Abstract The beta-decay of a tritium nucleus produces an entangled quantum system, a beta
Wave Mechanics Relevant sections in text: , 2.1
 Wave Mechanics Relevant sections in text: 1.1 1.6, 2.1 The wave function We will now create a model for the system that we call a particle in one dimension. To do this we should define states and observables.
Wave Mechanics Relevant sections in text: 1.1 1.6, 2.1 The wave function We will now create a model for the system that we call a particle in one dimension. To do this we should define states and observables.
Lecture notes 1. Standard physics vs. new physics. 1.1 The final state boundary condition
 Lecture notes 1 Standard physics vs. new physics The black hole information paradox has challenged our fundamental beliefs about spacetime and quantum theory. Which belief will have to change to resolve
Lecture notes 1 Standard physics vs. new physics The black hole information paradox has challenged our fundamental beliefs about spacetime and quantum theory. Which belief will have to change to resolve
Lecture 12: Particle in 1D boxes & Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Lecture 12: Particle in 1D boxes & Simple Harmonic Oscillator U(x) E Dx y(x) x Dx Lecture 12, p 1 Properties of Bound States Several trends exhibited by the particle-in-box states are generic to bound
Lecture 12: Particle in 1D boxes & Simple Harmonic Oscillator U(x) E Dx y(x) x Dx Lecture 12, p 1 Properties of Bound States Several trends exhibited by the particle-in-box states are generic to bound
1 Fundamental physical postulates. C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12
 C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
Theoretical Biophysics. Quantum Theory and Molecular Dynamics. Pawel Romanczuk WS 2017/18
 Theoretical Biophysics Quantum Theory and Molecular Dynamics Pawel Romanczuk WS 2017/18 http://lab.romanczuk.de/teaching/ 1 Introduction Two pillars of classical theoretical physics at the begin of 20th
Theoretical Biophysics Quantum Theory and Molecular Dynamics Pawel Romanczuk WS 2017/18 http://lab.romanczuk.de/teaching/ 1 Introduction Two pillars of classical theoretical physics at the begin of 20th
Introduction to Bell s theorem: the theory that solidified quantum mechanics
 Introduction to Bells theorem: the theory that solidified quantum mechanics Jia Wang Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, 930 N. University Ave., Ann Arbor, MI 48109 (Received November 30,
Introduction to Bells theorem: the theory that solidified quantum mechanics Jia Wang Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, 930 N. University Ave., Ann Arbor, MI 48109 (Received November 30,
5.4 Given the basis e 1, e 2 write the matrices that represent the unitary transformations corresponding to the following changes of basis:
 5 Representations 5.3 Given a three-dimensional Hilbert space, consider the two observables ξ and η that, with respect to the basis 1, 2, 3, arerepresentedby the matrices: ξ ξ 1 0 0 0 ξ 1 0 0 0 ξ 3, ξ
5 Representations 5.3 Given a three-dimensional Hilbert space, consider the two observables ξ and η that, with respect to the basis 1, 2, 3, arerepresentedby the matrices: ξ ξ 1 0 0 0 ξ 1 0 0 0 ξ 3, ξ
PHYS Concept Tests Fall 2009
 PHYS 30 Concept Tests Fall 009 In classical mechanics, given the state (i.e. position and velocity) of a particle at a certain time instant, the state of the particle at a later time A) cannot be determined
PHYS 30 Concept Tests Fall 009 In classical mechanics, given the state (i.e. position and velocity) of a particle at a certain time instant, the state of the particle at a later time A) cannot be determined
HW posted on web page HW10: Chap 14 Concept 8,20,24,26 Prob. 4,8. From Last Time
 HW posted on web page HW10: Chap 14 Concept 8,20,24,26 Prob. 4,8 From Last Time Philosophical effects in quantum mechanics Interpretation of the wave function: Calculation using the basic premises of quantum
HW posted on web page HW10: Chap 14 Concept 8,20,24,26 Prob. 4,8 From Last Time Philosophical effects in quantum mechanics Interpretation of the wave function: Calculation using the basic premises of quantum
