SOLUTIONS OF GAMES BY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS G. W. Brown and J. von Neumann. 1_. The purpose of this note is to give a new proof for the
|
|
|
- Dylan Geoffrey Jennings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3
4
5 -1- P SOLUTIONS OF GAMES BY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS G. W. Brown and J. von Neumann 1_. The purpose of this note is to give a new proof for the existence of a "value" and of M good strategies" for a zero-sum two-person game. This proof seems to have some interest because of two distinguishing traits: (a) Although the theorem to be proved is of an algebraical nature, a very simrle proof obtains by analytical means. (b) The proof is "constructive" in a sense that lends itself to utilization when actually computing the solutions of specific pames. The procedure could be "mechanized" with relative ease, both for digital" and for "analogy" methods. In the latter case it is probably much leas sensitive to the precision of the equipment, than the somewhat related problem of "linear equation solving" or "matrix inversion". The derivations which follow are ba^ed on results that were obtained independently by the two authors^ Further results of one of them (G.W.B.) are published elsewhere L1J. 2, Consider first the special ca^e of a symmetric game, i.e., where the "fame matrix" A,.ii,J 1,...,m) is anti3ymn,etric Numbers in square LracKets refer LO the bibliography at the end of this paper.
6 -2- P A - A A ij A Ji ' notations Write for vectors, x (x.), u - (u,), and use the u. j A IJ X J f(u.) - Max (Ü.u, M),' ; (x) - '-^u^ \ fix) - ^ i^u^ ) 2. Consider the differential equation system (2) dx ^ -/lu^ - /U) Xj. starting with a vector (3) x = tx 1 ), x 1 > Ü, _, x 1 (ix i i x. - 0 implies -rr - /(u. ) > 0, hence - 1. x > 0 can never go over into x, < 0, i.e., always U) x i > 0. Summing over all i gives d It \ ^ - x. 0UH1 - \ i 1 i.e., d 1 It tt ' 1 - i i - $[x), hence hxistence of a unique solution to this system is assured by virtue of the fact that the system is piecewise well-behaved, with matching of first derivatives at the boundaries. The related system obtained by droppihg the last term in (2) is piecewise a linear system, and has a growing solution, proportional to the solution of [2). The last term in [2) sinr-ly normalizes the solution to make 15) hold.
7 -3- P-U , x. - 1 can never go over into /_ x,. / I, i.e. always (5) Zx, - 1. i 1 Next, when ^(u.) > 0, then dfiu^ v- dx^ "JT -0(x) ^A^xj, hence always Jt Summing over all i gives 2 _ A^ ^lu^ ^(Uj) - 2 0(x) J J A ij^(u i )x J ' The first term on the right-hand side vanishes, because A. ^ is antisymmetric. The second term is eoual to /_ /(u. ) A..x. i 1 1J J J ZL.jTlu.lu.. Whenever /tu.) f 0, then P[\i. u,. Hence the above expression is equal to ( *[\x,]) 2 - V( x). s i 1 Therefore, 16) d^x^ (x) ^(x). Now clearly ( 7 ) 1 > ( x 1 1, ' < 0 ( x ) < l m H ( x ) )
8 -4- P-U Hence as long as H(x) > 0, also 0lx) > 0, and ^(x) Is de- creasing; also i-^u - 2 i>vu)r,.1 ^(xd^l^ixi^,. hence _ 1 _1 in (x)) 5 > mx n ^ t, 16) ilx) t VXJ < ^ ^ J. 1 ^tx o ) 7 t If ever ^(x) 0, then this remains true from then on (i.e. for all larger t ], and so (6) is true again. and so from (8) Finally from (7), 18) 1 1 (9) 0(x) < 2_ 1 ^(x ) 7 t o no) nv < 2 T 1 v V(x o )^ t 1
9 -5- P-U2 By (3), (9), (10) t > oo impllea ^(x)! 0, 0(x) -^ 0, and all ^(i^) -^ 0. That tht x, themselves have limits for t > 00 Is not clear; (2) and (10) do not seem to suffice to prove this Nevertheless, since the range (4), (5) of the x. ie compact, limit points x* - (x.) of the x - x, for t > ^ must exist. For any such x^ (O, (5) must again be true, and (10) gives that all <p{up - 0, i.e. all (11 ) ^_A i jx«< 0. j Hence any x^ - (xf) represents a "good strategy", and the "value" of the I symmetric) game is, as it should be, zero. Z^. Consider next an arbitrary game, i.e. one with an unrestricted "game matrix" B, * ^k - 1,...,p; i» 1,...,q). Various ways of reducing this to a symmetric game are known. They differ from each other, among other things, in the order m of the symmetric g^me, i.e. of the antisymmetric matrix f<4 4 \i»j " 1,...,n>) to which they lead. A very elegant method cf this type has been lately found [2] which gives the remarkably low
10 -6- P-U value m p q 1. One of the authors (J.v.N.) had obtained earlier ai.other method, which gives the larger value m pq. IT:.is is referred to, but not described, in [3j, page 1t»rf.) We will follow here the second procedure, partly because its underlying qualitative idea is simpler, and partly because, although its m is considerably larger than that of the other method (pq v». p q 1, cf. above), it leads ultimately to a set of differential equations in fewer variables (p q - 2 vs p» q, cf. the remarks at the end of ^,. ). The qualitative idea behind the method referred to is this: Assume that a player knew how to play every conceivable symmetric game A. Assume that he were asked to play a (not necessarily symmetric) game B. How could he then reduce it to known (symmetric) patterns? He could do it like this: He could imagine that he Is playing (simultaneously) two games B : Say B' and B". In B' he has the role of the first player, in B" he has the role of the second player for his opponent the positions are reversed. The total game A, consisting of B' and of B" together, is clearly symmetric. Hence the player will know how to play A -- hence also its parts, say B*, i.e. B. In spite of the apparent "practical" futility of this "reduction", it nevertheless expresses a valid mathematical procedure. The tnathematical procedure is as follows:
11
12
13
14
15
16 BLANK PAGE
March Algebra 2 Question 1. March Algebra 2 Question 1
 March Algebra 2 Question 1 If the statement is always true for the domain, assign that part a 3. If it is sometimes true, assign it a 2. If it is never true, assign it a 1. Your answer for this question
March Algebra 2 Question 1 If the statement is always true for the domain, assign that part a 3. If it is sometimes true, assign it a 2. If it is never true, assign it a 1. Your answer for this question
EOS 352 Continuum Dynamics Conservation of angular momentum
 EOS 352 Continuum Dynamics Conservation of angular momentum c Christian Schoof. Not to be copied, used, or revised without explicit written permission from the copyright owner The copyright owner explicitly
EOS 352 Continuum Dynamics Conservation of angular momentum c Christian Schoof. Not to be copied, used, or revised without explicit written permission from the copyright owner The copyright owner explicitly
II. Analysis of Linear Programming Solutions
 Optimization Methods Draft of August 26, 2005 II. Analysis of Linear Programming Solutions Robert Fourer Department of Industrial Engineering and Management Sciences Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois
Optimization Methods Draft of August 26, 2005 II. Analysis of Linear Programming Solutions Robert Fourer Department of Industrial Engineering and Management Sciences Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois
Rolle s theorem: from a simple theorem to an extremely powerful tool
 Rolle s theorem: from a simple theorem to an extremely powerful tool Christiane Rousseau, Université de Montréal November 10, 2011 1 Introduction How many solutions an equation or a system of equations
Rolle s theorem: from a simple theorem to an extremely powerful tool Christiane Rousseau, Université de Montréal November 10, 2011 1 Introduction How many solutions an equation or a system of equations
PRIMITIVE SPACES OF MATRICES OF BOUNDED RANK.II
 /. Austral. Math. Soc. (Series A) 34 (1983), 306-315 PRIMITIVE SPACES OF MATRICES OF BOUNDED RANK.II M. D. ATKINSON (Received 18 December 1981) Communicated by D. E. Taylor Abstract The classification
/. Austral. Math. Soc. (Series A) 34 (1983), 306-315 PRIMITIVE SPACES OF MATRICES OF BOUNDED RANK.II M. D. ATKINSON (Received 18 December 1981) Communicated by D. E. Taylor Abstract The classification
On second order sufficient optimality conditions for quasilinear elliptic boundary control problems
 On second order sufficient optimality conditions for quasilinear elliptic boundary control problems Vili Dhamo Technische Universität Berlin Joint work with Eduardo Casas Workshop on PDE Constrained Optimization
On second order sufficient optimality conditions for quasilinear elliptic boundary control problems Vili Dhamo Technische Universität Berlin Joint work with Eduardo Casas Workshop on PDE Constrained Optimization
Euler s Identity: why and how does e πi = 1?
 Euler s Identity: why and how does e πi = 1? Abstract In this dissertation, I want to show how e " = 1, reviewing every element that makes this possible and explore various examples of explaining this
Euler s Identity: why and how does e πi = 1? Abstract In this dissertation, I want to show how e " = 1, reviewing every element that makes this possible and explore various examples of explaining this
Physics 209 Fall 2002 Notes 5 Thomas Precession
 Physics 209 Fall 2002 Notes 5 Thomas Precession Jackson s discussion of Thomas precession is based on Thomas s original treatment, and on the later paper by Bargmann, Michel, and Telegdi. The alternative
Physics 209 Fall 2002 Notes 5 Thomas Precession Jackson s discussion of Thomas precession is based on Thomas s original treatment, and on the later paper by Bargmann, Michel, and Telegdi. The alternative
Game Theory. Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari. Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India August 2012
 Game Theory Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India August 2012 Chapter 7: Von Neumann - Morgenstern Utilities Note: This
Game Theory Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India August 2012 Chapter 7: Von Neumann - Morgenstern Utilities Note: This
EXERCISES. = {1, 4}, and. The zero coset is J. Thus, by (***), to say that J 4- a iu not zero, is to
 19 CHAPTER NINETEEN Whenever J is a prime ideal of a commutative ring with unity A, the quotient ring A/J is an integral domain. (The details are left as an exercise.) An ideal of a ring is called proper
19 CHAPTER NINETEEN Whenever J is a prime ideal of a commutative ring with unity A, the quotient ring A/J is an integral domain. (The details are left as an exercise.) An ideal of a ring is called proper
Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications. Lecture 4: 2-player zero-sum games, and the Minimax Theorem
 Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications Lecture 4: 2-player zero-sum games, and the Minimax Theorem Kousha Etessami 2-person zero-sum games A finite 2-person zero-sum (2p-zs) strategic game Γ, is a strategic
Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications Lecture 4: 2-player zero-sum games, and the Minimax Theorem Kousha Etessami 2-person zero-sum games A finite 2-person zero-sum (2p-zs) strategic game Γ, is a strategic
Local properties of plane algebraic curves
 Chapter 7 Local properties of plane algebraic curves Throughout this chapter let K be an algebraically closed field of characteristic zero, and as usual let A (K) be embedded into P (K) by identifying
Chapter 7 Local properties of plane algebraic curves Throughout this chapter let K be an algebraically closed field of characteristic zero, and as usual let A (K) be embedded into P (K) by identifying
Chapter 1: The Finite Element Method
 Chapter 1: The Finite Element Method Michael Hanke Read: Strang, p 428 436 A Model Problem Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation, Part Applications: u = fx), < x < 1 u) = u1) = D) axial deformation
Chapter 1: The Finite Element Method Michael Hanke Read: Strang, p 428 436 A Model Problem Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation, Part Applications: u = fx), < x < 1 u) = u1) = D) axial deformation
Quarter 2 400, , , , , , ,000 50,000
 Algebra 2 Quarter 2 Quadratic Functions Introduction to Polynomial Functions Hybrid Electric Vehicles Since 1999, there has been a growing trend in the sales of hybrid electric vehicles. These data show
Algebra 2 Quarter 2 Quadratic Functions Introduction to Polynomial Functions Hybrid Electric Vehicles Since 1999, there has been a growing trend in the sales of hybrid electric vehicles. These data show
Energy method for wave equations
 Energy method for wave equations Willie Wong Based on commit 5dfb7e5 of 2017-11-06 13:29 Abstract We give an elementary discussion of the energy method (and particularly the vector field method) in the
Energy method for wave equations Willie Wong Based on commit 5dfb7e5 of 2017-11-06 13:29 Abstract We give an elementary discussion of the energy method (and particularly the vector field method) in the
2 Two-Point Boundary Value Problems
 2 Two-Point Boundary Value Problems Another fundamental equation, in addition to the heat eq. and the wave eq., is Poisson s equation: n j=1 2 u x 2 j The unknown is the function u = u(x 1, x 2,..., x
2 Two-Point Boundary Value Problems Another fundamental equation, in addition to the heat eq. and the wave eq., is Poisson s equation: n j=1 2 u x 2 j The unknown is the function u = u(x 1, x 2,..., x
Double Binary Forms IV.*
 69 Double Binary Forms IV.* (1) Apolarity; (2) Automorphic Transformations. By Professor H. W. TURNBULL. (Bead 6th February 1928. Received 12th April 1. Introduction. The first part of the following investigation
69 Double Binary Forms IV.* (1) Apolarity; (2) Automorphic Transformations. By Professor H. W. TURNBULL. (Bead 6th February 1928. Received 12th April 1. Introduction. The first part of the following investigation
Prediction and Playing Games
 Prediction and Playing Games Vineel Pratap vineel@eng.ucsd.edu February 20, 204 Chapter 7 : Prediction, Learning and Games - Cesa Binachi & Lugosi K-Person Normal Form Games Each player k (k =,..., K)
Prediction and Playing Games Vineel Pratap vineel@eng.ucsd.edu February 20, 204 Chapter 7 : Prediction, Learning and Games - Cesa Binachi & Lugosi K-Person Normal Form Games Each player k (k =,..., K)
OF PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 EPSILON ENTROPY OF PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS 1. Introduction EDWARD C. POSNER and EUGENE R. RODEMICH JET PROPULSION LABORATORY CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY This paper summarizes recent work on the
EPSILON ENTROPY OF PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS 1. Introduction EDWARD C. POSNER and EUGENE R. RODEMICH JET PROPULSION LABORATORY CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY This paper summarizes recent work on the
necessita d'interrogare il cielo
 gigi nei necessia d'inegae i cie cic pe sax span s inuie a dispiegaa fma dea uce < affeandi ves i cen dea uce isnane " sienzi dei padi sie veic dei' anima 5 J i f H 5 f AL J) i ) L '3 J J "' U J J ö'
gigi nei necessia d'inegae i cie cic pe sax span s inuie a dispiegaa fma dea uce < affeandi ves i cen dea uce isnane " sienzi dei padi sie veic dei' anima 5 J i f H 5 f AL J) i ) L '3 J J "' U J J ö'
(c) For each α R \ {0}, the mapping x αx is a homeomorphism of X.
 A short account of topological vector spaces Normed spaces, and especially Banach spaces, are basic ambient spaces in Infinite- Dimensional Analysis. However, there are situations in which it is necessary
A short account of topological vector spaces Normed spaces, and especially Banach spaces, are basic ambient spaces in Infinite- Dimensional Analysis. However, there are situations in which it is necessary
THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM
 THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM W. PATRICK HOOPER The implicit function theorem is the following result: Theorem 1. Let f be a C 1 function from a neighborhood of a point a R n into R n. Suppose A = Df(a)
THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM W. PATRICK HOOPER The implicit function theorem is the following result: Theorem 1. Let f be a C 1 function from a neighborhood of a point a R n into R n. Suppose A = Df(a)
The Derivative. Appendix B. B.1 The Derivative of f. Mappings from IR to IR
 Appendix B The Derivative B.1 The Derivative of f In this chapter, we give a short summary of the derivative. Specifically, we want to compare/contrast how the derivative appears for functions whose domain
Appendix B The Derivative B.1 The Derivative of f In this chapter, we give a short summary of the derivative. Specifically, we want to compare/contrast how the derivative appears for functions whose domain
Zero sum games Proving the vn theorem. Zero sum games. Roberto Lucchetti. Politecnico di Milano
 Politecnico di Milano General form Definition A two player zero sum game in strategic form is the triplet (X, Y, f : X Y R) f (x, y) is what Pl1 gets from Pl2, when they play x, y respectively. Thus g
Politecnico di Milano General form Definition A two player zero sum game in strategic form is the triplet (X, Y, f : X Y R) f (x, y) is what Pl1 gets from Pl2, when they play x, y respectively. Thus g
1.3 Convergence of Regular Markov Chains
 Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 3 Applying the same argument to A T, which has the same λ 0 as A, yields the row sum bounds Corollary 0 Let P 0 be the transition matrix of a regular Markov chain
Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 3 Applying the same argument to A T, which has the same λ 0 as A, yields the row sum bounds Corollary 0 Let P 0 be the transition matrix of a regular Markov chain
RECOVERY OF NON-LINEAR CONDUCTIVITIES FOR CIRCULAR PLANAR GRAPHS
 RECOVERY OF NON-LINEAR CONDUCTIVITIES FOR CIRCULAR PLANAR GRAPHS WILL JOHNSON Abstract. We consider the problem of recovering nonlinear conductances in a circular planar graph. If the graph is critical
RECOVERY OF NON-LINEAR CONDUCTIVITIES FOR CIRCULAR PLANAR GRAPHS WILL JOHNSON Abstract. We consider the problem of recovering nonlinear conductances in a circular planar graph. If the graph is critical
6.2 Unitary and Hermitian operators
 6.2 Unitary and Hermitian operators Slides: Video 6.2.1 Using unitary operators Text reference: Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Section 4.10 (starting from Changing the representation of
6.2 Unitary and Hermitian operators Slides: Video 6.2.1 Using unitary operators Text reference: Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Section 4.10 (starting from Changing the representation of
Game Theory. Greg Plaxton Theory in Programming Practice, Spring 2004 Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Austin
 Game Theory Greg Plaxton Theory in Programming Practice, Spring 2004 Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Austin Bimatrix Games We are given two real m n matrices A = (a ij ), B = (b ij
Game Theory Greg Plaxton Theory in Programming Practice, Spring 2004 Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Austin Bimatrix Games We are given two real m n matrices A = (a ij ), B = (b ij
The Equivalence of Ergodicity and Weak Mixing for Infinitely Divisible Processes1
 Journal of Theoretical Probability. Vol. 10, No. 1, 1997 The Equivalence of Ergodicity and Weak Mixing for Infinitely Divisible Processes1 Jan Rosinski2 and Tomasz Zak Received June 20, 1995: revised September
Journal of Theoretical Probability. Vol. 10, No. 1, 1997 The Equivalence of Ergodicity and Weak Mixing for Infinitely Divisible Processes1 Jan Rosinski2 and Tomasz Zak Received June 20, 1995: revised September
Numerical Analysis and Methods for PDE I
 Numerical Analysis and Methods for PDE I A. J. Meir Department of Mathematics and Statistics Auburn University US-Africa Advanced Study Institute on Analysis, Dynamical Systems, and Mathematical Modeling
Numerical Analysis and Methods for PDE I A. J. Meir Department of Mathematics and Statistics Auburn University US-Africa Advanced Study Institute on Analysis, Dynamical Systems, and Mathematical Modeling
Arithmetic progressions of rectangles on a conic
 Notes on Number Theory and Discrete Mathematics ISSN 1310 5132 Vol. 20, 2014, No. 4, 53 57 Arithmetic progressions of rectangles on a conic Ajai Choudhry 13/4 A Clay Square, Lucknow 226001, India e-mail:
Notes on Number Theory and Discrete Mathematics ISSN 1310 5132 Vol. 20, 2014, No. 4, 53 57 Arithmetic progressions of rectangles on a conic Ajai Choudhry 13/4 A Clay Square, Lucknow 226001, India e-mail:
LINEARITY OF BEST APPROXIMATION: A CHARACTERIZATION OF ELLIPSOIDS 1)
 MATHEMATICS LINEARITY OF BEST APPROXIMATION: A CHARACTERIZATION OF ELLIPSOIDS 1) BY W. RUDIN 2) AND K. T. SMITH (Communicated by Prof. J. PoPKEN at the meeting of September 24, 1960) If n is a finite-dimensionai
MATHEMATICS LINEARITY OF BEST APPROXIMATION: A CHARACTERIZATION OF ELLIPSOIDS 1) BY W. RUDIN 2) AND K. T. SMITH (Communicated by Prof. J. PoPKEN at the meeting of September 24, 1960) If n is a finite-dimensionai
Introduction to Topology
 Introduction to Topology Randall R. Holmes Auburn University Typeset by AMS-TEX Chapter 1. Metric Spaces 1. Definition and Examples. As the course progresses we will need to review some basic notions about
Introduction to Topology Randall R. Holmes Auburn University Typeset by AMS-TEX Chapter 1. Metric Spaces 1. Definition and Examples. As the course progresses we will need to review some basic notions about
OPERATIONS RESEARCH CENTER. ^ l^ COPY $. /^ UPDATING THE PRODUCT FORM OF THE INVERSE FOR THE REVERSED SIMPLEX METHOD
 -,i.im»»-i.wu, i^~*^~mi^^mmmrim*^f~*^mmm _^,^. [ CO ORC 64-33 DECEMBER 1964 < UPDATING THE PRODUCT FORM OF THE INVERSE FOR THE REVERSED SIMPLEX METHOD COPY $. /^ ^QQFICHE J. ^ 3-^ by George B. Dantzig
-,i.im»»-i.wu, i^~*^~mi^^mmmrim*^f~*^mmm _^,^. [ CO ORC 64-33 DECEMBER 1964 < UPDATING THE PRODUCT FORM OF THE INVERSE FOR THE REVERSED SIMPLEX METHOD COPY $. /^ ^QQFICHE J. ^ 3-^ by George B. Dantzig
Local Stability of Strict Equilibria under Evolutionary Game Dynamics
 Local Stability of Strict Equilibria under Evolutionary Game Dynamics William H. Sandholm October 19, 2012 Abstract We consider the stability of strict equilibrium under deterministic evolutionary game
Local Stability of Strict Equilibria under Evolutionary Game Dynamics William H. Sandholm October 19, 2012 Abstract We consider the stability of strict equilibrium under deterministic evolutionary game
PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS MIDTERM
 PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS MIDTERM ERIN PEARSE. For b =,,..., ), find the explicit fundamental solution to the heat equation u + b u u t = 0 in R n 0, ). ) Letting G be what you find, show u 0 x) =
PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS MIDTERM ERIN PEARSE. For b =,,..., ), find the explicit fundamental solution to the heat equation u + b u u t = 0 in R n 0, ). ) Letting G be what you find, show u 0 x) =
ON THE CAUCHY EQUATION ON SPHERES
 Annales Mathematicae Silesianae 11. Katowice 1997, 89-99 Prace Naukowe Uniwersytetu Śląskiego nr 1665 ON THE CAUCHY EQUATION ON SPHERES ROMAN GER AND JUSTYNA SIKORSKA Abstract. We deal with a conditional
Annales Mathematicae Silesianae 11. Katowice 1997, 89-99 Prace Naukowe Uniwersytetu Śląskiego nr 1665 ON THE CAUCHY EQUATION ON SPHERES ROMAN GER AND JUSTYNA SIKORSKA Abstract. We deal with a conditional
Institutionen för matematik, KTH.
 Institutionen för matematik, KTH. Contents 7 Affine Varieties 1 7.1 The polynomial ring....................... 1 7.2 Hypersurfaces........................... 1 7.3 Ideals...............................
Institutionen för matematik, KTH. Contents 7 Affine Varieties 1 7.1 The polynomial ring....................... 1 7.2 Hypersurfaces........................... 1 7.3 Ideals...............................
Factorization in Integral Domains II
 Factorization in Integral Domains II 1 Statement of the main theorem Throughout these notes, unless otherwise specified, R is a UFD with field of quotients F. The main examples will be R = Z, F = Q, and
Factorization in Integral Domains II 1 Statement of the main theorem Throughout these notes, unless otherwise specified, R is a UFD with field of quotients F. The main examples will be R = Z, F = Q, and
Elliptic Curves and Public Key Cryptography
 Elliptic Curves and Public Key Cryptography Jeff Achter January 7, 2011 1 Introduction to Elliptic Curves 1.1 Diophantine equations Many classical problems in number theory have the following form: Let
Elliptic Curves and Public Key Cryptography Jeff Achter January 7, 2011 1 Introduction to Elliptic Curves 1.1 Diophantine equations Many classical problems in number theory have the following form: Let
II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics
 II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics Based on the results of the experiments described in the previous section, we recognize that real experiments do not behave quite as we expect. This section presents
II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics Based on the results of the experiments described in the previous section, we recognize that real experiments do not behave quite as we expect. This section presents
7 The Navier-Stokes Equations
 18.354/12.27 Spring 214 7 The Navier-Stokes Equations In the previous section, we have seen how one can deduce the general structure of hydrodynamic equations from purely macroscopic considerations and
18.354/12.27 Spring 214 7 The Navier-Stokes Equations In the previous section, we have seen how one can deduce the general structure of hydrodynamic equations from purely macroscopic considerations and
Homework 6 Math 309 Spring 2016
 Homework 6 Math 309 Spring 2016 Due May 18th Name: Solution: KEY: Do not distribute! Directions: No late homework will be accepted. The homework can be turned in during class or in the math lounge in Pedelford
Homework 6 Math 309 Spring 2016 Due May 18th Name: Solution: KEY: Do not distribute! Directions: No late homework will be accepted. The homework can be turned in during class or in the math lounge in Pedelford
Chapter 9. Mixed Extensions. 9.1 Mixed strategies
 Chapter 9 Mixed Extensions We now study a special case of infinite strategic games that are obtained in a canonic way from the finite games, by allowing mixed strategies. Below [0, 1] stands for the real
Chapter 9 Mixed Extensions We now study a special case of infinite strategic games that are obtained in a canonic way from the finite games, by allowing mixed strategies. Below [0, 1] stands for the real
2: LINEAR TRANSFORMATIONS AND MATRICES
 2: LINEAR TRANSFORMATIONS AND MATRICES STEVEN HEILMAN Contents 1. Review 1 2. Linear Transformations 1 3. Null spaces, range, coordinate bases 2 4. Linear Transformations and Bases 4 5. Matrix Representation,
2: LINEAR TRANSFORMATIONS AND MATRICES STEVEN HEILMAN Contents 1. Review 1 2. Linear Transformations 1 3. Null spaces, range, coordinate bases 2 4. Linear Transformations and Bases 4 5. Matrix Representation,
CHAPTER III THE CURVE AND THE EQUATION. The bisectors of the adjacent angles formed by two lines is. To solve any locus problem involves two things :
 CHAPTER III THE CURVE AND THE EQUATION 24. Locus of a point satisfying a given condition. The curve* (or group of curves) passing through all points which satisfy a given condition, and through no other
CHAPTER III THE CURVE AND THE EQUATION 24. Locus of a point satisfying a given condition. The curve* (or group of curves) passing through all points which satisfy a given condition, and through no other
x i x j x l ωk x j dx i dx j,
 Exterior Derivatives In this section we define a natural differential operator on smooth forms, called the exterior derivative. It is a generalization of the diffeential of a function. Motivations: Recall
Exterior Derivatives In this section we define a natural differential operator on smooth forms, called the exterior derivative. It is a generalization of the diffeential of a function. Motivations: Recall
Sample Examination VI 203
 Sample Examination VI 203 Section II Part A: Graphing Calculator MAY BE USED. 1. Two particles move in the xy-plane: Particle A moves along the graph of y = 1 + e- X and particle B moves along the graph
Sample Examination VI 203 Section II Part A: Graphing Calculator MAY BE USED. 1. Two particles move in the xy-plane: Particle A moves along the graph of y = 1 + e- X and particle B moves along the graph
Normed and Banach spaces
 Normed and Banach spaces László Erdős Nov 11, 2006 1 Norms We recall that the norm is a function on a vectorspace V, : V R +, satisfying the following properties x + y x + y cx = c x x = 0 x = 0 We always
Normed and Banach spaces László Erdős Nov 11, 2006 1 Norms We recall that the norm is a function on a vectorspace V, : V R +, satisfying the following properties x + y x + y cx = c x x = 0 x = 0 We always
CLASSIFICATION AND PRINCIPLE OF SUPERPOSITION FOR SECOND ORDER LINEAR PDE
 CLASSIFICATION AND PRINCIPLE OF SUPERPOSITION FOR SECOND ORDER LINEAR PDE 1. Linear Partial Differential Equations A partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation, for an unknown function u, that
CLASSIFICATION AND PRINCIPLE OF SUPERPOSITION FOR SECOND ORDER LINEAR PDE 1. Linear Partial Differential Equations A partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation, for an unknown function u, that
Chapter 2 Non-linear Equations
 Chapter 2 Non-linear Equations 2.1 First Examples of Non-linear Ordinary Differential Equations Before describing some general properties of non-linear equations, we find it useful to present some well-known
Chapter 2 Non-linear Equations 2.1 First Examples of Non-linear Ordinary Differential Equations Before describing some general properties of non-linear equations, we find it useful to present some well-known
POINT SET TOPOLOGY. Definition 2 A set with a topological structure is a topological space (X, O)
 POINT SET TOPOLOGY Definition 1 A topological structure on a set X is a family O P(X) called open sets and satisfying (O 1 ) O is closed for arbitrary unions (O 2 ) O is closed for finite intersections.
POINT SET TOPOLOGY Definition 1 A topological structure on a set X is a family O P(X) called open sets and satisfying (O 1 ) O is closed for arbitrary unions (O 2 ) O is closed for finite intersections.
Discretization Methods Exercise # 5
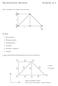 Discretization Methods Exercise # 5 Static calculation of a planar truss structure: a a F Six steps: 1. Discretization 2. Element matrices 3. Transformation 4. Assembly 5. Boundary conditions 6. Solution
Discretization Methods Exercise # 5 Static calculation of a planar truss structure: a a F Six steps: 1. Discretization 2. Element matrices 3. Transformation 4. Assembly 5. Boundary conditions 6. Solution
23 Elements of analytic ODE theory. Bessel s functions
 23 Elements of analytic ODE theory. Bessel s functions Recall I am changing the variables) that we need to solve the so-called Bessel s equation 23. Elements of analytic ODE theory Let x 2 u + xu + x 2
23 Elements of analytic ODE theory. Bessel s functions Recall I am changing the variables) that we need to solve the so-called Bessel s equation 23. Elements of analytic ODE theory Let x 2 u + xu + x 2
Convex Optimization Theory. Chapter 5 Exercises and Solutions: Extended Version
 Convex Optimization Theory Chapter 5 Exercises and Solutions: Extended Version Dimitri P. Bertsekas Massachusetts Institute of Technology Athena Scientific, Belmont, Massachusetts http://www.athenasc.com
Convex Optimization Theory Chapter 5 Exercises and Solutions: Extended Version Dimitri P. Bertsekas Massachusetts Institute of Technology Athena Scientific, Belmont, Massachusetts http://www.athenasc.com
Background on Coherent Systems
 2 Background on Coherent Systems 2.1 Basic Ideas We will use the term system quite freely and regularly, even though it will remain an undefined term throughout this monograph. As we all have some experience
2 Background on Coherent Systems 2.1 Basic Ideas We will use the term system quite freely and regularly, even though it will remain an undefined term throughout this monograph. As we all have some experience
Math 5588 Final Exam Solutions
 Math 5588 Final Exam Solutions Prof. Jeff Calder May 9, 2017 1. Find the function u : [0, 1] R that minimizes I(u) = subject to u(0) = 0 and u(1) = 1. 1 0 e u(x) u (x) + u (x) 2 dx, Solution. Since the
Math 5588 Final Exam Solutions Prof. Jeff Calder May 9, 2017 1. Find the function u : [0, 1] R that minimizes I(u) = subject to u(0) = 0 and u(1) = 1. 1 0 e u(x) u (x) + u (x) 2 dx, Solution. Since the
Definition 5.1. A vector field v on a manifold M is map M T M such that for all x M, v(x) T x M.
 5 Vector fields Last updated: March 12, 2012. 5.1 Definition and general properties We first need to define what a vector field is. Definition 5.1. A vector field v on a manifold M is map M T M such that
5 Vector fields Last updated: March 12, 2012. 5.1 Definition and general properties We first need to define what a vector field is. Definition 5.1. A vector field v on a manifold M is map M T M such that
Going from graphic solutions to algebraic
 Going from graphic solutions to algebraic 2 variables: Graph constraints Identify corner points of feasible area Find which corner point has best objective value More variables: Think about constraints
Going from graphic solutions to algebraic 2 variables: Graph constraints Identify corner points of feasible area Find which corner point has best objective value More variables: Think about constraints
WEYL S LEMMA, ONE OF MANY. Daniel W. Stroock
 WEYL S LEMMA, ONE OF MANY Daniel W Stroock Abstract This note is a brief, and somewhat biased, account of the evolution of what people working in PDE s call Weyl s Lemma about the regularity of solutions
WEYL S LEMMA, ONE OF MANY Daniel W Stroock Abstract This note is a brief, and somewhat biased, account of the evolution of what people working in PDE s call Weyl s Lemma about the regularity of solutions
REGULARITY FOR OBSTACLE PROBLEMS WITH APPLICATIONS TO THE FREE BOUNDARIES IN THE CONSTRAINED LEAST GRADIENT PROBLEM
 177 REGULARITY FOR OBSTACLE PROBLEMS WITH APPLICATIONS TO THE FREE BOUNDARIES IN THE CONSTRAINED LEAST GRADIENT PROBLEM Graham Williams The constrained least gradient problem involves minimizing in j'vujd:c
177 REGULARITY FOR OBSTACLE PROBLEMS WITH APPLICATIONS TO THE FREE BOUNDARIES IN THE CONSTRAINED LEAST GRADIENT PROBLEM Graham Williams The constrained least gradient problem involves minimizing in j'vujd:c
On the game-theoretic value of a linear transformation on a symmetric cone
 On the game-theoretic value of a linear transformation ona symmetric cone p. 1/25 On the game-theoretic value of a linear transformation on a symmetric cone M. Seetharama Gowda Department of Mathematics
On the game-theoretic value of a linear transformation ona symmetric cone p. 1/25 On the game-theoretic value of a linear transformation on a symmetric cone M. Seetharama Gowda Department of Mathematics
F I N I T E T E R M I N A T I 0 N GAME S
 F I N I T E T E R M I N A T I 0 N GAME S W I T H T I E by P E T E R G. HINMAN Abstract We consider the class of finite two-person games with perfect information in which the last player who can make a
F I N I T E T E R M I N A T I 0 N GAME S W I T H T I E by P E T E R G. HINMAN Abstract We consider the class of finite two-person games with perfect information in which the last player who can make a
Mathematical Olympiad for Girls
 UKMT UKMT UKMT United Kingdom Mathematics Trust Mathematical Olympiad for Girls Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust These are polished solutions and do not illustrate the process of failed
UKMT UKMT UKMT United Kingdom Mathematics Trust Mathematical Olympiad for Girls Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust These are polished solutions and do not illustrate the process of failed
Parity of the Number of Irreducible Factors for Composite Polynomials
 Parity of the Number of Irreducible Factors for Composite Polynomials Ryul Kim Wolfram Koepf Abstract Various results on parity of the number of irreducible factors of given polynomials over finite fields
Parity of the Number of Irreducible Factors for Composite Polynomials Ryul Kim Wolfram Koepf Abstract Various results on parity of the number of irreducible factors of given polynomials over finite fields
Infinite Limits. By Tuesday J. Johnson
 Infinite Limits By Tuesday J. Johnson Suggested Review Topics Algebra skills reviews suggested: Evaluating functions Graphing functions Working with inequalities Working with absolute values Trigonometric
Infinite Limits By Tuesday J. Johnson Suggested Review Topics Algebra skills reviews suggested: Evaluating functions Graphing functions Working with inequalities Working with absolute values Trigonometric
LECTURE 16: LIE GROUPS AND THEIR LIE ALGEBRAS. 1. Lie groups
 LECTURE 16: LIE GROUPS AND THEIR LIE ALGEBRAS 1. Lie groups A Lie group is a special smooth manifold on which there is a group structure, and moreover, the two structures are compatible. Lie groups are
LECTURE 16: LIE GROUPS AND THEIR LIE ALGEBRAS 1. Lie groups A Lie group is a special smooth manifold on which there is a group structure, and moreover, the two structures are compatible. Lie groups are
A GENERAL MEAN-VALUE THEOREM*
 A GENERAL MEAN-VALUE THEOREM* BY D. V. WIDDER In a paper published in 1906t, Professor G. D. Birkhoff treated the meanvalue and remainder theorems belonging to polynomial interpolation, in which the linear
A GENERAL MEAN-VALUE THEOREM* BY D. V. WIDDER In a paper published in 1906t, Professor G. D. Birkhoff treated the meanvalue and remainder theorems belonging to polynomial interpolation, in which the linear
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers. David Miller
 Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers David Miller Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector space Vector space We need a space in which our vectors exist
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers David Miller Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector space Vector space We need a space in which our vectors exist
* -)(- ~(A) 2, with A a self-adjoint operator. Such maps are also called. Matematisk Seminar. Mars 1964 No 4.
 Matematisk Seminar U~iversitetet i Oslo Mars 1964 No 4. Jordan homomorphisms of operator algebras, by Erling St0rnier A Jordan homomorphism of a ring into another ring is a linear map with the two multiplicative
Matematisk Seminar U~iversitetet i Oslo Mars 1964 No 4. Jordan homomorphisms of operator algebras, by Erling St0rnier A Jordan homomorphism of a ring into another ring is a linear map with the two multiplicative
1 Functions of Several Variables 2019 v2
 1 Functions of Several Variables 2019 v2 11 Notation The subject of this course is the study of functions f : R n R m The elements of R n, for n 2, will be called vectors so, if m > 1, f will be said to
1 Functions of Several Variables 2019 v2 11 Notation The subject of this course is the study of functions f : R n R m The elements of R n, for n 2, will be called vectors so, if m > 1, f will be said to
Chapter 1. Preliminaries. The purpose of this chapter is to provide some basic background information. Linear Space. Hilbert Space.
 Chapter 1 Preliminaries The purpose of this chapter is to provide some basic background information. Linear Space Hilbert Space Basic Principles 1 2 Preliminaries Linear Space The notion of linear space
Chapter 1 Preliminaries The purpose of this chapter is to provide some basic background information. Linear Space Hilbert Space Basic Principles 1 2 Preliminaries Linear Space The notion of linear space
Citation for published version (APA): Harinck, S. (2001). Conflict issues matter : how conflict issues influence negotiation
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Conflict issues matter : how conflict issues influence negotiation Harinck, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Harinck, S. (2001). Conflict
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Conflict issues matter : how conflict issues influence negotiation Harinck, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Harinck, S. (2001). Conflict
MTH 215: Introduction to Linear Algebra
 MTH 215: Introduction to Linear Algebra Lecture 5 Jonathan A. Chávez Casillas 1 1 University of Rhode Island Department of Mathematics September 20, 2017 1 LU Factorization 2 3 4 Triangular Matrices Definition
MTH 215: Introduction to Linear Algebra Lecture 5 Jonathan A. Chávez Casillas 1 1 University of Rhode Island Department of Mathematics September 20, 2017 1 LU Factorization 2 3 4 Triangular Matrices Definition
Lecture 2. MATH3220 Operations Research and Logistics Jan. 8, Pan Li The Chinese University of Hong Kong. Integer Programming Formulations
 Lecture 2 MATH3220 Operations Research and Logistics Jan. 8, 2015 Pan Li The Chinese University of Hong Kong 2.1 Agenda 1 2 3 2.2 : a linear program plus the additional constraints that some or all of
Lecture 2 MATH3220 Operations Research and Logistics Jan. 8, 2015 Pan Li The Chinese University of Hong Kong 2.1 Agenda 1 2 3 2.2 : a linear program plus the additional constraints that some or all of
Problem 1. CS205 Homework #2 Solutions. Solution
 CS205 Homework #2 s Problem 1 [Heath 3.29, page 152] Let v be a nonzero n-vector. The hyperplane normal to v is the (n-1)-dimensional subspace of all vectors z such that v T z = 0. A reflector is a linear
CS205 Homework #2 s Problem 1 [Heath 3.29, page 152] Let v be a nonzero n-vector. The hyperplane normal to v is the (n-1)-dimensional subspace of all vectors z such that v T z = 0. A reflector is a linear
1182 L. B. Beasley, S. Z. Song, ands. G. Lee matrix all of whose entries are 1 and =fe ij j1 i m 1 j ng denote the set of cells. The zero-term rank [5
 J. Korean Math. Soc. 36 (1999), No. 6, pp. 1181{1190 LINEAR OPERATORS THAT PRESERVE ZERO-TERM RANK OF BOOLEAN MATRICES LeRoy. B. Beasley, Seok-Zun Song, and Sang-Gu Lee Abstract. Zero-term rank of a matrix
J. Korean Math. Soc. 36 (1999), No. 6, pp. 1181{1190 LINEAR OPERATORS THAT PRESERVE ZERO-TERM RANK OF BOOLEAN MATRICES LeRoy. B. Beasley, Seok-Zun Song, and Sang-Gu Lee Abstract. Zero-term rank of a matrix
Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications. Lecture 7: The LP Duality Theorem
 Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications Lecture 7: The LP Duality Theorem Kousha Etessami recall LP s in Primal Form 1 Maximize c 1 x 1 + c 2 x 2 +... + c n x n a 1,1 x 1 + a 1,2 x 2 +... + a 1,n x n
Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications Lecture 7: The LP Duality Theorem Kousha Etessami recall LP s in Primal Form 1 Maximize c 1 x 1 + c 2 x 2 +... + c n x n a 1,1 x 1 + a 1,2 x 2 +... + a 1,n x n
First Digit Tally Marks Final Count
 Benford Test () Imagine that you are a forensic accountant, presented with the two data sets on this sheet of paper (front and back). Which of the two sets should be investigated further? Why? () () ()
Benford Test () Imagine that you are a forensic accountant, presented with the two data sets on this sheet of paper (front and back). Which of the two sets should be investigated further? Why? () () ()
Overview of normed linear spaces
 20 Chapter 2 Overview of normed linear spaces Starting from this chapter, we begin examining linear spaces with at least one extra structure (topology or geometry). We assume linearity; this is a natural
20 Chapter 2 Overview of normed linear spaces Starting from this chapter, we begin examining linear spaces with at least one extra structure (topology or geometry). We assume linearity; this is a natural
CH 59 SQUARE ROOTS. Every positive number has two square roots. Ch 59 Square Roots. Introduction
 59 CH 59 SQUARE ROOTS Introduction W e saw square roots when we studied the Pythagorean Theorem. They may have been hidden, but when the end of a right-triangle problem resulted in an equation like c =
59 CH 59 SQUARE ROOTS Introduction W e saw square roots when we studied the Pythagorean Theorem. They may have been hidden, but when the end of a right-triangle problem resulted in an equation like c =
THE CORONA FACTORIZATION PROPERTY AND REFINEMENT MONOIDS
 THE CORONA FACTORIZATION PROPERTY AND REFINEMENT MONOIDS EDUARD ORTEGA, FRANCESC PERERA, AND MIKAEL RØRDAM ABSTRACT. The Corona Factorization Property of a C -algebra, originally defined to study extensions
THE CORONA FACTORIZATION PROPERTY AND REFINEMENT MONOIDS EDUARD ORTEGA, FRANCESC PERERA, AND MIKAEL RØRDAM ABSTRACT. The Corona Factorization Property of a C -algebra, originally defined to study extensions
MATH 220: Problem Set 3 Solutions
 MATH 220: Problem Set 3 Solutions Problem 1. Let ψ C() be given by: 0, x < 1, 1 + x, 1 < x < 0, ψ(x) = 1 x, 0 < x < 1, 0, x > 1, so that it verifies ψ 0, ψ(x) = 0 if x 1 and ψ(x)dx = 1. Consider (ψ j )
MATH 220: Problem Set 3 Solutions Problem 1. Let ψ C() be given by: 0, x < 1, 1 + x, 1 < x < 0, ψ(x) = 1 x, 0 < x < 1, 0, x > 1, so that it verifies ψ 0, ψ(x) = 0 if x 1 and ψ(x)dx = 1. Consider (ψ j )
Ensembles and incomplete information
 p. 1/32 Ensembles and incomplete information So far in this course, we have described quantum systems by states that are normalized vectors in a complex Hilbert space. This works so long as (a) the system
p. 1/32 Ensembles and incomplete information So far in this course, we have described quantum systems by states that are normalized vectors in a complex Hilbert space. This works so long as (a) the system
Introduction to Algebraic and Geometric Topology Week 14
 Introduction to Algebraic and Geometric Topology Week 14 Domingo Toledo University of Utah Fall 2016 Computations in coordinates I Recall smooth surface S = {f (x, y, z) =0} R 3, I rf 6= 0 on S, I Chart
Introduction to Algebraic and Geometric Topology Week 14 Domingo Toledo University of Utah Fall 2016 Computations in coordinates I Recall smooth surface S = {f (x, y, z) =0} R 3, I rf 6= 0 on S, I Chart
SMALL ZEROS OF QUADRATIC FORMS WITH LINEAR CONDITIONS. Lenny Fukshansky. f ij X i Y j
 SALL ZEROS OF QUADRATIC FORS WITH LINEAR CONDITIONS Lenny Fukshansky Abstract. Given a quadratic form and linear forms in N + 1 variables with coefficients in a number field K, suppose that there exists
SALL ZEROS OF QUADRATIC FORS WITH LINEAR CONDITIONS Lenny Fukshansky Abstract. Given a quadratic form and linear forms in N + 1 variables with coefficients in a number field K, suppose that there exists
The Mollifier Theorem
 The Mollifier Theorem Definition of the Mollifier The function Tx Kexp 1 if x 1 2 1 x 0 if x 1, x R n where the constant K is chosen such that R n Txdx 1, is a test function on Rn. Note that Tx vanishes,
The Mollifier Theorem Definition of the Mollifier The function Tx Kexp 1 if x 1 2 1 x 0 if x 1, x R n where the constant K is chosen such that R n Txdx 1, is a test function on Rn. Note that Tx vanishes,
Lecture Notes on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS. Eusebius Doedel
 Lecture Notes on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel c Eusebius J. Doedel, 009 Contents Logic. Introduction............................................................................... Basic logical
Lecture Notes on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel c Eusebius J. Doedel, 009 Contents Logic. Introduction............................................................................... Basic logical
A primer on matrices
 A primer on matrices Stephen Boyd August 4, 2007 These notes describe the notation of matrices, the mechanics of matrix manipulation, and how to use matrices to formulate and solve sets of simultaneous
A primer on matrices Stephen Boyd August 4, 2007 These notes describe the notation of matrices, the mechanics of matrix manipulation, and how to use matrices to formulate and solve sets of simultaneous
WRT in 2D: Poisson Example
 WRT in 2D: Poisson Example Consider 2 u f on [, L x [, L y with u. WRT: For all v X N, find u X N a(v, u) such that v u dv v f dv. Follows from strong form plus integration by parts: ( ) 2 u v + 2 u dx
WRT in 2D: Poisson Example Consider 2 u f on [, L x [, L y with u. WRT: For all v X N, find u X N a(v, u) such that v u dv v f dv. Follows from strong form plus integration by parts: ( ) 2 u v + 2 u dx
UNCLASSIFIED Reptoduced. if ike ARMED SERVICES TECHNICAL INFORMATION AGENCY ARLINGTON HALL STATION ARLINGTON 12, VIRGINIA UNCLASSIFIED
 . UNCLASSIFIED. 273207 Reptoduced if ike ARMED SERVICES TECHNICAL INFORMATION AGENCY ARLINGTON HALL STATION ARLINGTON 12, VIRGINIA UNCLASSIFIED NOTICE: When government or other drawings, specifications
. UNCLASSIFIED. 273207 Reptoduced if ike ARMED SERVICES TECHNICAL INFORMATION AGENCY ARLINGTON HALL STATION ARLINGTON 12, VIRGINIA UNCLASSIFIED NOTICE: When government or other drawings, specifications
CS412: Lecture #17. Mridul Aanjaneya. March 19, 2015
 CS: Lecture #7 Mridul Aanjaneya March 9, 5 Solving linear systems of equations Consider a lower triangular matrix L: l l l L = l 3 l 3 l 33 l n l nn A procedure similar to that for upper triangular systems
CS: Lecture #7 Mridul Aanjaneya March 9, 5 Solving linear systems of equations Consider a lower triangular matrix L: l l l L = l 3 l 3 l 33 l n l nn A procedure similar to that for upper triangular systems
Review of matrices. Let m, n IN. A rectangle of numbers written like A =
 Review of matrices Let m, n IN. A rectangle of numbers written like a 11 a 12... a 1n a 21 a 22... a 2n A =...... a m1 a m2... a mn where each a ij IR is called a matrix with m rows and n columns or an
Review of matrices Let m, n IN. A rectangle of numbers written like a 11 a 12... a 1n a 21 a 22... a 2n A =...... a m1 a m2... a mn where each a ij IR is called a matrix with m rows and n columns or an
Deep Linear Networks with Arbitrary Loss: All Local Minima Are Global
 homas Laurent * 1 James H. von Brecht * 2 Abstract We consider deep linear networks with arbitrary convex differentiable loss. We provide a short and elementary proof of the fact that all local minima
homas Laurent * 1 James H. von Brecht * 2 Abstract We consider deep linear networks with arbitrary convex differentiable loss. We provide a short and elementary proof of the fact that all local minima
Final Exam May 4, 2016
 1 Math 425 / AMCS 525 Dr. DeTurck Final Exam May 4, 2016 You may use your book and notes on this exam. Show your work in the exam book. Work only the problems that correspond to the section that you prepared.
1 Math 425 / AMCS 525 Dr. DeTurck Final Exam May 4, 2016 You may use your book and notes on this exam. Show your work in the exam book. Work only the problems that correspond to the section that you prepared.
UNIT #3 LINEAR FUNCTIONS, EQUATIONS, AND THEIR ALGEBRA COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 Name: Date: Part I Questions UNIT #3 LINEAR FUNCTIONS, EQUATIONS, AND THEIR ALGEBRA COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II. The distance that a person drives at a constant speed varies directly with the amount of time
Name: Date: Part I Questions UNIT #3 LINEAR FUNCTIONS, EQUATIONS, AND THEIR ALGEBRA COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II. The distance that a person drives at a constant speed varies directly with the amount of time
direct or inverse variation. Write the equation that models the relationship.
 Name. Block Date Version A Algebra 2: Chapter 8 Test Review Directions #1&2: Determine if a variation relationship exists. Describe the data in the table as a direct or inverse variation. Write the equation
Name. Block Date Version A Algebra 2: Chapter 8 Test Review Directions #1&2: Determine if a variation relationship exists. Describe the data in the table as a direct or inverse variation. Write the equation
ON THE AVERAGE NUMBER OF REAL ROOTS OF A RANDOM ALGEBRAIC EQUATION
 ON THE AVERAGE NUMBER OF REAL ROOTS OF A RANDOM ALGEBRAIC EQUATION M. KAC 1. Introduction. Consider the algebraic equation (1) Xo + X x x + X 2 x 2 + + In-i^" 1 = 0, where the X's are independent random
ON THE AVERAGE NUMBER OF REAL ROOTS OF A RANDOM ALGEBRAIC EQUATION M. KAC 1. Introduction. Consider the algebraic equation (1) Xo + X x x + X 2 x 2 + + In-i^" 1 = 0, where the X's are independent random
98 Cours d analyse September 1, Chapter V. Determination of continuous functions of a single variable that satisfy certain conditions.
 98 Cours d analyse September 1, 2008 [98] Chapter V. Determination of continuous functions of a single variable that satisfy certain conditions. I. Research on a continuous function formed in such a manner
98 Cours d analyse September 1, 2008 [98] Chapter V. Determination of continuous functions of a single variable that satisfy certain conditions. I. Research on a continuous function formed in such a manner
The Power of One-State Turing Machines
 The Power of One-State Turing Machines Marzio De Biasi Jan 15, 2018 Abstract At first glance, one state Turing machines are very weak: the Halting problem for them is decidable, and, without memory, they
The Power of One-State Turing Machines Marzio De Biasi Jan 15, 2018 Abstract At first glance, one state Turing machines are very weak: the Halting problem for them is decidable, and, without memory, they
