Lecture 10: Vector Algebra: Orthogonal Basis
|
|
|
- Tamsin Dean
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 0: Vector Algebra: Orthogonal Basis Orthogonal Basis of a subspace Computing an orthogonal basis for a subspace using Gram-Schmidt Orthogonalization Process
2 Orthogonal Set Any set of vectors that are mutually orthogonal, is a an orthogonal set.
3 Orthonormal Set Any set of unit vectors that are mutually orthogonal, is a an orthonormal set. In other words, any orthogonal set is an orthonormal set if all the vectors in the set are unit vectors. Example: u, u 2, u 3 is an orthonormal set, where, 3 u =, u 2 = 6 2 6, u 3 =
4 An orthogonal set is Linearly Independent
5 Projection of vector b on vector a a b = a b cos θ Vector c is the image/perpendicular projection of b on a Direction of c is the same as a Magnitude of c is c = b cos θ = a b a If a is the unit vector of a, then vector c = a b a a b a = a a a c = a b = a b a a a b cos θ b b sin θ
6 Orthogonal Basis An orthogonal basis for a subspace W of R n is a basis for W that is also an orthogonal set. Example: 0 0, 0 0, 0 0 is basically the x, y, and z axis. It is an orthogonal basis in R 3, and it spans the whole R 3 space. It is also an orthogonal set.
7 Orthogonal Basis We know that given a basis of a subspace, any vector in that subspace will be a linear combination of the basis vectors. For example, if u and v are linearly independent and form the basis for a subspace S, then any vector y in S can be expressed as: y = c u + c 2 v But computing c and c 2 is not straight forward. v y On the other hand, if u and v form an orthogonal basis, then c = y u u y u = u u and c 2 = y v v y v = v v c 2 c u
8 Does not work if it is not Orthogonal basis y = c u + c 2 v But computing c and c 2 is not straight forward (yet). What is computed is, d = y u u = y u u u d 2 v y d 2 = y v v = y v v v c 2 c u d 8
9 Orthogonal Decomposition Theorem
10 Orthogonal Decomposition Theorem
11 Orthogonal Decomposition Theorem
12 Orthogonal Decomposition Theorem Example
13 Projection of a vector on a Subspace u and v are orthogonal 3D vectors. They span a plane (green plane) in 3D y is an arbitrary 3D vector out of the plane. y is the projection of y onto the plane. y = y u y v u + v u u v v The point y is also the closest point to y on the plane. y y is perpendicular to y, Span{u, v}, and hence u and v v u y y Perpendicular to y, u, v
14 Closest point of a vector to a span does not depend on the basis of that span y is an arbitrary 3D vector out of the plane. y is the projection of y onto the plane. y = x u + x 2 u 2 y = x 3 u 3 + x 4 u 4 y = x 5 u + x 6 u 3 u 2 u Coordinates of y change if the basis changes. But the vector y itself does not change. Hence the the closest point to y on the plane does not change. Even here, y y is perpendicular to y and Span{.,. } u 4 u 3 y y Perpendicular to y and the span
15 Closest point of a vector to a span does not depend on the basis of that span FINDING THE CLOSEST POINT OF A VECTOR TO A SPAN means : Finding the coordinates of the projection of the vector So, if you want to compute the closest point of a vector to a span, then find an appropriate basis with which you can compute the coordinates of the projection easily. What would be that basis? Answer: An orthogonal basis! u 4 u 3 y y u 2 u Perpendicular to y and the span
16 Projection on a span of non-orthogonal vectors How to find projection of any arbitrary 3D vector onto the span of two non-orthogonal, linearly independent vectors? u and u 2 are not orthogonal, but linearly independent vectors in 3D. y is an arbitrary 3D vector. Find the projection of y in the space spanned by u and u 2. a) First, find the orthogonal set of vectors v and v 2 that span the same subspace as u and u 2. In other words, find an orthogonal basis. b) Project y onto the space spanned by orthogonal v and v 2 vectors, as we earlier. v 2 u 2 u v y y
17 How to find an orthogonal basis?
18 How to find an orthogonal basis? Assume that the first vector u is in the orthogonal basis. Other vector(s) of the basis are computed that are perpendicular to u Let v = u Let v 2 = u 2 u 2v v v v We know that v 2 is perpendicular to v. v 2 is in the Span{u, u 2 } (Why?) So Span{u, u 2 } = Span{v, v 2 } And {v, v 2 } is an orthogonal basis Projection of y on to the Span{u, u 2 } v 2 u 2 u v y y y = y v v v v + y v 2 v 2 v 2 v 2
19 Gram-Schmidt Orthogonalization Process
20 Gram-Schmidt Orthogonalization Process Example:
21 Solving Inconsistent Systems
22 Solving Inconsistent Systems
23 Solving Inconsistent Systems Example : A trader buys and/or sells tomatoes and potatoes. (Negative number means buys, positive number means sells.) In the process, he either makes profit (positive number) or loss (negative number). A week s transaction is shown; find the approximate cost of tomatoes and potatoes. Tomatoes (tons) Potatoes (tons) Profit/Loss (in thousands)
24 Solving Inconsistent Systems t - 6p = t - 2p = 2 t + p = t + 7p = 6 t p = 2 6 The above equation might not have a solution (values of t and p that would satisfy that equation). So the best we can do is to find the values of t and p that would result in a vector on the right hand side that is as close as possible to the desired right hand side vector.
25 Solving Inconsistent Systems Example 2:
Math 3191 Applied Linear Algebra
 Math 9 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture : Orthogonal Projections, Gram-Schmidt Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 9Applied Linear Algebra p./ Orthonormal Sets A set of vectors {u, u,...,
Math 9 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture : Orthogonal Projections, Gram-Schmidt Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 9Applied Linear Algebra p./ Orthonormal Sets A set of vectors {u, u,...,
Section 6.2, 6.3 Orthogonal Sets, Orthogonal Projections
 Section 6. 6. Orthogonal Sets Orthogonal Projections Main Ideas in these sections: Orthogonal set = A set of mutually orthogonal vectors. OG LI. Orthogonal Projection of y onto u or onto an OG set {u u
Section 6. 6. Orthogonal Sets Orthogonal Projections Main Ideas in these sections: Orthogonal set = A set of mutually orthogonal vectors. OG LI. Orthogonal Projection of y onto u or onto an OG set {u u
Worksheet for Lecture 25 Section 6.4 Gram-Schmidt Process
 Worksheet for Lecture Name: Section.4 Gram-Schmidt Process Goal For a subspace W = Span{v,..., v n }, we want to find an orthonormal basis of W. Example Let W = Span{x, x } with x = and x =. Give an orthogonal
Worksheet for Lecture Name: Section.4 Gram-Schmidt Process Goal For a subspace W = Span{v,..., v n }, we want to find an orthonormal basis of W. Example Let W = Span{x, x } with x = and x =. Give an orthogonal
Math 261 Lecture Notes: Sections 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 and 6.4 Orthogonal Sets and Projections
 Math 6 Lecture Notes: Sections 6., 6., 6. and 6. Orthogonal Sets and Projections We will not cover general inner product spaces. We will, however, focus on a particular inner product space the inner product
Math 6 Lecture Notes: Sections 6., 6., 6. and 6. Orthogonal Sets and Projections We will not cover general inner product spaces. We will, however, focus on a particular inner product space the inner product
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Orthogonal sets Let V be a vector space with an inner product. Definition. Nonzero vectors v 1,v
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Orthogonal sets Let V be a vector space with an inner product. Definition. Nonzero vectors v 1,v
MTH 2310, FALL Introduction
 MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
Lecture 13: Orthogonal projections and least squares (Section ) Thang Huynh, UC San Diego 2/9/2018
 Lecture 13: Orthogonal projections and least squares (Section 3.2-3.3) Thang Huynh, UC San Diego 2/9/2018 Orthogonal projection onto subspaces Theorem. Let W be a subspace of R n. Then, each x in R n can
Lecture 13: Orthogonal projections and least squares (Section 3.2-3.3) Thang Huynh, UC San Diego 2/9/2018 Orthogonal projection onto subspaces Theorem. Let W be a subspace of R n. Then, each x in R n can
Orthonormal Bases; Gram-Schmidt Process; QR-Decomposition
 Orthonormal Bases; Gram-Schmidt Process; QR-Decomposition MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 205 Motivation When working with an inner product space, the most
Orthonormal Bases; Gram-Schmidt Process; QR-Decomposition MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 205 Motivation When working with an inner product space, the most
Section 6.4. The Gram Schmidt Process
 Section 6.4 The Gram Schmidt Process Motivation The procedures in 6 start with an orthogonal basis {u, u,..., u m}. Find the B-coordinates of a vector x using dot products: x = m i= x u i u i u i u i Find
Section 6.4 The Gram Schmidt Process Motivation The procedures in 6 start with an orthogonal basis {u, u,..., u m}. Find the B-coordinates of a vector x using dot products: x = m i= x u i u i u i u i Find
Orthogonal Complements
 Orthogonal Complements Definition Let W be a subspace of R n. If a vector z is orthogonal to every vector in W, then z is said to be orthogonal to W. The set of all such vectors z is called the orthogonal
Orthogonal Complements Definition Let W be a subspace of R n. If a vector z is orthogonal to every vector in W, then z is said to be orthogonal to W. The set of all such vectors z is called the orthogonal
Solutions to Review Problems for Chapter 6 ( ), 7.1
 Solutions to Review Problems for Chapter (-, 7 The Final Exam is on Thursday, June,, : AM : AM at NESBITT Final Exam Breakdown Sections % -,7-9,- - % -9,-,7,-,-7 - % -, 7 - % Let u u and v Let x x x x,
Solutions to Review Problems for Chapter (-, 7 The Final Exam is on Thursday, June,, : AM : AM at NESBITT Final Exam Breakdown Sections % -,7-9,- - % -9,-,7,-,-7 - % -, 7 - % Let u u and v Let x x x x,
Homework 5. (due Wednesday 8 th Nov midnight)
 Homework (due Wednesday 8 th Nov midnight) Use this definition for Column Space of a Matrix Column Space of a matrix A is the set ColA of all linear combinations of the columns of A. In other words, if
Homework (due Wednesday 8 th Nov midnight) Use this definition for Column Space of a Matrix Column Space of a matrix A is the set ColA of all linear combinations of the columns of A. In other words, if
MTH 2032 SemesterII
 MTH 202 SemesterII 2010-11 Linear Algebra Worked Examples Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education December 28, 2011 ii Contents Table of Contents
MTH 202 SemesterII 2010-11 Linear Algebra Worked Examples Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education December 28, 2011 ii Contents Table of Contents
Inner products. Theorem (basic properties): Given vectors u, v, w in an inner product space V, and a scalar k, the following properties hold:
 Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
Chapter 6: Orthogonality
 Chapter 6: Orthogonality (Last Updated: November 7, 7) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved around.. Inner products
Chapter 6: Orthogonality (Last Updated: November 7, 7) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved around.. Inner products
MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T. KEMP)
 MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T KEMP) Definition 01 If T (x) = Ax is a linear transformation from R n to R m then Nul (T ) = {x R n : T (x) = 0} = Nul (A) Ran (T ) = {Ax R m : x R n } = {b R m
MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T KEMP) Definition 01 If T (x) = Ax is a linear transformation from R n to R m then Nul (T ) = {x R n : T (x) = 0} = Nul (A) Ran (T ) = {Ax R m : x R n } = {b R m
Math 2331 Linear Algebra
 6. Orthogonal Projections Math 2 Linear Algebra 6. Orthogonal Projections Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math2 Jiwen He, University of
6. Orthogonal Projections Math 2 Linear Algebra 6. Orthogonal Projections Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math2 Jiwen He, University of
MATH Linear Algebra
 MATH 304 - Linear Algebra In the previous note we learned an important algorithm to produce orthogonal sequences of vectors called the Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization process. Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization
MATH 304 - Linear Algebra In the previous note we learned an important algorithm to produce orthogonal sequences of vectors called the Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization process. Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization
Linear Algebra. Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Fall A: Inner products
 Linear Algebra Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Fall 2011 6A: Inner products In this chapter, the field F = R or C. We regard F equipped with a conjugation χ : F F. If F =
Linear Algebra Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Fall 2011 6A: Inner products In this chapter, the field F = R or C. We regard F equipped with a conjugation χ : F F. If F =
LINEAR ALGEBRA SUMMARY SHEET.
 LINEAR ALGEBRA SUMMARY SHEET RADON ROSBOROUGH https://intuitiveexplanationscom/linear-algebra-summary-sheet/ This document is a concise collection of many of the important theorems of linear algebra, organized
LINEAR ALGEBRA SUMMARY SHEET RADON ROSBOROUGH https://intuitiveexplanationscom/linear-algebra-summary-sheet/ This document is a concise collection of many of the important theorems of linear algebra, organized
Math 3191 Applied Linear Algebra
 Math 191 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture 1: Inner Products, Length, Orthogonality Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 191Applied Linear Algebra p.1/ Motivation Not all linear systems have
Math 191 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture 1: Inner Products, Length, Orthogonality Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 191Applied Linear Algebra p.1/ Motivation Not all linear systems have
6. Orthogonality and Least-Squares
 Linear Algebra 6. Orthogonality and Least-Squares CSIE NCU 1 6. Orthogonality and Least-Squares 6.1 Inner product, length, and orthogonality. 2 6.2 Orthogonal sets... 8 6.3 Orthogonal projections... 13
Linear Algebra 6. Orthogonality and Least-Squares CSIE NCU 1 6. Orthogonality and Least-Squares 6.1 Inner product, length, and orthogonality. 2 6.2 Orthogonal sets... 8 6.3 Orthogonal projections... 13
The Gram Schmidt Process
 u 2 u The Gram Schmidt Process Now we will present a procedure, based on orthogonal projection, that converts any linearly independent set of vectors into an orthogonal set. Let us begin with the simple
u 2 u The Gram Schmidt Process Now we will present a procedure, based on orthogonal projection, that converts any linearly independent set of vectors into an orthogonal set. Let us begin with the simple
The Gram Schmidt Process
 The Gram Schmidt Process Now we will present a procedure, based on orthogonal projection, that converts any linearly independent set of vectors into an orthogonal set. Let us begin with the simple case
The Gram Schmidt Process Now we will present a procedure, based on orthogonal projection, that converts any linearly independent set of vectors into an orthogonal set. Let us begin with the simple case
Linear Models Review
 Linear Models Review Vectors in IR n will be written as ordered n-tuples which are understood to be column vectors, or n 1 matrices. A vector variable will be indicted with bold face, and the prime sign
Linear Models Review Vectors in IR n will be written as ordered n-tuples which are understood to be column vectors, or n 1 matrices. A vector variable will be indicted with bold face, and the prime sign
Vectors. Vectors and the scalar multiplication and vector addition operations:
 Vectors Vectors and the scalar multiplication and vector addition operations: x 1 x 1 y 1 2x 1 + 3y 1 x x n 1 = 2 x R n, 2 2 y + 3 2 2x = 2 + 3y 2............ x n x n y n 2x n + 3y n I ll use the two terms
Vectors Vectors and the scalar multiplication and vector addition operations: x 1 x 1 y 1 2x 1 + 3y 1 x x n 1 = 2 x R n, 2 2 y + 3 2 2x = 2 + 3y 2............ x n x n y n 2x n + 3y n I ll use the two terms
Lecture 4 Orthonormal vectors and QR factorization
 Orthonormal vectors and QR factorization 4 1 Lecture 4 Orthonormal vectors and QR factorization EE263 Autumn 2004 orthonormal vectors Gram-Schmidt procedure, QR factorization orthogonal decomposition induced
Orthonormal vectors and QR factorization 4 1 Lecture 4 Orthonormal vectors and QR factorization EE263 Autumn 2004 orthonormal vectors Gram-Schmidt procedure, QR factorization orthogonal decomposition induced
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2018 Lecture Notes Note 25
 EECS 6 Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 8 Lecture Notes Note 5 5. Speeding up OMP In the last lecture note, we introduced orthogonal matching pursuit OMP, an algorithm that can extract
EECS 6 Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 8 Lecture Notes Note 5 5. Speeding up OMP In the last lecture note, we introduced orthogonal matching pursuit OMP, an algorithm that can extract
Math 3C Lecture 25. John Douglas Moore
 Math 3C Lecture 25 John Douglas Moore June 1, 2009 Let V be a vector space. A basis for V is a collection of vectors {v 1,..., v k } such that 1. V = Span{v 1,..., v k }, and 2. {v 1,..., v k } are linearly
Math 3C Lecture 25 John Douglas Moore June 1, 2009 Let V be a vector space. A basis for V is a collection of vectors {v 1,..., v k } such that 1. V = Span{v 1,..., v k }, and 2. {v 1,..., v k } are linearly
A Primer in Econometric Theory
 A Primer in Econometric Theory Lecture 1: Vector Spaces John Stachurski Lectures by Akshay Shanker May 5, 2017 1/104 Overview Linear algebra is an important foundation for mathematics and, in particular,
A Primer in Econometric Theory Lecture 1: Vector Spaces John Stachurski Lectures by Akshay Shanker May 5, 2017 1/104 Overview Linear algebra is an important foundation for mathematics and, in particular,
Assignment #9: Orthogonal Projections, Gram-Schmidt, and Least Squares. Name:
 Assignment 9: Orthogonal Projections, Gram-Schmidt, and Least Squares Due date: Friday, April 0, 08 (:pm) Name: Section Number Assignment 9: Orthogonal Projections, Gram-Schmidt, and Least Squares Due
Assignment 9: Orthogonal Projections, Gram-Schmidt, and Least Squares Due date: Friday, April 0, 08 (:pm) Name: Section Number Assignment 9: Orthogonal Projections, Gram-Schmidt, and Least Squares Due
Dot product and linear least squares problems
 Dot product and linear least squares problems Dot Product For vectors u,v R n we define the dot product Note that we can also write this as u v = u,,u n u v = u v + + u n v n v v n = u v + + u n v n The
Dot product and linear least squares problems Dot Product For vectors u,v R n we define the dot product Note that we can also write this as u v = u,,u n u v = u v + + u n v n v v n = u v + + u n v n The
Math 2331 Linear Algebra
 6.2 Orthogonal Sets Math 233 Linear Algebra 6.2 Orthogonal Sets Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math233 Jiwen He, University of Houston
6.2 Orthogonal Sets Math 233 Linear Algebra 6.2 Orthogonal Sets Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math233 Jiwen He, University of Houston
LINEAR ALGEBRA 1, 2012-I PARTIAL EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS
 LINEAR ALGEBRA, -I PARTIAL EXAM SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS Problem (a) For each of the two matrices below, (i) determine whether it is diagonalizable, (ii) determine whether it is orthogonally diagonalizable,
LINEAR ALGEBRA, -I PARTIAL EXAM SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE PROBLEMS Problem (a) For each of the two matrices below, (i) determine whether it is diagonalizable, (ii) determine whether it is orthogonally diagonalizable,
The 'linear algebra way' of talking about "angle" and "similarity" between two vectors is called "inner product". We'll define this next.
 Orthogonality and QR The 'linear algebra way' of talking about "angle" and "similarity" between two vectors is called "inner product". We'll define this next. So, what is an inner product? An inner product
Orthogonality and QR The 'linear algebra way' of talking about "angle" and "similarity" between two vectors is called "inner product". We'll define this next. So, what is an inner product? An inner product
Problem # Max points possible Actual score Total 120
 FINAL EXAMINATION - MATH 2121, FALL 2017. Name: ID#: Email: Lecture & Tutorial: Problem # Max points possible Actual score 1 15 2 15 3 10 4 15 5 15 6 15 7 10 8 10 9 15 Total 120 You have 180 minutes to
FINAL EXAMINATION - MATH 2121, FALL 2017. Name: ID#: Email: Lecture & Tutorial: Problem # Max points possible Actual score 1 15 2 15 3 10 4 15 5 15 6 15 7 10 8 10 9 15 Total 120 You have 180 minutes to
which arises when we compute the orthogonal projection of a vector y in a subspace with an orthogonal basis. Hence assume that P y = A ij = x j, x i
 MODULE 6 Topics: Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization process We begin by observing that if the vectors {x j } N are mutually orthogonal in an inner product space V then they are necessarily linearly independent.
MODULE 6 Topics: Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization process We begin by observing that if the vectors {x j } N are mutually orthogonal in an inner product space V then they are necessarily linearly independent.
Math Linear Algebra
 Math 220 - Linear Algebra (Summer 208) Solutions to Homework #7 Exercise 6..20 (a) TRUE. u v v u = 0 is equivalent to u v = v u. The latter identity is true due to the commutative property of the inner
Math 220 - Linear Algebra (Summer 208) Solutions to Homework #7 Exercise 6..20 (a) TRUE. u v v u = 0 is equivalent to u v = v u. The latter identity is true due to the commutative property of the inner
Matrix Algebra for Engineers Jeffrey R. Chasnov
 Matrix Algebra for Engineers Jeffrey R. Chasnov The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematics Clear Water Bay, Kowloon
Matrix Algebra for Engineers Jeffrey R. Chasnov The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematics Clear Water Bay, Kowloon
The Gram-Schmidt Process 1
 The Gram-Schmidt Process In this section all vector spaces will be subspaces of some R m. Definition.. Let S = {v...v n } R m. The set S is said to be orthogonal if v v j = whenever i j. If in addition
The Gram-Schmidt Process In this section all vector spaces will be subspaces of some R m. Definition.. Let S = {v...v n } R m. The set S is said to be orthogonal if v v j = whenever i j. If in addition
MATH 31 - ADDITIONAL PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL
 MATH 3 - ADDITIONAL PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL MAIN TOPICS FOR THE FINAL EXAM:. Vectors. Dot product. Cross product. Geometric applications. 2. Row reduction. Null space, column space, row space, left
MATH 3 - ADDITIONAL PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL MAIN TOPICS FOR THE FINAL EXAM:. Vectors. Dot product. Cross product. Geometric applications. 2. Row reduction. Null space, column space, row space, left
6.1. Inner Product, Length and Orthogonality
 These are brief notes for the lecture on Friday November 13, and Monday November 1, 2009: they are not complete, but they are a guide to what I want to say on those days. They are guaranteed to be incorrect..1.
These are brief notes for the lecture on Friday November 13, and Monday November 1, 2009: they are not complete, but they are a guide to what I want to say on those days. They are guaranteed to be incorrect..1.
and u and v are orthogonal if and only if u v = 0. u v = x1x2 + y1y2 + z1z2. 1. In R 3 the dot product is defined by
 Linear Algebra [] 4.2 The Dot Product and Projections. In R 3 the dot product is defined by u v = u v cos θ. 2. For u = (x, y, z) and v = (x2, y2, z2), we have u v = xx2 + yy2 + zz2. 3. cos θ = u v u v,
Linear Algebra [] 4.2 The Dot Product and Projections. In R 3 the dot product is defined by u v = u v cos θ. 2. For u = (x, y, z) and v = (x2, y2, z2), we have u v = xx2 + yy2 + zz2. 3. cos θ = u v u v,
Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB
 Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional Plots Programming in
Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional Plots Programming in
There are two things that are particularly nice about the first basis
 Orthogonality and the Gram-Schmidt Process In Chapter 4, we spent a great deal of time studying the problem of finding a basis for a vector space We know that a basis for a vector space can potentially
Orthogonality and the Gram-Schmidt Process In Chapter 4, we spent a great deal of time studying the problem of finding a basis for a vector space We know that a basis for a vector space can potentially
Announcements Monday, November 19
 Announcements Monday, November 19 You should already have the link to view your graded midterm online. Course grades will be curved at the end of the semester. The percentage of A s, B s, and C s to be
Announcements Monday, November 19 You should already have the link to view your graded midterm online. Course grades will be curved at the end of the semester. The percentage of A s, B s, and C s to be
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 34: Review for Test 2.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 34: Review for Test 2. Topics for Test 2 Linear transformations (Leon 4.1 4.3) Matrix transformations Matrix of a linear mapping Similar matrices Orthogonality (Leon 5.1
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 34: Review for Test 2. Topics for Test 2 Linear transformations (Leon 4.1 4.3) Matrix transformations Matrix of a linear mapping Similar matrices Orthogonality (Leon 5.1
MTH 309Y 37. Inner product spaces. = a 1 b 1 + a 2 b a n b n
 MTH 39Y 37. Inner product spaces Recall: ) The dot product in R n : a. a n b. b n = a b + a 2 b 2 +...a n b n 2) Properties of the dot product: a) u v = v u b) (u + v) w = u w + v w c) (cu) v = c(u v)
MTH 39Y 37. Inner product spaces Recall: ) The dot product in R n : a. a n b. b n = a b + a 2 b 2 +...a n b n 2) Properties of the dot product: a) u v = v u b) (u + v) w = u w + v w c) (cu) v = c(u v)
Chapter 3 Transformations
 Chapter 3 Transformations An Introduction to Optimization Spring, 2014 Wei-Ta Chu 1 Linear Transformations A function is called a linear transformation if 1. for every and 2. for every If we fix the bases
Chapter 3 Transformations An Introduction to Optimization Spring, 2014 Wei-Ta Chu 1 Linear Transformations A function is called a linear transformation if 1. for every and 2. for every If we fix the bases
SOLUTION KEY TO THE LINEAR ALGEBRA FINAL EXAM 1 2 ( 2) ( 1) c a = 1 0
 SOLUTION KEY TO THE LINEAR ALGEBRA FINAL EXAM () We find a least squares solution to ( ) ( ) A x = y or 0 0 a b = c 4 0 0. 0 The normal equation is A T A x = A T y = y or 5 0 0 0 0 0 a b = 5 9. 0 0 4 7
SOLUTION KEY TO THE LINEAR ALGEBRA FINAL EXAM () We find a least squares solution to ( ) ( ) A x = y or 0 0 a b = c 4 0 0. 0 The normal equation is A T A x = A T y = y or 5 0 0 0 0 0 a b = 5 9. 0 0 4 7
orthogonal relations between vectors and subspaces Then we study some applications in vector spaces and linear systems, including Orthonormal Basis,
 5 Orthogonality Goals: We use scalar products to find the length of a vector, the angle between 2 vectors, projections, orthogonal relations between vectors and subspaces Then we study some applications
5 Orthogonality Goals: We use scalar products to find the length of a vector, the angle between 2 vectors, projections, orthogonal relations between vectors and subspaces Then we study some applications
2. Review of Linear Algebra
 2. Review of Linear Algebra ECE 83, Spring 217 In this course we will represent signals as vectors and operators (e.g., filters, transforms, etc) as matrices. This lecture reviews basic concepts from linear
2. Review of Linear Algebra ECE 83, Spring 217 In this course we will represent signals as vectors and operators (e.g., filters, transforms, etc) as matrices. This lecture reviews basic concepts from linear
Math 416, Spring 2010 Gram-Schmidt, the QR-factorization, Orthogonal Matrices March 4, 2010 GRAM-SCHMIDT, THE QR-FACTORIZATION, ORTHOGONAL MATRICES
 Math 46, Spring 00 Gram-Schmidt, the QR-factorization, Orthogonal Matrices March 4, 00 GRAM-SCHMIDT, THE QR-FACTORIZATION, ORTHOGONAL MATRICES Recap Yesterday we talked about several new, important concepts
Math 46, Spring 00 Gram-Schmidt, the QR-factorization, Orthogonal Matrices March 4, 00 GRAM-SCHMIDT, THE QR-FACTORIZATION, ORTHOGONAL MATRICES Recap Yesterday we talked about several new, important concepts
5.) For each of the given sets of vectors, determine whether or not the set spans R 3. Give reasons for your answers.
 Linear Algebra - Test File - Spring Test # For problems - consider the following system of equations. x + y - z = x + y + 4z = x + y + 6z =.) Solve the system without using your calculator..) Find the
Linear Algebra - Test File - Spring Test # For problems - consider the following system of equations. x + y - z = x + y + 4z = x + y + 6z =.) Solve the system without using your calculator..) Find the
Announcements Monday, November 20
 Announcements Monday, November 20 You already have your midterms! Course grades will be curved at the end of the semester. The percentage of A s, B s, and C s to be awarded depends on many factors, and
Announcements Monday, November 20 You already have your midterms! Course grades will be curved at the end of the semester. The percentage of A s, B s, and C s to be awarded depends on many factors, and
Inner Product Spaces
 Inner Product Spaces Introduction Recall in the lecture on vector spaces that geometric vectors (i.e. vectors in two and three-dimensional Cartesian space have the properties of addition, subtraction,
Inner Product Spaces Introduction Recall in the lecture on vector spaces that geometric vectors (i.e. vectors in two and three-dimensional Cartesian space have the properties of addition, subtraction,
Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II
 Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II Brian Borchers January 4, Linear Independence Definition The vectors v, v,..., v n are linearly independent if the system of equations c v + c v +...+ c n v n
Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II Brian Borchers January 4, Linear Independence Definition The vectors v, v,..., v n are linearly independent if the system of equations c v + c v +...+ c n v n
Lecture 9: Vector Algebra
 Lecture 9: Vector Algebra Linear combination of vectors Geometric interpretation Interpreting as Matrix-Vector Multiplication Span of a set of vectors Vector Spaces and Subspaces Linearly Independent/Dependent
Lecture 9: Vector Algebra Linear combination of vectors Geometric interpretation Interpreting as Matrix-Vector Multiplication Span of a set of vectors Vector Spaces and Subspaces Linearly Independent/Dependent
PRACTICE FINAL EXAM. why. If they are dependent, exhibit a linear dependence relation among them.
 Prof A Suciu MTH U37 LINEAR ALGEBRA Spring 2005 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Are the following vectors independent or dependent? If they are independent, say why If they are dependent, exhibit a linear dependence
Prof A Suciu MTH U37 LINEAR ALGEBRA Spring 2005 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Are the following vectors independent or dependent? If they are independent, say why If they are dependent, exhibit a linear dependence
2.4 Hilbert Spaces. Outline
 2.4 Hilbert Spaces Tom Lewis Spring Semester 2017 Outline Hilbert spaces L 2 ([a, b]) Orthogonality Approximations Definition A Hilbert space is an inner product space which is complete in the norm defined
2.4 Hilbert Spaces Tom Lewis Spring Semester 2017 Outline Hilbert spaces L 2 ([a, b]) Orthogonality Approximations Definition A Hilbert space is an inner product space which is complete in the norm defined
Lecture 1: Basic Concepts
 ENGG 5781: Matrix Analysis and Computations Lecture 1: Basic Concepts 2018-19 First Term Instructor: Wing-Kin Ma This note is not a supplementary material for the main slides. I will write notes such as
ENGG 5781: Matrix Analysis and Computations Lecture 1: Basic Concepts 2018-19 First Term Instructor: Wing-Kin Ma This note is not a supplementary material for the main slides. I will write notes such as
5 Compact linear operators
 5 Compact linear operators One of the most important results of Linear Algebra is that for every selfadjoint linear map A on a finite-dimensional space, there exists a basis consisting of eigenvectors.
5 Compact linear operators One of the most important results of Linear Algebra is that for every selfadjoint linear map A on a finite-dimensional space, there exists a basis consisting of eigenvectors.
Worksheet for Lecture 15 (due October 23) Section 4.3 Linearly Independent Sets; Bases
 Worksheet for Lecture 5 (due October 23) Name: Section 4.3 Linearly Independent Sets; Bases Definition An indexed set {v,..., v n } in a vector space V is linearly dependent if there is a linear relation
Worksheet for Lecture 5 (due October 23) Name: Section 4.3 Linearly Independent Sets; Bases Definition An indexed set {v,..., v n } in a vector space V is linearly dependent if there is a linear relation
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET
 IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning:
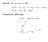 Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u 2 1 + u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning: u v = u v cos θ. u θ v 1 Reason: The opposite side is given by u v. u v 2 =
Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u 2 1 + u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning: u v = u v cos θ. u θ v 1 Reason: The opposite side is given by u v. u v 2 =
Diagonalizing Matrices
 Diagonalizing Matrices Massoud Malek A A Let A = A k be an n n non-singular matrix and let B = A = [B, B,, B k,, B n ] Then A n A B = A A 0 0 A k [B, B,, B k,, B n ] = 0 0 = I n 0 A n Notice that A i B
Diagonalizing Matrices Massoud Malek A A Let A = A k be an n n non-singular matrix and let B = A = [B, B,, B k,, B n ] Then A n A B = A A 0 0 A k [B, B,, B k,, B n ] = 0 0 = I n 0 A n Notice that A i B
Linear Algebra, Summer 2011, pt. 3
 Linear Algebra, Summer 011, pt. 3 September 0, 011 Contents 1 Orthogonality. 1 1.1 The length of a vector....................... 1. Orthogonal vectors......................... 3 1.3 Orthogonal Subspaces.......................
Linear Algebra, Summer 011, pt. 3 September 0, 011 Contents 1 Orthogonality. 1 1.1 The length of a vector....................... 1. Orthogonal vectors......................... 3 1.3 Orthogonal Subspaces.......................
Recall that any inner product space V has an associated norm defined by
 Hilbert Spaces Recall that any inner product space V has an associated norm defined by v = v v. Thus an inner product space can be viewed as a special kind of normed vector space. In particular every inner
Hilbert Spaces Recall that any inner product space V has an associated norm defined by v = v v. Thus an inner product space can be viewed as a special kind of normed vector space. In particular every inner
Math 18, Linear Algebra, Lecture C00, Spring 2017 Review and Practice Problems for Final Exam
 Math 8, Linear Algebra, Lecture C, Spring 7 Review and Practice Problems for Final Exam. The augmentedmatrix of a linear system has been transformed by row operations into 5 4 8. Determine if the system
Math 8, Linear Algebra, Lecture C, Spring 7 Review and Practice Problems for Final Exam. The augmentedmatrix of a linear system has been transformed by row operations into 5 4 8. Determine if the system
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 0 Fall Linear Algebra. These notes provide a review of basic concepts in linear algebra.
 DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 0 Fall 2016 Linear Algebra These notes provide a review of basic concepts in linear algebra. 1 Vector spaces You are no doubt familiar with vectors in R 2 or R 3, i.e. [ ] 1.1
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 0 Fall 2016 Linear Algebra These notes provide a review of basic concepts in linear algebra. 1 Vector spaces You are no doubt familiar with vectors in R 2 or R 3, i.e. [ ] 1.1
5. Orthogonal matrices
 L Vandenberghe EE133A (Spring 2017) 5 Orthogonal matrices matrices with orthonormal columns orthogonal matrices tall matrices with orthonormal columns complex matrices with orthonormal columns 5-1 Orthonormal
L Vandenberghe EE133A (Spring 2017) 5 Orthogonal matrices matrices with orthonormal columns orthogonal matrices tall matrices with orthonormal columns complex matrices with orthonormal columns 5-1 Orthonormal
Numerical Linear Algebra Chap. 2: Least Squares Problems
 Numerical Linear Algebra Chap. 2: Least Squares Problems Heinrich Voss voss@tu-harburg.de Hamburg University of Technology Institute of Numerical Simulation TUHH Heinrich Voss Numerical Linear Algebra
Numerical Linear Algebra Chap. 2: Least Squares Problems Heinrich Voss voss@tu-harburg.de Hamburg University of Technology Institute of Numerical Simulation TUHH Heinrich Voss Numerical Linear Algebra
LINEAR ALGEBRA W W L CHEN
 LINEAR ALGEBRA W W L CHEN c W W L Chen, 1997, 2008. This chapter is available free to all individuals, on the understanding that it is not to be used for financial gain, and may be downloaded and/or photocopied,
LINEAR ALGEBRA W W L CHEN c W W L Chen, 1997, 2008. This chapter is available free to all individuals, on the understanding that it is not to be used for financial gain, and may be downloaded and/or photocopied,
A Vector Space Justification of Householder Orthogonalization
 A Vector Space Justification of Householder Orthogonalization Ronald Christensen Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico August 28, 2015 Abstract We demonstrate
A Vector Space Justification of Householder Orthogonalization Ronald Christensen Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico August 28, 2015 Abstract We demonstrate
Announcements Monday, November 19
 Announcements Monday, November 19 You should already have the link to view your graded midterm online. Course grades will be curved at the end of the semester. The percentage of A s, B s, and C s to be
Announcements Monday, November 19 You should already have the link to view your graded midterm online. Course grades will be curved at the end of the semester. The percentage of A s, B s, and C s to be
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET
 IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS AND THEOREMS REFERENCE SHEET This is a (not quite comprehensive) list of definitions and theorems given in Math 1553. Pay particular attention to the ones in red. Study Tip For each
AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra)
 AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra) Lecture 5: Projectors and QR Factorization Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook Xiangmin Jiao Numerical Analysis I 1 / 14 Outline 1 Projectors 2 QR Factorization
AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra) Lecture 5: Projectors and QR Factorization Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook Xiangmin Jiao Numerical Analysis I 1 / 14 Outline 1 Projectors 2 QR Factorization
Matrix decompositions
 Matrix decompositions Zdeněk Dvořák May 19, 2015 Lemma 1 (Schur decomposition). If A is a symmetric real matrix, then there exists an orthogonal matrix Q and a diagonal matrix D such that A = QDQ T. The
Matrix decompositions Zdeněk Dvořák May 19, 2015 Lemma 1 (Schur decomposition). If A is a symmetric real matrix, then there exists an orthogonal matrix Q and a diagonal matrix D such that A = QDQ T. The
Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra)
 Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra) I.0 : Background Note. There is no corresponding section in the course notes, but as noted at the beginning of Unit I these are a few exercises which involve
Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra) I.0 : Background Note. There is no corresponding section in the course notes, but as noted at the beginning of Unit I these are a few exercises which involve
Orthogonality. Orthonormal Bases, Orthogonal Matrices. Orthogonality
 Orthonormal Bases, Orthogonal Matrices The Major Ideas from Last Lecture Vector Span Subspace Basis Vectors Coordinates in different bases Matrix Factorization (Basics) The Major Ideas from Last Lecture
Orthonormal Bases, Orthogonal Matrices The Major Ideas from Last Lecture Vector Span Subspace Basis Vectors Coordinates in different bases Matrix Factorization (Basics) The Major Ideas from Last Lecture
Announcements Monday, November 26
 Announcements Monday, November 26 Please fill out your CIOS survey! WeBWorK 6.6, 7.1, 7.2 are due on Wednesday. No quiz on Friday! But this is the only recitation on chapter 7. My office is Skiles 244
Announcements Monday, November 26 Please fill out your CIOS survey! WeBWorK 6.6, 7.1, 7.2 are due on Wednesday. No quiz on Friday! But this is the only recitation on chapter 7. My office is Skiles 244
Math 3191 Applied Linear Algebra
 Math 9 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture : Null and Column Spaces Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 9Applied Linear Algebra p./8 Announcements Study Guide posted HWK posted Math 9Applied
Math 9 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture : Null and Column Spaces Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 9Applied Linear Algebra p./8 Announcements Study Guide posted HWK posted Math 9Applied
Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra)
 Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra) I.0 : Background This does not correspond to a section in the course notes, but as noted at the beginning of Unit I it contains some exercises which involve
Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra) I.0 : Background This does not correspond to a section in the course notes, but as noted at the beginning of Unit I it contains some exercises which involve
1. Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal
 . Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal 3 9 matrix D such that A = P DP, for A =. 3 4 3 (a) P = 4, D =. 3 (b) P = 4, D =. (c) P = 4 8 4, D =. 3 (d) P
. Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal 3 9 matrix D such that A = P DP, for A =. 3 4 3 (a) P = 4, D =. 3 (b) P = 4, D =. (c) P = 4 8 4, D =. 3 (d) P
Linear Algebra Final Exam Study Guide Solutions Fall 2012
 . Let A = Given that v = 7 7 67 5 75 78 Linear Algebra Final Exam Study Guide Solutions Fall 5 explain why it is not possible to diagonalize A. is an eigenvector for A and λ = is an eigenvalue for A diagonalize
. Let A = Given that v = 7 7 67 5 75 78 Linear Algebra Final Exam Study Guide Solutions Fall 5 explain why it is not possible to diagonalize A. is an eigenvector for A and λ = is an eigenvalue for A diagonalize
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Second Edition, Serge Lange
 Introduction to Linear Algebra, Second Edition, Serge Lange Chapter I: Vectors R n defined. Addition and scalar multiplication in R n. Two geometric interpretations for a vector: point and displacement.
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Second Edition, Serge Lange Chapter I: Vectors R n defined. Addition and scalar multiplication in R n. Two geometric interpretations for a vector: point and displacement.
x 3y 2z = 6 1.2) 2x 4y 3z = 8 3x + 6y + 8z = 5 x + 3y 2z + 5t = 4 1.5) 2x + 8y z + 9t = 9 3x + 5y 12z + 17t = 7
 Linear Algebra and its Applications-Lab 1 1) Use Gaussian elimination to solve the following systems x 1 + x 2 2x 3 + 4x 4 = 5 1.1) 2x 1 + 2x 2 3x 3 + x 4 = 3 3x 1 + 3x 2 4x 3 2x 4 = 1 x + y + 2z = 4 1.4)
Linear Algebra and its Applications-Lab 1 1) Use Gaussian elimination to solve the following systems x 1 + x 2 2x 3 + 4x 4 = 5 1.1) 2x 1 + 2x 2 3x 3 + x 4 = 3 3x 1 + 3x 2 4x 3 2x 4 = 1 x + y + 2z = 4 1.4)
To find the least-squares solution to Ax = b, we project b onto Col A to obtain the vector ) b = proj ColA b,
 Least-Squares A famous application of linear algebra is the case study provided by the 1974 update of the North American Datum (pp. 373-374, a geodetic survey that keeps accurate measurements of distances
Least-Squares A famous application of linear algebra is the case study provided by the 1974 update of the North American Datum (pp. 373-374, a geodetic survey that keeps accurate measurements of distances
Section 6.1. Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality
 Section 6. Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Orientation Almost solve the equation Ax = b Problem: In the real world, data is imperfect. x v u But due to measurement error, the measured x is not
Section 6. Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Orientation Almost solve the equation Ax = b Problem: In the real world, data is imperfect. x v u But due to measurement error, the measured x is not
Assignment 1 Math 5341 Linear Algebra Review. Give complete answers to each of the following questions. Show all of your work.
 Assignment 1 Math 5341 Linear Algebra Review Give complete answers to each of the following questions Show all of your work Note: You might struggle with some of these questions, either because it has
Assignment 1 Math 5341 Linear Algebra Review Give complete answers to each of the following questions Show all of your work Note: You might struggle with some of these questions, either because it has
Practice Exam. 2x 1 + 4x 2 + 2x 3 = 4 x 1 + 2x 2 + 3x 3 = 1 2x 1 + 3x 2 + 4x 3 = 5
 Practice Exam. Solve the linear system using an augmented matrix. State whether the solution is unique, there are no solutions or whether there are infinitely many solutions. If the solution is unique,
Practice Exam. Solve the linear system using an augmented matrix. State whether the solution is unique, there are no solutions or whether there are infinitely many solutions. If the solution is unique,
MATH 22A: LINEAR ALGEBRA Chapter 4
 MATH 22A: LINEAR ALGEBRA Chapter 4 Jesús De Loera, UC Davis November 30, 2012 Orthogonality and Least Squares Approximation QUESTION: Suppose Ax = b has no solution!! Then what to do? Can we find an Approximate
MATH 22A: LINEAR ALGEBRA Chapter 4 Jesús De Loera, UC Davis November 30, 2012 Orthogonality and Least Squares Approximation QUESTION: Suppose Ax = b has no solution!! Then what to do? Can we find an Approximate
Conceptual Questions for Review
 Conceptual Questions for Review Chapter 1 1.1 Which vectors are linear combinations of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3)? 1.2 Compare the dot product of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3) to the product of their lengths.
Conceptual Questions for Review Chapter 1 1.1 Which vectors are linear combinations of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3)? 1.2 Compare the dot product of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3) to the product of their lengths.
1 Planar rotations. Math Abstract Linear Algebra Fall 2011, section E1 Orthogonal matrices and rotations
 Math 46 - Abstract Linear Algebra Fall, section E Orthogonal matrices and rotations Planar rotations Definition: A planar rotation in R n is a linear map R: R n R n such that there is a plane P R n (through
Math 46 - Abstract Linear Algebra Fall, section E Orthogonal matrices and rotations Planar rotations Definition: A planar rotation in R n is a linear map R: R n R n such that there is a plane P R n (through
7. Dimension and Structure.
 7. Dimension and Structure 7.1. Basis and Dimension Bases for Subspaces Example 2 The standard unit vectors e 1, e 2,, e n are linearly independent, for if we write (2) in component form, then we obtain
7. Dimension and Structure 7.1. Basis and Dimension Bases for Subspaces Example 2 The standard unit vectors e 1, e 2,, e n are linearly independent, for if we write (2) in component form, then we obtain
Orthogonal Projection. Hung-yi Lee
 Orthogonal Projection Hung-yi Lee Reference Textbook: Chapter 7.3, 7.4 Orthogonal Projection What is Orthogonal Complement What is Orthogonal Projection How to do Orthogonal Projection Application of Orthogonal
Orthogonal Projection Hung-yi Lee Reference Textbook: Chapter 7.3, 7.4 Orthogonal Projection What is Orthogonal Complement What is Orthogonal Projection How to do Orthogonal Projection Application of Orthogonal
Further Mathematical Methods (Linear Algebra)
 Further Mathematical Methods (Linear Algebra) Solutions For The 2 Examination Question (a) For a non-empty subset W of V to be a subspace of V we require that for all vectors x y W and all scalars α R:
Further Mathematical Methods (Linear Algebra) Solutions For The 2 Examination Question (a) For a non-empty subset W of V to be a subspace of V we require that for all vectors x y W and all scalars α R:
INNER PRODUCT SPACE. Definition 1
 INNER PRODUCT SPACE Definition 1 Suppose u, v and w are all vectors in vector space V and c is any scalar. An inner product space on the vectors space V is a function that associates with each pair of
INNER PRODUCT SPACE Definition 1 Suppose u, v and w are all vectors in vector space V and c is any scalar. An inner product space on the vectors space V is a function that associates with each pair of
Math 2331 Linear Algebra
 4.5 The Dimension of a Vector Space Math 233 Linear Algebra 4.5 The Dimension of a Vector Space Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ schiu/ Shang-Huan
4.5 The Dimension of a Vector Space Math 233 Linear Algebra 4.5 The Dimension of a Vector Space Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ schiu/ Shang-Huan
MATH 1120 (LINEAR ALGEBRA 1), FINAL EXAM FALL 2011 SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE VERSION
 MATH (LINEAR ALGEBRA ) FINAL EXAM FALL SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE VERSION Problem (a) For each matrix below (i) find a basis for its column space (ii) find a basis for its row space (iii) determine whether
MATH (LINEAR ALGEBRA ) FINAL EXAM FALL SOLUTIONS TO PRACTICE VERSION Problem (a) For each matrix below (i) find a basis for its column space (ii) find a basis for its row space (iii) determine whether
