additionalmathematicsadditionalmath ematicsadditionalmathematicsadditio nalmathematicsadditionalmathematic sadditionalmathematicsadditionalmat
|
|
|
- Mariah McLaughlin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 additionalmathematicsadditionalmath ematicsadditionalmathematicsadditio nalmathematicsadditionalmathematic sadditionalmathematicsadditionalmat FUNCTIONS hematicsadditionalmathematicsadditi Name onalmathematicsadditionalmathemati... csadditionalmathematicsadditionalma thematicsadditionalmathematicsadditi onalmathematicsadditionalmathemati csadditionalmathematicsadditionalma thematicsadditionalmathematicsadditi onalmathematicsadditionalmathemati csadditionalmathematicsadditionalma thematicsadditionalmathematicsadditi onalmathematicsadditionalmathemati csadditionalmathematicsadditionalma thematicsadditionalmathematicsadditi onalmathematicsadditionalmathemati
2 SET NOTATION The notation of set is { }. Examples. CHAPTER 1 : FUNCTIONS 1. A is the set of even numbers less than 1. A = {,, 6, 8, 10 }. B = { violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, red } B is... We can also use Venn Diagram to represent a set. RELATION A relation from set A to set B is the linking (or pairing) of the elements of set A to the elements of set B. 1.1 Represent a relation A relation between two sets can be represented by :- (a) arrow diagram (b) ordered pairs (c) graphs Example. A relation from set A = { -, 1,, ) to set B = { 1,, 9 } is given by power of for. Represent the relation using (a) arrow diagram
3 (b) ordered pairs (c) graph Activity 1 1. Given that set C = {,, 5 } and set D = {, 16, 18, 5 }. Represent the relation multiple of between set C to set D using (a) arrow diagram (b) ordered pairs. Represent the given relation using ordered pairs and graph. (a) child of A B Chandra Aisya Razif Chong Hasnul Lee Siva
4 (b) M has factor N Identify domain, codomain, object, image and range of a relation. Definition Domain - First set Codomain Second set Object Elements in the domain Image Elements in the codomain that are linked to the objects. Range set of images Example 1 Draw an arrow diagram to show a relation power of for from set A = { -, -, -,, } to set B = { - 9, -,, 9 }. Then, identify the (a) image for number (b) image for number (c) object for number (d) object for number 9 (e) domain (f) codomain (g) range of the relation.
5 Solution Example A relation is given in the form of ordered pairs, H = { (, 6), (, 8), (,10), (,8), (5,10), (5,15) }. Identify the (a) image of 5 (b) object of 8 (c) domain (d) range (e) codomain Example The relation below is shown in the graph. Set B Set A Identify the (a) image of (b) object of 15 (c) domain (d) range (e) codomain
6 Activity 1. Draw an arrow diagram to show a relation add to from set P = { 1,,,, 5 } to set Q = { 1,,,, 5, 6, 7, 8 }. From the diagram, state the (a) image of (b) object which its image is 6 (c) domain (d) codomain (e) range for the relation.. The relation that mapped set A = {,,, 5} onto set B = { 6, 8, 9 } is factor of. (a) Represent the relation using (i) arrow diagram (ii) ordered pairs (iii) graph (c) State the (i) domain (iii) range (v) object of (ii) codomain (iv) image of 8 1. Classifying the types of relation Type of relation 1. One to one relation Example of Arrow diagram Each object in the domain has only one image in the codomain. One to many relation Each object in the domain has more than one image in the range
7 . Many to one relation Each image in the range has more than one object in the domain but each object has only one image.. Many to many relation Each object in the domain has more than one image in the range and each image in the range has more than one object in the domain. State the type of relation shown by each of the following relation. Question 1. A element of B Type of relation Metane Ozone Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen. R = { (1,1), (,8), (,7), (,6), (5,5) }
8 . P power of Q B = { (,7), (,9), (,11), (5,9), (6,11) } 5. 5 Set B 1 1 Set A
9 . FUNCTIONS.1 Definition of a functions A functions is a special relation whereby for EVERY object in the domain, there is ONE AND ONLY ONE image in the codomain. Hence, the type of relations that are considered as a functions are (i) one to one relation (ii) many to one relation Examples Identify which of the following relations are functions. Give reason for your answer. Question (a) R = { (1,), (,), (5,6), (7,8) } Answer / Reason (b) A multiple of B (c) M 1 three times N 6 9 (d) K = { (May,1 days),(june,0 days), (July, 1 days),(feb,8 days)}
10 Activity Determine whether each of the following relation are considered as a function or not. Question Function / not a function 1. H = { (1,), (,), (5,7), (8,9) }. A March B 8 days April 0 days May 1 days. A B C D X Y Z. Set B Set A
11 . Express functions using function notation (1) A function can be represented using small letter such as f,g, h and etc. () (a) f : x y ( is read as function f maps x to y ) can also be written as f(x) = y. (b) g : x 5x -, hence g(x) = 5x - ( is read as 5x is the image of x under the function g ) (c) h : m m, hence h(m) = m. (d) Square of 16 f : x x or f(x) = x 6 6 domain codomain. Domain, object, image and range of a function Example 1 x g x Domain = { 0, 1, } Objects =.,.,.. Images =.,.,.. Range = {.,..,..} Example Find the image of f : x and range. x + given that x = { - 1, 1, }. State the domain, object
12 . Determine the image of a function given the object or vice versa. Example 1 (a) Given that f(x) = x 1. Find the image of x =. (b) Given that f ( x) x. Evaluate the value of f ( ). (c) A function h is defined as h : x 5x. Find the image for x = -. (d) Given the function m(x) = x the image for x = Find Example A function g is defined as g : x (a) g(0), g(- ), g(5), g(8) x, find the value of (b) State the value of x such that the function is not defined. Example Given that f : x x + 5. Find the object for which the image is 9.
13 Example Given the function g(x) = x 9. Find the value of the object that maps onto itself. Example 5 Given that function f(x) = x. Find the value of x such that f(x) = x. Activity 5 1. A function f is defined as f : x x +. Find a. f() b. f() c. f(x + 1).. A function f is defined by f : x x. Find (a) the object that has 9 as its image. (b) the object that is mapped onto itself.. A function f is defined as f : x x 1. (a) Find the image of -, -1, 0, 1,. (b) Find the objects that has 9 as it image.
14 . COMPOSITE FUNCTION.1 Composition of two functions f g A B C x f(x) g(x) (1) The figure above shows a function f that maps elements in set A to those in set B and the function g that maps set B to set C. The combined effect of the two functions can be represented by the function gf which is called the composite function of g and f. () fg = fg(x) = f[g(x)] gf () f = ff, f = fff or ff or f f and so on. Example For each pair of the following given function, find the composite function fg and gf. (a) f(x) = 5x, g(x) = x + (b) f(x) = 5x 1, g(x) = x +
15 (c) f : x x, g :x x (d) f : x 5, g : x 1 x x. Determine the image or object of a composite function Examples; 1. Given, f : x 5x and g : x x. Find (a) fg(x) (c) gf(x) (b) fg() (d) gf(- 1). Given that f : x, x 0 x (a) fg(x) and g :x x + 1. Find (b) gf(x)
16 (c) fg() (d) gf(). Given that f : x + x and g : x 8 x, x 0. Find the value of fg().. Functions f and g are defined as f :x x + and g : x x respectively. Find (a) f (b) g (c) f () (d) g ( ) 5. Functions f and g are defined as f(x) = x and g(x) = x 1 respectively. Find the value of x if gf(x) = 11.
17 Activity 6 1. Given f : x x + and g : x x 6. Find (a) fg ( x ) (b) gf ( x ) (c) gf ( ). Functions f and g are defined as f : x x - 5, g : x, x 0 respectively. x (a) Find the composite function gf and the value of gf(). (b) Determine f (x). Given f : x px + q and f : x 5x 8. Find the value of p and q ( p > 0).. INVERSE FUNCTION.1 Find the object, given its image and function by inverse mapping. f x f(x) f - 1 If f represent a function, the inverse function of f is denoted by f 1. ( take note that 1 f 1 f ) Therefore, if f : x y then f(x) = y if f 1 : y x then f 1 (y ) = x Example Function f is defined by f : x x 1.Find the value of a. f 1 (5) b. f 1 (- ) c. f 1 ()?
18 . Determining the inverse function Examples 1. Given f(x) = x + 1. Determine the inverse function f 1.. A function g is defined as g ( x ) = 5x - 8, determine g 1 (x).. Given that f : x x 1, find the inverse function f 1 (x). 5. A function g is defined as g : x x. Determine (a) g 1 (x) (b) the value of g 1 () (c) the value of k if g 1 (k)= k (d) g 1 h(x) if given h : x. x
19 5. Given that f : x x, x and g : x x. Find (a) f 1 (x) and state the value of x such that f 1 is not defined. (b) the value of f 1 g() 6. Given f : x x + k and its inverse function f 1 : x nx +. Find (a) the value of k and n (b) the value of f 1 f() 7. Given f(x) = x + 7 and g(x) = x + 1. Find (a) fg 1 (x) (b) the value of x such that gf(- x) = - 9
20 8. Given f : x p qx. determine (a) f 1 (x) in terms of p and q (b) the value of p and q if f 1 (8) = -1 and f() = - 7. Activity 8 1. Find the inverse function for each of the following (a) f : x x + (b) g : x x 7 (c) f : x, x 0 x (d) g : x x (e) f : x, x x. Given the function f : x x+, find the value of f 1 (5).. A function f is defined as f : x x 5, x 5 x 5. Find the value of f 1 (1) x a. Given that f : x, x x (a) the value of a (b) the value of f 1 (- ) and f(7) =. Find 5. Given the function f : x mx + n and its inverse function value of m and n. f x 8 : x. Find the 1-1
21 . The condition for the existence of an inverse function There are two types of relation that are considered as a functions that is (i) one to one (ii) many to one The reverse mapping for one to one relation is still one to one but the reverse mapping for many to one relation is not a function because it is one to many relation. Example Determine whether each of the following functions has inverse functions. Explain your answer. Question Answer (a) f (b) g.6 5.
22 Topical Test 1. Express the relation factor for between Set A = {, 6, 10, 15} and Set B = {,, 5} in the form of (a) graphs (b) ordered pairs. The arrow diagram shows the relation between Set A and Set B. r. s. t State the (a) domain (b) codomain (c) range (d) image for s (e) object for image f - 1 The figure above shows a function (a) the value of a and b (b) the image for x =. f : x ax bx. Find. Given the function f ( x) x 1 and g ( x) x. Find the composite functions (a) fg (b) gf (c) f ( x ) (d) g ( 1)
23 5. Given f ( x), x and g ( x) x 1. Find the value of x (a) fg (1) (b) g ( ) 6. Sketch the graph for the absolute function f ( x) 5 x in the domain 1 x. Hence, state the range of the function. 7. Given the function f : x x and the function g : x, x 0. Find x (a) the inverse function f 1 ( x) (b) the value of f 1 g() 8. Given the function Find f : x 10, where f ( 1) 5 and f ( ) 10. hx k (a) (b) the value of h and k the values of x such that f(x) = x 10. Functions f and g are defined as f x : x h x, and g : x x 1 (a) State the value of h. (b) Express the functions gf and f 1 ( x) (c) 1 Find the value of f g( ) 11. Given f(x) = px + q, f(0) = -5 and f() = 7. Find the value of p and q
1 FUNCTIONS _ 5 _ 1.0 RELATIONS
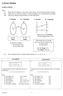 1 FUNCTIONS 1.0 RELATIONS Notes : (i) Four types of relations : one-to-one many-to-one one-to-many many-to-many. (ii) Three ways to represent relations : arrowed diagram set of ordered pairs graph. (iii)
1 FUNCTIONS 1.0 RELATIONS Notes : (i) Four types of relations : one-to-one many-to-one one-to-many many-to-many. (ii) Three ways to represent relations : arrowed diagram set of ordered pairs graph. (iii)
Math 110 Midterm 1 Study Guide October 14, 2013
 Name: For more practice exercises, do the study set problems in sections: 3.4 3.7, 4.1, and 4.2. 1. Find the domain of f, and express the solution in interval notation. (a) f(x) = x 6 D = (, ) or D = R
Name: For more practice exercises, do the study set problems in sections: 3.4 3.7, 4.1, and 4.2. 1. Find the domain of f, and express the solution in interval notation. (a) f(x) = x 6 D = (, ) or D = R
Functions. is the INPUT and is called the DOMAIN. is the OUTPUT and is called the RANGE.
 Functions Academic Skills Advice Function notation is another way of writing equations. For example: instead of writing y = 7x + 3, we could write f(x) = 7x + 3 (See lesson 2 for more information about
Functions Academic Skills Advice Function notation is another way of writing equations. For example: instead of writing y = 7x + 3, we could write f(x) = 7x + 3 (See lesson 2 for more information about
Quadratics. SPTA Mathematics Higher Notes
 H Quadratics SPTA Mathematics Higher Notes Quadratics are expressions with degree 2 and are of the form ax 2 + bx + c, where a 0. The Graph of a Quadratic is called a Parabola, and there are 2 types as
H Quadratics SPTA Mathematics Higher Notes Quadratics are expressions with degree 2 and are of the form ax 2 + bx + c, where a 0. The Graph of a Quadratic is called a Parabola, and there are 2 types as
Section 5.1 Composite Functions
 Section 5. Composite Functions Objective #: Form a Composite Function. In many cases, we can create a new function by taking the composition of two functions. For example, suppose f(x) x and g(x) x +.
Section 5. Composite Functions Objective #: Form a Composite Function. In many cases, we can create a new function by taking the composition of two functions. For example, suppose f(x) x and g(x) x +.
Higher Portfolio Quadratics and Polynomials
 Higher Portfolio Quadratics and Polynomials Higher 5. Quadratics and Polynomials Section A - Revision Section This section will help you revise previous learning which is required in this topic R1 I have
Higher Portfolio Quadratics and Polynomials Higher 5. Quadratics and Polynomials Section A - Revision Section This section will help you revise previous learning which is required in this topic R1 I have
C3 Revision Questions. (using questions from January 2006, January 2007, January 2008 and January 2009)
 C3 Revision Questions (using questions from January 2006, January 2007, January 2008 and January 2009) 1 2 1. f(x) = 1 3 x 2 + 3, x 2. 2 ( x 2) (a) 2 x x 1 Show that f(x) =, x 2. 2 ( x 2) (4) (b) Show
C3 Revision Questions (using questions from January 2006, January 2007, January 2008 and January 2009) 1 2 1. f(x) = 1 3 x 2 + 3, x 2. 2 ( x 2) (a) 2 x x 1 Show that f(x) =, x 2. 2 ( x 2) (4) (b) Show
Lesson 18: Problem Set Sample Solutions
 Problem Set Sample Solutions Problems 5 7 serve to review the process of computing f(g(x)) for given functions f and g in preparation for work with inverses of functions in Lesson 19. 1. Sketch the graphs
Problem Set Sample Solutions Problems 5 7 serve to review the process of computing f(g(x)) for given functions f and g in preparation for work with inverses of functions in Lesson 19. 1. Sketch the graphs
(a) Write down the value of q and of r. (2) Write down the equation of the axis of symmetry. (1) (c) Find the value of p. (3) (Total 6 marks)
 1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
Section 0.2 & 0.3 Worksheet. Types of Functions
 MATH 1142 NAME Section 0.2 & 0.3 Worksheet Types of Functions Now that we have discussed what functions are and some of their characteristics, we will explore different types of functions. Section 0.2
MATH 1142 NAME Section 0.2 & 0.3 Worksheet Types of Functions Now that we have discussed what functions are and some of their characteristics, we will explore different types of functions. Section 0.2
Examples 2: Composite Functions, Piecewise Functions, Partial Fractions
 Examples 2: Composite Functions, Piecewise Functions, Partial Fractions September 26, 206 The following are a set of examples to designed to complement a first-year calculus course. objectives are listed
Examples 2: Composite Functions, Piecewise Functions, Partial Fractions September 26, 206 The following are a set of examples to designed to complement a first-year calculus course. objectives are listed
, g : x x 6, Sketch, in a single diagram, the graphs of y = f(x) and y = f -1 (x), making clear the
 PAST QUESTION ON FUNCTIONS 1. Express x + 4x in the form (x + a) + b, stating the numerical values of a and b. The functions f and g are defined as follows : f : x x 4x, x, g : x x 6, x R (ii) (iii) Show
PAST QUESTION ON FUNCTIONS 1. Express x + 4x in the form (x + a) + b, stating the numerical values of a and b. The functions f and g are defined as follows : f : x x 4x, x, g : x x 6, x R (ii) (iii) Show
Revision Materials. Functions, Quadratics & Polynomials Skills Builder
 Mathematics Higher Revision Materials Functions, Quadratics & Polynomials Skills Builder Layout and content of the Unit Assessment will be different. This is not meant to be a carbon copy of the Unit Assessment.
Mathematics Higher Revision Materials Functions, Quadratics & Polynomials Skills Builder Layout and content of the Unit Assessment will be different. This is not meant to be a carbon copy of the Unit Assessment.
Precalculus Lesson 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models Mrs. Snow, Instructor
 Precalculus Lesson 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models Mrs. Snow, Instructor Let s review the definition of a polynomial. A polynomial function of degree n is a function of the form P(x) = a n x n + a
Precalculus Lesson 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models Mrs. Snow, Instructor Let s review the definition of a polynomial. A polynomial function of degree n is a function of the form P(x) = a n x n + a
Chapter 8. Exploring Polynomial Functions. Jennifer Huss
 Chapter 8 Exploring Polynomial Functions Jennifer Huss 8-1 Polynomial Functions The degree of a polynomial is determined by the greatest exponent when there is only one variable (x) in the polynomial Polynomial
Chapter 8 Exploring Polynomial Functions Jennifer Huss 8-1 Polynomial Functions The degree of a polynomial is determined by the greatest exponent when there is only one variable (x) in the polynomial Polynomial
1 Wyner PreCalculus Fall 2013
 1 Wyner PreCalculus Fall 2013 CHAPTER ONE: FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Summary, Terms, and Objectives Most of calculus and precalculus is based on functions. A function is a process that takes one or more
1 Wyner PreCalculus Fall 2013 CHAPTER ONE: FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Summary, Terms, and Objectives Most of calculus and precalculus is based on functions. A function is a process that takes one or more
SCHOOL OF BUSINESS, ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT BUSINESS MATHEMATICS / MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS
 SCHOOL OF BUSINESS, ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT BUSINESS MATHEMATICS / MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS UNIT 3 Moses Mwale e-mail: moses.mwale@ictar.ac.zm BBA 10 Business Mathematics Contents Unit 3: Functions and
SCHOOL OF BUSINESS, ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT BUSINESS MATHEMATICS / MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS UNIT 3 Moses Mwale e-mail: moses.mwale@ictar.ac.zm BBA 10 Business Mathematics Contents Unit 3: Functions and
Georgia Department of Education Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Framework CCGPS Advanced Algebra Unit 2
 Polynomials Patterns Task 1. To get an idea of what polynomial functions look like, we can graph the first through fifth degree polynomials with leading coefficients of 1. For each polynomial function,
Polynomials Patterns Task 1. To get an idea of what polynomial functions look like, we can graph the first through fifth degree polynomials with leading coefficients of 1. For each polynomial function,
Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra
 Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra 1. Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function f(x) = x 2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = x 2 + 2 *a. b. c. d.
Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra 1. Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function f(x) = x 2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = x 2 + 2 *a. b. c. d.
Math 2: Algebra 2, Geometry and Statistics Ms. Sheppard-Brick Chapter 4 Test Review
 Chapter 4 Test Review Students will be able to (SWBAT): Write an explicit and a recursive function rule for a linear table of values. Write an explicit function rule for a quadratic table of values. Determine
Chapter 4 Test Review Students will be able to (SWBAT): Write an explicit and a recursive function rule for a linear table of values. Write an explicit function rule for a quadratic table of values. Determine
1) The line has a slope of ) The line passes through (2, 11) and. 6) r(x) = x + 4. From memory match each equation with its graph.
 Review Test 2 Math 1314 Name Write an equation of the line satisfying the given conditions. Write the answer in standard form. 1) The line has a slope of - 2 7 and contains the point (3, 1). Use the point-slope
Review Test 2 Math 1314 Name Write an equation of the line satisfying the given conditions. Write the answer in standard form. 1) The line has a slope of - 2 7 and contains the point (3, 1). Use the point-slope
Regents Review Session #3 Functions
 Regents Review Session #3 Functions A relation is a set of ordered pairs. A function is a relation in which each element of the domain corresponds t exactly one element in the range. (Each x value is paired
Regents Review Session #3 Functions A relation is a set of ordered pairs. A function is a relation in which each element of the domain corresponds t exactly one element in the range. (Each x value is paired
3 FUNCTIONS. 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties. c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall
 c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2014 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from A to B is a rule that assigns to each element in the set
c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2014 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from A to B is a rule that assigns to each element in the set
f(x) x
 2 Function 2.1 Function notation The equation f(x) = x 2 + 3 defines a function f from the set R of real numbers to itself (written f : R R). This function accepts an input value x and returns an output
2 Function 2.1 Function notation The equation f(x) = x 2 + 3 defines a function f from the set R of real numbers to itself (written f : R R). This function accepts an input value x and returns an output
MTH4100 Calculus I. Lecture notes for Week 2. Thomas Calculus, Sections 1.3 to 1.5. Rainer Klages
 MTH4100 Calculus I Lecture notes for Week 2 Thomas Calculus, Sections 1.3 to 1.5 Rainer Klages School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary University of London Autumn 2009 Reading Assignment: read Thomas
MTH4100 Calculus I Lecture notes for Week 2 Thomas Calculus, Sections 1.3 to 1.5 Rainer Klages School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary University of London Autumn 2009 Reading Assignment: read Thomas
MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review
 MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review Topics Covered Section 1.1: Rectangular Coordinate System Section 1.3: Functions and Relations Section 1.4: Linear Equations in Two Variables and Linear Functions Section 1.5: Applications
MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review Topics Covered Section 1.1: Rectangular Coordinate System Section 1.3: Functions and Relations Section 1.4: Linear Equations in Two Variables and Linear Functions Section 1.5: Applications
Name: Date: Block: FUNCTIONS TEST STUDY GUIDE
 Algebra STUDY GUIDE AII.6, AII.7 Functions Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Test covers: Graphing using transformations FUNCTIONS TEST STUDY GUIDE Analyzing functions, including finding domain/range in
Algebra STUDY GUIDE AII.6, AII.7 Functions Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Test covers: Graphing using transformations FUNCTIONS TEST STUDY GUIDE Analyzing functions, including finding domain/range in
Review all the activities leading to Midterm 3. Review all the problems in the previous online homework sets (8+9+10).
 MA109, Activity 34: Review (Sections 3.6+3.7+4.1+4.2+4.3) Date: Objective: Additional Assignments: To prepare for Midterm 3, make sure that you can solve the types of problems listed in Activities 33 and
MA109, Activity 34: Review (Sections 3.6+3.7+4.1+4.2+4.3) Date: Objective: Additional Assignments: To prepare for Midterm 3, make sure that you can solve the types of problems listed in Activities 33 and
8 Building New Functions from Old Ones
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 2243: Business Calculus Dr. Marcel B. Finan 8 Building New Functions from Old Ones In this section we discuss various ways for building new functions from old ones. New functions
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2243: Business Calculus Dr. Marcel B. Finan 8 Building New Functions from Old Ones In this section we discuss various ways for building new functions from old ones. New functions
MAT 12 - SEC 021 PRECALCULUS SUMMER SESSION II 2014 LECTURE 3
 MAT 12 - SEC 021 PRECALCULUS SUMMER SESSION II 2014 LECTURE 3 JAMIE HADDOCK 1. Agenda Functions Composition Graphs Average Rate of Change..............................................................................................................
MAT 12 - SEC 021 PRECALCULUS SUMMER SESSION II 2014 LECTURE 3 JAMIE HADDOCK 1. Agenda Functions Composition Graphs Average Rate of Change..............................................................................................................
4) Have you met any functions during our previous lectures in this course?
 Definition: Let X and Y be sets. A function f from the set X to the set Y is a rule which associates to each element x X a unique element y Y. Notation: f : X Y f defined on X with values in Y. x y y =
Definition: Let X and Y be sets. A function f from the set X to the set Y is a rule which associates to each element x X a unique element y Y. Notation: f : X Y f defined on X with values in Y. x y y =
AP Calculus AB Summer Packet
 The accompanying problems are from the subjects covered in Algebra I, Algebra II, Pre-calculus, and Analytic Geometry. In Calculus you are expected to know all topics from these subjects. Included in this
The accompanying problems are from the subjects covered in Algebra I, Algebra II, Pre-calculus, and Analytic Geometry. In Calculus you are expected to know all topics from these subjects. Included in this
Theta Functions MAΘ National Convention 2018
 Theta Functions MAΘ National Convention 018 Note that choice stands for None of the above answers is correct 1. How many times do y = x and y = x 3 intersect? A) 0 B) 1 C) D) 3. Let f(x) = x + 19 and g(x)
Theta Functions MAΘ National Convention 018 Note that choice stands for None of the above answers is correct 1. How many times do y = x and y = x 3 intersect? A) 0 B) 1 C) D) 3. Let f(x) = x + 19 and g(x)
Answer all the questions
 SECTION A ( 38 marks) Answer all the questions 1 The following information refer to the set A and set B. Set A = { -3, -2, 2, 3 } Set B = { 4, 9 } The relations between set A and set B is defined by the
SECTION A ( 38 marks) Answer all the questions 1 The following information refer to the set A and set B. Set A = { -3, -2, 2, 3 } Set B = { 4, 9 } The relations between set A and set B is defined by the
A Level Maths summer preparation work
 A Level Maths summer preparation work Welcome to A Level Maths! We hope you are looking forward to two years of challenging and rewarding learning. You must make sure that you are prepared to study A Level
A Level Maths summer preparation work Welcome to A Level Maths! We hope you are looking forward to two years of challenging and rewarding learning. You must make sure that you are prepared to study A Level
FUNCTIONS - PART 2. If you are not familiar with any of the material below you need to spend time studying these concepts and doing some exercises.
 Introduction FUNCTIONS - PART 2 This handout is a summary of the basic concepts you should understand and be comfortable working with for the second math review module on functions. This is intended as
Introduction FUNCTIONS - PART 2 This handout is a summary of the basic concepts you should understand and be comfortable working with for the second math review module on functions. This is intended as
Section 4.4 Functions. CS 130 Discrete Structures
 Section 4.4 Functions CS 130 Discrete Structures Function Definitions Let S and T be sets. A function f from S to T, f: S T, is a subset of S x T where each member of S appears exactly once as the first
Section 4.4 Functions CS 130 Discrete Structures Function Definitions Let S and T be sets. A function f from S to T, f: S T, is a subset of S x T where each member of S appears exactly once as the first
March Algebra 2 Question 1. March Algebra 2 Question 1
 March Algebra 2 Question 1 If the statement is always true for the domain, assign that part a 3. If it is sometimes true, assign it a 2. If it is never true, assign it a 1. Your answer for this question
March Algebra 2 Question 1 If the statement is always true for the domain, assign that part a 3. If it is sometimes true, assign it a 2. If it is never true, assign it a 1. Your answer for this question
A. Evaluate log Evaluate Logarithms
 A. Evaluate log 2 16. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate Logarithms B. Evaluate. C. Evaluate. Evaluate Logarithms D. Evaluate log 17 17. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate. A. 4 B. 4 C. 2 D. 2 A. Evaluate log 8 512.
A. Evaluate log 2 16. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate Logarithms B. Evaluate. C. Evaluate. Evaluate Logarithms D. Evaluate log 17 17. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate. A. 4 B. 4 C. 2 D. 2 A. Evaluate log 8 512.
Math /Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined
 Math 400-001/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined using limits. As a particular case, the derivative of f(x)
Math 400-001/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined using limits. As a particular case, the derivative of f(x)
Core 3 (A2) Practice Examination Questions
 Core 3 (A) Practice Examination Questions Trigonometry Mr A Slack Trigonometric Identities and Equations I know what secant; cosecant and cotangent graphs look like and can identify appropriate restricted
Core 3 (A) Practice Examination Questions Trigonometry Mr A Slack Trigonometric Identities and Equations I know what secant; cosecant and cotangent graphs look like and can identify appropriate restricted
PMI Unit 2 Working With Functions
 Vertical Shifts Class Work 1. a) 2. a) 3. i) y = x 2 ii) Move down 2 6. i) y = x ii) Move down 1 4. i) y = 1 x ii) Move up 3 7. i) y = e x ii) Move down 4 5. i) y = x ii) Move up 1 Vertical Shifts Homework
Vertical Shifts Class Work 1. a) 2. a) 3. i) y = x 2 ii) Move down 2 6. i) y = x ii) Move down 1 4. i) y = 1 x ii) Move up 3 7. i) y = e x ii) Move down 4 5. i) y = x ii) Move up 1 Vertical Shifts Homework
Logarithms Dr. Laura J. Pyzdrowski
 1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory An exponential function of the form f(x) = a x, where a is a positive real number not equal to 1, is an example of a one-to-one function. This means
1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory An exponential function of the form f(x) = a x, where a is a positive real number not equal to 1, is an example of a one-to-one function. This means
Pre-Calculus Summer Math Packet 2018 Multiple Choice
 Pre-Calculus Summer Math Packet 208 Multiple Choice Page A Complete all work on separate loose-leaf or graph paper. Solve problems without using a calculator. Write the answers to multiple choice questions
Pre-Calculus Summer Math Packet 208 Multiple Choice Page A Complete all work on separate loose-leaf or graph paper. Solve problems without using a calculator. Write the answers to multiple choice questions
x f(x)
 1. Name three different reasons that a function can fail to be differential at a point. Give an example for each reason, and explain why your examples are valid. 2. Given the following table of values,
1. Name three different reasons that a function can fail to be differential at a point. Give an example for each reason, and explain why your examples are valid. 2. Given the following table of values,
x f(x)
 1. Name three different reasons that a function can fail to be differentiable at a point. Give an example for each reason, and explain why your examples are valid. 2. Given the following table of values,
1. Name three different reasons that a function can fail to be differentiable at a point. Give an example for each reason, and explain why your examples are valid. 2. Given the following table of values,
hard a problem o hard help e help problem, p help o problem a f hard g e f help help g please g o f problem g
 MATH2440 / SOLUTIONS FOR MIDTERM 2 (1) Let L := {a, b, d, e, p, r, o} and A := {hard, help, please, problem}. Consider the map f : L A sending a letter to the alphabetically first word in A in which it
MATH2440 / SOLUTIONS FOR MIDTERM 2 (1) Let L := {a, b, d, e, p, r, o} and A := {hard, help, please, problem}. Consider the map f : L A sending a letter to the alphabetically first word in A in which it
Math 121, Practice Questions for Final (Hints/Answers)
 Math 11, Practice Questions for Final Hints/Answers) 1. The graphs of the inverse functions are obtained by reflecting the graph of the original function over the line y = x. In each graph, the original
Math 11, Practice Questions for Final Hints/Answers) 1. The graphs of the inverse functions are obtained by reflecting the graph of the original function over the line y = x. In each graph, the original
Relations, Functions, Binary Relations (Chapter 1, Sections 1.2, 1.3)
 Relations, Functions, Binary Relations (Chapter 1, Sections 1.2, 1.3) CmSc 365 Theory of Computation 1. Relations Definition: Let A and B be two sets. A relation R from A to B is any set of ordered pairs
Relations, Functions, Binary Relations (Chapter 1, Sections 1.2, 1.3) CmSc 365 Theory of Computation 1. Relations Definition: Let A and B be two sets. A relation R from A to B is any set of ordered pairs
Lecture 9 4.1: Derivative Rules MTH 124
 Today we will see that the derivatives of classes of functions behave in similar ways. This is nice because by noticing this general pattern we can develop derivative rules which will make taking derivative
Today we will see that the derivatives of classes of functions behave in similar ways. This is nice because by noticing this general pattern we can develop derivative rules which will make taking derivative
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 2013/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 201/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 121 - Calculus 1, Fall 201/2014! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics
Introduction Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 201/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 121 - Calculus 1, Fall 201/2014! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics
Limits at Infinity. Horizontal Asymptotes. Definition (Limits at Infinity) Horizontal Asymptotes
 Limits at Infinity If a function f has a domain that is unbounded, that is, one of the endpoints of its domain is ±, we can determine the long term behavior of the function using a it at infinity. Definition
Limits at Infinity If a function f has a domain that is unbounded, that is, one of the endpoints of its domain is ±, we can determine the long term behavior of the function using a it at infinity. Definition
9/21/2018. Properties of Functions. Properties of Functions. Properties of Functions. Properties of Functions. Properties of Functions
 How can we prove that a function f is one-to-one? Whenever you want to prove something, first take a look at the relevant definition(s): x, y A (f(x) = f(y) x = y) f:r R f(x) = x 2 Disproof by counterexample:
How can we prove that a function f is one-to-one? Whenever you want to prove something, first take a look at the relevant definition(s): x, y A (f(x) = f(y) x = y) f:r R f(x) = x 2 Disproof by counterexample:
Limit Theorems. MATH 464/506, Real Analysis. J. Robert Buchanan. Summer Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Limit Theorems
 Limit s MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Bounded Functions Definition Let A R, let f : A R, and let c R be a cluster point of A. We say that f is bounded
Limit s MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Bounded Functions Definition Let A R, let f : A R, and let c R be a cluster point of A. We say that f is bounded
Sets and Functions. (As we will see, in describing a set the order in which elements are listed is irrelevant).
 Sets and Functions 1. The language of sets Informally, a set is any collection of objects. The objects may be mathematical objects such as numbers, functions and even sets, or letters or symbols of any
Sets and Functions 1. The language of sets Informally, a set is any collection of objects. The objects may be mathematical objects such as numbers, functions and even sets, or letters or symbols of any
Inverse Functions. One-to-one. Horizontal line test. Onto
 Inverse Functions One-to-one Suppose f : A B is a function. We call f one-to-one if every distinct pair of objects in A is assigned to a distinct pair of objects in B. In other words, each object of the
Inverse Functions One-to-one Suppose f : A B is a function. We call f one-to-one if every distinct pair of objects in A is assigned to a distinct pair of objects in B. In other words, each object of the
Unit 2 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey
 HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit 2 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) Determine for each of the following graphed relationships whether y is a function of x using the Vertical Line Test. 2) What are the outputs for
HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit 2 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) Determine for each of the following graphed relationships whether y is a function of x using the Vertical Line Test. 2) What are the outputs for
f(x) = 3x 2 3 g(x) = 5x 7 3 h(x) = 16x 1 4 k(x) = 10x 7 4 m(x) = 81x 2 7 n(x) = 3x 3 4 w(x) = 5x 1 4 2x 3 2 v(x) = 4x x 3 2
 W3D3 Function Operations Warm Up Lesson 35 Functions Operations Introduce Lesson with Brainstorm Carousal. Each group will spend 2 minutes at each station. The Paper will be divided into Notes about getting
W3D3 Function Operations Warm Up Lesson 35 Functions Operations Introduce Lesson with Brainstorm Carousal. Each group will spend 2 minutes at each station. The Paper will be divided into Notes about getting
Objectives for Composition and Inverse Function Activity
 Objectives for Composition and Inverse Function Activity Compose two functions give algebraically, by a table, by a graph, in words Decompose a function into two (or more) functions Compose more than two
Objectives for Composition and Inverse Function Activity Compose two functions give algebraically, by a table, by a graph, in words Decompose a function into two (or more) functions Compose more than two
MAC College Algebra
 MAC 05 - College Algebra Name Review for Test 2 - Chapter 2 Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact distance between the
MAC 05 - College Algebra Name Review for Test 2 - Chapter 2 Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact distance between the
_CH04_p pdf Page 52
 0000001071656491_CH04_p3-369.pdf Page 5 4.08 Algebra With Functions The basic rules of algebra tell you how the operations of addition and multiplication behave. Addition and multiplication are operations
0000001071656491_CH04_p3-369.pdf Page 5 4.08 Algebra With Functions The basic rules of algebra tell you how the operations of addition and multiplication behave. Addition and multiplication are operations
College Algebra. George Voutsadakis 1. LSSU Math 111. Lake Superior State University. 1 Mathematics and Computer Science
 College Algebra George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 111 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) College Algebra December 2014 1 / 74 Outline 1 Additional
College Algebra George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 111 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) College Algebra December 2014 1 / 74 Outline 1 Additional
Calculus Summer Math Practice. 1. Find inverse functions Describe in words how you use algebra to determine the inverse function.
 1 Calculus 2017-2018: Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun (kbraun@bdcs.org) Bishop Dunne Catholic School Calculus Summer Math Practice Please see the math department document for instructions on setting
1 Calculus 2017-2018: Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun (kbraun@bdcs.org) Bishop Dunne Catholic School Calculus Summer Math Practice Please see the math department document for instructions on setting
Honors Advanced Algebra Unit 3: Polynomial Functions November 9, 2016 Task 11: Characteristics of Polynomial Functions
 Honors Advanced Algebra Name Unit 3: Polynomial Functions November 9, 2016 Task 11: Characteristics of Polynomial Functions MGSE9 12.F.IF.7 Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features
Honors Advanced Algebra Name Unit 3: Polynomial Functions November 9, 2016 Task 11: Characteristics of Polynomial Functions MGSE9 12.F.IF.7 Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features
SPM Add Math Form 4 Chapter 3 Quadratic Functions
 CHAPTER 3 : QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Quadratic Functions and their Graphs Example 1: Identify the shapes of graphs of the following quadratic functions. 4x 5 (1 ) 5x 3 ( x )( x 3) Example : Determine the types
CHAPTER 3 : QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Quadratic Functions and their Graphs Example 1: Identify the shapes of graphs of the following quadratic functions. 4x 5 (1 ) 5x 3 ( x )( x 3) Example : Determine the types
Materials and Handouts - Warm-Up - Answers to homework #1 - Keynote and notes template - Tic Tac Toe grids - Homework #2
 Calculus Unit 1, Lesson 2: Composite Functions DATE: Objectives The students will be able to: - Evaluate composite functions using all representations Simplify composite functions Materials and Handouts
Calculus Unit 1, Lesson 2: Composite Functions DATE: Objectives The students will be able to: - Evaluate composite functions using all representations Simplify composite functions Materials and Handouts
Chapter 7 Algebra 2 Honors 1 Polynomials
 Chapter 7 Algebra 2 Honors 1 Polynomials Polynomial: - - Polynomials in one variable Degree Leading coefficient f(x) = 3x 3 2x + 4 f(2) = f(t) = f(y -1) = 3f(x) = Using your graphing calculator sketch/graph
Chapter 7 Algebra 2 Honors 1 Polynomials Polynomial: - - Polynomials in one variable Degree Leading coefficient f(x) = 3x 3 2x + 4 f(2) = f(t) = f(y -1) = 3f(x) = Using your graphing calculator sketch/graph
1. Definition of a Polynomial
 1. Definition of a Polynomial What is a polynomial? A polynomial P(x) is an algebraic expression of the form Degree P(x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 3 x 3 + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 Leading
1. Definition of a Polynomial What is a polynomial? A polynomial P(x) is an algebraic expression of the form Degree P(x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 3 x 3 + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 Leading
2.6 Logarithmic Functions. Inverse Functions. Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x?
 Inverse Functions Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 3 and g(x) = 3 x? Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x? Definition (One-to-One Function) A function f
Inverse Functions Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 3 and g(x) = 3 x? Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x? Definition (One-to-One Function) A function f
Analytic Geometry and Calculus I Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions 2/19/7
 Analytic Geometry and Calculus I Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions /19/7 Question 1 Write the following as an integer: log 4 (9)+log (5) We have: log 4 (9)+log (5) = ( log 4 (9)) ( log (5)) = 5 ( log
Analytic Geometry and Calculus I Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions /19/7 Question 1 Write the following as an integer: log 4 (9)+log (5) We have: log 4 (9)+log (5) = ( log 4 (9)) ( log (5)) = 5 ( log
ISLAMIYA ENGLISH SCHOOL ABU DHABI U. A. E.
 ISLAMIYA ENGLISH SCHOOL ABU DHABI U. A. E. MATHEMATICS ASSIGNMENT-1 GRADE-A/L-II(Sci) CHAPTER.NO.1,2,3(C3) Algebraic fractions,exponential and logarithmic functions DATE:18/3/2017 NAME.------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ISLAMIYA ENGLISH SCHOOL ABU DHABI U. A. E. MATHEMATICS ASSIGNMENT-1 GRADE-A/L-II(Sci) CHAPTER.NO.1,2,3(C3) Algebraic fractions,exponential and logarithmic functions DATE:18/3/2017 NAME.------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Rational and Radical Functions. College Algebra
 Rational and Radical Functions College Algebra Rational Function A rational function is a function that can be written as the quotient of two polynomial functions P(x) and Q(x) f x = P(x) Q(x) = a )x )
Rational and Radical Functions College Algebra Rational Function A rational function is a function that can be written as the quotient of two polynomial functions P(x) and Q(x) f x = P(x) Q(x) = a )x )
Example: f(x) = 2x² + 1 Solution: Math 2 VM Part 5 Quadratic Functions April 25, 2017
 Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 5 Quadratic Functions MATH 1 REVIEW THE CONCEPT OF FUNCTIONS The concept of a function is both a different way of thinking about equations and a different way of notating
Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 5 Quadratic Functions MATH 1 REVIEW THE CONCEPT OF FUNCTIONS The concept of a function is both a different way of thinking about equations and a different way of notating
Polynomial Degree Leading Coefficient. Sign of Leading Coefficient
 Chapter 1 PRE-TEST REVIEW Polynomial Functions MHF4U Jensen Section 1: 1.1 Power Functions 1) State the degree and the leading coefficient of each polynomial Polynomial Degree Leading Coefficient y = 2x
Chapter 1 PRE-TEST REVIEW Polynomial Functions MHF4U Jensen Section 1: 1.1 Power Functions 1) State the degree and the leading coefficient of each polynomial Polynomial Degree Leading Coefficient y = 2x
Name Advanced Math Functions & Statistics. Non- Graphing Calculator Section A. B. C.
 1. Compare and contrast the following graphs. Non- Graphing Calculator Section A. B. C. 2. For R, S, and T as defined below, which of the following products is undefined? A. RT B. TR C. TS D. ST E. RS
1. Compare and contrast the following graphs. Non- Graphing Calculator Section A. B. C. 2. For R, S, and T as defined below, which of the following products is undefined? A. RT B. TR C. TS D. ST E. RS
Function Notation We use the f(x) (read f of x) notation to represent a function. E.g. f(x) = 3x 1 Here, f is the name of the function, x is the
 Functions Informal definition of a function: A function between two sets is a rule that assigns to each member in the first set (called the domain) one and only one member in the second set (called the
Functions Informal definition of a function: A function between two sets is a rule that assigns to each member in the first set (called the domain) one and only one member in the second set (called the
Chapter 3. Graphing Linear Equations and Functions
 Chapter 3 Graphing Linear Equations and Functions 3.1 Plot Points in a Coordinate Plane Coordinate Plane- Two intersecting at a angle. x-axis the axis y-axis the axis The coordinate plane is divided into.
Chapter 3 Graphing Linear Equations and Functions 3.1 Plot Points in a Coordinate Plane Coordinate Plane- Two intersecting at a angle. x-axis the axis y-axis the axis The coordinate plane is divided into.
MA 109 College Algebra EXAM 3 - REVIEW
 MA 109 College Algebra EXAM - REVIEW Name: Sec.: 1. In the picture below, the graph of y = f(x) is the solid graph, and the graph of y = g(x) is the dashed graph. Find a formula for g(x). y (a) g(x) =f(2x)
MA 109 College Algebra EXAM - REVIEW Name: Sec.: 1. In the picture below, the graph of y = f(x) is the solid graph, and the graph of y = g(x) is the dashed graph. Find a formula for g(x). y (a) g(x) =f(2x)
1.1 Functions. Input (Independent or x) and output (Dependent or y) of a function. Range: Domain: Function Rule. Input. Output.
 1.1 Functions Function Function: A rule for a relationship between an input, or independent, quantity and an output, or dependent, quantity in which each input value uniquely determines one output value.
1.1 Functions Function Function: A rule for a relationship between an input, or independent, quantity and an output, or dependent, quantity in which each input value uniquely determines one output value.
f (x) = x 2 Chapter 2 Polynomial Functions Section 4 Polynomial and Rational Functions Shapes of Polynomials Graphs of Polynomials the form n
 Chapter 2 Functions and Graphs Section 4 Polynomial and Rational Functions Polynomial Functions A polynomial function is a function that can be written in the form a n n 1 n x + an 1x + + a1x + a0 for
Chapter 2 Functions and Graphs Section 4 Polynomial and Rational Functions Polynomial Functions A polynomial function is a function that can be written in the form a n n 1 n x + an 1x + + a1x + a0 for
1 Fundamental Concepts From Algebra & Precalculus
 Fundamental Concepts From Algebra & Precalculus. Review Exercises.. Simplify eac expression.. 5 7) [ 5)) ]. ) 5) 7) 9 + 8 5. 8 [ 5) 8 6)] [9 + 8 5 ]. 9 + 8 5 ) 8) + 5. 5 + [ )6)] 7) 7 + 6 5 6. 8 5 ) 6
Fundamental Concepts From Algebra & Precalculus. Review Exercises.. Simplify eac expression.. 5 7) [ 5)) ]. ) 5) 7) 9 + 8 5. 8 [ 5) 8 6)] [9 + 8 5 ]. 9 + 8 5 ) 8) + 5. 5 + [ )6)] 7) 7 + 6 5 6. 8 5 ) 6
Polynomial Review Problems
 Polynomial Review Problems 1. Find polynomial function formulas that could fit each of these graphs. Remember that you will need to determine the value of the leading coefficient. The point (0,-3) is on
Polynomial Review Problems 1. Find polynomial function formulas that could fit each of these graphs. Remember that you will need to determine the value of the leading coefficient. The point (0,-3) is on
MSM120 1M1 First year mathematics for civil engineers Revision notes 3
 MSM0 M First year mathematics for civil engineers Revision notes Professor Robert. Wilson utumn 00 Functions Definition of a function: it is a rule which, given a value of the independent variable (often
MSM0 M First year mathematics for civil engineers Revision notes Professor Robert. Wilson utumn 00 Functions Definition of a function: it is a rule which, given a value of the independent variable (often
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt Algebra 2 2
 6-7 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 2 Warm Up Identify all the real roots of each equation. 1. x 3 7x 2 + 8x + 16 = 0 1, 4 2. 2x 3 14x 12 = 0 1, 2, 3 3. x 4 + x 3 25x 2 27x = 0 4. x 4 26x 2 + 25
6-7 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 2 Warm Up Identify all the real roots of each equation. 1. x 3 7x 2 + 8x + 16 = 0 1, 4 2. 2x 3 14x 12 = 0 1, 2, 3 3. x 4 + x 3 25x 2 27x = 0 4. x 4 26x 2 + 25
Composition of Functions
 Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Composite and Inverse Functions Composition of Functions The composite function f g, the composition of f and g, is defined as (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). Recall that a function
Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Composite and Inverse Functions Composition of Functions The composite function f g, the composition of f and g, is defined as (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). Recall that a function
Chapter 3: Inequalities, Lines and Circles, Introduction to Functions
 QUIZ AND TEST INFORMATION: The material in this chapter is on Quiz 3 and Exam 2. You should complete at least one attempt of Quiz 3 before taking Exam 2. This material is also on the final exam and used
QUIZ AND TEST INFORMATION: The material in this chapter is on Quiz 3 and Exam 2. You should complete at least one attempt of Quiz 3 before taking Exam 2. This material is also on the final exam and used
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 2012/2013 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Fall 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Fall 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from Algebra
Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Fall 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Fall 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from Algebra
Note: The actual exam will consist of 20 multiple choice questions and 6 show-your-work questions. Extra questions are provided for practice.
 College Algebra - Unit 2 Exam - Practice Test Note: The actual exam will consist of 20 multiple choice questions and 6 show-your-work questions. Extra questions are provided for practice. MULTIPLE CHOICE.
College Algebra - Unit 2 Exam - Practice Test Note: The actual exam will consist of 20 multiple choice questions and 6 show-your-work questions. Extra questions are provided for practice. MULTIPLE CHOICE.
Section 6.1: Composite Functions
 Section 6.1: Composite Functions Def: Given two function f and g, the composite function, which we denote by f g and read as f composed with g, is defined by (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). In other words, the function
Section 6.1: Composite Functions Def: Given two function f and g, the composite function, which we denote by f g and read as f composed with g, is defined by (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). In other words, the function
Math 12 Final Exam Review 1
 Math 12 Final Exam Review 1 Part One Calculators are NOT PERMITTED for this part of the exam. 1. a) The sine of angle θ is 1 What are the 2 possible values of θ in the domain 0 θ 2π? 2 b) Draw these angles
Math 12 Final Exam Review 1 Part One Calculators are NOT PERMITTED for this part of the exam. 1. a) The sine of angle θ is 1 What are the 2 possible values of θ in the domain 0 θ 2π? 2 b) Draw these angles
10/22/16. 1 Math HL - Santowski SKILLS REVIEW. Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions. Lesson Objectives. (A) Rational Functions
 Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions SKILLS REVIEW! Use function composition to prove that the following two funtions are inverses of each other. 2x 3 f(x) = g(x) = 5 2 x 1 1 2 Lesson Objectives! The
Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions SKILLS REVIEW! Use function composition to prove that the following two funtions are inverses of each other. 2x 3 f(x) = g(x) = 5 2 x 1 1 2 Lesson Objectives! The
CUMULATIVE REVIEW (4 th Nine Weeks) Honors Algebra II Essential Question: What algebra skills should I possess when I leave Algebra II Honors?
 Name Class/Period Date CUMULATIVE REVIEW (4 th Nine Weeks) Honors Algebra II Essential Question: What algebra skills should I possess when I leave Algebra II Honors? Directions: You will be assigned different
Name Class/Period Date CUMULATIVE REVIEW (4 th Nine Weeks) Honors Algebra II Essential Question: What algebra skills should I possess when I leave Algebra II Honors? Directions: You will be assigned different
y+2 x 1 is in the range. We solve x as x =
 Dear Students, Here are sample solutions. The most fascinating thing about mathematics is that you can solve the same problem in many different ways. The correct answer will always be the same. Be creative
Dear Students, Here are sample solutions. The most fascinating thing about mathematics is that you can solve the same problem in many different ways. The correct answer will always be the same. Be creative
Calculus : Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun Bishop Dunne Catholic School. Calculus Summer Math Study Guide
 1 Calculus 2018-2019: Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun (kbraun@bdcs.org) Bishop Dunne Catholic School Name: Calculus Summer Math Study Guide After you have practiced the skills on Khan Academy (list
1 Calculus 2018-2019: Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun (kbraun@bdcs.org) Bishop Dunne Catholic School Name: Calculus Summer Math Study Guide After you have practiced the skills on Khan Academy (list
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELS
 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELS What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic functions. Write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of functions. Find minimum and
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELS What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic functions. Write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of functions. Find minimum and
Mathematics for Business and Economics - I. Chapter 5. Functions (Lecture 9)
 Mathematics for Business and Economics - I Chapter 5. Functions (Lecture 9) Functions The idea of a function is this: a correspondence between two sets D and R such that to each element of the first set,
Mathematics for Business and Economics - I Chapter 5. Functions (Lecture 9) Functions The idea of a function is this: a correspondence between two sets D and R such that to each element of the first set,
3 FUNCTIONS. 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties. c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall
 c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2016 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from the set A to the set B is a correspondence that assigns to
c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2016 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from the set A to the set B is a correspondence that assigns to
Further Topics in Functions
 Chapter 5 Further Topics in Functions 5. Function Composition Before we embark upon any further adventures with functions, we need to take some time to gather our thoughts and gain some perspective. Chapter
Chapter 5 Further Topics in Functions 5. Function Composition Before we embark upon any further adventures with functions, we need to take some time to gather our thoughts and gain some perspective. Chapter
Lesson 9 Exploring Graphs of Quadratic Functions
 Exploring Graphs of Quadratic Functions Graph the following system of linear inequalities: { y > 1 2 x 5 3x + 2y 14 a What are three points that are solutions to the system of inequalities? b Is the point
Exploring Graphs of Quadratic Functions Graph the following system of linear inequalities: { y > 1 2 x 5 3x + 2y 14 a What are three points that are solutions to the system of inequalities? b Is the point
Exponential Functions:
 Exponential Functions: An exponential function has the form f (x) = b x where b is a fixed positive number, called the base. Math 101-Calculus 1 (Sklensky) In-Class Work January 29, 2015 1 / 12 Exponential
Exponential Functions: An exponential function has the form f (x) = b x where b is a fixed positive number, called the base. Math 101-Calculus 1 (Sklensky) In-Class Work January 29, 2015 1 / 12 Exponential
