Vladimir Sobes 2, Luiz Leal 3, Andrej Trkov 4 and Matt Falk 5
|
|
|
- Barrie Foster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Study of the Required Fidelity for the Representation of Angular Distributions of Elastic Scattering in the Resolved Resonance Region for Nuclear Criticality Safety Applications 1 Vladimir Sobes 2, Luiz Leal 3, Andrej Trkov 4 and Matt Falk 5 2 Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN, USA, sobesv@ornl.gov 3 Institut de Radioprotection et de Sureté Nucléaire (IRSN), Fontenay aux Roses, Cedex, France 4 International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Vienna, Austria Two Sigma, New York, NY Abstract Angular distributions of elastic scattering in the resolved resonance region can be reconstructed from the resonance parameters directly, or they can be provided in a point-wise manner with respect to incident neutron energy in nuclear data files. This study investigates the required fidelity in energy for the accurate representation of the angular distributions of elastic scattering in the resolved resonance region with respect to the performance in neutron transport calculations for nuclear criticality safety applications. A dense energy grid such as that used to represent angle integrated cross sections in the resolved resonance region, is not necessary for representation of angular distributions. A reduction in the number of points in energy on the order 5 10 (a 5 10 reduction of storage) gives the same results in a wide variety of neutron transport problems simulated. I. INTRODUCTION The evaluated nuclear data file (ENDF) [1] format allows the evaluator to specify that the evaluation in the resolved resonance region (RRR) is suitable for angular distribution of elastic scattering to be reconstructed directly from the evaluated resonance parameters in File 2. Until now, this option has rarely been used. Instead, the angular distribution of elastic scattering has been provided in tabulated and/or Legendre order as a function of the incident particle energy in File 4. One reason to provide a point-wise evaluation of the angular distribution of elastic scattering is that until recently, nuclear data processing codes could not run the calculations needed to reconstruct the full differential cross section from the resonance parameters according to the Blatt and Biedenharn formalism [2] for all types of the R-Matrix theory used to describe the RRR. This capability was recently added to the prerelease of the NJOY [3] processing code. The NJOY methodology to process angular distribution of elastic scattering requires that the coefficients of expansion of the Legendre moments of angular distribution be reconstructed on the same energy grid as that constructed by the RECONR module. This ensures that the maximum error resulting from linear interpolation between adjacent energy points and the true angle-integrated cross section is less than a user-defined value, usually set to 0.1% relative error. Recent research indicates that such high fidelity in energy when representing coefficients of expansion for the Legendre moments of the angular distribution of elastic scattering is not necessary for neutron transport calculations being used for practical applications. The reconstructed angular distributions are applicable strictly at zero-kelvin temperature. Doppler-broadening of the scattering moments is an approximation. A consistent implementation in Monte Carlo (MC) codes would be to use a library at zero-kelvin and then sample the speed and direction of the target atom within the MC code. No known standard MC code is currently capable of doing this, so it is reasonable to thin the angular distributions to follow the broad trends. The actual number of points in energy necessary to preserve highly accurate results in neutron transport calculations is the subject of the present investigation. While the methodology used in NJOY to reconstruct the angular distributions of elastic scattering from the evaluated parameters of the RRR is conservative in terms of preserving the correct physics, it is not conservative on computer memory. To accommodate for nuclear data processing codes that have not yet implemented the Blatt and Biedenharn formalism calculation methodology for double differential cross section, the authors, as evaluators, recommend providing the coefficients of expansion in the Legendre moments of the angular distribution in a point-wise manner in File 4 with the explicit message in File 1. Resonance parameters are suitable for reconstructing the angular distributions of elastic scattering, but when such a capability is not available, a point-wise evaluation has been provided in File 4. To provide an ENDF file of reasonable size for users who do not have the Blatt and Biedenharn capability in their processing code, a study of techniques has been 1 This manuscript has been authored by UT-Battelle, LLC, under Contract No. DE-AC0500OR22725 with the US Department of Energy. The US Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the US Government retains a nonexclusive, paid-up, irrevocable, worldwide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this manuscript, or allow other to do so, for the US Government purposes. The Department of Energy will provide public access to these results of federally sponsored research in accordance with the DOE Public Access Plan \\ ( energy.gov/downloads/doe-public-access-plan).
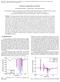
2 conducted to reduce the number of points in energy necessary to (1) represent angular distributions in the RRR, and (2) maintain a highly accurate representation of the physics of the RRR in the neutron transport calculations. Section III presents the techniques studied to reduce the number of points in energy to represent the angular distribution of elastic scattering. The tests to determine the performance of processed nuclear data files with different fidelity angular distributions in neutron transport problems are discussed in Section IV. Both successful and unsuccessful techniques for reducing the size of the pointwise file are presented. Detailed examples are presented showing how the proposed methodology is applied to the RRR evaluation of three isotopes: 16 O, 63 Cu and 65 Cu. II. BACKGROUND A neutron at a given incident energy scatters into solid angle dω. The preferred ENDF format method to represent and store angular distributions for elastic and inelastic scattering is the coefficients of Legendre polynomials. The definition of the coefficients, α l, is, α " E = %& ' ( (*) 34 σ - E, μ P " μ dμ, 54 where, σ s (E) is the angle integrated scattering cross section. The physical interpretation of the first two Legendre polynomials, P 1 (µ) = µ and P 2 (µ) = (3µ 2 1)/2, is straightforward. The first Legendre coefficient, α 1 (E), is often the primary determining factor of the amount of forward scattering. It determines whether more neutrons will scatter in the forward direction relative to their direction of motion, or if they will back scatter to return to their original location. The second Legendre coefficient, α 2 (E), indicates whether the scattering distribution of the isotope is enhanced in the forward/backward direction (α 2 > 0) or in the orthogonal direction (α 2 < 0). III. METHODOLOGY A careful study was performed to determine how to reduce the number of energy points necessary to represent the angular distributions of elastic scattering in terms of the Legendre coefficients. The goal was to find the minimum number of energy points necessary to represent the angular distributions while maintaining the highfidelity physical representation of the resonance phenomena present in the angular distributions. The study s success was measured by comparing performance of the evaluation with the reduced number of energy points in the angular distribution against the full fidelity representation in continuous-energy radiation transport codes. A progressive series of reductions was proposed (1) based on physics and mathematics, and a comprehensive testing system has been established. The first step in reducing the number of energy points in the point-wise representation was to successively relax the linear interpolation criteria. Originally, in the full fidelity representation, points are selected on 0.1% linear interpolation criteria. Therefore, at no point in the continuous function between any two consecutive points in the point-wise representation should the relative error exceed 0.1% when compared to the linear interpolation. The resulting reduction in the number of energy points is presented in Table I. A mathematical smoothing algorithm was applied to each reduced set of energy points that smoothed expansion in the coefficients. TABLE I. Number of Energy Points vs Linear Interpolation Criteria Used to Generate the Energy Grid. Interpolation 0.1% 10% 100% Criteria O Smoothed Cu Smoothed Cu Smoothed For such a significant reduction in the number of energy points, the visual effect on the coefficients of the Legendre expansion is nearly insignificant. Figure 1 presents a segment of the first coefficient of expansion of the angular distribution for 63 Cu in the RRR. Figure 2 shows a similar comparison for 16 O. Two reductions in the number of energy points are plotted, and the difference between the lines is minimal. To further reduce the numbers of energy points in the representation of the angular distributions, two successive physical approximations were made. The first approximation eliminated all resonances with associated orbital-angular momentum larger than zero. This is based on the understanding that the structure of the angular distributions of elastic scattering through the Blatt and Biedenharn formalism is dominated by the strong s-wave (orbital angular momentum equal to zero) resonances. Therefore, eliminating all higher orbital angular momentum resonances provides a systematic, physical way to reduce the number of energy points necessary to model major resonance features of angular distributions. Furthermore, all the smallest s-wave resonances can be eliminated if it is necessary to reduce the number of energy points even more dramatically. All the combinations and their final number of energy points for 63 Cu and 65 Cu are presented in Table II.
3 TABLE II. Number of Energy Points vs Physical Approximation Used to Generate the Reduced Energy Grid 63 Cu 65 Cu Interpolation criteria 10% 100% 10% 100% Eliminated p-waves Fig. 1. Coefficient of first moment in Legendre expansion of angular distribution of elastic scattering for 63 Cu in RRR for the 0.1% and the 100% relative error in the linear interpolation criteria, with smoothed versions. Fig. 2. Coefficient of first moment in Legendre expansion of angular distribution of elastic scattering for 16 O in RRR for the 0.1% and the 100% relative error in the energy range 500 kev and 6 MeV. The angular distribution files with the reduced number of energy points were first subjected to a seriesspecific MC neutron transport problem to test performance of the angular distribution reconstruction in neutron transport compared to results for nuclear data files processed with the NJOY angular distribution reconstruction capability. The second stage of testing was performed using sets of International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project (ICSBEP) [4] benchmark models with significant sensitivities to the isotopes of interest. The goal of this stage was to analyze performance of the processed nuclear data files in real applications. Eliminated p-waves (smoothed) Eliminated p-wave Reduced s-waves Eliminated p-wave Reduced s-waves (smoothed) Two dedicated computational exercises were devised with the geometry and neutron physics best suited to expose the impact of the angular distributions on neutron transport physics. One problem had a fixed-source, and the other was an eigenvalue-type problem. The fixed source problem consisted of a unidirectional point source of neutrons aimed at a dense sphere of the material of interest. The neutron source was mono-energetic, with energy selected as one of the test parameters. A wide detector was modeled on the other side of the target sphere, and tallies were taken in 50 energy bins and 10 different angular bins. The density of the target material was also varied as one of the test parameters to control the average number of scattering events and to govern how much the neutron slowed down before reaching the detector. This ensured that the angular distribution of elastic scattering was tested from the upper end of the resolved resonance region all the way to thermal energies. In the second specific test problem, a sphere with a radius of 10 cm centered at the origin was filled with one of the isotopes of interest ( 16 O, 63 Cu or 65 Cu) up to r = 7 cm. The remainder of the sphere was filled with 235 U in a homogenous mixture with 1 H. The U/H ratio was decreased until the energy of the average lethargy of neutrons causing fission was down in the resolved resonance region of the evaluation for the isotope of interest. The neutron current tallied in 50 energy bins and 10 cosine bins was recorded on the reflector/fuel boundary. The asymmetric geometry of this computational experiment tested the back scattering of the target isotopes in the resolved resonance region. The collective set of ICSBEP benchmarks used as a final test of the performance of the reduced angular distributions for 16 O is presented in Table III using the short-hand ICSBEP nomenclature. The ICSBEP benchmarks used to test performance of the reduced angular distributions of 63 Cu and 65 Cu are given in Table IV.
4 TABLE III. Collection of ICSBEP Benchmarks Used to Test Performance of the Reduced Angular Distribution of Elastic Scattering for 16 O. Benchmark Number ICSBEP Benchmark Name 1 LMT LMT ZED-2 TABLE IV. Collection of ICSBEP Benchmarks Used to Test Performance of the Reduced Angular Distribution of Elastic Scattering for 63 Cu and 65 Cu. Benchmark Number ICSBEP Benchmark Name 1 HMF HMF HMF HMF HMF HMF HMF HMF HMI HMI HMI HMI IMF IMF IMF IMF IMF IMF IMF IMF IMF IMF IMF IMF IMF IMI IMI IMI PMF-4001 IV. RESULTS Figure 3 presents the difference between the calculated tally results for two different cases. The Full Angular Distributions case indicates that the nuclear data file for 16 O was processed by NJOY with the angular distributions of elastic scattering calculated directly from the resonance parameters. In the Reduced Angular Distributions case, the processed file had the number of energy points necessary to represent the coefficients of the Legendre moments of expansion as a function of energy reduced to 6342 (10 % error). Fig. 3. Tally results for calculated neutron current across one face of a cube model filled with 16 O binned versus energy. In Figure 3, the example compares the effect of reducing the number of points in energy used to represent the coefficient of expansion in the Legendre moments of the angular distribution of elastic scattering of 16 O. Figure 3 suggests that thinning the angular distributions has no effect on this integral test. Multiple variations of this configuration were tested using different 16 O densities and sources, and all with the same conclusion as this example: without the elimination of isolated resonances, the angular distributions can be thinned to 10% relative error in the linear interpolation without a demonstrable effect in neutron transport calculations. From the set of two devised neutron transport test problems, it became evident that out of the proposed methodologies, only the mathematical reduction in the number of energy points necessary to represent the high fidelity angular distributions is viable. This also corresponds with the proposed distributions with the least reduction in the number of energy points. Table V provides an example of the deteriorating performance of the reduced angular distributions in transport calculations. Table V presents the tally scores for neutrons with energies between 31.8 kev and 55.7 kev for the cosine bin with a fixed-source energy of 300 kev (end of RRR for 63 Cu) and a target density corresponding to an average of 10 scattering events.
5 Table V. Tally Scores for Neutrons with Energies between 31.8 kev and 55.7 kev for Cosine Bin for the Fixed-Source Type Test Problem Using 63 Cu Angular Distribution File 0.1% criteria 10% criteria 100% criteria 10% criteria eliminated p-waves 10% criteria eliminated p-waves Reduced s-waves Tally Score Number of Energy Points Table V shows results obtained by varying the two input parameters for the fixed-source test problem and the eigenvalue test problem. The results clearly show that once the smaller resonances are eliminated from the angular distribution files, performance of the evaluation in the neutron transport calculations begins to decline. The comprehensive set of ICSBEP benchmarks for the two copper isotopes confirmed what was seen in the test problems. Figure 4 supports the findings shown in Figure 3 except for ICSBEP benchmarks sensitive to the two isotopes of copper for various reductions in the number of energy points in the representation of the angular distribution of elastic scattering. V. CONCLUSIONS A study was made of the different methodologies to reduce the number of energy points required to communicate angular distributions of elastic scattering in the RRR. Several approaches were considered, ranging from mathematical smoothing algorithms to physically intuitive manipulations of resonance parameters. A testing routine was established with a set of specifically devised neutron transport problems of both the eigenvalue and the fixed-source types, as well as a more general set of criticality safety benchmarks. Both types of testing were compared to the performance of the nuclear data files processed with the full fidelity model. Both types of testing showed the same general trend: mathematical smoothing of the angular distribution function is successful, while manipulations of resonance parameters based on physical intuition do not lead to consistent results in neutron transport calculations. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported by the US Department of Energy (DOE) Nuclear Criticality Safety Program, funded and managed by the National Nuclear Security Administration for DOE. The authors would like to thank Dr. A. C. (Skip) Kahler from Los Alamos National Laboratory for generously sharing the MCNP input files he developed based on the ICSBEP descriptions. REFERENCES 1. V. MCLANE, C. L. DUNFORD, and P. F. ROSE. ENDF-102, Data Formats and Procedures for the Evaluated Nuclear Data File, ENDF-6, written by the Members of the Cross Section Evaluation Working Group, ed. BNL-NCS-4495, Brookhaven National Laboratory, April Updated BNL- NCS-4495/04-Rev, ed. M. Herman (June 2005). 2. J. M. BLATT and L. C. BIEDENHARN. The Angular Distribution of Scattering and Reaction Cross Sections. Review of Modern Physics 24, 258 (1952). 3. R. E. MACFARLANE, D. W. MUIR, R. M. BOICOURT, The NJOY Nuclear Data Processing System: User s Manual, Vol. 1, Technical Report, Los Alamos National Laboratory (1982). 4. J. B. BRIGGS et al. International Handbook of Evaluated Criticality Safety Benchmark Experiments. Report NEA/DOC (95) 4 (2015).
6 k-effective % Criteria 10% Criteria 100% Criteria 10% Criteria Eliminated p-waves 10% Criteria Eliminated p-waves, Reduced s-waves Benchmark Number Fig. 4. k eff results for the set of 29 benchmarks described in Table IV for four different reductions of the number of energy points used to describe the angular distributions of elastic scattering for the two isotopes of copper. (The stochastic uncertainty on the calculations is below 10 pcm, which is smaller than the size of the markers.)
Invited. ENDF/B-VII data testing with ICSBEP benchmarks. 1 Introduction. 2 Discussion
 International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: 10.1051/ndata:07285 Invited ENDF/B-VII data testing with ICSBEP benchmarks A.C. Kahler and R.E. MacFarlane Los Alamos National
International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: 10.1051/ndata:07285 Invited ENDF/B-VII data testing with ICSBEP benchmarks A.C. Kahler and R.E. MacFarlane Los Alamos National
ORNL Nuclear Data Evaluation Accomplishments for FY 2013
 ORNL Nuclear Data Evaluation Accomplishments for FY 2013 L. Leal, V. Sobes, M. Pigni, K. Guber, G. Arbanas, D. Wiarda, M. Dunn (ORNL) and E. Ivanov, T. Ivanova, E. Letang (Institut de Radioprotection et
ORNL Nuclear Data Evaluation Accomplishments for FY 2013 L. Leal, V. Sobes, M. Pigni, K. Guber, G. Arbanas, D. Wiarda, M. Dunn (ORNL) and E. Ivanov, T. Ivanova, E. Letang (Institut de Radioprotection et
A TEMPERATURE DEPENDENT ENDF/B-VI.8 ACE LIBRARY FOR UO2, THO2, ZIRC4, SS AISI-348, H2O, B4C AND AG-IN-CD
 2009 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2009 Rio de Janeiro,RJ, Brazil, September27 to October 2, 2009 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-03-8 A TEMPERATURE
2009 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2009 Rio de Janeiro,RJ, Brazil, September27 to October 2, 2009 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-03-8 A TEMPERATURE
FRENDY: A new nuclear data processing system being developed at JAEA
 FRENDY: A new nuclear data processing system being developed at JAEA Kenichi Tada a, Yasunobu Nagaya, Satoshi Kunieda, Kenya Suyama, and Tokio Fukahori Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Tokai, Japan Abstract.
FRENDY: A new nuclear data processing system being developed at JAEA Kenichi Tada a, Yasunobu Nagaya, Satoshi Kunieda, Kenya Suyama, and Tokio Fukahori Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Tokai, Japan Abstract.
Upcoming features in Serpent photon transport mode
 Upcoming features in Serpent photon transport mode Toni Kaltiaisenaho VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Serpent User Group Meeting 2018 1/20 Outline Current photoatomic physics in Serpent Photonuclear
Upcoming features in Serpent photon transport mode Toni Kaltiaisenaho VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Serpent User Group Meeting 2018 1/20 Outline Current photoatomic physics in Serpent Photonuclear
Implementation of the CLUTCH method in the MORET code. Alexis Jinaphanh
 Implementation of the CLUTCH method in the MORET code Alexis Jinaphanh Institut de Radioprotection et de sûreté nucléaire (IRSN), PSN-EXP/SNC/LNC BP 17, 92262 Fontenay-aux-Roses, France alexis.jinaphanh@irsn.fr
Implementation of the CLUTCH method in the MORET code Alexis Jinaphanh Institut de Radioprotection et de sûreté nucléaire (IRSN), PSN-EXP/SNC/LNC BP 17, 92262 Fontenay-aux-Roses, France alexis.jinaphanh@irsn.fr
COVARIANCE DATA FOR 233 U IN THE RESOLVED RESONANCE REGION FOR CRITICALITY SAFETY APPLICATIONS
 Mathematics and Computation, Supercomputing, Reactor Physics and Nuclear and Biological Applications Palais des Papes, Avignon, France, September 12-15, 2005, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange
Mathematics and Computation, Supercomputing, Reactor Physics and Nuclear and Biological Applications Palais des Papes, Avignon, France, September 12-15, 2005, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange
CIELO Project. M. Herman 1) D. Brown 1), R. Capote 2), G. Nobre 1), A. Trkov 2) for the CIELO Collaboration 3)
 56Fe Evaluation for the CIELO Project M. Herman 1) D. Brown 1), R. Capote 2), G. Nobre 1), A. Trkov 2) for the CIELO Collaboration 3) 1) National Nuclear Data Center, Brookhaven National Laboratory, USA
56Fe Evaluation for the CIELO Project M. Herman 1) D. Brown 1), R. Capote 2), G. Nobre 1), A. Trkov 2) for the CIELO Collaboration 3) 1) National Nuclear Data Center, Brookhaven National Laboratory, USA
Processing of incident-neutron sub-library from ENDF/B-VII.1, JENDL-4.0 and JEFF-3.1.1
 Processing of incident-neutron sub-library from ENDF/B-VII.1, JENDL-4. and JEFF-3.1.1 M.P.W. Chin, A. Ferrari, V. Vlachoudis CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research), CH-1211 Geneva, Switzerland
Processing of incident-neutron sub-library from ENDF/B-VII.1, JENDL-4. and JEFF-3.1.1 M.P.W. Chin, A. Ferrari, V. Vlachoudis CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research), CH-1211 Geneva, Switzerland
Temperature treatment capabilites in Serpent 2(.1.24)
 Temperature treatment capabilites in Serpent 2(.1.24) Tuomas Viitanen Serpent User Group Meeting Knoxville, TN, USA OCt. 13 16, 2015 Introduction Temperature affects the neutron transport through: - Reaction
Temperature treatment capabilites in Serpent 2(.1.24) Tuomas Viitanen Serpent User Group Meeting Knoxville, TN, USA OCt. 13 16, 2015 Introduction Temperature affects the neutron transport through: - Reaction
Figure 1. Layout of fuel assemblies, taken from BEAVRS full core benchmark, to demonstrate the modeling capabilities of OpenMC.
 Treatment of Neutron Resonance Elastic Scattering Using Multipole Representation of Cross Sections in Monte Carlo Simulations Vivian Y. Tran Benoit Forget Abstract Predictive modeling and simulation plays
Treatment of Neutron Resonance Elastic Scattering Using Multipole Representation of Cross Sections in Monte Carlo Simulations Vivian Y. Tran Benoit Forget Abstract Predictive modeling and simulation plays
Introduction to Nuclear Data
 united nations educational, scientific and cultural organization the abdus salam international centre for theoretical physics international atomic energy agency SMR.1555-34 Workshop on Nuclear Reaction
united nations educational, scientific and cultural organization the abdus salam international centre for theoretical physics international atomic energy agency SMR.1555-34 Workshop on Nuclear Reaction
Comparative Analysis of Nuclear Cross Sections in Monte Carlo Methods for Medical Physics Applications
 Comparative Analysis of Nuclear Cross Sections in Monte Carlo Methods for Medical Physics Applications Christopher T. Myers 1 Georgia Institute of Technology Bernadette L. Kirk 2 Luiz C. Leal 2 Oak Ridge
Comparative Analysis of Nuclear Cross Sections in Monte Carlo Methods for Medical Physics Applications Christopher T. Myers 1 Georgia Institute of Technology Bernadette L. Kirk 2 Luiz C. Leal 2 Oak Ridge
VERIFICATION OF MONTE CARLO CALCULATIONS OF THE NEUTRON FLUX IN THE CAROUSEL CHANNELS OF THE TRIGA MARK II REACTOR, LJUBLJANA
 International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe 2002 Kranjska Gora, Slovenia, September 9-12, 2002 www.drustvo-js.si/gora2002 VERIFATION OF MONTE CARLO CALCULATIONS OF THE NEUTRON FLUX IN THE CAROUSEL
International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe 2002 Kranjska Gora, Slovenia, September 9-12, 2002 www.drustvo-js.si/gora2002 VERIFATION OF MONTE CARLO CALCULATIONS OF THE NEUTRON FLUX IN THE CAROUSEL
In the Memory of John Rowlands
 Introduction of the Resonance dependent scattering kernel in SERPENT In the Memory of John Rowlands Institute for Neutron Physics and Reactor Technology R. Dagan Institute for Neutron Physics and Reactor
Introduction of the Resonance dependent scattering kernel in SERPENT In the Memory of John Rowlands Institute for Neutron Physics and Reactor Technology R. Dagan Institute for Neutron Physics and Reactor
TENDL-2011 processing and criticality benchmarking
 JEF/DOC-1438 TENDL-2011 processing and criticality benchmarking Jean-Christophe C Sublet UK Atomic Energy Authority Culham Science Centre, Abingdon, OX14 3DB United Kingdom CCFE is the fusion research
JEF/DOC-1438 TENDL-2011 processing and criticality benchmarking Jean-Christophe C Sublet UK Atomic Energy Authority Culham Science Centre, Abingdon, OX14 3DB United Kingdom CCFE is the fusion research
Brief Review of the R-Matrix Theory
 Brief Review of the R-Matrix Theory L. C. Leal Introduction Resonance theory deals with the description of the nucleon-nucleus interaction and aims at the prediction of the experimental structure of cross
Brief Review of the R-Matrix Theory L. C. Leal Introduction Resonance theory deals with the description of the nucleon-nucleus interaction and aims at the prediction of the experimental structure of cross
Resonance Evaluations of 235 U for the CIELO Project
 Resonance Evaluations of 235 U for the CIELO Project L. Leal 1), A. Kahler 2), G. Noguere 3), O. Bouland 3), Y. Penneliau 3) 1) Oak Ridge National Laboratory 2) Los Alamos National Laboratory 3) CEA/Cadarache
Resonance Evaluations of 235 U for the CIELO Project L. Leal 1), A. Kahler 2), G. Noguere 3), O. Bouland 3), Y. Penneliau 3) 1) Oak Ridge National Laboratory 2) Los Alamos National Laboratory 3) CEA/Cadarache
Neutron Cross-Section Measurements at ORELA
 December 16, 2005 Paper for ORELA Proceedings Nuclear Science and Technology Division (94) Neutron Cross-Section Measurements at ORELA K. H. Guber, L. C. Leal, R. O. Sayer, P. E. Koehler, H. Derrien, D.
December 16, 2005 Paper for ORELA Proceedings Nuclear Science and Technology Division (94) Neutron Cross-Section Measurements at ORELA K. H. Guber, L. C. Leal, R. O. Sayer, P. E. Koehler, H. Derrien, D.
Nuclear Data Uncertainty Analysis in Criticality Safety. Oliver Buss, Axel Hoefer, Jens-Christian Neuber AREVA NP GmbH, PEPA-G (Offenbach, Germany)
 NUDUNA Nuclear Data Uncertainty Analysis in Criticality Safety Oliver Buss, Axel Hoefer, Jens-Christian Neuber AREVA NP GmbH, PEPA-G (Offenbach, Germany) Workshop on Nuclear Data and Uncertainty Quantification
NUDUNA Nuclear Data Uncertainty Analysis in Criticality Safety Oliver Buss, Axel Hoefer, Jens-Christian Neuber AREVA NP GmbH, PEPA-G (Offenbach, Germany) Workshop on Nuclear Data and Uncertainty Quantification
ENDF-6 Formats Manual
 CSEWG Document ENDF-102 Report BNL-90365-2009 Rev.1 ENDF-6 Formats Manual Data Formats and Procedures for the Evaluated Nuclear Data Files ENDF/B-VI and ENDF/B-VII Written by the Members of the Cross Sections
CSEWG Document ENDF-102 Report BNL-90365-2009 Rev.1 ENDF-6 Formats Manual Data Formats and Procedures for the Evaluated Nuclear Data Files ENDF/B-VI and ENDF/B-VII Written by the Members of the Cross Sections
INTERCOMPARISON OF CALCULATIONS FOR GODIVA AND JEZEBEL
 JEFF Report 16 INTERCOMPARISON OF CALCULATIONS FOR GODIVA AND JEZEBEL An intercomparison study organised by the JEFF Project, with contributions from Britain, France, the Netherlands and Switzerland December
JEFF Report 16 INTERCOMPARISON OF CALCULATIONS FOR GODIVA AND JEZEBEL An intercomparison study organised by the JEFF Project, with contributions from Britain, France, the Netherlands and Switzerland December
Reconstruction of Neutron Cross-sections and Sampling
 Reconstruction of Neutron Cross-sections and Sampling Harphool Kumawat Nuclear Physics Division, BARC 1 Outline Introduction Reconstruction of resonance cross-section Linearization of cross-section Unionization
Reconstruction of Neutron Cross-sections and Sampling Harphool Kumawat Nuclear Physics Division, BARC 1 Outline Introduction Reconstruction of resonance cross-section Linearization of cross-section Unionization
INDC International Nuclear Data Committee
 INDC(NDS)-0666 Distr. J INDC International Nuclear Data Committee How Accurate Are Our Processed ENDF Cross Sections? Dermott E. Cullen National Nuclear Data Center, Brookhaven National Laboratory (alumnus)
INDC(NDS)-0666 Distr. J INDC International Nuclear Data Committee How Accurate Are Our Processed ENDF Cross Sections? Dermott E. Cullen National Nuclear Data Center, Brookhaven National Laboratory (alumnus)
Assessment of the Unresolved Resonance Treatment for Cross-section and Covariance Representation
 Nuclear Science NEA/WPEC-32 NEA/NSC/WPEC/DOC(2011)430 International Evaluation Co-operation Volume 32 Assessment of the Unresolved Resonance Treatment for Cross-section and Covariance Representation A
Nuclear Science NEA/WPEC-32 NEA/NSC/WPEC/DOC(2011)430 International Evaluation Co-operation Volume 32 Assessment of the Unresolved Resonance Treatment for Cross-section and Covariance Representation A
Development of Multigroup Cross Section Generation Code MC 2-3 for Fast Reactor Analysis
 Development o Multigroup Cross Section Generation Code MC 2-3 or Fast Reactor Analysis International Conerence on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles December 7-11, 2009 Kyoto, Japan Changho Lee and
Development o Multigroup Cross Section Generation Code MC 2-3 or Fast Reactor Analysis International Conerence on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles December 7-11, 2009 Kyoto, Japan Changho Lee and
The Updated Version of Chinese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (CENDL-3.1)
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 59, No. 2, August 2011, pp. 1052 1056 The Updated Version of Chinese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (CENDL-3.1) Z. G. Ge, Z. X. Zhao and H. H. Xia China Nuclear
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 59, No. 2, August 2011, pp. 1052 1056 The Updated Version of Chinese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (CENDL-3.1) Z. G. Ge, Z. X. Zhao and H. H. Xia China Nuclear
JRPR. Current Status of ACE Format Libraries for MCNP at Nuclear Data Center of KAERI. Original Research. Introduction
 Journal of Radiation Protection and Research 216;41(3):191-195 pissn 258-1888 eissn 2466-2461 Current Status of ACE Format Libraries for MCNP at Nuclear Data Center of KAERI Do Heon Kim*, Choong-Sup Gil,
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research 216;41(3):191-195 pissn 258-1888 eissn 2466-2461 Current Status of ACE Format Libraries for MCNP at Nuclear Data Center of KAERI Do Heon Kim*, Choong-Sup Gil,
Needs for Nuclear Reactions on Actinides
 Needs for Nuclear Reactions on Actinides Mark Chadwick Los Alamos National Laboratory Talk at the Workshop on Nuclear Data Needs & Capabilities for Applications, May 27-29, 2015 Nuclear Data for National
Needs for Nuclear Reactions on Actinides Mark Chadwick Los Alamos National Laboratory Talk at the Workshop on Nuclear Data Needs & Capabilities for Applications, May 27-29, 2015 Nuclear Data for National
Status of Subgroup 24
 Status of Subgroup 24 M. Herman National Nuclear Data Center, BNL for SG24 mwherman@bnl.gov Brookhaven Science Associates SG 24 membership M. Herman (BNL) - Chairman C. Mattoon (BNL) S. Mughaghab (BNL)
Status of Subgroup 24 M. Herman National Nuclear Data Center, BNL for SG24 mwherman@bnl.gov Brookhaven Science Associates SG 24 membership M. Herman (BNL) - Chairman C. Mattoon (BNL) S. Mughaghab (BNL)
PIA and REWIND: Two New Methodologies for Cross Section Adjustment. G. Palmiotti and M. Salvatores
 PIA and REWIND: Two New Methodologies for Cross Section Adjustment G. Palmiotti and M. Salvatores Nuclear Systems Design and Analysis Division, Idaho National Laboratory, P.O. Box 1625, MS 3860, Idaho
PIA and REWIND: Two New Methodologies for Cross Section Adjustment G. Palmiotti and M. Salvatores Nuclear Systems Design and Analysis Division, Idaho National Laboratory, P.O. Box 1625, MS 3860, Idaho
ENDF-6 Formats Manual
 CSEWG Document ENDF-102 Report BNL-90365-2009 Rev.2 ENDF-6 Formats Manual Data Formats and Procedures for the Evaluated Nuclear Data Files ENDF/B-VI and ENDF/B-VII Written by the Members of the Cross Sections
CSEWG Document ENDF-102 Report BNL-90365-2009 Rev.2 ENDF-6 Formats Manual Data Formats and Procedures for the Evaluated Nuclear Data Files ENDF/B-VI and ENDF/B-VII Written by the Members of the Cross Sections
Photon transport mode in Serpent 2
 Photon transport mode in Serpent 2 Toni Kaltiaisenaho VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, LTD Serpent User Group Meeting, Knoxville, TN October 13 16, 215 October 14, 215 1/21 Outline Photon physics
Photon transport mode in Serpent 2 Toni Kaltiaisenaho VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, LTD Serpent User Group Meeting, Knoxville, TN October 13 16, 215 October 14, 215 1/21 Outline Photon physics
MOx Benchmark Calculations by Deterministic and Monte Carlo Codes
 MOx Benchmark Calculations by Deterministic and Monte Carlo Codes G.Kotev, M. Pecchia C. Parisi, F. D Auria San Piero a Grado Nuclear Research Group (GRNSPG), University of Pisa via Diotisalvi 2, 56122
MOx Benchmark Calculations by Deterministic and Monte Carlo Codes G.Kotev, M. Pecchia C. Parisi, F. D Auria San Piero a Grado Nuclear Research Group (GRNSPG), University of Pisa via Diotisalvi 2, 56122
TMS On-the-fly Temperature Treatment in Serpent
 TMS On-the-fly Temperature Treatment in Serpent Tuomas Viitanen & Jaakko Leppänen Serpent User Group Meeting, Cambridge, UK September 17 19, 2014 Effects of thermal motion on neutron transport On reaction
TMS On-the-fly Temperature Treatment in Serpent Tuomas Viitanen & Jaakko Leppänen Serpent User Group Meeting, Cambridge, UK September 17 19, 2014 Effects of thermal motion on neutron transport On reaction
Complete activation data libraries for all incident particles, all energies and including covariance data
 Complete activation data libraries for all incident particles, all energies and including covariance data Arjan Koning NRG Petten, The Netherlands Workshop on Activation Data EAF 2011 June 1-3 2011, Prague,
Complete activation data libraries for all incident particles, all energies and including covariance data Arjan Koning NRG Petten, The Netherlands Workshop on Activation Data EAF 2011 June 1-3 2011, Prague,
Covariance Generation using CONRAD and SAMMY Computer Codes
 Covariance Generation using CONRAD and SAMMY Computer Codes L. Leal a, C. De Saint Jean b, H. Derrien a, G. Noguere b, B. Habert b, and J. M. Ruggieri b a Oak Ridge National Laboratory b CEA, DEN, Cadarache
Covariance Generation using CONRAD and SAMMY Computer Codes L. Leal a, C. De Saint Jean b, H. Derrien a, G. Noguere b, B. Habert b, and J. M. Ruggieri b a Oak Ridge National Laboratory b CEA, DEN, Cadarache
CROSS SECTION WEIGHTING SPECTRUM FOR FAST REACTOR ANALYSIS
 2009 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2009 Rio de Janeiro,RJ, Brazil, September27 to October 2, 2009 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-03-8 CROSS SECTION
2009 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2009 Rio de Janeiro,RJ, Brazil, September27 to October 2, 2009 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-03-8 CROSS SECTION
Benchmark Tests of Gamma-Ray Production Data in JENDL-3 for Some Important Nuclides
 Journal of NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECFINOLOGY, 27[9], pp. 844~852 (September 1990). TECHNICAL REPORT Benchmark Tests of Gamma-Ray Production Data in JENDL-3 for Some Important Nuclides CAI Shao-huit, Akira
Journal of NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECFINOLOGY, 27[9], pp. 844~852 (September 1990). TECHNICAL REPORT Benchmark Tests of Gamma-Ray Production Data in JENDL-3 for Some Important Nuclides CAI Shao-huit, Akira
Neutronic analysis of SFR lattices: Serpent vs. HELIOS-2
 Neutronic analysis of SFR lattices: Serpent vs. HELIOS-2 E. Fridman 1, R. Rachamin 1, C. Wemple 2 1 Helmholtz Zentrum Dresden Rossendorf 2 Studsvik Scandpower Inc. Text optional: Institutsname Prof. Dr.
Neutronic analysis of SFR lattices: Serpent vs. HELIOS-2 E. Fridman 1, R. Rachamin 1, C. Wemple 2 1 Helmholtz Zentrum Dresden Rossendorf 2 Studsvik Scandpower Inc. Text optional: Institutsname Prof. Dr.
SENSITIVITY AND PERTURBATION THEORY IN FAST REACTOR CORE DESIGN
 Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 65, NO. 7s, 214, 25 29 SENSITIVITY AND PERTURBATION THEORY IN FAST REACTOR CORE DESIGN Jakub Lüley Branislav Vrban Štefan Čerba Ján Haščík Vladimír Nečas Sang-Ji
Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 65, NO. 7s, 214, 25 29 SENSITIVITY AND PERTURBATION THEORY IN FAST REACTOR CORE DESIGN Jakub Lüley Branislav Vrban Štefan Čerba Ján Haščík Vladimír Nečas Sang-Ji
: Y/LB-16,056 OAK RIDGE Y-12 PLANT
 Y-12 Report No.: Y/LB-16,056 OAK RIDGE Y-12 PLANT VERIFICATION OF URANIUM MASS AND ENRICHMENTS OF HIGHLY ENRICHED URANIUM (HEU) USING THE NUCLEAR MATERIALS IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM (NMIS) L. G. Chiang J.
Y-12 Report No.: Y/LB-16,056 OAK RIDGE Y-12 PLANT VERIFICATION OF URANIUM MASS AND ENRICHMENTS OF HIGHLY ENRICHED URANIUM (HEU) USING THE NUCLEAR MATERIALS IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM (NMIS) L. G. Chiang J.
Problem P7. Stéphanie Ménard. Dosimetry Department Fontenay-aux FRANCE IRSN QUADOS IRSN
 Problem P7 Stéphanie Ménard Dosimetry Department 92262 Fontenay-aux aux-roses FRANCE What are the applications of Gamma-Ray Spectrometry in Radiological Protection and in Safety? In the environment: after
Problem P7 Stéphanie Ménard Dosimetry Department 92262 Fontenay-aux aux-roses FRANCE What are the applications of Gamma-Ray Spectrometry in Radiological Protection and in Safety? In the environment: after
TENDL-TMC for dpa and pka
 WIR SCHAFFEN WISSEN HEUTE FÜR MORGEN D. Rochman, A.J. Koning, J.C. Sublet, M. Gilbert, H. Sjöstrand, P. Helgesson and H. Ferroukhi TENDL-TMC for dpa and pka Technical Meeting on Uncertainties for Radiation
WIR SCHAFFEN WISSEN HEUTE FÜR MORGEN D. Rochman, A.J. Koning, J.C. Sublet, M. Gilbert, H. Sjöstrand, P. Helgesson and H. Ferroukhi TENDL-TMC for dpa and pka Technical Meeting on Uncertainties for Radiation
CALIBRATION OF SCINTILLATION DETECTORS USING A DT GENERATOR Jarrod D. Edwards, Sara A. Pozzi, and John T. Mihalczo
 CALIBRATION OF SCINTILLATION DETECTORS USING A DT GENERATOR Jarrod D. Edwards, Sara A. Pozzi, and John T. Mihalczo Oak Ridge National Laboratory Oak Ridge, TN 37831-6010 PO Box 2008 Ms6010 ABSTRACT The
CALIBRATION OF SCINTILLATION DETECTORS USING A DT GENERATOR Jarrod D. Edwards, Sara A. Pozzi, and John T. Mihalczo Oak Ridge National Laboratory Oak Ridge, TN 37831-6010 PO Box 2008 Ms6010 ABSTRACT The
Optimizing HFIR Isotope Production through the Development of a Sensitivity-Informed Target Design Process 1
 Optimizing HFIR Isotope Production through the Development of a -Informed Design Process 1 Christopher Perfetti*, Susan Hogle, Seth Johnson, Bradley Rearden, and Thomas Evans Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Optimizing HFIR Isotope Production through the Development of a -Informed Design Process 1 Christopher Perfetti*, Susan Hogle, Seth Johnson, Bradley Rearden, and Thomas Evans Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
ADVANCED METHODOLOGY FOR SELECTING GROUP STRUCTURES FOR MULTIGROUP CROSS SECTION GENERATION
 ADVANCED METHODOLOGY FOR SELECTING GROUP STRUCTURES FOR MULTIGROUP CROSS SECTION GENERATION Arzu Alpan and Alireza Haghighat Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering Department The Pennsylvania State University
ADVANCED METHODOLOGY FOR SELECTING GROUP STRUCTURES FOR MULTIGROUP CROSS SECTION GENERATION Arzu Alpan and Alireza Haghighat Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering Department The Pennsylvania State University
DOPPLER COEFFICIENT OF REACTIVITY BENCHMARK CALCULATIONS FOR DIFFERENT ENRICHMENTS OF UO 2
 Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (M&C + SNA 2007) Monterey, California, April 15-19, 2007, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2007) DOPPLER COEFFICIENT OF REACTIVITY BENCHMARK
Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (M&C + SNA 2007) Monterey, California, April 15-19, 2007, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2007) DOPPLER COEFFICIENT OF REACTIVITY BENCHMARK
Sensitivity Computation with Monte Carlo Methods
 Sensitivity Computation with Monte Carlo Methods (Action C8, WPEC/Sg.39) E. Ivanov T. Ivanova WPEC/Sg. 39 Meeting Novembre 27-28, 2014 NEA, Issy-les-Moulineaux, 1 France General Remarks Objective of the
Sensitivity Computation with Monte Carlo Methods (Action C8, WPEC/Sg.39) E. Ivanov T. Ivanova WPEC/Sg. 39 Meeting Novembre 27-28, 2014 NEA, Issy-les-Moulineaux, 1 France General Remarks Objective of the
Serpent Monte Carlo Neutron Transport Code
 Serpent Monte Carlo Neutron Transport Code NEA Expert Group on Advanced Monte Carlo Techniques, Meeting September 17 2012 Jaakko Leppänen / Tuomas Viitanen VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Outline
Serpent Monte Carlo Neutron Transport Code NEA Expert Group on Advanced Monte Carlo Techniques, Meeting September 17 2012 Jaakko Leppänen / Tuomas Viitanen VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Outline
1 Introduction. É É â. EPJ Web of Conferences 42, (2013) C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013
 É É EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 05004 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134205004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Reactivity effect breakdown calculations with deterministic and stochastic
É É EPJ Web of Conferences 42, 05004 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20134205004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2013 Reactivity effect breakdown calculations with deterministic and stochastic
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF ALLEGRO MOX CORE. Bratislava, Iľkovičova 3, Bratislava, Slovakia
 SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF ALLEGRO MOX CORE Jakub Lüley 1, Ján Haščík 1, Vladimír Slugeň 1, Vladimír Nečas 1 1 Institute of Nuclear and Physical Engineering, Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava,
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF ALLEGRO MOX CORE Jakub Lüley 1, Ján Haščík 1, Vladimír Slugeň 1, Vladimír Nečas 1 1 Institute of Nuclear and Physical Engineering, Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava,
Benchmark Test of JENDL High Energy File with MCNP
 Benchmark Test of JENDL High Energy File with MCNP Masayuki WADA, Fujio MAEKAWA, Chikara KONNO Intense Neutron Source Laboratory, Department of Materials Science Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute,
Benchmark Test of JENDL High Energy File with MCNP Masayuki WADA, Fujio MAEKAWA, Chikara KONNO Intense Neutron Source Laboratory, Department of Materials Science Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute,
Comparison of the Monte Carlo Adjoint-Weighted and Differential Operator Perturbation Methods
 Progress in NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, Vol., pp.836-841 (011) ARTICLE Comparison of the Monte Carlo Adjoint-Weighted and Differential Operator Perturbation Methods Brian C. KIEDROWSKI * and Forrest
Progress in NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, Vol., pp.836-841 (011) ARTICLE Comparison of the Monte Carlo Adjoint-Weighted and Differential Operator Perturbation Methods Brian C. KIEDROWSKI * and Forrest
Monte Carlo Method: Theory and Exercises (1)
 united nations educational, scientific and cultural organization the abdus salam international centre for theoretical physics international atomic energy agency SMR.1555-12 Workshop on Nuclear Reaction
united nations educational, scientific and cultural organization the abdus salam international centre for theoretical physics international atomic energy agency SMR.1555-12 Workshop on Nuclear Reaction
VERIFICATION OFENDF/B-VII.0, ENDF/B-VII.1 AND JENDL-4.0 NUCLEAR DATA LIBRARIES FOR CRITICALITY CALCULATIONS USING NEA/NSC BENCHMARKS
 VERIFICATION OFENDF/B-VII.0, ENDF/B-VII.1 AND JENDL-4.0 NUCLEAR DATA LIBRARIES FOR CRITICALITY CALCULATIONS USING NEA/NSC BENCHMARKS Amine Bouhaddane 1, Gabriel Farkas 1, Ján Haščík 1, Vladimír Slugeň
VERIFICATION OFENDF/B-VII.0, ENDF/B-VII.1 AND JENDL-4.0 NUCLEAR DATA LIBRARIES FOR CRITICALITY CALCULATIONS USING NEA/NSC BENCHMARKS Amine Bouhaddane 1, Gabriel Farkas 1, Ján Haščík 1, Vladimír Slugeň
Monte Carlo Methods for Uncertainly Analysis Using the Bayesian R-Matrix Code SAMMY
 Monte Carlo Methods for Uncertainly Analysis Using the Bayesian R-Matrix Code SAMMY M.J. Rapp *, D.P. Barry, G. Leinweber, R.C. Block, and B.E. Epping Bechtel Marine Propulsion Corporation Knolls Atomic
Monte Carlo Methods for Uncertainly Analysis Using the Bayesian R-Matrix Code SAMMY M.J. Rapp *, D.P. Barry, G. Leinweber, R.C. Block, and B.E. Epping Bechtel Marine Propulsion Corporation Knolls Atomic
Perspective on CIELO. Michael Dunn Nuclear Data & Criticality Safety Group Leader. NEMEA-7 / CIELO Workshop Geel, Belgium November 5-8, 2013
 Perspective on CIELO Michael Dunn Nuclear Data & Criticality Safety Group Leader NEMEA-7 / CIELO Workshop Geel, Belgium November 5-8, 2013 Introductory Comments Perspective from multiple view points ORNL
Perspective on CIELO Michael Dunn Nuclear Data & Criticality Safety Group Leader NEMEA-7 / CIELO Workshop Geel, Belgium November 5-8, 2013 Introductory Comments Perspective from multiple view points ORNL
Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Methodologies for Fast Reactor Physics and Design at JAEA
 Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Methodologies for Fast Reactor Physics and Design at JAEA Kick off meeting of NEA Expert Group on Uncertainty Analysis for Criticality Safety Assessment IRSN, France
Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Methodologies for Fast Reactor Physics and Design at JAEA Kick off meeting of NEA Expert Group on Uncertainty Analysis for Criticality Safety Assessment IRSN, France
CHARACTERIZATION OF A RADIATION DETECTOR FOR AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS
 CHARACTERIZATION OF A RADIATION DETECTOR FOR AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS Leonardo de Holanda Mencarini 1,2, Claudio A. Federico 1,2 and Linda V. E. Caldas 1 1 Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares IPEN,
CHARACTERIZATION OF A RADIATION DETECTOR FOR AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS Leonardo de Holanda Mencarini 1,2, Claudio A. Federico 1,2 and Linda V. E. Caldas 1 1 Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares IPEN,
BENCHMARK CALCULATIONS FOR URANIUM 235
 BENCHMARK CALCULATIONS FOR URANIUM 235 Christopher J Dean, David Hanlon, Raymond J Perry AEA Technology - Nuclear Science, Room 347, Building A32, Winfrith, Dorchester, Dorset, DT2 8DH, United Kingdom
BENCHMARK CALCULATIONS FOR URANIUM 235 Christopher J Dean, David Hanlon, Raymond J Perry AEA Technology - Nuclear Science, Room 347, Building A32, Winfrith, Dorchester, Dorset, DT2 8DH, United Kingdom
On-the-Fly Sampling of Temperature-Dependent Thermal Neutron Scattering Data for Monte Carlo Simulations
 Please cite this article in press as: Pavlou, A.T., and Ji, W., On-the-fly sampling of temperaturedependent thermal neutron scattering data for Monte Carlo simulations. Ann. Nucl. Energy (2014). http://dx.doi.org
Please cite this article in press as: Pavlou, A.T., and Ji, W., On-the-fly sampling of temperaturedependent thermal neutron scattering data for Monte Carlo simulations. Ann. Nucl. Energy (2014). http://dx.doi.org
THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHREYER HONORS COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
 THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHREYER HONORS COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS TESTING THE LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NATIONAL LABORATORY SIMULATION OF NEUTRON AND GAMMA RAY EMISSION FROM FISSION AND PHOTOFISSION
THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHREYER HONORS COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS TESTING THE LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NATIONAL LABORATORY SIMULATION OF NEUTRON AND GAMMA RAY EMISSION FROM FISSION AND PHOTOFISSION
On-The-Fly Neutron Doppler Broadening for MCNP"
 LA-UR-12-00700" 2012-03-26! On-The-Fly Neutron Doppler Broadening for MCNP" Forrest Brown 1, William Martin 2, " Gokhan Yesilyurt 3, Scott Wilderman 2" 1 Monte Carlo Methods (XCP-3), LANL" 2 University
LA-UR-12-00700" 2012-03-26! On-The-Fly Neutron Doppler Broadening for MCNP" Forrest Brown 1, William Martin 2, " Gokhan Yesilyurt 3, Scott Wilderman 2" 1 Monte Carlo Methods (XCP-3), LANL" 2 University
Invited. The latest BROND-3 developments. 1 Introduction. 2 Cross section evaluations for actinides
 International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: 10.1051/ndata:07641 Invited The latest developments A.V. Ignatyuk a and B.I. Fursov Institute of Physics and Power Engineering,
International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: 10.1051/ndata:07641 Invited The latest developments A.V. Ignatyuk a and B.I. Fursov Institute of Physics and Power Engineering,
Presentation for the CIELO Meeting of the NEA 9-11 May 2016 Paris, France. The Chinese work on 56 Fe
 The Chinese work on 56 Fe Jing QIAN, Zhigang GE, Tingjin LIU, Hanlin LU, Xichao RUAN Guochang CHEN,Huanyu Huanyu ZHANG,Yangbo NIE China Nuclear Data Center(CNDC) China Institute of Atomic Energy(CIAE)
The Chinese work on 56 Fe Jing QIAN, Zhigang GE, Tingjin LIU, Hanlin LU, Xichao RUAN Guochang CHEN,Huanyu Huanyu ZHANG,Yangbo NIE China Nuclear Data Center(CNDC) China Institute of Atomic Energy(CIAE)
S. Ganesan. Theoretical Physics Division. Bhabha Atomic Research Centre. Trombay, Mumbai INDIA
 EXPERIENCES IN PROCESSING OF BASIC EVALUATED NUCLEAR DATA FILES: LINEARIZATION, RESONANCE RECONSTRUCTION, DOPPLER BROADENING AND CROSS SECTION AVERAGING By S. Ganesan Theoretical Physics Division Bhabha
EXPERIENCES IN PROCESSING OF BASIC EVALUATED NUCLEAR DATA FILES: LINEARIZATION, RESONANCE RECONSTRUCTION, DOPPLER BROADENING AND CROSS SECTION AVERAGING By S. Ganesan Theoretical Physics Division Bhabha
Y/DD-972. Methodology for Determination of the Upper Safety Limit for Criticality Calculations for Criticality Safety Analyses
 Methodology for Determination of the Upper Safety Limit for Criticality Calculations for Criticality Safety Analyses R. H. Smith H. J. Keener J. F. DeClue A. W. Krass Nuclear Criticality Safety Division
Methodology for Determination of the Upper Safety Limit for Criticality Calculations for Criticality Safety Analyses R. H. Smith H. J. Keener J. F. DeClue A. W. Krass Nuclear Criticality Safety Division
Lecture 3 Nuclear Data Neutron Interactions and Applications Spring 2010
 Lecture 3 Nuclear Data 22.106 Neutron Interactions and Applications Spring 2010 Common Misconceptions It s just a bunch of numbers ust give me the right value and stop changing it. Traditional evaluation
Lecture 3 Nuclear Data 22.106 Neutron Interactions and Applications Spring 2010 Common Misconceptions It s just a bunch of numbers ust give me the right value and stop changing it. Traditional evaluation
B. Morillon, L. Leal?, G. Noguere y, P. Romain, H. Duarte. April U, 238 U and 239 Pu JEFF-3.3T1 evaluations
 B. Morillon, L. Leal?, G. Noguere y, P. Romain, H. Duarte CEA,DAM,DIF F-9297 Arpajon, France y CEA,DEN Cadarache, France? IRSN 92260 Fontenay-aux-Roses, France April 206 239 Pu : what's new New FILES 2,
B. Morillon, L. Leal?, G. Noguere y, P. Romain, H. Duarte CEA,DAM,DIF F-9297 Arpajon, France y CEA,DEN Cadarache, France? IRSN 92260 Fontenay-aux-Roses, France April 206 239 Pu : what's new New FILES 2,
On-the-fly Doppler Broadening in Serpent
 On-the-fly Doppler Broadening in Serpent 1st International Serpent User Group Meeting 16.9.2011, Dresden Tuomas Viitanen VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Outline Fuel temperatures in neutronics
On-the-fly Doppler Broadening in Serpent 1st International Serpent User Group Meeting 16.9.2011, Dresden Tuomas Viitanen VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Outline Fuel temperatures in neutronics
Treatment of Implicit Effects with XSUSA.
 Treatment of Implicit Effects with Friederike Bostelmann 1,2, Andreas Pautz 2, Winfried Zwermann 1 1 Gesellschaft für Anlagen- und Reaktorsicherheit (GRS) ggmbh, Boltzmannstraße 14, 85748 Garching, Germany
Treatment of Implicit Effects with Friederike Bostelmann 1,2, Andreas Pautz 2, Winfried Zwermann 1 1 Gesellschaft für Anlagen- und Reaktorsicherheit (GRS) ggmbh, Boltzmannstraße 14, 85748 Garching, Germany
Analysis of High Enriched Uranyl Nitrate Solution Containing Cadmium
 INL/CON-05-01002 PREPRINT Analysis of High Enriched Uranyl Nitrate Solution Containing Cadmium PHYSOR-2006 Topical Meeting Soon Sam Kim September 2006 This is a preprint of a paper intended for publication
INL/CON-05-01002 PREPRINT Analysis of High Enriched Uranyl Nitrate Solution Containing Cadmium PHYSOR-2006 Topical Meeting Soon Sam Kim September 2006 This is a preprint of a paper intended for publication
From cutting-edge pointwise cross-section to groupwise reaction rate: A primer
 From cutting-edge pointwise cross-section to groupwise reaction rate: A primer Jean-Christophe Sublet a, Michael Fleming, and Mark R. Gilbert United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority, Culham Science Centre,
From cutting-edge pointwise cross-section to groupwise reaction rate: A primer Jean-Christophe Sublet a, Michael Fleming, and Mark R. Gilbert United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority, Culham Science Centre,
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF SCALE NUCLEAR ANALYSIS METHODS FOR HIGH TEMPERATURE GAS-COOLED REACTORS
 DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF SCALE NUCLEAR ANALYSIS METHODS FOR HIGH TEMPERATURE GAS-COOLED REACTORS Jess Gehin, Matthew Jessee, Mark Williams, Deokjung Lee, Sedat Goluoglu, Germina Ilas, Dan Ilas, Steve
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF SCALE NUCLEAR ANALYSIS METHODS FOR HIGH TEMPERATURE GAS-COOLED REACTORS Jess Gehin, Matthew Jessee, Mark Williams, Deokjung Lee, Sedat Goluoglu, Germina Ilas, Dan Ilas, Steve
Important Remarks on Latest Multigroup Libraries
 Progress in NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, Vol. 2, pp.341-345 (2011) ARTICLE Important Remarks on Latest Multigroup Libraries Chikara KONNO *, Kosuke TAKAKURA, Keitaro KONDO, Seiki OHNISHI, Kentaro OCHIAI
Progress in NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, Vol. 2, pp.341-345 (2011) ARTICLE Important Remarks on Latest Multigroup Libraries Chikara KONNO *, Kosuke TAKAKURA, Keitaro KONDO, Seiki OHNISHI, Kentaro OCHIAI
Dose Rates Modeling of Pressurized Water Reactor Primary Loop Components with SCALE6.0
 ABSTRACT Dose Rates Modeling of Pressurized Water Reactor Primary Loop Components with SCALE6.0 Mario Matijević, Dubravko Pevec, Krešimir Trontl University of Zagreb, Faculty of Electrical Engineering
ABSTRACT Dose Rates Modeling of Pressurized Water Reactor Primary Loop Components with SCALE6.0 Mario Matijević, Dubravko Pevec, Krešimir Trontl University of Zagreb, Faculty of Electrical Engineering
RESEARCH OPPORTUNITIES AT THE CNS (Y-12 AND PANTEX) NUCLEAR DETECTION AND SENSOR TESTING CENTERS (NDSTC)
 Y / DW-2319 RESEARCH OPPORTUNITIES AT THE CNS (Y-12 AND PANTEX) NUCLEAR DETECTION AND SENSOR TESTING CENTERS (NDSTC) Carter Hull 1 Carter.Hull@cns.doe.gov Jim Tallent 4, Dennis Tollefson 2, Martin Williamson
Y / DW-2319 RESEARCH OPPORTUNITIES AT THE CNS (Y-12 AND PANTEX) NUCLEAR DETECTION AND SENSOR TESTING CENTERS (NDSTC) Carter Hull 1 Carter.Hull@cns.doe.gov Jim Tallent 4, Dennis Tollefson 2, Martin Williamson
MUSE-4 BENCHMARK CALCULATIONS USING MCNP-4C AND DIFFERENT NUCLEAR DATA LIBRARIES
 MUSE-4 BENCHMARK CALCULATIONS USING MCNP-4C AND DIFFERENT NUCLEAR DATA LIBRARIES Nadia Messaoudi and Edouard Mbala Malambu SCK CEN Boeretang 200, B-2400 Mol, Belgium Email: nmessaou@sckcen.be Abstract
MUSE-4 BENCHMARK CALCULATIONS USING MCNP-4C AND DIFFERENT NUCLEAR DATA LIBRARIES Nadia Messaoudi and Edouard Mbala Malambu SCK CEN Boeretang 200, B-2400 Mol, Belgium Email: nmessaou@sckcen.be Abstract
New photon transport model in Serpent 2
 New photon transport model in Serpent 2 Toni Kaltiaisenaho VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Serpent User Group Meeting 1/20 Motivation On average, 8 prompt fission photons over an energy range
New photon transport model in Serpent 2 Toni Kaltiaisenaho VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Serpent User Group Meeting 1/20 Motivation On average, 8 prompt fission photons over an energy range
MCNP6: Fission Multiplicity Model Usage in Criticality Calculations
 MCNP6: Fission Multiplicity Model Usage in Criticality Calculations 1 Michael E. Rising, 1 Forrest B. Brown and 2 Mario I. Ortega 1 XCP-3 Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory 2 Department of Nuclear
MCNP6: Fission Multiplicity Model Usage in Criticality Calculations 1 Michael E. Rising, 1 Forrest B. Brown and 2 Mario I. Ortega 1 XCP-3 Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory 2 Department of Nuclear
Time Correlation Measurements of Heavily Shielded Uranium Metal. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, 1 Bethel Valley Road, Oak Ridge, TN 37831
 Time Correlation Measurements of Heavily Shielded Uranium Metal J. M. Crye **, S. M. McConchie, J. T. Mihalczo, K. E. Pena **, and H. L. Hall ** ** University of Tennessee, 303A Pasqua Engineering Bldg.,
Time Correlation Measurements of Heavily Shielded Uranium Metal J. M. Crye **, S. M. McConchie, J. T. Mihalczo, K. E. Pena **, and H. L. Hall ** ** University of Tennessee, 303A Pasqua Engineering Bldg.,
Validation of the MCNP computational model for neutron flux distribution with the neutron activation analysis measurement
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Validation of the MCNP computational model for neutron flux distribution with the neutron activation analysis measurement To cite this article: K
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Validation of the MCNP computational model for neutron flux distribution with the neutron activation analysis measurement To cite this article: K
SG39 Meeting May 16-17, Update on Continuous Energy Cross Section Adjustment. UC Berkeley / INL collaboration
 SG39 Meeting May 16-17, 2017 Update on Continuous Energy Cross Section Adjustment. UC Berkeley / INL collaboration Outline Presentation of the proposed methodology (you've already seen this) Results from
SG39 Meeting May 16-17, 2017 Update on Continuous Energy Cross Section Adjustment. UC Berkeley / INL collaboration Outline Presentation of the proposed methodology (you've already seen this) Results from
Neutron Generation from 10MeV Electron Beam to Produce Mo99
 From the SelectedWorks of Innovative Research Publications IRP India Winter January 1, 2015 Neutron Generation from 10MeV Electron Beam to Produce Mo99 Innovative Research Publications, IRP India, Innovative
From the SelectedWorks of Innovative Research Publications IRP India Winter January 1, 2015 Neutron Generation from 10MeV Electron Beam to Produce Mo99 Innovative Research Publications, IRP India, Innovative
A comparison between two evaluations of neutron multiplicity distributions
 Abstract A comparison between two evaluations of neutron multiplicity distributions J. P. February 22 nd 200 Applied Physics Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 7545, USA Within MCNP6,
Abstract A comparison between two evaluations of neutron multiplicity distributions J. P. February 22 nd 200 Applied Physics Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 7545, USA Within MCNP6,
New Neutron-Induced Cross-Section Measurements for Weak s-process Studies
 New Neutron-Induced Cross-Section Measurements for Weak s-process Studies Klaus H. Guber 1, D. Wiarda, L. C. Leal, H. Derrien, C. Ausmus, D. R. Brashear, J. A. White Nuclear Science and Technology Division,
New Neutron-Induced Cross-Section Measurements for Weak s-process Studies Klaus H. Guber 1, D. Wiarda, L. C. Leal, H. Derrien, C. Ausmus, D. R. Brashear, J. A. White Nuclear Science and Technology Division,
Monte Carlo Nuclear Data Assimilation via integral information
 Long-term international collaboration to improve nuclear data evaluation and evaluated data files meeting, 18-21 December 2017, IAEA, Vienna, Austria D. Rochman 1, E. Bauge 2, A.J. Koning 3 and J.Ch. Sublet
Long-term international collaboration to improve nuclear data evaluation and evaluated data files meeting, 18-21 December 2017, IAEA, Vienna, Austria D. Rochman 1, E. Bauge 2, A.J. Koning 3 and J.Ch. Sublet
EVALUATION OF NEUTRON INDUCED REACTIONS ON 238 U NUCLEUS
 EVALUATION OF NEUTRON INDUCED REACTIONS ON 238 U NUCLEUS UN complex 1/27 Roberto Capote, NAPC - Nuclear Data Section, IAEA, Austria Andrej Trkov, Jozef Stefan Institute, Slovenia Mihaela Sin, University
EVALUATION OF NEUTRON INDUCED REACTIONS ON 238 U NUCLEUS UN complex 1/27 Roberto Capote, NAPC - Nuclear Data Section, IAEA, Austria Andrej Trkov, Jozef Stefan Institute, Slovenia Mihaela Sin, University
The ENDF-6 file 7 and its possible evolutions with respect to the processing needs
 The ENDF-6 file 7 and its possible evolutions with respect to the processing needs Claude Mounier Commissariat à l Énergie Atomique et aux Énergies Alternatives (CEA) CEA-SACLAY DEN/DANS/DM2S/SERMA/LLPR,
The ENDF-6 file 7 and its possible evolutions with respect to the processing needs Claude Mounier Commissariat à l Énergie Atomique et aux Énergies Alternatives (CEA) CEA-SACLAY DEN/DANS/DM2S/SERMA/LLPR,
Researchers at the University of Missouri-Columbia have designed a triple crystal
 Childress, N. L. and W. H. Miller, MCNP Analysis and Optimization of a Triple Crystal Phoswich Detector, Nuclear Instruments and Methods, Section A, 490(1-2), 263-270 (Sept 1, 2002). Abstract Researchers
Childress, N. L. and W. H. Miller, MCNP Analysis and Optimization of a Triple Crystal Phoswich Detector, Nuclear Instruments and Methods, Section A, 490(1-2), 263-270 (Sept 1, 2002). Abstract Researchers
Implementation of new adjoint-based methods for sensitivity analysis and uncertainty quantication in Serpent
 Serpent UGM 2015 Knoxville, 1316 October 2015 Implementation of new adjoint-based methods for sensitivity analysis and uncertainty quantication in Serpent Manuele Auero & Massimiliano Fratoni UC Berkeley
Serpent UGM 2015 Knoxville, 1316 October 2015 Implementation of new adjoint-based methods for sensitivity analysis and uncertainty quantication in Serpent Manuele Auero & Massimiliano Fratoni UC Berkeley
Status of ENDF/B-VII.1 library
 Status of ENDF/B-VII.1 library Report to WPEC, May 12-13, 2011, NEA Headquarters, Paris, France M. Herman for CSEWG National Nuclear Data Center, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973-5000, USA
Status of ENDF/B-VII.1 library Report to WPEC, May 12-13, 2011, NEA Headquarters, Paris, France M. Herman for CSEWG National Nuclear Data Center, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973-5000, USA
in Cross-Section Data
 Sensitivity of Photoneutron Production to Perturbations in Cross-Section Data S. D. Clarke Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana S. A. Pozzi University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan E. Padovani
Sensitivity of Photoneutron Production to Perturbations in Cross-Section Data S. D. Clarke Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana S. A. Pozzi University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan E. Padovani
BENCHMARK EXPERIMENT OF NEUTRON RESONANCE SCATTERING MODELS IN MONTE CARLO CODES
 International Conference on Mathematics, Computational Methods & Reactor Physics (M&C 2009) Saratoga Springs, New York, May 3-7, 2009, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2009) BENCHMARK
International Conference on Mathematics, Computational Methods & Reactor Physics (M&C 2009) Saratoga Springs, New York, May 3-7, 2009, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2009) BENCHMARK
M.Cagnazzo Atominstitut, Vienna University of Technology Stadionallee 2, 1020 Wien, Austria
 Measurements of the In-Core Neutron Flux Distribution and Energy Spectrum at the Triga Mark II Reactor of the Vienna University of Technology/Atominstitut ABSTRACT M.Cagnazzo Atominstitut, Vienna University
Measurements of the In-Core Neutron Flux Distribution and Energy Spectrum at the Triga Mark II Reactor of the Vienna University of Technology/Atominstitut ABSTRACT M.Cagnazzo Atominstitut, Vienna University
Challenges in nuclear data evaluation of actinide nuclei
 Challenges in nuclear data evaluation of actinide nuclei 1 Roberto Capote NAPC - Nuclear Data Section, IAEA, Vienna, Austria Thanks to: Organizers for the invitation/support All collaborators o A. Trkov
Challenges in nuclear data evaluation of actinide nuclei 1 Roberto Capote NAPC - Nuclear Data Section, IAEA, Vienna, Austria Thanks to: Organizers for the invitation/support All collaborators o A. Trkov
On the Use of Shannon Entropy of the Fission Distribution for Assessing Convergence of Monte Carlo Criticality Calculations.
 Organized and hosted by the Canadian Nuclear Society. Vancouver, BC, Canada. 2006 September 10-14 On the Use of Shannon Entropy of the Fission Distribution for Assessing Convergence of Monte Carlo Criticality
Organized and hosted by the Canadian Nuclear Society. Vancouver, BC, Canada. 2006 September 10-14 On the Use of Shannon Entropy of the Fission Distribution for Assessing Convergence of Monte Carlo Criticality
ENDF8. M.B. Chadwick LANL. Mark Chadwick, LANL. WPEC-SG40 (CIELO), Paris, May17, Operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC for NNSA
 ENDF8 M.B. Chadwick LANL Mark Chadwick, LANL WPEC-SG40 (CIELO), Paris, May17, 2017 International CIELO Collaboration Experiments: Some of the many experimental facilities that measured new data supporting
ENDF8 M.B. Chadwick LANL Mark Chadwick, LANL WPEC-SG40 (CIELO), Paris, May17, 2017 International CIELO Collaboration Experiments: Some of the many experimental facilities that measured new data supporting
ECN-R SEPTEMBER \U Of. rl" 7 2Q. energy innovation ÜNR. A code for processing unresolved resonance data for MCNP A.
 SEPTEMBER 1994 ECN-R--94-020 \U Of. rl" 7 2Q energy innovation ÜNR A code for processing unresolved resonance data for MCNP A. HOGENBIRK VOL The Netherlands Energy Research Foundation ECN is the leading
SEPTEMBER 1994 ECN-R--94-020 \U Of. rl" 7 2Q energy innovation ÜNR A code for processing unresolved resonance data for MCNP A. HOGENBIRK VOL The Netherlands Energy Research Foundation ECN is the leading
