Errata for Robot Vision
|
|
|
- Caroline Taylor
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Errata for Robot Vision This is a list of known nontrivial bugs in Robot Vision 1986) by B.K.P. Horn, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA ISBN and McGraw-Hill, New York, NY ISBN If you know of any others, please advise the author by sending electronic mail to: bkph@csail.mit.edu or by sending hard-copy mail to: B.K.P. Horn, CSAIL, 3-D434, MIT, Cambridge MA 0139 USA Your help will be greatly appreciated. Thank you. Section.3, page 5. The expression for the diameter of the blur circle should be d z z z, Section 3., bottom of page 48 and top of page 49, interchange x-axis and y-axis in the text. Section 3., page 49, figure 3-: The circled X is not at the centroid it should be further to the left and higher. Section 3.3, page 55, the formulae for the second moments in the middle of the page are missing the term bx,y) in the integrands: I x bx,y)dx dy = x vx) dx & I y bx,y)dx dy = y hy) dy. Section 6.1, page 104, near end of paragraph, after the sentence: The transformation from the ideal image to that in the out-of-focus system is said to be a linear shift-invariant operation add If we ignore the slight change in scale and overall brightness resulting from the change in the distance from the lens to the image plane). Section 6.8, page 1: The equation below the middle of page should be: x + y σ ) L σ x, y) = e 1 x +y πσ 6 σ. The second sentence after this should read: It has a central depression of magnitude 1/πσ 4 ) and radius σ surrounded by a circular wall of maximum height e /πσ 4 ) and radius σ. Section 6.9, page 15 after the last equation on the page it should say:... and then drops smoothly to zero at rb =
2 Section 6.13, top of page 134: The integrand containing φ id ξ, η) has a spurious extra right parenthesis. Section 6.13, top of page 134: The integral for φ dd 0, 0) is missing a dx dy. Section 6.13, middle of page 136: The expression of the MTF of the optimal filter should read: H = id ii = H bb H H bb + nn. Section 7.1, just above middle of page 146: The first integral should contain F u, v), not Fu, v) and dudv instead of dx dy: fx,y)= 1 4π F u, v) e +iux+vy) dudv Section 7.1, just above middle of page 146: The second integral for fx,y) should contain dudv instead of dx dy. Section 7., near bottom of page 147: The integral for fx,y)should contain dudv instead of dx dy. Section 7., page 148. At the end of the section it should say something like:...so that the Fourier transform of fx,y)times gx, y) equals F u πk ) πl,v, w h k= l= a periodic superposition of copies of Fu, v). It should be clear that Fu, v), the Fourier transform of fx,y), can be recovered from this sum if Fu, v) is zero for u >π/wand for v >π/h, while Fu, v) cannot be recovered uniquely when this condition is not satisfied. Section 7.4, page 151, the sum for F mn should read: F mn = M k=0 and the sum for f kl should read: f kl = 1 MN M m=0 N l=0 N n=0 f kl e πi km M + ln N ). F mn e +πi km M + ln N ). Section 7.4, page 153, in two places: as above, the complex exponent needs a factor of. Section 7.8, page 155, problem 7-: the formula given is for g i,j, not f i,j. Section 8.3, top of page 165, formula is lacking a scale factor: ) E ) E + 1 Ei+1,j+1 E x y ɛ i,j ) E i,j+1 E i+1,j ) ).
3 Section 9.10, page 01, figure 9-8: The number 44, near the lower left hand corner of the figure, and below the number 36, should be 144. Section 10.7, page 14: For consistency with what follows, the equation for Eθ i,φ i ) should perhaps read: Eθ i,φ i ) = E δθ i θ s )δφ i φ s ), sin θ i although it is correct as it stands, since Eθ i,φ i ) is zero except where θ i = θ s. Section 10.9, near top of page 19: Change formula to read: L = 1 π E cos θ i for cos θ i 0, Section 10.16, page 34, problem 10-3: This problem can be solved more easily if a spherical coordinate system is chosen that has the poles where the plane containing the local tangent plane intersects the horizon, rather than one with the poles at the nadir. Section 10.16, page 41, problem 10-17: Change second sentence in part a) to read: Demonstrate that the corners of this triangle lie in the directions ŝ 3 ŝ 1, ŝ ŝ 3, and ŝ 1 ŝ. Section 11.1, below middle of page 46: The equations for xξ) and yξ) should contain θ 0 instead of θ: xξ) = x 0 + ξ cos θ 0 and yξ) = y 0 + ξ sin θ 0. Section 11.4, middle of page 56: the alternate solution is z = z 0 1 ax + bxy + cy ). Section 11-10, page 71, problem 11-7: In part e), change the equation to zr) = z 0 ± 1 r 4 k k cos k ). r and add the phrase when r 0 = k. Section 11-10, page 71, problem 11-9: In the second paragraph, change third sentence to read: A hyperboloid of one sheet is an example of a ruled surface. Section 11-10, page 75, problem 11-1: In part b) there is a sign error insert a minus sign before the λs in the right hand sides of the equations. change the two equations to read: Ex,y) Rp, q) ) Rp = λq xy p yy ), Ex,y) Rp, q) ) Rq = λp xy q xx ). 3
4 Section 1.6, page 88, middle of the page: There is a λ missing in the correction terms. Change the iterative update equations to read: u n+1 = u n kl kl λ 1 + λex + E y )E xu n kl + E yv n kl + E t)e x, v n+1 kl = v n kl λ 1 + λe x + E y )E xu n kl + E yv n kl + E t)e y. Section 13.9, page 317, near bottom of page: Change equation to read: F d x F d x y F d y + x F d x x + y F d y y = 0. Section 16.6, page 374, end of second paragraph of section, change sentence to read: In fact, the number of impulses per unit area on the Gaussian sphere approaches ρ times the inverse of the absolute value of the Gaussian curvature. Section 16.13, page 397, problem 16-7: Change solution to part b) to read: Rψ) = ab) a cos ψ) + b sin ψ) ) 3/. Section 16.13, page 399, problem 16-9: Change equation in part a) to read ρ X Y ψ) = ρ X ψ) + ρ Y ψ). Section 17.5, page 416: There is a sign error in the sixth equation from the top. The term u u r )y + v v r )x ) in the integrand should instead be u ur )y v v r )x ). Section 18.10, page 437, near bottom of page, the equation after the phrase: The norm of a quaternion is given by should read: q = q q = q + q q. Section 18.10, page 437, at the bottom of the page, change equation to read: q = cos θ + ω sin θ. Section 18.10, page 438, second sentence in second paragraph form the top, change to: Two antipodal points on this sphere correspond to a particular rotation. Section 18.1, page 450, problem 18-5, change middle equation to read: p q) p q) = p p) q q) = q p) q p). Section A.1, page 454, after the law of cosines for the angles, add:...and the so-called analogue formula is sin a cos B = cos b sin c sin b cos c cos A. 4
5 Section A.5., page 465, The extrema of f x,y,z) = 0 subject to... should be just The extrema of f x,y,z) subject to... Section A.5., page 466, We minimize abc +... should be We maximize abc +... Section A.6.1, page 470, in the equation after Using integration by parts, we see that there is a prime missing on the F f in the last integrand x η x)f f dx = [ ηx)f f ] x x ηx) d dx F f dx, 5
Errata for Robot Vision
 Errata for Robot Vision This is a list of known nontrivial bugs in Robot Vision 1986) by B.K.P. Horn, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA ISBN 0-6-08159-8 and McGraw-Hill, New York, NY ISBN 0-07-030349-5. Thanks
Errata for Robot Vision This is a list of known nontrivial bugs in Robot Vision 1986) by B.K.P. Horn, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA ISBN 0-6-08159-8 and McGraw-Hill, New York, NY ISBN 0-07-030349-5. Thanks
Errata for Robot Vision
 Errata for Robot Vision This is a list of known nontrivial bugs in Robot Vision 1986 by B.K.P. Horn, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA ISBN 0-262-08159-8 and McGraw-Hill, New York, NY ISBN 0-07-030349-5. If you
Errata for Robot Vision This is a list of known nontrivial bugs in Robot Vision 1986 by B.K.P. Horn, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA ISBN 0-262-08159-8 and McGraw-Hill, New York, NY ISBN 0-07-030349-5. If you
Review Sheet for the Final
 Review Sheet for the Final Math 6-4 4 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the absence
Review Sheet for the Final Math 6-4 4 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the absence
e x3 dx dy. 0 y x 2, 0 x 1.
 Problem 1. Evaluate by changing the order of integration y e x3 dx dy. Solution:We change the order of integration over the region y x 1. We find and x e x3 dy dx = y x, x 1. x e x3 dx = 1 x=1 3 ex3 x=
Problem 1. Evaluate by changing the order of integration y e x3 dx dy. Solution:We change the order of integration over the region y x 1. We find and x e x3 dy dx = y x, x 1. x e x3 dx = 1 x=1 3 ex3 x=
FFTs in Graphics and Vision. Homogenous Polynomials and Irreducible Representations
 FFTs in Graphics and Vision Homogenous Polynomials and Irreducible Representations 1 Outline The 2π Term in Assignment 1 Homogenous Polynomials Representations of Functions on the Unit-Circle Sub-Representations
FFTs in Graphics and Vision Homogenous Polynomials and Irreducible Representations 1 Outline The 2π Term in Assignment 1 Homogenous Polynomials Representations of Functions on the Unit-Circle Sub-Representations
7a3 2. (c) πa 3 (d) πa 3 (e) πa3
 1.(6pts) Find the integral x, y, z d S where H is the part of the upper hemisphere of H x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = a 2 above the plane z = a and the normal points up. ( 2 π ) Useful Facts: cos = 1 and ds = ±a sin
1.(6pts) Find the integral x, y, z d S where H is the part of the upper hemisphere of H x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = a 2 above the plane z = a and the normal points up. ( 2 π ) Useful Facts: cos = 1 and ds = ±a sin
Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1
 Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1 (a.g.kovalev@dpmms.cam.ac.uk) 1. Suppose that H is a hyperplane in Euclidean n-space R n defined by u x = c for some unit vector u and constant c. The reflection
Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1 (a.g.kovalev@dpmms.cam.ac.uk) 1. Suppose that H is a hyperplane in Euclidean n-space R n defined by u x = c for some unit vector u and constant c. The reflection
Corrections and Minor Revisions of Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences, third edition, by Mary L. Boas (deceased)
 Corrections and Minor Revisions of Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences, third edition, by Mary L. Boas (deceased) Updated December 6, 2017 by Harold P. Boas This list includes all errors known
Corrections and Minor Revisions of Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences, third edition, by Mary L. Boas (deceased) Updated December 6, 2017 by Harold P. Boas This list includes all errors known
Calculus of Variations and Computer Vision
 Calculus of Variations and Computer Vision Sharat Chandran Page 1 of 23 Computer Science & Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. http://www.cse.iitb.ernet.in/ sharat January 8,
Calculus of Variations and Computer Vision Sharat Chandran Page 1 of 23 Computer Science & Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. http://www.cse.iitb.ernet.in/ sharat January 8,
Discrete Wavelet Transformations: An Elementary Approach with Applications
 Discrete Wavelet Transformations: An Elementary Approach with Applications Errata Sheet March 6, 009 Please report any errors you find in the text to Patrick J. Van Fleet at pjvanfleet@stthomas.edu. The
Discrete Wavelet Transformations: An Elementary Approach with Applications Errata Sheet March 6, 009 Please report any errors you find in the text to Patrick J. Van Fleet at pjvanfleet@stthomas.edu. The
Review problems for the final exam Calculus III Fall 2003
 Review problems for the final exam alculus III Fall 2003 1. Perform the operations indicated with F (t) = 2t ı 5 j + t 2 k, G(t) = (1 t) ı + 1 t k, H(t) = sin(t) ı + e t j a) F (t) G(t) b) F (t) [ H(t)
Review problems for the final exam alculus III Fall 2003 1. Perform the operations indicated with F (t) = 2t ı 5 j + t 2 k, G(t) = (1 t) ı + 1 t k, H(t) = sin(t) ı + e t j a) F (t) G(t) b) F (t) [ H(t)
Errata for Vector and Geometric Calculus Printings 1-4
 October 21, 2017 Errata for Vector and Geometric Calculus Printings 1-4 Note: p. m (n) refers to page m of Printing 4 and page n of Printings 1-3. p. 31 (29), just before Theorem 3.10. f x(h) = [f x][h]
October 21, 2017 Errata for Vector and Geometric Calculus Printings 1-4 Note: p. m (n) refers to page m of Printing 4 and page n of Printings 1-3. p. 31 (29), just before Theorem 3.10. f x(h) = [f x][h]
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL EXAM. December 14, 2010, 9:00am-12:00 (3 hours)
 SOLUTIONS TO THE 18.02 FINAL EXAM BJORN POONEN December 14, 2010, 9:00am-12:00 (3 hours) 1) For each of (a)-(e) below: If the statement is true, write TRUE. If the statement is false, write FALSE. (Please
SOLUTIONS TO THE 18.02 FINAL EXAM BJORN POONEN December 14, 2010, 9:00am-12:00 (3 hours) 1) For each of (a)-(e) below: If the statement is true, write TRUE. If the statement is false, write FALSE. (Please
MATH H53 : Final exam
 MATH H53 : Final exam 11 May, 18 Name: You have 18 minutes to answer the questions. Use of calculators or any electronic items is not permitted. Answer the questions in the space provided. If you run out
MATH H53 : Final exam 11 May, 18 Name: You have 18 minutes to answer the questions. Use of calculators or any electronic items is not permitted. Answer the questions in the space provided. If you run out
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve. r (t) = 3 cos t, 0, 3 sin t, r ( 3π
 1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P 3, 3π, r t) 3 cos t, 4t, 3 sin t 3 ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. olution:
1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P 3, 3π, r t) 3 cos t, 4t, 3 sin t 3 ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. olution:
a Write down the coordinates of the point on the curve where t = 2. b Find the value of t at the point on the curve with coordinates ( 5 4, 8).
 Worksheet A 1 A curve is given by the parametric equations x = t + 1, y = 4 t. a Write down the coordinates of the point on the curve where t =. b Find the value of t at the point on the curve with coordinates
Worksheet A 1 A curve is given by the parametric equations x = t + 1, y = 4 t. a Write down the coordinates of the point on the curve where t =. b Find the value of t at the point on the curve with coordinates
1 4 (1 cos(4θ))dθ = θ 4 sin(4θ)
 M48M Final Exam Solutions, December 9, 5 ) A polar curve Let C be the portion of the cloverleaf curve r = sin(θ) that lies in the first quadrant a) Draw a rough sketch of C This looks like one quarter
M48M Final Exam Solutions, December 9, 5 ) A polar curve Let C be the portion of the cloverleaf curve r = sin(θ) that lies in the first quadrant a) Draw a rough sketch of C This looks like one quarter
ENGI Multiple Integration Page 8-01
 ENGI 345 8. Multiple Integration Page 8-01 8. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple integration include
ENGI 345 8. Multiple Integration Page 8-01 8. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple integration include
Sixth Term Examination Papers 9475 MATHEMATICS 3
 Sixth Term Examination Papers 9475 MATHEMATICS 3 Morning WEDNESDAY 26 JUNE 2013 Time: 3 hours Additional Materials: Answer Booklet Formulae Booklet INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Please read this page carefully,
Sixth Term Examination Papers 9475 MATHEMATICS 3 Morning WEDNESDAY 26 JUNE 2013 Time: 3 hours Additional Materials: Answer Booklet Formulae Booklet INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Please read this page carefully,
Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations
 Notes from phz 6607, Special and General Relativity University of Florida, Fall 2004, Detweiler Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations These notes are not a substitute in any manner for class lectures.
Notes from phz 6607, Special and General Relativity University of Florida, Fall 2004, Detweiler Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations These notes are not a substitute in any manner for class lectures.
Salmon: Lectures on partial differential equations
 6. The wave equation Of the 3 basic equations derived in the previous section, we have already discussed the heat equation, (1) θ t = κθ xx + Q( x,t). In this section we discuss the wave equation, () θ
6. The wave equation Of the 3 basic equations derived in the previous section, we have already discussed the heat equation, (1) θ t = κθ xx + Q( x,t). In this section we discuss the wave equation, () θ
Corrections to the First Printing: Chapter 6. This list includes corrections and clarifications through November 6, 1999.
 June 2,2 1 Corrections to the First Printing: Chapter 6 This list includes corrections and clarifications through November 6, 1999. We should have mentioned that our treatment of differential forms, especially
June 2,2 1 Corrections to the First Printing: Chapter 6 This list includes corrections and clarifications through November 6, 1999. We should have mentioned that our treatment of differential forms, especially
4 Partial Differentiation
 4 Partial Differentiation Many equations in engineering, physics and mathematics tie together more than two variables. For example Ohm s Law (V = IR) and the equation for an ideal gas, PV = nrt, which
4 Partial Differentiation Many equations in engineering, physics and mathematics tie together more than two variables. For example Ohm s Law (V = IR) and the equation for an ideal gas, PV = nrt, which
13 Spherical geometry
 13 Spherical geometry Let ABC be a triangle in the Euclidean plane. From now on, we indicate the interior angles A = CAB, B = ABC, C = BCA at the vertices merely by A, B, C. The sides of length a = BC
13 Spherical geometry Let ABC be a triangle in the Euclidean plane. From now on, we indicate the interior angles A = CAB, B = ABC, C = BCA at the vertices merely by A, B, C. The sides of length a = BC
Instructions: No books. No notes. Non-graphing calculators only. You are encouraged, although not required, to show your work.
 Exam 3 Math 850-007 Fall 04 Odenthal Name: Instructions: No books. No notes. Non-graphing calculators only. You are encouraged, although not required, to show your work.. Evaluate the iterated integral
Exam 3 Math 850-007 Fall 04 Odenthal Name: Instructions: No books. No notes. Non-graphing calculators only. You are encouraged, although not required, to show your work.. Evaluate the iterated integral
Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3
 Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 29, 2014 September 22, 2014 6:00pm Announcements This week we continue our discussion
Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 29, 2014 September 22, 2014 6:00pm Announcements This week we continue our discussion
Dr. Allen Back. Nov. 5, 2014
 Dr. Allen Back Nov. 5, 2014 12 lectures, 4 recitations left including today. a Most of what remains is vector integration and the integral theorems. b We ll start 7.1, 7.2,4.2 on Friday. c If you are not
Dr. Allen Back Nov. 5, 2014 12 lectures, 4 recitations left including today. a Most of what remains is vector integration and the integral theorems. b We ll start 7.1, 7.2,4.2 on Friday. c If you are not
Partial Differential Equations
 M3M3 Partial Differential Equations Solutions to problem sheet 3/4 1* (i) Show that the second order linear differential operators L and M, defined in some domain Ω R n, and given by Mφ = Lφ = j=1 j=1
M3M3 Partial Differential Equations Solutions to problem sheet 3/4 1* (i) Show that the second order linear differential operators L and M, defined in some domain Ω R n, and given by Mφ = Lφ = j=1 j=1
MATH20411 PDEs and Vector Calculus B
 MATH2411 PDEs and Vector Calculus B Dr Stefan Güttel Acknowledgement The lecture notes and other course materials are based on notes provided by Dr Catherine Powell. SECTION 1: Introctory Material MATH2411
MATH2411 PDEs and Vector Calculus B Dr Stefan Güttel Acknowledgement The lecture notes and other course materials are based on notes provided by Dr Catherine Powell. SECTION 1: Introctory Material MATH2411
MA 441 Advanced Engineering Mathematics I Assignments - Spring 2014
 MA 441 Advanced Engineering Mathematics I Assignments - Spring 2014 Dr. E. Jacobs The main texts for this course are Calculus by James Stewart and Fundamentals of Differential Equations by Nagle, Saff
MA 441 Advanced Engineering Mathematics I Assignments - Spring 2014 Dr. E. Jacobs The main texts for this course are Calculus by James Stewart and Fundamentals of Differential Equations by Nagle, Saff
11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System
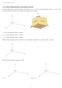 11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System In three dimensions, a point has three coordinates: (x,y,z). The normal orientation of the x, y, and z-axes is shown below. The three axes divide the region into
11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System In three dimensions, a point has three coordinates: (x,y,z). The normal orientation of the x, y, and z-axes is shown below. The three axes divide the region into
Study Guide/Practice Exam 3
 Study Guide/Practice Exam 3 This study guide/practice exam covers only the material since exam. The final exam, however, is cumulative so you should be sure to thoroughly study earlier material. The distribution
Study Guide/Practice Exam 3 This study guide/practice exam covers only the material since exam. The final exam, however, is cumulative so you should be sure to thoroughly study earlier material. The distribution
Type II hidden symmetries of the Laplace equation
 Type II hidden symmetries of the Laplace equation Andronikos Paliathanasis Larnaka, 2014 A. Paliathanasis (Univ. of Naples) Type II symmetries Larnaka, 2014 1 / 25 Plan of the Talk 1 The generic symmetry
Type II hidden symmetries of the Laplace equation Andronikos Paliathanasis Larnaka, 2014 A. Paliathanasis (Univ. of Naples) Type II symmetries Larnaka, 2014 1 / 25 Plan of the Talk 1 The generic symmetry
Higher Mathematics Course Notes
 Higher Mathematics Course Notes Equation of a Line (i) Collinearity: (ii) Gradient: If points are collinear then they lie on the same straight line. i.e. to show that A, B and C are collinear, show that
Higher Mathematics Course Notes Equation of a Line (i) Collinearity: (ii) Gradient: If points are collinear then they lie on the same straight line. i.e. to show that A, B and C are collinear, show that
UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN
 UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN TRINITY COLLEGE JS & SS Mathematics SS Theoretical Physics SS TSM Mathematics Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science school of mathematics Trinity Term 2015 Module MA3429
UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN TRINITY COLLEGE JS & SS Mathematics SS Theoretical Physics SS TSM Mathematics Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science school of mathematics Trinity Term 2015 Module MA3429
MATHEMATICS (2) Before you begin read these instructions carefully:
 NATURAL SCIENCES TRIPOS Part IA Wednesday, 13 June, 2018 9:00 am to 12:00 pm MATHEMATICS (2) Before you begin read these instructions carefully: The paper has two sections, A and B. Section A contains
NATURAL SCIENCES TRIPOS Part IA Wednesday, 13 June, 2018 9:00 am to 12:00 pm MATHEMATICS (2) Before you begin read these instructions carefully: The paper has two sections, A and B. Section A contains
Name: Instructor: Lecture time: TA: Section time:
 Math 222 Final May 11, 29 Name: Instructor: Lecture time: TA: Section time: INSTRUCTIONS READ THIS NOW This test has 1 problems on 16 pages worth a total of 2 points. Look over your test package right
Math 222 Final May 11, 29 Name: Instructor: Lecture time: TA: Section time: INSTRUCTIONS READ THIS NOW This test has 1 problems on 16 pages worth a total of 2 points. Look over your test package right
Rule ST1 (Symmetry). α β = β α for 1-forms α and β. Like the exterior product, the symmetric tensor product is also linear in each slot :
 2. Metrics as Symmetric Tensors So far we have studied exterior products of 1-forms, which obey the rule called skew symmetry: α β = β α. There is another operation for forming something called the symmetric
2. Metrics as Symmetric Tensors So far we have studied exterior products of 1-forms, which obey the rule called skew symmetry: α β = β α. There is another operation for forming something called the symmetric
CSC 125 :: Final Exam May 3 & 5, 2010
 CSC 125 :: Final Exam May 3 & 5, 2010 Name KEY (1 5) Complete the truth tables below: p Q p q p q p q p q p q T T T T F T T T F F T T F F F T F T T T F F F F F F T T 6-15. Match the following logical equivalences
CSC 125 :: Final Exam May 3 & 5, 2010 Name KEY (1 5) Complete the truth tables below: p Q p q p q p q p q p q T T T T F T T T F F T T F F F T F T T T F F F F F F T T 6-15. Match the following logical equivalences
A Probability Review
 A Probability Review Outline: A probability review Shorthand notation: RV stands for random variable EE 527, Detection and Estimation Theory, # 0b 1 A Probability Review Reading: Go over handouts 2 5 in
A Probability Review Outline: A probability review Shorthand notation: RV stands for random variable EE 527, Detection and Estimation Theory, # 0b 1 A Probability Review Reading: Go over handouts 2 5 in
j=1 ωj k E j. (3.1) j=1 θj E j, (3.2)
 3. Cartan s Structural Equations and the Curvature Form Let E,..., E n be a moving (orthonormal) frame in R n and let ωj k its associated connection forms so that: de k = n ωj k E j. (3.) Recall that ωj
3. Cartan s Structural Equations and the Curvature Form Let E,..., E n be a moving (orthonormal) frame in R n and let ωj k its associated connection forms so that: de k = n ωj k E j. (3.) Recall that ωj
Practice Problems for the Final Exam
 Math 114 Spring 2017 Practice Problems for the Final Exam 1. The planes 3x + 2y + z = 6 and x + y = 2 intersect in a line l. Find the distance from the origin to l. (Answer: 24 3 ) 2. Find the area of
Math 114 Spring 2017 Practice Problems for the Final Exam 1. The planes 3x + 2y + z = 6 and x + y = 2 intersect in a line l. Find the distance from the origin to l. (Answer: 24 3 ) 2. Find the area of
Mathematics of Physics and Engineering II: Homework problems
 Mathematics of Physics and Engineering II: Homework problems Homework. Problem. Consider four points in R 3 : P (,, ), Q(,, 2), R(,, ), S( + a,, 2a), where a is a real number. () Compute the coordinates
Mathematics of Physics and Engineering II: Homework problems Homework. Problem. Consider four points in R 3 : P (,, ), Q(,, 2), R(,, ), S( + a,, 2a), where a is a real number. () Compute the coordinates
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 2010 SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION
 Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Monday, January 9, 2012 3:10PM to 5:10PM Classical Physics Section 2. Electricity, Magnetism & Electrodynamics Two hours are permitted for
Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Monday, January 9, 2012 3:10PM to 5:10PM Classical Physics Section 2. Electricity, Magnetism & Electrodynamics Two hours are permitted for
Jim Lambers MAT 280 Summer Semester Practice Final Exam Solution. dy + xz dz = x(t)y(t) dt. t 3 (4t 3 ) + e t2 (2t) + t 7 (3t 2 ) dt
 Jim Lambers MAT 28 ummer emester 212-1 Practice Final Exam olution 1. Evaluate the line integral xy dx + e y dy + xz dz, where is given by r(t) t 4, t 2, t, t 1. olution From r (t) 4t, 2t, t 2, we obtain
Jim Lambers MAT 28 ummer emester 212-1 Practice Final Exam olution 1. Evaluate the line integral xy dx + e y dy + xz dz, where is given by r(t) t 4, t 2, t, t 1. olution From r (t) 4t, 2t, t 2, we obtain
and in each case give the range of values of x for which the expansion is valid.
 α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λ µ ν ξ ο π ρ σ τ υ ϕ χ ψ ω Mathematics is indeed dangerous in that it absorbs students to such a degree that it dulls their senses to everything else P Kraft Further Maths A (MFPD)
α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λ µ ν ξ ο π ρ σ τ υ ϕ χ ψ ω Mathematics is indeed dangerous in that it absorbs students to such a degree that it dulls their senses to everything else P Kraft Further Maths A (MFPD)
Homework 3 solutions Math 136 Gyu Eun Lee 2016 April 15. R = b a
 Homework 3 solutions Math 136 Gyu Eun Lee 2016 April 15 A problem may have more than one valid method of solution. Here we present just one. Arbitrary functions are assumed to have whatever regularity
Homework 3 solutions Math 136 Gyu Eun Lee 2016 April 15 A problem may have more than one valid method of solution. Here we present just one. Arbitrary functions are assumed to have whatever regularity
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems
 Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Contents. MATH 32B-2 (18W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables. 1 Multiple Integrals 3. 2 Vector Fields 9
 MATH 32B-2 (8W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Multiple Integrals 3 2 Vector Fields 9 3 Line and Surface Integrals 5 4 The Classical Integral Theorems 9 MATH 32B-2 (8W)
MATH 32B-2 (8W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Multiple Integrals 3 2 Vector Fields 9 3 Line and Surface Integrals 5 4 The Classical Integral Theorems 9 MATH 32B-2 (8W)
Math 210, Final Exam, Fall 2010 Problem 1 Solution. v cosθ = u. v Since the magnitudes of the vectors are positive, the sign of the dot product will
 Math, Final Exam, Fall Problem Solution. Let u,, and v,,3. (a) Is the angle between u and v acute, obtuse, or right? (b) Find an equation for the plane through (,,) containing u and v. Solution: (a) The
Math, Final Exam, Fall Problem Solution. Let u,, and v,,3. (a) Is the angle between u and v acute, obtuse, or right? (b) Find an equation for the plane through (,,) containing u and v. Solution: (a) The
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems
 Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON. a b. Name: Problem 1
 BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON Name: Problem 1 In this problem, we will use vectors to show that an angle formed by connecting a point on a circle to two
BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON Name: Problem 1 In this problem, we will use vectors to show that an angle formed by connecting a point on a circle to two
RAJASTHAN P.E.T. MATHS-1995
 RAJASTHAN P.E.T. MATHS-1995 1. The equation of the normal to the circle x2 + y2 = a2 at point (x y ) will be : (1) x y - xy = (2) xx - yy = (3) x y + xy = (4) xx + yy = 2. Equation of the bisector of the
RAJASTHAN P.E.T. MATHS-1995 1. The equation of the normal to the circle x2 + y2 = a2 at point (x y ) will be : (1) x y - xy = (2) xx - yy = (3) x y + xy = (4) xx + yy = 2. Equation of the bisector of the
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping
 Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
TRACKING and DETECTION in COMPUTER VISION Filtering and edge detection
 Technischen Universität München Winter Semester 0/0 TRACKING and DETECTION in COMPUTER VISION Filtering and edge detection Slobodan Ilić Overview Image formation Convolution Non-liner filtering: Median
Technischen Universität München Winter Semester 0/0 TRACKING and DETECTION in COMPUTER VISION Filtering and edge detection Slobodan Ilić Overview Image formation Convolution Non-liner filtering: Median
Math 23b Practice Final Summer 2011
 Math 2b Practice Final Summer 211 1. (1 points) Sketch or describe the region of integration for 1 x y and interchange the order to dy dx dz. f(x, y, z) dz dy dx Solution. 1 1 x z z f(x, y, z) dy dx dz
Math 2b Practice Final Summer 211 1. (1 points) Sketch or describe the region of integration for 1 x y and interchange the order to dy dx dz. f(x, y, z) dz dy dx Solution. 1 1 x z z f(x, y, z) dy dx dz
Solutions to Homework 5
 Solutions to Homework 5 1. Let z = f(x, y) be a twice continuously differentiable function of x and y. Let x = r cos θ and y = r sin θ be the equations which transform polar coordinates into rectangular
Solutions to Homework 5 1. Let z = f(x, y) be a twice continuously differentiable function of x and y. Let x = r cos θ and y = r sin θ be the equations which transform polar coordinates into rectangular
Sept , 17, 23, 29, 37, 41, 45, 47, , 5, 13, 17, 19, 29, 33. Exam Sept 26. Covers Sept 30-Oct 4.
 MATH 23, FALL 2013 Text: Calculus, Early Transcendentals or Multivariable Calculus, 7th edition, Stewart, Brooks/Cole. We will cover chapters 12 through 16, so the multivariable volume will be fine. WebAssign
MATH 23, FALL 2013 Text: Calculus, Early Transcendentals or Multivariable Calculus, 7th edition, Stewart, Brooks/Cole. We will cover chapters 12 through 16, so the multivariable volume will be fine. WebAssign
Math 550, Exam 1. 2/10/11.
 Math 55, Exam. //. Read problems carefully. Show all work. No notes, calculator, or text. The exam is approximately 5 percent of the total grade. There are points total. Partial credit may be given. Write
Math 55, Exam. //. Read problems carefully. Show all work. No notes, calculator, or text. The exam is approximately 5 percent of the total grade. There are points total. Partial credit may be given. Write
McGill University April 16, Advanced Calculus for Engineers
 McGill University April 16, 2014 Faculty of cience Final examination Advanced Calculus for Engineers Math 264 April 16, 2014 Time: 6PM-9PM Examiner: Prof. R. Choksi Associate Examiner: Prof. A. Hundemer
McGill University April 16, 2014 Faculty of cience Final examination Advanced Calculus for Engineers Math 264 April 16, 2014 Time: 6PM-9PM Examiner: Prof. R. Choksi Associate Examiner: Prof. A. Hundemer
Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations.
 1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
Calculus - II Multivariable Calculus. M.Thamban Nair. Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Calculus - II Multivariable Calculus M.Thamban Nair epartment of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Madras February 27 Revised: January 29 Contents Preface v 1 Functions of everal Variables 1 1.1
Calculus - II Multivariable Calculus M.Thamban Nair epartment of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Madras February 27 Revised: January 29 Contents Preface v 1 Functions of everal Variables 1 1.1
Week 7: Integration: Special Coordinates
 Week 7: Integration: Special Coordinates Introduction Many problems naturally involve symmetry. One should exploit it where possible and this often means using coordinate systems other than Cartesian coordinates.
Week 7: Integration: Special Coordinates Introduction Many problems naturally involve symmetry. One should exploit it where possible and this often means using coordinate systems other than Cartesian coordinates.
c) xy 3 = cos(7x +5y), y 0 = y3 + 7 sin(7x +5y) 3xy sin(7x +5y) d) xe y = sin(xy), y 0 = ey + y cos(xy) x(e y cos(xy)) e) y = x ln(3x + 5), y 0
 Some Math 35 review problems With answers 2/6/2005 The following problems are based heavily on problems written by Professor Stephen Greenfield for his Math 35 class in spring 2005. His willingness to
Some Math 35 review problems With answers 2/6/2005 The following problems are based heavily on problems written by Professor Stephen Greenfield for his Math 35 class in spring 2005. His willingness to
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1
 OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
Moment of inertia. Contents. 1 Introduction and simple cases. January 15, Introduction. 1.2 Examples
 Moment of inertia January 15, 016 A systematic account is given of the concept and the properties of the moment of inertia. Contents 1 Introduction and simple cases 1 1.1 Introduction.............. 1 1.
Moment of inertia January 15, 016 A systematic account is given of the concept and the properties of the moment of inertia. Contents 1 Introduction and simple cases 1 1.1 Introduction.............. 1 1.
Change of Variables, Parametrizations, Surface Integrals
 Chapter 8 Change of Variables, Parametrizations, Surface Integrals 8. he transformation formula In evaluating any integral, if the integral depends on an auxiliary function of the variables involved, it
Chapter 8 Change of Variables, Parametrizations, Surface Integrals 8. he transformation formula In evaluating any integral, if the integral depends on an auxiliary function of the variables involved, it
MATH 12 CLASS 23 NOTES, NOV Contents 1. Change of variables: the Jacobian 1
 MATH 12 CLASS 23 NOTES, NOV 11 211 Contents 1. Change of variables: the Jacobian 1 1. Change of variables: the Jacobian So far, we have seen three examples of situations where we change variables to help
MATH 12 CLASS 23 NOTES, NOV 11 211 Contents 1. Change of variables: the Jacobian 1 1. Change of variables: the Jacobian So far, we have seen three examples of situations where we change variables to help
Sixth Term Examination Papers 9470 MATHEMATICS 2 MONDAY 12 JUNE 2017
 Sixth Term Examination Papers 9470 MATHEMATICS 2 MONDAY 12 JUNE 2017 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES AND INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES six six Calculators are not permitted. Please wait to be told you may begin
Sixth Term Examination Papers 9470 MATHEMATICS 2 MONDAY 12 JUNE 2017 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES AND INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES six six Calculators are not permitted. Please wait to be told you may begin
(b) Find the range of h(x, y) (5) Use the definition of continuity to explain whether or not the function f(x, y) is continuous at (0, 0)
 eview Exam Math 43 Name Id ead each question carefully. Avoid simple mistakes. Put a box around the final answer to a question (use the back of the page if necessary). For full credit you must show your
eview Exam Math 43 Name Id ead each question carefully. Avoid simple mistakes. Put a box around the final answer to a question (use the back of the page if necessary). For full credit you must show your
CALCULUS III. Paul Dawkins
 CALCULUS III Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... iii Outline... iv Three Dimensional Space... Introduction... The -D Coordinate System... Equations of Lines... 9 Equations of Planes... 5 Quadric
CALCULUS III Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... iii Outline... iv Three Dimensional Space... Introduction... The -D Coordinate System... Equations of Lines... 9 Equations of Planes... 5 Quadric
( ) ( ) Math 17 Exam II Solutions
 Math 7 Exam II Solutions. Sketch the vector field F(x,y) -yi + xj by drawing a few vectors. Draw the vectors associated with at least one point in each quadrant and draw the vectors associated with at
Math 7 Exam II Solutions. Sketch the vector field F(x,y) -yi + xj by drawing a few vectors. Draw the vectors associated with at least one point in each quadrant and draw the vectors associated with at
II. DIFFERENTIABLE MANIFOLDS. Washington Mio CENTER FOR APPLIED VISION AND IMAGING SCIENCES
 II. DIFFERENTIABLE MANIFOLDS Washington Mio Anuj Srivastava and Xiuwen Liu (Illustrations by D. Badlyans) CENTER FOR APPLIED VISION AND IMAGING SCIENCES Florida State University WHY MANIFOLDS? Non-linearity
II. DIFFERENTIABLE MANIFOLDS Washington Mio Anuj Srivastava and Xiuwen Liu (Illustrations by D. Badlyans) CENTER FOR APPLIED VISION AND IMAGING SCIENCES Florida State University WHY MANIFOLDS? Non-linearity
Calculus III. Math 233 Spring Final exam May 3rd. Suggested solutions
 alculus III Math 33 pring 7 Final exam May 3rd. uggested solutions This exam contains twenty problems numbered 1 through. All problems are multiple choice problems, and each counts 5% of your total score.
alculus III Math 33 pring 7 Final exam May 3rd. uggested solutions This exam contains twenty problems numbered 1 through. All problems are multiple choice problems, and each counts 5% of your total score.
(a) The points (3, 1, 2) and ( 1, 3, 4) are the endpoints of a diameter of a sphere.
 MATH 4 FINAL EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS Problem. a) The points,, ) and,, 4) are the endpoints of a diameter of a sphere. i) Determine the center and radius of the sphere. ii) Find an equation for the sphere.
MATH 4 FINAL EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS Problem. a) The points,, ) and,, 4) are the endpoints of a diameter of a sphere. i) Determine the center and radius of the sphere. ii) Find an equation for the sphere.
3 2 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) 3. a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1
 Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and engineering.
 Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Mathematics of Physics and Engineering II: Homework answers You are encouraged to disagree with everything that follows. P R and i j k 2 1 1
 Mathematics of Physics and Engineering II: Homework answers You are encouraged to disagree with everything that follows Homework () P Q = OQ OP =,,,, =,,, P R =,,, P S = a,, a () The vertex of the angle
Mathematics of Physics and Engineering II: Homework answers You are encouraged to disagree with everything that follows Homework () P Q = OQ OP =,,,, =,,, P R =,,, P S = a,, a () The vertex of the angle
Algebra I Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.701 Algebra I Fall 007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.701 007 Geometry of the Special Unitary
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.701 Algebra I Fall 007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.701 007 Geometry of the Special Unitary
MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework
 MATH 332, (Vector Analysis), Summer 2005: Homework 1 Instructor: Ivan Avramidi MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework Set 1. (Scalar Product, Equation of a Plane, Vector Product) Sections: 1.9,
MATH 332, (Vector Analysis), Summer 2005: Homework 1 Instructor: Ivan Avramidi MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework Set 1. (Scalar Product, Equation of a Plane, Vector Product) Sections: 1.9,
MIT 2.71/2.710 Optics 10/31/05 wk9-a-1. The spatial frequency domain
 10/31/05 wk9-a-1 The spatial frequency domain Recall: plane wave propagation x path delay increases linearly with x λ z=0 θ E 0 x exp i2π sinθ + λ z i2π cosθ λ z plane of observation 10/31/05 wk9-a-2 Spatial
10/31/05 wk9-a-1 The spatial frequency domain Recall: plane wave propagation x path delay increases linearly with x λ z=0 θ E 0 x exp i2π sinθ + λ z i2π cosθ λ z plane of observation 10/31/05 wk9-a-2 Spatial
Errata and Updates for ASM Exam MAS-I (First Edition) Sorted by Date
 Errata for ASM Exam MAS-I Study Manual (First Edition) Sorted by Date 1 Errata and Updates for ASM Exam MAS-I (First Edition) Sorted by Date Practice Exam 5 Question 6 is defective. See the correction
Errata for ASM Exam MAS-I Study Manual (First Edition) Sorted by Date 1 Errata and Updates for ASM Exam MAS-I (First Edition) Sorted by Date Practice Exam 5 Question 6 is defective. See the correction
Errata and Updates for ASM Exam MAS-I (First Edition) Sorted by Page
 Errata for ASM Exam MAS-I Study Manual (First Edition) Sorted by Page 1 Errata and Updates for ASM Exam MAS-I (First Edition) Sorted by Page Practice Exam 5 Question 6 is defective. See the correction
Errata for ASM Exam MAS-I Study Manual (First Edition) Sorted by Page 1 Errata and Updates for ASM Exam MAS-I (First Edition) Sorted by Page Practice Exam 5 Question 6 is defective. See the correction
Module Two: Differential Calculus(continued) synopsis of results and problems (student copy)
 Module Two: Differential Calculus(continued) synopsis of results and problems (student copy) Srikanth K S 1 Syllabus Taylor s and Maclaurin s theorems for function of one variable(statement only)- problems.
Module Two: Differential Calculus(continued) synopsis of results and problems (student copy) Srikanth K S 1 Syllabus Taylor s and Maclaurin s theorems for function of one variable(statement only)- problems.
Dr. Allen Back. Oct. 6, 2014
 Dr. Allen Back Oct. 6, 2014 Distribution Min=48 Max=100 Q1=74 Median=83 Q3=91.5 mean = 81.48 std. dev. = 12.5 Distribution Distribution: (The letters will not be directly used.) Scores Freq. 100 2 98-99
Dr. Allen Back Oct. 6, 2014 Distribution Min=48 Max=100 Q1=74 Median=83 Q3=91.5 mean = 81.48 std. dev. = 12.5 Distribution Distribution: (The letters will not be directly used.) Scores Freq. 100 2 98-99
Solutions to Sample Questions for Final Exam
 olutions to ample Questions for Final Exam Find the points on the surface xy z 3 that are closest to the origin. We use the method of Lagrange Multipliers, with f(x, y, z) x + y + z for the square of the
olutions to ample Questions for Final Exam Find the points on the surface xy z 3 that are closest to the origin. We use the method of Lagrange Multipliers, with f(x, y, z) x + y + z for the square of the
MATH 131P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER 12, 2012
 MATH 3P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER, This is a closed ook, closed notes, no calculators/computers exam. There are 6 prolems. Write your solutions to Prolems -3 in lue ook #, and your solutions to
MATH 3P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER, This is a closed ook, closed notes, no calculators/computers exam. There are 6 prolems. Write your solutions to Prolems -3 in lue ook #, and your solutions to
The minus sign indicates that the centroid is located below point E. We will relocate the axis as shown in Figure (1) and take discard the sign:
 AOE 304: Thin Walled Structures Solutions to Consider a cantilever beam as shown in the attached figure. At the tip of the beam, a bending moment M = 1000 N-m is applied at an angle θ with respect to the
AOE 304: Thin Walled Structures Solutions to Consider a cantilever beam as shown in the attached figure. At the tip of the beam, a bending moment M = 1000 N-m is applied at an angle θ with respect to the
Mathematics (Course B) Lent Term 2005 Examples Sheet 2
 N12d Natural Sciences, Part IA Dr M. G. Worster Mathematics (Course B) Lent Term 2005 Examples Sheet 2 Please communicate any errors in this sheet to Dr Worster at M.G.Worster@damtp.cam.ac.uk. Note that
N12d Natural Sciences, Part IA Dr M. G. Worster Mathematics (Course B) Lent Term 2005 Examples Sheet 2 Please communicate any errors in this sheet to Dr Worster at M.G.Worster@damtp.cam.ac.uk. Note that
Math 497C Mar 3, Curves and Surfaces Fall 2004, PSU
 Math 497C Mar 3, 2004 1 Curves and Surfaces Fall 2004, PSU Lecture Notes 10 2.3 Meaning of Gaussian Curvature In the previous lecture we gave a formal definition for Gaussian curvature K in terms of the
Math 497C Mar 3, 2004 1 Curves and Surfaces Fall 2004, PSU Lecture Notes 10 2.3 Meaning of Gaussian Curvature In the previous lecture we gave a formal definition for Gaussian curvature K in terms of the
Created by T. Madas LINE INTEGRALS. Created by T. Madas
 LINE INTEGRALS LINE INTEGRALS IN 2 DIMENSIONAL CARTESIAN COORDINATES Question 1 Evaluate the integral ( x + 2y) dx, C where C is the path along the curve with equation y 2 = x + 1, from ( ) 0,1 to ( )
LINE INTEGRALS LINE INTEGRALS IN 2 DIMENSIONAL CARTESIAN COORDINATES Question 1 Evaluate the integral ( x + 2y) dx, C where C is the path along the curve with equation y 2 = x + 1, from ( ) 0,1 to ( )
14.1. Multiple Integration. Iterated Integrals and Area in the Plane. Iterated Integrals. Iterated Integrals. MAC2313 Calculus III - Chapter 14
 14 Multiple Integration 14.1 Iterated Integrals and Area in the Plane Objectives Evaluate an iterated integral. Use an iterated integral to find the area of a plane region. Copyright Cengage Learning.
14 Multiple Integration 14.1 Iterated Integrals and Area in the Plane Objectives Evaluate an iterated integral. Use an iterated integral to find the area of a plane region. Copyright Cengage Learning.
1. Find and classify the extrema of h(x, y) = sin(x) sin(y) sin(x + y) on the square[0, π] [0, π]. (Keep in mind there is a boundary to check out).
![1. Find and classify the extrema of h(x, y) = sin(x) sin(y) sin(x + y) on the square[0, π] [0, π]. (Keep in mind there is a boundary to check out). 1. Find and classify the extrema of h(x, y) = sin(x) sin(y) sin(x + y) on the square[0, π] [0, π]. (Keep in mind there is a boundary to check out).](/thumbs/87/97246100.jpg) . Find and classify the extrema of hx, y sinx siny sinx + y on the square[, π] [, π]. Keep in mind there is a boundary to check out. Solution: h x cos x sin y sinx + y + sin x sin y cosx + y h y sin x
. Find and classify the extrema of hx, y sinx siny sinx + y on the square[, π] [, π]. Keep in mind there is a boundary to check out. Solution: h x cos x sin y sinx + y + sin x sin y cosx + y h y sin x
3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity
 3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity 55 3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity Overview: Second derivatives are useful for understanding how the linear approximation varies
3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity 55 3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity Overview: Second derivatives are useful for understanding how the linear approximation varies
PRACTICE PROBLEMS. Please let me know if you find any mistakes in the text so that i can fix them. 1. Mixed partial derivatives.
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS Please let me know if you find any mistakes in the text so that i can fix them. 1.1. Let Show that f is C 1 and yet How is that possible? 1. Mixed partial derivatives f(x, y) = {xy x
PRACTICE PROBLEMS Please let me know if you find any mistakes in the text so that i can fix them. 1.1. Let Show that f is C 1 and yet How is that possible? 1. Mixed partial derivatives f(x, y) = {xy x
ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic concepts: Find y(x) where x is the independent and y the dependent varible, based on an equation involving x, y(x), y 0 (x),...e.g.: y 00 (x) = 1+y(x) y0 (x) 1+x or,
ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic concepts: Find y(x) where x is the independent and y the dependent varible, based on an equation involving x, y(x), y 0 (x),...e.g.: y 00 (x) = 1+y(x) y0 (x) 1+x or,
Practice problems for Exam 1. a b = (2) 2 + (4) 2 + ( 3) 2 = 29
 Practice problems for Exam.. Given a = and b =. Find the area of the parallelogram with adjacent sides a and b. A = a b a ı j k b = = ı j + k = ı + 4 j 3 k Thus, A = 9. a b = () + (4) + ( 3)
Practice problems for Exam.. Given a = and b =. Find the area of the parallelogram with adjacent sides a and b. A = a b a ı j k b = = ı j + k = ı + 4 j 3 k Thus, A = 9. a b = () + (4) + ( 3)
MA232A Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geometry School of Mathematics, Trinity College Michaelmas Term 2017 Vector Algebra and Spherical Trigonometry
 MA232A Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geometry School of Mathematics, Trinity College Michaelmas Term 2017 Vector Algebra and Spherical Trigonometry David R. Wilkins 3.1. Vectors in Three-Dimensional Euclidean
MA232A Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geometry School of Mathematics, Trinity College Michaelmas Term 2017 Vector Algebra and Spherical Trigonometry David R. Wilkins 3.1. Vectors in Three-Dimensional Euclidean
x + ye z2 + ze y2, y + xe z2 + ze x2, z and where T is the
 1.(8pts) Find F ds where F = x + ye z + ze y, y + xe z + ze x, z and where T is the T surface in the pictures. (The two pictures are two views of the same surface.) The boundary of T is the unit circle
1.(8pts) Find F ds where F = x + ye z + ze y, y + xe z + ze x, z and where T is the T surface in the pictures. (The two pictures are two views of the same surface.) The boundary of T is the unit circle
