THEORY OF SPIN HALL EFFECT AND INTERFACE SPIN-ORBIT COUPLING
|
|
|
- Logan Townsend
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THEORY OF SPIN HALL EFFECT AND INTERFACE SPIN-ORBIT COUPLING CURRENT-INDUCED SPIN POLARIZATION AND SPIN - ORBIT TORQUE IN GRAPHENE Anna Dyrdał, Łukasz Karwacki, Józef Barnaś Mesoscopic Physics Division, Faculty of Physics Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań, Poland NANOSPIN: Nanoscale spin torque devices for spin electronics Summarizing MEETING, 11th-12th of July 2016
2 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION: SPIN ORBIT DRIVEN PHENOMENA MICROSCOPIC MECHANISMS LEADING TO AHE/SHE SPIN TORQUES DUE TO SPIN-ORBIT COUPLING SHE AND CISP IN SEMICONDUCTOR HETEROSTRUCTURES WITH RASHBA SOI DETERMINATION OF SPIN-ORBIT TORQUES: THEORETICAL DESCRIPTION OF HARMONIC HALL VOLTAGE MEASUREMENTS PHENOMENOLOGICAL DESCRIPTION OF SOTs DRIFT-DIFFUSION MODEL FOR Ta CoFeB - literature model for Ta CoFeB by Kim et.al. - results for trilayer spin-diffusion model of Ta interface CoFeB TRILAYER SPIN-DIFFUSION MODEL: SUMMARY AHE IN Ta CoFeB ANOTHER APPROACHES 2/22
3 SPIN-ORBIT DRIVEN PHENOMENA ANOMALOUS HALL EFFECT CURRENT-INDUCED SPIN POLARIZATION THERMAL CURRENT-INDUCED SPIN POLARIZATION SPIN HALL EFFECT SPIN NERNST EFFECT SPIN HALL TORQUE Nature Physics 10, (2014) INVERSE SPIN HALL EFFECT SPIN-ORBIT TORQUE 3/22
4 INTRINSIC CONTRIBUTION BAND STRUCTURE TOPOLOGY MICROSCOPIC MECHANISMS An external electric field leads to an interband coherence that gives rise to contribution to the transverse velocity an anomalous velocity related to Berry phase curvature anomalous velocity Intrinsic spin Hall conductivity for 4d and 5d transition metals (microscopic tight-binding calculations); γ a quasiparticle damping rate Tanaka, T., H. Kontani, M. Naito, T. Naito, D. Hirashima, K. Yamada, and J. Inoue, 2008, Phys. Rev. B 77, J. Sinova et al., Rev. Mod Phys. 87, 1213 (2015); G. Vignale, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 23, 3 (2010); J. Schliemann, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 20, 1015 (2006); M. I. Dyakonov and A. V. Khaetskii, in Spin Physics in Semiconductors edited by M. I. Dyakonov, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2008, Chap. 8; 4/22
5 EXTRINSIC CONTRIBUTION MICROSCOPIC MECHANISMS SKEW SCATTERING SIDE JUMP EXTRINSIC SIDE-JUMP: The contribution arising from the non-spin-orbit coupled part of the wave-packet scattering off the spin-orbit coupled disordered. INTRINSIC SIDE-JUMP: The contribution arising from the spin-orbit coupled part of the wave-packet formed by the Bloch electrons scattering off the scalar potential alone without spin-orbit coupling. J. Sinova et al., Rev. Mod Phys. 87, 1213 (2015); G. Vignale, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 23, 3 (2010); J. Schliemann, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 20, 1015 (2006); A. Crépieux, P. Bruno, Phys. Rev. B 64, (2001); M. I. Dyakonov and A. V. Khaetskii, in Spin Physics in Semiconductors edited by M. I. Dyakonov, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2008, Chap. 8; 5/22
6 MICROSCOPIC MECHANISMS: EXPERIMENTAL DATA vs THEORY ANOMALOUS HALL EFFECT HIGH CONDUCTIVITY REGIME skew-scattering mechanism dominate GOOD METAL REGIME scattering-independent mechanisms or side jump dominate SPIN HALL EFFECT BAD-METAL-HOPPING REGIME there is currently no theory which predicts the observed scaling N. Nagaosa et al., Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 1539 (2010); J. Sinova et al., Rev. Mod Phys. 87, 1213 (2015) 6/22
7 CISP IN 2D ELECTRON GAS WITH RASHBA SOI J. Sinova et al., Rev. Mod. Phys. 87, 1213 (2015) J. Sinova et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, (2004) N. A. Sinitsyn et al., Phys. Rev. B 70, (R) (2004) V.M. Edelstein, Sol. State Communs. 73, 233 (1990) C. Gorini et al., Phys. Rv. B 78, (2008) P. Schwab et al., Phys. Rev. B, Europhysics Lett. 90, (2010) L. Golub et al., Phys. Rev. B 84, (2011) A.Dyrdal et al., Phys. Rev. B 87, (2013) 7/22
8 SPIN-ORBIT TORQUES LLG EQUATION: eff SPIN TRANSFER TORQUE IN SPIN VALVES SPIN HALL TORQUE SPIN ORBIT (RASHBA) TORQE. Sinova et al., Rev. Mod Phys. 87, 1213 (2015); X. Fan et al., Nature Communications 4, 1799 (2013); P. Gambardella, I. M. Miron, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A, 369, 3175 (2011); 8/22
9 DETERMINATION OF THE SOTs HARMONIC HALL VOLATGE MEASUREMENTS M. Hayashi, J. Kim, M. Yamanouchi, and H. Ohno, Quantitative characterization of the spin-orbit torque using harmonic Hall voltage measurements, PHYSICAL REVIEW B 89, (2014) J. Kim, J. Sinha, M. Hayashi, M. Yamanouchi, S. Fukami, T. Suzuki, S. Mitani and H. Ohno, Layer thickness dependence of the current-induced effective field vector in Ta CoFeB MgO, NATURE MATERIALS 12, 240 (2013),, 9/22
10 DETERMINATION OF THE SOTs HARMONIC HALL VOLATGE MEASUREMENTS M. Hayashi, J. Kim, M. Yamanouchi, and H. Ohno, Quantitative characterization of the spin-orbit torque using harmonic Hall voltage measurements, PHYSICAL REVIEW B 89, (2014) J. Kim, J. Sinha, M. Hayashi, M. Yamanouchi, S. Fukami, T. Suzuki, S. Mitani and H. Ohno, Layer thickness dependence of the current-induced effective field vector in Ta CoFeB MgO, NATURE MATERIALS 12, 240 (2013) LANDAU-LIFSHITZ-GILBERT (LLG) EQUATION p - represents the magnetization direction of the reference layer in the STT case or average spin direction of electrons diffusing into the magnetic layer in SOT case 10/22
11 MOTIVATION: PHENOMENOLOGICAL DESCRIPTION OF SOTs J. Kim, J. Sinha, S. Mitani, M. Hayashi, S. Takahashi, S. Maekawa, M. Yamanouchi, and H. Ohno, Anomalous temperature dependence of current-induced torques in CoFeB/MgO heterostructures with Ta-based underlayers, PHYSICAL REVIEW B 89, (2014) DRIFT-DIFFUSION FORMALISM BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: 11/22
12 MOTIVATION: RESULTS PHENOMENOLOGICAL DESCRIPTION OF SOTs J. Kim, J. Sinha, S. Mitani, M. Hayashi, S. Takahashi, S. Maekawa, M. Yamanouchi, and H. Ohno, Anomalous temperature dependence of current-induced torques in CoFeB/MgO heterostructures with Ta-based underlayers, PHYSICAL REVIEW B 89, (2014) 12/22
13 EFFECTS ON INTERFACE PHENOMENOLOGICAL DESCRIPTION OF SOTs The NM layer and the FM layer affect the electronic strucyure of each other close to the interface the magnetic proximity effect can induce a magnetic moment in the NM layer (the material with strong SOC) the spin-orbit proximity effect can induce spin-orbit effects in the FM layer lattice mismatch between materials: thickness fluctuations, formation of dislocation spin backflow (even from a well-ordered interface) spin memory loss due to intermixing and disorder at the NM FM interface 13/22
14 PHENOMENOLOGICAL DESCRIPTION OF SOTs EFFECTS ON INTERFACE: TRILAYER SPIN DIFFUSION MODEL BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: 14/22
15 PHENOMENOLOGICAL DESCRIPTION OF SOTs EFFECTS ON INTERFACE: TRILAYER SPIN DIFFUSION MODEL DAMPING-LIKE AND FIELD-LIKE TORQUE EFFICIENCY: WITHOUT INTERFACE LAYER 15/22
16 PHENOMENOLOGICAL DESCRIPTION OF SOTs EFFECTS ON INTERFACE: TRILAYER SPIN DIFFUSION MODEL RESULTS 16/22
17 TRILAYER SPIN DIFFUSION MODEL : SUMMARY Im[G MIX ] comparable in size to its real counterpart large angle rotation of the spin direction of spin current presence of spin Hall torque Negative Re[G MIX ]!!! model failure poor band matching between NM and the FM layers flow of spin current from the FM layer to the NM layer AHE or SHE in FM layer should be checked! 17/22
18 ANOMALOUS HALL EFFECT IN Ta CoFeB 18/22
19 TRILAYER SPIN DIFFUSION MODEL : SUMMARY Im[G MIX ] comparable in size to its real counterpart large angle rotation of the spin direction of spin current presence of spin Hall torque Negative Re[G MIX ]!!! model failure poor band matching between NM and the FM layers flow of spin current from the FM layer to the NM layer AHE or SHE in FM layer should be checked! FURTHER MODIFICATION OF TRILAYER SPIN DIFFUSION MODEL ( SH SH) J Iy??? SOC at the interface! SOC in the FM? 19/22
20 ANOTHER APPROACHES BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: spin currents generated by interfacial spin-orbit scattering additional spin-torque due to spin polarization that arises at the interface the torque on magnetization at the interface - conductance matrix - THE RASHBA MODEL OF SOC - torkance tensor - - conductivity tensor - - torkivity tensors - 20/22
21 ANOTHER APPROACHES spin pumping conductivity is given by retarded and advanced Green functions disoredrs included explicitly SOC at the interface backflow current 21/22
22 ANOTHER APPROACHES 22/22
Mesoscopic Spintronics
 Mesoscopic Spintronics Taro WAKAMURA (Université Paris-Sud) Lecture 2 Today s Topics 2.1 Anomalous Hall effect and spin Hall effect 2.2 Spin Hall effect measurements 2.3 Interface effects Anomalous Hall
Mesoscopic Spintronics Taro WAKAMURA (Université Paris-Sud) Lecture 2 Today s Topics 2.1 Anomalous Hall effect and spin Hall effect 2.2 Spin Hall effect measurements 2.3 Interface effects Anomalous Hall
Spin-orbit effects in graphene and graphene-like materials. Józef Barnaś
 Spin-orbit effects in graphene and graphene-like materials Józef Barnaś Faculty of Physics, Adam Mickiewicz University, Poznań & Institute of Molecular Physics PAN, Poznań In collaboration with: A. Dyrdał,
Spin-orbit effects in graphene and graphene-like materials Józef Barnaś Faculty of Physics, Adam Mickiewicz University, Poznań & Institute of Molecular Physics PAN, Poznań In collaboration with: A. Dyrdał,
Lecture I. Spin Orbitronics
 Lecture I Spin Orbitronics Alireza Qaiumzadeh Radboud University (RU) Institute for Molecules and Materials (IMM) Theory of Condensed Matter group (TCM) What We Talk About When We Talk About Spin Orbitronics
Lecture I Spin Orbitronics Alireza Qaiumzadeh Radboud University (RU) Institute for Molecules and Materials (IMM) Theory of Condensed Matter group (TCM) What We Talk About When We Talk About Spin Orbitronics
Spin orbit torque driven magnetic switching and memory. Debanjan Bhowmik
 Spin orbit torque driven magnetic switching and memory Debanjan Bhowmik Spin Transfer Torque Fixed Layer Free Layer Fixed Layer Free Layer Current coming out of the fixed layer (F2) is spin polarized in
Spin orbit torque driven magnetic switching and memory Debanjan Bhowmik Spin Transfer Torque Fixed Layer Free Layer Fixed Layer Free Layer Current coming out of the fixed layer (F2) is spin polarized in
Gauge Concepts in Theoretical Applied Physics
 Gauge Concepts in Theoretical Applied Physics Seng Ghee Tan, Mansoor BA Jalil Data Storage Institute, A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research) Computational Nanoelectronics and Nano-device
Gauge Concepts in Theoretical Applied Physics Seng Ghee Tan, Mansoor BA Jalil Data Storage Institute, A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research) Computational Nanoelectronics and Nano-device
Expecting the unexpected in the spin Hall effect: from fundamental to practical
 Expecting the unexpected in the spin Hall effect: from fundamental to practical JAIRO SINOVA Texas A&M University Institute of Physics ASCR Institute of Physics ASCR Tomas Jungwirth, Vít Novák, et al Hitachi
Expecting the unexpected in the spin Hall effect: from fundamental to practical JAIRO SINOVA Texas A&M University Institute of Physics ASCR Institute of Physics ASCR Tomas Jungwirth, Vít Novák, et al Hitachi
Spin pumping in Ferromagnet-Topological Insulator-Ferromagnet Heterostructures Supplementary Information.
 Spin pumping in Ferromagnet-Topological Insulator-Ferromagnet Heterostructures Supplementary Information. A.A. Baker,, 2 A.I. Figueroa, 2 L.J. Collins-McIntyre, G. van der Laan, 2 and T., a) Hesjedal )
Spin pumping in Ferromagnet-Topological Insulator-Ferromagnet Heterostructures Supplementary Information. A.A. Baker,, 2 A.I. Figueroa, 2 L.J. Collins-McIntyre, G. van der Laan, 2 and T., a) Hesjedal )
Mesoscopic Spintronics
 Mesoscopic Spintronics Taro WAKAMURA (Université Paris-Sud) Lecture 1 Today s Topics 1.1 History of Spintronics 1.2 Fudamentals in Spintronics Spin-dependent transport GMR and TMR effect Spin injection
Mesoscopic Spintronics Taro WAKAMURA (Université Paris-Sud) Lecture 1 Today s Topics 1.1 History of Spintronics 1.2 Fudamentals in Spintronics Spin-dependent transport GMR and TMR effect Spin injection
Spin-resolved Hall effect driven by spin-orbit coupling. Physical Review B - Condensed Matter And Materials Physics, 2005, v. 71 n.
 Title Spin-resolved Hall effect driven by spin-orbit coupling Author(s) Li, J; Hu, L; Shen, SQ Citation Physical Review B - Condensed Matter And Materials Physics, 2005, v. 71 n. 24 Issued Date 2005 URL
Title Spin-resolved Hall effect driven by spin-orbit coupling Author(s) Li, J; Hu, L; Shen, SQ Citation Physical Review B - Condensed Matter And Materials Physics, 2005, v. 71 n. 24 Issued Date 2005 URL
0.002 ( ) R xy
 a b z 0.002 x H y R xy () 0.000-0.002 0 90 180 270 360 (degree) Supplementary Figure 1. Planar Hall effect resistance as a function of the angle of an in-plane field. a, Schematic of the planar Hall resistance
a b z 0.002 x H y R xy () 0.000-0.002 0 90 180 270 360 (degree) Supplementary Figure 1. Planar Hall effect resistance as a function of the angle of an in-plane field. a, Schematic of the planar Hall resistance
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Quasiparticle-mediated spin Hall effect in a superconductor T. Wakamura 1, H. Akaike 2, Y. Omori 1, Y. Niimi 1, S. Takahashi 3, A. Fujimaki 2, S. Maekawa 4,5 and YoshiChika Otani 1,6 1 Institute for Solid
Quasiparticle-mediated spin Hall effect in a superconductor T. Wakamura 1, H. Akaike 2, Y. Omori 1, Y. Niimi 1, S. Takahashi 3, A. Fujimaki 2, S. Maekawa 4,5 and YoshiChika Otani 1,6 1 Institute for Solid
An Overview of Spintronics in 2D Materials
 An Overview of Spintronics in 2D Materials Wei Han ( 韩伟 ) 1 2014 ICQM Outline I. Introduction to spintronics (Lecture I) II. Spin injection and detection in 2D (Lecture I) III. Putting magnetic moment
An Overview of Spintronics in 2D Materials Wei Han ( 韩伟 ) 1 2014 ICQM Outline I. Introduction to spintronics (Lecture I) II. Spin injection and detection in 2D (Lecture I) III. Putting magnetic moment
Spin orbit torques and Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction in dualinterfaced
 Supplementary Information Spin orbit torques and Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction in dualinterfaced Co-Ni multilayers Jiawei Yu, Xuepeng Qiu, Yang Wu, Jungbum Yoon, Praveen Deorani, Jean Mourad Besbas,
Supplementary Information Spin orbit torques and Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction in dualinterfaced Co-Ni multilayers Jiawei Yu, Xuepeng Qiu, Yang Wu, Jungbum Yoon, Praveen Deorani, Jean Mourad Besbas,
Lecture I. Spin Orbitronics
 Lecture I Spin Orbitronics Alireza Qaiumzadeh Radboud University (RU) Institute for Molecules and Materials (IMM) Theory of Condensed Matter group (TCM) What We Talk About When We Talk About Spin Orbitronics
Lecture I Spin Orbitronics Alireza Qaiumzadeh Radboud University (RU) Institute for Molecules and Materials (IMM) Theory of Condensed Matter group (TCM) What We Talk About When We Talk About Spin Orbitronics
Magnetic skyrmions. See also talks online by Tokura, Tchernyshyov. Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University
 See also talks online by Tokura, Tchernyshyov Magnetic skyrmions Rembert Duine with Marianne Knoester (UU) Jairo Sinova (Texas A&M, Mainz) ArXiv 1310.2850 Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University
See also talks online by Tokura, Tchernyshyov Magnetic skyrmions Rembert Duine with Marianne Knoester (UU) Jairo Sinova (Texas A&M, Mainz) ArXiv 1310.2850 Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University
Optical studies of current-induced magnetization
 Optical studies of current-induced magnetization Virginia (Gina) Lorenz Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign PHYS403, December 5, 2017 The scaling of electronics John Bardeen,
Optical studies of current-induced magnetization Virginia (Gina) Lorenz Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign PHYS403, December 5, 2017 The scaling of electronics John Bardeen,
MSE 7025 Magnetic Materials (and Spintronics)
 MSE 7025 Magnetic Materials (and Spintronics) Lecture 14: Spin Transfer Torque And the future of spintronics research Chi-Feng Pai cfpai@ntu.edu.tw Course Outline Time Table Week Date Lecture 1 Feb 24
MSE 7025 Magnetic Materials (and Spintronics) Lecture 14: Spin Transfer Torque And the future of spintronics research Chi-Feng Pai cfpai@ntu.edu.tw Course Outline Time Table Week Date Lecture 1 Feb 24
Effect of heavy metal layer thickness on spin-orbit torque and current-induced. switching in Hf CoFeB MgO structures 90095, USA USA.
 Effect of heavy metal layer thickness on spin-orbit torque and current-induced switching in Hf CoFeB MgO structures Mustafa Akyol, 1, 2 Wanjun Jiang, 3 Guoqiang Yu, 1 Yabin Fan, 1 Mustafa Gunes, 4 Ahmet
Effect of heavy metal layer thickness on spin-orbit torque and current-induced switching in Hf CoFeB MgO structures Mustafa Akyol, 1, 2 Wanjun Jiang, 3 Guoqiang Yu, 1 Yabin Fan, 1 Mustafa Gunes, 4 Ahmet
Anomalous Hall effect in multiband disordered systems: from the metallic to the hopping regime
 Anomalous Hall effect in multiband disordered systems: from the metallic to the hopping regime JAIRO SINOVA Texas A&M University Institute of Physics ASCR Texas A&M University Xiong-Jun Liu, Xin Liu (Nankai)
Anomalous Hall effect in multiband disordered systems: from the metallic to the hopping regime JAIRO SINOVA Texas A&M University Institute of Physics ASCR Texas A&M University Xiong-Jun Liu, Xin Liu (Nankai)
Analytical expression for the harmonic Hall voltages in evaluating spin orbit torques
 Analytical expression for the harmonic all voltages in evaluating spin orbit torques Masamitsu ayashi National Institute for Materials Science, Tsukuba 35-47, Japan Solid understanding of current induced
Analytical expression for the harmonic all voltages in evaluating spin orbit torques Masamitsu ayashi National Institute for Materials Science, Tsukuba 35-47, Japan Solid understanding of current induced
Experimental discovery of the spin-hall effect in Rashba spin-orbit coupled semiconductor systems
 Experimental discovery of the spin-hall effect in Rashba spin-orbit coupled semiconductor systems J. Wunderlich, 1 B. Kästner, 1,2 J. Sinova, 3 T. Jungwirth 4,5 1 Hitachi Cambridge Laboratory, Cambridge
Experimental discovery of the spin-hall effect in Rashba spin-orbit coupled semiconductor systems J. Wunderlich, 1 B. Kästner, 1,2 J. Sinova, 3 T. Jungwirth 4,5 1 Hitachi Cambridge Laboratory, Cambridge
Spin-torque nano-oscillators trends and challenging
 Domain Microstructure and Dynamics in Magnetic Elements Heraklion, Crete, April 8 11, 2013 Spin-torque nano-oscillators trends and challenging N H ext S Giovanni Finocchio Department of Electronic Engineering,
Domain Microstructure and Dynamics in Magnetic Elements Heraklion, Crete, April 8 11, 2013 Spin-torque nano-oscillators trends and challenging N H ext S Giovanni Finocchio Department of Electronic Engineering,
Introduction to Spintronics and Spin Caloritronics. Tamara Nunner Freie Universität Berlin
 Introduction to Spintronics and Spin Caloritronics Tamara Nunner Freie Universität Berlin Outline Format of seminar How to give a presentation How to search for scientific literature Introduction to spintronics
Introduction to Spintronics and Spin Caloritronics Tamara Nunner Freie Universität Berlin Outline Format of seminar How to give a presentation How to search for scientific literature Introduction to spintronics
Magnetic oscillations driven by the spin Hall effect in 3-terminal magnetic tunnel junction. devices. Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853
 Magnetic oscillations driven by the spin Hall ect in 3-terminal magnetic tunnel junction devices Luqiao Liu 1, Chi-Feng Pai 1, D. C. Ralph 1,2, R. A. Buhrman 1 1 Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853 2
Magnetic oscillations driven by the spin Hall ect in 3-terminal magnetic tunnel junction devices Luqiao Liu 1, Chi-Feng Pai 1, D. C. Ralph 1,2, R. A. Buhrman 1 1 Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853 2
Spin-orbit torque in Pt/CoNiCo/Pt symmetric devices
 Spin-orbit torque in Pt/CoNiCo/Pt symmetric devices Meiyin Yang 1, Kaiming Cai 1, Hailang Ju 2, Kevin William Edmonds 3, Guang Yang 4, Shuai Liu 2, Baohe Li 2, Bao Zhang 1, Yu Sheng 1, ShouguoWang 4, Yang
Spin-orbit torque in Pt/CoNiCo/Pt symmetric devices Meiyin Yang 1, Kaiming Cai 1, Hailang Ju 2, Kevin William Edmonds 3, Guang Yang 4, Shuai Liu 2, Baohe Li 2, Bao Zhang 1, Yu Sheng 1, ShouguoWang 4, Yang
Spin Hall effect and related issues. Dept of Physics Taiwan Normal Univ. Ming-Che Chang
 Spin Hall effect and related issues Dept of Physics Taiwan Normal Univ. Ming-Che Chang Basic spin interactions in semiconductors (Dyakonov, cond-mat/0401369) spin-orbit interaction required for optical
Spin Hall effect and related issues Dept of Physics Taiwan Normal Univ. Ming-Che Chang Basic spin interactions in semiconductors (Dyakonov, cond-mat/0401369) spin-orbit interaction required for optical
Spin wave assisted current induced magnetic. domain wall motion
 Spin wave assisted current induced magnetic domain wall motion Mahdi Jamali, 1 Hyunsoo Yang, 1,a) and Kyung-Jin Lee 2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore,
Spin wave assisted current induced magnetic domain wall motion Mahdi Jamali, 1 Hyunsoo Yang, 1,a) and Kyung-Jin Lee 2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore,
Ferromagnetism and Anomalous Hall Effect in Graphene
 Ferromagnetism and Anomalous Hall Effect in Graphene Jing Shi Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of California, Riverside Graphene/YIG Introduction Outline Proximity induced ferromagnetism Quantized
Ferromagnetism and Anomalous Hall Effect in Graphene Jing Shi Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of California, Riverside Graphene/YIG Introduction Outline Proximity induced ferromagnetism Quantized
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/24306 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Verhagen, T.G.A. Title: Magnetism and magnetization dynamics in thin film ferromagnets
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/24306 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Verhagen, T.G.A. Title: Magnetism and magnetization dynamics in thin film ferromagnets
Spin-transfer torques and emergent electrodynamics in magnetic Skyrmion crystals
 Spin-transfer torques and emergent electrodynamics in magnetic Skyrmion crystals Universität zu Köln collaboration: K. Everschor, B. Binz, A. Rosch Universität zu Köln R. Duine Utrecht University T. Schulz,
Spin-transfer torques and emergent electrodynamics in magnetic Skyrmion crystals Universität zu Köln collaboration: K. Everschor, B. Binz, A. Rosch Universität zu Köln R. Duine Utrecht University T. Schulz,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 23 Oct 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 23 Oct 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 23 Oct 2010](/thumbs/74/70896570.jpg) Robust to impurity-scattering spin Hall effect in two-dimensional electron gas arxiv:11.49v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 23 Oct 21 V. K. Dugaev 1,2, M. Inglot 1, E. Ya. Sherman 3,4, and J. Barnaś 5, 1 Department
Robust to impurity-scattering spin Hall effect in two-dimensional electron gas arxiv:11.49v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 23 Oct 21 V. K. Dugaev 1,2, M. Inglot 1, E. Ya. Sherman 3,4, and J. Barnaś 5, 1 Department
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES
 PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES Jasprit Singh University of Michigan McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES Jasprit Singh University of Michigan McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal
Spin dynamics in Bi 2 Se 3 /ferromagnet heterostructures
 Spin dynamics in Bi 2 Se 3 /ferromagnet heterostructures Hyunsoo Yang Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore eleyang@nus.edu.sg Outline Spin-orbit torque (SOT) engineering
Spin dynamics in Bi 2 Se 3 /ferromagnet heterostructures Hyunsoo Yang Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore eleyang@nus.edu.sg Outline Spin-orbit torque (SOT) engineering
Berry Phase Effects on Electronic Properties
 Berry Phase Effects on Electronic Properties Qian Niu University of Texas at Austin Collaborators: D. Xiao, W. Yao, C.P. Chuu, D. Culcer, J.R.Shi, Y.G. Yao, G. Sundaram, M.C. Chang, T. Jungwirth, A.H.MacDonald,
Berry Phase Effects on Electronic Properties Qian Niu University of Texas at Austin Collaborators: D. Xiao, W. Yao, C.P. Chuu, D. Culcer, J.R.Shi, Y.G. Yao, G. Sundaram, M.C. Chang, T. Jungwirth, A.H.MacDonald,
Physics in Quasi-2D Materials for Spintronics Applications
 Physics in Quasi-2D Materials for Spintronics Applications Topological Insulators and Graphene Ching-Tzu Chen IBM TJ Watson Research Center May 13, 2016 2016 C-SPIN Topological Spintronics Device Workshop
Physics in Quasi-2D Materials for Spintronics Applications Topological Insulators and Graphene Ching-Tzu Chen IBM TJ Watson Research Center May 13, 2016 2016 C-SPIN Topological Spintronics Device Workshop
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures
 Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
Topological insulators
 http://www.physik.uni-regensburg.de/forschung/fabian Topological insulators Jaroslav Fabian Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Regensburg Stara Lesna, 21.8.212 DFG SFB 689 what are topological
http://www.physik.uni-regensburg.de/forschung/fabian Topological insulators Jaroslav Fabian Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Regensburg Stara Lesna, 21.8.212 DFG SFB 689 what are topological
Spin transfer torque and magnetization dynamics in in-plane and out-of-plane magnetized spin valves
 Spin transfer torque and magnetization dynamics in in-plane and out-of-plane magnetized spin valves Pavel Baláž Institute of Molecular Physics in Poznań Polish Academy of Sciences and Faculty of Physics
Spin transfer torque and magnetization dynamics in in-plane and out-of-plane magnetized spin valves Pavel Baláž Institute of Molecular Physics in Poznań Polish Academy of Sciences and Faculty of Physics
Planar Hall Effect Based Characterization of Spin Orbital Torques in Ta/CoFeB/MgO Structures
 Planar Hall Effect Based Characterization of Spin Orbital Torques in Ta/CoFeB/MgO Structures Mahdi Jamali 1, Zhengyang Zhao 1, Mahendra DC 2, Delin Zhang 1, Hongshi Li 3, Angeline K. Smith 1, Jian-Ping
Planar Hall Effect Based Characterization of Spin Orbital Torques in Ta/CoFeB/MgO Structures Mahdi Jamali 1, Zhengyang Zhao 1, Mahendra DC 2, Delin Zhang 1, Hongshi Li 3, Angeline K. Smith 1, Jian-Ping
Valley Hall effect in electrically spatial inversion symmetry broken bilayer graphene
 NPSMP2015 Symposium 2015/6/11 Valley Hall effect in electrically spatial inversion symmetry broken bilayer graphene Yuya Shimazaki 1, Michihisa Yamamoto 1, 2, Ivan V. Borzenets 1, Kenji Watanabe 3, Takashi
NPSMP2015 Symposium 2015/6/11 Valley Hall effect in electrically spatial inversion symmetry broken bilayer graphene Yuya Shimazaki 1, Michihisa Yamamoto 1, 2, Ivan V. Borzenets 1, Kenji Watanabe 3, Takashi
Spin relaxation of conduction electrons Jaroslav Fabian (Institute for Theoretical Physics, Uni. Regensburg)
 Spin relaxation of conduction electrons Jaroslav Fabian (Institute for Theoretical Physics, Uni. Regensburg) :Syllabus: 1. Introductory description 2. Elliott-Yafet spin relaxation and spin hot spots 3.
Spin relaxation of conduction electrons Jaroslav Fabian (Institute for Theoretical Physics, Uni. Regensburg) :Syllabus: 1. Introductory description 2. Elliott-Yafet spin relaxation and spin hot spots 3.
Observation of the intrinsic inverse spin Hall effect in Ni 80 Fe 20. Yuichiro Ando, Teruya Shinjo and Masashi Shiraishi * #
 Observation of the intrinsic inverse spin Hall effect in Ni 80 Fe 20 Ayaka Tsukahara #, Yuta Kitamura #, Eiji Shikoh, Yuichiro Ando, Teruya Shinjo and Masashi Shiraishi * # Graduate School of Engineering
Observation of the intrinsic inverse spin Hall effect in Ni 80 Fe 20 Ayaka Tsukahara #, Yuta Kitamura #, Eiji Shikoh, Yuichiro Ando, Teruya Shinjo and Masashi Shiraishi * # Graduate School of Engineering
Quantitative characterization of the spin orbit torque using harmonic Hall voltage measurements
 Quantitative characterization of the spin orbit torque using harmonic all voltage measurements Masamitsu ayashi and Junyeon Kim National Institute for Materials Science, Tsukuba 35-47, Japan Michihiko
Quantitative characterization of the spin orbit torque using harmonic all voltage measurements Masamitsu ayashi and Junyeon Kim National Institute for Materials Science, Tsukuba 35-47, Japan Michihiko
Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology
 EQPCM, ISSP, U. Tokyo June, 2013 Berry curvature and topological phases for magnons Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology Collaborators: R. Shindou (Tokyo Tech. Peking Univ.)
EQPCM, ISSP, U. Tokyo June, 2013 Berry curvature and topological phases for magnons Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology Collaborators: R. Shindou (Tokyo Tech. Peking Univ.)
Mesoscopic Spin Hall Effect in Multiprobe Semiconductor Bridges
 Mesoscopic Spin Hall Effect in Multiprobe Semiconductor Bridges Branislav K. Nikolić, Liviu P. Zârbo, and Satofumi Souma Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark, DE 19716-2570
Mesoscopic Spin Hall Effect in Multiprobe Semiconductor Bridges Branislav K. Nikolić, Liviu P. Zârbo, and Satofumi Souma Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark, DE 19716-2570
Transient grating measurements of spin diffusion. Joe Orenstein UC Berkeley and Lawrence Berkeley National Lab
 Transient grating measurements of spin diffusion Joe Orenstein UC Berkeley and Lawrence Berkeley National Lab LBNL, UC Berkeley and UCSB collaboration Chris Weber, Nuh Gedik, Joel Moore, JO UC Berkeley
Transient grating measurements of spin diffusion Joe Orenstein UC Berkeley and Lawrence Berkeley National Lab LBNL, UC Berkeley and UCSB collaboration Chris Weber, Nuh Gedik, Joel Moore, JO UC Berkeley
Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS. An Introduction to Theory and Experiment
 Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS An Introduction to Theory and Experiment With 230 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS An Introduction to Theory and Experiment With 230 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Two-terminal spin orbit torque magnetoresistive random access memory
 Two-terminal spin orbit torque magnetoresistive random access memory Noriyuki Sato 1, Fen Xue 1,3, Robert M. White 1,2, Chong Bi 1, and Shan X. Wang 1,2,* 1 Stanford University, Department of Electrical
Two-terminal spin orbit torque magnetoresistive random access memory Noriyuki Sato 1, Fen Xue 1,3, Robert M. White 1,2, Chong Bi 1, and Shan X. Wang 1,2,* 1 Stanford University, Department of Electrical
Current-induced four-state magnetization switching by spin-orbit torques in. perpendicular ferromagnetic trilayers
 Current-induced four-state magnetization switching by spin-orbit torques in perpendicular ferromagnetic trilayers Y. Sheng, 1,2 Y. C. Li, 2,3 X. Q. Ma, 1 K. Y. Wang 2,3,4 1 Department of Physics, University
Current-induced four-state magnetization switching by spin-orbit torques in perpendicular ferromagnetic trilayers Y. Sheng, 1,2 Y. C. Li, 2,3 X. Q. Ma, 1 K. Y. Wang 2,3,4 1 Department of Physics, University
Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects. Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST
 YKIS2007 (Kyoto) Nov.16, 2007 Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST Introduction Spin Hall effect spin Hall effect in
YKIS2007 (Kyoto) Nov.16, 2007 Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST Introduction Spin Hall effect spin Hall effect in
Physics of Semiconductors
 Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Concepts in Spin Electronics
 Concepts in Spin Electronics Edited by Sadamichi Maekawa Institutefor Materials Research, Tohoku University, Japan OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of Contributors xiii 1 Optical phenomena in magnetic
Concepts in Spin Electronics Edited by Sadamichi Maekawa Institutefor Materials Research, Tohoku University, Japan OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of Contributors xiii 1 Optical phenomena in magnetic
Spin orbit interaction induced spin-separation in platinum nanostructures
 Spin orbit interaction induced spin-separation in platinum nanostructures Koong Chee Weng 1,2, N. Chandrasekhar 1,2, Christian Miniatura 1,3 Berthold-Georg Englert 1,4 1 Department of Physics, National
Spin orbit interaction induced spin-separation in platinum nanostructures Koong Chee Weng 1,2, N. Chandrasekhar 1,2, Christian Miniatura 1,3 Berthold-Georg Englert 1,4 1 Department of Physics, National
Room-temperature perpendicular magnetization switching through giant spin-orbit torque from sputtered Bi x Se (1-x) topological insulator material
 Room-temperature perpendicular magnetization switching through giant spin-orbit torque from sputtered Bi x Se (1-x) topological insulator material Mahendra DC 1, Mahdi Jamali 2, Jun-Yang Chen 2, Danielle
Room-temperature perpendicular magnetization switching through giant spin-orbit torque from sputtered Bi x Se (1-x) topological insulator material Mahendra DC 1, Mahdi Jamali 2, Jun-Yang Chen 2, Danielle
Spin Hall magnetoresistance in metallic bilayers
 Spin Hall magnetoresistance in metallic bilayers Junyeon Kim 1, Peng Sheng 1, Saburo Takahashi, Seiji Mitani 1 and Masamitsu Hayashi 1* 1 National Institute for Materials Science, Tsukuba 35-47, Japan
Spin Hall magnetoresistance in metallic bilayers Junyeon Kim 1, Peng Sheng 1, Saburo Takahashi, Seiji Mitani 1 and Masamitsu Hayashi 1* 1 National Institute for Materials Science, Tsukuba 35-47, Japan
Observation of the intrinsic inverse spin Hall effect from ferromagnet
 Observation of the intrinsic inverse spin Hall effect from ferromagnet Ayaka Tsukahara #, Yuta Kitamura #, Eiji Shikoh, Yuichiro Ando, Teruya Shinjo and Masashi Shiraishi * # Graduate School of Engineering
Observation of the intrinsic inverse spin Hall effect from ferromagnet Ayaka Tsukahara #, Yuta Kitamura #, Eiji Shikoh, Yuichiro Ando, Teruya Shinjo and Masashi Shiraishi * # Graduate School of Engineering
Extrinsically vs. intrinsically driven spin Hall effect in disordered mesoscopic multiterminal bars
 February 2007 EPL, 77 (2007) 47004 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/77/47004 www.epljournal.org Extrinsically vs. intrinsically driven spin Hall effect in disordered mesoscopic multiterminal bars B. K. Nikolić and
February 2007 EPL, 77 (2007) 47004 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/77/47004 www.epljournal.org Extrinsically vs. intrinsically driven spin Hall effect in disordered mesoscopic multiterminal bars B. K. Nikolić and
Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures
 B. Halperin Spin lecture 1 Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures Behavior of non-equilibrium spin populations. Spin relaxation and spin transport. How does one produce
B. Halperin Spin lecture 1 Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures Behavior of non-equilibrium spin populations. Spin relaxation and spin transport. How does one produce
Damping of magnetization dynamics
 Damping of magnetization dynamics Andrei Kirilyuk! Radboud University, Institute for Molecules and Materials, Nijmegen, The Netherlands 1 2 Landau-Lifshitz equation N Heff energy gain:! torque equation:
Damping of magnetization dynamics Andrei Kirilyuk! Radboud University, Institute for Molecules and Materials, Nijmegen, The Netherlands 1 2 Landau-Lifshitz equation N Heff energy gain:! torque equation:
Mott Relation for Anomalous Hall and Nernst effects in
 Mott Relation for Anomalous Hall and Nernst effects in Ga -x Mn x As Ferromagnetic Semiconductors Yong Pu, Daichi Chiba 2, Fumihiro Matsukura 2, Hideo Ohno 2 and Jing Shi Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Mott Relation for Anomalous Hall and Nernst effects in Ga -x Mn x As Ferromagnetic Semiconductors Yong Pu, Daichi Chiba 2, Fumihiro Matsukura 2, Hideo Ohno 2 and Jing Shi Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Spintronics at Nanoscale
 Colloquium@NTHU Sep 22, 2004 Spintronics at Nanoscale Hsiu-Hau Lin Nat l Tsing-Hua Univ & Nat l Center for Theoretical Sciences What I have been doing Spintronics: Green s function theory for diluted magnetic
Colloquium@NTHU Sep 22, 2004 Spintronics at Nanoscale Hsiu-Hau Lin Nat l Tsing-Hua Univ & Nat l Center for Theoretical Sciences What I have been doing Spintronics: Green s function theory for diluted magnetic
Recent developments in spintronic
 Recent developments in spintronic Tomas Jungwirth nstitute of Physics ASCR, Prague University of Nottingham in collaboration with Hitachi Cambridge, University of Texas, Texas A&M University - Spintronics
Recent developments in spintronic Tomas Jungwirth nstitute of Physics ASCR, Prague University of Nottingham in collaboration with Hitachi Cambridge, University of Texas, Texas A&M University - Spintronics
Observation of an anti-damping spin-orbit torque originating from the Berry curvature
 Observation of an anti-damping spin-orbit torque originating from the Berry curvature H. Kurebayashi, 1, 2, Jairo Sinova, 3, 4, 5 D. Fang, 1 A. C. Irvine, 1 T. D. Skinner, 1 J. Wunderlich, 5, 6 V. Novák,
Observation of an anti-damping spin-orbit torque originating from the Berry curvature H. Kurebayashi, 1, 2, Jairo Sinova, 3, 4, 5 D. Fang, 1 A. C. Irvine, 1 T. D. Skinner, 1 J. Wunderlich, 5, 6 V. Novák,
Spin Current and Spin Seebeck Effect
 at Rome, Italy (September 18, 2013) Spin Current and Spin Seebeck Effect Sadamichi Maekawa Advanced Science Research Center (ASRC), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tokai and CREST-JST. Co-workers:
at Rome, Italy (September 18, 2013) Spin Current and Spin Seebeck Effect Sadamichi Maekawa Advanced Science Research Center (ASRC), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tokai and CREST-JST. Co-workers:
Metals: the Drude and Sommerfeld models p. 1 Introduction p. 1 What do we know about metals? p. 1 The Drude model p. 2 Assumptions p.
 Metals: the Drude and Sommerfeld models p. 1 Introduction p. 1 What do we know about metals? p. 1 The Drude model p. 2 Assumptions p. 2 The relaxation-time approximation p. 3 The failure of the Drude model
Metals: the Drude and Sommerfeld models p. 1 Introduction p. 1 What do we know about metals? p. 1 The Drude model p. 2 Assumptions p. 2 The relaxation-time approximation p. 3 The failure of the Drude model
Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface
 Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface Ilya Eremin Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Uni Bochum Work done in collaboration with: F. Nogueira
Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface Ilya Eremin Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Uni Bochum Work done in collaboration with: F. Nogueira
Abstract. I. Introduction
 Temperature dependence of spin diffusion length and spin Hall angle in Au and Pt Miren Isasa 1, Estitxu Villamor 1, Luis E. Hueso 1,2, Martin Gradhand 3 and Fèlix Casanova 1,2 1 CIC nanogune, 20018 Donostia-San
Temperature dependence of spin diffusion length and spin Hall angle in Au and Pt Miren Isasa 1, Estitxu Villamor 1, Luis E. Hueso 1,2, Martin Gradhand 3 and Fèlix Casanova 1,2 1 CIC nanogune, 20018 Donostia-San
Room temperature spin-orbit torque switching induced by a
 Room temperature spin-orbit torque switching induced by a topological insulator Jiahao Han 1, A. Richardella 2, Saima Siddiqui 1, Joseph Finley 1, N. Samarth 2 and Luqiao Liu 1* 1 Department of Electrical
Room temperature spin-orbit torque switching induced by a topological insulator Jiahao Han 1, A. Richardella 2, Saima Siddiqui 1, Joseph Finley 1, N. Samarth 2 and Luqiao Liu 1* 1 Department of Electrical
Interband effects and orbital suceptibility of multiband tight-binding models
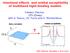 Interband effects and orbital suceptibility of multiband tight-binding models Frédéric Piéchon LPS (Orsay) with A. Raoux, J-N. Fuchs and G. Montambaux Orbital suceptibility Berry curvature ky? kx GDR Modmat,
Interband effects and orbital suceptibility of multiband tight-binding models Frédéric Piéchon LPS (Orsay) with A. Raoux, J-N. Fuchs and G. Montambaux Orbital suceptibility Berry curvature ky? kx GDR Modmat,
Spin transfer torque devices utilizing the giant spin Hall effect of tungsten
 Spin transfer torque devices utilizing the giant spin Hall effect of tungsten Chi-Feng Pai, 1,a) Luqiao Liu, 1 Y. Li, 1 H. W. Tseng, 1 D. C. Ralph 1,2 and R. A. Buhrman 1 1 Cornell University, Ithaca,
Spin transfer torque devices utilizing the giant spin Hall effect of tungsten Chi-Feng Pai, 1,a) Luqiao Liu, 1 Y. Li, 1 H. W. Tseng, 1 D. C. Ralph 1,2 and R. A. Buhrman 1 1 Cornell University, Ithaca,
Spin Funneling for Enhanced Spin Injection into Ferromagnets: Supplementary Information
 Spin Funneling for Enhanced Spin Injection into Ferromagnets: Supplementary Information Shehrin Sayed, Vinh Q. Diep, Kerem Yunus Camsari, and Supriyo Datta School of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Spin Funneling for Enhanced Spin Injection into Ferromagnets: Supplementary Information Shehrin Sayed, Vinh Q. Diep, Kerem Yunus Camsari, and Supriyo Datta School of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Tutorial: Berry phase and Berry curvature in solids
 Tutorial: Berry phase and Berry curvature in solids Justin Song Division of Physics, Nanyang Technological University (Singapore) & Institute of High Performance Computing (Singapore) Funding: (Singapore)
Tutorial: Berry phase and Berry curvature in solids Justin Song Division of Physics, Nanyang Technological University (Singapore) & Institute of High Performance Computing (Singapore) Funding: (Singapore)
Berry Phase Effects on Charge and Spin Transport
 Berry Phase Effects on Charge and Spin Transport Qian Niu 牛谦 University of Texas at Austin 北京大学 Collaborators: Shengyuan Yang, C.P. Chuu, D. Xiao, W. Yao, D. Culcer, J.R.Shi, Y.G. Yao, G. Sundaram, M.C.
Berry Phase Effects on Charge and Spin Transport Qian Niu 牛谦 University of Texas at Austin 北京大学 Collaborators: Shengyuan Yang, C.P. Chuu, D. Xiao, W. Yao, D. Culcer, J.R.Shi, Y.G. Yao, G. Sundaram, M.C.
An Intrinsic Spin Orbit Torque Nano-Oscillator
 arxiv:188.933v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 28 Aug 218 An Intrinsic Spin Orbit Torque Nano-Oscillator M. Haidar, 1 A. A. Awad, 1 M. Dvornik, 1 R. Khymyn, 1 A. Houshang, 1 J. Åkerman 1,2 1 Physics Department, University
arxiv:188.933v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 28 Aug 218 An Intrinsic Spin Orbit Torque Nano-Oscillator M. Haidar, 1 A. A. Awad, 1 M. Dvornik, 1 R. Khymyn, 1 A. Houshang, 1 J. Åkerman 1,2 1 Physics Department, University
Enhanced spin orbit torques by oxygen incorporation in tungsten films
 Enhanced spin orbit torques by oxygen incorporation in tungsten films Timothy Phung IBM Almaden Research Center, San Jose, California, USA 1 Motivation: Memory devices based on spin currents Spin Transfer
Enhanced spin orbit torques by oxygen incorporation in tungsten films Timothy Phung IBM Almaden Research Center, San Jose, California, USA 1 Motivation: Memory devices based on spin currents Spin Transfer
Switching of perpendicular magnetization by spin-orbit torques in the absence of. external magnetic fields. California 90095, United States
 Switching of perpendicular magnetization by spin-orbit torques in the absence of external magnetic fields Guoqiang Yu 1 *, Pramey Upadhyaya 1, Yabin Fan 1, Juan G Alzate 1, Wanjun Jiang 1, Kin L. Wong
Switching of perpendicular magnetization by spin-orbit torques in the absence of external magnetic fields Guoqiang Yu 1 *, Pramey Upadhyaya 1, Yabin Fan 1, Juan G Alzate 1, Wanjun Jiang 1, Kin L. Wong
Magnetism (Spins) Seen in a New Light. Muhammad Sabieh Anwar
 Magnetism (Spins) Seen in a New Light Muhammad Sabieh Anwar sabieh@lums.edu.pk Spring College on Optics, LUMS, 2016 Graphene and topological insulators Classes of Spintronic Effects Current induced torque
Magnetism (Spins) Seen in a New Light Muhammad Sabieh Anwar sabieh@lums.edu.pk Spring College on Optics, LUMS, 2016 Graphene and topological insulators Classes of Spintronic Effects Current induced torque
Strong Spin Hall Effect in the Antiferromagnet PtMn. Abstract
 Strong Spin Hall Effect in the Antiferromagnet Yongxi Ou 1, Shengjie Shi 1, D. C. Ralph 1,2, and R. A. Buhrman 1,* 1 Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853, USA 2 Kavli Institute at Cornell, Ithaca,
Strong Spin Hall Effect in the Antiferromagnet Yongxi Ou 1, Shengjie Shi 1, D. C. Ralph 1,2, and R. A. Buhrman 1,* 1 Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853, USA 2 Kavli Institute at Cornell, Ithaca,
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities
 Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
Topological Hall effect studied in simple models
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 74, 045327 2006 Topological Hall effect studied in simple models G. Metalidis* and P. Bruno Max-Planck-Institut für Mikrostrukturphysik, Weinberg 2, D-06120 Halle, Germany Received 24
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 74, 045327 2006 Topological Hall effect studied in simple models G. Metalidis* and P. Bruno Max-Planck-Institut für Mikrostrukturphysik, Weinberg 2, D-06120 Halle, Germany Received 24
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Magnetization switching through giant spin-orbit torque in a magnetically doped topological insulator heterostructure Yabin Fan, 1,,* Pramey Upadhyaya, 1, Xufeng Kou, 1, Murong Lang, 1 So Takei, 2 Zhenxing
Magnetization switching through giant spin-orbit torque in a magnetically doped topological insulator heterostructure Yabin Fan, 1,,* Pramey Upadhyaya, 1, Xufeng Kou, 1, Murong Lang, 1 So Takei, 2 Zhenxing
Influence of dephasing on the quantum Hall effect and the spin Hall effect
 Influence of dephasing on the quantum Hall effect and the spin Hall effect Yanxia Xing, 1 Qing-feng Sun, 1, * and Jian Wang 2 1 Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics and Institute of
Influence of dephasing on the quantum Hall effect and the spin Hall effect Yanxia Xing, 1 Qing-feng Sun, 1, * and Jian Wang 2 1 Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics and Institute of
Controllable chirality-induced geometrical Hall effect in a frustrated highlycorrelated
 Supplementary Information Controllable chirality-induced geometrical Hall effect in a frustrated highlycorrelated metal B. G. Ueland, C. F. Miclea, Yasuyuki Kato, O. Ayala Valenzuela, R. D. McDonald, R.
Supplementary Information Controllable chirality-induced geometrical Hall effect in a frustrated highlycorrelated metal B. G. Ueland, C. F. Miclea, Yasuyuki Kato, O. Ayala Valenzuela, R. D. McDonald, R.
Fokker-Planck calculation of spintorque switching rates: comparison with telegraph-noise data
 Fokker-Planck calculation of spintorque switching rates: comparison with telegraph-noise data P. B.Visscher and D. M. Apalkov Department of Physics and Astronomy The University of Alabama This project
Fokker-Planck calculation of spintorque switching rates: comparison with telegraph-noise data P. B.Visscher and D. M. Apalkov Department of Physics and Astronomy The University of Alabama This project
Magnetic switching by spin torque from the spin Hall effect
 Magnetic switching by spin torque from the spin Hall effect Luqiao Liu 1, O. J. Lee 1, T. J. Gudmundsen 1, D. C. Ralph 1,2 and R. A. Buhrman 1 1 Cornell University and 2 Kavli Institute at Cornell, Ithaca,
Magnetic switching by spin torque from the spin Hall effect Luqiao Liu 1, O. J. Lee 1, T. J. Gudmundsen 1, D. C. Ralph 1,2 and R. A. Buhrman 1 1 Cornell University and 2 Kavli Institute at Cornell, Ithaca,
CURRENT-INDUCED MAGNETIC DYNAMICS IN NANOSYSTEMS
 CURRENT-INDUCED MAGNETIC DYNAMICS IN NANOSYSTEMS J. Barna Department of Physics Adam Mickiewicz University & Institute of Molecular Physics, Pozna, Poland In collaboration: M Misiorny, I Weymann, AM University,
CURRENT-INDUCED MAGNETIC DYNAMICS IN NANOSYSTEMS J. Barna Department of Physics Adam Mickiewicz University & Institute of Molecular Physics, Pozna, Poland In collaboration: M Misiorny, I Weymann, AM University,
TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES
 TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES 1) Berry curvature in superlattice bands 2) Energy scales for Moire superlattices 3) Spin-Hall effect in graphene Leonid Levitov (MIT) @ ISSP U Tokyo MIT Manchester
TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES 1) Berry curvature in superlattice bands 2) Energy scales for Moire superlattices 3) Spin-Hall effect in graphene Leonid Levitov (MIT) @ ISSP U Tokyo MIT Manchester
Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators
 Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
Matching domain wall configuration and spin-orbit torques for very efficient domain-wall motion
 Matching domain wall configuration and spin-orbit torques for very efficient domain-wall motion A.V. Khvalkovskiy 1, V. Cros 2, D. Apalkov 1, V. Nikitin 1, M. Krounbi 1, K.A. Zvezdin 3, A. Anane 2, J.
Matching domain wall configuration and spin-orbit torques for very efficient domain-wall motion A.V. Khvalkovskiy 1, V. Cros 2, D. Apalkov 1, V. Nikitin 1, M. Krounbi 1, K.A. Zvezdin 3, A. Anane 2, J.
Gauge Physics of Spin Hall Effect
 Gauge Physics of Spin Hall Effect (1) Data Storage Institute, A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research), DSI Building, 5 Engineering Drive 1, Singapore 117608 (2) Computational Nanoelectronics
Gauge Physics of Spin Hall Effect (1) Data Storage Institute, A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research), DSI Building, 5 Engineering Drive 1, Singapore 117608 (2) Computational Nanoelectronics
Temperature dependence of spin diffusion length in silicon by Hanle-type spin. precession
 Temperature dependence of spin diffusion length in silicon by Hanle-type spin precession T. Sasaki 1,a), T. Oikawa 1, T. Suzuki 2, M. Shiraishi 3, Y. Suzuki 3, and K. Noguchi 1 SQ Research Center, TDK
Temperature dependence of spin diffusion length in silicon by Hanle-type spin precession T. Sasaki 1,a), T. Oikawa 1, T. Suzuki 2, M. Shiraishi 3, Y. Suzuki 3, and K. Noguchi 1 SQ Research Center, TDK
Interface control of the magnetic chirality in TaN CoFeB MgO heterosctructures
 Interface control of the magnetic chirality in TaN CoFeB MgO heterosctructures Jacob Torrejon 1, Junyeon Kim 1, Jaivardhan Sinha 1, Seiji Mitani 1 and Masamitsu Hayashi 1* 1 National Institute for Materials
Interface control of the magnetic chirality in TaN CoFeB MgO heterosctructures Jacob Torrejon 1, Junyeon Kim 1, Jaivardhan Sinha 1, Seiji Mitani 1 and Masamitsu Hayashi 1* 1 National Institute for Materials
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2008 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2008](/thumbs/72/67207946.jpg) Ballistic Intrinsic Spin-Hall Effect in HgTe Nanostructures C. Brüne 1, A. Roth 1, E.G. Novik 1, M. König 1, H. Buhmann 1, E.M. Hankiewicz, W. Hanke, J. Sinova 3, and L. W. Molenkamp 1 1 Physikalisches
Ballistic Intrinsic Spin-Hall Effect in HgTe Nanostructures C. Brüne 1, A. Roth 1, E.G. Novik 1, M. König 1, H. Buhmann 1, E.M. Hankiewicz, W. Hanke, J. Sinova 3, and L. W. Molenkamp 1 1 Physikalisches
The Physics of Nanoelectronics
 The Physics of Nanoelectronics Transport and Fluctuation Phenomena at Low Temperatures Tero T. Heikkilä Low Temperature Laboratory, Aalto University, Finland OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of symbols
The Physics of Nanoelectronics Transport and Fluctuation Phenomena at Low Temperatures Tero T. Heikkilä Low Temperature Laboratory, Aalto University, Finland OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of symbols
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 63, NO. 11, NOVEMBER
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 63, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2016 4499 All-Spin-Orbit Switching of Perpendicular Magnetization Mohammad Kazemi, Student Member, IEEE, Graham E. Rowlands, Shengjie Shi,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 63, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2016 4499 All-Spin-Orbit Switching of Perpendicular Magnetization Mohammad Kazemi, Student Member, IEEE, Graham E. Rowlands, Shengjie Shi,
Universal conductance fluctuation of mesoscopic systems in the metal-insulator crossover regime
 Universal conductance fluctuation of mesoscopic systems in the metal-insulator crossover regime Zhenhua Qiao, Yanxia Xing, and Jian Wang* Department of Physics and the Center of Theoretical and Computational
Universal conductance fluctuation of mesoscopic systems in the metal-insulator crossover regime Zhenhua Qiao, Yanxia Xing, and Jian Wang* Department of Physics and the Center of Theoretical and Computational
Hall Effect. Sergio O. Valenzuela. ICREA and Centre d Investigació en Nanociència i Nanotecnologia (ICN-CSIC), Barcelona.
 Nonlocal Spin Detection and the Spin Hall Effect Sergio O. Valenzuela Sergio.Valenzuela.icn@uab.es ICREA and Centre d Investigació en Nanociència i Nanotecnologia (ICN-CSIC), Barcelona CEMAG 2009 Zaragoza,
Nonlocal Spin Detection and the Spin Hall Effect Sergio O. Valenzuela Sergio.Valenzuela.icn@uab.es ICREA and Centre d Investigació en Nanociència i Nanotecnologia (ICN-CSIC), Barcelona CEMAG 2009 Zaragoza,
Determination of the Interfacial Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya Interaction (idmi) in the Inversion Symmetry Broken Systems
 Determination of the Interfacial Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya Interaction (idmi) in the Inversion Symmetry Broken Systems 27 Nov. 2015 Chun-Yeol You (cyyou@inha.ac.kr) Dept. of Physics, Inha University, Korea
Determination of the Interfacial Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya Interaction (idmi) in the Inversion Symmetry Broken Systems 27 Nov. 2015 Chun-Yeol You (cyyou@inha.ac.kr) Dept. of Physics, Inha University, Korea
Spin Orbit Coupling (SOC) in Graphene
 Spin Orbit Coupling (SOC) in Graphene MMM, Mirko Rehmann, 12.10.2015 Motivation Weak intrinsic SOC in graphene: [84]: Phys. Rev. B 80, 235431 (2009) [85]: Phys. Rev. B 82, 125424 (2010) [86]: Phys. Rev.
Spin Orbit Coupling (SOC) in Graphene MMM, Mirko Rehmann, 12.10.2015 Motivation Weak intrinsic SOC in graphene: [84]: Phys. Rev. B 80, 235431 (2009) [85]: Phys. Rev. B 82, 125424 (2010) [86]: Phys. Rev.
Spin transverse force on spin current in an electric field
 Title Spin transverse force on spin current in an electric field Author(s) Shen, SQ Citation Physical Review Letters, 005, v. 95 n. 18 Issued Date 005 URL http://hdl.handle.net/107/146197 Rights Physical
Title Spin transverse force on spin current in an electric field Author(s) Shen, SQ Citation Physical Review Letters, 005, v. 95 n. 18 Issued Date 005 URL http://hdl.handle.net/107/146197 Rights Physical
