C Nitrogen and others. D Oxygen and carbon
|
|
|
- Solomon Jacobs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 6.5A Knw that an element is a pure substance represented by chemical symbls. Knw AN ELEMENT IS A PURE SUBSTANCE REPRESENTED BY CHEMICAL SYMBOLS Element a pure substance that cannt be brken dwn chemically int simpler substances Chemical symbl represents the name f an element and is written as a capital letter r a capital letter fllwed by a lwercase letter Pssible examples may include: H: hydrgen He: helium N: nitrgen O: xygen C: carbn Cl: chlrine Na: sdium Ca: calcium 1 (5A) Which f the fllwing is the symbl fr chlrine? A Ch C Cl B C D Ce 2 (5A) The chemical symbl Ca represents A chlrine C carbn B cesium D calcium 5 (5B) Accrding t the Abundance f Elements in the Earth's Crust table abve, what percentage f the Earth's crust is made up f Ca and Na cmbined? A 7 B 2 6.5B Recgnize that a limited number f the many knwn elements cmprise the largest prtin f slid Earth, living matter, ceans, and the atmsphere. Recgnize A LIMITED NUMBER OF ELEMENTS COMPRISE THE LARGEST PORTION OF SOLID EARTH, LIVING MATTER, OCEANS, AND THE ATMOSPHERE Slid Earth O: xygen Si: silicn Living matter (SPONCH)* S: sulfur P: phsphrus O: xygen N: nitrgen C: carbn H: hydrgen Oceans O: xygen H: hydrgen Cl: chlrine Na: sdium Atmsphere N: nitrgen O: xygen 3 (5B) Accrding t the Abundance f Elements in Living Organisms table abve, mst mass f living rganisms is made up f which tw elements? A Hydrgen and xygen B Oxygen and nitrgen C Nitrgen and thers D Oxygen and carbn 4 (5A) Which f the fllwing is nt an element? C 5 D 28 6 (5A) The chemical frmula fr baking sda, a cmmn husehld chemical is NaHCO 3. Hw many elements are in this cmpund? A Helium B Nitrgen C Water D Sdium
2 6.5C Differentiate between elements and cmpunds n the mst basic level. Differentiate BETWEEN ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS ON THE MOST BASIC LEVEL Elements A pure substance made up f ne kind f atm Building blcks f all matter Organized n the Peridic Table f the elements Prperties can be used t identify different elements Subscripts identify hw many atms are in a substance Pssible examples f elements may include: C O2 N H2 Cmpund A pure substance made by chemically cmbining tw r mre elements The prprtin f each element in a cmpund is cnstant (if the subscript is changed, the substance is changed) Pssible examples f cmpunds may include: CO2: carbn dixide CO: carbn mnxide H2O: water NaCl: sdium chlride C6H12O6: glucse CaCO3: calcium carbnate SiO2: silicn dixide 7 (5C) Water has the chemical frmula H 2 O. Which statement crrectly states the number f hydrgen and xygen atms present in the chemical frmula fr water? A There is an equal number f hydrgen and xygen. B There is ne hydrgen atm fr every tw xygen atms. C There are tw hydrgen atms fr every ne xygen atm. D There are tw hydrgen atms fr every fur xygen atms. 10 (5D) A student had a beaker with a small amunt f baking sda. The student added a few drps f pickle juice t the baking sda and bserved fizzing and bubbling. Based n bservatin, which f these can the student cnclude? F A chemical reactin prduced a slid. G N chemical reactin tk place. H Only a physical change happened. J A chemical reactin prduced a gas. 11 (5D) Tw liquids are mixed tgether. Which f the fllwing des NOT identify the frmatin f a new substance? F A gas is prduced. G One liquid disslves int the ther. H The temperature changes. 6.5D Identify the frmatin f a new substance by using the evidence f a pssible chemical change such as prductin f a gas, change in temperature, prductin f a precipitate, r clr change. Students may be assessed by being asked t classify the prducts r reactants f a chemical equatin as an element r a cmpund. Identify THE FORMATION OF A NEW SUBSTANCE USING THE EVIDENCE OF A POSSIBLE CHEMICAL CHANGE Physical change change which alters the physical prperties f a substance withut changing its identity Chemical change the frmatin f a new substance with different prperties; cannt be undne by physical means Identify evidence f chemical change Prductin f a gas Odr Bubbling Change in temperature Prductin f a precipitate Precipitate the frmatin f slids frm a slutin Clr change (permanent) Prductin f light 8 (5D) Which clumn in the abve Physical and Chemical Changes table includes nly chemical changes? A A C C B B D D MCO 3 MO + CO 2 9 (5C) The prducts in the chemical equatin abve are best classified as F ne cmpund and ne element G tw elements H ne element and tw cmpunds J tw cmpunds J A slid is frmed. 12 (5D) During a science class investigatin, a teacher places a small amunt f sugar in a spn and heats it ver a candle. Which f the fllwing wuld be the best evidence that a change in the chemical prperties f the sugar has taken place? F The sugar gets htter G The sugar gets larger H The sugar turns int a liquid J The sugar turns black.
3 6.6A Cmpare metals, nnmetals, and metallids using physical prperties such as luster, cnductivity, r malleability. Cmpare METALS, NONMETALS, AND METALLOIDS USING PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Physical prperties Luster Cnductivity Malleability Magnetism Ductility States f matter Density Students must knw definitins and characteristics f the physical prperties f metals, nnmetals, and metallids in rder t classify substances by thse physical prperties. 13 (6A) A student is implementing an investigatin f physical prperties using samples f metals, nnmetals, and metallids. She used a battery, wires, and a bulb t test if each f the samples will cmplete the circuit causing the bulb t light. Next, she shined a bright light n each f the samples. Which physical prperties is the student investigating? A Streak and hardness B Luster and cnductivity C Streak and cnductivity 16 (6C) A student is testing several minerals in science class. First, the student scratched the minerals acrss a tile and then scratched the minerals with a cpper penny and a steel tl. What physical prperties is the student testing? F Clr and state G Streak and hardness H Luster and cnductivity J ph and fracture 6.6B Calculate density t identify an unknwn substance. Calculate DENSITY TO IDENTIFY AN UNKNOWN SUBSTANCE Density the amunt f matter that will fit int a given amunt f space Using, calculate density f bjects Density is measured in grams/cubic centimeter (g/cm 3 ) r grams/millimeter (g/ml) Use density t identify / classify an unknwn substance The density f a substance des nt change regardless f the quantity f the substance Vlume the amunt f space that a substance r bject ccupies Using L x W x H, calculate the vlume f a regularly shaped bject Using water displacement, determine the vlume f an irregularly shaped bject Using a graduated cylinder, determine the vlume f a liquid Vlume f a liquid is measured in milliliters (ml) Vlume f slids is measured in cubic centimeters (cm 3 ) 1 milliliter (ml) is equal t 1 cm 3 Mass the amunt f matter in smething Using a triple beam balance r spring scale determine the mass (g) f an bject D Hardness and luster 14 (6A) Cpper is a cmmn metal. Which f the fllwing prperties des this metal mst likely have? F Lw cnductivity, lw malleability, and lw luster G High cnductivity, high malleability, and lw luster H Lw cnductivity, high malleability, and high luster J High cnductivity, high malleability, and high luster 15 (6B) A student needs t find the density f a cube. Each side f the cube measures 3 cm and the mass f the cube is 12 g. What is the apprximate density f the cube? 17 (6B) A student measured the mass and vlume f a metal sample using a triple beam balance and a graduated cylinder. The sample has a mass f 16.7 grams and a vlume f 4.4 cm 3. What is the density f the metal sample? 6.6C Test the physical prperties f minerals, including hardness, clr, luster, and streak. Test PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF MINERALS Physical prperty prperty f matter that can be bserved withut changing the cmpsitin r identity f the matter Hardness - Mhs Hardness Scale Clr Luster Streak A 0.4 g/cm 3 C 4.0 g/cm 3 B 2.25 g/cm 3 D 36 g/cm 3 18 (6C) Hw the surface f a mineral appears when it reflects light is knwn as A streak C cnductivity B luster D hardness
4 6.8A Cmpare and cntrast ptential and kinetic energy. 6.8B Identify and describe the changes in psitin, directin, and speed f an bject when acted upn by unbalanced frces. Cmpare, Cntrast POTENTIAL AND KINETIC ENERGY Ptential energy stred energy f an bject because f its psitin r shape Psitin (pint f greatest and least ptential energy) Kinetic energy energy f mtin Psitin (pint f greatest and least kinetic energy) Transfrmatin (relatinship) between ptential and kinetic energy Pssible examples f transfrmatins between ptential and kinetic energy: Rller casters Buncing balls Pendulums Rubber bands Identify, Describe CHANGES TO AN OBJECT WHEN ACTED UPON BY UNBALANCED FORCES Balanced frces equal and ppsite frces n an bject that result in n change in psitin, directin, r mtin Unbalanced frces unequal frces n an bject that may result in a change in psitin, directin, r mtin Acceleratin change in an bject s mtin; caused by unbalanced frces Psitin (displacement) Directin Mtin Speed Examples f acceleratin Starting / stpping Speeding up / slwing dwn Changing directin 19 (8A) Accrding t the abve diagram, at what pint wuld the rller caster car have the greatest ptential energy? F 3 G 4 H 5 J 6 20 (8A) Accrding t the abve diagram, at what pint wuld the rller caster car have the greatest kinetic energy? A 3 B 4 C 5 D 6 22 (8B) Refer t the infrmatin and diagram abve. As the ball rises in the air, it is acted n by the frce f gravity. This frce causes the ball t F slw dwn, change directin, and then speed up until it falls t the grund G speed up, keep its same directin, and then slw dwn as it falls t the grund H travel at the same speed until it hits the grund J travel in the same directin until it hits the grund 6.8C Calculate average speed using distance and time measurements. Calculate AVERAGE SPEED USING MEASUREMENTS Fr example: 12.6 m / 9 s (STAAR Spring 2014 Administratin, Item #38). Average speed Students may be required t cnvert units f measure (minutes t hurs) prir t calculatins. 21 (8C) Observe the inclined plane and ball in the abve image. If the ball rlls dwn the inclined plane in the directin f the arrw in 2.42 secnds, what is the average speed f the ball during the rll? F 4.96 m/s H 1.65 m/s G 2.07 m/s J 1.24 m/s 23 (8C) Refer t the abve infrmatin and table. What was the average speed f the wind-up-ty during the three trials t the nearest hundredth f a cm/s? F cm/s G 6.50 cm/s H cm/s J 8.20 cm/s
5 6.8D Measure and graph changes in mtin. Measure, Graph CHANGES IN MOTION Distance ver time Speed ver time Interpreting and cmparing graph lines shwing the fllwing scenaris Cnstant speed Increasing speed Decreasing speed N mtin (stpped) 24 (8D) A dg walks away frm hme at a cnstant pace fr 20 minutes. Next, he stps fr a 10 minute nap under a tree. Finally, he walks back hme at a cnstant pace and cmes t a stp. Which graph belw best represents the mtin f the dg in terms f distance frm hme ver time? 26 (8D) The graph abve shws the mtin f a car. Which statement belw best describes the mtin f the car? 6.8E Investigate hw inclined planes and pulleys can be used t change the amunt f frce t mve an bject. Investigate HOW THE AMOUNT OF FORCE NEEDED TO MOVE AN OBJECT CAN BE CHANGED Using simple machines t change the amunt f frce r the directin t mve an bject Mving an bject with an inclined plane Mving an bject withut an inclined plane When raising an bject t a specific height, the amunt f frce will be less when using an inclined plane cmpared t the amunt f frce needed t d the same wrk withut an inclined plane. Mving an bject with a pulley Single fixed pulley (des nt change frce; nly directin) Single mvable pulley (changes frce) Cmpund pulley (changes frce) Mving an bject withut a pulley F H G J 25 (8E) Which inclined plane requires the mst frce t push the ball t the tp? F G A The car is stpped fr tw minutes, travels at a cnstant speed fr tw minutes, and then stps. B The car is stpped fr tw minutes, increases its speed ver tw minutes, and then stps. C The car travels at a cnstant speed fr tw minutes, increases its speed ver tw minutes and then travels at a cnstant speed fr tw mre minutes. D The car increases its speed fr tw minutes, travels at a cnstant speed fr tw minutes and then increases its speed ver the next tw minutes. H J
6 6.9A Investigate methds f thermal energy transfer, including cnductin, cnvectin, and radiatin. 6.9B Verify thrugh investigatins that thermal energy mves in a predictable pattern frm warmer t cler until all the substances attain the same temperature such as an ice cube melting 6.9C Demnstrate energy transfrmatins such as energy in a flashlight battery changes frm chemical energy t electrical energy t light energy. Investigate METHODS OF THERMAL ENERGY TRANSFER Thermal energy can be transferred frm ne system t anther (r frm a system t its envirnment) in different ways Cnductin transfer f heat thrugh direct cntact frm a warmer substance t a cler substance Cnvectin transfer f thermal energy, in a liquid r gas, in which the warmer substance rises and the cler substance sinks; frms a current Radiatin the transfer f energy frm a light surce (e.g., Sun, fire, light bulb, burner) t an bject r substance Investigate, Verify THERMAL ENERGY MOVES IN A PREDICTABLE PATTERN Thermal energy mvement Frm warmer t cler Until all the substances attain the same temperature Ice cube melting Additinal pssible examples may include: Cnvectin tanks / tubes Demnstrate ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS Transfrmatins between frms f energy Chemical Thermal Light (radiant) Mechanical Electrical Example f energy transfrmatin Energy in a flashlight battery changes frm chemical energy t electrical energy t light energy Pssible additinal examples may include: Ht air balln rising An engine causing a car t mve A wind turbine system A hydrelectric pwer plant One animal cnsuming anther animal An animal cnsuming a plant (prducer) 27 (9A) The diagram abve shws an ice cube placed in a ht pan. Thermal energy is being transferred t the ice cube frm the pan shwn abve by F cnvectin H radiatin G cnductin J cnservatin 28 (9B) An ice cube is placed nt a ht pan that is sitting n the cunter tp as shwn abve. Hw will the thermal energy mve? A The cldness will mve frm the pan t the ice cube. B The cldness will mve frm the ice cube t the pan. C The heat will travel frm the pan t the ice cube. D The heat will mve frm the ice cube t the pan. 29 (9A) A student is drinking a cup f ht chclate as they sit by a campfire n a chilly evening. They knw that the cup f ht chclate transfers thermal energy t the surrunding air. The heated air ver their cup f ht chclate expands and rises and is replaced by cler, denser air. This methd f energy transfer is F cnvectin H cnductin G cndensatin J radiatin 30 (9B) A student is investigating hw heat mves. The student heated a nail t 100 C and placed it int 250 ml f 20 C water. What is the mst likely temperature f the water and the nail 30 minutes later? F The water is 10 C, and the nail is 110 C. G The water is 40 C, and the nail is 40 C. H The water is 70 C, and the nail is 40 C. J The water is 100 C, and the nail is 70 C. 31 (9C) Electrical energy is being prduced by transfrmatin frm nuclear energy and added t ur natin's pwer grid. Sme f the electrical pwer yu use may cme frm nuclear energy. Use the flw map t see hw energy is transfrmed frm nuclear t electrical. Identify the energy transfrmatins f each step in the diagram abve. Example: Radiactive atms are split in a nuclear reactr t heat water t steam. nuclear energy t thermal energy Part A. The spinning turbine turns an electrical generatr. t Part B. Electrical energy frm the generatr is sent acrss pwer lines t d such things as turn n lights. t
7 6.10A Build a mdel t illustrate the structural layers f Earth, including the inner cre, uter cre, mantle, crust, asthensphere, and lithsphere. 6.10B Classify rcks as metamrphic, igneus, r sedimentary by the prcesses f their frmatin. Build A MODEL TO ILLUSTRATE THE STRUCTURAL LAYERS OF EARTH Inner cre Outer cre Mantle Crust Asthensphere Lithsphere Classify ROCKS BY THE PROCESS OF THEIR FORMATION Types f rcks Metamrphic Frmed when igneus r sedimentary rcks are put under heat and / r pressure in the Earth s crust Igneus Frmed when crystallized thrugh melting and cling Magma Lava Sedimentary Frmed thrugh the accumulatin f sediment Cmpactin prcess by which verlying pressure frm rcks and sil reduces the size r vlume f sediments Cementatin prcess f binding and hardening sediments int hard rck Sedimentatin the depsitin f slid material frm being suspended in a fluid (water) Rck cycle the cntinual prcess by which rcks can be changed int different types f rck 32 (10A) Sme students use an apple t represent the Earth. What is the best reasn t use an apple fr this cmparisn? F The skin f an apple is very thin, and the crust f the Earth is very thin. G The flesh f an apple is made f the same material all the way thrugh, and the interir f the Earth is the same all the way thrugh. H The seeds f the apple are very light in cmparisn t the rest f the apple, and the cre f the Earth is als made f very light matter. J The stem f the apple cmes frm the cre and the Nrth Ple cmes frm the Earth s cre. 33 (10A) A student wanted t make a mdel f the Earth. The student decided t cut a giant Styrfam ball in half and paint the layers n it t shw their thickness. Which mdel belw best represents the layers f the Earth? F H J G 34 (10B) A student made peanut butter bars by pressing a layer f graham cracker crumbs int a baking pan. Next, the student added a layer f a peanut butter mixture and then added a layer f crushed peanuts. Lastly, the student added a layer f chclate frsting. The prcess f making peanut butter bars is mst like the frmatin f what type f rck? A Igneus C Sedimentary 35 B Metamrphic D Magma What prcess is ccurring at lcatin W? A Pressure and cementatin B Weathering and ersin C Heating and melting D Cling and hardening
8 6.11A Describe the physical prperties, lcatins, and mvements f the Sun, planets, Galilean mns, meters, asterids, and cmets. 6.11B Understand that gravity is the frce that gverns the mtin f ur slar system. Describe PHYSICAL PROPERTIES, LOCATIONS, AND MOVEMENTS OF OBJECTS THAT COMPRISE THE SOLAR SYSTEM Physical prperties f bjects Temperature Cmparative size / mass Cmpsitin Terrestrials vs. gas giants Atmsphere Lcatin f bjects Relative distance frm Sun Mvement f bjects Orbits Rtatin Revlutin Objects in the slar system Sun Planets Galilean mns Asterids Meters Cmets Understand GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS THE MOTION OF OUR SOLAR SYSTEM Gravity frce f attractin between tw bjects due t their masses Larger masses have a larger gravitatinal frce than smaller masses Recgnize gravitatinal attractin (frce) between Sun and Mn Sun and planets Planets travel in a curved path (ellipse) instead f a straight line Planets and their mn(s) Sun and ther bjects in ur slar system Mtin f ur slar system Revlutin Orbit 36 (11B) On which planet wuld a persn weigh the least? A Jupiter C Mercury B Venus D Earth 37 (11A) Scientists bserved a rcky, rtating bject rbiting in space. It was 250 km wide. The rcky bject was lcated several times farther away frm the Sun than the Earth. The bject is mst likely F Venus H Mars G the Mn J an asterid 38 (11B) The Sun is the center f ur slar system and creates a large amunt f gravitatinal frce. If this system lst the Sun, what wuld happen t the planets? F The planets wuld explde. G The planets wuld stp mving. H The planets wuld travel in a straight line. 39 (11A) Which f the fllwing represents characteristics f the fur planets farthest frm the Sun? F Smaller planets G Gas giants H Rcky (terrestrial) planets J 3 r less mns 40 (11A) Which graph illustrates the diameter f the inner planets? A B J The planets wuld cntinue n their same path. C
9 6.11C Describe the histry and future f space explratin, including the types f equipment and transprtatin needed fr space travel. Describe THE HISTORY AND FUTURE OF SPACE EXPLORATION Histry and Future First liquid fueled rcket (Gddard) First rcket t reach space (Vn Braun) First artificial satellite (Sputnik 1) First csmnaut t rbit the Earth (Yuri) Explratin f the mn (Apll prgram) First human t walk n the Mn (Armstrng) U.S. Space Shuttle Prgram Hubble Space Telescpe Internatinal Space Statin Prgram Mars Explratin Prgram Outer planetary unmanned explratin Types f equipment and transprtatin Rckets Satellites Space shuttles Space prbes Space statin 41 (11C) A prbe is a vehicle designed t carry instruments, but nt crew. T which f the fllwing places wuld we mst likely send a prbe? F The Internatinal Space Statin G Inside the Sun H Muntain tp J Saturn 42 (11C) Over time, NASA has develped many different vehicles t carry men and wmen int space. These craft have changed t allw lnger stays in space, carry mre astrnauts, and cnduct mre investigatins. Until recently, the U.S. has used the space shuttle. The space shuttle differed frm previus space vehicles because it 43 (11C) This diagram prvides sme imprtant dates in the histry f space explratin as it relates t the mn. After scientists had a clear picture f the surface f the Mn, they landed an unmanned craft befre risking human life. The Sviets landed the first unmanned craft n the Mn, named Luna 9. Which f the fllwing is the mst reasnable time perid fr this missin t have taken place? A Smetime befre 1959 B Between 1959 and 1965 F was reusable C Between 1965 and 1969 G culd carry mre than ne persn D Smetime after 1969 H culd travel beynd Earth's rbit J was airtight
C Nitrogen and others. D Oxygen and carbon
 6.5A Knw that an element is a pure substance represented by chemical symbls. Knw AN ELEMENT IS A PURE SUBSTANCE REPRESENTED BY CHEMICAL SYMBOLS Element a pure substance that cannt be brken dwn chemically
6.5A Knw that an element is a pure substance represented by chemical symbls. Knw AN ELEMENT IS A PURE SUBSTANCE REPRESENTED BY CHEMICAL SYMBOLS Element a pure substance that cannt be brken dwn chemically
First Semester 6 th Grade Exam Review
 Name: Perid First Semester 6 th Grade Exam Review Exam Schedule: Tuesday, Dec. 18 th -4 th Perid Wednesday, Dec 19 th - 2 nd & 7 th Perids Thursday, Dec. 20 th - 3 rd and 6 th Perids Friday, Dec. 21 th
Name: Perid First Semester 6 th Grade Exam Review Exam Schedule: Tuesday, Dec. 18 th -4 th Perid Wednesday, Dec 19 th - 2 nd & 7 th Perids Thursday, Dec. 20 th - 3 rd and 6 th Perids Friday, Dec. 21 th
Benchmark review 2014
 Benchmark review 2014 Elements vs Cmpunds: 1. What is the difference between an element and a cmpund? Element = a pure substance Cmpund = 2 r mre elements chemically cmbined 2. What are elements represented
Benchmark review 2014 Elements vs Cmpunds: 1. What is the difference between an element and a cmpund? Element = a pure substance Cmpund = 2 r mre elements chemically cmbined 2. What are elements represented
Matter Content from State Frameworks and Other State Documents
 Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 Spring, 2016
 OBJECTIVES 1. Ft Pressure EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 Spring, 2016 Determine the surface area f an bject. Given the weight and surface area, calculate the pressure. 2. Measuring Vlume & Mass Prvided a
OBJECTIVES 1. Ft Pressure EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 Spring, 2016 Determine the surface area f an bject. Given the weight and surface area, calculate the pressure. 2. Measuring Vlume & Mass Prvided a
Chapter 1 Notes Using Geography Skills
 Chapter 1 Ntes Using Gegraphy Skills Sectin 1: Thinking Like a Gegrapher Gegraphy is used t interpret the past, understand the present, and plan fr the future. Gegraphy is the study f the Earth. It is
Chapter 1 Ntes Using Gegraphy Skills Sectin 1: Thinking Like a Gegrapher Gegraphy is used t interpret the past, understand the present, and plan fr the future. Gegraphy is the study f the Earth. It is
Science 9 Unit 2: Atoms, Elements and Compounds
 Science 9 Unit 2: Atms, Elements and Cmpunds demnstrate a knwledge f WHMIS standards by using prper techniques fr handling and dispsing f lab materials (209-7) cmpare earlier cnceptins f the structure
Science 9 Unit 2: Atms, Elements and Cmpunds demnstrate a knwledge f WHMIS standards by using prper techniques fr handling and dispsing f lab materials (209-7) cmpare earlier cnceptins f the structure
ASTRODYNAMICS. o o o. Early Space Exploration. Kepler's Laws. Nicolaus Copernicus ( ) Placed Sun at center of solar system
 ASTRODYNAMICS Early Space Explratin Niclaus Cpernicus (1473-1543) Placed Sun at center f slar system Shwed Earth rtates n its axis nce a day Thught planets rbit in unifrm circles (wrng!) Jhannes Kepler
ASTRODYNAMICS Early Space Explratin Niclaus Cpernicus (1473-1543) Placed Sun at center f slar system Shwed Earth rtates n its axis nce a day Thught planets rbit in unifrm circles (wrng!) Jhannes Kepler
Accelerated Chemistry POGIL: Half-life
 Name: Date: Perid: Accelerated Chemistry POGIL: Half-life Why? Every radiistpe has a characteristic rate f decay measured by its half-life. Half-lives can be as shrt as a fractin f a secnd r as lng as
Name: Date: Perid: Accelerated Chemistry POGIL: Half-life Why? Every radiistpe has a characteristic rate f decay measured by its half-life. Half-lives can be as shrt as a fractin f a secnd r as lng as
Chapter One. Matter and Energy - Chemistry the study of matter and its changes the "central science" Natural Laws
 Chapter One Matter and Measurement http://www.chemistry.armstrng.edu/ nivens/curse_list.htm OWL HOMEWORK REQUIRED!!! Matter and Energy - Chemistry the study f matter and its changes the "central science"
Chapter One Matter and Measurement http://www.chemistry.armstrng.edu/ nivens/curse_list.htm OWL HOMEWORK REQUIRED!!! Matter and Energy - Chemistry the study f matter and its changes the "central science"
Examples: 1. How much heat is given off by a 50.0 g sample of copper when it cools from 80.0 to 50.0 C?
 NOTES: Thermchemistry Part 1 - Heat HEAT- TEMPERATURE - Thermchemistry: the study f energy (in the frm f heat) changes that accmpany physical & chemical changes heat flws frm high t lw (ht cl) endthermic
NOTES: Thermchemistry Part 1 - Heat HEAT- TEMPERATURE - Thermchemistry: the study f energy (in the frm f heat) changes that accmpany physical & chemical changes heat flws frm high t lw (ht cl) endthermic
A Chemical Reaction occurs when the of a substance changes.
 Perid: Unit 8 Chemical Reactin- Guided Ntes Chemical Reactins A Chemical Reactin ccurs when the f a substance changes. Chemical Reactin: ne r mre substances are changed int ne r mre new substances by the
Perid: Unit 8 Chemical Reactin- Guided Ntes Chemical Reactins A Chemical Reactin ccurs when the f a substance changes. Chemical Reactin: ne r mre substances are changed int ne r mre new substances by the
Study Guide: PS. 10 Motion, Forces, Work & Simple Machines DESCRIBING MOTION SPEED
 DESCRIBING MOTION Distance: hw far smething has mved; SI unit meters (m) Reference pint: nn-mving bject used as a cmparisn pint t detect an bject s mtin. Displacement: the distance between the starting
DESCRIBING MOTION Distance: hw far smething has mved; SI unit meters (m) Reference pint: nn-mving bject used as a cmparisn pint t detect an bject s mtin. Displacement: the distance between the starting
Student Exploration: Cell Energy Cycle
 Name: Date: Student Explratin: Cell Energy Cycle Vcabulary: aerbic respiratin, anaerbic respiratin, ATP, cellular respiratin, chemical energy, chlrphyll, chlrplast, cytplasm, glucse, glyclysis, mitchndria,
Name: Date: Student Explratin: Cell Energy Cycle Vcabulary: aerbic respiratin, anaerbic respiratin, ATP, cellular respiratin, chemical energy, chlrphyll, chlrplast, cytplasm, glucse, glyclysis, mitchndria,
NGSS High School Physics Domain Model
 NGSS High Schl Physics Dmain Mdel Mtin and Stability: Frces and Interactins HS-PS2-1: Students will be able t analyze data t supprt the claim that Newtn s secnd law f mtin describes the mathematical relatinship
NGSS High Schl Physics Dmain Mdel Mtin and Stability: Frces and Interactins HS-PS2-1: Students will be able t analyze data t supprt the claim that Newtn s secnd law f mtin describes the mathematical relatinship
EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 FALLF, 2017
 OBJECTIVES 1. Ft Pressure EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 FALLF, 2017 Determine the surface area f an bject. Given the weight and surface area, calculate the pressure. 2. Measuring Vlume & Mass Prvided a
OBJECTIVES 1. Ft Pressure EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 FALLF, 2017 Determine the surface area f an bject. Given the weight and surface area, calculate the pressure. 2. Measuring Vlume & Mass Prvided a
Electric Current and Resistance
 Electric Current and Resistance Electric Current Electric current is the rate f flw f charge thrugh sme regin f space The SI unit f current is the ampere (A) 1 A = 1 C / s The symbl fr electric current
Electric Current and Resistance Electric Current Electric current is the rate f flw f charge thrugh sme regin f space The SI unit f current is the ampere (A) 1 A = 1 C / s The symbl fr electric current
making triangle (ie same reference angle) ). This is a standard form that will allow us all to have the X= y=
 Intrductin t Vectrs I 21 Intrductin t Vectrs I 22 I. Determine the hrizntal and vertical cmpnents f the resultant vectr by cunting n the grid. X= y= J. Draw a mangle with hrizntal and vertical cmpnents
Intrductin t Vectrs I 21 Intrductin t Vectrs I 22 I. Determine the hrizntal and vertical cmpnents f the resultant vectr by cunting n the grid. X= y= J. Draw a mangle with hrizntal and vertical cmpnents
Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry. Topic 1: Principles of chemistry. Chemical formulae, equations and calculations. Notes.
 Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Tpic 1: Principles f chemistry Chemical frmulae, equatins and calculatins Ntes 1.25 write wrd equatins and balanced chemical equatins (including state symbls): fr reactins studied
Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Tpic 1: Principles f chemistry Chemical frmulae, equatins and calculatins Ntes 1.25 write wrd equatins and balanced chemical equatins (including state symbls): fr reactins studied
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
 Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I)
 1 General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I) CDS Chapter 14: Physical Prperties f Gases Observatin 1: Pressure- Vlume Measurements n Gases The spring f air is measured as pressure, defined as the
1 General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I) CDS Chapter 14: Physical Prperties f Gases Observatin 1: Pressure- Vlume Measurements n Gases The spring f air is measured as pressure, defined as the
Chapter 11: Atmosphere
 Chapter 11: Atmsphere Sectin 1: Atmspheric Basics Objectives 1. Describe the cmpsitin f the atmsphere. 2. Cmpare and cntrast the varius layers f the atmsphere. 3. Identify three methds f transferring energy
Chapter 11: Atmsphere Sectin 1: Atmspheric Basics Objectives 1. Describe the cmpsitin f the atmsphere. 2. Cmpare and cntrast the varius layers f the atmsphere. 3. Identify three methds f transferring energy
Chapter 30: Stars. B. The Solar Interior 1. Core : the combining of lightweight nuclei into heavier nuclei
 Chapter 30: Stars Sectin 1: The Sun Objectives 1. Explre the structure f the Sun. 2. Describe the slar activity cycle and hw the Sun affects Earth. 3. Cmpare the different types f spectra. A. Prperties
Chapter 30: Stars Sectin 1: The Sun Objectives 1. Explre the structure f the Sun. 2. Describe the slar activity cycle and hw the Sun affects Earth. 3. Cmpare the different types f spectra. A. Prperties
4 Fe + 3 O 2 2 Fe 2 O 3
 UNIT 7: STOICHIOMETRY NOTES (chapter 9) INTRO TO STOICHIOMETRY Reactin Stichimetry: Stichimetry is simply a way t shw f smething this is. Relatinship between a given and an unknwn: GIVEN UNKNOWN Type 1
UNIT 7: STOICHIOMETRY NOTES (chapter 9) INTRO TO STOICHIOMETRY Reactin Stichimetry: Stichimetry is simply a way t shw f smething this is. Relatinship between a given and an unknwn: GIVEN UNKNOWN Type 1
Lesson 8: Types of Matter
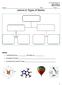 NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 8: Types f Matter Matter: anything that has and takes up Examples f matter: Examples that are NOT matter: _ 1 Pure substances: Elements and Cmpunds a material that has a
NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 8: Types f Matter Matter: anything that has and takes up Examples f matter: Examples that are NOT matter: _ 1 Pure substances: Elements and Cmpunds a material that has a
CHEM 103 Calorimetry and Hess s Law
 CHEM 103 Calrimetry and Hess s Law Lecture Ntes March 23, 2006 Prf. Sevian Annuncements Exam #2 is next Thursday, March 30 Study guide, practice exam, and practice exam answer key are already psted n the
CHEM 103 Calrimetry and Hess s Law Lecture Ntes March 23, 2006 Prf. Sevian Annuncements Exam #2 is next Thursday, March 30 Study guide, practice exam, and practice exam answer key are already psted n the
Differentiation Applications 1: Related Rates
 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Unit 9: The Mole- Guided Notes What is a Mole?
 Unit 9: The Mle- Guided Ntes What is a Mle? A mle is a name fr a specific f things Similar t a r a One mle is equal t 602 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 That s 602 with zers A mle is NOT an abbreviatin
Unit 9: The Mle- Guided Ntes What is a Mle? A mle is a name fr a specific f things Similar t a r a One mle is equal t 602 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 That s 602 with zers A mle is NOT an abbreviatin
14. Which shows the direction of the centripetal force acting on a mass spun in a vertical circle?
 Physics 0 Public Exam Questins Unit 1: Circular Mtin NAME: August 009---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. Which describes
Physics 0 Public Exam Questins Unit 1: Circular Mtin NAME: August 009---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. Which describes
14. Which shows the direction of the centripetal force acting on a mass spun in a vertical circle?
 Physics 3204 Public Exam Questins Unit 1: Circular Mtin NAME: August 2009---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12. Which
Physics 3204 Public Exam Questins Unit 1: Circular Mtin NAME: August 2009---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12. Which
AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY
 AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY Energy- the capacity t d wrk r t prduce heat 1 st Law f Thermdynamics: Law f Cnservatin f Energy- energy can be cnverted frm ne frm t anther but it can be neither
AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY Energy- the capacity t d wrk r t prduce heat 1 st Law f Thermdynamics: Law f Cnservatin f Energy- energy can be cnverted frm ne frm t anther but it can be neither
Exhibit Alignment with SC Science Standards 8 th Grade
 Scientific Inquiry Standard 8-1: The student will demnstrate an understanding f technlgical design and scientific inquiry, including prcess skills, mathematical thinking, cntrlled investigative design
Scientific Inquiry Standard 8-1: The student will demnstrate an understanding f technlgical design and scientific inquiry, including prcess skills, mathematical thinking, cntrlled investigative design
Lesson 8 Types of Matter
 Lessn 8 Types f Matter D Nw 6Ga, 6I 10.30.18 Take ut HW 6.13 t be checked. In CJ, cpy dwn inf frm CJ bard. Keep CJs ut and pen n desk. On DO NOW PAGE #4, cpy and answer the questins: 1. In KCl (aq), is
Lessn 8 Types f Matter D Nw 6Ga, 6I 10.30.18 Take ut HW 6.13 t be checked. In CJ, cpy dwn inf frm CJ bard. Keep CJs ut and pen n desk. On DO NOW PAGE #4, cpy and answer the questins: 1. In KCl (aq), is
Unit 14 Thermochemistry Notes
 Name KEY Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 14 Thermchemistry Ntes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
Name KEY Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 14 Thermchemistry Ntes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
SPH3U1 Lesson 06 Kinematics
 PROJECTILE MOTION LEARNING GOALS Students will: Describe the mtin f an bject thrwn at arbitrary angles thrugh the air. Describe the hrizntal and vertical mtins f a prjectile. Slve prjectile mtin prblems.
PROJECTILE MOTION LEARNING GOALS Students will: Describe the mtin f an bject thrwn at arbitrary angles thrugh the air. Describe the hrizntal and vertical mtins f a prjectile. Slve prjectile mtin prblems.
Phys101 Final Code: 1 Term: 132 Wednesday, May 21, 2014 Page: 1
 Phys101 Final Cde: 1 Term: 1 Wednesday, May 1, 014 Page: 1 Q1. A car accelerates at.0 m/s alng a straight rad. It passes tw marks that are 0 m apart at times t = 4.0 s and t = 5.0 s. Find the car s velcity
Phys101 Final Cde: 1 Term: 1 Wednesday, May 1, 014 Page: 1 Q1. A car accelerates at.0 m/s alng a straight rad. It passes tw marks that are 0 m apart at times t = 4.0 s and t = 5.0 s. Find the car s velcity
Introduction to Spacetime Geometry
 Intrductin t Spacetime Gemetry Let s start with a review f a basic feature f Euclidean gemetry, the Pythagrean therem. In a twdimensinal crdinate system we can relate the length f a line segment t the
Intrductin t Spacetime Gemetry Let s start with a review f a basic feature f Euclidean gemetry, the Pythagrean therem. In a twdimensinal crdinate system we can relate the length f a line segment t the
Study Guide Physics Pre-Comp 2013
 I. Scientific Measurement Metric Units S.I. English Length Meter (m) Feet (ft.) Mass Kilgram (kg) Pund (lb.) Weight Newtn (N) Ounce (z.) r pund (lb.) Time Secnds (s) Secnds (s) Vlume Liter (L) Galln (gal)
I. Scientific Measurement Metric Units S.I. English Length Meter (m) Feet (ft.) Mass Kilgram (kg) Pund (lb.) Weight Newtn (N) Ounce (z.) r pund (lb.) Time Secnds (s) Secnds (s) Vlume Liter (L) Galln (gal)
Lecture 13: Electrochemical Equilibria
 3.012 Fundamentals f Materials Science Fall 2005 Lecture 13: 10.21.05 Electrchemical Equilibria Tday: LAST TIME...2 An example calculatin...3 THE ELECTROCHEMICAL POTENTIAL...4 Electrstatic energy cntributins
3.012 Fundamentals f Materials Science Fall 2005 Lecture 13: 10.21.05 Electrchemical Equilibria Tday: LAST TIME...2 An example calculatin...3 THE ELECTROCHEMICAL POTENTIAL...4 Electrstatic energy cntributins
https://goo.gl/eaqvfo SUMMER REV: Half-Life DUE DATE: JULY 2 nd
 NAME: DUE DATE: JULY 2 nd AP Chemistry SUMMER REV: Half-Life Why? Every radiistpe has a characteristic rate f decay measured by its half-life. Half-lives can be as shrt as a fractin f a secnd r as lng
NAME: DUE DATE: JULY 2 nd AP Chemistry SUMMER REV: Half-Life Why? Every radiistpe has a characteristic rate f decay measured by its half-life. Half-lives can be as shrt as a fractin f a secnd r as lng
CHE 105 EXAMINATION III November 11, 2010
 CHE 105 EXAMINATION III Nvember 11, 2010 University f Kentucky Department f Chemistry READ THESE DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY BEFORE STARTING THE EXAMINATION! It is extremely imprtant that yu fill in the answer
CHE 105 EXAMINATION III Nvember 11, 2010 University f Kentucky Department f Chemistry READ THESE DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY BEFORE STARTING THE EXAMINATION! It is extremely imprtant that yu fill in the answer
Unit 11 Solutions- Guided Notes. What are alloys? What is the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures?
 Name: Perid: Unit 11 Slutins- Guided Ntes Mixtures: What is a mixture and give examples? What is a pure substance? What are allys? What is the difference between hetergeneus and hmgeneus mixtures? Slutins:
Name: Perid: Unit 11 Slutins- Guided Ntes Mixtures: What is a mixture and give examples? What is a pure substance? What are allys? What is the difference between hetergeneus and hmgeneus mixtures? Slutins:
Chem 163 Section: Team Number: ALE 24. Voltaic Cells and Standard Cell Potentials. (Reference: 21.2 and 21.3 Silberberg 5 th edition)
 Name Chem 163 Sectin: Team Number: ALE 24. Vltaic Cells and Standard Cell Ptentials (Reference: 21.2 and 21.3 Silberberg 5 th editin) What des a vltmeter reading tell us? The Mdel: Standard Reductin and
Name Chem 163 Sectin: Team Number: ALE 24. Vltaic Cells and Standard Cell Ptentials (Reference: 21.2 and 21.3 Silberberg 5 th editin) What des a vltmeter reading tell us? The Mdel: Standard Reductin and
SCIENCE 10: CHEMISTRY,
 , 1 Atmic Thery and Bnding The Nucleus - The particles that make up an atm are called subatmic particles - The three subatmic particles are prtns, neutrns and electrns. - Prtns, which have a +1 (psitive)
, 1 Atmic Thery and Bnding The Nucleus - The particles that make up an atm are called subatmic particles - The three subatmic particles are prtns, neutrns and electrns. - Prtns, which have a +1 (psitive)
NUPOC STUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY. Navy Recruiting Command
 NUPOC SUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY Navy Recruiting Cmmand CHEMISRY. ph represents the cncentratin f H ins in a slutin, [H ]. ph is a lg scale base and equal t lg[h ]. A ph f 7 is a neutral slutin. PH < 7 is acidic
NUPOC SUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY Navy Recruiting Cmmand CHEMISRY. ph represents the cncentratin f H ins in a slutin, [H ]. ph is a lg scale base and equal t lg[h ]. A ph f 7 is a neutral slutin. PH < 7 is acidic
Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam
 Chemistry 114 First Hur Exam Please shw all wrk fr partial credit Name: (4 pints) 1. (12 pints) Espress is made by frcing very ht water under high pressure thrugh finely grund, cmpacted cffee. (Wikipedia)
Chemistry 114 First Hur Exam Please shw all wrk fr partial credit Name: (4 pints) 1. (12 pints) Espress is made by frcing very ht water under high pressure thrugh finely grund, cmpacted cffee. (Wikipedia)
Interference is when two (or more) sets of waves meet and combine to produce a new pattern.
 Interference Interference is when tw (r mre) sets f waves meet and cmbine t prduce a new pattern. This pattern can vary depending n the riginal wave directin, wavelength, amplitude, etc. The tw mst extreme
Interference Interference is when tw (r mre) sets f waves meet and cmbine t prduce a new pattern. This pattern can vary depending n the riginal wave directin, wavelength, amplitude, etc. The tw mst extreme
N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) 2NH 3 (g) o Three mole ratios can be derived from the balanced equation above: Example: Li(s) + O 2 (g) Li 2 O(s)
 Chapter 9 - Stichimetry Sectin 9.1 Intrductin t Stichimetry Types f Stichimetry Prblems Given is in mles and unknwn is in mles. Given is in mles and unknwn is in mass (grams). Given is in mass and unknwn
Chapter 9 - Stichimetry Sectin 9.1 Intrductin t Stichimetry Types f Stichimetry Prblems Given is in mles and unknwn is in mles. Given is in mles and unknwn is in mass (grams). Given is in mass and unknwn
Chapter 9 Chemical Reactions NOTES
 Chapter 9 Chemical Reactins NOTES Chemical Reactins Chemical reactin: Chemical change 4 Indicatrs f Chemical Change: (1) (2) (3) (4) Cnsist f reactants (starting materials) and prducts (substances frmed)
Chapter 9 Chemical Reactins NOTES Chemical Reactins Chemical reactin: Chemical change 4 Indicatrs f Chemical Change: (1) (2) (3) (4) Cnsist f reactants (starting materials) and prducts (substances frmed)
PHOTOSYNTHESIS THE PRACTICALS 16 APRIL 2014
 PHOTOSYNTHESIS THE PRACTICALS 16 APRIL 2014 Lessn Descriptin In this lessn, we will: Review the prcess f phtsynthesis Study the starch test in leaves Study the varius practicals testing phtsynthesis Lk
PHOTOSYNTHESIS THE PRACTICALS 16 APRIL 2014 Lessn Descriptin In this lessn, we will: Review the prcess f phtsynthesis Study the starch test in leaves Study the varius practicals testing phtsynthesis Lk
Lab 1 The Scientific Method
 INTRODUCTION The fllwing labratry exercise is designed t give yu, the student, an pprtunity t explre unknwn systems, r universes, and hypthesize pssible rules which may gvern the behavir within them. Scientific
INTRODUCTION The fllwing labratry exercise is designed t give yu, the student, an pprtunity t explre unknwn systems, r universes, and hypthesize pssible rules which may gvern the behavir within them. Scientific
Chapter 17: Thermodynamics: Spontaneous and Nonspontaneous Reactions and Processes
 Chapter 17: hermdynamics: Spntaneus and Nnspntaneus Reactins and Prcesses Learning Objectives 17.1: Spntaneus Prcesses Cmparing and Cntrasting the hree Laws f hermdynamics (1 st Law: Chap. 5; 2 nd & 3
Chapter 17: hermdynamics: Spntaneus and Nnspntaneus Reactins and Prcesses Learning Objectives 17.1: Spntaneus Prcesses Cmparing and Cntrasting the hree Laws f hermdynamics (1 st Law: Chap. 5; 2 nd & 3
How can standard heats of formation be used to calculate the heat of a reaction?
 Answer Key ALE 28. ess s Law and Standard Enthalpies Frmatin (Reerence: Chapter 6 - Silberberg 4 th editin) Imprtant!! Fr answers that invlve a calculatin yu must shw yur wrk neatly using dimensinal analysis
Answer Key ALE 28. ess s Law and Standard Enthalpies Frmatin (Reerence: Chapter 6 - Silberberg 4 th editin) Imprtant!! Fr answers that invlve a calculatin yu must shw yur wrk neatly using dimensinal analysis
1.2.1 Vectors. 1 P age. Examples What is the reference vector angle for a vector that points 50 degrees east of south?
 1.2.1 Vectrs Definitins Vectrs are represented n paper by arrws directin = magnitude = Examples f vectrs: Examples What is the reference vectr angle fr a vectr that pints 50 degrees east f suth? What is
1.2.1 Vectrs Definitins Vectrs are represented n paper by arrws directin = magnitude = Examples f vectrs: Examples What is the reference vectr angle fr a vectr that pints 50 degrees east f suth? What is
Space Shuttle Ascent Mass vs. Time
 Space Shuttle Ascent Mass vs. Time Backgrund This prblem is part f a series that applies algebraic principles in NASA s human spaceflight. The Space Shuttle Missin Cntrl Center (MCC) and the Internatinal
Space Shuttle Ascent Mass vs. Time Backgrund This prblem is part f a series that applies algebraic principles in NASA s human spaceflight. The Space Shuttle Missin Cntrl Center (MCC) and the Internatinal
Chapter One Atoms and Elements
 S u m m e r S c h l 2 0 1 4 S c i e n c e S T P a g e 1 Chapter One Atms and Elements Histry f the Atm Daltn s Atmic Mdel Daltn thught f atms as slid, indivisible balls f different Thmsn s Atmic Mdel Thmsn
S u m m e r S c h l 2 0 1 4 S c i e n c e S T P a g e 1 Chapter One Atms and Elements Histry f the Atm Daltn s Atmic Mdel Daltn thught f atms as slid, indivisible balls f different Thmsn s Atmic Mdel Thmsn
Name: Period: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
1 Course Notes in Introductory Physics Jeffrey Seguritan
 Intrductin & Kinematics I Intrductin Quickie Cncepts Units SI is standard system f units used t measure physical quantities. Base units that we use: meter (m) is standard unit f length kilgram (kg) is
Intrductin & Kinematics I Intrductin Quickie Cncepts Units SI is standard system f units used t measure physical quantities. Base units that we use: meter (m) is standard unit f length kilgram (kg) is
State of matter characteristics solid Retains shape and volume
 **See attachment fr graphs States f matter The fundamental difference between states f matter is the distance between particles Gas Ttal disrder Much empty space Particles have cmpletely freedm f mtin
**See attachment fr graphs States f matter The fundamental difference between states f matter is the distance between particles Gas Ttal disrder Much empty space Particles have cmpletely freedm f mtin
Pipetting 101 Developed by BSU CityLab
 Discver the Micrbes Within: The Wlbachia Prject Pipetting 101 Develped by BSU CityLab Clr Cmparisns Pipetting Exercise #1 STUDENT OBJECTIVES Students will be able t: Chse the crrect size micrpipette fr
Discver the Micrbes Within: The Wlbachia Prject Pipetting 101 Develped by BSU CityLab Clr Cmparisns Pipetting Exercise #1 STUDENT OBJECTIVES Students will be able t: Chse the crrect size micrpipette fr
NOTES. Name: Date: Topic: Periodic Table & Atoms Notes. Period: Matter
 NOTES Unit: Tpic: Peridic Table & Atms Ntes Name: Date: Perid: Matter Atmic Structure The term matter describes all f the physical substances arund us. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
NOTES Unit: Tpic: Peridic Table & Atms Ntes Name: Date: Perid: Matter Atmic Structure The term matter describes all f the physical substances arund us. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
"1 O O O. -U -7 P fl> 1 3. jff. (t) o o 1-7- PAa s: A - o 0'»«-« "Tf O ") ftt Ti 0 -- CO -1 O. fa n. i,, I. -n F en 2.0»- 4 T2. -5 Ut.
 crv/ 3 P -U -7 P fl> 1 3 (t) jff?- "1 s P 9-1-7- ~* PAa s: A - "C '»«-«in i,, I ftt Ti -- c 4 T2-5 Ut j 3 C -1 p fa n l> -n F en 2.»- "Tf ") r . x 2 "Z * "! t :.!, 21,, V\ C fn
crv/ 3 P -U -7 P fl> 1 3 (t) jff?- "1 s P 9-1-7- ~* PAa s: A - "C '»«-«in i,, I ftt Ti -- c 4 T2-5 Ut j 3 C -1 p fa n l> -n F en 2.»- "Tf ") r . x 2 "Z * "! t :.!, 21,, V\ C fn
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND PHYSICAL SCIENCE
 ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND PHYSICAL SCIENCE The Peridic Table f Elements (PTE): Families Stick Tgether Allys and Cmpunds Lessn 3 Nte: this lessn culd take up t three class sessins
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND PHYSICAL SCIENCE The Peridic Table f Elements (PTE): Families Stick Tgether Allys and Cmpunds Lessn 3 Nte: this lessn culd take up t three class sessins
Pacing Guide TEKS. Unit 1 Scientific Process Skills and Investigations
 Pacing Guide Unit Scientific Process Skills and Investigations Lab Safety/ Use of Tools Measurement Process Skills and Investigations 6.(A) demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations
Pacing Guide Unit Scientific Process Skills and Investigations Lab Safety/ Use of Tools Measurement Process Skills and Investigations 6.(A) demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations
Types of Energy COMMON MISCONCEPTIONS CHEMICAL REACTIONS INVOLVE ENERGY
 CHEMICAL REACTIONS INVOLVE ENERGY The study energy and its transrmatins is knwn as thermdynamics. The discussin thermdynamics invlve the cncepts energy, wrk, and heat. Types Energy Ptential energy is stred
CHEMICAL REACTIONS INVOLVE ENERGY The study energy and its transrmatins is knwn as thermdynamics. The discussin thermdynamics invlve the cncepts energy, wrk, and heat. Types Energy Ptential energy is stred
Chapter Outline 4/28/2014. P-V Work. P-V Work. Isolated, Closed and Open Systems. Exothermic and Endothermic Processes. E = q + w
 Islated, Clsed and Open Systems 9.1 Energy as a Reactant r a Prduct 9.2 Transferring Heat and Ding Wrk 9.5 Heats f Reactin and Calrimetry 9.6 Hess s Law and Standard Heats f Reactin 9.7 Heats f Reactin
Islated, Clsed and Open Systems 9.1 Energy as a Reactant r a Prduct 9.2 Transferring Heat and Ding Wrk 9.5 Heats f Reactin and Calrimetry 9.6 Hess s Law and Standard Heats f Reactin 9.7 Heats f Reactin
Group Color: Subgroup Number: How Science Works. Grade 5. Module 2. Class Question: Scientist (Your Name): Teacher s Name: SciTrek Volunteer s Name:
 Grup Clr: Subgrup Number: Hw Science Wrks Grade 5 Mdule 2 Class Questin: Scientist (Yur Name): Teacher s Name: SciTrek Vlunteer s Name: VOCABULARY Science: The study f the material wrld using human reasn.
Grup Clr: Subgrup Number: Hw Science Wrks Grade 5 Mdule 2 Class Questin: Scientist (Yur Name): Teacher s Name: SciTrek Vlunteer s Name: VOCABULARY Science: The study f the material wrld using human reasn.
Lecture 16 Thermodynamics II
 Lecture 16 Thermdynamics II Calrimetry Hess s Law Enthalpy r Frmatin Cpyright 2013, 2011, 2009, 2008 AP Chem Slutins. All rights reserved. Fur Methds fr Finding H 1) Calculate it using average bnd enthalpies
Lecture 16 Thermdynamics II Calrimetry Hess s Law Enthalpy r Frmatin Cpyright 2013, 2011, 2009, 2008 AP Chem Slutins. All rights reserved. Fur Methds fr Finding H 1) Calculate it using average bnd enthalpies
Chemistry 20 Lesson 11 Electronegativity, Polarity and Shapes
 Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
OSIRIS-REx Frequently Asked Questions
 OSIRIS-REx Frequently Asked Questins What is the OSIRIS-REx Missin? The OSIRIS-REx missin is NASA New Frntiers missin t return a sample f an asterid t the Earth. Missin cst is apprximately $800 millin
OSIRIS-REx Frequently Asked Questins What is the OSIRIS-REx Missin? The OSIRIS-REx missin is NASA New Frntiers missin t return a sample f an asterid t the Earth. Missin cst is apprximately $800 millin
Weathering. Title: Chemical and Mechanical Weathering. Grade Level: Subject/Content: Earth and Space Science
 Weathering Title: Chemical and Mechanical Weathering Grade Level: 9-12 Subject/Cntent: Earth and Space Science Summary f Lessn: Students will test hw chemical and mechanical weathering can affect a rck
Weathering Title: Chemical and Mechanical Weathering Grade Level: 9-12 Subject/Cntent: Earth and Space Science Summary f Lessn: Students will test hw chemical and mechanical weathering can affect a rck
Downloaded from Downloaded from
 MATTER IN OUR SURROUNDINGS Date Diagram Observatin Explanatin Cnclusin ACTIVITY 1.1 (10 marks) date n which the experiment was perfrmed. I have drawn a diagram. My diagram is neat. My diagram is well labeled.
MATTER IN OUR SURROUNDINGS Date Diagram Observatin Explanatin Cnclusin ACTIVITY 1.1 (10 marks) date n which the experiment was perfrmed. I have drawn a diagram. My diagram is neat. My diagram is well labeled.
THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM SECTION 27.1 Tools of Astronomy
 Name Date Perid THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM SECTION 27.1 Tls f Astrnmy (45 pints this side) In yur textbk, read abut electrmagnetic radiatin and telescpes. Use each f the terms belw just nce t cmplete the
Name Date Perid THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM SECTION 27.1 Tls f Astrnmy (45 pints this side) In yur textbk, read abut electrmagnetic radiatin and telescpes. Use each f the terms belw just nce t cmplete the
QCE Chemistry. Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, Chemistry: Revision Notes. By Sophie (1 ATAR)
 QCE Chemistry Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, 2017 11 Chemistry: Revisin Ntes By Sphie (1 ATAR) Pwered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.rg) Yur ntes authr, Sphie. Sphie achieved an ATAR f 1 in 2016 while
QCE Chemistry Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, 2017 11 Chemistry: Revisin Ntes By Sphie (1 ATAR) Pwered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.rg) Yur ntes authr, Sphie. Sphie achieved an ATAR f 1 in 2016 while
Lecture 4. The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Lecture 4. The First Law f Thermdynamics THERMODYNAMICS: Basic Cncepts Thermdynamics: (frm the Greek therme, meaning "heat" and, dynamis, meaning "pwer") is the study f energy cnversin between heat and
Lecture 4. The First Law f Thermdynamics THERMODYNAMICS: Basic Cncepts Thermdynamics: (frm the Greek therme, meaning "heat" and, dynamis, meaning "pwer") is the study f energy cnversin between heat and
Solution to HW14 Fall-2002
 Slutin t HW14 Fall-2002 CJ5 10.CQ.003. REASONING AND SOLUTION Figures 10.11 and 10.14 shw the velcity and the acceleratin, respectively, the shadw a ball that underges unirm circular mtin. The shadw underges
Slutin t HW14 Fall-2002 CJ5 10.CQ.003. REASONING AND SOLUTION Figures 10.11 and 10.14 shw the velcity and the acceleratin, respectively, the shadw a ball that underges unirm circular mtin. The shadw underges
LESSON 09: EARTH S STRUCTURE
 G E O S C I E N C E : E A R T H A N D F I R E G E O S C I E N C E S : E A R T H A N D F I R E LESSON 09: EARTH S STRUCTURE READING & RESEARCH Read KSE Earth s Structure, pp. 8-9. Read DSE Structure f the
G E O S C I E N C E : E A R T H A N D F I R E G E O S C I E N C E S : E A R T H A N D F I R E LESSON 09: EARTH S STRUCTURE READING & RESEARCH Read KSE Earth s Structure, pp. 8-9. Read DSE Structure f the
Semester 2 AP Chemistry Unit 12
 Cmmn In Effect and Buffers PwerPint The cmmn in effect The shift in equilibrium caused by the additin f a cmpund having an in in cmmn with the disslved substance The presence f the excess ins frm the disslved
Cmmn In Effect and Buffers PwerPint The cmmn in effect The shift in equilibrium caused by the additin f a cmpund having an in in cmmn with the disslved substance The presence f the excess ins frm the disslved
Chapter 3 Forensic Laboratory Techniques Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved
 Chapter 3 Frensic Labratry Techniques Intrductin Objectives 1. Distinguish between physical and chemical prperties. 2. Describe presumptive and cnfirmatry tests. 3. Cmpare and cntrast different types f
Chapter 3 Frensic Labratry Techniques Intrductin Objectives 1. Distinguish between physical and chemical prperties. 2. Describe presumptive and cnfirmatry tests. 3. Cmpare and cntrast different types f
Midterm Review Notes - Unit 1 Intro
 Midterm Review Ntes - Unit 1 Intr 3 States f Matter Slid definite shape, definite vlume, very little mlecular mvement Liquid definite vlume, takes shape f cntainer, mlecules mve faster Gas des nt have
Midterm Review Ntes - Unit 1 Intr 3 States f Matter Slid definite shape, definite vlume, very little mlecular mvement Liquid definite vlume, takes shape f cntainer, mlecules mve faster Gas des nt have
Name: Period: Date: ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
Name: Perid: Date: ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
o Land and water both are heated by solar radiation, but land
 Benchmark: SC.D.l.4.1 The student knws hw climatic patterns n Earth result frm an interplay f many factrs (Earth's tpgraphy, its rtatin'tn its axis, slar radiatin, the transfer f heat energy where the
Benchmark: SC.D.l.4.1 The student knws hw climatic patterns n Earth result frm an interplay f many factrs (Earth's tpgraphy, its rtatin'tn its axis, slar radiatin, the transfer f heat energy where the
Unit C Review Notes. Theory of Deep Time
 Unit C Review Ntes Thery f Deep Time Types f evidence: Anecdtal vs. Instrumental Direct vs. Indirect Relative dating vs. radiactive dating Steps t calculating the age f a mineral using radiactive dating:
Unit C Review Ntes Thery f Deep Time Types f evidence: Anecdtal vs. Instrumental Direct vs. Indirect Relative dating vs. radiactive dating Steps t calculating the age f a mineral using radiactive dating:
Science Unit Grades 7-9 Lesson 3: Craftsmen Chemistry
 Lessn Descriptin Science Unit Grades 7-9 Lessn 3: Craftsmen Chemistry N matter where yu are Chemistry is nt far away. It can be smething as simple as cking an egg r as elabrate as sending rckets int space.
Lessn Descriptin Science Unit Grades 7-9 Lessn 3: Craftsmen Chemistry N matter where yu are Chemistry is nt far away. It can be smething as simple as cking an egg r as elabrate as sending rckets int space.
Examples: Everything in the universe is made up of matter. How atoms are form the. Solids Liquids Gases. The a substance has, If a substance has
 Matter What is Matter? Examples: Everything in the universe is made up f matter Hw atms are frm the The States f Matter There are main states f matter Slids Liquids Gases What causes the different States
Matter What is Matter? Examples: Everything in the universe is made up f matter Hw atms are frm the The States f Matter There are main states f matter Slids Liquids Gases What causes the different States
Phy 212: General Physics II 1 Chapter 18 Worksheet 3/20/2008
 Phy 1: General Physics II 1 hapter 18 rksheet 3/0/008 Thermal Expansin: 1. A wedding ring cmpsed f pure gld (inner diameter = 1.5 x 10 - m) is placed n a persn s finger (diameter = 1.5 x 10 - m). Bth the
Phy 1: General Physics II 1 hapter 18 rksheet 3/0/008 Thermal Expansin: 1. A wedding ring cmpsed f pure gld (inner diameter = 1.5 x 10 - m) is placed n a persn s finger (diameter = 1.5 x 10 - m). Bth the
5 th grade Common Core Standards
 5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
/ / Chemistry. Chapter 1 Chemical Foundations
 Name Chapter 1 Chemical Fundatins Advanced Chemistry / / Metric Cnversins All measurements in chemistry are made using the metric system. In using the metric system yu must be able t cnvert between ne
Name Chapter 1 Chemical Fundatins Advanced Chemistry / / Metric Cnversins All measurements in chemistry are made using the metric system. In using the metric system yu must be able t cnvert between ne
Physics 2B Chapter 23 Notes - Faraday s Law & Inductors Spring 2018
 Michael Faraday lived in the Lndn area frm 1791 t 1867. He was 29 years ld when Hand Oersted, in 1820, accidentally discvered that electric current creates magnetic field. Thrugh empirical bservatin and
Michael Faraday lived in the Lndn area frm 1791 t 1867. He was 29 years ld when Hand Oersted, in 1820, accidentally discvered that electric current creates magnetic field. Thrugh empirical bservatin and
GASES. PV = nrt N 2 CH 4 CO 2 O 2 HCN N 2 O NO 2. Pressure & Boyle s Law Temperature & Charles s Law Avogadro s Law IDEAL GAS LAW
 GASES Pressure & Byle s Law Temperature & Charles s Law Avgadr s Law IDEAL GAS LAW PV = nrt N 2 CH 4 CO 2 O 2 HCN N 2 O NO 2 Earth s atmsphere: 78% N 2 21% O 2 sme Ar, CO 2 Sme Cmmn Gasses Frmula Name
GASES Pressure & Byle s Law Temperature & Charles s Law Avgadr s Law IDEAL GAS LAW PV = nrt N 2 CH 4 CO 2 O 2 HCN N 2 O NO 2 Earth s atmsphere: 78% N 2 21% O 2 sme Ar, CO 2 Sme Cmmn Gasses Frmula Name
Part One: Heat Changes and Thermochemistry. This aspect of Thermodynamics was dealt with in Chapter 6. (Review)
 CHAPTER 18: THERMODYNAMICS AND EQUILIBRIUM Part One: Heat Changes and Thermchemistry This aspect f Thermdynamics was dealt with in Chapter 6. (Review) A. Statement f First Law. (Sectin 18.1) 1. U ttal
CHAPTER 18: THERMODYNAMICS AND EQUILIBRIUM Part One: Heat Changes and Thermchemistry This aspect f Thermdynamics was dealt with in Chapter 6. (Review) A. Statement f First Law. (Sectin 18.1) 1. U ttal
How do scientists measure trees? What is DBH?
 Hw d scientists measure trees? What is DBH? Purpse Students develp an understanding f tree size and hw scientists measure trees. Students bserve and measure tree ckies and explre the relatinship between
Hw d scientists measure trees? What is DBH? Purpse Students develp an understanding f tree size and hw scientists measure trees. Students bserve and measure tree ckies and explre the relatinship between
Fall 2013 Physics 172 Recitation 3 Momentum and Springs
 Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
CHEM Thermodynamics. Change in Gibbs Free Energy, G. Review. Gibbs Free Energy, G. Review
 Review Accrding t the nd law f Thermdynamics, a prcess is spntaneus if S universe = S system + S surrundings > 0 Even thugh S system
Review Accrding t the nd law f Thermdynamics, a prcess is spntaneus if S universe = S system + S surrundings > 0 Even thugh S system
How can standard heats of formation be used to calculate the heat of a reaction?
 Name Chem 161, Sectin: Grup Number: ALE 28. Hess s Law and Standard Enthalpies Frmatin (Reerence: Chapter 6 - Silberberg 5 th editin) Imprtant!! Fr answers that invlve a calculatin yu must shw yur wrk
Name Chem 161, Sectin: Grup Number: ALE 28. Hess s Law and Standard Enthalpies Frmatin (Reerence: Chapter 6 - Silberberg 5 th editin) Imprtant!! Fr answers that invlve a calculatin yu must shw yur wrk
Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan
 Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan Questin 1 6 Pints Classify each f the fllwing mlecules as plar r nnplar? a) NO + : c) CH 2 Cl 2 : b) XeF 4 : Questin 2 The hypthetical mlecule PY 3 Z 2 has the general
Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan Questin 1 6 Pints Classify each f the fllwing mlecules as plar r nnplar? a) NO + : c) CH 2 Cl 2 : b) XeF 4 : Questin 2 The hypthetical mlecule PY 3 Z 2 has the general
Therefore the atomic diameter is 5 orders of magnitude ( times) greater than the m
 Orders f Magnitude Pwers f 10 are referred t as rders f magnitude e.g. smething a thusand times larger (10 3 ) is three rders f magnitude bigger. A prtn has a diameter f the rder ~10-15 m The diameter
Orders f Magnitude Pwers f 10 are referred t as rders f magnitude e.g. smething a thusand times larger (10 3 ) is three rders f magnitude bigger. A prtn has a diameter f the rder ~10-15 m The diameter
