Properties of Commutators and Schroedinger Operators and Applications to Quantum Computing
|
|
|
- August McCoy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Research Technology (IJEART) Properties of Commutators and Schroedinger Operators and Applications to Quantum Computing N. B. Okelo Abstract In this paper we study the properties of Hilbert space operators, commutatorsand Schroedinger equation. We also explore their applications in quantum physics and explain the links between the abstract mathematics and the reality in the physical sense. Index Terms Commutators, Schrödinger equation, IT where c 1 =x, c 2 =y, c 3 =z and x 1 =i, x 2 =, x 3 =k. Notice that the components of the vector are the constants c. In Dirac notation, this would become: R c x (2.3) I. INTRODUCTION Hilbert spaces are complete inner product spaces with a lot o interesting properties[2]. Operators on Hilbert spaces are also very interesting with a lot of applications to quantum physics. In this paper, we consider general Hilbert space operators, commutators and Schrödinger equations[1] and explore their applications to quantum mechanics. II. PRELIMINARIES Consider some vector which can have complex components to be symbolized by a. The dual or conugate of the vector will be symbolized by a a *. a. Thus, There is some set of basis vectors that can be multiplied by constant coefficients and added together to give a. a c x1 c2 x2... c x 1 (1.1) The constant c can be complex. The basis vectors form the basis or vector space. There can be one to an infinite number of basis vectors. As an example, consider a position vector R in three dimensions. We can choose to represent the vector in a variety of vector spaces, each with different basis vectors. Let s use the familiar rectangular vector space with the three basis vectors of i,, k. We can write R as R = xi + y +zk = c x (2.2) N. B. Okelo, School of Mathematics and Actuarial Science, Jaramogi Oginga Odinga University of Science and Technology, P. O. Box , Bondo-Kenya This example uses a conventional vector quantity, namely position. But one can extend the concept of vector to include unconventional quantities. For instance, a function all of the values of x. The vector has a component (x) for each basis vector. Note that there are an infinite number of basis vectors in this case! We can therefore write an expression for the vector as ( x) x dx x dx( x ) (2.4) Any two vectors in a vector space S satisfy closure under addition and scalar multiplication. Formally, if a, b S, then a b b a S c a c b 1 2 S (2.5) We now define an operation between 2 vectors called the scalar product such that the product is a scalar (it can be complex). We also require that if the scalar product is performed between a vector and one of the basis vectors, then the scalar is the coefficient c: that scalar product b a b a b a so b a = a number x a c and so that For ordinary vectors, the scalar product is simply the dot product. Consider our position vector example above. Note that the x-component of vector R can be found by taking the dot product of R with i=x 1 : x x R x R 1 1 (2.6) 23
2 Properties of Commutators and Schroedinger Operators and Applications to Quantum Computing For a function, then, we can find the value of the function (x) [one of the components of vector ] by taking the scalar product between x [the basis vector ] and vector : ( x) x (2.7) Properties of Vectors Now that we have defined vectors and the scalar product, we can list some properties. Note that c is a scalar which can be complex. Substituting (2.7) into (2.4) gives x dx x (2.8) and we now have the definition for a unit operator. Examining (2.8) we see that b c a c b a b a a' b a b a' b a a b * a a 0 and is real a 0 0 (2.14) x dx x 1 (2.9) This unit operator is useful in deriving expressions and in vector algebra as we shall see immediately. What happens if we take the scalar product of two vectors that are functions of x? Let the two functions be (x) and (x). Let the two vectors representing the functions be and. Then the scalar product of the two vectors is. Let us use the unit operator to write x dx x (2.10) III. BASIC CONCEPTS These definitions involving the scalar product should look very familiar based on your experience with regular vectors. The magnitude of a a a 1/ 2. Vectors a and b are orthogonal if a b 0. Vector a is a unit vector if a a 1. A unit vector is also called a normalized vector. Two vectors are orthonormal if they are orthogonal and if they are both normalized. IV. DIRAC DELTA FUNCTION Bringing the two vectors into the integrand gives x dx x (2.11) Now we have established in (2.7) that we can write. Taking the complex ( x) x and ( x) x conugate of the second expression gives so that (2.11) becomes *( x) x * x (2.12) *( x) ( x) dx (2.13) Equation (2.13) tells us how to evaluate the scalar product of two vectors that are functions. *Notice that the scalar product is written with a bracket sometimes still used. While we are discussing vector theory as developed by Dirac, it is interesting to see how he came upon the delta function which bears his name. Consider inserting the unit operator into the bracket expression for the function x) in (2.7): ( x) x x' dx' x' x x' dx' ( x') (2.15) Notice that we have distinguished x and x. The unit operator must integrate over all possible values of x while x is ust one of the possible values of x. Now the left side is the value of at one value of x (x =x) while the right side involves a sum of the values of at all values of x. There is no way that this can be true unless the scalar product x x' has an interesting property. Namely, x x' 0 unless x=x and if x=x then the integral of x x must give one. Dirac called this strange scalar product the delta function: x x' ( x x') (2.16) 24
3 where ( x x') 0 ( x x') dx' 1 International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Research Technology (IJEART) for x' x for x' = x V. OPERATOR THEORY Operators operate on vectors to give other vectors: A a b (2.17) We will be dealing with linear operators: A a b A a A b (2.18) A c a ca a (ii) VI. SOME PROPERTIES OF OPERATORS A B a A a B a A B a B A a AB a BA a AB a A B a b A a b A a (i) *usually (2.19) The quantum states of a physical system are identified as vectors. In practice, this means that the wavefunctions are viewed as function vectors. The components of the vectors are the values of the wavefunctions. The components can change with position and time. This means the function vectors can point in different directions as position and time vary. If we fix the time to one value or have a time-independent system, then the basis vectors are the position values x in one dimension. Dynamic variables (physical quantities of the motion like position, momentum, energy) have corresponding linear operators. These quantities are also referred to as observables since they can be measured or observed. We have already listed these operators in Part 1. We will now simply use our notation of ^ above the operators instead of using curly brackets. For instance, the momentum operator is p i x. In classical mechanics, the order of dynamic variables in equations doesn t matter. In quantum mechanics, the order of these variables in equations is very important! This is because of how some of them operate on the wavefunction. Formally, we can say that operators do not generally commute in quantum mechanics. For instance, x, p xp px 0. In addition to being linear, the adoint of an operator of a dynamic variable is equal to the operator ( A A ). Such operators are called self-adoint. For example, the adoint of the momentum operator is p p i x * Operators usually do not commute. We define the commutator of two operators as If the operators do commute, then A, B AB BA (2.20) A, B 0. It is convenient to define the adoint of an operator as follows. Operator A has an adoint, denoted by A that b A a * a A b We will say more about the adoint below. such (2.21) We have developed a general definition of a vector, the scalar product, an operator, and various properties in a purely abstract, mathematical sense. What is the connection to quantum physics? Let us briefly describe the connection. We can demonstrate this by considering the momentum operator operating on the wavefunction of a free particle. The wavefunction is of the form ( x, t) Ae i kx t so ( ) i( kxt ) p i i( ik) Ae k x p k k k. Now assuming that the wavefunction is normalized. The complex conugate of this scalar product is simply the scalar product itself: p * ( k)* k p This fact, combined with the definition of the adoint as expressed in (2.21), gives 25
4 Properties of Commutators and Schroedinger Operators and Applications to Quantum Computing p p * p This can only be true if p p, i.e. the operator is self-adoint. The fact that operators of dynamic variables are self-adoint can be used in the solving of certain physical systems, as we will see. Let us examine the result of this connection between mathematics, Dirac notation, and physics in more detail. We now write a one-dimensional, time-dependent wavefunction x,t) as a vector. The normalization of the wavefunction is expressed as *( x, t) ( x, t) dx 1 (2.22) How do we express an average value of a dyanmic variable? We already know how to evaluate it. For example, to find the average value of position x we evaluate the integral x x dx * (2.23) vector and obtain another vector that is parallel to the first. The resulting vector is ust a multiple of the original vector. This original vector and the operator have a very special relationship! Usually, an operator will change the direction of a vector. In general terms, if A a c a where c is a number (can be complex) then we call a an eigenvector of operator A and c the eigenvalue. Equation (2.26) then is an eigenvalue equation, and since the Hamiltonian is the total energy operator, we call the energy eigenvector, (x) the energy eigenfunction or energy eigenstate, and E the energy eigenvalue. For a physical sysytem in which energy is quantized, there are different eigenstates corresponding to the different energy eigenvalues. More than eigenstate may have the same energy. Such states are called degenerate. Eigenstates & Measurement We can now state some postulates about the measurement process in quantum mechanics in relation to the theory we have ust developed. We will make these postulates specific to the Hamiltonian and the energy eigenstates and eigenvalues, but they apply to any operator corresponding to a dynamic variable and its associated eigenstates and eigenvectors. Examine this equation a bit closer. We can view the 1. If a quantum system is in an eigenstate of the the operator x. This gives a new vector. (2) Now evaluate the scalar product of this new vector with the conugate of (2.24) x x x The expression x is ust short-hand for the middle expression and is commonly used. Can you write the full Dirac notation expression and the integral expression for the average momentum of the particle? p p? (2.25) VII. SCHROEDINGER OPERATORS We can now express the one-dimensional time-independent Schroedinger equation as H E (2.26) You should verify that this is equivalent to the familiar differential equation version we have been using. In terms of operator theory, this equation says that you operate on a operator H, then a measurement of the energy will certainly give the eigenvalue E as a result. 2. If the system is in a state such that a measurement of H is certain to give one particular result then the state is an eigenstate of corresponding to H. H and the result is the eigenvalue E 3. The result of measuring the energy is one of the energy eigenvalues. If the system was not originally in an eigenstate then the measurement causes the system to "ump" into an eigenstate. Corollary: If a measurement is repeated "immediately" after it is performed, the result must be unchanged. Thus the state to which the system umped as a result of the first measurement must be an eigenstate with an eigenvalue corresponding to the measured value. 4. Every energy eigenvalue is a possible result of the measurement of the energy. 5. If the energy is measured with the system in a particular state, the eigenstates into which the system may ump due to the measurement are such that the original state is dependent on them, i.e. the original state is a linear combination of the eigenstates. 26
5 International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Research Technology (IJEART) Corollary: Since the original state can be any state, every state must be dependent on the eigenstates to which the system may ump. The eigenstates form a complete set of states. An operator whose eigenstates form a complete set is called an observable. 6. Suppose the system is in a state (not necessarily an eigenstate) and a measurement of the energy is made a large number of times, with the system being put back into the original state after each measurement. Then, the average of all of those measurements is E H assuming that is normalized. REFERENCES [1] John K. On schroedinger equations, IJRT, 2(3)(2010)3-9. [2] Kitaneh G. K., On Commutator approximants, J. Operator Theory, %(2)(2008),
Lecture 6. Four postulates of quantum mechanics. The eigenvalue equation. Momentum and energy operators. Dirac delta function. Expectation values
 Lecture 6 Four postulates of quantum mechanics The eigenvalue equation Momentum and energy operators Dirac delta function Expectation values Objectives Learn about eigenvalue equations and operators. Learn
Lecture 6 Four postulates of quantum mechanics The eigenvalue equation Momentum and energy operators Dirac delta function Expectation values Objectives Learn about eigenvalue equations and operators. Learn
The quantum state as a vector
 The quantum state as a vector February 6, 27 Wave mechanics In our review of the development of wave mechanics, we have established several basic properties of the quantum description of nature:. A particle
The quantum state as a vector February 6, 27 Wave mechanics In our review of the development of wave mechanics, we have established several basic properties of the quantum description of nature:. A particle
Mathematical Formulation of the Superposition Principle
 Mathematical Formulation of the Superposition Principle Superposition add states together, get new states. Math quantity associated with states must also have this property. Vectors have this property.
Mathematical Formulation of the Superposition Principle Superposition add states together, get new states. Math quantity associated with states must also have this property. Vectors have this property.
PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations
 PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations 1 Τhe continuous spectrum-a n So far we have seen problems where the involved operators have a discrete spectrum of eigenfunctions and eigenvalues.! n
PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations 1 Τhe continuous spectrum-a n So far we have seen problems where the involved operators have a discrete spectrum of eigenfunctions and eigenvalues.! n
2. As we shall see, we choose to write in terms of σ x because ( X ) 2 = σ 2 x.
 Section 5.1 Simple One-Dimensional Problems: The Free Particle Page 9 The Free Particle Gaussian Wave Packets The Gaussian wave packet initial state is one of the few states for which both the { x } and
Section 5.1 Simple One-Dimensional Problems: The Free Particle Page 9 The Free Particle Gaussian Wave Packets The Gaussian wave packet initial state is one of the few states for which both the { x } and
Chapter 2. Linear Algebra. rather simple and learning them will eventually allow us to explain the strange results of
 Chapter 2 Linear Algebra In this chapter, we study the formal structure that provides the background for quantum mechanics. The basic ideas of the mathematical machinery, linear algebra, are rather simple
Chapter 2 Linear Algebra In this chapter, we study the formal structure that provides the background for quantum mechanics. The basic ideas of the mathematical machinery, linear algebra, are rather simple
1 Mathematical preliminaries
 1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space
 Physics 342 Lecture 16 Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space Lecture 16 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1st, 2010 We have seen the importance of the plane wave solutions to the potentialfree Schrödinger
Physics 342 Lecture 16 Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space Lecture 16 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1st, 2010 We have seen the importance of the plane wave solutions to the potentialfree Schrödinger
Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors,
 chmy564-19 Fri 18jan19 Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors, 3. Theorems vs. Postulates Scalar (inner) prod.
chmy564-19 Fri 18jan19 Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors, 3. Theorems vs. Postulates Scalar (inner) prod.
Harmonic Oscillator I
 Physics 34 Lecture 7 Harmonic Oscillator I Lecture 7 Physics 34 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, February th, 008 We can manipulate operators, to a certain extent, as we would algebraic expressions. By considering
Physics 34 Lecture 7 Harmonic Oscillator I Lecture 7 Physics 34 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, February th, 008 We can manipulate operators, to a certain extent, as we would algebraic expressions. By considering
BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS. Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5
 BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5 Interesting things happen when electrons are confined to small regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an
BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5 Interesting things happen when electrons are confined to small regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an
II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics
 II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics Based on the results of the experiments described in the previous section, we recognize that real experiments do not behave quite as we expect. This section presents
II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics Based on the results of the experiments described in the previous section, we recognize that real experiments do not behave quite as we expect. This section presents
1 The postulates of quantum mechanics
 1 The postulates of quantum mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics were derived after a long process of trial and error. These postulates provide a connection between the physical world and the
1 The postulates of quantum mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics were derived after a long process of trial and error. These postulates provide a connection between the physical world and the
Introduction to Electronic Structure Theory
 Introduction to Electronic Structure Theory C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology June 2002 Last Revised: June 2003 1 Introduction The purpose of these
Introduction to Electronic Structure Theory C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology June 2002 Last Revised: June 2003 1 Introduction The purpose of these
Harmonic Oscillator with raising and lowering operators. We write the Schrödinger equation for the harmonic oscillator in one dimension as follows:
 We write the Schrödinger equation for the harmonic oscillator in one dimension as follows: H ˆ! = "!2 d 2! + 1 2µ dx 2 2 kx 2! = E! T ˆ = "! 2 2µ d 2 dx 2 V ˆ = 1 2 kx 2 H ˆ = ˆ T + ˆ V (1) where µ is
We write the Schrödinger equation for the harmonic oscillator in one dimension as follows: H ˆ! = "!2 d 2! + 1 2µ dx 2 2 kx 2! = E! T ˆ = "! 2 2µ d 2 dx 2 V ˆ = 1 2 kx 2 H ˆ = ˆ T + ˆ V (1) where µ is
Time part of the equation can be separated by substituting independent equation
 Lecture 9 Schrödinger Equation in 3D and Angular Momentum Operator In this section we will construct 3D Schrödinger equation and we give some simple examples. In this course we will consider problems where
Lecture 9 Schrödinger Equation in 3D and Angular Momentum Operator In this section we will construct 3D Schrödinger equation and we give some simple examples. In this course we will consider problems where
1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation
 1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation A. M. Steane, Exeter College, Oxford University 1.1 Introduction These pages are intended to help you get a feel for the mathematics behind Quantum Mechanics. The
1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation A. M. Steane, Exeter College, Oxford University 1.1 Introduction These pages are intended to help you get a feel for the mathematics behind Quantum Mechanics. The
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 5, January 27, 2006
 Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 5, January 27, 2006 Solved Homework (Homework for grading is also due today) We are told
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 5, January 27, 2006 Solved Homework (Homework for grading is also due today) We are told
An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually).
 Formalism of Quantum Mechanics Operators Engel 3.2 An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually). Example: In QM, most operators are linear:
Formalism of Quantum Mechanics Operators Engel 3.2 An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually). Example: In QM, most operators are linear:
Page 404. Lecture 22: Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 2008/11/19 Date Revised: 2008/11/19
 Page 404 Lecture : Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 008/11/19 Date Revised: 008/11/19 Coordinate Basis Section 6. The One-Dimensional Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Coordinate Basis Page
Page 404 Lecture : Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 008/11/19 Date Revised: 008/11/19 Coordinate Basis Section 6. The One-Dimensional Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Coordinate Basis Page
df(x) = h(x) dx Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 2009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation
 Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation Linearity of differential equation Partial vs. Ordinary Differential Equations
Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation Linearity of differential equation Partial vs. Ordinary Differential Equations
2. Introduction to quantum mechanics
 2. Introduction to quantum mechanics 2.1 Linear algebra Dirac notation Complex conjugate Vector/ket Dual vector/bra Inner product/bracket Tensor product Complex conj. matrix Transpose of matrix Hermitian
2. Introduction to quantum mechanics 2.1 Linear algebra Dirac notation Complex conjugate Vector/ket Dual vector/bra Inner product/bracket Tensor product Complex conj. matrix Transpose of matrix Hermitian
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 7, February 1, 2006
 Chem 350/450 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 006 Christopher J. Cramer ecture 7, February 1, 006 Solved Homework We are given that A is a Hermitian operator such that
Chem 350/450 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 006 Christopher J. Cramer ecture 7, February 1, 006 Solved Homework We are given that A is a Hermitian operator such that
1 Dirac Notation for Vector Spaces
 Theoretical Physics Notes 2: Dirac Notation This installment of the notes covers Dirac notation, which proves to be very useful in many ways. For example, it gives a convenient way of expressing amplitudes
Theoretical Physics Notes 2: Dirac Notation This installment of the notes covers Dirac notation, which proves to be very useful in many ways. For example, it gives a convenient way of expressing amplitudes
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case:
 The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
1. Quantum Mechanics, Cohen Tannoudji, Chapters Linear Algebra, Schaum Series 3. Quantum Chemistry Ch. 6
 Lecture # Today s Program 1. Recap: Classical States, Hamiltonians and time evolution. First postulate The description of a state of a system. 3. Second postulate physical quantities. 4. Linear operators.
Lecture # Today s Program 1. Recap: Classical States, Hamiltonians and time evolution. First postulate The description of a state of a system. 3. Second postulate physical quantities. 4. Linear operators.
Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics. EE270 Fall 2017
 Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics Properties of Vector Spaces Unit vectors ~xi form a basis which spans the space and which are orthonormal ( if i = j ~xi
Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics Properties of Vector Spaces Unit vectors ~xi form a basis which spans the space and which are orthonormal ( if i = j ~xi
Lecture #1. Review. Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1
 L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 0 Fall Linear Algebra. These notes provide a review of basic concepts in linear algebra.
 DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 0 Fall 2016 Linear Algebra These notes provide a review of basic concepts in linear algebra. 1 Vector spaces You are no doubt familiar with vectors in R 2 or R 3, i.e. [ ] 1.1
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 0 Fall 2016 Linear Algebra These notes provide a review of basic concepts in linear algebra. 1 Vector spaces You are no doubt familiar with vectors in R 2 or R 3, i.e. [ ] 1.1
Perturbation Theory 1
 Perturbation Theory 1 1 Expansion of Complete System Let s take a look of an expansion for the function in terms of the complete system : (1) In general, this expansion is possible for any complete set.
Perturbation Theory 1 1 Expansion of Complete System Let s take a look of an expansion for the function in terms of the complete system : (1) In general, this expansion is possible for any complete set.
1 Fundamental physical postulates. C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12
 C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
Physics 741 Graduate Quantum Mechanics 1 Solutions to Midterm Exam, Fall x i x dx i x i x x i x dx
 Physics 74 Graduate Quantum Mechanics Solutions to Midterm Exam, Fall 4. [ points] Consider the wave function x Nexp x ix (a) [6] What is the correct normaliation N? The normaliation condition is. exp,
Physics 74 Graduate Quantum Mechanics Solutions to Midterm Exam, Fall 4. [ points] Consider the wave function x Nexp x ix (a) [6] What is the correct normaliation N? The normaliation condition is. exp,
Vector Spaces in Quantum Mechanics
 Chapter 8 Vector Spaces in Quantum Mechanics We have seen in the previous Chapter that there is a sense in which the state of a quantum system can be thought of as being made up of other possible states.
Chapter 8 Vector Spaces in Quantum Mechanics We have seen in the previous Chapter that there is a sense in which the state of a quantum system can be thought of as being made up of other possible states.
Vector spaces and operators
 Vector spaces and operators Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 2013 22 August, 2013 1 Outline 2 Setting up 3 Exploring 4 Keywords and References Quantum states are vectors We saw that
Vector spaces and operators Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 2013 22 August, 2013 1 Outline 2 Setting up 3 Exploring 4 Keywords and References Quantum states are vectors We saw that
Chapter Two Elements of Linear Algebra
 Chapter Two Elements of Linear Algebra Previously, in chapter one, we have considered single first order differential equations involving a single unknown function. In the next chapter we will begin to
Chapter Two Elements of Linear Algebra Previously, in chapter one, we have considered single first order differential equations involving a single unknown function. In the next chapter we will begin to
We start with some important background material in classical and quantum mechanics.
 Chapter Basics We start with some important background material in classical and quantum mechanics.. Classical mechanics Lagrangian mechanics Compared to Newtonian mechanics, Lagrangian mechanics has the
Chapter Basics We start with some important background material in classical and quantum mechanics.. Classical mechanics Lagrangian mechanics Compared to Newtonian mechanics, Lagrangian mechanics has the
Quantum Physics Notes-7 Operators, Observables, Understanding QM. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 1
 Quantum Physics 2005 Notes-7 Operators, Observables, Understanding QM Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 A summary of this section This section of notes is a brief overview of the ideas in chapters 0-2 of Morrison.
Quantum Physics 2005 Notes-7 Operators, Observables, Understanding QM Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 A summary of this section This section of notes is a brief overview of the ideas in chapters 0-2 of Morrison.
On the quantum theory of rotating electrons
 Zur Quantentheorie des rotierenden Elektrons Zeit. f. Phys. 8 (98) 85-867. On the quantum theory of rotating electrons By Friedrich Möglich in Berlin-Lichterfelde. (Received on April 98.) Translated by
Zur Quantentheorie des rotierenden Elektrons Zeit. f. Phys. 8 (98) 85-867. On the quantum theory of rotating electrons By Friedrich Möglich in Berlin-Lichterfelde. (Received on April 98.) Translated by
Lecture Notes 2: Review of Quantum Mechanics
 Quantum Field Theory for Leg Spinners 18/10/10 Lecture Notes 2: Review of Quantum Mechanics Lecturer: Prakash Panangaden Scribe: Jakub Závodný This lecture will briefly review some of the basic concepts
Quantum Field Theory for Leg Spinners 18/10/10 Lecture Notes 2: Review of Quantum Mechanics Lecturer: Prakash Panangaden Scribe: Jakub Závodný This lecture will briefly review some of the basic concepts
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations
 Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
Quantum Mechanics crash course (For the scholar with an higher education in mathematics) Fabio Grazioso :48
 Quantum Mechanics crash course (For the scholar with an higher education in mathematics) Fabio Grazioso 2015-03-23 19:48 1 Contents 1 Mathematical definitions 3 11 Hilbert space 3 12 Operators on the Hilbert
Quantum Mechanics crash course (For the scholar with an higher education in mathematics) Fabio Grazioso 2015-03-23 19:48 1 Contents 1 Mathematical definitions 3 11 Hilbert space 3 12 Operators on the Hilbert
1 Infinite-Dimensional Vector Spaces
 Theoretical Physics Notes 4: Linear Operators In this installment of the notes, we move from linear operators in a finitedimensional vector space (which can be represented as matrices) to linear operators
Theoretical Physics Notes 4: Linear Operators In this installment of the notes, we move from linear operators in a finitedimensional vector space (which can be represented as matrices) to linear operators
The Particle in a Box
 Page 324 Lecture 17: Relation of Particle in a Box Eigenstates to Position and Momentum Eigenstates General Considerations on Bound States and Quantization Continuity Equation for Probability Date Given:
Page 324 Lecture 17: Relation of Particle in a Box Eigenstates to Position and Momentum Eigenstates General Considerations on Bound States and Quantization Continuity Equation for Probability Date Given:
Quantum Mechanics- I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Quantum Mechanics- I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 4 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics I In today s lecture I will essentially be talking
Quantum Mechanics- I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 4 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics I In today s lecture I will essentially be talking
MODELING MATTER AT NANOSCALES. 4. Introduction to quantum treatments Outline of the principles and the method of quantum mechanics
 MODELING MATTER AT NANOSCALES 4. Introduction to quantum treatments 4.01. Outline of the principles and the method of quantum mechanics 1 Why quantum mechanics? Physics and sizes in universe Knowledge
MODELING MATTER AT NANOSCALES 4. Introduction to quantum treatments 4.01. Outline of the principles and the method of quantum mechanics 1 Why quantum mechanics? Physics and sizes in universe Knowledge
Quantum Mechanics Solutions
 Quantum Mechanics Solutions (a (i f A and B are Hermitian, since (AB = B A = BA, operator AB is Hermitian if and only if A and B commute So, we know that [A,B] = 0, which means that the Hilbert space H
Quantum Mechanics Solutions (a (i f A and B are Hermitian, since (AB = B A = BA, operator AB is Hermitian if and only if A and B commute So, we know that [A,B] = 0, which means that the Hilbert space H
Waves and the Schroedinger Equation
 Waves and the Schroedinger Equation 5 april 010 1 The Wave Equation We have seen from previous discussions that the wave-particle duality of matter requires we describe entities through some wave-form
Waves and the Schroedinger Equation 5 april 010 1 The Wave Equation We have seen from previous discussions that the wave-particle duality of matter requires we describe entities through some wave-form
On common eigenbases of commuting operators
 On common eigenbases of commuting operators Paolo Glorioso In this note we try to answer the question: Given two commuting Hermitian operators A and B, is each eigenbasis of A also an eigenbasis of B?
On common eigenbases of commuting operators Paolo Glorioso In this note we try to answer the question: Given two commuting Hermitian operators A and B, is each eigenbasis of A also an eigenbasis of B?
C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/05 Fall 2005 Lecture 11
 C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/05 Fall 2005 Lecture 11 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/05 Fall 2005 Lecture 11 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Classical harmonic oscillator Linear force acting on a particle (Hooke s law): F =!kx From Newton s law: F = ma = m d x dt =!kx " d x dt + # x = 0, # = k / m Position and momentum solutions oscillate in
Classical harmonic oscillator Linear force acting on a particle (Hooke s law): F =!kx From Newton s law: F = ma = m d x dt =!kx " d x dt + # x = 0, # = k / m Position and momentum solutions oscillate in
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Outline
 Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Outline 1. General structure of quantum mechanics. 8.04 was based primarily on wave mechanics. We review that foundation with the intent to build a more formal basis
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Outline 1. General structure of quantum mechanics. 8.04 was based primarily on wave mechanics. We review that foundation with the intent to build a more formal basis
Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam 2 Solutions
 Chemistry 46 Fall 7 Dr. Jean M. Standard Name SAMPE EXAM Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam Solutions.) ( points) Answer the following questions by selecting the correct answer from the choices provided. a.)
Chemistry 46 Fall 7 Dr. Jean M. Standard Name SAMPE EXAM Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam Solutions.) ( points) Answer the following questions by selecting the correct answer from the choices provided. a.)
Lecture #5: Begin Quantum Mechanics: Free Particle and Particle in a 1D Box
 561 Fall 017 Lecture #5 page 1 Last time: Lecture #5: Begin Quantum Mechanics: Free Particle and Particle in a 1D Box 1-D Wave equation u x = 1 u v t * u(x,t): displacements as function of x,t * nd -order:
561 Fall 017 Lecture #5 page 1 Last time: Lecture #5: Begin Quantum Mechanics: Free Particle and Particle in a 1D Box 1-D Wave equation u x = 1 u v t * u(x,t): displacements as function of x,t * nd -order:
SCE3337 Quantum Mechanics III (Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Optics) Teaching Team
 SCE3337 Quantum Mechanics III 1 SCE3337 Quantum Mechanics III (Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Optics) Teaching Team Dr Robert Sang Robert Sang can be found in Science II Level Room.15, non-personal contact
SCE3337 Quantum Mechanics III 1 SCE3337 Quantum Mechanics III (Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Optics) Teaching Team Dr Robert Sang Robert Sang can be found in Science II Level Room.15, non-personal contact
The Hamiltonian and the Schrödinger equation Consider time evolution from t to t + ɛ. As before, we expand in powers of ɛ; we have. H(t) + O(ɛ 2 ).
 Lecture 12 Relevant sections in text: 2.1 The Hamiltonian and the Schrödinger equation Consider time evolution from t to t + ɛ. As before, we expand in powers of ɛ; we have U(t + ɛ, t) = I + ɛ ( īh ) H(t)
Lecture 12 Relevant sections in text: 2.1 The Hamiltonian and the Schrödinger equation Consider time evolution from t to t + ɛ. As before, we expand in powers of ɛ; we have U(t + ɛ, t) = I + ɛ ( īh ) H(t)
{(V0-E)Ψ(x) if x < 0 or x > L
 This is our first example of a bound state system. A bound state is an eigenstate of the Hamiltonian with eigenvalue E that has asymptotically E < V(x) as x Couple of general theorems, (for single dimension)
This is our first example of a bound state system. A bound state is an eigenstate of the Hamiltonian with eigenvalue E that has asymptotically E < V(x) as x Couple of general theorems, (for single dimension)
Physics 342 Lecture 26. Angular Momentum. Lecture 26. Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I
 Physics 342 Lecture 26 Angular Momentum Lecture 26 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, April 2nd, 2010 We know how to obtain the energy of Hydrogen using the Hamiltonian operator but given a particular
Physics 342 Lecture 26 Angular Momentum Lecture 26 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, April 2nd, 2010 We know how to obtain the energy of Hydrogen using the Hamiltonian operator but given a particular
Lecture-XXVI. Time-Independent Schrodinger Equation
 Lecture-XXVI Time-Independent Schrodinger Equation Time Independent Schrodinger Equation: The time-dependent Schrodinger equation: Assume that V is independent of time t. In that case the Schrodinger equation
Lecture-XXVI Time-Independent Schrodinger Equation Time Independent Schrodinger Equation: The time-dependent Schrodinger equation: Assume that V is independent of time t. In that case the Schrodinger equation
Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017)
 Lecture 1 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 1 Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017) 1.1 Simultaneous Diagonalization In the last lecture, we discussed the situations in which two operators can be simultaneously
Lecture 1 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 1 Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017) 1.1 Simultaneous Diagonalization In the last lecture, we discussed the situations in which two operators can be simultaneously
The Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 The Simple Harmonic Oscillator Asaf Pe er 1 November 4, 215 This part of the course is based on Refs [1] [3] 1 Introduction We return now to the study of a 1-d stationary problem: that of the simple harmonic
The Simple Harmonic Oscillator Asaf Pe er 1 November 4, 215 This part of the course is based on Refs [1] [3] 1 Introduction We return now to the study of a 1-d stationary problem: that of the simple harmonic
Topic 2: The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thin
 The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
Chapter III. Quantum Computation. Mathematical preliminaries. A.1 Complex numbers. A.2 Linear algebra review
 Chapter III Quantum Computation These lecture notes are exclusively for the use of students in Prof. MacLennan s Unconventional Computation course. c 2017, B. J. MacLennan, EECS, University of Tennessee,
Chapter III Quantum Computation These lecture notes are exclusively for the use of students in Prof. MacLennan s Unconventional Computation course. c 2017, B. J. MacLennan, EECS, University of Tennessee,
Physics 505 Homework No. 1 Solutions S1-1
 Physics 505 Homework No s S- Some Preliminaries Assume A and B are Hermitian operators (a) Show that (AB) B A dx φ ABψ dx (A φ) Bψ dx (B (A φ)) ψ dx (B A φ) ψ End (b) Show that AB [A, B]/2+{A, B}/2 where
Physics 505 Homework No s S- Some Preliminaries Assume A and B are Hermitian operators (a) Show that (AB) B A dx φ ABψ dx (A φ) Bψ dx (B (A φ)) ψ dx (B A φ) ψ End (b) Show that AB [A, B]/2+{A, B}/2 where
Lecture 7. More dimensions
 Lecture 7 More dimensions 67 68 LECTURE 7. MORE DIMENSIONS 7.1 Introduction In this lecture we generalize the concepts introduced so far to systems that evolve in more than one spatial dimension. While
Lecture 7 More dimensions 67 68 LECTURE 7. MORE DIMENSIONS 7.1 Introduction In this lecture we generalize the concepts introduced so far to systems that evolve in more than one spatial dimension. While
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS
 MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics
 Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics are often stated in textbooks. There are two main properties of physics upon which these postulates are based: 1)the probability
Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics are often stated in textbooks. There are two main properties of physics upon which these postulates are based: 1)the probability
Matrix Representation
 Matrix Representation Matrix Rep. Same basics as introduced already. Convenient method of working with vectors. Superposition Complete set of vectors can be used to express any other vector. Complete set
Matrix Representation Matrix Rep. Same basics as introduced already. Convenient method of working with vectors. Superposition Complete set of vectors can be used to express any other vector. Complete set
B. Physical Observables Physical observables are represented by linear, hermitian operators that act on the vectors of the Hilbert space. If A is such
 G25.2651: Statistical Mechanics Notes for Lecture 12 I. THE FUNDAMENTAL POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS The fundamental postulates of quantum mechanics concern the following questions: 1. How is the physical
G25.2651: Statistical Mechanics Notes for Lecture 12 I. THE FUNDAMENTAL POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS The fundamental postulates of quantum mechanics concern the following questions: 1. How is the physical
Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics.
 Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics. R. C. Johnson March 10, 2015 1 Brief review of the language and concepts of Quantum Mechanics. We begin with a review of the basic concepts involved in the quantum
Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics. R. C. Johnson March 10, 2015 1 Brief review of the language and concepts of Quantum Mechanics. We begin with a review of the basic concepts involved in the quantum
Mathematical Structures of Quantum Mechanics
 msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page 1 #1 Mathematical Structures of Quantum Mechanics Kow Lung Chang Physics Department, National Taiwan University msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page 2 #2 msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page i #3 TO
msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page 1 #1 Mathematical Structures of Quantum Mechanics Kow Lung Chang Physics Department, National Taiwan University msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page 2 #2 msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page i #3 TO
Path integrals and the classical approximation 1 D. E. Soper 2 University of Oregon 14 November 2011
 Path integrals and the classical approximation D. E. Soper University of Oregon 4 November 0 I offer here some background for Sections.5 and.6 of J. J. Sakurai, Modern Quantum Mechanics. Introduction There
Path integrals and the classical approximation D. E. Soper University of Oregon 4 November 0 I offer here some background for Sections.5 and.6 of J. J. Sakurai, Modern Quantum Mechanics. Introduction There
ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline:
 ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline: Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation Solutions to thetime-dependent Schrödinger Equation Expansion of Energy Eigenstates Things you
ECE 487 Lecture 6 : Time-Dependent Quantum Mechanics I Class Outline: Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation Solutions to thetime-dependent Schrödinger Equation Expansion of Energy Eigenstates Things you
Quantum Mechanics Exercises and solutions
 Quantum Mechanics Exercises and solutions P.J. Mulders Department of Physics and Astronomy, Faculty of Sciences, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam De Boelelaan 181, 181 HV Amsterdam, the Netherlands email:
Quantum Mechanics Exercises and solutions P.J. Mulders Department of Physics and Astronomy, Faculty of Sciences, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam De Boelelaan 181, 181 HV Amsterdam, the Netherlands email:
Quantum Mechanics II
 Quantum Mechanics II Prof. Boris Altshuler March 8, 011 1 Lecture 19 1.1 Second Quantization Recall our results from simple harmonic oscillator. We know the Hamiltonian very well so no need to repeat here.
Quantum Mechanics II Prof. Boris Altshuler March 8, 011 1 Lecture 19 1.1 Second Quantization Recall our results from simple harmonic oscillator. We know the Hamiltonian very well so no need to repeat here.
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2004 Assignment 3
 Quantum Physics II (8.5) Fall 24 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 3, 24 September 23, 24 7:pm This week we continue to study the basic principles of quantum
Quantum Physics II (8.5) Fall 24 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 3, 24 September 23, 24 7:pm This week we continue to study the basic principles of quantum
Lecture 4 (Sep. 18, 2017)
 Lecture 4 8.3 Quantum Theory I, Fall 07 Lecture 4 (Sep. 8, 07) 4. Measurement 4.. Spin- Systems Last time, we said that a general state in a spin- system can be written as ψ = c + + + c, (4.) where +,
Lecture 4 8.3 Quantum Theory I, Fall 07 Lecture 4 (Sep. 8, 07) 4. Measurement 4.. Spin- Systems Last time, we said that a general state in a spin- system can be written as ψ = c + + + c, (4.) where +,
Lecture notes for Atomic and Molecular Physics, FYSC11, HT Joachim Schnadt
 Lecture notes for Atomic and Molecular Physics, FYSC11, HT 015 Joachim Schnadt August 31, 016 Chapter 1 Before we really start 1.1 What have you done previously? Already in FYSA1 you have seen nearly all
Lecture notes for Atomic and Molecular Physics, FYSC11, HT 015 Joachim Schnadt August 31, 016 Chapter 1 Before we really start 1.1 What have you done previously? Already in FYSA1 you have seen nearly all
Physics 221A Fall 2010 Notes 1 The Mathematical Formalism of Quantum Mechanics
 Physics 221A Fall 2010 Notes 1 The Mathematical Formalism of Quantum Mechanics 1. Introduction The prerequisites for Physics 221A include a full year of undergraduate quantum mechanics. In this semester
Physics 221A Fall 2010 Notes 1 The Mathematical Formalism of Quantum Mechanics 1. Introduction The prerequisites for Physics 221A include a full year of undergraduate quantum mechanics. In this semester
Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 14 Coupling of Angular Momenta
 Physics 1A Fall 1996 Notes 14 Coupling of Angular Momenta In these notes we will discuss the problem of the coupling or addition of angular momenta. It is assumed that you have all had experience with
Physics 1A Fall 1996 Notes 14 Coupling of Angular Momenta In these notes we will discuss the problem of the coupling or addition of angular momenta. It is assumed that you have all had experience with
Lecture 5: Harmonic oscillator, Morse Oscillator, 1D Rigid Rotor
 Lecture 5: Harmonic oscillator, Morse Oscillator, 1D Rigid Rotor It turns out that the boundary condition of the wavefunction going to zero at infinity is sufficient to quantize the value of energy that
Lecture 5: Harmonic oscillator, Morse Oscillator, 1D Rigid Rotor It turns out that the boundary condition of the wavefunction going to zero at infinity is sufficient to quantize the value of energy that
Formalism of quantum mechanics
 Formalism of quantum mechanics August 22, 204 Contents Introduction 2 Classical physics 3 Quantum physics 3 4 Harmonic oscillator 0 Introduction Quite a bit of the serious mathematical theory of self-adjoint
Formalism of quantum mechanics August 22, 204 Contents Introduction 2 Classical physics 3 Quantum physics 3 4 Harmonic oscillator 0 Introduction Quite a bit of the serious mathematical theory of self-adjoint
Lecture 5 (Sep. 20, 2017)
 Lecture 5 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 22 Lecture 5 (Sep. 20, 2017) 5.1 The Position Operator In the last class, we talked about operators with a continuous spectrum. A prime eample is the position
Lecture 5 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 22 Lecture 5 (Sep. 20, 2017) 5.1 The Position Operator In the last class, we talked about operators with a continuous spectrum. A prime eample is the position
This is the important completeness relation,
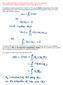 Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Ch 125a Problem Set 1
 Ch 5a Problem Set Due Monday, Oct 5, 05, am Problem : Bra-ket notation (Dirac notation) Bra-ket notation is a standard and convenient way to describe quantum state vectors For example, φ is an abstract
Ch 5a Problem Set Due Monday, Oct 5, 05, am Problem : Bra-ket notation (Dirac notation) Bra-ket notation is a standard and convenient way to describe quantum state vectors For example, φ is an abstract
Basic Quantum Mechanics Prof. Ajoy Ghatak Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Basic Quantum Mechanics Prof. Ajoy Ghatak Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module No. # 07 Bra-Ket Algebra and Linear Harmonic Oscillator II Lecture No. # 02 Dirac s Bra and
Basic Quantum Mechanics Prof. Ajoy Ghatak Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module No. # 07 Bra-Ket Algebra and Linear Harmonic Oscillator II Lecture No. # 02 Dirac s Bra and
Physics 221A Fall 2017 Notes 1 The Mathematical Formalism of Quantum Mechanics
 Copyright c 2017 by Robert G. Littlejohn Physics 221A Fall 2017 Notes 1 The Mathematical Formalism of Quantum Mechanics 1. Introduction The prerequisites for Physics 221A include a full year of undergraduate
Copyright c 2017 by Robert G. Littlejohn Physics 221A Fall 2017 Notes 1 The Mathematical Formalism of Quantum Mechanics 1. Introduction The prerequisites for Physics 221A include a full year of undergraduate
Physics-I. Dr. Anurag Srivastava. Web address: Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus
 Physics-I Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus Syllabus Electrodynamics: Maxwell s equations: differential
Physics-I Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus Syllabus Electrodynamics: Maxwell s equations: differential
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Assignment 3
 Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 00 Assignment Readings The readings below will take you through the material for Problem Sets and 4. Cohen-Tannoudji Ch. II, III. Shankar Ch. 1 continues to be helpful. Sakurai
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 00 Assignment Readings The readings below will take you through the material for Problem Sets and 4. Cohen-Tannoudji Ch. II, III. Shankar Ch. 1 continues to be helpful. Sakurai
04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics
 04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics () States are represented by vectors of length. A physical system is represented by a linear vector space (the space of all its possible states). () Properties
04. Five Principles of Quantum Mechanics () States are represented by vectors of length. A physical system is represented by a linear vector space (the space of all its possible states). () Properties
Representation theory and quantum mechanics tutorial Spin and the hydrogen atom
 Representation theory and quantum mechanics tutorial Spin and the hydrogen atom Justin Campbell August 3, 2017 1 Representations of SU 2 and SO 3 (R) 1.1 The following observation is long overdue. Proposition
Representation theory and quantum mechanics tutorial Spin and the hydrogen atom Justin Campbell August 3, 2017 1 Representations of SU 2 and SO 3 (R) 1.1 The following observation is long overdue. Proposition
Lecture 10: Solving the Time-Independent Schrödinger Equation. 1 Stationary States 1. 2 Solving for Energy Eigenstates 3
 Contents Lecture 1: Solving the Time-Independent Schrödinger Equation B. Zwiebach March 14, 16 1 Stationary States 1 Solving for Energy Eigenstates 3 3 Free particle on a circle. 6 1 Stationary States
Contents Lecture 1: Solving the Time-Independent Schrödinger Equation B. Zwiebach March 14, 16 1 Stationary States 1 Solving for Energy Eigenstates 3 3 Free particle on a circle. 6 1 Stationary States
ECE 501b Homework #4 Due: 10/22/2012
 1. Game Strategy: Consider a multiplayer boardgame that takes place on the following board and with the following rules: 7 8 9 10 6 11 5 12 4 3 2 1 The board contains six squares that are property (the
1. Game Strategy: Consider a multiplayer boardgame that takes place on the following board and with the following rules: 7 8 9 10 6 11 5 12 4 3 2 1 The board contains six squares that are property (the
Self-adjoint extensions of symmetric operators
 Self-adjoint extensions of symmetric operators Simon Wozny Proseminar on Linear Algebra WS216/217 Universität Konstanz Abstract In this handout we will first look at some basics about unbounded operators.
Self-adjoint extensions of symmetric operators Simon Wozny Proseminar on Linear Algebra WS216/217 Universität Konstanz Abstract In this handout we will first look at some basics about unbounded operators.
Statistical Interpretation
 Physics 342 Lecture 15 Statistical Interpretation Lecture 15 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, February 29th, 2008 Quantum mechanics is a theory of probability densities given that we now have an
Physics 342 Lecture 15 Statistical Interpretation Lecture 15 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, February 29th, 2008 Quantum mechanics is a theory of probability densities given that we now have an
Chapter 2 Approximation Methods Can be Used When Exact Solutions to the Schrödinger Equation Can Not be Found.
 Chapter 2 Approximation Methods Can be Used When Exact Solutions to the Schrödinger Equation Can Not be Found. In applying quantum mechanics to 'real' chemical problems, one is usually faced with a Schrödinger
Chapter 2 Approximation Methods Can be Used When Exact Solutions to the Schrödinger Equation Can Not be Found. In applying quantum mechanics to 'real' chemical problems, one is usually faced with a Schrödinger
Quantum mechanics. Chapter The quantum mechanical formalism
 Chapter 5 Quantum mechanics 5.1 The quantum mechanical formalism The realisation, by Heisenberg, that the position and momentum of a quantum mechanical particle cannot be measured simultaneously renders
Chapter 5 Quantum mechanics 5.1 The quantum mechanical formalism The realisation, by Heisenberg, that the position and momentum of a quantum mechanical particle cannot be measured simultaneously renders
Quantum Physics 2006/07
 Quantum Physics 6/7 Lecture 7: More on the Dirac Equation In the last lecture we showed that the Dirac equation for a free particle i h t ψr, t = i hc α + β mc ψr, t has plane wave solutions ψr, t = exp
Quantum Physics 6/7 Lecture 7: More on the Dirac Equation In the last lecture we showed that the Dirac equation for a free particle i h t ψr, t = i hc α + β mc ψr, t has plane wave solutions ψr, t = exp
-state problems and an application to the free particle
 -state problems and an application to the free particle Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 2013 3 September, 2013 Outline 1 Outline 2 The Hilbert space 3 A free particle 4 Keywords
-state problems and an application to the free particle Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 2013 3 September, 2013 Outline 1 Outline 2 The Hilbert space 3 A free particle 4 Keywords
The Schrodinger Wave Equation (Engel 2.4) In QM, the behavior of a particle is described by its wave function Ψ(x,t) which we get by solving:
 When do we use Quantum Mechanics? (Engel 2.1) Basically, when λ is close in magnitude to the dimensions of the problem, and to the degree that the system has a discrete energy spectrum The Schrodinger
When do we use Quantum Mechanics? (Engel 2.1) Basically, when λ is close in magnitude to the dimensions of the problem, and to the degree that the system has a discrete energy spectrum The Schrodinger
The Dirac Approach to Quantum Theory. Paul Renteln. Department of Physics California State University 5500 University Parkway San Bernardino, CA 92407
 November 2009 The Dirac Approach to Quantum Theory Paul Renteln Department of Physics California State University 5500 University Parkway San Bernardino, CA 92407 c Paul Renteln, 1996,2009 Table of Contents
November 2009 The Dirac Approach to Quantum Theory Paul Renteln Department of Physics California State University 5500 University Parkway San Bernardino, CA 92407 c Paul Renteln, 1996,2009 Table of Contents
