CRYSTAL MEASUREMENT AND AXIAL RATIO LABORATORY
|
|
|
- Lambert Stanley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CRYSTAL MEASUREMENT AND AXIAL RATIO LABORATORY George R. McCormick Department of Geology The University of Iowa Iowa City, Iowa Goals of the Exercise This exercise is designed to help you understand relationships among external morphology of crystals (their shape and faces), internal structure (unit cell shape, edge measurements, and volume), Hermann-Mauguin notation for the 32 crystal classes, and Miller Indices of forms and faces. When you look up the information on any mineral in a standard reference or text book such as Dana's Manual of Mineralogy (Klein and Hurlbut, 1993) or Introduction to the Rock Forming Minerals (Deer, Howie, and Zussman, 1966) you will note that the following crystallographic information is given: crystal class in Hermann-Mauguin notation, axial ratios (relative unit cell lengths), absolute unit cell lengths (in Ångstrom units), and common crystal forms present in terms of Miller Indices. Some references may also give Φ (Phi) and ρ (Rho) values for each form. These values have been determined by measurement of the external form of the crystal and can be used to plot the forms or faces on a Wulff stereographic projection. This exercise should help you to understand and use this standard mineralogical information. Before proceeding with the exercise you should have an understanding of the symmetry elements present in the 32 crystal classes and how they are represented by Hermann-Mauguin notation. You should also understand the differences between the axial ratio and absolute cell lengths of a mineral, the meaning and use of Miller Indices, and how mineral faces and forms are plotted on a Wulff stereographic projection. These subjects are covered with examples in most mineralogy textbooks. How Crystals are Measured Each crystal face can be identified by two angular measurements, Φ (Phi) and ρ (Rho). The Rho angle is the angle measured along a great circle from the c-crystallographic axis to the face pole (a line perpendicular to the face). The Phi angle is the angle measured in the plane of the equator of the crystal from the + b axis to the great circle in which the face pole is located. These measurements are similar to the latitude and longitude of any geographic location on earth. Longitude is measured from the Greenwich meridian (a great circle passing through the north and south poles) in the plane of the equator to the great circle on which the geographic location is located. Latitude is measured along a great circle from the equator to the geographic location. Great circles are circles that pass through both the north and south pole (longitude in geographical terms); small circles are planes parallel to the equator (latitude in geographical terms). Measurement are made by an instrument called a goniometer. These can range from very sophisticated two-circle models with microscope and telescope to a very simple one made with a protractor and ruler. All goniometers are designed to measure the interfacial angles between perpendiculars to faces (face poles). Examples of goniometers and how to use them are found in mineralogy textbooks such as Manual of Mineralogy, (Klein and Hurlbut, 1993). Measurements on a goniometer are usually made in zones. All faces are said to be in a zone if they all lie parallel to one crystallographic direction, e.g. all faces parallel to a c- crystallographic axis are in the same zone. The sum of all angles measured between face poles in a zone should be 360. If the total is not 360 a mistake has been made -- either a number was read wrong or an angle missed that should be measured.
2 Faces are grouped together in forms. Each face in a form has the same angular relationship to each of the crystallographic axes. The Form symbol chosen is that for the most positive face, e.g. for a cube there are 6 faces (001), (001 ), (100), ( 1 00 ), (010), (0 1 0) and the form symbol chosen is {100}. Notice that braces are used to indicate forms. The Wulff Stereographic Projection Once a crystal has been measured and each face assigned Φ and ρ values, one can then plot the faces on a Wulff stereonet (also known as an equal angle net) to determine the symmetry of the crystal, and thus, to determine the crystal class to which it belongs. The description of the method of plotting faces on a Wulff projection are found in all mineralogy textbooks such as Manual of Mineralogy (Klein and Hurlbut, 1993). Calculating the Axial Ratio After you have measured a crystal, plotted all the faces on a stereographic projection, determined all the symmetry elements present, and determined the crystal system to which the crystal belongs, you are then ready to calculate the axial ratios. You first must chose a face that cuts all three crystallographic axes and arbitrarily give it the Miller Index (111). This is called a parametral plane. When more than one form cuts all three crystallographic axes it is customary to take the form with the larger faces as the parametral plane, however, either one could be chosen. It is not necessary to calculate an axial ratio for an isometric crystal because all three crystallographic axes are the same length and all angles are 90. However, it is possible to calculate axial ratios for a crystal in any of the other crystal systems. Axial ratio's for the tetragonal and hexagonal crystal systems are written a:c where a = 1 (by convention) and the axial ratio's for the orthorhombic, monoclinic and triclinic crystal systems are written as a:b:c where b = 1 (also by convention). This exercise deals only with crystals in the tetragonal and orthorhombic crystal systems to simplify the calculations needed. Calculations for other crystal systems are simplified by a matrix algebra approach (see Gibbs, this volume). The equations for a and c are as follows: a = h (cot Φ) / k c = l (tan ρ) ( cos Φ) / k where h, k, and l are from the Miller Index for the face (hkl) and are all one if the face is (111). Calculation of Miller Indices Once an axial ratio is determined for a crystal by the equations above, it is possible to calculate the Miller Index of each face or form on the crystal using the same equations in a slightly different form as shown below: k / h = (cot Φ) / a k / l = (tan ρ) (cos Φ) / c Keep in mind that once an axial ratio is determined for a crystal, the same value for a and c should be used to calculate the Miller Index of each face. There are several exceptions: (1) Any face that cuts one axis and is parallel to two other axes can be indexed by inspection, e.g. (001), (010), or (001); and (2) it is not possible to calculate the Miller Index for any face parallel to the b-axis as the angle Φ = 90 and thus the cosine and cotangent values in the above formulas would be 0. A practical solution to the problem is to exchange the a and b values in the axial ratio, divide a, b, and c with the old a value, and use the new a and c values in the above equation for that face (a:b:c is a:1:c = 1:a:c = 1/a : a/a : c/a). (See the worked example.)
3 A Checklist for Crystal Measurement 1) Make a sketch of the mineral and label each face with a small letter such as a, b, c, etc. to identify the face. 2) Measure all interfacial angles by zones and list the angles for each zone. 3) Chose an orientation for the mineral and make an angle table of Φ and ρ values. 4) Plot each face on a Wulff projection using the Φ and ρ values for each face. 5) Determine the symmetry elements that are present from the arrangement of the faces, mark the symmetry on the net, from this determine the crystal class, and label your diagram with the Hermann-Mauguin notation for that class. 6) Choose one face which cuts all three axes as the parametral plane and arbitrarily give it the Miller Index (1 1 1). 7) Calculate the axial ratio. 8) Group the faces into forms and make a Table of Forms. 9) Calculate the Miller Index for each of the remaining forms. References Klein, C. and Hurlbut, C.S., Jr., (1993) Manual of Mineralogy, 21st Edition: New York, John Wiley and Sons, 681p. Deer, W.A., Howie, R.A., and Zussman, J. (1966) An Introduction to the Rock-Forming Minerals: New York, John Wiley and Sons, 528p. Notes for the Instructor The example and four crystal measurement problems have been drawn using the computer program SHAPE (see both Brock and Velbel, this volume). Both a single drawing and stereo pair are given for each problem. The stereo pair drawings can be used with the normal stereoscope used to read air photographs. The interfacial angles were calculated by the SHAPE program. If you have access to SHAPE you can design other crystal problems or have students generate the crystal drawing on the computer and then make the calculations ask for in this exercise.
4 Some geology departments still have access to wooden crystal models (Krantz models). Students can make a simple goniometer with a plastic protractor and ruler and then measure the interfacial angles on the wooden models. They then can make the drawings and angle tables themselves rather than using the computer program.
5 Example of a Crystal Measurement and Calculation The crystal drawing and interfacial table for a crystal are shown below: n m g h k l Interfacial Angles a Λ b = b Λ c = c Λ d = d Λ e = e Λ f = f Λ a = f e a d b c a Λ g = g Λ h = h Λ d = d Λ i = i Λ j = j Λ a = r q i j o p b Λ k = k Λ m = m Λ e = e Λ q = q Λ o = o Λ b = f Λ n = n Λ l = l Λ c = c Λ p = p Λ r = r Λ f = Orient the crystal so that the a,b, and c crystallographic axes are parallel to symmetry axes and calculate the Φ and ρ values for each face.
6 Angle Table: face Φ ρ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Wulff Projection of all Faces and Symmetry Hermann-Mauguin symbol for the symmetry shown is 2/m 2/m 2/m.
7 Table of Forms Form Miller Index Φ ρ a,d {100} b,c,e,f {110} k,l,m,n,o,p,q,r {111} g,h,i,j {201} Calculation of the Axial Ratio Use the Parametral plane (111) which you have arbitrarily chosen because it cuts all three crystallographic axes. a = h (cot Φ) / k = 1 (cot ) / 1 = 1.63 c = l (tan ρ) (cos Φ) / k = 1 (1.537) (0.852) / 1 = 1.31 a:b:c = 1.63:1:1.31 Calculation of the Miller Index for Each Form {111} This is the parametral form and is arbitrarily chosen as (111). {100} Each face in this form cuts only one axis and is parallel to the other two axes. The index is chosen by inspection. {110} This form is parallel to the c-axis and cuts the a- and b-axes, thus, only one equation is needed. k / h = (cot Φ) / a = 1.63 / 1.63 = 1 / 1; thus the Miller Index is (110) {201} Whenever a face has a Φ value of 90 the above equations will not work because the cotangent and cosine functions are 0 for 90. A simple trick can be used to get rid of this Φ = 90 problem by rotating the crystal 90 and making Φ = 0. a:b:c = 1.63:1:1.31 exchange the a and b axes thus b:a:c = 1:1.63:1.31 Divide through by 1.63 (1/1.63):(1.63/1.63):(1.31/1.63) = 0.613:1:0.804 Use the axial ratio a:b:c = 0.613:1:0.804 together with Φ = 0 and the ρ value for the form to calculate the Miller Index. The faces of the form are all parallel to the new a-axis so the h value in the new Miller Index will be 0 and only the following equation need be used: k / l = (tan ρ)(cos Φ) / c = (tan )(cos 0 ) / = (1.608)(1) / = 2/1 The Miller Index would be (021), however, if the crystal is rotated back to its original position according to the original axial ratio (a exchanged for b), then the Miller Index is (201).
8 CRYSTAL MEASUREMENT EXERCISES Crystal #1 Interfacial Angles a Λ b = 90 b Λ c = 90 c Λ d = 90 d Λ a = 90 d h l a g k e i c j f b e Λ i = i Λ k = k Λ g = g Λ e = h Λ l = l Λ j = j Λ f = f Λ h = 96.41
9 Crystal #2 g h v o p w f a i n u x y m j t q e b l s k r d c Interfacial Angles a Λ b = 45 y Λ k = b Λ c = 45 k Λ c = c Λ d = 45 c Λ r = d Λ e = 45 r Λ z = e Λ f = 45 z Λ v = f Λ g = 45 v Λ g = g Λ h = 45 g Λ o = h Λ a = 45 o Λ y = y Λ j = j Λ b = b Λq = q Λ z = z Λ u = u Λ f = f Λ n = z y Λ p = p Λ h = h Λ w = w Λ z = z Λ s = s Λ d = d Λ l = l Λ y = y Λ i = i Λ a = a Λ x = x Λ z = z Λ t = t Λ e = e Λ m = 60.02
10 Crystal # 3 f j n i g h e d a b c m k l Interfacial Angles a Λ b = b Λ c = c Λ d = d Λ e = e Λ f = f Λ g = g Λ b = b Λ k = k Λ m = m Λ e = e Λ i = i Λ g = j Λ f = f Λ n = n Λ l = l Λ c = c Λ h = h Λ j =
11 Crystal # 4 e d a b c Interfacial Angles a Λ g = g Λ m = m Λ v = v Λ p = p Λ j = j Λ a = j p k q u i f o l t v r s h n m g a Λ b = b Λ f = f Λ l = l Λ r = r Λ v = v Λ t = t Λ o = o Λ i = i Λ d = d Λ a = a Λ e = e Λ k = k Λ q = q Λ u = u Λ v = v Λ s = s Λ n = n Λ h = h Λ c = c Λ a = h/n edge Λ f/l edge = 82.02
GEOL. 40 ELEMENTARY MINERALOGY
 CRYSTAL DESCRIPTION AND CALCULATION A. INTRODUCTION This exercise develops the framework necessary for describing a crystal. In essence we shall discuss how we fix the position of any crystallographic
CRYSTAL DESCRIPTION AND CALCULATION A. INTRODUCTION This exercise develops the framework necessary for describing a crystal. In essence we shall discuss how we fix the position of any crystallographic
Crystallographic Calculations
 Page 1 of 7 EENS 2110 Tulane University Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson This page last updated on 07-Sep-2010 Crystallographic calculations involve the following: 1. Miller Indices (hkl) 2. Axial ratios
Page 1 of 7 EENS 2110 Tulane University Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson This page last updated on 07-Sep-2010 Crystallographic calculations involve the following: 1. Miller Indices (hkl) 2. Axial ratios
Axial Ratios, Parameters, Miller Indices
 Page 1 of 7 EENS 2110 Tulane University Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Axial Ratios, Parameters, Miller Indices This document last updated on 07-Sep-2016 We've now seen how crystallographic axes can
Page 1 of 7 EENS 2110 Tulane University Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Axial Ratios, Parameters, Miller Indices This document last updated on 07-Sep-2016 We've now seen how crystallographic axes can
Symmetry. 2-D Symmetry. 2-D Symmetry. Symmetry. EESC 2100: Mineralogy 1. Symmetry Elements 1. Rotation. Symmetry Elements 1. Rotation.
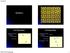 Symmetry a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation Operation Motif = the symbol for a two-fold rotation EESC 2100: Mineralogy 1 a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation
Symmetry a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation Operation Motif = the symbol for a two-fold rotation EESC 2100: Mineralogy 1 a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation
Mineralogy Problem Set Crystal Systems, Crystal Classes
 Mineralogy Problem Set Crystal Systems, Crystal Classes (1) For each of the three accompanying plane patterns: (a) Use a ruler to draw solid lines to show where there are mirror planes on the pattern.
Mineralogy Problem Set Crystal Systems, Crystal Classes (1) For each of the three accompanying plane patterns: (a) Use a ruler to draw solid lines to show where there are mirror planes on the pattern.
Introduction to Crystallography and Mineral Crystal Systems by Mike and Darcy Howard Part 6: The Hexagonal System
 Introduction to Crystallography and Mineral Crystal Systems by Mike and Darcy Howard Part 6: The Hexagonal System Now we will consider the only crystal system that has 4 crystallographic axes! You will
Introduction to Crystallography and Mineral Crystal Systems by Mike and Darcy Howard Part 6: The Hexagonal System Now we will consider the only crystal system that has 4 crystallographic axes! You will
Crystal Chem Crystallography
 Crystal Chem Crystallography Chemistry behind minerals and how they are assembled Bonding properties and ideas governing how atoms go together Mineral assembly precipitation/ crystallization and defects
Crystal Chem Crystallography Chemistry behind minerals and how they are assembled Bonding properties and ideas governing how atoms go together Mineral assembly precipitation/ crystallization and defects
Symmetry Crystallography
 Crystallography Motif: the fundamental part of a symmetric design that, when repeated, creates the whole pattern In 3-D, translation defines operations which move the motif into infinitely repeating patterns
Crystallography Motif: the fundamental part of a symmetric design that, when repeated, creates the whole pattern In 3-D, translation defines operations which move the motif into infinitely repeating patterns
The structure of liquids and glasses. The lattice and unit cell in 1D. The structure of crystalline materials. Describing condensed phase structures
 Describing condensed phase structures Describing the structure of an isolated small molecule is easy to do Just specify the bond distances and angles How do we describe the structure of a condensed phase?
Describing condensed phase structures Describing the structure of an isolated small molecule is easy to do Just specify the bond distances and angles How do we describe the structure of a condensed phase?
St. Xavier s College Mumbai
 St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2016 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.1.01 - Introduction to Mineralogy and Crystallography o
St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2016 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.1.01 - Introduction to Mineralogy and Crystallography o
Earth Materials Lab 2 - Lattices and the Unit Cell
 Earth Materials Lab 2 - Lattices and the Unit Cell Unit Cell Minerals are crystallographic solids and therefore are made of atoms arranged into lattices. The average size hand specimen is made of more
Earth Materials Lab 2 - Lattices and the Unit Cell Unit Cell Minerals are crystallographic solids and therefore are made of atoms arranged into lattices. The average size hand specimen is made of more
TILES, TILES, TILES, TILES, TILES, TILES
 3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Structure Lecture 15 TILES, TILES, TILES, TILES, TILES, TILES Photo courtesy of Chris Applegate. Homework for Fri Nov 4 Study: Allen and Thomas from 3.1.1 to 3.1.4 and 3.2.1, 3.2.4
3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Structure Lecture 15 TILES, TILES, TILES, TILES, TILES, TILES Photo courtesy of Chris Applegate. Homework for Fri Nov 4 Study: Allen and Thomas from 3.1.1 to 3.1.4 and 3.2.1, 3.2.4
St. Xavier s College Mumbai. Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2017 onwards)
 St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.1.01 - Introduction to Mineralogy and Crystallography o
St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.1.01 - Introduction to Mineralogy and Crystallography o
Structural Geology, GEOL 330 Fold mapping lab: Even folds get parasites Spring, 2012
 Structural Geology, GEOL 330 Name: Fold mapping lab: Even folds get parasites Spring, 2012 This exercise is meant to mimic a field experience in which you, the student, will measure beddingcleavage relationships
Structural Geology, GEOL 330 Name: Fold mapping lab: Even folds get parasites Spring, 2012 This exercise is meant to mimic a field experience in which you, the student, will measure beddingcleavage relationships
Overview - Macromolecular Crystallography
 Overview - Macromolecular Crystallography 1. Overexpression and crystallization 2. Crystal characterization and data collection 3. The diffraction experiment 4. Phase problem 1. MIR (Multiple Isomorphous
Overview - Macromolecular Crystallography 1. Overexpression and crystallization 2. Crystal characterization and data collection 3. The diffraction experiment 4. Phase problem 1. MIR (Multiple Isomorphous
n-dimensional, infinite, periodic array of points, each of which has identical surroundings.
 crystallography ll Lattice n-dimensional, infinite, periodic array of points, each of which has identical surroundings. use this as test for lattice points A2 ("bcc") structure lattice points Lattice n-dimensional,
crystallography ll Lattice n-dimensional, infinite, periodic array of points, each of which has identical surroundings. use this as test for lattice points A2 ("bcc") structure lattice points Lattice n-dimensional,
Biaxial Minerals This document last updated on 27-Oct-2014
 1 of 18 10/27/2014 1:10 PM EENS 2110 Tulane University Biaxial Minerals Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson This document last updated on 27-Oct-2014 All minerals that crystallize in the orthorhombic, monoclinic,
1 of 18 10/27/2014 1:10 PM EENS 2110 Tulane University Biaxial Minerals Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson This document last updated on 27-Oct-2014 All minerals that crystallize in the orthorhombic, monoclinic,
Section 8.1 Vector and Parametric Equations of a Line in
 Section 8.1 Vector and Parametric Equations of a Line in R 2 In this section, we begin with a discussion about how to find the vector and parametric equations of a line in R 2. To find the vector and parametric
Section 8.1 Vector and Parametric Equations of a Line in R 2 In this section, we begin with a discussion about how to find the vector and parametric equations of a line in R 2. To find the vector and parametric
Foundations of Mathematics and Pre-Calculus 10. Sample Questions for Algebra and Number. Teacher Version
 Foundations of Mathematics and Pre-Calculus 0 Sample Questions for Algebra and Number Teacher Version Instructions. You may require a protractor and a ruler (metric and imperial) for paper versions of
Foundations of Mathematics and Pre-Calculus 0 Sample Questions for Algebra and Number Teacher Version Instructions. You may require a protractor and a ruler (metric and imperial) for paper versions of
Analytical Methods for Materials
 Analytical Methods for Materials Lesson 11 Crystallography and Crystal Structures, Part 3 Suggested Reading Chapter 6 in Waseda Chapter 1 in F.D. Bloss, Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry: An Introduction,
Analytical Methods for Materials Lesson 11 Crystallography and Crystal Structures, Part 3 Suggested Reading Chapter 6 in Waseda Chapter 1 in F.D. Bloss, Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry: An Introduction,
UNIT I SOLID STATE PHYSICS
 UNIT I SOLID STATE PHYSICS CHAPTER 1 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE 1.1 INTRODUCTION When two atoms are brought together, two kinds of forces: attraction and repulsion come into play. The force of attraction increases
UNIT I SOLID STATE PHYSICS CHAPTER 1 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE 1.1 INTRODUCTION When two atoms are brought together, two kinds of forces: attraction and repulsion come into play. The force of attraction increases
Mineralogy ( ) Chapter 5: Crystallography
 Hashemite University Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of earth and environmental sciences Mineralogy (1201220) Chapter 5: Crystallography Dr. Faten Al-Slaty First Semester 2015/2016
Hashemite University Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of earth and environmental sciences Mineralogy (1201220) Chapter 5: Crystallography Dr. Faten Al-Slaty First Semester 2015/2016
Lecture 2 Symmetry in the solid state -
 Lecture 2 Symmetry in the solid state - Part II: Crystallographic coordinates and Space Groups. 1 Coordinate systems in crystallography and the mathematical form of the symmetry operators 1.1 Introduction
Lecture 2 Symmetry in the solid state - Part II: Crystallographic coordinates and Space Groups. 1 Coordinate systems in crystallography and the mathematical form of the symmetry operators 1.1 Introduction
Tables of crystallographic properties of double antisymmetry space groups
 Tables of crystallographic properties of double antisymmetry space groups Mantao Huang a, Brian K. VanLeeuwen a, Daniel B. Litvin b and Venkatraman Gopalan a * a Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
Tables of crystallographic properties of double antisymmetry space groups Mantao Huang a, Brian K. VanLeeuwen a, Daniel B. Litvin b and Venkatraman Gopalan a * a Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
Fundamentals. Crystal patterns and crystal structures. Lattices, their symmetry and related basic concepts
 Fundamentals. Crystal patterns and crystal structures. Lattices, their symmetry and related basic concepts Didactic material for the MaThCryst schools, France massimo.nespolo@univ-lorraine.fr Ideal vs.
Fundamentals. Crystal patterns and crystal structures. Lattices, their symmetry and related basic concepts Didactic material for the MaThCryst schools, France massimo.nespolo@univ-lorraine.fr Ideal vs.
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 2013/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 201/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 121 - Calculus 1, Fall 201/2014! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics
Introduction Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 201/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 121 - Calculus 1, Fall 201/2014! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics
Introduction to crystallography The unitcell The resiprocal space and unitcell Braggs law Structure factor F hkl and atomic scattering factor f zθ
 Introduction to crystallography The unitcell The resiprocal space and unitcell Braggs law Structure factor F hkl and atomic scattering factor f zθ Introduction to crystallography We divide materials into
Introduction to crystallography The unitcell The resiprocal space and unitcell Braggs law Structure factor F hkl and atomic scattering factor f zθ Introduction to crystallography We divide materials into
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 2012/2013 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Fall 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Fall 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from Algebra
Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Fall 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Fall 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from Algebra
CHAPTER 3 THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 CHAPTER THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Fundamental Concepts.1 What is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? Atomic structure relates to the number of protons
CHAPTER THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Fundamental Concepts.1 What is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? Atomic structure relates to the number of protons
Crystallography basics
 Crystallography basics 1 ? 2 Family of planes (hkl) - Family of plane: parallel planes and equally spaced. The indices correspond to the plane closer to the origin which intersects the cell at a/h, b/k
Crystallography basics 1 ? 2 Family of planes (hkl) - Family of plane: parallel planes and equally spaced. The indices correspond to the plane closer to the origin which intersects the cell at a/h, b/k
Basics of crystallography
 Basics of crystallography 1 Family of planes (hkl) - Family of plane: parallel planes and equally spaced. The indices correspond to the plane closer to the origin which intersects the cell at a/h, b/k
Basics of crystallography 1 Family of planes (hkl) - Family of plane: parallel planes and equally spaced. The indices correspond to the plane closer to the origin which intersects the cell at a/h, b/k
PX-CBMSO Course (2) of Symmetry
 PX-CBMSO Course (2) The mathematical description of Symmetry y PX-CBMSO-June 2011 Cele Abad-Zapatero University of Illinois at Chicago Center for Pharmaceutical Biotechnology. Lecture no. 2 This material
PX-CBMSO Course (2) The mathematical description of Symmetry y PX-CBMSO-June 2011 Cele Abad-Zapatero University of Illinois at Chicago Center for Pharmaceutical Biotechnology. Lecture no. 2 This material
Chapter 2 Introduction to Phenomenological Crystal Structure
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Phenomenological Crystal Structure 2.1 Crystal Structure An ideal crystal represents a periodic pattern generated by infinite, regular repetition of identical microphysical structural
Chapter 2 Introduction to Phenomenological Crystal Structure 2.1 Crystal Structure An ideal crystal represents a periodic pattern generated by infinite, regular repetition of identical microphysical structural
SOLID STATE 18. Reciprocal Space
 SOLID STATE 8 Reciprocal Space Wave vectors and the concept of K-space can simplify the explanation of several properties of the solid state. They will be introduced to provide more information on diffraction
SOLID STATE 8 Reciprocal Space Wave vectors and the concept of K-space can simplify the explanation of several properties of the solid state. They will be introduced to provide more information on diffraction
Angles and Applications
 CHAPTER 1 Angles and Applications 1.1 Introduction Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics concerned with the measurement of the parts, sides, and angles of a triangle. Plane trigonometry, which is the
CHAPTER 1 Angles and Applications 1.1 Introduction Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics concerned with the measurement of the parts, sides, and angles of a triangle. Plane trigonometry, which is the
Structural Geology, GEOL 330 Spring 2012
 Developing the Magic Eye for folds This lab exercise is designed to get you thinking about the chronology of structural processes and and the resultant map patterns in areas with flat topography. You may
Developing the Magic Eye for folds This lab exercise is designed to get you thinking about the chronology of structural processes and and the resultant map patterns in areas with flat topography. You may
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Winter 2012/2013 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Winter 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Winter 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from
Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Winter 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Winter 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from
INTRODUCTION TO THE PETROGRAPHIC MICROSCOPE AND RELIEF, BECKE LINE, AND OBLIQUE ILLUMINATION
 GLY 4200C LAB EXERCISE 10 INTRODUCTION TO THE PETROGRAPHIC MICROSCOPE AND RELIEF, BECKE LINE, AND OBLIQUE ILLUMINATION Locate all of the following microscope parts. Refer to Figure1 1) Eyepiece (note the
GLY 4200C LAB EXERCISE 10 INTRODUCTION TO THE PETROGRAPHIC MICROSCOPE AND RELIEF, BECKE LINE, AND OBLIQUE ILLUMINATION Locate all of the following microscope parts. Refer to Figure1 1) Eyepiece (note the
1/2, 1/2,1/2, is the center of a cube. Induces of lattice directions and crystal planes (a) Directions in a crystal Directions in a crystal are
 Crystallography Many materials in nature occur as crystals. Examples include the metallic elements gold, copper and silver, ionic compounds such as salt (e.s. NaCl); ceramics, rutile TiO2; and nonmetallic
Crystallography Many materials in nature occur as crystals. Examples include the metallic elements gold, copper and silver, ionic compounds such as salt (e.s. NaCl); ceramics, rutile TiO2; and nonmetallic
Topic Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching Activities Resources On-Line Resources
 UNIT 3 Trigonometry and Vectors (P1) Recommended Prior Knowledge. Students will need an understanding and proficiency in the algebraic techniques from either O Level Mathematics or IGCSE Mathematics. Context.
UNIT 3 Trigonometry and Vectors (P1) Recommended Prior Knowledge. Students will need an understanding and proficiency in the algebraic techniques from either O Level Mathematics or IGCSE Mathematics. Context.
Chemical Crystallography
 Chemical Crystallography Prof Andrew Goodwin Michaelmas 2014 Recap: Lecture 1 Why does diffraction give a Fourier transform? k i = k s = 2π/λ k i k s k i k s r l 1 = (λ/2π) k i r l 2 = (λ/2π) k s r Total
Chemical Crystallography Prof Andrew Goodwin Michaelmas 2014 Recap: Lecture 1 Why does diffraction give a Fourier transform? k i = k s = 2π/λ k i k s k i k s r l 1 = (λ/2π) k i r l 2 = (λ/2π) k s r Total
Section 2. Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate.
 Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct
Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky Section 2 Locating Astronomical Objects in the Night Sky What Do You See? What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct
Field Trip to Tempe Butte
 Synopsis Field Trip to Tempe Butte So far you have been identifying rocks and mapping their locations without actually going there. Now it is your chance to put it all together and see real rocks out in
Synopsis Field Trip to Tempe Butte So far you have been identifying rocks and mapping their locations without actually going there. Now it is your chance to put it all together and see real rocks out in
Mathematics Teachers Enrichment Program MTEP 2012 Trigonometry and Bearings
 Mathematics Teachers Enrichment Program MTEP 2012 Trigonometry and Bearings Trigonometry in Right Triangles A In right ABC, AC is called the hypotenuse. The vertices are labelled using capital letters.
Mathematics Teachers Enrichment Program MTEP 2012 Trigonometry and Bearings Trigonometry in Right Triangles A In right ABC, AC is called the hypotenuse. The vertices are labelled using capital letters.
GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity
 Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity I. Geomagnetism The earth's magnetic field can be viewed as a simple bar magnet located near the center of
Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity I. Geomagnetism The earth's magnetic field can be viewed as a simple bar magnet located near the center of
Crystallography Reading: Warren, Chapters 2.1, 2.2, 2.6, 8 Surface symmetry: Can be a clue to underlying structure. Examples:
 Crystallography Reading: Warren, Chapters 2.1, 2.2, 2.6, 8 Surface symmetry: Can be a clue to underlying structure. Examples: Snow (SnowCrystals.com) Bismuth (Bao, Kavanagh, APL 98 66103 (2005) Hexagonal,
Crystallography Reading: Warren, Chapters 2.1, 2.2, 2.6, 8 Surface symmetry: Can be a clue to underlying structure. Examples: Snow (SnowCrystals.com) Bismuth (Bao, Kavanagh, APL 98 66103 (2005) Hexagonal,
MATHEMATICS UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED HIGHER TIER
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3300U60-1 S17-3300U60-1 MATHEMATICS UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED HIGHER TIER TUESDAY, 20 JUNE 2017 AFTERNOON 1 hour 45 minutes For s use ADDITIONAL
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3300U60-1 S17-3300U60-1 MATHEMATICS UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED HIGHER TIER TUESDAY, 20 JUNE 2017 AFTERNOON 1 hour 45 minutes For s use ADDITIONAL
Vector Algebra II: Scalar and Vector Products
 Chapter 2 Vector Algebra II: Scalar and Vector Products ------------------- 2 a b = 0, φ = 90 The vectors are perpendicular to each other 49 Check the result geometrically by completing the diagram a =(4,
Chapter 2 Vector Algebra II: Scalar and Vector Products ------------------- 2 a b = 0, φ = 90 The vectors are perpendicular to each other 49 Check the result geometrically by completing the diagram a =(4,
Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1
 Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1 (a.g.kovalev@dpmms.cam.ac.uk) 1. Suppose that H is a hyperplane in Euclidean n-space R n defined by u x = c for some unit vector u and constant c. The reflection
Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1 (a.g.kovalev@dpmms.cam.ac.uk) 1. Suppose that H is a hyperplane in Euclidean n-space R n defined by u x = c for some unit vector u and constant c. The reflection
World Time-Day Calculator Lab
 Background: Time zones around the Earth are bounded by imaginary lines called lines of longitude, or meridians. On a globe or map of the world, they are the lines that are perpendicular to the equator.
Background: Time zones around the Earth are bounded by imaginary lines called lines of longitude, or meridians. On a globe or map of the world, they are the lines that are perpendicular to the equator.
Crystallographic Symmetry. Jeremy Karl Cockcroft
 Crystallographic Symmetry Jeremy Karl Cockcroft Why bother? To describe crystal structures Simplifies the description, e.g. NaCl structure Requires coordinates for just 2 atoms + space group symmetry!
Crystallographic Symmetry Jeremy Karl Cockcroft Why bother? To describe crystal structures Simplifies the description, e.g. NaCl structure Requires coordinates for just 2 atoms + space group symmetry!
Marquette University
 Marquette University 2 0 7 C O M P E T I T I V E S C H O L A R S H I P E X A M I N A T I O N I N M A T H E M A T I C S Do not open this booklet until you are directed to do so.. Fill out completely the
Marquette University 2 0 7 C O M P E T I T I V E S C H O L A R S H I P E X A M I N A T I O N I N M A T H E M A T I C S Do not open this booklet until you are directed to do so.. Fill out completely the
Student Exploration: Vectors
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Vectors Vocabulary: component, dot product, magnitude, resultant, scalar, unit vector notation, vector Prior Knowledge Question (Do this BEFORE using the Gizmo.) An airplane
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Vectors Vocabulary: component, dot product, magnitude, resultant, scalar, unit vector notation, vector Prior Knowledge Question (Do this BEFORE using the Gizmo.) An airplane
Section 6.2 Notes Page Trigonometric Functions; Unit Circle Approach
 Section Notes Page Trigonometric Functions; Unit Circle Approach A unit circle is a circle centered at the origin with a radius of Its equation is x y = as shown in the drawing below Here the letter t
Section Notes Page Trigonometric Functions; Unit Circle Approach A unit circle is a circle centered at the origin with a radius of Its equation is x y = as shown in the drawing below Here the letter t
USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB
 USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB 1. Explain the main differences between using a star wheel and a star chart to find things in the night sky. 2. Explain the terms Hour Angle, Meridian and
USING YOUR FIELD GUIDE AND STAR CHARTS PRELAB 1. Explain the main differences between using a star wheel and a star chart to find things in the night sky. 2. Explain the terms Hour Angle, Meridian and
The Mohr Stress Diagram. Edvard Munch as a young geologist!
 The Mohr Stress Diagram Edvard Munch as a young geologist! Material in the chapter is covered in Chapter 7 in Fossen s text The Mohr Stress Diagram A means by which two stresses acting on a plane of known
The Mohr Stress Diagram Edvard Munch as a young geologist! Material in the chapter is covered in Chapter 7 in Fossen s text The Mohr Stress Diagram A means by which two stresses acting on a plane of known
A shape which can be divided by a straight line, so that each part is the mirror image of the other has reflective symmetry.
 SYMMETRY There are two kinds of symmetry: a) reflective symmetry b) rotational symmetry a) Reflective Symmetry A shape which can be divided by a straight line, so that each part is the image of the other
SYMMETRY There are two kinds of symmetry: a) reflective symmetry b) rotational symmetry a) Reflective Symmetry A shape which can be divided by a straight line, so that each part is the image of the other
The time they chose was the Vernal Equinox of March 20, 2000, at 7:30 AM Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Right Ascension Offset
 Star Coordinates and the Celestial Dome Astronomers have mapped out the sky in the shape of a spherical dome the Celestial Sphere, where earth is just a tiny spec at the center of the dome. The celestial
Star Coordinates and the Celestial Dome Astronomers have mapped out the sky in the shape of a spherical dome the Celestial Sphere, where earth is just a tiny spec at the center of the dome. The celestial
The function x² + y² = 1, is the algebraic function that describes a circle with radius = 1.
 8.3 The Unit Circle Outline Background Trig Function Information Unit circle Relationship between unit circle and background information 6 Trigonometric Functions Values of 6 Trig Functions The Unit Circle
8.3 The Unit Circle Outline Background Trig Function Information Unit circle Relationship between unit circle and background information 6 Trigonometric Functions Values of 6 Trig Functions The Unit Circle
2.1 Identifying Patterns
 I. Foundations for Functions 2.1 Identifying Patterns: Leaders' Notes 2.1 Identifying Patterns Overview: Objective: s: Materials: Participants represent linear relationships among quantities using concrete
I. Foundations for Functions 2.1 Identifying Patterns: Leaders' Notes 2.1 Identifying Patterns Overview: Objective: s: Materials: Participants represent linear relationships among quantities using concrete
We need to be able to describe planes and directions.
 We need to be able to describe planes and directions. Miller Indices & XRD 1 2 Determining crystal structure and identifying materials (B) Plastic deformation Plastic deformation and mechanical properties
We need to be able to describe planes and directions. Miller Indices & XRD 1 2 Determining crystal structure and identifying materials (B) Plastic deformation Plastic deformation and mechanical properties
Celestial Coordinate Systems
 Celestial Coordinate Systems Introduction How does one go about describing the position of an object in the sky? Astronomers cannot rely on the imprecise method of merely pointing at an object. There must
Celestial Coordinate Systems Introduction How does one go about describing the position of an object in the sky? Astronomers cannot rely on the imprecise method of merely pointing at an object. There must
Chapter 4. Crystallography. 4.1 The crystalline state
 Crystallography Atoms form bonds which attract them to one another. When you put many atoms together and they form bonds amongst themselves, are there any rules as to how they order themselves? Can we
Crystallography Atoms form bonds which attract them to one another. When you put many atoms together and they form bonds amongst themselves, are there any rules as to how they order themselves? Can we
Location and Distance on Earth (Chapter 22 part 1)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Location and Distance on Earth (Chapter 22 part 1) For this assignment you will require: a calculator, protractor, and a metric ruler, and an
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Location and Distance on Earth (Chapter 22 part 1) For this assignment you will require: a calculator, protractor, and a metric ruler, and an
Latitude and Longitude Pre Test
 Name Date Latitude and Longitude Pre Test Multiple Choice Directions: For questions, 1 10 circle the answer that letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 1 point each. 1. To locate
Name Date Latitude and Longitude Pre Test Multiple Choice Directions: For questions, 1 10 circle the answer that letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 1 point each. 1. To locate
Röntgenpraktikum. M. Oehzelt. (based on the diploma thesis of T. Haber [1])
![Röntgenpraktikum. M. Oehzelt. (based on the diploma thesis of T. Haber [1]) Röntgenpraktikum. M. Oehzelt. (based on the diploma thesis of T. Haber [1])](/thumbs/91/106501237.jpg) Röntgenpraktikum M. Oehzelt (based on the diploma thesis of T. Haber [1]) October 21, 2004 Contents 1 Fundamentals 2 1.1 X-Ray Radiation......................... 2 1.1.1 Bremsstrahlung......................
Röntgenpraktikum M. Oehzelt (based on the diploma thesis of T. Haber [1]) October 21, 2004 Contents 1 Fundamentals 2 1.1 X-Ray Radiation......................... 2 1.1.1 Bremsstrahlung......................
Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3
 Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3 Day 1 Objective I will understand maps can be used to find locations on Earth and to represent information about features on Earth s Surface I will understand
Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3 Day 1 Objective I will understand maps can be used to find locations on Earth and to represent information about features on Earth s Surface I will understand
A web based crystallographic tool for the construction of nanoparticles
 A web based crystallographic tool for the construction of nanoparticles Alexios Chatzigoulas 16/5/2018 + = 1 Outline Introduction Motivation Crystallography theory Creation of a web based crystallographic
A web based crystallographic tool for the construction of nanoparticles Alexios Chatzigoulas 16/5/2018 + = 1 Outline Introduction Motivation Crystallography theory Creation of a web based crystallographic
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 03 Symmetry in Perfect Solids Worked Examples Stated without prove to be in the lecture.
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 03 Symmetry in Perfect Solids Worked Examples Stated without prove to be in the lecture.
Lecture 1 Symmetry in the solid state -
 Lecture 1 Symmetry in the solid state - Part I: Simple patterns and groups 1 Symmetry operators: key concepts Operators: transform (move) the whole pattern (i.e., the attributes, or content, of all points
Lecture 1 Symmetry in the solid state - Part I: Simple patterns and groups 1 Symmetry operators: key concepts Operators: transform (move) the whole pattern (i.e., the attributes, or content, of all points
(b: 5 pts) A thin plastic rod of length 4.5 m has been rubbed with a wool cloth, and has gained a net charge
 Problem 1 (25 pts). (a: 5 pts) student claimed that the formula for the electric field outside a cube of edge length L, carrying a uniformly distributed charge Q, at a distance x from the center of the
Problem 1 (25 pts). (a: 5 pts) student claimed that the formula for the electric field outside a cube of edge length L, carrying a uniformly distributed charge Q, at a distance x from the center of the
Nove fizickohemijske metode. Ivana Radosavljevic Evans Durham University, UK
 Nove fizickohemijske metode Ivana Radosavljevic Evans Durham University, UK Nove fizickohemijske metode: Metode zasnovane na sinhrotronskom zracenju Plan predavanja: Difrakcione metode strukturne karakterizacije
Nove fizickohemijske metode Ivana Radosavljevic Evans Durham University, UK Nove fizickohemijske metode: Metode zasnovane na sinhrotronskom zracenju Plan predavanja: Difrakcione metode strukturne karakterizacije
Part I. PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts:
 Student Name: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory #13 Structural Geology II Drawing and Analyzing Folds and Faults Grade: Introduction & Purpose: Structural geology is the study of how geologic rock units
Student Name: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory #13 Structural Geology II Drawing and Analyzing Folds and Faults Grade: Introduction & Purpose: Structural geology is the study of how geologic rock units
VECTORS. 3-1 What is Physics? 3-2 Vectors and Scalars CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 3 VECTORS 3-1 What is Physics? Physics deals with a great many quantities that have both size and direction, and it needs a special mathematical language the language of vectors to describe those
CHAPTER 3 VECTORS 3-1 What is Physics? Physics deals with a great many quantities that have both size and direction, and it needs a special mathematical language the language of vectors to describe those
GY-343 Petrology Petrographic Microscope Laboratory
 Introduction to the Petrographic Microscope In this laboratory you will be using the petrographic microscope to analyze thin sections of various types of igneous rocks. You will be assigned a thin section
Introduction to the Petrographic Microscope In this laboratory you will be using the petrographic microscope to analyze thin sections of various types of igneous rocks. You will be assigned a thin section
5 Symmetries and point group in a nut shell
 30 Phys520.nb 5 Symmetries and point group in a nut shell 5.1. Basic ideas: 5.1.1. Symmetry operations Symmetry: A system remains invariant under certain operation. These operations are called symmetry
30 Phys520.nb 5 Symmetries and point group in a nut shell 5.1. Basic ideas: 5.1.1. Symmetry operations Symmetry: A system remains invariant under certain operation. These operations are called symmetry
Analytical Methods for Materials
 Analytical Methods for Materials Laboratory Module # Crystal Structure Determination for Non-Cubic Crystals Suggested Reading 1. Y. Waseda, E. Matsubara, and K. Shinoda, X-ray Diffraction Crystallography,
Analytical Methods for Materials Laboratory Module # Crystal Structure Determination for Non-Cubic Crystals Suggested Reading 1. Y. Waseda, E. Matsubara, and K. Shinoda, X-ray Diffraction Crystallography,
Structure of Earth Materials
 12.108 Structure of Earth Materials I. Lecture 1: Minerals and Symmetry Operations Definition of a mineral A mineral is a naturally occurring homogeneous solid usually formed by inorganic processes. It
12.108 Structure of Earth Materials I. Lecture 1: Minerals and Symmetry Operations Definition of a mineral A mineral is a naturally occurring homogeneous solid usually formed by inorganic processes. It
10-7. The Law of Sines. Vocabulary. Solutions to cos = k When 0 < < 180. Solutions to sin = k When 0 < < 180. Lesson. Mental Math
 Chapter 10 Lesson 10-7 The Law of Sines Vocabulary solving a triangle BIG IDE Given S or S in a triangle, the Law of Sines enables you to fi nd the lengths of the remaining sides. One of the most important
Chapter 10 Lesson 10-7 The Law of Sines Vocabulary solving a triangle BIG IDE Given S or S in a triangle, the Law of Sines enables you to fi nd the lengths of the remaining sides. One of the most important
7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS
 7-1 7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS 7.1 THE MOHR CIRCLE The discussions in Chapters and 5 were largely concerned with vertical stresses. A more detailed examination of soil behaviour requires a knowledge
7-1 7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS 7.1 THE MOHR CIRCLE The discussions in Chapters and 5 were largely concerned with vertical stresses. A more detailed examination of soil behaviour requires a knowledge
1. Write down the term 2. Write down the book definition 3. Put the definition in your own words 4. Draw an image and/or put a Real Life Example
 Unit 1 Vocabulary 1. Write down the term 2. Write down the book definition 3. Put the definition in your own words 4. Draw an image and/or put a Real Life Example Absolute Location Where Is It EXACTLY?
Unit 1 Vocabulary 1. Write down the term 2. Write down the book definition 3. Put the definition in your own words 4. Draw an image and/or put a Real Life Example Absolute Location Where Is It EXACTLY?
Homework 1 (not graded) X-ray Diffractometry CHE Multiple Choice. 1. One of the methods of reducing exposure to radiation is to minimize.
 Homework 1 (not graded) X-ray Diffractometry CHE 380.45 Multiple Choice 1. One of the methods of reducing exposure to radiation is to minimize. a) distance b) humidity c) time d) speed e) shielding 2.
Homework 1 (not graded) X-ray Diffractometry CHE 380.45 Multiple Choice 1. One of the methods of reducing exposure to radiation is to minimize. a) distance b) humidity c) time d) speed e) shielding 2.
Introduction to Statics
 Introduction to Statics.PDF Edition Version 0.95 Unit 7 Vector Products Helen Margaret Lester Plants Late Professor Emerita Wallace Starr Venable Emeritus Associate Professor West Virginia University,
Introduction to Statics.PDF Edition Version 0.95 Unit 7 Vector Products Helen Margaret Lester Plants Late Professor Emerita Wallace Starr Venable Emeritus Associate Professor West Virginia University,
- 5π 2. a. a. b. b. In 5 7, convert to a radian measure without using a calculator
 4-1 Skills Objective A In 1 and, the measure of a rotation is given. a. Convert the measure to revolutions. b. On the circle draw a central angle showing the given rotation. 1. 5. radians - a. a. b. b.
4-1 Skills Objective A In 1 and, the measure of a rotation is given. a. Convert the measure to revolutions. b. On the circle draw a central angle showing the given rotation. 1. 5. radians - a. a. b. b.
NMR Shifts. I Introduction and tensor/crystal symmetry.
 NMR Shifts. I Introduction and tensor/crystal symmetry. These notes were developed for my group as introduction to NMR shifts and notation. 1) Basic shift definitions and notation: For nonmagnetic materials,
NMR Shifts. I Introduction and tensor/crystal symmetry. These notes were developed for my group as introduction to NMR shifts and notation. 1) Basic shift definitions and notation: For nonmagnetic materials,
Course Outline and Objectives. MA 1453 Precalculus with Graphing Calculators
 Effective Fall 2011 Course Outline and Objectives MA 1453 Precalculus with Graphing Calculators TEXT: Precalculus, 5 th Edition, by Faires and DeFranza ISBN 978-0-8400-6862-0 NOTE: A graphing calculator
Effective Fall 2011 Course Outline and Objectives MA 1453 Precalculus with Graphing Calculators TEXT: Precalculus, 5 th Edition, by Faires and DeFranza ISBN 978-0-8400-6862-0 NOTE: A graphing calculator
Thank you for your participation Good Luck!
 Friday, September 11, 2009 Choose 10 different numbers from {0, 1, 2,, 14} and put them into the following circles. If there is an edge between two circles, then take the absolute value of their difference.
Friday, September 11, 2009 Choose 10 different numbers from {0, 1, 2,, 14} and put them into the following circles. If there is an edge between two circles, then take the absolute value of their difference.
Vector equations of lines in the plane and 3-space (uses vector addition & scalar multiplication).
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.6: Lines and Planes From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Plotting points, sketching vectors. Be able to find the component form a vector given
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.6: Lines and Planes From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Plotting points, sketching vectors. Be able to find the component form a vector given
Resolution: maximum limit of diffraction (asymmetric)
 Resolution: maximum limit of diffraction (asymmetric) crystal Y X-ray source 2θ X direct beam tan 2θ = Y X d = resolution 2d sinθ = λ detector 1 Unit Cell: two vectors in plane of image c* Observe: b*
Resolution: maximum limit of diffraction (asymmetric) crystal Y X-ray source 2θ X direct beam tan 2θ = Y X d = resolution 2d sinθ = λ detector 1 Unit Cell: two vectors in plane of image c* Observe: b*
An elementary argument for the magnetic field outside a solenoid. Abstract
 An elementary argument for the magnetic field outside a solenoid Aritro Pathak Department of Mathematics Brandeis University (Dated: October 26, 2016) arxiv:1610.07876v1 [physics.gen-ph] 17 Oct 2016 Abstract
An elementary argument for the magnetic field outside a solenoid Aritro Pathak Department of Mathematics Brandeis University (Dated: October 26, 2016) arxiv:1610.07876v1 [physics.gen-ph] 17 Oct 2016 Abstract
Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition
 Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition 1 Appendix A : Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values Sets A set is a collection of objects with an important
Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition 1 Appendix A : Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values Sets A set is a collection of objects with an important
Lattices and Symmetry Scattering and Diffraction (Physics)
 Lattices and Symmetry Scattering and Diffraction (Physics) James A. Kaduk INEOS Technologies Analytical Science Research Services Naperville IL 60566 James.Kaduk@innovene.com 1 Harry Potter and the Sorcerer
Lattices and Symmetry Scattering and Diffraction (Physics) James A. Kaduk INEOS Technologies Analytical Science Research Services Naperville IL 60566 James.Kaduk@innovene.com 1 Harry Potter and the Sorcerer
Practice Problems Set II
 P1. For the HCP crystal structure, (a) show that the ideal c/a ratio is 1.633; (b) show that the atomic packing factor for HCP is 0.74. (a) A sketch of one-third of an HCP unit cell is shown below. Consider
P1. For the HCP crystal structure, (a) show that the ideal c/a ratio is 1.633; (b) show that the atomic packing factor for HCP is 0.74. (a) A sketch of one-third of an HCP unit cell is shown below. Consider
GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles. Name
 GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles Name Instructions: Follow the directions given. Take a picture (with your phone) of your work showing final pole locations on the globe. Print pictures and turn
GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles Name Instructions: Follow the directions given. Take a picture (with your phone) of your work showing final pole locations on the globe. Print pictures and turn
Using Proportions to Solve Percent Problems (page 562)
 LESSON Name 81 Using Proportions to Solve Percent Problems (page 562) Percent problems can be solved using proportions. Make and complete a percent box. (The total is always 100.) 1. Write in the known
LESSON Name 81 Using Proportions to Solve Percent Problems (page 562) Percent problems can be solved using proportions. Make and complete a percent box. (The total is always 100.) 1. Write in the known
Vectors. both a magnitude and a direction. Slide Pearson Education, Inc.
 Vectors A quantity that is fully described The velocity vector has both a magnitude and a direction. by a single number is called a scalar quantity (i.e., mass, temperature, volume). A quantity having
Vectors A quantity that is fully described The velocity vector has both a magnitude and a direction. by a single number is called a scalar quantity (i.e., mass, temperature, volume). A quantity having
College Physics 201 Graphing Review and Analysis
 Northern Michigan University Graphing Review and Analysis Page-1 College Physics 201 Graphing Review and Analysis Materials: Graph paper, ruler, pencil and calculator. 1 Purpose The goal of these laboratory
Northern Michigan University Graphing Review and Analysis Page-1 College Physics 201 Graphing Review and Analysis Materials: Graph paper, ruler, pencil and calculator. 1 Purpose The goal of these laboratory
Algebra/Trigonometry Review Notes
 Algebra/Trigonometry Review Notes MAC 41 Calculus for Life Sciences Instructor: Brooke Quinlan Hillsborough Community College ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR CALCULUS 1 TOPIC 1: POLYNOMIAL BASICS, POLYNOMIAL END BEHAVIOR,
Algebra/Trigonometry Review Notes MAC 41 Calculus for Life Sciences Instructor: Brooke Quinlan Hillsborough Community College ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR CALCULUS 1 TOPIC 1: POLYNOMIAL BASICS, POLYNOMIAL END BEHAVIOR,
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS MINERALS LAB 1 HANDOUT
 EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS MINERALS LAB 1 HANDOUT Sources: Cornell EAS302 lab, UMass Lowell 89.301 Mineralogy, LHRIC.org The Petrographic Microscope As you know, light is an electromagnetic
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS MINERALS LAB 1 HANDOUT Sources: Cornell EAS302 lab, UMass Lowell 89.301 Mineralogy, LHRIC.org The Petrographic Microscope As you know, light is an electromagnetic
Analytical Methods for Materials
 Analytical Methods for Materials Lesson 15 Reciprocal Lattices and Their Roles in Diffraction Studies Suggested Reading Chs. 2 and 6 in Tilley, Crystals and Crystal Structures, Wiley (2006) Ch. 6 M. DeGraef
Analytical Methods for Materials Lesson 15 Reciprocal Lattices and Their Roles in Diffraction Studies Suggested Reading Chs. 2 and 6 in Tilley, Crystals and Crystal Structures, Wiley (2006) Ch. 6 M. DeGraef
