conditional expression \LET E2 let x == E1 E2 local definition formulae
|
|
|
- Derek Banks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Z notation This file is a translation of the German original which can be found at uni-muenchen.de/lehre/ws0203/gse/z-notation. The following tables provide an overview of the notation used in Z. The L A TEXinput format is accepted by most Z tools, e.g. Z/Eves or Jaza. However, you need the file zed-csp.sty or z-eves.sty, respectively to compile your latex source file. All inputs must be declared inside a zed environment, i.e. between \begin{zed} and \end{zed}. declarations and definitions [type] [type] basic type id params == expr id params == expr shortcut T ::= c d \ldata U \rdata \begin{axdef} x: T \end{axdef} \begin{gendef}[x] x: X \end{gendef} \begin{schema}{s} x: T \end{schema} T ::= c d U x : T [X] x : X S x : T definition of free types axiomatic definitions generic definitions schema definition S \defs [x:t ] S = [x : T ] schema definition in horizontal notation schema expressions Id, Id!, Id?, Id_n Id, Id!, Id?, Id n decorations (n digit) \Delta S S shortcut for S S \Xi S ΞS shortcut for S S θs = θs \lnot S, S \land T, S \lor T \forall S \exists S S, S T, S T x : T S x : T S logical schema conjunctions quantifiers (also possible: 1 ) S \hide (x) S \ (x) Hiding, same as x : T S, where T is the type of x in S S \project T S T projection, same as (S T) \ ( x), where x represents all variables in S which are not in T S \semi T S o 9 T sequential composition S \pipe T S>>T pipe-composition \pre S pre S precondition (hiding of output and striked out variables, respectively) 1
2 expressions \{ E \} {x : T E} set comprehension (E optional), e.g. {x : Z x > 5 x x} = {36, 49, 64,...} (\lambda E) (λ x : T E) λ-expression, same as {x : T (x, E)} f x f x function application (\mu E) (µ x : T E) unique specification (E optional), e.g. (µ x : N 1 x x = x x + x) = 2 \IF \THEN E1 \ELSE E2 if then E1 else E2 conditional expression \LET E2 let x == E1 E2 local definition formulae x = y, x \neq y x = y, x y (in-)equality x \in S, x \notin S x S, x / S (non-)membership S \subseteq T S T subset S \subset T S T proper subset \lnot negation \land Q Q conjunction \lor Q Q disjunction \implies Q Q implication \iff Q Q equivalence \forall x : T universal quantifier \exists x : T existential quantifier \exists_1 1 x : T unique existence a \inrel{r} b a R b infix-relation, same as (a, b) R sets \emptyset empty set \{a, b\} {a, b} enumeration of finite sets S \cup T, S \cap T S T, S T union, intersection S \setminus T S \ T complement \power S, \power_1 S S, 1 S power set ( 1 S = S \ ) S \cross T S T cartesian product \bigcup TT TT generalized union, a TT S TT a S \bigcap TT TT generalized intersection, a TT S TT a S 2
3 pairs and tuples (a, b) (a, b) pair and tuple construction (arbitrary arity) a \mapsto b a b ordered pair ( maplet ), same as (a, b) t.n t.n selection of the nth component, e.g. (a, b, c).2 = b first p first p first component, first(a, b) = a (same as p.1) second p second p second component, second(a, b) = b (same as p.2) relations X \rel Y X Y set of relations, X Y = (X Y) \dom R dom R domain, dom R = { x : X; y : Y x R y x } \ran R ran R range, ran R = { x : X; y : Y x R y y } \id X id X identity relation, id X = (λ x : X x) Q \comp R Q o 9 R composition of relations, Q o 9 R = { x : X; z : Z ( y : Y x Q y y R z) x z } R \circ Q R Q backward composition, R Q = Q o 9 R, (f g) x = f (g x) R \inv R inverse relation, R = { x : X; y : Y x R y y x } A \dres R A R domain restriction, A R = { x : X; y : Y x R y x A x y } A \ndres R A R domain anti-restriction, A R = { x : X; y : Y x R y x / A x y } A \rres R A R range restriction, A R = { x : X; y : Y x R y y B x y } A \nrres R A R range anti-restriction, A R = { x : X; y : Y x R y y / B x y } R \limg A \rimg R( A ) relational mapping, R( A ) = ran(a R) Q \oplus R Q R overwriting, Q R = (dom R Q) R R \plus R + transitive closure, R + = { Q : X X R Q Q o 9 Q Q } R \star R reflexive transitive closure, R = id X R + Rˆ{k} R k relational iteration, R 0 = id X, R k+1 = R o 9 R k, R k = (R ) k functions X \pfun Y X Y partial function, { R : X Y x : X; y 1, y 2 : Y x R y 1 x R y 2 y 1 = y 2 } X \fun Y X Y total function, X Y = { f : X Y dom f = X} X \pinj Y X Y partial injection, { f : X Y x 1, x 2 : dom f f x 1 = f x 2 x 1 = x 2 } X \inj Y X Y total injection, X Y = (X Y) (X Y) X \psurj Y X Y partial surjection, X Y = { f : X Y ran f = B } X \surj Y X Y total surjection, X Y = (X Y) (X Y) X \bij Y X Y bijection, X Y = (X Y) (X Y) 3
4 numbers \num Z integers \nat N natural numbers, N = { n : Z n 0 } \nat_1 N 1 positive natural numbers, N 1 = N \ {0} +, -, * +,, arithmetic operations (Z Z Z) \div, \mod div, mod division, modulo (Z (Z \ {0}) Z) <, \leq, >, \geq <,, >, arithmetic comparisons (Z Z) succ succ successor (N N) a \upto b a.. b intervals, a.. b = { n : Z a n n b } min S, max S min S, max S minimum/maximum element of a set of number (if ex.) min S = (µ m : S ( n : S m n)) finite sets \finset S F S set of the finite subsets of S, F S = { s : S n : N f : 1.. n S ran f = S } \finset_1 S F 1 S non-empty finite subsets, F 1 S = F S \ \# S #S cardinality of a finite set, #S = (µ n : N ( f : 1.. n S ran f = S)) X \ffun Y X Y finite partial function, X Y = { f : X Y dom f F X } X \finj Y X Y finite partial injection, X Y = (X Y) (X Y) multisets \bag S bag S multiset over S, bag S = (S N 1 ) \lbag a, a, b\rbag [[a, a, b]] enumeration of finite subsets, same as {a 2, b 1} B \bcount x B x frequency of x in B, B x = (λ x : S 0) B n \otimes B n B scaling, n B = (λ x : dom B x n (B x)) x \inbag B x in B membership in a multiset, x in B x dom B A \subbageq B A B sub-multiset relation, A B x : S A x B x A \uplus B A B multiset union, (A B) x = A x + B x A \uminus B A B multiset complement, (A B) x = max {0, A x B x} items s items s multiset of the elements of a sequence, (items s) x = #(s {x}) 4
5 finite sequences \seq S seq S set of the finite sequences of S, seq S = { s : N S n : N dom s = 1.. n } \seq_1 S seq 1 S non-empty sequence, seq 1 S = { s : seq S #s > 0 } \iseq S iseq S duplicate-free sequence, iseq S = (seq S) (N S) \langle a, a, b \rangle a, a, b enumeration of a finite sequence, same as { 1 a, 2 a, 3 b } s \cat t s t concatenation, s t = s { n : dom t (n + #s) t(n) } rev s rev s inversion, rev s = (λ n : dom s s(#s n + 1)) head s head s first element, head s = s(1) tail s tail s remainder of the sequence, tail s = (λ n : 1.. #s 1 s(n + 1)) last s last s last element, last s = s(#s) front s front s sequence without the last element, front s = (1.. #s 1) s squash f squash f compactification, (µ g : 1.. #f dom f g o 9 succ o 9 g ( < )) o 9 f A \extract s A s extraction of the elemente using indexes in A, A s = squash (A s) s \filter A s A subsequence of the elements of s which are contained in A, s A = squash (s A) s \prefix t s prefix t prefix relation, s prefix t v : seq S s v = t s \suffix t s suffix t suffix relation, s suffix t v : seq S v s = t s \inseq t s in t subsequence, s in t u, v : seq S u s v = t \dcat s / s concatenation of all sequences in s, / =, #s > 1 / s = (head s) ( / tail s) 5
Sets. Slides by Christopher M. Bourke Instructor: Berthe Y. Choueiry. Fall 2007
 Slides by Christopher M. Bourke Instructor: Berthe Y. Choueiry Fall 2007 1 / 42 Computer Science & Engineering 235 Introduction to Discrete Mathematics Sections 2.1, 2.2 of Rosen Introduction I Introduction
Slides by Christopher M. Bourke Instructor: Berthe Y. Choueiry Fall 2007 1 / 42 Computer Science & Engineering 235 Introduction to Discrete Mathematics Sections 2.1, 2.2 of Rosen Introduction I Introduction
Sets. Slides by Christopher M. Bourke Instructor: Berthe Y. Choueiry. Spring 2006
 Slides by Christopher M. Bourke Instructor: Berthe Y. Choueiry Spring 2006 1 / 1 Computer Science & Engineering 235 Introduction to Discrete Mathematics Sections 1.6 1.7 of Rosen Introduction I We ve already
Slides by Christopher M. Bourke Instructor: Berthe Y. Choueiry Spring 2006 1 / 1 Computer Science & Engineering 235 Introduction to Discrete Mathematics Sections 1.6 1.7 of Rosen Introduction I We ve already
 The Z/EVES Mathematical Toolkit Version 2.2 for Z/EVES Version 1.5 TR-97-5493-05a Mark Saaltink Release date: September 1997 ORA Canada 267 Richmond Road, Suite 100 Ottawa, Ontario K1Z 6X3 CANADA Z/EVES
The Z/EVES Mathematical Toolkit Version 2.2 for Z/EVES Version 1.5 TR-97-5493-05a Mark Saaltink Release date: September 1997 ORA Canada 267 Richmond Road, Suite 100 Ottawa, Ontario K1Z 6X3 CANADA Z/EVES
Basic Propositional Logic. Inductive Theory of the Natural Numbers. Conjunction. Equivalence. Negation and Inequivalence. Implication.
 McMaster University COMPSCI&SFWRENG 2DM3 Dept. of Computing and Software Theorem List 4 Dr. W. Kahl 2017-12-09 The names listed here are precisely the names used in the preloaded material you are already
McMaster University COMPSCI&SFWRENG 2DM3 Dept. of Computing and Software Theorem List 4 Dr. W. Kahl 2017-12-09 The names listed here are precisely the names used in the preloaded material you are already
Z Support in the HiVe Mathematical Toolkit
 Z Support in the HiVe Mathematical Toolkit Brendan Mahony, Jim McCarthy, Linh Vu, Kylie Williams Command, Control, Communications and Intelligence Division Defence Science and Technology Organisation DSTO
Z Support in the HiVe Mathematical Toolkit Brendan Mahony, Jim McCarthy, Linh Vu, Kylie Williams Command, Control, Communications and Intelligence Division Defence Science and Technology Organisation DSTO
Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics.
 MAT 200, Logic, Language and Proof, Fall 2015 Summary Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics. Definition. A proposition is a sentence which is either true or false. Truth table for the connective or :
MAT 200, Logic, Language and Proof, Fall 2015 Summary Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics. Definition. A proposition is a sentence which is either true or false. Truth table for the connective or :
Propositional Logic, Predicates, and Equivalence
 Chapter 1 Propositional Logic, Predicates, and Equivalence A statement or a proposition is a sentence that is true (T) or false (F) but not both. The symbol denotes not, denotes and, and denotes or. If
Chapter 1 Propositional Logic, Predicates, and Equivalence A statement or a proposition is a sentence that is true (T) or false (F) but not both. The symbol denotes not, denotes and, and denotes or. If
Automata Theory for Presburger Arithmetic Logic
 Automata Theory for Presburger Arithmetic Logic References from Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages & Computation and Constraints in Computational Logic Theory & Application Presented by Masood
Automata Theory for Presburger Arithmetic Logic References from Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages & Computation and Constraints in Computational Logic Theory & Application Presented by Masood
Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 1
 Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 1 Sets, Languages, Logic Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 1 p.1/72 Sets, Languages, Logic Today Course Overview Administrivia Sets Theory (Review?)
Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 1 Sets, Languages, Logic Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 1 p.1/72 Sets, Languages, Logic Today Course Overview Administrivia Sets Theory (Review?)
2.1 Sets. Definition 1 A set is an unordered collection of objects. Important sets: N, Z, Z +, Q, R.
 2. Basic Structures 2.1 Sets Definition 1 A set is an unordered collection of objects. Important sets: N, Z, Z +, Q, R. Definition 2 Objects in a set are called elements or members of the set. A set is
2. Basic Structures 2.1 Sets Definition 1 A set is an unordered collection of objects. Important sets: N, Z, Z +, Q, R. Definition 2 Objects in a set are called elements or members of the set. A set is
COMP2111 Glossary. Kai Engelhardt. Contents. 1 Symbols. 1 Symbols 1. 2 Hoare Logic 3. 3 Refinement Calculus 5. rational numbers Q, real numbers R.
 COMP2111 Glossary Kai Engelhardt Revision: 1.3, May 18, 2018 Contents 1 Symbols 1 2 Hoare Logic 3 3 Refinement Calculus 5 1 Symbols Booleans B = {false, true}, natural numbers N = {0, 1, 2,...}, integers
COMP2111 Glossary Kai Engelhardt Revision: 1.3, May 18, 2018 Contents 1 Symbols 1 2 Hoare Logic 3 3 Refinement Calculus 5 1 Symbols Booleans B = {false, true}, natural numbers N = {0, 1, 2,...}, integers
Discrete Mathematics. W. Ethan Duckworth. Fall 2017, Loyola University Maryland
 Discrete Mathematics W. Ethan Duckworth Fall 2017, Loyola University Maryland Contents 1 Introduction 4 1.1 Statements......................................... 4 1.2 Constructing Direct Proofs................................
Discrete Mathematics W. Ethan Duckworth Fall 2017, Loyola University Maryland Contents 1 Introduction 4 1.1 Statements......................................... 4 1.2 Constructing Direct Proofs................................
Part IA Numbers and Sets
 Part IA Numbers and Sets Definitions Based on lectures by A. G. Thomason Notes taken by Dexter Chua Michaelmas 2014 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Part IA Numbers and Sets Definitions Based on lectures by A. G. Thomason Notes taken by Dexter Chua Michaelmas 2014 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Mathematical Preliminaries. Sipser pages 1-28
 Mathematical Preliminaries Sipser pages 1-28 Mathematical Preliminaries This course is about the fundamental capabilities and limitations of computers. It has 3 parts 1. Automata Models of computation
Mathematical Preliminaries Sipser pages 1-28 Mathematical Preliminaries This course is about the fundamental capabilities and limitations of computers. It has 3 parts 1. Automata Models of computation
Sets, Logic, Relations, and Functions
 Sets, Logic, Relations, and Functions Andrew Kay September 28, 2014 Abstract This is an introductory text, not a comprehensive study; these notes contain mainly definitions, basic results, and examples.
Sets, Logic, Relations, and Functions Andrew Kay September 28, 2014 Abstract This is an introductory text, not a comprehensive study; these notes contain mainly definitions, basic results, and examples.
MATH 215 Sets (S) Definition 1 A set is a collection of objects. The objects in a set X are called elements of X.
 MATH 215 Sets (S) Definition 1 A set is a collection of objects. The objects in a set X are called elements of X. Notation 2 A set can be described using set-builder notation. That is, a set can be described
MATH 215 Sets (S) Definition 1 A set is a collection of objects. The objects in a set X are called elements of X. Notation 2 A set can be described using set-builder notation. That is, a set can be described
Contents Propositional Logic: Proofs from Axioms and Inference Rules
 Contents 1 Propositional Logic: Proofs from Axioms and Inference Rules... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.1.1 An Example Demonstrating the Use of Logic in Real Life... 2 1.2 The Pure Propositional Calculus...
Contents 1 Propositional Logic: Proofs from Axioms and Inference Rules... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.1.1 An Example Demonstrating the Use of Logic in Real Life... 2 1.2 The Pure Propositional Calculus...
CSE 1400 Applied Discrete Mathematics Definitions
 CSE 1400 Applied Discrete Mathematics Definitions Department of Computer Sciences College of Engineering Florida Tech Fall 2011 Arithmetic 1 Alphabets, Strings, Languages, & Words 2 Number Systems 3 Machine
CSE 1400 Applied Discrete Mathematics Definitions Department of Computer Sciences College of Engineering Florida Tech Fall 2011 Arithmetic 1 Alphabets, Strings, Languages, & Words 2 Number Systems 3 Machine
Outline. Sets. Relations. Functions. Products. Sums 2 / 40
 Mathematical Background Outline Sets Relations Functions Products Sums 2 / 40 Outline Sets Relations Functions Products Sums 3 / 40 Sets Basic Notations x S membership S T subset S T proper subset S fin
Mathematical Background Outline Sets Relations Functions Products Sums 2 / 40 Outline Sets Relations Functions Products Sums 3 / 40 Sets Basic Notations x S membership S T subset S T proper subset S fin
Section 0. Sets and Relations
 0. Sets and Relations 1 Section 0. Sets and Relations NOTE. Mathematics is the study of ideas, not of numbers!!! The idea from modern algebra which is the focus of most of this class is that of a group
0. Sets and Relations 1 Section 0. Sets and Relations NOTE. Mathematics is the study of ideas, not of numbers!!! The idea from modern algebra which is the focus of most of this class is that of a group
Contribution of Problems
 Exam topics 1. Basic structures: sets, lists, functions (a) Sets { }: write all elements, or define by condition (b) Set operations: A B, A B, A\B, A c (c) Lists ( ): Cartesian product A B (d) Functions
Exam topics 1. Basic structures: sets, lists, functions (a) Sets { }: write all elements, or define by condition (b) Set operations: A B, A B, A\B, A c (c) Lists ( ): Cartesian product A B (d) Functions
Final Exam Review. 2. Let A = {, { }}. What is the cardinality of A? Is
 1. Describe the elements of the set (Z Q) R N. Is this set countable or uncountable? Solution: The set is equal to {(x, y) x Z, y N} = Z N. Since the Cartesian product of two denumerable sets is denumerable,
1. Describe the elements of the set (Z Q) R N. Is this set countable or uncountable? Solution: The set is equal to {(x, y) x Z, y N} = Z N. Since the Cartesian product of two denumerable sets is denumerable,
586 Index. vertex, 369 disjoint, 236 pairwise, 272, 395 disjoint sets, 236 disjunction, 33, 36 distributive laws
 Index absolute value, 135 141 additive identity, 254 additive inverse, 254 aleph, 465 algebra of sets, 245, 278 antisymmetric relation, 387 arcsine function, 349 arithmetic sequence, 208 arrow diagram,
Index absolute value, 135 141 additive identity, 254 additive inverse, 254 aleph, 465 algebra of sets, 245, 278 antisymmetric relation, 387 arcsine function, 349 arithmetic sequence, 208 arrow diagram,
COMP9020 Lecture 3 Session 2, 2016 Sets, Functions, and Sequences. Revision: 1.3
 1 COMP9020 Lecture 3 Session 2, 2016 Sets, Functions, and Sequences Revision: 1.3 2 Divisibility Let m, n Z. m n means m is a divisor of n, defined by n = km for some k Z (Also stated as: n is divisible
1 COMP9020 Lecture 3 Session 2, 2016 Sets, Functions, and Sequences Revision: 1.3 2 Divisibility Let m, n Z. m n means m is a divisor of n, defined by n = km for some k Z (Also stated as: n is divisible
Axiomatic set theory. Chapter Why axiomatic set theory?
 Chapter 1 Axiomatic set theory 1.1 Why axiomatic set theory? Essentially all mathematical theories deal with sets in one way or another. In most cases, however, the use of set theory is limited to its
Chapter 1 Axiomatic set theory 1.1 Why axiomatic set theory? Essentially all mathematical theories deal with sets in one way or another. In most cases, however, the use of set theory is limited to its
Mid-Semester Quiz Second Semester, 2012
 THE AUSTRALIAN NATIONAL UNIVERSITY Mid-Semester Quiz Second Semester, 2012 COMP2600 (Formal Methods for Software Engineering) Writing Period: 1 hour duration Study Period: 10 minutes duration Permitted
THE AUSTRALIAN NATIONAL UNIVERSITY Mid-Semester Quiz Second Semester, 2012 COMP2600 (Formal Methods for Software Engineering) Writing Period: 1 hour duration Study Period: 10 minutes duration Permitted
Sets McGraw-Hill Education
 Sets A set is an unordered collection of objects. The objects in a set are called the elements, or members of the set. A set is said to contain its elements. The notation a A denotes that a is an element
Sets A set is an unordered collection of objects. The objects in a set are called the elements, or members of the set. A set is said to contain its elements. The notation a A denotes that a is an element
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Concepts of Mathematics MATH 352
 Lecture Notes 1 Basic Concepts of Mathematics MATH 352 Ivan Avramidi New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology Socorro, NM 87801 June 3, 2004 Author: Ivan Avramidi; File: absmath.tex; Date: June 11,
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Concepts of Mathematics MATH 352 Ivan Avramidi New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology Socorro, NM 87801 June 3, 2004 Author: Ivan Avramidi; File: absmath.tex; Date: June 11,
A Semester Course in Basic Abstract Algebra
 A Semester Course in Basic Abstract Algebra Marcel B. Finan Arkansas Tech University c All Rights Reserved December 29, 2011 1 PREFACE This book is an introduction to abstract algebra course for undergraduates
A Semester Course in Basic Abstract Algebra Marcel B. Finan Arkansas Tech University c All Rights Reserved December 29, 2011 1 PREFACE This book is an introduction to abstract algebra course for undergraduates
Logic, Sets, and Proofs
 Logic, Sets, and Proofs David A. Cox and Catherine C. McGeoch Amherst College 1 Logic Logical Operators. A logical statement is a mathematical statement that can be assigned a value either true or false.
Logic, Sets, and Proofs David A. Cox and Catherine C. McGeoch Amherst College 1 Logic Logical Operators. A logical statement is a mathematical statement that can be assigned a value either true or false.
Notation Index. gcd(a, b) (greatest common divisor) NT-16
 Notation Index (for all) B A (all functions) B A = B A (all functions) SF-18 (n) k (falling factorial) SF-9 a R b (binary relation) C(n,k) = n! k! (n k)! (binomial coefficient) SF-9 n! (n factorial) SF-9
Notation Index (for all) B A (all functions) B A = B A (all functions) SF-18 (n) k (falling factorial) SF-9 a R b (binary relation) C(n,k) = n! k! (n k)! (binomial coefficient) SF-9 n! (n factorial) SF-9
Informal Statement Calculus
 FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICS Branches of Logic 1. Theory of Computations (i.e. Recursion Theory). 2. Proof Theory. 3. Model Theory. 4. Set Theory. Informal Statement Calculus STATEMENTS AND CONNECTIVES Example
FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICS Branches of Logic 1. Theory of Computations (i.e. Recursion Theory). 2. Proof Theory. 3. Model Theory. 4. Set Theory. Informal Statement Calculus STATEMENTS AND CONNECTIVES Example
Sets. We discuss an informal (naive) set theory as needed in Computer Science. It was introduced by G. Cantor in the second half of the nineteenth
 Sets We discuss an informal (naive) set theory as needed in Computer Science. It was introduced by G. Cantor in the second half of the nineteenth century. Most students have seen sets before. This is intended
Sets We discuss an informal (naive) set theory as needed in Computer Science. It was introduced by G. Cantor in the second half of the nineteenth century. Most students have seen sets before. This is intended
Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes
 Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes These notes form a brief summary of what has been covered during the lectures. All the definitions must be memorized and understood. Statements
Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes These notes form a brief summary of what has been covered during the lectures. All the definitions must be memorized and understood. Statements
n Empty Set:, or { }, subset of all sets n Cardinality: V = {a, e, i, o, u}, so V = 5 n Subset: A B, all elements in A are in B
 Discrete Math Review Discrete Math Review (Rosen, Chapter 1.1 1.7, 5.5) TOPICS Sets and Functions Propositional and Predicate Logic Logical Operators and Truth Tables Logical Equivalences and Inference
Discrete Math Review Discrete Math Review (Rosen, Chapter 1.1 1.7, 5.5) TOPICS Sets and Functions Propositional and Predicate Logic Logical Operators and Truth Tables Logical Equivalences and Inference
Table of mathematical symbols - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Página 1 de 13 Table of mathematical symbols From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia For the HTML codes of mathematical symbols see mathematical HTML. Note: This article contains special characters. The
Página 1 de 13 Table of mathematical symbols From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia For the HTML codes of mathematical symbols see mathematical HTML. Note: This article contains special characters. The
Today s Topics. Methods of proof Relationships to logical equivalences. Important definitions Relationships to sets, relations Special functions
 Today s Topics Set identities Methods of proof Relationships to logical equivalences Functions Important definitions Relationships to sets, relations Special functions Set identities help us manipulate
Today s Topics Set identities Methods of proof Relationships to logical equivalences Functions Important definitions Relationships to sets, relations Special functions Set identities help us manipulate
COMP 633: Parallel Computing Fall 2018 Written Assignment 1: Sample Solutions
 COMP 633: Parallel Computing Fall 2018 Written Assignment 1: Sample Solutions September 12, 2018 I. The Work-Time W-T presentation of EREW sequence reduction Algorithm 2 in the PRAM handout has work complexity
COMP 633: Parallel Computing Fall 2018 Written Assignment 1: Sample Solutions September 12, 2018 I. The Work-Time W-T presentation of EREW sequence reduction Algorithm 2 in the PRAM handout has work complexity
EQUIVALENCE RELATIONS (NOTES FOR STUDENTS) 1. RELATIONS
 EQUIVALENCE RELATIONS (NOTES FOR STUDENTS) LIOR SILBERMAN Version 1.0 compiled September 9, 2015. 1.1. List of examples. 1. RELATIONS Equality of real numbers: for some x,y R we have x = y. For other pairs
EQUIVALENCE RELATIONS (NOTES FOR STUDENTS) LIOR SILBERMAN Version 1.0 compiled September 9, 2015. 1.1. List of examples. 1. RELATIONS Equality of real numbers: for some x,y R we have x = y. For other pairs
Sets and Functions. MATH 464/506, Real Analysis. J. Robert Buchanan. Summer Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Sets and Functions
 Sets and Functions MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Notation x A means that element x is a member of set A. x / A means that x is not a member of A.
Sets and Functions MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Notation x A means that element x is a member of set A. x / A means that x is not a member of A.
Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. statement. sentential connectives. negation. conjunction. disjunction
 Copyright & License Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. statement sentential connectives negation conjunction disjunction implication or conditional antecedant & consequent hypothesis
Copyright & License Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. statement sentential connectives negation conjunction disjunction implication or conditional antecedant & consequent hypothesis
A B is shaded A B A B
 NION: Let and be subsets of a universal set. The union of sets and is the set of all elements in that belong to or to or to both, and is denoted. Symbolically: = {x x or x } EMMPLE: Let = {a, b, c, d,
NION: Let and be subsets of a universal set. The union of sets and is the set of all elements in that belong to or to or to both, and is denoted. Symbolically: = {x x or x } EMMPLE: Let = {a, b, c, d,
Exclusive Disjunction
 Exclusive Disjunction Recall A statement is a declarative sentence that is either true or false, but not both. If we have a declarative sentence s, p: s is true, and q: s is false, can we rewrite s is
Exclusive Disjunction Recall A statement is a declarative sentence that is either true or false, but not both. If we have a declarative sentence s, p: s is true, and q: s is false, can we rewrite s is
Math Fall 2014 Final Exam Solutions
 Math 2001-003 Fall 2014 Final Exam Solutions Wednesday, December 17, 2014 Definition 1. The union of two sets X and Y is the set X Y consisting of all objects that are elements of X or of Y. The intersection
Math 2001-003 Fall 2014 Final Exam Solutions Wednesday, December 17, 2014 Definition 1. The union of two sets X and Y is the set X Y consisting of all objects that are elements of X or of Y. The intersection
Foundations of Mathematics
 Foundations of Mathematics L. Brian Lawrence Department of Mathematics George Mason University Fairfax, VA 22030 4444 U.S.A. e mail: blawrenc@mail.gmu.edu January 1, 2007 Preface This set of notes is an
Foundations of Mathematics L. Brian Lawrence Department of Mathematics George Mason University Fairfax, VA 22030 4444 U.S.A. e mail: blawrenc@mail.gmu.edu January 1, 2007 Preface This set of notes is an
Automata and Languages
 Automata and Languages Prof. Mohamed Hamada Software Engineering Lab. The University of Aizu Japan Mathematical Background Mathematical Background Sets Relations Functions Graphs Proof techniques Sets
Automata and Languages Prof. Mohamed Hamada Software Engineering Lab. The University of Aizu Japan Mathematical Background Mathematical Background Sets Relations Functions Graphs Proof techniques Sets
1.4 Cardinality. Tom Lewis. Fall Term Tom Lewis () 1.4 Cardinality Fall Term / 9
 1.4 Cardinality Tom Lewis Fall Term 2006 Tom Lewis () 1.4 Cardinality Fall Term 2006 1 / 9 Outline 1 Functions 2 Cardinality 3 Cantor s theorem Tom Lewis () 1.4 Cardinality Fall Term 2006 2 / 9 Functions
1.4 Cardinality Tom Lewis Fall Term 2006 Tom Lewis () 1.4 Cardinality Fall Term 2006 1 / 9 Outline 1 Functions 2 Cardinality 3 Cantor s theorem Tom Lewis () 1.4 Cardinality Fall Term 2006 2 / 9 Functions
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH. Winter
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Winter 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi17/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Determine whether a relation is an equivalence relation by determining whether it is Reflexive Symmetric
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Winter 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi17/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Determine whether a relation is an equivalence relation by determining whether it is Reflexive Symmetric
Lecturecise 22 Weak monadic second-order theory of one successor (WS1S)
 Lecturecise 22 Weak monadic second-order theory of one successor (WS1S) 2013 Reachability in the Heap Many programs manipulate linked data structures (lists, trees). To express many important properties
Lecturecise 22 Weak monadic second-order theory of one successor (WS1S) 2013 Reachability in the Heap Many programs manipulate linked data structures (lists, trees). To express many important properties
Proving simple set properties...
 Proving simple set properties... Part 1: Some examples of proofs over sets Fall 2013 Proving simple set properties... Fall 2013 1 / 17 Introduction Overview: Learning outcomes In this session we will...
Proving simple set properties... Part 1: Some examples of proofs over sets Fall 2013 Proving simple set properties... Fall 2013 1 / 17 Introduction Overview: Learning outcomes In this session we will...
1. (B) The union of sets A and B is the set whose elements belong to at least one of A
 1. (B) The union of sets A and B is the set whose elements belong to at least one of A or B. Thus, A B = { 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 5}. 2. (A) The intersection of sets A and B is the set whose elements belong to
1. (B) The union of sets A and B is the set whose elements belong to at least one of A or B. Thus, A B = { 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 5}. 2. (A) The intersection of sets A and B is the set whose elements belong to
MODEL ANSWERS TO THE SEVENTH HOMEWORK. (b) We proved in homework six, question 2 (c) that. But we also proved homework six, question 2 (a) that
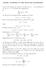 MODEL ANSWERS TO THE SEVENTH HOMEWORK 1. Let X be a finite set, and let A, B and A 1, A 2,..., A n be subsets of X. Let A c = X \ A denote the complement. (a) χ A (x) = A. x X (b) We proved in homework
MODEL ANSWERS TO THE SEVENTH HOMEWORK 1. Let X be a finite set, and let A, B and A 1, A 2,..., A n be subsets of X. Let A c = X \ A denote the complement. (a) χ A (x) = A. x X (b) We proved in homework
Notes for Math 290 using Introduction to Mathematical Proofs by Charles E. Roberts, Jr.
 Notes for Math 290 using Introduction to Mathematical Proofs by Charles E. Roberts, Jr. Chapter : Logic Topics:. Statements, Negation, and Compound Statements.2 Truth Tables and Logical Equivalences.3
Notes for Math 290 using Introduction to Mathematical Proofs by Charles E. Roberts, Jr. Chapter : Logic Topics:. Statements, Negation, and Compound Statements.2 Truth Tables and Logical Equivalences.3
Background for Discrete Mathematics
 Background for Discrete Mathematics Huck Bennett Northwestern University These notes give a terse summary of basic notation and definitions related to three topics in discrete mathematics: logic, sets,
Background for Discrete Mathematics Huck Bennett Northwestern University These notes give a terse summary of basic notation and definitions related to three topics in discrete mathematics: logic, sets,
Discrete Mathematics Review
 CS 1813 Discrete Mathematics Discrete Mathematics Review or Yes, the Final Will Be Comprehensive 1 Truth Tables for Logical Operators P Q P Q False False False P Q False P Q False P Q True P Q True P True
CS 1813 Discrete Mathematics Discrete Mathematics Review or Yes, the Final Will Be Comprehensive 1 Truth Tables for Logical Operators P Q P Q False False False P Q False P Q False P Q True P Q True P True
3. Only sequences that were formed by using finitely many applications of rules 1 and 2, are propositional formulas.
 1 Chapter 1 Propositional Logic Mathematical logic studies correct thinking, correct deductions of statements from other statements. Let us make it more precise. A fundamental property of a statement is
1 Chapter 1 Propositional Logic Mathematical logic studies correct thinking, correct deductions of statements from other statements. Let us make it more precise. A fundamental property of a statement is
Informatics 1 - Computation & Logic: Tutorial 3
 Informatics 1 - Computation & Logic: Tutorial 3 Counting Week 5: 16-20 October 2016 Please attempt the entire worksheet in advance of the tutorial, and bring all work with you. Tutorials cannot function
Informatics 1 - Computation & Logic: Tutorial 3 Counting Week 5: 16-20 October 2016 Please attempt the entire worksheet in advance of the tutorial, and bring all work with you. Tutorials cannot function
Lecture 2: Axiomatic semantics
 Chair of Software Engineering Trusted Components Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Lecture 2: Axiomatic semantics Reading assignment for next week Ariane paper and response (see course page) Axiomatic semantics
Chair of Software Engineering Trusted Components Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Lecture 2: Axiomatic semantics Reading assignment for next week Ariane paper and response (see course page) Axiomatic semantics
With Question/Answer Animations. Chapter 2
 With Question/Answer Animations Chapter 2 Chapter Summary Sets The Language of Sets Set Operations Set Identities Functions Types of Functions Operations on Functions Sequences and Summations Types of
With Question/Answer Animations Chapter 2 Chapter Summary Sets The Language of Sets Set Operations Set Identities Functions Types of Functions Operations on Functions Sequences and Summations Types of
Chapter 0. Introduction: Prerequisites and Preliminaries
 Chapter 0. Sections 0.1 to 0.5 1 Chapter 0. Introduction: Prerequisites and Preliminaries Note. The content of Sections 0.1 through 0.6 should be very familiar to you. However, in order to keep these notes
Chapter 0. Sections 0.1 to 0.5 1 Chapter 0. Introduction: Prerequisites and Preliminaries Note. The content of Sections 0.1 through 0.6 should be very familiar to you. However, in order to keep these notes
Introduction to Proofs
 Introduction to Proofs Notes by Dr. Lynne H. Walling and Dr. Steffi Zegowitz September 018 The Introduction to Proofs course is organised into the following nine sections. 1. Introduction: sets and functions
Introduction to Proofs Notes by Dr. Lynne H. Walling and Dr. Steffi Zegowitz September 018 The Introduction to Proofs course is organised into the following nine sections. 1. Introduction: sets and functions
Analysis 1. Lecture Notes 2013/2014. The original version of these Notes was written by. Vitali Liskevich
 Analysis 1 Lecture Notes 2013/2014 The original version of these Notes was written by Vitali Liskevich followed by minor adjustments by many Successors, and presently taught by Misha Rudnev University
Analysis 1 Lecture Notes 2013/2014 The original version of these Notes was written by Vitali Liskevich followed by minor adjustments by many Successors, and presently taught by Misha Rudnev University
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH. Fall
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Determine whether a relation is an equivalence relation by determining whether it is Reflexive Symmetric
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Determine whether a relation is an equivalence relation by determining whether it is Reflexive Symmetric
Lecture Notes on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS. Eusebius Doedel
 Lecture Notes on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel c Eusebius J. Doedel, 009 Contents Logic. Introduction............................................................................... Basic logical
Lecture Notes on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel c Eusebius J. Doedel, 009 Contents Logic. Introduction............................................................................... Basic logical
Relating Abstract Datatypes and Z-Schemata
 Relating Abstract Datatypes and Z-Schemata Hubert Baumeister University of Munich, Institute of Computer Science, Oettingenstr. 67, D-80358 Munich, Germany baumeist@informatik.uni-muenchen.de Abstract.
Relating Abstract Datatypes and Z-Schemata Hubert Baumeister University of Munich, Institute of Computer Science, Oettingenstr. 67, D-80358 Munich, Germany baumeist@informatik.uni-muenchen.de Abstract.
INTRODUCTION TO RELATIONAL DATABASE SYSTEMS
 INTRODUCTION TO RELATIONAL DATABASE SYSTEMS DATENBANKSYSTEME 1 (INF 3131) Torsten Grust Universität Tübingen Winter 2017/18 1 THE RELATIONAL ALGEBRA The Relational Algebra (RA) is a query language for
INTRODUCTION TO RELATIONAL DATABASE SYSTEMS DATENBANKSYSTEME 1 (INF 3131) Torsten Grust Universität Tübingen Winter 2017/18 1 THE RELATIONAL ALGEBRA The Relational Algebra (RA) is a query language for
On Recognizable Languages of Infinite Pictures
 On Recognizable Languages of Infinite Pictures Equipe de Logique Mathématique CNRS and Université Paris 7 LIF, Marseille, Avril 2009 Pictures Pictures are two-dimensional words. Let Σ be a finite alphabet
On Recognizable Languages of Infinite Pictures Equipe de Logique Mathématique CNRS and Université Paris 7 LIF, Marseille, Avril 2009 Pictures Pictures are two-dimensional words. Let Σ be a finite alphabet
Contribution of Problems
 Exam topics 1. Basic structures: sets, lists, functions (a) Sets { }: write all elements, or define by condition (b) Set operations: A B, A B, A\B, A c (c) Lists ( ): Cartesian product A B (d) Functions
Exam topics 1. Basic structures: sets, lists, functions (a) Sets { }: write all elements, or define by condition (b) Set operations: A B, A B, A\B, A c (c) Lists ( ): Cartesian product A B (d) Functions
Foundations of Mathematics
 Foundations of Mathematics L. Pedro Poitevin 1. Preliminaries 1.1. Sets We will naively think of a set as a collection of mathematical objects, called its elements or members. To indicate that an object
Foundations of Mathematics L. Pedro Poitevin 1. Preliminaries 1.1. Sets We will naively think of a set as a collection of mathematical objects, called its elements or members. To indicate that an object
On Recognizable Languages of Infinite Pictures
 On Recognizable Languages of Infinite Pictures Equipe de Logique Mathématique CNRS and Université Paris 7 JAF 28, Fontainebleau, Juin 2009 Pictures Pictures are two-dimensional words. Let Σ be a finite
On Recognizable Languages of Infinite Pictures Equipe de Logique Mathématique CNRS and Université Paris 7 JAF 28, Fontainebleau, Juin 2009 Pictures Pictures are two-dimensional words. Let Σ be a finite
Chapter 2 Sets, Relations and Functions
 Chapter 2 Sets, Relations and Functions Key Topics Sets Set Operations Russell s Paradox Relations Composition of Relations Reflexive, Symmetric and Transitive Relations Functions Partial and Total Functions
Chapter 2 Sets, Relations and Functions Key Topics Sets Set Operations Russell s Paradox Relations Composition of Relations Reflexive, Symmetric and Transitive Relations Functions Partial and Total Functions
HANDOUT AND SET THEORY. Ariyadi Wijaya
 HANDOUT LOGIC AND SET THEORY Ariyadi Wijaya Mathematics Education Department Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science Yogyakarta State University 2009 1 Mathematics Education Department Faculty of Mathematics
HANDOUT LOGIC AND SET THEORY Ariyadi Wijaya Mathematics Education Department Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science Yogyakarta State University 2009 1 Mathematics Education Department Faculty of Mathematics
18.S097 Introduction to Proofs IAP 2015 Lecture Notes 1 (1/5/2015)
 18.S097 Introduction to Proofs IAP 2015 Lecture Notes 1 (1/5/2015) 1. Introduction The goal for this course is to provide a quick, and hopefully somewhat gentle, introduction to the task of formulating
18.S097 Introduction to Proofs IAP 2015 Lecture Notes 1 (1/5/2015) 1. Introduction The goal for this course is to provide a quick, and hopefully somewhat gentle, introduction to the task of formulating
Rigorous Software Development CSCI-GA
 Rigorous Software Development CSCI-GA 3033-009 Instructor: Thomas Wies Spring 2013 Lecture 2 Alloy Analyzer Analyzes micro models of software Helps to identify key properties of a software design find
Rigorous Software Development CSCI-GA 3033-009 Instructor: Thomas Wies Spring 2013 Lecture 2 Alloy Analyzer Analyzes micro models of software Helps to identify key properties of a software design find
Mathematics Review for Business PhD Students
 Mathematics Review for Business PhD Students Anthony M. Marino Department of Finance and Business Economics Marshall School of Business Lecture 1: Introductory Material Sets The Real Number System Functions,
Mathematics Review for Business PhD Students Anthony M. Marino Department of Finance and Business Economics Marshall School of Business Lecture 1: Introductory Material Sets The Real Number System Functions,
Introduction to Automata
 Introduction to Automata Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr 1 /
Introduction to Automata Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr 1 /
Spring Based on Partee, ter Meulen, & Wall (1993), Mathematical Methods in Linguistics
 1 / 17 L545 Spring 2013 Based on Partee, ter Meulen, & Wall (1993), Mathematical Methods in Linguistics 2 / 17 Why set theory? Set theory sets the foundation for much of mathematics For us: provides precise
1 / 17 L545 Spring 2013 Based on Partee, ter Meulen, & Wall (1993), Mathematical Methods in Linguistics 2 / 17 Why set theory? Set theory sets the foundation for much of mathematics For us: provides precise
CS 455/555: Mathematical preliminaries
 CS 455/555: Mathematical preliminaries Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2019 SETS AND RELATIONS Sets: Operations: intersection, union, difference, Cartesian product Big, powerset (2 A ) Partition (π 2 A, π, i j
CS 455/555: Mathematical preliminaries Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2019 SETS AND RELATIONS Sets: Operations: intersection, union, difference, Cartesian product Big, powerset (2 A ) Partition (π 2 A, π, i j
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH WINTER
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH WINTER 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi16/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Define and differentiate between important sets Use correct notation when describing sets: {...}, intervals
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH WINTER 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi16/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Define and differentiate between important sets Use correct notation when describing sets: {...}, intervals
Relations, Functions, and Sequences
 MCS-236: Graph Theory Handout #A3 San Skulrattanakulchai Gustavus Adolphus College Sep 13, 2010 Relations, Functions, and Sequences Relations An ordered pair can be constructed from any two mathematical
MCS-236: Graph Theory Handout #A3 San Skulrattanakulchai Gustavus Adolphus College Sep 13, 2010 Relations, Functions, and Sequences Relations An ordered pair can be constructed from any two mathematical
Decidability of WS1S and S1S (An Exposition) Exposition by William Gasarch-U of MD
 1 Introduction Decidability of WS1S and S1S (An Exposition) Exposition by William Gasarch-U of MD We are going to prove that a (small) fragment of mathematics is decidable. 1. A Formula allows variables
1 Introduction Decidability of WS1S and S1S (An Exposition) Exposition by William Gasarch-U of MD We are going to prove that a (small) fragment of mathematics is decidable. 1. A Formula allows variables
COT3100 SI Final Exam Review
 1 Symbols COT3100 SI Final Exam Review Jarrett Wendt Spring 2018 You ve learned a plethora of new Mathematical symbols this semester. Let s see if you know them all and what they re used for. How many
1 Symbols COT3100 SI Final Exam Review Jarrett Wendt Spring 2018 You ve learned a plethora of new Mathematical symbols this semester. Let s see if you know them all and what they re used for. How many
CHAPTER 0: BACKGROUND (SPRING 2009 DRAFT)
 CHAPTER 0: BACKGROUND (SPRING 2009 DRAFT) MATH 378, CSUSM. SPRING 2009. AITKEN This chapter reviews some of the background concepts needed for Math 378. This chapter is new to the course (added Spring
CHAPTER 0: BACKGROUND (SPRING 2009 DRAFT) MATH 378, CSUSM. SPRING 2009. AITKEN This chapter reviews some of the background concepts needed for Math 378. This chapter is new to the course (added Spring
Unifying Theories of Programming
 1&2 Unifying Theories of Programming Unifying Theories of Programming 3&4 Theories Unifying Theories of Programming designs predicates relations reactive CSP processes Jim Woodcock University of York May
1&2 Unifying Theories of Programming Unifying Theories of Programming 3&4 Theories Unifying Theories of Programming designs predicates relations reactive CSP processes Jim Woodcock University of York May
SETS AND FUNCTIONS JOSHUA BALLEW
 SETS AND FUNCTIONS JOSHUA BALLEW 1. Sets As a review, we begin by considering a naive look at set theory. For our purposes, we define a set as a collection of objects. Except for certain sets like N, Z,
SETS AND FUNCTIONS JOSHUA BALLEW 1. Sets As a review, we begin by considering a naive look at set theory. For our purposes, we define a set as a collection of objects. Except for certain sets like N, Z,
CHAPTER 1 SETS AND EVENTS
 CHPTER 1 SETS ND EVENTS 1.1 Universal Set and Subsets DEFINITION: set is a well-defined collection of distinct elements in the universal set. This is denoted by capital latin letters, B, C, If an element
CHPTER 1 SETS ND EVENTS 1.1 Universal Set and Subsets DEFINITION: set is a well-defined collection of distinct elements in the universal set. This is denoted by capital latin letters, B, C, If an element
CHAPTER 1. Preliminaries. 1 Set Theory
 CHAPTER 1 Preliminaries 1 et Theory We assume that the reader is familiar with basic set theory. In this paragraph, we want to recall the relevant definitions and fix the notation. Our approach to set
CHAPTER 1 Preliminaries 1 et Theory We assume that the reader is familiar with basic set theory. In this paragraph, we want to recall the relevant definitions and fix the notation. Our approach to set
ABOUT THE CLASS AND NOTES ON SET THEORY
 ABOUT THE CLASS AND NOTES ON SET THEORY About the Class Evaluation. Final grade will be based 25%, 25%, 25%, 25%, on homework, midterm 1, midterm 2, final exam. Exam dates. Midterm 1: Oct 4. Midterm 2:
ABOUT THE CLASS AND NOTES ON SET THEORY About the Class Evaluation. Final grade will be based 25%, 25%, 25%, 25%, on homework, midterm 1, midterm 2, final exam. Exam dates. Midterm 1: Oct 4. Midterm 2:
Type equations in linear format
 Strona 1 z 9 Support / Word / Word 2010 Help and How-to / Equations Linear format equations and Math AutoCorrect in Word 2010 Applies to: Microsoft Word 2010 Some of the content in this topic may not be
Strona 1 z 9 Support / Word / Word 2010 Help and How-to / Equations Linear format equations and Math AutoCorrect in Word 2010 Applies to: Microsoft Word 2010 Some of the content in this topic may not be
Introduction. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Introduction Logic is concerned mainly with two concepts: truth and provability. These concepts have been investigated extensively for centuries, by philosophers, linguists, and mathematicians.
Chapter 1 Introduction Logic is concerned mainly with two concepts: truth and provability. These concepts have been investigated extensively for centuries, by philosophers, linguists, and mathematicians.
Fuzzy and Rough Sets Part I
 Fuzzy and Rough Sets Part I Decision Systems Group Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology Aim Present aspects of fuzzy and rough sets.
Fuzzy and Rough Sets Part I Decision Systems Group Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology Aim Present aspects of fuzzy and rough sets.
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH WINTER
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH WINTER 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi16/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Evaluate which proof technique(s) is appropriate for a given proposition Direct proof Proofs by contraposition
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH WINTER 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi16/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Evaluate which proof technique(s) is appropriate for a given proposition Direct proof Proofs by contraposition
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH SPRING
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH SPRING 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse20-ac/ Today's learning goals Evaluate which proof technique(s) is appropriate for a given proposition Direct proof Proofs by contraposition
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH SPRING 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse20-ac/ Today's learning goals Evaluate which proof technique(s) is appropriate for a given proposition Direct proof Proofs by contraposition
Reading 11 : Relations and Functions
 CS/Math 240: Introduction to Discrete Mathematics Fall 2015 Reading 11 : Relations and Functions Instructor: Beck Hasti and Gautam Prakriya In reading 3, we described a correspondence between predicates
CS/Math 240: Introduction to Discrete Mathematics Fall 2015 Reading 11 : Relations and Functions Instructor: Beck Hasti and Gautam Prakriya In reading 3, we described a correspondence between predicates
COMP1002 exam study sheet
 COMP1002 exam study sheet Propositional statement: expression that has a truth value (true/false). It is a tautology if it is always true, contradiction if always false. Logic connectives: negation ( not
COMP1002 exam study sheet Propositional statement: expression that has a truth value (true/false). It is a tautology if it is always true, contradiction if always false. Logic connectives: negation ( not
0 Logical Background. 0.1 Sets
 0 Logical Background 0.1 Sets In this course we will use the term set to simply mean a collection of things which have a common property such as the totality of positive integers or the collection of points
0 Logical Background 0.1 Sets In this course we will use the term set to simply mean a collection of things which have a common property such as the totality of positive integers or the collection of points
Mathematics Review for Business PhD Students Lecture Notes
 Mathematics Review for Business PhD Students Lecture Notes Anthony M. Marino Department of Finance and Business Economics Marshall School of Business University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-0804
Mathematics Review for Business PhD Students Lecture Notes Anthony M. Marino Department of Finance and Business Economics Marshall School of Business University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-0804
Opleiding Informatica
 Opleiding Informatica Tape-quantifying Turing machines in the arithmetical hierarchy Simon Heijungs Supervisors: H.J. Hoogeboom & R. van Vliet BACHELOR THESIS Leiden Institute of Advanced Computer Science
Opleiding Informatica Tape-quantifying Turing machines in the arithmetical hierarchy Simon Heijungs Supervisors: H.J. Hoogeboom & R. van Vliet BACHELOR THESIS Leiden Institute of Advanced Computer Science
Foundations of Mathematics
 Foundations of Mathematics Andrew Monnot 1 Construction of the Language Loop We must yield to a cyclic approach in the foundations of mathematics. In this respect we begin with some assumptions of language
Foundations of Mathematics Andrew Monnot 1 Construction of the Language Loop We must yield to a cyclic approach in the foundations of mathematics. In this respect we begin with some assumptions of language
REVIEW QUESTIONS. Chapter 1: Foundations: Sets, Logic, and Algorithms
 REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 1: Foundations: Sets, Logic, and Algorithms 1. Why can t a Venn diagram be used to prove a statement about sets? 2. Suppose S is a set with n elements. Explain why the power set
REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 1: Foundations: Sets, Logic, and Algorithms 1. Why can t a Venn diagram be used to prove a statement about sets? 2. Suppose S is a set with n elements. Explain why the power set
