Introduction to Vectors
|
|
|
- Timothy Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Vectors 1. Which of the following natural phenomena would serve as the best time standard? a. The mean orbit radius of the earth. b. The period of audible sound waves. c. The time for one inhalation or ehalation. d. The time it takes a leaf to fall from a tree to the ground. e. The speed of the Mississippi River.. Using the prefies given in Table 1.4 of our tet, how would ou epress a. 4 Gg b. 4 Tg c. 4 mg d. 4 ng e. 4 cg g? 3. If m=ρ V, where ρ is a constant of proportionalit, the kg is the unit of m, and the m 3 is the unit of V, what is the unit of ρ? a. kg m 3 b. kg c. m 3 d. kg m 3 3 e. m kg 4. If = 1 at, with meters the units of, and seconds the units of t, what are the units of a? a. m b. s c. ms d. s m e. m s 1
2 Introduction and Vectors 5. ssuming that m and t have different dimensions, which of the following would be phsicall meaningful? a. mt b. m+ t c. m t d. m + t m mt e. m t 6. If the mass densit of a kg mass is 10 4 kg m 3, what volume in m 3 does the mass occup to the nearest order of magnitude? a b. 10 c d e What is the order of magnitude of the age of a 40-ear-old person in seconds? a b c d e woman walks 00 m west, then 300 m north, then 00 m south, then 00 m east. What is her displacement? a. 100 m E b. 100 m W c. 100 m N d. 100 m S e. The displacement is zero. 9. car traveled 300 km west, then 50 km south, then 150 km east, then 50 km north. What distance did it travel in km? a. 950 b. 850 c. 150 d. 50 e. 300
3 Chapter The magnitude of vector is 3 m and that of vector is 4 m. What is the largest magnitude in meters that their sum ma have? a. 5 b. 6 c. 7 d. 8 e The magnitude of vector is 3 m and that of vector is 4 m. What is the smallest magnitude in meters that their sum ma have? a. 1 b. c. 3 d. 4 e The magnitude of vector is 3 m and that of vector is 4 m. What is the largest magnitude in meters that their difference ma have? a. 5 b. 6 c. 7 d. 8 e The magnitude of vector is 3 m and that of vector is 4 m. What is the smallest magnitude in meters that their difference ma have? a. 1 b. c. 3 d. 4 e. 5
4 4 Introduction and Vectors 14. Given the vectors below, which vector has negative components in both the and directions? a. b. c. d. e. 15. Given the vectors below, which vector has a negative component in the direction and a positive component in the direction? a. b. c. d. e.
5 Chapter In which diagram does the sum + of the vectors and have a positive component in the direction? a. b. c. d. e. 17. In which diagram does the difference of the vectors and have a negative component in the direction? a. b. c. d. e.
6 6 Introduction and Vectors 18. Given the vectors below, which vector has a zero component in the direction? a. b. c. d. e. 19. Which of the following is a scalar? a. Displacement b. Force c. Velocit d. cceleration e. Distance 0. Which of the following is a vector? a. Momentum b. Temperature c. Volume d. Mass e. Densit
7 Chapter Two vectors are shown in each diagram below. In which diagram is the sum of the two vectors equal to zero? a. b. c. d. e.. woman starts from the origin and walks 50 m west. Then she walks 15 m east. What is her displacement? a. 15 m W b. 35 m W c. 50 m W d. 65 m W e. 75 m E 3. scuba diver dives at an angle of 60 with the horizontal and swims 30 m to the top of a reef. How far under water in meters is the top of the reef? a. 15 b. 6 c. 4 d. 18 e. 1
8 8 Introduction and Vectors 4. woman starts at the origin and walks 9 m along the -ais. She then turns 90 and walks parallel to the - ais for 1 m. How far in meters is she from the origin? a. 9 b. 1 c. 15 d. 18 e What is the densit in kg m 3 of a solid cube that measures m on a side and has a mass of 343 kg? a. 100 b. 80 c. 490 d e What is the mass in kilograms of two liters of helium, where " = cm 3 3? ρ He = kg m a b c d e If T = π ", where T is measured in seconds and " is measured in meters, what are the units of g? g a. ms b. s m c. kg s d. s kg e. 1 s
9 Chapter If K = 1 mv, where m is measured in kilograms and v in m s, what are the units of K? a. s kg b. m s c. kg s m d. kg m s s e. kg m 9. light ear is the distance light travels in a ear. If the speed of light is c = m s, how man meters are there in a light ear? Use 365 das/ear, 4 hours/da, 60 minutes/hour, 60 seconds/minute and.54 cm/inch. a b c d e cubic foot of water spills on a floor. It covers 5. 8 ft. How deep is the water in centimeters? a..34 b c d e If an average human heart beats 70 times per minute, the best estimate of the number of times a heart will beat in 80 ears is: a b c d e. 10 9
10 10 Introduction and Vectors 3. Suppose that the average number of books each student carries is and that one of the states of the United States has ten percent of the 100 million students in the countr. How man books are being carried in the state in question? a b c d e What is the area in cm of a computer disk whose diameter is 5.5 inches? a. 1.6 b c d. 87 e Four of the products below give conversions from miles per hour to cm per second that are dimensionall or numericall incorrect. Which one is correct? a. mi f. cm 1 h min h mi f 60 min 60 s b. mi in. cm 100 cm 1 h min h mi f m 60 min 60 s c. mi d h 36 in.54 cm mi 1 h d min f 60 min 600 s d. mi in. cm 1 h min h mi in 60 min 60 s e. mi f 1 in. cm 1 h min h mi f in 60 min 60 s 35. Two points in the plane have coordinates (1.0, 1.0) and (5.0,.0) in centimeters. What is the distance between the points in centimeters? a. 1.0 b..0 c. 3.0 d. 4.0 e. 5.0
11 Chapter What are the polar coordinates of the point (8.0, 6.0)? a. r = 80., θ = 53 b. r = 10, θ = 37 c. r = 10, θ = 53 d. r = 65., θ = 30 e. r = 75., θ = 61 a f= F H G I K J π 37. What are the Cartesian coordinates of the point r, θ 0.,? 4 a. (1.4, 1.4) b. (.8,.8) c. (1.0, 3.0) F π πi d., HG 4 K J e. (0.0,.0) 38. If = 14 and = 13, what is r? a. 15 b. 16 c. 17 d. 18 e If = 1 and = 13, what is r? a. 1 b. 14 c. 16 d. 18 e If = cm and = cm, what is θ? a b c d e. 43.1
12 1 Introduction and Vectors 41. If = 1 cm and = 14 cm, what is θ? a. 50 b. 48 c. 7. d. 41 e If a vector has an component of 11 and a component of 13, what is the magnitude of this vector? a. 16 b. 17 c. 18 d. 19 e Three vectors are given b = i # + 3 # j, = 3 i # # j and C = # i+ # j. What is the sum of the three vectors? a. 3 # i+ # j b. # j 3i # c. # j+ 3i # d. # i+ # j e. 3 # i+ # j 44. person walks 50 m north, then 50 m west, then 5 m south. t what angle measured from the east direction would the person have had to walk to go directl to the destination reached? a. 6 b. 153 c. 63 d. 116 e If a = [ 15, 80 ], and b = 1 # i 16 # j, what is the magnitude of a b? a. 15 b. 35 c. 3 d. 5.0 e. 3
13 46. vector,, when added to the vector C = 3i# + 4# j, ields a resultant vector which is in the positive direction and has a magnitude equal to that of C. What is the magnitude of? a. 3. b. 6.3 c. 9.5 d. 18 e. 5.0 Chapter If vector is added to vector, the result is 6 # i+ # j. If is subtracted from, the result is 4# i+ 7# j. What is the magnitude of? a. 5.1 b. 4.1 c. 5.4 d. 5.8 e If C = [. 5 cm, 80 ], i.e., the magnitude and direction of C are.5 cm and 80 D = [ 3. 5 cm, 10 ], and $ E= D C, what is the direction of E to the nearest degree? a. 47 b. 35 c. 43 d. 34 e If = 1 # i 16 # j and = 4 i# + 10 # j, what is the magnitude of the vector C=? a. 4 b. c. 64 d. 90 e vector is added to = 6i# 8# j. The resultant vector is in the positive direction and has a magnitude equal to. What is the magnitude of? a. 11 b. 5.1 c. 7.1 d. 8.3 e. 1.
14 14 Introduction and Vectors 51. If = 1 # i 16 # j and = 4 i# + 10 # j, what is the direction of the vector C=? a. 49 b. 41 c. 90 d. +49 e If C = (10 m, 30 ) and D = (5 m, 130 ), what is the magnitude of the sum of these two vectors in meters? a. 0 b. 35 c. 15 d. 5 e The three forces shown act on a particle. What is the magnitude of the resultant of these three forces? 65 N 30 N 30 0 a. 7 N b. 33 N c. 36 N d. 4 N e. 105 N 54. In scientific notation with the correct number of significant figures, the correct value of the sum is: a b c d e
15 Chapter In scientific notation with the correct number of significant figures, the correct value of the difference is: a b c d e batter in a baseball game hits a home run and runs around the bases. The magnitude of her displacement when she returns to home plate is: a. 0 m. b. twice the distance from home plate to second base. c. the total distance around the bases. d. not defined unless we know the angles between the lines from base to base. e. not defined since a real game is not a phsics problem. 57. Given two non-zero vectors and such that = and =, which one of the following can never be correct? a. + = b. + = c. + =0 d. + = e. + = 58. Of the possible representations of a 100 m race given below, the one that phsicists would not usuall use is a a. mental representation. b. graphical representation. c. pictorial representation. d. theatrical representation. e. mathematical representation.
16 16 Introduction and Vectors 59. Which answer below has the correct units and correct number of significant figures for z when z is m m obtained b the calculation z =? 1.1 m m a m b m c m d m e m 60. The dimension of distance is length, ", and the dimension of time is time, t. What are the dimensions of flow rate for a liquid eiting a pipe, where the flow rate is the volume leaving the pipe in unit time? L" a. t b. c. d. NM O QP L" N M O t Q P L" 3 N M O t Q P L" 3 3 N M O t Q P e. " 3 t 61. The dimension of distance is length, ", and the dimension of time is time, t. What are the dimensions of g the quantit defined b, where L is the length of a pendulum and g is the acceleration of gravit, L 980. m s? L" a. NM O QP L t " O b. c. d. e. NM t QP L " N M O t Q P L 1 O NM t QP L1 NM O QP t
17 Chapter Gold has a densit of kg m 3. One atomic mass of gold, 197 g, contains atoms. What volume in cubic meters does this atom mass occup? a b c d e problem ma be solved more easil when alternative representations are used. The best strateg is to formulate representations in an order that assists in understanding the phsical principles involved. Of the orders given below, the one that will work best most often is: a. pictorial representation, mathematical representation, tabular representation, mental representation b. pictorial representation, mental representation, mathematical representation, tabular representation c. mathematical representation, pictorial representation, tabular representation, mental representation d. mathematical representation, tabular representation, mental representation, pictorial representation e. mental representation, pictorial representation, tabular representation, mathematical representation 64. If each frame of a motion picture film is 35 cm high, and 4 frames go b in a second, estimate how man frames are needed to show a two hour long movie. a b c d e. This cannot be determined without knowing how man reels were used. 65. scientific eplanation of an observation is provided b a. repeating the eperiment and getting the same numbers. b. describing the procedures for performing the eperiment. c. listing all the equations that were solved. d. giving definitions of the smbols used in the equations. e. combining the eperimental results with reasoning to answer the question how do we know? 66. The magnitude of the vector is written as. The magnitude + of the vector sum +, is a.. b.. c.. d.. e. 4.
18 18 Introduction and Vectors 67. Given two non-zero vectors, and, such that = = =, the sum + satisfies a b. 0< + <. c. +. d. < + <. e Given two non-zero vectors, and, such that = = =, the difference satisfies a. 0. b. 0 < <. c. 0. d. 0< <. e The population of the United States is now over 90 million people. The number of bars of soap used at home in a ear is closest to a b c d e You find that a line to the top of a clindrical water tower makes an angle of 8 with a line to the base of the tower when ou are 100 m from the base of the tower. How tall is the tower? a. 47 m. b. 53 m. c. 88 m. d. 100 m. e. 188 m.
19 a f and D = a5 m, If C = 10 m, 30 a. 37 b. 53 c. 17 d. 143 e n analsis model consists of a. a detailed summar of all characteristics of all parts of the sstem. b. a summar in which insignificant details have been ignored. c. a problem of the same general tpe that has been solved before. d. a view in three dimensions following engineering graphics rules. e. a combination of (a) and (d) above. f, what is the direction of the sum of these two vectors? Chapter 1 19
Physical Measurement
 Order of Magnitude Estimations: estimations to the nearest power of ten The ranges of magnitude that occur in the universe: Sizes: 10-15 m to 10 +25 m (subnuclear particles to etent of the visible universe).
Order of Magnitude Estimations: estimations to the nearest power of ten The ranges of magnitude that occur in the universe: Sizes: 10-15 m to 10 +25 m (subnuclear particles to etent of the visible universe).
CHAPTER 1 MEASUREMENTS AND VECTORS
 CHPTER 1 MESUREMENTS ND VECTORS 1 CHPTER 1 MESUREMENTS ND VECTORS 1.1 UNITS ND STNDRDS n phsical quantit must have, besides its numerical value, a standard unit. It will be meaningless to sa that the distance
CHPTER 1 MESUREMENTS ND VECTORS 1 CHPTER 1 MESUREMENTS ND VECTORS 1.1 UNITS ND STNDRDS n phsical quantit must have, besides its numerical value, a standard unit. It will be meaningless to sa that the distance
Regular Physics - Notes Ch. 1
 Regular Phsics - Notes Ch. 1 What is Phsics? the stud of matter and energ and their relationships; the stud of the basic phsical laws of nature which are often stated in simple mathematical equations.
Regular Phsics - Notes Ch. 1 What is Phsics? the stud of matter and energ and their relationships; the stud of the basic phsical laws of nature which are often stated in simple mathematical equations.
Physics Lab 1 - Measurements
 Phsics 203 - Lab 1 - Measurements Introduction An phsical science requires measurement. This lab will involve making several measurements of the fundamental units of length, mass, and time. There is no
Phsics 203 - Lab 1 - Measurements Introduction An phsical science requires measurement. This lab will involve making several measurements of the fundamental units of length, mass, and time. There is no
Assessment Readiness. 28 Unit 1 MIXED REVIEW. 1. Look at each number. Is the number between 2π and
 MODULE 1 1. Look at each number. Is the number between π and 5? Select or for epressions A C. A. 6 _ 3 5π B. C. 3 5. Consider the number - 11 15. A. The number is rational. True False B. The number can
MODULE 1 1. Look at each number. Is the number between π and 5? Select or for epressions A C. A. 6 _ 3 5π B. C. 3 5. Consider the number - 11 15. A. The number is rational. True False B. The number can
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is phsics? Phsics deals with the behavior and composition of matter and its interactions at the most fundamental level. 1 Classical Phsics Classical phsics: (1600-1900)
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is phsics? Phsics deals with the behavior and composition of matter and its interactions at the most fundamental level. 1 Classical Phsics Classical phsics: (1600-1900)
10. The dimensional formula for c) 6% d) 7%
 UNIT. One of the combinations from the fundamental phsical constants is hc G. The unit of this epression is a) kg b) m 3 c) s - d) m. If the error in the measurement of radius is %, then the error in the
UNIT. One of the combinations from the fundamental phsical constants is hc G. The unit of this epression is a) kg b) m 3 c) s - d) m. If the error in the measurement of radius is %, then the error in the
Math 122 Fall Solutions to Homework #5. ( ) 2 " ln x. y = x 2
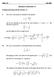 Math 1 Fall 8 Solutions to Homework #5 Problems from Pages 383-38 (Section 7.) 6. The curve in this problem is defined b the equation: = ( ) " ln and we are interested in the part of the curve between
Math 1 Fall 8 Solutions to Homework #5 Problems from Pages 383-38 (Section 7.) 6. The curve in this problem is defined b the equation: = ( ) " ln and we are interested in the part of the curve between
Physics: Momentum, Work, Energy, Power
 Name: ate: 1. The momentum of a 5-kilogram object moving at 6 meters per second is. 1 kg m/sec. 5 kg m/sec. 11 kg m/sec. 30 kg m/sec 2. 60-kilogram student running at 3.0 meters per second has a kinetic
Name: ate: 1. The momentum of a 5-kilogram object moving at 6 meters per second is. 1 kg m/sec. 5 kg m/sec. 11 kg m/sec. 30 kg m/sec 2. 60-kilogram student running at 3.0 meters per second has a kinetic
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS
 CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
2.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System
 . The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
So, whether or not something is moving depends on your frame of reference.
 When an object changes position relative to a reference point. (Frame of reference) Not from where she s sitting, but from space, the earth rotates and the wall with it. So, whether or not something is
When an object changes position relative to a reference point. (Frame of reference) Not from where she s sitting, but from space, the earth rotates and the wall with it. So, whether or not something is
Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Chapter 3 Vectors and Coordinate Systems
 Phsics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 3 Vectors and Coordinate Sstems Spring, 2008 Ho Jung Paik Coordinate Sstems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate sstem consists of a
Phsics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 3 Vectors and Coordinate Sstems Spring, 2008 Ho Jung Paik Coordinate Sstems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate sstem consists of a
AP Physics Math Review Packet
 AP Physics Math Review Packet The science of physics was developed to help explain the physics environment around us. Many of the subjects covered in this class will help you understand the physical world
AP Physics Math Review Packet The science of physics was developed to help explain the physics environment around us. Many of the subjects covered in this class will help you understand the physical world
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The current definition of the standard meter of length is based on 1) A) the length of
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The current definition of the standard meter of length is based on 1) A) the length of
PHYSICS PART II SECTION- I. Straight objective Type
 PHYSICS PAT II SECTION- I Straight objective Tpe This section contains 9 multiple choice questions numbered to 1. Each question has choices,, (C) and, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.. A parallel plate
PHYSICS PAT II SECTION- I Straight objective Tpe This section contains 9 multiple choice questions numbered to 1. Each question has choices,, (C) and, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.. A parallel plate
4) If a woman weighs 125 lb, her mass expressed in kilograms is x kg, where x is. A) less than 15. B) greater than 15. Answer: A
 Topic 1 Units, Conversions, and Estimation 1.1 Conceptual Questions 1) The current definition of the standard meter of length is based on A) the distance between the earthʹs equator and north pole. B)
Topic 1 Units, Conversions, and Estimation 1.1 Conceptual Questions 1) The current definition of the standard meter of length is based on A) the distance between the earthʹs equator and north pole. B)
C) D) 2. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope to pull a cart.
 1. Which graph best represents the relationship between the acceleration of an object falling freely near the surface of Earth and the time that it falls? 2. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope
1. Which graph best represents the relationship between the acceleration of an object falling freely near the surface of Earth and the time that it falls? 2. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope
St. Mary's H.S. Physics. Midterm Review
 Name Midterm Review St. Mary's H.S. Physics 1. If a car accelerates uniformly from rest to 15 meters per second over a distance of 100. meters, the magnitude of the car s acceleration is A) 0.15 m/s 2
Name Midterm Review St. Mary's H.S. Physics 1. If a car accelerates uniformly from rest to 15 meters per second over a distance of 100. meters, the magnitude of the car s acceleration is A) 0.15 m/s 2
11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
 Locker LESSON 11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as f (). Also A..A,
Locker LESSON 11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as f (). Also A..A,
MOST OF THESE PROBLEMS CAN BE SOLVED BY HAND USING PROPERTIES OF THE REAL NUMBERS. PROB- LEMS THAT REQUIRE TECHNOLOGY ARE INDICATED WITH A (*)
 STEP PROGRAM FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS BANK OF QUESTIONS MOST OF THESE PROBLEMS CAN BE SOLVED BY HAND USING PROPERTIES OF THE REAL NUMBERS. PROB- LEMS THAT REQUIRE TECHNOLOGY ARE INDICATED WITH A (*) SCIENTIFIC
STEP PROGRAM FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS BANK OF QUESTIONS MOST OF THESE PROBLEMS CAN BE SOLVED BY HAND USING PROPERTIES OF THE REAL NUMBERS. PROB- LEMS THAT REQUIRE TECHNOLOGY ARE INDICATED WITH A (*) SCIENTIFIC
Introduction Direct Variation Rates of Change Scatter Plots. Introduction. EXAMPLE 1 A Mathematical Model
 APPENDIX B Mathematical Modeling B1 Appendi B Mathematical Modeling B.1 Modeling Data with Linear Functions Introduction Direct Variation Rates of Change Scatter Plots Introduction The primar objective
APPENDIX B Mathematical Modeling B1 Appendi B Mathematical Modeling B.1 Modeling Data with Linear Functions Introduction Direct Variation Rates of Change Scatter Plots Introduction The primar objective
Review for the Final Exam
 Calculus Lia Vas. Integrals. Evaluate the following integrals. (a) ( x 4 x 2 ) dx (b) (2 3 x + x2 4 ) dx (c) (3x + 5) 6 dx (d) x 2 dx x 3 + (e) x 9x 2 dx (f) x dx x 2 (g) xe x2 + dx (h) 2 3x+ dx (i) x
Calculus Lia Vas. Integrals. Evaluate the following integrals. (a) ( x 4 x 2 ) dx (b) (2 3 x + x2 4 ) dx (c) (3x + 5) 6 dx (d) x 2 dx x 3 + (e) x 9x 2 dx (f) x dx x 2 (g) xe x2 + dx (h) 2 3x+ dx (i) x
Fluid force problems
 Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter 5: Basic applications of integration Section 1 Fluid force problems What ou need to know alread: How to use the four step process to set up an integral. What
Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter 5: Basic applications of integration Section 1 Fluid force problems What ou need to know alread: How to use the four step process to set up an integral. What
Convert 36 inches to feet. Show your work so that a classmate can follow what you did and why you did it. Remember 12inches = 1 foot
 Convert 36 inches to feet. Show your work so that a classmate can follow what you did and why you did it. Remember 12inches = 1 foot 1 NASA had originally planned on firing the rocket engines to put Mars
Convert 36 inches to feet. Show your work so that a classmate can follow what you did and why you did it. Remember 12inches = 1 foot 1 NASA had originally planned on firing the rocket engines to put Mars
Chapter 3. Vectors. θ that the vector forms with i ˆ is 15. I. Vectors and Scalars
 Chapter 3. Vectors I. Vectors and Scalars 1. What type of quantity does the odometer of a car measure? a) vector; b) scalar; c) neither scalar nor vector; d) both scalar and vector. 2. What type of quantity
Chapter 3. Vectors I. Vectors and Scalars 1. What type of quantity does the odometer of a car measure? a) vector; b) scalar; c) neither scalar nor vector; d) both scalar and vector. 2. What type of quantity
Physics 121, Sections 1 and 2, Winter 2011 Instructor: Scott Bergeson Exam #3 April 16 April 21, 2011 RULES FOR THIS TEST:
 Physics 121, Sections 1 and 2, Winter 2011 Instructor: Scott Bergeson Exam #3 April 16 April 21, 2011 RULES FOR THIS TEST: This test is closed book. You may use a dictionary. You may use your own calculator
Physics 121, Sections 1 and 2, Winter 2011 Instructor: Scott Bergeson Exam #3 April 16 April 21, 2011 RULES FOR THIS TEST: This test is closed book. You may use a dictionary. You may use your own calculator
Summary and Vocabulary
 Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Summar and Vocabular The functions studied in this chapter are all based on direct and inverse variation. When k and n >, formulas of the form = k n define direct-variation functions,
Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Summar and Vocabular The functions studied in this chapter are all based on direct and inverse variation. When k and n >, formulas of the form = k n define direct-variation functions,
Regents Physics. Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems
 Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Review of Exponent Rules
 Page Review of Eponent Rules Math : Unit Radical and Rational Functions Rule : Multipling Powers With the Same Base Multipl Coefficients, Add Eponents. h h h. ( )( ). (6 )(6 ). (m n )(m n ). ( 8ab)( a
Page Review of Eponent Rules Math : Unit Radical and Rational Functions Rule : Multipling Powers With the Same Base Multipl Coefficients, Add Eponents. h h h. ( )( ). (6 )(6 ). (m n )(m n ). ( 8ab)( a
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Coordinate Systems. Cartesian Coordinate System. Lectures 5 and 6 Vectors.
 PC1221 Fundamentals of Phsics I Lectures 5 and 6 Vectors Dr Ta Seng Chuan 1 Ground ules Switch off our handphone and pager Switch off our laptop computer and keep it No talking while lecture is going on
PC1221 Fundamentals of Phsics I Lectures 5 and 6 Vectors Dr Ta Seng Chuan 1 Ground ules Switch off our handphone and pager Switch off our laptop computer and keep it No talking while lecture is going on
Chapter 5 Assessment. 164 Chapter 5 Measurements and Calculations. 8. Write each of the following numbers in standard scientific notation. a.
 Chapter 5 Assessment All exercises with blue numbers have answers in the back of this book. 5.1 Scientific Notation and Units A. Scientific Notation 1. When the number 98,145 is written in standard scientific
Chapter 5 Assessment All exercises with blue numbers have answers in the back of this book. 5.1 Scientific Notation and Units A. Scientific Notation 1. When the number 98,145 is written in standard scientific
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND MATHEMATICAL CONCEPTS. s K J =
 CHPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS CONCEPTUL QUESTIONS 1. RESONING ND SOLUTION The quantit tan is dimensionless and has no units. The units of the ratio /v are m F = m s s (m / s) H G I m K J
CHPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS CONCEPTUL QUESTIONS 1. RESONING ND SOLUTION The quantit tan is dimensionless and has no units. The units of the ratio /v are m F = m s s (m / s) H G I m K J
s_3x03 Page 1 Physics Samples
 Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
Chapter 2 Measurement and Problem Solving
 Measurement and Problem Solving What Is a Measurement? Quantitative observation. Comparison to an agreed upon standard. Every measurement has a number and a unit. 2 A Measurement The unit tells you to
Measurement and Problem Solving What Is a Measurement? Quantitative observation. Comparison to an agreed upon standard. Every measurement has a number and a unit. 2 A Measurement The unit tells you to
INTRODUCTION AND MATHMATICAL Concepts. 1. Which one of the following is an SI base unit? (a) gram (c) newton (e) kilogram
 chapter INTRODUCTION AND MATHMATICAL Concepts Section 1.2 Units Section 1.3 The Role of Units in Problem Solving 1. Which one of the following is an SI base unit? (a) gram (c) newton (e) kilogram (b) slug
chapter INTRODUCTION AND MATHMATICAL Concepts Section 1.2 Units Section 1.3 The Role of Units in Problem Solving 1. Which one of the following is an SI base unit? (a) gram (c) newton (e) kilogram (b) slug
Solutions to Physics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 3 CHAPTER 3
 Solutions to Phsics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 3 CHAPTE 3 1. We choose the west and south coordinate sstem shown. For the components of the resultant we have W W = D 1 + D cos
Solutions to Phsics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 3 CHAPTE 3 1. We choose the west and south coordinate sstem shown. For the components of the resultant we have W W = D 1 + D cos
Dynamics-Newton's 2nd Law
 1. A constant unbalanced force is applied to an object for a period of time. Which graph best represents the acceleration of the object as a function of elapsed time? 2. The diagram below shows a horizontal
1. A constant unbalanced force is applied to an object for a period of time. Which graph best represents the acceleration of the object as a function of elapsed time? 2. The diagram below shows a horizontal
Name Date Class MEASUREMENTS AND THEIR UNCERTAINTY
 3.1 MEASUREMENTS AND THEIR UNCERTAINTY Section Review Objectives Convert measurements to scientific notation Distinguish among the accuracy, precision, and error of a measurement Identify the number of
3.1 MEASUREMENTS AND THEIR UNCERTAINTY Section Review Objectives Convert measurements to scientific notation Distinguish among the accuracy, precision, and error of a measurement Identify the number of
Let s try an example of Unit Analysis. Your friend gives you this formula: x=at. You have to figure out if it s right using Unit Analysis.
 Lecture 1 Introduction to Measurement - SI sstem Dimensional nalsis / Unit nalsis Unit Conversions Vectors and Mathematics International Sstem of Units (SI) Table 1.1, p.5 The Seven Base Units What is
Lecture 1 Introduction to Measurement - SI sstem Dimensional nalsis / Unit nalsis Unit Conversions Vectors and Mathematics International Sstem of Units (SI) Table 1.1, p.5 The Seven Base Units What is
1 What is Science? Worksheets CHAPTER CHAPTER OUTLINE
 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. What is Science? Worksheets CSS AP Physics 1 2015-16 Summer Assignment Part 1 of 3 CHAPTER 1 What is Science? Worksheets CHAPTER OUTLINE 1.1 Scientific Inquiry 1.2 Fundamental Units
www.ck12.org Chapter 1. What is Science? Worksheets CSS AP Physics 1 2015-16 Summer Assignment Part 1 of 3 CHAPTER 1 What is Science? Worksheets CHAPTER OUTLINE 1.1 Scientific Inquiry 1.2 Fundamental Units
One Dimensional Motion. Motion in x or y only
 One Dimensional Motion Motion in x or y only Scalar vs. Vector Scalar Defined as quantity with magnitude (size) only Example: 3 m, 62 seconds, 4.2 miles EASY Math!!! Vector Defined as quantity with magnitude
One Dimensional Motion Motion in x or y only Scalar vs. Vector Scalar Defined as quantity with magnitude (size) only Example: 3 m, 62 seconds, 4.2 miles EASY Math!!! Vector Defined as quantity with magnitude
Students must be prepared to take a quiz on pre-calculus material by the 2 nd day of class.
 AP Calculus AB Students must be prepared to take a quiz on pre-calculus material by the nd day of class. You must be able to complete each of these problems Uwith and without the use of a calculatoru (unless
AP Calculus AB Students must be prepared to take a quiz on pre-calculus material by the nd day of class. You must be able to complete each of these problems Uwith and without the use of a calculatoru (unless
Vectors. An Introduction
 Vectors An Introduction There are two kinds of quantities Scalars are quantities that have magnitude only, such as position speed time mass Vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction,
Vectors An Introduction There are two kinds of quantities Scalars are quantities that have magnitude only, such as position speed time mass Vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction,
Dynamics-Newton's 2nd Law
 1. A constant unbalanced force is applied to an object for a period of time. Which graph best represents the acceleration of the object as a function of elapsed time? 2. The diagram below shows a horizontal
1. A constant unbalanced force is applied to an object for a period of time. Which graph best represents the acceleration of the object as a function of elapsed time? 2. The diagram below shows a horizontal
4-5 Compute with Scientific Notation
 1. About 1 10 6 fruit flies weigh 1.3 10 2 pounds. How much does one fruit fly weigh? Write in scientific notation. Divide the weight of the fruit flies by the number of fruit flies to find the weight
1. About 1 10 6 fruit flies weigh 1.3 10 2 pounds. How much does one fruit fly weigh? Write in scientific notation. Divide the weight of the fruit flies by the number of fruit flies to find the weight
b(n) = 4n, where n represents the number of students in the class. What is the independent
 Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing movie tickets that sell for $ each C The cost,, after a $ discount,
Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing movie tickets that sell for $ each C The cost,, after a $ discount,
One dimensional Motion test 8/24
 8/16/017 One dimensional Motion test 8/4 The Nature of Science Observation: important first step toward scientific theory; requires imagination to tell what is important. Theories: created to explain observations;
8/16/017 One dimensional Motion test 8/4 The Nature of Science Observation: important first step toward scientific theory; requires imagination to tell what is important. Theories: created to explain observations;
What You ll Learn Identify direct variation. Use direct variation to solve problems.
 AM_S_C_L_3.indd Page // 3: PM s-user /Volumes//GO/CORE_READING/TENNESSEE/ANCILLARY... Proportionalit and Linear Relationships Teach the Concept Lesson - Direct Variation Interactive Stud Guide See pages
AM_S_C_L_3.indd Page // 3: PM s-user /Volumes//GO/CORE_READING/TENNESSEE/ANCILLARY... Proportionalit and Linear Relationships Teach the Concept Lesson - Direct Variation Interactive Stud Guide See pages
THIS IS A CLASS SET - DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER
 THIS IS A CLASS SET - DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER ALGEBRA EOC PRACTICE Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing
THIS IS A CLASS SET - DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER ALGEBRA EOC PRACTICE Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing
CHAPTER-OPENING QUESTION
 g B This snowboarder fling through the air shows an eample of motion in two dimensions. In the absence of air resistance, the path would be a perfect parabola. The gold arrow represents the downward acceleration
g B This snowboarder fling through the air shows an eample of motion in two dimensions. In the absence of air resistance, the path would be a perfect parabola. The gold arrow represents the downward acceleration
9 (0, 3) and solve equations to earn full credit.
 Math 0 Intermediate Algebra II Final Eam Review Page of Instructions: (6, ) Use our own paper for the review questions. For the final eam, show all work on the eam. (-6, ) This is an algebra class do not
Math 0 Intermediate Algebra II Final Eam Review Page of Instructions: (6, ) Use our own paper for the review questions. For the final eam, show all work on the eam. (-6, ) This is an algebra class do not
Review of Scientific Notation and Significant Figures
 II-1 Scientific Notation Review of Scientific Notation and Significant Figures Frequently numbers that occur in physics and other sciences are either very large or very small. For example, the speed of
II-1 Scientific Notation Review of Scientific Notation and Significant Figures Frequently numbers that occur in physics and other sciences are either very large or very small. For example, the speed of
Learning Plan 4 Chapter 9
 Learning Plan 4 Chapter 9 Question The population of a country reached 309.5 million people. The total area is 3.25 million square miles. What is the population density for the country? Round to the nearest
Learning Plan 4 Chapter 9 Question The population of a country reached 309.5 million people. The total area is 3.25 million square miles. What is the population density for the country? Round to the nearest
9.2 Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY
 9. Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY QUESTIONS 9.H Energy.doc 1. A 500 kilogram car is driving at 15 meters/second. Calculate its kinetic energy? How much does
9. Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY QUESTIONS 9.H Energy.doc 1. A 500 kilogram car is driving at 15 meters/second. Calculate its kinetic energy? How much does
Chapter 3 Solutions. *3.1 x = r cos θ = (5.50 m) cos 240 = (5.50 m)( 0.5) = 2.75 m. y = r sin θ = (5.50 m) sin 240 = (5.50 m)( 0.866) = 4.
 Chapter 3 Solutions *3.1 = r cos θ = (5.50 m) cos 240 = (5.50 m)( 0.5) = 2.75 m = r sin θ = (5.50 m) sin 240 = (5.50 m)( 0.866) = 4.76 m 3.2 (a) d = ( 2 1 ) 2 + ( 2 1 ) 2 = (2.00 [ 3.00] 2 ) + ( 4.00 3.00)
Chapter 3 Solutions *3.1 = r cos θ = (5.50 m) cos 240 = (5.50 m)( 0.5) = 2.75 m = r sin θ = (5.50 m) sin 240 = (5.50 m)( 0.866) = 4.76 m 3.2 (a) d = ( 2 1 ) 2 + ( 2 1 ) 2 = (2.00 [ 3.00] 2 ) + ( 4.00 3.00)
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7
 Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
Chapter 6 Motion in Two Dimensions
 Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 6 Motion in Two Dimensions Section Review 6.1 1. What is the word for the horizontal distance a projectile travels? 2. What does it mean to say a projectile
Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 6 Motion in Two Dimensions Section Review 6.1 1. What is the word for the horizontal distance a projectile travels? 2. What does it mean to say a projectile
Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction
 Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction 1. A particle moves from x 1 = 30 cm to x 2 = 40 cm. The displacement of this particle is A. 30 cm B. 40 cm C. 70 cm
Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction 1. A particle moves from x 1 = 30 cm to x 2 = 40 cm. The displacement of this particle is A. 30 cm B. 40 cm C. 70 cm
Mechanics. Time (s) Distance (m) Velocity (m/s) Acceleration (m/s 2 ) = + displacement/time.
 Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
The diagram below shows a block on a horizontal frictionless surface. A 100.-newton force acts on the block at an angle of 30. above the horizontal.
 Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maximum or minimum values.
 8 LESSON 5- MAX/MIN APPLICATIONS (OPTIMIZATION) One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maimum or minimum values. Procedure:. Choose variables and/or draw a labeled figure..
8 LESSON 5- MAX/MIN APPLICATIONS (OPTIMIZATION) One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maimum or minimum values. Procedure:. Choose variables and/or draw a labeled figure..
REVIEW PACKET FOR END OF COURSE EXAM
 Math H REVIEW PACKET FOR END OF COURSE EXAM DO NOT WRITE ON PACKET! Do on binder paper, show support work. On this packet leave all fractional answers in improper fractional form (ecept where appropriate
Math H REVIEW PACKET FOR END OF COURSE EXAM DO NOT WRITE ON PACKET! Do on binder paper, show support work. On this packet leave all fractional answers in improper fractional form (ecept where appropriate
Accuracy, Precision, and Significant Figures
 Accuracy, Precision, and Significant Figures Bởi: OpenStaxCollege A double-pan mechanical balance is used to compare different masses. Usually an object with unknown mass is placed in one pan and objects
Accuracy, Precision, and Significant Figures Bởi: OpenStaxCollege A double-pan mechanical balance is used to compare different masses. Usually an object with unknown mass is placed in one pan and objects
AP Physics I Summer Work
 AP Physics I Summer Work 2018 (20 points) Please complete the following set of questions and word problems. Answers will be reviewed in depth during the first week of class followed by an assessment based
AP Physics I Summer Work 2018 (20 points) Please complete the following set of questions and word problems. Answers will be reviewed in depth during the first week of class followed by an assessment based
Measurement: Length, Area and Volume Part I
 IDS 101 Name Measurement: Length, Area and Volume Part I If we ask someone the size of a common object, such as a dime or penny, most people come pretty close to the actual size. However, objects that
IDS 101 Name Measurement: Length, Area and Volume Part I If we ask someone the size of a common object, such as a dime or penny, most people come pretty close to the actual size. However, objects that
1Write and graph. 2Solve problems. Now. Then. Why? New Vocabulary
 Direct Variation Then You found rates of change of linear functions. (Lesson -) Now Write and graph direct variation equations. Solve problems involving direct variation. Wh? Bianca is saving her mone
Direct Variation Then You found rates of change of linear functions. (Lesson -) Now Write and graph direct variation equations. Solve problems involving direct variation. Wh? Bianca is saving her mone
Problems to practice for FINAL. 1. Below is the graph of a function ( ) At which of the marked values ( and ) is: (a) ( ) greatest = (b) ( ) least
 Problems to practice for FINAL. Below is the graph of a function () At which of the marked values ( and ) is: (a) () greatest = (b) () least = (c) () the greatest = (d) () the least = (e) () = = (f) ()
Problems to practice for FINAL. Below is the graph of a function () At which of the marked values ( and ) is: (a) () greatest = (b) () least = (c) () the greatest = (d) () the least = (e) () = = (f) ()
Motion Graphs Practice
 Name Motion Graphs Practice d vs. t Graphs d vs. t Graphs d vs. t Graphs 1. The graph below represents the relationship between velocity and time of travel for a toy car moving in a straight line. 3. The
Name Motion Graphs Practice d vs. t Graphs d vs. t Graphs d vs. t Graphs 1. The graph below represents the relationship between velocity and time of travel for a toy car moving in a straight line. 3. The
1. Two forces act concurrently on an object on a horizontal, frictionless surface, as shown in the diagram below.
 Name Vectors Practice 1. Two forces act concurrently on an object on a horizontal, frictionless surface, as shown in the diagram below. What additional force, when applied to the object, will establish
Name Vectors Practice 1. Two forces act concurrently on an object on a horizontal, frictionless surface, as shown in the diagram below. What additional force, when applied to the object, will establish
END OF COURSE ALGEBRA I
 VIRGINIA STANDARDS OF LEARNING Spring 008 Released Test END OF COURSE ALGERA I Form M08, CORE Propert of the Virginia Department of Education 008 b the Commonwealth of Virginia, Department of Education,
VIRGINIA STANDARDS OF LEARNING Spring 008 Released Test END OF COURSE ALGERA I Form M08, CORE Propert of the Virginia Department of Education 008 b the Commonwealth of Virginia, Department of Education,
Written Homework problems. Spring (taken from Giancoli, 4 th edition)
 Written Homework problems. Spring 014. (taken from Giancoli, 4 th edition) HW1. Ch1. 19, 47 19. Determine the conversion factor between (a) km / h and mi / h, (b) m / s and ft / s, and (c) km / h and m
Written Homework problems. Spring 014. (taken from Giancoli, 4 th edition) HW1. Ch1. 19, 47 19. Determine the conversion factor between (a) km / h and mi / h, (b) m / s and ft / s, and (c) km / h and m
π (sinπ ) + cos π + C = C = 0 C = 1
 National Mu Alpha Theta Diff EQ page Mississippi, 00 Differential Equations Topic Test: Complete Solutions Note: For each problem, where there is no choice (e), assume (e) none of the above.. State the
National Mu Alpha Theta Diff EQ page Mississippi, 00 Differential Equations Topic Test: Complete Solutions Note: For each problem, where there is no choice (e), assume (e) none of the above.. State the
Components of a Vector
 Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
2.1 Intercepts; Symmetry; Graphing Key Equations
 Ch. Graphs.1 Intercepts; Smmetr; Graphing Ke Equations 1 Find Intercepts from an Equation MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. List the
Ch. Graphs.1 Intercepts; Smmetr; Graphing Ke Equations 1 Find Intercepts from an Equation MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. List the
Physics 207, Lecture 2, Sept. 8
 Physics 207, Lecture 2, Sept. 8 Goals: (Highlights of Chaps. 1 & 2.1-2.4) 2.4) Units and scales, order of magnitude calculations, significant digits (on your own for the most part) Distinguish between
Physics 207, Lecture 2, Sept. 8 Goals: (Highlights of Chaps. 1 & 2.1-2.4) 2.4) Units and scales, order of magnitude calculations, significant digits (on your own for the most part) Distinguish between
Scalars distance speed mass time volume temperature work and energy
 Scalars and Vectors scalar is a quantit which has no direction associated with it, such as mass, volume, time, and temperature. We sa that scalars have onl magnitude, or size. mass ma have a magnitude
Scalars and Vectors scalar is a quantit which has no direction associated with it, such as mass, volume, time, and temperature. We sa that scalars have onl magnitude, or size. mass ma have a magnitude
Algebra I. Administered May 2014 RELEASED
 STAAR State of Teas Assessments of Academic Readiness Algebra I Administered Ma 0 RELEASED Copright 0, Teas Education Agenc. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited
STAAR State of Teas Assessments of Academic Readiness Algebra I Administered Ma 0 RELEASED Copright 0, Teas Education Agenc. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited
RELEASED. Go to next page. 2. The graph shows the acceleration of a car over time.
 1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
Physical Science Chapter 11. Motion
 Physical Science Chapter 11 Motion Motion Definition An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Relative Motion Relative motion is movement in relation to a REFERENCE POINT.
Physical Science Chapter 11 Motion Motion Definition An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Relative Motion Relative motion is movement in relation to a REFERENCE POINT.
Directions: This is a practice final exam which covers all chapters in this course. (A) (B) 3 10 (C) 10 3 (D) (E) None of the above
 MAT 1012 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Page 1 of 28 Directions: This is a practice final exam which covers all chapters in this course. Question: 1 Simplify. 9 Question: 2 Write the number 1000 using an exponent
MAT 1012 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Page 1 of 28 Directions: This is a practice final exam which covers all chapters in this course. Question: 1 Simplify. 9 Question: 2 Write the number 1000 using an exponent
Physics 211 Fall 2009 Exam 3 Version D
 Physics 211 Fall 2009 xam 3 Version Instructions e sure to answer every question. Follow the rules shown on the screen for filling in the Scantron form. ach problem is worth 10% of the exam. When you are
Physics 211 Fall 2009 xam 3 Version Instructions e sure to answer every question. Follow the rules shown on the screen for filling in the Scantron form. ach problem is worth 10% of the exam. When you are
Physics 211 Fall 2009 Exam 3 Version A
 Physics 211 Fall 2009 xam 3 Version Instructions e sure to answer every question. Follow the rules shown on the screen for filling in the Scantron form. ach problem is worth 10% of the exam. When you are
Physics 211 Fall 2009 xam 3 Version Instructions e sure to answer every question. Follow the rules shown on the screen for filling in the Scantron form. ach problem is worth 10% of the exam. When you are
the distance from the top to the bottom of an object height a measurement of how heavy something is weight
 height the distance from the top to the bottom of an object weight a measurement of how heavy something is length the distance from one side of an object to another measure to find the number that shows
height the distance from the top to the bottom of an object weight a measurement of how heavy something is length the distance from one side of an object to another measure to find the number that shows
Bellringer Day In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules?
 Bellringer Day 01 1. In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules? Lab Safety Video Lab Safety Map See if you can identify the lab safety equipment around the room. You can discuss
Bellringer Day 01 1. In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules? Lab Safety Video Lab Safety Map See if you can identify the lab safety equipment around the room. You can discuss
SCIENTIFIC MEASUREMENTS
 SCIENTIFIC MEASUREMENTS Textbook References: Textbook 4 th, Appendix A-1 & C-1 Textbook 5 th, Appendix B Lesson Objectives: By Studying this chapter, you will learn 1. What the fundamental quantities of
SCIENTIFIC MEASUREMENTS Textbook References: Textbook 4 th, Appendix A-1 & C-1 Textbook 5 th, Appendix B Lesson Objectives: By Studying this chapter, you will learn 1. What the fundamental quantities of
Page 1. Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is A) 34 m B) 30.
 Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
Find the integral. 12) 15)
 Find the location of the indicated absolute etremum within the specified domain. ) Minimum of f() = /- /; [0, ] 8) Maimum h() ) Minimum of f() = - + - ; [-, ] ) Minimum of f() = ( + )/; [-, ] ) Maimum
Find the location of the indicated absolute etremum within the specified domain. ) Minimum of f() = /- /; [0, ] 8) Maimum h() ) Minimum of f() = - + - ; [-, ] ) Minimum of f() = ( + )/; [-, ] ) Maimum
Identify the domain and the range of the relation from the graph. 8)
 INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST Use the given conditions to write an equation for the line. 1) a) Passing through (, -) and parallel to = - +. b) Passing through (, 7) and parallel to - 3 = 10 c)
INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST Use the given conditions to write an equation for the line. 1) a) Passing through (, -) and parallel to = - +. b) Passing through (, 7) and parallel to - 3 = 10 c)
Ordered pair: Domain: Range:
 Sec 2.1 Relations Learning Objectives: 1. Understand relations. 2. Find the domain and the range of a relation. 3. Graph a relation defined b an equation. 1. Understand relations Relation eists when the
Sec 2.1 Relations Learning Objectives: 1. Understand relations. 2. Find the domain and the range of a relation. 3. Graph a relation defined b an equation. 1. Understand relations Relation eists when the
Introduction to Kinematics. Motion, Forces and Energy
 Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Math 0302 Course Review
 89 Solve the following: Math 0302 Course Review ) 4y + 23 = 47 2) 6(2y + 3) 4 = 2y 22 3) 5y+ 6 2y 4 3 = 2 4) 2+6 7 = 3 5) = 7 y + pg (solve for y) 6) 2 7 + 6 = 0 7) ac bc = ab + vh (solve for a) 8) 2 =
89 Solve the following: Math 0302 Course Review ) 4y + 23 = 47 2) 6(2y + 3) 4 = 2y 22 3) 5y+ 6 2y 4 3 = 2 4) 2+6 7 = 3 5) = 7 y + pg (solve for y) 6) 2 7 + 6 = 0 7) ac bc = ab + vh (solve for a) 8) 2 =
CCR Math - Grade 7 Practice Test
 R Math - Grade 7 Practice Test You may use a calculator for questions -7.. Use the picture below to answer the question. A B What is the probability of spinning a? A. B.. D. 5 3 5 3 5 A 3 Go on to the
R Math - Grade 7 Practice Test You may use a calculator for questions -7.. Use the picture below to answer the question. A B What is the probability of spinning a? A. B.. D. 5 3 5 3 5 A 3 Go on to the
[ ] 4. Math 70 Intermediate Algebra II Final Exam Review Page 1 of 19. Instructions:
![[ ] 4. Math 70 Intermediate Algebra II Final Exam Review Page 1 of 19. Instructions: [ ] 4. Math 70 Intermediate Algebra II Final Exam Review Page 1 of 19. Instructions:](/thumbs/80/81204581.jpg) Math Intermediate Algebra II Final Eam Review Page of 9 Instructions: Use our own paper for the review questions. For the final eam, show all work on the eam. This is an algebra class do not guess! Write
Math Intermediate Algebra II Final Eam Review Page of 9 Instructions: Use our own paper for the review questions. For the final eam, show all work on the eam. This is an algebra class do not guess! Write
BC VECTOR PROBLEMS. 13. Find the area of the parallelogram having AB and AC as adjacent sides: A(2,1,3), B(1,4,2), C( 3,2,7) 14.
 For problems 9 use: u (,3) v (3, 4) s (, 7). w =. 3u v = 3. t = 4. 7u = u w (,3,5) 5. wt = t (,, 4) 6. Find the measure of the angle between w and t to the nearest degree. 7. Find the unit vector having
For problems 9 use: u (,3) v (3, 4) s (, 7). w =. 3u v = 3. t = 4. 7u = u w (,3,5) 5. wt = t (,, 4) 6. Find the measure of the angle between w and t to the nearest degree. 7. Find the unit vector having
Phys 221. Chapter 3. Vectors A. Dzyubenko Brooks/Cole
 Phs 221 Chapter 3 Vectors adzubenko@csub.edu http://www.csub.edu/~adzubenko 2014. Dzubenko 2014 rooks/cole 1 Coordinate Sstems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate sstem consists
Phs 221 Chapter 3 Vectors adzubenko@csub.edu http://www.csub.edu/~adzubenko 2014. Dzubenko 2014 rooks/cole 1 Coordinate Sstems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate sstem consists
Measurement. Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure.
 chapter 32 Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You ll Learn how to estimate
chapter 32 Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You ll Learn how to estimate
= = =
 . D - To evaluate the expression, we can regroup the numbers and the powers of ten, multiply, and adjust the decimal and exponent to put the answer in correct scientific notation format: 5 0 0 7 = 5 0
. D - To evaluate the expression, we can regroup the numbers and the powers of ten, multiply, and adjust the decimal and exponent to put the answer in correct scientific notation format: 5 0 0 7 = 5 0
Physics 11 (Fall 2012) Chapter 1: Representing Motion
 Physics 11 (Fall 2012) Chapter 1: Representing Motion Anyone who has never made a mistake has never tried anything new. Albert Einstein Experience is the name that everyone gives to his mistakes. Oscar
Physics 11 (Fall 2012) Chapter 1: Representing Motion Anyone who has never made a mistake has never tried anything new. Albert Einstein Experience is the name that everyone gives to his mistakes. Oscar
