( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 2. ELEC 201 Electric Circuit Analysis I Lecture 8(a) RL and RC Circuits: Single Switch 11/9/2017. Driven RL Circuit: Equation
|
|
|
- Lydia Jacobs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 /9/7 Dren rcut: Equaton EE Electrc rcut Analyss I ecture 8(a) an rcuts: Sngle Swtch THE ITADE, THE MIITAY OEGE OF SOUTH AOINA All sles an content 7 Moultre courtesy Street, of harleston, Dr. Gregory S 949 J. Mazzaro s Intally, (a) the source s turne off, an (b) no energy s store, so (c) no current flows. s After the swtch changes, s V The nuctor has not yet ha tme to bul up current: A long tme after the swtch has been close,, ( ) V, t t just before t just after t (nuctor acts as a short crcut) Dren rcut: Equaton Dren rcut: Soluton ( ) V V t ( t) V Wrtng KV after the swtch changes, V V ( t) ( t) V V ( t ) ( t) homogeneous, frst-orer fferental equaton 3 Sole the fferental equaton by guess & check constant? snusoal? exponental ecay? exponental rse? t I e I I I ( ) I V I V 4
2 /9/7 Dren rcut: Soluton Dren rcut: Soluton V t ( t) V V t ( t) V V t V V t e ( e ) substtute nto the ff eq V V V V e e V ( e ) t tme constant of the crcut, a measure of how much tme s requre to charge/scharge 5 6 Example: Dren rcut Example: Dren rcut Plot the oltages s,, an for µs < t < µs. kω Plot the oltages s,, an for µs < t < µs. kω s V 5 mh ( t ) t I e V ( ) ( ) t kω 5 mh ( 5 ma)( ) I e I e I V kω 5 ma t e s 5 mh ( t ) t t e e 4 4t 5 5 ma kω V 7 8
3 /9/7 Example: Dren rcut Example: Dren rcut Plot the oltages s,, an for µs < t < µs. s kω V 5 mh s ( t) t < V t t < e V t t < t e V t ( t) 4t ( t) 4 s kω V 5 mh t t e 4t ( 5 mh) ( 5 ma)( ) t ( t) ( t) ( )( )( e ) e t 5 4 V t -e-6:e-7:e-6; _s ().* (t > ); _ (*exp(-4e4*t)).* (t > ); _ ( - *exp(-4e4*t)).* (t > ); plot(t/^-6,_s,'-',t/^-6,... _,'--',t/^-6,_,'-.') axs([-inf Inf - ]) legen('_s','_','_') ylabel('voltage (V)') xlabel('tme (\mus)') 9 Dren rcut: Equaton s s After the swtch changes, s V The capactor has not yet ha tme to bul up oltage: A long tme after the swtch has been close, Intally, (a) the source s turne off, an (b) no energy s store., ( ) V, t t just before t just after t (capactor acts as an open crcut) Dren rcut: Equaton Wrtng KV after the swtch changes, ( ) V V V V V ( t ) ( t ) homogeneous, frst-orer fferental equaton 3
4 /9/7 Dren rcut: Soluton Dren rcut: Soluton V ( t ) ( t ) ( ) V V ( t ) ( t ) ( ) V Sole the fferental equaton by guess & check t V e V V V ( ) V V V V 3 Substtute the exponental soluton nto the fferental equaton t t V ( V ) e ( V ) ( V ) e 4 t t V V e Dren rcut: Soluton rcut: PSpce V ( t ) ( t ) ( ) V Smulate ths crcut an plot the oltages an for < t < ms. t ms 4 kω V 5 nf ( t ) t V e tme constant of the crcut, a measure of how much tme s requre to charge/scharge Sw_tlose & Sw_tOpen, EVA lbrary 5 6 4
5 /9/7 Source-Free rcut Source-Free rcut t ( t) ( ) V energy store ntally no source rops to zero oer tme energy store ntally no source ( t ) ( t ) V ( ) rops to zero oer tme V e t V t V e t.368 V 7 8 Source-Free rcut: PSpce Source-Free rcut: PSpce Smulate ths crcut an plot the oltage an current for < t < µs. Assume that, at t, the oltage across the capactor s mv. 4 nf 6 kω Smulate ths crcut an plot the oltage an current for < t < µs. Assume that, at t, the oltage across the capactor s mv. 4 nf 6 kω IPINT part, SPEIA lbrary I ntal conon oltage for a capactor (n Volts) current for an nuctor (n Amps) 9 5
6 /9/7 Source-Free rcut: PSpce & rcut: General Soluton Smulate ths crcut an plot the oltage an current for < t < µs. Assume that, at t, the oltage across the capactor s mv. th 5 kω 4 nf µs 4 nf 6 kω The transent response (all oltages an currents) wthn a sngle-equalent-energy-storage-element crcut follow ths general form: crcut x t X e X X x X X x crcut th th th th t I e I t V e V t where th s the Theenn equalent resstance seen at the termnals of the energy storage element., General Soluton: Proceure () Ientfy the crcut as a transent or crcut. (e.g. not an crcut) () Assume that the crcut response ( or ) wll follow the general soluton: x t X e X 3 X x X X x (3) If necessary, etermne equalent nuctance ( eq ) or capactance ( eq ) by approprate seres/parallel combnatons. (4) Sole for the ntal nuctor current () or capactor oltage (). (5) Sole for the fnal nuctor current ( ) or capactor oltage ( ). (6) Determne the Theenn equalent resstance seen by the energy-storage element (nuctor or capactor), th. ompute / th or th. (7) Substtute results from steps 4, 5, 6 nto the general soluton (step ). (8) To sole for / that s not for the nuctor/capactor, use crcut analyss (KV, K, etc.) to sole for that partcular /. 6
Boise State University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 212L Circuit Analysis and Design Lab
 Bose State Unersty Department of Electrcal and omputer Engneerng EE 1L rcut Analyss and Desgn Lab Experment #8: The Integratng and Dfferentatng Op-Amp rcuts 1 Objectes The objectes of ths laboratory experment
Bose State Unersty Department of Electrcal and omputer Engneerng EE 1L rcut Analyss and Desgn Lab Experment #8: The Integratng and Dfferentatng Op-Amp rcuts 1 Objectes The objectes of ths laboratory experment
Boise State University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 212L Circuit Analysis and Design Lab
 Bose State Unersty Department of Electrcal and omputer Engneerng EE 1L rcut Analyss and Desgn Lab Experment #8: The Integratng and Dfferentatng Op-Amp rcuts 1 Objectes The objectes of ths laboratory experment
Bose State Unersty Department of Electrcal and omputer Engneerng EE 1L rcut Analyss and Desgn Lab Experment #8: The Integratng and Dfferentatng Op-Amp rcuts 1 Objectes The objectes of ths laboratory experment
CHAPTER 8 COMPLETE RESPONSE OF RC & RL CIRCUITS
 HAPTER 8 OMPETE RESPONSE OF R & R IRUITS The order of the crcut s defned by the number of rreducble storage elements n the crcut. In ths chapter, we wll fnd the complete response of a frst-order crcut;
HAPTER 8 OMPETE RESPONSE OF R & R IRUITS The order of the crcut s defned by the number of rreducble storage elements n the crcut. In ths chapter, we wll fnd the complete response of a frst-order crcut;
( ) = ( ) + ( 0) ) ( )
 EETOMAGNETI OMPATIBIITY HANDBOOK 1 hapter 9: Transent Behavor n the Tme Doman 9.1 Desgn a crcut usng reasonable values for the components that s capable of provdng a tme delay of 100 ms to a dgtal sgnal.
EETOMAGNETI OMPATIBIITY HANDBOOK 1 hapter 9: Transent Behavor n the Tme Doman 9.1 Desgn a crcut usng reasonable values for the components that s capable of provdng a tme delay of 100 ms to a dgtal sgnal.
(b) i(t) for t 0. (c) υ 1 (t) and υ 2 (t) for t 0. Solution: υ 2 (0 ) = I 0 R 1 = = 10 V. υ 1 (0 ) = 0. (Given).
 Problem 5.37 Pror to t =, capactor C 1 n the crcut of Fg. P5.37 was uncharged. For I = 5 ma, R 1 = 2 kω, = 5 kω, C 1 = 3 µf, and C 2 = 6 µf, determne: (a) The equvalent crcut nvolvng the capactors for
Problem 5.37 Pror to t =, capactor C 1 n the crcut of Fg. P5.37 was uncharged. For I = 5 ma, R 1 = 2 kω, = 5 kω, C 1 = 3 µf, and C 2 = 6 µf, determne: (a) The equvalent crcut nvolvng the capactors for
ELEC 201 Electric Circuit Analysis I Lecture 9(a) RLC Circuits: Introduction
 //6 All le courey of Dr. Gregory J. Mazzaro EE Elecrc rcu Analy I ecure 9(a) rcu: Inroucon THE ITADE, THE MIITAY OEGE OF SOUTH AOINA 7 Moulre Sree, harleon, S 949 V Sere rcu: Analog Dcoery _ 5 Ω pf eq
//6 All le courey of Dr. Gregory J. Mazzaro EE Elecrc rcu Analy I ecure 9(a) rcu: Inroucon THE ITADE, THE MIITAY OEGE OF SOUTH AOINA 7 Moulre Sree, harleon, S 949 V Sere rcu: Analog Dcoery _ 5 Ω pf eq
UNIVERSITY OF UTAH ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT. 10k. 3mH. 10k. Only one current in the branch:
 UNIERSITY OF UTH ELECTRICL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING DEPRTMENT ECE 70 HOMEWORK #6 Soluton Summer 009. fter beng closed a long tme, the swtch opens at t = 0. Fnd (t) for t > 0. t = 0 0kΩ 0kΩ 3mH Step : (Redraw
UNIERSITY OF UTH ELECTRICL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING DEPRTMENT ECE 70 HOMEWORK #6 Soluton Summer 009. fter beng closed a long tme, the swtch opens at t = 0. Fnd (t) for t > 0. t = 0 0kΩ 0kΩ 3mH Step : (Redraw
Lecture #4 Capacitors and Inductors Energy Stored in C and L Equivalent Circuits Thevenin Norton
 EES ntro. electroncs for S Sprng 003 Lecture : 0/03/03 A.R. Neureuther Verson Date 0/0/03 EES ntroducton to Electroncs for omputer Scence Andrew R. Neureuther Lecture # apactors and nductors Energy Stored
EES ntro. electroncs for S Sprng 003 Lecture : 0/03/03 A.R. Neureuther Verson Date 0/0/03 EES ntroducton to Electroncs for omputer Scence Andrew R. Neureuther Lecture # apactors and nductors Energy Stored
CHAPTER 13. Exercises. E13.1 The emitter current is given by the Shockley equation:
 HPT 3 xercses 3. The emtter current s gen by the Shockley equaton: S exp VT For operaton wth, we hae exp >> S >>, and we can wrte VT S exp VT Solng for, we hae 3. 0 6ln 78.4 mv 0 0.784 5 4.86 V VT ln 4
HPT 3 xercses 3. The emtter current s gen by the Shockley equaton: S exp VT For operaton wth, we hae exp >> S >>, and we can wrte VT S exp VT Solng for, we hae 3. 0 6ln 78.4 mv 0 0.784 5 4.86 V VT ln 4
Energy Storage Elements: Capacitors and Inductors
 CHAPTER 6 Energy Storage Elements: Capactors and Inductors To ths pont n our study of electronc crcuts, tme has not been mportant. The analyss and desgns we hae performed so far hae been statc, and all
CHAPTER 6 Energy Storage Elements: Capactors and Inductors To ths pont n our study of electronc crcuts, tme has not been mportant. The analyss and desgns we hae performed so far hae been statc, and all
Physics 114 Exam 2 Fall 2014 Solutions. Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
INDUCTANCE. RC Cicuits vs LR Circuits
 INDUTANE R cuts vs LR rcuts R rcut hargng (battery s connected): (1/ )q + (R)dq/ dt LR rcut = (R) + (L)d/ dt q = e -t/ R ) = / R(1 - e -(R/ L)t ) q ncreases from 0 to = dq/ dt decreases from / R to 0 Dschargng
INDUTANE R cuts vs LR rcuts R rcut hargng (battery s connected): (1/ )q + (R)dq/ dt LR rcut = (R) + (L)d/ dt q = e -t/ R ) = / R(1 - e -(R/ L)t ) q ncreases from 0 to = dq/ dt decreases from / R to 0 Dschargng
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 28: INDUCTION AND INDUCTANCE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
EE215 FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 EE215 FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TaChang Chen Unersty of Washngton, Bothell Sprng 2010 EE215 1 WEEK 8 FIRST ORDER CIRCUIT RESPONSE May 21 st, 2010 EE215 2 1 QUESTIONS TO ANSWER Frst order crcuts
EE215 FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING TaChang Chen Unersty of Washngton, Bothell Sprng 2010 EE215 1 WEEK 8 FIRST ORDER CIRCUIT RESPONSE May 21 st, 2010 EE215 2 1 QUESTIONS TO ANSWER Frst order crcuts
PHYSICS - CLUTCH 1E CH 28: INDUCTION AND INDUCTANCE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
matter consists, measured in coulombs (C) 1 C of charge requires electrons Law of conservation of charge: charge cannot be created or
 Basc Concepts Oerew SI Prefxes Defntons: Current, Voltage, Power, & Energy Passe sgn conenton Crcut elements Ideal s Portland State Unersty ECE 221 Basc Concepts Ver. 1.24 1 Crcut Analyss: Introducton
Basc Concepts Oerew SI Prefxes Defntons: Current, Voltage, Power, & Energy Passe sgn conenton Crcut elements Ideal s Portland State Unersty ECE 221 Basc Concepts Ver. 1.24 1 Crcut Analyss: Introducton
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Winter 16 Final, March 16, 2016
 ME140 - Lnear rcuts - Wnter 16 Fnal, March 16, 2016 Instructons () The exam s open book. You may use your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator wth no communcaton capabltes. () You have
ME140 - Lnear rcuts - Wnter 16 Fnal, March 16, 2016 Instructons () The exam s open book. You may use your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator wth no communcaton capabltes. () You have
G = G 1 + G 2 + G 3 G 2 +G 3 G1 G2 G3. Network (a) Network (b) Network (c) Network (d)
 Massachusetts Insttute of Technology Department of Electrcal Engneerng and Computer Scence 6.002 í Electronc Crcuts Homework 2 Soluton Handout F98023 Exercse 21: Determne the conductance of each network
Massachusetts Insttute of Technology Department of Electrcal Engneerng and Computer Scence 6.002 í Electronc Crcuts Homework 2 Soluton Handout F98023 Exercse 21: Determne the conductance of each network
Diode. Current HmAL Voltage HVL Simplified equivalent circuit. V γ. Reverse bias. Forward bias. Designation: Symbol:
 Dode Materal: Desgnaton: Symbol: Poste Current flow: ptype ntype Anode Cathode Smplfed equalent crcut Ideal dode Current HmAL 0 8 6 4 2 Smplfed model 0.5.5 2 V γ eal dode Voltage HVL V γ closed open V
Dode Materal: Desgnaton: Symbol: Poste Current flow: ptype ntype Anode Cathode Smplfed equalent crcut Ideal dode Current HmAL 0 8 6 4 2 Smplfed model 0.5.5 2 V γ eal dode Voltage HVL V γ closed open V
I. INTRODUCTION. There are two other circuit elements that we will use and are special cases of the above elements. They are:
 I. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Crcut Theory Fundamentals In ths course we study crcuts wth non-lnear elements or deces (dodes and transstors). We wll use crcut theory tools to analyze these crcuts. Snce some of tools
I. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Crcut Theory Fundamentals In ths course we study crcuts wth non-lnear elements or deces (dodes and transstors). We wll use crcut theory tools to analyze these crcuts. Snce some of tools
TUTORIAL PROBLEMS. E.1 KCL, KVL, Power and Energy. Q.1 Determine the current i in the following circuit. All units in VAΩ,,
 196 E TUTORIAL PROBLEMS E.1 KCL, KVL, Power and Energy Q.1 Determne the current n the followng crcut. 3 5 3 8 9 6 5 Appendx E Tutoral Problems 197 Q. Determne the current and the oltage n the followng
196 E TUTORIAL PROBLEMS E.1 KCL, KVL, Power and Energy Q.1 Determne the current n the followng crcut. 3 5 3 8 9 6 5 Appendx E Tutoral Problems 197 Q. Determne the current and the oltage n the followng
6.3.7 Example with Runga Kutta 4 th order method
 6.3.7 Example wth Runga Kutta 4 th order method Agan, as an example, 3 machne, 9 bus system shown n Fg. 6.4 s agan consdered. Intally, the dampng of the generators are neglected (.e. d = 0 for = 1, 2,
6.3.7 Example wth Runga Kutta 4 th order method Agan, as an example, 3 machne, 9 bus system shown n Fg. 6.4 s agan consdered. Intally, the dampng of the generators are neglected (.e. d = 0 for = 1, 2,
6.01: Introduction to EECS I Lecture 7 March 15, 2011
 6.0: Introducton to EECS I Lecture 7 March 5, 20 6.0: Introducton to EECS I Crcuts The Crcut Abstracton Crcuts represent systems as connectons of elements through whch currents (through arables) flow and
6.0: Introducton to EECS I Lecture 7 March 5, 20 6.0: Introducton to EECS I Crcuts The Crcut Abstracton Crcuts represent systems as connectons of elements through whch currents (through arables) flow and
Physics 4B. A positive value is obtained, so the current is counterclockwise around the circuit.
 Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
Linearity. If kx is applied to the element, the output must be ky. kx ky. 2. additivity property. x 1 y 1, x 2 y 2
 Lnearty An element s sad to be lnear f t satsfes homogenety (scalng) property and addte (superposton) property. 1. homogenety property Let x be the nput and y be the output of an element. x y If kx s appled
Lnearty An element s sad to be lnear f t satsfes homogenety (scalng) property and addte (superposton) property. 1. homogenety property Let x be the nput and y be the output of an element. x y If kx s appled
Physics 114 Exam 2 Spring Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam Sprng 013 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red wth the amount beng
Physcs 114 Exam Sprng 013 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red wth the amount beng
Advanced Circuits Topics - Part 1 by Dr. Colton (Fall 2017)
 Advanced rcuts Topcs - Part by Dr. olton (Fall 07) Part : Some thngs you should already know from Physcs 0 and 45 These are all thngs that you should have learned n Physcs 0 and/or 45. Ths secton s organzed
Advanced rcuts Topcs - Part by Dr. olton (Fall 07) Part : Some thngs you should already know from Physcs 0 and 45 These are all thngs that you should have learned n Physcs 0 and/or 45. Ths secton s organzed
Electrical Circuits 2.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER
 CHAPTE Electrcal Crcuts. INTODUCTION In ths chapter, we brefly revew the three types of basc passve electrcal elements: resstor, nductor and capactor. esstance Elements: Ohm s Law: The voltage drop across
CHAPTE Electrcal Crcuts. INTODUCTION In ths chapter, we brefly revew the three types of basc passve electrcal elements: resstor, nductor and capactor. esstance Elements: Ohm s Law: The voltage drop across
Complex Numbers, Signals, and Circuits
 Complex Numbers, Sgnals, and Crcuts 3 August, 009 Complex Numbers: a Revew Suppose we have a complex number z = x jy. To convert to polar form, we need to know the magntude of z and the phase of z. z =
Complex Numbers, Sgnals, and Crcuts 3 August, 009 Complex Numbers: a Revew Suppose we have a complex number z = x jy. To convert to polar form, we need to know the magntude of z and the phase of z. z =
Chapter 9 Complete Response of Circuits with Two Storage Elements
 hapter 9 omplete Response of rcuts wth Two Storage Elements In hapter 8, we had rreducble storage element and a frst order crcut. In hapter 9, we wll hae rreducble storage elements and therefore, a second
hapter 9 omplete Response of rcuts wth Two Storage Elements In hapter 8, we had rreducble storage element and a frst order crcut. In hapter 9, we wll hae rreducble storage elements and therefore, a second
DC Circuits. Crossing the emf in this direction +ΔV
 DC Crcuts Delverng a steady flow of electrc charge to a crcut requres an emf devce such as a battery, solar cell or electrc generator for example. mf stands for electromotve force, but an emf devce transforms
DC Crcuts Delverng a steady flow of electrc charge to a crcut requres an emf devce such as a battery, solar cell or electrc generator for example. mf stands for electromotve force, but an emf devce transforms
Physics Electricity and Magnetism Lecture 12 - Inductance, RL Circuits. Y&F Chapter 30, Sect 1-4
 Physcs - lectrcty and Magnetsm ecture - Inductance, Crcuts Y&F Chapter 30, Sect - 4 Inductors and Inductance Self-Inductance Crcuts Current Growth Crcuts Current Decay nergy Stored n a Magnetc Feld nergy
Physcs - lectrcty and Magnetsm ecture - Inductance, Crcuts Y&F Chapter 30, Sect - 4 Inductors and Inductance Self-Inductance Crcuts Current Growth Crcuts Current Decay nergy Stored n a Magnetc Feld nergy
I. INTRODUCTION. 1.1 Circuit Theory Fundamentals
 I. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Crcut Theory Fundamentals Crcut theory s an approxmaton to Maxwell s electromagnetc equatons n order to smplfy analyss of complcated crcuts. A crcut s made of seeral elements (boxes
I. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Crcut Theory Fundamentals Crcut theory s an approxmaton to Maxwell s electromagnetc equatons n order to smplfy analyss of complcated crcuts. A crcut s made of seeral elements (boxes
ELCT 503: Semiconductors. Fall 2014
 EL503 Semconductors Fall 2014 Lecture 09: BJ rcut Analyss Dr. Hassan Mostafa د. حسن مصطفى hmostafa@aucegypt.edu EL 503: Semconductors ntroducton npn transstor pnp transstor EL 503: Semconductors ntroducton
EL503 Semconductors Fall 2014 Lecture 09: BJ rcut Analyss Dr. Hassan Mostafa د. حسن مصطفى hmostafa@aucegypt.edu EL 503: Semconductors ntroducton npn transstor pnp transstor EL 503: Semconductors ntroducton
6.01: Introduction to EECS 1 Week 6 October 15, 2009
 6.0: ntroducton to EECS Week 6 October 5, 2009 6.0: ntroducton to EECS Crcuts The Crcut Abstracton Crcuts represent systems as connectons of component through whch currents (through arables) flow and across
6.0: ntroducton to EECS Week 6 October 5, 2009 6.0: ntroducton to EECS Crcuts The Crcut Abstracton Crcuts represent systems as connectons of component through whch currents (through arables) flow and across
Electricity and Magnetism Lecture 13 - Physics 121 Electromagnetic Oscillations in LC & LCR Circuits,
 lectrcty and Magnetsm ecture 3 - Physcs lectromagnetc Oscllatons n & rcuts, Y&F hapter 3, Sec. 5-6 Alternatng urrent rcuts, Y&F hapter 3, Sec. - Summary: and crcuts Mechancal Harmonc Oscllator rcut Oscllatons
lectrcty and Magnetsm ecture 3 - Physcs lectromagnetc Oscllatons n & rcuts, Y&F hapter 3, Sec. 5-6 Alternatng urrent rcuts, Y&F hapter 3, Sec. - Summary: and crcuts Mechancal Harmonc Oscllator rcut Oscllatons
FE REVIEW OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS)
 FE EIEW OPEATIONAL AMPLIFIES (OPAMPS) 1 The Opamp An opamp has two nputs and one output. Note the opamp below. The termnal labeled wth the () sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth the () sgn
FE EIEW OPEATIONAL AMPLIFIES (OPAMPS) 1 The Opamp An opamp has two nputs and one output. Note the opamp below. The termnal labeled wth the () sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth the () sgn
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design
 EE C45 ME C8 Introducton to MEM Desgn Fall 7 Prof. Clark T.C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrcal Engneerng & Computer cences Unersty of Calforna at Berkeley Berkeley, C 947 Dscusson: eew of Op mps EE C45: Introducton
EE C45 ME C8 Introducton to MEM Desgn Fall 7 Prof. Clark T.C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrcal Engneerng & Computer cences Unersty of Calforna at Berkeley Berkeley, C 947 Dscusson: eew of Op mps EE C45: Introducton
FE REVIEW OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 8/25/2010
 FE REVEW OPERATONAL AMPLFERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 1 The Op-amp 2 An op-amp has two nputs and one output. Note the op-amp below. The termnal labeled l wth the (-) sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth
FE REVEW OPERATONAL AMPLFERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 1 The Op-amp 2 An op-amp has two nputs and one output. Note the op-amp below. The termnal labeled l wth the (-) sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth
Week 11: Differential Amplifiers
 ELE 0A Electronc rcuts Week : Dfferental Amplfers Lecture - Large sgnal analyss Topcs to coer A analyss Half-crcut analyss eadng Assgnment: hap 5.-5.8 of Jaeger and Blalock or hap 7. - 7.3, of Sedra and
ELE 0A Electronc rcuts Week : Dfferental Amplfers Lecture - Large sgnal analyss Topcs to coer A analyss Half-crcut analyss eadng Assgnment: hap 5.-5.8 of Jaeger and Blalock or hap 7. - 7.3, of Sedra and
A capacitor is simply two pieces of metal near each other, separated by an insulator or air. A capacitor is used to store charge and energy.
 -1 apactors A capactor s smply two peces of metal near each other, separate by an nsulator or ar. A capactor s use to store charge an energy. A parallel-plate capactor conssts of two parallel plates separate
-1 apactors A capactor s smply two peces of metal near each other, separate by an nsulator or ar. A capactor s use to store charge an energy. A parallel-plate capactor conssts of two parallel plates separate
EMF induced in a coil by moving a bar magnet. Induced EMF: Faraday s Law. Induction and Oscillations. Electromagnetic Induction.
 Inducton and Oscllatons Ch. 3: Faraday s Law Ch. 3: AC Crcuts Induced EMF: Faraday s Law Tme-dependent B creates nduced E In partcular: A changng magnetc flux creates an emf n a crcut: Ammeter or voltmeter.
Inducton and Oscllatons Ch. 3: Faraday s Law Ch. 3: AC Crcuts Induced EMF: Faraday s Law Tme-dependent B creates nduced E In partcular: A changng magnetc flux creates an emf n a crcut: Ammeter or voltmeter.
Lecture 10: Small Signal Device Parameters
 Lecture 0: Small Sgnal Dece Parameters 06009 Lecture 9, Hgh Speed Deces 06 Lecture : Ballstc FETs Lu: 0, 394 06009 Lecture 9, Hgh Speed Deces 06 Large Sgnal / Small Sgnal e I E c I C The electrcal sgnal
Lecture 0: Small Sgnal Dece Parameters 06009 Lecture 9, Hgh Speed Deces 06 Lecture : Ballstc FETs Lu: 0, 394 06009 Lecture 9, Hgh Speed Deces 06 Large Sgnal / Small Sgnal e I E c I C The electrcal sgnal
Copyright 2004 by Oxford University Press, Inc.
 JT as an Amplfer &a Swtch, Large Sgnal Operaton, Graphcal Analyss, JT at D, asng JT, Small Sgnal Operaton Model, Hybrd P-Model, TModel. Lecture # 7 1 Drecton of urrent Flow & Operaton for Amplfer Applcaton
JT as an Amplfer &a Swtch, Large Sgnal Operaton, Graphcal Analyss, JT at D, asng JT, Small Sgnal Operaton Model, Hybrd P-Model, TModel. Lecture # 7 1 Drecton of urrent Flow & Operaton for Amplfer Applcaton
Physics Courseware Electronics
 Physcs ourseware Electroncs ommon emtter amplfer Problem 1.- In the followg ommon Emtter mplfer calculate: a) The Q pot, whch s the D base current (I ), the D collector current (I ) and the voltage collector
Physcs ourseware Electroncs ommon emtter amplfer Problem 1.- In the followg ommon Emtter mplfer calculate: a) The Q pot, whch s the D base current (I ), the D collector current (I ) and the voltage collector
1.4 Small-signal models of BJT
 1.4 Small-sgnal models of J Analog crcuts often operate wth sgnal levels that are small compared to the bas currents and voltages n the crcut. Under ths condton, ncremental or small-sgnal models can be
1.4 Small-sgnal models of J Analog crcuts often operate wth sgnal levels that are small compared to the bas currents and voltages n the crcut. Under ths condton, ncremental or small-sgnal models can be
UNIT I BASIC CIRCUIT CONCEPTS
 UNIT I BASIC CIRCUIT CONCEPTS Crcut elements Krchhoff s Law V-I Relatonshp of R,L and C Independent and Dependent sources Smple Resstve crcuts Networks reducton Voltage dvson current source transformaton.
UNIT I BASIC CIRCUIT CONCEPTS Crcut elements Krchhoff s Law V-I Relatonshp of R,L and C Independent and Dependent sources Smple Resstve crcuts Networks reducton Voltage dvson current source transformaton.
Lecture 14: More MOS Circuits and the Differential Amplifier
 Lecture 4: More MOS rcuts an the Dfferental Aplfer Gu-Yeon We Dson of nneern an Apple Scences Harar Unersty uyeon@eecs.harar.eu We Oerew Rean S&S: hapter 5.0, 6.~, 6.6 ackroun Han seen soe of the basc
Lecture 4: More MOS rcuts an the Dfferental Aplfer Gu-Yeon We Dson of nneern an Apple Scences Harar Unersty uyeon@eecs.harar.eu We Oerew Rean S&S: hapter 5.0, 6.~, 6.6 ackroun Han seen soe of the basc
Circuits II EE221. Instructor: Kevin D. Donohue. Instantaneous, Average, RMS, and Apparent Power, and, Maximum Power Transfer, and Power Factors
 Crcuts II EE1 Unt 3 Instructor: Ken D. Donohue Instantaneous, Aerage, RMS, and Apparent Power, and, Maxmum Power pp ransfer, and Power Factors Power Defntons/Unts: Work s n unts of newton-meters or joules
Crcuts II EE1 Unt 3 Instructor: Ken D. Donohue Instantaneous, Aerage, RMS, and Apparent Power, and, Maxmum Power pp ransfer, and Power Factors Power Defntons/Unts: Work s n unts of newton-meters or joules
Formulation of Circuit Equations
 ECE 570 Sesson 2 IC 752E Computer Aded Engneerng for Integrated Crcuts Formulaton of Crcut Equatons Bascs of crcut modelng 1. Notaton 2. Crcut elements 3. Krchoff laws 4. ableau formulaton 5. Modfed nodal
ECE 570 Sesson 2 IC 752E Computer Aded Engneerng for Integrated Crcuts Formulaton of Crcut Equatons Bascs of crcut modelng 1. Notaton 2. Crcut elements 3. Krchoff laws 4. ableau formulaton 5. Modfed nodal
Transfer Functions. Convenient representation of a linear, dynamic model. A transfer function (TF) relates one input and one output: ( ) system
 Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Electrical Circuits II (ECE233b)
 Electrcal Crcuts (ECE33b SteadyState Power Analyss Anests Dounas The Unersty of Western Ontaro Faculty of Engneerng Scence SteadyState Power Analyss (t AC crcut: The steady state oltage and current can
Electrcal Crcuts (ECE33b SteadyState Power Analyss Anests Dounas The Unersty of Western Ontaro Faculty of Engneerng Scence SteadyState Power Analyss (t AC crcut: The steady state oltage and current can
EE 2006 Electric Circuit Analysis Fall September 04, 2014 Lecture 02
 EE 2006 Electrc Crcut Analyss Fall 2014 September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 For Your Informaton Course Webpage http://www.d.umn.edu/~jngba/electrc_crcut_analyss_(ee_2006).html You can fnd on the webpage: Lecture:
EE 2006 Electrc Crcut Analyss Fall 2014 September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 For Your Informaton Course Webpage http://www.d.umn.edu/~jngba/electrc_crcut_analyss_(ee_2006).html You can fnd on the webpage: Lecture:
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Winter 16 Midterm, February 5
 Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Wnter 16 Mdterm, February 5 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Wnter 16 Mdterm, February 5 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Lecture 27 Bipolar Junction Transistors
 Lecture 27 polar Juncton Transstors ELETRIAL ENGINEERING: PRINIPLES AND APPLIATIONS, Fourth Edton, by Allan R. Hambley, 2008 Pearson Educaton, Inc. polar Juncton Transstors 1. Understand bpolar juncton
Lecture 27 polar Juncton Transstors ELETRIAL ENGINEERING: PRINIPLES AND APPLIATIONS, Fourth Edton, by Allan R. Hambley, 2008 Pearson Educaton, Inc. polar Juncton Transstors 1. Understand bpolar juncton
Traffic Signal Control. Signalized Intersection Analysis and Level of Service. Traffic Signal Control. Traffic Signal Control 11/4/2009
 Sgnalze Intersecton nalyss an Leel of Serce CE3 Transportaton Engneerng Dr. hme bel-rahm Traffc Sgnal Control Pretme sgnal whose tmng (cycle length, green tme, an so on) s fxe oer specfe tme peros an oes
Sgnalze Intersecton nalyss an Leel of Serce CE3 Transportaton Engneerng Dr. hme bel-rahm Traffc Sgnal Control Pretme sgnal whose tmng (cycle length, green tme, an so on) s fxe oer specfe tme peros an oes
November 5, 2002 SE 180: Earthquake Engineering SE 180. Final Project
 SE 8 Fnal Project Story Shear Frame u m Gven: u m L L m L L EI ω ω Solve for m Story Bendng Beam u u m L m L Gven: m L L EI ω ω Solve for m 3 3 Story Shear Frame u 3 m 3 Gven: L 3 m m L L L 3 EI ω ω ω
SE 8 Fnal Project Story Shear Frame u m Gven: u m L L m L L EI ω ω Solve for m Story Bendng Beam u u m L m L Gven: m L L EI ω ω Solve for m 3 3 Story Shear Frame u 3 m 3 Gven: L 3 m m L L L 3 EI ω ω ω
Selected Student Solutions for Chapter 2
 /3/003 Assessment Prolems Selected Student Solutons for Chapter. Frst note that we know the current through all elements n the crcut except the 6 kw resstor (the current n the three elements to the left
/3/003 Assessment Prolems Selected Student Solutons for Chapter. Frst note that we know the current through all elements n the crcut except the 6 kw resstor (the current n the three elements to the left
Flyback Converter in DCM
 Flyback Converter n CM m 1:n V O V S m I M m 1 1 V CCM: wth O V I I n and S 2 1 R L M m M m s m 1 CM: IM 2 m 1 1 V 1 Borderlne: O VS I n wth V nv 2 1 R 2 L 1 M m s O S m CM f R > R 2n crt 2 L m 2 (1 )
Flyback Converter n CM m 1:n V O V S m I M m 1 1 V CCM: wth O V I I n and S 2 1 R L M m M m s m 1 CM: IM 2 m 1 1 V 1 Borderlne: O VS I n wth V nv 2 1 R 2 L 1 M m s O S m CM f R > R 2n crt 2 L m 2 (1 )
Prof. Paolo Colantonio a.a
 Pro. Paolo olantono a.a. 3 4 Let s consder a two ports network o Two ports Network o L For passve network (.e. wthout nternal sources or actve devces), a general representaton can be made by a sutable
Pro. Paolo olantono a.a. 3 4 Let s consder a two ports network o Two ports Network o L For passve network (.e. wthout nternal sources or actve devces), a general representaton can be made by a sutable
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer Negate feedback β s the feedback transfer functon S o S S o o S S o f S S S S fb
55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer Negate feedback β s the feedback transfer functon S o S S o o S S o f S S S S fb
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Circuits and Electronics Spring 2001
 Massachusetts Insttute of Technology Department of Electrcal Engneerng and Computer Scence Read Chapters 11 through 12. 6.002 Crcuts and Electroncs Sprng 2001 Homework #5 Handout S01031 Issued: 3/8/2001
Massachusetts Insttute of Technology Department of Electrcal Engneerng and Computer Scence Read Chapters 11 through 12. 6.002 Crcuts and Electroncs Sprng 2001 Homework #5 Handout S01031 Issued: 3/8/2001
6.3.4 Modified Euler s method of integration
 6.3.4 Modfed Euler s method of ntegraton Before dscussng the applcaton of Euler s method for solvng the swng equatons, let us frst revew the basc Euler s method of numercal ntegraton. Let the general from
6.3.4 Modfed Euler s method of ntegraton Before dscussng the applcaton of Euler s method for solvng the swng equatons, let us frst revew the basc Euler s method of numercal ntegraton. Let the general from
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PUTRAJAYA CAMPUS FINAL EXAMINATION SPECIAL SEMESTER 2013 / 2014
 OLLEGE OF ENGNEENG PUTAJAYA AMPUS FNAL EXAMNATON SPEAL SEMESTE 03 / 04 POGAMME SUBJET ODE SUBJET : Bachelor of Electrcal & Electroncs Engneerng (Honours) Bachelor of Electrcal Power Engneerng (Honours)
OLLEGE OF ENGNEENG PUTAJAYA AMPUS FNAL EXAMNATON SPEAL SEMESTE 03 / 04 POGAMME SUBJET ODE SUBJET : Bachelor of Electrcal & Electroncs Engneerng (Honours) Bachelor of Electrcal Power Engneerng (Honours)
3.2 Terminal Characteristics of Junction Diodes (pp )
 /9/008 secton3_termnal_characterstcs_of_juncton_odes.doc /6 3. Termnal Characterstcs of Juncton odes (pp.47-53) A Juncton ode I.E., A real dode! Smlar to an deal dode, ts crcut symbol s: HO: The Juncton
/9/008 secton3_termnal_characterstcs_of_juncton_odes.doc /6 3. Termnal Characterstcs of Juncton odes (pp.47-53) A Juncton ode I.E., A real dode! Smlar to an deal dode, ts crcut symbol s: HO: The Juncton
Chapter 6 Electrical Systems and Electromechanical Systems
 ME 43 Systems Dynamcs & Control Chapter 6: Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems Chapter 6 Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems 6. INTODUCTION A. Bazoune The majorty of engneerng systems
ME 43 Systems Dynamcs & Control Chapter 6: Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems Chapter 6 Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems 6. INTODUCTION A. Bazoune The majorty of engneerng systems
I 2 V V. = 0 write 1 loop equation for each loop with a voltage not in the current set of equations. or I using Ohm s Law V 1 5.
 Krchoff s Laws Drect: KL, KL, Ohm s Law G G Ohm s Law: 6 (always get equaton/esor) Ω 5 Ω 6Ω 4 KL: : 5 : 5 eq. are dependent (n general, get n ndep. for nodes) KL: 4 wrte loop equaton for each loop wth
Krchoff s Laws Drect: KL, KL, Ohm s Law G G Ohm s Law: 6 (always get equaton/esor) Ω 5 Ω 6Ω 4 KL: : 5 : 5 eq. are dependent (n general, get n ndep. for nodes) KL: 4 wrte loop equaton for each loop wth
Common Base Configuration
 ommon Base onfguraton nput caracterstcs: s. B wt B const Output caracterstc: s. B wt const Pcture from ref [2] S. Lneykn, ntroducton to electroncs Slde [53] ommon Base Termnal caracterstcs [2] α BO FB
ommon Base onfguraton nput caracterstcs: s. B wt B const Output caracterstc: s. B wt const Pcture from ref [2] S. Lneykn, ntroducton to electroncs Slde [53] ommon Base Termnal caracterstcs [2] α BO FB
i I (I + i) 3/27/2006 Circuits ( F.Robilliard) 1
 4V I 2V (I + ) 0 0 --- 3V 1 2 4Ω 6Ω 3Ω 3/27/2006 Crcuts ( F.obllard) 1 Introducton: Electrcal crcuts are ubqutous n the modern world, and t s dffcult to oerstate ther mportance. They range from smple drect
4V I 2V (I + ) 0 0 --- 3V 1 2 4Ω 6Ω 3Ω 3/27/2006 Crcuts ( F.obllard) 1 Introducton: Electrcal crcuts are ubqutous n the modern world, and t s dffcult to oerstate ther mportance. They range from smple drect
S-Domain Analysis. s-domain Circuit Analysis. EE695K VLSI Interconnect. Time domain (t domain) Complex frequency domain (s domain) Laplace Transform L
 EE695K S nterconnect S-Doman naly -Doman rcut naly Tme doman t doman near rcut aplace Tranform omplex frequency doman doman Tranformed rcut Dfferental equaton lacal technque epone waveform aplace Tranform
EE695K S nterconnect S-Doman naly -Doman rcut naly Tme doman t doman near rcut aplace Tranform omplex frequency doman doman Tranformed rcut Dfferental equaton lacal technque epone waveform aplace Tranform
ELE B7 Power Systems Engineering. Power Flow- Introduction
 ELE B7 Power Systems Engneerng Power Flow- Introducton Introducton to Load Flow Analyss The power flow s the backbone of the power system operaton, analyss and desgn. It s necessary for plannng, operaton,
ELE B7 Power Systems Engneerng Power Flow- Introducton Introducton to Load Flow Analyss The power flow s the backbone of the power system operaton, analyss and desgn. It s necessary for plannng, operaton,
College of Engineering Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering. Test 2
 Name: Student D Number: Secton Number: 01/0/03/04 A/B Lecturer: Dr Jamaludn/ Dr Azn Wat/ Dr Jehana Ermy/ Prof Md Zan Table Number: ollege of Engneerng Department of Electroncs and ommuncaton Engneerng
Name: Student D Number: Secton Number: 01/0/03/04 A/B Lecturer: Dr Jamaludn/ Dr Azn Wat/ Dr Jehana Ermy/ Prof Md Zan Table Number: ollege of Engneerng Department of Electroncs and ommuncaton Engneerng
Lecture 8: Small signal parameters and hybrid-π model Lecture 9, High Speed Devices 2016
 Lecture 8: Small sgnal parameters and hbrdπ model π 08006 Lecture 9, Hgh Speed Deces 06 Lecture 8: Small sgnal parameters and hbrdπ model Lterature: Twoport networks Transstors for hgh frequences How to
Lecture 8: Small sgnal parameters and hbrdπ model π 08006 Lecture 9, Hgh Speed Deces 06 Lecture 8: Small sgnal parameters and hbrdπ model Lterature: Twoport networks Transstors for hgh frequences How to
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 R. W. Erckson Department of Electrcal, Computer, and Energy Engneerng Unersty of Colorado, Boulder 3.5. Example: ncluson of semconductor conducton losses n the boost conerter model Boost conerter example
R. W. Erckson Department of Electrcal, Computer, and Energy Engneerng Unersty of Colorado, Boulder 3.5. Example: ncluson of semconductor conducton losses n the boost conerter model Boost conerter example
3. MODELING OF PARALLEL THREE-PHASE CURRENT-UNIDIRECTIONAL CONVERTERS 3. MODELING OF PARALLEL THREE-PHASE CURRENT-
 3. MOEING OF PARAE THREE-PHASE URRENT-UNIIRETIONA ONERTERS 3. MOEING OF PARAE THREE-PHASE URRENT- UNIIRETIONA ONERTERS Ths chater eelos the moels of the arallel three-hase current-unrectonal swtch base
3. MOEING OF PARAE THREE-PHASE URRENT-UNIIRETIONA ONERTERS 3. MOEING OF PARAE THREE-PHASE URRENT- UNIIRETIONA ONERTERS Ths chater eelos the moels of the arallel three-hase current-unrectonal swtch base
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Fall 13 Midterm, October 31
 Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Fall 13 Mdterm, October 31 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Fall 13 Mdterm, October 31 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
5.6 Small-Signal Operation and Models
 3/16/2011 secton 5_6 Small Sgnal Operaton and Models 1/2 5.6 Small-Sgnal Operaton and Models Readng Assgnment: 443-458 Now let s examne how we use BJTs to construct amplfers! The frst mportant desgn rule
3/16/2011 secton 5_6 Small Sgnal Operaton and Models 1/2 5.6 Small-Sgnal Operaton and Models Readng Assgnment: 443-458 Now let s examne how we use BJTs to construct amplfers! The frst mportant desgn rule
Key component in Operational Amplifiers
 Key component n Operatonal Amplfers Objectve of Lecture Descrbe how dependent voltage and current sources functon. Chapter.6 Electrcal Engneerng: Prncples and Applcatons Chapter.6 Fundamentals of Electrc
Key component n Operatonal Amplfers Objectve of Lecture Descrbe how dependent voltage and current sources functon. Chapter.6 Electrcal Engneerng: Prncples and Applcatons Chapter.6 Fundamentals of Electrc
Chapter 6. Operational Amplifier. inputs can be defined as the average of the sum of the two signals.
 6 Operatonal mpler Chapter 6 Operatonal mpler CC Symbol: nput nput Output EE () Non-nvertng termnal, () nvertng termnal nput mpedance : Few mega (ery hgh), Output mpedance : Less than (ery low) Derental
6 Operatonal mpler Chapter 6 Operatonal mpler CC Symbol: nput nput Output EE () Non-nvertng termnal, () nvertng termnal nput mpedance : Few mega (ery hgh), Output mpedance : Less than (ery low) Derental
Fundamental loop-current method using virtual voltage sources technique for special cases
 Fundamental loop-current method usng vrtual voltage sources technque for specal cases George E. Chatzaraks, 1 Marna D. Tortorel 1 and Anastasos D. Tzolas 1 Electrcal and Electroncs Engneerng Departments,
Fundamental loop-current method usng vrtual voltage sources technque for specal cases George E. Chatzaraks, 1 Marna D. Tortorel 1 and Anastasos D. Tzolas 1 Electrcal and Electroncs Engneerng Departments,
Physics 1202: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda
 Physcs 122: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems start ths Thursday Team 1: Hend Ouda, Mke Glnsk, Stephane Auger Team 2: Analese Bruder, Krsten Dean, Alson Smth Offce hours: Monday 2:3-3:3
Physcs 122: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems start ths Thursday Team 1: Hend Ouda, Mke Glnsk, Stephane Auger Team 2: Analese Bruder, Krsten Dean, Alson Smth Offce hours: Monday 2:3-3:3
Graphical Analysis of a BJT Amplifier
 4/6/2011 A Graphcal Analyss of a BJT Amplfer lecture 1/18 Graphcal Analyss of a BJT Amplfer onsder agan ths smple BJT amplfer: ( t) = + ( t) O O o B + We note that for ths amplfer, the output oltage s
4/6/2011 A Graphcal Analyss of a BJT Amplfer lecture 1/18 Graphcal Analyss of a BJT Amplfer onsder agan ths smple BJT amplfer: ( t) = + ( t) O O o B + We note that for ths amplfer, the output oltage s
VI. Transistor Amplifiers
 VI. Transstor Amplfers 6. Introducton In ths secton we wll use the transstor small-sgnal model to analyze and desgn transstor amplfers. There are two ssues that we need to dscuss frst: ) What are the mportant
VI. Transstor Amplfers 6. Introducton In ths secton we wll use the transstor small-sgnal model to analyze and desgn transstor amplfers. There are two ssues that we need to dscuss frst: ) What are the mportant
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer S o S ε S o ( S β S ) o Negate feedback S S o + β β s the feedback transfer functon
55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer S o S ε S o ( S β S ) o Negate feedback S S o + β β s the feedback transfer functon
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Fall 10 Midterm, October 28
 M140 - Lnear rcuts - Fall 10 Mdterm, October 28 nstructons () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
M140 - Lnear rcuts - Fall 10 Mdterm, October 28 nstructons () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
University of Bahrain College of Science Dept. of Physics PHYCS 102 FINAL EXAM
 Unversty o Bahran College o Scence Dept. o Physcs PHYCS 10 FINAL XAM Date: 15/1/001 Tme:Two Hours Name:-------------------------------------------------ID#---------------------- Secton:----------------
Unversty o Bahran College o Scence Dept. o Physcs PHYCS 10 FINAL XAM Date: 15/1/001 Tme:Two Hours Name:-------------------------------------------------ID#---------------------- Secton:----------------
FTCS Solution to the Heat Equation
 FTCS Soluton to the Heat Equaton ME 448/548 Notes Gerald Recktenwald Portland State Unversty Department of Mechancal Engneerng gerry@pdx.edu ME 448/548: FTCS Soluton to the Heat Equaton Overvew 1. Use
FTCS Soluton to the Heat Equaton ME 448/548 Notes Gerald Recktenwald Portland State Unversty Department of Mechancal Engneerng gerry@pdx.edu ME 448/548: FTCS Soluton to the Heat Equaton Overvew 1. Use
Inductor = (coil of wire)
 A student n 1120 emaled me to ask how much extra he should expect to pay on hs electrc bll when he strngs up a standard 1-strand box of ccle holday lghts outsde hs house. (total, cumulatve cost)? Try to
A student n 1120 emaled me to ask how much extra he should expect to pay on hs electrc bll when he strngs up a standard 1-strand box of ccle holday lghts outsde hs house. (total, cumulatve cost)? Try to
Thermal-Fluids I. Chapter 18 Transient heat conduction. Dr. Primal Fernando Ph: (850)
 hermal-fluds I Chapter 18 ransent heat conducton Dr. Prmal Fernando prmal@eng.fsu.edu Ph: (850) 410-6323 1 ransent heat conducton In general, he temperature of a body vares wth tme as well as poston. In
hermal-fluds I Chapter 18 ransent heat conducton Dr. Prmal Fernando prmal@eng.fsu.edu Ph: (850) 410-6323 1 ransent heat conducton In general, he temperature of a body vares wth tme as well as poston. In
V V. This calculation is repeated now for each current I.
 Page1 Page2 The power supply oltage V = +5 olts and the load resstor R = 1 k. For the range of collector bas currents, I = 0.5 ma, 1 ma, 2.5 ma, 4 ma and 4.5 ma, determne the correspondng collector-to-emtter
Page1 Page2 The power supply oltage V = +5 olts and the load resstor R = 1 k. For the range of collector bas currents, I = 0.5 ma, 1 ma, 2.5 ma, 4 ma and 4.5 ma, determne the correspondng collector-to-emtter
Important Instructions to the Examiners:
 Summer 0 Examnaton Subject & Code: asc Maths (70) Model Answer Page No: / Important Instructons to the Examners: ) The Answers should be examned by key words and not as word-to-word as gven n the model
Summer 0 Examnaton Subject & Code: asc Maths (70) Model Answer Page No: / Important Instructons to the Examners: ) The Answers should be examned by key words and not as word-to-word as gven n the model
Announcements. Lecture #2
 Announcements Lectures wll be n 4 LeConte begnnng Frday 8/29 Addtonal dscusson TA Denns Chang (Sectons 101, 105) Offce hours: Mo 2-3 PM; Th 5-6 PM Lab sectons begn Tuesday 9/2 Read Experment #1 onlne Download
Announcements Lectures wll be n 4 LeConte begnnng Frday 8/29 Addtonal dscusson TA Denns Chang (Sectons 101, 105) Offce hours: Mo 2-3 PM; Th 5-6 PM Lab sectons begn Tuesday 9/2 Read Experment #1 onlne Download
Lecture 5: Operational Amplifiers and Op Amp Circuits
 Lecture 5: peratonal mplers and p mp Crcuts Gu-Yeon We Dson o Engneerng and ppled Scences Harard Unersty guyeon@eecs.harard.edu We erew eadng S&S: Chapter Supplemental eadng Background rmed wth our crcut
Lecture 5: peratonal mplers and p mp Crcuts Gu-Yeon We Dson o Engneerng and ppled Scences Harard Unersty guyeon@eecs.harard.edu We erew eadng S&S: Chapter Supplemental eadng Background rmed wth our crcut
Signalized Intersections LOS. Signalized Intersection Analysis and Level of Service. Signalized Intersections LOS. Lane Grouping 11/17/2009
 Sgnalze Intersecton nalyss an Leel of Serce CE3 Transportaton Engneerng Dr. hme bel-rahm Sgnalze Intersectons LOS Recall that leel of serce (LOS) s a qualtate assessment of faclty operatons base upon a
Sgnalze Intersecton nalyss an Leel of Serce CE3 Transportaton Engneerng Dr. hme bel-rahm Sgnalze Intersectons LOS Recall that leel of serce (LOS) s a qualtate assessment of faclty operatons base upon a
The Decibel and its Usage
 The Decbel and ts Usage Consder a two-stage amlfer system, as shown n Fg.. Each amlfer rodes an ncrease of the sgnal ower. Ths effect s referred to as the ower gan,, of the amlfer. Ths means that the sgnal
The Decbel and ts Usage Consder a two-stage amlfer system, as shown n Fg.. Each amlfer rodes an ncrease of the sgnal ower. Ths effect s referred to as the ower gan,, of the amlfer. Ths means that the sgnal
Logic effort and gate sizing
 EEN454 Dgtal Integrated rcut Desgn Logc effort and gate szng EEN 454 Introducton hp desgners face a bewlderng arra of choces What s the best crcut topolog for a functon? How man stages of logc gve least
EEN454 Dgtal Integrated rcut Desgn Logc effort and gate szng EEN 454 Introducton hp desgners face a bewlderng arra of choces What s the best crcut topolog for a functon? How man stages of logc gve least
Coupling Element and Coupled circuits. Coupled inductor Ideal transformer Controlled sources
 Couplng Element and Coupled crcuts Coupled nductor Ideal transformer Controlled sources Couplng Element and Coupled crcuts Coupled elements hae more that one branch and branch oltages or branch currents
Couplng Element and Coupled crcuts Coupled nductor Ideal transformer Controlled sources Couplng Element and Coupled crcuts Coupled elements hae more that one branch and branch oltages or branch currents
Chapter 2 Problem Solutions 2.1 R v = Peak diode current i d (max) = R 1 K 0.6 I 0 I 0
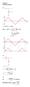 Chapter Problem Solutons. K γ.6, r f Ω For v, v.6 r + f ( 9.4) +. v 9..6 9.. v v v v v T ln and S v T ln S v v.3 8snωt (a) vs 3.33snωt 6 3.33 Peak dode current d (max) (b) P v s (max) 3.3 (c) T o π vo(
Chapter Problem Solutons. K γ.6, r f Ω For v, v.6 r + f ( 9.4) +. v 9..6 9.. v v v v v T ln and S v T ln S v v.3 8snωt (a) vs 3.33snωt 6 3.33 Peak dode current d (max) (b) P v s (max) 3.3 (c) T o π vo(
ECE 320 Energy Conversion and Power Electronics Dr. Tim Hogan. Chapter 1: Introduction and Three Phase Power
 ECE 3 Energy Conerson and Power Electroncs Dr. Tm Hogan Chapter : ntroducton and Three Phase Power. eew of Basc Crcut Analyss Defntons: Node - Electrcal juncton between two or more deces. Loop - Closed
ECE 3 Energy Conerson and Power Electroncs Dr. Tm Hogan Chapter : ntroducton and Three Phase Power. eew of Basc Crcut Analyss Defntons: Node - Electrcal juncton between two or more deces. Loop - Closed
CHAPTER 7 ENERGY BALANCES SYSTEM SYSTEM. * What is energy? * Forms of Energy. - Kinetic energy (KE) - Potential energy (PE) PE = mgz
 SYSTM CHAPTR 7 NRGY BALANCS 1 7.1-7. SYSTM nergy & 1st Law of Thermodynamcs * What s energy? * Forms of nergy - Knetc energy (K) K 1 mv - Potental energy (P) P mgz - Internal energy (U) * Total nergy,
SYSTM CHAPTR 7 NRGY BALANCS 1 7.1-7. SYSTM nergy & 1st Law of Thermodynamcs * What s energy? * Forms of nergy - Knetc energy (K) K 1 mv - Potental energy (P) P mgz - Internal energy (U) * Total nergy,
