Clip 181 Histograms A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H Clip 182 Probability 'And' and 'Or' Questions Clip 183 Stratified Sampling...
|
|
|
- Lora Fletcher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Grade A and A* topics Page Clip 155 Recurring Decimals Clip 156 Fractional and Negative Indices Clip 157 Surds A and B Clip 158 Rationalising the Denominator Clip 159 Direct and Inverse Proportion A and B Clip 160 Upper and Lower Bounds A, B and C Clip 161 Solving Quadratic Equations A, B, C and D Clip 16 Proof Clip 163 Algebraic Fractions A and B Clip 164 Rearranging Difficult Formulae Clip 165 Simultaneous Equations With a Quadratic Clip 166 Gradients of Lines Clip 167 Transformations of Functions A, B, C and D Clip 168 Graphs of Trigonometric Functions A and B Clip 169 Transformations of Trigonometric Functions Clip 170 Graphs of Eponential Functions Clip 171 Enlargements by Negative Scale Factors Clip 17 Equations of Circles Clip 173 Sine and Cosine Rules A and B Clip 174 Pythagoras in 3D Clip 175 Trigonometry in 3D Clip 176 Areas of Triangles Using ½absinC Clip 177 Cones and Spheres A and B Clip 178 Segments and Frustums Clip 179 Congruent Triangles A and B Clip 180 Vectors A, B, C, D and E Clip 181 Histograms A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H Clip 18 Probability 'And' and 'Or' Questions Clip 183 Stratified Sampling A and B
3 MathsWatch Clip 155 Recurring Decimals 1) a) Convert the recurring decimal 036. to a fraction in its simplest form. 8 b) Prove that the recurring decimal 07. = 11 ) a) Change 4 9 to a decimal. 19 b) Prove that the recurring decimal 057. = 33 3) a) Change 3 to a decimal b) Prove that the recurring decimal 045. = 33 4) a) Change 1 6 to a decimal. 5 b) Prove that the recurring decimal = 37 5) a) Convert the recurring decimal 061. to a fraction in its simplest form. b) Prove that the recurring decimal 07. = ) a) Convert the recurring decimal 5. to a fraction in its simplest form. 3 b) Prove that the recurring decimal = Page 155
4 MathsWatch Clip 156 Fractional and Negative Indices 1) Simplify the following: a) y 4 y 5 b) 6 c) (p 4 ) 5 d) ( 3 ) e) ( 4 ) f) ( 3 ) 5 g) 7 h) t 5 t 3 ) Work out the value of the following, leaving your answer in fraction form when necessary a) 5 0 b) 4 c) 5 3 d) 49 e) f) 3 g) 16 h) 7 i) ) 5 5 can be written in the form 5 n. Calculate the value of n. 4) 8 can be written in the form n. Calculate the value of n. 5) a =, b = y Epress in terms of a and b (i) (ii) + y (iii) + y Page 156
5 MathsWatch Clip 157 Surds 1) Simplify the following: a) 7 7 b) 3 3 c) 0 d) 4 e) 7 f) 00 g) 5 4) Epand and simplify where possible: a) ( 1+ )( 1 ) b) ( 3+ 5)( 5) c) ( 3+ )( 3+ 4) d) ( 5 3)( 5+ 1) e) ( + 7)( 7) f) ( 6 3) ) Simplify the following: 5) Work out the following, giving your answer in its simplest form: a) 18 b) 8 3 c) 99 d) 45 0 e) f) ) Epand and simplify where possible: a) 3( 3 3) b) ( 6+ ) c) 7( + 3 7) d) ( 3 8) a) b) c) d) e) f) ( 5+ 3)( 5 3) ( 4 5)( 4+ 5) 11 ( 3 )( 3+ ) 14 ( 3+ 1) 3 ( 5+ 3) 0 ( 5 5)( + 5) 0 Page 157A
6 MathsWatch Clip 157 Surds 1) 5 = 5 k a) Write down the value of k. b) Epand and simplify ( + 5 )(1 + 5 ) Give your answer in the form a + b c where a, b and c are integers. ) The diagram shows a right-angled triangle with lengths of sides as indicated. The area of the triangle is A cm 6 cm Show that A = k giving the value of k. 3 3) a) Find the value of 64 3 b) Given that 8 18 a + b find the value of a and the value of b. =, where a and b are integers, 4) Work out ( + 3)( 3) Give your answer in its simplest form. Page 157B
7 MathsWatch Clip 158 Rationalising the Denominator 1) Rationalise the denominator, simplifying where possible: a) b) 3 c) 3 7 d) 5 10 e) f) 15 3 g) 1 7 ) Rationalise the denominator of 1 3 3) Rationalise the denominator of giving the answer in the form p Page 158
8 MathsWatch Clip 159 Direct and Inverse Proportion 1) M is directly proportional to L 3. When L =, M = 160 Find the value of M when L = 3 ) y is directly proportional to. When = 500, y = 10 a) Find a formula for y in terms of. b) Calculate the value of y when = 350 3) D is proportional to S. D = 900 when S = 0 Calculate the value of D when S = 5 4) P is inversely proportional to V. When V = 8, P = 6 a) Find a formula for P in terms of V. b) Calculate the value of P when V = 5) The time, T seconds, for a hot sphere to cool is proportional to the square root of the surface area, A m, of the sphere. When A = 100, T = 30. Find the value of T when A = 60. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. Page 159A
9 MathsWatch Clip 159 Direct and Inverse Proportion 1) is directly proportional to y. When = 1, then y = 3. a) Epress in terms of y. b) Find the value of when y is equal to 10. ) a is inversely proportional to b. When a = 1, then b = 4. a) Find a formula for a in terms of b. b) Find the value of a when b is equal to 8. c) Find the value of b when a is equal to 4. 3) The variables u and v are in inverse proportion to one another. When u = 3, then v = 8. Find the value of u when v = 1. 4) p is directly proportional to the square of q. p = 75 when q = 5 a) Epress p in terms of q. b) Work out the value of p when q = 7. c) Work out the positive value of q when p = 7. 5) y is directly proportional to. When = 3, then y = 36. a) Epress y in terms of. z is inversely proportional to. When = 4, z =. b) Show that z = c y n, where c and n are numbers and c > 0. You must find the values of c and n. Page 159B
10 MathsWatch Clip 160 Upper and Lower Bounds 1) Here is a rectangle. a = 8.4 cm correct to 1 decimal place. b = 3.6 cm correct to 1 decimal place. b a a) Calculate the upper bound of the area of the rectangle. Write down all the figures on your calculator. b) Find the area of this rectangle correct to an appropriate number of significant figures. ) Terry measured the length and the width of a rectangle. He measured the length to be 745 mm correct to the nearest 5 mm. He measured the width to be 300 mm correct to the nearest 5 mm. a) Calculate the lower bound for the area of this rectangle. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. b) Calculate the upper bound for the perimeter of the rectangle. 3) The voltage V of an electronic circuit is given by the formula where I is the current in amps and R is the resistance in ohms. V = I R Given that V = 17 correct to three significant figures, R = 1.4 correct to three significant figures, calculate the lower bound of I. 4) Sara drove for 37 miles, correct to the nearest mile. She used 7. litres of petrol, to the nearest tenth of a litre. Petrol consumption = Number of miles travelled Number of litres of petrol used Work out the upper bound for the petrol consumption for Sara s journey. Give your answer correct to decimal places. Page 160A
11 MathsWatch Clip 160 Upper and Lower Bounds 1) The length of the rectangle, a, is 45 cm correct to the nearest cm. b The width of the rectangle, b, is 6 cm correct to the nearest cm. a Calculate the upper bound for the area of the rectangle. Write down all the figures on your calculator display. ) A field is in the shape of a rectangle. The width of the field is 6 metres, measured to the nearest metre. a) Work out the upper bound of the width of the field. The length of the field is 135 metres, measured to the nearest 5 metres. b) Work out the upper bound for the perimeter of the field. 3) A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a speed V metres per second. The height, H metres, to which it rises is given by H = V g where g m/s is the acceleration due to gravity. V = 4.4 correct to 3 significant figures. g = 9.8 correct to significant figures. (i) Write down the lower bound of g. (ii) Calculate the upper bound of H. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. 4) v = a b a = 6.43 correct to decimal places. b = correct to 3 decimal places. By considering bounds, work out the value of v to a suitable degree of accuracy. You must show all your working and give a reason for your final answer. Page 160B
12 MathsWatch Clip 160 Upper and Lower Bounds 1) A = 11.3 correct to 1 decimal place B = 300 correct to 1 significant figure C = 9 correct to the nearest integer a) Calculate the upper bound for A + B. b) Calculate the lower bound for B C. c) Calculate the least possible value of AC. d) Calculate the greatest possible value of A + B B + C ) An estimate of the acceleration due to gravity can be found using the formula: L g = T sin Using T = 1. correct to 1 decimal place L = 4.50 correct to decimal places = 40 correct to the nearest integer a) Calculate the lower bound for the value of g. Give your answer correct to 3 decimal places. b) Calculate the upper bound for the value of g. Give your answer correct to 3 decimal places. 3) The diagram shows a triangle ABC. C AB = 73mm correct to significant figures. BC = 80mm correct to 1 significant figure. Diagram NOT accurately drawn A a) Write the upper and lower bounds of both AB and BC. B AB upper =... BC upper =... AB lower =... BC lower =... b) Calculate the upper bound for the area of the triangle ABC....mm Angle CAB = c) Calculate the lower bound for the value of tan. Page 160C
13 MathsWatch Clip 161 Solve Quadratics Using the Formula 1) Solve the equation = 0 Give your answers correct to 3 decimal places. ) Solve the equation = 0 Give your answers correct to 3 significant figures. 3) Solve the equation 3 = 0 Give your answers correct to 3 significant figures. 4) Solve the equation 7 + = 0 Give your answers correct to 3 significant figures. 5) Solve the equation = 0 Give your answers correct to 3 significant figures. 6) Solve the equation 3 0 = 0 Give your answers correct to 3 significant figures. 7) Solve the equation = 0 8) Solve the equation = 0 Give your answers correct to 3 significant figures. 9) + 10 = 300 Find the positive value of. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. 10) ( + )( 3) = 1 a) Show that 7 = 0 b) Solve the equation 7 = 0 Give your answers correct to 3 significant figures. Page 161A
14 MathsWatch Clip 161 Solve Quadratics Using the Formula 1) The diagram shows a cuboid. All the measurements are in cm. The volume of the cuboid is 5 cm 3. a) Show that 4 5 = 0 for > b) Solve the quadratic equation 4 5 = 0 Give your solutions correct to 3 significant figures. You must show your working. ) The diagram below shows a large rectangle of length ( + 6) cm and width cm. A smaller rectangle of length cm and width 3 cm is cut out and removed The area of the shape that is left is 100 cm. a) Show that = 0 b) Calculate the length of the smaller rectangle. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. Page 161B
15 MathsWatch Clip 161 Solve Quadratics Using the Formula 1) The diagram shows a 6-sided shape. All the corners are right angles. All the measurements are given in centimetres. The area of the shape is 94 cm. a) Show that = 0 b) Solve the equation = 0 Give your solutions correct to 3 significant figures. ) The diagram shows a 6-sided shape. All the corners are right angles All the measurements are given in centimetres. The area of the shape is 33 cm. Work out the length of the longest side of the shape. Give your answer correct to significant figures. Page 161C
16 MathsWatch Clip 161 Completing the Square 1) Show that if y = then y 19 for all values of. ) Show that if y = then y 5 for all values of. 3) The epression can be written in the form ( + p) + q for all values of. Find the values of p and q. 4) Given that = ( p) + q for all values of, find the value of p and the value of q. 5) For all values of, + 6 = ( + p) + q a) Find the values of p and q. b) Find the minimum value of ) For all values of, 8 5 = ( p) + q a) Find the value of p and the value of q. y b) On the aes, sketch the graph of y = 8 5. O c) Find the coordinates of the minimum point on the graph of y = ) The epression 10 can be written in the form p ( q) for all values of. a) Find the values of p and q. b) The epression 10 has a maimum value. (i) Find the maimum value of 10. (ii) State the value of for which this maimum value occurs. Page 161D
17 MathsWatch Clip 16 Proof 1) Show algebraically that the sum of two consecutive numbers is always odd. ) Show algebraically that the product of two even numbers is always a multiple of four. 3) Show algebraically that the square of an odd number is always odd. 4) Prove, using algebra, that the difference between the squares of any two consecutive even numbers is always a multiple of four. 5) n is an integer. Prove that (n + 1)(n + 3) + (n + 1)(n ) is not a multiple of. 6) Prove that (4n + 1) (4n 1) is a multiple of eight for all positive integer values of n. 7) Prove algebraically that the sum of the squares of any three consecutive even numbers is always a multiple of four. Page 16
18 MathsWatch Clip 163 Algebraic Fractions 1) Simplify fully a) b) 10 y 5y 3 c) 18 ab ab 3 d) e) ab 14 ab 3 3 6ab 3 f) 5y+ 5y 10y ) Simplify fully a) b) c) ) a) Factorise b) Simplify Page 163A
19 MathsWatch Clip 163 Algebraic Fractions 1) Write as single fractions in their simplest form a) b) c) d) ) a) Factorise b) Write as a single fraction in its simplest form ) Solve a) b) c) d) e) f) = = = = = = 1 Page 163B
20 MathsWatch Clip 164 Rearranging Difficult Fomulae 1) Make c the subject of the formula. v = a + 3b + c ) Make t the subject of the formula. A = π t + 5t 3) Make s the subject of the formula. R = 3s + π s + t l 4) k = m l a) Make l the subject of the formula. b) Make m the subject of the formula. 5) A k ( = + 5) 3 Make the subject of the formula. 6) R = u+ v u+ v Make u the subject of the formula. 7) 3+ y = y Make y the subject of the formula. 8) a 3 = 5 4b Rearrange this formula to give a in terms of b. 9) S = πd h + d Rearrange this formula to make h the subject. Page 164
21 MathsWatch Clip 165 Simultaneous Equations with a Quadratic 1) Solve these simultaneous equations. y = y = 6 ) Solve these simultaneous equations. y = 4 y = 3 3) Solve these simultaneous equations. y = 13 y = + 4) Solve these simultaneous equations. y = 35 y = 5 5) Solve these simultaneous equations. + y = 6 y + 6 = 6) Sarah said that the line y = 7 cuts the curve + y = 5 at two points. a) By eliminating y show that Sarah is not correct. b) By eliminating y, find the solutions to the simultaneous equations + y = 5 y = 3 9 Page 165
22 MathsWatch Clip 166 Gradients of Lines 1) y B (10, 7) A (0, ) 0 A is the point (0, ) B is the point (10, 7) a) Write down the equation of the straight line which passes through points A and B. b) Find the equation of the line perpendicular to AB passing through B. ) A straight line has equation y = 5 The point P lies on the straight line. The y coordinate of P is -6 a) Find the coordinate of P. A straight line L is parallel to y = 5 and passes through the point (3, ). b) Find the equation of line L. c) Find the equation of the line that is perpendicular to line L and passes through point (3, ). 3) In the diagram A is the point (0, -) B is the point (-4, ) C is the point (0, ) a) Find the equation of the line that passes through C and is parallel to AB. b) Find the equation of the line that passes through C and is perpendicular to AB. y 3 B C O A -3 Page 166
23 MathsWatch Clip 167 Transformations of Functions 1) The graph of y = f() is shown on the grids. a) On this grid, sketch the graph of y = f ( 3) y y = f() O b) On this grid sketch the graph of y = f() 6 y 5 4 y = f() O Page 167A
24 MathsWatch Clip 167 Transformations of Functions 1) y (, 4) y = f() O The diagram shows part of the curve with equation y = f(). The coordinates of the maimum point of this curve are (, 4). Write down the coordinates of the maimum point of the curve with equation a) y = f( ) b) y = f() ) y = f() y - O 4 6 The curve with equation y = f() is translated so that the point at (0, 0) is mapped onto the point (4, 0). Find the equation of the translated curve. Page 167B
25 MathsWatch Clip 167 Transformations of Functions 1) The graph of y = f() is shown on the grid. 5 y y = f() graph G O The graph G is a translation of the graph of y = f(). a) Write down, in terms of f, the equation of graph G. The graph of y = f() has a maimum point at (-4, 3). b) Write down the coordinates of the maimum point of the graph y = f(-). ) This is a sketch of the curve with the equation y = f(). The only minimum point of the curve is at P (3, -4). y y = f() o P (3, -4) a) Write down the coordinates of the minimum point of the curve with the equation y = f( ) b) Write down the coordinates of the minimum point of the curve with the equation y = f( + 5) + 6 Page 167C
26 MathsWatch Clip 167 Transformations of Functions 1) This is a sketch of the curve with equation y = f(). It passes through the origin O. The only verte of the curve is at A (1, -1) a) Write down the coordinates of the verte of the curve with equation (i) y = f( 3) (ii) y = f() 5 (iii) y = f() (iv) y = f() y A (1, -1) b) The curve y = has been translated to give the curve y = f(). Find f() in terms of. ) The graph of y = f() is shown on the grids. a) On this grid, sketch the graph of y = f( 1) b) On this grid, sketch the graph of y = f() 3) Sketch the graph of y = ( ) + 3 State the coordinates of the verte. Page 167D
27 MathsWatch Clip 168 Graphs of Trigonometric Functions 1) On the aes below below, draw a sketch-graph to show y = sin 1 y Given that sin 30 = 0.5, write down the value of: (i) sin 150 (ii) sin 330 ) On the aes below, draw a sketch-graph to show y = cos 1 y Given that cos 60 = 0.5, write down the value of: (i) cos 10 (ii) cos 40 Page 168A
28 MathsWatch Clip 168 Graphs of Trigonometric Functions 1) On the aes below, draw a sketch-graph to show y = tan y ) The diagram below shows the graph of y = cos a + b, for values of between 0 and 300. Work out the values of a and b. ) Here is the graph of the curve y = cos for 0 < < 360. y a) Use the graph to solve cos = 0.75 for 0 < < 360 b) Use the graph to solve cos = for < < Page 168B
29 MathsWatch Clip 169 Transformations of Trigonometric Functions 1) The diagram below shows the graph of y = sin, for values of between 0 and 360. y B A The curve cuts the ais at the point A. The graph has a maimum at the point B. a) (i) Write down the coordinates of A. (ii) Write down the coordinates of B. b) On the same diagram, sketch the graph of y = sin + 1 for values of between 0 and 360. ) The diagram below shows the graph of y = cos a + b, for values of between 0 and 300. Work out the values of a and b. y Page 169
30 MathsWatch Clip 170 Graphs of Eponential Functions 1) y (4, 375) (1, 3) The sketch-graph shows a curve with equation y = pq. The curve passes through the points (1, 3) and (4, 375). Calculate the value of p and the value of q. ) The graph shows the number of bacteria living in a petri dish. The number N of bacteria at time t is given by the relation: N = a b t The curve passes through the point (0, 400). a) Use this information to show that a = 400. The curve also passes through (, 900). b) Use this information to find the value of b. Number of bacteria N t c) Work out the number of bacteria in the dish at time t = 3. Time (hours) Page 170
31 MathsWatch Clip 171 Enlargements by Negative Scale Factors 1) Enlarge triangle T by scale factor - using coordinates (, ) as the centre of enlargement. y T O ) Describe fully the single transformation which maps triangle T to triangle U. y U O T Page 171
32 MathsWatch Clip 17 Equations of Circles 1) Find the equation of a circle with radius 3 and centre the origin. y O ) a) Draw the graph of + y = 6.5 y O b) By drawing the line + y = 1.5, solve the equations + y = y = 1.5 Page 17
33 MathsWatch Clip 173 Sine and Cosine Rules 1) Work out the size of the angle marked. Give your answer correct to one decimal place. 11 cm 13 cm 30 ) ABC is a triangle. AC = 8 cm BC = 9 cm Angle ACB = 43 Calculate the length of AB. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. A 8 cm 9 cm 43 B C 3) The lengths of the sides of a triangle are 4.1 cm, 5.4 cm and 7.8 cm. Calculate the size of the largest angle of the triangle. Give your answer correct to 1 decimal place. 4.1 cm 5.4 cm 7.8 cm 4) Find the missing lengths, cm and y cm, in this triangle. Give your answers to 3 significant figures. y cm Page 173A
34 MathsWatch Clip 173 Sine and Cosine Rules 1) P 14 cm Q 8 cm S 64 R PQRS is a trapezium. PQ is parallel to SR. Angle PSR = 90 Angle PRS = 64 PQ = 14 cm. PS = 8 cm. a) Work out the length of PR. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. b) Work out the length of QR. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. ) AC = 9 cm AB = 3 cm DE = 0 cm Angle ABC = angle CBD = angle BDE = 90 C E 0 cm 9 cm A 3 cm B 50 D a) Calculate the length of CD. Give your answer to 3 significant figures. b) Calculate the length of CE. Give your answer to 3 significant figures. Page 173B
35 MathsWatch Clip 174 1) The diagram shows a bo in the shape of a cuboid. AB = 6cm, BC = 4cm, CG = 3cm Pythagoras in 3D H G A string runs diagonally across the bo from A to G. E F 3cm Calculate the length of the string AG. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. D 4cm C A 6cm B ) The diagram shows a bo in the shape of a cuboid. AB = 8cm, BC = 11cm H G A string runs diagonally across the bo from D to F and is 18cm long. Calculate the length AE. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. E A D 18cm 8cm B F C 11cm 3) The diagram shows a wedge in the shape of a prism. Angle BFC is a right angle. String runs diagonally across the wedge from A to C. Calculate the length AC Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. A E D 0cm B C 8cm F 17cm 4) Two points, P and Q, lie on coordinate aes. y Find the distance PQ to 1 decimal place. Q (7, 5, ) P (, 3, 1) z Page 174
36 MathsWatch Clip 175 Trigonometry in 3D 1) The diagram shows a wedge. The base of the wedge is a horizontal rectangle measuring 80 cm by 60 cm. The sloping face ABRS makes an angle of 1 to the horizontal. S R D C 1 80 cm A 60 cm B Calculate the angle that AR makes with the horizontal plane ABCD. Give your answer correct to 1 decimal place. ) The diagram shows a bo in the shape of a cuboid. A string runs diagonally across the bo from C to E. H G E F 5 cm D C A 30 cm B 40 cm a) Work out the length of the string CE. Give your answer correct to 1 decimal place. b) Work out the angle between the string CE and the horizontal plane ABCD. Give your answer correct to 1 decimal place. Page 175
37 MathsWatch Clip 176 Areas of Triangles Using ½abSinC 1) A B Diagram NOT accurately drawn. ABC is a triangle. AC = 8 cm. BC = 10 cm Angle ACB = 4 Calculate the area of triangle ABC. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. 8 cm 10 cm 4 C ) C Diagram NOT accurately drawn. 18 cm ABC is a triangle. AB = 0 cm. BC = 18 cm Angle ABC = 144 B cm A Calculate the area of triangle ABC. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. 3) C Diagram NOT accurately drawn. 3 cm 31 cm ABC is a triangle. AC = 3 cm. BC = 31 cm Angle BAC = 54 Angle ABC = 39 A B Calculate the area of triangle ABC. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. Page 176
38 MathsWatch Clip 177 Cones and Spheres 1) A cone has a base radius of 4 cm and a vertical height of 8 cm. a) Calculate the volume of the cone. Take to be Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. b) Use Pythagoras Theorem to find the slant height of the cone. Give your answer correct to 1 decimal place. 8 cm c) Find the curved surface area of the cone. Take to be Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. 4 cm ) A sphere has a radius of 1cm. a) Calculate the volume of the sphere. Take to be Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. 1 cm b) Find the curved surface area of the sphere. Take to be Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. 3) A cone has a base radius of 8 cm and a slant height of 10 cm. Calculate the volume of the cone. Leave your answer in terms of. 10 cm 8 cm Page 177A
39 MathsWatch Clip 177 Cones and Spheres 1) h The diagram shows a solid cone and a solid hemisphere. The cone has a base of radius cm and a height of h cm. The hemisphere has a base of radius cm. The surface area of the cone is equal to the surface area of the hemisphere. Find an epression for h in terms of. ) h A cylinder has base radius cm and height cm. A cone has base radius cm and height h cm. The volume of the cylinder and the volume of the cone are equal. Find h in terms of. Give your answer in its simplest form. Page 177B
40 MathsWatch Clip 178 Segments and Frustums 1) Find the area of the segment shaded in the diagram below. Take to be Give your answer to 3 significant figures. A 6 cm O cm B ) The diagram shows a cone of height 40 cm and base radius 10 cm. A smaller cone of height 8 cm is removed to form a frustum. 8 cm 40 cm r r 10 cm 10 cm Taking to be 3.14 a) Work out the radius r of the base of the smaller cone. Calculate, to the nearest cm 3 b) The volume of the larger cone. c) The volume of the smaller cone. d) The volume of the frustum. Page 178
41 MathsWatch Clip 179 Congruent Triangles 1) ABCD is a quadrilateral. A B D AB is parallel to DC. DA is parallel to CB. C Prove that triangle ABD is congruent to triangle CDB. ) P Q T S R PQRS is a square. PTS and SUR are equilateral triangles. U a) Prove that triangle USP is congruent to triangle TSR. X is the point such that RUXT is a parallelogram. b) Prove that UP = UX Page 179A
42 MathsWatch Clip 179 1) Congruent Triangles A P Q B The diagram shows a triangle ABC. PQRB is a parallelogram where P is the midpoint of AB, Q is the midpoint of AC, and R is the midpoint of BC. R C Prove that triangle APQ and triangle QRC are congruent. You must give reasons for each stage of your proof. ) A B D C ABC is an equilateral triangle. D lies on BC. AD is perpendicular to BC. a) Prove that triangle ADC is congruent to triangle ADB. 1 b) Hence, prove that BD = AB Page 179B
43 MathsWatch Clip 180 1) C Vectors A Q O B X In the diagram, OA = 4a and OB = 4b OAC, OBX and BQC are all straight lines. AC = OA and BQ : QC = 1 : 3 a) Find, in terms of a and b, the vectors which represent (i) (ii) BC AQ Given that BX = 8b b) Show that AQX is a straight line. ) a A P B O 3b OAB is a triangle. OA = a OB = 3b a) Find AB in terms of a and b. P is a point on AB such that AP : PB = : 3 b) Show that OP is parallel to the vector a + b. Page 180A
44 MathsWatch Clip 180 1) Vectors P M b O a T OPT is a triangle. M is the midpoint of OP. OT = a TP = b a) Epress OM in terms of a and b. b) Epress TM in terms of a and b. Give your answer in its simplest form. ) A a P O OAB is a triangle. OA = a, OB = b b B a) Find the vector AB in terms of a and b. P is the point on AB so that AP : PB = : 1 b) Find the vector OP in terms of a and b. Give your answer in its simplest form. Page 180B
45 MathsWatch Clip 180 Vectors 1) A a P O OAB is a triangle. OA = a, OB = b b B a) Find the vector AB in terms of a and b. P is the point on AB so that AP : PB = 3 : 1 b) Show that OP = (a + 3b) 5 ) OX = a + b O 4a + 3b Y OY = 4a + 3b a + b X a) Epress the vector XY in terms of a and b Give your answer in its simplest form. XYZ is a straight line. XY : YZ = : 3 b) Epress the vector OZ in terms of a and b Give your answer in its simplest form. O Z 4a + 3b Y a + b X Page 180C
46 MathsWatch Clip 180 Vectors 1) The diagram shows a trapezium PQRS. PQ = a and QR = b. PS is three times the length of QR. Q b R Diagram NOT accurately drawn a P S Find, in terms of a and b, epressions for a) QP b) PR c) PS d) QS ) In triangle ABC, P and Q are the midpoints of AB and AC. AP = p and AQ = q. p A q Diagram NOT accurately drawn a) Find, in terms of p and q, epressions for P Q (i) PQ (ii) AB (iii) AC (iv) BC B C b) Use your results from (a) to prove that PQ is parallel to BC. 3) B D b C Diagram NOT accurately drawn O a A OAB is a triangle. D is the midpoint of OB. C is the midpoint of AB. OA = a and OB = b (i) Find OC in terms of a and b. (ii) Show that DC is parallel to OA. Page 180D
47 MathsWatch Clip 180 Vectors 1) P p Q q Diagram NOT accurately drawn U q R T S X PQRSTU is a regular heagon. PQ = p QR = q PS = q a) Find the vector PR in terms of p and q. PR = RX b) Prove that PQ is parallel to SX ) B M C Diagram NOT accurately drawn A N ABCD is a trapezium with BC parallel to AD. D AB = 3 b BC = 3 a AD = 9 a M is the midpoint of BC and N is the midpoint of AD. a) Find the vector MN in terms of a and b. X is the midpoint of MN and Y is the midpoint of CD. b) Prove that XY is parallel to AD. Page 180E
48 MathsWatch Clip 181 Histograms 1) The table and histogram give some information about the weights of parcels received at a post office during one Thursday. Frequency density Weight (w) kg a) Use the histogram to complete the frequency table. Weight (w) kg Frequency 0 < w < 40 < w < 3 3 < w < < w < < w < 8 b) Use the table to complete the histogram. Page 181A
49 MathsWatch Clip 181 Histograms 1) The incomplete table and histogram give some information about the heights (in cm) of some plants. Height (h cm) Frequency 100 < h < < h < < h < < h < < h < Frequency density Height (h cm) a) Use the histogram to complete the table. b) Use the table to complete the histogram. Page 181B
50 MathsWatch Clip 181 Histograms 1) Paul asked the students in his class how many hours they used the internet for last week. The incomplete histogram was drawn using his results. Frequency density Hours used Eight students used the internet for between 10 and 15 hours. Si students used it for between 0 and 10 hours. a) Use this information to complete the histogram. No students used the internet for more than 30 hours. b) Work out how many students Paul asked. Page 181C
51 MathsWatch Clip 181 Histograms 1) Some trains from Nottingham to Leeds were late. The incomplete table and histogram give some information about how late the trains were. Minutes late (t) Frequency 0 < t < < t < < t < 0 0 < t < < t < 50 8 Frequency density Minutes late (t) a) Use the information in the histogram to complete the table. b) Use the information in the table to complete the histogram. Page 181D
52 MathsWatch Clip 181 Histograms 1) The table and histogram give information about how long, in minutes, some students took to complete a set of homework. Time (t) in minutes Frequency 0 < t < < t < < t < < t < < t < Frequency density Time (minutes) a) Use the information in the histogram to complete the table. b) Use the table to complete the histogram. Page 181E
53 MathsWatch Clip 181 Histograms 1) The incomplete histogram and table give some information about the distances some students travel to school. Frequency density Distance (d km) a) Use the information in the histogram to complete the frequency table. Distance (d km) Frequency 0 < d < < d < < d < 0 0 < d < < d < b) Use the information in the table to complete the histogram. Page 181F
54 MathsWatch Clip 181 Histograms 1) There are 100 pupils in Year 11. The time taken by each pupil to answer a question was recorded. The following grouped frequency distribution was obtained. Time, t seconds 0 < t < < t < 0 0 < t < < t < < t < 60 Number of pupils Draw a histogram to illustrate the distribution on the graph paper below. Time taken to answer in seconds Time, t seconds Page 181G
55 MathsWatch Clip 181 1) The table gives information about the heights, in centimetres, of some 18 year old students. Use the table to draw a histogram. Histograms Height (h cm) Frequency 135 < h < < h < < h < < h < < h < ) The histogram shows the amount of time, in hours, that students spend on their homework per week. Use the histogram to complete the table Hours spent on homework per week Time (t hours) Frequency 0 < t < ½ ½ < t < 1 1 < t < < t < < t < 5 Page 181H
56 MathsWatch Clip 18 Probability And & Or Questions 1) Jordan designs a game for a school fair. He has two 8-sided spinners. The spinners are equally likely to land on each of their sides. One spinner has 3 blue sides, yellow sides and 3 white sides. The other spinner has blue sides, green sides and 4 white sides. Calculate the probability that the two spinners will land on the same colour. ) The probability that it will snow in Paris on Christmas day is a) Work out the probability that it will snow in Paris on both Christmas day 015 and Christmas day 016. b) Work out the probability that it will snow in Paris on either Christmas Day 015 or Christmas Day 016, but not on both. 3) A bag contains black beads, 5 yellow beads and 3 red beads. Natalie takes a bead at random from the bag, records its colour and replaces it. She does this two more times. Work out the probability that, of the three beads Natalie takes, eactly two are the same colour. Page 18
57 MathsWatch Clip 183 Stratified Sampling 1) Ellen wants to do a survey with Years 9, 10 and 11 at her school. The table shows the number of students in each of these year groups. Year 11 Year 10 Year Ellen takes a sample of 50 students stratified by year group. Work out the number of students from Year 10 in the sample. ) The table shows information about the year groups of 1000 students in a school. Year group Number in year Tony takes a sample of 50 of these students, stratified by year group. Calculate the number of Year 8 students he should have in his sample. 3) The table shows information about Ben s collection of 65 coins. Country Number of coins France Spain Germany Italy Total Ben takes a sample of 50 coins stratified by country. Work out the number of coins from Italy in this sample. 4) Male Female Lower sith Upper sith The table gives information about the number of students in the two years of a sith form. Amy wants to interview some of these students. She takes a random sample of 70 students stratified by year and by gender. Work out the number of students in the sample who are male and in the lower sith. Page 183A
58 MathsWatch Clip 183 Stratified Sampling 1) The table below shows the number of employees in each section of a company. Department Managerial Sales Technical Production Number of employees A survey on job satisfaction is to be carried out. a) Eplain why a simple random sample of employees is unsuitable. b) A stratified random sample of 100 is used. Complete the table below to show how many employees from each department will be included. Department Managerial Sales Technical Production Number of employees in sample ) MathsWatch High-School has 798 pupils. The size of each year group is shown below. Year Group Boys Girls The headteacher wants to find out the opinions of the pupils on changing the timing of the school day. A stratified sample of 80 pupils is taken. a) Complete the table below to show the numbers of pupils to be sampled. Year Group Boys in Sample Girls in Sample The table below shows the number of pupils in the sample who answered YES to a change in the timing of the school day. Year Group Boys in Sample Girls in Sample who answered YES who answered YES b) Use the table to estimate the percentage of pupils in the school who would answer YES to the question. Page 183B
Solve Quadratics Using the Formula
 Clip 6 Solve Quadratics Using the Formula a + b + c = 0, = b± b 4 ac a ) Solve the equation + 4 + = 0 Give our answers correct to decimal places. ) Solve the equation + 8 + 6 = 0 ) Solve the equation =
Clip 6 Solve Quadratics Using the Formula a + b + c = 0, = b± b 4 ac a ) Solve the equation + 4 + = 0 Give our answers correct to decimal places. ) Solve the equation + 8 + 6 = 0 ) Solve the equation =
Practice Papers Set D Higher Tier A*
 Practice Papers Set D Higher Tier A* 1380 / 2381 Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number.
Practice Papers Set D Higher Tier A* 1380 / 2381 Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number.
Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) A* Paper (not for the faint hearted) Higher Tier
 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) A* Paper (not for the faint hearted) Higher Tier Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses,
Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) A* Paper (not for the faint hearted) Higher Tier Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses,
Questions Q1. x =... (Total for Question is 4 marks) Q2. Write down the value of (i) 7. (ii) 5 1. (iii) 9 ½. (Total for Question is 3 marks) Q3.
 Questions Q1. The equation x 3 6x = 72 has a solution between 4 and 5 Use a trial and improvement method to find this solution. Give your answer correct to one decimal place. You must show all your working.
Questions Q1. The equation x 3 6x = 72 has a solution between 4 and 5 Use a trial and improvement method to find this solution. Give your answer correct to one decimal place. You must show all your working.
Paper Reference. Mathematics A Paper 5 (Non Calculator) Higher Tier Tuesday 8 June 2004 Afternoon Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 5505 05 Signature Paper Reference(s) 5505/05 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 5 (Non Calculator) Higher Tier Tuesday 8 June 2004 Afternoon
Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 5505 05 Signature Paper Reference(s) 5505/05 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 5 (Non Calculator) Higher Tier Tuesday 8 June 2004 Afternoon
1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. accurately drawn. x + 2. x + 4. x + 2
 1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. 2 x + 3 Diagram NOT accurately drawn x + 2 x + 4 x + 2 The length of the rectangle is 2x + 3. The width of the rectangle is x + 4. The length
1. Peter cuts a square out of a rectangular piece of metal. 2 x + 3 Diagram NOT accurately drawn x + 2 x + 4 x + 2 The length of the rectangle is 2x + 3. The width of the rectangle is x + 4. The length
GCSE Mathematics. Higher Tier. Paper 3D (Non-Calculator) Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes. For Edexcel. Name
 For Edexcel Name GCSE Mathematics Paper 3D (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Materials required Ruler, protractor, compasses, pen, pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used. Instructions
For Edexcel Name GCSE Mathematics Paper 3D (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Materials required Ruler, protractor, compasses, pen, pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used. Instructions
Practice Papers Set D
 Practice Papers Set D Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer
Practice Papers Set D Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer
Sixth Form Entrance Mathematics
 Sixth Form Entrance 2016 Mathematics 1 hour Attempt all questions if possible. Do not worry if there are topics you have never covered; do your best on whatever you can attempt. Questions are not necessarily
Sixth Form Entrance 2016 Mathematics 1 hour Attempt all questions if possible. Do not worry if there are topics you have never covered; do your best on whatever you can attempt. Questions are not necessarily
Paper Reference. Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 5540H 4H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 5540H/4H Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A (Linear) 2540 Paper 4 (Calculator) Higher Tier Wednesday 12 November 2008 Morning
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 5540H 4H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 5540H/4H Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A (Linear) 2540 Paper 4 (Calculator) Higher Tier Wednesday 12 November 2008 Morning
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, pair of compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Sample Assessment Material Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Sample Assessment Material Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Mathematics A. Edexcel GCSE S37709A. Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier. Sample Assessment Material Time: 1 hour 45 minutes.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Centre Number Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Sample Assessment Material Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Centre Number Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Sample Assessment Material Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Aiming for Grade 6-8: Study Programme
 Aiming for Grade 6-8: Study Programme Week A1: Similar Triangles Triangle ABC is similar to triangle PQR. Angle ABC = angle PQR. Angle ACB = angle PRQ. Calculate the length of: i PQ ii AC Week A: Enlargement
Aiming for Grade 6-8: Study Programme Week A1: Similar Triangles Triangle ABC is similar to triangle PQR. Angle ABC = angle PQR. Angle ACB = angle PRQ. Calculate the length of: i PQ ii AC Week A: Enlargement
Mathematics 4306/2H (Specification A)
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Time allowed 2 hours General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2010 Mathematics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Time allowed 2 hours General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2010 Mathematics
Grade 9 type questions. GCSE style questions arranged by topic
 Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edecel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Mathematics Grade 9 type questions GCSE style questions arranged by topic Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edecel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Mathematics Grade 9 type questions GCSE style questions arranged by topic Candidate Number
General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Pages 3 Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier 4 5 6 7 Mathematics (Linear) B Paper 2 Calculator
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Pages 3 Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier 4 5 6 7 Mathematics (Linear) B Paper 2 Calculator
Paper Reference. Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 3 (Non-Calculator)
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 1380H 3H Paper Reference(s) 1380H/3H Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 3 (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Mock Paper Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Surname Signature
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 1380H 3H Paper Reference(s) 1380H/3H Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 3 (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Mock Paper Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Surname Signature
Recurring Decimals. Mathswatch. Clip ) a) Convert the recurring decimal 036. to a fraction in its simplest form.
 Clip Recurring Decimals ) a) Convert the recurring decimal 06. to a fraction in its simplest form. 8 b) Prove that the recurring decimal 07. = ) a) Change 4 9 to a decimal. 9 b) Prove that the recurring
Clip Recurring Decimals ) a) Convert the recurring decimal 06. to a fraction in its simplest form. 8 b) Prove that the recurring decimal 07. = ) a) Change 4 9 to a decimal. 9 b) Prove that the recurring
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3HR Centre Number Wednesday 14 May 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3HR Centre Number Wednesday 14 May 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3H Centre Number Monday 8 January 2018 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3H Centre Number Monday 8 January 2018 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Paper 3 Unseen Topics
 Paper 3 Unseen Topics This is a collection of questions based on the topics that are so far UNSEEN or are usually more prominent Make sure you revise all topics as it is very likely topics from Paper 1
Paper 3 Unseen Topics This is a collection of questions based on the topics that are so far UNSEEN or are usually more prominent Make sure you revise all topics as it is very likely topics from Paper 1
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics A Paper 3HR Friday 10 May 2013 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Higher Tier Paper Reference 4MA0/3HR
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics A Paper 3HR Friday 10 May 2013 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Higher Tier Paper Reference 4MA0/3HR
Wednesday 15 January 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4H Centre Number Wednesday 15 January 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4H Centre Number Wednesday 15 January 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number
Wednesday 11 January 2012 Morning Time: 2 hours
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 3H Wednesday 11 January 2012 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference 4MA0/3H
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 3H Wednesday 11 January 2012 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference 4MA0/3H
Instructions. Information. Advice
 Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the
Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the
E Math (4048/01) Total marks : (a) Simplify 3 2x 1. Answer. [2] (b) Factorise 6x. 2. Factorise completely 4ax 12by 16ay 3bx
![E Math (4048/01) Total marks : (a) Simplify 3 2x 1. Answer. [2] (b) Factorise 6x. 2. Factorise completely 4ax 12by 16ay 3bx E Math (4048/01) Total marks : (a) Simplify 3 2x 1. Answer. [2] (b) Factorise 6x. 2. Factorise completely 4ax 12by 16ay 3bx](/thumbs/83/88085790.jpg) Requirement : Answer all questions Total marks : 80 Duration : 2 hour 1. (a) Simplify 3 2x 1 1. Answer. [1] (b) Factorise 6x 18xy. Answer. [1] 2. Factorise completely 4ax 12by 16ay 3bx. Prepared by Mr
Requirement : Answer all questions Total marks : 80 Duration : 2 hour 1. (a) Simplify 3 2x 1 1. Answer. [1] (b) Factorise 6x 18xy. Answer. [1] 2. Factorise completely 4ax 12by 16ay 3bx. Prepared by Mr
Name. GCSE Mathematics. Paper 3D (Non-Calculator) Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes
 For Edexcel Name GCSE Mathematics Paper 3D (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Materials required Ruler, protractor, compasses, pen, pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used. Instructions
For Edexcel Name GCSE Mathematics Paper 3D (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Materials required Ruler, protractor, compasses, pen, pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used. Instructions
3301/1H. MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 3301/1H Higher Tier Paper 1 Non-Calculator. General Certificate of Secondary Education November 2005
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education November 2005 MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 330/H Higher Tier Paper Non-Calculator
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education November 2005 MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 330/H Higher Tier Paper Non-Calculator
Created by T. Madas 2D VECTORS. Created by T. Madas
 2D VECTORS Question 1 (**) Relative to a fixed origin O, the point A has coordinates ( 2, 3). The point B is such so that AB = 3i 7j, where i and j are mutually perpendicular unit vectors lying on the
2D VECTORS Question 1 (**) Relative to a fixed origin O, the point A has coordinates ( 2, 3). The point B is such so that AB = 3i 7j, where i and j are mutually perpendicular unit vectors lying on the
C accurately drawn. Calculate the upper bound for the area of triangle ABC. .. mm 2 (2)
 1. C Diagram NOT accurately drawn A B The diagram shows a triangle ABC. Angle ABC is exactly 90. AB = 83 mm correct to 2 significant figures. BC = 90 mm correct to 1 significant figures. (a) Calculate
1. C Diagram NOT accurately drawn A B The diagram shows a triangle ABC. Angle ABC is exactly 90. AB = 83 mm correct to 2 significant figures. BC = 90 mm correct to 1 significant figures. (a) Calculate
*P59022A0228* International GCSE Mathematics Formulae sheet Higher Tier DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA
 Arithmetic series Sum to n terms, S n = n 2 The quadratic equation International GCSE Mathematics Formulae sheet Higher Tier [2a + (n 1)d] Area The solutions of ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where a ¹ 0 are given
Arithmetic series Sum to n terms, S n = n 2 The quadratic equation International GCSE Mathematics Formulae sheet Higher Tier [2a + (n 1)d] Area The solutions of ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where a ¹ 0 are given
Instructions. Information. Advice
 Instructions Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided
Instructions Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided
Teddington School Sixth Form
 Teddington School Sith Form AS / A level Maths Induction and Key Course Materials 016-018 Introduction The Mathematics Department at Teddington School are delighted that you would like to continue your
Teddington School Sith Form AS / A level Maths Induction and Key Course Materials 016-018 Introduction The Mathematics Department at Teddington School are delighted that you would like to continue your
Methods in Mathematics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Monday 11 November 013
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Monday 11 November 013
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4HR Centre Number Tuesday 16 January 2018 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4HR Centre Number Tuesday 16 January 2018 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, pair of compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Thursday 25 May 2017 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Thursday 25 May 2017 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper
GCSE style questions arranged by topic
 Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edecel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics A* type questions Model Answers GCSE style questions arranged by topic Higher Tier
Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edecel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics A* type questions Model Answers GCSE style questions arranged by topic Higher Tier
4306/1H. General Certificate of Secondary Education November MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 4306/1H Higher Tier Paper 1 Non-calculator
 Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education November 2009 MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 4306/1H Higher Tier Paper
Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education November 2009 MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 4306/1H Higher Tier Paper
1.30 pm 2.30 pm. Mathematics Module M4 Paper 1 (Non-calculator) Higher Tier [GMM41] 1 hour.
![1.30 pm 2.30 pm. Mathematics Module M4 Paper 1 (Non-calculator) Higher Tier [GMM41] 1 hour. 1.30 pm 2.30 pm. Mathematics Module M4 Paper 1 (Non-calculator) Higher Tier [GMM41] 1 hour.](/thumbs/89/98210090.jpg) Centre Number 71 Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2006 Mathematics Module M4 Paper 1 (Non-calculator) Higher Tier [GMM41] GMM41 MONDAY 5 JUNE 1.30 pm 2.30 pm TIME 1 hour. INSTRUCTIONS
Centre Number 71 Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2006 Mathematics Module M4 Paper 1 (Non-calculator) Higher Tier [GMM41] GMM41 MONDAY 5 JUNE 1.30 pm 2.30 pm TIME 1 hour. INSTRUCTIONS
Mock GCSE Paper Calculator allowed for all questions
 Foundation Higher Mock GCSE Paper Calculator allowed for all questions MATHSWATCH Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Name: Question number Marks Score Question number Marks Score 1 3 14 3 2 2 15 4 3 2 16 8 4 5 17
Foundation Higher Mock GCSE Paper Calculator allowed for all questions MATHSWATCH Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Name: Question number Marks Score Question number Marks Score 1 3 14 3 2 2 15 4 3 2 16 8 4 5 17
Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work
 Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work The summer assignment element should take no longer than hours to complete. Your summer assignment for each course must be submitted in the relevant first
Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work The summer assignment element should take no longer than hours to complete. Your summer assignment for each course must be submitted in the relevant first
General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Pages 3 Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier 4 5 6 7 Mathematics (Linear) B Paper 1 Non-calculator
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Pages 3 Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier 4 5 6 7 Mathematics (Linear) B Paper 1 Non-calculator
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time)
 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 998 MATHEMATICS / UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions. ALL questions are of equal value.
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 998 MATHEMATICS / UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions. ALL questions are of equal value.
International GCSE Mathematics Formulae sheet Higher Tier. In any triangle ABC. Sine Rule = = Cosine Rule a 2 = b 2 + c 2 2bccos A
 Arithmetic series Sum to n terms, S n = n 2 The quadratic equation International GCSE Mathematics Formulae sheet Higher Tier [2a + (n 1)d] Area The solutions of ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where a ¹ 0 are given
Arithmetic series Sum to n terms, S n = n 2 The quadratic equation International GCSE Mathematics Formulae sheet Higher Tier [2a + (n 1)d] Area The solutions of ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where a ¹ 0 are given
Higher Tier Practice Paper 1B (Set N) Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 1MA0 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1MA0 Paper 1H (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Practice Paper 1B (Set N) Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Ruler graduated in centimetres and
1MA0 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1MA0 Paper 1H (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Practice Paper 1B (Set N) Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Ruler graduated in centimetres and
Practice Papers Set D
 Practice Papers Set D Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer
Practice Papers Set D Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer
Further Mathematics Summer work booklet
 Further Mathematics Summer work booklet Further Mathematics tasks 1 Skills You Should Have Below is the list of the skills you should be confident with before starting the A-Level Further Maths course:
Further Mathematics Summer work booklet Further Mathematics tasks 1 Skills You Should Have Below is the list of the skills you should be confident with before starting the A-Level Further Maths course:
General Certificate of Secondary Education Mathematics. Unit T4 (With calculator) Higher Tier [GMT41] TUESDAY 27 MAY, 9.15am 11.
![General Certificate of Secondary Education Mathematics. Unit T4 (With calculator) Higher Tier [GMT41] TUESDAY 27 MAY, 9.15am 11. General Certificate of Secondary Education Mathematics. Unit T4 (With calculator) Higher Tier [GMT41] TUESDAY 27 MAY, 9.15am 11.](/thumbs/89/98286845.jpg) Centre Number 71 Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 Mathematics Unit T4 (With calculator) Higher Tier [GMT41] MV18 TUESDAY 27 MAY, 9.15am 11.15am TIME 2 hours, plus your additional
Centre Number 71 Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 Mathematics Unit T4 (With calculator) Higher Tier [GMT41] MV18 TUESDAY 27 MAY, 9.15am 11.15am TIME 2 hours, plus your additional
GCSE 185/05. MATHEMATICS (2 Tier) HIGHER TIER PAPER 2. P.M. MONDAY, 2 June hours. Candidate Name. Centre Number.
 Candidate Name Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 185/05 MATHEMATICS (2 Tier) HIGHER TIER PAPER 2 P.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2008 2 hours For Examiner s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
Candidate Name Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 185/05 MATHEMATICS (2 Tier) HIGHER TIER PAPER 2 P.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2008 2 hours For Examiner s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time)
 N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 996 MATHEMATICS /3 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions. ALL
N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 996 MATHEMATICS /3 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions. ALL
81-E 2. Ans. : 2. Universal set U = { 2, 3, 5, 6, 10 }, subset A = { 5, 6 }. The diagram which represents A / is. Ans. : ( SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK )
 81-E 2 General Instructions : i) The question-cum-answer booklet contains two Parts, Part A & Part B. ii) iii) iv) Part A consists of 60 questions and Part B consists of 16 questions. Space has been provided
81-E 2 General Instructions : i) The question-cum-answer booklet contains two Parts, Part A & Part B. ii) iii) iv) Part A consists of 60 questions and Part B consists of 16 questions. Space has been provided
GCSE Mathematics Calculator Higher Tier Free Practice Paper 1 hour 45 minutes
 First Name Last Name Date Total Marks / 100 marks MathsMadeEasy GCSE Mathematics Calculator Higher Tier Free Practice Paper 1 hour 45 minutes Answers at: http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/gcsemathspastpapers-higher.htm
First Name Last Name Date Total Marks / 100 marks MathsMadeEasy GCSE Mathematics Calculator Higher Tier Free Practice Paper 1 hour 45 minutes Answers at: http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/gcsemathspastpapers-higher.htm
COMMON UNITS OF PERIMITER ARE METRE
 MENSURATION BASIC CONCEPTS: 1.1 PERIMETERS AND AREAS OF PLANE FIGURES: PERIMETER AND AREA The perimeter of a plane figure is the total length of its boundary. The area of a plane figure is the amount of
MENSURATION BASIC CONCEPTS: 1.1 PERIMETERS AND AREAS OF PLANE FIGURES: PERIMETER AND AREA The perimeter of a plane figure is the total length of its boundary. The area of a plane figure is the amount of
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4H Centre Number Tuesday 19 January 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4H Centre Number Tuesday 19 January 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number
Make the Grade. A Programme for Success. Target Grade A
 Make the Grade A Programme for Success Target Grade A MAKE THE GRADE NUMBER 1. a) Find the Highest Common Factor of 36 and 84 b) Find the Least Common Multiple of 28 and 42 2. a) Write the following numbers
Make the Grade A Programme for Success Target Grade A MAKE THE GRADE NUMBER 1. a) Find the Highest Common Factor of 36 and 84 b) Find the Least Common Multiple of 28 and 42 2. a) Write the following numbers
Methods in Mathematics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Monday 10 November 2014
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Monday 10 November 2014
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Electronic calculator
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Electronic calculator
2016 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW
 FEB EXAM 06 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW Find the values of k for which the line y 6 is a tangent to the curve k 7 y. Find also the coordinates of the point at which this tangent touches the curve.
FEB EXAM 06 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW Find the values of k for which the line y 6 is a tangent to the curve k 7 y. Find also the coordinates of the point at which this tangent touches the curve.
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 4 4 0 0 4 H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 4400/4H London Examinations IGCSE Mathematics Paper 4H Higher Tier Tuesday 16 November 2010 Morning Time: 2 hours
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 4 4 0 0 4 H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 4400/4H London Examinations IGCSE Mathematics Paper 4H Higher Tier Tuesday 16 November 2010 Morning Time: 2 hours
Paper Reference. Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 4 (Calculator) Monday 14 November 2011 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 1 3 8 0 4 H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 1380/4H Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 4 (Calculator) Higher Tier Monday 14 November 2011 Morning
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 1 3 8 0 4 H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 1380/4H Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Paper 4 (Calculator) Higher Tier Monday 14 November 2011 Morning
Working Out Your Grade
 Working Out Your Grade Please note: these files are matched to the most recent version of our book. Don t worry you can still use the files with older versions of the book, but the answer references will
Working Out Your Grade Please note: these files are matched to the most recent version of our book. Don t worry you can still use the files with older versions of the book, but the answer references will
GCSE Mathematics Non-Calculator Higher Tier Mock 1, paper 1 1 hour 45 minutes. Materials needed for examination
 First Name Last Name Date Total Marks / 100 marks MathsMadeEasy GCSE Mathematics Non-Calculator Higher Tier Mock 1, paper 1 1 hour 45 minutes 3 Instructions Write your name and other details in the boxes
First Name Last Name Date Total Marks / 100 marks MathsMadeEasy GCSE Mathematics Non-Calculator Higher Tier Mock 1, paper 1 1 hour 45 minutes 3 Instructions Write your name and other details in the boxes
Geometry Midterm Exam Review 3. Square BERT is transformed to create the image B E R T, as shown.
 1. Reflect FOXY across line y = x. 3. Square BERT is transformed to create the image B E R T, as shown. 2. Parallelogram SHAQ is shown. Point E is the midpoint of segment SH. Point F is the midpoint of
1. Reflect FOXY across line y = x. 3. Square BERT is transformed to create the image B E R T, as shown. 2. Parallelogram SHAQ is shown. Point E is the midpoint of segment SH. Point F is the midpoint of
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4H Centre Number Monday 1 January 015 Afternoon Time: hours Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4H Centre Number Monday 1 January 015 Afternoon Time: hours Candidate Number
(b) Find the value of 25 (2) June 2011 Unit 2 (Modular) Higher Non- Calculator- Q15
 1.1 (a) Find the value of 5 0 1 3 (b) Find the value of 27 (c) Find the value of 2 3 1.2 Write down the value of (i) 7 0 (ii) 5 1 1 2 (iii) 9 March 2012 Unit 2 (Modular) Higher Non-Calculator Q11 (Total
1.1 (a) Find the value of 5 0 1 3 (b) Find the value of 27 (c) Find the value of 2 3 1.2 Write down the value of (i) 7 0 (ii) 5 1 1 2 (iii) 9 March 2012 Unit 2 (Modular) Higher Non-Calculator Q11 (Total
Mathematics (Linear) 4365/1H
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2014 Mathematics (Linear)
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2014 Mathematics (Linear)
HIGHER GCSE MATHS 2014 PRACTISE QUESTIONS FOR THE CALCULATOR PAPER
 HIGHER GCSE MATHS 2014 PRACTISE QUESTIONS FOR THE CALCULATOR PAPER 1 (a) Use your calculator to work out 21.5 5.8 2.36 Write down all the figures on your calculator display. (b) Write down your answer
HIGHER GCSE MATHS 2014 PRACTISE QUESTIONS FOR THE CALCULATOR PAPER 1 (a) Use your calculator to work out 21.5 5.8 2.36 Write down all the figures on your calculator display. (b) Write down your answer
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3HR Centre Number Monday 8 January 2018 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3HR Centre Number Monday 8 January 2018 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
TEST CODE FORM TP JANUARY 2015 C A R I B B E A N E X A M I N A T I O N S C O U N C I L
 TEST CODE 01234020 FORM TP 2015017 JANUARY 2015 C A R I B B E A N E X A M I N A T I O N S C O U N C I L CARIBBEAN SECONDARY EDUCATION CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Paper 02 General Proficiency 2
TEST CODE 01234020 FORM TP 2015017 JANUARY 2015 C A R I B B E A N E X A M I N A T I O N S C O U N C I L CARIBBEAN SECONDARY EDUCATION CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Paper 02 General Proficiency 2
GCSE Mathematics (Linear) Formulae: Higher Tier
 Name: Target Test 2 GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Formulae: Higher Tier You must not write on this formulae page. Anything you write on this formulae page will gain NO credit. Volume of a prism = area
Name: Target Test 2 GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1380 Formulae: Higher Tier You must not write on this formulae page. Anything you write on this formulae page will gain NO credit. Volume of a prism = area
Mathematics Paper 1 (Non-Calculator)
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Mock Set 2 Spring 2017 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Higher
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Mock Set 2 Spring 2017 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Higher
Mathematics A Level 1/2 Paper 2H
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Level 1/2 Paper 2H Specimen Paper Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference 4MA1/2H
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Level 1/2 Paper 2H Specimen Paper Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference 4MA1/2H
2016 Calculator Test 1 Name:
 2016 Calculator Test 1 Name: GCSE Mathematics 1MA0 Formulae: Higher Tier You must not write on this formulae page. Anything you write on this formulae page will gain NO credit. Volume of prism = area of
2016 Calculator Test 1 Name: GCSE Mathematics 1MA0 Formulae: Higher Tier You must not write on this formulae page. Anything you write on this formulae page will gain NO credit. Volume of prism = area of
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4HR Centre Number Monday 12 January 2015 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4HR Centre Number Monday 12 January 2015 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Sp Assume: Previous coverage up to Level 8
 Assume: Previous coverage up to Level 8 Recap: Levels 7 and 8 Core: Higher Levels Hrs Topic Notes Eamples References Page (3). INDICES: STANDARD FORM R: Inde notation Positive integer powers only 5 3 4
Assume: Previous coverage up to Level 8 Recap: Levels 7 and 8 Core: Higher Levels Hrs Topic Notes Eamples References Page (3). INDICES: STANDARD FORM R: Inde notation Positive integer powers only 5 3 4
Mathematics A A* Type Questions 1H
 Write our name here Surname Other names In the stle of: Edecel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A A* Tpe Questions 1H Etra topics that occur less frequentl, for students working towards an A* Candidate Number
Write our name here Surname Other names In the stle of: Edecel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A A* Tpe Questions 1H Etra topics that occur less frequentl, for students working towards an A* Candidate Number
Methods in Mathematics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Tuesday 17 June 2014 Morning
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Tuesday 17 June 2014 Morning
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel Certificate Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3H Friday 10 May 2013 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel Certificate Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3H Friday 10 May 2013 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper
Mathematics A *P49304A0128* Pearson Edexcel GCSE P49304A. Paper 2 (Calculator) Higher Tier. Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Wednesday 2 November 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Wednesday 2 November 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Wednesday 2 November 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier
GCSE Mathematics Calculator Higher Tier Mock 2, paper 2 ANSWERS. 1 hour 45 minutes. Legend used in answers
 MathsMadeEasy GCSE Mathematics Calculator Higher Tier Mock 2, paper 2 ANSWERS 1 hour 45 minutes 3 Legend used in answers Blue dotted boxes instructions or key points Start with a column or row that has
MathsMadeEasy GCSE Mathematics Calculator Higher Tier Mock 2, paper 2 ANSWERS 1 hour 45 minutes 3 Legend used in answers Blue dotted boxes instructions or key points Start with a column or row that has
Paper Reference. 5525/05 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A Paper 5 (Non-Calculator) Monday 5 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 5 5 2 5 0 5 Signature Paper Reference(s) 5525/05 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 5 (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Examiner s use only Team
Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 5 5 2 5 0 5 Signature Paper Reference(s) 5525/05 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 5 (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Examiner s use only Team
Methods in Mathematics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Centre Number Candidate Number Edexcel GCSE Methods in Mathematics Unit 2: Methods 2 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Tuesday 21 June 2011 Morning Time:
Write your name here Surname Other names Centre Number Candidate Number Edexcel GCSE Methods in Mathematics Unit 2: Methods 2 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Tuesday 21 June 2011 Morning Time:
Methods in Mathematics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Monday 17 June 2013 Morning Time:
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Monday 17 June 2013 Morning Time:
*P40669A02024* Diagram NOT accurately drawn A O C. In the diagram A LV WKH SRLQW í B is the point (0, 4) C LV WKH SRLQW í
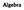 Algebra 16 y Diagram NOT accurately drawn B A O C x In the diagram A LV WKH SRLQW í B is the point (0, 4) C LV WKH SRLQW í Find an equation of the line that passes through C and is perpendicular to AB....
Algebra 16 y Diagram NOT accurately drawn B A O C x In the diagram A LV WKH SRLQW í B is the point (0, 4) C LV WKH SRLQW í Find an equation of the line that passes through C and is perpendicular to AB....
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3H Centre Number Monday 11 January 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3H Centre Number Monday 11 January 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number
GCSE Mathematics. Higher Tier. Paper 3J (Non-Calculator) Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes. For Edexcel. Name
 For Edexcel Name GCSE Mathematics Paper 3J (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Materials required Ruler, protractor, compasses, pen, pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used. Instructions
For Edexcel Name GCSE Mathematics Paper 3J (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Materials required Ruler, protractor, compasses, pen, pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used. Instructions
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4HR Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4HR Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
BUMPER BETWEEN PAPERS 2 and 3 PRACTICE PAPER (Q1 to Q32)
 BUMPER BETWEEN PAPERS 2 and 3 PRACTICE PAPER (Q1 to Q32) HIGHER TIER (Summer 2017) QUESTIONS Not A best Guess paper. Neither is it a prediction... only the examiners know what is going to come up! Fact!
BUMPER BETWEEN PAPERS 2 and 3 PRACTICE PAPER (Q1 to Q32) HIGHER TIER (Summer 2017) QUESTIONS Not A best Guess paper. Neither is it a prediction... only the examiners know what is going to come up! Fact!
General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June Time allowed 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark Mathematics General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2015 43603H
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark Mathematics General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 2015 43603H
GCSE style questions arranged by topic
 Write our name here Surname Other names In the stle of: Pearson Edecel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics A* tpe questions GCSE stle questions arranged b topic Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write our name here Surname Other names In the stle of: Pearson Edecel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics A* tpe questions GCSE stle questions arranged b topic Higher Tier Paper Reference
Instructions. Information. Advice
 For each question in this paper, less than 10% of Higher Tier students gained full marks can you do so? Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page
For each question in this paper, less than 10% of Higher Tier students gained full marks can you do so? Instructions Information Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page
184/09 MATHEMATICS HIGHER TIER PAPER 1. P.M. MONDAY, 4 June (2 Hours) CALCULATORS ARE NOT TO BE USED FOR THIS PAPER
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number WELSH JOINT EDUCATION COMMITTEE General Certificate of Secondary Education CYD-BWYLLGOR ADDYSG CYMRU Tystysgrif Gyffredinol Addysg Uwchradd 184/09 MATHEMATICS
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number WELSH JOINT EDUCATION COMMITTEE General Certificate of Secondary Education CYD-BWYLLGOR ADDYSG CYMRU Tystysgrif Gyffredinol Addysg Uwchradd 184/09 MATHEMATICS
 Geometry 3 SIMILARITY & CONGRUENCY Congruency: When two figures have same shape and size, then they are said to be congruent figure. The phenomena between these two figures is said to be congruency. CONDITIONS
Geometry 3 SIMILARITY & CONGRUENCY Congruency: When two figures have same shape and size, then they are said to be congruent figure. The phenomena between these two figures is said to be congruency. CONDITIONS
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4H Centre Number Tuesday 17 January 2017 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 4H Centre Number Tuesday 17 January 2017 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
GCSE Mathematics. Higher Tier. Paper 3G (Non-Calculator) Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes. For Edexcel. Name
 For Edexcel Name GCSE Mathematics Paper 3G (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Materials required Ruler, protractor, compasses, pen, pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used. Instructions
For Edexcel Name GCSE Mathematics Paper 3G (Non-Calculator) Higher Tier Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Materials required Ruler, protractor, compasses, pen, pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used. Instructions
Year 12 into 13 Maths Bridging Tasks
 Year 1 into 13 Maths Bridging Tasks Topics covered: Surds Indices Curve sketching Linear equations Quadratics o Factorising o Completing the square Differentiation Factor theorem Circle equations Trigonometry
Year 1 into 13 Maths Bridging Tasks Topics covered: Surds Indices Curve sketching Linear equations Quadratics o Factorising o Completing the square Differentiation Factor theorem Circle equations Trigonometry
Mathematics A Paper 3HR
 P45864A 2016 Pearson Education Ltd. 1/1/1/1/ Write your name here Surname Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3HR Thursday 26 May 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Centre Number Other names
P45864A 2016 Pearson Education Ltd. 1/1/1/1/ Write your name here Surname Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 3HR Thursday 26 May 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Centre Number Other names
Higher. Ch 19 Pythagoras, Trigonometry and Vectors. Bilton
 Higher Ch 19 Pythagoras, Trigonometry and Vectors Bilton Questions Q1. Triangle ABC has perimeter 20 cm. AB = 7 cm. BC = 4 cm. By calculation, deduce whether triangle ABC is a right angled triangle. (Total
Higher Ch 19 Pythagoras, Trigonometry and Vectors Bilton Questions Q1. Triangle ABC has perimeter 20 cm. AB = 7 cm. BC = 4 cm. By calculation, deduce whether triangle ABC is a right angled triangle. (Total
Part (1) Second : Trigonometry. Tan
 Part (1) Second : Trigonometry (1) Complete the following table : The angle Ratio 42 12 \ Sin 0.3214 Cas 0.5321 Tan 2.0625 (2) Complete the following : 1) 46 36 \ 24 \\ =. In degrees. 2) 44.125 = in degrees,
Part (1) Second : Trigonometry (1) Complete the following table : The angle Ratio 42 12 \ Sin 0.3214 Cas 0.5321 Tan 2.0625 (2) Complete the following : 1) 46 36 \ 24 \\ =. In degrees. 2) 44.125 = in degrees,
