Loop parallelization using compiler analysis
|
|
|
- Hillary Pearson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Loop parallelization using compiler analysis
2 Which of these loops is parallel? How can we determine this automatically using compiler analysis?
3 Organization of a Modern Compiler Source Program Front-end syntax analysis + type-checking + symbol table High-level Intermediate Representation loops,array references are preserved) Middle1 loop-level transformations Low-level Intermediate Representation array references converted into low level operations, loops converted to control flow) Low-level intermediate Representation Middle2 conventional optimizations Back-end Assembly Code register allocation instruction selection
4 "! # $ ) * * +, # *.- / / =< > A 2 CB D@EFG IHE J KML N IOE PE J Q Q DSRT Q Q D N IOE NU VW U H W O QC XE OO U CN E N I IXIO E C E N I O Q ZHH F V U I W NU O QC Z[E I N Q I X JJ J Q D OQ Q G J Q Q D N IOE / 01 \ 3 4 ] \ \ 3 ^ _ 1 ` ] \ \ / 01 a 3 \< 4 ] a \ 3 ] a \ b ] \ \ / 01 a 3 \< 4 / 01 c 3 \< 4 a ] a c ed 3 ] a \? ] c \ f
5 GF Q ZH OG Q F J IOEN PE h Z g N QVR D@EFG IHE K L J Q D OQ
6 Š ŒŒŒ # o ), l # # $ ˆ Š ˆ. Š ˆ. Š ˆ Š ˆ. Š Œ ŒŒ Ž ˆ. oƒ + ) # J DO I = 1, N DO J = 1,M S M 1 1 N I # ) #! * #! * - ƒ!
7 Intuition about systems of linear inequalities Equality line 2D), plane 3D), hyperplane > 3D) Inequality half-plane 2D), half-space>2d) y 3x+4y = 12 x 3x + 4y <= 12 Region described by inequality is convex if two points are in region, all points in between them are in region)
8 Intuition about systems of linear inequalities Conjunction of inequalties = intersection of half-spaces => some convex region y <= 4 y x >= - 3x+4y <= 12 x 3x - 3y <= 9 Region described by inequalities is a convex polyhedron if two points are in region, all points in between them are in region)
9 $ + * + + * $, * - + # # + * ) - n ) #, + ) # ) - k # # # * $ + m # # -
10 ± ² ³ ² µ ² ± µ š ž ¹ œ ž Ÿ º»¼»œ ½ ½ ¾ ¾ ¾ ž ¹ ¾ ¾ º¾»»œ ½ ½ ¾ ¾ p # À # # * Á  Á à p Ä Á Â Ä Á Ã Ä Ž ÅÇÆur ts t ~ uw ut vt È É p Ê Á Â Ë Á à Šy v Ì vt vuu ÍÎ w { v s r xw É p #! # # * Á Ï Á Ð p Ä Á ÏÒÑ Á Ð Ä Ž Å u vt È t ~ uw t ruæ ts É p Ê Á Ð Ë Á Ï Å y v Ì vt vuu ÍÎ w { v s r xw É p # + + # # * Á  Á  p Ä Á Â Ñ Á Â Ä Ž ÅÇÆur rts x z u } uwv Ì uw utè É p Ê Á Â Ê Á  Šy v Ì vt vuu Í Î w { v s r xw É f
11 í ä ä î è æè é ä ä ì è æè ä ä è æè Ú Û Ú Û Û Ú Û Ú Û Û Š # # Á  Á à à ½ ½ ¾ ¾ ½ ž Ÿ ± ³ ðï ã Ü å ß æëê ã Ü å ß ã Ü å ß æëê ã Ü å ß ã Ü å ß æ ç ã Ü å ß ß â Û à Þ Þ Ü â Ú Þ Þ ß Ý Ûáà Þ Þ Ü Ý Ú Þ Þ Ù o ) # # - À # * ˆØ  ˆ ž ¹ ¾ ¾ º¾»Õ»œ Ÿ ½ Ÿ Ö»œ Ÿ º»¼»œ Ÿ Ÿ»œ Ÿ ½ ½ ¾ ¾ ¾ š ž ¹ ž Ÿ Ô ¹ ¹ š ž ¹ œ ž ¹ ¹ ² ³ ² µ ² ² Óµ ± µ
12 ø ö ù óø ï òñ óô õò ó úö ù úò öúò üúû ûõò úý öúþ ò ú ö õò õÿ ø ü ÿ
13 ï
14 ! " $# ) ) * +, * +, / < ê < = >? û? ô ûõò úý >@ ô óóúò õ ü BA < < = < = < ï C
15 0D BA < < = < = < ûõò úý úe üüú ú ö òô úó? G H I KJ õ ü F ÿÿ ü> L L L L L L L A A < A < A < < M M M M M M M N O O O O O O O P A A A Q R R R R R R R S ï T
16 ! U " $# ) ) " $# V ) ) * + V -. *. + XW V/ Z [ \ ] Z [ \ZB^_ a`i b c d egf a` b _h \ A i = i j ò kú@ óÿ úe ô õ ù? ô öú@ ] òô ó òô úó ú@ ú l ø õÿ ô üúóô m ôò ú l ø õÿ ô üúóô ï n
17 oqp r sut r vxw o p y s t y v z p r { p y } oop r p y vq~ o t r { t y vv z 9 BA i = i ƒ i 9 BA i = i 0 0 ˆ
18 0 4 " $# ) ) " $# V * + V -. *. + XW V/ -... Z [ \ ] Z [ \ZB^_ a`i b c d egf a` b _h \ BA i = i ˆŠ
19 0 Œ Ž Ž š š œ š ž šÿ š Ÿœ š š š Z \ < Z \ Z \ < Z \ j ª k «[ < ª G ª ± ² F ² ª ³ ² ˆµ
20 ˆ ˆ Min s and max s in loop bounds mayseem weird, but actually they describe general polyhedral iteration spaces! J U1 L1 L2 U2 I For a given I, the J co-ordinate of a point in the iteration space of the loop nest satisfies maxl1i),l2i)) <= J <= minu1i),u2i))
21 ¹ º» ¼ ½» ¾ ¹ ¼ º ½ ½»¹ ¹ ¾ ¹ ¼ À º º Á 2 À¼ ¾ Ž àŽ ÃÂ Ä Å ª ³ ² Æ«@ ª Ç ª? È? ³ ª > ² ɲ ² > ² ²³ Ê ª G ÌË ÌË A Æ? ³ ³ l ³ k Å ² ª ª ²³ È F³ ³ Å ª ³ ² Ê k Å F Ç Ç ª «F³ >? k G ª ³ ² ª ² È F Ç Í > ² ų Ê Î Î ³ ª Î Î ³ ª ³ ² Å ²³ l Å ³ ª ³ ˆÏ
22 Ð À Ñ» ¹ ¹¼ ¼ ¹ º ¼ ½ ¼ ¹ ¾ ¾» 2» ¼ 2» ¹»»¹ ¼ ¾ º ½» Ñ ¼ ¾» º ½ ¼ ¾ º» 0 ¾» 0 ¼ ¹ ¼» ¾ À»¹ ¼» ¾ Ñ ¾» ~ Ò ÓKÔ 4 Õ 2Ö 2Ö ¾ Ö» 0 ¹ ¾ ½ ¹ ¾¹ Ö¼ º Ö 4 ؈
23 ˆ C Presentation sequence - one equation, several variables 2 x + 3 y = - several equations, several variables 2x + 3 y + z = 3x + 4 y = 3 - equations inequalities 2x + 3 y = x <= y <= -9 Diophatine equations use integer Gaussian elimination Solve equalities first then use Fourier-Motzkin elimination
24 ˆ T One equation, many variables Thm The linear Diophatine equation a1 x1 + a2 x an xn = c has integer solutions iff gcda1,a2,...,an) divides c. Examples 1) 2x = 3 No solutions 2) 2x = One solution x = 3 3) 2x + y = 3 GCD2,1) = 1 which divides 3. Solutions x = t, y = 3-2t) 4) 2x + 3y = 3 GCD2,3) = 1 which divides 3. Let z = x + floor3/2) y = x + y Rewrite equation as 2z + y = 3 Solutions z = t => x = 3t - 3) y = 3-2t) y = 3-2t) Intuition Think of underdetermined systems of eqns over reals. Caution Integer constraint => Diophantine system may have no solns
25 ˆ n Thm The linear Diophatine equation a1 x1 + a2 x an xn = c has integer solutions iff gcda1,a2,...,an) divides c. Proof Base case WLOG, assume that all coefficients a1,a2,...an are positive. We prove only the IF case by induction, the proof in the other direction is trivial. Induction is on minsmallest coefficient, number of variables). If # of variables = 1), then equation is a1 x1 = c which has integer solutions if a1 divides c. If smallest coefficient = 1), then gcda1,a2,...,an) = 1 which divides c. Wlog, assume that a1 = 1, and observe that the equation has solutions of the form c - a2 t2 - a3 t an tn, t2, t3,...tn). Inductive case Suppose smallest coefficient is a1, and let t = x1 + floora2/a1) x flooran/a1) xn In terms of this variable, the equation can be rewritten as a1) t + a2 mod a1) x an mod a1) xn = c 1) where we assume that all terms with zero coefficient have been deleted. Observe that 1) has integer solutions iff original equation does too. Now gcda,b) = gcda mod b, b) => gcda1,a2,...,an) = gcda1, a2 mod a1),..,an mod a1)) => gcda1, a2 mod a1),..,an mod a1)) divides c. If a1 is the smallest co-efficient in 1), we are left with 1 variable base case. Otherwise, the size of the smallest co-efficient has decreased, so we have made progress in the induction.
26 Ï Summary Eqn a1 x1 + a2 x an xn = c - Does this have integer solutions? = Does gcda1,a2,...,an) divide c?
27 Ï ˆ Systems of Diophatine Equations Key idea use integer Gaussian elimination Example 2x + 3y + 4z = x - y + 2z = => x y z = It is not easy to determine if this Diophatine system has solutions. Easy special case lower triangular matrix x y = => x = y = 3 z z = arbitrary integer Question Can we convert general integer matrix into equivalent lower triangular system? INTEGER GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION
28 Ï ã Unimodular Column Operations a) Interchange two columns b) Negate a column Check Let x,y satisfy first eqn. Let x,y satisfy second eqn. x = y, y = x Check x = x, y = - y c) Add an integer multiple of one column to another n = Check x = x + n y y = y
29 Ï ä Example x y z = => => => => x x = = => y y = 3 z z = t => x y z = t 4-2t = -1 t
30 $ Systems of Inequalities 1
31 Given system of inequalities of the form Ax b $ Goals determine if system has an integer solution enumerate all integer solutions 2
32 bounds for x 2) and 3) Upper bounds for x 1) and 4) Lower bounds for y 2) and 4) Upper bounds for y 1) and 3) Lower $ Running example 3x + 4y 1 1) 4x + y 2) 4x y 20 3) 2x 3y 9 4) 3
33 $ MATLAB graphs y 2x 3y= 9 4x+y= x+4y=1 4x y= x 4
34 $ Code for enumerating integer points in polyhedron see graph) Outer loop, Inner loop X DO =d4=3e,b4=13c DO X=dmax1=3 4y=3 9=2 + 3y=2)e,bmin + y=4 14 y=4)c... Outer loop X, Inner loop DO X=1, 9 DO =dmax4 3y=4 4x 20)=)e,bmin 4x= 2x + 9)=3)c... How do we can determine loop bounds?
35 elimination variable elimination technique for Fourier-Motzkin inequalities $ 3x + 4y 1 ) 4x + y ) 4x y 20 ) 2x 3y 9 ) Let us project out x. First, express all inequalities as upper or lower bounds on x. x 1=3 4y=3 9) x 14 y=4 10) x + y=4 11) x 9=2 + 3y=2 12)
36 any y, if there is an x that satises all inequalities, then every For bound on x must be less than or equal to every upper bound lower a new system of inequalities from each pair upper,lower) Generate bounds. $ on x. + y=4 1=3 4y=3Inequalities3 1) + y=4 9=2 + 3y=2Inequalities3 4) 14 y=4 1=3 4y=3Inequalities2 1) 14 y=4 9=2 + 3y=2Inequalities2 4)
37 $ Simplify y 4=3 y 3 y 104= y 4=13 => max4=3 3) y min104= 4=13) => 4=3 y 4=13 This means there are rational solutions to original system of inequalities.
38 $ We can now express solutions in closed form as follows 4=3 y 4=3 max1=3 4y=3 9=2 + 3y=2) x min + y=4 14 y=4) 9
39 elimination iterative algorithm Fourier-Motzkin step Iterative $ obtain reduced system by projecting out a variable if reduced system has a rational solution, so does the original Termination no variables left Projection along variable x Divide inequalities into three categories a 1 y + a 2 z + c 1 no x) b 1 x c 2 + b 2 y + b 3 z + upper bound) d 1 x c 3 + d 2 y + d 3 z + lower bound) New system of inequalities All inequalities that do not involve x Each pair lower,upper) bounds gives rise to one inequality b 1 [c 3 + d 2 y + d 3 z + ] d 1 [c 2 + b 2 y + b 3 z + ] 10
40 If y 1 z 1 ) satises the reduced system, then Theorem 1 y 1 z 1 ) satises the original system, where x 1 is a rational x $ number between min1=b 1 c 2 + b 2 y 1 + b 3 z 1 + ) ) over all upper bounds) and max1=d 1 c 3 + d 2 y 1 + d 3 z 1 + ) ) over all lower bounds) Proof trivial 11
41 If reduced system has no integer solutions, neither does Corollary original system. the true Reduced system has integer solutions => original system Not too. does problem Multiplying one inequality by b 1 and other by d 1 is Key guaranteed to preserve "integrality" cf. equalities) not projection If all upper bound coecients b i Exact coecients d i bound $ What can we conclude about integer solutions? original system - no integers in original polyhedron - projected system contains integers [ ] X projected system or all lower happen to be 1, then integer solution to reduced system implies integer solution to original system. 12
42 because there are integers between 4/3 and 4/13, we cannot Just there are integers in feasible region. assume if gap between lower and upper bounds is greater than or However, to 1 for some integer value of y, there must be an integer in equal More accurate algorithm for determining existence $ y 2x 3y= 9 4x+y= x+4y=1 4x y= x feasible region. 1
43 shadow region of y for which gap between upper and lower Dark of x is guaranteed to be greater than or equal to 1. bounds $ Determining dark shadow region Ordinary FM elimination x u, x l => u l Dark shadow x u, x l => u l + 1 1
44 $ For our example, dark shadow projection along x gives system + y=4 1=3 4y=3 + 1Inequalities3 1) + y=4 9=2 + 3y=2 + 1Inequalities3 4) 14 y=4 1=3 4y=3 + 1Inequalities2 1) 14 y=4 9=2 + 3y=2 + 1Inequalities2 4) => /13 y 1/3 There is an integer value of y in this range => integer in polyhedron. 1
45 More accurate estimate of dark shadow y x = 1/b1c2+b2y+b3z+...) y1 x = 1/d1c3+d2y+d3z+...) gap is some multiple of 1/b1 gap is some multiple of 1/d1 $ For integer values of y1,z1,..., there is no integer value x1 between lower and upper bounds if 1/d1c3+d2y1+d3z1+...) - 1/b1c2+b2y1+b3z1+...) +1/b1+1/d1 <= 1 This means there is an integer between upper and lower bounds if 1/d1c3+d2y1+d3z1+...) - 1/b1c2+b2y1+b3z1+...) +1/b1+1/d1 > 1 To convert this to >=, notice that smallest change of lhs value is 1/b1d1. So the inequality is => 1/d1c3+d2y1+d3z1+...) - 1/b1c2+b2y1+b3z1+...) +1/b1+1/d1 >= 1 + 1/b1d1 1/d1c3+d2y1+d3z1+...) - 1/b1c2+b2y1+b3z1+...) >= 1-1/b1)1-1/d1) 19
46 If b 1 = 1) or d 1 = 1), dark shadow constraint = real Note constraint shadow $ 20
47 $ Example 3x 1 4y 4x 20 + y Real shadow 20 + y) y) Dark shadow 20 + y) y) 12 Dark shadow improved) 20 + y) y) 21
48 may still be integer points nestled closely between an upper There lower bound. and $ What if dark shadow has no integers? dark shadow [ ] X projected system 22
49 One enumeration idea splintering dark shadow $ X Scan the corners with hyperplanes, looking for integer points. Generate a succession of problems in which each lower bound is replaced with a sequence of hyperplanes. How many hyperplanes are needed? Equation for lower bound x = 1/b1c2+b2y+b3z+...) Hyperplanes x = 1/b1c2+b2y+b3z+...) x = 1/b1c2+b2y+b3z+...)+ 1/b1 x = 1/b1c2+b2y+b3z+...)+ 2/b1 x = 1/b1c2+b2y+b3z+...)+ 3/b1... x = 1/b1c2+b2y+b3z+...)+ 1 in dark shadow region if this is integer, so is ) 24
50 Summary Two integer linear programming problems Is there an integer point within a polyhedron Ax b where A is an integer matrix and b is an integer vector? used for dependence analysis Enumerate the integer points within a polyhedron Ax b where A is an integer matrix and b is an integer vector. used for code generation after affine loop transformation
Front-end. Organization of a Modern Compiler. Middle1. Middle2. Back-end. converted to control flow) Representation
 register allocation instruction selection Code Low-level intermediate Representation Back-end Assembly array references converted into low level operations, loops converted to control flow Middle2 Low-level
register allocation instruction selection Code Low-level intermediate Representation Back-end Assembly array references converted into low level operations, loops converted to control flow Middle2 Low-level
Organization of a Modern Compiler. Middle1
 Organization of a Modern Compiler Source Program Front-end syntax analysis + type-checking + symbol table High-level Intermediate Representation (loops,array references are preserved) Middle1 loop-level
Organization of a Modern Compiler Source Program Front-end syntax analysis + type-checking + symbol table High-level Intermediate Representation (loops,array references are preserved) Middle1 loop-level
Organization of a Modern Compiler. Front-end. Middle1. Back-end DO I = 1, N DO J = 1,M S 1 1 N. Source Program
 Organization of a Modern Compiler ource Program Front-end snta analsis + tpe-checking + smbol table High-level ntermediate Representation (loops,arra references are preserved) Middle loop-level transformations
Organization of a Modern Compiler ource Program Front-end snta analsis + tpe-checking + smbol table High-level ntermediate Representation (loops,arra references are preserved) Middle loop-level transformations
 ! " # $! % & '! , ) ( + - (. ) ( ) * + / 0 1 2 3 0 / 4 5 / 6 0 ; 8 7 < = 7 > 8 7 8 9 : Œ Š ž P P h ˆ Š ˆ Œ ˆ Š ˆ Ž Ž Ý Ü Ý Ü Ý Ž Ý ê ç è ± ¹ ¼ ¹ ä ± ¹ w ç ¹ è ¼ è Œ ¹ ± ¹ è ¹ è ä ç w ¹ ã ¼ ¹ ä ¹ ¼ ¹ ±
! " # $! % & '! , ) ( + - (. ) ( ) * + / 0 1 2 3 0 / 4 5 / 6 0 ; 8 7 < = 7 > 8 7 8 9 : Œ Š ž P P h ˆ Š ˆ Œ ˆ Š ˆ Ž Ž Ý Ü Ý Ü Ý Ž Ý ê ç è ± ¹ ¼ ¹ ä ± ¹ w ç ¹ è ¼ è Œ ¹ ± ¹ è ¹ è ä ç w ¹ ã ¼ ¹ ä ¹ ¼ ¹ ±
Framework for functional tree simulation applied to 'golden delicious' apple trees
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Theses Theses and Dissertations Spring 2015 Framework for functional tree simulation applied to 'golden delicious' apple trees Marek Fiser Purdue University
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Theses Theses and Dissertations Spring 2015 Framework for functional tree simulation applied to 'golden delicious' apple trees Marek Fiser Purdue University
An Introduction to Optimal Control Applied to Disease Models
 An Introduction to Optimal Control Applied to Disease Models Suzanne Lenhart University of Tennessee, Knoxville Departments of Mathematics Lecture1 p.1/37 Example Number of cancer cells at time (exponential
An Introduction to Optimal Control Applied to Disease Models Suzanne Lenhart University of Tennessee, Knoxville Departments of Mathematics Lecture1 p.1/37 Example Number of cancer cells at time (exponential
LA PRISE DE CALAIS. çoys, çoys, har - dis. çoys, dis. tons, mantz, tons, Gas. c est. à ce. C est à ce. coup, c est à ce
 > ƒ? @ Z [ \ _ ' µ `. l 1 2 3 z Æ Ñ 6 = Ð l sl (~131 1606) rn % & +, l r s s, r 7 nr ss r r s s s, r s, r! " # $ s s ( ) r * s, / 0 s, r 4 r r 9;: < 10 r mnz, rz, r ns, 1 s ; j;k ns, q r s { } ~ l r mnz,
> ƒ? @ Z [ \ _ ' µ `. l 1 2 3 z Æ Ñ 6 = Ð l sl (~131 1606) rn % & +, l r s s, r 7 nr ss r r s s s, r s, r! " # $ s s ( ) r * s, / 0 s, r 4 r r 9;: < 10 r mnz, rz, r ns, 1 s ; j;k ns, q r s { } ~ l r mnz,
" #$ P UTS W U X [ZY \ Z _ `a \ dfe ih j mlk n p q sr t u s q e ps s t x q s y i_z { U U z W } y ~ y x t i e l US T { d ƒ ƒ ƒ j s q e uˆ ps i ˆ p q y
 " #$ +. 0. + 4 6 4 : + 4 ; 6 4 < = =@ = = =@ = =@ " #$ P UTS W U X [ZY \ Z _ `a \ dfe ih j mlk n p q sr t u s q e ps s t x q s y i_z { U U z W } y ~ y x t i e l US T { d ƒ ƒ ƒ j s q e uˆ ps i ˆ p q y h
" #$ +. 0. + 4 6 4 : + 4 ; 6 4 < = =@ = = =@ = =@ " #$ P UTS W U X [ZY \ Z _ `a \ dfe ih j mlk n p q sr t u s q e ps s t x q s y i_z { U U z W } y ~ y x t i e l US T { d ƒ ƒ ƒ j s q e uˆ ps i ˆ p q y h
An Example file... log.txt
 # ' ' Start of fie & %$ " 1 - : 5? ;., B - ( * * B - ( * * F I / 0. )- +, * ( ) 8 8 7 /. 6 )- +, 5 5 3 2( 7 7 +, 6 6 9( 3 5( ) 7-0 +, => - +< ( ) )- +, 7 / +, 5 9 (. 6 )- 0 * D>. C )- +, (A :, C 0 )- +,
# ' ' Start of fie & %$ " 1 - : 5? ;., B - ( * * B - ( * * F I / 0. )- +, * ( ) 8 8 7 /. 6 )- +, 5 5 3 2( 7 7 +, 6 6 9( 3 5( ) 7-0 +, => - +< ( ) )- +, 7 / +, 5 9 (. 6 )- 0 * D>. C )- +, (A :, C 0 )- +,
General Neoclassical Closure Theory: Diagonalizing the Drift Kinetic Operator
 General Neoclassical Closure Theory: Diagonalizing the Drift Kinetic Operator E. D. Held eheld@cc.usu.edu Utah State University General Neoclassical Closure Theory:Diagonalizing the Drift Kinetic Operator
General Neoclassical Closure Theory: Diagonalizing the Drift Kinetic Operator E. D. Held eheld@cc.usu.edu Utah State University General Neoclassical Closure Theory:Diagonalizing the Drift Kinetic Operator
Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory
 Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory p. 1/21 Decision Making:
Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory p. 1/21 Decision Making:
QUESTIONS ON QUARKONIUM PRODUCTION IN NUCLEAR COLLISIONS
 International Workshop Quarkonium Working Group QUESTIONS ON QUARKONIUM PRODUCTION IN NUCLEAR COLLISIONS ALBERTO POLLERI TU München and ECT* Trento CERN - November 2002 Outline What do we know for sure?
International Workshop Quarkonium Working Group QUESTIONS ON QUARKONIUM PRODUCTION IN NUCLEAR COLLISIONS ALBERTO POLLERI TU München and ECT* Trento CERN - November 2002 Outline What do we know for sure?
OC330C. Wiring Diagram. Recommended PKH- P35 / P50 GALH PKA- RP35 / RP50. Remarks (Drawing No.) No. Parts No. Parts Name Specifications
 G G " # $ % & " ' ( ) $ * " # $ % & " ( + ) $ * " # C % " ' ( ) $ * C " # C % " ( + ) $ * C D ; E @ F @ 9 = H I J ; @ = : @ A > B ; : K 9 L 9 M N O D K P D N O Q P D R S > T ; U V > = : W X Y J > E ; Z
G G " # $ % & " ' ( ) $ * " # $ % & " ( + ) $ * " # C % " ' ( ) $ * C " # C % " ( + ) $ * C D ; E @ F @ 9 = H I J ; @ = : @ A > B ; : K 9 L 9 M N O D K P D N O Q P D R S > T ; U V > = : W X Y J > E ; Z
Data Dependences and Parallelization. Stanford University CS243 Winter 2006 Wei Li 1
 Data Dependences and Parallelization Wei Li 1 Agenda Introduction Single Loop Nested Loops Data Dependence Analysis 2 Motivation DOALL loops: loops whose iterations can execute in parallel for i = 11,
Data Dependences and Parallelization Wei Li 1 Agenda Introduction Single Loop Nested Loops Data Dependence Analysis 2 Motivation DOALL loops: loops whose iterations can execute in parallel for i = 11,
Examination paper for TFY4240 Electromagnetic theory
 Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4240 Electromagnetic theory Academic contact during examination: Associate Professor John Ove Fjærestad Phone: 97 94 00 36 Examination date: 16 December 2015
Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4240 Electromagnetic theory Academic contact during examination: Associate Professor John Ove Fjærestad Phone: 97 94 00 36 Examination date: 16 December 2015
Complex Analysis. PH 503 Course TM. Charudatt Kadolkar Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Complex Analysis PH 503 Course TM Charudatt Kadolkar Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati ii Copyright 2000 by Charudatt Kadolkar Preface Preface Head These notes were prepared during the lectures
Complex Analysis PH 503 Course TM Charudatt Kadolkar Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati ii Copyright 2000 by Charudatt Kadolkar Preface Preface Head These notes were prepared during the lectures
Optimal Control of PDEs
 Optimal Control of PDEs Suzanne Lenhart University of Tennessee, Knoville Department of Mathematics Lecture1 p.1/36 Outline 1. Idea of diffusion PDE 2. Motivating Eample 3. Big picture of optimal control
Optimal Control of PDEs Suzanne Lenhart University of Tennessee, Knoville Department of Mathematics Lecture1 p.1/36 Outline 1. Idea of diffusion PDE 2. Motivating Eample 3. Big picture of optimal control
Constructive Decision Theory
 Constructive Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Constructive Decision Theory p. 1/2 Savage s Approach Savage s approach to decision
Constructive Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Constructive Decision Theory p. 1/2 Savage s Approach Savage s approach to decision
B œ c " " ã B œ c 8 8. such that substituting these values for the B 3 's will make all the equations true
 System of Linear Equations variables Ð unknowns Ñ B" ß B# ß ÞÞÞ ß B8 Æ Æ Æ + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, "" " "# # "8 8 " + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, #" " ## # #8 8 # ã + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, 3" " 3# # 38 8 3 ã + 7" B" + 7# B#
System of Linear Equations variables Ð unknowns Ñ B" ß B# ß ÞÞÞ ß B8 Æ Æ Æ + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, "" " "# # "8 8 " + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, #" " ## # #8 8 # ã + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, 3" " 3# # 38 8 3 ã + 7" B" + 7# B#
Max. Input Power (W) Input Current (Arms) Dimming. Enclosure
 Product Overview XI025100V036NM1M Input Voltage (Vac) Output Power (W) Output Voltage Range (V) Output urrent (A) Efficiency@ Max Load and 70 ase Max ase Temp. ( ) Input urrent (Arms) Max. Input Power
Product Overview XI025100V036NM1M Input Voltage (Vac) Output Power (W) Output Voltage Range (V) Output urrent (A) Efficiency@ Max Load and 70 ase Max ase Temp. ( ) Input urrent (Arms) Max. Input Power
ALTER TABLE Employee ADD ( Mname VARCHAR2(20), Birthday DATE );
 !! "# $ % & '( ) # * +, - # $ "# $ % & '( ) # *.! / 0 "# "1 "& # 2 3 & 4 4 "# $ % & '( ) # *!! "# $ % & # * 1 3 - "# 1 * #! ) & 3 / 5 6 7 8 9 ALTER ; ? @ A B C D E F G H I A = @ A J > K L ; ?
!! "# $ % & '( ) # * +, - # $ "# $ % & '( ) # *.! / 0 "# "1 "& # 2 3 & 4 4 "# $ % & '( ) # *!! "# $ % & # * 1 3 - "# 1 * #! ) & 3 / 5 6 7 8 9 ALTER ; ? @ A B C D E F G H I A = @ A J > K L ; ?
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants Teaching-Learning Points A matri is an ordered rectanguar arra (arrangement) of numbers and encosed b capita bracket [ ]. These numbers are caed eements of the matri. Matri is
Matrices and Determinants Teaching-Learning Points A matri is an ordered rectanguar arra (arrangement) of numbers and encosed b capita bracket [ ]. These numbers are caed eements of the matri. Matri is
Principal Secretary to Government Haryana, Town & Country Planning Department, Haryana, Chandigarh.
 1 From To Principal Secretary to Government Haryana, Town & Country Planning Department, Haryana, Chandigarh. The Director General, Town & Country Planning Department, Haryana, Chandigarh. Memo No. Misc-2339
1 From To Principal Secretary to Government Haryana, Town & Country Planning Department, Haryana, Chandigarh. The Director General, Town & Country Planning Department, Haryana, Chandigarh. Memo No. Misc-2339
A Functional Quantum Programming Language
 A Functional Quantum Programming Language Thorsten Altenkirch University of Nottingham based on joint work with Jonathan Grattage and discussions with V.P. Belavkin supported by EPSRC grant GR/S30818/01
A Functional Quantum Programming Language Thorsten Altenkirch University of Nottingham based on joint work with Jonathan Grattage and discussions with V.P. Belavkin supported by EPSRC grant GR/S30818/01
SOLAR MORTEC INDUSTRIES.
 SOLAR MORTEC INDUSTRIES www.mortecindustries.com.au Wind Regions Region A Callytharra Springs Gascoyne Junction Green Head Kununurra Lord Howe Island Morawa Toowoomba Wittanoom Bourke Region B Adelaide
SOLAR MORTEC INDUSTRIES www.mortecindustries.com.au Wind Regions Region A Callytharra Springs Gascoyne Junction Green Head Kununurra Lord Howe Island Morawa Toowoomba Wittanoom Bourke Region B Adelaide
The University of Bath School of Management is one of the oldest established management schools in Britain. It enjoys an international reputation for
 The University of Bath School of Management is one of the oldest established management schools in Britain. It enjoys an international reputation for the quality of its teaching and research. Its mission
The University of Bath School of Management is one of the oldest established management schools in Britain. It enjoys an international reputation for the quality of its teaching and research. Its mission
A PRACTICAL ALGORITHM FOR EXACT ARRAY DEPENDENCE ANALYSIS
 A PRACTICAL ALGORITHM FOR EXACT ARRAY DEPENDENCE ANALYSIS 10/11/05 Slide 1 Introduction We describe the Omega Test which is a new method for dependence analysis. It combines new methods from integer programming
A PRACTICAL ALGORITHM FOR EXACT ARRAY DEPENDENCE ANALYSIS 10/11/05 Slide 1 Introduction We describe the Omega Test which is a new method for dependence analysis. It combines new methods from integer programming
Vectors. Teaching Learning Point. Ç, where OP. l m n
 Vectors 9 Teaching Learning Point l A quantity that has magnitude as well as direction is called is called a vector. l A directed line segment represents a vector and is denoted y AB Å or a Æ. l Position
Vectors 9 Teaching Learning Point l A quantity that has magnitude as well as direction is called is called a vector. l A directed line segment represents a vector and is denoted y AB Å or a Æ. l Position
4.3 Laplace Transform in Linear System Analysis
 4.3 Laplace Transform in Linear System Analysis The main goal in analysis of any dynamic system is to find its response to a given input. The system response in general has two components: zero-state response
4.3 Laplace Transform in Linear System Analysis The main goal in analysis of any dynamic system is to find its response to a given input. The system response in general has two components: zero-state response
Planning for Reactive Behaviors in Hide and Seek
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Center for Human Modeling and Simulation Department of Computer & Information Science May 1995 Planning for Reactive Behaviors in Hide and Seek Michael B. Moore
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Center for Human Modeling and Simulation Department of Computer & Information Science May 1995 Planning for Reactive Behaviors in Hide and Seek Michael B. Moore
Vector analysis. 1 Scalars and vectors. Fields. Coordinate systems 1. 2 The operator The gradient, divergence, curl, and Laplacian...
 Vector analysis Abstract These notes present some background material on vector analysis. Except for the material related to proving vector identities (including Einstein s summation convention and the
Vector analysis Abstract These notes present some background material on vector analysis. Except for the material related to proving vector identities (including Einstein s summation convention and the
Symbols and dingbats. A 41 Α a 61 α À K cb ➋ à esc. Á g e7 á esc. Â e e5 â. Ã L cc ➌ ã esc ~ Ä esc : ä esc : Å esc * å esc *
 Note: Although every effort ws tken to get complete nd ccurte tble, the uhtor cn not be held responsible for ny errors. Vrious sources hd to be consulted nd MIF hd to be exmined to get s much informtion
Note: Although every effort ws tken to get complete nd ccurte tble, the uhtor cn not be held responsible for ny errors. Vrious sources hd to be consulted nd MIF hd to be exmined to get s much informtion
New method for solving nonlinear sum of ratios problem based on simplicial bisection
 V Ù â ð f 33 3 Vol33, No3 2013 3 Systems Engineering Theory & Practice Mar, 2013 : 1000-6788(2013)03-0742-06 : O2112!"#$%&')(*)+),-))/0)1)23)45 : A 687:9 1, ;:= 2 (1?@ACBEDCFHCFEIJKLCFFM, NCO 453007;
V Ù â ð f 33 3 Vol33, No3 2013 3 Systems Engineering Theory & Practice Mar, 2013 : 1000-6788(2013)03-0742-06 : O2112!"#$%&')(*)+),-))/0)1)23)45 : A 687:9 1, ;:= 2 (1?@ACBEDCFHCFEIJKLCFFM, NCO 453007;
This document has been prepared by Sunder Kidambi with the blessings of
 Ö À Ö Ñ Ø Ò Ñ ÒØ Ñ Ý Ò Ñ À Ö Ñ Ò Ú º Ò Ì ÝÊ À Å Ú Ø Å Ê ý Ú ÒØ º ÝÊ Ú Ý Ê Ñ º Å º ² ºÅ ý ý ý ý Ö Ð º Ñ ÒÜ Æ Å Ò Ñ Ú «Ä À ý ý This document has been prepared by Sunder Kidambi with the blessings of Ö º
Ö À Ö Ñ Ø Ò Ñ ÒØ Ñ Ý Ò Ñ À Ö Ñ Ò Ú º Ò Ì ÝÊ À Å Ú Ø Å Ê ý Ú ÒØ º ÝÊ Ú Ý Ê Ñ º Å º ² ºÅ ý ý ý ý Ö Ð º Ñ ÒÜ Æ Å Ò Ñ Ú «Ä À ý ý This document has been prepared by Sunder Kidambi with the blessings of Ö º
ETIKA V PROFESII PSYCHOLÓGA
 P r a ž s k á v y s o k á š k o l a p s y c h o s o c i á l n í c h s t u d i í ETIKA V PROFESII PSYCHOLÓGA N a t á l i a S l o b o d n í k o v á v e d ú c i p r á c e : P h D r. M a r t i n S t r o u
P r a ž s k á v y s o k á š k o l a p s y c h o s o c i á l n í c h s t u d i í ETIKA V PROFESII PSYCHOLÓGA N a t á l i a S l o b o d n í k o v á v e d ú c i p r á c e : P h D r. M a r t i n S t r o u
Pharmacological and genomic profiling identifies NF-κB targeted treatment strategies for mantle cell lymphoma
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Med. 0, 87 9 (014) Pharmacoogica and genomic profiing identifies NF-κB targeted treatment strategies for mante ce ymphoma Rami Raha, Mareie Fric, Rodrigo Romero, Joshua M Korn, Robert
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Med. 0, 87 9 (014) Pharmacoogica and genomic profiing identifies NF-κB targeted treatment strategies for mante ce ymphoma Rami Raha, Mareie Fric, Rodrigo Romero, Joshua M Korn, Robert
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 REDCLIFF MUNICIPAL PLANNING COMMISSION FOR COMMENT/DISCUSSION DATE: TOPIC: April 27 th, 2018 Bylaw 1860/2018, proposed amendments to the Land Use Bylaw regarding cannabis
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 REDCLIFF MUNICIPAL PLANNING COMMISSION FOR COMMENT/DISCUSSION DATE: TOPIC: April 27 th, 2018 Bylaw 1860/2018, proposed amendments to the Land Use Bylaw regarding cannabis
Connection equations with stream variables are generated in a model when using the # $ % () operator or the & ' %
 7 9 9 7 The two basic variable types in a connector potential (or across) variable and flow (or through) variable are not sufficient to describe in a numerically sound way the bi-directional flow of matter
7 9 9 7 The two basic variable types in a connector potential (or across) variable and flow (or through) variable are not sufficient to describe in a numerically sound way the bi-directional flow of matter
Block-tridiagonal matrices
 Block-tridiagonal matrices. p.1/31 Block-tridiagonal matrices - where do these arise? - as a result of a particular mesh-point ordering - as a part of a factorization procedure, for example when we compute
Block-tridiagonal matrices. p.1/31 Block-tridiagonal matrices - where do these arise? - as a result of a particular mesh-point ordering - as a part of a factorization procedure, for example when we compute
$%! & (, -3 / 0 4, 5 6/ 6 +7, 6 8 9/ 5 :/ 5 A BDC EF G H I EJ KL N G H I. ] ^ _ ` _ ^ a b=c o e f p a q i h f i a j k e i l _ ^ m=c n ^
![$%! & (, -3 / 0 4, 5 6/ 6 +7, 6 8 9/ 5 :/ 5 A BDC EF G H I EJ KL N G H I. ] ^ _ ` _ ^ a b=c o e f p a q i h f i a j k e i l _ ^ m=c n ^ $%! & (, -3 / 0 4, 5 6/ 6 +7, 6 8 9/ 5 :/ 5 A BDC EF G H I EJ KL N G H I. ] ^ _ ` _ ^ a b=c o e f p a q i h f i a j k e i l _ ^ m=c n ^](/thumbs/92/108125918.jpg) ! #" $%! & ' ( ) ) (, -. / ( 0 1#2 ' ( ) ) (, -3 / 0 4, 5 6/ 6 7, 6 8 9/ 5 :/ 5 ;=? @ A BDC EF G H I EJ KL M @C N G H I OPQ ;=R F L EI E G H A S T U S V@C N G H IDW G Q G XYU Z A [ H R C \ G ] ^ _ `
! #" $%! & ' ( ) ) (, -. / ( 0 1#2 ' ( ) ) (, -3 / 0 4, 5 6/ 6 7, 6 8 9/ 5 :/ 5 ;=? @ A BDC EF G H I EJ KL M @C N G H I OPQ ;=R F L EI E G H A S T U S V@C N G H IDW G Q G XYU Z A [ H R C \ G ] ^ _ `
CONVEX OPTIMIZATION OVER POSITIVE POLYNOMIALS AND FILTER DESIGN. Y. Genin, Y. Hachez, Yu. Nesterov, P. Van Dooren
 CONVEX OPTIMIZATION OVER POSITIVE POLYNOMIALS AND FILTER DESIGN Y. Genin, Y. Hachez, Yu. Nesterov, P. Van Dooren CESAME, Université catholique de Louvain Bâtiment Euler, Avenue G. Lemaître 4-6 B-1348 Louvain-la-Neuve,
CONVEX OPTIMIZATION OVER POSITIVE POLYNOMIALS AND FILTER DESIGN Y. Genin, Y. Hachez, Yu. Nesterov, P. Van Dooren CESAME, Université catholique de Louvain Bâtiment Euler, Avenue G. Lemaître 4-6 B-1348 Louvain-la-Neuve,
: œ Ö: =? À =ß> real numbers. œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example,! is translated to :)
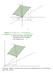 â SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö =? > @ À =ß> real numbers : SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö: =? > @ À =ß> real numbers œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example, is translated to :) á In general: Adding a vector :
â SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö =? > @ À =ß> real numbers : SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö: =? > @ À =ß> real numbers œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example, is translated to :) á In general: Adding a vector :
Advanced Restructuring Compilers. Advanced Topics Spring 2009 Prof. Robert van Engelen
 Advanced Restructuring Compilers Advanced Topics Spring 2009 Prof. Robert van Engelen Overview Data and control dependences The theory and practice of data dependence analysis K-level loop-carried dependences
Advanced Restructuring Compilers Advanced Topics Spring 2009 Prof. Robert van Engelen Overview Data and control dependences The theory and practice of data dependence analysis K-level loop-carried dependences
Lecture 16: Modern Classification (I) - Separating Hyperplanes
 Lecture 16: Modern Classification (I) - Separating Hyperplanes Outline 1 2 Separating Hyperplane Binary SVM for Separable Case Bayes Rule for Binary Problems Consider the simplest case: two classes are
Lecture 16: Modern Classification (I) - Separating Hyperplanes Outline 1 2 Separating Hyperplane Binary SVM for Separable Case Bayes Rule for Binary Problems Consider the simplest case: two classes are
Building Products Ltd. G Jf. CIN No. L26922KA199SPLC018990
 Building Products Ltd.! #$%&'( )*$+.+/'12 3454*67 89 :;= >?? @*;;* ABCDEFGHH @!EJ KLM OGGO RS*4$ST U$+V.+W'X6 $Y Z74' [4%\*67 ]^_ `?a bc>de fg>h> iddjkl mno ApqCDEFrHHHO @ce @sbt?u @vwx yz PD @ Q { }~
Building Products Ltd.! #$%&'( )*$+.+/'12 3454*67 89 :;= >?? @*;;* ABCDEFGHH @!EJ KLM OGGO RS*4$ST U$+V.+W'X6 $Y Z74' [4%\*67 ]^_ `?a bc>de fg>h> iddjkl mno ApqCDEFrHHHO @ce @sbt?u @vwx yz PD @ Q { }~
Books. Book Collection Editor. Editor. Name Name Company. Title "SA" A tree pattern. A database instance
 "! # #%$ $ $ & & & # ( # ) $ + $, -. 0 1 1 1 2430 5 6 78 9 =?
"! # #%$ $ $ & & & # ( # ) $ + $, -. 0 1 1 1 2430 5 6 78 9 =?
Block vs. Stream cipher
 Block vs. Stream cipher Idea of a block cipher: partition the text into relatively large (e.g. 128 bits) blocks and encode each block separately. The encoding of each block generally depends on at most
Block vs. Stream cipher Idea of a block cipher: partition the text into relatively large (e.g. 128 bits) blocks and encode each block separately. The encoding of each block generally depends on at most
Computer Systems Organization. Plan for Today
 Computer Systems Organization "!#%$&(' *),+-/. 021 345$&7634 098 :;!/.:?$&4@344A$&76 Plan for Today 1 ! ILP Limit Study #"%$'&)('*+-,.&/ 0 1+-*2 435&)$'768&9,:+8&.* &:>@7ABAC&ED(
Computer Systems Organization "!#%$&(' *),+-/. 021 345$&7634 098 :;!/.:?$&4@344A$&76 Plan for Today 1 ! ILP Limit Study #"%$'&)('*+-,.&/ 0 1+-*2 435&)$'768&9,:+8&.* &:>@7ABAC&ED(
1. Allstate Group Critical Illness Claim Form: When filing Critical Illness claim, please be sure to include the following:
 Dear Policyholder, Per your recent request, enclosed you will find the following forms: 1. Allstate Group Critical Illness Claim Form: When filing Critical Illness claim, please be sure to include the
Dear Policyholder, Per your recent request, enclosed you will find the following forms: 1. Allstate Group Critical Illness Claim Form: When filing Critical Illness claim, please be sure to include the
A Theory of Universal AI
 A Theory of Universa AI Literature Marcus Hutter Kircherr, Li, and Vitanyi Presenter Prashant J. Doshi CS594: Optima Decision Maing A Theory of Universa Artificia Inteigence p.1/18 Roadmap Caim Bacground
A Theory of Universa AI Literature Marcus Hutter Kircherr, Li, and Vitanyi Presenter Prashant J. Doshi CS594: Optima Decision Maing A Theory of Universa Artificia Inteigence p.1/18 Roadmap Caim Bacground
Testing SUSY Dark Matter
 Testing SUSY Dark Matter Wi de Boer, Markus Horn, Christian Sander Institut für Experientelle Kernphysik Universität Karlsruhe Wi.de.Boer@cern.ch http://hoe.cern.ch/ deboerw SPACE Part Elba, May 7, CMSSM
Testing SUSY Dark Matter Wi de Boer, Markus Horn, Christian Sander Institut für Experientelle Kernphysik Universität Karlsruhe Wi.de.Boer@cern.ch http://hoe.cern.ch/ deboerw SPACE Part Elba, May 7, CMSSM
Towards a High Level Quantum Programming Language
 MGS Xmas 04 p.1/?? Towards a High Level Quantum Programming Language Thorsten Altenkirch University of Nottingham based on joint work with Jonathan Grattage and discussions with V.P. Belavkin supported
MGS Xmas 04 p.1/?? Towards a High Level Quantum Programming Language Thorsten Altenkirch University of Nottingham based on joint work with Jonathan Grattage and discussions with V.P. Belavkin supported
Harlean. User s Guide
 Harlean User s Guide font faq HOW TO INSTALL YOUR FONT You will receive your files as a zipped folder. For instructions on how to unzip your folder, visit LauraWorthingtonType.com/faqs/. Your font is available
Harlean User s Guide font faq HOW TO INSTALL YOUR FONT You will receive your files as a zipped folder. For instructions on how to unzip your folder, visit LauraWorthingtonType.com/faqs/. Your font is available
Finding small factors of integers. Speed of the number-field sieve. D. J. Bernstein University of Illinois at Chicago
 The number-field sieve Finding small factors of integers Speed of the number-field sieve D. J. Bernstein University of Illinois at Chicago Prelude: finding denominators 87366 22322444 in R. Easily compute
The number-field sieve Finding small factors of integers Speed of the number-field sieve D. J. Bernstein University of Illinois at Chicago Prelude: finding denominators 87366 22322444 in R. Easily compute
6. Convert 5021 centimeters to kilometers. 7. How many seconds are in a leap year? 8. Convert the speed 5.30 m/s to km/h.
 % " ' ) 2 3 1 2 3 + + 4 2 3 L L CHAPTER A Physics Toolkit Practice Problems Mathematics and Physics pages page 5 For each problem, give the rewritten equation you would use and the answer. 1. A lightbulb
% " ' ) 2 3 1 2 3 + + 4 2 3 L L CHAPTER A Physics Toolkit Practice Problems Mathematics and Physics pages page 5 For each problem, give the rewritten equation you would use and the answer. 1. A lightbulb
Applications of Discrete Mathematics to the Analysis of Algorithms
 Applications of Discrete Mathematics to the Analysis of Algorithms Conrado Martínez Univ. Politècnica de Catalunya, Spain May 2007 Goal Given some algorithm taking inputs from some set Á, we would like
Applications of Discrete Mathematics to the Analysis of Algorithms Conrado Martínez Univ. Politècnica de Catalunya, Spain May 2007 Goal Given some algorithm taking inputs from some set Á, we would like
Queues, Stack Modules, and Abstract Data Types. CS2023 Winter 2004
 Queues Stack Modules and Abstact Data Types CS2023 Wnte 2004 Outcomes: Queues Stack Modules and Abstact Data Types C fo Java Pogammes Chapte 11 (11.5) and C Pogammng - a Moden Appoach Chapte 19 Afte the
Queues Stack Modules and Abstact Data Types CS2023 Wnte 2004 Outcomes: Queues Stack Modules and Abstact Data Types C fo Java Pogammes Chapte 11 (11.5) and C Pogammng - a Moden Appoach Chapte 19 Afte the
Synchronizing Automata Preserving a Chain of Partial Orders
 Synchronizing Automata Preserving a Chain of Partial Orders M. V. Volkov Ural State University, Ekaterinburg, Russia CIAA 2007, Prague, Finland, 16.07.07 p.1/25 Synchronizing automata We consider DFA:.
Synchronizing Automata Preserving a Chain of Partial Orders M. V. Volkov Ural State University, Ekaterinburg, Russia CIAA 2007, Prague, Finland, 16.07.07 p.1/25 Synchronizing automata We consider DFA:.
F O R SOCI AL WORK RESE ARCH
 7 TH EUROPE AN CONFERENCE F O R SOCI AL WORK RESE ARCH C h a l l e n g e s i n s o c i a l w o r k r e s e a r c h c o n f l i c t s, b a r r i e r s a n d p o s s i b i l i t i e s i n r e l a t i o n
7 TH EUROPE AN CONFERENCE F O R SOCI AL WORK RESE ARCH C h a l l e n g e s i n s o c i a l w o r k r e s e a r c h c o n f l i c t s, b a r r i e r s a n d p o s s i b i l i t i e s i n r e l a t i o n
UNIQUE FJORDS AND THE ROYAL CAPITALS UNIQUE FJORDS & THE NORTH CAPE & UNIQUE NORTHERN CAPITALS
 Q J j,. Y j, q.. Q J & j,. & x x. Q x q. ø. 2019 :. q - j Q J & 11 Y j,.. j,, q j q. : 10 x. 3 x - 1..,,. 1-10 ( ). / 2-10. : 02-06.19-12.06.19 23.06.19-03.07.19 30.06.19-10.07.19 07.07.19-17.07.19 14.07.19-24.07.19
Q J j,. Y j, q.. Q J & j,. & x x. Q x q. ø. 2019 :. q - j Q J & 11 Y j,.. j,, q j q. : 10 x. 3 x - 1..,,. 1-10 ( ). / 2-10. : 02-06.19-12.06.19 23.06.19-03.07.19 30.06.19-10.07.19 07.07.19-17.07.19 14.07.19-24.07.19
Subrings and Ideals 2.1 INTRODUCTION 2.2 SUBRING
 Subrings and Ideals Chapter 2 2.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter, we discuss, subrings, sub fields. Ideals and quotient ring. We begin our study by defining a subring. If (R, +, ) is a ring and S is a non-empty
Subrings and Ideals Chapter 2 2.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter, we discuss, subrings, sub fields. Ideals and quotient ring. We begin our study by defining a subring. If (R, +, ) is a ring and S is a non-empty
AN IDENTIFICATION ALGORITHM FOR ARMAX SYSTEMS
 AN IDENTIFICATION ALGORITHM FOR ARMAX SYSTEMS First the X, then the AR, finally the MA Jan C. Willems, K.U. Leuven Workshop on Observation and Estimation Ben Gurion University, July 3, 2004 p./2 Joint
AN IDENTIFICATION ALGORITHM FOR ARMAX SYSTEMS First the X, then the AR, finally the MA Jan C. Willems, K.U. Leuven Workshop on Observation and Estimation Ben Gurion University, July 3, 2004 p./2 Joint
Remainders. We learned how to multiply and divide in elementary
 Remainders We learned how to multiply and divide in elementary school. As adults we perform division mostly by pressing the key on a calculator. This key supplies the quotient. In numerical analysis and
Remainders We learned how to multiply and divide in elementary school. As adults we perform division mostly by pressing the key on a calculator. This key supplies the quotient. In numerical analysis and
Homomorphism Preservation Theorem. Albert Atserias Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Barcelona, Spain
 Homomorphism Preservation Theorem Albert Atserias Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Barcelona, Spain Structure of the talk 1. Classical preservation theorems 2. Preservation theorems in finite model
Homomorphism Preservation Theorem Albert Atserias Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Barcelona, Spain Structure of the talk 1. Classical preservation theorems 2. Preservation theorems in finite model
DISSIPATIVE SYSTEMS. Lectures by. Jan C. Willems. K.U. Leuven
 DISSIPATIVE SYSTEMS Lectures by Jan C. Willems K.U. Leuven p.1/26 LYAPUNOV FUNCTIONS Consider the classical dynamical system, the flow with, the state, and Denote the set of solutions, the vector-field.
DISSIPATIVE SYSTEMS Lectures by Jan C. Willems K.U. Leuven p.1/26 LYAPUNOV FUNCTIONS Consider the classical dynamical system, the flow with, the state, and Denote the set of solutions, the vector-field.
Damping Ring Requirements for 3 TeV CLIC
 Damping Ring Requirements for 3 TeV CLIC Quantity Symbol Value Bunch population N b 9 4.1 10 No. of bunches/train k bt 154 Repetition frequency f r 100 Hz Horizontal emittance γε x 7 4.5 10 m Vertical
Damping Ring Requirements for 3 TeV CLIC Quantity Symbol Value Bunch population N b 9 4.1 10 No. of bunches/train k bt 154 Repetition frequency f r 100 Hz Horizontal emittance γε x 7 4.5 10 m Vertical
Homework #2: assignments/ps2/ps2.htm Due Thursday, March 7th.
 Homework #2: http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs612/2002sp/ assignments/ps2/ps2.htm Due Thursday, March 7th. 1 Transformations and Dependences 2 Recall: Polyhedral algebra tools for determining emptiness
Homework #2: http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs612/2002sp/ assignments/ps2/ps2.htm Due Thursday, March 7th. 1 Transformations and Dependences 2 Recall: Polyhedral algebra tools for determining emptiness
Stochastic invariances and Lamperti transformations for Stochastic Processes
 Stochastic invariances and Lamperti transformations for Stochastic Processes Pierre Borgnat, Pierre-Olivier Amblard, Patrick Flandrin To cite this version: Pierre Borgnat, Pierre-Olivier Amblard, Patrick
Stochastic invariances and Lamperti transformations for Stochastic Processes Pierre Borgnat, Pierre-Olivier Amblard, Patrick Flandrin To cite this version: Pierre Borgnat, Pierre-Olivier Amblard, Patrick
Obtain from theory/experiment a value for the absorbtion cross-section. Calculate the number of atoms/ions/molecules giving rise to the line.
 Line Emission Observations of spectral lines offer the possibility of determining a wealth of information about an astronomical source. A usual plan of attack is :- Identify the line. Obtain from theory/experiment
Line Emission Observations of spectral lines offer the possibility of determining a wealth of information about an astronomical source. A usual plan of attack is :- Identify the line. Obtain from theory/experiment
Optimization of a parallel 3d-FFT with non-blocking collective operations
 Optimization of a parallel 3d-FFT with non-blocking collective operations Chair of Computer Architecture Technical University of Chemnitz Département de Physique Théorique et Appliquée Commissariat à l
Optimization of a parallel 3d-FFT with non-blocking collective operations Chair of Computer Architecture Technical University of Chemnitz Département de Physique Théorique et Appliquée Commissariat à l
A Study on the Analysis of Measurement Errors of Specific Gravity Meter
 HWAHAK KONGHAK Vol. 40, No. 6, December, 2002, pp. 676-680 (2001 7 2, 2002 8 5 ) A Study on the Analysis of Measurement Errors of Specific Gravity Meter Kang-Jin Lee, Jae-Young Her, Young-Cheol Ha, Seung-Hee
HWAHAK KONGHAK Vol. 40, No. 6, December, 2002, pp. 676-680 (2001 7 2, 2002 8 5 ) A Study on the Analysis of Measurement Errors of Specific Gravity Meter Kang-Jin Lee, Jae-Young Her, Young-Cheol Ha, Seung-Hee
4 Powers of an Element; Cyclic Groups
 4 Powers of an Element; Cyclic Groups Notation When considering an abstract group (G, ), we will often simplify notation as follows x y will be expressed as xy (x y) z will be expressed as xyz x (y z)
4 Powers of an Element; Cyclic Groups Notation When considering an abstract group (G, ), we will often simplify notation as follows x y will be expressed as xy (x y) z will be expressed as xyz x (y z)
Optimal data-independent point locations for RBF interpolation
 Optimal dataindependent point locations for RF interpolation S De Marchi, R Schaback and H Wendland Università di Verona (Italy), Universität Göttingen (Germany) Metodi di Approssimazione: lezione dell
Optimal dataindependent point locations for RF interpolation S De Marchi, R Schaback and H Wendland Università di Verona (Italy), Universität Göttingen (Germany) Metodi di Approssimazione: lezione dell
Systems of Equations 1. Systems of Linear Equations
 Lecture 1 Systems of Equations 1. Systems of Linear Equations [We will see examples of how linear equations arise here, and how they are solved:] Example 1: In a lab experiment, a researcher wants to provide
Lecture 1 Systems of Equations 1. Systems of Linear Equations [We will see examples of how linear equations arise here, and how they are solved:] Example 1: In a lab experiment, a researcher wants to provide
Fast Fourier Transform Solvers and Preconditioners for Quadratic Spline Collocation
 Fast Fourier Transform Solvers and Preconditioners for Quadratic Spline Collocation Christina C. Christara and Kit Sun Ng Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Toronto, Ontario M5S 3G4,
Fast Fourier Transform Solvers and Preconditioners for Quadratic Spline Collocation Christina C. Christara and Kit Sun Ng Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Toronto, Ontario M5S 3G4,
Differentiating Functions & Expressions - Edexcel Past Exam Questions
 - Edecel Past Eam Questions. (a) Differentiate with respect to (i) sin + sec, (ii) { + ln ()}. 5-0 + 9 Given that y =, ¹, ( -) 8 (b) show that = ( -). (6) June 05 Q. f() = e ln, > 0. (a) Differentiate
- Edecel Past Eam Questions. (a) Differentiate with respect to (i) sin + sec, (ii) { + ln ()}. 5-0 + 9 Given that y =, ¹, ( -) 8 (b) show that = ( -). (6) June 05 Q. f() = e ln, > 0. (a) Differentiate
JEE(Advanced) 2015 TEST PAPER WITH ANSWER. (HELD ON SUNDAY 24 th MAY, 2015) PART - III : MATHEMATICS
 PART - III : JEE(Advanced) 5 Final Eam/Paper-/Code- JEE(Advanced) 5 TEST PAPER WITH ANSWER (HELD ON SUNDAY 4 th MAY, 5) SECTION : (Maimum Marks : ) This section contains EIGHT questions. The answer to
PART - III : JEE(Advanced) 5 Final Eam/Paper-/Code- JEE(Advanced) 5 TEST PAPER WITH ANSWER (HELD ON SUNDAY 4 th MAY, 5) SECTION : (Maimum Marks : ) This section contains EIGHT questions. The answer to
A Language for Task Orchestration and its Semantic Properties
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCES A Language for Task Orchestration and its Semantic Properties David Kitchin, William Cook and Jayadev Misra Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Austin
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCES A Language for Task Orchestration and its Semantic Properties David Kitchin, William Cook and Jayadev Misra Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Austin
( ) Chapter 6 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Exercise Set The greatest common factor is x + 3.
 Chapter 6 Exercise Set 6.1 1. A prime number is an integer greater than 1 that has exactly two factors, itself and 1. 3. To factor an expression means to write the expression as the product of factors.
Chapter 6 Exercise Set 6.1 1. A prime number is an integer greater than 1 that has exactly two factors, itself and 1. 3. To factor an expression means to write the expression as the product of factors.
Optimizing Stresses for Testing DRAM Cell Defects Using Electrical Simulation
 Optimizing Stresses for Testing RAM Cell efects Using Electrical Simulation Zaid Al-Ars Ad J. van de Goor Faculty of Information Technology and Systems Section of Computer Engineering elft University of
Optimizing Stresses for Testing RAM Cell efects Using Electrical Simulation Zaid Al-Ars Ad J. van de Goor Faculty of Information Technology and Systems Section of Computer Engineering elft University of
Multilevel Preconditioning of Graph-Laplacians: Polynomial Approximation of the Pivot Blocks Inverses
 Multilevel Preconditioning of Graph-Laplacians: Polynomial Approximation of the Pivot Blocks Inverses P. Boyanova 1, I. Georgiev 34, S. Margenov, L. Zikatanov 5 1 Uppsala University, Box 337, 751 05 Uppsala,
Multilevel Preconditioning of Graph-Laplacians: Polynomial Approximation of the Pivot Blocks Inverses P. Boyanova 1, I. Georgiev 34, S. Margenov, L. Zikatanov 5 1 Uppsala University, Box 337, 751 05 Uppsala,
Mathematical Optimisation, Chpt 2: Linear Equations and inequalities
 Mathematical Optimisation, Chpt 2: Linear Equations and inequalities Peter J.C. Dickinson p.j.c.dickinson@utwente.nl http://dickinson.website version: 12/02/18 Monday 5th February 2018 Peter J.C. Dickinson
Mathematical Optimisation, Chpt 2: Linear Equations and inequalities Peter J.C. Dickinson p.j.c.dickinson@utwente.nl http://dickinson.website version: 12/02/18 Monday 5th February 2018 Peter J.C. Dickinson
Final exam: Computer-controlled systems (Datorbaserad styrning, 1RT450, 1TS250)
 Uppsala University Department of Information Technology Systems and Control Professor Torsten Söderström Final exam: Computer-controlled systems (Datorbaserad styrning, RT450, TS250) Date: December 9,
Uppsala University Department of Information Technology Systems and Control Professor Torsten Söderström Final exam: Computer-controlled systems (Datorbaserad styrning, RT450, TS250) Date: December 9,
ÇÙÐ Ò ½º ÅÙÐ ÔÐ ÔÓÐÝÐÓ Ö Ñ Ò Ú Ö Ð Ú Ö Ð ¾º Ä Ò Ö Ö Ù Ð Ý Ó ËÝÑ ÒÞ ÔÓÐÝÒÓÑ Ð º Ì ÛÓ¹ÐÓÓÔ ÙÒÖ Ö Ô Û Ö Ö ÖÝ Ñ ¹ ÝÓÒ ÑÙÐ ÔÐ ÔÓÐÝÐÓ Ö Ñ
 ÅÙÐ ÔÐ ÔÓÐÝÐÓ Ö Ñ Ò ÝÒÑ Ò Ò Ö Ð Ö Ò Ó Ò Ö ÀÍ ÖÐ Òµ Ó Ò ÛÓÖ Û Ö Ò ÖÓÛÒ Ö Ú ½ ¼¾º ¾½ Û Åº Ä Ö Ö Ú ½ ¼¾º ¼¼ Û Äº Ñ Ò Ëº Ï ÒÞ ÖÐ Å ÒÞ ½ º¼ º¾¼½ ÇÙÐ Ò ½º ÅÙÐ ÔÐ ÔÓÐÝÐÓ Ö Ñ Ò Ú Ö Ð Ú Ö Ð ¾º Ä Ò Ö Ö Ù Ð Ý Ó ËÝÑ
ÅÙÐ ÔÐ ÔÓÐÝÐÓ Ö Ñ Ò ÝÒÑ Ò Ò Ö Ð Ö Ò Ó Ò Ö ÀÍ ÖÐ Òµ Ó Ò ÛÓÖ Û Ö Ò ÖÓÛÒ Ö Ú ½ ¼¾º ¾½ Û Åº Ä Ö Ö Ú ½ ¼¾º ¼¼ Û Äº Ñ Ò Ëº Ï ÒÞ ÖÐ Å ÒÞ ½ º¼ º¾¼½ ÇÙÐ Ò ½º ÅÙÐ ÔÐ ÔÓÐÝÐÓ Ö Ñ Ò Ú Ö Ð Ú Ö Ð ¾º Ä Ò Ö Ö Ù Ð Ý Ó ËÝÑ
A Beamforming Method for Blind Calibration of Time-Interleaved A/D Converters
 A Beamforming Method for Blind Calibration of Time-nterleaved A/D Converters Bernard C. Levy University of California, Davis Joint wor with Steve Huang September 30, 200 Outline 1 Motivation Problem Formulation
A Beamforming Method for Blind Calibration of Time-nterleaved A/D Converters Bernard C. Levy University of California, Davis Joint wor with Steve Huang September 30, 200 Outline 1 Motivation Problem Formulation
ETNA Kent State University
 Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 17, pp. 76-92, 2004. Copyright 2004,. ISSN 1068-9613. ETNA STRONG RANK REVEALING CHOLESKY FACTORIZATION M. GU AND L. MIRANIAN Ý Abstract. For any symmetric
Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 17, pp. 76-92, 2004. Copyright 2004,. ISSN 1068-9613. ETNA STRONG RANK REVEALING CHOLESKY FACTORIZATION M. GU AND L. MIRANIAN Ý Abstract. For any symmetric
 n P! " # $ % & % & ' ( ) * + % $, $ -. $ -..! " # ) & % $/ $ - 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 8 7 9 9 : 3 ; 1 7 < 9 : 5 = > : 9? @ A B C D E F G HI J G H K D L M N O P Q R S T U V M Q P W X X Y W X X Z [ Y \ ] M
n P! " # $ % & % & ' ( ) * + % $, $ -. $ -..! " # ) & % $/ $ - 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 8 7 9 9 : 3 ; 1 7 < 9 : 5 = > : 9? @ A B C D E F G HI J G H K D L M N O P Q R S T U V M Q P W X X Y W X X Z [ Y \ ] M
Saturday, April 23, Dependence Analysis
 Dependence Analysis Motivating question Can the loops on the right be run in parallel? i.e., can different processors run different iterations in parallel? What needs to be true for a loop to be parallelizable?
Dependence Analysis Motivating question Can the loops on the right be run in parallel? i.e., can different processors run different iterations in parallel? What needs to be true for a loop to be parallelizable?
1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide
 Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Fall 2013 1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide 1.1 Problems The following are some problems, some of which will appear on the final exam. 1.1.1 Number
Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Fall 2013 1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide 1.1 Problems The following are some problems, some of which will appear on the final exam. 1.1.1 Number
Robert Krzyzanowski Algebra (Dummit and Foote) Chapter 1.1. These problems implicitly make use of the following lemma (stated casually in the book).
 Chapter 11 These problems implicitly make use of the following lemma (stated casually in the book) Lemma If akß æb is a group and L K is closed under æ then æ is associative in L Proof We know æ is associative
Chapter 11 These problems implicitly make use of the following lemma (stated casually in the book) Lemma If akß æb is a group and L K is closed under æ then æ is associative in L Proof We know æ is associative
PART IV LIVESTOCK, POULTRY AND FISH PRODUCTION
 ! " $#%(' ) PART IV LIVSTOCK, POULTRY AND FISH PRODUCTION Table (93) MAIN GROUPS OF ANIMAL PRODUCTS Production 1000 M.T Numbers 1000 Head Type 2012 Numbers Cattle 54164.5 53434.6 Buffaloes 4304.51 4292.51
! " $#%(' ) PART IV LIVSTOCK, POULTRY AND FISH PRODUCTION Table (93) MAIN GROUPS OF ANIMAL PRODUCTS Production 1000 M.T Numbers 1000 Head Type 2012 Numbers Cattle 54164.5 53434.6 Buffaloes 4304.51 4292.51
SCOTT PLUMMER ASHTON ANTONETTI
 2742 A E E E, UE, AAAMA 3802 231 EE AEA 38,000-cre dversfed federl cmus 41,000 emloyees wth 72+ dfferent gences UE roosed 80-cre mster-lnned develoment 20 home stes 3,000F of vllgestyle retl 100,000 E
2742 A E E E, UE, AAAMA 3802 231 EE AEA 38,000-cre dversfed federl cmus 41,000 emloyees wth 72+ dfferent gences UE roosed 80-cre mster-lnned develoment 20 home stes 3,000F of vllgestyle retl 100,000 E
ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2/WG2 N2
 ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2/WG2 N2 2000-04-13 Universal Multiple-Octet Coded Character Set International Organization for Standardization Organisation Internationale de Normalisation Œåæäóíàðîäíàß îðãàíèçàöèß ïî
ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2/WG2 N2 2000-04-13 Universal Multiple-Octet Coded Character Set International Organization for Standardization Organisation Internationale de Normalisation Œåæäóíàðîäíàß îðãàíèçàöèß ïî
Manifold Regularization
 Manifold Regularization Vikas Sindhwani Department of Computer Science University of Chicago Joint Work with Mikhail Belkin and Partha Niyogi TTI-C Talk September 14, 24 p.1 The Problem of Learning is
Manifold Regularization Vikas Sindhwani Department of Computer Science University of Chicago Joint Work with Mikhail Belkin and Partha Niyogi TTI-C Talk September 14, 24 p.1 The Problem of Learning is
TELEMATICS LINK LEADS
 EEAICS I EADS UI CD PHOE VOICE AV PREIU I EADS REQ E E A + A + I A + I E B + E + I B + E + I B + E + H B + I D + UI CD PHOE VOICE AV PREIU I EADS REQ D + D + D + I C + C + C + C + I G G + I G + I G + H
EEAICS I EADS UI CD PHOE VOICE AV PREIU I EADS REQ E E A + A + I A + I E B + E + I B + E + I B + E + H B + I D + UI CD PHOE VOICE AV PREIU I EADS REQ D + D + D + I C + C + C + C + I G G + I G + I G + H
Sample Exam 1: Chapters 1, 2, and 3
 L L 1 ' ] ^, % ' ) 3 Sample Exam 1: Chapters 1, 2, and 3 #1) Consider the lineartime invariant system represented by Find the system response and its zerostate and zeroinput components What are the response
L L 1 ' ] ^, % ' ) 3 Sample Exam 1: Chapters 1, 2, and 3 #1) Consider the lineartime invariant system represented by Find the system response and its zerostate and zeroinput components What are the response
Section 1.3 Functions and Their Graphs 19
 23. 0 1 2 24. 0 1 2 y 0 1 0 y 1 0 0 Section 1.3 Functions and Their Graphs 19 3, Ÿ 1, 0 25. y œ 26. y œ œ 2, 1 œ, 0 Ÿ " 27. (a) Line through a!ß! band a"ß " b: y œ Line through a"ß " band aß! b: y œ 2,
23. 0 1 2 24. 0 1 2 y 0 1 0 y 1 0 0 Section 1.3 Functions and Their Graphs 19 3, Ÿ 1, 0 25. y œ 26. y œ œ 2, 1 œ, 0 Ÿ " 27. (a) Line through a!ß! band a"ß " b: y œ Line through a"ß " band aß! b: y œ 2,
Deciding Presburger Arithmetic
 Deciding Presburger Arithmetic Michael Norrish Michael.Norrish@nicta.com.au National ICT Australia Michael Norrish (National ICT Australia) LSS2006: Presburger Arithmetic 1 / 62 Outline 1 Introduction
Deciding Presburger Arithmetic Michael Norrish Michael.Norrish@nicta.com.au National ICT Australia Michael Norrish (National ICT Australia) LSS2006: Presburger Arithmetic 1 / 62 Outline 1 Introduction
Some emission processes are intrinsically polarised e.g. synchrotron radiation.
 Polarisation Some emission processes are intrinsically polarised e.g. synchrotron radiation. B e linearly polarised emission circularly polarised emission Scattering processes can either increase or decrease
Polarisation Some emission processes are intrinsically polarised e.g. synchrotron radiation. B e linearly polarised emission circularly polarised emission Scattering processes can either increase or decrease
Here are proofs for some of the results about diagonalization that were presented without proof in class.
 Suppose E is an 8 8 matrix. In what follows, terms like eigenvectors, eigenvalues, and eigenspaces all refer to the matrix E. Here are proofs for some of the results about diagonalization that were presented
Suppose E is an 8 8 matrix. In what follows, terms like eigenvectors, eigenvalues, and eigenspaces all refer to the matrix E. Here are proofs for some of the results about diagonalization that were presented
