Episode 212: Newton s third law of motion
|
|
|
- Charla Daniels
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Episode 212: Newton s third law of motion Newton s third law of motion causes problems to physicists at many levels and it is worthwhile spending a little time developing a clear approach to the concept to avoid confusion in later work. There are a number of difficulties in teaching this concept: the pervasiveness of its application misconceptions from previous experience the difficulty of a convincing demonstration use of the concept is either trivial or mathematical. Recognising these difficulties is half the battle; the other half is ensuring that your own understanding is sound! Summary Discussion: Newton s third law. (15 minutes) Demonstration: The third law. (10 minutes) Questions: For discussion or homework. (15 minutes) Discussion: Newton s third law Ask the class to state Newton s third law. Hope that you get the archaic answer: Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. If you do you can proceed to ask what that statement actually means and ask the students to give examples. This discussion is likely to reveal a number of misconceptions. Give the law in the form: If body A exerts a force on body B then body B will exert the same force on body A but the force will be in the opposite direction. This could be thought of as a law of conservation of force. Make sure that the students are clear about the following aspects of a Newton s third-law pair of forces : The two forces act on two different bodies. Both forces are always of the same type (i.e. both gravitational, both electrostatic, etc.). The forces are equal in magnitude. The forces are opposite in direction. The example of a book on a table is useful at this point. 1
2 Ask about the two forces acting on the book; this will often elicit the response, the weight of the book and the reaction force of the table. These forces are present but are not a Newton s thirdlaw pair they are not the same type of force, and they act on the same object. When you take away the table the weight of the book remains. There are two Newton pairs here: (i) The pull of the Earth on the book and the pull of the book on the Earth (gravitational forces) and (ii) the push of the book on the table and the push of the table on the book (contact forces). Notice that in each case removing one force makes the other vanish. The situation may be clarified with the use of a suitable diagram. It may help to draw up a table of typical Newton pair situations as shown below: Situation Body A Body B Type of force Satellite in orbit around Earth Satellite Earth gravitational Of course, many situations involve more than one Newton pair. Demonstration: The third law A very basic demonstration but how many Newton pairs are there here? TAP 212-1: Newton s third law Another demonstration might be to show two bar magnets. Choose one that is stronger than the other; demonstrate this by showing that one can lift a greater iron weight than the other. Ask: If the two magnets attract one another, will one pull more strongly than the other? The answer is, no. You can feel that they pull each other equally. (This is because the force is proportional to the strength of each.) 2
3 If magnet A pulled magnet B more strongly than B pulled A, you could attach B to the front of your car and lean out, holding A in front. Your car would move effortlessly! Questions: N S N For discussion or homework Question 1 is one of the oldest brain teasers in physics and is certainly worth discussing. If your students are competent mathematicians they will enjoy the other question, if not you may prefer to go through them with the class. Note that some students decide for themselves that Newton s Third Law is an idealised notion, and that the two forces may not be exactly equal and opposite this is wrong! TAP 212-2: Questions on Newton s Third Law 3
4 TAP 212-1: Newton s third law Demonstration Apparatus: Electronic balance set to measure in newtons Spring balance Lab stands as scaffolding 8.31 Attach the spring balance (newtonmeter) to the scale pan (use adhesive tape and exercise great care not to damage the scale pan). As the pan registers an upward force the spring balance registers an equal and opposite downward force. But what are the Newton pairs here? 4
5 Practical advice Try not to use too many pairs of forces. 5
6 TAP 212-2: Questions on Newton s third law 1. This question is adapted from the book Thinking Physics is Gedanken Physics and is one of the most well known physics puzzles. If the force on the carriage is equal and opposite to the force on the horse how can the horse pull the carriage? Is the answer: (a) The horse cannot pull the carriage because the carriage pulls as hard on the horse as the horse pulls on the carriage. (b) The carriage moves because the horse pulls slightly harder on the carriage (c) The horse pulls the carriage before it has time to react. (d) The horse can pull the carriage only if the horse is heavier than the carriage. (e) Another explanation. What might it be? 6
7 2. A builder s crane is a simple device that allows a person to haul himself/herself up using a pulley. The builder has a mass of 75 kg and the cradle a mass of 35 kg. The builder pulls on the rope with a force of 650 N. The rope will exert a force of 650 N upwards on the man and 650 N upwards on the cradle. (a) Explain why the net upward force on the man is: force exerted by the floor of the lift (F) (weight of man 650 N) (b) Explain why the net force on the cradle is: 650N weight of the lift force man exerts on the cradle (F) (c) Calculate the acceleration of the cradle and the force exerted by the man on the floor of the cradle. To do this you will have to use the two equations given in (a) and (b). The net force in (a) is equal to mass of man x acceleration of man. The net force in (b) is equal to the mass of the cradle x acceleration of the cradle. As the acceleration of both man and cradle is the same you can solve these equations simultaneously. 7
8 Answers and worked solutions 1 The answer is (e), of course. The horse is joined to the ground by its hooves whilst the carriage rolls on wheels. This means that one force pulls on the carriage whilst other of the Newton pair pulls on the Earth and horse. 2 (c) This is solved by simultaneous equations. Force on man = F ( ) = 75 a Force on cradle = F = 35 a Acceleration = 2 m s -2 Force = 235 N 8
Lesson 11: Newton s Third Law: Quantitative
 11.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Lesson 11: Newton s Third Law: Quantitative The goal of this experiment is to determine a mathematical relationship between the force that object A exerts on object B and
11.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Lesson 11: Newton s Third Law: Quantitative The goal of this experiment is to determine a mathematical relationship between the force that object A exerts on object B and
Chapter 4. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. continued
 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Quiz 3 4.7 The Gravitational Force Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the universe exerts an attractive force on every other
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Quiz 3 4.7 The Gravitational Force Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the universe exerts an attractive force on every other
Force mediated by a field - long range: action at a distance: The attractive or repulsion between two stationary charged objects.
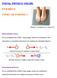 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DYNAMICS TYPES O ORCES 1 Electrostatic force orce mediated by a field - long range: action at a distance: The attractive or repulsion between two stationary charged objects. AB A
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DYNAMICS TYPES O ORCES 1 Electrostatic force orce mediated by a field - long range: action at a distance: The attractive or repulsion between two stationary charged objects. AB A
Forces and Newton s Laws Reading Notes. Give an example of a force you have experienced continuously all your life.
 Forces and Newton s Laws Reading Notes Name: Section 4-1: Force What is force? Give an example of a force you have experienced continuously all your life. Give an example of a situation where an object
Forces and Newton s Laws Reading Notes Name: Section 4-1: Force What is force? Give an example of a force you have experienced continuously all your life. Give an example of a situation where an object
Lecture 4. Newton s 3rd law and Friction
 Lecture 4 Newton s 3rd law and Friction Newtons First Law or Law of Inertia If no net external force is applied to an object, its velocity will remain constant ("inert"). OR A body cannot change its state
Lecture 4 Newton s 3rd law and Friction Newtons First Law or Law of Inertia If no net external force is applied to an object, its velocity will remain constant ("inert"). OR A body cannot change its state
Lesson 6: How to Calculate Kinetic Energy
 KREUTTER:WORK AND ENERGY 1 Lesson 6: How to Calculate Kinetic Energy 6.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) In a car crash testing facility, engineers evaluate the reaction of a car to a front impact.
KREUTTER:WORK AND ENERGY 1 Lesson 6: How to Calculate Kinetic Energy 6.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) In a car crash testing facility, engineers evaluate the reaction of a car to a front impact.
GRADE 6: Physical processes 3. UNIT 6P.3 6 hours. The effects of forces. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 6: Physical processes 3 The effects of forces UNIT 6P.3 6 hours About this unit This unit is the third of three units on physical processes for Grade 3 and the second of two on forces. It builds
GRADE 6: Physical processes 3 The effects of forces UNIT 6P.3 6 hours About this unit This unit is the third of three units on physical processes for Grade 3 and the second of two on forces. It builds
Lesson 1: How can you describe motion?
 Lesson 1 Summary Use with pp. 407 409 Lesson 1: How can you describe motion? Vocabulary velocity the speed and direction of an object s motion Types of Motion Motion is movement. When you see something
Lesson 1 Summary Use with pp. 407 409 Lesson 1: How can you describe motion? Vocabulary velocity the speed and direction of an object s motion Types of Motion Motion is movement. When you see something
Chapter 3: Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapter 3: Newton s Laws of Motion Mini Investigation: Predicting Forces, page 113 Answers may vary. Sample answers: A. I predicted the reading in question 3 would be the sum of the readings from questions
Chapter 3: Newton s Laws of Motion Mini Investigation: Predicting Forces, page 113 Answers may vary. Sample answers: A. I predicted the reading in question 3 would be the sum of the readings from questions
Concept of Force Challenge Problem Solutions
 Concept of Force Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1: Force Applied to Two Blocks Two blocks sitting on a frictionless table are pushed from the left by a horizontal force F, as shown below. a) Draw
Concept of Force Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1: Force Applied to Two Blocks Two blocks sitting on a frictionless table are pushed from the left by a horizontal force F, as shown below. a) Draw
Engage I 1. What do you think about this design? If the car were to suddenly stop, what would happen to the child? Why?
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 4.a Nature of Forces Outcomes Define force. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion. Describe inertia and describe its relationship to mass. Draw free-body diagrams to represent
AP Physics 1 Lesson 4.a Nature of Forces Outcomes Define force. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion. Describe inertia and describe its relationship to mass. Draw free-body diagrams to represent
Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion Force and Mass Units of Chapter 5 Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion The Vector Nature of Forces: Forces in Two Dimensions
Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion Force and Mass Units of Chapter 5 Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion The Vector Nature of Forces: Forces in Two Dimensions
MEI Mechanics 1. Applying Newton s second law along a line
 MEI Mechanics 1 Applying Newton s second law along a line Chapter assessment 1. (a) The following two questions are about the motion of a car of mass 1500 kg, travelling along a straight, horizontal road.
MEI Mechanics 1 Applying Newton s second law along a line Chapter assessment 1. (a) The following two questions are about the motion of a car of mass 1500 kg, travelling along a straight, horizontal road.
HSC PHYSICS ONLINE B F BA. repulsion between two negatively charged objects. attraction between a negative charge and a positive charge
 HSC PHYSICS ONLINE DYNAMICS TYPES O ORCES Electrostatic force (force mediated by a field - long range: action at a distance) the attractive or repulsion between two stationary charged objects. AB A B BA
HSC PHYSICS ONLINE DYNAMICS TYPES O ORCES Electrostatic force (force mediated by a field - long range: action at a distance) the attractive or repulsion between two stationary charged objects. AB A B BA
The Concept of Force. field forces d) The gravitational force of attraction between two objects. f) Force a bar magnet exerts on a piece of iron.
 Lecture 3 The Laws of Motion OUTLINE 5.1 The Concept of Force 5.2 Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames 5.3 Mass 5.4 Newton s Second Law 5.5 The Gravitational Force and Weight 5.6 Newton s Third Law 5.8
Lecture 3 The Laws of Motion OUTLINE 5.1 The Concept of Force 5.2 Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames 5.3 Mass 5.4 Newton s Second Law 5.5 The Gravitational Force and Weight 5.6 Newton s Third Law 5.8
Unit 2 Part 2: Forces Note 1: Newton`s Universal Law of Gravitation. Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation states: Gravity. Where: G = M = r =
 Unit 2 Part 2: Forces Note 1: Newton`s Universal Law of Gravitation Gravity Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation states: Where: G = = M = m = r = Ex 1: What is the force of gravity exerted on a 70.0 kg
Unit 2 Part 2: Forces Note 1: Newton`s Universal Law of Gravitation Gravity Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation states: Where: G = = M = m = r = Ex 1: What is the force of gravity exerted on a 70.0 kg
Chapter Seven Notes: Newton s Third Law of Motion Action and Reaction
 Chapter Seven Notes: Newton s Third Law of Motion Action and Reaction A force is always part of a mutual action that involves another force. A mutual action is an interaction between one thing and another
Chapter Seven Notes: Newton s Third Law of Motion Action and Reaction A force is always part of a mutual action that involves another force. A mutual action is an interaction between one thing and another
Forces and Newton s Laws
 chapter 3 section 1 Forces Forces and Newton s Laws What You ll Learn how force and motion are related what friction is between objects the difference between mass and weight Before You Read When you hit
chapter 3 section 1 Forces Forces and Newton s Laws What You ll Learn how force and motion are related what friction is between objects the difference between mass and weight Before You Read When you hit
Q2. A book whose mass is 2 kg rests on a table. Find the magnitude of the force exerted by the table on the book.
 AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A change in state of motion means a change in an object s velocity, therefore
AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A change in state of motion means a change in an object s velocity, therefore
Solving two-body problems with Newton s Second Law. Example Static and Kinetic Friction. Section 5.1 Friction 10/15/13
 Solving two-body problems with Newton s Second Law You ll get multiple equations from the x and y directions, these equations can be solved simultaneously to find unknowns 1. Draw a separate free body
Solving two-body problems with Newton s Second Law You ll get multiple equations from the x and y directions, these equations can be solved simultaneously to find unknowns 1. Draw a separate free body
Newton s Wagon. Materials. friends rocks wagon balloon fishing line tape stopwatch measuring tape. Lab Time Part 1
 Newton s Wagon Overview: The natural state of objects is to follow a straight line. In fact, Newton s First Law of Motion states that objects in motion will tend to stay in motion unless they are acted
Newton s Wagon Overview: The natural state of objects is to follow a straight line. In fact, Newton s First Law of Motion states that objects in motion will tend to stay in motion unless they are acted
Year 11 Physics Tutorial 84C2 Newton s Laws of Motion
 Year 11 Physics Tutorial 84C2 Newton s Laws of Motion Module Topic 8.4 Moving About 8.4.C Forces Name Date Set 1 Calculating net force 1 A trolley was moved to the right by a force applied to a cord attached
Year 11 Physics Tutorial 84C2 Newton s Laws of Motion Module Topic 8.4 Moving About 8.4.C Forces Name Date Set 1 Calculating net force 1 A trolley was moved to the right by a force applied to a cord attached
2. FORCE AND MOTION. In the above, the objects are being moved by a push or pull. A push or pull acting on objects is called a force.
 2. FORCE AND MOTION Force We do many jobs in our daily life like lifting things, moving things from one place to another, cutting objects, etc. To do these jobs, we have to move. We are surrounded by a
2. FORCE AND MOTION Force We do many jobs in our daily life like lifting things, moving things from one place to another, cutting objects, etc. To do these jobs, we have to move. We are surrounded by a
Physics 9 Friday, January 15, 2016
 Physics 9 Friday, January 15, 2016 Handing out HW1, due Monday 1/25. Homework help sessions start next week (Thu 1/21 and Sun 1/24). You read Giancoli s chapter 4 for today: it was a review of Newton s
Physics 9 Friday, January 15, 2016 Handing out HW1, due Monday 1/25. Homework help sessions start next week (Thu 1/21 and Sun 1/24). You read Giancoli s chapter 4 for today: it was a review of Newton s
Episode 211: Newton s second law of motion
 Episode 211: Newton s second law of motion This episode concerns Newton s second law. Your students will probably have met the second law in the form F = ma; many will have performed experiments to demonstrate
Episode 211: Newton s second law of motion This episode concerns Newton s second law. Your students will probably have met the second law in the form F = ma; many will have performed experiments to demonstrate
Motor. Cable. Elevator
 Q4.1 An elevator is being lifted at a constant speed by a steel cable attached to an electric motor. There is no air resistance, nor is there any friction between the elevator and the walls of the elevator
Q4.1 An elevator is being lifted at a constant speed by a steel cable attached to an electric motor. There is no air resistance, nor is there any friction between the elevator and the walls of the elevator
UNIT 4: FORCES IN NATURE Test review: 4_1_ Forces in nature. Fundamentals
 UNIT 4: FORCES IN NATURE Test review: 4_1_ Forces in nature. Fundamentals 1. Contact forces are examples of which of the fundamental forces? a. Strong c. Weak b. Electromagnetic d. Gravitational 2. The
UNIT 4: FORCES IN NATURE Test review: 4_1_ Forces in nature. Fundamentals 1. Contact forces are examples of which of the fundamental forces? a. Strong c. Weak b. Electromagnetic d. Gravitational 2. The
Unit 2 Forces. Fundamental Forces
 Lesson14.notebook July 10, 2013 Unit 2 Forces Fundamental Forces Today's goal: I can identify/name applied forces and draw appropriate free body diagrams (FBD's). There are 4 fundamental forces Gravity
Lesson14.notebook July 10, 2013 Unit 2 Forces Fundamental Forces Today's goal: I can identify/name applied forces and draw appropriate free body diagrams (FBD's). There are 4 fundamental forces Gravity
Name Date Hour Table
 Name Date Hour Table Chapter 3 Pre-AP Directions: Use the clues to create your word bank for the word search. Put the answer to each question with its number in the word bank box. Then find each word in
Name Date Hour Table Chapter 3 Pre-AP Directions: Use the clues to create your word bank for the word search. Put the answer to each question with its number in the word bank box. Then find each word in
1D Motion: Review Packet Problem 1: Consider the following eight velocity vs. time graphs. Positive velocity is forward velocity.
 Name: 1D Motion: Review Packet Problem 1: Consider the following eight velocity vs. time graphs. Positive velocity is forward velocity. Graph A Graph B Graph C Graph D Graph E Graph F Graph G Graph H (a)
Name: 1D Motion: Review Packet Problem 1: Consider the following eight velocity vs. time graphs. Positive velocity is forward velocity. Graph A Graph B Graph C Graph D Graph E Graph F Graph G Graph H (a)
POGIL: Newton s First Law of Motion and Statics. Part 1: Net Force Model: Read the following carefully and study the diagrams that follow.
 POGIL: Newton s First Law of Motion and Statics Name Purpose: To become familiar with the forces acting on an object at rest Part 1: Net Force Model: Read the following carefully and study the diagrams
POGIL: Newton s First Law of Motion and Statics Name Purpose: To become familiar with the forces acting on an object at rest Part 1: Net Force Model: Read the following carefully and study the diagrams
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01T Fall Term 2004
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.0T Fall Term 2004 Problem Set 3: Newton's Laws of Motion, Motion: Force, Mass, and Acceleration, Vectors in Physics Solutions Problem
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.0T Fall Term 2004 Problem Set 3: Newton's Laws of Motion, Motion: Force, Mass, and Acceleration, Vectors in Physics Solutions Problem
Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass: Section 5.1
Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass: Section 5.1
AP Physics 1 Review. On the axes below draw the horizontal force acting on this object as a function of time.
 P Physics Review. Shown is the velocity versus time graph for an object that is moving in one dimension under the (perhaps intermittent) action of a single horizontal force. Velocity, m/s Time, s On the
P Physics Review. Shown is the velocity versus time graph for an object that is moving in one dimension under the (perhaps intermittent) action of a single horizontal force. Velocity, m/s Time, s On the
Force. The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object.
 Force The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object. Forces do not always give rise to motion. Forces can be equal and opposite. Force is a vector
Force The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object. Forces do not always give rise to motion. Forces can be equal and opposite. Force is a vector
July 19 - Work and Energy 1. Name Date Partners
 July 19 - Work and Energy 1 Name Date Partners WORK AND ENERGY Energy is the only life and is from the Body; and Reason is the bound or outward circumference of energy. Energy is eternal delight. William
July 19 - Work and Energy 1 Name Date Partners WORK AND ENERGY Energy is the only life and is from the Body; and Reason is the bound or outward circumference of energy. Energy is eternal delight. William
LAB 6: WORK AND ENERGY
 89 Name Date Partners LAB 6: WORK AND ENERGY OBJECTIVES Energy is the only life and is from the Body; and Reason is the bound or outward circumference of energy. Energy is eternal delight. William Blake
89 Name Date Partners LAB 6: WORK AND ENERGY OBJECTIVES Energy is the only life and is from the Body; and Reason is the bound or outward circumference of energy. Energy is eternal delight. William Blake
PHYSICS. Chapter 5 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
Lab #5: Newton s First Law
 Lab #5: Newton s First Law Reading Assignment: Chapter 5 Chapter 6, Sections 6-1 through 6-3, Section 6-5 Introduction: A common misnomer is that astronauts experience zero g s during space flight. In
Lab #5: Newton s First Law Reading Assignment: Chapter 5 Chapter 6, Sections 6-1 through 6-3, Section 6-5 Introduction: A common misnomer is that astronauts experience zero g s during space flight. In
UNIT 4 NEWTON S THIRD LAW, FORCE DIAGRAMS AND FORCES. Objectives. To understand and be able to apply Newton s Third Law
 UNIT 4 NEWTON S THIRD LAW, FORCE DIAGRAMS AND FORCES Objectives To understand and be able to apply Newton s Third Law To be able to determine the object that is exerting a particular force To understand
UNIT 4 NEWTON S THIRD LAW, FORCE DIAGRAMS AND FORCES Objectives To understand and be able to apply Newton s Third Law To be able to determine the object that is exerting a particular force To understand
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapter 5 Force and Motion Chapter Goal: To establish a connection between force and motion. Slide 5-2 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-3 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-4 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-5 Chapter 5 Preview
Chapter 5 Force and Motion Chapter Goal: To establish a connection between force and motion. Slide 5-2 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-3 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-4 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-5 Chapter 5 Preview
II. Universal Gravitation - Newton 4th Law
 Periodic Motion I. Circular Motion - kinematics & centripetal acceleration - dynamics & centripetal force - centrifugal force II. Universal Gravitation - Newton s 4 th Law - force fields & orbits III.
Periodic Motion I. Circular Motion - kinematics & centripetal acceleration - dynamics & centripetal force - centrifugal force II. Universal Gravitation - Newton s 4 th Law - force fields & orbits III.
7.1 Interacting Systems p Action/reaction pairs p Newton s Third Law p Ropes and Pulleys p.
 7.1 Interacting Systems p. 183-185 7.2 Action/reaction pairs p. 185-189 7.3 Newton s Third Law p. 189-194 7.4 Ropes and Pulleys p. 194-198 7.5 Interacting-system Problems p. 198-202 1 7.1 Interacting Systems
7.1 Interacting Systems p. 183-185 7.2 Action/reaction pairs p. 185-189 7.3 Newton s Third Law p. 189-194 7.4 Ropes and Pulleys p. 194-198 7.5 Interacting-system Problems p. 198-202 1 7.1 Interacting Systems
13) Two skaters, an 82-kg man and a 48-kg woman, are standing on ice. The woman pushes on the man with a force of 45 Newtons due east.
 Lab 14: Two Ball Race ; Egg Drop - The Law of Force and Acceleration (Newtonʼs 2nd Law) - Distance and velocity vs. time graphs for constant acceleration - Solving problems with force, mass and acceleration
Lab 14: Two Ball Race ; Egg Drop - The Law of Force and Acceleration (Newtonʼs 2nd Law) - Distance and velocity vs. time graphs for constant acceleration - Solving problems with force, mass and acceleration
Reading Quiz. Chapter 5. Physics 111, Concordia College
 Reading Quiz Chapter 5 1. The coefficient of static friction is A. smaller than the coefficient of kinetic friction. B. equal to the coefficient of kinetic friction. C. larger than the coefficient of kinetic
Reading Quiz Chapter 5 1. The coefficient of static friction is A. smaller than the coefficient of kinetic friction. B. equal to the coefficient of kinetic friction. C. larger than the coefficient of kinetic
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 4 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
INTRO VIDEO REVIEW QUIZ
 DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS PRE-DP PHYSICS INTRO VIDEO Newton's Third Law of Motion REVIEW QUIZ 1. What is force? 2. Name Newton s First Law of Motion. 3. What is inertia? 4. What is the chemistry
DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS PRE-DP PHYSICS INTRO VIDEO Newton's Third Law of Motion REVIEW QUIZ 1. What is force? 2. Name Newton s First Law of Motion. 3. What is inertia? 4. What is the chemistry
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
 Section 2.17: Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation Gravity is an attractive force that exists between all objects that have mass. It is the force that keeps us stuck to the earth and the moon orbiting
Section 2.17: Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation Gravity is an attractive force that exists between all objects that have mass. It is the force that keeps us stuck to the earth and the moon orbiting
PHYSICS 231 Laws of motion PHY 231
 PHYSICS 231 Laws of motion 1 Newton s Laws First Law: If the net force exerted on an object is zero the object continues in its original state of motion; if it was at rest, it remains at rest. If it was
PHYSICS 231 Laws of motion 1 Newton s Laws First Law: If the net force exerted on an object is zero the object continues in its original state of motion; if it was at rest, it remains at rest. If it was
Chapter 6 Dynamics I: Motion Along a Line
 Chapter 6 Dynamics I: Motion Along a Line Chapter Goal: To learn how to solve linear force-and-motion problems. Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Preview Slide 6-3 Chapter 6 Preview Slide 6-4 Chapter 6 Preview Slide
Chapter 6 Dynamics I: Motion Along a Line Chapter Goal: To learn how to solve linear force-and-motion problems. Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Preview Slide 6-3 Chapter 6 Preview Slide 6-4 Chapter 6 Preview Slide
Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 3 Wednesday February 2, 2011
 Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 3 Wednesday February 2, 2011 Make sure your name is on your homework, and please box your final answer. Because we will be giving partial credit, be sure to attempt all
Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 3 Wednesday February 2, 2011 Make sure your name is on your homework, and please box your final answer. Because we will be giving partial credit, be sure to attempt all
Friction Can Be Rough
 10.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Friction Can Be Rough Observe the following experiment: Rest a brick on a rough surface. Tie a string around the brick and attach a large spring scale to it. Pull the scale
10.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Friction Can Be Rough Observe the following experiment: Rest a brick on a rough surface. Tie a string around the brick and attach a large spring scale to it. Pull the scale
1. (P2.1A) The picture below shows a ball rolling along a table at 1 second time intervals. What is the object s average velocity after 6 seconds?
 PHYSICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW FIRST SEMESTER (01/2017) UNIT 1 Motion P2.1 A Calculate the average speed of an object using the change of position and elapsed time. P2.1B Represent the velocities for linear
PHYSICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW FIRST SEMESTER (01/2017) UNIT 1 Motion P2.1 A Calculate the average speed of an object using the change of position and elapsed time. P2.1B Represent the velocities for linear
Welcome to Forces an anticipation guide A force is defined as a push or a pull When answering the following true or false statements, offer a
 Welcome to Forces an anticipation guide A force is defined as a push or a pull When answering the following true or false statements, offer a real-life example that justifies your answer. You haven t answered
Welcome to Forces an anticipation guide A force is defined as a push or a pull When answering the following true or false statements, offer a real-life example that justifies your answer. You haven t answered
S2 Physics Forces. Pupil Booklet
 Name: Class: S2 Physics Forces Pupil Booklet Learning Outcomes Homework Exercises Unit Summary SCN 3-07a By contributing to investigations of energy loss due to friction, I can suggest ways of improving
Name: Class: S2 Physics Forces Pupil Booklet Learning Outcomes Homework Exercises Unit Summary SCN 3-07a By contributing to investigations of energy loss due to friction, I can suggest ways of improving
Physics B Newton s Laws AP Review Packet
 Force A force is a push or pull on an object. Forces cause an object to accelerate To speed up To slow down To change direction Unit: Newton (SI system) Newton s First Law The Law of Inertia. A body in
Force A force is a push or pull on an object. Forces cause an object to accelerate To speed up To slow down To change direction Unit: Newton (SI system) Newton s First Law The Law of Inertia. A body in
A force is a push or a pull.
 A force is a push or a pull. Contact forces arise from physical contact. Action at adistance forces do not require contact and include gravity and electrical forces. 1 Force is a vector [F]=[Newton]=[N]
A force is a push or a pull. Contact forces arise from physical contact. Action at adistance forces do not require contact and include gravity and electrical forces. 1 Force is a vector [F]=[Newton]=[N]
Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion Newtonian Mechanics Mass Mass is an intrinsic characteristic of a body The mass of a body is the characteristic that relates a force on the body to the resulting acceleration.
Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion Newtonian Mechanics Mass Mass is an intrinsic characteristic of a body The mass of a body is the characteristic that relates a force on the body to the resulting acceleration.
What is a Force? Free-Body diagrams. Contact vs. At-a-Distance 11/28/2016. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion What is a Force? In generic terms: a force is a push or a pull exerted on an object that could cause one of the following to occur: A linear acceleration of the object
Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion What is a Force? In generic terms: a force is a push or a pull exerted on an object that could cause one of the following to occur: A linear acceleration of the object
Mass & Weight. weight a force acting on a body due to the gravitational attraction pulling that body to another. NOT constant.
 Mass & Weight mass how much stuff a body has. Doesn t change. Is responsible for the inertial properties of a body. The greater the mass, the greater the force required to achieve some acceleration: Fnet
Mass & Weight mass how much stuff a body has. Doesn t change. Is responsible for the inertial properties of a body. The greater the mass, the greater the force required to achieve some acceleration: Fnet
Section /07/2013. PHY131H1F University of Toronto Class 9 Preclass Video by Jason Harlow. Based on Knight 3 rd edition Ch. 5, pgs.
 PHY131H1F University of Toronto Class 9 Preclass Video by Jason Harlow Based on Knight 3 rd edition Ch. 5, pgs. 116-133 Section 5.1 A force is a push or a pull What is a force? What is a force? A force
PHY131H1F University of Toronto Class 9 Preclass Video by Jason Harlow Based on Knight 3 rd edition Ch. 5, pgs. 116-133 Section 5.1 A force is a push or a pull What is a force? What is a force? A force
Tue Sept 15. Dynamics - Newton s Laws of Motion. Forces: Identifying Forces Free-body diagram Affect on Motion
 Tue Sept 15 Assignment 4 Friday Pre-class Thursday Lab - Print, do pre-lab Closed toed shoes Exam Monday Oct 5 7:15-9:15 PM email me if class conflict or extended time Dynamics - Newton s Laws of Motion
Tue Sept 15 Assignment 4 Friday Pre-class Thursday Lab - Print, do pre-lab Closed toed shoes Exam Monday Oct 5 7:15-9:15 PM email me if class conflict or extended time Dynamics - Newton s Laws of Motion
Some Facts About Force ASSIGNMENT. 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below : EDULABZ
 Some Facts About Force ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below : List : body, magnet, 10, itself, earth, friction, slide, gravity, opposite, electric,
Some Facts About Force ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below : List : body, magnet, 10, itself, earth, friction, slide, gravity, opposite, electric,
Four naturally occuring forces
 Forces System vs Environment: system the object the force is applied to environment the world around the object that exerts the force Type Forces: Contact is applied by touching Long range exerted without
Forces System vs Environment: system the object the force is applied to environment the world around the object that exerts the force Type Forces: Contact is applied by touching Long range exerted without
Exam 1 Solutions. Kinematics and Newton s laws of motion
 Exam 1 Solutions Kinematics and Newton s laws of motion No. of Students 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 PHY231 Spring 2012 Midterm Exam 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Raw Score 1. In which
Exam 1 Solutions Kinematics and Newton s laws of motion No. of Students 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 PHY231 Spring 2012 Midterm Exam 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Raw Score 1. In which
Forces and motion. 1 Explaining motion. 2 Identifying forces. 1 of 9
 1 of 9 Forces and motion 1 Explaining motion The reason why force is an important idea in physics is because the motion of any object can be explained by the forces acting on the object. The procedure
1 of 9 Forces and motion 1 Explaining motion The reason why force is an important idea in physics is because the motion of any object can be explained by the forces acting on the object. The procedure
SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION.
 MOTION & FORCES SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION. A. CALCULATE VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. B. APPLY NEWTON S THREE LAWS TO EVERYDAY SITUATIONS BY EXPLAINING THE
MOTION & FORCES SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION. A. CALCULATE VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. B. APPLY NEWTON S THREE LAWS TO EVERYDAY SITUATIONS BY EXPLAINING THE
Concept of Force and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Concept of Force and Newton s Laws of Motion 8.01 W02D2 Chapter 7 Newton s Laws of Motion, Sections 7.1-7.4 Chapter 8 Applications of Newton s Second Law, Sections 8.1-8.4.1 Announcements W02D3 Reading
Concept of Force and Newton s Laws of Motion 8.01 W02D2 Chapter 7 Newton s Laws of Motion, Sections 7.1-7.4 Chapter 8 Applications of Newton s Second Law, Sections 8.1-8.4.1 Announcements W02D3 Reading
PS113 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s laws of motion
 PS113 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s laws of motion 1 The concepts of force and mass A force is described as the push or pull between two objects There are two kinds of forces 1. Contact forces where two
PS113 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s laws of motion 1 The concepts of force and mass A force is described as the push or pull between two objects There are two kinds of forces 1. Contact forces where two
An Accelerating Hockey Puck
 Example 5.1 An Accelerating Hockey Puck A hockey puck having a mass of 0.30 kg slides on the frictionless, horizontal surface of an ice rink. Two hockey sticks strike the puck simultaneously, exerting
Example 5.1 An Accelerating Hockey Puck A hockey puck having a mass of 0.30 kg slides on the frictionless, horizontal surface of an ice rink. Two hockey sticks strike the puck simultaneously, exerting
Chapter Four Holt Physics. Forces and the Laws of Motion
 Chapter Four Holt Physics Forces and the Laws of Motion Physics Force and the study of dynamics 1.Forces - a. Force - a push or a pull. It can change the motion of an object; start or stop movement; and,
Chapter Four Holt Physics Forces and the Laws of Motion Physics Force and the study of dynamics 1.Forces - a. Force - a push or a pull. It can change the motion of an object; start or stop movement; and,
Physics 101. Hour Exam I Fall Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name:
 Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. This is a closed book exam. You have ninety (90) minutes to complete it.
Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. This is a closed book exam. You have ninety (90) minutes to complete it.
LAB 6: WORK AND ENERGY
 93 Name Date Partners LAB 6: WORK AND ENERGY OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Energy is the only life and is from the Body; and Reason is the bound or outward circumference of energy. Energy is eternal delight. William
93 Name Date Partners LAB 6: WORK AND ENERGY OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Energy is the only life and is from the Body; and Reason is the bound or outward circumference of energy. Energy is eternal delight. William
Chapter 5 Gravitation Chapter 6 Work and Energy
 Chapter 5 Gravitation Chapter 6 Work and Energy Chapter 5 (5.6) Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation (5.7) Gravity Near the Earth s Surface Chapter 6 (today) Work Done by a Constant Force Kinetic Energy,
Chapter 5 Gravitation Chapter 6 Work and Energy Chapter 5 (5.6) Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation (5.7) Gravity Near the Earth s Surface Chapter 6 (today) Work Done by a Constant Force Kinetic Energy,
Newton s First Law and IRFs
 Goals: Physics 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 22 Recognize different types of forces and know how they act on an object in a particle representation Identify forces and draw a Free Body Diagram Solve 1D and 2D
Goals: Physics 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 22 Recognize different types of forces and know how they act on an object in a particle representation Identify forces and draw a Free Body Diagram Solve 1D and 2D
UNIQUE SCIENCE ACADEMY General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 UNIQUE SIENE EMY General ertificate of Education Ordinary Level PHYSIS 995054/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice ugust 2010 lass 2 1 91 hour dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser Soft
UNIQUE SIENE EMY General ertificate of Education Ordinary Level PHYSIS 995054/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice ugust 2010 lass 2 1 91 hour dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser Soft
Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Physics I Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass:
Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Physics I Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass:
Main points of today s lecture: Normal force Newton s 3 d Law Frictional forces: kinetic friction: static friction Examples. Physic 231 Lecture 9
 Main points of today s lecture: Normal force Newton s 3 d Law Frictional forces: kinetic friction: static friction Examples. Physic 3 Lecture 9 f N k = µ k f N s < µ s Atwood s machine Consider the Atwood
Main points of today s lecture: Normal force Newton s 3 d Law Frictional forces: kinetic friction: static friction Examples. Physic 3 Lecture 9 f N k = µ k f N s < µ s Atwood s machine Consider the Atwood
Physics 2A Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Physics 2A Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion There is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeare It s not what happens to you that determines how far you will
Physics 2A Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion There is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeare It s not what happens to you that determines how far you will
Newton s Law of Motion
 Newton s Law of Motion Physics 211 Syracuse University, Physics 211 Spring 2019 Walter Freeman February 7, 2019 W. Freeman Newton s Law of Motion February 7, 2019 1 / 21 Announcements Homework 3 due next
Newton s Law of Motion Physics 211 Syracuse University, Physics 211 Spring 2019 Walter Freeman February 7, 2019 W. Freeman Newton s Law of Motion February 7, 2019 1 / 21 Announcements Homework 3 due next
Motion *All matter in the universe is constantly at motion Motion an object is in motion if its position is changing
 Aim: What is motion? Do Now: Have you ever seen a race? Describe what occurred during it. Homework: Vocabulary Define: Motion Point of reference distance displacement speed velocity force Textbook: Read
Aim: What is motion? Do Now: Have you ever seen a race? Describe what occurred during it. Homework: Vocabulary Define: Motion Point of reference distance displacement speed velocity force Textbook: Read
(a) On the dots below that represent the students, draw and label free-body diagrams showing the forces on Student A and on Student B.
 2003 B1. (15 points) A rope of negligible mass passes over a pulley of negligible mass attached to the ceiling, as shown above. One end of the rope is held by Student A of mass 70 kg, who is at rest on
2003 B1. (15 points) A rope of negligible mass passes over a pulley of negligible mass attached to the ceiling, as shown above. One end of the rope is held by Student A of mass 70 kg, who is at rest on
Circle the correct answer. For those questions involving calculations, working MUST be shown to receive credit.
 Dynamics Assignment 3 Name: Multiple Choice. Circle the correct answer. For those questions involving calculations, working MUST be shown to receive credit. 1. Which statement is always true regarding
Dynamics Assignment 3 Name: Multiple Choice. Circle the correct answer. For those questions involving calculations, working MUST be shown to receive credit. 1. Which statement is always true regarding
The Laws of Motion. Gravity and Friction
 The Laws of Motion Gravity and Friction Types of Forces Think about all the things you pushed or pulled today. You might have pushed toothpaste out of a tube. Maybe you pulled out a chair to sit down.
The Laws of Motion Gravity and Friction Types of Forces Think about all the things you pushed or pulled today. You might have pushed toothpaste out of a tube. Maybe you pulled out a chair to sit down.
This book was developed in collaboration with Region 4 Education Service Center, Houston, Texas.
 This book was developed in collaboration with Region 4 Education Service Center, Houston, Texas. Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. The following materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property
This book was developed in collaboration with Region 4 Education Service Center, Houston, Texas. Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. The following materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property
Chapter Introduction. Motion. Motion. Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Motion Graphing Motion Forces Chapter Wrap-Up What is the relationship between motion and forces? What do you think? Before you begin, decide
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Motion Graphing Motion Forces Chapter Wrap-Up What is the relationship between motion and forces? What do you think? Before you begin, decide
Concept of Force Concept Questions
 Concept of Force Concept Questions Question 1: You are pushing a wooden crate across the floor at constant speed. You decide to turn the crate on end, reducing by half the surface area in contact with
Concept of Force Concept Questions Question 1: You are pushing a wooden crate across the floor at constant speed. You decide to turn the crate on end, reducing by half the surface area in contact with
Free-Body Diagrams: Introduction
 Free-Body Diagrams: Introduction Learning Goal: To learn to draw free-body diagrams for various real-life situations. Imagine that you are given a description of a real-life situation and are asked to
Free-Body Diagrams: Introduction Learning Goal: To learn to draw free-body diagrams for various real-life situations. Imagine that you are given a description of a real-life situation and are asked to
CHAPTER 2. FORCE and Motion. CHAPTER s Objectives
 19 CHAPTER 2 FORCE and Motion CHAPTER s Objectives To define a force To understand the relation between force and motion In chapter 1, we understood that the Greek philosopher Aristotle was the first who
19 CHAPTER 2 FORCE and Motion CHAPTER s Objectives To define a force To understand the relation between force and motion In chapter 1, we understood that the Greek philosopher Aristotle was the first who
3/17/2018. Interacting Objects. Interacting Objects
 Example 0 - Iris drags a sled containing her baby brother across the floor at a constant speed. She pulls the sled at a 20 degree above the horizontal. Draw a FBD and write out N2L for both x and y directions.
Example 0 - Iris drags a sled containing her baby brother across the floor at a constant speed. She pulls the sled at a 20 degree above the horizontal. Draw a FBD and write out N2L for both x and y directions.
Lecture 7: More on Newton s Laws
 Lecture 7: More on Newton s Laws Other Important Aspects of the Second Law: Note that = ma is a vector equation, i.e., it is equivalent to saying: = ma x y z = ma = ma An object accelerates in the same
Lecture 7: More on Newton s Laws Other Important Aspects of the Second Law: Note that = ma is a vector equation, i.e., it is equivalent to saying: = ma x y z = ma = ma An object accelerates in the same
Virbations and Waves
 Virbations and Waves 1.1 Observe and find a pattern Try the following simple experiments and describe common patterns concerning the behavior of the block. (a) Fill in the table that follows. Experiment
Virbations and Waves 1.1 Observe and find a pattern Try the following simple experiments and describe common patterns concerning the behavior of the block. (a) Fill in the table that follows. Experiment
Practice Test for Midterm Exam
 A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
Friction Can Be Rough
 8.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Friction Can Be Rough Perform the following experiment: Rest a brick on a rough surface. Tie a string around the brick and attach a large spring scale to it. Pull the scale
8.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Friction Can Be Rough Perform the following experiment: Rest a brick on a rough surface. Tie a string around the brick and attach a large spring scale to it. Pull the scale
PHYSICS. Chapter 5 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
Bell Ringer: What is Newton s 3 rd Law? Which force acts downward? Which force acts upward when two bodies are in contact?
 Bell Ringer: What is Newton s 3 rd Law? Which force acts downward? Which force acts upward when two bodies are in contact? Does the moon attract the Earth with the same force that the Earth attracts the
Bell Ringer: What is Newton s 3 rd Law? Which force acts downward? Which force acts upward when two bodies are in contact? Does the moon attract the Earth with the same force that the Earth attracts the
How Do Objects Move? Describing Motion. Different Kinds of Motion
 How Do Objects Move? Describing Motion Different Kinds of Motion Motion is everywhere. The planets are in motion around the Sun. Cars are in motion as they are driven down the street. There s even motion
How Do Objects Move? Describing Motion Different Kinds of Motion Motion is everywhere. The planets are in motion around the Sun. Cars are in motion as they are driven down the street. There s even motion
Yanbu University College. General Studies Department. Phsc001 Course (111) Chapter2 (forces) Worksheet Solutions
 1 Yanbu University College General Studies Department Phsc001 Course (111) Chapter2 (forces) Worksheet Solutions 2 Chapter 2 Worksheet Part 1 Matching: Match the definitions with the given concepts. 1.
1 Yanbu University College General Studies Department Phsc001 Course (111) Chapter2 (forces) Worksheet Solutions 2 Chapter 2 Worksheet Part 1 Matching: Match the definitions with the given concepts. 1.
Chapter 12 Forces and Motion
 Chapter 12 Forces and Motion GOAL: Students will be able to interpret and apply Newton s three laws of motion and analyze the motion of an object in terms of its position, velocity, and acceleration. Standard:
Chapter 12 Forces and Motion GOAL: Students will be able to interpret and apply Newton s three laws of motion and analyze the motion of an object in terms of its position, velocity, and acceleration. Standard:
