CHEE 319 Process Dynamics and Control
|
|
|
- Karen Anderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHEE 319 Process Dynamics and Control Winter 2012 Instructor: M.Guay TAs: S. Dougherty, D. Park and E. Moshksar 1
2 Organization Instructor: Dr. Martin Guay Office: Dupuis 406 Phone: Web: 2
3 Schedule Lectures: (DUN 14 (for today only), JEF 127) Monday 10:30 11:20 Wednesday 9:30 10:20 Friday 8:30 9:20 Tutorials: Section A (DUP 244) Friday 9:30 10:20 Section B (DUP 244) Friday 10:30 11:20 Office Hours (MG): Monday 15:30 17:00 (Tentative) Tuesday 15:30 17:00 3
4 References All lectures will be available online Derivations will be done on the board Powerpoint slides are to support lectures Textbook (highly recommended) D.E. Seborg,, T.F. Edgar, D.A. Mellichamp, Process Dynamics and Control (2nd or 3rd Edition),, Wiley, NJ (2003, 2009). 4
5 Grading Grading Midterm (TBDIC) 25% Assignments 15% Final Exam 60% 5
6 Guidelines i) Assignments Problems will be assigned every week. Although they will not be marked, weekly tutorials will be concentrated on the solution of the problems and on questions that may arise from the course. Collaboration is encouraged throughout the course. It is recommended that the students develop their own individual solutions. There will be a set of assignments that will be marked. They are to be completed in groups of 4-5. With one assignment per group. ii) Exams Midterm exam will be open-book. Textbooks, course notes and assignments will be allowed. The final will be closed-book. The timing of the midterm exam will be decided in class. (Likely to be after reading week.) 6
7 Course Objectives By the end of this course the student should be able to: derive transfer function models from process models and process data recognize important process dynamic features of SISO linear dynamical systems apply modern control theory to design a controller for uncertain SISO linear dynamical systems understand the trade-off in performance that arise in the design of a controller 7
8 Teaching Approach and Expectations Each student is ultimately responsible for learning the material in a course. Every professor is responsible for presenting the course material in a manner that facilitates learning as much as possible for the class as a whole. 8
9 Teaching Approach and Expectations In fulfilling this contract, I expect that you will actively and constructively participate in the course. ask questions whenever something is not clear, help each other understand the course material, perform all assigned reading on time, arrive on-time for class, be courteous to each other and myself, provide me with feedback / suggestions as to how the course and my delivery can be improved. 9
10 Teaching Approach and Expectations In return you should expect me to: treat each of you with courtesy and respect, be committed to help you understand and master the course material, by being available for out of class assistance, by providing competent teaching assistants, by working to continually improve the course, treat each question or concern seriously and answer these to the best of my ability. Class discussions and student participation are encouraged as much as possible, in and out of the classroom 10
11 Course Outline 1. Introduction 2. Modeling for control 3. Solution of Linear ODEs using Laplace transforms 4. Transfer function models of mechanical systems 5. Analysis of Continuous-time Linear Systems 6. SISO Control System Analysis 7. Synthesis of SISO Controllers 8. SISO Controller Design 11
12 Introduction Feedback systems are commonplace in almost every aspect of life Standing, walking, running etc are all forms of control systems where the central nervous system reacts to various biosensor mechanisms Gene regulation is controlled by complex responses that trigger various biological mechanisms In engineering applications, feedback systems arise in the design of control systems Aircraft flight control, satellite s altitude control Automotive control Communication systems Robotics Manugfacturing systems and industrial process cotnrol Control is the hidden technology It s s everywhere, but hidden by the machinery. 12
13 Introduction Feedback systems: Interconnection of two systems System 1 System 2 E.g. Glucose concentration regulation: System 1 is the liver System 2 is the pancreas the output of interest,, is glucose concentration the input of interest,, is insulin release rate 13
14 Control What is a feedback controller? Process Controller A controller is a system designed to regulate a given process Process typically obeys physical and chemical conservation laws Controller obeys laws of mathematics and logic (sometimes intelligent) e.g. - Riding a bike (human controller) - Driving a car - Automatic control (computer programmed to control) 14
15 Control A controlled process is a system which is comprised of two interacting systems: e.g. Most controlled systems are feedback control systems Disturbances Process Outputs Action intervene Controller Observation monitor The controller is designed to provide regulation of process outputs in the presence of disturbances 15
16 Classical Feedback Control Control is meant to provide regulation of process outputs about a reference, r, despite inherent disturbances d r + - e Controller u Process y Classical Feedback Control System The deviation of the plant output, e=(r-y), from its intended reference is used to make appropriate adjustments in the plant input, u 16
17 Feedforward Control Feedforward control is used to remove the effect of measurable disturbances Disturbance M Nominal Input + + C ff Input Correction A Corrected Input P 17
18 Open-loop vs. Closed-loop Feedback control is an example of closed-loop control: The process output is sent back to the controller before affecting the process Process Control Open-loop control Control Process Controller affects the behavior of Process in a non reactive way 18
19 Control goes back to the 19th century Central theme in many important areas Major impact in flight f control We know how to construct airplanes. Men also know how to build engines. Inability to balance and steer still confronts students of the flying problem.. When one feature has been worked out, the age of flying will have arrived, for all other difficulties are of minor importance. Wilbur Wright (1901) 19
20 Historical Perspective History of flight control is a testament to the importance of control theory Wright Brothers 1903 Sperry s s Autopilot 1912 V1 and V2 (A4) 1942 Robert E. Lee 1947 Sputnik 1957 Apollo 1969 Mars Pathfinder
21 Examples e.g. Landing on Mars 21
22 Historical Perspective The feedback amplifier Invented by Black (1928) to improve signal strength Enables telephone calls over long distances Input + Output - Open-loop amplification Becomes Amplification of the feedback amplifier depends on feedback gain 22
23 Historical Perspective The invention of the feedback amplifier is fundamental Forms the basis for the design of world wide telephone/television networks Confirms the importance of feedback system design Nyquist stability theorem 1932 Bode s work on feedback design 1940 Provides the framework for modern control system theory and control system design 23
24 Historical Perspective By 1940, the magic of feedback was understood An extra component to be considered for process design to: Keep key variables constant Stabilize unstable systems Reduce the effects of disturbances and process variations Main drawback: can de-stabilize stable processes Principles of feedback applied in: Power electronics Industrial process control Flight control Telecommunications But, the similarities between all applications were not understood yet. 24
25 Historical Perspective From 40s, a new field emerges Similarities between applications are understood leading to the unification of Solid theoretical framework Sound design methodology Design principles Applications Modern Control systems Well established body of ideas, concepts, theory and design methods. Wide and growing scope of applications Remains a very active area of research and development 25
26 Introduction In engineering applications, the design of a control system is essential to ensure: Good Process Operation Process Safety Product Quality Minimization of Environmental Impact 26
27 Introduction What is the purpose of a control system? To maintain important process characteristics at desired targets despite the effects of external perturbations. Perturbations Plant Processing objectives Market Economy Climate Upsets... Safety Make $$$ Environment... Control 27
28 Introduction Dynamics: Study of the transient behavior of processes Control: the use of process dynamics for the improvement of process operation and performance the use of process dynamics to alleviate the effect of undesirable (unstable) process behaviors 28
29 What do we mean by process, plant or system? Introduction A process (plant or system),, is an operation that takes an INPUT or a DISTURBANCE and gives an OUTPUT Information Flow INPUT: ( ) Something that you can manipulate DISTURBANCE: ( ) Something that comes as a result of some outside phenomenon OUTPUT: ( ) An observable quantity that we want to regulate 29
30 Examples The speed of an automobile Inputs Friction Engine Aerodynamic Friction Process Force of Engine Output Speed 30
31 Examples Stirred tank heater T in, w M Inputs T in w Q Q Process T, w Output T 31
32 Block representations Block diagrams are models of the physical systems Input variables Process Output variables System Physical Boundary Transfer of fundamental quantities Mass, Energy and Momentum Physical Operation Abstract 32
33 Introduction What is required for the development of a control system? 1. Process Understanding Required measurements Dynamic model Required actuators Understand design limitations 2. Process Instrumentation Appropriate sensor and actuator selection Integration in control system Communication and computer architecture 3. Process Control Appropriate control strategy 33
34 Examples Measure, adjust Controller Heater + - C A M P Tank Thermocouple Feedback control Controller: where Q: Is this positive or negative feedback? 34
35 Example Cruise Control Friction Engine Process Speed Controller Human or Computer 35
36 Classical Control Control is meant to provide regulation of process outputs about a reference, r, despite inherent disturbances d r + - e Controller u Process y Classical Feedback Control System The deviation of the plant output, e=(r-y), from its intended reference is used to make appropriate adjustments in the plant input, u 36
37 Control Process is a combination of sensors and actuators Controller is a computer (or operator) that performs the required manipulations d r + - e Computer C Actuator A P y Process M Sensor e.g. Classical feedback control loop 37
38 Examples Driving an automobile r + - e Driver C Steering A M P Automobile y Visual and tactile measurement Desired trajectory r Actual trajectory y 38
39 Examples Stirred-Tank Heater T in, w Heater Q T, w T R + - e Controller C TC Thermocouple Heater A M T in, w P Tank y Thermocouple 39
40 Examples Measure T i, adjust Q T i M C A P Q i + + ΔQ Q Feedforward Control 40
41 Feedforward Control Feedforward control is used to remove the effect of measurable disturbances Disturbance M Nominal Input + + C ff Input Correction A Corrected Input P 41
42 Identification of all process variables Control Nomenclature Inputs Outputs (affect process) (result of process) Inputs Disturbance variables Variables affecting process that are due to external forces Manipulated variables Things that we can directly affect 42
43 Control Nomenclature Outputs Measured speed of a car Unmeasured acceleration of a car Control variables important observable quantities that we want to regulate can be measured or unmeasured Disturbances Manipulated Process Other Control Controller 43
44 Examples The speed of an automobile Friction Variables Engine force: u Car speed: v Friction force: f fric Aerodynamic forces: f aero Road inclination: Force of Engine 44
45 Example Variables Inputs Outputs Disturbances Manipulated Measured Unmeasured Control Task: Classify the variables 45
46 Example w i, T i P c L w c, T ci h T P o wc, Tco Variables w i, w o : T i, T o : w c : P c : P o : T ci, T co : h: Tank inlet and outlet mass flows Tank inlet and outlet temperatures Cooling jacket mass flow Position of cooling jacket inlet valve Position of tank outlet valve Cooling jacket inlet and outlet temperatures Tank liquid level T w o, T o 46
47 Example Variables Inputs Outputs Disturbances Manipulated Measured Unmeasured Control w i T i T ci w c h w o T o P c P o Task: Classify the variables 47
48 Process Control and Modeling In designing a controller, we must Define control objectives Develop a process model Design controller based on model Test through simulation Implement to real process r Tune and monitor e Controller u d Process y Model Design Implementation 48
49 Control System Development Control development is usually carried out following these important steps Define Objectives Develop a process model Design controller based on model Test by Simulation Implement and Tune Monitor Performance Often an iterative process, based on performance we may decide to retune, redesign or remodel a given control system 49
50 Control System Development Objectives What are we trying to control? Process modeling What do we need? Mechanistic and/or empirical Controller design How do we use the knowledge of process behavior to reach our process control objectives? What variables should we measure? What variables should we control? What are the best manipulated variables? What is the best controller structure? 50
51 Control System Development Implement and tune the controlled process Test by simulation incorporate control strategy to the process hardware theory rarely transcends to reality tune and re-tune Monitor performance periodic retuning and redesign is often necessary based on sensitivity of process or market demands statistical methods can be used to monitor performance 51
Subject: Introduction to Process Control. Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring Content
 v CHEG 461 : Process Dynamics and Control Subject: Introduction to Process Control Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring 2014 Dr. Costas Kiparissides Content 1. Introduction to Process Dynamics and Control 2.
v CHEG 461 : Process Dynamics and Control Subject: Introduction to Process Control Week 01, Lectures 01 02, Spring 2014 Dr. Costas Kiparissides Content 1. Introduction to Process Dynamics and Control 2.
Advanced Aerospace Control. Marco Lovera Dipartimento di Scienze e Tecnologie Aerospaziali, Politecnico di Milano
 Advanced Aerospace Control Dipartimento di Scienze e Tecnologie Aerospaziali, Politecnico di Milano ICT for control systems engineering School of Industrial and Information Engineering Aeronautical Engineering
Advanced Aerospace Control Dipartimento di Scienze e Tecnologie Aerospaziali, Politecnico di Milano ICT for control systems engineering School of Industrial and Information Engineering Aeronautical Engineering
ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS. Instructor: S. P. Bhattacharyya* (Dr. B.) 1/18
 ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS Instructor: S. P. Bhattacharyya* (Dr. B.) 1/18 Course information Course Duration: 14 weeks Divided into 7 units, each of two weeks duration, 5 lectures, 1 test Each unit
ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS Instructor: S. P. Bhattacharyya* (Dr. B.) 1/18 Course information Course Duration: 14 weeks Divided into 7 units, each of two weeks duration, 5 lectures, 1 test Each unit
What is flight dynamics? AE540: Flight Dynamics and Control I. What is flight control? Is the study of aircraft motion and its characteristics.
 KING FAHD UNIVERSITY Department of Aerospace Engineering AE540: Flight Dynamics and Control I Instructor Dr. Ayman Hamdy Kassem What is flight dynamics? Is the study of aircraft motion and its characteristics.
KING FAHD UNIVERSITY Department of Aerospace Engineering AE540: Flight Dynamics and Control I Instructor Dr. Ayman Hamdy Kassem What is flight dynamics? Is the study of aircraft motion and its characteristics.
Astronomy 001 Online SP16 Syllabus (Section 8187)
 Astronomy 001 Online SP16 Syllabus (Section 8187) Instructor: Elizabeth Bell Email (best way to contact me): bellea@wlac.edu Classroom: online Office Hours: online by appointment Prerequisite: None REQUIRED:
Astronomy 001 Online SP16 Syllabus (Section 8187) Instructor: Elizabeth Bell Email (best way to contact me): bellea@wlac.edu Classroom: online Office Hours: online by appointment Prerequisite: None REQUIRED:
AE 200 Engineering Analysis and Control of Aerospace Systems
 Instructor Info Credit Class Days / Time Office Location: ENG 272C Office Hours: Monday 4:00pm 6:30pm Email: kamran.turkoglu@sjsu.edu 3 units Tuesday, 6:00pm 8:45pm Classroom CL 222 Prerequisites TA: Contact
Instructor Info Credit Class Days / Time Office Location: ENG 272C Office Hours: Monday 4:00pm 6:30pm Email: kamran.turkoglu@sjsu.edu 3 units Tuesday, 6:00pm 8:45pm Classroom CL 222 Prerequisites TA: Contact
Solid foundations has been a hallmark of the control community
 A Broad Picture There are examples of control from ancient time but control became widely used in the industries that emerged in the 19 th and 20 th centuries: steam power, electric power, ships, aircrafts,
A Broad Picture There are examples of control from ancient time but control became widely used in the industries that emerged in the 19 th and 20 th centuries: steam power, electric power, ships, aircrafts,
CH 331 Syllabus Fall 2012
 Instructor Information: Dr. Daniel J. T. Myles Office: Gilbert Hall 145 Phone: 541-737-6756 E-mail: daniel.myles@oregonstate.edu All course information, updates, and announcements are posted via Blackboard
Instructor Information: Dr. Daniel J. T. Myles Office: Gilbert Hall 145 Phone: 541-737-6756 E-mail: daniel.myles@oregonstate.edu All course information, updates, and announcements are posted via Blackboard
Overview of the Seminar Topic
 Overview of the Seminar Topic Simo Särkkä Laboratory of Computational Engineering Helsinki University of Technology September 17, 2007 Contents 1 What is Control Theory? 2 History
Overview of the Seminar Topic Simo Särkkä Laboratory of Computational Engineering Helsinki University of Technology September 17, 2007 Contents 1 What is Control Theory? 2 History
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6
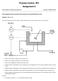 Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Chemistry 14C: Structure of Organic Molecules - Winter 2017 Version 56
 Chemistry 14C: Structure of Organic Molecules - Winter 2017 Version 56 Instructor: Dr. Steven A. Hardinger Office: Young Hall 3077C harding@chem.ucla.edu Office hours: Monday and Tuesday 2:00-2:50 PM Teaching
Chemistry 14C: Structure of Organic Molecules - Winter 2017 Version 56 Instructor: Dr. Steven A. Hardinger Office: Young Hall 3077C harding@chem.ucla.edu Office hours: Monday and Tuesday 2:00-2:50 PM Teaching
Control System Design
 ELEC ENG 4CL4: Control System Design Notes for Lecture #1 Monday, January 6, 2003 Instructor: Dr. Ian C. Bruce Room CRL-229, Ext. 26984 ibruce@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Office Hours: TBA Teaching Assistants:
ELEC ENG 4CL4: Control System Design Notes for Lecture #1 Monday, January 6, 2003 Instructor: Dr. Ian C. Bruce Room CRL-229, Ext. 26984 ibruce@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Office Hours: TBA Teaching Assistants:
Office Hours: Mon., Wed before and after class or by appointment.
 Instructor: Long Beach Community College Chemistry 2 Introductory General Chemistry Section 70320 Spring 2013 MW 8:00 9:25 AM, Lecture, Room D314 M 9:35 10:40, Prelab lecture, Room D304 M 10:50 12:55 PM,
Instructor: Long Beach Community College Chemistry 2 Introductory General Chemistry Section 70320 Spring 2013 MW 8:00 9:25 AM, Lecture, Room D314 M 9:35 10:40, Prelab lecture, Room D304 M 10:50 12:55 PM,
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Dynamics 2
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Dynamics 2 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) office hour: LEE
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Dynamics 2 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) office hour: LEE
MATH4406 (Control Theory) Unit 1: Introduction Prepared by Yoni Nazarathy, July 21, 2012
 MATH4406 (Control Theory) Unit 1: Introduction Prepared by Yoni Nazarathy, July 21, 2012 Unit Outline Introduction to the course: Course goals, assessment, etc... What is Control Theory A bit of jargon,
MATH4406 (Control Theory) Unit 1: Introduction Prepared by Yoni Nazarathy, July 21, 2012 Unit Outline Introduction to the course: Course goals, assessment, etc... What is Control Theory A bit of jargon,
Automatic Control (TSRT15): Lecture 1
 Automatic Control (TSRT15): Lecture 1 Tianshi Chen* Division of Automatic Control Dept. of Electrical Engineering Email: tschen@isy.liu.se Phone: 13-282226 Office: B-house extrance 25-27 * All lecture
Automatic Control (TSRT15): Lecture 1 Tianshi Chen* Division of Automatic Control Dept. of Electrical Engineering Email: tschen@isy.liu.se Phone: 13-282226 Office: B-house extrance 25-27 * All lecture
Control Systems I. Lecture 1: Introduction. Suggested Readings: Åström & Murray Ch. 1, Guzzella Ch. 1. Emilio Frazzoli
 Control Systems I Lecture 1: Introduction Suggested Readings: Åström & Murray Ch. 1, Guzzella Ch. 1 Emilio Frazzoli Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control D-MAVT ETH Zürich September 22, 2017 E. Frazzoli
Control Systems I Lecture 1: Introduction Suggested Readings: Åström & Murray Ch. 1, Guzzella Ch. 1 Emilio Frazzoli Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control D-MAVT ETH Zürich September 22, 2017 E. Frazzoli
ELEC4631 s Lecture 2: Dynamic Control Systems 7 March Overview of dynamic control systems
 ELEC4631 s Lecture 2: Dynamic Control Systems 7 March 2011 Overview of dynamic control systems Goals of Controller design Autonomous dynamic systems Linear Multi-input multi-output (MIMO) systems Bat flight
ELEC4631 s Lecture 2: Dynamic Control Systems 7 March 2011 Overview of dynamic control systems Goals of Controller design Autonomous dynamic systems Linear Multi-input multi-output (MIMO) systems Bat flight
Mathematical Description of Light
 Mathematical Description of Light Thursday, 8/24/2006 Physics 158 Peter Beyersdorf Document info 1 Class Outline Introductions/Announcements Properties of light Mathematical description of transverse waves
Mathematical Description of Light Thursday, 8/24/2006 Physics 158 Peter Beyersdorf Document info 1 Class Outline Introductions/Announcements Properties of light Mathematical description of transverse waves
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY
 Fall 2013 DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY Tuesday, Thursday 9:30-10:45 a.m. Room 401 ESB ChE 435 Chemical Process Control - Process Dynamics, Instrumentation & Control Instructor:
Fall 2013 DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY Tuesday, Thursday 9:30-10:45 a.m. Room 401 ESB ChE 435 Chemical Process Control - Process Dynamics, Instrumentation & Control Instructor:
REMOTE SENSING OF THE ATMOSPHERE AND OCEANS
 EAS 6145 SPRING 2007 REMOTE SENSING OF THE ATMOSPHERE AND OCEANS Instructor: Prof. Irina N. Sokolik office 2258, phone 404-894-6180 isokolik@eas.gatech.edu Meeting Time: Mondays: 3:05-4:25 PM Wednesdays:
EAS 6145 SPRING 2007 REMOTE SENSING OF THE ATMOSPHERE AND OCEANS Instructor: Prof. Irina N. Sokolik office 2258, phone 404-894-6180 isokolik@eas.gatech.edu Meeting Time: Mondays: 3:05-4:25 PM Wednesdays:
Physics 141 Course Information
 Physics 141 Course Information General Physics I - Mechanics Spring 2008 Instructors: Office Hours: Textbook: Online Homework: Disclaimer: Nikos Varelas 2134 SES (312) 996-3415 varelas@uic.edu Charles
Physics 141 Course Information General Physics I - Mechanics Spring 2008 Instructors: Office Hours: Textbook: Online Homework: Disclaimer: Nikos Varelas 2134 SES (312) 996-3415 varelas@uic.edu Charles
Physics 141 Course Information
 Physics 141 Course Information General Physics I - Mechanics Spring 2009 Instructors: Office Hours: Textbook: Online Homework: Disclaimer: Nikos Varelas 2134 SES (312) 996-3415 varelas@uic.edu Adrian Barkan
Physics 141 Course Information General Physics I - Mechanics Spring 2009 Instructors: Office Hours: Textbook: Online Homework: Disclaimer: Nikos Varelas 2134 SES (312) 996-3415 varelas@uic.edu Adrian Barkan
ENVIRONMENT AND NATURAL RESOURCES 3700 Introduction to Spatial Information for Environment and Natural Resources. (2 Credit Hours) Semester Syllabus
 ENVIRONMENT AND NATURAL RESOURCES 3700 Introduction to Spatial Information for Environment and Natural Resources COURSE INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Kris Jaeger Assistant Professor 359 Kottman Hall (Mondays and Tuesdays)
ENVIRONMENT AND NATURAL RESOURCES 3700 Introduction to Spatial Information for Environment and Natural Resources COURSE INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Kris Jaeger Assistant Professor 359 Kottman Hall (Mondays and Tuesdays)
PHYSICS 564 Introduction to Particle Physics I
 PHYSICS 564 Introduction to Particle Physics I Prof. Norbert Neumeister Department of Physics Purdue University Fall 2016 http://www.physics.purdue.edu/phys564 Course Format Lectures: Time: Tuesday, Thursday
PHYSICS 564 Introduction to Particle Physics I Prof. Norbert Neumeister Department of Physics Purdue University Fall 2016 http://www.physics.purdue.edu/phys564 Course Format Lectures: Time: Tuesday, Thursday
Monday May 12, :00 to 1:30 AM
 ASTRONOMY 108: Descriptive Astronomy Spring 2008 Instructor: Hugh Gallagher Office: Physical Science Building 130 Phone, Email: 436-3177, gallagha@oneonta.edu Office Hours: M 2:00-3:00 PM, Th 10:00-11:00
ASTRONOMY 108: Descriptive Astronomy Spring 2008 Instructor: Hugh Gallagher Office: Physical Science Building 130 Phone, Email: 436-3177, gallagha@oneonta.edu Office Hours: M 2:00-3:00 PM, Th 10:00-11:00
Welcome to Physics 161 Elements of Physics Fall 2018, Sept 4. Wim Kloet
 Welcome to Physics 161 Elements of Physics Fall 2018, Sept 4 Wim Kloet 1 Lecture 1 TOPICS Administration - course web page - contact details Course materials - text book - iclicker - syllabus Course Components
Welcome to Physics 161 Elements of Physics Fall 2018, Sept 4 Wim Kloet 1 Lecture 1 TOPICS Administration - course web page - contact details Course materials - text book - iclicker - syllabus Course Components
Stellar Astronomy 1401 Spring 2009
 Stellar Astronomy 1401 Spring 2009 Instructor: Ron Wilhelm Office: Science Building Room 9 Contact information: Office Hours: 742-4707 or ron.wilhelm@ttu.edu MWF 10:00-11:00 PM T & Th 11:30-12:30 AM Or
Stellar Astronomy 1401 Spring 2009 Instructor: Ron Wilhelm Office: Science Building Room 9 Contact information: Office Hours: 742-4707 or ron.wilhelm@ttu.edu MWF 10:00-11:00 PM T & Th 11:30-12:30 AM Or
AS 101: The Solar System (Spring 2017) Course Syllabus
 AS 101: The Solar System (Spring 2017) Course Syllabus Instructor: Professor Wen Li Office: CAS 501 Phone: 617-353-7439 Email: wenli77@bu.edu Office hours: Mondays 3:30 5:00 pm, Wednesdays 3:30 5:00 pm,
AS 101: The Solar System (Spring 2017) Course Syllabus Instructor: Professor Wen Li Office: CAS 501 Phone: 617-353-7439 Email: wenli77@bu.edu Office hours: Mondays 3:30 5:00 pm, Wednesdays 3:30 5:00 pm,
CE261 ENGINEERING MECHANICS - DYNAMICS
 CE1 ENGINEERING MECHANICS - DYNAMICS Instructor JORGE A. RAMÍREZ, PH.D. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Water Resources, Hydrologic and Environmental Sciences Division Civil Engineering Department A Engineering Bldg.
CE1 ENGINEERING MECHANICS - DYNAMICS Instructor JORGE A. RAMÍREZ, PH.D. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Water Resources, Hydrologic and Environmental Sciences Division Civil Engineering Department A Engineering Bldg.
Course Staff. Textbook
 Course Staff CS311H: Discrete Mathematics Intro and Propositional Logic Instructor: Işıl Dillig Instructor: Prof. Işıl Dillig TAs: Jacob Van Geffen, Varun Adiga, Akshay Gupta Class meets every Monday,
Course Staff CS311H: Discrete Mathematics Intro and Propositional Logic Instructor: Işıl Dillig Instructor: Prof. Işıl Dillig TAs: Jacob Van Geffen, Varun Adiga, Akshay Gupta Class meets every Monday,
Chemistry A Course Syllabus
 Chemistry A Course Syllabus Course Description: Chemistry A is designed to acquaint you with topics in chemistry, including the science of chemistry, matter and energy, atomic structure, the periodic table,
Chemistry A Course Syllabus Course Description: Chemistry A is designed to acquaint you with topics in chemistry, including the science of chemistry, matter and energy, atomic structure, the periodic table,
CHEMISTRY 3A INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY SPRING
 CHEMISTRY 3A INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY SPRING ---- 2007 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Phil Reedy Office: Cunningham 321 Telephone: 954-5671 email: preedy@deltacollege.edu WEBSITES: www.deltacollege.edu/emp/preedy www.preparatorychemistry.com
CHEMISTRY 3A INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY SPRING ---- 2007 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Phil Reedy Office: Cunningham 321 Telephone: 954-5671 email: preedy@deltacollege.edu WEBSITES: www.deltacollege.edu/emp/preedy www.preparatorychemistry.com
AS The Astronomical Universe. Prof. Merav Opher - Fall 2013
 SYLLABUS AS 102 - The Astronomical Universe Prof. Merav Opher - Fall 2013 Course Catalog Summary: The birth and death of stars; red giants, white dwarfs, black holes; our galaxy, the Milky Way, and other
SYLLABUS AS 102 - The Astronomical Universe Prof. Merav Opher - Fall 2013 Course Catalog Summary: The birth and death of stars; red giants, white dwarfs, black holes; our galaxy, the Milky Way, and other
Advanced Analytical Chemistry The University of Toledo Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry CHEM / /
 Advanced Analytical Chemistry The University of Toledo Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry CHEM 4305 001/6300 001/8300 001 Instructor: Emanuela Gionfriddo Email: emanuela.gionfriddo@utoledo.edu Office
Advanced Analytical Chemistry The University of Toledo Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry CHEM 4305 001/6300 001/8300 001 Instructor: Emanuela Gionfriddo Email: emanuela.gionfriddo@utoledo.edu Office
Welcome to Physics 211! General Physics I
 Welcome to Physics 211! General Physics I Physics 211 Fall 2015 Lecture 01-1 1 Physics 215 Honors & Majors Are you interested in becoming a physics major? Do you have a strong background in physics and
Welcome to Physics 211! General Physics I Physics 211 Fall 2015 Lecture 01-1 1 Physics 215 Honors & Majors Are you interested in becoming a physics major? Do you have a strong background in physics and
Control of MIMO processes. 1. Introduction. Control of MIMO processes. Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes
 Control of MIMO processes Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes Statistical Process Control Feedforward and ratio control Cascade control Split range and selective control Control
Control of MIMO processes Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes Statistical Process Control Feedforward and ratio control Cascade control Split range and selective control Control
CDS 101/110a: Lecture 1.1 Introduction to Feedback & Control. CDS 101/110 Course Sequence
 CDS 101/110a: Lecture 1.1 Introduction to Feedback & Control Richard M. Murray 28 September 2015 Goals: Give an overview of CDS 101/110: course structure & administration Define feedback systems and learn
CDS 101/110a: Lecture 1.1 Introduction to Feedback & Control Richard M. Murray 28 September 2015 Goals: Give an overview of CDS 101/110: course structure & administration Define feedback systems and learn
CHAPTER 5 ROBUSTNESS ANALYSIS OF THE CONTROLLER
 114 CHAPTER 5 ROBUSTNESS ANALYSIS OF THE CONTROLLER 5.1 INTRODUCTION Robust control is a branch of control theory that explicitly deals with uncertainty in its approach to controller design. It also refers
114 CHAPTER 5 ROBUSTNESS ANALYSIS OF THE CONTROLLER 5.1 INTRODUCTION Robust control is a branch of control theory that explicitly deals with uncertainty in its approach to controller design. It also refers
(Refer Slide Time: 1:42)
 Control Engineering Prof. Madan Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 21 Basic Principles of Feedback Control (Contd..) Friends, let me get started
Control Engineering Prof. Madan Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 21 Basic Principles of Feedback Control (Contd..) Friends, let me get started
Geography 1103: Spatial Thinking
 Geography 1103: Spatial Thinking Lecture: T\TH 8:00-9:15 am (McEniry 401) Lab: Wed 2:00-4:30 pm (McEniry 420) Instructor: Dr. Elizabeth C. Delmelle Email: edelmell@uncc.edu Office: McEniry 419 Phone: 704-687-5932
Geography 1103: Spatial Thinking Lecture: T\TH 8:00-9:15 am (McEniry 401) Lab: Wed 2:00-4:30 pm (McEniry 420) Instructor: Dr. Elizabeth C. Delmelle Email: edelmell@uncc.edu Office: McEniry 419 Phone: 704-687-5932
ECE 516: System Control Engineering
 ECE 516: System Control Engineering This course focuses on the analysis and design of systems control. This course will introduce time-domain systems dynamic control fundamentals and their design issues
ECE 516: System Control Engineering This course focuses on the analysis and design of systems control. This course will introduce time-domain systems dynamic control fundamentals and their design issues
Physics 343: Modern Physics Autumn 2015
 Physics 343: Modern Physics Autumn 2015 Course Information Instructor: Dr. David A. Macaluso Office: C.H. Clapp Building, room 119 Telephone: (406) 243-6641 Email: david.macaluso@umontana.edu Lectures:
Physics 343: Modern Physics Autumn 2015 Course Information Instructor: Dr. David A. Macaluso Office: C.H. Clapp Building, room 119 Telephone: (406) 243-6641 Email: david.macaluso@umontana.edu Lectures:
Chapter 0 Introduction. Advanced Urban Analysis E. - Spatial Analysis and GIS Educational background. 0.1 Introducing myself
 Course #716-26 Advanced Urban Analysis E Chapter 0 Introduction Lecture Title: - Spatial Analysis and GIS Instructor: Yukio Sadahiro 0.1 Introducing myself 0.1.1 Educational background Yukio Sadahiro Associate
Course #716-26 Advanced Urban Analysis E Chapter 0 Introduction Lecture Title: - Spatial Analysis and GIS Instructor: Yukio Sadahiro 0.1 Introducing myself 0.1.1 Educational background Yukio Sadahiro Associate
CHE 717, Chemical Reaction Engineering, Fall 2016 COURSE SYLLABUS
 Page 1 of 5 CHE 717, Chemical Reaction Engineering, Fall 2016 COURSE SYLLABUS engineeringonline.ncsu.edu/onlinecourses/coursehomepages/fall-2016/che717.html Instructor: Prof. Jason Haugh 3100 Partners
Page 1 of 5 CHE 717, Chemical Reaction Engineering, Fall 2016 COURSE SYLLABUS engineeringonline.ncsu.edu/onlinecourses/coursehomepages/fall-2016/che717.html Instructor: Prof. Jason Haugh 3100 Partners
ASTR 4 Solar System Astronom y
 Lectures: M thru F, :30-:0 am Location: De Anza Planetarium ASTR 4 Solar System Astronom y Marek Cichanski Office: S-a cichanskimarek@fhda.edu (40) 4-4 Office Hours: M thru F, :30 0:0 am In This Syllabus
Lectures: M thru F, :30-:0 am Location: De Anza Planetarium ASTR 4 Solar System Astronom y Marek Cichanski Office: S-a cichanskimarek@fhda.edu (40) 4-4 Office Hours: M thru F, :30 0:0 am In This Syllabus
Chemistry 020. Intersession 2007 Course Outline. Instructor: Kay Calvin ChB
 Chemistry 020 Intersession 2007 Course Outline Instructor: Kay Calvin ChB 117 E-mail: kcalvin@uwo.ca Course Website: http://instruct.uwo.ca/chemistry/020inter Course information will also be posted on
Chemistry 020 Intersession 2007 Course Outline Instructor: Kay Calvin ChB 117 E-mail: kcalvin@uwo.ca Course Website: http://instruct.uwo.ca/chemistry/020inter Course information will also be posted on
EG4321/EG7040. Nonlinear Control. Dr. Matt Turner
 EG4321/EG7040 Nonlinear Control Dr. Matt Turner EG4321/EG7040 [An introduction to] Nonlinear Control Dr. Matt Turner EG4321/EG7040 [An introduction to] Nonlinear [System Analysis] and Control Dr. Matt
EG4321/EG7040 Nonlinear Control Dr. Matt Turner EG4321/EG7040 [An introduction to] Nonlinear Control Dr. Matt Turner EG4321/EG7040 [An introduction to] Nonlinear [System Analysis] and Control Dr. Matt
Black Boxes & White Noise
 Black Boxes & White Noise The Evolution of Automatic Control K. J. Åström Lund Institute of Technology Lund, Sweden 1. Introduction 2. Early Ideas 3. A Discipline Emerges 4. The Second Wave 5. Conclusions
Black Boxes & White Noise The Evolution of Automatic Control K. J. Åström Lund Institute of Technology Lund, Sweden 1. Introduction 2. Early Ideas 3. A Discipline Emerges 4. The Second Wave 5. Conclusions
Physics 162a Quantum Mechanics
 Physics 162a Quantum Mechanics 1 Introduction Syllabus for Fall 2009 This is essentially a standard first-year course in quantum mechanics, the basic language for describing physics at the atomic and subatomic
Physics 162a Quantum Mechanics 1 Introduction Syllabus for Fall 2009 This is essentially a standard first-year course in quantum mechanics, the basic language for describing physics at the atomic and subatomic
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 1
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 1 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 9, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 1 January 9, 2013 1 / 27 Outline Course in general Description Grading
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 1 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 9, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 1 January 9, 2013 1 / 27 Outline Course in general Description Grading
Quantum Mechanics CHEM/ENCH 313
 Quantum Mechanics CHEM/ENCH 313 Instructor: Soran Jahangiri Instructor Contact Information Email: soran.jahangiri@chem.queensu.ca Office: Chernoff Hall, Room 313 Office Hours: Monday 2:30PM - 3:30PM, Tuesday
Quantum Mechanics CHEM/ENCH 313 Instructor: Soran Jahangiri Instructor Contact Information Email: soran.jahangiri@chem.queensu.ca Office: Chernoff Hall, Room 313 Office Hours: Monday 2:30PM - 3:30PM, Tuesday
Process Dynamics And Control Chemical Engineering
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with process dynamics and
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with process dynamics and
Text: Lutgens and Tarbuck, The Atmosphere (14 th ed.), Quick Start: Preparing Effectively for Each Class
 Montgomery College, Rockville AOSC100 Weather and Climate (CRN#31633) Syllabus Spring 2019 Text: Lutgens and Tarbuck, The Atmosphere (14 th ed.), 2019 Instructor: Bill Krayer, Adjunct Professor Office:
Montgomery College, Rockville AOSC100 Weather and Climate (CRN#31633) Syllabus Spring 2019 Text: Lutgens and Tarbuck, The Atmosphere (14 th ed.), 2019 Instructor: Bill Krayer, Adjunct Professor Office:
University Studies Natural Science Course Renewal
 Chemistry 213: Principles of Chemistry II (Lecture and Lab - 4 s.h.) The purpose of this general chemistry course is to provide students with the knowledge to understand and appreciate our world/universe
Chemistry 213: Principles of Chemistry II (Lecture and Lab - 4 s.h.) The purpose of this general chemistry course is to provide students with the knowledge to understand and appreciate our world/universe
A SURVEY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 1315 TuTr 9:35-10:55 am, Boggs B6
 GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Spring 2004 A SURVEY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 1315 TuTr 9:35-10:55 am, Boggs B6 Instructor: Marcus Weck Office: Boggs 3-85 Phone:
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Spring 2004 A SURVEY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 1315 TuTr 9:35-10:55 am, Boggs B6 Instructor: Marcus Weck Office: Boggs 3-85 Phone:
Chemistry Organic Chemistry II, Spring 2018
 Chemistry 2320 Organic Chemistry II, Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Tom Chang Office: Widtsoe 337 Phone: 797-3545 Email: tom.chang@usu.edu Meeting Time/Place: MWF 10:30-11:20 am, Eccles Business Building
Chemistry 2320 Organic Chemistry II, Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Tom Chang Office: Widtsoe 337 Phone: 797-3545 Email: tom.chang@usu.edu Meeting Time/Place: MWF 10:30-11:20 am, Eccles Business Building
KOMAR UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (KUST)
 Course Title Course Code General Chemistry I and Lab CHM1410C General Chemistry I No. of Credits Department All Departments College Science and Engineering Pre-requisites Course Code Course Coordinator(s)
Course Title Course Code General Chemistry I and Lab CHM1410C General Chemistry I No. of Credits Department All Departments College Science and Engineering Pre-requisites Course Code Course Coordinator(s)
Systems Analysis and Control
 Systems Analysis and Control Matthew M. Peet Arizona State University Lecture 1: Introduction to Control Systems What is this class about? Control is the study of how to make things do what you want. The
Systems Analysis and Control Matthew M. Peet Arizona State University Lecture 1: Introduction to Control Systems What is this class about? Control is the study of how to make things do what you want. The
Astronomy Course Syllabus
 Astronomy Course Syllabus Course: ASTR& 100 Title: Survey of Astronomy Section: DE Term: 2017 Spring Days: Online Time: Online Location: Online Instructor: Julie Masura Phone None E-mail: Canvas intranet
Astronomy Course Syllabus Course: ASTR& 100 Title: Survey of Astronomy Section: DE Term: 2017 Spring Days: Online Time: Online Location: Online Instructor: Julie Masura Phone None E-mail: Canvas intranet
GEOL 443 SYLLABUS. Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, Spring 2013 Tuesday & Thursday 8:00 a.m. 9:15 a.m., PLS Date Subject Reading
 GEOL 443 SYLLABUS Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, Spring 2013 Tuesday & Thursday 8:00 a.m. 9:15 a.m., PLS 1113 Date Subject Reading Jan 24 Introduction: Overview of petrology, rocks. Structure and Chapter
GEOL 443 SYLLABUS Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, Spring 2013 Tuesday & Thursday 8:00 a.m. 9:15 a.m., PLS 1113 Date Subject Reading Jan 24 Introduction: Overview of petrology, rocks. Structure and Chapter
CHAPTER 13: FEEDBACK PERFORMANCE
 When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Apply two methods for evaluating control performance: simulation and frequency response Apply general guidelines for the effect of -
When I complete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Apply two methods for evaluating control performance: simulation and frequency response Apply general guidelines for the effect of -
Physics 18, Introductory Physics I for Biological Sciences Spring 2010
 Physics 18 page 1/6 Physics 18, Introductory Physics I for Biological Sciences Spring 2010 - Course Description - Instructor: Dr. Derrick Kiley Office: AOB 176; Office Phone 209 228-3076 E-mail Address:
Physics 18 page 1/6 Physics 18, Introductory Physics I for Biological Sciences Spring 2010 - Course Description - Instructor: Dr. Derrick Kiley Office: AOB 176; Office Phone 209 228-3076 E-mail Address:
Essentials of Physics PHYS 101 Spring, 2007
 Essentials of Physics PHYS 101 Spring, 2007 Instructor: Dr. Dean Livelybrooks E-mail: dlivelyb@hendrix2; 346-5855 Office: 225 Willamette Hall Office hours: U10:00, H14:00 TAs: Anthony Clark E-mail: aclark@uoregon.edu
Essentials of Physics PHYS 101 Spring, 2007 Instructor: Dr. Dean Livelybrooks E-mail: dlivelyb@hendrix2; 346-5855 Office: 225 Willamette Hall Office hours: U10:00, H14:00 TAs: Anthony Clark E-mail: aclark@uoregon.edu
CAS GE 365 Introduction to Geographical Information Systems. The Applications of GIS are endless
 Spring 2007 CAS GE 365 Introduction to Geographical Information Systems Boston University Department of Geography and Environment The Applications of GIS are endless images from www.esri.com CAS GE 365
Spring 2007 CAS GE 365 Introduction to Geographical Information Systems Boston University Department of Geography and Environment The Applications of GIS are endless images from www.esri.com CAS GE 365
Biology 351 Plant Kingdom Fall Department of Biology 111 Miller Science ;
 Biology 351 Plant Kingdom Fall 2011 Instructor: Text: Meeting Time: Office Hours: Dr. Donald B. Pratt Department of Biology 111 Miller Science 468-2038; prattdb@sfasu.edu Biology of Plants, 7 th edition,
Biology 351 Plant Kingdom Fall 2011 Instructor: Text: Meeting Time: Office Hours: Dr. Donald B. Pratt Department of Biology 111 Miller Science 468-2038; prattdb@sfasu.edu Biology of Plants, 7 th edition,
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1
 Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
Introduction to GIS (GEOG 401) Spring 2014, 3 credit hours
 Introduction to GIS (GEOG 401) Spring 2014, 3 credit hours Instructors: Guangxing Wang, Ph.D. Email: gxwang@siu.edu Phone: (618) 453-6017 Office: 4442 Faner Hall Office hours: M& W&F 9:00am-11:00am or
Introduction to GIS (GEOG 401) Spring 2014, 3 credit hours Instructors: Guangxing Wang, Ph.D. Email: gxwang@siu.edu Phone: (618) 453-6017 Office: 4442 Faner Hall Office hours: M& W&F 9:00am-11:00am or
Chemistry 103: Basic General Chemistry (4.0 Credits) Fall Semester Prerequisites: Placement or concurrent enrollment in DEVM F105 or higher
 Chemistry 103: Basic General Chemistry (4.0 Credits) Fall Semester 2017 Instructor: Dr. Kriya L. Dunlap Office: WRRB 230 Telephone: 474-2766 (office) Email: kldunlap@alaska.edu Lecture: MWF 3:30 4:30,
Chemistry 103: Basic General Chemistry (4.0 Credits) Fall Semester 2017 Instructor: Dr. Kriya L. Dunlap Office: WRRB 230 Telephone: 474-2766 (office) Email: kldunlap@alaska.edu Lecture: MWF 3:30 4:30,
Plan of the Lecture. Today s topic: what is feedback control? past, present, future
 Plan of the Lecture Today s topic: what is feedback control? past, present, future Plan of the Lecture Today s topic: what is feedback control? past, present, future Goal: get comfortable with the idea
Plan of the Lecture Today s topic: what is feedback control? past, present, future Plan of the Lecture Today s topic: what is feedback control? past, present, future Goal: get comfortable with the idea
GIST 4302/5302: Spatial Analysis and Modeling
 GIST 4302/5302: Spatial Analysis and Modeling Spring 2016 Lectures: Tuesdays & Thursdays 12:30pm-1:20pm, Science 234 Labs: GIST 4302: Monday 1:00-2:50pm or Tuesday 2:00-3:50pm GIST 5302: Wednesday 2:00-3:50pm
GIST 4302/5302: Spatial Analysis and Modeling Spring 2016 Lectures: Tuesdays & Thursdays 12:30pm-1:20pm, Science 234 Labs: GIST 4302: Monday 1:00-2:50pm or Tuesday 2:00-3:50pm GIST 5302: Wednesday 2:00-3:50pm
Process Fluid Mechanics
 Process Fluid Mechanics CENG 2220 Instructor: Francesco Ciucci, Room 2577A (Lift 27-29), Tel: 2358 7187, email: francesco.ciucci@ust.hk. Office Hours: Tuesday 17:00-18:00 or by email appointment Teaching
Process Fluid Mechanics CENG 2220 Instructor: Francesco Ciucci, Room 2577A (Lift 27-29), Tel: 2358 7187, email: francesco.ciucci@ust.hk. Office Hours: Tuesday 17:00-18:00 or by email appointment Teaching
Physics Fundamentals of Astronomy
 Physics 1303.010 Fundamentals of Astronomy Course Information Meeting Place & Time ASU Planetarium (VIN P-02) TR 09:30-10:45 AM Spring 2018 Instructor Dr. Kenneth Carrell Office: VIN 119 Phone: (325) 942-2136
Physics 1303.010 Fundamentals of Astronomy Course Information Meeting Place & Time ASU Planetarium (VIN P-02) TR 09:30-10:45 AM Spring 2018 Instructor Dr. Kenneth Carrell Office: VIN 119 Phone: (325) 942-2136
Wilson Area School District Planned Course Guide
 Wilson Area School District Planned Course Guide Title of planned course: AP Physics C: Mechanics Subject Area: Science Grade Level: 11-12 Course Description: AP Physics C: Mechanics is a nationwide course
Wilson Area School District Planned Course Guide Title of planned course: AP Physics C: Mechanics Subject Area: Science Grade Level: 11-12 Course Description: AP Physics C: Mechanics is a nationwide course
Reglerteknik, TNG028. Lecture 1. Anna Lombardi
 Reglerteknik, TNG028 Lecture 1 Anna Lombardi Today lecture We will try to answer the following questions: What is automatic control? Where can we nd automatic control? Why do we need automatic control?
Reglerteknik, TNG028 Lecture 1 Anna Lombardi Today lecture We will try to answer the following questions: What is automatic control? Where can we nd automatic control? Why do we need automatic control?
Mechanics of Material 11/29/2017. General Information
 General Information Assistant Lecturer: Asmaa Ab. Mustafa Email : asmaa.abdulmajeed@ishik.edu.iq Department : Civil Engineering Course Title : Engineering Mechanics I Code : Credit : 2 Office Hour : Monday
General Information Assistant Lecturer: Asmaa Ab. Mustafa Email : asmaa.abdulmajeed@ishik.edu.iq Department : Civil Engineering Course Title : Engineering Mechanics I Code : Credit : 2 Office Hour : Monday
Welcome to Astronomy 141!
 Welcome to Astronomy 141! Prof. Richard Pogge Winter Quarter 2012 Prof. Richard Pogge Education: B.Sc. in Physics, Caltech (1983) Ph.D. in Astrophysics UC Santa Cruz (1988) Postdoc at UT Austin & OSU OSU
Welcome to Astronomy 141! Prof. Richard Pogge Winter Quarter 2012 Prof. Richard Pogge Education: B.Sc. in Physics, Caltech (1983) Ph.D. in Astrophysics UC Santa Cruz (1988) Postdoc at UT Austin & OSU OSU
CHEMISTRY 152 (CRN 80670) Survey of Organic and Bioorganic Chemistry (3 credits) Course Syllabus Spring 2009
 CHEMISTRY 152 (CRN 8070) Survey of Organic and Bioorganic Chemistry (3 credits) Course Syllabus Spring 2009 Instructor: Adele McCurdy Casaschi, PhD, Assistant Professor of Chemistry Office: Bilger 27b,
CHEMISTRY 152 (CRN 8070) Survey of Organic and Bioorganic Chemistry (3 credits) Course Syllabus Spring 2009 Instructor: Adele McCurdy Casaschi, PhD, Assistant Professor of Chemistry Office: Bilger 27b,
Introduction MEAM 535. What is MEAM 535? Audience. Advanced topics in dynamics
 What is MEAM 535? Advanced topics in dynamics Audience Review of Newtonian mechanics MEAM 535 Introduction Analytical mechanics: Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Special topics: Stability of dynamical systems,
What is MEAM 535? Advanced topics in dynamics Audience Review of Newtonian mechanics MEAM 535 Introduction Analytical mechanics: Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Special topics: Stability of dynamical systems,
Acknowledgements. Control System. Tracking. CS122A: Embedded System Design 4/24/2007. A Simple Introduction to Embedded Control Systems (PID Control)
 Acknowledgements A Simple Introduction to Embedded Control Systems (PID Control) The material in this lecture is adapted from: F. Vahid and T. Givargis, Embedded System Design A Unified Hardware/Software
Acknowledgements A Simple Introduction to Embedded Control Systems (PID Control) The material in this lecture is adapted from: F. Vahid and T. Givargis, Embedded System Design A Unified Hardware/Software
Department of Mechanical Engineering MECH 221 (with MECH 224 & MATH 255) Engineering Science I
 Department of Mechanical Engineering MECH 221 (with MECH 224 & MATH 255) Engineering Science I Calendar Description: Rigid body kinetics and kinematics, basic electrical circuits, work and power, stress
Department of Mechanical Engineering MECH 221 (with MECH 224 & MATH 255) Engineering Science I Calendar Description: Rigid body kinetics and kinematics, basic electrical circuits, work and power, stress
Fundamental Principles of Process Control
 Fundamental Principles of Process Control Motivation for Process Control Safety First: people, environment, equipment The Profit Motive: meeting final product specs minimizing waste production minimizing
Fundamental Principles of Process Control Motivation for Process Control Safety First: people, environment, equipment The Profit Motive: meeting final product specs minimizing waste production minimizing
COURSE SYLLABUS AND INSTRUCTOR PLAN GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY I CHEM Dr. Vanessa Castleberry
 WACO, TEXAS COURSE SYLLABUS AND INSTRUCTOR PLAN GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY I CHEM - 1411-50 Dr. Vanessa Castleberry Spring 2012 Course Description: Covers the fundamental laws, theories, and concepts
WACO, TEXAS COURSE SYLLABUS AND INSTRUCTOR PLAN GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY I CHEM - 1411-50 Dr. Vanessa Castleberry Spring 2012 Course Description: Covers the fundamental laws, theories, and concepts
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1
 Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
Systems Engineering/Process Control L1 What is Systems Engineering/Process Control? Graphical system representations Fundamental control principles Reading: Systems Engineering and Process Control: 1.1
Chemistry 401: Modern Inorganic Chemistry (3 credits) Fall 2017
 Chemistry 401: Modern Inorganic Chemistry (3 credits) Fall 2017 Monday, Wednesday, Friday 9:10-10:00 am in Troy G5 Syllabus Instructor: Professor Qiang Zhang Office: Troy 220 Phone: 509-335-1269 Email:
Chemistry 401: Modern Inorganic Chemistry (3 credits) Fall 2017 Monday, Wednesday, Friday 9:10-10:00 am in Troy G5 Syllabus Instructor: Professor Qiang Zhang Office: Troy 220 Phone: 509-335-1269 Email:
ME264 Thermodynamics
 ME264 Thermodynamics Spring 2016 Syllabus Instructor: Dr. Özgür Uğraş Baran 1 Course Information Basic Information Required or elective Course Credit (Hours/ECTS credits) Required (3-0-0/6) Class Hours
ME264 Thermodynamics Spring 2016 Syllabus Instructor: Dr. Özgür Uğraş Baran 1 Course Information Basic Information Required or elective Course Credit (Hours/ECTS credits) Required (3-0-0/6) Class Hours
Controlled variable- T (house interior temperature) Manipulated variable- Q (heat from the furnace) 1-1
 1.1 a) True b) True c) True d) False e) True 1.2 Q L Q T TC ON/OFF SWITCH Controlled variable- T (house interior temperature) Manipulated variable- Q (heat from the furnace) Solution Manual for Process
1.1 a) True b) True c) True d) False e) True 1.2 Q L Q T TC ON/OFF SWITCH Controlled variable- T (house interior temperature) Manipulated variable- Q (heat from the furnace) Solution Manual for Process
(Refer Slide Time: 00:01:30 min)
 Control Engineering Prof. M. Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 3 Introduction to Control Problem (Contd.) Well friends, I have been giving you various
Control Engineering Prof. M. Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 3 Introduction to Control Problem (Contd.) Well friends, I have been giving you various
Simulation of Quadruple Tank Process for Liquid Level Control
 Simulation of Quadruple Tank Process for Liquid Level Control Ritika Thusoo 1, Sakshi Bangia 2 1 M.Tech Student, Electronics Engg, Department, YMCA University of Science and Technology, Faridabad 2 Assistant
Simulation of Quadruple Tank Process for Liquid Level Control Ritika Thusoo 1, Sakshi Bangia 2 1 M.Tech Student, Electronics Engg, Department, YMCA University of Science and Technology, Faridabad 2 Assistant
Required Materials For complete material(s) information, refer to
 Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Organic Chemistry 2 Course Description CH 245. Organic
Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Organic Chemistry 2 Course Description CH 245. Organic
Physics Fundamentals of Astronomy
 Physics 1303.010 Fundamentals of Astronomy Course Information Meeting Place & Time ASU Planetarium (VIN P-02) MWF 09:00-09:50 AM Spring 2017 Instructor Dr. Kenneth Carrell Office: VIN 119 Phone: (325)
Physics 1303.010 Fundamentals of Astronomy Course Information Meeting Place & Time ASU Planetarium (VIN P-02) MWF 09:00-09:50 AM Spring 2017 Instructor Dr. Kenneth Carrell Office: VIN 119 Phone: (325)
Research Project Summaries and Homework (all equally graded): 60% Final: 30% Attendance/Participation: 10%
 GEOL 520 001 Adv Topic:Igm/Metam Petrology Syllabus Professor Dr. Justin Filiberto Office Hours: Open Door Park 203 Course Time: M W F 9 9:50 Parkinson 101 Email: Filiberto@siu.edu Phone: 618 453 4849
GEOL 520 001 Adv Topic:Igm/Metam Petrology Syllabus Professor Dr. Justin Filiberto Office Hours: Open Door Park 203 Course Time: M W F 9 9:50 Parkinson 101 Email: Filiberto@siu.edu Phone: 618 453 4849
Physics 162b Quantum Mechanics
 Physics 162b Quantum Mechanics Syllabus for Winter/Spring 2017 1 Course description Physics 162b is a second-semester graduate course in advanced quantum mechanics. We will open with some advanced topics
Physics 162b Quantum Mechanics Syllabus for Winter/Spring 2017 1 Course description Physics 162b is a second-semester graduate course in advanced quantum mechanics. We will open with some advanced topics
Index. INDEX_p /15/02 3:08 PM Page 765
 INDEX_p.765-770 11/15/02 3:08 PM Page 765 Index N A Adaptive control, 144 Adiabatic reactors, 465 Algorithm, control, 5 All-pass factorization, 257 All-pass, frequency response, 225 Amplitude, 216 Amplitude
INDEX_p.765-770 11/15/02 3:08 PM Page 765 Index N A Adaptive control, 144 Adiabatic reactors, 465 Algorithm, control, 5 All-pass factorization, 257 All-pass, frequency response, 225 Amplitude, 216 Amplitude
Process Control Hardware Fundamentals
 Unit-1: Process Control Process Control Hardware Fundamentals In order to analyse a control system, the individual components that make up the system must be understood. Only with this understanding can
Unit-1: Process Control Process Control Hardware Fundamentals In order to analyse a control system, the individual components that make up the system must be understood. Only with this understanding can
Dublin City Schools Science Graded Course of Study Physical Science
 I. Content Standard: Students demonstrate an understanding of the composition of physical systems and the concepts and principles that describe and predict physical interactions and events in the natural
I. Content Standard: Students demonstrate an understanding of the composition of physical systems and the concepts and principles that describe and predict physical interactions and events in the natural
Honors Physics 1 for Scientists and Engineers
 Honors Physics 1 for Scientists and Engineers Physics 0475, University of Pittsburgh (Fall 2017) Syllabus Course Information Meeting Time: Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri: 11:00-11:50 AM Thaw Hall 102 Instructor
Honors Physics 1 for Scientists and Engineers Physics 0475, University of Pittsburgh (Fall 2017) Syllabus Course Information Meeting Time: Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri: 11:00-11:50 AM Thaw Hall 102 Instructor
Physics 2D Lecture Slides Lecture 1: Jan
 Physics 2D Lecture Slides Lecture 1: Jan 3 2005 Vivek Sharma UCSD Physics 1 Modern Physics (PHYS 2D) Exploration of physical ideas and phenomena related to High velocities and acceleration ( Einstein s
Physics 2D Lecture Slides Lecture 1: Jan 3 2005 Vivek Sharma UCSD Physics 1 Modern Physics (PHYS 2D) Exploration of physical ideas and phenomena related to High velocities and acceleration ( Einstein s
San José State University Aerospace Engineering Department AE168: Aerospace Vehicle Dynamics & Control Fall 2016
 San José State University Aerospace Engineering Department AE168: Aerospace Vehicle Dynamics & Control Fall 216 Course and Contact Information Instructor: Office Location: Email: Office Hours: Class Days/Time:
San José State University Aerospace Engineering Department AE168: Aerospace Vehicle Dynamics & Control Fall 216 Course and Contact Information Instructor: Office Location: Email: Office Hours: Class Days/Time:
SPH4U: COURSE OUTLINE
 SPH4U: COURSE OUTLINE COURSE OUTLINE This course will enable students to deepen their understanding of physics concepts and theories. Students will investigate a variety of physics concepts including kinematics,
SPH4U: COURSE OUTLINE COURSE OUTLINE This course will enable students to deepen their understanding of physics concepts and theories. Students will investigate a variety of physics concepts including kinematics,
