Searching for Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers with Parallel Computing
|
|
|
- May Jones
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Searching for Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers with Parallel Computing Przemysław Dąbrowski, Grzegorz Łabuzek, Tomasz Rachwalik, Janusz Szmidt Military Communication Institute ul. Warszawska 22A, Zegrze, Poland Abstract. Nonlinear feedback shift registers (NLFSRs) are used to construct pseudorandom generators for stream ciphers. Their theory is not so complete as that of linear feedback shift registers (LFSRs). In general, it is not known how to construct all NLFSRs with maximum period. The direct method is to search for such registers with suitable properties. Advanced technology of parallel computing has been applied both in software and hardware to search for maximum period NLFSRs having a fairly simple algebraic normal form. Key words: nonlinear feedback shift registers, maximum period, quadratic m-sequences, parallel computing, FPGA implementation. 1 Introduction Feedback shift register (FSR) sequences have been widely used in many areas of communication theory, as key stream generators in stream ciphers cryptosystems, pseudorandom number generators in many cryptographic primitives, in the design of correlators for spread spectrum communication systems, global positioning systems or radar systems, and as testing vectors in hardware design. Golomb s book [6] is a pioneering one that discusses this type of sequences. A modern treatment of the subject is contained in the book of Golomb and Gong [7]. The theory of linear feedback shift registers (LFSRs) is quite well understood. In particular, it is known how to construct LFSRs with maximum period; they correspond to primitive polynomials over the binary field F 2. The order n of FSR is the number of its cells and an FSR can generate a binary sequence of period up to 2 n. The main drawback of primitive LFSRs is that their linear complexity is equal to their order. In recent years, nonlinear feedback shift registers (NLFSRs) have received much attention in designing numerous cryptographic algorithms such as stream ciphers and lightweight block ciphers to provide security in communication systems. In most cases, NLFSRs have much greater linear complexity than LFSRs of the same period. However, there are no general methods of designing maximum period NLFSRs. The construction of a special class of NLFSRs with maximum period has been given by Mykkeltveit et al. [11]. Recently, maximum period NLFSRs of order up to n = 64 have been constructed in the paper of Mandal and Gong [9], but these NLFSRs have very complicated algebraic normal form (ANF). Dubrova [3] has given an example of a Galois shift register of order n = 100 generating a sequence with maximum period but this sequence does not have the de Bruijn property; i.e., some patterns of n-bits appear more than once in the sequence. In this article the approach from the papers of Gammel, Goettfert, and Kniffler [5] and Chan, Games, and Rushanan [2] is followed. NLFSRs having a simple algebraic normal form and maximum period are directly found by exhaustive searching. In particular, the conjecture posed in [2] on the existence of maximum period NLFSRs whose feedback functions have linear terms and one quadratic term has been experimentally investigated. Like the notion of linear m-sequence, these NLFSRs generate quadratic m-sequences. The conjecture has been verified up to order n = 29. Quadratic m-sequences of this type up to order n = 21 have been classified according to the weight (number of terms) of primitive polynomials involved. These experimental investigations support the Chan, Games and Rushanan conjecture of the existence of a special type of quadratic m-sequences for each order n. Our experiments have applied parallel computing. NLFSRs generating quadratic m-sequences have been found by using three servers with 54 CPU cores. The investigations from the previous paper [12] have also been continued using the Field Programmable Gate Arrays to find maximum period NLFSRs. Nonlinear feedback shift registers have been applied in [13] to construct modified alternating step generators.
2 2 Przemysław Dąbrowski, Grzegorz Łabuzek, Tomasz Rachwalik, Janusz Szmidt 2 Feedback Shift Registers In this section, the definitions and basic facts about feedback shift registers are given. We use F 2 to denote the binary finite field. F 2 [x] denotes the ring of polynomials in the indeterminate x and with coefficients from F 2. Let F n 2 be the n-dimensional vector space over F 2 consisting of all n-tuples of elements of F 2. Any function from F n 2 to F 2 is referred to as a Boolean function of n variables. A sequence of elements s = (s 0,s 1,...) of F 2 is called a binary sequence. A sequence s = (s i ) i=0 is called periodic if there is a positive integer p such that s i+p = s i for all i 0. The least positive integer with this property is called the period of s. A binary feedback shift register of order n is a mapping F from F n 2 into F n 2 of the form F : (x 0,x 1,...,x n 1 ) (x 1,x 2,...,x n 1,f(x 0,x 1,...,x n 1 )), where f is a Boolean function of n variables which is called the feedback function. The shift register is called a linear feedback shift register (LFSR) if F is a linear transformation from the vector space F n 2 into itself. Otherwise, the shift register is called a nonlinear feedback shift register (NLFSR). The shift register is called nonsingular if the mapping F is a bijection. Further, we will consider only nonsingular and mostly nonlinear feedback shift registers. It can be proved (see e.g. [6]) that the feedback function of a nonsingular feedback shift register has the form f(x 0,x 1,...,x n 1 ) = x 0 +g(x 1,...,x n 1 ), (1) where g is a Boolean function of n 1 variables. Consider a binary sequence s = (s i ) i=0 whose first n terms s 0,s 1,...,s n 1 are given and whose remaining terms are uniquely determined by the recurrence relation s i+n = f(s i,s i+1,...,s i+n 1 ) for all i 0. (2) We call s an output sequence of the feedback shift register given by (1). The binaryn-tuple(s 0,s 1,...,s n 1 ) is called the initial state vector of the sequence s or the initial state of the feedback shift register. The recurrence relation (2) can be implemented in hardware as a special electronic switching circuit consisting of n memory cells which is controlled by an external clock to generate the sequence s. Definition 1. A de Bruijn sequence of order n is a sequence of period 2 n of elements of F 2 in which all different binary n-tuples appear in each period exactly once. It was proved by Flye Sainte-Marie [4] in 1894 and independently by de Bruijn [1] in 1946 that the number of cyclically non-equivalent sequences satisfying Definition 1 is equal to B n = 2 2n 1 n. Definition 2. A modified de Bruijn sequence of order n is a sequence of period 2 n 1 obtainned from the de Bruijn sequence of order n by removing one zero from all tuples of n consecutive zeros. In 1990 Mayhew and Golomb [10] investigated sequences satisfying Definition 2 and calculated their linear complexity. These sequences were called by Gammel et al. [5] primitive. In the case of linear feedback shift registers such sequences are generated by primitive polynomials from the ring F 2 [x] and their theory is quite well understood [6 8]. The task is to find primitive NLFSRs with a simple algebraic normal form and this is a time consuming work. An effective method of constructing such primitive NLFSRs is not known and one has to search for them. Gammel et al. [5] found simple primitive NLFSRs up to order 34 used in the design of the stream cipher Achterbahn, but neither the method of searching nor the average time needed to find such good NLFSRs have been revealed. A search for primitive NLFSRs with special purpose hardware devices has been undertaken in [12]. The present paper is a continuation of the previous investigations with additional application of software implementations on parallel cores. The search is restricted to looking for nonlinear primitive NLFSRs with a simple ANF. 3 Quadratic m-sequences Chen, Games and Rushanan [2] have investigated the case when the feedback function (1) is a quadratic Boolean function of n variables; i.e., it has the following algebraic normal form: f(x 0,x 1,...,x n 1 ) = a ij x i x j. (3) 0 i j n 1
3 Searching for Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers with Parallel Computing 3 Let us note that x 2 i = x i for all i 0, hence the coefficients a ii correspond to the linear terms of the function f. The recurrence (2) corresponding to the quadratic function (3) has the form s n+k = a ij s i+k s j+k (4) 0 i j n 1 for all k 0. The authors of [2] have introduced a notion of quadratic m-sequences by analogy to the linear ones. Definition 3. A binary sequence s is called a quadratic m-sequence of order n if it satisfies the quadratic recurrence (4) and has period 2 n 1. The authors of [2] have studied algorithmic generation of special form quadratic m-sequences and enumerated them up to order n = 12. Namely, they considered quadratic Boolean functions of the form where i j, 1 i,j n 1 and f(x 0,x 1,...,x n 1 ) = g(x 0,x 1,...,x n 1 )+x i +x i x j (5) g(x 0,x 1,...,x n 1 ) = x 0 +c 1 x 1 + +c n 1 x n 1 is a linear function which generates the m-sequence, i.e., the corresponding polynomial in the ring F 2 [x] p(x) = x n +c n 1 x n 1 + +c 1 x+1 (6) is primitive. Primitive polynomials of degree n have their roots in the finite Galois field GF(2 n ); these roots are primitive elements (generators) of the multiplicative group GF(2 n ). It is known that there is a one-to-one correspondence between linear m-sequences of period 2 n 1 and primitive polynomials of degree n. The number of primitive polynomials of degree n is equal to ϕ(2 n 1)/n, where ϕ(.) is the Euler function. The proofs of all these facts can be found in the books [6 8]. The quadratic recurrences corresponding to Boolean functions (5) are modifications of the linear one. The term x i +x i x j introduces a non-linear perturbation to the given m-sequence. The states of the LFSR for which the function x i +x i x j equals 1 break or join the corresponding cycles of the LFSR. The case when after running over all states of the FSR we get only one cycle is the sought-for NLFSR. In fact, this is a random phenomenon. The relevant discussion has been presented in [2]. In practice, not all primitive polynomials and terms x i +x i x j lead to a suitable coincidence giving a quadratic m-sequence. 4 Software implementation We have searched for quadratic m-sequences of order n generated by Boolean functions of the form (5) using our software. The procedure is the following: one generates all primitive polynomials of a given degree n; for a given primitive polynomial all terms x i +x i x j are checked to find a feedback function of NLFSR generating a quadratic m-sequence. The maximum period can only be verified by calculating all states of the NLFSR for given i and j. The procedure has been implemented in standard C programming language to speed the search up and for portability. The numbers ( ) of special form quadratic m-sequences for orders n up to 21 are presented in the Appendix, Tables 1 and 2 (k denotes the number of terms of primitive polynomials of a given degree). For n large checking the period is the most time consuming part of the algorithm. It can be seen from the tables that for the number of terms of the primitive polynomial (6) near n/2, the number of quadratic m-sequences found has a maximum. However, the algorithm can be computed in parallel, which speeds up the search. Nowadays multi-core and multi-thread computing environments are widespread even in desktop PCs. The client-server program has been developed to split the searching space into parts. The server program controls the distribution of subtasks and sends client programs jobs to perform using IP packets. The client is a Linux/Windows program receiving subtasks from the server, doing its jobs and sending back the results. The subtasks are performed as threads on multi-core computers. The server program collects results from all clients over TCP/IP networks. It is worth noting that the subtasks are distributed to platform independent clients (Windows, Linux, Mac OS X). The loss of a client due to e.g. power failure
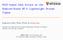
4 4 Przemysław Dąbrowski, Grzegorz Łabuzek, Tomasz Rachwalik, Janusz Szmidt or no network connection is no problem for our server program, because it sends the lost subtasks once again to other clients. The feedback functions of special form quadratic m-sequences up to order n = 29 are given in the Appendix. The above results have been found by using three servers with overall 54 threads connected through an TCP/IP network at Military Communication Institute Interoperability Laboratory 1. This turned out to be a coarse-grain type work in parallel computing due to low communication between clients and server and using distributed memory. In the future we hope our software can be ported to high-performance computing using Open MPI API to find more quadratic m-sequences for greater orders. 5 Hardware implementation One way to search for NLFSRs in hardware is to duplicate a searching module. For this purpose, the hardware platform containing Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) of Altera EP3C80 and the microcontroller have been used. 32 independent programmable searching modules in one EP3C80 device have been fit. The duplicated modules are managed by the control machine which detects the module readiness and directs the result to the output interface of FPGA. The microcontroller transfers the resulting vector to a computer by Ethernet interface. The diagram of a single module is shown in Figure 1. EI RNG CS CB M&X PPF VM SR Fig. 1. The diagram of a single searching module The former version [12] consisted of multiplexers and an XOR block called M&X which was configured by the coefficients buffer CB. The present version adds a primitive polynomial feedback PPF which helps to find a NLFSR feedback functions faster. In this search, random numbers for M&X are taken from RNG. The coefficients are downloaded byte by byte into the coefficient selector CS, where their values and repetitions are checked. Then the bytes go to CB, whose task is to store combinations of coefficients during the test. The multiplexers partially define the random feedback function of NLFSR according to the data buffered in CB. Their outputs are connected to the XOR gate with a feedback function from PPF. The result of XOR feeds the shift register SR. The SR is set with a seed value at the beginning of a searching process by the verification machine VM and it starts shifting. After the first repetition of the seed the test is finished. An acceptable result is sent to the Ethernet interface EI by VM. An unacceptable result starts a new process of random generation and testing. The tests have been carried out on seven such platforms. The results of the search are given in the Appendix. 1 The equipment has been purchased thanks to a grant of the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education decision no 6251/IA/690/2012.
5 Searching for Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers with Parallel Computing 5 6 Conclusion In the paper, we have searched for NLFSRs generating modified de Bruijn sequences. Methods of parallel computing have been applied both in software and hardware to speed the search up. The software has been used to look for special form quadratic m-sequences. An enumeration of all quadratic m-sequences up to order n = 21 generated by feedback functions with the term x i +x i x j and linear terms defined by primitive polynomials has been provided and classified by the weights of these polynomials. The conjecture of Chan, Games and Rushanan [2] has been verified numerically up to order n = 29 for NLFSRs whose feedback functions have the special algebraic normal form. Hardware search of NLFSRs is a continuation of the previous work [12]. The feedback functions of the registers of orders n = 29,30 and 31 we found are expressed in terms of negations of some arguments; this gives simpler formulae than ANFs and it is suitable for implementation. References 1. N. G. de Bruijn. A combinatorial problem. Indag. Math., 8(1946), pp A. H. Chan, R. A. Games, J. J. Rushanan. On the quadratic m-sequences. Proceedings of Fast Software Encryption. LNCS vol. 809, pp Springer-Verlag, E. Dubrova. A scalable method for constructing Galois NLFSRs with period 2 n 1 using cross-join pairs. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, vol. 59(1)(2013), pp C. Flye Sainte-Marie. Solution to question nr. 48. L Intermédiaire des Mathématiciens 1(1894). pp B. M. Gammel, R. Goetffert, O. Kniffler. Achterbahn 128/80. The estream project, S. W. Golomb. Shift Register Sequences. San Francisco, Holden-Day, 1967, revised edition, Laguna Hills, CA, Aegean Park Press, S. W. Golomb, G. Gong. Signal Design for Good Correlation. For Wireless Communication, Cryptography, and Radar. Cambridge University Press, R. Lidl, H. Niederreiter. Introduction to Finite Fields and their Applications (Revisited Edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge(1994). 9. K. Mandal, G. Gong. Cryptographically strong de Bruijn sequences with large periods. Selected Areas in Cryptography. L. R. Knudsen, K. Wu (Eds.). LNCS, vol. 7707, pp Springer-Verlag G. L. Mayhew, S. W. Golomb. Linear spans of modified de Bruijn sequences. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, 36(5)(1990), pp J. Mykkeltveit, M-K. Siu, P. Tong. On the cyclic structure of some nonlinear shift register sequences. Inform. and Control, vol. 43(1979), pp T. Rachwalik, J. Szmidt, R. Wicik, J. Zabłocki. Generation of nonlinear feedback shift registers with special purpose hardware Military Communications and Information Systems Conference. MCC 2012, pp IEEE Xplore Digital Library. Cryptology eprint Archive, 2012/ R. Wicik, T. Rachwalik. Modified alternating step generators. Submitted to MCC2013. Appendix The feedback functions of the form (5) generating quadratic m-sequences up to order n = 29: n = 22, x 0 +x 3 +x 7 +x 9 +x 13 +x 14 +x 18 +x 19 +x 20 +x 5 x 11 n = 23, x 0 +x 6 +x 8 +x 9 +x 11 +x 13 +x 14 +x 15 +x 17 +x 19 +x 20 +x 21 +x 22 +x 2 x 10 n = 24, x 0 +x 9 +x 10 +x 14 +x 16 +x 17 +x 19 +x 10 x 15 n = 25, x 0 +x 1 +x 3 +x 5 +x 8 +x 10 +x 12 +x 15 +x 16 +x 18 +x 19 +x 22 +x 23 +x 5 x 12 n = 26, x 0 +x 2 +x 4 +x 5 +x 8 +x 15 +x 19 +x 21 +x 22 +x 6 x 16 n = 27, x 0 +x 1 +x 2 +x 4 +x 8 +x 10 +x 11 +x 14 +x 17 +x 19 +x 21 +x 6 x 10 n = 28, x 0 +x 4 +x 5 +x 6 +x 8 +x 11 +x 14 +x 18 +x 19 +x 21 +x 22 +x 26 +x 27 +x 8 x 27 n = 29, x 0 +x 3 +x 5 +x 6 +x 11 +x 12 +x 16 +x 19 +x 22 +x 23 +x 27 +x 20 x 28 The nonlinear feedback functions of shift registers of order n found with the FPGA devices: n = 26, x 0 +x 13 +x 14 +x 19 +x 23 +x 18 x 22 x 23 x 25 n = 27, x 0 +x 3 +x 5 +x 9 +x 10 +x 11 +x 18 +x 20 +x 24 +x 9 x 11 x 23 x 26 n = 28, x 0 +x 1 +x 8 +x 17 +x 18 +x 19 +x 21 +x 22 +x 23 +x 4 x 11 x 14 x 18
6 6 Przemysław Dąbrowski, Grzegorz Łabuzek, Tomasz Rachwalik, Janusz Szmidt n = 29, x 0 +x 1 +x 3 +x 4 +x 13 +x 16 +x 18 +x 19 +x 20 +x 22 +x 23 +x 27 + x 6 x 10 x 19 x 20 x 21 x 24 x 26 x 27 + x 6 x 10 x 19 x 20 x 21 x 24 x 26 x 27 n = 30, x 0 +x 4 +x 7 +x 8 +x 9 +x 10 +x 11 +x 12 +x 13 +x 14 +x 15 +x 22 +x 27 +x 28 + x 1 x 3 x 7 x 9 x 11 x 13 x 15 x 19 x 20 x 24 x 25 x 27 + x 1 x 3 x 7 x 9 x 11 x 13 x 15 x 19 x 20 x 24 x 25 x 27 n = 31, x 0 +x 2 +x 6 +x 7 +x 8 +x 9 +x 10 +x 14 +x 15 +x 16 +x 20 +x 21 +x 26 +x 29 + x 4 x 5 x 7 x 9 x 12 x 19 x 21 x 22 x 24 x 25 x 26 x 29 + x 4 x 5 x 7 x 9 x 12 x 19 x 21 x 22 x 24 x 25 x 26 x 29 where x i = x i +1 Table 1. The number of the special form quadratic m-sequences of orders 4 n 12 n = 4 n = 5 n = 6 n = 7 n = 8 n = 9 n = 10 n = 11 n = 12 k k k k k k k k k total 4 total 10 total 12 total 24 total 20 total 24 total 34 total 56 total 28 Table 2. The number of the special form quadratic m-sequences of orders 13 n 21 n = 13 n = 14 n = 15 n = 16 n = 17 n = 18 n = 19 n = 20 n = 21 k k k k k k k k k total 96 total 84 total 88 total 50 total 124 total 104 total 180 total 72 total 172
Modified Alternating Step Generators
 Modified Alternating Step Generators Robert Wicik, Tomasz Rachwalik Military Communication Institute Warszawska 22A, 05-130 Zegrze, Poland {r.wicik, t.rachwalik}@wil.waw.pl Abstract. Irregular clocking
Modified Alternating Step Generators Robert Wicik, Tomasz Rachwalik Military Communication Institute Warszawska 22A, 05-130 Zegrze, Poland {r.wicik, t.rachwalik}@wil.waw.pl Abstract. Irregular clocking
Cryptographic D-morphic Analysis and Fast Implementations of Composited De Bruijn Sequences
 Cryptographic D-morphic Analysis and Fast Implementations of Composited De Bruijn Sequences Kalikinkar Mandal, and Guang Gong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo,
Cryptographic D-morphic Analysis and Fast Implementations of Composited De Bruijn Sequences Kalikinkar Mandal, and Guang Gong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo,
A Scalable Method for Constructing Galois NLFSRs with Period 2 n 1 using Cross-Join Pairs
 A Scalable Method for Constructing Galois NLFSRs with Period 2 n 1 using Cross-Join Pairs Elena Dubrova Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Forum 12, 164 4 Kista, Sweden {dubrova}@kth.se Abstract. This
A Scalable Method for Constructing Galois NLFSRs with Period 2 n 1 using Cross-Join Pairs Elena Dubrova Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Forum 12, 164 4 Kista, Sweden {dubrova}@kth.se Abstract. This
THEORETICAL SIMPLE POWER ANALYSIS OF THE GRAIN STREAM CIPHER. A. A. Zadeh and Howard M. Heys
 THEORETICAL SIMPLE POWER ANALYSIS OF THE GRAIN STREAM CIPHER A. A. Zadeh and Howard M. Heys Electrical and Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland
THEORETICAL SIMPLE POWER ANALYSIS OF THE GRAIN STREAM CIPHER A. A. Zadeh and Howard M. Heys Electrical and Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland
Filtering Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers using Welch-Gong Transformations for Securing RFID Applications
 Filtering Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers using Welch-Gong Transformations for Securing RFID Applications Kalikinkar Mandal, and Guang Gong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University
Filtering Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers using Welch-Gong Transformations for Securing RFID Applications Kalikinkar Mandal, and Guang Gong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University
On The Nonlinearity of Maximum-length NFSR Feedbacks
 On The Nonlinearity of Maximum-length NFSR Feedbacks Meltem Sönmez Turan National Institute of Standards and Technology meltem.turan@nist.gov Abstract. Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) are the main
On The Nonlinearity of Maximum-length NFSR Feedbacks Meltem Sönmez Turan National Institute of Standards and Technology meltem.turan@nist.gov Abstract. Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) are the main
De Bruijn Sequences from Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers
 De Bruijn Sequences from Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers Ming Li and Dongdai Lin State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing
De Bruijn Sequences from Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers Ming Li and Dongdai Lin State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing
Minimal polynomials of the modified de Bruijn sequences
 Discrete Applied Mathematics 156 (2008) 1549 1553 www.elsevier.com/locate/dam Minimal polynomials of the modified de Bruijn sequences Gohar M. Kyureghyan Department of Mathematics, Otto-von-Guericke University
Discrete Applied Mathematics 156 (2008) 1549 1553 www.elsevier.com/locate/dam Minimal polynomials of the modified de Bruijn sequences Gohar M. Kyureghyan Department of Mathematics, Otto-von-Guericke University
STREAM CIPHER. Chapter - 3
 STREAM CIPHER Chapter - 3 S t r e a m C i p h e r P a g e 38 S t r e a m C i p h e r P a g e 39 STREAM CIPHERS Stream cipher is a class of symmetric key algorithm that operates on individual bits or bytes.
STREAM CIPHER Chapter - 3 S t r e a m C i p h e r P a g e 38 S t r e a m C i p h e r P a g e 39 STREAM CIPHERS Stream cipher is a class of symmetric key algorithm that operates on individual bits or bytes.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs. Cross-coupled NOR gates
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
New Implementations of the WG Stream Cipher
 New Implementations of the WG Stream Cipher Hayssam El-Razouk, Arash Reyhani-Masoleh, and Guang Gong Abstract This paper presents two new hardware designs of the WG-28 cipher, one for the multiple output
New Implementations of the WG Stream Cipher Hayssam El-Razouk, Arash Reyhani-Masoleh, and Guang Gong Abstract This paper presents two new hardware designs of the WG-28 cipher, one for the multiple output
Linear Feedback Shift Registers
 Linear Feedback Shift Registers Pseudo-Random Sequences A pseudo-random sequence is a periodic sequence of numbers with a very long period. Golomb's Principles G1: The # of zeros and ones should be as
Linear Feedback Shift Registers Pseudo-Random Sequences A pseudo-random sequence is a periodic sequence of numbers with a very long period. Golomb's Principles G1: The # of zeros and ones should be as
L9: Galois Fields. Reading material
 L9: Galois Fields Reading material Muzio & Wesselkamper Multiple-valued switching theory, p. 3-5, - 4 Sasao, Switching theory for logic synthesis, pp. 43-44 p. 2 - Advanced Logic Design L9 - Elena Dubrova
L9: Galois Fields Reading material Muzio & Wesselkamper Multiple-valued switching theory, p. 3-5, - 4 Sasao, Switching theory for logic synthesis, pp. 43-44 p. 2 - Advanced Logic Design L9 - Elena Dubrova
Nonlinear feedback shift registers and generating of binary de Bruijn sequences
 Nonlinear feedback shift registers and generating of binary de Bruijn sequences Christian Ebne Vivelid November 21, 2016 Master's thesis Department of Informatics University of Bergen 1 Introduction Cryptology
Nonlinear feedback shift registers and generating of binary de Bruijn sequences Christian Ebne Vivelid November 21, 2016 Master's thesis Department of Informatics University of Bergen 1 Introduction Cryptology
Cryptanalysis of Achterbahn
 Cryptanalysis of Achterbahn Thomas Johansson 1, Willi Meier 2, and Frédéric Muller 3 1 Department of Information Technology, Lund University P.O. Box 118, 221 00 Lund, Sweden thomas@it.lth.se 2 FH Aargau,
Cryptanalysis of Achterbahn Thomas Johansson 1, Willi Meier 2, and Frédéric Muller 3 1 Department of Information Technology, Lund University P.O. Box 118, 221 00 Lund, Sweden thomas@it.lth.se 2 FH Aargau,
Computing the biases of parity-check relations
 Computing the biases of parity-check relations Anne Canteaut INRIA project-team SECRET B.P. 05 7853 Le Chesnay Cedex, France Email: Anne.Canteaut@inria.fr María Naya-Plasencia INRIA project-team SECRET
Computing the biases of parity-check relations Anne Canteaut INRIA project-team SECRET B.P. 05 7853 Le Chesnay Cedex, France Email: Anne.Canteaut@inria.fr María Naya-Plasencia INRIA project-team SECRET
Appendix A. Pseudo-random Sequence (Number) Generators
 Communication Systems Security, Appendix A, Draft, L. Chen and G. Gong, 2008 1 Appendix A. Pseudo-random Sequence (Number) Generators In this appendix, we introduce how to design pseudo-random sequence
Communication Systems Security, Appendix A, Draft, L. Chen and G. Gong, 2008 1 Appendix A. Pseudo-random Sequence (Number) Generators In this appendix, we introduce how to design pseudo-random sequence
Linear Cellular Automata as Discrete Models for Generating Cryptographic Sequences
 Linear Cellular Automata as Discrete Models for Generating Cryptographic Sequences A Fúster-Sabater P Caballero-Gil 2 Institute of Applied Physics, CSIC Serrano 44, 286 Madrid, Spain Email: amparo@ieccsices
Linear Cellular Automata as Discrete Models for Generating Cryptographic Sequences A Fúster-Sabater P Caballero-Gil 2 Institute of Applied Physics, CSIC Serrano 44, 286 Madrid, Spain Email: amparo@ieccsices
Cryptographically Robust Large Boolean Functions. Debdeep Mukhopadhyay CSE, IIT Kharagpur
 Cryptographically Robust Large Boolean Functions Debdeep Mukhopadhyay CSE, IIT Kharagpur Outline of the Talk Importance of Boolean functions in Cryptography Important Cryptographic properties Proposed
Cryptographically Robust Large Boolean Functions Debdeep Mukhopadhyay CSE, IIT Kharagpur Outline of the Talk Importance of Boolean functions in Cryptography Important Cryptographic properties Proposed
Affine equivalence in the AES round function
 Discrete Applied Mathematics 148 (2005) 161 170 www.elsevier.com/locate/dam Affine equivalence in the AES round function A.M. Youssef a, S.E. Tavares b a Concordia Institute for Information Systems Engineering,
Discrete Applied Mathematics 148 (2005) 161 170 www.elsevier.com/locate/dam Affine equivalence in the AES round function A.M. Youssef a, S.E. Tavares b a Concordia Institute for Information Systems Engineering,
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 26 Error Correction Codes, Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs)
 EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 26 Error Correction Codes, Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) Nov 21, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 Lec26-ECC Page 1 Outline Error detection using parity Hamming
EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 26 Error Correction Codes, Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) Nov 21, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 Lec26-ECC Page 1 Outline Error detection using parity Hamming
Resilience to Distinguishing Attacks on WG-7 Cipher and Their Generalizations
 Resilience to Distinguishing Attacks on WG-7 Cipher and Their Generalizations Guang Gong, Mark Aagaard and Xinxin Fan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Waterloo, Waterloo,
Resilience to Distinguishing Attacks on WG-7 Cipher and Their Generalizations Guang Gong, Mark Aagaard and Xinxin Fan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Waterloo, Waterloo,
Design of Pseudo-Random Spreading Sequences for CDMA Systems
 Design of Pseudo-Random Spreading Sequences for CDMA Systems Jian Ren and Tongtong Li Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Michigan State University, 2120 Engineering Building East Lansing,
Design of Pseudo-Random Spreading Sequences for CDMA Systems Jian Ren and Tongtong Li Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Michigan State University, 2120 Engineering Building East Lansing,
Simulation study of using shift registers based on 16 th Degree Primitive Polynomials
 Simulation study of using shift registers based on 16 th Degree Primitive Polynomials Mirella Amelia Mioc Abstract Almost all of the major applications in the specific Fields of Communication used a well-known
Simulation study of using shift registers based on 16 th Degree Primitive Polynomials Mirella Amelia Mioc Abstract Almost all of the major applications in the specific Fields of Communication used a well-known
MILP-based Cube Attack on the Reduced-Round WG-5 Lightweight Stream Cipher
 MILP-based Cube Attack on the Reduced-Round WG-5 Lightweight Stream Cipher Raghvendra Rohit, Riham AlTawy, & Guang Gong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo Waterloo,
MILP-based Cube Attack on the Reduced-Round WG-5 Lightweight Stream Cipher Raghvendra Rohit, Riham AlTawy, & Guang Gong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo Waterloo,
Linear Cellular Automata as Discrete Models for Generating Cryptographic Sequences
 Linear Cellular Automata as Discrete Models for Generating Cryptographic Sequences Pino Caballero-Gil Faculty of Mathematics. University of La Laguna 38271. La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain. pcaballe@ull.es
Linear Cellular Automata as Discrete Models for Generating Cryptographic Sequences Pino Caballero-Gil Faculty of Mathematics. University of La Laguna 38271. La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain. pcaballe@ull.es
A New Distinguisher on Grain v1 for 106 rounds
 A New Distinguisher on Grain v1 for 106 rounds Santanu Sarkar Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology, Sardar Patel Road, Chennai 600036, India. sarkar.santanu.bir@gmail.com Abstract.
A New Distinguisher on Grain v1 for 106 rounds Santanu Sarkar Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology, Sardar Patel Road, Chennai 600036, India. sarkar.santanu.bir@gmail.com Abstract.
Outline. EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec 18 Error Coding. In the real world. Our beautiful digital world.
 Outline EECS 150 - Components and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 18 Error Coding Errors and error models Parity and Hamming Codes (SECE) Errors in Communications LFSRs Cyclic Redundancy Check
Outline EECS 150 - Components and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 18 Error Coding Errors and error models Parity and Hamming Codes (SECE) Errors in Communications LFSRs Cyclic Redundancy Check
A GENERAL FRAMEWORK FOR GUESS-AND-DETERMINE AND TIME-MEMORY-DATA TRADE-OFF ATTACKS ON STREAM CIPHERS
 A GENERAL FRAMEWORK FOR GUESS-AND-DETERMINE AND TIME-MEMORY-DATA TRADE-OFF ATTACKS ON STREAM CIPHERS Guanhan Chew, Khoongming Khoo DSO National Laboratories, 20 Science Park Drive, Singapore 118230 cguanhan,kkhoongm@dso.org.sg
A GENERAL FRAMEWORK FOR GUESS-AND-DETERMINE AND TIME-MEMORY-DATA TRADE-OFF ATTACKS ON STREAM CIPHERS Guanhan Chew, Khoongming Khoo DSO National Laboratories, 20 Science Park Drive, Singapore 118230 cguanhan,kkhoongm@dso.org.sg
Maximum Correlation Analysis of Nonlinear S-boxes in Stream Ciphers
 Maximum Correlation Analysis of Nonlinear S-boxes in Stream Ciphers Muxiang Zhang 1 and Agnes Chan 2 1 GTE Laboratories Inc., 40 Sylvan Road LA0MS59, Waltham, MA 02451 mzhang@gte.com 2 College of Computer
Maximum Correlation Analysis of Nonlinear S-boxes in Stream Ciphers Muxiang Zhang 1 and Agnes Chan 2 1 GTE Laboratories Inc., 40 Sylvan Road LA0MS59, Waltham, MA 02451 mzhang@gte.com 2 College of Computer
Gurgen Khachatrian Martun Karapetyan
 34 International Journal Information Theories and Applications, Vol. 23, Number 1, (c) 2016 On a public key encryption algorithm based on Permutation Polynomials and performance analyses Gurgen Khachatrian
34 International Journal Information Theories and Applications, Vol. 23, Number 1, (c) 2016 On a public key encryption algorithm based on Permutation Polynomials and performance analyses Gurgen Khachatrian
Transform Domain Analysis of DES. Guang Gong and Solomon W. Golomb. University of Southern California. Tels and
 Transform Domain Analysis of DES Guang Gong and Solomon W. Golomb Communication Sciences Institute University of Southern California Electrical Engineering-Systems, EEB # 500 Los Angeles, California 90089-2565
Transform Domain Analysis of DES Guang Gong and Solomon W. Golomb Communication Sciences Institute University of Southern California Electrical Engineering-Systems, EEB # 500 Los Angeles, California 90089-2565
On the Design of Trivium
 On the Design of Trivium Yun Tian, Gongliang Chen, Jianhua Li School of Information Security Engineering, Shanghai Jiaotong University, China ruth tian@sjtu.edu.cn, chengl@sjtu.edu.cn, lijh888@sjtu.edu.cn
On the Design of Trivium Yun Tian, Gongliang Chen, Jianhua Li School of Information Security Engineering, Shanghai Jiaotong University, China ruth tian@sjtu.edu.cn, chengl@sjtu.edu.cn, lijh888@sjtu.edu.cn
On the computation of best second order approximations of Boolean Functions ΕΤΗΣΙΑ ΕΚΘΕΣΗ 2010
 Introduction Boolean functions 2nd order nonlinearity Summary ARXH PROSTASIAS_APOLOGISMOS 2010.indd 1 20/04/2011 12:54 ΜΜ On the computation of best second order approximations of Boolean Functions ΕΤΗΣΙΑ
Introduction Boolean functions 2nd order nonlinearity Summary ARXH PROSTASIAS_APOLOGISMOS 2010.indd 1 20/04/2011 12:54 ΜΜ On the computation of best second order approximations of Boolean Functions ΕΤΗΣΙΑ
Existence of Cyclic Hadamard Difference Sets and its Relation to Binary Sequences with Ideal Autocorrelation
 14 JOURNAL OF COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKS, VOL.1, NO.1, MARCH 1999 Existence of Cyclic Hadamard Difference Sets and its Relation to Binary Sequences with Ideal Autocorrelation Jeong-Heon Kim and Hong-Yeop
14 JOURNAL OF COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKS, VOL.1, NO.1, MARCH 1999 Existence of Cyclic Hadamard Difference Sets and its Relation to Binary Sequences with Ideal Autocorrelation Jeong-Heon Kim and Hong-Yeop
Nonlinear Equivalence of Stream Ciphers
 Sondre Rønjom 1 and Carlos Cid 2 1 Crypto Technology Group, Norwegian National Security Authority, Bærum, Norway 2 Information Security Group, Royal Holloway, University of London Egham, United Kingdom
Sondre Rønjom 1 and Carlos Cid 2 1 Crypto Technology Group, Norwegian National Security Authority, Bærum, Norway 2 Information Security Group, Royal Holloway, University of London Egham, United Kingdom
The Adjacency Graphs of Linear Feedback Shift Registers with Primitive-like Characteristic Polynomials
 The Adjacency Graphs of Linear Feedback Shift Registers with Primitive-like Characteristic Polynomials Ming Li and Dongdai Lin State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Institute of Information Engineering,
The Adjacency Graphs of Linear Feedback Shift Registers with Primitive-like Characteristic Polynomials Ming Li and Dongdai Lin State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Institute of Information Engineering,
SOBER Cryptanalysis. Daniel Bleichenbacher and Sarvar Patel Bell Laboratories Lucent Technologies
 SOBER Cryptanalysis Daniel Bleichenbacher and Sarvar Patel {bleichen,sarvar}@lucent.com Bell Laboratories Lucent Technologies Abstract. SOBER is a new stream cipher that has recently been developed by
SOBER Cryptanalysis Daniel Bleichenbacher and Sarvar Patel {bleichen,sarvar}@lucent.com Bell Laboratories Lucent Technologies Abstract. SOBER is a new stream cipher that has recently been developed by
EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec 26 CRCs, LFSRs (and a little power)
 EECS 150 - Components and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 26 CRCs, LFSRs (and a little power) avid Culler Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler
EECS 150 - Components and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 26 CRCs, LFSRs (and a little power) avid Culler Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler
Cryptanalysis of the Stream Cipher ABC v2
 Cryptanalysis of the Stream Cipher ABC v2 Hongjun Wu and Bart Preneel Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, ESAT/SCD-COSIC Kasteelpark Arenberg 10, B-3001 Leuven-Heverlee, Belgium {wu.hongjun,bart.preneel}@esat.kuleuven.be
Cryptanalysis of the Stream Cipher ABC v2 Hongjun Wu and Bart Preneel Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, ESAT/SCD-COSIC Kasteelpark Arenberg 10, B-3001 Leuven-Heverlee, Belgium {wu.hongjun,bart.preneel}@esat.kuleuven.be
Nonlinear Shi, Registers: A Survey and Open Problems. Tor Helleseth University of Bergen NORWAY
 Nonlinear Shi, Registers: A Survey and Open Problems Tor Helleseth University of Bergen NORWAY Outline ntroduc9on Nonlinear Shi> Registers (NLFSRs) Some basic theory De Bruijn Graph De Bruijn graph Golomb
Nonlinear Shi, Registers: A Survey and Open Problems Tor Helleseth University of Bergen NORWAY Outline ntroduc9on Nonlinear Shi> Registers (NLFSRs) Some basic theory De Bruijn Graph De Bruijn graph Golomb
Trace Representation of Legendre Sequences
 C Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 24, 343 348, 2001 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Trace Representation of Legendre Sequences JEONG-HEON KIM School of Electrical and
C Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 24, 343 348, 2001 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Trace Representation of Legendre Sequences JEONG-HEON KIM School of Electrical and
A Five-Round Algebraic Property of the Advanced Encryption Standard
 A Five-Round Algebraic Property of the Advanced Encryption Standard Jianyong Huang, Jennifer Seberry and Willy Susilo Centre for Computer and Information Security Research (CCI) School of Computer Science
A Five-Round Algebraic Property of the Advanced Encryption Standard Jianyong Huang, Jennifer Seberry and Willy Susilo Centre for Computer and Information Security Research (CCI) School of Computer Science
Constructing a Ternary FCSR with a Given Connection Integer
 Constructing a Ternary FCSR with a Given Connection Integer Lin Zhiqiang 1,2 and Pei Dingyi 1,2 1 School of Mathematics and Information Sciences, Guangzhou University, China 2 State Key Laboratory of Information
Constructing a Ternary FCSR with a Given Connection Integer Lin Zhiqiang 1,2 and Pei Dingyi 1,2 1 School of Mathematics and Information Sciences, Guangzhou University, China 2 State Key Laboratory of Information
AN EFFICIENT PRNG FOR STREAM CIPHERS BASED ON HYBRID CELLULAR AUTOMATA WITH NONLINEAR FEEDBACK
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volume 16, Special Issue 2015, pp. 367-374 AN EFFICIENT PRNG FOR STREAM CIPHERS BASED ON HYBRID CELLULAR AUTOMATA
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volume 16, Special Issue 2015, pp. 367-374 AN EFFICIENT PRNG FOR STREAM CIPHERS BASED ON HYBRID CELLULAR AUTOMATA
Analysis of Some Quasigroup Transformations as Boolean Functions
 M a t h e m a t i c a B a l k a n i c a New Series Vol. 26, 202, Fasc. 3 4 Analysis of Some Quasigroup Transformations as Boolean Functions Aleksandra Mileva Presented at MASSEE International Conference
M a t h e m a t i c a B a l k a n i c a New Series Vol. 26, 202, Fasc. 3 4 Analysis of Some Quasigroup Transformations as Boolean Functions Aleksandra Mileva Presented at MASSEE International Conference
Cryptanalysis of the Stream Cipher DECIM
 Cryptanalysis of the Stream Cipher DECIM Hongjun Wu and Bart Preneel Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, ESAT/SCD-COSIC Kasteelpark Arenberg 10, B-3001 Leuven-Heverlee, Belgium {wu.hongjun, bart.preneel}@esat.kuleuven.be
Cryptanalysis of the Stream Cipher DECIM Hongjun Wu and Bart Preneel Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, ESAT/SCD-COSIC Kasteelpark Arenberg 10, B-3001 Leuven-Heverlee, Belgium {wu.hongjun, bart.preneel}@esat.kuleuven.be
Improved Cascaded Stream Ciphers Using Feedback
 Improved Cascaded Stream Ciphers Using Feedback Lu Xiao 1, Stafford Tavares 1, Amr Youssef 2, and Guang Gong 3 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Queen s University, {xiaolu, tavares}@ee.queensu.ca
Improved Cascaded Stream Ciphers Using Feedback Lu Xiao 1, Stafford Tavares 1, Amr Youssef 2, and Guang Gong 3 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Queen s University, {xiaolu, tavares}@ee.queensu.ca
Smart Hill Climbing Finds Better Boolean Functions
 Smart Hill Climbing Finds Better Boolean Functions William Millan, Andrew Clark and Ed Dawson Information Security Research Centre Queensland University of Technology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane, Queensland,
Smart Hill Climbing Finds Better Boolean Functions William Millan, Andrew Clark and Ed Dawson Information Security Research Centre Queensland University of Technology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane, Queensland,
Algebraic attack on stream ciphers Master s Thesis
 Comenius University Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics Department of Computer Science Algebraic attack on stream ciphers Master s Thesis Martin Vörös Bratislava, 2007 Comenius University Faculty
Comenius University Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics Department of Computer Science Algebraic attack on stream ciphers Master s Thesis Martin Vörös Bratislava, 2007 Comenius University Faculty
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) 4-bit LFSR
 Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) These are n-bit counters exhibiting pseudo-random behavior. Built from simple shift-registers with a small number of xor gates. Used for: random number generation
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) These are n-bit counters exhibiting pseudo-random behavior. Built from simple shift-registers with a small number of xor gates. Used for: random number generation
Division of Trinomials by Pentanomials and Orthogonal Arrays
 Division of Trinomials by Pentanomials and Orthogonal Arrays School of Mathematics and Statistics Carleton University daniel@math.carleton.ca Joint work with M. Dewar, L. Moura, B. Stevens and Q. Wang
Division of Trinomials by Pentanomials and Orthogonal Arrays School of Mathematics and Statistics Carleton University daniel@math.carleton.ca Joint work with M. Dewar, L. Moura, B. Stevens and Q. Wang
Linear Approximations for 2-round Trivium
 Linear Approximations for 2-round Trivium Meltem Sönmez Turan 1, Orhun Kara 2 1 Institute of Applied Mathematics, Middle East Technical University Ankara, Turkey msonmez@metu.edu.tr 2 TUBITAK-UEKAE, Gebze,
Linear Approximations for 2-round Trivium Meltem Sönmez Turan 1, Orhun Kara 2 1 Institute of Applied Mathematics, Middle East Technical University Ankara, Turkey msonmez@metu.edu.tr 2 TUBITAK-UEKAE, Gebze,
Sequences, DFT and Resistance against Fast Algebraic Attacks
 Sequences, DFT and Resistance against Fast Algebraic Attacks Guang Gong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1, CANADA Email. ggong@calliope.uwaterloo.ca
Sequences, DFT and Resistance against Fast Algebraic Attacks Guang Gong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1, CANADA Email. ggong@calliope.uwaterloo.ca
2. Accelerated Computations
 2. Accelerated Computations 2.1. Bent Function Enumeration by a Circular Pipeline Implemented on an FPGA Stuart W. Schneider Jon T. Butler 2.1.1. Background A naive approach to encoding a plaintext message
2. Accelerated Computations 2.1. Bent Function Enumeration by a Circular Pipeline Implemented on an FPGA Stuart W. Schneider Jon T. Butler 2.1.1. Background A naive approach to encoding a plaintext message
Low complexity bit-parallel GF (2 m ) multiplier for all-one polynomials
 Low complexity bit-parallel GF (2 m ) multiplier for all-one polynomials Yin Li 1, Gong-liang Chen 2, and Xiao-ning Xie 1 Xinyang local taxation bureau, Henan, China. Email:yunfeiyangli@gmail.com, 2 School
Low complexity bit-parallel GF (2 m ) multiplier for all-one polynomials Yin Li 1, Gong-liang Chen 2, and Xiao-ning Xie 1 Xinyang local taxation bureau, Henan, China. Email:yunfeiyangli@gmail.com, 2 School
Stream Ciphers: Cryptanalytic Techniques
 Stream Ciphers: Cryptanalytic Techniques Thomas Johansson Department of Electrical and Information Technology. Lund University, Sweden ECRYPT Summer school 2007 (Lund University) Stream Ciphers: Cryptanalytic
Stream Ciphers: Cryptanalytic Techniques Thomas Johansson Department of Electrical and Information Technology. Lund University, Sweden ECRYPT Summer school 2007 (Lund University) Stream Ciphers: Cryptanalytic
1 The Algebraic Normal Form
 1 The Algebraic Normal Form Boolean maps can be expressed by polynomials this is the algebraic normal form (ANF). The degree as a polynomial is a first obvious measure of nonlinearity linear (or affine)
1 The Algebraic Normal Form Boolean maps can be expressed by polynomials this is the algebraic normal form (ANF). The degree as a polynomial is a first obvious measure of nonlinearity linear (or affine)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks April 3, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec21-db3 Page 1 Fixed Shifters / Rotators fixed shifters hardwire the shift amount into the circuit.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks April 3, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec21-db3 Page 1 Fixed Shifters / Rotators fixed shifters hardwire the shift amount into the circuit.
New Construction of Single Cycle T-function Families
 New Construction of Single Cycle T-function Families Shiyi ZHANG 1, Yongjuan WANG, Guangpu GAO Luoyang Foreign Language University, Luoyang, Henan Province, China Abstract The single cycle T-function is
New Construction of Single Cycle T-function Families Shiyi ZHANG 1, Yongjuan WANG, Guangpu GAO Luoyang Foreign Language University, Luoyang, Henan Province, China Abstract The single cycle T-function is
A SHORT SURVEY OF P-ARY PSEUDO-RANDOM SEQUENCES. Zhaneta Tasheva
 JOURNAL SCIENCE EDUCATION INNOVATION, VOL. 2. 2014 Association Scientific and Applied Research International Journal Original Contribution ISSN 1314-9784 A SHORT SURVEY OF P-ARY PSEUDO-RANDOM SEQUENCES
JOURNAL SCIENCE EDUCATION INNOVATION, VOL. 2. 2014 Association Scientific and Applied Research International Journal Original Contribution ISSN 1314-9784 A SHORT SURVEY OF P-ARY PSEUDO-RANDOM SEQUENCES
Distinguishing Stream Ciphers with Convolutional Filters
 Distinguishing Stream Ciphers with Convolutional Filters Joan Daemen and Gilles Van Assche STMicroelectronics Smart Cards ICs Division Excelsiorlaan 44 46, 930 Zaventem, Belgium February 5, 2005 Abstract
Distinguishing Stream Ciphers with Convolutional Filters Joan Daemen and Gilles Van Assche STMicroelectronics Smart Cards ICs Division Excelsiorlaan 44 46, 930 Zaventem, Belgium February 5, 2005 Abstract
Least Period of Linear Recurring Sequences over a Finite Field
 Degree Project Least Period of Linear Recurring Sequences over a Finite Field 2012-02-29 Author: Sajid Hanif Subject: Mathematics Level: Master Course code: 5MA12E Abstract This thesis deals with fundamental
Degree Project Least Period of Linear Recurring Sequences over a Finite Field 2012-02-29 Author: Sajid Hanif Subject: Mathematics Level: Master Course code: 5MA12E Abstract This thesis deals with fundamental
Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates. Textbook Chapter 3
 Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates Textbook Chapter 3 Basic Logic Gates XOR CMPE12 Summer 2009 02-2 Truth Table The most basic representation of a logic function Lists the output for all possible
Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates Textbook Chapter 3 Basic Logic Gates XOR CMPE12 Summer 2009 02-2 Truth Table The most basic representation of a logic function Lists the output for all possible
Linear Extension Cube Attack on Stream Ciphers ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 Malaysian Journal of Mathematical Sciences 9(S) June: 139-156 (015) Special ssue: The 4 th nternational Cryptology and nformation Security Conference 014 (Cryptology 014) MALAYSAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATCAL
Malaysian Journal of Mathematical Sciences 9(S) June: 139-156 (015) Special ssue: The 4 th nternational Cryptology and nformation Security Conference 014 (Cryptology 014) MALAYSAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATCAL
Stream ciphers I. Thomas Johansson. May 16, Dept. of EIT, Lund University, P.O. Box 118, Lund, Sweden
 Dept. of EIT, Lund University, P.O. Box 118, 221 00 Lund, Sweden thomas@eit.lth.se May 16, 2011 Outline: Introduction to stream ciphers Distinguishers Basic constructions of distinguishers Various types
Dept. of EIT, Lund University, P.O. Box 118, 221 00 Lund, Sweden thomas@eit.lth.se May 16, 2011 Outline: Introduction to stream ciphers Distinguishers Basic constructions of distinguishers Various types
Section VI.33. Finite Fields
 VI.33 Finite Fields 1 Section VI.33. Finite Fields Note. In this section, finite fields are completely classified. For every prime p and n N, there is exactly one (up to isomorphism) field of order p n,
VI.33 Finite Fields 1 Section VI.33. Finite Fields Note. In this section, finite fields are completely classified. For every prime p and n N, there is exactly one (up to isomorphism) field of order p n,
B. Cyclic Codes. Primitive polynomials are the generator polynomials of cyclic codes.
 B. Cyclic Codes A cyclic code is a linear block code with the further property that a shift of a codeword results in another codeword. These are based on polynomials whose elements are coefficients from
B. Cyclic Codes A cyclic code is a linear block code with the further property that a shift of a codeword results in another codeword. These are based on polynomials whose elements are coefficients from
PREDICTING MASKED LINEAR PSEUDORANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS OVER FINITE FIELDS
 PREDICTING MASKED LINEAR PSEUDORANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS OVER FINITE FIELDS JAIME GUTIERREZ, ÁLVAR IBEAS, DOMINGO GÓMEZ-PEREZ, AND IGOR E. SHPARLINSKI Abstract. We study the security of the linear generator
PREDICTING MASKED LINEAR PSEUDORANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS OVER FINITE FIELDS JAIME GUTIERREZ, ÁLVAR IBEAS, DOMINGO GÓMEZ-PEREZ, AND IGOR E. SHPARLINSKI Abstract. We study the security of the linear generator
The LILI-128 Keystream Generator
 The LILI-128 Keystream Generator E. Dawson 1 A. Clark 1 J. Golić 2 W. Millan 1 L. Penna 1 L. Simpson 1 1 Information Security Research Centre, Queensland University of Technology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane
The LILI-128 Keystream Generator E. Dawson 1 A. Clark 1 J. Golić 2 W. Millan 1 L. Penna 1 L. Simpson 1 1 Information Security Research Centre, Queensland University of Technology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane
Thesis Research Notes
 Thesis Research Notes Week 26-2012 Christopher Wood June 29, 2012 Abstract This week was devoted to reviewing some classical literature on the subject of Boolean functions and their application to cryptography.
Thesis Research Notes Week 26-2012 Christopher Wood June 29, 2012 Abstract This week was devoted to reviewing some classical literature on the subject of Boolean functions and their application to cryptography.
Towards non-linear feedbacks
 Towards non-linear feedbacks Who? Cédric Lauradoux When? December 2, 2008 Applications of sequences BPSK Data Carrier m t IV Init s n K k t f Φ Φ c t s 1 s n s 1 PRNG Spread spectrum Boolean functions
Towards non-linear feedbacks Who? Cédric Lauradoux When? December 2, 2008 Applications of sequences BPSK Data Carrier m t IV Init s n K k t f Φ Φ c t s 1 s n s 1 PRNG Spread spectrum Boolean functions
A Synoptic of Software Implementation for Shift Registers Based on 16 th Degree Primitive Polynomials
 A Synoptic of Software Implementation for Shift Registers Based on 16 th Degree Primitive Polynomials Mirella Amelia Mioc Integrated Center for research, development and innovation in Advanced Materials,
A Synoptic of Software Implementation for Shift Registers Based on 16 th Degree Primitive Polynomials Mirella Amelia Mioc Integrated Center for research, development and innovation in Advanced Materials,
Counting Two-State Transition-Tour Sequences
 Counting Two-State Transition-Tour Sequences Nirmal R. Saxena & Edward J. McCluskey Center for Reliable Computing, ERL 460 Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305
Counting Two-State Transition-Tour Sequences Nirmal R. Saxena & Edward J. McCluskey Center for Reliable Computing, ERL 460 Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305
FResCA: A Fault-Resistant Cellular Automata Based Stream Cipher
 FResCA: A Fault-Resistant Cellular Automata Based Stream Cipher Jimmy Jose 1,2 Dipanwita Roy Chowdhury 1 1 Crypto Research Laboratory, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of
FResCA: A Fault-Resistant Cellular Automata Based Stream Cipher Jimmy Jose 1,2 Dipanwita Roy Chowdhury 1 1 Crypto Research Laboratory, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of
Stream Ciphers. Çetin Kaya Koç Winter / 20
 Çetin Kaya Koç http://koclab.cs.ucsb.edu Winter 2016 1 / 20 Linear Congruential Generators A linear congruential generator produces a sequence of integers x i for i = 1,2,... starting with the given initial
Çetin Kaya Koç http://koclab.cs.ucsb.edu Winter 2016 1 / 20 Linear Congruential Generators A linear congruential generator produces a sequence of integers x i for i = 1,2,... starting with the given initial
Cryptanalysis of the Light-Weight Cipher A2U2 First Draft version
 Cryptanalysis of the Light-Weight Cipher A2U2 First Draft version Mohamed Ahmed Abdelraheem, Julia Borghoff, Erik Zenner Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800 Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark {M.A.Abdelraheem,J.Borghoff,E.Zenner}@mat.dtu.dk
Cryptanalysis of the Light-Weight Cipher A2U2 First Draft version Mohamed Ahmed Abdelraheem, Julia Borghoff, Erik Zenner Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800 Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark {M.A.Abdelraheem,J.Borghoff,E.Zenner}@mat.dtu.dk
Maximum Length Linear Feedback Shift Registers
 Maximum Length Linear Feedback Shift Registers (c) Peter Fischer Institute for Computer Engineering (ZITI) Heidelberg University, Germany email address: peterfischer@zitiuni-heidelbergde February 23, 2018
Maximum Length Linear Feedback Shift Registers (c) Peter Fischer Institute for Computer Engineering (ZITI) Heidelberg University, Germany email address: peterfischer@zitiuni-heidelbergde February 23, 2018
Public-key Cryptography: Theory and Practice
 Public-key Cryptography Theory and Practice Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Appendix A: Symmetric Techniques Block Ciphers A block cipher f of block-size
Public-key Cryptography Theory and Practice Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Appendix A: Symmetric Techniques Block Ciphers A block cipher f of block-size
Third-order nonlinearities of some biquadratic monomial Boolean functions
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Third-order nonlinearities of some biquadratic monomial Boolean functions Brajesh Kumar Singh Received: April 01 / Accepted: date Abstract In this
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Third-order nonlinearities of some biquadratic monomial Boolean functions Brajesh Kumar Singh Received: April 01 / Accepted: date Abstract In this
Analysis of Modern Stream Ciphers
 Analysis of Modern Stream Ciphers Josef Pieprzyk Centre for Advanced Computing Algorithms and Cryptography, Macquarie University, Australia CANS - Singapore - December 2007 estream Outline 1. estream Project
Analysis of Modern Stream Ciphers Josef Pieprzyk Centre for Advanced Computing Algorithms and Cryptography, Macquarie University, Australia CANS - Singapore - December 2007 estream Outline 1. estream Project
Cryptography Lecture 3. Pseudorandom generators LFSRs
 Cryptography Lecture 3 Pseudorandom generators LFSRs Remember One Time Pad is ideal With OTP you need the same transmission capacity via an already secure channel for the key as you can then secure via
Cryptography Lecture 3 Pseudorandom generators LFSRs Remember One Time Pad is ideal With OTP you need the same transmission capacity via an already secure channel for the key as you can then secure via
Some long-period random number generators using shifts and xors
 ANZIAM J. 48 (CTAC2006) pp.c188 C202, 2007 C188 Some long-period random number generators using shifts and xors Richard P. Brent 1 (Received 6 July 2006; revised 2 July 2007) Abstract Marsaglia recently
ANZIAM J. 48 (CTAC2006) pp.c188 C202, 2007 C188 Some long-period random number generators using shifts and xors Richard P. Brent 1 (Received 6 July 2006; revised 2 July 2007) Abstract Marsaglia recently
FPGA accelerated multipliers over binary composite fields constructed via low hamming weight irreducible polynomials
 FPGA accelerated multipliers over binary composite fields constructed via low hamming weight irreducible polynomials C. Shu, S. Kwon and K. Gaj Abstract: The efficient design of digit-serial multipliers
FPGA accelerated multipliers over binary composite fields constructed via low hamming weight irreducible polynomials C. Shu, S. Kwon and K. Gaj Abstract: The efficient design of digit-serial multipliers
4.3 General attacks on LFSR based stream ciphers
 67 4.3 General attacks on LFSR based stream ciphers Recalling our initial discussion on possible attack scenarios, we now assume that z = z 1,z 2,...,z N is a known keystream sequence from a generator
67 4.3 General attacks on LFSR based stream ciphers Recalling our initial discussion on possible attack scenarios, we now assume that z = z 1,z 2,...,z N is a known keystream sequence from a generator
Parallel Cube Tester Analysis of the CubeHash One-Way Hash Function
 Parallel Cube Tester Analysis of the CubeHash One-Way Hash Function Alan Kaminsky Department of Computer Science B. Thomas Golisano College of Computing and Information Sciences Rochester Institute of
Parallel Cube Tester Analysis of the CubeHash One-Way Hash Function Alan Kaminsky Department of Computer Science B. Thomas Golisano College of Computing and Information Sciences Rochester Institute of
LINEAR FEEDBACK SHIFT REGISTER BASED UNIQUE RANDOM NUMBER GENERATOR
 LINEAR FEEDBACK SHIFT REGISTER BASED UNIQUE RANDOM NUMBER GENERATOR HARSH KUMAR VERMA 1 & RAVINDRA KUMAR SINGH 2 1,2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Dr. B. R. Ambedkar National Institute
LINEAR FEEDBACK SHIFT REGISTER BASED UNIQUE RANDOM NUMBER GENERATOR HARSH KUMAR VERMA 1 & RAVINDRA KUMAR SINGH 2 1,2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Dr. B. R. Ambedkar National Institute
ACORN: A Lightweight Authenticated Cipher (v3)
 ACORN: A Lightweight Authenticated Cipher (v3) Designer and Submitter: Hongjun Wu Division of Mathematical Sciences Nanyang Technological University wuhongjun@gmail.com 2016.09.15 Contents 1 Specification
ACORN: A Lightweight Authenticated Cipher (v3) Designer and Submitter: Hongjun Wu Division of Mathematical Sciences Nanyang Technological University wuhongjun@gmail.com 2016.09.15 Contents 1 Specification
FPGA Implementation of Pseudo Noise Sequences based on Quadratic Residue Theory
 FPGA Implementation of Pseudo Noise Sequences based on Quadratic Residue Theory A. Rajagopal Dept. of E&C, K.L. Sudha Dept.of E&C, Dundi Ajay Dept. of E&C, ABSTRACT Pseudo Noise (PN) sequences are defined
FPGA Implementation of Pseudo Noise Sequences based on Quadratic Residue Theory A. Rajagopal Dept. of E&C, K.L. Sudha Dept.of E&C, Dundi Ajay Dept. of E&C, ABSTRACT Pseudo Noise (PN) sequences are defined
Introduction to Modern Cryptography. (1) Finite Groups, Rings and Fields. (2) AES - Advanced Encryption Standard
 Introduction to Modern Cryptography Lecture 3 (1) Finite Groups, Rings and Fields (2) AES - Advanced Encryption Standard +,0, and -a are only notations! Review - Groups Def (group): A set G with a binary
Introduction to Modern Cryptography Lecture 3 (1) Finite Groups, Rings and Fields (2) AES - Advanced Encryption Standard +,0, and -a are only notations! Review - Groups Def (group): A set G with a binary
A note on López-Dahab coordinates
 A note on López-Dahab coordinates Tanja Lange Faculty of Mathematics, Matematiktorvet - Building 303, Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800 Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark tanja@hyperelliptic.org Abstract López-Dahab
A note on López-Dahab coordinates Tanja Lange Faculty of Mathematics, Matematiktorvet - Building 303, Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800 Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark tanja@hyperelliptic.org Abstract López-Dahab
Cryptanalysis of Sosemanuk and SNOW 2.0 Using Linear Masks
 Cryptanalysis of Sosemanuk and SNOW 2.0 Using Linear Masks Jung-Keun Lee, Dong Hoon Lee, and Sangwoo Park ETRI Network & Communication Security Division, 909 Jeonmin-dong, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, Korea Abstract.
Cryptanalysis of Sosemanuk and SNOW 2.0 Using Linear Masks Jung-Keun Lee, Dong Hoon Lee, and Sangwoo Park ETRI Network & Communication Security Division, 909 Jeonmin-dong, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, Korea Abstract.
CONSTRUCTING Boolean functions on odd number of variables n having nonlinearity greater than the bent
 Patterson-Wiedemann type functions on 21 variables with Nonlinearity greater than Bent Concatenation bound Selçuk Kavut and Subhamoy Maitra 1 Abstract Nonlinearity is one of the most challenging combinatorial
Patterson-Wiedemann type functions on 21 variables with Nonlinearity greater than Bent Concatenation bound Selçuk Kavut and Subhamoy Maitra 1 Abstract Nonlinearity is one of the most challenging combinatorial
The Filter-Combiner Model for Memoryless Synchronous Stream Ciphers
 The Filter-Combiner Model for Memoryless Synchronous Stream Ciphers Palash Sarkar Cryptology Research Centre Applied Statistics Unit Indian Statistical Institute 203, B.T. Road, Kolkata 700035 India palash@isical.ac.in
The Filter-Combiner Model for Memoryless Synchronous Stream Ciphers Palash Sarkar Cryptology Research Centre Applied Statistics Unit Indian Statistical Institute 203, B.T. Road, Kolkata 700035 India palash@isical.ac.in
PARALLEL MULTIPLICATION IN F 2
 PARALLEL MULTIPLICATION IN F 2 n USING CONDENSED MATRIX REPRESENTATION Christophe Negre Équipe DALI, LP2A, Université de Perpignan avenue P Alduy, 66 000 Perpignan, France christophenegre@univ-perpfr Keywords:
PARALLEL MULTIPLICATION IN F 2 n USING CONDENSED MATRIX REPRESENTATION Christophe Negre Équipe DALI, LP2A, Université de Perpignan avenue P Alduy, 66 000 Perpignan, France christophenegre@univ-perpfr Keywords:
A Byte-Based Guess and Determine Attack on SOSEMANUK
 A Byte-Based Guess and Determine Attack on SOSEMANUK Xiutao Feng, Jun Liu, Zhaocun Zhou, Chuankun Wu and Dengguo Feng State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Institute of Software, Chinese Academy
A Byte-Based Guess and Determine Attack on SOSEMANUK Xiutao Feng, Jun Liu, Zhaocun Zhou, Chuankun Wu and Dengguo Feng State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Institute of Software, Chinese Academy
AES side channel attacks protection using random isomorphisms
 Rostovtsev A.G., Shemyakina O.V., St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University AES side channel attacks protection using random isomorphisms General method of side-channel attacks protection, based on random
Rostovtsev A.G., Shemyakina O.V., St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University AES side channel attacks protection using random isomorphisms General method of side-channel attacks protection, based on random
Characterizations on Algebraic Immunity for Multi-Output Boolean Functions
 Characterizations on Algebraic Immunity for Multi-Output Boolean Functions Xiao Zhong 1, and Mingsheng Wang 3 1. Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China. Graduate School
Characterizations on Algebraic Immunity for Multi-Output Boolean Functions Xiao Zhong 1, and Mingsheng Wang 3 1. Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China. Graduate School
Information redundancy
 Information redundancy Information redundancy add information to date to tolerate faults error detecting codes error correcting codes data applications communication memory p. 2 - Design of Fault Tolerant
Information redundancy Information redundancy add information to date to tolerate faults error detecting codes error correcting codes data applications communication memory p. 2 - Design of Fault Tolerant
CRC Press has granted the following specific permissions for the electronic version of this book:
 This is a Chapter from the Handbook of Applied Cryptography, by A. Menezes, P. van Oorschot, and S. Vanstone, CRC Press, 1996. For further information, see www.cacr.math.uwaterloo.ca/hac CRC Press has
This is a Chapter from the Handbook of Applied Cryptography, by A. Menezes, P. van Oorschot, and S. Vanstone, CRC Press, 1996. For further information, see www.cacr.math.uwaterloo.ca/hac CRC Press has
