Lecture 4 February 16, 2016
|
|
|
- Erika Eaton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MIT 6.854/18.415: Advaced Algorithms Sprig 16 Prof. Akur Moitra Lecture 4 February 16, 16 Scribe: Be Eysebach, Devi Neal 1 Last Time Cosistet Hashig - hash fuctios that evolve well Radom Trees - routig schemes that deal with icosistet views Today: Distict Elemets ad Cout-Mi Sketch. What ca we do if we ca t store data, oly stream it? Distict Elemets Problem: Cout the umber of distict elemets i a sequece X 1, X,..., X. For example, how may uique words did Shakespeare use? Naively this problem takes O(N) space, where N is the umber of distict elemets i the sequece. For Shakespeare s total vocabulary, N 35,. However, it turs out that you ca do much better tha the aive method if you are willig to accept some level of approximatio. There s a famous quote from a 3 paper by Mariae Durad ad Philippe Flajolet: Usig oly memory equivalet to 5 lies of prited text, you ca estimate with a typical accuracy of 5% ad i a sigle pass the total vocabulary of Shakespeare..1 Usig a Sigle Hash Fuctio Idea: Choose a radom hash fuctio h : U [, 1] ad pass oce through the data, hashig each item ad storig oly the miimum of h(x 1 ), h(x ),..., h(x i ),.... Let Y mi i {h(x i )} be the miimum, ad let N be the true umber of distict elemets. Lemma 1. E[Y ] = 1 1
2 Proof. E[Y ] = = 1 1 [ = = 1 P[Y z]dz (1 z) N dz ] (1 1 z)n+1 With some thought, you ca cofirm that E[Y ] is the same as the probability of choosig umbers i the iterval [, 1] ad havig the last umber be the miimum. By symmetry, this probability is 1 N+1. So, if we estimate N by 1 Y 1, we ll at least get the right aswer i expectatio. To show that we also get the right aswer with good probability, we re goig to use the Chebyshev tail boud to boud the probability that our estimate for Y is close to its expectatio. To do this, we must first compute the variace of Y. Lemma. Proof. V ar[y ] ( 1 ) V ar[y ] = E[Y ] E[Y ] 1 ( ) 1 = z N(1 z) N 1 dz = ()(N + ) 1 ()() ()() 1 ()() ( ) 1 = Ufortuately, we caot apply Chebyshev directly because the variace of Y is too large. I particular, Chebyshev oly gives error resolutio dow to size of Y s stadard deviatio (i.e. V ar[y ]). Zero is oe stadard deviatio below E[Y ], so Chebyshev would oly tell us that P[Y = ] is some costat. This is bad because we caot solve N = 1 Y 1 whe Y =. We wat P[Y = ] to be very small.
3 . k Hash Fuctios Fortuately, we ca apply the stadard techique of reducig the variace of our estimate via repetitio. Idea [Flajolet-Marti]: Use k hash fuctios h 1,..., h k : U [, 1]. Now, evaluate each hash fuctio o each item i the sequece, storig the miimum for each hash fuctio separately. Let Ȳ 1 k k i=1 Y i be the average miimum. The variace of the sum of idepedet radom variables is the sum of their variaces. Thus, V ar[ȳ ] = 1 k k i=1 Y 1 i, k(n+1) where we ve used Lemma for the iequality. Applyig Chebyshev: [ P Ȳ 1 ɛ ] V ar[ȳ ) ] 1 kɛ ( ɛ N+1 with proba- Thus, our estimate for the umber of distict elemets,, satisfies 1Ȳ N+1 1+ɛ 1 Ȳ N+1 1 ɛ bility at least 1 1. For small ɛ, this guaratee is equivalet to: kɛ (1 O(ɛ))N 1 Y 1 (1 + O(ɛ))N We eed to set k = O(1/ɛ ) to get a ɛ accurate estimate with probability 9/1, for example. I practice, we do t eed our hash fuctios to map to arbitrary real umbers. It is sufficiet to use legth O(log ) biary strigs. For more details, see [1]. 3 Heavy Hitters We ca compute may statistics about a stream of data beyod the umber of distict elemets. Oe particularly popular ad practically useful goal is to fid elemets that appear frequetly i the stream. These items are simply called frequet items or sometimes heavy hitters. 3.1 Misra-Gries, 198 [3] We begi with a straight forward versio of the heavy hitters problem: Give a sequece of elemets X 1, X,..., X, output a list with at most k values, esurig that every elemet which occurs at least k times i the sequece is o the list. Note that there ca oly be k such items, although there could be fewer. We allow false positives i the list. Here s the algorithm: iitialize empty list for each item if item o list icremet its couter else if legth(list) < k 3
4 add item to list set item s couter to 1 else throw away item decremet couter of every item i list delete items i list with couter = Fact: Sice the Misra-Gries algorithm stores k couters with value at most, it uses O(k log ) space. Lemma 3. Let f x deote the frequecy of item x. Whe Misra Gries termiates, the couter for x is at least f x k+1. Note that x could have a couter equal to, i which case it will ot be o the list. Proof. The fial value of x s couter is equal to the umber of times it appears i our sequece, f x, mius the umber of times x was throw out because the list was full at the time. We argue that this umber ca t be higher tha k+1. Whe a item is throw out, each elemet cotaied i the list is decremeted. Additioally, x s virtual couter is effectively decremeted from 1 to. Sice the etire list must be filled, this correspods to k + 1 tokes beig destroyed every time x is throw out. There are a total of tokes received, so this evet ca occur at most k+1 times. We coclude that the couter for x is at least f x k+1. So, if f x > k+1, it will appear o the list at the ed of the algorithm, as desired. 3. Cout-Mi Sketch We ca also solve a more ambitious versio of the heavy hitters problem: Give a sequece X 1, X,..., X, compute f x to withi additive error ɛ. Note that a additive approximatio is more meaigful for heavier items i the list ad becomes meaigless whe f x ɛ. We will use the Cout-Mi Sketch (Cormode, Muthukrisha 5 []). Choose l radom hash fuctios h 1,..., h l : U {1,,..., b}. Iitialize a l b array CMS[l][b] with zeros. The, as elemets X i i the sequece are streamed i, for each hash fuctio h j ( ), icremet the (j, h j (X i )) etry of the table. To estimate the frequecy of item x, compute Cout(x) = mi j { CMS[j][h j (x)] } Claim 4. For ay fixed item x ad idex j, CMS[j][h j (x)] f x. Proof. We icremet CMS[j][h j (x)] each time we see x. However, this etry will be icremeted if h j (y) = h j (x) for some other item y x that also appears i the stream. Hece the iequality. 4
5 3..1 Aalysis Let z j CMS[j][h j (x)], ad ote that z j = f x + y x,h j (y)=h j (x) f y. We wat to examie the expected value of z j : E[z j ] = f x + y x f y P[h j (x) = h j (y)] = f x + 1 b y x f x + 1 b = f x + b y f y f y Note that z j is a biased estimator: its expected value is greater tha f x, the quatity we hope to estimate. Now, we wat to show that z j is close to f x. Usig the Markov Boud whe b = ɛ, P[z j ɛ] 1 Whe we have l hash fuctios, our estimate is the miimum z j. Our estimate is bad iff every z j is much larger tha f x : P[(mi z j ) f x + ɛ] = P[ j, z j f x + ɛ] j 1 l Settig l = O(log()), we get P[(mi j z j ) f x + ɛ] 1. Accordigly, our estimate is accurate up to ɛ error with high probability. 3.. Compariso with Misra Gries By settig ɛ = 1 k, the Cout-Mi sketch solves almost the same problem as Misra-Gries. The key differece is that the Cout-Mi sketch guaratees that for every x, if Cout(x) is large the x is a heavy hitter. I Misra-Gries, a item o the retured list might ot be a heavy hitter. We pay for this guaratee i space. Misra-Gries takes O(k log()) space, while the Cout-Mi sketch requires O(k log ()) space (settig ɛ = 1 k ad otig that each couter stores a value of at most ). Also ote that Cout-Mi oly obtais its solutio with high probability. Misra-Gries is determiistic ad so it always succeeds. 5
6 Refereces [1] Flajolet, Philippe ad Marti, Nigel Probabilistic coutig algorithms for data base applicatios. I Joural of Computer ad System Scieces, Volume 31, Number. pp [] Cormode, Graham, ad Muthukrisha, S. 5. A improved data stream summary: the cout-mi sketch ad its applicatios. I Joural of Algorithms. pp [3] Misra, Jayadev ad Gries, David Fidig repeated elemets. I Sciece of Computer Programmig. pp
Lecture 4: Unique-SAT, Parity-SAT, and Approximate Counting
 Advaced Complexity Theory Sprig 206 Lecture 4: Uique-SAT, Parity-SAT, ad Approximate Coutig Prof. Daa Moshkovitz Scribe: Aoymous Studet Scribe Date: Fall 202 Overview I this lecture we begi talkig about
Advaced Complexity Theory Sprig 206 Lecture 4: Uique-SAT, Parity-SAT, ad Approximate Coutig Prof. Daa Moshkovitz Scribe: Aoymous Studet Scribe Date: Fall 202 Overview I this lecture we begi talkig about
Problem Set 2 Solutions
 CS271 Radomess & Computatio, Sprig 2018 Problem Set 2 Solutios Poit totals are i the margi; the maximum total umber of poits was 52. 1. Probabilistic method for domiatig sets 6pts Pick a radom subset S
CS271 Radomess & Computatio, Sprig 2018 Problem Set 2 Solutios Poit totals are i the margi; the maximum total umber of poits was 52. 1. Probabilistic method for domiatig sets 6pts Pick a radom subset S
Lecture 2 February 8, 2016
 MIT 6.854/8.45: Advaced Algorithms Sprig 206 Prof. Akur Moitra Lecture 2 February 8, 206 Scribe: Calvi Huag, Lih V. Nguye I this lecture, we aalyze the problem of schedulig equal size tasks arrivig olie
MIT 6.854/8.45: Advaced Algorithms Sprig 206 Prof. Akur Moitra Lecture 2 February 8, 206 Scribe: Calvi Huag, Lih V. Nguye I this lecture, we aalyze the problem of schedulig equal size tasks arrivig olie
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.070J Fall 2013 Lecture 2 9/9/2013. Large Deviations for i.i.d. Random Variables
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.070J Fall 2013 Lecture 2 9/9/2013 Large Deviatios for i.i.d. Radom Variables Cotet. Cheroff boud usig expoetial momet geeratig fuctios. Properties of a momet
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.070J Fall 2013 Lecture 2 9/9/2013 Large Deviatios for i.i.d. Radom Variables Cotet. Cheroff boud usig expoetial momet geeratig fuctios. Properties of a momet
Optimally Sparse SVMs
 A. Proof of Lemma 3. We here prove a lower boud o the umber of support vectors to achieve geeralizatio bouds of the form which we cosider. Importatly, this result holds ot oly for liear classifiers, but
A. Proof of Lemma 3. We here prove a lower boud o the umber of support vectors to achieve geeralizatio bouds of the form which we cosider. Importatly, this result holds ot oly for liear classifiers, but
Lecture 4: April 10, 2013
 TTIC/CMSC 1150 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 01 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 4: April 10, 01 Scribe: Haris Agelidakis 1 Chebyshev s Iequality recap I the previous lecture, we used Chebyshev s iequality to get a
TTIC/CMSC 1150 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 01 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 4: April 10, 01 Scribe: Haris Agelidakis 1 Chebyshev s Iequality recap I the previous lecture, we used Chebyshev s iequality to get a
Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2007 Luca Trevisan Lecture 22
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2007 Luca Trevisa Lecture 22 Aother Importat Distributio The Geometric Distributio Questio: A biased coi with Heads probability p is tossed repeatedly util the first
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2007 Luca Trevisa Lecture 22 Aother Importat Distributio The Geometric Distributio Questio: A biased coi with Heads probability p is tossed repeatedly util the first
Basics of Probability Theory (for Theory of Computation courses)
 Basics of Probability Theory (for Theory of Computatio courses) Oded Goldreich Departmet of Computer Sciece Weizma Istitute of Sciece Rehovot, Israel. oded.goldreich@weizma.ac.il November 24, 2008 Preface.
Basics of Probability Theory (for Theory of Computatio courses) Oded Goldreich Departmet of Computer Sciece Weizma Istitute of Sciece Rehovot, Israel. oded.goldreich@weizma.ac.il November 24, 2008 Preface.
An Introduction to Randomized Algorithms
 A Itroductio to Radomized Algorithms The focus of this lecture is to study a radomized algorithm for quick sort, aalyze it usig probabilistic recurrece relatios, ad also provide more geeral tools for aalysis
A Itroductio to Radomized Algorithms The focus of this lecture is to study a radomized algorithm for quick sort, aalyze it usig probabilistic recurrece relatios, ad also provide more geeral tools for aalysis
Lecture 3: August 31
 36-705: Itermediate Statistics Fall 018 Lecturer: Siva Balakrisha Lecture 3: August 31 This lecture will be mostly a summary of other useful expoetial tail bouds We will ot prove ay of these i lecture,
36-705: Itermediate Statistics Fall 018 Lecturer: Siva Balakrisha Lecture 3: August 31 This lecture will be mostly a summary of other useful expoetial tail bouds We will ot prove ay of these i lecture,
Disjoint set (Union-Find)
 CS124 Lecture 7 Fall 2018 Disjoit set (Uio-Fid) For Kruskal s algorithm for the miimum spaig tree problem, we foud that we eeded a data structure for maitaiig a collectio of disjoit sets. That is, we eed
CS124 Lecture 7 Fall 2018 Disjoit set (Uio-Fid) For Kruskal s algorithm for the miimum spaig tree problem, we foud that we eeded a data structure for maitaiig a collectio of disjoit sets. That is, we eed
Probability 2 - Notes 10. Lemma. If X is a random variable and g(x) 0 for all x in the support of f X, then P(g(X) 1) E[g(X)].
![Probability 2 - Notes 10. Lemma. If X is a random variable and g(x) 0 for all x in the support of f X, then P(g(X) 1) E[g(X)]. Probability 2 - Notes 10. Lemma. If X is a random variable and g(x) 0 for all x in the support of f X, then P(g(X) 1) E[g(X)].](/thumbs/90/101606445.jpg) Probability 2 - Notes 0 Some Useful Iequalities. Lemma. If X is a radom variable ad g(x 0 for all x i the support of f X, the P(g(X E[g(X]. Proof. (cotiuous case P(g(X Corollaries x:g(x f X (xdx x:g(x
Probability 2 - Notes 0 Some Useful Iequalities. Lemma. If X is a radom variable ad g(x 0 for all x i the support of f X, the P(g(X E[g(X]. Proof. (cotiuous case P(g(X Corollaries x:g(x f X (xdx x:g(x
Lecture 2: Concentration Bounds
 CSE 52: Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms I Sprig 206 Lecture 2: Cocetratio Bouds Lecturer: Shaya Oveis Ghara March 30th Scribe: Syuzaa Sargsya Disclaimer: These otes have ot bee subjected to the usual scrutiy
CSE 52: Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms I Sprig 206 Lecture 2: Cocetratio Bouds Lecturer: Shaya Oveis Ghara March 30th Scribe: Syuzaa Sargsya Disclaimer: These otes have ot bee subjected to the usual scrutiy
There is no straightforward approach for choosing the warmup period l.
 B. Maddah INDE 504 Discrete-Evet Simulatio Output Aalysis () Statistical Aalysis for Steady-State Parameters I a otermiatig simulatio, the iterest is i estimatig the log ru steady state measures of performace.
B. Maddah INDE 504 Discrete-Evet Simulatio Output Aalysis () Statistical Aalysis for Steady-State Parameters I a otermiatig simulatio, the iterest is i estimatig the log ru steady state measures of performace.
# fixed points of g. Tree to string. Repeatedly select the leaf with the smallest label, write down the label of its neighbour and remove the leaf.
 Combiatorics Graph Theory Coutig labelled ad ulabelled graphs There are 2 ( 2) labelled graphs of order. The ulabelled graphs of order correspod to orbits of the actio of S o the set of labelled graphs.
Combiatorics Graph Theory Coutig labelled ad ulabelled graphs There are 2 ( 2) labelled graphs of order. The ulabelled graphs of order correspod to orbits of the actio of S o the set of labelled graphs.
4.1 Sigma Notation and Riemann Sums
 0 the itegral. Sigma Notatio ad Riema Sums Oe strategy for calculatig the area of a regio is to cut the regio ito simple shapes, calculate the area of each simple shape, ad the add these smaller areas
0 the itegral. Sigma Notatio ad Riema Sums Oe strategy for calculatig the area of a regio is to cut the regio ito simple shapes, calculate the area of each simple shape, ad the add these smaller areas
6.3 Testing Series With Positive Terms
 6.3. TESTING SERIES WITH POSITIVE TERMS 307 6.3 Testig Series With Positive Terms 6.3. Review of what is kow up to ow I theory, testig a series a i for covergece amouts to fidig the i= sequece of partial
6.3. TESTING SERIES WITH POSITIVE TERMS 307 6.3 Testig Series With Positive Terms 6.3. Review of what is kow up to ow I theory, testig a series a i for covergece amouts to fidig the i= sequece of partial
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics
 SDS 321: Itroductio to Probability ad Statistics Lecture 23: Cotiuous radom variables- Iequalities, CLT Puramrita Sarkar Departmet of Statistics ad Data Sciece The Uiversity of Texas at Austi www.cs.cmu.edu/
SDS 321: Itroductio to Probability ad Statistics Lecture 23: Cotiuous radom variables- Iequalities, CLT Puramrita Sarkar Departmet of Statistics ad Data Sciece The Uiversity of Texas at Austi www.cs.cmu.edu/
Feedback in Iterative Algorithms
 Feedback i Iterative Algorithms Charles Byre (Charles Byre@uml.edu), Departmet of Mathematical Scieces, Uiversity of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, MA 01854 October 17, 2005 Abstract Whe the oegative system
Feedback i Iterative Algorithms Charles Byre (Charles Byre@uml.edu), Departmet of Mathematical Scieces, Uiversity of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, MA 01854 October 17, 2005 Abstract Whe the oegative system
Information Theory and Statistics Lecture 4: Lempel-Ziv code
 Iformatio Theory ad Statistics Lecture 4: Lempel-Ziv code Łukasz Dębowski ldebowsk@ipipa.waw.pl Ph. D. Programme 203/204 Etropy rate is the limitig compressio rate Theorem For a statioary process (X i)
Iformatio Theory ad Statistics Lecture 4: Lempel-Ziv code Łukasz Dębowski ldebowsk@ipipa.waw.pl Ph. D. Programme 203/204 Etropy rate is the limitig compressio rate Theorem For a statioary process (X i)
Lecture 19: Convergence
 Lecture 19: Covergece Asymptotic approach I statistical aalysis or iferece, a key to the success of fidig a good procedure is beig able to fid some momets ad/or distributios of various statistics. I may
Lecture 19: Covergece Asymptotic approach I statistical aalysis or iferece, a key to the success of fidig a good procedure is beig able to fid some momets ad/or distributios of various statistics. I may
OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES
 OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES Peter M. Maurer Why Hashig is θ(). As i biary search, hashig assumes that keys are stored i a array which is idexed by a iteger. However, hashig attempts to bypass
OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES Peter M. Maurer Why Hashig is θ(). As i biary search, hashig assumes that keys are stored i a array which is idexed by a iteger. However, hashig attempts to bypass
Topic 9: Sampling Distributions of Estimators
 Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2018 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2018 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
Hashing and Amortization
 Lecture Hashig ad Amortizatio Supplemetal readig i CLRS: Chapter ; Chapter 7 itro; Sectio 7.. Arrays ad Hashig Arrays are very useful. The items i a array are statically addressed, so that isertig, deletig,
Lecture Hashig ad Amortizatio Supplemetal readig i CLRS: Chapter ; Chapter 7 itro; Sectio 7.. Arrays ad Hashig Arrays are very useful. The items i a array are statically addressed, so that isertig, deletig,
Lecture 5: April 17, 2013
 TTIC/CMSC 350 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 203 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 5: April 7, 203 Scribe: Somaye Hashemifar Cheroff bouds recap We recall the Cheroff/Hoeffdig bouds we derived i the last lecture idepedet
TTIC/CMSC 350 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 203 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 5: April 7, 203 Scribe: Somaye Hashemifar Cheroff bouds recap We recall the Cheroff/Hoeffdig bouds we derived i the last lecture idepedet
Lecture 2: April 3, 2013
 TTIC/CMSC 350 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 203 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 2: April 3, 203 Scribe: Shubhedu Trivedi Coi tosses cotiued We retur to the coi tossig example from the last lecture agai: Example. Give,
TTIC/CMSC 350 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 203 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 2: April 3, 203 Scribe: Shubhedu Trivedi Coi tosses cotiued We retur to the coi tossig example from the last lecture agai: Example. Give,
Frequentist Inference
 Frequetist Iferece The topics of the ext three sectios are useful applicatios of the Cetral Limit Theorem. Without kowig aythig about the uderlyig distributio of a sequece of radom variables {X i }, for
Frequetist Iferece The topics of the ext three sectios are useful applicatios of the Cetral Limit Theorem. Without kowig aythig about the uderlyig distributio of a sequece of radom variables {X i }, for
Topic 9: Sampling Distributions of Estimators
 Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2018 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2018 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
Lecture 14: Graph Entropy
 15-859: Iformatio Theory ad Applicatios i TCS Sprig 2013 Lecture 14: Graph Etropy March 19, 2013 Lecturer: Mahdi Cheraghchi Scribe: Euiwoog Lee 1 Recap Bergma s boud o the permaet Shearer s Lemma Number
15-859: Iformatio Theory ad Applicatios i TCS Sprig 2013 Lecture 14: Graph Etropy March 19, 2013 Lecturer: Mahdi Cheraghchi Scribe: Euiwoog Lee 1 Recap Bergma s boud o the permaet Shearer s Lemma Number
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 Solutios to Quiz : Sprig 006 Problem : Each of the followig statemets is either True or False. There will be o partial credit give for the True False questios, thus ay explaatios will ot be graded. Please
Solutios to Quiz : Sprig 006 Problem : Each of the followig statemets is either True or False. There will be o partial credit give for the True False questios, thus ay explaatios will ot be graded. Please
IP Reference guide for integer programming formulations.
 IP Referece guide for iteger programmig formulatios. by James B. Orli for 15.053 ad 15.058 This documet is iteded as a compact (or relatively compact) guide to the formulatio of iteger programs. For more
IP Referece guide for iteger programmig formulatios. by James B. Orli for 15.053 ad 15.058 This documet is iteded as a compact (or relatively compact) guide to the formulatio of iteger programs. For more
HOMEWORK 2 SOLUTIONS
 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS CSE 55 RANDOMIZED AND APPROXIMATION ALGORITHMS 1. Questio 1. a) The larger the value of k is, the smaller the expected umber of days util we get all the coupos we eed. I fact if = k
HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS CSE 55 RANDOMIZED AND APPROXIMATION ALGORITHMS 1. Questio 1. a) The larger the value of k is, the smaller the expected umber of days util we get all the coupos we eed. I fact if = k
Lecture 9: Hierarchy Theorems
 IAS/PCMI Summer Sessio 2000 Clay Mathematics Udergraduate Program Basic Course o Computatioal Complexity Lecture 9: Hierarchy Theorems David Mix Barrigto ad Alexis Maciel July 27, 2000 Most of this lecture
IAS/PCMI Summer Sessio 2000 Clay Mathematics Udergraduate Program Basic Course o Computatioal Complexity Lecture 9: Hierarchy Theorems David Mix Barrigto ad Alexis Maciel July 27, 2000 Most of this lecture
Randomized Algorithms I, Spring 2018, Department of Computer Science, University of Helsinki Homework 1: Solutions (Discussed January 25, 2018)
 Radomized Algorithms I, Sprig 08, Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Helsiki Homework : Solutios Discussed Jauary 5, 08). Exercise.: Cosider the followig balls-ad-bi game. We start with oe black
Radomized Algorithms I, Sprig 08, Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Helsiki Homework : Solutios Discussed Jauary 5, 08). Exercise.: Cosider the followig balls-ad-bi game. We start with oe black
CS 330 Discussion - Probability
 CS 330 Discussio - Probability March 24 2017 1 Fudametals of Probability 11 Radom Variables ad Evets A radom variable X is oe whose value is o-determiistic For example, suppose we flip a coi ad set X =
CS 330 Discussio - Probability March 24 2017 1 Fudametals of Probability 11 Radom Variables ad Evets A radom variable X is oe whose value is o-determiistic For example, suppose we flip a coi ad set X =
Lecture 9: Expanders Part 2, Extractors
 Lecture 9: Expaders Part, Extractors Topics i Complexity Theory ad Pseudoradomess Sprig 013 Rutgers Uiversity Swastik Kopparty Scribes: Jaso Perry, Joh Kim I this lecture, we will discuss further the pseudoradomess
Lecture 9: Expaders Part, Extractors Topics i Complexity Theory ad Pseudoradomess Sprig 013 Rutgers Uiversity Swastik Kopparty Scribes: Jaso Perry, Joh Kim I this lecture, we will discuss further the pseudoradomess
Linear Regression Demystified
 Liear Regressio Demystified Liear regressio is a importat subject i statistics. I elemetary statistics courses, formulae related to liear regressio are ofte stated without derivatio. This ote iteds to
Liear Regressio Demystified Liear regressio is a importat subject i statistics. I elemetary statistics courses, formulae related to liear regressio are ofte stated without derivatio. This ote iteds to
n outcome is (+1,+1, 1,..., 1). Let the r.v. X denote our position (relative to our starting point 0) after n moves. Thus X = X 1 + X 2 + +X n,
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2008 David Wager Note 9 Variace Questio: At each time step, I flip a fair coi. If it comes up Heads, I walk oe step to the right; if it comes up Tails, I walk oe
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2008 David Wager Note 9 Variace Questio: At each time step, I flip a fair coi. If it comes up Heads, I walk oe step to the right; if it comes up Tails, I walk oe
( ) = p and P( i = b) = q.
 MATH 540 Radom Walks Part 1 A radom walk X is special stochastic process that measures the height (or value) of a particle that radomly moves upward or dowward certai fixed amouts o each uit icremet of
MATH 540 Radom Walks Part 1 A radom walk X is special stochastic process that measures the height (or value) of a particle that radomly moves upward or dowward certai fixed amouts o each uit icremet of
Homework 5 Solutions
 Homework 5 Solutios p329 # 12 No. To estimate the chace you eed the expected value ad stadard error. To do get the expected value you eed the average of the box ad to get the stadard error you eed the
Homework 5 Solutios p329 # 12 No. To estimate the chace you eed the expected value ad stadard error. To do get the expected value you eed the average of the box ad to get the stadard error you eed the
Output Analysis and Run-Length Control
 IEOR E4703: Mote Carlo Simulatio Columbia Uiversity c 2017 by Marti Haugh Output Aalysis ad Ru-Legth Cotrol I these otes we describe how the Cetral Limit Theorem ca be used to costruct approximate (1 α%
IEOR E4703: Mote Carlo Simulatio Columbia Uiversity c 2017 by Marti Haugh Output Aalysis ad Ru-Legth Cotrol I these otes we describe how the Cetral Limit Theorem ca be used to costruct approximate (1 α%
Lecture 6: Coupon Collector s problem
 Radomized Algorithms Lecture 6: Coupo Collector s problem Sotiris Nikoletseas Professor CEID - ETY Course 2017-2018 Sotiris Nikoletseas, Professor Radomized Algorithms - Lecture 6 1 / 16 Variace: key features
Radomized Algorithms Lecture 6: Coupo Collector s problem Sotiris Nikoletseas Professor CEID - ETY Course 2017-2018 Sotiris Nikoletseas, Professor Radomized Algorithms - Lecture 6 1 / 16 Variace: key features
ST5215: Advanced Statistical Theory
 ST525: Advaced Statistical Theory Departmet of Statistics & Applied Probability Tuesday, September 7, 2 ST525: Advaced Statistical Theory Lecture : The law of large umbers The Law of Large Numbers The
ST525: Advaced Statistical Theory Departmet of Statistics & Applied Probability Tuesday, September 7, 2 ST525: Advaced Statistical Theory Lecture : The law of large umbers The Law of Large Numbers The
Rademacher Complexity
 EECS 598: Statistical Learig Theory, Witer 204 Topic 0 Rademacher Complexity Lecturer: Clayto Scott Scribe: Ya Deg, Kevi Moo Disclaimer: These otes have ot bee subjected to the usual scrutiy reserved for
EECS 598: Statistical Learig Theory, Witer 204 Topic 0 Rademacher Complexity Lecturer: Clayto Scott Scribe: Ya Deg, Kevi Moo Disclaimer: These otes have ot bee subjected to the usual scrutiy reserved for
CS161: Algorithm Design and Analysis Handout #10 Stanford University Wednesday, 10 February 2016
 CS161: Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Hadout #10 Staford Uiversity Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Lecture #11: Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Topics: Example midterm problems ad solutios from a log time ago Sprig
CS161: Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Hadout #10 Staford Uiversity Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Lecture #11: Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Topics: Example midterm problems ad solutios from a log time ago Sprig
Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2005 Clancy/Wagner Notes 21. Some Important Distributions
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2005 Clacy/Wager Notes 21 Some Importat Distributios Questio: A biased coi with Heads probability p is tossed repeatedly util the first Head appears. What is the
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2005 Clacy/Wager Notes 21 Some Importat Distributios Questio: A biased coi with Heads probability p is tossed repeatedly util the first Head appears. What is the
7.1 Convergence of sequences of random variables
 Chapter 7 Limit theorems Throughout this sectio we will assume a probability space (Ω, F, P), i which is defied a ifiite sequece of radom variables (X ) ad a radom variable X. The fact that for every ifiite
Chapter 7 Limit theorems Throughout this sectio we will assume a probability space (Ω, F, P), i which is defied a ifiite sequece of radom variables (X ) ad a radom variable X. The fact that for every ifiite
Shannon s noiseless coding theorem
 18.310 lecture otes May 4, 2015 Shao s oiseless codig theorem Lecturer: Michel Goemas I these otes we discuss Shao s oiseless codig theorem, which is oe of the foudig results of the field of iformatio
18.310 lecture otes May 4, 2015 Shao s oiseless codig theorem Lecturer: Michel Goemas I these otes we discuss Shao s oiseless codig theorem, which is oe of the foudig results of the field of iformatio
Chapter 2 The Solution of Numerical Algebraic and Transcendental Equations
 Chapter The Solutio of Numerical Algebraic ad Trascedetal Equatios Itroductio I this chapter we shall discuss some umerical methods for solvig algebraic ad trascedetal equatios. The equatio f( is said
Chapter The Solutio of Numerical Algebraic ad Trascedetal Equatios Itroductio I this chapter we shall discuss some umerical methods for solvig algebraic ad trascedetal equatios. The equatio f( is said
Lecture 16: Monotone Formula Lower Bounds via Graph Entropy. 2 Monotone Formula Lower Bounds via Graph Entropy
 15-859: Iformatio Theory ad Applicatios i TCS CMU: Sprig 2013 Lecture 16: Mootoe Formula Lower Bouds via Graph Etropy March 26, 2013 Lecturer: Mahdi Cheraghchi Scribe: Shashak Sigh 1 Recap Graph Etropy:
15-859: Iformatio Theory ad Applicatios i TCS CMU: Sprig 2013 Lecture 16: Mootoe Formula Lower Bouds via Graph Etropy March 26, 2013 Lecturer: Mahdi Cheraghchi Scribe: Shashak Sigh 1 Recap Graph Etropy:
w (1) ˆx w (1) x (1) /ρ and w (2) ˆx w (2) x (2) /ρ.
 2 5. Weighted umber of late jobs 5.1. Release dates ad due dates: maximimizig the weight of o-time jobs Oce we add release dates, miimizig the umber of late jobs becomes a sigificatly harder problem. For
2 5. Weighted umber of late jobs 5.1. Release dates ad due dates: maximimizig the weight of o-time jobs Oce we add release dates, miimizig the umber of late jobs becomes a sigificatly harder problem. For
Ada Boost, Risk Bounds, Concentration Inequalities. 1 AdaBoost and Estimates of Conditional Probabilities
 CS8B/Stat4B Sprig 008) Statistical Learig Theory Lecture: Ada Boost, Risk Bouds, Cocetratio Iequalities Lecturer: Peter Bartlett Scribe: Subhrasu Maji AdaBoost ad Estimates of Coditioal Probabilities We
CS8B/Stat4B Sprig 008) Statistical Learig Theory Lecture: Ada Boost, Risk Bouds, Cocetratio Iequalities Lecturer: Peter Bartlett Scribe: Subhrasu Maji AdaBoost ad Estimates of Coditioal Probabilities We
1 Hash tables. 1.1 Implementation
 Lecture 8 Hash Tables, Uiversal Hash Fuctios, Balls ad Bis Scribes: Luke Johsto, Moses Charikar, G. Valiat Date: Oct 18, 2017 Adapted From Virgiia Williams lecture otes 1 Hash tables A hash table is a
Lecture 8 Hash Tables, Uiversal Hash Fuctios, Balls ad Bis Scribes: Luke Johsto, Moses Charikar, G. Valiat Date: Oct 18, 2017 Adapted From Virgiia Williams lecture otes 1 Hash tables A hash table is a
ACO Comprehensive Exam 9 October 2007 Student code A. 1. Graph Theory
 1. Graph Theory Prove that there exist o simple plaar triagulatio T ad two distict adjacet vertices x, y V (T ) such that x ad y are the oly vertices of T of odd degree. Do ot use the Four-Color Theorem.
1. Graph Theory Prove that there exist o simple plaar triagulatio T ad two distict adjacet vertices x, y V (T ) such that x ad y are the oly vertices of T of odd degree. Do ot use the Four-Color Theorem.
Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 22
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2008 David Wager Note 22 I.I.D. Radom Variables Estimatig the bias of a coi Questio: We wat to estimate the proportio p of Democrats i the US populatio, by takig
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2008 David Wager Note 22 I.I.D. Radom Variables Estimatig the bias of a coi Questio: We wat to estimate the proportio p of Democrats i the US populatio, by takig
Topic 9: Sampling Distributions of Estimators
 Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2016 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2016 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
Skip Lists. Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 S 3 S S 1
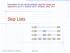 Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for
Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for
MATH 472 / SPRING 2013 ASSIGNMENT 2: DUE FEBRUARY 4 FINALIZED
 MATH 47 / SPRING 013 ASSIGNMENT : DUE FEBRUARY 4 FINALIZED Please iclude a cover sheet that provides a complete setece aswer to each the followig three questios: (a) I your opiio, what were the mai ideas
MATH 47 / SPRING 013 ASSIGNMENT : DUE FEBRUARY 4 FINALIZED Please iclude a cover sheet that provides a complete setece aswer to each the followig three questios: (a) I your opiio, what were the mai ideas
CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutions
 CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutios assigmet due July 6, 016 writte by Jāis Lazovskis maximum poits: 33 Some questios from CLRS. Questios marked with a asterisk were ot graded. 1 Use the defiitio of
CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutios assigmet due July 6, 016 writte by Jāis Lazovskis maximum poits: 33 Some questios from CLRS. Questios marked with a asterisk were ot graded. 1 Use the defiitio of
Chapter 3. Strong convergence. 3.1 Definition of almost sure convergence
 Chapter 3 Strog covergece As poited out i the Chapter 2, there are multiple ways to defie the otio of covergece of a sequece of radom variables. That chapter defied covergece i probability, covergece i
Chapter 3 Strog covergece As poited out i the Chapter 2, there are multiple ways to defie the otio of covergece of a sequece of radom variables. That chapter defied covergece i probability, covergece i
Carleton College, Winter 2017 Math 121, Practice Final Prof. Jones. Note: the exam will have a section of true-false questions, like the one below.
 Carleto College, Witer 207 Math 2, Practice Fial Prof. Joes Note: the exam will have a sectio of true-false questios, like the oe below.. True or False. Briefly explai your aswer. A icorrectly justified
Carleto College, Witer 207 Math 2, Practice Fial Prof. Joes Note: the exam will have a sectio of true-false questios, like the oe below.. True or False. Briefly explai your aswer. A icorrectly justified
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2012 Alistair Sinclair Note 15
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics ad Probability Theory Sprig 2012 Alistair Siclair Note 15 Some Importat Distributios The first importat distributio we leared about i the last Lecture Note is the biomial distributio
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics ad Probability Theory Sprig 2012 Alistair Siclair Note 15 Some Importat Distributios The first importat distributio we leared about i the last Lecture Note is the biomial distributio
Axioms of Measure Theory
 MATH 532 Axioms of Measure Theory Dr. Neal, WKU I. The Space Throughout the course, we shall let X deote a geeric o-empty set. I geeral, we shall ot assume that ay algebraic structure exists o X so that
MATH 532 Axioms of Measure Theory Dr. Neal, WKU I. The Space Throughout the course, we shall let X deote a geeric o-empty set. I geeral, we shall ot assume that ay algebraic structure exists o X so that
7.1 Convergence of sequences of random variables
 Chapter 7 Limit Theorems Throughout this sectio we will assume a probability space (, F, P), i which is defied a ifiite sequece of radom variables (X ) ad a radom variable X. The fact that for every ifiite
Chapter 7 Limit Theorems Throughout this sectio we will assume a probability space (, F, P), i which is defied a ifiite sequece of radom variables (X ) ad a radom variable X. The fact that for every ifiite
CS:3330 (Prof. Pemmaraju ): Assignment #1 Solutions. (b) For n = 3, we will have 3 men and 3 women with preferences as follows: m 1 : w 3 > w 1 > w 2
 Shiyao Wag CS:3330 (Prof. Pemmaraju ): Assigmet #1 Solutios Problem 1 (a) Cosider iput with me m 1, m,..., m ad wome w 1, w,..., w with the followig prefereces: All me have the same prefereces for wome:
Shiyao Wag CS:3330 (Prof. Pemmaraju ): Assigmet #1 Solutios Problem 1 (a) Cosider iput with me m 1, m,..., m ad wome w 1, w,..., w with the followig prefereces: All me have the same prefereces for wome:
CS284A: Representations and Algorithms in Molecular Biology
 CS284A: Represetatios ad Algorithms i Molecular Biology Scribe Notes o Lectures 3 & 4: Motif Discovery via Eumeratio & Motif Represetatio Usig Positio Weight Matrix Joshua Gervi Based o presetatios by
CS284A: Represetatios ad Algorithms i Molecular Biology Scribe Notes o Lectures 3 & 4: Motif Discovery via Eumeratio & Motif Represetatio Usig Positio Weight Matrix Joshua Gervi Based o presetatios by
4.1 SIGMA NOTATION AND RIEMANN SUMS
 .1 Sigma Notatio ad Riema Sums Cotemporary Calculus 1.1 SIGMA NOTATION AND RIEMANN SUMS Oe strategy for calculatig the area of a regio is to cut the regio ito simple shapes, calculate the area of each
.1 Sigma Notatio ad Riema Sums Cotemporary Calculus 1.1 SIGMA NOTATION AND RIEMANN SUMS Oe strategy for calculatig the area of a regio is to cut the regio ito simple shapes, calculate the area of each
11. Hash Tables. m is not too large. Many applications require a dynamic set that supports only the directory operations INSERT, SEARCH and DELETE.
 11. Hash Tables May applicatios require a dyamic set that supports oly the directory operatios INSERT, SEARCH ad DELETE. A hash table is a geeralizatio of the simpler otio of a ordiary array. Directly
11. Hash Tables May applicatios require a dyamic set that supports oly the directory operatios INSERT, SEARCH ad DELETE. A hash table is a geeralizatio of the simpler otio of a ordiary array. Directly
SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES
 SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES Read Sectio 1.5 (pages 5 9) Overview I Sectio 1.5 we lear to work with summatio otatio ad formulas. We will also itroduce a brief overview of sequeces,
SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES Read Sectio 1.5 (pages 5 9) Overview I Sectio 1.5 we lear to work with summatio otatio ad formulas. We will also itroduce a brief overview of sequeces,
Advanced Stochastic Processes.
 Advaced Stochastic Processes. David Gamarik LECTURE 2 Radom variables ad measurable fuctios. Strog Law of Large Numbers (SLLN). Scary stuff cotiued... Outlie of Lecture Radom variables ad measurable fuctios.
Advaced Stochastic Processes. David Gamarik LECTURE 2 Radom variables ad measurable fuctios. Strog Law of Large Numbers (SLLN). Scary stuff cotiued... Outlie of Lecture Radom variables ad measurable fuctios.
Lecture 2. The Lovász Local Lemma
 Staford Uiversity Sprig 208 Math 233A: No-costructive methods i combiatorics Istructor: Ja Vodrák Lecture date: Jauary 0, 208 Origial scribe: Apoorva Khare Lecture 2. The Lovász Local Lemma 2. Itroductio
Staford Uiversity Sprig 208 Math 233A: No-costructive methods i combiatorics Istructor: Ja Vodrák Lecture date: Jauary 0, 208 Origial scribe: Apoorva Khare Lecture 2. The Lovász Local Lemma 2. Itroductio
ECE 901 Lecture 12: Complexity Regularization and the Squared Loss
 ECE 90 Lecture : Complexity Regularizatio ad the Squared Loss R. Nowak 5/7/009 I the previous lectures we made use of the Cheroff/Hoeffdig bouds for our aalysis of classifier errors. Hoeffdig s iequality
ECE 90 Lecture : Complexity Regularizatio ad the Squared Loss R. Nowak 5/7/009 I the previous lectures we made use of the Cheroff/Hoeffdig bouds for our aalysis of classifier errors. Hoeffdig s iequality
Infinite Sequences and Series
 Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
Lecture 12: September 27
 36-705: Itermediate Statistics Fall 207 Lecturer: Siva Balakrisha Lecture 2: September 27 Today we will discuss sufficiecy i more detail ad the begi to discuss some geeral strategies for costructig estimators.
36-705: Itermediate Statistics Fall 207 Lecturer: Siva Balakrisha Lecture 2: September 27 Today we will discuss sufficiecy i more detail ad the begi to discuss some geeral strategies for costructig estimators.
The random version of Dvoretzky s theorem in l n
 The radom versio of Dvoretzky s theorem i l Gideo Schechtma Abstract We show that with high probability a sectio of the l ball of dimesio k cε log c > 0 a uiversal costat) is ε close to a multiple of the
The radom versio of Dvoretzky s theorem i l Gideo Schechtma Abstract We show that with high probability a sectio of the l ball of dimesio k cε log c > 0 a uiversal costat) is ε close to a multiple of the
CS 171 Lecture Outline October 09, 2008
 CS 171 Lecture Outlie October 09, 2008 The followig theorem comes very hady whe calculatig the expectatio of a radom variable that takes o o-egative iteger values. Theorem: Let Y be a radom variable that
CS 171 Lecture Outlie October 09, 2008 The followig theorem comes very hady whe calculatig the expectatio of a radom variable that takes o o-egative iteger values. Theorem: Let Y be a radom variable that
Solutions to selected exercise of Randomized Algorithms
 Solutios to selected exercise of Radomized Algorithms Zhag Qi December 5, 006 Chapter. Problem.7. We first prove that e λx λ(e x ) Whe x = 0, LHS = RHS = 0. Ad whe x > 0, (e λx ) = λe λx λe x = [λ(e x
Solutios to selected exercise of Radomized Algorithms Zhag Qi December 5, 006 Chapter. Problem.7. We first prove that e λx λ(e x ) Whe x = 0, LHS = RHS = 0. Ad whe x > 0, (e λx ) = λe λx λe x = [λ(e x
6.895 Essential Coding Theory October 20, Lecture 11. This lecture is focused in comparisons of the following properties/parameters of a code:
 6.895 Essetial Codig Theory October 0, 004 Lecture 11 Lecturer: Madhu Suda Scribe: Aastasios Sidiropoulos 1 Overview This lecture is focused i comparisos of the followig properties/parameters of a code:
6.895 Essetial Codig Theory October 0, 004 Lecture 11 Lecturer: Madhu Suda Scribe: Aastasios Sidiropoulos 1 Overview This lecture is focused i comparisos of the followig properties/parameters of a code:
Economics Spring 2015
 1 Ecoomics 400 -- Sprig 015 /17/015 pp. 30-38; Ch. 7.1.4-7. New Stata Assigmet ad ew MyStatlab assigmet, both due Feb 4th Midterm Exam Thursday Feb 6th, Chapters 1-7 of Groeber text ad all relevat lectures
1 Ecoomics 400 -- Sprig 015 /17/015 pp. 30-38; Ch. 7.1.4-7. New Stata Assigmet ad ew MyStatlab assigmet, both due Feb 4th Midterm Exam Thursday Feb 6th, Chapters 1-7 of Groeber text ad all relevat lectures
STAT Homework 1 - Solutions
 STAT-36700 Homework 1 - Solutios Fall 018 September 11, 018 This cotais solutios for Homework 1. Please ote that we have icluded several additioal commets ad approaches to the problems to give you better
STAT-36700 Homework 1 - Solutios Fall 018 September 11, 018 This cotais solutios for Homework 1. Please ote that we have icluded several additioal commets ad approaches to the problems to give you better
Sieve Estimators: Consistency and Rates of Convergence
 EECS 598: Statistical Learig Theory, Witer 2014 Topic 6 Sieve Estimators: Cosistecy ad Rates of Covergece Lecturer: Clayto Scott Scribe: Julia Katz-Samuels, Brado Oselio, Pi-Yu Che Disclaimer: These otes
EECS 598: Statistical Learig Theory, Witer 2014 Topic 6 Sieve Estimators: Cosistecy ad Rates of Covergece Lecturer: Clayto Scott Scribe: Julia Katz-Samuels, Brado Oselio, Pi-Yu Che Disclaimer: These otes
Lecture #20. n ( x p i )1/p = max
 COMPSCI 632: Approximatio Algorithms November 8, 2017 Lecturer: Debmalya Paigrahi Lecture #20 Scribe: Yua Deg 1 Overview Today, we cotiue to discuss about metric embeddigs techique. Specifically, we apply
COMPSCI 632: Approximatio Algorithms November 8, 2017 Lecturer: Debmalya Paigrahi Lecture #20 Scribe: Yua Deg 1 Overview Today, we cotiue to discuss about metric embeddigs techique. Specifically, we apply
(A sequence also can be thought of as the list of function values attained for a function f :ℵ X, where f (n) = x n for n 1.) x 1 x N +k x N +4 x 3
 MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
b i u x i U a i j u x i u x j
 M ath 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecture 1 9 N ov. 1 6, 2 0 0 9 ) S ecod- Order Elliptic Equatios: Weak S olutios 1. Defiitios. I this ad the followig two lectures we will study the boudary value problem Here
M ath 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecture 1 9 N ov. 1 6, 2 0 0 9 ) S ecod- Order Elliptic Equatios: Weak S olutios 1. Defiitios. I this ad the followig two lectures we will study the boudary value problem Here
Econ 325/327 Notes on Sample Mean, Sample Proportion, Central Limit Theorem, Chi-square Distribution, Student s t distribution 1.
 Eco 325/327 Notes o Sample Mea, Sample Proportio, Cetral Limit Theorem, Chi-square Distributio, Studet s t distributio 1 Sample Mea By Hiro Kasahara We cosider a radom sample from a populatio. Defiitio
Eco 325/327 Notes o Sample Mea, Sample Proportio, Cetral Limit Theorem, Chi-square Distributio, Studet s t distributio 1 Sample Mea By Hiro Kasahara We cosider a radom sample from a populatio. Defiitio
Statistics 511 Additional Materials
 Cofidece Itervals o mu Statistics 511 Additioal Materials This topic officially moves us from probability to statistics. We begi to discuss makig ifereces about the populatio. Oe way to differetiate probability
Cofidece Itervals o mu Statistics 511 Additioal Materials This topic officially moves us from probability to statistics. We begi to discuss makig ifereces about the populatio. Oe way to differetiate probability
Because it tests for differences between multiple pairs of means in one test, it is called an omnibus test.
 Math 308 Sprig 018 Classes 19 ad 0: Aalysis of Variace (ANOVA) Page 1 of 6 Itroductio ANOVA is a statistical procedure for determiig whether three or more sample meas were draw from populatios with equal
Math 308 Sprig 018 Classes 19 ad 0: Aalysis of Variace (ANOVA) Page 1 of 6 Itroductio ANOVA is a statistical procedure for determiig whether three or more sample meas were draw from populatios with equal
Lecture 10 October Minimaxity and least favorable prior sequences
 STATS 300A: Theory of Statistics Fall 205 Lecture 0 October 22 Lecturer: Lester Mackey Scribe: Brya He, Rahul Makhijai Warig: These otes may cotai factual ad/or typographic errors. 0. Miimaxity ad least
STATS 300A: Theory of Statistics Fall 205 Lecture 0 October 22 Lecturer: Lester Mackey Scribe: Brya He, Rahul Makhijai Warig: These otes may cotai factual ad/or typographic errors. 0. Miimaxity ad least
Machine Learning Brett Bernstein
 Machie Learig Brett Berstei Week 2 Lecture: Cocept Check Exercises Starred problems are optioal. Excess Risk Decompositio 1. Let X = Y = {1, 2,..., 10}, A = {1,..., 10, 11} ad suppose the data distributio
Machie Learig Brett Berstei Week 2 Lecture: Cocept Check Exercises Starred problems are optioal. Excess Risk Decompositio 1. Let X = Y = {1, 2,..., 10}, A = {1,..., 10, 11} ad suppose the data distributio
Lecture 11: Pseudorandom functions
 COM S 6830 Cryptography Oct 1, 2009 Istructor: Rafael Pass 1 Recap Lecture 11: Pseudoradom fuctios Scribe: Stefao Ermo Defiitio 1 (Ge, Ec, Dec) is a sigle message secure ecryptio scheme if for all uppt
COM S 6830 Cryptography Oct 1, 2009 Istructor: Rafael Pass 1 Recap Lecture 11: Pseudoradom fuctios Scribe: Stefao Ermo Defiitio 1 (Ge, Ec, Dec) is a sigle message secure ecryptio scheme if for all uppt
Estimation for Complete Data
 Estimatio for Complete Data complete data: there is o loss of iformatio durig study. complete idividual complete data= grouped data A complete idividual data is the oe i which the complete iformatio of
Estimatio for Complete Data complete data: there is o loss of iformatio durig study. complete idividual complete data= grouped data A complete idividual data is the oe i which the complete iformatio of
Introductory Analysis I Fall 2014 Homework #7 Solutions
 Itroductory Aalysis I Fall 214 Homework #7 Solutios Note: There were a couple of typos/omissios i the formulatio of this homework. Some of them were, I believe, quite obvious. The fact that the statemet
Itroductory Aalysis I Fall 214 Homework #7 Solutios Note: There were a couple of typos/omissios i the formulatio of this homework. Some of them were, I believe, quite obvious. The fact that the statemet
Recursive Algorithms. Recurrences. Recursive Algorithms Analysis
 Recursive Algorithms Recurreces Computer Sciece & Egieerig 35: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M Bourke cbourke@cseuledu A recursive algorithm is oe i which objects are defied i terms of other objects
Recursive Algorithms Recurreces Computer Sciece & Egieerig 35: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M Bourke cbourke@cseuledu A recursive algorithm is oe i which objects are defied i terms of other objects
Lecture 11: Hash Functions and Random Oracle Model
 CS 7810 Foudatios of Cryptography October 16, 017 Lecture 11: Hash Fuctios ad Radom Oracle Model Lecturer: Daiel Wichs Scribe: Akshar Varma 1 Topic Covered Defiitio of Hash Fuctios Merkle-Damgaård Theorem
CS 7810 Foudatios of Cryptography October 16, 017 Lecture 11: Hash Fuctios ad Radom Oracle Model Lecturer: Daiel Wichs Scribe: Akshar Varma 1 Topic Covered Defiitio of Hash Fuctios Merkle-Damgaård Theorem
The multiplicative structure of finite field and a construction of LRC
 IERG6120 Codig for Distributed Storage Systems Lecture 8-06/10/2016 The multiplicative structure of fiite field ad a costructio of LRC Lecturer: Keeth Shum Scribe: Zhouyi Hu Notatios: We use the otatio
IERG6120 Codig for Distributed Storage Systems Lecture 8-06/10/2016 The multiplicative structure of fiite field ad a costructio of LRC Lecturer: Keeth Shum Scribe: Zhouyi Hu Notatios: We use the otatio
Seunghee Ye Ma 8: Week 5 Oct 28
 Week 5 Summary I Sectio, we go over the Mea Value Theorem ad its applicatios. I Sectio 2, we will recap what we have covered so far this term. Topics Page Mea Value Theorem. Applicatios of the Mea Value
Week 5 Summary I Sectio, we go over the Mea Value Theorem ad its applicatios. I Sectio 2, we will recap what we have covered so far this term. Topics Page Mea Value Theorem. Applicatios of the Mea Value
Math 152. Rumbos Fall Solutions to Review Problems for Exam #2. Number of Heads Frequency
 Math 152. Rumbos Fall 2009 1 Solutios to Review Problems for Exam #2 1. I the book Experimetatio ad Measuremet, by W. J. Youde ad published by the by the Natioal Sciece Teachers Associatio i 1962, the
Math 152. Rumbos Fall 2009 1 Solutios to Review Problems for Exam #2 1. I the book Experimetatio ad Measuremet, by W. J. Youde ad published by the by the Natioal Sciece Teachers Associatio i 1962, the
Binomial Distribution
 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 Overview Example: coi tossed three times Defiitio Formula Recall that a r.v. is discrete if there are either a fiite umber of possible
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 Overview Example: coi tossed three times Defiitio Formula Recall that a r.v. is discrete if there are either a fiite umber of possible
Lecture 12: November 13, 2018
 Mathematical Toolkit Autum 2018 Lecturer: Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 12: November 13, 2018 1 Radomized polyomial idetity testig We will use our kowledge of coditioal probability to prove the followig lemma,
Mathematical Toolkit Autum 2018 Lecturer: Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 12: November 13, 2018 1 Radomized polyomial idetity testig We will use our kowledge of coditioal probability to prove the followig lemma,
Chapter 6. Advanced Counting Techniques
 Chapter 6 Advaced Coutig Techiques 6.: Recurrece Relatios Defiitio: A recurrece relatio for the sequece {a } is a equatio expressig a i terms of oe or more of the previous terms of the sequece: a,a2,a3,,a
Chapter 6 Advaced Coutig Techiques 6.: Recurrece Relatios Defiitio: A recurrece relatio for the sequece {a } is a equatio expressig a i terms of oe or more of the previous terms of the sequece: a,a2,a3,,a
