UNCORRECTED. Australian curriculum MEASUREMENT AND GEOMETRY
|
|
|
- Darren Parrish
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3 3 3C 3D 3 3F 3G 3H 3I 3J Chpter Wht you will lern Pythgors theorem Finding the shorter sides pplying Pythgors theorem Pythgors in three dimensions (tending) Trigonometri rtios Finding side lengths Solving for the denomintor Finding n ngle pplying trigonometry (tending) erings (tending) 3Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry ustrlin urriulum MSURMNT ND GOMTRY Pythgors nd Trigonometry Investigte Pythgors theorem nd its pplition to solving simple prolems involving right-ngled tringles Use similrity to investigte the onstny of the sine, osine nd tngent rtios for given ngle in right-ngled tringles pply trigonometry to solve right-ngled tringle prolems Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
2 Stellites Stellite nvigtion systems work y determining where you re nd lulting how fr it is to where you wnt to go. Distnes re worked out using the mthemtis of trigonometry. The position of the stellite, your position nd your destintion re three points whih form tringle. This tringle n e divided into two right-ngled tringles nd, using two known ngles nd one side length, the distne etween where you re nd your destintion n e found using sine, osine nd tngent funtions. Similr tehniques re used to nvigte the ses, study the strs nd mp our plnet, rth. Online resoures Chpter pre-test Videos of ll worked emples Intertive widgets Intertive wlkthroughs Downlodle HOTsheets ess to HOTmths ustrlin Curriulum ourses Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
3 144 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3 Pythgors theorem Pythgors ws orn on the Greek islnd of Smos in the 6th entury C. He reeived privileged edution nd trvelled to gypt nd Persi where he developed his ides in mthemtis nd philosophy. He settled in Crotone Itly where he founded shool. His mny students nd followers were lled the Pythgorens nd under the guidne of Pythgors, lived very strutured life with strit rules. They imed to e pure, selfsuffiient nd wise, where men nd women were treted eqully nd ll property ws onsidered ommunl. They strove to perfet their physil nd mentl form nd mde mny dvnes in their understnding of the world through mthemtis. The Pythgorens disovered the fmous theorem, whih is nmed fter Pythgors, nd the eistene of irrtionl numers suh s 2, whih nnot e written down s frtion or terminting deiml. Suh numers nnot The Pythgoren rotherhood in nient Greee e mesured etly with ruler with frtionl prts nd were thought to e unnturl. The Pythgorens lled these numers unutterle numers nd it is elieved tht ny memer of the rotherhood who mentioned these numers in puli would e put to deth. Let s strt: Mthing the res of squres Look t this right-ngled tringle nd the squres drwn on eh side. h squre is divided into smller setions. Cn you see how the prts of the two smller squres would fit into the lrger squre? Wht is the re of eh squre if the side lengths of the right-ngled tringle re, nd s mrked? Wht do the nswers to the ove two questions suggest out the reltionship etween, nd? Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
4 Mesurement nd Geometry 14 The longest side of right-ngled tringle is lled the hypotenuse nd is opposite the right ngle. The theorem of Pythgors sys tht the squre of the length of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the squres of the lengths of the other two sides. For the tringle shown, it is: 2 = squre of the hypotenuse squres of the two shorter sides The theorem n e illustrted in digrm like the one on the right. The sum of the res of the two smller squres ( ) is the sme s the re of the lrgest squre ( 2 ). Lengths n e epressed with et vlues using surds. 2, 28 nd 2 3 re emples of surds. When epressed s deiml, surd is n infinite non-reurring deiml with no pttern. For emple: 2 = mple 1 Finding the length of the hypotenuse re = 2 re = 2 re = 2 Find the length of the hypotenuse in these right-ngled tringles. Round to two deiml ples in prt SOLUTION 2 = = = 169 = 169 = 13 XPLNTION 7 Write the rule nd sustitute the lengths of the two shorter sides. If 2 = 169 then = 169 = 13. Key ides Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
5 146 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 2 = = = = = (to 2 d.p.) The order for nd does not mtter sine = Round s required. mple 2 Finding the length of the hypotenuse using et vlues Find the length of the hypotenuse in this right-ngled tringle, leving your nswer s n et vlue. SOLUTION 2 = = = 29 = 29 erise 3 2 XPLNTION pply Pythgors theorem to find the vlue of. press the nswer etly using surd. 1 Stte the length of the hypotenuse ( units) in these right-ngled tringles (½) 2 Write down Pythgors theorem using the given pronumerls for these right-ngled tringles. For emple: z 2 = 2 + y 2. y j k z l 3 vlute the following, rounding to two deiml ples in prts g nd h d e 36 f g 24 h UNDRSTNDING Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
6 Mesurement nd Geometry 147 mple 1 mple 1 mple Find the length of the hypotenuse in eh of the following right-ngled tringles d 12 e 24 g h Find the length of the hypotenuse in eh of these right-ngled tringles, orret to two deiml ples. 3 d e Find the length of the hypotenuse in these tringles, leving your nswer s n et vlue d 6 1 e (½) 4 8(½) 4 8(½) 1 f i f f FLUNCY 3 Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
7 148 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3 7 Find the length of the hypotenuse in eh of these right-ngled tringles, rounding to two deiml ples where neessry. Convert to the units indited in red. 1.2 m 0 mm d 1.3 m 18 mm 8 m e 12 m 90 mm 1.01 km 40 m f 1 m m 8.2 mm 8 For eh of these tringles, first lulte the length of the hypotenuse then find the perimeter, orret to two deiml ples. 2 m 2.37 m 2 m 1 m d m m 3 m e mm 9 Find the perimeter of this tringle. (Hint: You will need to find nd C first.) f.16 m 3.2 m , Find the length of the digonl steel re required to support wll of length 3. m nd height 2.6 m. Give your nswer orret to one deiml ple. 12 m 9 m 3. m 11 heliopter hovers t height of 10 m ove the ground nd is horizontl distne of 200 m from eon on the ground. Find the diret distne of the heliopter from the eon m C 2.6 m FLUNCY PROLM-SOLVING Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
8 Mesurement nd Geometry miniture roket lsts off t n ngle of 4 nd trvels in stright line. fter few seonds, rehes height of 30 m ove the ground. t this point it hs lso overed horizontl distne of 30 m. How fr hs the roket trvelled to the nerest metre? 13 Find the length of the longest rod tht will fit inside ylinder of height 2.1 m nd with irulr end surfe of 1.2 m dimeter. Give your nswer orret to one deiml ple. 14 For the shpe on the right, find the vlue of: y (s frtion) 3 m y m m 4 m 2 63 m? 4 30 m 1.2 m 1 One wy to hek whether four-sided figure is retngle is to ensure tht oth its digonls re the sme length. Wht should the length of the digonls e if retngle hs side lengths 3 m nd m? nswer to two deiml ples. 30 m 2.1 m 16 We know tht if the tringle hs right ngle, then 2 = The onverse of this is tht if 2 = then the tringle must hve right ngle. Test if 2 = to see if these tringles must hve right ngle. They my not e drwn to sle e d f.4 1 1, , 17 PROLM-SOLVING RSONING 3 Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
9 10 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3 17 Tringle C is right-ngled isoseles tringle, nd D is perpendiulr to C. If DC = 4 m nd D = 4 m: find the length of C orret to two deiml ples stte the length of orret to two deiml ples use Pythgors theorem nd C to hek tht the length of C is twie the length of DC. Kennels nd kites D C 18 dog kennel hs the dimensions shown in the digrm on the m right. Give your nswers to eh of the following orret to two deiml ples. Wht is the width, in m, of the kennel? Dog h m Wht is the totl height, h m, of the kennel? 1 m If the sloping height of the roof ws to e redued from m to 0 m, wht differene would this mke to the totl height of the kennel? (ssume tht the width is the sme s in prt.) d Wht is the length of the sloping height of the roof of new kennel if it is to hve totl height of 1.2 m? (The height of the kennel without the roof is still 1 m nd its width is unhnged.) 19 The frme of kite is onstruted with si piees of timer dowel. The four piees round the outer edge re two 30 m piees nd two 0 m piees. The top end of the kite is to form right ngle. Find the length of eh of the digonl piees required to omplete the onstrution. nswer to two deiml ples. 0 m 30 m 18, 19 RSONING NRICHMNT Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
10 Mesurement nd Geometry 11 3 Finding the shorter sides Throughout history, mthemtiins hve utilised known theorems to eplore new ides, disover new theorems nd solve wider rnge of prolems. Similrly, Pythgors knew tht his right-ngled tringle theorem ould e mnipulted so tht the length of one of the shorter sides of tringle n e found if the length of the other two sides re known. We know tht the sum 7 = n e written s differene 3 = 7 4. Likewise, if 2 = then 2 = 2 2 or 2 = 2 2. pplying this to right-ngled tringle mens tht we n now find the length of one of the shorter sides if the other two sides re known. Let s strt: True or flse elow re some mthemtil sttements relting to right-ngled tringle with hypotenuse nd the two shorter sides nd. If we know the length of the rne ji nd the horizontl distne it etends, Pythgors theorem enles us to lulte its vertil height. Some of these mthemtil sttements re true nd some re flse. Cn you sort them into true nd flse groups? = 2 = = = 2 = = 2 2 = = 2 When finding the length of side: 2 = sustitute known vlues into Pythgors rule 2 2 = solve this eqution to find the unknown vlue. 62 = For emple: 400 = 2 If = 30 then sutrt 16 from oth sides. = 20 If 2 = 14 then tke the squre root of oth sides. = 14 is n et nswer ( surd). = 3.74 is rounded deiml nswer. 2 1 Key ides Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
11 12 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry mple 3 Finding the length of shorter side In eh of the following, find the vlue of the pronumerl. Round your nswer in prt to two deiml ples nd give n et nswer to prt SOLUTION = = = 64 = 64 = = = = = = = 9 = 6.0 (to 2 d.p.) 2 = 9 2 ( 9 = = 3 = 3 ) erise 3 XPLNTION Write the rule nd sustitute the known sides. Squre 1 nd 17. Sutrt 22 from oth sides. Tke the squre root of oth sides. Write the rule. Sutrt 7.76 from oth sides. Tke the squre root of oth sides. Round to two deiml ples. Two sides re of length. dd like terms nd then divide oth sides y 2. Tke the squre root of oth sides. To epress s n et nswer, do not round. Different forms re possile. 1(½), Find the vlue of or in these equtions. (oth nd re positive numers.) = 196 = = 144 d 2 = 400 e = 2 f = 62 g = 100 h = If = 100, deide if the following re true or flse. 2 = = = d = e = 6 f = 10 UNDRSTNDING Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
12 Mesurement nd Geometry 13 mple 3 mple 3 3 (½) 3 (½), 6 3 (½), 6 3 In eh of the following find the vlue of the pronumerl d e In eh of the following, find the vlue of the pronumerl. press your nswers orret to two deiml ples d f 4 e f Find the length of the unknown side of eh of these tringles, orret to two deiml ples where neessry. Convert to the units shown in red. 40 m 180 m 1 m 2.3 m d 0. m 3000 m 2 km e 13 m 0 mm f mm 80 mm 6 m FLUNCY 3 Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
13 14 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3 mple 3 6 In eh of the following, find the vlue of s n et nswer. 4 7 For eh of the following digrms, find the vlue of. Give n et nswer eh time m ommunition tower is supported y 3 m les strething from the top of the tower to position t ground level. Find the distne from the se of the tower to the point where the le rehes the ground, orret to one deiml ple , 8, 10 9 The se of ldder lening ginst vertil wll is 1. m from the se of the wll. If the ldder is. m long, find how high the top of the ldder is ove the ground, orret to one deiml ple m Ldder. m 1. m 32 m 10 If television hs sreen size of 63 m it mens tht the digonl length of the sreen is 63 m. If the vertil height of 63 m sreen is 39 m, find how wide the sreen is to the nerest entimetre m vertil fene post is supported y 2.27 m r, s shown in the digrm on the right. Find the distne (d metres) from the se of the post to where the support enters the ground. Give your nswer orret to two deiml ples. Fene 2.27 m d m 9 11 Wll 1.3 m FLUNCY PROLM-SOLVING Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
14 Mesurement nd Geometry 1 12 For these questions note tht ( 2 ) 2 = 4 2 nd ( 3 ) 2 = 9 2. In eh of the following find the vlue of s n et nswer right-ngled tringle hs hypotenuse mesuring m. Find the lengths of the other sides if their lengths re in the given rtio. Give n et nswer. Hint: You n drw tringle like the one shown for prt. 1 to 3 2 to 3 to 7 The power of et vlues 14 Consider this digrm nd the unknown length. d m 3 m 12, 13 plin wht needs to e found first efore n e lulted. Now try lulting the vlue s n et vlue. Ws it neessry to lulte the vlue of or ws 2 enough? Wht prolems might e enountered if the vlue of ws lulted nd rounded efore the vlue of is found? 1 In the digrm elow, OD = 3 nd = C = CD = 1. d Using et vlues find the length of: i OC ii O iii O Round your nswer in prt iii to one deiml ple nd use tht length to relulte the lengths of O, OC nd OD (orret to two deiml ples) strting with O. plin the differene etween the given length OD = 3 nd your nswer for OD in prt. Investigte how hnging the side length ffets your nswers to prts to ove. O 3 D 1 C 14, m RSONING NRICHMNT 3 Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
15 16 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3C Key ides pplying Pythgors theorem Initilly it my not e ovious tht Pythgors theorem n e used to help solve prtiulr prolem. With further investigtion, however, it my e possile to identify nd drw in rightngled tringle whih n help solve the prolem. s long s two sides of the right-ngled tringle re known, the length of the third side n e found. Let s strt: The iggest squre Imgine trying to ut the lrgest squre from irle of ertin size nd lulting the side length of the squre. Drwing simple digrm s shown does not initilly revel right-ngled tringle. If the irle hs dimeter of 2 m, n you find good position to drw the dimeter tht lso helps to form right-ngled tringle? Cn you determine the side length of the lrgest squre? Wht perentge of the re of irle does the lrgest squre oupy? The length of eh le on the nz ridge, Sydney n e lulted using Pythgors theorem. When pplying Pythgors theorem, follow these steps. Identify nd drw right-ngled tringles whih my help to solve the prolem. Lel the sides with their lengths or with letter (pronumerl) if the length is unknown. Use Pythgors theorem to solve for the unknown. Solve the prolem y mking ny further lultions nd nswering in words. mple 4 pplying Pythgors theorem Two skysrpers re loted 2 m prt nd le links the tops of the two uildings. Find the length of the le if the uildings re 0 m nd 80 m in height. Give your nswer orret to two deiml ples. Cle 2 m Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
16 Mesurement nd Geometry 17 SOLUTION XPLNTION Let m e the length of the le. m 2 m 2 = = = = 12 = 12 = m The le is 39.0 m long. erise 3C Drw right-ngled tringle nd lel the mesurements nd pronumerls. 0 m 80 0 = 30 m m 2 m 2 m 80 m Set up n eqution using Pythgors theorem nd solve for. nswer the question in words. 1 Mth eh prolem (, or ) with oth digrm (, or C) nd its solution (I, II, III). Two trees stnd 20 m I The kite is flying t height prt nd they re 32 m 3 km km of 30.9 m. nd 47 m tll. Wht is the distne etween the tops km 2 km of the two trees? mn wlks due north for 2 km then north-est for 3 km. How fr north is he from his strting point? kite is flying with kite string of length 3 m. Its horizontl distne from its nhor point is 17 m. How high is the kite flying? C m m 20 m 17 m 3 m = 1 m 1 1 II The distne etween the top of the two trees is 2 m. III The mn hs wlked totl of = 4.12 km north from his strting point. UNDRSTNDING Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
17 18 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3C mple 4 2 Two skysrpers re loted 2 m prt nd le of length 62.3 m links the tops of the two uildings. If the tller uilding is 200 metres tll, wht is the height of the shorter uilding? Give your nswer orret to one deiml ple. 3 Two poles re loted 2 m prt. wire links the tops of the two poles. Find the length of the wire if the poles re 2.8 m nd m in height. Give your nswer orret to one deiml ple. 4 grge is to e uilt with skillion roof ( roof with single slope). The mesurements re given in the digrm. Clulte the pith line length, to the nerest millimetre. llow 00 mm for eh of the eves. Two ushwlkers re stnding on different mountin sides. ording to their mps, one of them is t height of 2120 m nd the other is t height of 160 m. If the horizontl distne etween them is 90 m, find the diret distne etween the two ushwlkers. Give your nswer orret to the nerest metre. ves 1700 mm 2.8 m Pith line 2600 mm 2 m ves m 2800 mm 6 Find the diret distne etween the points nd in eh of the following, orret to one deiml ple. 10 m 1.9 m 4 m 6 m m m 2 m d 2 2, 4, m 3.9 m 7.1 m 2.7 m 2.6 m 2, 4, 6(½) FLUNCY Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
18 Mesurement nd Geometry m rdio mst is supported y si les in two sets of three les. They re nhored to the ground t n equl distne from the mst. The top set of three les is tthed t point 20 m elow the top of the mst. h le in the lower set of three les is 60 m long nd is tthed t height of 30 m ove the ground. If ll the les hve to e repled, find the totl length of le required. Give your nswer orret to two deiml ples. 8 In prtiulr irle of rdius 2 m, is dimeter nd C is point on the irumferene. ngle C is right ngle. The hord C is 1 m in length. Drw the tringle C s desried, nd mrk in ll the importnt informtion. Find the length of C orret to one deiml ple. 9 suspension ridge is uilt with two vertil pylons nd two stright ems of equl length tht re positioned to etend from the top of the pylons to meet t point C ove the entre of the ridge, s shown in the digrm on the right. Clulte the vertil height of the point C ove the tops of the pylons. Clulte the distne etween the pylons, tht is, the length of the spn of the ridge orret to one deiml ple. 2 m 10 Two irles of rdii 10 m nd 1 m respetively re pled inside squre. Find the perimeter of the squre to the nerest entimetre. Hint: first find the digonl length of the squre using the digrm on the right. 7, 8 8, 9 Pylon 6 m C C Rod 2 m Pylon 72 m 8 10 PROLM-SOLVING 3C Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
19 160 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3C 11 It is possile to find the length of the shorter sides of right-ngled isoseles tringle if only the hypotenuse length is known. Find the et vlue of in this right-ngled isoseles tringle. Now find the et vlue of in this digrm. Finlly, use your results from ove to find the length of in this digrm orret to one deiml ple. 12 Use the method outlined in Question 11 for this prolem. In n rmy nvigtion eerise, group of soldiers hiked due south from se mp for 2. km to wter hole. From there, they turned 4 to the left, to hed south-est for 1.6 km to resting point. When the soldiers were t the resting point, how fr (orret to one deiml ple): est were they from the wter hole? south were they from the wter hole? were they in stright line from se mp? Folding pper squre piee of pper, CD, of side length 20 m is folded to form right-ngled tringle C. The pper is folded seond time to form right-ngled tringle s shown in the digrm elow. D C C d , 12 Find the length of C orret to two deiml ples. Find the perimeter of eh of the following, orret to one deiml ple where neessry: i squre CD ii tringle C iii tringle Use Pythgors theorem nd your nswer for prt to onfirm tht = in tringle. Investigte how hnging the initil side length hnges the nswers to the ove. 13 RSONING NRICHMNT Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
20 Mesurement nd Geometry 161 3D Pythgors in three dimensions XTNDING If you ut solid to form ross-setion two-dimensionl shpe is reveled. From tht ross-setion it my e possile to identify right-ngled tringle tht n e used to find unknown lengths. These lengths n then tell us informtion out the three-dimensionl solid. You n visulise right-ngled tringles in ll sorts of different solids. The glss pyrmid t the Plis du Louvre, Pris, is mde up of totl of 70 tringulr nd 603 rhomus-shped glss segments together forming mny right-ngled tringles. Let s strt: How mny tringles in pyrmid? Here is drwing of squre-sed pyrmid. y drwing lines from ny verte to the entre of the se nd nother point, how mny different right-ngled tringles n you visulise nd drw? The tringles ould e inside or on the outside surfe of the pyrmid. Right-ngled tringles n e identified in mny three-dimensionl solids. It is importnt to try to drw ny identified right-ngled tringle using seprte digrm. Key ides Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
21 162 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry mple Using Pythgors in 3D The length of the digonl on the se of retngulr prism is 8.3 m nd the retngulr prism s height is 3.9 m. Find the distne from one orner of the retngulr prism to the opposite orner. Give your nswer orret to two deiml ples. SOLUTION Let d m e the distne required. d m 8.3 m d 2 = = 84.1 d = m The distne from one orner of the retngulr prism to the opposite orner is pproimtely 9.17 m. erise 3D XPLNTION 8.3 m Drw right-ngled tringle nd lel ll the mesurements nd pronumerls. Use Pythgors theorem. Round to two deiml ples. Write your nswer in words. 1 Deide if the following shded regions would form right-ngled tringles. d Right ylinder Cue e Right one Cue 1 1 f Cone Retngulr prism 3.9 m UNDRSTNDING Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
22 Mesurement nd Geometry 163 mple 2 g Tringulr prism h Tetrhedron (regulr tringulrsed pyrmid) i Right squre-sed pyrmid (pe ove entre of se) Find the distne, d units, from one orner to the opposite orner in eh of the following retngulr prisms. Give your nswers orret to two deiml ples. d mm d m mm 10 mm m 8.91 m 0.32 m d m 0.1 m 3 Find the slnt height, s units, of eh of the following ones. Give your nswers orret to one deiml ple. 1. m 3 m 2 m s m 1.7 m s m 2.3 m 3 m 4 Find the length to the nerest millimetre of the longest rod tht will fit inside ylinder of the following dimensions. Dimeter 10 m nd height 1 m Rdius 2.8 mm nd height 4.2 mm Dimeter m nd height 0.01 m s m 2 4(½),, 6 Rod UNDRSTNDING FLUNCY 3D Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
23 164 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3D The ue in the digrm on the right hs 1 m sides. D Find the length of C s n et vlue. Hene, find the length of D orret to one deiml ple. 6 Consider the shpe shown. Find the length of C s n et vlue. Hene, find the length of D orret to one deiml ple. F 12 m 7 7, 8 C D 4 m C 8 m 7 miner mkes lim to irulr piee of lnd with rdius of 40 m from given point, nd is entitled to dig to depth of 2 m. If the miner n dig tunnels t ny ngle, find the length of the longest stright tunnel tht he n dig, to the nerest metre. 8 owl is in the shpe of hemisphere (hlf sphere) with rdius 10 m. The surfe of the wter in the ontiner hs rdius of 7 m. How deep is the wter? Give your nswer to two deiml ples. 9 ue of side length l sits inside sphere of rdius r so tht the verties of the ue sit on the sphere. Find the rtio r : l. 10 There re different wys to pproh finding the height of pyrmid depending on wht informtion is given. For eh of the following squre-sed pyrmids, find: i the et length (using surd) of the digonl on the se ii the height of the pyrmid orret to two deiml ples. 4 m 2 m m m 8, 9 10, 11 FLUNCY PROLM-SOLVING RSONING Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
24 Mesurement nd Geometry For this retngulr prism nswer these questions. Find the et length. Find orret to two deiml ples. Find the length C using your result from prt nd then round to two deiml ples. d Find the length C using your result from 7 4 prt nd then round to two deiml ples. e How n you eplin the differene etween your results from prts nd d ove? Spider rwl 12 spider rwls from one orner,, of the eiling of room to the opposite orner, G, on the floor. The room is retngulr prism with dimensions s given in the digrm on the right. ssuming the spider rwls in diret line etween points, find how fr (orret to two deiml ples) the spider rwls if it rwls from to G vi: i ii C iii D iv F H F G 6.2 m Investigte other pths to determine the shortest distne tht the spider ould rwl in order to trvel from point to point G. (Hint: onsider drwing net for the solid.) D C 2 C 4. m 3.9 m 12 RSONING NRICHMNT 3D Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
25 166 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3 Trigonometri rtios The rnh of mthemtis lled trigonometry dels with the reltionship etween the side lengths nd ngles in tringles. Trigonometry dtes k to the nient gyptin nd ylonin ivilistions where si form of trigonometry ws used in the uilding of pyrmids nd in the study of stronomy. The first tle of vlues inluding hord nd r lengths on irle for given ngle ws reted y Hipprhus in the 2nd entury C in Greee. These tles of vlues helped to lulte the position of the plnets. out three enturies si form of trigonometry ws used in the uilding of pyrmids in nient gypt. lter, Cludius Ptolemy dvned the study of trigonometry writing 13 ooks lled the lmgest. Ptolemy lso developed tles of vlues linking the sides nd ngles of tringle nd produed mny theorems whih use the sine, osine nd tngent funtions. Let s strt: Constny of sine, osine nd tngent In geometry we would sy tht similr tringles hve the sme shpe ut re of different size. Here re three similr right-ngled tringles. The ngle q (thet) is the sme for ll three tringles We will now lulte three speil rtios: sine, osine nd tngent for the ngle q in the ove tringles. We use the sides lelled Hypotenuse (H), Opposite (O) nd djent () s shown t right. Complete this tle simplifying ll frtions. Wht do you notie out the vlue of: ( ) O sin q i.e. for ll three tringles? H ( os q i.e. ) for ll three tringles? H ( ) O tn q i.e. for ll three tringles? Why re the three rtios (sin q, os q nd tn q ) the sme for ll three tringles? Disuss. Tringle Hypotenuse (H) O H (sin q ) 13 C djent () H (os q ) Opposite (O) C = O (tn q ) 1 36 = 12 1 Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
26 Mesurement nd Geometry 167 For right-ngled tringle with nother ngle nmed q : The hypotenuse is the longest side, opposite the 90 ngle The opposite side is opposite q The djent side is net to q ut not the hypotenuse. Opposite Hypotenuse djent Opposite djent q Hypotenuse For right-ngled tringle with given ngle q, the three rtios sine (sin), osine (os) nd tngent (tn) re given y: length of the opposite side sine of ngle q (or sin q ) = length of the hypotenuse length of the djent side osine of ngle q (or os q ) = length of the hypotenuse length of the opposite side tngent of ngle q (or tn q ) = length of the djent side For ny right-ngled tringle with the sme ngles, these rtios re lwys the sme. The term SOHCHTO is useful when trying to rememer the three rtios. sin = Opposite Hypotenuse SOH CH TO os = djent Hypotenuse mple 6 Lelling the sides of tringles tn = Opposite djent Copy this tringle nd lel the sides s opposite to q (O), djent to q () or hypotenuse (H). SOLUTION O H XPLNTION q H q Drw the tringle nd lel the side opposite the right ngle s hypotenuse (H), the side opposite the ngle q s opposite (O) nd the remining side net to the ngle q s djent (). O Key ides Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
27 168 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry mple 7 Writing trigonometri rtios Write trigonometri rtio (in frtion form) for eh of the following tringles. 7 9 SOLUTION os q = H = 7 sin q = O H = 4 9 tn q = O = 3 erise 3 4 XPLNTION () (H) 7 () 1 Write the missing word in these sentenes. H stnds for the word. O stnds for the word. stnds for the word. d sin q = Hypotenuse. e os q = djent. f tn q = Opposite. () 4 (O) 9 (H) (H) 3 (O) (O) Side length 7 is opposite the right ngle so it is the hypotenuse (H). Side length is djent to ngle q so it is the djent (). Side length 9 is opposite the right ngle so it is the hypotenuse (H). Side length 4 is opposite ngle q so it is the opposite (O). Side length is the djent side to ngle q so it is the djent (). Side length 3 is opposite ngle q so it is the opposite (O). 1, 2(½), 3 3 H O 3 UNDRSTNDING Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
28 Mesurement nd Geometry 169 mple 6 mple 7 2 Copy eh of these tringles nd lel the sides s opposite to q (O), djent to q () or hypotenuse (H). d e f 3 For the tringle shown, stte the length of the side whih orresponds to: the hypotenuse the side opposite ngle q the side opposite ngle α d the side djent to ngle q e the side djent to ngle α. 3 4 Write trigonometri rtio (in frtion form) for eh of the following tringles nd simplify where possile d 4 e f y 6 g t h 4t 3 g 4 6 4(½), 7 6 i y 3 q h α 4 4(½),, 6(½), 7 UNDRSTNDING FLUNCY 3 Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
29 170 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3 Here re two similr tringles nd i Write the rtio sin q (s frtion) for tringle. ii Write the rtio sin q (s frtion) for tringle. iii Wht do you notie out your two nswers from prts i nd ii ove? i Write the rtio os q (s frtion) for tringle. ii Write the rtio os q (s frtion) for tringle. iii Wht do you notie out your two nswers from prts i nd ii ove? i Write the rtio tn q (s frtion) for tringle. ii Write the rtio tn q (s frtion) for tringle. iii Wht do you notie out your two nswers from prts i nd ii ove? 6 For eh of these tringles, write rtio (in simplified frtion form) for sin q, os q nd tn q For the tringle shown on the right, write rtio (in frtion form) for: sin q sin α os q α d tn α e os α f tn q vertil flg pole sts shdow 20 m long. If the pole is 1 m high, find the rtio for tn q. 1 m , 9 9, , 11 FLUNCY PROLM-SOLVING 20 m We n use trigonometry to lulte the ngle of the shdow tht the pole sts. Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
30 Mesurement nd Geometry The fde of Romn temple hs the given mesurements elow. Write down the rtio for: sin q os q tn q m 10 For eh of the following: 3m 4m The Pntheon, Romn temple tht ws uilt in 126 C. i Use Pythgors theorem to find the unknown side. ii Find the rtios for sin q, os q nd tn q q Drw right-ngled tringle nd mrk one of the ngles s q. Mrk in the length of the opposite side s 1 units nd the length of the hypotenuse s 17 units. Using Pythgors theorem, find the length of the djent side. Determine the rtios for sin q, os q nd tn q. 12 This tringle hs ngles 90, 60 nd 30 nd side lengths 1, 2 nd 3. Write rtio for: i sin 30 ii os 30 iii tn 30 iv sin 60 v os 60 vi tn 60 Wht do you notie out the following pirs of rtios? i os 30 nd sin 60 ii sin 30 nd os , 13 d PROLM-SOLVING RSONING 3 Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
31 172 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3 13 Mesure ll the side lengths of this tringle to the nerest millimetre. Use your mesurements from prt to find n pproimte rtio for: i os 40 ii sin 40 iii tn 40 iv sin 0 v tn 0 vi os 0 40 Do you notie nything out the trigonometri rtios for 40 nd 0? 14 Deide if it is possile to drw right-ngled tringle with the given properties. plin. tn q = 1 sin q = 1 os q = 0 d sin q > 1 or os q > 1 Pythgoren etensions 1 Given tht q is ute nd os q = 4, find sin q nd tn q. Hint: use Pythgors theorem. For eh of the following, drw right-ngled tringle then use it to find the other two trigonometri rtios. d i sin q = 1 ii os q = 1 iii tn q = Use your results from prt to lulte (os q ) 2 + (sin q ) 2. Wht do you notie? vlute (os q ) 2 + (sin q ) 2 for other omintions of os q nd sin q. Reserh nd desrie wht you hve found. 4 1 RSONING NRICHMNT Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
32 Mesurement nd Geometry 173 3F Finding side lengths For similr tringles we know tht the rtio of orresponding sides is lwys the sme. This implies tht the three trigonometri rtios for similr right-ngled tringles re lso onstnt if the internl ngles re equl. Sine nient times, mthemtiins hve ttempted to tulte these rtios for vrying ngles. Here re the rtios for some ngles in right-ngled tringle, orret to three deiml ples. ngle ( q ) sin q os q tn q undefined Trigonometri tles in 400-yer old uropen ook. In modern times these vlues n e evluted using lultors to high degree of ury nd n e used to help solve prolems involving tringles with unknown side lengths. Let s strt: Clultor strt-up ll sientifi or CS lultors n produe urte vlues of sin q, os q nd tn q. nsure tht your lultor is in degree mode. Chek the vlues in the ove tle to ensure tht you re using the lultor orretly. Use tril nd error to find (to the nerest degree) n ngle q whih stisfies these onditions: sin q = 0.44 os q = 0.88 tn q = 9.14 If q is in degrees, the rtios for sin q, os q nd tn q n urtely e found using lultor in degree mode. If the ngles nd one side length of right-ngled tringle re known then the other side lengths n e found using the sin q, os q or tn q rtios sin 30 = 3 = 3 sin os 42 = 7.2 = 7.2 os tn 71 = 4 = 4 tn 71 Key ides Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
33 174 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry mple 8 Using lultor Use lultor to evlute the following, orret to two deiml ples. sin 0 os 16 tn 77 SOLUTION XPLNTION sin 0 = 0.77 (to 2 d.p.) sin 0 = the 3rd deiml ple is greter thn 4 so round up. os 16 = 0.96 (to 2 d.p.) os 16 = the 3rd deiml ple is less thn so round down. tn 77 = 4.33 (to 2 d.p.) tn 77 = the 3rd deiml ple is less thn so round down. mple 9 Solving for in the numertor of trigonometri rtio Find the vlue of in the eqution os 20 =, orret to two deiml ples. 3 SOLUTION os 20 = 3 = 3 os 20 = 2.82 (to 2 d.p.) mple 10 Finding side lengths XPLNTION For eh tringle, find the vlue of orret to two deiml ples Multiply oth sides of the eqution y 3 nd round s required Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
34 Mesurement nd Geometry 17 SOLUTION XPLNTION sin 38 = O sin 38 = 7 tn 42 = O tn 42 = 4 = 7 sin 38 = 4.31 (to 2 d.p.) = 4 tn 42 os 24 = H os 24 = 10 erise 3F = 3.60 (to 2 d.p.) = 10 os 24 = 9.14 (to 2 d.p.) Sine the opposite side (O) nd the hypotenuse (H) re involved, the sin q rtio must e used. Multiply oth sides y 7 nd evlute using lultor. Sine the opposite side (O) nd the djent side () re involved, the tn q rtio must e used. Multiply oth sides y 4 nd evlute. Sine the djent side () nd the hypotenuse (H) re involved, the os q rtio must e used. Multiply oth sides y 10. (O) 1 For the mrked ngle q, deide if represents the length of the opposite (O), djent () or hypotenuse (H) side. 2 Deide if you would use sin q = O H, os q = H or tn q = O to help find the vlue of in these tringles. Do not find the vlue of, just stte whih rtio would e used (½) (O) (H) 7(H) 38 () 42 4 () 24 (O) () 10 (H) UNDRSTNDING Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
35 176 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3F mple 8 mple 9 mple Use lultor to evlute the following orret to two deiml ples. sin 20 os 37 tn 64 e os 84 f tn 14.1 g sin 27.4 In eh of the following, find the vlue of orret to two deiml ples. sin 0 = tn 81 4 = os 33 3 = 6 d g os 7 = 3. = tn e h sin 24 = 4.2 = sin f i d h sin 47 os 76.2 tn 42 = 10 = os For the tringles given elow, find the vlue of orret to two deiml ples d e i m f j n g k o 4 (½) (½) h l p (½) 6, my wlks.4 m up rmp whih is inlined t 12 to the horizontl. How high (orret to two deiml ples) is she ove her strting point? m UNDRSTNDING FLUNCY PROLM-SOLVING Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
36 Mesurement nd Geometry Kne wnted to mesure the width of river. He pled two mrkers, nd, 72 m prt long the nk. C is point diretly opposite mrker. Kne mesured ngle C to e 32. Find the width of the river orret to two deiml ples. 8 One end of 12.2 m rope is tied to ot. The other end is tied to n nhor, whih is holding the ot stedy in the wter. If the nhor is mking n ngle of 34 with the vertil, how deep is the wter? Give your nswer orret to two deiml ples m 9 Find the length in these digrms. Round to two deiml ples where neessry m 10.6 m For this right-ngled tringle: Find the vlue of C. Clulte the vlue of orret to three deiml ples using the sine rtio. Clulte the vlue of orret to three deiml ples ut insted use the osine rtio. d Comment on your nswers to prts nd. 11 Complementry ngles sum to 90. Find the omplementry ngles to these ngles. i 10 ii 28 iii vlute: i sin 10 nd os 80 iii os 4 nd sin 36 Wht do you notie in prt? d Complete the following. i sin 20 = os iii os 36 = sin ii iv ii iv 4 m sin 28 nd os 62 os 81 nd sin 9 sin 9 = os os 73 = sin iv C 2 width m 34 10, 11 C PROLM-SOLVING RSONING 3F Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
37 178 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3F t vlues 12 2, 3 nd 1 2 re emples of et vlues. d For the tringle shown (right), use Pythgors theorem to find the et length C. Use your result from prt to write down the et vlues of: i sin 4 ii os 4 iii tn 4 For this tringle (right) use Pythgors theorem to find the et length C. Use your result from prt to write down the et vlues of: i sin 30 ii os 30 iii tn 30 iv sin 60 v os 60 vi tn 60 This digrm y the third entury D Chinese mthemtiin Liu Hui shows how to mesure the height of mountin on se islnd using right-ngled tringles. This method of surveying eme known s tringultion. 1 C C NRICHMNT Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
38 Mesurement nd Geometry 179 3G Solving for the denomintor So fr we hve onstruted trigonometri rtios using pronumerl whih hs lwys ppered in the numertor. For emple: = sin 40. This mkes it esy to solve for where oth sides of the eqution n e multiplied y. If, however, the pronumerl ppers in the denomintor there re numer of lgeri steps tht n e tken to find the solution. Let s strt: Solution steps Three students ttempt to solve sin 40 = for. Nik sys = sin 40 Shree sys = sin 40 Dori sys = 1 sin 40 Whih student hs the orret solution? Cn you show the lgeri steps tht support the orret nswer? If the unknown vlue of trigonometri rtio is in the denomintor, you need to rerrnge the eqution to mke the pronumerl the sujet. For emple: For the tringle shown, os 30 = Multiplying oth sides y os 30 = Dividing oth sides y os 30 = os mple 11 Solving for in the denomintor Solve for in the eqution os 3 = 2, orret to two deiml ples. SOLUTION XPLNTION Key ides os 3 = 2 os 3 = 2 = 2 os 3 = 2.44 (to 2 d.p.) Multiply oth sides of the eqution y. Divide oth sides of the eqution y os 3. vlute nd round to two deiml ples. Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
39 180 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry mple 12 Finding side lengths Find the vlues of the pronumerls orret to two deiml ples. 28 SOLUTION sin 3 = O H sin 3 = sin 3 = 3 = sin 3 tn 28 = O tn 28 = 19 tn 28 = 19 erise 3G = 8.72 (to 2 d.p.) 19 = tn 28 = 3.73 y 2 = = y = y = (to 2 d.p.) y XPLNTION 19 Sine the opposite side (O) is given (O) nd we require the hypotenuse (H), use sin q. (H) 3 () Multiply oth sides of the eqution y then divide oth sides of the eqution y sin 3. vlute on lultor nd round to two deiml ples. Sine the opposite side (O) is given nd the djent () is required, use tn q. Multiply oth sides of the eqution y. () 28 (H) y 19 (O) Divide oth sides of the eqution y tn 28 nd round the nswer to two deiml ples. Find y y using Pythgors theorem nd 19 sustitute the et vlue of, i.e. tn 28 lterntively, y n e found y using sin q. () 28 (H) y 1 Solve these simple equtions for. 4 = 2 20 = 4 1 = d 2 = 100 e = 3 1 2(½) 2(½) f 10 = 2. g 2. = h 12 = (O) Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph UNDRSTNDING
40 Mesurement nd Geometry 181 mple 11 mple 12 mple For eh of the following equtions, find the vlue of orret to two deiml ples. d g os 43 = 3 tn 64 = 2 sin 38.3 =.9 e h sin 36 = 4 os 67 = 4 = tn 21.4 f i tn 9 = 6 sin 12 = = os 32 Find the vlue of orret to two deiml ples using the sine, osine or tngent rtios. d e i f j g 3 4(½) (½) h 26 3 k 2 l Find the vlue of eh pronumerl orret to one deiml ple. d y y 8 4 e y f 9.6 g h n 23 y m (½), 6, 6, 7 kite is flying t height of 27 m ove the nhor point. If the string is inlined t 42 to the horizontl, find the length of the string, orret to the nerest metre. 27 m y 6, 7 42 UNDRSTNDING FLUNCY PROLM-SOLVING 3G Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
41 182 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 3G 6 prglider flying t height of 800 m desends t n ngle of 12 to the horizontl. How fr (to the nerest metre) hs it trvelled in desending to the ground? 7 Find the perimeter of these tringles, orret to one deiml ple. m Distne in desent 20 m In lulting the vlue of for this tringle, orret to two deiml ples, two students ome up with these nswers. m = sin 31 = 0.2 = 9.62 = sin 31 = m Whih of the ove two nswers is more orret nd why? Wht dvie would you give to the student whose nswer is not urte? Find the differene in the nswers if the different methods ( nd ) re used to lulte the vlue of orret to two deiml ples in these tringles. i 19 ii m 10 m 8 m 120 m Linking tn q to sin q nd os q 9 For this tringle find, orret to three deiml ples: C i ii C Clulte these rtios to two deiml ples. 4 m i sin 20 ii os 20 iii tn sin 20 vlute os 20 using your results from prt. Wht do you notie? d For this tringle with side lengths, nd, find n epression for: sin q i sin q ii os q iii tn q iv os q e Simplify your epression for prt d iv. Wht do you notie? 8 9 m PROLM-SOLVING RSONING NRICHMNT Using CS lultor 3G: Trigonometry This tivity is in the intertive tetook in the form of printle PDF. Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
42 Mesurement nd Geometry 183 Progress quiz 38pt 3/ 38pt 3/ 38pt 3C 38pt 3D t 38pt Find the length of the missing side in these right-ngled tringles. Round to two deiml ples. 4.4 Find the et vlue of in these right-ngled tringles. 4 ldder 230 m long is pled 0 m from the edge of uilding, how fr up the side of the uilding will this ldder reh? Round to one deiml ple Find the length of the digonls of these prisms, orret to one deiml ple. 6 m 6 m 6 m Consider the tringle C. d Nme the hypotenuse. Nme the side djent to ngle C. Write the rtio for os q. Write the rtio for tn q. 3 4 C 10 m 6 m 4 m Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
43 184 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry 38pt 3F/G 38pt 3F/G 38pt 3G 38pt 3 G Solve for, orret to two deiml ples. = 12.7 os 4 tn 30 = 12 sin 6 = 8.4 Find the vlues of the pronumerls, orret to two deiml ples Find the perimeter of this tringle, orret to two deiml ples. 6 m 40 Tringle C is equilterl with perimeter of 12 m. Find: C the height D using ny suitle method, orret to three deiml ples D 60 the re of the tringle C, orret to one deiml ple. Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
44 Mesurement nd Geometry 18 3H Finding n ngle Logilly, if you n use trigonometry to find side length of right-ngled tringle given one ngle nd one side, you should e le to find n ngle if you re given two sides. We know tht sin 30 = 1 2 so if we were to determine q if sin q = 1 2, the nswer would e q = 30. ( ) We write this s q = sin 1 1 = 30 2 nd we sy tht the inverse sine of 1 2 is 30. Clultors n e used to help solve prolems using inverse sine (sin 1 ), inverse osine (os 1 ) nd inverse tngent (tn 1 ). For ngles in degrees, ensure your lultor is in degree mode. Let s strt: Tril nd error n e slow We know tht for this tringle, sin q = Guess the ngle q. For your guess use lultor to see if sin q = 1 3 = Updte your guess nd use your lultor to hek one gin. 3 Repet this tril-nd-error ( ) proess until you think you hve the ngle q orret to three deiml ples. Now evlute sin 1 1 nd hek your guess. 3 Inverse sine (sin 1 ), inverse osine (os 1 ) nd inverse tngent (tn 1 ) n e used to find ngles in right-ngled tringles. sin q = ( ) mens q = sin 1 os q = ( ) mens q = os 1 tn q = ( ) mens q = tn 1 Note tht sin 1 does not men 1 sin. 2 1 Key ides Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
45 186 Chpter 3 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry mple 13 Using inverse trigonometri rtios Find the vlue of q to the level of ury indited. sin q = (nerest degree) SOLUTION sin q = tn q = 1 2 q = sin 1 (0.3907) = 23 (to nerest degree) q = tn 1 ( 1 2 ) = 26.6 (to 1 d.p.) mple 14 Finding n ngle Find the vlue of q to the nerest degree. SOLUTION sin q = O H = 6 10 q = sin 1 ( 6 10 = 37 erise 3H ) tn q = 1 (one deiml ple) 2 XPLNTION Use the sin 1 key on your lultor. Round to the nerest whole numer. Use the tn 1 key on your lultor nd round the nswer to one deiml ple XPLNTION Sine the opposite side (O) nd the hypotenuse (H) re given, use sin q. (H) 10 () 6 (O) Use the sin 1 key on your lultor nd round s required. 1, 2, 3(½), Use lultor to evlute the following rounding to two deiml ples. sin 1 (0.2) sin 1 (0.9) os 1 (0.7) d os 1 (0.43) e tn 1 (0.) f tn 1 (2.) UNDRSTNDING Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
46 Mesurement nd Geometry 187 mple 13 mple 13 mple 14 2 Write the missing numer. If sin 30 = 1 2 then 30 = sin 1 ( ). If os 0 = 0.64 then = os 1 (0.64). If tn 4 = 1 then = tn 1 ( ). 3 vlute eh of the following to the nerest degree. sin 1 (0.7324) os 1 (0.9763) tn 1 (0.3321) d tn 1 (1.23) e sin 1 (0.4126) f os 1 (0.7462) g os 1 (0.1971) h sin 1 (0.2247) i tn 1 (0.041) 4 Whih trigonometri rtio should e used to solve for q? Find the vlue of q to the nerest degree. sin q = 0. os q = 0. tn q = 1 d os q = e sin q = f tn q = g sin q = 1 h tn q = i os q = 0 j os q = k os q = 1 l sin q = Find the ngle q orret to two deiml ples. sin q = 4 sin q = 1 sin q = d os q = 1 e os q = 4 f os q = g tn q = 3 h tn q = 8 i tn q = 12 Find the vlue of q to the nerest degree e 9 13 f 7 11 g 6(½), (½) d d h (½) UNDRSTNDING FLUNCY 3H Unorreted 3rd smple pges Cmridge University Press Greenwood et l., 201 ISN Ph
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? IN THIS CHAPTER YOU WILL:
 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? 1 01 Squres, squre roots nd surds 1 02 Pythgors theorem 1 03 Finding the hypotenuse 1 04 Finding shorter side 1 05 Mixed prolems 1 06 Testing for right-ngled tringles
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? 1 01 Squres, squre roots nd surds 1 02 Pythgors theorem 1 03 Finding the hypotenuse 1 04 Finding shorter side 1 05 Mixed prolems 1 06 Testing for right-ngled tringles
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
Activities. 4.1 Pythagoras' Theorem 4.2 Spirals 4.3 Clinometers 4.4 Radar 4.5 Posting Parcels 4.6 Interlocking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes and Solutions
 MEP: Demonstrtion Projet UNIT 4: Trigonometry UNIT 4 Trigonometry tivities tivities 4. Pythgors' Theorem 4.2 Spirls 4.3 linometers 4.4 Rdr 4.5 Posting Prels 4.6 Interloking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes nd
MEP: Demonstrtion Projet UNIT 4: Trigonometry UNIT 4 Trigonometry tivities tivities 4. Pythgors' Theorem 4.2 Spirls 4.3 linometers 4.4 Rdr 4.5 Posting Prels 4.6 Interloking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes nd
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q5 of Paper 2
 Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM,TRIGONOMETRY,BEARINGS AND THREE DIMENSIONAL PROBLEMS
 PYTHGORS THEOREM,TRIGONOMETRY,ERINGS ND THREE DIMENSIONL PROLEMS 1.1 PYTHGORS THEOREM: 1. The Pythgors Theorem sttes tht the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the squres of the other two sides
PYTHGORS THEOREM,TRIGONOMETRY,ERINGS ND THREE DIMENSIONL PROLEMS 1.1 PYTHGORS THEOREM: 1. The Pythgors Theorem sttes tht the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the squres of the other two sides
Naming the sides of a right-angled triangle
 6.2 Wht is trigonometry? The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigonon (tringle) nd metron (mesurement). Thus, it literlly mens to mesure tringle. Trigonometry dels with the reltionship
6.2 Wht is trigonometry? The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigonon (tringle) nd metron (mesurement). Thus, it literlly mens to mesure tringle. Trigonometry dels with the reltionship
GM1 Consolidation Worksheet
 Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1. Given a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
 1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
Pythagoras Theorem. Pythagoras Theorem. Curriculum Ready ACMMG: 222, 245.
 Pythgors Theorem Pythgors Theorem Curriulum Redy ACMMG:, 45 www.mthletis.om Fill in these spes with ny other interesting fts you n find out Pythgors. In the world of Mthemtis, Pythgors is legend. He lived
Pythgors Theorem Pythgors Theorem Curriulum Redy ACMMG:, 45 www.mthletis.om Fill in these spes with ny other interesting fts you n find out Pythgors. In the world of Mthemtis, Pythgors is legend. He lived
Trigonometry. Trigonometry. labelling conventions. Evaluation of areas of non-right-angled triangles using the formulas A = 1 ab sin (C )
 8 8 Pythgors theorem 8 Pythgoren trids 8 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 8D Trigonometri rtios 8E The sine rule 8F miguous se of the sine rule 8G The osine rule 8H Speil tringles 8I re of tringles res
8 8 Pythgors theorem 8 Pythgoren trids 8 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 8D Trigonometri rtios 8E The sine rule 8F miguous se of the sine rule 8G The osine rule 8H Speil tringles 8I re of tringles res
Pythagoras Theorem. The area of the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides
 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry Pythgors Theorem The hypotenuse of right-ngled tringle is the longest side The hypotenuse is lwys opposite the right-ngle 2 = 2 + 2 or 2 = 2-2 or 2 = 2-2 The re of the
Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry Pythgors Theorem The hypotenuse of right-ngled tringle is the longest side The hypotenuse is lwys opposite the right-ngle 2 = 2 + 2 or 2 = 2-2 or 2 = 2-2 The re of the
3 Angle Geometry. 3.1 Measuring Angles. 1. Using a protractor, measure the marked angles.
 3 ngle Geometry MEP Prtie ook S3 3.1 Mesuring ngles 1. Using protrtor, mesure the mrked ngles. () () (d) (e) (f) 2. Drw ngles with the following sizes. () 22 () 75 120 (d) 90 (e) 153 (f) 45 (g) 180 (h)
3 ngle Geometry MEP Prtie ook S3 3.1 Mesuring ngles 1. Using protrtor, mesure the mrked ngles. () () (d) (e) (f) 2. Drw ngles with the following sizes. () 22 () 75 120 (d) 90 (e) 153 (f) 45 (g) 180 (h)
MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS 1.6
 MTHMTIS N STTISTIS 1.6 pply geometri resoning in solving prolems ternlly ssessed 4 redits S 91031 inding unknown ngles When finding the size of unknown ngles in figure, t lest two steps of resoning will
MTHMTIS N STTISTIS 1.6 pply geometri resoning in solving prolems ternlly ssessed 4 redits S 91031 inding unknown ngles When finding the size of unknown ngles in figure, t lest two steps of resoning will
ONLINE PAGE PROOFS. Trigonometry Kick off with CAS 12.2 Trigonometry 12.3 Pythagorean triads
 12 12.1 Kik off with S 12.2 Trigonometry 12.3 Pythgoren trids Trigonometry 12.4 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 12.5 Trigonometri rtios 12.6 The sine rule 12.7 miguous se of the sine rule 12.8 The osine
12 12.1 Kik off with S 12.2 Trigonometry 12.3 Pythgoren trids Trigonometry 12.4 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 12.5 Trigonometri rtios 12.6 The sine rule 12.7 miguous se of the sine rule 12.8 The osine
Pythagoras theorem and surds
 HPTER Mesurement nd Geometry Pythgors theorem nd surds In IE-EM Mthemtis Yer 8, you lernt out the remrkle reltionship etween the lengths of the sides of right-ngled tringle. This result is known s Pythgors
HPTER Mesurement nd Geometry Pythgors theorem nd surds In IE-EM Mthemtis Yer 8, you lernt out the remrkle reltionship etween the lengths of the sides of right-ngled tringle. This result is known s Pythgors
CHENG Chun Chor Litwin The Hong Kong Institute of Education
 PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
Trigonometry. cosθ. sinθ tanθ. Mathletics Instant Workbooks. Copyright
 Student Book - Series K- sinθ tnθ osθ Mtletis Instnt Workooks Copyrigt Student Book - Series K Contents Topis Topi - Nming te sides of rigt-ngled tringle Topi 2 - Te trigonometri rtios Topi 3 - Using lultor
Student Book - Series K- sinθ tnθ osθ Mtletis Instnt Workooks Copyrigt Student Book - Series K Contents Topis Topi - Nming te sides of rigt-ngled tringle Topi 2 - Te trigonometri rtios Topi 3 - Using lultor
Similar Right Triangles
 Geometry V1.noteook Ferury 09, 2012 Similr Right Tringles Cn I identify similr tringles in right tringle with the ltitude? Cn I identify the proportions in right tringles? Cn I use the geometri mens theorems
Geometry V1.noteook Ferury 09, 2012 Similr Right Tringles Cn I identify similr tringles in right tringle with the ltitude? Cn I identify the proportions in right tringles? Cn I use the geometri mens theorems
Section 1.3 Triangles
 Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
Geometry of the Circle - Chords and Angles. Geometry of the Circle. Chord and Angles. Curriculum Ready ACMMG: 272.
 Geometry of the irle - hords nd ngles Geometry of the irle hord nd ngles urriulum Redy MMG: 272 www.mthletis.om hords nd ngles HRS N NGLES The irle is si shpe nd so it n e found lmost nywhere. This setion
Geometry of the irle - hords nd ngles Geometry of the irle hord nd ngles urriulum Redy MMG: 272 www.mthletis.om hords nd ngles HRS N NGLES The irle is si shpe nd so it n e found lmost nywhere. This setion
Non Right Angled Triangles
 Non Right ngled Tringles Non Right ngled Tringles urriulum Redy www.mthletis.om Non Right ngled Tringles NON RIGHT NGLED TRINGLES sin i, os i nd tn i re lso useful in non-right ngled tringles. This unit
Non Right ngled Tringles Non Right ngled Tringles urriulum Redy www.mthletis.om Non Right ngled Tringles NON RIGHT NGLED TRINGLES sin i, os i nd tn i re lso useful in non-right ngled tringles. This unit
Shape and measurement
 C H A P T E R 5 Shpe nd mesurement Wht is Pythgors theorem? How do we use Pythgors theorem? How do we find the perimeter of shpe? How do we find the re of shpe? How do we find the volume of shpe? How do
C H A P T E R 5 Shpe nd mesurement Wht is Pythgors theorem? How do we use Pythgors theorem? How do we find the perimeter of shpe? How do we find the re of shpe? How do we find the volume of shpe? How do
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 9: Roots, Real Numbers and The Pythagorean Theorem
 HS Pre-Alger Notes Unit 9: Roots, Rel Numers nd The Pythgoren Theorem Roots nd Cue Roots Syllus Ojetive 5.4: The student will find or pproximte squre roots of numers to 4. CCSS 8.EE.-: Evlute squre roots
HS Pre-Alger Notes Unit 9: Roots, Rel Numers nd The Pythgoren Theorem Roots nd Cue Roots Syllus Ojetive 5.4: The student will find or pproximte squre roots of numers to 4. CCSS 8.EE.-: Evlute squre roots
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals
 AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
LESSON 11: TRIANGLE FORMULAE
 . THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
. THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
12.4 Similarity in Right Triangles
 Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
Trigonometry and Constructive Geometry
 Trigonometry nd Construtive Geometry Trining prolems for M2 2018 term 1 Ted Szylowie tedszy@gmil.om 1 Leling geometril figures 1. Prtie writing Greek letters. αβγδɛθλµπψ 2. Lel the sides, ngles nd verties
Trigonometry nd Construtive Geometry Trining prolems for M2 2018 term 1 Ted Szylowie tedszy@gmil.om 1 Leling geometril figures 1. Prtie writing Greek letters. αβγδɛθλµπψ 2. Lel the sides, ngles nd verties
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday 17 October 2012 Geometry II: Side Lengths
 Intermedite Mth Cirles Wednesdy 17 Otoer 01 Geometry II: Side Lengths Lst week we disussed vrious ngle properties. As we progressed through the evening, we proved mny results. This week, we will look t
Intermedite Mth Cirles Wednesdy 17 Otoer 01 Geometry II: Side Lengths Lst week we disussed vrious ngle properties. As we progressed through the evening, we proved mny results. This week, we will look t
5. Every rational number have either terminating or repeating (recurring) decimal representation.
 CHAPTER NUMBER SYSTEMS Points to Rememer :. Numer used for ounting,,,,... re known s Nturl numers.. All nturl numers together with zero i.e. 0,,,,,... re known s whole numers.. All nturl numers, zero nd
CHAPTER NUMBER SYSTEMS Points to Rememer :. Numer used for ounting,,,,... re known s Nturl numers.. All nturl numers together with zero i.e. 0,,,,,... re known s whole numers.. All nturl numers, zero nd
SAMPLE. Trigonometry. Naming the sides of a right-angled triangle
 H P T E R 7 Trigonometry How re sin, os nd tn defined using right-ngled tringle? How n the trigonometri rtios e used to find the side lengths or ngles in right-ngled tringles? Wht is ment y n ngle of elevtion
H P T E R 7 Trigonometry How re sin, os nd tn defined using right-ngled tringle? How n the trigonometri rtios e used to find the side lengths or ngles in right-ngled tringles? Wht is ment y n ngle of elevtion
THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
 THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM The Pythgoren Theorem is one of the most well-known nd widely used theorems in mthemtis. We will first look t n informl investigtion of the Pythgoren Theorem, nd then pply this
THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM The Pythgoren Theorem is one of the most well-known nd widely used theorems in mthemtis. We will first look t n informl investigtion of the Pythgoren Theorem, nd then pply this
4.3 The Sine Law and the Cosine Law
 4.3 Te Sine Lw nd te osine Lw Te ee Tower is te tllest prt of nd s rliment uildings. ronze mst, wi flies te ndin flg, stnds on top of te ee Tower. From point 25 m from te foot of te tower, te ngle of elevtion
4.3 Te Sine Lw nd te osine Lw Te ee Tower is te tllest prt of nd s rliment uildings. ronze mst, wi flies te ndin flg, stnds on top of te ee Tower. From point 25 m from te foot of te tower, te ngle of elevtion
Comparing the Pre-image and Image of a Dilation
 hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
m A 1 1 A ! and AC 6
 REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
21.1 Using Formulae Construct and Use Simple Formulae Revision of Negative Numbers Substitution into Formulae
 MEP Jmi: STRAND G UNIT 1 Formule: Student Tet Contents STRAND G: Alger Unit 1 Formule Student Tet Contents Setion 1.1 Using Formule 1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule 1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers 1.4
MEP Jmi: STRAND G UNIT 1 Formule: Student Tet Contents STRAND G: Alger Unit 1 Formule Student Tet Contents Setion 1.1 Using Formule 1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule 1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers 1.4
Perimeter, area and volume
 6 Perimeter, re nd volume Syllus topi M. Perimeter, re nd volume This topi will develop your skills to ompetently solve prolems involving perimeter, re, volume nd pity. Outomes Clulte the re of irles nd
6 Perimeter, re nd volume Syllus topi M. Perimeter, re nd volume This topi will develop your skills to ompetently solve prolems involving perimeter, re, volume nd pity. Outomes Clulte the re of irles nd
Lesson 2: The Pythagorean Theorem and Similar Triangles. A Brief Review of the Pythagorean Theorem.
 27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
5Trigonometric UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS. ratios and their applications
 5Trigonometri rtios nd their pplitions 5.1 Kik off with CS 5.2 Trigonometry of right-ngled tringles 5.3 Elevtion, depression nd erings 5.4 The sine rule 5.5 The osine rule 5.6 rs, setors nd segments 5.7
5Trigonometri rtios nd their pplitions 5.1 Kik off with CS 5.2 Trigonometry of right-ngled tringles 5.3 Elevtion, depression nd erings 5.4 The sine rule 5.5 The osine rule 5.6 rs, setors nd segments 5.7
Perimeter and Area. Mathletics Instant Workbooks. Copyright
 Perimeter nd Are Student Book - Series J- L B Mthletis Instnt Workooks Copyright Student Book - Series J Contents Topis Topi - Plne shpes Topi 2 - Perimeter of regulr shpes Topi 3 - Perimeter of irregulr
Perimeter nd Are Student Book - Series J- L B Mthletis Instnt Workooks Copyright Student Book - Series J Contents Topis Topi - Plne shpes Topi 2 - Perimeter of regulr shpes Topi 3 - Perimeter of irregulr
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL. Part 1. What and Why.?
 SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
Basic Angle Rules 5. A Short Hand Geometric Reasons. B Two Reasons. 1 Write in full the meaning of these short hand geometric reasons.
 si ngle Rules 5 6 Short Hnd Geometri Resons 1 Write in full the mening of these short hnd geometri resons. Short Hnd Reson Full Mening ) se s isos Δ re =. ) orr s // lines re =. ) sum s t pt = 360. d)
si ngle Rules 5 6 Short Hnd Geometri Resons 1 Write in full the mening of these short hnd geometri resons. Short Hnd Reson Full Mening ) se s isos Δ re =. ) orr s // lines re =. ) sum s t pt = 360. d)
Mathematics SKE: STRAND F. F1.1 Using Formulae. F1.2 Construct and Use Simple Formulae. F1.3 Revision of Negative Numbers
 Mthemtis SKE: STRAND F UNIT F1 Formule: Tet STRAND F: Alger F1 Formule Tet Contents Setion F1.1 Using Formule F1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule F1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers F1.4 Sustitution into Formule
Mthemtis SKE: STRAND F UNIT F1 Formule: Tet STRAND F: Alger F1 Formule Tet Contents Setion F1.1 Using Formule F1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule F1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers F1.4 Sustitution into Formule
April 8, 2017 Math 9. Geometry. Solving vector problems. Problem. Prove that if vectors and satisfy, then.
 pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
Something found at a salad bar
 Nme PP Something found t sld r 4.7 Notes RIGHT TRINGLE hs extly one right ngle. To solve right tringle, you n use things like SOH-H-TO nd the Pythgoren Theorem. n OLIQUE TRINGLE hs no right ngles. To solve
Nme PP Something found t sld r 4.7 Notes RIGHT TRINGLE hs extly one right ngle. To solve right tringle, you n use things like SOH-H-TO nd the Pythgoren Theorem. n OLIQUE TRINGLE hs no right ngles. To solve
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
 PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
Numbers and indices. 1.1 Fractions. GCSE C Example 1. Handy hint. Key point
 GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
Plotting Ordered Pairs Using Integers
 SAMPLE Plotting Ordered Pirs Using Integers Ple two elsti nds on geoord to form oordinte xes shown on the right to help you solve these prolems.. Wht letter of the lphet does eh set of pirs nme?. (, )
SAMPLE Plotting Ordered Pirs Using Integers Ple two elsti nds on geoord to form oordinte xes shown on the right to help you solve these prolems.. Wht letter of the lphet does eh set of pirs nme?. (, )
4Measurement and geometry. Trigonometry
 4Mesurement nd geometry In the seond entury BCE, the Greek stronomer Hipprhus ould lulte distnes to the Moon nd the Sun nd he ws the first sientist to hrt the positions of over 850 strs. How ws he le to
4Mesurement nd geometry In the seond entury BCE, the Greek stronomer Hipprhus ould lulte distnes to the Moon nd the Sun nd he ws the first sientist to hrt the positions of over 850 strs. How ws he le to
S2 (2.2) Pythagoras.notebook March 04, 2016
 S2 (2.2) Pythgors.noteook Mrh 04, 2016 Dily Prtie 16.12.2015 Q1. Multiply out nd simplify 9x 3(2x + 1) Q2. Solve the eqution 3(2x + 4) = 18 Q3. If 1 = $1.30, how muh is 50 in dollrs? Tody we will e lerning
S2 (2.2) Pythgors.noteook Mrh 04, 2016 Dily Prtie 16.12.2015 Q1. Multiply out nd simplify 9x 3(2x + 1) Q2. Solve the eqution 3(2x + 4) = 18 Q3. If 1 = $1.30, how muh is 50 in dollrs? Tody we will e lerning
MCH T 111 Handout Triangle Review Page 1 of 3
 Hnout Tringle Review Pge of 3 In the stuy of sttis, it is importnt tht you e le to solve lgeri equtions n tringle prolems using trigonometry. The following is review of trigonometry sis. Right Tringle:
Hnout Tringle Review Pge of 3 In the stuy of sttis, it is importnt tht you e le to solve lgeri equtions n tringle prolems using trigonometry. The following is review of trigonometry sis. Right Tringle:
8Similarity UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS. 8.1 Kick off with CAS 8.2 Similar objects 8.3 Linear scale factors. 8.4 Area and volume scale factors 8.
 8.1 Kick off with S 8. Similr ojects 8. Liner scle fctors 8Similrity 8. re nd volume scle fctors 8. Review U N O R R E TE D P G E PR O O FS 8.1 Kick off with S Plese refer to the Resources t in the Prelims
8.1 Kick off with S 8. Similr ojects 8. Liner scle fctors 8Similrity 8. re nd volume scle fctors 8. Review U N O R R E TE D P G E PR O O FS 8.1 Kick off with S Plese refer to the Resources t in the Prelims
Green s Theorem. (2x e y ) da. (2x e y ) dx dy. x 2 xe y. (1 e y ) dy. y=1. = y e y. y=0. = 2 e
 Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
Applications of trigonometry
 3 3 3 3 3D 3E 3F 3G 3H Review of right-ngled tringles erings Using the sine rule to find side lengths Using the sine rule to find ngles re of tringle Using the osine rule to find side lengths Using the
3 3 3 3 3D 3E 3F 3G 3H Review of right-ngled tringles erings Using the sine rule to find side lengths Using the sine rule to find ngles re of tringle Using the osine rule to find side lengths Using the
Lesson 2.1 Inductive Reasoning
 Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
= x x 2 = 25 2
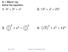 9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
2.1 ANGLES AND THEIR MEASURE. y I
 .1 ANGLES AND THEIR MEASURE Given two interseting lines or line segments, the mount of rottion out the point of intersetion (the vertex) required to ring one into orrespondene with the other is lled the
.1 ANGLES AND THEIR MEASURE Given two interseting lines or line segments, the mount of rottion out the point of intersetion (the vertex) required to ring one into orrespondene with the other is lled the
9.1 Day 1 Warm Up. Solve the equation = x x 2 = March 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythagorean Theorem 1
 9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
8 Measurement. How is measurement used in your home? 8E Area of a circle 8B Circumference of a circle. 8A Length and perimeter
 8A Length nd perimeter 8E Are of irle 8B Cirumferene of irle 8F Surfe re 8C Are of retngles nd tringles 8G Volume of prisms 8D Are of other qudrilterls 8H Are nd volume onversions SA M PL E Mesurement
8A Length nd perimeter 8E Are of irle 8B Cirumferene of irle 8F Surfe re 8C Are of retngles nd tringles 8G Volume of prisms 8D Are of other qudrilterls 8H Are nd volume onversions SA M PL E Mesurement
The Ellipse. is larger than the other.
 The Ellipse Appolonius of Perg (5 B.C.) disovered tht interseting right irulr one ll the w through with plne slnted ut is not perpendiulr to the is, the intersetion provides resulting urve (oni setion)
The Ellipse Appolonius of Perg (5 B.C.) disovered tht interseting right irulr one ll the w through with plne slnted ut is not perpendiulr to the is, the intersetion provides resulting urve (oni setion)
In right-angled triangles the square on the side subtending the right angle is equal to the squares on the sides containing the right angle.
 Mth 3329-Uniform Geometries Leture 06 1. Review of trigonometry While we re looking t Eulid s Elements, I d like to look t some si trigonometry. Figure 1. The Pythgoren theorem sttes tht if = 90, then
Mth 3329-Uniform Geometries Leture 06 1. Review of trigonometry While we re looking t Eulid s Elements, I d like to look t some si trigonometry. Figure 1. The Pythgoren theorem sttes tht if = 90, then
Project 6: Minigoals Towards Simplifying and Rewriting Expressions
 MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
Math Lesson 4-5 The Law of Cosines
 Mth-1060 Lesson 4-5 The Lw of osines Solve using Lw of Sines. 1 17 11 5 15 13 SS SSS Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. We need nother eqution. h Drop nd ltitude
Mth-1060 Lesson 4-5 The Lw of osines Solve using Lw of Sines. 1 17 11 5 15 13 SS SSS Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. Every pir of loops will hve unknowns. We need nother eqution. h Drop nd ltitude
Linear Algebra Introduction
 Introdution Wht is Liner Alger out? Liner Alger is rnh of mthemtis whih emerged yers k nd ws one of the pioneer rnhes of mthemtis Though, initilly it strted with solving of the simple liner eqution x +
Introdution Wht is Liner Alger out? Liner Alger is rnh of mthemtis whih emerged yers k nd ws one of the pioneer rnhes of mthemtis Though, initilly it strted with solving of the simple liner eqution x +
Ellipses. The second type of conic is called an ellipse.
 Ellipses The seond type of oni is lled n ellipse. Definition of Ellipse An ellipse is the set of ll points (, y) in plne, the sum of whose distnes from two distint fied points (foi) is onstnt. (, y) d
Ellipses The seond type of oni is lled n ellipse. Definition of Ellipse An ellipse is the set of ll points (, y) in plne, the sum of whose distnes from two distint fied points (foi) is onstnt. (, y) d
Integration. antidifferentiation
 9 Integrtion 9A Antidifferentition 9B Integrtion of e, sin ( ) nd os ( ) 9C Integrtion reognition 9D Approimting res enlosed funtions 9E The fundmentl theorem of integrl lulus 9F Signed res 9G Further
9 Integrtion 9A Antidifferentition 9B Integrtion of e, sin ( ) nd os ( ) 9C Integrtion reognition 9D Approimting res enlosed funtions 9E The fundmentl theorem of integrl lulus 9F Signed res 9G Further
MEP Practice Book ES3. 1. Calculate the size of the angles marked with a letter in each diagram. None to scale
 ME rctice ook ES3 3 ngle Geometr 3.3 ngle Geometr 1. lculte the size of the ngles mrked with letter in ech digrm. None to scle () 70 () 20 54 65 25 c 36 (d) (e) (f) 56 62 d e 60 40 70 70 f 30 g (g) (h)
ME rctice ook ES3 3 ngle Geometr 3.3 ngle Geometr 1. lculte the size of the ngles mrked with letter in ech digrm. None to scle () 70 () 20 54 65 25 c 36 (d) (e) (f) 56 62 d e 60 40 70 70 f 30 g (g) (h)
Algebra Basics. Algebra Basics. Curriculum Ready ACMNA: 133, 175, 176, 177, 179.
 Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 33 75 76 77 79 www.mthletis.om Fill in the spes with nything you lredy know out Alger Creer Opportunities: Arhitets eletriins plumers et. use it to do importnt lultions. Give this
Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 33 75 76 77 79 www.mthletis.om Fill in the spes with nything you lredy know out Alger Creer Opportunities: Arhitets eletriins plumers et. use it to do importnt lultions. Give this
2. There are an infinite number of possible triangles, all similar, with three given angles whose sum is 180.
 SECTION 8-1 11 CHAPTER 8 Setion 8 1. There re n infinite numer of possile tringles, ll similr, with three given ngles whose sum is 180. 4. If two ngles α nd β of tringle re known, the third ngle n e found
SECTION 8-1 11 CHAPTER 8 Setion 8 1. There re n infinite numer of possile tringles, ll similr, with three given ngles whose sum is 180. 4. If two ngles α nd β of tringle re known, the third ngle n e found
UNCORRECTED SAMPLE PAGES. Australian curriculum NUMBER AND ALGEBRA
 7A 7B 7C 7D 7E 7F 7G 7H 7I 7J 7K Chpter Wht ou will lern 7Prols nd other grphs Eploring prols Skething prols with trnsformtions Skething prols using ftoristion Skething ompleting the squre Skething using
7A 7B 7C 7D 7E 7F 7G 7H 7I 7J 7K Chpter Wht ou will lern 7Prols nd other grphs Eploring prols Skething prols with trnsformtions Skething prols using ftoristion Skething ompleting the squre Skething using
Topics Covered: Pythagoras Theorem Definition of sin, cos and tan Solving right-angle triangles Sine and cosine rule
 Trigonometry Topis overed: Pythgors Theorem Definition of sin, os nd tn Solving right-ngle tringles Sine nd osine rule Lelling right-ngle tringle Opposite (Side opposite the ngle θ) Hypotenuse (Side opposite
Trigonometry Topis overed: Pythgors Theorem Definition of sin, os nd tn Solving right-ngle tringles Sine nd osine rule Lelling right-ngle tringle Opposite (Side opposite the ngle θ) Hypotenuse (Side opposite
Chapter 8 Roots and Radicals
 Chpter 8 Roots nd Rdils 7 ROOTS AND RADICALS 8 Figure 8. Grphene is n inredily strong nd flexile mteril mde from ron. It n lso ondut eletriity. Notie the hexgonl grid pttern. (redit: AlexnderAIUS / Wikimedi
Chpter 8 Roots nd Rdils 7 ROOTS AND RADICALS 8 Figure 8. Grphene is n inredily strong nd flexile mteril mde from ron. It n lso ondut eletriity. Notie the hexgonl grid pttern. (redit: AlexnderAIUS / Wikimedi
Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework. Solving for Obtuse Angles QUIZ ( ) More Trig Word Problems QUIZ ( )
 UNIT 5 TRIGONOMETRI RTIOS Dte Lesson Text TOPI Homework pr. 4 5.1 (48) Trigonometry Review WS 5.1 # 3 5, 9 11, (1, 13)doso pr. 6 5. (49) Relted ngles omplete lesson shell & WS 5. pr. 30 5.3 (50) 5.3 5.4
UNIT 5 TRIGONOMETRI RTIOS Dte Lesson Text TOPI Homework pr. 4 5.1 (48) Trigonometry Review WS 5.1 # 3 5, 9 11, (1, 13)doso pr. 6 5. (49) Relted ngles omplete lesson shell & WS 5. pr. 30 5.3 (50) 5.3 5.4
8Similarity ONLINE PAGE PROOFS. 8.1 Kick off with CAS 8.2 Similar objects 8.3 Linear scale factors. 8.4 Area and volume scale factors 8.
 8.1 Kick off with S 8. Similr ojects 8. Liner scle fctors 8Similrity 8.4 re nd volume scle fctors 8. Review Plese refer to the Resources t in the Prelims section of your eookplus for comprehensive step-y-step
8.1 Kick off with S 8. Similr ojects 8. Liner scle fctors 8Similrity 8.4 re nd volume scle fctors 8. Review Plese refer to the Resources t in the Prelims section of your eookplus for comprehensive step-y-step
m m m m m m m m P m P m ( ) m m P( ) ( ). The o-ordinte of the point P( ) dividing the line segment joining the two points ( ) nd ( ) eternll in the r
 CO-ORDINTE GEOMETR II I Qudrnt Qudrnt (-.+) (++) X X - - - 0 - III IV Qudrnt - Qudrnt (--) - (+-) Region CRTESIN CO-ORDINTE SSTEM : Retngulr Co-ordinte Sstem : Let X' OX nd 'O e two mutull perpendiulr
CO-ORDINTE GEOMETR II I Qudrnt Qudrnt (-.+) (++) X X - - - 0 - III IV Qudrnt - Qudrnt (--) - (+-) Region CRTESIN CO-ORDINTE SSTEM : Retngulr Co-ordinte Sstem : Let X' OX nd 'O e two mutull perpendiulr
2 Calculate the size of each angle marked by a letter in these triangles.
 Cmridge Essentils Mthemtics Support 8 GM1.1 GM1.1 1 Clculte the size of ech ngle mrked y letter. c 2 Clculte the size of ech ngle mrked y letter in these tringles. c d 3 Clculte the size of ech ngle mrked
Cmridge Essentils Mthemtics Support 8 GM1.1 GM1.1 1 Clculte the size of ech ngle mrked y letter. c 2 Clculte the size of ech ngle mrked y letter in these tringles. c d 3 Clculte the size of ech ngle mrked
UNCORRECTED. Australian curriculum NUMBER AND ALGEBRA
 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F 0G 0H Chpter Wht ou will lern Qudrti equtions (Etending) Solving + = 0 nd = d (Etending) Solving + + = 0 (Etending) Applitions of qudrti equtions (Etending) The prol Skething = with diltions
0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F 0G 0H Chpter Wht ou will lern Qudrti equtions (Etending) Solving + = 0 nd = d (Etending) Solving + + = 0 (Etending) Applitions of qudrti equtions (Etending) The prol Skething = with diltions
Lesson 2.1 Inductive Reasoning
 Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I)
 /0 BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I) SAMPLE TEST PLACEMENT EXAMINATION Downlod the omplete Study Pket: http://www.glendle.edu/studypkets Students who hve tken yer of high shool lger or its equivlent with grdes
/0 BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I) SAMPLE TEST PLACEMENT EXAMINATION Downlod the omplete Study Pket: http://www.glendle.edu/studypkets Students who hve tken yer of high shool lger or its equivlent with grdes
6.5 Improper integrals
 Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
Proving the Pythagorean Theorem
 Proving the Pythgoren Theorem W. Bline Dowler June 30, 2010 Astrt Most people re fmilir with the formul 2 + 2 = 2. However, in most ses, this ws presented in lssroom s n solute with no ttempt t proof or
Proving the Pythgoren Theorem W. Bline Dowler June 30, 2010 Astrt Most people re fmilir with the formul 2 + 2 = 2. However, in most ses, this ws presented in lssroom s n solute with no ttempt t proof or
Trigonometry. VCEcoverage. Area of study. Units 3 & 4 Geometry and trigonometry
 Trigonometry 9 VEcoverge re of study Units & Geometry nd trigonometry In this ch chpter 9 Pythgors theorem 9 Pythgoren trids 9 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 9D Trigonometric rtios 9E The sine rule
Trigonometry 9 VEcoverge re of study Units & Geometry nd trigonometry In this ch chpter 9 Pythgors theorem 9 Pythgoren trids 9 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 9D Trigonometric rtios 9E The sine rule
I1.1 Pythagoras' Theorem. I1.2 Further Work With Pythagoras' Theorem. I1.3 Sine, Cosine and Tangent. I1.4 Finding Lengths in Right Angled Triangles
 UNIT I1 Pythgors' Theorem nd Trigonometric Rtios: Tet STRAND I: Geometry nd Trigonometry I1 Pythgors' Theorem nd Trigonometric Rtios Tet Contents Section I1.1 Pythgors' Theorem I1. Further Work With Pythgors'
UNIT I1 Pythgors' Theorem nd Trigonometric Rtios: Tet STRAND I: Geometry nd Trigonometry I1 Pythgors' Theorem nd Trigonometric Rtios Tet Contents Section I1.1 Pythgors' Theorem I1. Further Work With Pythgors'
We use metres to measure length. There are 100 centimetres in a metre. a 6 m = cm b 3 m = cm c 9 m = cm
 Units of length metres We use metres to mesure length. There re 00 entimetres in metre. 00 m = m Convert these metres to entimetres: 6 m = m 3 m = m 9 m = m 600 300 900 Estimte nd then mesure the length
Units of length metres We use metres to mesure length. There re 00 entimetres in metre. 00 m = m Convert these metres to entimetres: 6 m = m 3 m = m 9 m = m 600 300 900 Estimte nd then mesure the length
( ) 1. 1) Let f( x ) = 10 5x. Find and simplify f( 2) and then state the domain of f(x).
 Mth 15 Fettermn/DeSmet Gustfson/Finl Em Review 1) Let f( ) = 10 5. Find nd simplif f( ) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = +. Find nd simplif f(1) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = 8.
Mth 15 Fettermn/DeSmet Gustfson/Finl Em Review 1) Let f( ) = 10 5. Find nd simplif f( ) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = +. Find nd simplif f(1) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = 8.
SAMPLE EVALUATION ONLY
 mesurement nd geometry topic 5 Geometry 5.1 Overview Why lern this? Geometry llows us to explore our world in very preise wy. uilders, rhitets, surveyors nd engineers use knowledge of geometry to ensure
mesurement nd geometry topic 5 Geometry 5.1 Overview Why lern this? Geometry llows us to explore our world in very preise wy. uilders, rhitets, surveyors nd engineers use knowledge of geometry to ensure
Geometry. Trigonometry of Right Triangles. Slide 2 / 240. Slide 1 / 240. Slide 3 / 240. Slide 4 / 240. Slide 6 / 240.
 Slide 1 / 240 Slide 2 / 240 New Jerse enter for Tehing nd Lerning Progressive Mthemtis Inititive This mteril is mde freel ville t www.njtl.org nd is intended for the non-ommeril use of students nd tehers.
Slide 1 / 240 Slide 2 / 240 New Jerse enter for Tehing nd Lerning Progressive Mthemtis Inititive This mteril is mde freel ville t www.njtl.org nd is intended for the non-ommeril use of students nd tehers.
Special Numbers, Factors and Multiples
 Specil s, nd Student Book - Series H- + 3 + 5 = 9 = 3 Mthletics Instnt Workooks Copyright Student Book - Series H Contents Topics Topic - Odd, even, prime nd composite numers Topic - Divisiility tests
Specil s, nd Student Book - Series H- + 3 + 5 = 9 = 3 Mthletics Instnt Workooks Copyright Student Book - Series H Contents Topics Topic - Odd, even, prime nd composite numers Topic - Divisiility tests
MTH 4-16a Trigonometry
 MTH 4-16 Trigonometry Level 4 [UNIT 5 REVISION SECTION ] I cn identify the opposite, djcent nd hypotenuse sides on right-ngled tringle. Identify the opposite, djcent nd hypotenuse in the following right-ngled
MTH 4-16 Trigonometry Level 4 [UNIT 5 REVISION SECTION ] I cn identify the opposite, djcent nd hypotenuse sides on right-ngled tringle. Identify the opposite, djcent nd hypotenuse in the following right-ngled
Lesson 8.1 Graphing Parametric Equations
 Lesson 8.1 Grphing Prmetric Equtions 1. rete tle for ech pir of prmetric equtions with the given vlues of t.. x t 5. x t 3 c. x t 1 y t 1 y t 3 y t t t {, 1, 0, 1, } t {4,, 0,, 4} t {4, 0,, 4, 8}. Find
Lesson 8.1 Grphing Prmetric Equtions 1. rete tle for ech pir of prmetric equtions with the given vlues of t.. x t 5. x t 3 c. x t 1 y t 1 y t 3 y t t t {, 1, 0, 1, } t {4,, 0,, 4} t {4, 0,, 4, 8}. Find
Instructions to students: Use your Text Book and attempt these questions.
 Instrutions to students: Use your Text Book nd ttempt these questions. Due Dte: 16-09-2018 Unit 2 Chpter 8 Test Slrs nd vetors Totl mrks 50 Nme: Clss: Dte: Setion A Selet the est nswer for eh question.
Instrutions to students: Use your Text Book nd ttempt these questions. Due Dte: 16-09-2018 Unit 2 Chpter 8 Test Slrs nd vetors Totl mrks 50 Nme: Clss: Dte: Setion A Selet the est nswer for eh question.
Introduction to Olympiad Inequalities
 Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Chapter 9 Definite Integrals
 Chpter 9 Definite Integrls In the previous chpter we found how to tke n ntiderivtive nd investigted the indefinite integrl. In this chpter the connection etween ntiderivtives nd definite integrls is estlished
Chpter 9 Definite Integrls In the previous chpter we found how to tke n ntiderivtive nd investigted the indefinite integrl. In this chpter the connection etween ntiderivtives nd definite integrls is estlished
I1 = I2 I1 = I2 + I3 I1 + I2 = I3 + I4 I 3
 2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
Calculus Module C21. Areas by Integration. Copyright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technology All Rights Reserved.
 Clculus Module C Ares Integrtion Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 7. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Mrch, 9 Introduction to Ares Integrtion Sttement of Prerequisite
Clculus Module C Ares Integrtion Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 7. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Mrch, 9 Introduction to Ares Integrtion Sttement of Prerequisite
Part I: Study the theorem statement.
 Nme 1 Nme 2 Nme 3 A STUDY OF PYTHAGORAS THEOREM Instrutions: Together in groups of 2 or 3, fill out the following worksheet. You my lift nswers from the reding, or nswer on your own. Turn in one pket for
Nme 1 Nme 2 Nme 3 A STUDY OF PYTHAGORAS THEOREM Instrutions: Together in groups of 2 or 3, fill out the following worksheet. You my lift nswers from the reding, or nswer on your own. Turn in one pket for
This chapter will show you What you should already know Quick check 111
 1 Pythgors theorem 2 Finding shorter side 3 Solving prolems using Pythgors theorem This chpter will show you how to use Pythgors theorem in right-ngled tringles how to solve prolems using Pythgors theorem
1 Pythgors theorem 2 Finding shorter side 3 Solving prolems using Pythgors theorem This chpter will show you how to use Pythgors theorem in right-ngled tringles how to solve prolems using Pythgors theorem
1.3 SCALARS AND VECTORS
 Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
3.1 Review of Sine, Cosine and Tangent for Right Angles
 Foundtions of Mth 11 Section 3.1 Review of Sine, osine nd Tngent for Right Tringles 125 3.1 Review of Sine, osine nd Tngent for Right ngles The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigon,
Foundtions of Mth 11 Section 3.1 Review of Sine, osine nd Tngent for Right Tringles 125 3.1 Review of Sine, osine nd Tngent for Right ngles The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigon,
H (2a, a) (u 2a) 2 (E) Show that u v 4a. Explain why this implies that u v 4a, with equality if and only u a if u v 2a.
 Chpter Review 89 IGURE ol hord GH of the prol 4. G u v H (, ) (A) Use the distne formul to show tht u. (B) Show tht G nd H lie on the line m, where m ( )/( ). (C) Solve m for nd sustitute in 4, otining
Chpter Review 89 IGURE ol hord GH of the prol 4. G u v H (, ) (A) Use the distne formul to show tht u. (B) Show tht G nd H lie on the line m, where m ( )/( ). (C) Solve m for nd sustitute in 4, otining
Student Book SERIES. Measurement. Name
 Student Book Nme Series Contents Topi Units of length (pp. 9) metres entimetres metres nd entimetres millimetres perimeter length nd deiml nottion onnet nd lok pply te ompleted Topi Are (pp. 0 5) squre
Student Book Nme Series Contents Topi Units of length (pp. 9) metres entimetres metres nd entimetres millimetres perimeter length nd deiml nottion onnet nd lok pply te ompleted Topi Are (pp. 0 5) squre
