Section 4: Linear Equations, Functions, and Inequalities
|
|
|
- Tamsyn Willis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topic 1: Arithmetic Sequences Topic 2: Rate of Change of Linear Functions Topic 3: Interpreting Rate of Change and yy-intercept in a Real-World Context - Part Topic 4: Interpreting Rate of Change and yy-intercept in a Real-World Context - Part Topic 5: Introduction to Systems of Equations Topic 6: Finding Solution Sets to Systems of Equations Using Substitution and Graphing Topic 7: Using Equivalent Systems of Equations Topic 8: Finding Solution Sets to Systems of Equations Using Elimination Topic 9: Solution Sets to Inequalities with Two Variables Topic 10: Finding Solution Sets to Systems of Linear Inequalities Visit AlgebraNation.com or search "Algebra Nation" in your phone or tablet's app store to watch the videos that go along with this workbook! 85
2 The following Mathematics Florida Standards will be covered in this section: A-CED Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities; graph equations on coordinate axes with labels and scales. A-CED Represent constraints by equations or inequalities, and by systems of equations and/or inequalities, and interpret solutions as viable or non-viable options in a modeling context. For example, represent inequalities describing nutritional and cost constraints on combinations of different foods. A-REI Prove that, given a system of two equations in two variables, replacing one equation by the sum of that equation and a multiple of the other produces a system with the same solutions. A-REI Solve systems of linear equations exactly and approximately (e.g., with graphs), focusing on pairs of linear equations in two variables. A-REI Understand that the graph of an equation in two variables is the set of all its solutions plotted in the coordinate plane, often forming a curve (which could be a line). A-REI Explain why the xx-coordinates of the points where the graphs of the equations yy = ff(xx) and yy = gg(xx) intersect are the solutions of the equation ff(xx) = gg(xx); find the solutions approximately, e.g., using technology to graph the functions, make tables of values, or find successive approximations. Include cases where ff(xx) and/or gg(xx) are linear, rational, absolute value, and exponential functions. A-REI Graph the solutions to a linear inequality in two variables as a half-plane (excluding the boundary in the case of a strict inequality), and graph the solution set to a system of linear inequalities in two variables as the intersection of the corresponding halfplanes. F-BF Write a function that describes a relationship between two quantities. a. Determine an explicit expression, a recursive process, or steps for calculation from a context. F-IF Recognize that sequences are functions, sometimes defined recursively, whose domain is a subset of the integers. For example, the Fibonacci sequence is defined recursively by ff(0) = ff(1) = 1, ff(nn + 1) = ff(nn) + ff(nn 1) for nn 1. F-IF.3.7a - Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features of the graph, by hand in simple cases and using technology in more complicated cases. a. Graph linear and quadratic functions and show intercepts, maxima, and minima. F-LE Construct linear and exponential functions, including arithmetic and geometric sequences, given a graph, a description of a relationship, or two input/output pairs (including reading these from a table). F-LE Interpret the parameters in a linear or exponential function in terms of a context. S-ID Interpret the slope (rate of change) and the intercept (constant term) of a linear model in the context of the data. 86
3 Section 4: Linear Equations, Functions, and Inequalities Section 4 Topic 1 Arithmetic Sequences Let s look at the following sequence of numbers: 3, 8, 13, 18, 23,. We can represent this sequence in a table: Term Number Sequence Term Term Function Notation 1 aa, 3 ff(1) a formula to find the 1 st term 2 aa 0 8 a formula to find the 2 nd term Ø Ø The at the end means that this goes on forever. 3, 8, 13, 18, and 23 are the actual of this sequence. 3 aa 1 13 ff(3) a formula to find the term 4 aa 3 ff(4) a formula to find the term 5 aa 4 a formula to find the term Ø There are 5 terms in this sequence so far: o o o o o 3 is the 1 st term. 8 is the 2 nd term. 13 is the term. 18 is the term. 23 is the term. nn aa 7 ff(nn) a formula to find the term How can we find the 9 th term of this sequence? This is an example of an arithmetic sequence. Ø This is a sequence where each term is the of the previous term and a common difference, dd. 87
4 One way is to start by finding the previous term: Term Number Sequence Term Term 1 aa, 3 ff(1) 3 Function Notation 2 aa 0 8 = 3 + ff(2) aa 1 13 = 8 + ff(3) aa 3 18 = 13 + ff(4) aa 4 23 = + 5 ff(5) aa = ff(6) aa? ff(7) Let s look at another way to find unknown terms: Term Number Sequence Term Term 1 aa, 3 ff(1) 3 Function Notation 2 aa 0 8 = ff(2) 3 + 5(1) 3 aa 1 13 = = ff(3) aa, + 5(2) 4 aa 3 18 = = ff(4) aa, + 5(3) 5 aa 4 23 = = ff(5) aa, + 5(4) 6 aa = 7 aa? 28 = = = = ff(6) aa, + 5(5) ff(7) aa, + 5(6) 8 ff(8) = = ff(8) 9 aa A ff(9) aa A 43 = = ff(9) Write a general equation that we could use to find any term in the sequence. Write a general equation that we could use to find any term in the sequence. This is a recursive formula. Ø In order to solve for a term, you must know the value of its preceding term. Can you think of a situation where the recursive formula would take a long time to use? This is an explicit formula. Ø To solve for a term, you need to know the first term of the sequence and the difference by which the sequence is increasing or decreasing. 88
5 Let s Practice! 1. Consider the sequence 10, 4, 2, 8,. a. Write a recursive formula for the sequence. b. Write an explicit formula for the sequence. c. Find the 42 nd term of the sequence. BEAT THE TEST! 1. Yohanna is conditioning all summer to prepare for her high school s varsity soccer team tryouts. She is incorporating walking planks into her daily training plan. Every day, she will complete four more walking planks than the day before. Part A: Yohanna starts with five walking planks on the first day. Write an explicit formula that can be used to find the number of walking planks she completes on any given day. Try It! 2. Consider the sequence 7, 17, 27, 37,. a. Find the next three terms of the sequence. b. Write a recursive formula for the sequence. c. Write an explicit formula for the sequence. Part B: How many walking planks will Yohanna do on the 12 th day? A 49 B 53 C 59 D 64 d. Find the 33 rd term of the sequence. 89
6 2. The following figures were created with squares, where each side of the squares has a length of exactly one unit. AA, represents the area of the first figure, AA 0 represents the area of the second figure, and so on. Based on this pattern, what would be the rule for the area of the nn EF figure when nn > 1? Section 4 Topic 2 Rate of Change of Linear Functions Génesis reads 16 pages of The Fault in Our Stars every day. Zully reads 8 pages every day of the same book. Represent both situations on the graphs below using the same scales on the axes for both graphs. AA, = 1 nn = 1 AA 0 = 4 nn = 2 AA 1 = 7 nn = 3 Graph 1: Génesis s Reading Speed Graph 2: Zully s Reading Speed A AA 7 = 2AA 7I, 2 B AA 7 = 2AA 7I, + 4 C AA 7 = AA 7I, + 3 D AA 7 = AA 7I, + 2 Algebra Wall Want some help? You can always ask questions on the Algebra Wall and receive help from other students, teachers, and Study Experts. You can also help others on the Algebra Wall and earn Karma Points for doing so. Go to AlgebraNation.com to learn more and get started! 90
7 Aaron loves Cherry Coke. Each mini-can contains 100 calories. Jacobe likes to munch on carrot snack packs. Each snack pack contains 40 calories. Represent both situations on the graphs below using the same scales for both graphs. What is the rate of change for each of the graphs? Graph 1: per Graph 2: per Graph 3: per Graph 3: Aaron s Calorie Intake Graph 4: Jacobe s Calorie Intake Graph 4: per This is also called the of the line. We can also find slope by looking at the JFK7LM N7 O JFK7LM N7 P or QNRM QS7. What is the slope of the following graph? What does the slope represent? In each of the graphs, we were finding the rate of change in the given situation. 91
8 Let s Practice! 1. Consider the following graph. 2. Freedom High School collected data on the GPA of various students and the number of hours they spend studying each week. A scatterplot of the data is shown below with the line of best fit. Keisha s Vacation Souvenirs Souvenirs Purchased Days of Vacation a. What is the rate of change of the graph? a. What is the slope of the line of best fit? b. What does the rate of change represent? b. What does the slope represent? 92
9 Try It! 3. Sarah s parents give her a $ allowance at the beginning of each month. Sarah spends her allowance on comic books. The graph below represents the amount of money Sarah spent on comic books last month. Sarah s Expenses BEAT THE TEST! 1. A cleaning service cleans many apartments each day. The following table shows the number of hours the cleaners spend cleaning and the number of apartments they clean during that time. Apartment Cleaning Amount of Allowance Left (in dollars) Time (Hours) Apartments Cleaned Part A: Represent the situation on the graph below. Number of Comic Books Purchased a. What is the rate of change? b. What does the rate of change represent? 93
10 Part B: The data suggest a linear relationship between the number of hours spent cleaning and the number of apartments cleaned. Assuming the relationship is linear, what does the rate of change represent in the context of this relationship? A B C D The number of apartments cleaned after one hour. The number of hours it took to clean one apartment. The number of apartments cleaned each hour. The number of apartments cleaned before the company started cleaning. Section 4 Topic 3 Interpreting Rate of Change and yy-intercept in a Real-World Context Part 1 The T-Mobile ONE family plan includes four lines and unlimited data, calls, and texts for $ per month, including taxes and fees. There is an activation fee of $ Define the variable and write a function that represents this situation. Represent the situation on a graph. Part C: Which equation describes the relationship between the time elapsed and the number of apartments cleaned? A yy = xx B yy = xx + 2 C yy = 2xx D yy = 2xx + 2 Algebra Wall Want some help? You can always ask questions on the Algebra Wall and receive help from other students, teachers, and Study Experts. You can also help others on the Algebra Wall and earn Karma Points for doing so. Go to AlgebraNation.com to learn more and get started! What is the slope of the line? What does the slope represent? 94
11 At what point does the line intersect the yy-axis? What does this point represent? b. Represent the situation on a graph. The yy-value of the point where the graph intersects the yy-axis is the yy-intercept. Let s Practice! 1. You saved $ to spend over the summer. You decide to budget $25.00 to spend each week. a. Define the variable and write a function that represents this situation. c. What is the slope of the line? What does the slope represent? d. What is different about the slope of this line compared to our earlier problem? Why is it different? e. What is the yy-intercept? What does this point represent? 95
12 Try It! 2. Consider the following graph. Consider the three functions that you wrote regarding the cell phone plan, summer spending habits, and the community pool membership. What do you notice about the constant term and the coefficient of the xx term? Ø Ø The constant term is the. The coefficient of the xx is the or. These functions are written in slope-intercept form. We can use slope-intercept form to graph any linear equation. a. What is the slope of the line? What does the slope represent? The coefficient of xx is the slope and the constant term is the yy-intercept ONLY if the equation is in slope-intercept form, yy = mmmm + bb. b. What is the yy-intercept? What does the yy-intercept represent? c. Define the variables and write a function that represents this situation. d. What does each point represent? Algebra Wall Want some help? You can always ask questions on the Algebra Wall and receive help from other students, teachers, and Study Experts. You can also help others on the Algebra Wall and earn Karma Points for doing so. Go to AlgebraNation.com to learn more and get started! 96
13 Section 4 Topic 4 Interpreting Rate of Change and yy-intercept in a Real-World Context Part 2 Let s Practice! 1. Graph yy = 2xx Consider the equation 2xx + 5yy = 10. a. How does this equation look different from slope-intercept form of an equation? b. Rewrite the equation in slope-intercept form. c. Identify the slope and yy-intercept. d. Graph the equation. 97
14 Try It! 3. Graph the equation 4xx 5yy = 10. BEAT THE TEST! 1. Line tt, EEEEEE, and FFFFFF are shown on the coordinate grid below. Which of the following statements are true? Select all that apply. The slope of AAAA is equal to the slope of BBBB. The slope of AAAA is equal to the slope of line tt. The slope of line tt is equal to ab ca. The slope of line tt is equal to de ef. The yy-intercept of line tt is 2. Line tt represents a discrete function. 98
15 2. The senior class at Elizabeth High School sold tickets to raise money for prom. The graph below represents the situation. Section 4 Topic 5 Introduction to Systems of Equations A system of equations is a set of two or more equations. Consider the following system of equations. Line 1: 2xx yy = 5 Line 2: 2xx + yy = 1 Graph the system of equations on the coordinate plane below. Part A: How much did one ticket cost? Part B: How much money did the senior class have at the start of the fundraiser? Algebra Wall Want some help? You can always ask questions on the Algebra Wall and receive help from other students, teachers, and Study Experts. You can also help others on the Algebra Wall and earn Karma Points for doing so. Go to AlgebraNation.com to learn more and get started! Recall that a solution to a linear equation is any ordered pair that makes that equation a true statement. 99
16 What do you notice about the point ( 2, 5)? Let s Practice! 1. Consider the following system of equations made up of Line 1 and Line 2. Line 1: 5xx + 2yy = 8 Line 2: 3xx 2yy = 4 What do you notice about the point (1, 7)? Complete the following sentences. a. The ordered pair ( 2, 5) is a solution to o line 1. o line 2. o the system of equations. What do you notice about the point ( 1, 3)? b. The ordered pair (2, 1) is a solution to o line 1. o line 2. o the system of equations. What do you notice about the point (1, 1)? c. The ordered pair (0, 4) is a solution to o line 1. o line 2. o the system of equations. 100
17 2. Is there ever a time when a system of equations will not have a solution? If so, sketch an example. 4. Consider the following system of equations. 4xx + 3yy = 3 2xx 5yy = 5 a. Sketch the graph the system of equations. Try It! 3. Consider the following system of equations. xx yy = 3 2xx + 2yy = 6 a. Sketch the graph of the system of equations. b. What is the solution to the system? b. What can be said about the solution to this system of equations? 101
18 BEAT THE TEST! 1. Consider the following system of equations. xx + yy = 5 2xx yy = 2 Part A: Sketch the graph of the system of equations. 2. Two linear functions in a coordinate plane have no points of intersection. Which pair of functions does not intersect? A 6xx + 2yy = 12 and 20xx + 10yy = 14 B 4xx + 2yy = 12 and 20xx + 10yy = 30 C 6xx + 2yy = 12 and yy = 0.5xx 0.6 D 10xx + 10yy = 6 and yy = 0.5xx 0.6 Part B: Determine the solution to the system of equations. Part C: Create a third equation that could be added to the system so that the solution does not change. Graph the line on the coordinate plane above. Algebra Wall Want some help? You can always ask questions on the Algebra Wall and receive help from other students, teachers, and Study Experts. You can also help others on the Algebra Wall and earn Karma Points for doing so. Go to AlgebraNation.com to learn more and get started! 102
19 Section 4 Topic 6 Finding Solution Sets to Systems of Equations Using Substitution and Graphing b. Represent the two situations on the graph below. We are able to use systems of equations to solve many realworld problems. One method of solving systems of equations is by graphing like we did in the previous video. Let s Practice! 1. Brianna s lacrosse coach suggested that she practice yoga to improve her flexibility. Yoga-ta Try This! Yoga Studio has two membership plans. Plan A costs $20.00 per month plus $10.00 per class. Plan B costs $ per month for unlimited classes. a. Define the variables and write two functions to represent the monthly cost of each plan. c. What is the rate of change for each plan? d. What does the rate of change represent in this situation? e. What do the yy-intercepts of the graphs represent? 103
20 2. Brianna is trying to determine which plan is more appropriate for the number of classes she wants to attend. a. When will the two plans cost exactly the same? b. When is Plan A the better deal? Try It! 3. Vespa Scooter Rental rents scooters for $45.00 and $0.25 per mile. Scottie s Scooter Rental rents scooters for $35.00 and $0.30 per mile. a. Define the variables and write two functions to represent the situation. c. When is Plan B the better deal? b. Represent the two situations on the graph below. We can also help Brianna determine the best plan for herself without graphing. Consider our two equations again. We want to know when the total costs would be equal. Ø Set the two plans equal to each other and solve for the number of visits. Ø This method is called solving by. c. What is the rate of change of each line? What do they represent? d. What do the yy-intercepts of each line represent? 104
21 It s difficult to find the solution by looking at the graph. In such cases, it s better to use substitution to solve the problem. 4. Use the substitution method to help the renter determine when the two scooter rentals will cost the same amount. a. When will renting a scooter from Vespa Scooter Rental cost the same as renting a scooter from Scottie s Scooter Rental? BEAT THE TEST! 1. Lyle and Shaun open savings accounts at the same time. Lyle deposits $100 initially and adds $20 per week. Shaun deposits $500 initially and adds $10 per week. Lyle wants to know when he will have the same amount in his savings account as Shaun has. Part A: Write two equations to represent the amounts of money Lyle and Shaun have in their accounts. b. Describe a situation when renting from Vespa Scooter Rental would be a better deal than renting from Scottie s Scooter Rental. Part B: Which method would you use to solve the problem, substitution or graphing? Explain your answer. Part C: After how many weeks of making the additional deposits will Lyle have the same amount of money as Shaun has? Algebra Wall Want some help? You can always ask questions on the Algebra Wall and receive help from other students, teachers, and Study Experts. You can also help others on the Algebra Wall and earn Karma Points for doing so. Go to AlgebraNation.com to learn more and get started! 105
22 Section 4 Topic 7 Using Equivalent Systems of Equations An ordered pair that satisfies all equations in a system is called the to that system. If two systems of equations have the same solution, they are called systems. Let s explore how to write equivalent systems of equations. Consider the following system of equations: Equation A: xx + yy = 4 Equation B: xx yy = 6 The solution to this system is (5, 1). We can also see this when we graph the lines. Describe the result when we multiply either of the equations by some factor. Use this process to write an equivalent system. 106
23 Consider the original system of equations again. Equation A: xx + yy = 4 Equation B: xx yy = 6 What is the resulting equation when we add the two equations in the system together? What is the resulting equation when we subtract the second equation from the first equation? Graph the new equation on the same coordinate plane with our original system. Graph the new equation on the same coordinate plane with our original system. Algebraically, show that (5, 1) is also a solution to the difference of the two lines. Algebraically, show that (5, 1) is also a solution to the sum of the two lines. 107
24 Let s revisit the original system: Equation A: xx + yy = 4 Equation B: xx yy = 6 Graph Equation D on the same coordinate plane with our original system. Complete the following steps to show that replacing one equation by the sum of that equation and a multiple of the other equation produces a system with the same solutions. Create Equation C by multiplying Equation A by 2. Create Equation D by finding the sum of Equation B and Equation C. Algebraically, show that (5, 1) is a solution to the Equation D. 108
25 Let s Practice! 1. Consider the following system, which has a solution of (2, 5). MM, NN, PP, RR, SS, and TT are non-zero real numbers. Try It! MMMM + NNNN = PP RRRR + SSSS = TT Write two new equations that could be used to create an equivalent system of equations. 2. List three ways to write new equations that can be used to create equivalent systems. BEAT THE TEST! AAAA + BBBB = CC 1. The system has the solution (1, 3), where DDDD + EEEE = FF AA, BB, CC, DD, EE, and FF are non-zero real numbers. Select all the systems of equations with the same solution. AA DD xx + BB EE yy = CC FF DDDD + EEEE = FF (2AA + DD)xx + (2BB + EE)yy = CC + 2FF DDDD + EEEE = FF AAAA + BBBB = CC 3DDDD 3EEEE = 3FF AA 5DD xx + BB 5EE yy = CC 5FF DDDD + EEEE = FF AAAA + (BB + EE)yy = CC AA + DD xx + EEEE = CC + FF Algebra Wall Want some help? You can always ask questions on the Algebra Wall and receive help from other students, teachers, and Study Experts. You can also help others on the Algebra Wall and earn Karma Points for doing so. Go to AlgebraNation.com to learn more and get started! 109
26 Section 4 Topic 8 Finding Solution Sets to Systems of Equations Using Elimination Consider the following system of equations: 2xx + yy = 8 xx 2yy = 1 Write an equivalent system that will eliminate one of the variables when you add the equations. Let s Practice! 1. Ruxin and Andre were invited to a Super Bowl party. They were asked to bring pizzas and sodas. Ruxin brought three pizzas and four bottles of soda and spent $ Andre brought five pizzas and two bottles of soda and spent $ a. Write a system of equations to represent the situation. Determine the solution to the system of equations. b. Write an equivalent system that will eliminate one of the variables when you add the equations. Describe what the graph of the two systems would look like. This method of solving a system is called. c. Solve the system to determine the cost of one pizza and one bottle of soda. 110
27 Try It! BEAT THE TEST! 2. Jazmin and Justine went shopping for back to school clothes. Jazmin purchased three shirts and one pair of shorts and spent $ Justine bought four shirts and three pairs of shorts and spent $ Complete the following table. Solve by Elimination: 2xx 3yy = 8 3xx + 4yy = 46 a. Assuming all the shirts cost the same amount and all the shorts cost the same amount, write a system of equations to represent each girl s shopping spree. Operations Equations Labels 2xx 3yy = 8 3xx + 4yy = 46 Equation 1 Equation 2 6xx + 9yy = 24 New Equation 1 b. Use the elimination method to solve for the price of one pair of shorts. Multiply Equation 2 by 2. New Equation 2 6xx + 9yy = 24 6xx + 8yy = 92 17yy = 68 Divide by 17. Solve for xx. Write xx and yy as coordinates. (, ) Solution to the system 111
28 2. Which of the systems of equations below could not be used to solve the following system for xx and yy? A 6xx + 4yy = 24 2xx 4yy = 10 B 6xx + 4yy = 24 4xx + 8yy = 20 C 18xx + 12yy = 72 6xx + 12yy = 30 D 12xx + 8yy = 48 4xx + 8yy = 10 6xx + 4yy = 24 2xx + 4yy = 10 Section 4 Topic 9 Solution Sets to Inequalities with Two Variables Consider the following linear inequality. yy 2xx 1 Underline each ordered pair (xx, yy) that is a solution to the above inequality. (0, 5) (4, 1) ( 1, 1) (1, 1) (3, 0) ( 2, 3) (4, 3) ( 1, 3) Plot each solution as a point (xx, yy) in the coordinate plane. Algebra Wall Want some help? You can always ask questions on the Algebra Wall and receive help from other students, teachers, and Study Experts. You can also help others on the Algebra Wall and earn Karma Points for doing so. Go to AlgebraNation.com to learn more and get started! Graph the line yy = 2xx 1 in the same coordinate plane. What do you notice about the solutions to the inequality yy 2xx 1 and the graph of the line yy = 2xx 1? 112
29 Let s Practice! c. Graph the region of the solutions to the inequality. 1. The senior class is raising money for Grad Bash. The students parents are donating cakes. The students plan to sell entire cakes for $20.00 each and slices of cake for $3.00 each. If they need over $500.00, how many of each should they sell? a. List two possibilities for the number of whole cakes and cake slices students could sell to reach their goal of raising at least $ b. Write an inequality to represent the situation. d. What is the difference between the ordered pairs that fall on the line and the ones that fall in the shaded area? e. What does the xx-intercept represent? 113
30 Try It! c. Graph the region of the solutions to the inequality. 2. The freshman class wants to include at least 120 people in performances at a pep rally. Each skit will have 15 people, and each dance routine will feature 12 people. a. List two possible combinations of skits and dance routines. b. Write an inequality to represent the situation. d. What does the yy-intercept represent? 114
31 BEAT THE TEST! 1. Coach De Leon purchases sports equipment. Basketballs cost $20.00 each and soccer balls cost $18.00 each. He has a budget of $ The graph shown below represents the number of basketballs and soccer balls he can buy given his budget constraint. Part B: Determine whether these combinations of basketballs, bb, and soccer balls, ss, can be purchased within the budget. bb = 55 ss = 33 bb = 22 ss = 44 bb = 77 ss = 33 bb = 00 ss = 88 bb = 88 ss = 00 bb = 66 ss = 33 bb = 44 ss = 77 Yes No Part A: Write an inequality to represent the situation. Algebra Wall Want some help? You can always ask questions on the Algebra Wall and receive help from other students, teachers, and Study Experts. You can also help others on the Algebra Wall and earn Karma Points for doing so. Go to AlgebraNation.com to learn more and get started! 115
32 Section 4 Topic 10 Finding Solution Sets to Systems of Linear Inequalities Juan must purchase car insurance. He needs to earn at least $50.00 a week to cover the payments. The most he can work each week is 8 hours because of football practice. Juan can earn $10.00 per hour mowing yards and $12.00 per hour washing cars. The system 10xx + 12yy 50 xx + yy 8 Define the variables. represents Juan s situation. Let s Practice! 1. Bristol is having a party and has invited 24 friends. She plans to purchase sodas that cost $5.00 for a 12-pack and chips that cost $3.00 per bag. She wants each friend to have at least two sodas. Bristol s budget is $ a. Write a system of inequalities to represent the situation. b. Graph the region using boundary lines to show the solutions to the inequality. The graph below depicts Juan s situation. Interpret the graph and identify two different solutions. c. Name two different solutions for Bristol s situation. 116
33 Try It! 2. Anna is an avid reader. Her generous grandparents gave her money for her birthday, and she decided to spend at most $ on books. Reading Spot is running a special: all paperback books are $8.00 and hardback books are $ Anna wants to purchase at least 12 books. BEAT THE TEST! 1. Tatiana is reviewing for the Algebra 1 final exam. She made this graph representing a system of inequalities: a. Write a system of inequalities to represent the situation. b. Graph the region of the solutions to the inequality. Part A: Underline the ordered pairs below that represent solutions to the system of inequalities. ( 8, 3) ( 3, 8) 1, 9 4, 9 (9, 6) (0, 9) (5, 5) ( 5, 10) ( 9, 1) ( 2, 7) (1, 6) (0, 0) c. Name two different solutions for Anna s situation. Part B: Derive the system of inequalities that describes the region of the graph Tatiana drew. 117
34 2. Consider the system of inequalities below. 3yy 2xx yy xx + 12 THIS PAGE WAS INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK Which of the following points are in the solution set? Select all that apply. 4, 3 (1, 6) (2, 4) 5, 5 (3, 2) Test Yourself! Practice Tool Great job! You have reached the end of this section. Now it s time to try the Test Yourself! Practice Tool, where you can practice all the skills and concepts you learned in this section. Log in to Algebra Nation and try out the Test Yourself! Practice Tool so you can see how well you know these topics! 118
Section 4 Topic 1 Arithmetic Sequences
 Section 4 Topic 1 Arithmetic Sequences Let s look at the following sequence of numbers: 3, 8, 13, 18, 23,.... Ø Ø Ø The at the end means that this sequence goes on forever. 3, 8, 13, 18, and 23 are the
Section 4 Topic 1 Arithmetic Sequences Let s look at the following sequence of numbers: 3, 8, 13, 18, 23,.... Ø Ø Ø The at the end means that this sequence goes on forever. 3, 8, 13, 18, and 23 are the
Section 2: Equations and Inequalities
 Topic 1: Equations: True or False?... 29 Topic 2: Identifying Properties When Solving Equations... 31 Topic 3: Solving Equations... 34 Topic 4: Solving Equations Using the Zero Product Property... 36 Topic
Topic 1: Equations: True or False?... 29 Topic 2: Identifying Properties When Solving Equations... 31 Topic 3: Solving Equations... 34 Topic 4: Solving Equations Using the Zero Product Property... 36 Topic
Section 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions Part 1
 Section 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions Part 1 Topic 1: Real-World Examples of Quadratic Functions... 121 Topic 2: Factoring Quadratic Expressions... 125 Topic 3: Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring...
Section 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions Part 1 Topic 1: Real-World Examples of Quadratic Functions... 121 Topic 2: Factoring Quadratic Expressions... 125 Topic 3: Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring...
Section 3: Introduction to Functions
 Topic 1: Input and Output Values... 55 Topic 2: Representing, Naming, and Evaluating Functions... 58 Topic 3: Adding and Subtracting Functions... 60 Topic 4: Multiplying Functions... 62 Topic 5: Closure
Topic 1: Input and Output Values... 55 Topic 2: Representing, Naming, and Evaluating Functions... 58 Topic 3: Adding and Subtracting Functions... 60 Topic 4: Multiplying Functions... 62 Topic 5: Closure
5 1 Worksheet MATCHING: For # 1 4, match each graph to its equation. Not all equations will be used. 1) 2) 3) 4)
 Algebra 1 Name: Per: 5 1 Worksheet MATCHING: For # 1 4, match each graph to its equation. Not all equations will be used. 1) 2) 3) 4) A) yy = xx 3 B) yy = xx + 3 C) yy = 1 2 xx 3 D) yy = xx 3 E) yy = 2
Algebra 1 Name: Per: 5 1 Worksheet MATCHING: For # 1 4, match each graph to its equation. Not all equations will be used. 1) 2) 3) 4) A) yy = xx 3 B) yy = xx + 3 C) yy = 1 2 xx 3 D) yy = xx 3 E) yy = 2
Name Period Date DRAFT
 Name Period Date Equations and Inequalities Student Packet 4: Inequalities EQ4.1 EQ4.2 EQ4.3 Linear Inequalities in One Variable Add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers. Write expressions, equations,
Name Period Date Equations and Inequalities Student Packet 4: Inequalities EQ4.1 EQ4.2 EQ4.3 Linear Inequalities in One Variable Add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers. Write expressions, equations,
Section 2 Topic 1 Equations: True or False?
 Section 2: Equations and Inequalities Section 2 Topic 1 Equations: True or False? Consider the statement 4 + 5 = 2 + 7. This is a mathematically correct sentence. Is the sentence true or false? True Consider
Section 2: Equations and Inequalities Section 2 Topic 1 Equations: True or False? Consider the statement 4 + 5 = 2 + 7. This is a mathematically correct sentence. Is the sentence true or false? True Consider
Section 8 Topic 1 Comparing Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Functions Part 1
 Section 8: Summary of Functions Section 8 Topic 1 Comparing Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Functions Part 1 Complete the table below to describe the characteristics of linear functions. Linear Functions
Section 8: Summary of Functions Section 8 Topic 1 Comparing Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Functions Part 1 Complete the table below to describe the characteristics of linear functions. Linear Functions
Section 2 Equations and Inequalities
 Section 2 Equations and Inequalities The following Mathematics Florida Standards will be covered in this section: MAFS.912.A-SSE.1.2 Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. MAFS.912.A-REI.1.1
Section 2 Equations and Inequalities The following Mathematics Florida Standards will be covered in this section: MAFS.912.A-SSE.1.2 Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. MAFS.912.A-REI.1.1
Inequalities Chapter Test
 Inequalities Chapter Test Part 1: For questions 1-9, circle the answer that best answers the question. 1. Which graph best represents the solution of 8 4x < 4 A. B. C. D. 2. Which of the following inequalities
Inequalities Chapter Test Part 1: For questions 1-9, circle the answer that best answers the question. 1. Which graph best represents the solution of 8 4x < 4 A. B. C. D. 2. Which of the following inequalities
Section 2.2 Objectives
 Section 2.2 Objectives Solve multi-step equations using algebra properties of equality. Solve equations that have no solution and equations that have infinitely many solutions. Solve equations with rational
Section 2.2 Objectives Solve multi-step equations using algebra properties of equality. Solve equations that have no solution and equations that have infinitely many solutions. Solve equations with rational
ALGEBRA 1 SEMESTER 1 INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS Courses: Algebra 1 S1 (#2201) and Foundations in Algebra 1 S1 (#7769)
 Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Ramal goes to the grocery store and buys pounds of apples and pounds of bananas. Apples cost dollars per
Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Ramal goes to the grocery store and buys pounds of apples and pounds of bananas. Apples cost dollars per
Algebra I Practice Exam
 Algebra I This practice assessment represents selected TEKS student expectations for each reporting category. These questions do not represent all the student expectations eligible for assessment. Copyright
Algebra I This practice assessment represents selected TEKS student expectations for each reporting category. These questions do not represent all the student expectations eligible for assessment. Copyright
Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie. Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks
 Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by
Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by
UNIT 5 INEQUALITIES CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher:
 UNIT 5 INEQUALITIES 2015-2016 CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Topic(s) Page(s) Unit 5 Vocabulary 2 Writing and Graphing Inequalities 3 8 Solving One-Step Inequalities 9 15 Solving Multi-Step Inequalities
UNIT 5 INEQUALITIES 2015-2016 CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Topic(s) Page(s) Unit 5 Vocabulary 2 Writing and Graphing Inequalities 3 8 Solving One-Step Inequalities 9 15 Solving Multi-Step Inequalities
Foundations of Math. Chapter 3 Packet. Table of Contents
 Foundations of Math Chapter 3 Packet Name: Table of Contents Notes #43 Solving Systems by Graphing Pg. 1-4 Notes #44 Solving Systems by Substitution Pg. 5-6 Notes #45 Solving by Graphing & Substitution
Foundations of Math Chapter 3 Packet Name: Table of Contents Notes #43 Solving Systems by Graphing Pg. 1-4 Notes #44 Solving Systems by Substitution Pg. 5-6 Notes #45 Solving by Graphing & Substitution
SOLVING LINEAR INEQUALITIES
 Topic 15: Solving linear inequalities 65 SOLVING LINEAR INEQUALITIES Lesson 15.1 Inequalities on the number line 15.1 OPENER Consider the inequality x > 7. 1. List five numbers that make the inequality
Topic 15: Solving linear inequalities 65 SOLVING LINEAR INEQUALITIES Lesson 15.1 Inequalities on the number line 15.1 OPENER Consider the inequality x > 7. 1. List five numbers that make the inequality
Section 3 Topic 1 Input and Output Values
 Section 3: Introduction to Functions Section 3 Topic 1 Input and Output Values A function is a relationship between input and output. Ø Ø Domain is the set of values of x used for the input of the function.
Section 3: Introduction to Functions Section 3 Topic 1 Input and Output Values A function is a relationship between input and output. Ø Ø Domain is the set of values of x used for the input of the function.
June Dear Future Algebra 2 Trig Student,
 June 016 Dear Future Algebra Trig Student, Welcome to Algebra /Trig! Since we have so very many topics to cover during our 016-17 school year, it is important that each one of you is able to complete these
June 016 Dear Future Algebra Trig Student, Welcome to Algebra /Trig! Since we have so very many topics to cover during our 016-17 school year, it is important that each one of you is able to complete these
Simple Inequalities Involving Addition and Subtraction. Unit 3 Inequalities.notebook. November 18, Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Simple Inequalities Addition/Subtraction Simple Inequalities Multiplication/Division Two-Step and Multiple-Step Inequalities Solving Compound Inequalities Special Cases of Compound Inequalities
Table of Contents Simple Inequalities Addition/Subtraction Simple Inequalities Multiplication/Division Two-Step and Multiple-Step Inequalities Solving Compound Inequalities Special Cases of Compound Inequalities
Sample: Do Not Reproduce LF6 STUDENT PAGES LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS. Name Period Date
 Name Period Date LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LF6.1 LF6.2 LF6.3 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Understand the definition of a system of linear equations Understand
Name Period Date LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LF6.1 LF6.2 LF6.3 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Understand the definition of a system of linear equations Understand
Final Exam Study Guide
 Algebra 2 Alei - Desert Academy 2011-12 Name: Date: Block: Final Exam Study Guide 1. Which of the properties of real numbers is illustrated below? a + b = b + a 2. Convert 6 yards to inches. 3. How long
Algebra 2 Alei - Desert Academy 2011-12 Name: Date: Block: Final Exam Study Guide 1. Which of the properties of real numbers is illustrated below? a + b = b + a 2. Convert 6 yards to inches. 3. How long
Section 1: Expressions
 Topic 1: Using Expressions to Represent Real-World Situations... 3 Topic 2: Understanding Polynomial Expressions... 6 Topic 3: Algebraic Expressions Using the Distributive Property... 9 Topic 4: Algebraic
Topic 1: Using Expressions to Represent Real-World Situations... 3 Topic 2: Understanding Polynomial Expressions... 6 Topic 3: Algebraic Expressions Using the Distributive Property... 9 Topic 4: Algebraic
Algebra 1 PAP Fall Exam Review
 Name: Pd: 2016-2017 Algebra 1 PAP Fall Exam Review 1. A collection of nickels and quarters has a value of $7.30. The value of the quarters is $0.80 less than triple the value of the nickels. Which system
Name: Pd: 2016-2017 Algebra 1 PAP Fall Exam Review 1. A collection of nickels and quarters has a value of $7.30. The value of the quarters is $0.80 less than triple the value of the nickels. Which system
3.1 NOTES Solving Systems of Linear Equations Graphically
 3.1 NOTES Solving Systems of Linear Equations Graphically A system of two linear equations in two variables x and y consist of two equations of the following form: Ax + By = C Equation 1 Dx + Ey = F Equation
3.1 NOTES Solving Systems of Linear Equations Graphically A system of two linear equations in two variables x and y consist of two equations of the following form: Ax + By = C Equation 1 Dx + Ey = F Equation
Math Class: Algebra I. Summer Review Packet DUE DATE:
 Name: 2014-15 Math Class: Algebra I Summer Review Packet DUE DATE: About Algebra I Algebra I teaches students to think, reason, and communicate mathematically. Students use variables to determine solutions
Name: 2014-15 Math Class: Algebra I Summer Review Packet DUE DATE: About Algebra I Algebra I teaches students to think, reason, and communicate mathematically. Students use variables to determine solutions
Math 3 Unit 4: Rational Functions
 Math Unit : Rational Functions Unit Title Standards. Equivalent Rational Expressions A.APR.6. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions A.APR.7. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions A.APR.7.
Math Unit : Rational Functions Unit Title Standards. Equivalent Rational Expressions A.APR.6. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions A.APR.7. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions A.APR.7.
Algebra I. Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities. Slide 1 / 179. Slide 2 / 179. Slide 3 / 179. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 179 Algebra I Slide 2 / 179 Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities 2015-04-23 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 179 Click on the topic to go to that section 8th Grade Review of
Slide 1 / 179 Algebra I Slide 2 / 179 Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities 2015-04-23 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 179 Click on the topic to go to that section 8th Grade Review of
Name Algebra 1 Midterm Review Period. = 10 4x e) x ) Solve for y: a) 6x 3y = 12 b) 4y 8x = 16
 Name Algebra 1 Date Midterm Review Period 1) Solve each equation: a) x 2x + 2 = 3 b) 5 5 + 9 = 13 c) 64 = 9x +1 d) x 7 2 = 10 4x e) x + 2 3 = 3x 2) Solve for y: a) 6x 3y = 12 b) 4y 8x = 16 3) Solve and
Name Algebra 1 Date Midterm Review Period 1) Solve each equation: a) x 2x + 2 = 3 b) 5 5 + 9 = 13 c) 64 = 9x +1 d) x 7 2 = 10 4x e) x + 2 3 = 3x 2) Solve for y: a) 6x 3y = 12 b) 4y 8x = 16 3) Solve and
Name: Systems 2.1. Ready Topic: Determine if given value is a solution and solve systems of equations
 Name: Systems 2.1 Ready, Set, Go! Ready Topic: Determine if given value is a solution and solve systems of equations TE-16 1. Graph both equations on the same axes. Then determine which ordered pair is
Name: Systems 2.1 Ready, Set, Go! Ready Topic: Determine if given value is a solution and solve systems of equations TE-16 1. Graph both equations on the same axes. Then determine which ordered pair is
Part 1 will be selected response. Each selected response item will have 3 or 4 choices.
 Items on this review are grouped by Unit and Topic. A calculator is permitted on the Algebra 1 A Semester Exam. The Algebra 1 A Semester Exam will consist of two parts. Part 1 will be selected response.
Items on this review are grouped by Unit and Topic. A calculator is permitted on the Algebra 1 A Semester Exam. The Algebra 1 A Semester Exam will consist of two parts. Part 1 will be selected response.
Algebra I Solving & Graphing Inequalities
 Slide 1 / 182 Slide 2 / 182 Algebra I Solving & Graphing Inequalities 2016-01-11 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 182 Table of Contents Simple Inequalities Addition/Subtraction click on the topic to go to that
Slide 1 / 182 Slide 2 / 182 Algebra I Solving & Graphing Inequalities 2016-01-11 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 182 Table of Contents Simple Inequalities Addition/Subtraction click on the topic to go to that
Practice Ace Problems
 Unit 5: Moving Straight Ahead Investigation 3: Solving Equations using tables and Graphs Practice Ace Problems Directions: Please complete the necessary problems to earn a maximum of 16 points according
Unit 5: Moving Straight Ahead Investigation 3: Solving Equations using tables and Graphs Practice Ace Problems Directions: Please complete the necessary problems to earn a maximum of 16 points according
Lesson 1: Writing Equations Using Symbols
 Lesson 1 Lesson 1: Writing Equations Using Symbols Classwork Exercises Write each of the following statements using symbolic language. 1. The sum of four consecutive even integers is 28. 2. A number is
Lesson 1 Lesson 1: Writing Equations Using Symbols Classwork Exercises Write each of the following statements using symbolic language. 1. The sum of four consecutive even integers is 28. 2. A number is
UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES. Solving Equations and Inequalities in One Variable
 UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES This unit investigates linear equations and inequalities. Students create linear equations and inequalities and use them to solve problems. They
UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES This unit investigates linear equations and inequalities. Students create linear equations and inequalities and use them to solve problems. They
Equations and Inequalities in One Variable
 Name Date lass Equations and Inequalities in One Variable. Which of the following is ( r ) 5 + + s evaluated for r = 8 and s =? A 3 B 50 58. Solve 3x 9= for x. A B 7 3. What is the best first step for
Name Date lass Equations and Inequalities in One Variable. Which of the following is ( r ) 5 + + s evaluated for r = 8 and s =? A 3 B 50 58. Solve 3x 9= for x. A B 7 3. What is the best first step for
Define the word inequality
 Warm Up: Define the word inequality Agenda: Objective- Students can solve linear inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. Define Inequalities One & Two
Warm Up: Define the word inequality Agenda: Objective- Students can solve linear inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. Define Inequalities One & Two
4. Based on the table below, what is the joint relative frequency of the people surveyed who do not have a job and have a savings account?
 Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 Common Semester 1 Final Review 1. How many surveyed do not like PS4 and do not like X-Box? 2. What percent of people surveyed like the X-Box, but not the PS4? 3. What is the
Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 Common Semester 1 Final Review 1. How many surveyed do not like PS4 and do not like X-Box? 2. What percent of people surveyed like the X-Box, but not the PS4? 3. What is the
4. Based on the table below, what is the joint relative frequency of the people surveyed who do not have a job and have a savings account?
 Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 Common Semester 1 Final Review Like PS4 1. How many surveyed do not like PS4 and do not like X-Box? 2. What percent of people surveyed like the X-Box, but not the PS4? 3.
Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 Common Semester 1 Final Review Like PS4 1. How many surveyed do not like PS4 and do not like X-Box? 2. What percent of people surveyed like the X-Box, but not the PS4? 3.
Week of December 11 th to December 15 th, nd 9 weeks Algebra 1 (Periods 1, 2, 3)
 Week of December 11 th to December 15 th, 2017 2 nd 9 weeks 12/11 Review for Midterm Exam Chapters 1-6 12/12 Review for Midterm Exam Chapters 1-6 Exam Review Chapters 1-6 Exam Review Chapters 1-6 12/13
Week of December 11 th to December 15 th, 2017 2 nd 9 weeks 12/11 Review for Midterm Exam Chapters 1-6 12/12 Review for Midterm Exam Chapters 1-6 Exam Review Chapters 1-6 Exam Review Chapters 1-6 12/13
Systems of Equations Unit Five ONE NONE INFINITE
 Systems of Equations Unit Five ONE NONE INFINITE Standards: 8.EE.8 Analyze and solve pairs of simultaneous linear equations. a. Understand that solutions to a system of two linear equations in two variables
Systems of Equations Unit Five ONE NONE INFINITE Standards: 8.EE.8 Analyze and solve pairs of simultaneous linear equations. a. Understand that solutions to a system of two linear equations in two variables
MATH NATION Algebra Scope and Sequence TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: EXPRESSIONS... 2 SECTION 2: EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES... 4 SECTION 3: INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONS... 7 SECTION 4: LINEAR EQUATIONS, FUNCTIONS, AND INEQUALITIES... 10 SECTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: EXPRESSIONS... 2 SECTION 2: EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES... 4 SECTION 3: INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONS... 7 SECTION 4: LINEAR EQUATIONS, FUNCTIONS, AND INEQUALITIES... 10 SECTION
Practice EOC Questions
 Practice EOC Questions 1 One of the events at a high school track meet is the pole vault. The pole vaulter runs toward the crossbar and uses a pole to attempt to vault over the bar. Josh collects data
Practice EOC Questions 1 One of the events at a high school track meet is the pole vault. The pole vaulter runs toward the crossbar and uses a pole to attempt to vault over the bar. Josh collects data
Section 2.3 Objectives
 Section 2.3 Objectives Use the inequality symbols to compare two numbers. Determine if a given value is a solution of an inequality. Solve simple inequalities. Graph the solutions to inequalities on the
Section 2.3 Objectives Use the inequality symbols to compare two numbers. Determine if a given value is a solution of an inequality. Solve simple inequalities. Graph the solutions to inequalities on the
Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming
 Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to solve linear equations students should be able to graph linear equations students should be able to create linear equations
Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to solve linear equations students should be able to graph linear equations students should be able to create linear equations
4. The table shows the number of toll booths driven through compared to the cost of using a Toll Tag.
 ALGEBRA 1 Fall 2016 Semester Exam Review Name 1. According to the data shown below, which would be the best prediction of the average cost of a -bedroom house in Georgetown in the year 2018? Year Average
ALGEBRA 1 Fall 2016 Semester Exam Review Name 1. According to the data shown below, which would be the best prediction of the average cost of a -bedroom house in Georgetown in the year 2018? Year Average
California Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Standards Map Algebra I
 A Correlation of Pearson CME Project Algebra 1 Common Core 2013 to the California Common Core State s for Mathematics s Map Algebra I California Common Core State s for Mathematics s Map Algebra I Indicates
A Correlation of Pearson CME Project Algebra 1 Common Core 2013 to the California Common Core State s for Mathematics s Map Algebra I California Common Core State s for Mathematics s Map Algebra I Indicates
Algebra I Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN)
 Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN) Use properties of rational and irrational numbers N-RN.3 Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational; that the sum of a rational
Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN) Use properties of rational and irrational numbers N-RN.3 Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational; that the sum of a rational
Mathematics I Resources for EOC Remediation
 Mathematics I Resources for EOC Remediation CED Creating Equations Cluster: HSA CED.A.1 HSA CED.A.2 HSA CED.A.3 HSA CED.A.4 The information in this document is intended to demonstrate the depth and rigor
Mathematics I Resources for EOC Remediation CED Creating Equations Cluster: HSA CED.A.1 HSA CED.A.2 HSA CED.A.3 HSA CED.A.4 The information in this document is intended to demonstrate the depth and rigor
Dublin City Schools Mathematics Graded Course of Study Algebra I Philosophy
 Philosophy The Dublin City Schools Mathematics Program is designed to set clear and consistent expectations in order to help support children with the development of mathematical understanding. We believe
Philosophy The Dublin City Schools Mathematics Program is designed to set clear and consistent expectations in order to help support children with the development of mathematical understanding. We believe
CCGPS Coordinate Algebra. EOCT Review Units 1 and 2
 CCGPS Coordinate Algebra EOCT Review Units 1 and 2 Unit 1: Relationships Among Quantities Key Ideas Unit Conversions A quantity is a an exact amount or measurement. A quantity can be exact or approximate
CCGPS Coordinate Algebra EOCT Review Units 1 and 2 Unit 1: Relationships Among Quantities Key Ideas Unit Conversions A quantity is a an exact amount or measurement. A quantity can be exact or approximate
ALGEBRA 1 UNIT 3 WORKBOOK CHAPTER 6
 ALGEBRA 1 UNIT 3 WORKBOOK CHAPTER 6 FALL 2014 0 1 Algebra 1 Section 6.1 Notes: Graphing Systems of Equations System of Equations: a set of two or more equations with the same variables, graphed in the
ALGEBRA 1 UNIT 3 WORKBOOK CHAPTER 6 FALL 2014 0 1 Algebra 1 Section 6.1 Notes: Graphing Systems of Equations System of Equations: a set of two or more equations with the same variables, graphed in the
Complete Week 18 Package
 Complete Week 18 Package Jeanette Stein Table of Contents Unit 4 Pacing Chart -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Day 86 Bellringer --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Complete Week 18 Package Jeanette Stein Table of Contents Unit 4 Pacing Chart -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Day 86 Bellringer --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sequenced Units for Arizona s College and Career Ready Standards MA35 Personal Finance Year at a Glance
 Unit 1: Prepare a Budget (20 days) Unit 2: Employment Basics (15 days) Unit 3: Modeling a Business (20 days) Unit 4: Banking Services (15 days) Unit 5: Consumer Credit (15 days) Unit 6: Automobile Ownership
Unit 1: Prepare a Budget (20 days) Unit 2: Employment Basics (15 days) Unit 3: Modeling a Business (20 days) Unit 4: Banking Services (15 days) Unit 5: Consumer Credit (15 days) Unit 6: Automobile Ownership
HW A) SWBAT identify the properties of operations Create flashcards or a some type of foldable that shows the following properties of operations
 HW A) SWBAT identify the properties of operations Create flashcards or a some type of foldable that shows the following properties of operations including examples: HW B) SWBAT apply properties of operations
HW A) SWBAT identify the properties of operations Create flashcards or a some type of foldable that shows the following properties of operations including examples: HW B) SWBAT apply properties of operations
Algebra I Sample Unit Outline
 Algebra I Sample Unit Outline Organizing Theme Topic Unit 1: Intro. to Topic 2 Topic 3 Topic 4 Topic 5 Topic 6 Topic 7 Topic 8 Topic 9 Build functions that model situations Unit 1: Intro. to Data- Summarize,
Algebra I Sample Unit Outline Organizing Theme Topic Unit 1: Intro. to Topic 2 Topic 3 Topic 4 Topic 5 Topic 6 Topic 7 Topic 8 Topic 9 Build functions that model situations Unit 1: Intro. to Data- Summarize,
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES. ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra I Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra I Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
FSA Algebra I End-of-Course Review Packet. Algebra and Modeling
 FSA Algebra I End-of-Course Review Packet Algebra and Modeling Table of Contents MAFS.912.A-APR.1.1 EOC Practice... 3 MAFS.912.A-CE1.1 EOC Practice... 5 MAFS.912.A-REI.2.3 EOC Practice... 7 MAFS.912.A-CE1.4
FSA Algebra I End-of-Course Review Packet Algebra and Modeling Table of Contents MAFS.912.A-APR.1.1 EOC Practice... 3 MAFS.912.A-CE1.1 EOC Practice... 5 MAFS.912.A-REI.2.3 EOC Practice... 7 MAFS.912.A-CE1.4
Algebra I Notes Linear Inequalities in One Variable and Unit 3 Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
 PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students must have a clear understanding of signed numbers and their operations students must understand meaning of operations and how they relate to one another students must be able
PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students must have a clear understanding of signed numbers and their operations students must understand meaning of operations and how they relate to one another students must be able
GSE Algebra 1. Unit Two Information. Curriculum Map: Reasoning with Linear Equations & Inequalities
 GSE Algebra 1 Unit Two Information EOCT Domain & Weight: Equations 30% Curriculum Map: Reasoning with Linear Equations & Inequalities Content Descriptors: Concept 1: Create equations that describe numbers
GSE Algebra 1 Unit Two Information EOCT Domain & Weight: Equations 30% Curriculum Map: Reasoning with Linear Equations & Inequalities Content Descriptors: Concept 1: Create equations that describe numbers
7 = 8 (Type a simplified fraction.)
 Student: Date: Assignment: Exponential and Radical Equations 1. Perform the indicated computation. Write the answer in scientific notation. 3. 10 6 10. 3. 4. 3. 10 6 10 = (Use the multiplication symbol
Student: Date: Assignment: Exponential and Radical Equations 1. Perform the indicated computation. Write the answer in scientific notation. 3. 10 6 10. 3. 4. 3. 10 6 10 = (Use the multiplication symbol
Algebra I. Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities. 8th Grade Review. Slide 1 / 179 Slide 2 / 179. Slide 4 / 179. Slide 3 / 179.
 Slide 1 / 179 Slide 2 / 179 lgebra I Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities 2015-04-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 179 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section 8th Grade Review of Systems
Slide 1 / 179 Slide 2 / 179 lgebra I Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities 2015-04-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 179 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section 8th Grade Review of Systems
Chapter 4: Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 4: Systems of Equations and Inequalities 4.1 Systems of Equations A system of two linear equations in two variables x and y consist of two equations of the following form: Equation 1: ax + by =
Chapter 4: Systems of Equations and Inequalities 4.1 Systems of Equations A system of two linear equations in two variables x and y consist of two equations of the following form: Equation 1: ax + by =
Mathematics Standards for High School Algebra I
 Mathematics Standards for High School Algebra I Algebra I is a course required for graduation and course is aligned with the College and Career Ready Standards for Mathematics in High School. Throughout
Mathematics Standards for High School Algebra I Algebra I is a course required for graduation and course is aligned with the College and Career Ready Standards for Mathematics in High School. Throughout
ALGEBRA I SEMESTER EXAMS PRACTICE MATERIALS SEMESTER Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm. A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = cm 2. 6.
 1. Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = 57.66 cm 2 6.2 cm A rectangle s sides are measured to be 6.2 cm and 9.3 cm. What is the rectangle s area rounded to the correct number of significant
1. Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = 57.66 cm 2 6.2 cm A rectangle s sides are measured to be 6.2 cm and 9.3 cm. What is the rectangle s area rounded to the correct number of significant
Unit 5 SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS
 MATH 8 Unit 5 SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS By the end of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Solve simultaneous linear equations by graphing. 2. Understand what it means to solve a system of equations.
MATH 8 Unit 5 SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS By the end of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Solve simultaneous linear equations by graphing. 2. Understand what it means to solve a system of equations.
Unit 5. Linear equations and inequalities OUTLINE. Topic 13: Solving linear equations. Topic 14: Problem solving with slope triangles
 Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Algebra Performance Level Descriptors
 Limited A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for Algebra. A student at this level has an emerging ability to A student whose performance
Limited A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for Algebra. A student at this level has an emerging ability to A student whose performance
Algebra 1 Fall Review
 Name Algebra 1 Fall Review 2013-2014 Date 1. Write an inequality to best represent the graph shown at right. (A.1.D.) m: b: inequality: 2. Write an inequality to best describe the graph shown at right.
Name Algebra 1 Fall Review 2013-2014 Date 1. Write an inequality to best represent the graph shown at right. (A.1.D.) m: b: inequality: 2. Write an inequality to best describe the graph shown at right.
Algebra I Final Study Guide
 2011-2012 Algebra I Final Study Guide Short Answer Source: www.cityoforlando.net/public_works/stormwater/rain/rainfall.htm 1. For which one month period was the rate of change in rainfall amounts in Orlando
2011-2012 Algebra I Final Study Guide Short Answer Source: www.cityoforlando.net/public_works/stormwater/rain/rainfall.htm 1. For which one month period was the rate of change in rainfall amounts in Orlando
Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations. Unit Calendar
 Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations Unit Calendar Date Topic Homework Nov 5 (A ) 6.1 Solving Linear Inequalities +/- 6.2 Solving Linear Inequalities x/ 6.3 Solving
Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations Unit Calendar Date Topic Homework Nov 5 (A ) 6.1 Solving Linear Inequalities +/- 6.2 Solving Linear Inequalities x/ 6.3 Solving
High School Algebra I Scope and Sequence by Timothy D. Kanold
 High School Algebra I Scope and Sequence by Timothy D. Kanold First Semester 77 Instructional days Unit 1: Understanding Quantities and Expressions (10 Instructional days) N-Q Quantities Reason quantitatively
High School Algebra I Scope and Sequence by Timothy D. Kanold First Semester 77 Instructional days Unit 1: Understanding Quantities and Expressions (10 Instructional days) N-Q Quantities Reason quantitatively
Midterm: Wednesday, January 23 rd at 8AM Midterm Review
 Name: Algebra 1 CC Period: Midterm: Wednesday, January 23 rd at 8AM Midterm Review Unit 1: Building Blocks of Algebra Number Properties (Distributive, Commutative, Associative, Additive, Multiplicative)
Name: Algebra 1 CC Period: Midterm: Wednesday, January 23 rd at 8AM Midterm Review Unit 1: Building Blocks of Algebra Number Properties (Distributive, Commutative, Associative, Additive, Multiplicative)
Eureka Math. Grade 8, Module 4. Student File_B. Contains Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials
 A Story of Ratios Eureka Math Grade 8, Module 4 Student File_B Contains, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may be reproduced,
A Story of Ratios Eureka Math Grade 8, Module 4 Student File_B Contains, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may be reproduced,
4) Solve for this system using your graphing
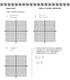 Algebra Unit 5 HW Day 1 SOLVING GRAPHICALLY Graph the following systems: 1) x 2y 12 y 2x 6 2) y x 2 6x 2y 10 ) x y 9 4) Solve for this system using your graphing x calculator. [You will still need to put
Algebra Unit 5 HW Day 1 SOLVING GRAPHICALLY Graph the following systems: 1) x 2y 12 y 2x 6 2) y x 2 6x 2y 10 ) x y 9 4) Solve for this system using your graphing x calculator. [You will still need to put
Unit 5. Linear equations and inequalities OUTLINE. Topic 13: Solving linear equations. Topic 14: Problem solving with slope triangles
 Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Lesson 1: Successive Differences in Polynomials
 Lesson 1 Lesson 1: Successive Differences in Polynomials Classwork Opening Exercise John noticed patterns in the arrangement of numbers in the table below. 2.4 3.4 4.4 5.4 6.4 5.76 11.56 19.36 29.16 40.96
Lesson 1 Lesson 1: Successive Differences in Polynomials Classwork Opening Exercise John noticed patterns in the arrangement of numbers in the table below. 2.4 3.4 4.4 5.4 6.4 5.76 11.56 19.36 29.16 40.96
The Keystones of Algebra 1
 The Keystones of Algebra 1 The Top Ten Keystones of Algebra 1 You should be able to 1) Simplify a radical expression. 2) Solve an equation. 3) Solve and graph an inequality on a number line. 4) Manipulate
The Keystones of Algebra 1 The Top Ten Keystones of Algebra 1 You should be able to 1) Simplify a radical expression. 2) Solve an equation. 3) Solve and graph an inequality on a number line. 4) Manipulate
Unit 2 Linear Functions and Systems of Linear Functions Algebra 1
 Number of Days: MS 44 10/16/17 12/22/17 HS 44 10/16/17 12/22/17 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Unit 2 builds upon students prior knowledge of linear models. Students learn function notation and develop
Number of Days: MS 44 10/16/17 12/22/17 HS 44 10/16/17 12/22/17 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Unit 2 builds upon students prior knowledge of linear models. Students learn function notation and develop
INEQUALITIES Modeling Linear Inequalities Common Core Standards
 F Inequalities, Lesson 3, Modeling Linear Inequalities (r. 2018) INEQUALITIES Modeling Linear Inequalities Common Core Standards A-CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to
F Inequalities, Lesson 3, Modeling Linear Inequalities (r. 2018) INEQUALITIES Modeling Linear Inequalities Common Core Standards A-CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to
The steps in Raya s solution to 2.5 (6.25x + 0.5) = 11 are shown. Select the correct reason for line 4 of Raya s solution.
 A.CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear functions. Unit 2: Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities The perimeter
A.CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear functions. Unit 2: Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities The perimeter
Unit Test Linear equations and Inequalities
 Unit Test Linear equations and Inequalities Name: Date: Directions: Select the best answer for the following questions. (2 points each) 7L 1. The steps for solving are: 1) Read the problem and label variables,
Unit Test Linear equations and Inequalities Name: Date: Directions: Select the best answer for the following questions. (2 points each) 7L 1. The steps for solving are: 1) Read the problem and label variables,
Name Class Date. Determine whether each number is a solution of the given inequality.
 3-1 Practice Form G Inequalities and Their Graphs Write an inequality that represents each verbal expression. 1. v is greater 10. 2. b is less than or equal to 1. 3. the product of g and 2 is less than
3-1 Practice Form G Inequalities and Their Graphs Write an inequality that represents each verbal expression. 1. v is greater 10. 2. b is less than or equal to 1. 3. the product of g and 2 is less than
Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation
 Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation Algebraically 2( x 3) = 12 Graphically 2( x 3) = 12 2. Solve the following equations algebraically a. 5w 15 2w = 2(w 5) b. 1
Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation Algebraically 2( x 3) = 12 Graphically 2( x 3) = 12 2. Solve the following equations algebraically a. 5w 15 2w = 2(w 5) b. 1
Midterm Review Fall 2018
 Midterm Review Fall 018 Topics List: Unit 1 Simplifying Expressions Evaluating Linear Equations Dimensional Analysis Consecutive Number Equations Linear Equation Word Problems Representing Linear Equations
Midterm Review Fall 018 Topics List: Unit 1 Simplifying Expressions Evaluating Linear Equations Dimensional Analysis Consecutive Number Equations Linear Equation Word Problems Representing Linear Equations
Algebra 1 S1 (#2201) Foundations in Algebra 1 S1 (#7769)
 Instructional Materials for WCSD Math Common Finals The Instructional Materials are for student and teacher use and are aligned to the Course Guides for the following courses: Algebra 1 S1 (#2201) Foundations
Instructional Materials for WCSD Math Common Finals The Instructional Materials are for student and teacher use and are aligned to the Course Guides for the following courses: Algebra 1 S1 (#2201) Foundations
Name: 2016 Algebra 1 Final Exam Review-GL Period:
 Name: 06 Algebra Final Exam Review-GL Period:. A regular polygon s perimeter is a multiple of the side length. For a square, the relationship between the perimeter, p, and the side length, s, is described
Name: 06 Algebra Final Exam Review-GL Period:. A regular polygon s perimeter is a multiple of the side length. For a square, the relationship between the perimeter, p, and the side length, s, is described
Transition to College Math and Statistics
 Transition to College Math and Statistics Summer Work 016 due date: third day of class estimated time: 10 hours (for planning purposes only; work until you finish) Dear College Algebra Students, This assignment
Transition to College Math and Statistics Summer Work 016 due date: third day of class estimated time: 10 hours (for planning purposes only; work until you finish) Dear College Algebra Students, This assignment
Name. Check with teacher. equation: a. Can you find. a. (-2, -3) b. (1, 3) c. (2, 5) d. (-2, -6) a. (-2, 6) b. (-1, 1) c. (1, 3) d. (0, 0) Explain why
 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations: Graphing Name Part I - Warm Up with ONE EQUATION: a. Which of the following is a solution to the equation: y 3x 1? a. (-2, -3) b. (1, 3) c. (2, 5) d. (-2, -6) Partt II
7.1 Solving Systems of Equations: Graphing Name Part I - Warm Up with ONE EQUATION: a. Which of the following is a solution to the equation: y 3x 1? a. (-2, -3) b. (1, 3) c. (2, 5) d. (-2, -6) Partt II
8 th Grade Domain 2: Algebra and Functions (40%) Sara
 8 th Grade Domain 2: Algebra and Functions (40%) 1. Tara creates a budget for her weekly expenses. The graph shows how much money is in the account at different times. Find the slope of the line and tell
8 th Grade Domain 2: Algebra and Functions (40%) 1. Tara creates a budget for her weekly expenses. The graph shows how much money is in the account at different times. Find the slope of the line and tell
Moving Straight Ahead - Unit Test Review Sheet
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Moving Straight Ahead - Unit Test Review Sheet Short Answer 1. Use the graph at the right. a. Find the slope of the line. b. Find the equation of the line. 2. Does the table below
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Moving Straight Ahead - Unit Test Review Sheet Short Answer 1. Use the graph at the right. a. Find the slope of the line. b. Find the equation of the line. 2. Does the table below
Throughout Algebra I, students should continue to develop proficiency with the Common Core's eight Standards for Mathematical Practice:
 In the three years prior to Algebra I, students have already begun their study of algebraic concepts. They have investigated variables and expressions, solved equations, constructed and analyzed tables,
In the three years prior to Algebra I, students have already begun their study of algebraic concepts. They have investigated variables and expressions, solved equations, constructed and analyzed tables,
ALGEBRA I Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN)
 Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN) Use properties of rational and irrational numbers Additional N-RN.3 Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational; that the sum of
Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN) Use properties of rational and irrational numbers Additional N-RN.3 Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational; that the sum of
Standard Description Agile Mind Lesson / Activity Page / Link to Resource
 Publisher: Agile Mind, Inc Date: 19-May-14 Course and/or Algebra I Grade Level: TN Core Standard Standard Description Agile Mind Lesson / Activity Page / Link to Resource Create equations that describe
Publisher: Agile Mind, Inc Date: 19-May-14 Course and/or Algebra I Grade Level: TN Core Standard Standard Description Agile Mind Lesson / Activity Page / Link to Resource Create equations that describe
To determine the slope or rate of change of a linear function, use m =, positive slopes, rises from left to right, negative
 Common Core Regents Review Linear Functions The standard form for a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m represents the slope and b represents the y-intercept. To determine the slope or rate of change
Common Core Regents Review Linear Functions The standard form for a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m represents the slope and b represents the y-intercept. To determine the slope or rate of change
Looking Ahead to Chapter 4
 Looking Ahead to Chapter Focus In Chapter, you will learn about functions and function notation, and you will find the domain and range of a function. You will also learn about real numbers and their properties,
Looking Ahead to Chapter Focus In Chapter, you will learn about functions and function notation, and you will find the domain and range of a function. You will also learn about real numbers and their properties,
N-Q2. Define appropriate quantities for the purpose of descriptive modeling.
 Unit 1 Expressions Use properties of rational and irrational numbers. N-RN3. Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational; that the sum of a rational number and an irrational number
Unit 1 Expressions Use properties of rational and irrational numbers. N-RN3. Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational; that the sum of a rational number and an irrational number
ALGEBRA I. 2. Rewrite expressions involving radicals and rational exponents using the properties of exponents. (N-RN2)
 ALGEBRA I The Algebra I course builds on foundational mathematical content learned by students in Grades K-8 by expanding mathematics understanding to provide students with a strong mathematics education.
ALGEBRA I The Algebra I course builds on foundational mathematical content learned by students in Grades K-8 by expanding mathematics understanding to provide students with a strong mathematics education.
The Top 11 Keystones of Algebra 1
 The Top 11 Keystones of Algebra 1 The Top Eleven Keystones of Algebra 1 You should be able to 1) Simplify a radical expression. 2) Solve an equation. 3) Solve and graph an inequality on a number line.
The Top 11 Keystones of Algebra 1 The Top Eleven Keystones of Algebra 1 You should be able to 1) Simplify a radical expression. 2) Solve an equation. 3) Solve and graph an inequality on a number line.
ALGEBRA I SEMESTER EXAMS PRACTICE MATERIALS SEMESTER (1.1) Examine the dotplots below from three sets of data Set A
 1. (1.1) Examine the dotplots below from three sets of data. 0 2 4 6 8 10 Set A 0 2 4 6 8 10 Set 0 2 4 6 8 10 Set C The mean of each set is 5. The standard deviations of the sets are 1.3, 2.0, and 2.9.
1. (1.1) Examine the dotplots below from three sets of data. 0 2 4 6 8 10 Set A 0 2 4 6 8 10 Set 0 2 4 6 8 10 Set C The mean of each set is 5. The standard deviations of the sets are 1.3, 2.0, and 2.9.
