CONTROL OF THE HUMIDITY AND TEMPERATURE IN AN ATRIUM BY COOLING THE SURFACE OF A POND IN THE ATRIUM
|
|
|
- Posy Allen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CONTROL OF THE HUMIDITY AND TEMPERATURE IN AN ATRIUM BY COOLING THE SURFACE OF A POND IN THE ATRIUM Masamch Ena, Yasufum Kaaguch, Shge Nshzaa, and Hdeho Maeda Graduate School of Engneerng, Hoado Unversty Address: N-1 W-8, Ktau, Saoro Jaan ABSTRACT Ths aer resents a method for dynamc numercal analyss of the thermal envronment n an atrum. In ths study, the quantty of condensaton on and the quantty of evaoraton from the surface of ater n a small ool (ater surface area, 1m 2 ) ere exermentally measured, and changes n the vertcal dstrbutons of humdty and temerature n an atrum ere numercally calculated by usng the Successve Integraton Method. The analyss as carred out usng BASIC language softare. The atrum used as the model for ths study as 6 m 2 n floor area, m n heght, and had a ond th a surface area of 5 m 2. The arflo beteen the atrum and outdoor s naturally ventlated n summer. If the temerature of the surface of the ond s mantaned at less than degrees Celsus, the estmated rate of vaor condensaton n summer s 6 g/h. Ths ould allo the cool and lo humdty ar to be crculated to other arts of the buldng. A cooled surface of a ond n an atrum ould therefore functon as a tye of dehumdfer, le an ar-condtonng system. and such a ventlated envronment ould be benefcal for the health of aged eole. Moreover, cold fresh ar nfltratng nto the atrum n nter can be heated by solar radaton enetratng through the glazed roof, and ths armed ar can be crculated to other arts such as the ards. On the other hand, one dsadvantage of an atrum s that the temerature of the ar heated by solar radaton enetratng through the glazed roof n summer s too hgh for the ar to be used as ventlaton for other arts of the buldng. There s, hoever, one relatvely easy ay to solve ths roblem. Snce many atrums have artfcal onds bult nsde them, the ater n the ond could be revented from evaoratng by eeng the ater surface temerature loer than de-ont temerature, and ths ould lead to vaor condensaton, hch ould cool the fresh ar comng nto the atrum from outsde. Ths dea 4) ould enable both the humdty and temerature n an atrum to be controlled. It ould also reduce the coolng load of the buldng n summer and the roblem of condensaton on the glazed roof n nter. INTRODUCTION Many nsttutons for the elderly have recently been bult n Jaan due to the agng socety. In Hoado, the northernmost sland of Jaan, aroxmately ten ne nsttutons for the aged are currently beng constructed every year. In nter, t s dffcult for the resdents of nsttutons for the aged n Hoado to go outdoors because of the large amount of sno and the frozen sdeals. In such cold and snoy regons, a glasscovered sace le atrums could rovde deal laces for aged eole to exercse n nter ). For examle, such a sace n a buldng can rovde several benefts for the occuants of the buldng, esecally f the buldng s a resdental faclty for aged eole. For one, a hgh level of ventlaton s requred to elmnate the unleasant odor caused by ards annexed for aged eole, summer nter Fg. 1 System of ventlaton for the buldng 1
2 Secfcaton for numercal smulaton: EConvectve heat transfer coeffcent Celng : C=.495Hc+4.74 (uard) Wall : C=.411Hc+2.51 Floor : C=.11Hc+4.2 (uard) : C=.1Hc+1.4 (donard) C: convectve heat transfer coeffcent [W/m 2 K] HC: convectve heat flux [W/m 2 ] EIn ths smulaton, nd effect and ar leaage of the atrum s neglgble. EConsttutons of each all as follos Heat balance equatons: () Imagnary zones dθ c γ V + dt () Wall surfaces A Mosture balance equatons: Imagnary zones dx γ = α A cl l SW NS ( x j x ) Y V = Q j + dt γ NS ( θ ) ( ) l θ + cγq W j θ j θ ( H H ) + α A ( θ θ ) + ε β α ( θ θ ) + W = m () Pond c j l r l dθ c γ V c q = γ dt + α A c SW ( θ θ ) + A ( H H ) c ( θ j θ ) + ε βlα r( θ l θ ) A rz W + SW m Secton of glass covered sace Fg. 2 Consttutons of each all n the Atrum T2<T<T1 T<T<T2 T<T a) exchanged ventlaton of oen ar c :secfc γ : densty [g/m ] V α Q W Y Z : : volume of a room, zone, : radatve heat transfer : quantty : heat gan (solar radaton, human body, etc.) [W] : mosture gan (human body) [g/h] quantty of condensaton or of A :area H H : loss of heat [Wh/gK] of all surface, :nflo of heat flux from the all surface [W/ u] ε : absorbtvty of q heat flux through the surroundng alls : ncdent factor to of ventlaton from sace j to [m /h] x : humdty rato of ar [g/g'] β r l j m ond [ u] all surface coeffcen t [W/ uk] radaton ond [m ] θ : temerature of ar, all surface, ater [ Ž] : quantty of crculated through the ater ond r : latent heat of vaorzaton [Wh/g] evaoraton [g/ uh] [W/ u] [m /h] Ta<T2 T<Ta<T1 T1<Ta b) sutable ventlaton beteen one sace and another j : neghborng@ sace number of sace, sace l : to hch all surface number of all surface faced and all surface : ond : ater NS : neghborng saces faces, outdoor to sace c : coolng ater SW : surroundng alls T<T2<T1 T<T2 T2<T1 c) recrocal ventlaton beteen one sace and another Fg. Modelng of arflo aths beteen magnary dvsons n the atrum 2
3 In ths study, the thermal envronment of an atrum n an nsttuton for the aged as numercally calculated ). These results ere used to determne the best ays (1) to mrove the thermal envronment of an atrum hen the roof s oened for buoyant convecton and to cool the atrum sace by natural ventlaton n summer, and (2) to crculate ar that has been cooled and dehumdfed by a ond n an atrum to other arts of the buldng and thereby reduce energy costs. ANALSIS METHOD The Successve Integraton Method 1) as used for the analyss, BASIC language softare as used for the numercal calculaton. An llustraton of the ventlaton system used n the nsttuton s shon n Fgure 1, and the modelng arflo aths n the atrum s shon n Fgure. Dry-bulb temerature s horzontally contoured n some actual measurements n a sace th a hgh celng, such as an atrum, and the sace s dvded nto the magnary dvsons of uer zone, mddle zone and loer zones (.e., occued sace) such as Bloc Model 2). The heat transfer th resect to the consttuent alls n the sace s dvded nto convecton and radaton comonents 2). The magnary alls beteen three zones are transarent to the radaton comonent, each zone has heat and arflo balances, resectvely. The all surfaces do not emt or absorb vaor. The temerature n each ard s mantaned at 27 degrees Celsus, eeng RH 6 %. Fresh ar nto each ard s ventlated through the atrum by the forced ventlaton system (2 ac/h) throughout the year. The olluted ar s alays exhausted from the ards to outsde. Fgure 4 shos the floor lan and a cross secton of the subject buldng used as the model for ths study. The buldng s a resdental nsttuton for elderly eole (current number of resdents, 9 n both the East and West ards). There s an artfcal ond contanng cooled ater on the floor level of the atrum. The roof of the atrum has oenngs (.e., exhaust oenngs for fre smoe) to allo arm ar near the roof level to be exhausted and fresh ar from outsde to enter the atrum by the buoyant ventlaton 2). When usng the eather data n Saoro (.e., outdoor ar temerature, de ont temerature, solar radaton [ncludng the beamed comonent on a normal face and the dffuse comonent] of HASP standard data), hourly data n summer as shon Degree Celsus Fg. 4 Floor lan and a cross secton of the buldng Elased tme Outdoor temerature Relatve humdty Fg. 5 Fluctuatons n outdoor temerature and relatve humdty n summer n Saoro n Fgure 5 s made u an average value of the same tme durng 2-ee of the hottest erod. Anng cloths under the glazed roof absorb about 5 % of solar radaton enetratng through the glazed roof, and the ar armed by the absorbed heat of the cloths accelerates the buoyant ventlaton through the exhaust oenng n the roof. Changes n the area of sunshne on each all ere calculated before the dynamc numercal analyss of the thermal envronments n the atrum s started, the solar radaton on each all surface s estmated by the above changes n the area of sunshne. The quantty of condensaton on and quantty of evaoraton from the ater surface ere exermentally measured by usng a small ool contanng ater th a surface area of 1 m 2. The vaor transfer on the surface of a ond as calculated from the measurement results by usng the follong aroxmated equatons 4).
4 Condensaton: Z=(14.8*v+45.5){df+.68(1-RH)} Maeda-Ena C=.6*v+4.1 Evaoraton: Z=(169.4*v+41.){df+.54(1-RH)} Kaaguch-Ena C=5.4*v+7.4 here Z: quantty of condensaton or of evaoraton [g/(m 2 h)] v: ar velocty on the ater surface [m/s] df: dfference beteen vaor ressure n room ar and on the ater surface [Pa] RH: relatve humdty [%] Changes n the dstrbutons of temerature and humdty n the atrum sace and changes n the thermal load for the ards can easly be calculated by the above BASIC language softare. SETTING CONDITIONS We examned 17 cases n hch the enetraton coeffcent, ater surface area, ar velocty and ater temerature ere vared ( Table 1). In case, the ards are drectly ventlated from outdoor. Effect of ater surface temerature: The effect of mantanng ater surface temerature at beteen 1 and degrees Celsus, of exhaustng arm ar by buoyant convecton and on energy costs and amenty erformance n the occued zone of the atrum and n the ards ere examned. Effect of sheld cloths: If the anng cloths are not used, the enetraton coeffcent of the glazed roof s. One mert of an atrum s to mae the occuants feel as f they are n an outdoor sace, hch ould not be ossble f the anng cloths shelded too much of the glazed roof. The enetraton coeffcent as therefore controlled at the value of.5. Effect of ar velocty: Ar velocty strongly affects the quantty of condensaton on and the quantty of evaoraton from the ater surface. The ar velocty at the ater surface level as mantaned n the range of.25 to 1. m/s. RESULTS & DISCUSSION Table 1 Settng condtons Penetraton Water surface area Ar velocty Water temerature coeffcent [u] [m/s] [Degree Celsus] Case.5 Case1 Case2.2 Case no control Case no control Temerature [Degree Celsus] Temerature[Degree Celsus] CASE CASE 1 CASE 2 CASE CASE 4 CASE 5 CASE 6 CASE 7 CASE 8 CASE 9 CASE 1 CASE 11 CASE 12 CASE 1 CASE 14 CASE 15 CASE 16 Max. OT Average OT Mn. OT Max. ar tem. Average. ar tem. Mn. ar tem. Fg. 6 Thermal envronments n the occuant zones Elased tme OT Uer Mddle Lo er Outdoor Fg. 7 Fluctuatons n temerature n each of the three zones of the atrum Fgure 6 shos the thermal envronment of the occuant zone n each of the 17 cases lsted n Table 1. The results for cases 1 to case, hch are thout onds, are bases for dscussng the effect of a cooled surface of a ond n an atrum. In case 1, the oeratve temerature (OT) n the occuant zone rose as hgh as.6 degrees, a temerature hch s not comfortable for occuants. When the enetraton coeffcent of anng cloths to solar radaton as set to.5, the temerature of the loer zone as less than 29 degree Celsus. Even n case 7, here there s a ond n the atrum, the ater surface temerature rose to more than degrees Celsus due to the ar temerature n the atrum. On the other hand, n case 8, here anng cloths ere used, thermal amenty could be mantaned due to the decrease 4
5 8 Quantty of condensaton [g/h] Humdty rato [g/g'] Quantty of condensaton daly[g/day] Elased tme Case1 Fg. 9 Fluctuatons n humdty rato n the loer zone Elased tme Case1 Fg. 8 Fluctuatons n quantty of condensaton Fg. 1 Comarson of the quanttes of condensaton n the ar temerature of the loer zone, as shon n Fgure 7. Fgure 8 shos the quantty of vaor condensaton on the ater surface, Negatve values ndcate the quantty of vaor evaoraton. Fgure 9 shos the changes n humdty rato n the loer zone. The humdty rato n the loer zone decreases th decrease n the ater surface temerature. Thus, ater surface temerature affects the humdty n the loer zone. Fgure 1 shos the quantty of vaor condensaton throughout the day under varous condtons. If the ater n the onds s not cooled, t constantly evaorates. Condensaton s greatly affected by the ater surface area and ar velocty at ater surface level. Fgure 11 and Fgure 12 sho the sum of radaton heat, convecton heat and latent heat absorbed on the ater surface f the ond as cooled. Each s llustrated as the value er the floor area. The ater temerature af- Case1 Amount of thermal load [W/u] Case1 Radaton Convecton Latent heat Fg.11 Thermal load reduced th cool ater surface at ea tme Amount of thermal load [Wh/u ] Case1 Radaton Convecton Latent heat Fg. 12 Integral thermal load reduced daly th cool ater surface Amount of thermal load [W/u] Case Case1 Case2 Case Case1 Frst floor Second floor Fg. 1 Sensble thermal load rovded by ventlaton through atrum sace at ea tme Amount of thermal load [W/u] Case Case1 Case2 Case Case1 Frst floor Second floor Fg. 14 Latent thermal load rovded by ventlaton through atrum sace at ea tme 5
6 fects the amount of condensaton or evaoraton. If the ater temerature ll not be et loer than the de ont temerature n the loer zone, the latent heat to evaorate from the ater surface becomes the thermal load to the ards hch are ar-condtoned. The maxmum thermal load n case 8 s 1-tmes greater than that n case 11. Fgure 1 and Fgure 14 sho the thermal loads n each case hen ventlatng nto the ards through the atrum. The thermal loads ere exressed as the values er the floor area of ards. If anng cloths are not used, the ea load rses to about 4 W/m 2 as the total heat. The thermal load s greatly affected by solar radaton enetratng through the glazed roof. In comarson th case hch s the atrum thout a ond and case 8 hch s the atrum th a ond, the effects of a ond can be dscussed, and also n the same ay from case 9 to case 16, the effects of the ond can be evaluated. The cooled ond can decrease the total heat of 6.4 W/m 2 to the maxmum of thermal load. Artfcal onds, hch are often bult n atrums for esthetc urose, can become a source of hgh humdty f there s no control of the ater temerature. On the other hand, f the ater temerature s et loer than the de ont temerature, the cool ater surface can act as a tye of dehumdfer by causng vaor to condense. REFERENCE 1) N. Aratan, N. Sasa, M. Ena: A Successve Integraton Method for the Analyss of the Thermal Envronment of Buldng, Buldng Scence Seres 9 of NBS,.5-16,1971 2) M. Ena, N. Aratan, K. Kubota, H. Matsumura: Modelng of a Hgh Celng Sace for Numercal Analyss of Thermal Envronment Wth Inhomogeneous Temerature Dstrbuton, and Alcaton of Three Zones Model to Glass-Covered Saces by Usng Successve Integraton Method, Journal of Archt. Plann. Envron. Engng, AIJ, No.419,.21-29, 1991 ) S. Yamamoto, M. Ena, N. Aratan: Thermal Envronment n an Atrum Sace as an Insttuton for the Elderly n a Wnter Cty, Proceedngs of PLEA1997 KUSHIRO Smulaton & Montorng,.91-96, ) M. Ena, H. Maeda, T. Mor, N. Aratan, Y. Kaaguch: Control of Humd Condton n a Large Well by the Cool Runnng Water, Transactons of the Heatng, Ar-Condtonng and Santary Engneers of Jaan No.72,.47-56, 1999 CONCLUSIONS In ths study, e nvestgated the effect on amenty and energy conservaton n an atrum of (1) sheldng solar radaton by the use of anng cloths under the glazed roof of an atrum, (2) usng oenngs n the roof of an atrum as a mean to rovde fresh ar to other arts of the buldng and to exhaust arm ar from the atrum n summer, () coolng the surface of a ond n an atrum. The merts of an atrum as art of a buldng used for elderly eole are as follos: (1) the hgh level of ventlaton needed to elmnate the unleasant odor caused by ards s benefcal for the health of aged eole, and (2) ar that cool and of lo humdty can be crculated throughout the buldng f the surface of a ond n the atrum s cooled. 6
CHE-201. I n t r o d u c t i o n t o Chemical E n g i n e e r i n g. C h a p t e r 6. Multiphase Systems
 I n t r o d u c t o n t o Chemcal E n g n e e r n g CHE-201 I N S T R U C T O R : D r. N a b e e l S a l m b o - G h a n d e r C h a t e r 6 Multhase Systems Introductory Statement: Phase s a state of
I n t r o d u c t o n t o Chemcal E n g n e e r n g CHE-201 I N S T R U C T O R : D r. N a b e e l S a l m b o - G h a n d e r C h a t e r 6 Multhase Systems Introductory Statement: Phase s a state of
Air Age Equation Parameterized by Ventilation Grouped Time WU Wen-zhong
 Appled Mechancs and Materals Submtted: 2014-05-07 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vols. 587-589, pp 449-452 Accepted: 2014-05-10 do:10.4028/www.scentfc.net/amm.587-589.449 Onlne: 2014-07-04 2014 Trans Tech Publcatons,
Appled Mechancs and Materals Submtted: 2014-05-07 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vols. 587-589, pp 449-452 Accepted: 2014-05-10 do:10.4028/www.scentfc.net/amm.587-589.449 Onlne: 2014-07-04 2014 Trans Tech Publcatons,
Simulation of Heat Transfer during Artificial Ground Freezing Combined with Groundwater Flow
 Smulaton of Heat Transfer durng Artfcal Ground Freezng Combned th Groundater Flo Ru Hu *1, Quan Lu 1 1 School of Earth Scence and Engneerng, Hoha Unversty, Nanjng, Chna *Correspondng author: No.8 Fochengx
Smulaton of Heat Transfer durng Artfcal Ground Freezng Combned th Groundater Flo Ru Hu *1, Quan Lu 1 1 School of Earth Scence and Engneerng, Hoha Unversty, Nanjng, Chna *Correspondng author: No.8 Fochengx
Aerodynamic database for low-rise buildings
 Aerodynamc database for low-rse buldngs. Introducton An aerodynamc database has been constructed by the Tokyo Polytechnc Unversty as one art of the Wnd Effects on Buldngs and Urban Envronment, the 2st
Aerodynamc database for low-rse buldngs. Introducton An aerodynamc database has been constructed by the Tokyo Polytechnc Unversty as one art of the Wnd Effects on Buldngs and Urban Envronment, the 2st
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Heat Transfer
 Prncples of Food and Boprocess Engneerng (FS 31) Solutons to Example Problems on Heat Transfer 1. We start wth Fourer s law of heat conducton: Q = k A ( T/ x) Rearrangng, we get: Q/A = k ( T/ x) Here,
Prncples of Food and Boprocess Engneerng (FS 31) Solutons to Example Problems on Heat Transfer 1. We start wth Fourer s law of heat conducton: Q = k A ( T/ x) Rearrangng, we get: Q/A = k ( T/ x) Here,
Model and program for the prediction of the indoor air temperature and the indoor air relative humidity
 Insttute of Buldng Clmatology, Faculty of Archtecture, Dresden Unversty of Technology, Germany Model and program for the predcton of the ndoor ar temperature and the ndoor ar relatve humdty Dr.-Ing. A.
Insttute of Buldng Clmatology, Faculty of Archtecture, Dresden Unversty of Technology, Germany Model and program for the predcton of the ndoor ar temperature and the ndoor ar relatve humdty Dr.-Ing. A.
Airflow and Contaminant Simulation with CONTAM
 Arflow and Contamnant Smulaton wth CONTAM George Walton, NIST CHAMPS Developers Workshop Syracuse Unversty June 19, 2006 Network Analogy Electrc Ppe, Duct & Ar Wre Ppe, Duct, or Openng Juncton Juncton
Arflow and Contamnant Smulaton wth CONTAM George Walton, NIST CHAMPS Developers Workshop Syracuse Unversty June 19, 2006 Network Analogy Electrc Ppe, Duct & Ar Wre Ppe, Duct, or Openng Juncton Juncton
MASS TRANSFER Lesson 1 BY DR. ARI SEPPÄLÄ AALTO UNIVERSITY
 SS TRNSFER 2015 Lesson 1 BY DR. RI SEPPÄLÄ LTO UNIVERSITY Structure of the course 6 lessons by r Seälä and Tuula Noonen 5 excercse lessons (one homework roblem n each excercse) by Votto Kotaho (1/6 onts)
SS TRNSFER 2015 Lesson 1 BY DR. RI SEPPÄLÄ LTO UNIVERSITY Structure of the course 6 lessons by r Seälä and Tuula Noonen 5 excercse lessons (one homework roblem n each excercse) by Votto Kotaho (1/6 onts)
Research & Reviews: Journal of Engineering and Technology
 Research & Revews: Journal of Engneerng and Technology Case Study to Smulate Convectve Flows and Heat Transfer n Arcondtoned Spaces Hussen JA 1 *, Mazlan AW 1 and Hasanen MH 2 1 Department of Mechancal
Research & Revews: Journal of Engneerng and Technology Case Study to Smulate Convectve Flows and Heat Transfer n Arcondtoned Spaces Hussen JA 1 *, Mazlan AW 1 and Hasanen MH 2 1 Department of Mechancal
The Analysis of Convection Experiment
 Internatonal Conference on Appled Scence and Engneerng Innovaton (ASEI 5) The Analyss of Convecton Experment Zlong Zhang School of North Chna Electrc Power Unversty, Baodng 7, Chna 469567@qq.com Keywords:
Internatonal Conference on Appled Scence and Engneerng Innovaton (ASEI 5) The Analyss of Convecton Experment Zlong Zhang School of North Chna Electrc Power Unversty, Baodng 7, Chna 469567@qq.com Keywords:
A Particle Filter Algorithm based on Mixing of Prior probability density and UKF as Generate Importance Function
 Advanced Scence and Technology Letters, pp.83-87 http://dx.do.org/10.14257/astl.2014.53.20 A Partcle Flter Algorthm based on Mxng of Pror probablty densty and UKF as Generate Importance Functon Lu Lu 1,1,
Advanced Scence and Technology Letters, pp.83-87 http://dx.do.org/10.14257/astl.2014.53.20 A Partcle Flter Algorthm based on Mxng of Pror probablty densty and UKF as Generate Importance Functon Lu Lu 1,1,
Elastic Collisions. Definition: two point masses on which no external forces act collide without losing any energy.
 Elastc Collsons Defnton: to pont asses on hch no external forces act collde thout losng any energy v Prerequstes: θ θ collsons n one denson conservaton of oentu and energy occurs frequently n everyday
Elastc Collsons Defnton: to pont asses on hch no external forces act collde thout losng any energy v Prerequstes: θ θ collsons n one denson conservaton of oentu and energy occurs frequently n everyday
Priority Queuing with Finite Buffer Size and Randomized Push-out Mechanism
 ICN 00 Prorty Queung wth Fnte Buffer Sze and Randomzed Push-out Mechansm Vladmr Zaborovsy, Oleg Zayats, Vladmr Muluha Polytechncal Unversty, Sant-Petersburg, Russa Arl 4, 00 Content I. Introducton II.
ICN 00 Prorty Queung wth Fnte Buffer Sze and Randomzed Push-out Mechansm Vladmr Zaborovsy, Oleg Zayats, Vladmr Muluha Polytechncal Unversty, Sant-Petersburg, Russa Arl 4, 00 Content I. Introducton II.
A large scale tsunami run-up simulation and numerical evaluation of fluid force during tsunami by using a particle method
 A large scale tsunam run-up smulaton and numercal evaluaton of flud force durng tsunam by usng a partcle method *Mtsuteru Asa 1), Shoch Tanabe 2) and Masaharu Isshk 3) 1), 2) Department of Cvl Engneerng,
A large scale tsunam run-up smulaton and numercal evaluaton of flud force durng tsunam by usng a partcle method *Mtsuteru Asa 1), Shoch Tanabe 2) and Masaharu Isshk 3) 1), 2) Department of Cvl Engneerng,
Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Analyss of Varance and Desgn of Exerments-I MODULE III LECTURE - 2 EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN MODELS Dr. Shalabh Deartment of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanur 2 We consder the models
Analyss of Varance and Desgn of Exerments-I MODULE III LECTURE - 2 EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN MODELS Dr. Shalabh Deartment of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanur 2 We consder the models
Hans-Joachim Kretzschmar and Katja Knobloch
 Sulementary Backward Equatons for the Industral Formulaton IAPWS-IF of Water and Steam for Fast Calculatons of Heat Cycles, Bolers, and Steam Turbnes Hans-Joachm Kretzschmar and Katja Knobloch Deartment
Sulementary Backward Equatons for the Industral Formulaton IAPWS-IF of Water and Steam for Fast Calculatons of Heat Cycles, Bolers, and Steam Turbnes Hans-Joachm Kretzschmar and Katja Knobloch Deartment
Operating conditions of a mine fan under conditions of variable resistance
 Paper No. 11 ISMS 216 Operatng condtons of a mne fan under condtons of varable resstance Zhang Ynghua a, Chen L a, b, Huang Zhan a, *, Gao Yukun a a State Key Laboratory of Hgh-Effcent Mnng and Safety
Paper No. 11 ISMS 216 Operatng condtons of a mne fan under condtons of varable resstance Zhang Ynghua a, Chen L a, b, Huang Zhan a, *, Gao Yukun a a State Key Laboratory of Hgh-Effcent Mnng and Safety
ENERGY SAVING SOLAR FACADE FOR NON-RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS FOR CLIMATIC CONDITION IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC
 ENERGY SAVING SOLAR FACADE FOR NON-RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS FOR CLIMATIC CONDITION IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC Jr Sedlak and Mlos Kalousek Department of Buldng Desgn Engneerng, Faculty of Cvl Engneerng, Techncal
ENERGY SAVING SOLAR FACADE FOR NON-RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS FOR CLIMATIC CONDITION IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC Jr Sedlak and Mlos Kalousek Department of Buldng Desgn Engneerng, Faculty of Cvl Engneerng, Techncal
Thermal-Fluids I. Chapter 18 Transient heat conduction. Dr. Primal Fernando Ph: (850)
 hermal-fluds I Chapter 18 ransent heat conducton Dr. Prmal Fernando prmal@eng.fsu.edu Ph: (850) 410-6323 1 ransent heat conducton In general, he temperature of a body vares wth tme as well as poston. In
hermal-fluds I Chapter 18 ransent heat conducton Dr. Prmal Fernando prmal@eng.fsu.edu Ph: (850) 410-6323 1 ransent heat conducton In general, he temperature of a body vares wth tme as well as poston. In
Adsorption: A gas or gases from a mixture of gases or a liquid (or liquids) from a mixture of liquids is bound physically to the surface of a solid.
 Searatons n Chemcal Engneerng Searatons (gas from a mxture of gases, lquds from a mxture of lquds, solds from a soluton of solds n lquds, dssolved gases from lquds, solvents from gases artally/comletely
Searatons n Chemcal Engneerng Searatons (gas from a mxture of gases, lquds from a mxture of lquds, solds from a soluton of solds n lquds, dssolved gases from lquds, solvents from gases artally/comletely
NUMERICAL SIMULATION ON AIR DISTRIBUTION OF A TENNIS HALL IN WINTER AND EVALUATION ON INDOOR THERMAL ENVIRONMENT
 Engneerng Revew, Vol. 34, Issue 2, 109-118, 2014. 109 NUMERICAL SIMULATION ON AIR DISTRIBUTION OF A TENNIS HALL IN WINTER AND EVALUATION ON INDOOR THERMAL ENVIRONMENT X. Su 1* G. Han 2 F. Chen 3 1 School
Engneerng Revew, Vol. 34, Issue 2, 109-118, 2014. 109 NUMERICAL SIMULATION ON AIR DISTRIBUTION OF A TENNIS HALL IN WINTER AND EVALUATION ON INDOOR THERMAL ENVIRONMENT X. Su 1* G. Han 2 F. Chen 3 1 School
Section 8.1 Exercises
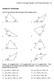 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Model Reference Adaptive Temperature Control of the Electromagnetic Oven Process in Manufacturing Process
 RECENT ADVANCES n SIGNAL PROCESSING, ROBOTICS and AUTOMATION Model Reference Adatve Temerature Control of the Electromagnetc Oven Process n Manufacturng Process JIRAPHON SRISERTPOL SUPOT PHUNGPHIMAI School
RECENT ADVANCES n SIGNAL PROCESSING, ROBOTICS and AUTOMATION Model Reference Adatve Temerature Control of the Electromagnetc Oven Process n Manufacturng Process JIRAPHON SRISERTPOL SUPOT PHUNGPHIMAI School
Heating and ventilation in milking parlours
 Agronomy Research 13(1), 245 252, 2015 Heatng and ventlaton n mlkng parlours J. Papez * and P. Kc Czech Unversty of Lfe Scences Prague, Faculty of Engneerng, Kamycka 129, 16521 Prague 6, Czech Republc;
Agronomy Research 13(1), 245 252, 2015 Heatng and ventlaton n mlkng parlours J. Papez * and P. Kc Czech Unversty of Lfe Scences Prague, Faculty of Engneerng, Kamycka 129, 16521 Prague 6, Czech Republc;
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #3: Hydraulic Head and Fluid Potential. p o. p o + p
 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #3: Hydraulc Head and Flud Potental What makes water flow? Consder ressure Water Level o A Water Level C o o + B Pressure at A atmosherc (
1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #3: Hydraulc Head and Flud Potental What makes water flow? Consder ressure Water Level o A Water Level C o o + B Pressure at A atmosherc (
Advanced Topics in Optimization. Piecewise Linear Approximation of a Nonlinear Function
 Advanced Tocs n Otmzaton Pecewse Lnear Aroxmaton of a Nonlnear Functon Otmzaton Methods: M8L Introducton and Objectves Introducton There exsts no general algorthm for nonlnear rogrammng due to ts rregular
Advanced Tocs n Otmzaton Pecewse Lnear Aroxmaton of a Nonlnear Functon Otmzaton Methods: M8L Introducton and Objectves Introducton There exsts no general algorthm for nonlnear rogrammng due to ts rregular
Digital PI Controller Equations
 Ver. 4, 9 th March 7 Dgtal PI Controller Equatons Probably the most common tye of controller n ndustral ower electroncs s the PI (Proortonal - Integral) controller. In feld orented motor control, PI controllers
Ver. 4, 9 th March 7 Dgtal PI Controller Equatons Probably the most common tye of controller n ndustral ower electroncs s the PI (Proortonal - Integral) controller. In feld orented motor control, PI controllers
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Chapter 8 Balances on Nonreactive Processes 8.1 Elements of Energy Balances Calculations 8.1a Reference States A Review
 Chater 8 Balances on Nonreactve Processes 8.1 Elements of Energy Balances Calculatons 8.1a Reference States A Revew We can never know the absolute values of U and H for a seces at a gven state. t Fortunately,
Chater 8 Balances on Nonreactve Processes 8.1 Elements of Energy Balances Calculatons 8.1a Reference States A Revew We can never know the absolute values of U and H for a seces at a gven state. t Fortunately,
MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF TUBE HEAT EXCHANGERS
 Chemcal and Process Engneerng 3 ( ) 7-9 DOI:.478/v76---y MAHEMAICAL MODELLING OF UBE HEA EXCHANGERS WIH COMPLEX FLOW ARRANGEMEN Dad aler * Marcn rojan Jan aler Craco Unversty of Scence And echnology (AGH)
Chemcal and Process Engneerng 3 ( ) 7-9 DOI:.478/v76---y MAHEMAICAL MODELLING OF UBE HEA EXCHANGERS WIH COMPLEX FLOW ARRANGEMEN Dad aler * Marcn rojan Jan aler Craco Unversty of Scence And echnology (AGH)
Chapter 13: Multiple Regression
 Chapter 13: Multple Regresson 13.1 Developng the multple-regresson Model The general model can be descrbed as: It smplfes for two ndependent varables: The sample ft parameter b 0, b 1, and b are used to
Chapter 13: Multple Regresson 13.1 Developng the multple-regresson Model The general model can be descrbed as: It smplfes for two ndependent varables: The sample ft parameter b 0, b 1, and b are used to
EXPERT CONTROL BASED ON NEURAL NETWORKS FOR CONTROLLING GREENHOUSE ENVIRONMENT
 EXPERT CONTROL BASED ON NEURAL NETWORKS FOR CONTROLLING GREENHOUSE ENVIRONMENT Le Du Bejng Insttute of Technology, Bejng, 100081, Chna Abstract: Keyords: Dependng upon the nonlnear feature beteen neural
EXPERT CONTROL BASED ON NEURAL NETWORKS FOR CONTROLLING GREENHOUSE ENVIRONMENT Le Du Bejng Insttute of Technology, Bejng, 100081, Chna Abstract: Keyords: Dependng upon the nonlnear feature beteen neural
ESCI Cloud Physics and Precipitation Processes Lesson 4 - Convection Dr. DeCaria
 References: ESCI 340 - Cloud Physcs and Precptaton Processes Lesson 4 - Convecton Dr. DeCara Glossary of Meteorology, 2nd ed., Amercan Meteorologcal Socety A Short Course n Cloud Physcs, 3rd ed., Rogers
References: ESCI 340 - Cloud Physcs and Precptaton Processes Lesson 4 - Convecton Dr. DeCara Glossary of Meteorology, 2nd ed., Amercan Meteorologcal Socety A Short Course n Cloud Physcs, 3rd ed., Rogers
THERMODYNAMICS. Temperature
 HERMODYNMICS hermodynamcs s the henomenologcal scence whch descrbes the behavor of macroscoc objects n terms of a small number of macroscoc arameters. s an examle, to descrbe a gas n terms of volume ressure
HERMODYNMICS hermodynamcs s the henomenologcal scence whch descrbes the behavor of macroscoc objects n terms of a small number of macroscoc arameters. s an examle, to descrbe a gas n terms of volume ressure
Lecture # 02: Pressure measurements and Measurement Uncertainties
 AerE 3L & AerE343L Lecture Notes Lecture # 0: Pressure measurements and Measurement Uncertantes Dr. Hu H Hu Deartment of Aerosace Engneerng Iowa State Unversty Ames, Iowa 500, U.S.A Mechancal Pressure
AerE 3L & AerE343L Lecture Notes Lecture # 0: Pressure measurements and Measurement Uncertantes Dr. Hu H Hu Deartment of Aerosace Engneerng Iowa State Unversty Ames, Iowa 500, U.S.A Mechancal Pressure
Physics 3 (PHYF144) Chap 2: Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics System. Quantity Positive Negative
 Physcs (PHYF hap : Heat and the Frst aw of hermodynamcs -. Work and Heat n hermodynamc Processes A thermodynamc system s a system that may exchange energy wth ts surroundngs by means of heat and work.
Physcs (PHYF hap : Heat and the Frst aw of hermodynamcs -. Work and Heat n hermodynamc Processes A thermodynamc system s a system that may exchange energy wth ts surroundngs by means of heat and work.
A NEW FILTERED DYNAMIC SUBGRID-SCALE MODEL FOR LARGE EDDY SIMULATION OF INDOOR AIRFLOW
 A NEW FILTERED DYNAMIC SUBGRID-SCALE MODEL FOR LARGE EDDY SIMULATION OF INDOOR AIRFLOW We Zhang and Qngyan Chen Buldng Technology Program Massachusetts Insttute of Technology 77 Mass. Ave., Cambrdge, MA
A NEW FILTERED DYNAMIC SUBGRID-SCALE MODEL FOR LARGE EDDY SIMULATION OF INDOOR AIRFLOW We Zhang and Qngyan Chen Buldng Technology Program Massachusetts Insttute of Technology 77 Mass. Ave., Cambrdge, MA
Stateof the art of urbanmesoscale modelling and possible use of the Helsinki testbed data
 Stateof the art of urbanmesoscale modellng and possble use of the Helsnk testbed data Alberto Martll CIEMAT, Madrd, Span alberto.martll@cemat.es Snce the orgn of mesoscale meteorologcal modelng, urban
Stateof the art of urbanmesoscale modellng and possble use of the Helsnk testbed data Alberto Martll CIEMAT, Madrd, Span alberto.martll@cemat.es Snce the orgn of mesoscale meteorologcal modelng, urban
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION
 NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
Hopfield Training Rules 1 N
 Hopfeld Tranng Rules To memorse a sngle pattern Suppose e set the eghts thus - = p p here, s the eght beteen nodes & s the number of nodes n the netor p s the value requred for the -th node What ll the
Hopfeld Tranng Rules To memorse a sngle pattern Suppose e set the eghts thus - = p p here, s the eght beteen nodes & s the number of nodes n the netor p s the value requred for the -th node What ll the
Lab 2e Thermal System Response and Effective Heat Transfer Coefficient
 58:080 Expermental Engneerng 1 OBJECTIVE Lab 2e Thermal System Response and Effectve Heat Transfer Coeffcent Warnng: though the experment has educatonal objectves (to learn about bolng heat transfer, etc.),
58:080 Expermental Engneerng 1 OBJECTIVE Lab 2e Thermal System Response and Effectve Heat Transfer Coeffcent Warnng: though the experment has educatonal objectves (to learn about bolng heat transfer, etc.),
Influence of the PCM Layer Location on the Multilayer Wall Thermal Performance
 Open Journal of Energy Effcency, 207, 6, -3 http://www.scrp.org/journal/ojee ISSN Onlne: 269-2645 ISSN Prnt: 269-2637 Influence of the PCM Layer Locaton on the Multlayer Wall Thermal Performance Yanna
Open Journal of Energy Effcency, 207, 6, -3 http://www.scrp.org/journal/ojee ISSN Onlne: 269-2645 ISSN Prnt: 269-2637 Influence of the PCM Layer Locaton on the Multlayer Wall Thermal Performance Yanna
Comparison of Regression Lines
 STATGRAPHICS Rev. 9/13/2013 Comparson of Regresson Lnes Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analyss Summary... 4 Plot of Ftted Model... 6 Condtonal Sums of Squares... 6 Analyss Optons... 7 Forecasts... 8 Confdence
STATGRAPHICS Rev. 9/13/2013 Comparson of Regresson Lnes Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analyss Summary... 4 Plot of Ftted Model... 6 Condtonal Sums of Squares... 6 Analyss Optons... 7 Forecasts... 8 Confdence
On the Connectedness of the Solution Set for the Weak Vector Variational Inequality 1
 Journal of Mathematcal Analyss and Alcatons 260, 15 2001 do:10.1006jmaa.2000.7389, avalable onlne at htt:.dealbrary.com on On the Connectedness of the Soluton Set for the Weak Vector Varatonal Inequalty
Journal of Mathematcal Analyss and Alcatons 260, 15 2001 do:10.1006jmaa.2000.7389, avalable onlne at htt:.dealbrary.com on On the Connectedness of the Soluton Set for the Weak Vector Varatonal Inequalty
Natural Convection in a Rectangular Enclosure with Colliding Boundary Layers
 Journal of Appled Mathematcs & Bonformatcs, vol.4, no.2, 2014, 85-97 ISSN: 1792-6602 (prnt), 1792-6939 (onlne) Scenpress Ltd, 2014 Natural Convecton n a Rectangular Enclosure wth Colldng Boundary Layers
Journal of Appled Mathematcs & Bonformatcs, vol.4, no.2, 2014, 85-97 ISSN: 1792-6602 (prnt), 1792-6939 (onlne) Scenpress Ltd, 2014 Natural Convecton n a Rectangular Enclosure wth Colldng Boundary Layers
STUDY ON TWO PHASE FLOW IN MICRO CHANNEL BASED ON EXPERI- MENTS AND NUMERICAL EXAMINATIONS
 Blucher Mechancal Engneerng Proceedngs May 0, vol., num. www.proceedngs.blucher.com.br/evento/0wccm STUDY ON TWO PHASE FLOW IN MICRO CHANNEL BASED ON EXPERI- MENTS AND NUMERICAL EXAMINATIONS Takahko Kurahash,
Blucher Mechancal Engneerng Proceedngs May 0, vol., num. www.proceedngs.blucher.com.br/evento/0wccm STUDY ON TWO PHASE FLOW IN MICRO CHANNEL BASED ON EXPERI- MENTS AND NUMERICAL EXAMINATIONS Takahko Kurahash,
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 4: Work, Energy and Linear Momentum Due Friday March 1 st
 EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
ME6750 Thermoelectrics Design and Materials
 ME6750 Thermoelectrcs Desgn and Materals HoSung Lee, PhD Professor of Mechancal and Aerospace Engneerng Western Mchgan Unversty July, 017 1 Outlne Part I Desgn of Thermoelectrc Generators and Coolers Part
ME6750 Thermoelectrcs Desgn and Materals HoSung Lee, PhD Professor of Mechancal and Aerospace Engneerng Western Mchgan Unversty July, 017 1 Outlne Part I Desgn of Thermoelectrc Generators and Coolers Part
instance, most of building simulation programs use 1- h time step since weather files normally give hourly values.
 Seventh Internatonal IBPSA Conference Ro de Janero, Brazl August 13-15, 21 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF BUILDING HYGROTHERMAL BEHAIOR Nathan Mendes and Gerson H. dos Santos Pontfcal Catholc Unversty of Paraná PUC/CCET
Seventh Internatonal IBPSA Conference Ro de Janero, Brazl August 13-15, 21 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF BUILDING HYGROTHERMAL BEHAIOR Nathan Mendes and Gerson H. dos Santos Pontfcal Catholc Unversty of Paraná PUC/CCET
Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer
 Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
A Numerical Study of Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow past Single Tube
 A Numercal Study of Heat ransfer and Flud Flow past Sngle ube ZEINAB SAYED ABDEL-REHIM Mechancal Engneerng Natonal Research Center El-Bohos Street, Dokk, Gza EGYP abdelrehmz@yahoo.com Abstract: - A numercal
A Numercal Study of Heat ransfer and Flud Flow past Sngle ube ZEINAB SAYED ABDEL-REHIM Mechancal Engneerng Natonal Research Center El-Bohos Street, Dokk, Gza EGYP abdelrehmz@yahoo.com Abstract: - A numercal
(T > w) F R = T - w. Going up. T - w = ma
 ANSES Suspended Acceleratng-Objects A resultant orce causes a syste to accelerate. he drecton o the acceleraton s n the drecton o the resultant orce. As llustrated belo, hen suspended objects accelerate,
ANSES Suspended Acceleratng-Objects A resultant orce causes a syste to accelerate. he drecton o the acceleraton s n the drecton o the resultant orce. As llustrated belo, hen suspended objects accelerate,
APPENDIX F A DISPLACEMENT-BASED BEAM ELEMENT WITH SHEAR DEFORMATIONS. Never use a Cubic Function Approximation for a Non-Prismatic Beam
 APPENDIX F A DISPACEMENT-BASED BEAM EEMENT WITH SHEAR DEFORMATIONS Never use a Cubc Functon Approxmaton for a Non-Prsmatc Beam F. INTRODUCTION { XE "Shearng Deformatons" }In ths appendx a unque development
APPENDIX F A DISPACEMENT-BASED BEAM EEMENT WITH SHEAR DEFORMATIONS Never use a Cubc Functon Approxmaton for a Non-Prsmatc Beam F. INTRODUCTION { XE "Shearng Deformatons" }In ths appendx a unque development
6.3.4 Modified Euler s method of integration
 6.3.4 Modfed Euler s method of ntegraton Before dscussng the applcaton of Euler s method for solvng the swng equatons, let us frst revew the basc Euler s method of numercal ntegraton. Let the general from
6.3.4 Modfed Euler s method of ntegraton Before dscussng the applcaton of Euler s method for solvng the swng equatons, let us frst revew the basc Euler s method of numercal ntegraton. Let the general from
Negative Binomial Regression
 STATGRAPHICS Rev. 9/16/2013 Negatve Bnomal Regresson Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Statstcal Model... 3 Analyss Summary... 4 Analyss Optons... 7 Plot of Ftted Model... 8 Observed Versus Predcted... 10 Predctons...
STATGRAPHICS Rev. 9/16/2013 Negatve Bnomal Regresson Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Statstcal Model... 3 Analyss Summary... 4 Analyss Optons... 7 Plot of Ftted Model... 8 Observed Versus Predcted... 10 Predctons...
Problem #1. Known: All required parameters. Schematic: Find: Depth of freezing as function of time. Strategy:
 BEE 3500 013 Prelm Soluton Problem #1 Known: All requred parameter. Schematc: Fnd: Depth of freezng a functon of tme. Strategy: In thee mplfed analy for freezng tme, a wa done n cla for a lab geometry,
BEE 3500 013 Prelm Soluton Problem #1 Known: All requred parameter. Schematc: Fnd: Depth of freezng a functon of tme. Strategy: In thee mplfed analy for freezng tme, a wa done n cla for a lab geometry,
MODERN TECHNOLOGIES. I. Lee, C. Kang, J. Yun, J. Jeun, and G. Kim
 1 A STUDY OF AERODYNAMICS IN AGRICULTURE MODERN TECHNOLOGIES I. Lee, C. Kang, J. Yun, J. Jeun, and G. Km The authors are In-Bok Lee, ASAE Member, Junor researcher; Chang-Ho Kang, Senor researcher; Jn-Ha
1 A STUDY OF AERODYNAMICS IN AGRICULTURE MODERN TECHNOLOGIES I. Lee, C. Kang, J. Yun, J. Jeun, and G. Km The authors are In-Bok Lee, ASAE Member, Junor researcher; Chang-Ho Kang, Senor researcher; Jn-Ha
Chapter 3 Describing Data Using Numerical Measures
 Chapter 3 Student Lecture Notes 3-1 Chapter 3 Descrbng Data Usng Numercal Measures Fall 2006 Fundamentals of Busness Statstcs 1 Chapter Goals To establsh the usefulness of summary measures of data. The
Chapter 3 Student Lecture Notes 3-1 Chapter 3 Descrbng Data Usng Numercal Measures Fall 2006 Fundamentals of Busness Statstcs 1 Chapter Goals To establsh the usefulness of summary measures of data. The
Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Analyss of Varance and Desgn of Exerments-I MODULE II LECTURE - GENERAL LINEAR HYPOTHESIS AND ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE Dr. Shalabh Deartment of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanur 3.
Analyss of Varance and Desgn of Exerments-I MODULE II LECTURE - GENERAL LINEAR HYPOTHESIS AND ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE Dr. Shalabh Deartment of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanur 3.
Lecture 3 Examples and Problems
 Lecture 3 Examles and Problems Mechancs & thermodynamcs Equartton Frst Law of Thermodynamcs Ideal gases Isothermal and adabatc rocesses Readng: Elements Ch. 1-3 Lecture 3, 1 Wllam Thomson (1824 1907) a.k.a.
Lecture 3 Examles and Problems Mechancs & thermodynamcs Equartton Frst Law of Thermodynamcs Ideal gases Isothermal and adabatc rocesses Readng: Elements Ch. 1-3 Lecture 3, 1 Wllam Thomson (1824 1907) a.k.a.
Effect of loading frequency on the settlement of granular layer
 Effect of loadng frequency on the settlement of granular layer Akko KONO Ralway Techncal Research Insttute, Japan Takash Matsushma Tsukuba Unversty, Japan ABSTRACT: Cyclc loadng tests were performed both
Effect of loadng frequency on the settlement of granular layer Akko KONO Ralway Techncal Research Insttute, Japan Takash Matsushma Tsukuba Unversty, Japan ABSTRACT: Cyclc loadng tests were performed both
9.2 Seismic Loads Using ASCE Standard 7-93
 CHAPER 9: Wnd and Sesmc Loads on Buldngs 9.2 Sesmc Loads Usng ASCE Standard 7-93 Descrpton A major porton of the Unted States s beleved to be subject to sesmc actvty suffcent to cause sgnfcant structural
CHAPER 9: Wnd and Sesmc Loads on Buldngs 9.2 Sesmc Loads Usng ASCE Standard 7-93 Descrpton A major porton of the Unted States s beleved to be subject to sesmc actvty suffcent to cause sgnfcant structural
b ), which stands for uniform distribution on the interval a x< b. = 0 elsewhere
 Fall Analyss of Epermental Measurements B. Esensten/rev. S. Errede Some mportant probablty dstrbutons: Unform Bnomal Posson Gaussan/ormal The Unform dstrbuton s often called U( a, b ), hch stands for unform
Fall Analyss of Epermental Measurements B. Esensten/rev. S. Errede Some mportant probablty dstrbutons: Unform Bnomal Posson Gaussan/ormal The Unform dstrbuton s often called U( a, b ), hch stands for unform
Statistical Energy Analysis for High Frequency Acoustic Analysis with LS-DYNA
 14 th Internatonal Users Conference Sesson: ALE-FSI Statstcal Energy Analyss for Hgh Frequency Acoustc Analyss wth Zhe Cu 1, Yun Huang 1, Mhamed Soul 2, Tayeb Zeguar 3 1 Lvermore Software Technology Corporaton
14 th Internatonal Users Conference Sesson: ALE-FSI Statstcal Energy Analyss for Hgh Frequency Acoustc Analyss wth Zhe Cu 1, Yun Huang 1, Mhamed Soul 2, Tayeb Zeguar 3 1 Lvermore Software Technology Corporaton
Turbulence classification of load data by the frequency and severity of wind gusts. Oscar Moñux, DEWI GmbH Kevin Bleibler, DEWI GmbH
 Turbulence classfcaton of load data by the frequency and severty of wnd gusts Introducton Oscar Moñux, DEWI GmbH Kevn Blebler, DEWI GmbH Durng the wnd turbne developng process, one of the most mportant
Turbulence classfcaton of load data by the frequency and severty of wnd gusts Introducton Oscar Moñux, DEWI GmbH Kevn Blebler, DEWI GmbH Durng the wnd turbne developng process, one of the most mportant
Confidence intervals for weighted polynomial calibrations
 Confdence ntervals for weghted olynomal calbratons Sergey Maltsev, Amersand Ltd., Moscow, Russa; ur Kalambet, Amersand Internatonal, Inc., Beachwood, OH e-mal: kalambet@amersand-ntl.com htt://www.chromandsec.com
Confdence ntervals for weghted olynomal calbratons Sergey Maltsev, Amersand Ltd., Moscow, Russa; ur Kalambet, Amersand Internatonal, Inc., Beachwood, OH e-mal: kalambet@amersand-ntl.com htt://www.chromandsec.com
November 5, 2002 SE 180: Earthquake Engineering SE 180. Final Project
 SE 8 Fnal Project Story Shear Frame u m Gven: u m L L m L L EI ω ω Solve for m Story Bendng Beam u u m L m L Gven: m L L EI ω ω Solve for m 3 3 Story Shear Frame u 3 m 3 Gven: L 3 m m L L L 3 EI ω ω ω
SE 8 Fnal Project Story Shear Frame u m Gven: u m L L m L L EI ω ω Solve for m Story Bendng Beam u u m L m L Gven: m L L EI ω ω Solve for m 3 3 Story Shear Frame u 3 m 3 Gven: L 3 m m L L L 3 EI ω ω ω
Numerical Transient Heat Conduction Experiment
 Numercal ransent Heat Conducton Experment OBJECIVE 1. o demonstrate the basc prncples of conducton heat transfer.. o show how the thermal conductvty of a sold can be measured. 3. o demonstrate the use
Numercal ransent Heat Conducton Experment OBJECIVE 1. o demonstrate the basc prncples of conducton heat transfer.. o show how the thermal conductvty of a sold can be measured. 3. o demonstrate the use
HEAT TRANSFER IN ELECTRONIC PACKAGE SUBMITTED TO TIME-DEPENDANT CLIMATIC CONDITIONS
 ISTP-16, 005, PRAGUE 16 TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA HEAT TRANSFER IN ELECTRONIC PACKAGE SUBMITTED TO TIME-DEPENDANT CLIMATIC CONDITIONS Valére Ménard*, Phlppe Reulet**, Davd Nörtershäuser*,
ISTP-16, 005, PRAGUE 16 TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA HEAT TRANSFER IN ELECTRONIC PACKAGE SUBMITTED TO TIME-DEPENDANT CLIMATIC CONDITIONS Valére Ménard*, Phlppe Reulet**, Davd Nörtershäuser*,
Orientation Model of Elite Education and Mass Education
 Proceedngs of the 8th Internatonal Conference on Innovaton & Management 723 Orentaton Model of Elte Educaton and Mass Educaton Ye Peng Huanggang Normal Unversty, Huanggang, P.R.Chna, 438 (E-mal: yepeng@hgnc.edu.cn)
Proceedngs of the 8th Internatonal Conference on Innovaton & Management 723 Orentaton Model of Elte Educaton and Mass Educaton Ye Peng Huanggang Normal Unversty, Huanggang, P.R.Chna, 438 (E-mal: yepeng@hgnc.edu.cn)
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. D Alembert s Principle and The Lagrangian-1
 P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
Indeterminate pin-jointed frames (trusses)
 Indetermnate pn-jonted frames (trusses) Calculaton of member forces usng force method I. Statcal determnacy. The degree of freedom of any truss can be derved as: w= k d a =, where k s the number of all
Indetermnate pn-jonted frames (trusses) Calculaton of member forces usng force method I. Statcal determnacy. The degree of freedom of any truss can be derved as: w= k d a =, where k s the number of all
1. Governing Equations
 1. Governng Equatons 1a. Governng Equatons for Mean Varables The governng equatons descrbe the varaton n space and tme of the zonal, merdonal and vertcal wnd components, densty, temperature, specfc humdty
1. Governng Equatons 1a. Governng Equatons for Mean Varables The governng equatons descrbe the varaton n space and tme of the zonal, merdonal and vertcal wnd components, densty, temperature, specfc humdty
Evaluating Thermodynamic Properties in LAMMPS
 D. Keffer ME 64 Det. of Materals cence & Engneerng Unversty of ennessee Knoxvlle Evaluatng hermodynamc Proertes n LAMMP Davd Keffer Deartment of Materals cence & Engneerng Unversty of ennessee Knoxvlle
D. Keffer ME 64 Det. of Materals cence & Engneerng Unversty of ennessee Knoxvlle Evaluatng hermodynamc Proertes n LAMMP Davd Keffer Deartment of Materals cence & Engneerng Unversty of ennessee Knoxvlle
Environmental Lab. Don Pugh. Ergonomics
 Envronmental Lab Don Pugh Ergonomcs 1. Introducton The purpose of ths lab s to measure aspects of the envronment, specfcally nose, heat, humdty, and lghtng and to relate these factors to human productvty
Envronmental Lab Don Pugh Ergonomcs 1. Introducton The purpose of ths lab s to measure aspects of the envronment, specfcally nose, heat, humdty, and lghtng and to relate these factors to human productvty
Lecture 5.8 Flux Vector Splitting
 Lecture 5.8 Flux Vector Splttng 1 Flux Vector Splttng The vector E n (5.7.) can be rewrtten as E = AU (5.8.1) (wth A as gven n (5.7.4) or (5.7.6) ) whenever, the equaton of state s of the separable form
Lecture 5.8 Flux Vector Splttng 1 Flux Vector Splttng The vector E n (5.7.) can be rewrtten as E = AU (5.8.1) (wth A as gven n (5.7.4) or (5.7.6) ) whenever, the equaton of state s of the separable form
Numerical Analysis of Natural Ventilation System in a Studio Apartment in Bangladesh
 Numercal Analyss of Natural Ventlaton System n a Studo Apartment n Bangladesh K.M Arful Kabr 1, a) Md. Rakbul Hasan 2, b) and Md. Abdul Hakm Khan 1 1 Bangladesh Unversty of Engneerng and Technology, Dhaka-1000,
Numercal Analyss of Natural Ventlaton System n a Studo Apartment n Bangladesh K.M Arful Kabr 1, a) Md. Rakbul Hasan 2, b) and Md. Abdul Hakm Khan 1 1 Bangladesh Unversty of Engneerng and Technology, Dhaka-1000,
Moderator & Moderator System
 NPTL Chemcal ngneerng Nuclear Reactor Technology Moderator & Moderator System K.S. Rajan Professor, School of Chemcal & Botechnology SASTRA Unversty Jont Intatve of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page of
NPTL Chemcal ngneerng Nuclear Reactor Technology Moderator & Moderator System K.S. Rajan Professor, School of Chemcal & Botechnology SASTRA Unversty Jont Intatve of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page of
Turbulent Heat Transfer Modelling in a Vessel Stirred by a Pitched Blade Turbine Impeller
 Turbulent Heat Transfer Modellng n a Vessel Strred by a Ptched Blade Turbne Impeller BARBARA ZAKRZEWSKA, ZDZISŁAW JAWORSKI Chemcal Engneerng Faculty Szczecn Unversty of Technology Al. Pastó 42, 70-065
Turbulent Heat Transfer Modellng n a Vessel Strred by a Ptched Blade Turbne Impeller BARBARA ZAKRZEWSKA, ZDZISŁAW JAWORSKI Chemcal Engneerng Faculty Szczecn Unversty of Technology Al. Pastó 42, 70-065
The impact of global change on low-elevation blue-ice areas in Antarctica: a thermo-hydrodynamic modelling study
 50 Annals of Glacology 46 2007 The mpact of global change on lo-elevaton blue-ce areas n Antarctca: a thermo-hydrodynamc modellng study Ka RASMUS, 1 Ake BECKMANN 2 1 Fnnsh Envronment Insttute, PO Box 140,
50 Annals of Glacology 46 2007 The mpact of global change on lo-elevaton blue-ce areas n Antarctca: a thermo-hydrodynamc modellng study Ka RASMUS, 1 Ake BECKMANN 2 1 Fnnsh Envronment Insttute, PO Box 140,
SIMULATION STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT URBAN CANYONS ELEMENT TO THE CANYON THERMAL ENVIRONMENT. Faculty of Eng.
 SIMULATION STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT URBAN CANYONS ELEMENT TO THE CANYON THERMAL ENVIRONMENT Naoko Yamaoka 1, Harunor Yoshda 2, Mtsuo Tanabe 3 Mchko Yamashta 1, and Takuma Koga 1 1 Graduate Student,
SIMULATION STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT URBAN CANYONS ELEMENT TO THE CANYON THERMAL ENVIRONMENT Naoko Yamaoka 1, Harunor Yoshda 2, Mtsuo Tanabe 3 Mchko Yamashta 1, and Takuma Koga 1 1 Graduate Student,
Natural Convection with Localized Heating and Cooling on Opposite Vertical Walls in an Enclosure
 The SIJ Transactons on Computer Networks & Communcaton Engneerng (CNCE), Vol. 1, No. 4, September-October 013 Natural Convecton wth Localzed Heatng and Coolng on Opposte Vertcal Walls n an Enclosure Marura
The SIJ Transactons on Computer Networks & Communcaton Engneerng (CNCE), Vol. 1, No. 4, September-October 013 Natural Convecton wth Localzed Heatng and Coolng on Opposte Vertcal Walls n an Enclosure Marura
Thermodynamics Second Law Entropy
 Thermodynamcs Second Law Entropy Lana Sherdan De Anza College May 8, 2018 Last tme the Boltzmann dstrbuton (dstrbuton of energes) the Maxwell-Boltzmann dstrbuton (dstrbuton of speeds) the Second Law of
Thermodynamcs Second Law Entropy Lana Sherdan De Anza College May 8, 2018 Last tme the Boltzmann dstrbuton (dstrbuton of energes) the Maxwell-Boltzmann dstrbuton (dstrbuton of speeds) the Second Law of
Dynamic Contact Problem for Slide Hinge
 Open Journal of Appled Scences Supplement01 world Congress on Engneerng and Technology Dynamc Contact Problem for Slde Hnge Kazunor Shnohara JAXA's Engneerng Dgtal Innovaton Center (JEDI) Japan Aerospace
Open Journal of Appled Scences Supplement01 world Congress on Engneerng and Technology Dynamc Contact Problem for Slde Hnge Kazunor Shnohara JAXA's Engneerng Dgtal Innovaton Center (JEDI) Japan Aerospace
COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD
 COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD Ákos Jósef Lengyel, István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer, Professor of Mechancs, Insttute of Appled Mechancs, Unversty of Mskolc, Mskolc-Egyetemváros,
COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD Ákos Jósef Lengyel, István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer, Professor of Mechancs, Insttute of Appled Mechancs, Unversty of Mskolc, Mskolc-Egyetemváros,
THE EFFECT OF BEAM TO COLUMN CONNECTION IN ARC PORTAL FRAME
 THE EFFECT OF BEAM TO COLUMN CONNECTON N ARC PORTAL FRAME Asko Keronen Rakenteden Mekankka, Vol. 26 No 2 1993, ss. 35-5 SUMMARY A full scale rc (renforced concrete) portal frame has been bult n order to
THE EFFECT OF BEAM TO COLUMN CONNECTON N ARC PORTAL FRAME Asko Keronen Rakenteden Mekankka, Vol. 26 No 2 1993, ss. 35-5 SUMMARY A full scale rc (renforced concrete) portal frame has been bult n order to
FORCED CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER FROM A RECTANGULAR CYLINDER: EFFECT OF ASPECT RATIO
 ISTP-,, PRAGUE TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA FORCED CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER FROM A RECTANGULAR CYLINDER: EFFECT OF ASPECT RATIO Mohammad Rahnama*, Seyed-Mad Hasheman*, Mousa Farhad**
ISTP-,, PRAGUE TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA FORCED CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER FROM A RECTANGULAR CYLINDER: EFFECT OF ASPECT RATIO Mohammad Rahnama*, Seyed-Mad Hasheman*, Mousa Farhad**
MODELLING OF VENTILATION AIRFLOW RATES OF SOLAR CHIMNEYS FOR BUILDING INTERGRATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVICES
 MODELLING OF VENTILATION AIRFLOW RATES OF SOLAR CHIMNEYS FOR BUILDING INTERGRATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVICES A.G. L, Ph.D., P. Jones, Ph.D., P.G. Zhao, L.P. Wang ABSTRACT Heat transfer process and natural
MODELLING OF VENTILATION AIRFLOW RATES OF SOLAR CHIMNEYS FOR BUILDING INTERGRATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVICES A.G. L, Ph.D., P. Jones, Ph.D., P.G. Zhao, L.P. Wang ABSTRACT Heat transfer process and natural
A Novel Control Strategy for Superconducting Magnetic Energy Storage Unit to Improve Power System Stability
 Proceedngs of the CEECE December 4, 3, Dhaka, Bangladesh A Novel Control Strategy for Suerconductng Magnetc Energy Storage Unt to mrove Poer System Stablty M.G. Rabban *, M.R.. Shekh **, and M.F. Hossan
Proceedngs of the CEECE December 4, 3, Dhaka, Bangladesh A Novel Control Strategy for Suerconductng Magnetc Energy Storage Unt to mrove Poer System Stablty M.G. Rabban *, M.R.. Shekh **, and M.F. Hossan
Turbulent Natural Convection of Heat with Localized Heating and Cooling on Adjacent Vertical Walls in an Enclosure
 Internatonal Journal of Scence and esearch (IJS ISSN (Onlne: 319-7064 Turbulent Natural Convecton of Heat wth Localzed Heatng and Coolng on Adacent Vertcal Walls n an Enclosure 1 Chrstopher Onchaga, J.K.Sgey,
Internatonal Journal of Scence and esearch (IJS ISSN (Onlne: 319-7064 Turbulent Natural Convecton of Heat wth Localzed Heatng and Coolng on Adacent Vertcal Walls n an Enclosure 1 Chrstopher Onchaga, J.K.Sgey,
Statistical Evaluation of WATFLOOD
 tatstcal Evaluaton of WATFLD By: Angela MacLean, Dept. of Cvl & Envronmental Engneerng, Unversty of Waterloo, n. ctober, 005 The statstcs program assocated wth WATFLD uses spl.csv fle that s produced wth
tatstcal Evaluaton of WATFLD By: Angela MacLean, Dept. of Cvl & Envronmental Engneerng, Unversty of Waterloo, n. ctober, 005 The statstcs program assocated wth WATFLD uses spl.csv fle that s produced wth
The Decibel and its Usage
 The Decbel and ts Usage Consder a two-stage amlfer system, as shown n Fg.. Each amlfer rodes an ncrease of the sgnal ower. Ths effect s referred to as the ower gan,, of the amlfer. Ths means that the sgnal
The Decbel and ts Usage Consder a two-stage amlfer system, as shown n Fg.. Each amlfer rodes an ncrease of the sgnal ower. Ths effect s referred to as the ower gan,, of the amlfer. Ths means that the sgnal
Parameter Estimation for Dynamic System using Unscented Kalman filter
 Parameter Estmaton for Dynamc System usng Unscented Kalman flter Jhoon Seung 1,a, Amr Atya F. 2,b, Alexander G.Parlos 3,c, and Klto Chong 1,4,d* 1 Dvson of Electroncs Engneerng, Chonbuk Natonal Unversty,
Parameter Estmaton for Dynamc System usng Unscented Kalman flter Jhoon Seung 1,a, Amr Atya F. 2,b, Alexander G.Parlos 3,c, and Klto Chong 1,4,d* 1 Dvson of Electroncs Engneerng, Chonbuk Natonal Unversty,
ONE DIMENSIONAL TRIANGULAR FIN EXPERIMENT. Technical Advisor: Dr. D.C. Look, Jr. Version: 11/03/00
 ONE IMENSIONAL TRIANGULAR FIN EXPERIMENT Techncal Advsor: r..c. Look, Jr. Verson: /3/ 7. GENERAL OJECTIVES a) To understand a one-dmensonal epermental appromaton. b) To understand the art of epermental
ONE IMENSIONAL TRIANGULAR FIN EXPERIMENT Techncal Advsor: r..c. Look, Jr. Verson: /3/ 7. GENERAL OJECTIVES a) To understand a one-dmensonal epermental appromaton. b) To understand the art of epermental
Uncertainty and auto-correlation in. Measurement
 Uncertanty and auto-correlaton n arxv:1707.03276v2 [physcs.data-an] 30 Dec 2017 Measurement Markus Schebl Federal Offce of Metrology and Surveyng (BEV), 1160 Venna, Austra E-mal: markus.schebl@bev.gv.at
Uncertanty and auto-correlaton n arxv:1707.03276v2 [physcs.data-an] 30 Dec 2017 Measurement Markus Schebl Federal Offce of Metrology and Surveyng (BEV), 1160 Venna, Austra E-mal: markus.schebl@bev.gv.at
Analysis of Unsteady Aerodynamics of a Car Model with Radiator in Dynamic Pitching Motion using LS-DYNA
 Analyss of Unsteady Aerodynamcs of a Car Model wth Radator n Dynamc Ptchng Moton usng LS-DYNA Yusuke Nakae 1, Jro Takamtsu 1, Hrosh Tanaka 1, Tsuyosh Yasuk 1 1 Toyota Motor Corporaton 1 Introducton Recently,
Analyss of Unsteady Aerodynamcs of a Car Model wth Radator n Dynamc Ptchng Moton usng LS-DYNA Yusuke Nakae 1, Jro Takamtsu 1, Hrosh Tanaka 1, Tsuyosh Yasuk 1 1 Toyota Motor Corporaton 1 Introducton Recently,
Lecture 13 APPROXIMATION OF SECOMD ORDER DERIVATIVES
 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS: FDM: Appromaton of Second Order Dervatves Lecture APPROXIMATION OF SECOMD ORDER DERIVATIVES. APPROXIMATION OF SECOND ORDER DERIVATIVES Second order dervatves appear n dffusve
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS: FDM: Appromaton of Second Order Dervatves Lecture APPROXIMATION OF SECOMD ORDER DERIVATIVES. APPROXIMATION OF SECOND ORDER DERIVATIVES Second order dervatves appear n dffusve
Chapter 11: Simple Linear Regression and Correlation
 Chapter 11: Smple Lnear Regresson and Correlaton 11-1 Emprcal Models 11-2 Smple Lnear Regresson 11-3 Propertes of the Least Squares Estmators 11-4 Hypothess Test n Smple Lnear Regresson 11-4.1 Use of t-tests
Chapter 11: Smple Lnear Regresson and Correlaton 11-1 Emprcal Models 11-2 Smple Lnear Regresson 11-3 Propertes of the Least Squares Estmators 11-4 Hypothess Test n Smple Lnear Regresson 11-4.1 Use of t-tests
Lecture #06 Hotwire anemometry: Fundamentals and instrumentation
 AerE 344 Lecture otes Lecture #06 Hotwre anemometry: Fundamentals and nstrumentaton Dr. Hu Hu Department of Aerospace Engneerng Iowa State Unversty Ames, Iowa 500, U.S.A Thermal anemometers: Techncal Fundamentals
AerE 344 Lecture otes Lecture #06 Hotwre anemometry: Fundamentals and nstrumentaton Dr. Hu Hu Department of Aerospace Engneerng Iowa State Unversty Ames, Iowa 500, U.S.A Thermal anemometers: Techncal Fundamentals
Managing Capacity Through Reward Programs. on-line companion page. Byung-Do Kim Seoul National University College of Business Administration
 Managng Caacty Through eward Programs on-lne comanon age Byung-Do Km Seoul Natonal Unversty College of Busness Admnstraton Mengze Sh Unversty of Toronto otman School of Management Toronto ON M5S E6 Canada
Managng Caacty Through eward Programs on-lne comanon age Byung-Do Km Seoul Natonal Unversty College of Busness Admnstraton Mengze Sh Unversty of Toronto otman School of Management Toronto ON M5S E6 Canada
