CYCLOSTATIONARITY-BASED BLIND CLASSIFICATION OF ANALOG AND DIGITAL MODULATIONS
|
|
|
- Griselda Whitehead
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
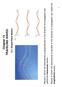
1 CYCLOSAIONARIY-BASED BLIND CLASSIFICAION OF ANALOG AND DIGIAL MODULAIONS Oavia A. Dobe Ali Abdi 2 Yehekel Ba-Ne 2 Wei Su 3 Fauly of Eng. Applied Siene Memoial Univeiy of Newfoundl S. John NL AB 3X5 Canada 2 CCSPR Dep. of ECE New Jeey Iniue of ehnology Newak NJ 72 USA 3 RDECOM Fo Monmouh NJ 773 USA dobe@eng.mun.a abdi@adm.nji.edu bane@yegal.nji.edu wei.u@u.amy.mil Aba - he poblem of blind analog digial modulaion laifiaion i akled in hi pape. A yloaionaiy-baed laifie i popoed whih doe no euie eimaion of aie phae feueny offe ignal noie powe iming eovey a pepoeing ak. Numeial imulaion ae pefomed o validae heoeial developmen. I. INRODUCION Blind modulaion laifiaion (MC i a majo ak of an inelligen eeive wih boh miliay ommeial appliaion []. A modulaion laifie eenially involve wo ep i.e. ignal pepoeing modulaion eogniion. Pepoeing ak may inlude eimaion of aie phae feueny offe ignal noie powe iming eovey e. Depending on he laifiaion algoihm employed in he eond ep diffeen pepoeing ak an be euied. Claifiaion algoihm whih ely le on pepoeing ae ough. Reeah on MC ha been aied ou fo a lea a deade []-[9]. Many algoihm popoed in he lieaue adde he digial modulaion laifiaion poblem []-[5]. A uvey of uh laifiaion ehniue i peened in []. Nonehele laifiaion of analog digial modulaion i of inee a ome exiing yem ill ue analog ommuniaion ehniue. Algoihm fo he eogniion of analog digial modulaion ae alo popoed in he lieaue [5]-[8]. Howeve he pefomane of mo of hee algoihm i peened unde he aumpion of pefe pepoeing i an ubanially degade wih model mimahe uh a aie phae feueny offe. In hi pape we popoe a novel algoihm whih exploi ignal yloaionaiy fo analog digial modulaion laifiaion. he algoihm doe no euie eimaion of aie phae feueny offe ignal noie powe iming eovey in he pepoeing ep i appliable o he following pool of modulaion: ampliude modulaion (AM double ideb (DSB ingle ideb (SSB M-ay phae hif keying (M-PSK M-ay uadaue ampliude modulaion (M-QAM. he e of he pape i oganized a follow. he ignal model oeponding aiial haaeizaion ae peened in Seion II he popoed yloaionaiy-baed laifiaion algoihm i inodued in Seion III imulaion eul ae given in Seion IV onluion ae dawn in Seion V. empoal yloaionaiy paamee ae defined in Appendix A eul fo he fi- / o eond-ode yloaionaiy of he ignal of inee ae deived in Appendix B. II. SIGNAL MODEL AND CORRESPONDING SAISICAL CHARACERIAION A. Signal Model Le he eeived baeb wavefom ( be he um jθ j2π f ( = e e ( + w( ( whee θ i he aie phae f i he aie feueny offe ( = I ( + jq ( i he anmied ignal wih modulaion i w ( = wi( + jwq( i zeo-mean omplex Gauian noie of powe N wih indexe I Q ing fo in-phae uadaue epeively j =. he in-phae uadaue noie omponen wi ( wq ( ae zeo-mean unoelaed Gauian poee unoelaed wih (. he anmied ignal i given by ( = A( +µ Ax( fo i=am ( = Ax( fo i=dsb ( = A( x( ± jx (( fo i=ssb ( = A k px( k ε fo i=m-psk k M-QAM whee A i he ignal ampliude µ A i he modulaion index x( i he zeo-mean eal-valued b-limied modulaing ignal ( x( i he Hilbe anfom of x( px ( i he anmi pule hape i he ymbol peiod ε epeen a iming eo wih ε< k = k I + jk Q i he ymbol anmied wihin he k h peiod dawn fom he ignal onellaion i i=m-psk M-QAM M i he numbe of poin in he ignal onellaion []. he daa ymbol { k } ae aumed o be zeo-mean independen idenially diibued ( om vaiable wih { i ki } ( { i kq } unoelaed. A he eeive-ide nomalizaion of he ignal i aied ou wih epe o he eeived ignal powe o emove any ale fao fom daa hen ampling i pefomed a a ampling ae f (no aliaing ou []. he nomalized diee-ime ignal i ( k: = ( / S + N wih S a he ignal powe. = kf
2 B. Cyloaionaiy of Signal of Inee Reul deived in Appendix B fo he fi- /o eond-ode yli empoal umulan funion (CCF of he ignal of inee ae peened in he euel wih emphai on hei appliaion o modulaion laifiaion. he fi-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF of AM DSB SSB M-PSK M-QAM nomalized diee-ime eeived ignal a yle feueny (CF β ae a follow jθ /2 (AM ( β = Ae ( S + N wih β= f f (2 ( i ( β = any β i = DSB SSB M-PSK M-QAM. (3 One an hu onlude ha he eeived AM ignal exhibi fiode yloaionaiy wheea all ohe ignal of inee do no. hi popey of he AM ignal i exploied fo i eogniion. he eond-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF of DSB SSB M-PSK M-QAM M 4 BPSK nomalized diee-ime eeived ignal a CF β delay τ ae a follow (DSB 2 2 j 2 f f j θ π τ x (; βτ = A ( S + N e e m ( τ f (4 wih 2 f f β= mx( τ f a he eond-ode/ zeoonjugae momen of xk ( = x ( = kf ( i (; β τ = any β i =SSB M-PSK M-QAM M 4(5 2 j2πγfε (BPSK (; βτ = A ( S + N f e (6 j2θ j2π fτf j2πγk e e px ( k px ( k+τ e k = wih 2 f f β=γ+ γ= f k/ k inege 2 p X ( k = p X ( kf. = hu fo i=dsb BPSK (; βτ a CF β= 2 f f 2 ff + f k/ 2 epeively wheea fo i=ssb M-PSK M-QAM M 4 (; β τ = any β. hi popey i exploied hee o diinguih beween DSB BPSK SSB M-PSK M-QAM M 4. he eond-ode/ one-onjugae CCF of DSB SSB M-PSK M-QAM nomalized diee-ime eeived ignal a CF β delay τ ae a follow 2 j 2 f f π τ x (DSB (; βτ = 2 A ( S + N e m ( τf (7 + w( β; τ wih β= mx( τ f a he eond-ode/ one-onjugae momen of x( k (; w βτ a he of eond-ode/ one-onjugae yli umulan of wk ( = w ( / S+ N a CF β delay τ = kf 2 j2π fτf (SSB (; βτ =2 A ( S + N e (8 ( mx( τf m jm ( x( τf + w( β; τ wih β = m( (. x a he Hilbe anfom of m (. x 2 j2πγfε j2π fτf (; βτ = A ( S + N f e e (9 * j2πγk px ( k px ( k+τ e + w( β; τ k = wih β=γ= f k/ k inege 2 i=m-psk M-QAM M 2 * a he omplex onjugae. hu fo i = DSB SSB (; β τ a β = only wheea fo i=m-psk M-QAM M 2 (; β τ a β= f k/ k inege 2. hi popey i exploied o diinguih beween DSB BPSK a well a beween SSB M-PSK M-QAM M 4. III. PROPOSED CYCLOSAIONARIY-BASED CLASSIFIER he binay deiion ee algoihm popoed fo blind eogniion of analog digial modulaion i depied in Fig.. A eah node of he ee ignal yloaionaiy i exploied o make a deiion on he modulaion foma of he eeived ignal. A. Binay Deiion-ee Claifiaion Algoihm A Node of he ee diiminaion beween AM DSB SSB M-PSK M-QAM M 2 i pefomed by exploiing he peene of a CF in he fi-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF of he AM ignal. he eogniion poe i blindly pefomed oniing of he following wo ep: Sep I: he magniude of he fi-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF i eimaed fom he finie lengh eeived daa euene a idae CF β' ove he [ //2 ange. Fo an AM ignal a peak ou in hi magniude a CF β= f f i value deeae wih a eduion in he ignal o noie aio (SNR defined a SNR:= S/ N (ee (2. hu below a eain SNR he value of hi peak beome ompaable wih he aiially inignifian pike whih appea in he eimaed CCF magniude a idae CF β' β due o he finie lengh of daa euene 3 (example ae povided fo illuaion in Seion IV. If a peak i deeed in he eimaed magniude of he fi-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF Sep II i applied o he idae CF oeponding o hi peak. Ohewie i i deided ha he modulaion foma i no AM. Sep II: he yloaionaiy e developed in [2] i ued o e he idae CF oeponding o he peak deeed in Sep I. Definiion of he empoal yloaionaiy paamee i given in Appendix A. 2 Noe ha he inege k ake value in a denumeable e whih depend on he yloaionaiy ode ignal bwidh [2]. 3 Appaenly wih a finie lengh daa euene neihe he fi-ode eimaed CCF of AM a idae β β ' no of DSB SSB M-PSK M-QAM M 2 a any idae CF β ' ae idenially zeo. Noe ha eul of Appendix B need o be undeood a aympoial value whih ae obained by aveaging ove an infinie-ime ineval.
3 Deail on hi e ae given in Seion III. B. If he eed idae CF β ' i deided o be indeed a CF β he ignal i idenified a AM; ohewie a belonging o he DSB SSB M-PSK M-QAM ignal la. A Node 2 diiminaion beween DSB BPSK SSB M-PSK M-QAM M 4 i pefomed by exploiing he peene of a CF in he eond-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF of he DSB BPSK ignal fo zeo delay ( τ=. he laifiaion poe i imila o ha fo Node. A Node 3 Node 4 diiminaion beween DSB BPSK SSB M-PSK M-QAM M 4 i epeively pefomed by exploiing he peene of non-zeo CF in he eond-ode/ one-onjugae CCF of M-PSK M-QAM ignal M 2 fo zeo-delay ( τ=. he laifiaion poe i imila o ha fo Node wih Sep I applied o he ixh-ode/ hee-onjugae yli empoal momen funion (CMF Sep II o he eond-ode/ one-onjugae CCF. he eondode/ one-onjugae CCF magniude i no ued in Sep I a i value a non-zeo CF β=± f / i low even a high SNR peak oeponding o hee CF anno be diinguihed fom he aiially inignifian pike whih appea due o eimaion baed on a finie lengh daa euene. Inead he wo ymmei peak ae idenified fom he ixh-ode/ hee-onjugae CMF magniude 4. he idae CF whih oepond o he highe peak ou of he wo i hen eed in Sep II. I i o be noed ha he laifiaion poe doe no euie knowledge of he aie phae feueny offe ignal noie powe iming eovey. In addiion i i o be noed ha laifiaion beyond Node 4 an be pefomed by applying ohe algoihm popoed in lieaue uh a []-[3] fo linea digial modulaion [7] fo SSB ignal. B. Cyloaionaiy e A menioned in Seion III. A he yloaionaiy e developed in [2] i ued o hek he peene of a CF a eah node l l =...4 of he popoed laifiaion algoihm. he e i fomulaed a a wo hypohei-eing poblem i.e. H : he eed idae CF β ' i no a CF H : he eed idae CF β ' i indeed a CF. he e oni of hee ep i applied hee fo zeo delay 5 a follow. Sep : he nh-ode/ -onjugae CCF 5 i eimaed fom K ample a he idae CF β ' eleed in Sep I fo zeo delay i.e. ˆ ( β'; 5. hen he veo 4 By uing he yli umulan-o-momen fomula along wih (2-(22 (25-(26 one an eaily pove ha he magniude of he ixh-ode/ hee-onjugae CMF a β=± f / i geae han ha of he eondode/ one-onjugae CCF a he ame CF. 5 Fo Node n = = fo Node 2 n = 2 = fo Node 3 4 n = 2 =. ˆ : [Re{ ˆ ( '; } Im{ ˆ ( '; }] ( ( = K β K n n β 5 ( i fomed wih Re{.} Im{.} a he eal imaginay pa epeively. Sep 2: he aii ˆ = K Σ n n n ˆ ˆ 5 ( i ompued fo he eed idae CF β '. Hee - denoe maix anpoe invee epeively ˆ Σ i n an eimae of he maix Re {( Q + Q / 2} Im {( Q Q / 2} Σ = 5 (2 n Im {( Q + Q /2} Re {( Q Q /2} whee ( K ( K Q : = lim Cum[ ˆ ( β'; ˆ ( β'; ] n K ( K ( K* Q = ˆ β ˆ β K : lim Cum[ ( '; ( '; ] wih Cum[.] a he umulan opeao 6. he ovaiane Q Q ae given epeively by 7 8 [2] K = k n K = +ξ ξ= j2π2 β' k j2 πβ' ξ Q lim K Cum[ L ( k; L ( k ; ] e e K * = =- n K k= ξ +ξ j2 π( β' ξ Q lim K Cum[ L ( k; L ( k ; ] e whee L ((* ( ( k n i u i ; : = ( k i he n h-ode/ u = -onjugae lag podu of ( k fo zeo delay-veo wih ( u u =... n a a poible onjugaion o ha he oal numbe of onjugaion i. Sep 3: he aii 5 eimaed a eed idae CF β ' fo zeo delay i ompaed again a hehold Γ ( l ( l l =...4 fo deiion-making. If 5 one deide ha he eed idae CF i indeed a CF fo zeo delay; ohewie i i no delaed a CF. he hehold i e fo a given pobabiliy of ( l ( K ( l fale alam PF = P{ n H} 5 l =...4 by aking ino aoun ha 5 ha an aympoi χ 2 diibuion wih wo degee of feedom unde H [2]. 5 IV. SIMULAION RESULS A. Simulaion Seup Fo he geneaion of analog ignal he modulaing ignal x( i obained by low-pa fileing a euene of zeo-mean Gauian om numbe wih uni vaiane. he analog ignal 6 Fo he umulan definiion ee e.g. [3] Ch.2. 7 Noe ha hee eualiie ae alway valid if n = wheea only fo a zeo-mean poe if n = 2. 8 Fo he ovaiane eimao ee e.g. [2] e. (48. 5
4 ae aled o ha he ignal powe i. Fo he AM ignal he modulaion index µ A i omly hoen beween. Fo he linea digial modulaion la we imulae BPSK QPSK 8-PSK 6-QAM 64-QAM wih uni vaiane onellaion. he ignal powe i alo e o he pule hape px ( i oo-aied oine wih.25 oll-off fao []. he ignal bwidh i B = 3 KHz. A he eeive-ide a low-pa file i ued o eliminae he ou-of-b noie he eeived ignal i ampled a a ae f = 48 KHz. he obevaion ineval available 4 a he eeive i eond whih yield K = 4.8 ample. he SNR i defined a he ignal powe o he noie powe a he oupu of eeive file. All eeived ignal ae affeed by a phae θ unifomly diibued ove [ π π a aie feueny offe f f =.. In addiion linea digial ignal ae affeed by a iming eo ε wih ε =.8. B. Eimaed CCF Magniude Saii Ued fo Deiion- Making hehold Seing he magniude of he fi-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF of AM BPSK ignal ae given fo illuaion in Fig. 2 a b a -db -2dB SNR epeively. Fo AM one an noie he peak in ˆ (AM ( β ' a β=β= ' f. f = a well a he eduion of i value wih a deeae in SNR. On he ohe h non-zeo pike due o eimaion baed on a finie lengh daa ( euene ae o be noed in ˆ K ( i ( β ' i=am DSB. Baed on ˆ ( β'; 5 he aii 5 i alulaed a eah node l l =...4 aoding o (. A Kaie window of lengh 6 paamee wa ued o ompue he ovaiane eimae in (2 8. A eah node l he aii i ompaed again a hehold Γ ( l ( (2 l =...4. Hee Γ =Γ =8.42 (3 (4 Γ =Γ =3.86. hee value oepond o a 4 pobabiliy of fale alam of 3 epeively [4] ae e baed on he eimaed value of he aii ued fo deiion-making. C. Claifiaion Pefomane o evaluae he pefomane of he popoed laifiaion algoihm we define he aveage pobabiliy of oe ( l 2 ( li li laifiaion a eah node l l =... 4 a P = 2 P li = ( i i wih P l l a he aveage pobabiliy o hooe he banh l i l i = 2 when indeed he banh l i i he oe hoie. he ( i i pobabiliy l l ( N li mod ( l ( i i li P i fuhe ompued a P / i N = mod wih ( l N i mod a he numbe of poible modulaion fo he l i h banh ( i P l i a he pobabiliy o hooe he l i h banh when he ( li i h ignal i anmied i =... Nmod. Fo example wih ( ( ( l = (Node l = (AM banh N mod = P = P. ( i he P l i i eimaed baed on 3 Mone Calo ial. he aveage pobabiliy of oe laifiaion a eah node ( l of he popoed binay deiion ee algoihm P l =...4 i ploed veu SNR in Fig. 3. A Node ( l = a pobabiliy of oe laifiaion of one i ahieved a SNR a low a -23dB o diiminae AM fom DSB SSB BPSK QPSK 8-PSK 6-QAM 64-QAM. A Node 2 ( l = 2 uh a pefomane i aained a SNR a low a -8dB o diiminae DSB BPSK fom SSB QPSK 8-PSK 6-QAM 64-QAM. A Node 3 4 ( l = 3 4 5dB SNR i euied o diiminae wih pobabiliy one beween DSB BPSK SSB QPSK 8-PSK 6-QAM 64-QAM epeively. Noe ha he aii whih i uenly ued a Node 3 4 an be applied o diinguih beween analog digial modulaion a Node i.e. o diiminae AM DSB SSB fom M-PSK M-QAM. Howeve highe SNR would be euied o ahieve he ame laifiaion pefomane a Node hu he pefomane of he whole laifie would be limied. I i alo o be noed ha eul peviouly peened ae ahieved fo eond obevaion ineval. Appaenly if a lage obevaion ineval i available a he eeive-ide he eimae will be moe auae whih in un will eul in a bee laifiaion pefomane. V. CONCLUSION A yloaionaiy-baed binay deiion ee algoihm ha been popoed fo analog digial modulaion laifiaion. he algoihm povide a good laifiaion pefomane in addiive Gauian noie doe no euie eimaion of aie phae feueny offe ignal noie powe iming eovey in he pepoeing ep. REFERENCES [] O. A. Dobe A. Abdi Y. Ba-Ne W. Su A uvey of auomai modulaion laifiaion ehniue: Claial appoahe new end o be publihed in IEE Po. Commun. 26. [2] O. A. Dobe Y. Ba-Ne W. Su Highe-ode yli umulan fo high ode modulaion laifiaion in Po. IEEE MILCOM 23 pp [3] C. M. Spoone Claifiaion of ohannel ommuniaion ignal uing yli umulan in Po. ASILOMAR 995 pp [4] O. A. Dobe A. Abdi Y. Ba-Ne W. Su Seleion ombining fo modulaion eogniion in fading hannel in Po. IEEE MILCOM 25 pp.-7. [5] E. E. Azzouz A. K. Ni Auomai Modulaion Reogniion of Communiaion Signal. Kluwe 996. [6] Y.. Chan L. G. Gadboi P. Yanouni Idenifiaion of he modulaion ype of a ignal Signal Poe. vol. 6 pp [7] O. A. Dobe A. Abdi Y. Ba-Ne W. Su he laifiaion of join analog digial modulaion in Po. IEEE MILCOM 25 pp.-6. [8] Y. O. Al-Jalili Idenifiaion algoihm of uppe ideb lowe ideb SSB ignal Signal Poe. vol. 42 pp
5 [9] W. A. Gadne Cyloaionaiy in Communiaion Signal Poeing. New Yok: IEEE Pe 994. [] A. B. Calon P. B. Cilly J. C. Ruledge Communiaion Syem 4h ed. MGaw Hill 22. [] A. Napoliano Cyli highe-ode aii: inpu/oupu elaion fo diee- oninuou-ime MIMO linea almo-peiodially imevaian yem Signal Poe. vol. 42 pp [2] A. V. Dawade G. B. Giannaki Saiial e fo peene of yloaionaiy IEEE an. Signal Poe. vol. 42 pp [3] C. L. Nikia A. P. Peopulu Highe-Ode Spea Analyi: A Nonlinea Signal Poeing Famewok. Penie Hall 993 [4] M. Abamowiz I. A. Segun Hbook of Mahemaial Funion. New Yok: Dove Publiaion 972. [5] R. C. Cabo A noe on he appliaion of he Hilbe anfom o ime delay eimaion IEEE an. Aou. Speeh Signal Poeing vol. 29 pp APPENDIX A: EMPORAL CYCLOSAIONARIY PARAMEERS In he faion-of-ime (FO pobabiliy famewok ignal ae modeled a ime-eie ahe han ealizaion of ohai poee [9] []. hu wih he FO pobabiliy appoah aiial paamee ae defined hough infinie-ime aveage ahe han enemble aveage. hi appoah i ubeuenly ued o peen empoal yloaionaiy paamee. Le ( be a oninuou-ime omplex-valued ime-eie L % (; τ % be he n h-ode/ -onjugae lag podu of ( defined a L n % ((* ( (; i u i : = ( + u= u (3 whee τ % = [% τ = % τ2... % τ n] i he delay-veo. he ime-eie ( i aid o be n h-ode yloaionay fo a given onjugaion onfiguaion ( -onjugae if m% % I L% % e d I /2 j2πα% ( α % ; τ : = lim ( ; τ I I /2 j2πα : =< L% % ( ; e (4 exi i non-zeo fo ome delay veo a denumeable e of eal α% wih α % [9]. E. (4 define he CMF wih α% a CF. I i o be noed ha CMF aie fom a onideaion of he finie-engh addiive ine-wave omponen in he lag podu. he um of all uh omponen i given by he empoal momen funion (MF [9] { α} j 2πα m% ( ; τ % :=E % [ L% ( ; τ % ] = m% ( α% ; τ % e % (5 ( i ( i m ( i n n α κ % % m whee κ % = { α% : m% ( α% ; } { α% E } [.] i he expeaion opeao in he FO pobabiliy famewok whih eplae he uual opeao E[.] in he ohai famewok. hi aually pefom a ine-wave exaion opeaion i.e. i exa all addiive ine-wave omponen exien in i agumen. he n h-ode/ -onjugae empoal umulan funion (CF of ( an be expeed in em of he n h- lowe-ode MF by uing he momen-o-umulan fomula [9] % ( ; : = Cum[ (... ( +τ % ( + ] ( i ( i(* ((* i n ((* i n n n = m ( i {... } % z= z nz z ( (! ( ; (6 whee {... } i a paiion of = { 2... n} wih z z =... a non-empy dijoin ube of o ha hei eunion i i he numbe of he ube in a paiion ( n z i a delay veo whoe omponen ae elemen of { } n u u= wih indie peified by z n z i he numbe of elemen in he ube z fom whih z oepond o onjugae em. Noe ha z= nz = n z= z =. Fuhemoe % ( i (; un ou o be an almo-peiodi funion of ime ha an be wien a [9] % % % % % e πβ (7 j 2 % ( i (; τ = ( i ( ; β κ % β τ % whee % % % I % % e d (8 I /2 j2πβ% ( i (; β τ = lim ( i (; I τ I /2 i he n h-ode/ -onjugae CCF a CF β % κ % = { β% : % ( β% ; }. By uing (5 (6 (7 he n h-ode/ -onjugae CCF of ( a a CF β % an be expeed a [9] % % % ( i (; β τ = ( (! {... } m ( i =β % α% z= z α% % z nz z ( ; (9 whee α % = [ α%... α% ] i a e of CF i a -dimenional one veo. E. (9 i efeed o a he yli momen-oumulan fomula. A imila expeion an be wien o expe he CMF a a funion of CCF. hi i efeed o a he yli umulan-o-momen fomula i given by [9] m% ( ( α i % ; = ( i ( β ; {... } % % % =α z= z % z nz (2 β z whee β % = [ β%... β% ] i a e of CF. Fo he diee-ime ignal ( ( k i = ( obained by = kf ampling he oninuou-ime ignal ( a a ampling ae f he n h-ode/ -onjugae CCF he e of CF ae epeively given a (unde he aumpion of no aliaing [] % f f (2 (; β τ = ( β ; τ κ = { β [ /2;/2 : β = β% / f ( i ( β; τ } (22 whee τ = f wih omponen τ u = uf u =... n. Eimao of he yloaionaiy paamee defined in he FO famewok ae obained by onideing finie-ime aveage onvege aympoially o he ue value whih ae he infinie-ime aveage of he ame uaniie [9].
6 APPENDIX B: DERIVAIONS OF (2-(9 Subeuenly fi- / o eond-ode empoal yloaionaiy paamee of he ignal of inee ae deived. Wih a zeo-mean puely aionay modulaing ignal x( 9 by uing (3 (4 wih he ignal given in ( aking ino aoun he aiial popeie of he noie one an eaily how ha he fi-ode/ zeo-onjugae CMF of he eeived ignal ( i = AM DSB SSB ae a follow (AM j2πα% m% (AM ( α% :=< ( e jθ j j2 f 2 j Ae f e θ π e A( Ax( e πα % α= % (23 =< + µ = ohewie m% ( i ( α % = any α% i=dsb SSB. (24 A he fi-ode CMF CCF ae idenial (23 (24 hold alo fo he fi-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF i.e. % ( β % = m% ( α% β % =α% i=am DSB SSB. he n h-ode/ -onjugae CCF of linea digial modulaion i [2]-[3] n n j2πγε % jθ( n2 j2 π f ( u uτu % = (; β % = A e e e n (25 n (* u j2πγ% p ( +τ % e d+ % ( β% ; u= X u w n whee β=γ+ % % ( n2 f (26 wih γ=k % / k inege i he n h-ode/ -onjugae n umulan fo he ignal onellaion i i=m-psk M-QAM ( u i he opional minu ign aoiaed wih he opional onjugaion (* u u =... n. Noe ha % w(; β% n in (25 i non-zeo only fo n 2 =... n β=. Fo value of he n h-ode / -onjugae umulan fo diffeen linea digial modulaion ( n =...8 =... n ee e.g. [2]-[3]. n Odd-ode umulan (n odd eual zeo fo ymmei ignal onellaion [2]. hu wih = he fi-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF of M-PSK M-QAM ignal beome zeo i.e. % ( β % = any β % i=m-psk M-QAM. Seond-ode yloaionaiy i ubeuenly inveigaed fo DSB SSB M-PSK M-QAM ignal. One an eaily how ha he eond-ode/ zeo-onjugae CMF of he eeived ignal ( i=dsb SSB ae a follow (DSB (DSB j2πα% m% (DSB ( ατ % ;% :=< ( ( +τ % e = 2 j 2θ j2π f Ae e m% x( α % = 2 f (27 = ohewie m% ( ατ % ;% (SSB (SSB j2 :=< ( ( +τ e πα % % = any α%. (28 (SSB 9 Baed on hi aumpion one an eaily how ha < ( x ( = j2πα% j2πα% < xx ( ( + τ % e =< ( xx ((( + τ % e = any α %. he ideniie m% x = m% x( ( m% xx =m% xx( ( ( [] ae ued o deive (28 wih m% x : =< x(( x +τ % m% x : =< x(( x + τ % ( ( ( m% xx : =< x(( x +τ % ( ( m% xx : =< x(( x + τ % ( (. A he fi-ode CMF eual zeo fo i = DSB SSB a well a fo he noie w ( he yli momen-o-umulan fomula yield he eualiy of eond-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF CFM i.e. % (; β% τ % = m% ( α% ; β % =α% i = DSB SSB. By applying (25 wih n = 2 = = [ ] = fo i=bpsk = fo i=m-psk M-QAM M 4 [2] he eond-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF of M-PSK M-QAM ignal ae found a 2 j2πγε % j2θ j2π f A e e e j2πγ% % ( βτ %; % = px ( px ( e d i BPSK +τ % = (29 i = M-PSK M-QAM M 4 whee β % =γ+ % 2 f wih γ=k % / k inege. Similaly one an how ha he eond-ode/ one-onjugae CMF of he DSB SSB ignal ae given epeively a (DSB ( DSB * j2πα% m% ( ατ % ;% := ( ( ( + e ( DSB 2 j2π f 2 Ae mx( τ + mw( α% ; τ α % = = % % % % (3 ohewie m% ( ατ % ;% := ( ( ( + e (SSB (SSB * j2πα% (SSB 2 j2π f 2 Ae ( m% x( jm% x( + m% w( α% ; α % = = m ( (3 ohewie * whee m% x : =< x( x ( + τ % m( % ( x i he Hilbe anfom of m% ( x. he ideniy m% xx = mx( τ ( (% % [5] wih * m% xx : =< x( x ( + τ % ( ( i ued in deiving (3. Noe ha m% x = m% x( m% xx = m% xx( ( ( a x( i a ealvalued ignal. By uing he yli momen-o-umulan fomula one an eaily how ha he eond-ode/ one-onjugae CCF CMF of ( i= DSB SSB ae epeively eual. In ohe wod % (; β% τ % = m% ( α% ; β % =α% i= DSB SSB. Fo i=m-psk M-QAM by applying (25 wih n = 2 = = [2] i beome aighfowad ha 2 j2πγε % j2π f % (; βτ % % = A e e (32 * j2πγ% px ( px ( +τ % e d+ % w( β% ; wih β=γ=k % % / k inege. Wih he eul peviouly deived fo oninuou-ime ignal by applying (2 (22 aking ino aoun ignal nomalizaion one an eaily obain (2-(9 fo he nomalized diee-ime ignal.
7 AM DSB SSB BPSK QPSK 8-PSK 6-QAM 64-QAM DSB SSB BPSK QPSK 8-PSK 6-QAM 64-QAM No ( ( Ye DSB No (2 Ye AM (2 DSB BPSK SSB QPSK 8-PSK 6-QAM 64-QAM No (3 (4 Ye No ( (3 (4 Ye K β' β' BPSK Fig.. Popoed yloaionaiy-baed binay deiion ee laifiaion algoihm. SSB QPSK 8-PSK 6-QAM 64-QAM.35.3 ^(K (AM (β' ^(K (BPSK (β' Cidae yle feueny β'.2 a Cidae yle feueny β'.4 ^(K (AM (β' ^(K (BPSK (β' Cidae yle feueny β' Fig. 2. he eimaed fi-ode/ zeo-onjugae CCF magniude of AM BPSK ignal veu idae CF wih 4 K = 4.8 ample a SNR=-dB b SNR=-2dB. b Cidae yle feueny β'.95 l = l =2 l =3 l =4.9 P ( l SNR (db Fig. 3. he aveage pobabiliy of oe laifiaion veu SNR a eah node l l =... 4.
Consider a Binary antipodal system which produces data of δ (t)
 Modulaion Polem PSK: (inay Phae-hi keying) Conide a inay anipodal yem whih podue daa o δ ( o + δ ( o inay and epeively. Thi daa i paed o pule haping ile and he oupu o he pule haping ile i muliplied y o(
Modulaion Polem PSK: (inay Phae-hi keying) Conide a inay anipodal yem whih podue daa o δ ( o + δ ( o inay and epeively. Thi daa i paed o pule haping ile and he oupu o he pule haping ile i muliplied y o(
Multicode DS-CDMA With Joint Transmit/Receive Frequency-domain Equalization
 Muliode DS-CDMA Wih Join Tanmi/Reeive Fequeny-domain Equalizaion Kazuki TAKEDA iomihi TOMEBA and Fumiyuki ADACI Dep. of Eleial and Communiaion Engineeing, Gaduae Shool of Engineeing, Tohoku Univeiy 6-6-5,
Muliode DS-CDMA Wih Join Tanmi/Reeive Fequeny-domain Equalizaion Kazuki TAKEDA iomihi TOMEBA and Fumiyuki ADACI Dep. of Eleial and Communiaion Engineeing, Gaduae Shool of Engineeing, Tohoku Univeiy 6-6-5,
Final Exam. Tuesday, December hours, 30 minutes
 an Faniso ae Univesi Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 04 Final Exam Tuesda, Deembe 6 hous, 30 minues Name: Insuions. This is losed book, losed noes exam.. No alulaos of an kind ae allowed. 3. how all he alulaions.
an Faniso ae Univesi Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 04 Final Exam Tuesda, Deembe 6 hous, 30 minues Name: Insuions. This is losed book, losed noes exam.. No alulaos of an kind ae allowed. 3. how all he alulaions.
Molecular Evolution and Phylogeny. Based on: Durbin et al Chapter 8
 Molecula Evoluion and hylogeny Baed on: Dubin e al Chape 8. hylogeneic Tee umpion banch inenal node leaf Topology T : bifucaing Leave - N Inenal node N+ N- Lengh { i } fo each banch hylogeneic ee Topology
Molecula Evoluion and hylogeny Baed on: Dubin e al Chape 8. hylogeneic Tee umpion banch inenal node leaf Topology T : bifucaing Leave - N Inenal node N+ N- Lengh { i } fo each banch hylogeneic ee Topology
Low-complexity Algorithms for MIMO Multiplexing Systems
 Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Combinatorial Approach to M/M/1 Queues. Using Hypergeometric Functions
 Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
8.1. a) For step response, M input is u ( t) Taking inverse Laplace transform. as α 0. Ideal response, K c. = Kc Mτ D + For ramp response, 8-1
 8. a For ep repone, inpu i u, U Y a U α α Y a α α Taking invere Laplae ranform a α e e / α / α A α 0 a δ 0 e / α a δ deal repone, α d Y i Gi U i δ Hene a α 0 a i For ramp repone, inpu i u, U Soluion anual
8. a For ep repone, inpu i u, U Y a U α α Y a α α Taking invere Laplae ranform a α e e / α / α A α 0 a δ 0 e / α a δ deal repone, α d Y i Gi U i δ Hene a α 0 a i For ramp repone, inpu i u, U Soluion anual
Coupled Mass Transport and Reaction in LPCVD Reactors
 ople Ma Tanpo an eaion in LPV eao ile A in B e.g., SiH 4 in H Sepaae eao ino o egion, inaafe & annla b - oniniy Eqn: : onveion-iffion iffion-eaion Eqn Ampion! ile peie i in majo aie ga e.g., H isih 4!
ople Ma Tanpo an eaion in LPV eao ile A in B e.g., SiH 4 in H Sepaae eao ino o egion, inaafe & annla b - oniniy Eqn: : onveion-iffion iffion-eaion Eqn Ampion! ile peie i in majo aie ga e.g., H isih 4!
Add the transfer payments and subtract the total taxes from (1): Using these definitions, the above becomes: The Saving and Investment Equation:
 San Fanio Sae Univei Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 06 Poblem e 5 Conumpion-Saving Deiion and Riadian Equivalene. (0 poin. Saving and Invemen equaion. a. Deive he aving and invemen equaion. The fomula fo GDP uing
San Fanio Sae Univei Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 06 Poblem e 5 Conumpion-Saving Deiion and Riadian Equivalene. (0 poin. Saving and Invemen equaion. a. Deive he aving and invemen equaion. The fomula fo GDP uing
MEEN 617 Handout #11 MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Systems with VISCOUS DAMPING
 MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
Reinforcement learning
 Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
Let. x y. denote a bivariate time series with zero mean.
 Linear Filer Le x y : T denoe a bivariae ime erie wih zero mean. Suppoe ha he ime erie {y : T} i conruced a follow: y a x The ime erie {y : T} i aid o be conruced from {x : T} by mean of a Linear Filer.
Linear Filer Le x y : T denoe a bivariae ime erie wih zero mean. Suppoe ha he ime erie {y : T} i conruced a follow: y a x The ime erie {y : T} i aid o be conruced from {x : T} by mean of a Linear Filer.
The shortest path between two truths in the real domain passes through the complex domain. J. Hadamard
 Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
General Non-Arbitrage Model. I. Partial Differential Equation for Pricing A. Traded Underlying Security
 1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
Transmit Beamforming with Reduced Channel State Information in MIMO-OFDM Wireless Systems
 anmi Beamfoming wih Reduced Channel Sae Infomaion in MIMO-OFDM Wiele Syem Seung-Hyeon Yang, Jae-Yun Ko, and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Elecical Engineeing and INMC Seoul Naional Univeiy Seoul, Koea Email:
anmi Beamfoming wih Reduced Channel Sae Infomaion in MIMO-OFDM Wiele Syem Seung-Hyeon Yang, Jae-Yun Ko, and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Elecical Engineeing and INMC Seoul Naional Univeiy Seoul, Koea Email:
QUASI-EXTREMUM SCALAR CONTROL FOR INDUCTION TRACTION MOTORS: RESULTS OF SIMULATION. Rodica Feştilă* Vasile Tulbure** Eva Dulf * Clement Feştilă*
 QUAI-EXEMUM CALA CONOL FO INDUCION ACION MOO: EUL OF IMULAION odia Feşilă aile ulbue Eva Dulf Cleen Feşilă Depaen of Auoai Conol, ehnial Univeiy of Cluj-Napoa, Fauly of Auoaion and Copue iene, 6-8 Baiiu,
QUAI-EXEMUM CALA CONOL FO INDUCION ACION MOO: EUL OF IMULAION odia Feşilă aile ulbue Eva Dulf Cleen Feşilă Depaen of Auoai Conol, ehnial Univeiy of Cluj-Napoa, Fauly of Auoaion and Copue iene, 6-8 Baiiu,
Surface Contents Author Index
 uae onen Auho Inde IAP VOLUME IV PA 2 OMMIION II i an Aug.2-22 EM ALIBAION OF INELLIGEN PHOOGAMMEON Heping PAN 1 hunen HANG 2 1 Digial Inelligene eeah ene hool o emoe ening and Inomaion EngineeingWuhan
uae onen Auho Inde IAP VOLUME IV PA 2 OMMIION II i an Aug.2-22 EM ALIBAION OF INELLIGEN PHOOGAMMEON Heping PAN 1 hunen HANG 2 1 Digial Inelligene eeah ene hool o emoe ening and Inomaion EngineeingWuhan
L. Yaroslavsky. Image data fusion. Processing system. Input scene. Output images
 L. Yaolavk Image daa fuion Poceing em Inpu cene Oupu image Muli componen imaging and eoaion model Conide an M componen imaging em and aume ha each image of M componen can be decibed in a domain of a ceain
L. Yaolavk Image daa fuion Poceing em Inpu cene Oupu image Muli componen imaging and eoaion model Conide an M componen imaging em and aume ha each image of M componen can be decibed in a domain of a ceain
 WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 31 Signal & Syem Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #27 C-T Syem: Laplace Tranform Power Tool for yem analyi Reading Aignmen: Secion 6.1 6.3 of Kamen and Heck 1/18 Coure Flow Diagram The arrow here how concepual
EECE 31 Signal & Syem Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #27 C-T Syem: Laplace Tranform Power Tool for yem analyi Reading Aignmen: Secion 6.1 6.3 of Kamen and Heck 1/18 Coure Flow Diagram The arrow here how concepual
7 Wave Equation in Higher Dimensions
 7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
Support Vector Machines
 Suppo Veco Machine CSL 3 ARIFICIAL INELLIGENCE SPRING 4 Suppo Veco Machine O, Kenel Machine Diciminan-baed mehod olean cla boundaie Suppo veco coni of eample cloe o bounday Kenel compue imilaiy beeen eample
Suppo Veco Machine CSL 3 ARIFICIAL INELLIGENCE SPRING 4 Suppo Veco Machine O, Kenel Machine Diciminan-baed mehod olean cla boundaie Suppo veco coni of eample cloe o bounday Kenel compue imilaiy beeen eample
Exponential and Logarithmic Equations and Properties of Logarithms. Properties. Properties. log. Exponential. Logarithmic.
 Eponenial and Logaihmic Equaions and Popeies of Logaihms Popeies Eponenial a a s = a +s a /a s = a -s (a ) s = a s a b = (ab) Logaihmic log s = log + logs log/s = log - logs log s = s log log a b = loga
Eponenial and Logaihmic Equaions and Popeies of Logaihms Popeies Eponenial a a s = a +s a /a s = a -s (a ) s = a s a b = (ab) Logaihmic log s = log + logs log/s = log - logs log s = s log log a b = loga
Lecture 17: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System:
 Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Representing Knowledge. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Properties of BNs. Independence? Reachability (the Bayes Ball) Example
 C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
Today - Lecture 13. Today s lecture continue with rotations, torque, Note that chapters 11, 12, 13 all involve rotations
 Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Introduction to SLE Lecture Notes
 Inroducion o SLE Lecure Noe May 13, 16 - The goal of hi ecion i o find a ufficien condiion of λ for he hull K o be generaed by a imple cure. I urn ou if λ 1 < 4 hen K i generaed by a imple curve. We will
Inroducion o SLE Lecure Noe May 13, 16 - The goal of hi ecion i o find a ufficien condiion of λ for he hull K o be generaed by a imple cure. I urn ou if λ 1 < 4 hen K i generaed by a imple curve. We will
Lecture-V Stochastic Processes and the Basic Term-Structure Equation 1 Stochastic Processes Any variable whose value changes over time in an uncertain
 Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
Lecture 18: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System: general kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximation
 Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
8.5 Circles and Lengths of Segments
 LenghofSegmen20052006.nb 1 8.5 Cicle and Lengh of Segmen In hi ecion we will how (and in ome cae pove) ha lengh of chod, ecan, and angen ae elaed in ome nal way. We will look a hee heoem ha ae hee elaionhip
LenghofSegmen20052006.nb 1 8.5 Cicle and Lengh of Segmen In hi ecion we will how (and in ome cae pove) ha lengh of chod, ecan, and angen ae elaed in ome nal way. We will look a hee heoem ha ae hee elaionhip
UT Austin, ECE Department VLSI Design 5. CMOS Gate Characteristics
 La moule: CMOS Tranior heory Thi moule: DC epone Logic Level an Noie Margin Tranien epone Delay Eimaion Tranior ehavior 1) If he wih of a ranior increae, he curren will ) If he lengh of a ranior increae,
La moule: CMOS Tranior heory Thi moule: DC epone Logic Level an Noie Margin Tranien epone Delay Eimaion Tranior ehavior 1) If he wih of a ranior increae, he curren will ) If he lengh of a ranior increae,
Part I. Labor- Leisure Decision (15 pts)
 Eon 509 Sping 204 Final Exam S. Paene Pa I. Labo- Leisue Deision (5 ps. Conside he following sai eonom given b he following equaions. Uili ln( H ln( l whee H sands fo he househ f f Poduion: Ah whee f sands
Eon 509 Sping 204 Final Exam S. Paene Pa I. Labo- Leisue Deision (5 ps. Conside he following sai eonom given b he following equaions. Uili ln( H ln( l whee H sands fo he househ f f Poduion: Ah whee f sands
Sections 3.1 and 3.4 Exponential Functions (Growth and Decay)
 Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Problem Set If all directed edges in a network have distinct capacities, then there is a unique maximum flow.
 CSE 202: Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Winer 2013 Problem Se 3 Inrucor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Due on: Tue. Feb 26, 2013 Inrucion For your proof, you may ue any lower bound, algorihm or daa rucure from he ex
CSE 202: Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Winer 2013 Problem Se 3 Inrucor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Due on: Tue. Feb 26, 2013 Inrucion For your proof, you may ue any lower bound, algorihm or daa rucure from he ex
Laplace Transform. Inverse Laplace Transform. e st f(t)dt. (2)
 Laplace Tranform Maoud Malek The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranform named in honor of mahemaician and aronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace, who ued he ranform in hi work on probabiliy heory. I i a powerful
Laplace Tranform Maoud Malek The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranform named in honor of mahemaician and aronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace, who ued he ranform in hi work on probabiliy heory. I i a powerful
Inference for A One Way Factorial Experiment. By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo
 Infeence fo A One Way Factoial Expeiment By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo. Intoduction We develop etimating equation fo Facto Level mean in a completely andomized one way factoial expeiment. Thi development
Infeence fo A One Way Factoial Expeiment By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo. Intoduction We develop etimating equation fo Facto Level mean in a completely andomized one way factoial expeiment. Thi development
Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) - State Feedback Design
 Linear Quadrai Regulaor (LQR) - Sae Feedbak Design A sysem is expressed in sae variable form as x = Ax + Bu n m wih x( ) R, u( ) R and he iniial ondiion x() = x A he sabilizaion problem using sae variable
Linear Quadrai Regulaor (LQR) - Sae Feedbak Design A sysem is expressed in sae variable form as x = Ax + Bu n m wih x( ) R, u( ) R and he iniial ondiion x() = x A he sabilizaion problem using sae variable
Degree of Approximation of a Class of Function by (C, 1) (E, q) Means of Fourier Series
 IAENG Inenaional Jounal of Applied Mahemaic, 4:, IJAM_4 7 Degee of Appoximaion of a Cla of Funcion by C, E, q Mean of Fouie Seie Hae Kihna Nigam and Kuum Shama Abac In hi pape, fo he fi ime, we inoduce
IAENG Inenaional Jounal of Applied Mahemaic, 4:, IJAM_4 7 Degee of Appoximaion of a Cla of Funcion by C, E, q Mean of Fouie Seie Hae Kihna Nigam and Kuum Shama Abac In hi pape, fo he fi ime, we inoduce
4/3/2017. PHY 712 Electrodynamics 9-9:50 AM MWF Olin 103
 PHY 7 Eleodnais 9-9:50 AM MWF Olin 0 Plan fo Leue 0: Coninue eading Chap Snhoon adiaion adiaion fo eleon snhoon deies adiaion fo asonoial objes in iula obis 0/05/07 PHY 7 Sping 07 -- Leue 0 0/05/07 PHY
PHY 7 Eleodnais 9-9:50 AM MWF Olin 0 Plan fo Leue 0: Coninue eading Chap Snhoon adiaion adiaion fo eleon snhoon deies adiaion fo asonoial objes in iula obis 0/05/07 PHY 7 Sping 07 -- Leue 0 0/05/07 PHY
MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH
 Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]](/thumbs/91/106162145.jpg) ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
Sample Final Exam (finals03) Covering Chapters 1-9 of Fundamentals of Signals & Systems
 Sample Final Exam Covering Chaper 9 (final04) Sample Final Exam (final03) Covering Chaper 9 of Fundamenal of Signal & Syem Problem (0 mar) Conider he caual opamp circui iniially a re depiced below. I LI
Sample Final Exam Covering Chaper 9 (final04) Sample Final Exam (final03) Covering Chaper 9 of Fundamenal of Signal & Syem Problem (0 mar) Conider he caual opamp circui iniially a re depiced below. I LI
Randomized Perfect Bipartite Matching
 Inenive Algorihm Lecure 24 Randomized Perfec Biparie Maching Lecurer: Daniel A. Spielman April 9, 208 24. Inroducion We explain a randomized algorihm by Ahih Goel, Michael Kapralov and Sanjeev Khanna for
Inenive Algorihm Lecure 24 Randomized Perfec Biparie Maching Lecurer: Daniel A. Spielman April 9, 208 24. Inroducion We explain a randomized algorihm by Ahih Goel, Michael Kapralov and Sanjeev Khanna for
On The Estimation of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complete Block Designs
 Mahemaical Theoy and Modeling ISSN 45804 (Pape ISSN 505 (Online Vol.6, No.7, 06 www.iise.og On The Esimaion of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complee Bloc Designs EFFANGA, EFFANGA OKON AND BASSE, E.
Mahemaical Theoy and Modeling ISSN 45804 (Pape ISSN 505 (Online Vol.6, No.7, 06 www.iise.og On The Esimaion of Two Missing Values in Randomized Complee Bloc Designs EFFANGA, EFFANGA OKON AND BASSE, E.
The sudden release of a large amount of energy E into a background fluid of density
 10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
Relative Positioning Method of Using Single-frequency Model for Formation Flying Missions
 Inenaional Induial Infomaic and Compue Engineeing Confeence (IIICEC 205) Relaive Poiioning Mehod of Uing Single-fequency Model fo Fomaion Flying Miion Hanyi Shi, Qizi Huangpeng2,a, Yuanyuan Qiao3,4, Yong
Inenaional Induial Infomaic and Compue Engineeing Confeence (IIICEC 205) Relaive Poiioning Mehod of Uing Single-fequency Model fo Fomaion Flying Miion Hanyi Shi, Qizi Huangpeng2,a, Yuanyuan Qiao3,4, Yong
Graphs III - Network Flow
 Graph III - Nework Flow Flow nework eup graph G=(V,E) edge capaciy w(u,v) 0 - if edge doe no exi, hen w(u,v)=0 pecial verice: ource verex ; ink verex - no edge ino and no edge ou of Aume every verex v
Graph III - Nework Flow Flow nework eup graph G=(V,E) edge capaciy w(u,v) 0 - if edge doe no exi, hen w(u,v)=0 pecial verice: ource verex ; ink verex - no edge ino and no edge ou of Aume every verex v
STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE WEIBULL DISTRIBUTION
 Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
Identification of Fault Locations using Transient State Estimation
 denificaion of Faul Locaion uing Tanien Sae Eimaion K. K.C. Yu, Suden Membe, EEE and N. R. Waon, Senio Membe, EEE Abac n a lage cale elecical powe yem, idenificaion of yem faul can be a ediou ak. Unexpeced
denificaion of Faul Locaion uing Tanien Sae Eimaion K. K.C. Yu, Suden Membe, EEE and N. R. Waon, Senio Membe, EEE Abac n a lage cale elecical powe yem, idenificaion of yem faul can be a ediou ak. Unexpeced
Engineering Accreditation. Heat Transfer Basics. Assessment Results II. Assessment Results. Review Definitions. Outline
 Hea ansfe asis Febua 7, 7 Hea ansfe asis a Caeo Mehanial Engineeing 375 Hea ansfe Febua 7, 7 Engineeing ediaion CSUN has aedied pogams in Civil, Eleial, Manufauing and Mehanial Engineeing Naional aediing
Hea ansfe asis Febua 7, 7 Hea ansfe asis a Caeo Mehanial Engineeing 375 Hea ansfe Febua 7, 7 Engineeing ediaion CSUN has aedied pogams in Civil, Eleial, Manufauing and Mehanial Engineeing Naional aediing
Fall 2014 Final Exam (250 pts)
 Eon 509 Fall 04 Final Exam (50 ps S. Paene Pa I. Answe ONLY ONE of he quesions below. (45 poins. Explain he onep of Riadian Equivalene. Wha ae he ondiions ha mus be saisfied fo i o h? Riadian Equivalene-
Eon 509 Fall 04 Final Exam (50 ps S. Paene Pa I. Answe ONLY ONE of he quesions below. (45 poins. Explain he onep of Riadian Equivalene. Wha ae he ondiions ha mus be saisfied fo i o h? Riadian Equivalene-
, on the power of the transmitter P t fed to it, and on the distance R between the antenna and the observation point as. r r t
 Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Chapter Finite Difference Method for Ordinary Differential Equations
 Chape 8.7 Finie Diffeence Mehod fo Odinay Diffeenial Eqaions Afe eading his chape, yo shold be able o. Undesand wha he finie diffeence mehod is and how o se i o solve poblems. Wha is he finie diffeence
Chape 8.7 Finie Diffeence Mehod fo Odinay Diffeenial Eqaions Afe eading his chape, yo shold be able o. Undesand wha he finie diffeence mehod is and how o se i o solve poblems. Wha is he finie diffeence
12. Nyquist Sampling, Pulse-Amplitude Modulation, and Time- Division Multiplexing
 Nyqui Sapling, Pule-Apliude Modulaion, and Tie Diviion Muliplexing on Mac 2. Nyqui Sapling, Pule-Apliude Modulaion, and Tie- Diviion Muliplexing Many analogue counicaion ye are ill in wide ue oday. Thee
Nyqui Sapling, Pule-Apliude Modulaion, and Tie Diviion Muliplexing on Mac 2. Nyqui Sapling, Pule-Apliude Modulaion, and Tie- Diviion Muliplexing Many analogue counicaion ye are ill in wide ue oday. Thee
Lecture 9. Transport Properties in Mesoscopic Systems. Over the last 1-2 decades, various techniques have been developed to synthesize
 eue 9. anspo Popeies in Mesosopi Sysems Ove he las - deades, vaious ehniques have been developed o synhesize nanosuued maeials and o fabiae nanosale devies ha exhibi popeies midway beween he puely quanum
eue 9. anspo Popeies in Mesosopi Sysems Ove he las - deades, vaious ehniques have been developed o synhesize nanosuued maeials and o fabiae nanosale devies ha exhibi popeies midway beween he puely quanum
Sensors, Signals and Noise
 Sensors, Signals and Noise COURSE OUTLINE Inroducion Signals and Noise: 1) Descripion Filering Sensors and associaed elecronics rv 2017/02/08 1 Noise Descripion Noise Waveforms and Samples Saisics of Noise
Sensors, Signals and Noise COURSE OUTLINE Inroducion Signals and Noise: 1) Descripion Filering Sensors and associaed elecronics rv 2017/02/08 1 Noise Descripion Noise Waveforms and Samples Saisics of Noise
The International Diversification Puzzle when Goods Prices are Sticky: It s Really about Exchange-Rate Hedging, not Equity Portfolios
 The Inenaional Diveificaion Puzzle when Good Pice ae Sicky: I eally abou Exchange-ae edging, no Equiy Pofolio by CALES ENGEL AND AKITO MATSUMOTO Appendix A. Soluion of he Dynamic Model An equilibium aifie
The Inenaional Diveificaion Puzzle when Good Pice ae Sicky: I eally abou Exchange-ae edging, no Equiy Pofolio by CALES ENGEL AND AKITO MATSUMOTO Appendix A. Soluion of he Dynamic Model An equilibium aifie
On Control Problem Described by Infinite System of First-Order Differential Equations
 Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
Problem Set #1. i z. the complex propagation constant. For the characteristic impedance:
 Problem Se # Problem : a) Using phasor noaion, calculae he volage and curren waves on a ransmission line by solving he wave equaion Assume ha R, L,, G are all non-zero and independen of frequency From
Problem Se # Problem : a) Using phasor noaion, calculae he volage and curren waves on a ransmission line by solving he wave equaion Assume ha R, L,, G are all non-zero and independen of frequency From
Flow networks. Flow Networks. A flow on a network. Flow networks. The maximum-flow problem. Introduction to Algorithms, Lecture 22 December 5, 2001
 CS 545 Flow Nework lon Efra Slide courey of Charle Leieron wih mall change by Carola Wenk Flow nework Definiion. flow nework i a direced graph G = (V, E) wih wo diinguihed verice: a ource and a ink. Each
CS 545 Flow Nework lon Efra Slide courey of Charle Leieron wih mall change by Carola Wenk Flow nework Definiion. flow nework i a direced graph G = (V, E) wih wo diinguihed verice: a ource and a ink. Each
#5 Demodulation and Detection Error due to Noise
 06 Q Wirele Communicaion Engineering #5 Demodulaion and Deecion Error due o Noie Kei Sakaguci akaguci@mobile.ee. Jul 8, 06 Coure Scedule Dae Tex Conen # June 7, 7 Inroducion o wirele communicaion em #
06 Q Wirele Communicaion Engineering #5 Demodulaion and Deecion Error due o Noie Kei Sakaguci akaguci@mobile.ee. Jul 8, 06 Coure Scedule Dae Tex Conen # June 7, 7 Inroducion o wirele communicaion em #
Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway
 Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
Primal and Weakly Primal Sub Semi Modules
 Aein Inenionl Jounl of Conepoy eeh Vol 4 No ; Jnuy 204 Pil nd Wekly Pil ub ei odule lik Bineh ub l hei Depen Jodn Univeiy of iene nd Tehnology Ibid 220 Jodn Ab Le be ouive eiing wih ideniy nd n -ei odule
Aein Inenionl Jounl of Conepoy eeh Vol 4 No ; Jnuy 204 Pil nd Wekly Pil ub ei odule lik Bineh ub l hei Depen Jodn Univeiy of iene nd Tehnology Ibid 220 Jodn Ab Le be ouive eiing wih ideniy nd n -ei odule
Control Systems -- Final Exam (Spring 2006)
 6.5 Conrol Syem -- Final Eam (Spring 6 There are 5 prolem (inluding onu prolem oal poin. (p Given wo marie: (6 Compue A A e e. (6 For he differenial equaion [ ] ; y u A wih ( u( wha i y( for >? (8 For
6.5 Conrol Syem -- Final Eam (Spring 6 There are 5 prolem (inluding onu prolem oal poin. (p Given wo marie: (6 Compue A A e e. (6 For he differenial equaion [ ] ; y u A wih ( u( wha i y( for >? (8 For
Network Flow. Data Structures and Algorithms Andrei Bulatov
 Nework Flow Daa Srucure and Algorihm Andrei Bulao Algorihm Nework Flow 24-2 Flow Nework Think of a graph a yem of pipe We ue hi yem o pump waer from he ource o ink Eery pipe/edge ha limied capaciy Flow
Nework Flow Daa Srucure and Algorihm Andrei Bulao Algorihm Nework Flow 24-2 Flow Nework Think of a graph a yem of pipe We ue hi yem o pump waer from he ource o ink Eery pipe/edge ha limied capaciy Flow
Chapter 7: Inverse-Response Systems
 Chaper 7: Invere-Repone Syem Normal Syem Invere-Repone Syem Baic Sar ou in he wrong direcion End up in he original eady-ae gain value Two or more yem wih differen magniude and cale in parallel Main yem
Chaper 7: Invere-Repone Syem Normal Syem Invere-Repone Syem Baic Sar ou in he wrong direcion End up in he original eady-ae gain value Two or more yem wih differen magniude and cale in parallel Main yem
The distribution of the interval of the Cox process with shot noise intensity for insurance claims and its moments
 The diibuion of he ineval of he Cox poce wih ho noie ineniy fo inuance claim and i momen Angelo Daio, Ji-Wook Jang Depamen of Saiic, London School of Economic and Poliical Science, Houghon See, London
The diibuion of he ineval of he Cox poce wih ho noie ineniy fo inuance claim and i momen Angelo Daio, Ji-Wook Jang Depamen of Saiic, London School of Economic and Poliical Science, Houghon See, London
Topic 3. Single factor ANOVA: Introduction [ST&D Chapter 7] 3.1. The F distribution [ST&D p. 99]
![Topic 3. Single factor ANOVA: Introduction [ST&D Chapter 7] 3.1. The F distribution [ST&D p. 99] Topic 3. Single factor ANOVA: Introduction [ST&D Chapter 7] 3.1. The F distribution [ST&D p. 99]](/thumbs/95/124150085.jpg) Topic 3. Single faco ANOVA: Inoducion [ST&D Chape 7] "The analyi of vaiance i moe han a echnique fo aiical analyi. Once i i undeood, ANOVA i a ool ha can povide an inigh ino he naue of vaiaion of naual
Topic 3. Single faco ANOVA: Inoducion [ST&D Chape 7] "The analyi of vaiance i moe han a echnique fo aiical analyi. Once i i undeood, ANOVA i a ool ha can povide an inigh ino he naue of vaiaion of naual
Revision of Lecture Eight
 Revision of Lectue Eight Baseband equivalent system and equiements of optimal tansmit and eceive filteing: (1) achieve zeo ISI, and () maximise the eceive SNR Thee detection schemes: Theshold detection
Revision of Lectue Eight Baseband equivalent system and equiements of optimal tansmit and eceive filteing: (1) achieve zeo ISI, and () maximise the eceive SNR Thee detection schemes: Theshold detection
Lecture 26: Leapers and Creepers
 Lecue 6: Leape and Ceepe Scibe: Geain Jone (and Main Z. Bazan) Depamen of Economic, MIT May, 5 Inoducion Thi lecue conide he analyi of he non-epaable CTRW in which he diibuion of ep ize and ime beween
Lecue 6: Leape and Ceepe Scibe: Geain Jone (and Main Z. Bazan) Depamen of Economic, MIT May, 5 Inoducion Thi lecue conide he analyi of he non-epaable CTRW in which he diibuion of ep ize and ime beween
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
 COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
Variance and Covariance Processes
 Vaiance and Covaiance Pocesses Pakash Balachandan Depamen of Mahemaics Duke Univesiy May 26, 2008 These noes ae based on Due s Sochasic Calculus, Revuz and Yo s Coninuous Maingales and Bownian Moion, Kaazas
Vaiance and Covaiance Pocesses Pakash Balachandan Depamen of Mahemaics Duke Univesiy May 26, 2008 These noes ae based on Due s Sochasic Calculus, Revuz and Yo s Coninuous Maingales and Bownian Moion, Kaazas
Then the number of elements of S of weight n is exactly the number of compositions of n into k parts.
 Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
18.03SC Unit 3 Practice Exam and Solutions
 Sudy Guide on Sep, Dela, Convoluion, Laplace You can hink of he ep funcion u() a any nice mooh funcion which i for < a and for > a, where a i a poiive number which i much maller han any ime cale we care
Sudy Guide on Sep, Dela, Convoluion, Laplace You can hink of he ep funcion u() a any nice mooh funcion which i for < a and for > a, where a i a poiive number which i much maller han any ime cale we care
Stochastic dynamics of ion channels in sensory cilia: regulation by feedback
 Sohai dynai of ion hannel in enoy ilia: egulaion by feedbak Manoj Gopalakihnan MPI-PKS Pee Boowki Main Zapooky Fank Jülihe 4/9/5 MPI-PKS, -4-5 `Duing he pa deade, he olfaoy ye ha eeged fo elaive obuiy
Sohai dynai of ion hannel in enoy ilia: egulaion by feedbak Manoj Gopalakihnan MPI-PKS Pee Boowki Main Zapooky Fank Jülihe 4/9/5 MPI-PKS, -4-5 `Duing he pa deade, he olfaoy ye ha eeged fo elaive obuiy
Computer Propagation Analysis Tools
 Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Mahgoub Transform Method for Solving Linear Fractional Differential Equations
 Mahgoub Transform Mehod for Solving Linear Fraional Differenial Equaions A. Emimal Kanaga Puhpam 1,* and S. Karin Lydia 2 1* Assoiae Professor&Deparmen of Mahemais, Bishop Heber College Tiruhirappalli,
Mahgoub Transform Mehod for Solving Linear Fraional Differenial Equaions A. Emimal Kanaga Puhpam 1,* and S. Karin Lydia 2 1* Assoiae Professor&Deparmen of Mahemais, Bishop Heber College Tiruhirappalli,
Estimation and Confidence Intervals: Additional Topics
 Chapte 8 Etimation and Confidence Inteval: Additional Topic Thi chapte imply follow the method in Chapte 7 fo foming confidence inteval The text i a bit dioganized hee o hopefully we can implify Etimation:
Chapte 8 Etimation and Confidence Inteval: Additional Topic Thi chapte imply follow the method in Chapte 7 fo foming confidence inteval The text i a bit dioganized hee o hopefully we can implify Etimation:
A Theoretical Model of a Voltage Controlled Oscillator
 A Theoreical Model of a Volage Conrolled Ocillaor Yenming Chen Advior: Dr. Rober Scholz Communicaion Science Iniue Univeriy of Souhern California UWB Workhop, April 11-1, 6 Inroducion Moivaion The volage
A Theoreical Model of a Volage Conrolled Ocillaor Yenming Chen Advior: Dr. Rober Scholz Communicaion Science Iniue Univeriy of Souhern California UWB Workhop, April 11-1, 6 Inroducion Moivaion The volage
Algorithmic Discrete Mathematics 6. Exercise Sheet
 Algorihmic Dicree Mahemaic. Exercie Shee Deparmen of Mahemaic SS 0 PD Dr. Ulf Lorenz 7. and 8. Juni 0 Dipl.-Mah. David Meffer Verion of June, 0 Groupwork Exercie G (Heap-Sor) Ue Heap-Sor wih a min-heap
Algorihmic Dicree Mahemaic. Exercie Shee Deparmen of Mahemaic SS 0 PD Dr. Ulf Lorenz 7. and 8. Juni 0 Dipl.-Mah. David Meffer Verion of June, 0 Groupwork Exercie G (Heap-Sor) Ue Heap-Sor wih a min-heap
The Residual Graph. 11 Augmenting Path Algorithms. Augmenting Path Algorithm. Augmenting Path Algorithm
 Augmening Pah Algorihm Greedy-algorihm: ar wih f (e) = everywhere find an - pah wih f (e) < c(e) on every edge augmen flow along he pah repea a long a poible The Reidual Graph From he graph G = (V, E,
Augmening Pah Algorihm Greedy-algorihm: ar wih f (e) = everywhere find an - pah wih f (e) < c(e) on every edge augmen flow along he pah repea a long a poible The Reidual Graph From he graph G = (V, E,
ADAPTIVE BACKSTEPPING CONTROL FOR WIND TURBINES WITH DOUBLY-FED INDUCTION GENERATOR UNDER UNKNOWN PARAMETERS
 Jounal of Theoeial and Applied Infomaion Tehnology 5 h Sepembe 6. Vol.9. No. 5-6 JATIT LLS. All igh eeved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jai.og E-ISSN: 87-95 ADAPTIVE BAKSTEPPING ONTROL FOR WIND TURBINES WITH DOUBLY-FED
Jounal of Theoeial and Applied Infomaion Tehnology 5 h Sepembe 6. Vol.9. No. 5-6 JATIT LLS. All igh eeved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jai.og E-ISSN: 87-95 ADAPTIVE BAKSTEPPING ONTROL FOR WIND TURBINES WITH DOUBLY-FED
EE Control Systems LECTURE 2
 Copyrigh F.L. Lewi 999 All righ reerved EE 434 - Conrol Syem LECTURE REVIEW OF LAPLACE TRANSFORM LAPLACE TRANSFORM The Laplace ranform i very ueful in analyi and deign for yem ha are linear and ime-invarian
Copyrigh F.L. Lewi 999 All righ reerved EE 434 - Conrol Syem LECTURE REVIEW OF LAPLACE TRANSFORM LAPLACE TRANSFORM The Laplace ranform i very ueful in analyi and deign for yem ha are linear and ime-invarian
Orthotropic Materials
 Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u
![[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u [ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u](/thumbs/89/100187624.jpg) Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
Chapter 7. Interference
 Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
International Journal of Mathematical Archive-5(6), 2014, Available online through ISSN
 Inenaional Jonal o Mahemaical Achive-6, 0, 09-8 Availale online hogh www.ijma.ino ISSN 9 06 EXISENCE OF NONOSCILLAORY SOLUIONS OF A CLASS OF NONLINEAR NEURAL DELAY DIFFERENIAL EQUAIONS OF HIRD ORDER K
Inenaional Jonal o Mahemaical Achive-6, 0, 09-8 Availale online hogh www.ijma.ino ISSN 9 06 EXISENCE OF NONOSCILLAORY SOLUIONS OF A CLASS OF NONLINEAR NEURAL DELAY DIFFERENIAL EQUAIONS OF HIRD ORDER K
The Production of Well-Being: Conventional Goods, Relational Goods and Status Goods
 The Poducion of Well-Bein: Convenional Good, Relaional Good and Sau Good Aloy Pinz Iniue of Public Economic II Univeiy of Müne, Gemany New Diecion in Welfae II, OECD Pai July 06 08, 2011 Conen 1. Inoducion
The Poducion of Well-Bein: Convenional Good, Relaional Good and Sau Good Aloy Pinz Iniue of Public Economic II Univeiy of Müne, Gemany New Diecion in Welfae II, OECD Pai July 06 08, 2011 Conen 1. Inoducion
Control Volume Derivation
 School of eospace Engineeing Conol Volume -1 Copyigh 1 by Jey M. Seizman. ll ighs esee. Conol Volume Deiaion How o cone ou elaionships fo a close sysem (conol mass) o an open sysem (conol olume) Fo mass
School of eospace Engineeing Conol Volume -1 Copyigh 1 by Jey M. Seizman. ll ighs esee. Conol Volume Deiaion How o cone ou elaionships fo a close sysem (conol mass) o an open sysem (conol olume) Fo mass
Multiphase Shift Keying (MPSK) Lecture 8. Constellation. Decision Regions. s i. 2 T cos 2π f c t iφ 0 t As iφ 1 t. t As. A c i.
 π fc uliphase Shif Keying (PSK) Goals Lecure 8 Be able o analyze PSK modualion s i Ac i Ac Pcos π f c cos π f c iφ As iφ π i p p As i sin π f c p Be able o analyze QA modualion Be able o quanify he radeoff
π fc uliphase Shif Keying (PSK) Goals Lecure 8 Be able o analyze PSK modualion s i Ac i Ac Pcos π f c cos π f c iφ As iφ π i p p As i sin π f c p Be able o analyze QA modualion Be able o quanify he radeoff
The Production of Polarization
 Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
The Residual Graph. 12 Augmenting Path Algorithms. Augmenting Path Algorithm. Augmenting Path Algorithm
 Augmening Pah Algorihm Greedy-algorihm: ar wih f (e) = everywhere find an - pah wih f (e) < c(e) on every edge augmen flow along he pah repea a long a poible The Reidual Graph From he graph G = (V, E,
Augmening Pah Algorihm Greedy-algorihm: ar wih f (e) = everywhere find an - pah wih f (e) < c(e) on every edge augmen flow along he pah repea a long a poible The Reidual Graph From he graph G = (V, E,
To become more mathematically correct, Circuit equations are Algebraic Differential equations. from KVL, KCL from the constitutive relationship
 Laplace Tranform (Lin & DeCarlo: Ch 3) ENSC30 Elecric Circui II The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranformaion. I ranform: f ( ) F( ) ime variable complex variable From Euler > Lagrange > Laplace. Hence,
Laplace Tranform (Lin & DeCarlo: Ch 3) ENSC30 Elecric Circui II The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranformaion. I ranform: f ( ) F( ) ime variable complex variable From Euler > Lagrange > Laplace. Hence,
Lecture 22 Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
and substitute in to the 1 st period budget constraint b. Derive the utility maximization condition (10 pts)
 Eon 50 Sping 06 Midem Examinaion (00 ps S.L. Paene Ovelapping Geneaions Model (50 ps Conside he following he Ovelapping Geneaions model whee people live wo peiods. Eah geneaion has he same numbe of people.
Eon 50 Sping 06 Midem Examinaion (00 ps S.L. Paene Ovelapping Geneaions Model (50 ps Conside he following he Ovelapping Geneaions model whee people live wo peiods. Eah geneaion has he same numbe of people.
Lecture 5. Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons, and Light
 Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
TRAVELING WAVES. Chapter Simple Wave Motion. Waves in which the disturbance is parallel to the direction of propagation are called the
 Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
Introduction to Congestion Games
 Algorihmic Game Theory, Summer 2017 Inroducion o Congeion Game Lecure 1 (5 page) Inrucor: Thoma Keelheim In hi lecure, we ge o know congeion game, which will be our running example for many concep in game
Algorihmic Game Theory, Summer 2017 Inroducion o Congeion Game Lecure 1 (5 page) Inrucor: Thoma Keelheim In hi lecure, we ge o know congeion game, which will be our running example for many concep in game
The Non-Truncated Bulk Arrival Queue M x /M/1 with Reneging, Balking, State-Dependent and an Additional Server for Longer Queues
 Alied Maheaical Sciece Vol. 8 o. 5 747-75 The No-Tucaed Bul Aival Queue M x /M/ wih Reei Bali Sae-Deede ad a Addiioal Seve fo Loe Queue A. A. EL Shebiy aculy of Sciece Meofia Uiveiy Ey elhebiy@yahoo.co
Alied Maheaical Sciece Vol. 8 o. 5 747-75 The No-Tucaed Bul Aival Queue M x /M/ wih Reei Bali Sae-Deede ad a Addiioal Seve fo Loe Queue A. A. EL Shebiy aculy of Sciece Meofia Uiveiy Ey elhebiy@yahoo.co
Interpolation and Pulse Shaping
 EE345S Real-Time Digial Signal Proceing Lab Spring 2006 Inerpolaion and Pule Shaping Prof. Brian L. Evan Dep. of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering The Univeriy of Texa a Auin Lecure 7 Dicree-o-Coninuou
EE345S Real-Time Digial Signal Proceing Lab Spring 2006 Inerpolaion and Pule Shaping Prof. Brian L. Evan Dep. of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering The Univeriy of Texa a Auin Lecure 7 Dicree-o-Coninuou
