Fermi s Golden Rule and Simple Feynman Rules
|
|
|
- Samuel Bradley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fermi s Golden Rule and Simple Feynman Rules ; December 5, 2013
2 Outline Golden Rule 1 Golden Rule 2
3 Recipe For the Golden Rule For both decays rates and cross sections we need: The invariant amplitude M Phase space available M comes from evaluating the relevant Feynman diagram Phase space depends on the masses, momentum and energy of the particles
4 The more phase space available to the final products the higher the probability the reaction will occur π + (139.6MeV ) e + (0.51MeV ) + ν e m = 139.1MeV (1) π + (139.6MeV ) π0 (135.0) + e + (0.51MeV ) + ν e m = 4.1MeV (2) In decay (1) there is a larger mass decrease so there are more ways to distribute momentum to the three reactants This means decay (1) has a higher probability than decay (2)
5 Fermi s Golden rules says the transition rate is essentially the product of phase space and M Decay rate for 1 -> n Γ = S M 2 (2π) 4 δ 4 (p 1 p 2 p 3... p n ) 2 m 1 n x 2πδ(pj 2 mj 2 c2 )θ(pj 0 ) d 4 p j (2π) 4 j=2 cross section for > n σ = S 2 4 (p 1 p 2 ) 2 (m 1 m 2 c 2 ) 2 M 2 (2π) 4 δ 4 (p 1 + p 2 p 3... p n x n j=3 2πδ(p 2 j m 2 j c2 )θ(p 0 j ) d 4 p j (2π) 4
6 Γ = S 2 m 1 M 2 (2π) 4 δ 4 (p 1 p 2 p 3... p n ) x n j=2 2πδ(p 2 j m 2 j c2 )θ(p 0 j ) d 4 p j (2π) 4 S is a statistical factor which corrects for double counting S = (1/s 1!)(1/s 2!)...(1/s n!) Phase space constraints Outgoing particles lie on their mass shell p 2 j = m 2 j c 2 δ(p 2 j m 2 j c 4 ) Outgoing energies are positive θ(p 0 j ) Energy and momentum are conserved δ 4 (p 1 p 2 p 3... p n )
7 Example: Two Particle Decay Γ = S 2 m 1 M 2 (2π) 4 δ 4 (p 1 p 2 p 3 ) x(2π) 2 δ(p 2 2 m2 2 c2 )θ(p 0 2 )δ(p2 3 m2 3 c2 )θ(p 0 3 )d 4 p 2 d 4 p 3 (2π) 8 Using the identity δ(x 2 a 2 ) = 1 [δ(x a) + δ(x + a)] 2a We can integrate over dp2 0 and dp0 3 pj 0 = p j 2 + mj 2c2
8 Γ = S 32 π 2 m 1 M 2 δ4 (p 1 p 2 p 3 )d 4 p 2 d 4 p 3 p 22 + m22 c2 p m2 3 c2 If we go to the center of mass frame p 1 = 0 and p 2 = p 3 and the integral over d 3 p 3 becomes easy S Γ = 32 π 2 M δ(m 1c p m2 2 c2 p m2 2 c2 )d 3 p 2 m 1 p 22 + m22 c2 p m2 2 c2 This can be further simplified if we use spherical coordinates
9 Cross Section Golden Rule σ = S 2 4 (p 1 p 2 ) 2 (m 1 m 2 c 2 ) 2 M 2 (2π) 4 δ 4 (p 1 + p 2 p 3... p n x n j=3 2πδ(p 2 j m 2 j c2 )θ(p 0 j ) d 4 p j (2π) 4 Phase space constraints Outgoing particles lie on their mass shell p 2 j = m 2 j c 2 δ(p 2 j m 2 j c 4 ) Outgoing energies are positive θ(p 0 j ) Energy and momentum are conserved δ 4 (p 1 p 2 p 3... p n )
10 Example: Two Particle Scattering Consider in the CM frame p 2 = p 1 (p 1 p 2 ) 2 (m 1 m 2 c 2 ) 2 = (E 1 + E 2 ) p 1 /c Doing the same delta function manipulations as before x M δ[(e E 2 )/c 2 σ = (8π) 2 Sc (E 1 + E 2 ) p 1 p m2 3 c2 p m2 4 c2 ] d p p 3 p m23 c m24 c2
11 Using d 3 p = p 2 dpdω we can integrate over p and determine the differential cross section u = p m2 3 c2 + p m2 4 c2 du dp = up p 23 + m23 c2 p m2 4 c2 dσ dω = 2 (8π) 2 Sc (E 1 + E 2 ) p 1 M 2 δ[(e 1 + E 2 )/c u] p u du dσ dω = ( c)2 (8π) 2 S M 2 (E 1 + E 2 ) 2 p f p i
12 Simple To calculate M we need to use the Feynman rules for the corresponding Feynman diagram e γ g q e + q This section will give the rules for a primitive diagram such as the following B A C Real Feynamn diagrams will have further complications mostly due to spin
13 1. Notation: Label all incoming and outionig four-momenta and give a direction for their momentum k 2 q k 3 k 1 k 4 Label all internal momenta (q in this case) where momentum direction is arbitary 2. Vertex factors: For each vertex write a factor -ig. Where g is a coupling constant and is considered a small parameter. 3. Propagators: For each interal line write a factor of i q 2 j m 2 j c2
14 4. Conservation of energy and mentum: For each vertex write a delta function (2π) 4 δ 4 (k 1 + k 2 ) Where the k s are the four momenta coming into the vertex k 2 q k 3 k 1 k 4 5. Integrate over internal momenta: For each internal line write d 4 q j (2π) 4 and integrate over the internal momenta. 6. Cancel the delta function: The result will have a factor (2π) 4 δ 4 (k 1 + k 2 k 3 k 4 ). Erase this factor, multiply by i, and the result is M
15 Example. Golden Rule 1. Label all momenta k 2 k 1 q k 3 k 4 2. We have to vertices ( ig) 2 3. One internal momenta i q 2 m 2 qc 2 4. Two vertices (2π) 8 δ(k 1 k 2 q)δ(q + k 4 k 3 ) 5. One internal line d 4 q (2π) 4
16 So far M = ( ig) 2 i (2π) 8 δ(k q 2 mqc k 2 q)δ(q + k 4 k 3 ) d 4 q Simplifing and integrating M = ig 2 (2π) 4 (k 3 k 4 ) 2 m 2 qc 2 δ(k 1 k 2 k 3 + k 4 ) (2π) 4 6. Erasing the delta function and multiplying by i we arrive at M. M = g 2 (2π) 4 (k 3 k 4 ) 2 m 2 qc 2
THE FEYNMAN RULES. < f S i >. \ f >
 THE FEYNMAN RULES I. Introduction: Very generally, interactions can be viewed as the result of a scattering operator (S), a unitary operator acting on an initial state (\i >) leading to a multitude of
THE FEYNMAN RULES I. Introduction: Very generally, interactions can be viewed as the result of a scattering operator (S), a unitary operator acting on an initial state (\i >) leading to a multitude of
2 Feynman rules, decay widths and cross sections
 2 Feynman rules, decay widths and cross sections 2.1 Feynman rules Normalization In non-relativistic quantum mechanics, wave functions of free particles are normalized so that there is one particle in
2 Feynman rules, decay widths and cross sections 2.1 Feynman rules Normalization In non-relativistic quantum mechanics, wave functions of free particles are normalized so that there is one particle in
Lorentz invariant scattering cross section and phase space
 Chapter 3 Lorentz invariant scattering cross section and phase space In particle physics, there are basically two observable quantities : Decay rates, Scattering cross-sections. Decay: p p 2 i a f p n
Chapter 3 Lorentz invariant scattering cross section and phase space In particle physics, there are basically two observable quantities : Decay rates, Scattering cross-sections. Decay: p p 2 i a f p n
Pion Lifetime. A. George January 18, 2012
 Pion Lifetime A. George January 18, 01 Abstract We derive the expected lifetime of the pion, assuming only the Feynman Rules, Fermi s Golden Rule, the Dirac Equation and its corollary, the completeness
Pion Lifetime A. George January 18, 01 Abstract We derive the expected lifetime of the pion, assuming only the Feynman Rules, Fermi s Golden Rule, the Dirac Equation and its corollary, the completeness
Scattering amplitudes and the Feynman rules
 Scattering amplitudes and the Feynman rules based on S-10 We have found Z( J ) for the phi-cubed theory and now we can calculate vacuum expectation values of the time ordered products of any number of
Scattering amplitudes and the Feynman rules based on S-10 We have found Z( J ) for the phi-cubed theory and now we can calculate vacuum expectation values of the time ordered products of any number of
Lecture 6:Feynman diagrams and QED
 Lecture 6:Feynman diagrams and QED 0 Introduction to current particle physics 1 The Yukawa potential and transition amplitudes 2 Scattering processes and phase space 3 Feynman diagrams and QED 4 The weak
Lecture 6:Feynman diagrams and QED 0 Introduction to current particle physics 1 The Yukawa potential and transition amplitudes 2 Scattering processes and phase space 3 Feynman diagrams and QED 4 The weak
Intercollegiate post-graduate course in High Energy Physics. Paper 1: The Standard Model
 Brunel University Queen Mary, University of London Royal Holloway, University of London University College London Intercollegiate post-graduate course in High Energy Physics Paper 1: The Standard Model
Brunel University Queen Mary, University of London Royal Holloway, University of London University College London Intercollegiate post-graduate course in High Energy Physics Paper 1: The Standard Model
Cross-sections. Kevin Cahill for 524 January 24, There are two standard ways of normalizing states. We have been using continuum normalization
 Cross-sections Kevin Cahill for 54 January 4, 013 1 Fermi s Golden Rule There are two standard ways of normalizing states. We have been using continuum normalization p p = δ (3) (p p). (1) The other way
Cross-sections Kevin Cahill for 54 January 4, 013 1 Fermi s Golden Rule There are two standard ways of normalizing states. We have been using continuum normalization p p = δ (3) (p p). (1) The other way
Quantum Electrodynamics Test
 MSc in Quantum Fields and Fundamental Forces Quantum Electrodynamics Test Monday, 11th January 2010 Please answer all three questions. All questions are worth 20 marks. Use a separate booklet for each
MSc in Quantum Fields and Fundamental Forces Quantum Electrodynamics Test Monday, 11th January 2010 Please answer all three questions. All questions are worth 20 marks. Use a separate booklet for each
Decays and Scattering. Decay Rates Cross Sections Calculating Decays Scattering Lifetime of Particles
 Decays and Scattering Decay Rates Cross Sections Calculating Decays Scattering Lifetime of Particles 1 Decay Rates There are THREE experimental probes of Elementary Particle Interactions - bound states
Decays and Scattering Decay Rates Cross Sections Calculating Decays Scattering Lifetime of Particles 1 Decay Rates There are THREE experimental probes of Elementary Particle Interactions - bound states
The path integral for photons
 The path integral for photons based on S-57 We will discuss the path integral for photons and the photon propagator more carefully using the Lorentz gauge: as in the case of scalar field we Fourier-transform
The path integral for photons based on S-57 We will discuss the path integral for photons and the photon propagator more carefully using the Lorentz gauge: as in the case of scalar field we Fourier-transform
Quantum Field Theory Spring 2019 Problem sheet 3 (Part I)
 Quantum Field Theory Spring 2019 Problem sheet 3 (Part I) Part I is based on material that has come up in class, you can do it at home. Go straight to Part II. 1. This question will be part of a take-home
Quantum Field Theory Spring 2019 Problem sheet 3 (Part I) Part I is based on material that has come up in class, you can do it at home. Go straight to Part II. 1. This question will be part of a take-home
Loop corrections in Yukawa theory based on S-51
 Loop corrections in Yukawa theory based on S-51 Similarly, the exact Dirac propagator can be written as: Let s consider the theory of a pseudoscalar field and a Dirac field: the only couplings allowed
Loop corrections in Yukawa theory based on S-51 Similarly, the exact Dirac propagator can be written as: Let s consider the theory of a pseudoscalar field and a Dirac field: the only couplings allowed
Decays of the Higgs Boson
 Decays of te Higgs Boson Daniel Odell April 8, 5 We will calculate various decay modes of te Higgs boson. We start wit te decay of te Higgs to a fermion-antifermion pair. f f Figure : f f First, we ll
Decays of te Higgs Boson Daniel Odell April 8, 5 We will calculate various decay modes of te Higgs boson. We start wit te decay of te Higgs to a fermion-antifermion pair. f f Figure : f f First, we ll
Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics I
 Physics 56400 Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics I Lecture 16 Fall 018 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Review of Lecture 15 When we introduced a (classical) electromagnetic field, the Dirac equation
Physics 56400 Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics I Lecture 16 Fall 018 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Review of Lecture 15 When we introduced a (classical) electromagnetic field, the Dirac equation
Feynman Diagrams. e + e µ + µ scattering
 Feynman Diagrams Pictorial representations of amplitudes of particle reactions, i.e scatterings or decays. Greatly reduce the computation involved in calculating rate or cross section of a physical process,
Feynman Diagrams Pictorial representations of amplitudes of particle reactions, i.e scatterings or decays. Greatly reduce the computation involved in calculating rate or cross section of a physical process,
QFT. Unit 11: Cross Sections and Decay Rates
 QFT Unit 11: Cross Sections and Decay Rates Decays and Collisions n When it comes to elementary particles, there are only two things that ever really happen: One particle decays into stuff Two particles
QFT Unit 11: Cross Sections and Decay Rates Decays and Collisions n When it comes to elementary particles, there are only two things that ever really happen: One particle decays into stuff Two particles
Lecture 3 (Part 1) Physics 4213/5213
 September 8, 2000 1 FUNDAMENTAL QED FEYNMAN DIAGRAM Lecture 3 (Part 1) Physics 4213/5213 1 Fundamental QED Feynman Diagram The most fundamental process in QED, is give by the definition of how the field
September 8, 2000 1 FUNDAMENTAL QED FEYNMAN DIAGRAM Lecture 3 (Part 1) Physics 4213/5213 1 Fundamental QED Feynman Diagram The most fundamental process in QED, is give by the definition of how the field
Textbook Problem 4.2: We begin by developing Feynman rules for the theory at hand. The Hamiltonian clearly
 PHY 396 K. Solutions for problem set #10. Textbook Problem 4.2: We begin by developing Feynman rules for the theory at hand. The Hamiltonian clearly decomposes into Ĥ = Ĥ0 + ˆV where and Ĥ 0 = Ĥfree Φ
PHY 396 K. Solutions for problem set #10. Textbook Problem 4.2: We begin by developing Feynman rules for the theory at hand. The Hamiltonian clearly decomposes into Ĥ = Ĥ0 + ˆV where and Ĥ 0 = Ĥfree Φ
LSZ reduction for spin-1/2 particles
 LSZ reduction for spin-1/2 particles based on S-41 In order to describe scattering experiments we need to construct appropriate initial and final states and calculate scattering amplitude. Summary of free
LSZ reduction for spin-1/2 particles based on S-41 In order to describe scattering experiments we need to construct appropriate initial and final states and calculate scattering amplitude. Summary of free
REVIEW REVIEW. A guess for a suitable initial state: Similarly, let s consider a final state: Summary of free theory:
 LSZ reduction for spin-1/2 particles based on S-41 In order to describe scattering experiments we need to construct appropriate initial and final states and calculate scattering amplitude. Summary of free
LSZ reduction for spin-1/2 particles based on S-41 In order to describe scattering experiments we need to construct appropriate initial and final states and calculate scattering amplitude. Summary of free
Homework 4: Fermi s Golden Rule and Feynman Diagrams
 Homework 4: Fermi s Golden Rule and Feynman Diagrams 1 Proton-Proton Total Cross Section In this problem, we are asked to find the approximate radius of the proton from the TOTEM data for the total proton
Homework 4: Fermi s Golden Rule and Feynman Diagrams 1 Proton-Proton Total Cross Section In this problem, we are asked to find the approximate radius of the proton from the TOTEM data for the total proton
Decays, resonances and scattering
 Structure of matter and energy scales Subatomic physics deals with objects of the size of the atomic nucleus and smaller. We cannot see subatomic particles directly, but we may obtain knowledge of their
Structure of matter and energy scales Subatomic physics deals with objects of the size of the atomic nucleus and smaller. We cannot see subatomic particles directly, but we may obtain knowledge of their
Physics 444: Quantum Field Theory 2. Homework 2.
 Physics 444: Quantum Field Theory Homework. 1. Compute the differential cross section, dσ/d cos θ, for unpolarized Bhabha scattering e + e e + e. Express your results in s, t and u variables. Compute the
Physics 444: Quantum Field Theory Homework. 1. Compute the differential cross section, dσ/d cos θ, for unpolarized Bhabha scattering e + e e + e. Express your results in s, t and u variables. Compute the
Units. In this lecture, natural units will be used:
 Kinematics Reminder: Lorentz-transformations Four-vectors, scalar-products and the metric Phase-space integration Two-body decays Scattering The role of the beam-axis in collider experiments Units In this
Kinematics Reminder: Lorentz-transformations Four-vectors, scalar-products and the metric Phase-space integration Two-body decays Scattering The role of the beam-axis in collider experiments Units In this
Fundamental Interactions (Forces) of Nature
 Chapter 14 Fundamental Interactions (Forces) of Nature Interaction Gauge Boson Gauge Boson Mass Interaction Range (Force carrier) Strong Gluon 0 short-range (a few fm) Weak W ±, Z M W = 80.4 GeV/c 2 short-range
Chapter 14 Fundamental Interactions (Forces) of Nature Interaction Gauge Boson Gauge Boson Mass Interaction Range (Force carrier) Strong Gluon 0 short-range (a few fm) Weak W ±, Z M W = 80.4 GeV/c 2 short-range
Unitarity, Dispersion Relations, Cutkosky s Cutting Rules
 Unitarity, Dispersion Relations, Cutkosky s Cutting Rules 04.06.0 For more information about unitarity, dispersion relations, and Cutkosky s cutting rules, consult Peskin& Schröder, or rather Le Bellac.
Unitarity, Dispersion Relations, Cutkosky s Cutting Rules 04.06.0 For more information about unitarity, dispersion relations, and Cutkosky s cutting rules, consult Peskin& Schröder, or rather Le Bellac.
Properties of the S-matrix
 Properties of the S-matrix In this chapter we specify the kinematics, define the normalisation of amplitudes and cross sections and establish the basic formalism used throughout. All mathematical functions
Properties of the S-matrix In this chapter we specify the kinematics, define the normalisation of amplitudes and cross sections and establish the basic formalism used throughout. All mathematical functions
Ultraviolet Divergences
 Ultraviolet Divergences In higher-order perturbation theory we encounter Feynman graphs with closed loops, associated with unconstrained momenta. For every such momentum k µ, we have to integrate over
Ultraviolet Divergences In higher-order perturbation theory we encounter Feynman graphs with closed loops, associated with unconstrained momenta. For every such momentum k µ, we have to integrate over
Kern- und Teilchenphysik I Lecture 2: Fermi s golden rule
 Kern- und Teilchenphysik I Lecture 2: Fermi s golden rule (adapted from the Handout of Prof. Mark Thomson) Prof. Nico Serra Dr. Patrick Owen, Mr. Davide Lancierini http://www.physik.uzh.ch/de/lehre/phy211/hs2017.html
Kern- und Teilchenphysik I Lecture 2: Fermi s golden rule (adapted from the Handout of Prof. Mark Thomson) Prof. Nico Serra Dr. Patrick Owen, Mr. Davide Lancierini http://www.physik.uzh.ch/de/lehre/phy211/hs2017.html
Summary of free theory: one particle state: vacuum state is annihilated by all a s: then, one particle state has normalization:
 The LSZ reduction formula based on S-5 In order to describe scattering experiments we need to construct appropriate initial and final states and calculate scattering amplitude. Summary of free theory:
The LSZ reduction formula based on S-5 In order to describe scattering experiments we need to construct appropriate initial and final states and calculate scattering amplitude. Summary of free theory:
Experimental Aspects of Deep-Inelastic Scattering. Kinematics, Techniques and Detectors
 1 Experimental Aspects of Deep-Inelastic Scattering Kinematics, Techniques and Detectors 2 Outline DIS Structure Function Measurements DIS Kinematics DIS Collider Detectors DIS process description Dirac
1 Experimental Aspects of Deep-Inelastic Scattering Kinematics, Techniques and Detectors 2 Outline DIS Structure Function Measurements DIS Kinematics DIS Collider Detectors DIS process description Dirac
Lecture 3. Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams
 Lecture 3 Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams Natural Units & the Planck Scale Review of Relativistic Kinematics Cross-Sections, Matrix Elements & Phase Space Decay Rates, Lifetimes & Branching Fractions
Lecture 3 Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams Natural Units & the Planck Scale Review of Relativistic Kinematics Cross-Sections, Matrix Elements & Phase Space Decay Rates, Lifetimes & Branching Fractions
Textbook Problem 4.2: We begin by developing Feynman rules for the theory at hand. The Hamiltonian clearly decomposes into Ĥ = Ĥ0 + ˆV where
 PHY 396 K. Solutions for problem set #11. Textbook Problem 4.2: We begin by developing Feynman rules for the theory at hand. The Hamiltonian clearly decomposes into Ĥ = Ĥ0 + ˆV where Ĥ 0 = Ĥfree Φ + Ĥfree
PHY 396 K. Solutions for problem set #11. Textbook Problem 4.2: We begin by developing Feynman rules for the theory at hand. The Hamiltonian clearly decomposes into Ĥ = Ĥ0 + ˆV where Ĥ 0 = Ĥfree Φ + Ĥfree
Quantum Mechanics II
 Quantum Mechanics II Prof. Boris Altshuler April, 20 Lecture 2. Scattering Theory Reviewed Remember what we have covered so far for scattering theory. We separated the Hamiltonian similar to the way in
Quantum Mechanics II Prof. Boris Altshuler April, 20 Lecture 2. Scattering Theory Reviewed Remember what we have covered so far for scattering theory. We separated the Hamiltonian similar to the way in
Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2013
 Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2013 Lecture 3: Feynman Diagrams, Decays and Scattering Feynman Diagrams continued Decays, Scattering and Fermi s Golden Rule Anti-matter? 1 Notation
Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2013 Lecture 3: Feynman Diagrams, Decays and Scattering Feynman Diagrams continued Decays, Scattering and Fermi s Golden Rule Anti-matter? 1 Notation
Scattering Theory. In quantum mechanics the basic observable is the probability
 Scattering Theory In quantum mechanics the basic observable is the probability P = ψ + t ψ t 2, for a transition from and initial state, ψ t, to a final state, ψ + t. Since time evolution is unitary this
Scattering Theory In quantum mechanics the basic observable is the probability P = ψ + t ψ t 2, for a transition from and initial state, ψ t, to a final state, ψ + t. Since time evolution is unitary this
Phys 622 Problems Chapter 6
 1 Problem 1 Elastic scattering Phys 622 Problems Chapter 6 A heavy scatterer interacts with a fast electron with a potential V (r) = V e r/r. (a) Find the differential cross section dσ dω = f(θ) 2 in the
1 Problem 1 Elastic scattering Phys 622 Problems Chapter 6 A heavy scatterer interacts with a fast electron with a potential V (r) = V e r/r. (a) Find the differential cross section dσ dω = f(θ) 2 in the
Maxwell s equations. electric field charge density. current density
 Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
4. The Standard Model
 4. The Standard Model Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 4. The Standard Model 1 In this section... Standard Model particle content Klein-Gordon equation Antimatter Interaction
4. The Standard Model Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 4. The Standard Model 1 In this section... Standard Model particle content Klein-Gordon equation Antimatter Interaction
Poincaré Invariant Calculation of the Three-Body Bound State Energy and Wave Function
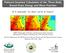 Poincaré Invariant Calculation of the Three-Body Bound State Energy and Wave Function q [fm ] 8 6 4 M. R. Hadizadeh, Ch. Elster and W. N. Polyzou log Ψ nr 8 7 7 7 3 3 7 7 3 3 4 6 8 log Ψ r p [fm ] 8 4
Poincaré Invariant Calculation of the Three-Body Bound State Energy and Wave Function q [fm ] 8 6 4 M. R. Hadizadeh, Ch. Elster and W. N. Polyzou log Ψ nr 8 7 7 7 3 3 7 7 3 3 4 6 8 log Ψ r p [fm ] 8 4
Lecture 8 Feynman diagramms. SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2
 Lecture 8 Feynman diagramms SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 Photon propagator Electron-proton scattering by an exchange of virtual photons ( Dirac-photons ) (1) e - virtual
Lecture 8 Feynman diagramms SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 Photon propagator Electron-proton scattering by an exchange of virtual photons ( Dirac-photons ) (1) e - virtual
1. Kinematics, cross-sections etc
 1. Kinematics, cross-sections etc A study of kinematics is of great importance to any experiment on particle scattering. It is necessary to interpret your measurements, but at an earlier stage to determine
1. Kinematics, cross-sections etc A study of kinematics is of great importance to any experiment on particle scattering. It is necessary to interpret your measurements, but at an earlier stage to determine
Non-relativistic scattering
 Non-relativistic scattering Contents Scattering theory 2. Scattering amplitudes......................... 3.2 The Born approximation........................ 5 2 Virtual Particles 5 3 The Yukawa Potential
Non-relativistic scattering Contents Scattering theory 2. Scattering amplitudes......................... 3.2 The Born approximation........................ 5 2 Virtual Particles 5 3 The Yukawa Potential
Feynman Diagrams of the Standard Model Sedigheh Jowzaee
 tglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Feynman Diagrams of the Standard Model Sedigheh Jowzaee PhD Seminar, 5 July 01 Outlook Introduction to the standard model Basic information Feynman diagram Feynman rules
tglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Feynman Diagrams of the Standard Model Sedigheh Jowzaee PhD Seminar, 5 July 01 Outlook Introduction to the standard model Basic information Feynman diagram Feynman rules
Electroweak Physics. Krishna S. Kumar. University of Massachusetts, Amherst
 Electroweak Physics Krishna S. Kumar University of Massachusetts, Amherst Acknowledgements: M. Grunewald, C. Horowitz, W. Marciano, C. Quigg, M. Ramsey-Musolf, www.particleadventure.org Electroweak Physics
Electroweak Physics Krishna S. Kumar University of Massachusetts, Amherst Acknowledgements: M. Grunewald, C. Horowitz, W. Marciano, C. Quigg, M. Ramsey-Musolf, www.particleadventure.org Electroweak Physics
2P + E = 3V 3 + 4V 4 (S.2) D = 4 E
 PHY 396 L. Solutions for homework set #19. Problem 1a): Let us start with the superficial degree of divergence. Scalar QED is a purely bosonic theory where all propagators behave as 1/q at large momenta.
PHY 396 L. Solutions for homework set #19. Problem 1a): Let us start with the superficial degree of divergence. Scalar QED is a purely bosonic theory where all propagators behave as 1/q at large momenta.
Beta functions in quantum electrodynamics
 Beta functions in quantum electrodynamics based on S-66 Let s calculate the beta function in QED: the dictionary: Note! following the usual procedure: we find: or equivalently: For a theory with N Dirac
Beta functions in quantum electrodynamics based on S-66 Let s calculate the beta function in QED: the dictionary: Note! following the usual procedure: we find: or equivalently: For a theory with N Dirac
Weak interactions, parity, helicity
 Lecture 10 Weak interactions, parity, helicity SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 Weak decay of particles The weak interaction is also responsible for the β + -decay of atomic
Lecture 10 Weak interactions, parity, helicity SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 Weak decay of particles The weak interaction is also responsible for the β + -decay of atomic
. α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λ μ Aμ ν(x) ξ ο π ρ ς σ τ υ φ χ ψ ω. Α Β Γ Δ Ε Ζ Η Θ Ι Κ Λ Μ Ν Ξ Ο Π Ρ Σ Τ Υ Φ Χ Ψ Ω. Friday April 1 ± ǁ
 . α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λ μ Aμ ν(x) ξ ο π ρ ς σ τ υ φ χ ψ ω. Α Β Γ Δ Ε Ζ Η Θ Ι Κ Λ Μ Ν Ξ Ο Π Ρ Σ Τ Υ Φ Χ Ψ Ω Friday April 1 ± ǁ 1 Chapter 5. Photons: Covariant Theory 5.1. The classical fields 5.2. Covariant
. α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λ μ Aμ ν(x) ξ ο π ρ ς σ τ υ φ χ ψ ω. Α Β Γ Δ Ε Ζ Η Θ Ι Κ Λ Μ Ν Ξ Ο Π Ρ Σ Τ Υ Φ Χ Ψ Ω Friday April 1 ± ǁ 1 Chapter 5. Photons: Covariant Theory 5.1. The classical fields 5.2. Covariant
Lecture 11 Perturbative calculation
 M.Krawczyk, AFZ Particles and Universe 11 1 Particles and Universe Lecture 11 Perturbative calculation Maria Krawczyk, Aleksander F. Żarnecki Faculty of Physics UW I.Theory of elementary particles description
M.Krawczyk, AFZ Particles and Universe 11 1 Particles and Universe Lecture 11 Perturbative calculation Maria Krawczyk, Aleksander F. Żarnecki Faculty of Physics UW I.Theory of elementary particles description
Quantum Field Theory II
 Quantum Field Theory II PHYS-P 622 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory Chapters: 13, 14, 16-21, 26-28, 51, 52, 61-68, 44, 53, 69-74, 30-32, 84-86, 75,
Quantum Field Theory II PHYS-P 622 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory Chapters: 13, 14, 16-21, 26-28, 51, 52, 61-68, 44, 53, 69-74, 30-32, 84-86, 75,
Calculating cross-sections in Compton scattering processes
 Calculating cross-sections in Compton scattering processes Fredrik Björkeroth School of Physics & Astronomy, University of Southampton January 6, 4. Abstract We consider the phenomenon of Compton scattering
Calculating cross-sections in Compton scattering processes Fredrik Björkeroth School of Physics & Astronomy, University of Southampton January 6, 4. Abstract We consider the phenomenon of Compton scattering
REVIEW REVIEW. Quantum Field Theory II
 Quantum Field Theory II PHYS-P 622 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory Chapters: 13, 14, 16-21, 26-28, 51, 52, 61-68, 44, 53, 69-74, 30-32, 84-86, 75,
Quantum Field Theory II PHYS-P 622 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory Chapters: 13, 14, 16-21, 26-28, 51, 52, 61-68, 44, 53, 69-74, 30-32, 84-86, 75,
Quantum Field Theory II
 Quantum Field Theory II PHYS-P 622 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory Chapters: 13, 14, 16-21, 26-28, 51, 52, 61-68, 44, 53, 69-74, 30-32, 84-86, 75,
Quantum Field Theory II PHYS-P 622 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory Chapters: 13, 14, 16-21, 26-28, 51, 52, 61-68, 44, 53, 69-74, 30-32, 84-86, 75,
Dynamics of Resonances in Strongly Interacting Matter
 in Strongly Interacting Matter (Resonance transport) J. Knoll 1, F. Riek 1, Yu.B. Ivanov 1,2, D. Voskresensky 1,3 1 GSI 2 Kurchatov Inst. (Moscow) 3 Moscow Ins. for Physics and Engineering Outline 1 2
in Strongly Interacting Matter (Resonance transport) J. Knoll 1, F. Riek 1, Yu.B. Ivanov 1,2, D. Voskresensky 1,3 1 GSI 2 Kurchatov Inst. (Moscow) 3 Moscow Ins. for Physics and Engineering Outline 1 2
Particle Physics (SH/IM)
 Particle Physics (SH/IM) Spring Semester 2011 Dr Victoria Martin Lecture Notes Introductory Material 0.1 Organisation Teaching Weeks: 16 January - 17 February; 27 February - 6 April Lectures Tuesday 12:10-13:00
Particle Physics (SH/IM) Spring Semester 2011 Dr Victoria Martin Lecture Notes Introductory Material 0.1 Organisation Teaching Weeks: 16 January - 17 February; 27 February - 6 April Lectures Tuesday 12:10-13:00
1 Introduction. 2 Relativistic Kinematics. 2.1 Particle Decay
 1 Introduction Relativistic Kinematics.1 Particle Decay Due to time dilation, the decay-time (i.e. lifetime) of the particle in its restframe is related to the decay-time in the lab frame via the following
1 Introduction Relativistic Kinematics.1 Particle Decay Due to time dilation, the decay-time (i.e. lifetime) of the particle in its restframe is related to the decay-time in the lab frame via the following
Review of scalar field theory. Srednicki 5, 9, 10
 Review of scalar field theory Srednicki 5, 9, 10 2 The LSZ reduction formula based on S-5 In order to describe scattering experiments we need to construct appropriate initial and final states and calculate
Review of scalar field theory Srednicki 5, 9, 10 2 The LSZ reduction formula based on S-5 In order to describe scattering experiments we need to construct appropriate initial and final states and calculate
SFI = F T exp i d4x int.(x) I
 MANDL AND SHAW Chapter 5. Photons: Covariant Theory 5.1. The classical field theory 5.2. Covariant quantization 5.3. The photon propagator Problems; 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Chapter 6. The S-Matrix Expansion 6.1.
MANDL AND SHAW Chapter 5. Photons: Covariant Theory 5.1. The classical field theory 5.2. Covariant quantization 5.3. The photon propagator Problems; 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Chapter 6. The S-Matrix Expansion 6.1.
Cross Section for the Reaction P+P Into H+K + +K - By Feynmann Rules
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Cross Section for the Reaction P+P Into H+K + +K - By Feynmann Rules Sonali Pattnaik 1 Anjana Acharya 2 Department Of Physics,Veer
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Cross Section for the Reaction P+P Into H+K + +K - By Feynmann Rules Sonali Pattnaik 1 Anjana Acharya 2 Department Of Physics,Veer
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Quantum Mechanics Qualifying Examination. January 7, 2013 (Tuesday) 9:00 am - 12:00 noon
 University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Quantum Mechanics Qualifying Examination January 7, 13 Tuesday 9: am - 1: noon Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Quantum Mechanics Qualifying Examination January 7, 13 Tuesday 9: am - 1: noon Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions
Two particle elastic scattering at 1-loop
 Two particle elastic scattering at 1-loop based on S-20 Let s use our rules to calculate two-particle elastic scattering amplitude in, theory in 6 dimensions including all one-loop corrections: For the
Two particle elastic scattering at 1-loop based on S-20 Let s use our rules to calculate two-particle elastic scattering amplitude in, theory in 6 dimensions including all one-loop corrections: For the
Physics 217 Solution Set #5 Fall 2016
 Physics 217 Solution Set #5 Fall 2016 1. Repeat the computation of problem 3 of Problem Set 4, but this time use the full relativistic expression for the matrix element. Show that the resulting spin-averaged
Physics 217 Solution Set #5 Fall 2016 1. Repeat the computation of problem 3 of Problem Set 4, but this time use the full relativistic expression for the matrix element. Show that the resulting spin-averaged
Cross sections and decay rates
 3 Cross sections and decay rates In the preceding chapter we explained how to obtain a Feynman diagram expansion for Green s functions that describe the interaction between a number of external sources.
3 Cross sections and decay rates In the preceding chapter we explained how to obtain a Feynman diagram expansion for Green s functions that describe the interaction between a number of external sources.
be stationary under variations in A, we obtain Maxwell s equations in the form ν J ν = 0. (7.5)
 Chapter 7 A Synopsis of QED We will here sketch the outlines of quantum electrodynamics, the theory of electrons and photons, and indicate how a calculation of an important physical quantity can be carried
Chapter 7 A Synopsis of QED We will here sketch the outlines of quantum electrodynamics, the theory of electrons and photons, and indicate how a calculation of an important physical quantity can be carried
Interactions and Fields
 Interactions and Fields Quantum Picture of Interactions Yukawa Theory Boson Propagator Feynman Diagrams Electromagnetic Interactions Renormalization and Gauge Invariance Strong Interactions Weak and Electroweak
Interactions and Fields Quantum Picture of Interactions Yukawa Theory Boson Propagator Feynman Diagrams Electromagnetic Interactions Renormalization and Gauge Invariance Strong Interactions Weak and Electroweak
6. QED. Particle and Nuclear Physics. Dr. Tina Potter. Dr. Tina Potter 6. QED 1
 6. QED Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 6. QED 1 In this section... Gauge invariance Allowed vertices + examples Scattering Experimental tests Running of alpha Dr. Tina Potter
6. QED Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 6. QED 1 In this section... Gauge invariance Allowed vertices + examples Scattering Experimental tests Running of alpha Dr. Tina Potter
Feynman Amplitude for Dirac and Majorana Neutrinos
 EJTP 13, No. 35 (2016) 73 78 Electronic Journal of Theoretical Physics Feynman Amplitude for Dirac and Majorana Neutrinos Asan Damanik Department of Physics Education Faculty of Teacher Training and Education,
EJTP 13, No. 35 (2016) 73 78 Electronic Journal of Theoretical Physics Feynman Amplitude for Dirac and Majorana Neutrinos Asan Damanik Department of Physics Education Faculty of Teacher Training and Education,
Physics 218. Quantum Field Theory. Professor Dine. Green s Functions and S Matrices from the Operator (Hamiltonian) Viewpoint
 Physics 28. Quantum Field Theory. Professor Dine Green s Functions and S Matrices from the Operator (Hamiltonian) Viewpoint Field Theory in a Box Consider a real scalar field, with lagrangian L = 2 ( µφ)
Physics 28. Quantum Field Theory. Professor Dine Green s Functions and S Matrices from the Operator (Hamiltonian) Viewpoint Field Theory in a Box Consider a real scalar field, with lagrangian L = 2 ( µφ)
Theory of Elementary Particles homework XI (July??)
 Theory of Elementary Particles homework XI (July??) At the head of your report, please write your name, student ID number and a list of problems that you worked on in a report (like II-1, II-3, IV- ).
Theory of Elementary Particles homework XI (July??) At the head of your report, please write your name, student ID number and a list of problems that you worked on in a report (like II-1, II-3, IV- ).
Renormalization of the Yukawa Theory Physics 230A (Spring 2007), Hitoshi Murayama
 Renormalization of the Yukawa Theory Physics 23A (Spring 27), Hitoshi Murayama We solve Problem.2 in Peskin Schroeder. The Lagrangian density is L 2 ( µφ) 2 2 m2 φ 2 + ψ(i M)ψ ig ψγ 5 ψφ. () The action
Renormalization of the Yukawa Theory Physics 23A (Spring 27), Hitoshi Murayama We solve Problem.2 in Peskin Schroeder. The Lagrangian density is L 2 ( µφ) 2 2 m2 φ 2 + ψ(i M)ψ ig ψγ 5 ψφ. () The action
Neutron Beta-Decay. Christopher B. Hayes. December 6, 2012
 Neutron Beta-Decay Christopher B. Hayes December 6, 2012 Abstract A Detailed account of the V-A theory of neutron beta decay is presented culminating in a precise calculation of the neutron lifetime. 1
Neutron Beta-Decay Christopher B. Hayes December 6, 2012 Abstract A Detailed account of the V-A theory of neutron beta decay is presented culminating in a precise calculation of the neutron lifetime. 1
The Exchange Model. Lecture 2. Quantum Particles Experimental Signatures The Exchange Model Feynman Diagrams. Eram Rizvi
 The Exchange Model Lecture 2 Quantum Particles Experimental Signatures The Exchange Model Feynman Diagrams Eram Rizvi Royal Institution - London 14 th February 2012 Outline A Century of Particle Scattering
The Exchange Model Lecture 2 Quantum Particles Experimental Signatures The Exchange Model Feynman Diagrams Eram Rizvi Royal Institution - London 14 th February 2012 Outline A Century of Particle Scattering
QFT. Chapter 14: Loop Corrections to the Propagator
 QFT Chapter 14: Loop Corrections to the Propagator Overview Here we turn to our next major topic: loop order corrections. We ll consider the effect on the propagator first. This has at least two advantages:
QFT Chapter 14: Loop Corrections to the Propagator Overview Here we turn to our next major topic: loop order corrections. We ll consider the effect on the propagator first. This has at least two advantages:
ψ( ) k (r) which take the asymtotic form far away from the scattering center: k (r) = E kψ (±) φ k (r) = e ikr
 Scattering Theory Consider scattering of two particles in the center of mass frame, or equivalently scattering of a single particle from a potential V (r), which becomes zero suciently fast as r. The initial
Scattering Theory Consider scattering of two particles in the center of mass frame, or equivalently scattering of a single particle from a potential V (r), which becomes zero suciently fast as r. The initial
Particle Physics WS 2012/13 ( )
 Particle Physics WS 2012/13 (13.11.2012) Stephanie Hansmann-Menzemer Physikalisches Institut, INF 226, 3.101 Content of Today Up to now: first order non-resonant e+e- cross-section dσ e.g. (e + e μ + μ
Particle Physics WS 2012/13 (13.11.2012) Stephanie Hansmann-Menzemer Physikalisches Institut, INF 226, 3.101 Content of Today Up to now: first order non-resonant e+e- cross-section dσ e.g. (e + e μ + μ
Derivation of Electro Weak Unification and Final Form of Standard Model with QCD and Gluons 1 W W W 3
 Derivation of Electro Weak Unification and Final Form of Standard Model with QCD and Gluons 1 W 1 + 2 W 2 + 3 W 3 Substitute B = cos W A + sin W Z 0 Sum over first generation particles. up down Left handed
Derivation of Electro Weak Unification and Final Form of Standard Model with QCD and Gluons 1 W 1 + 2 W 2 + 3 W 3 Substitute B = cos W A + sin W Z 0 Sum over first generation particles. up down Left handed
Lecture: Scattering theory
 Lecture: Scattering theory 30.05.2012 SS2012: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 Part I: Scattering theory: Classical trajectoriest and cross-sections Quantum Scattering 2 I. Scattering
Lecture: Scattering theory 30.05.2012 SS2012: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 Part I: Scattering theory: Classical trajectoriest and cross-sections Quantum Scattering 2 I. Scattering
Vacuum Energy and Effective Potentials
 Vacuum Energy and Effective Potentials Quantum field theories have badly divergent vacuum energies. In perturbation theory, the leading term is the net zero-point energy E zeropoint = particle species
Vacuum Energy and Effective Potentials Quantum field theories have badly divergent vacuum energies. In perturbation theory, the leading term is the net zero-point energy E zeropoint = particle species
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Monday 7 June, 004 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 48 THE STANDARD MODEL Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Monday 7 June, 004 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 48 THE STANDARD MODEL Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start
Landau s Fermi Liquid Theory
 Thors Hans Hansson Stockholm University Outline 1 Fermi Liquids Why, What, and How? Why Fermi liquids? What is a Fermi liquids? Fermi Liquids How? 2 Landau s Phenomenological Approach The free Fermi gas
Thors Hans Hansson Stockholm University Outline 1 Fermi Liquids Why, What, and How? Why Fermi liquids? What is a Fermi liquids? Fermi Liquids How? 2 Landau s Phenomenological Approach The free Fermi gas
Hadronic structure functions in the e + e ΛΛ reaction
 Hadronic structure functions in the e + e ΛΛ reaction Göran Fäldt a, Andrzej Kupsc a a Division of Nuclear Physics, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Uppsala University, Box 516, 75120 Uppsala, Sweden
Hadronic structure functions in the e + e ΛΛ reaction Göran Fäldt a, Andrzej Kupsc a a Division of Nuclear Physics, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Uppsala University, Box 516, 75120 Uppsala, Sweden
MHV Vertices and On-Shell Recursion Relations
 0-0 MHV Vertices and On-Shell Recursion Relations Peter Svrček Stanford University/SLAC QCD 2006 May 12th 2006 In December 2003, Witten proposed a string theory in twistor space dual to perturbative gauge
0-0 MHV Vertices and On-Shell Recursion Relations Peter Svrček Stanford University/SLAC QCD 2006 May 12th 2006 In December 2003, Witten proposed a string theory in twistor space dual to perturbative gauge
Particle Physics 2018 Final Exam (Answers with Words Only)
 Particle Physics 2018 Final Exam (Answers with Words Only) This was a hard course that likely covered a lot of new and complex ideas. If you are feeling as if you could not possibly recount all of the
Particle Physics 2018 Final Exam (Answers with Words Only) This was a hard course that likely covered a lot of new and complex ideas. If you are feeling as if you could not possibly recount all of the
Introductory Lectures on Collider Physics
 Introductory Lectures on Collider Physics Tim M.P. Tait Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Irvine, California 92697 (Dated: June 14, 2011) 1 pa p1 pa p1 Q = p1 - pa V(x) pb
Introductory Lectures on Collider Physics Tim M.P. Tait Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Irvine, California 92697 (Dated: June 14, 2011) 1 pa p1 pa p1 Q = p1 - pa V(x) pb
PHY 396 L. Solutions for homework set #20.
 PHY 396 L. Solutions for homework set #. Problem 1 problem 1d) from the previous set): At the end of solution for part b) we saw that un-renormalized gauge invariance of the bare Lagrangian requires Z
PHY 396 L. Solutions for homework set #. Problem 1 problem 1d) from the previous set): At the end of solution for part b) we saw that un-renormalized gauge invariance of the bare Lagrangian requires Z
Physics 217 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Fall u(p,λ) by any method of your choosing.
 Physics 27 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Fall 206. The helicity spinor u(p, λ satisfies u(p,λu(p,λ = 2m. ( In parts (a and (b, you may assume that m 0. (a Evaluate u(p,λ by any method of your choosing. Using the
Physics 27 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Fall 206. The helicity spinor u(p, λ satisfies u(p,λu(p,λ = 2m. ( In parts (a and (b, you may assume that m 0. (a Evaluate u(p,λ by any method of your choosing. Using the
Chapter 10: Multi- Electron Atoms Optical Excitations
 Chapter 10: Multi- Electron Atoms Optical Excitations To describe the energy levels in multi-electron atoms, we need to include all forces. The strongest forces are the forces we already discussed in Chapter
Chapter 10: Multi- Electron Atoms Optical Excitations To describe the energy levels in multi-electron atoms, we need to include all forces. The strongest forces are the forces we already discussed in Chapter
Lecture-05 Perturbation Theory and Feynman Diagrams
 Lecture-5 Perturbation Theory and Feynman Diagrams U. Robkob, Physics-MUSC SCPY639/428 September 3, 218 From the previous lecture We end up at an expression of the 2-to-2 particle scattering S-matrix S
Lecture-5 Perturbation Theory and Feynman Diagrams U. Robkob, Physics-MUSC SCPY639/428 September 3, 218 From the previous lecture We end up at an expression of the 2-to-2 particle scattering S-matrix S
L = 1 2 µφ µ φ m2 2 φ2 λ 0
 Physics 6 Homework solutions Renormalization Consider scalar φ 4 theory, with one real scalar field and Lagrangian L = µφ µ φ m φ λ 4 φ4. () We have seen many times that the lowest-order matrix element
Physics 6 Homework solutions Renormalization Consider scalar φ 4 theory, with one real scalar field and Lagrangian L = µφ µ φ m φ λ 4 φ4. () We have seen many times that the lowest-order matrix element
 More Energetics of Alpha Decay The energy released in decay, Q, is determined by the difference in mass of the parent nucleus and the decay products, which include the daughter nucleus and the particle.
More Energetics of Alpha Decay The energy released in decay, Q, is determined by the difference in mass of the parent nucleus and the decay products, which include the daughter nucleus and the particle.
OUTLINE. CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion
 Weak Interactions OUTLINE CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion CHARGED WEAK INTERACTIONS OF QUARKS - Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism - Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Weak Interactions OUTLINE CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion CHARGED WEAK INTERACTIONS OF QUARKS - Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism - Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Physics 216 Spring The Optical Theorem
 Physics 6 Spring 0 The Optical Theorem. The probability currents In the quantum theory of scattering, the optical theorem is a consequence of the conservation of probability. As usual, we define ρ(x,t)
Physics 6 Spring 0 The Optical Theorem. The probability currents In the quantum theory of scattering, the optical theorem is a consequence of the conservation of probability. As usual, we define ρ(x,t)
A Calculation of the Differential Cross Section for Compton Scattering in Tree-Level Quantum Electrodynamics
 A Calculation of the Differential Cross Section for Compton Scattering in Tree-Level Quantum Electrodynamics Declan Millar D.Millar@soton.ac.uk School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Southampton,
A Calculation of the Differential Cross Section for Compton Scattering in Tree-Level Quantum Electrodynamics Declan Millar D.Millar@soton.ac.uk School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Southampton,
9 Lorentz Invariant phase-space
 9 Lorentz Invariant phae-space 9. Cro-ection The cattering amplitude M q,q 2,out p, p 2,in i the amplitude for a tate p, p 2 to make a tranition into the tate q,q 2. The tranition probability i the quare
9 Lorentz Invariant phae-space 9. Cro-ection The cattering amplitude M q,q 2,out p, p 2,in i the amplitude for a tate p, p 2 to make a tranition into the tate q,q 2. The tranition probability i the quare
Outline. Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction. Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks. Neutral Weak Interaction. Electroweak Unification
 Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
A short Introduction to Feynman Diagrams
 A short Introduction to Feynman Diagrams J. Bijnens, November 2008 This assumes knowledge at the level of Chapter two in G. Kane, Modern Elementary Particle Physics. This note is more advanced than needed
A short Introduction to Feynman Diagrams J. Bijnens, November 2008 This assumes knowledge at the level of Chapter two in G. Kane, Modern Elementary Particle Physics. This note is more advanced than needed
11.D.2. Collision Operators
 11.D.. Collision Operators (11.94) can be written as + p t m h+ r +p h+ p = C + h + (11.96) where C + is the Boltzmann collision operator defined by [see (11.86a) for convention of notations] C + g(p)
11.D.. Collision Operators (11.94) can be written as + p t m h+ r +p h+ p = C + h + (11.96) where C + is the Boltzmann collision operator defined by [see (11.86a) for convention of notations] C + g(p)
Drude-Schwarzschild Metric and the Electrical Conductivity of Metals
 Drude-Schwarzschild Metric and the Electrical Conductivity of Metals P. R. Silva - Retired associate professor Departamento de Física ICEx Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais email: prsilvafis@gmail.com
Drude-Schwarzschild Metric and the Electrical Conductivity of Metals P. R. Silva - Retired associate professor Departamento de Física ICEx Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais email: prsilvafis@gmail.com
