The World of Elementary Particle Physics Demystified
|
|
|
- August Cox
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The World of Elementary Particle Physics Demystified Eduardo Pontón - IFT & ICTP/SAIFR IFT - Perimeter - ICTP/SAIFR Journeys into Theoretical Physics, July 18-23
2 Plan 1. What are these lectures about 2. How do we know what we know 3. Field Theory and Symmetries 4. Hidden Symmetry and the Higgs Boson
3 Part I Our Subject Matter
4 Particle Physics Perseus Galaxy Cluster What do YOU mean?? Gold Dust? Installation inspired by the search for the Higgs boson (by Becs Andrews) Atoms of Niobium (41) and Selenium (34)
5 Particle Physics typically understood as the realm of subatomic particles Quantum mechanical effects an essential component!
6 It will be useful to recall some facts in the context of the birth of Quantum Mechanics!
7 Planck's law for black-body radiation: For radiation at temperature T, average energy in volume V with frequencies between! and! + d! : hde(!)i = V ~ 2 c 3! 3 d! e ~! 1 = dn(!) ~! e ~! 1 Planck, 1900 Number of modes in V and [!,! + d!] dn(!) = V!2 d! 2 c 3 Einstein s formula for mean energy fluctuations in a black body: h( E) 2 i = hde(!)i2 dn(!) + ~!hde(!)i Einstein, 1909
8 To derive it, just need to recall a bit of statistical mechanics: Canonical Partition Function: Z = X n e E n Obtain average energy by differentiating w.r.t. : hei 1 Z X n E n e E n log Differentiating w.r.t. again, we can obtain the mean square energy fluctuation: h( E) 2 i = he 2 i hei Upshot: can easily get the energy fluctuation, if we know the energy as a function of temperature!
9 Einstein just applied this to Planck s law: h( E) 2 ~! hde(!)i = dn(!) e ~! 1 and for any frequency: dn(!) ~! 1 Rayleigh-Jeans law ~! 1 ~! Wien s formula dn(!) ~! e h( E) 2 i = hde(!)i2 dn(!) + ~!hde(!)i Then he proceeded to interpret the result
10 h( E) 2 i = hde(!)i2 dn(!) + ~!hde(!)i To interpret the linear term The quadratic term is exactly what is obtained for classical waves (Homework!) Recall that for an ideal gas, i.e. N non-interacting particles: hei = 3 2 Nk BT = 3N 2 Hence: The concept of wave-particle duality was born: h( E) 2 = k B T hei the effects of the two causes of fluctuations [waves and particles] act like fluctuations from mutually independent causes (additivity of the two terms) Einstein (1909) Attempts at obtaining this from dynamics (as time averages) could only give one or the other term
11 vs
12 In our typical particle physics experiments, we see the events as particles: they resemble the electron-by-electron setup! But we are interested in the underlying distribution (in different variables) In addition, the experimental conditions we are focusing on are such that the particles are moving close to the speed of light! Theoretician perspective: need to be able to compute quantum mechanical amplitudes that reflect the properties of special relativity: No inertial frame is special (laws appear the same in any) Nothing travels faster than the speed of light (causality structure) Amplitudes must allow a probabilistic interpretation (unitarity) Quantum Mechanics + Special Relativity = Quantum Field Theory
13 If we want to be more precise: Quantum Field Theory of Point Particles A point particle type specified by: mass & spin (or helicity, if massless) What if the fundamental constituents were string-like, or even more complex? A matter of scales: if our probe cannot resolve the string/brane, we will be able to describe its physics by QFT
14 The lesson is more general: Protons/nuclei can look point-like under many experimental conditions Atoms/molecules can look point-like to a typical human QFT can be used to describe any such system it has nothing to do with the system being fundamental But QFT becomes essential when the energies are such that particles can be produced the realm we want to explore here!
15 The Quantum Harmonic Oscillator (if you need a review) Quadratic Hamiltonian: H = 1 2 ˆp2 +! 2ˆx 2 r ~ ˆx = 2! a + a Define creation and annihilation operators via: r ~! ˆp = i a a 2 H = N + 1 Which diagonalize the Hamiltonian: ~! N = a a 2 n-quanta/particle states obeying Bose-Einstein statistics: 1i = a 0i ni = 1 p n! (a ) n 0i [a, a ]=1 [a, a] =[a,a ]=0
16 Let us go back to the wave-particle puzzle h( E) 2 i = hde(!)i2 dn(!) + ~!hde(!)i which had to wait until 1925 for a satisfactory solution (Pasqual Jordan in the Dreimännerarbeit) Since the E&M field (in a box) is a set of decoupled simple harmonic oscillators, we can quantize each one, following the quantum mechanical treatment known to apply to a single oscillator. Considering a 1D case: (as Jordan did) r ~ box of size L and wavevectors k n = n/l =! n (x, t) = X n 2! n a n e i! nt+k n x +h.c. [a n,a n 0 ]= n,n 0 [a n,a n 0]=[a n,a n 0 ]=0
17 Considering a 1D case: box of size L and wavevectors r ~ k n = n/l =! n (x, t) = X n 2! n a n e i! nt+k n x +h.c. [a n,a n 0 ]= n,n 0 [a n,a n 0]=[a n,a n 0 ]=0 The energy density is found to be H = 1 2L Z L 0 dx (@ t ) 2 +(@ x ) 2 = X n (N n )~! n By putting the oscillators in a thermal bath at temperature T, and computing the mean square energy fluctuations in a small segment a << L, the two terms were recovered: h( E) 2 i = hde(!)i2 dn(!) + ~!hde(!)i For a detailed derivation see: Duncan & Janssen, arxiv: These considerations, together with the seminal papers by Dirac (1926,1927), gave birth to Quantum Field Theory
18 Upshot: the canonical quantization of a field (continuous) incorporates automatically the concept of a particle (discreteness)
19 In addition: the formalism allows to describe the creation and destruction of quanta (particles) (provided energy and momentum can be conserved) Note also that the quantum mechanical treatment of the E&M field had to be intrinsically relativistic
20 Dimensional Analysis The only difference between a rut and a grave are the dimensions Ellen Glasgow Existence of (maximum) universal speed: c = m/s Universal unit of action: ~ = (40) ev s Universal Boltzmann constant: k B = (78) ev/k Since we are interested in quantum, relativistic systems, better to measure velocities and action in units of c and! ~ Natural units: c = ~ = k B =1 Then any mass/energy scale is associated with a length scale through the Compton wavelength: and to a time scale through c. o = ~/(mc) Everything is energy and that s all there is to it. Match the frequency of the reality you want and you cannot help but get that reality. It can be no other way. This is physics. Pseudo-scientific quote, probably from a channeler named Darryl Anka who has assigned the words to an entity named Bashar!!
21 Dimensional Analysis Some useful reference scales: Most of the mass we see around us comes from the mass of protons/neutrons Nucleon mass: m p 1 GeV = 10 9 ev kg Associated length scale: o p (1/5) m = (1/5) Fermi Associated time scale: s Note: the charge radius of the proton is about 1 Fermi Sometimes dimensionless constants have a crucial effect on the physics. Compare to the hydrogen atom. The underlying mass scale is: m e 0.5 MeV = ev m p /2000 Relevant energy scale is and the length scale is a 0 = o e / E 0 = m e 10 ev o e 2000 o p A big, non-relativistic system because 1/137 1
22 The Standard Model Mendeleev s Table
23 Particles and Particles
24 Rutherford at his Lab. A Paradigm
25 Seeing Particles ~B P.A.M. Dirac (1931) Discovery of the Positron (1932) C. Anderson Cloud chamber s picture of cosmic radiation
26 Simpler Times Cloud Chamber (muons, alpha and beta radiation) Alpha Particles (Polonium)
27 16 GeV beam entering a liquid-h 2 bubble chamber at CERN (~1970)
28 The discovery of neutral currents by the Gargamelle bubble chamber (1973)
29 ... A Long Way
30 Find an LHC Guide/FAQ with lots of interesting information at: Brochure Eng.pdf
Lecture 01. Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics
 Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics Particle Astrophysics Particle physics Fundamental constituents of nature Most basic building blocks Describe all particles and interactions Shortest length
Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics Particle Astrophysics Particle physics Fundamental constituents of nature Most basic building blocks Describe all particles and interactions Shortest length
Atoms, nuclei, particles
 Atoms, nuclei, particles Nikolaos Kidonakis Physics for Georgia Academic Decathlon September 2016 Age-old questions What are the fundamental particles of matter? What are the fundamental forces of nature?
Atoms, nuclei, particles Nikolaos Kidonakis Physics for Georgia Academic Decathlon September 2016 Age-old questions What are the fundamental particles of matter? What are the fundamental forces of nature?
THERMAL HISTORY OF THE UNIVERSE
 M. Pettini: Introduction to Cosmology Lecture 7 THERMAL HISTORY OF THE UNIVERSE The Universe today is bathed in an all-pervasive radiation field, the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) which we introduced
M. Pettini: Introduction to Cosmology Lecture 7 THERMAL HISTORY OF THE UNIVERSE The Universe today is bathed in an all-pervasive radiation field, the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) which we introduced
The Building Blocks of Nature
 The Building Blocks of Nature PCES 15.1 Schematic picture of constituents of an atom, & rough length scales. The size quoted for the nucleus here (10-14 m) is too large- a single nucleon has size 10-15
The Building Blocks of Nature PCES 15.1 Schematic picture of constituents of an atom, & rough length scales. The size quoted for the nucleus here (10-14 m) is too large- a single nucleon has size 10-15
Overview. The quest of Particle Physics research is to understand the fundamental particles of nature and their interactions.
 Overview The quest of Particle Physics research is to understand the fundamental particles of nature and their interactions. Our understanding is about to take a giant leap.. the Large Hadron Collider
Overview The quest of Particle Physics research is to understand the fundamental particles of nature and their interactions. Our understanding is about to take a giant leap.. the Large Hadron Collider
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 3: Quantum Mechanics
 Introduction to particle physics Lecture 3: Quantum Mechanics Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2010 Outline 1 Planck s hypothesis 2 Substantiating Planck s claim 3 More quantisation: Bohr
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 3: Quantum Mechanics Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2010 Outline 1 Planck s hypothesis 2 Substantiating Planck s claim 3 More quantisation: Bohr
Elementary particles and typical scales in high energy physics
 Elementary particles and typical scales in high energy physics George Jorjadze Free University of Tbilisi Zielona Gora - 23.01.2017 GJ Elementary particles and typical scales in HEP Lecture 1 1/18 Contents
Elementary particles and typical scales in high energy physics George Jorjadze Free University of Tbilisi Zielona Gora - 23.01.2017 GJ Elementary particles and typical scales in HEP Lecture 1 1/18 Contents
High Energy Physics. QuarkNet summer workshop June 24-28, 2013
 High Energy Physics QuarkNet summer workshop June 24-28, 2013 1 The Birth of Particle Physics In 1896, Thompson showed that electrons were particles, not a fluid. In 1905, Einstein argued that photons
High Energy Physics QuarkNet summer workshop June 24-28, 2013 1 The Birth of Particle Physics In 1896, Thompson showed that electrons were particles, not a fluid. In 1905, Einstein argued that photons
Structure of matter, 1
 Structure of matter, 1 In the hot early universe, prior to the epoch of nucleosynthesis, even the most primitive nuclear material i.e., protons and neutrons could not have existed. Earlier than 10 5 s
Structure of matter, 1 In the hot early universe, prior to the epoch of nucleosynthesis, even the most primitive nuclear material i.e., protons and neutrons could not have existed. Earlier than 10 5 s
The Dark Side of the Higgs Field and General Relativity
 The Dark Side of the Higgs Field and General Relativity The gravitational force attracting the matter, causing concentration of the matter in a small space and leaving much space with low matter concentration:
The Dark Side of the Higgs Field and General Relativity The gravitational force attracting the matter, causing concentration of the matter in a small space and leaving much space with low matter concentration:
Physics 214 Experimental Particle Physics. Lecture 1 What to expect.
 Physics 214 Experimental Particle Physics Lecture 1 What to expect. We ll start with a grand tour. I do not expect you to understand this tour in detail. Instead, think of it as an orientation to which
Physics 214 Experimental Particle Physics Lecture 1 What to expect. We ll start with a grand tour. I do not expect you to understand this tour in detail. Instead, think of it as an orientation to which
INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS Class Mechanics My office (for now): Dantziger B Room 121 My Phone: x85200 Office hours: Call ahead, or better yet, email... Even better than office
INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS Class Mechanics My office (for now): Dantziger B Room 121 My Phone: x85200 Office hours: Call ahead, or better yet, email... Even better than office
Quantum Gravity and Entanglement
 Quantum Gravity and Entanglement The magnetic induction creates a negative electric field, causing an electromagnetic inertia responsible for the relativistic mass change; it is the mysterious Higgs Field
Quantum Gravity and Entanglement The magnetic induction creates a negative electric field, causing an electromagnetic inertia responsible for the relativistic mass change; it is the mysterious Higgs Field
Physics 214 Experimental Particle Physics. Lecture 1 What to expect.
 Physics 214 Experimental Particle Physics Lecture 1 What to expect. We ll start with a grand tour. I do not expect you to understand this tour in detail. Instead, think of it as an orientation to which
Physics 214 Experimental Particle Physics Lecture 1 What to expect. We ll start with a grand tour. I do not expect you to understand this tour in detail. Instead, think of it as an orientation to which
Quantum Physics and General Relativity
 Quantum Physics and General Relativity The self maintained electric potential of the accelerating charges equivalent with the General Relativity space-time curvature, and since it is true on the quantum
Quantum Physics and General Relativity The self maintained electric potential of the accelerating charges equivalent with the General Relativity space-time curvature, and since it is true on the quantum
CHAPTER 2: POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS
 CHAPTER 2: POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS Basics of Quantum Mechanics - Why Quantum Physics? - Classical mechanics (Newton's mechanics) and Maxwell's equations (electromagnetics theory) can explain MACROSCOPIC
CHAPTER 2: POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS Basics of Quantum Mechanics - Why Quantum Physics? - Classical mechanics (Newton's mechanics) and Maxwell's equations (electromagnetics theory) can explain MACROSCOPIC
Microcosmos. Elementary Particle Physics. I. Quantum world II. CERN: past & present III. Particle physics matters! IV. Astroparticle physics
 Elementary Particle Physics Microcosmos I. Quantum world II. CERN: past & present III. Particle physics matters! IV. Astroparticle physics Frank Linde Nikhef & UvA +31-205925001 f.linde@nikhef.nl Dark
Elementary Particle Physics Microcosmos I. Quantum world II. CERN: past & present III. Particle physics matters! IV. Astroparticle physics Frank Linde Nikhef & UvA +31-205925001 f.linde@nikhef.nl Dark
14 Lecture 14: Early Universe
 PHYS 652: Astrophysics 70 14 Lecture 14: Early Universe True science teaches us to doubt and, in ignorance, to refrain. Claude Bernard The Big Picture: Today we introduce the Boltzmann equation for annihilation
PHYS 652: Astrophysics 70 14 Lecture 14: Early Universe True science teaches us to doubt and, in ignorance, to refrain. Claude Bernard The Big Picture: Today we introduce the Boltzmann equation for annihilation
Higgs Field and Quantum Gravity
 Higgs Field and Quantum Gravity The magnetic induction creates a negative electric field, causing an electromagnetic inertia responsible for the relativistic mass change; it is the mysterious Higgs Field
Higgs Field and Quantum Gravity The magnetic induction creates a negative electric field, causing an electromagnetic inertia responsible for the relativistic mass change; it is the mysterious Higgs Field
Quanta to Quarks. Science Teachers Workshop 2014 Workshop Session. Adrian Manning
 Quanta to Quarks Science Teachers Workshop 2014 Workshop Session Adrian Manning The Quanta to Quarks module! The Quanta to Quarks module ultimately deals with some of the most fundamental questions about
Quanta to Quarks Science Teachers Workshop 2014 Workshop Session Adrian Manning The Quanta to Quarks module! The Quanta to Quarks module ultimately deals with some of the most fundamental questions about
NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHYSICS (PH242) PARTICLE PHYSICS
 NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHYSICS (PH242) PARTICLE PHYSICS History of Elementary Particles THE CLASSICAL ERA (1897-1932) Elementary particle physics was born in 1897 with J.J. Thomson s discovery of the ELECTRONS
NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHYSICS (PH242) PARTICLE PHYSICS History of Elementary Particles THE CLASSICAL ERA (1897-1932) Elementary particle physics was born in 1897 with J.J. Thomson s discovery of the ELECTRONS
PHYS3113, 3d year Statistical Mechanics Tutorial problems. Tutorial 1, Microcanonical, Canonical and Grand Canonical Distributions
 1 PHYS3113, 3d year Statistical Mechanics Tutorial problems Tutorial 1, Microcanonical, Canonical and Grand Canonical Distributions Problem 1 The macrostate probability in an ensemble of N spins 1/2 is
1 PHYS3113, 3d year Statistical Mechanics Tutorial problems Tutorial 1, Microcanonical, Canonical and Grand Canonical Distributions Problem 1 The macrostate probability in an ensemble of N spins 1/2 is
Elementary Particle Physics Glossary. Course organiser: Dr Marcella Bona February 9, 2016
 Elementary Particle Physics Glossary Course organiser: Dr Marcella Bona February 9, 2016 1 Contents 1 Terms A-C 5 1.1 Accelerator.............................. 5 1.2 Annihilation..............................
Elementary Particle Physics Glossary Course organiser: Dr Marcella Bona February 9, 2016 1 Contents 1 Terms A-C 5 1.1 Accelerator.............................. 5 1.2 Annihilation..............................
Exam Results. Force between charges. Electric field lines. Other particles and fields
 Exam: Exam scores posted on Learn@UW No homework due next week Exam Results F D C BC B AB A Phy107 Fall 2006 1 Particles and fields We have talked about several particles Electron,, proton, neutron, quark
Exam: Exam scores posted on Learn@UW No homework due next week Exam Results F D C BC B AB A Phy107 Fall 2006 1 Particles and fields We have talked about several particles Electron,, proton, neutron, quark
Name Final Exam December 7, 2015
 Name Final Exam December 7, 015 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Part I: Multiple Choice (mixed new and review questions)
Name Final Exam December 7, 015 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Part I: Multiple Choice (mixed new and review questions)
Physics 102: Lecture 24. Bohr vs. Correct Model of Atom. Physics 102: Lecture 24, Slide 1
 Physics 102: Lecture 24 Bohr vs. Correct Model of Atom Physics 102: Lecture 24, Slide 1 Plum Pudding Early Model for Atom positive and negative charges uniformly distributed throughout the atom like plums
Physics 102: Lecture 24 Bohr vs. Correct Model of Atom Physics 102: Lecture 24, Slide 1 Plum Pudding Early Model for Atom positive and negative charges uniformly distributed throughout the atom like plums
Particle Physics Dr. Alexander Mitov Handout 2 : The Dirac Equation
 Dr. A. Mitov Particle Physics 45 Particle Physics Dr. Alexander Mitov µ + e - e + µ - µ + e - e + µ - µ + e - e + µ - µ + e - e + µ - Handout 2 : The Dirac Equation Dr. A. Mitov Particle Physics 46 Non-Relativistic
Dr. A. Mitov Particle Physics 45 Particle Physics Dr. Alexander Mitov µ + e - e + µ - µ + e - e + µ - µ + e - e + µ - µ + e - e + µ - Handout 2 : The Dirac Equation Dr. A. Mitov Particle Physics 46 Non-Relativistic
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 12-1A: INTERACTIONS OF MATTER WITH RADIATION Questions From Reading Activity? Essential Idea: The microscopic quantum world offers a range of phenomena,
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 12-1A: INTERACTIONS OF MATTER WITH RADIATION Questions From Reading Activity? Essential Idea: The microscopic quantum world offers a range of phenomena,
Gravitational Repulsion of Matter and Antimatter
 Gravitational Repulsion of Matter and Antimatter The changing acceleration of the electrons explains the created negative electric field of the magnetic induction, the electromagnetic inertia, the changing
Gravitational Repulsion of Matter and Antimatter The changing acceleration of the electrons explains the created negative electric field of the magnetic induction, the electromagnetic inertia, the changing
Gravitational Magnetic Force
 Gravitational Magnetic Force The curved space-time around current loops and solenoids carrying arbitrarily large steady electric currents is obtained from the numerical resolution of the coupled Einstein-Maxwell
Gravitational Magnetic Force The curved space-time around current loops and solenoids carrying arbitrarily large steady electric currents is obtained from the numerical resolution of the coupled Einstein-Maxwell
Physics Oct A Quantum Harmonic Oscillator
 Physics 301 5-Oct-2005 9-1 A Quantum Harmonic Oscillator The quantum harmonic oscillator (the only kind there is, really) has energy levels given by E n = (n + 1/2) hω, where n 0 is an integer and the
Physics 301 5-Oct-2005 9-1 A Quantum Harmonic Oscillator The quantum harmonic oscillator (the only kind there is, really) has energy levels given by E n = (n + 1/2) hω, where n 0 is an integer and the
John Ellison University of California, Riverside. Quarknet 2008 at UCR
 Overview of Particle Physics John Ellison University of California, Riverside Quarknet 2008 at UCR 1 Particle Physics What is it? Study of the elementary constituents of matter And the fundamental forces
Overview of Particle Physics John Ellison University of California, Riverside Quarknet 2008 at UCR 1 Particle Physics What is it? Study of the elementary constituents of matter And the fundamental forces
CHAPTER 1. SPECIAL RELATIVITY AND QUANTUM MECHANICS
 CHAPTER 1. SPECIAL RELATIVITY AND QUANTUM MECHANICS 1.1 PARTICLES AND FIELDS The two great structures of theoretical physics, the theory of special relativity and quantum mechanics, have been combined
CHAPTER 1. SPECIAL RELATIVITY AND QUANTUM MECHANICS 1.1 PARTICLES AND FIELDS The two great structures of theoretical physics, the theory of special relativity and quantum mechanics, have been combined
Physics 424: Dr. Justin Albert (call me Justin!)
 Physics 424: Dr. Justin Albert (call me Justin!) A Brief History of Particle Physics Discoveries (Or: Figuring out What the Universe is Made Of ) Looking Inside the Atom: e -, p, and n! 1897: J.J. Thomson
Physics 424: Dr. Justin Albert (call me Justin!) A Brief History of Particle Physics Discoveries (Or: Figuring out What the Universe is Made Of ) Looking Inside the Atom: e -, p, and n! 1897: J.J. Thomson
Higgs boson may appear to be a technihiggs
 Higgs boson may appear to be a technihiggs The discovered elusive Higgs boson, first predicted theoretically, turns out to may have been a different particle after all. A team of international researchers
Higgs boson may appear to be a technihiggs The discovered elusive Higgs boson, first predicted theoretically, turns out to may have been a different particle after all. A team of international researchers
Quantum Decoherence due to Gravitational Time Dilation
 Quantum Decoherence due to Gravitational Time Dilation Gravitational time dilation causes decoherence of composite quantum systems. Even if gravitons are there, it s probable that we would never be able
Quantum Decoherence due to Gravitational Time Dilation Gravitational time dilation causes decoherence of composite quantum systems. Even if gravitons are there, it s probable that we would never be able
The energy of this state comes from the dispersion relation:
 Homework 6 Solutions Problem 1: Kittel 7-2 a The method is the same as for the nonrelativistic gas. A particle confined in a box of volume L 3 is described by a the set of wavefunctions ψ n sinn x πx/l
Homework 6 Solutions Problem 1: Kittel 7-2 a The method is the same as for the nonrelativistic gas. A particle confined in a box of volume L 3 is described by a the set of wavefunctions ψ n sinn x πx/l
Einstein s Theory Relativistic 0 < v < c. No Absolute Time. Quantization, Zero point energy position & momentum obey Heisenberg uncertainity rule
 Lecture: March 27, 2019 Classical Mechanics Particle is described by position & velocity Quantum Mechanics Particle is described by wave function Probabilistic description Newton s equation non-relativistic
Lecture: March 27, 2019 Classical Mechanics Particle is described by position & velocity Quantum Mechanics Particle is described by wave function Probabilistic description Newton s equation non-relativistic
The Scale-Symmetric Theory as the Origin of the Standard Model
 Copyright 2017 by Sylwester Kornowski All rights reserved The Scale-Symmetric Theory as the Origin of the Standard Model Sylwester Kornowski Abstract: Here we showed that the Scale-Symmetric Theory (SST)
Copyright 2017 by Sylwester Kornowski All rights reserved The Scale-Symmetric Theory as the Origin of the Standard Model Sylwester Kornowski Abstract: Here we showed that the Scale-Symmetric Theory (SST)
Particle Physics. Michaelmas Term 2011 Prof. Mark Thomson. Handout 2 : The Dirac Equation. Non-Relativistic QM (Revision)
 Particle Physics Michaelmas Term 2011 Prof. Mark Thomson + e - e + - + e - e + - + e - e + - + e - e + - Handout 2 : The Dirac Equation Prof. M.A. Thomson Michaelmas 2011 45 Non-Relativistic QM (Revision)
Particle Physics Michaelmas Term 2011 Prof. Mark Thomson + e - e + - + e - e + - + e - e + - + e - e + - Handout 2 : The Dirac Equation Prof. M.A. Thomson Michaelmas 2011 45 Non-Relativistic QM (Revision)
Lecture notes for QFT I (662)
 Preprint typeset in JHEP style - PAPER VERSION Lecture notes for QFT I (66) Martin Kruczenski Department of Physics, Purdue University, 55 Northwestern Avenue, W. Lafayette, IN 47907-036. E-mail: markru@purdue.edu
Preprint typeset in JHEP style - PAPER VERSION Lecture notes for QFT I (66) Martin Kruczenski Department of Physics, Purdue University, 55 Northwestern Avenue, W. Lafayette, IN 47907-036. E-mail: markru@purdue.edu
Energy Level Energy Level Diagrams for Diagrams for Simple Hydrogen Model
 Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics Lecture 20: Real Hydrogen Atom /Identical particles http://www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/361 physics edu/ugrad/361 Prof. Sean Oh Last time Hydrogen atom: electron in
Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics Lecture 20: Real Hydrogen Atom /Identical particles http://www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/361 physics edu/ugrad/361 Prof. Sean Oh Last time Hydrogen atom: electron in
Outline. Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction. Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks. Neutral Weak Interaction. Electroweak Unification
 Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICS. \Hp. Ni Jun TSINGHUA. Physics. From Quantum Field Theory. to Classical Mechanics. World Scientific. Vol.2. Report and Review in
 LONDON BEIJING HONG TSINGHUA Report and Review in Physics Vol2 PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICS From Quantum Field Theory to Classical Mechanics Ni Jun Tsinghua University, China NEW JERSEY \Hp SINGAPORE World Scientific
LONDON BEIJING HONG TSINGHUA Report and Review in Physics Vol2 PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICS From Quantum Field Theory to Classical Mechanics Ni Jun Tsinghua University, China NEW JERSEY \Hp SINGAPORE World Scientific
Chapter 32 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 32 Lecture Notes Physics 2424 - Strauss Formulas: mc 2 hc/2πd 1. INTRODUCTION What are the most fundamental particles and what are the most fundamental forces that make up the universe? For a brick
Chapter 32 Lecture Notes Physics 2424 - Strauss Formulas: mc 2 hc/2πd 1. INTRODUCTION What are the most fundamental particles and what are the most fundamental forces that make up the universe? For a brick
Lecture 11 Perturbative calculation
 M.Krawczyk, AFZ Particles and Universe 11 1 Particles and Universe Lecture 11 Perturbative calculation Maria Krawczyk, Aleksander F. Żarnecki Faculty of Physics UW I.Theory of elementary particles description
M.Krawczyk, AFZ Particles and Universe 11 1 Particles and Universe Lecture 11 Perturbative calculation Maria Krawczyk, Aleksander F. Żarnecki Faculty of Physics UW I.Theory of elementary particles description
THE STANDARD MODEL OF MATTER
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THE STANDARD MODEL OF MATTER The "Standard Model" of subatomic and sub nuclear physics is an intricate, complex and often subtle thing and a complete study of it is beyond the scope
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THE STANDARD MODEL OF MATTER The "Standard Model" of subatomic and sub nuclear physics is an intricate, complex and often subtle thing and a complete study of it is beyond the scope
Beyond the standard model? From last time. What does the SM say? Grand Unified Theories. Unifications: now and the future
 From last time Quantum field theory is a relativistic quantum theory of fields and interactions. Fermions make up matter, and bosons mediate the forces by particle exchange. Lots of particles, lots of
From last time Quantum field theory is a relativistic quantum theory of fields and interactions. Fermions make up matter, and bosons mediate the forces by particle exchange. Lots of particles, lots of
Chapter 46. Particle Physics and Cosmology
 Chapter 46 Particle Physics and Cosmology Atoms as Elementary Particles Atoms From the Greek for indivisible Were once thought to be the elementary particles Atom constituents Proton, neutron, and electron
Chapter 46 Particle Physics and Cosmology Atoms as Elementary Particles Atoms From the Greek for indivisible Were once thought to be the elementary particles Atom constituents Proton, neutron, and electron
Complementi di Fisica Lectures 7-9
 Complementi di Fisica Lectures 7-9 Livio Lanceri Università di Trieste Trieste, 07/09-10-2012 Course Outline - Reminder Quantum Mechanics: an introduction Waves as particles and particles as waves (the
Complementi di Fisica Lectures 7-9 Livio Lanceri Università di Trieste Trieste, 07/09-10-2012 Course Outline - Reminder Quantum Mechanics: an introduction Waves as particles and particles as waves (the
STSF2223 Quantum Mechanics I
 STSF2223 Quantum Mechanics I What is quantum mechanics? Why study quantum mechanics? How does quantum mechanics get started? What is the relation between quantum physics with classical physics? Where is
STSF2223 Quantum Mechanics I What is quantum mechanics? Why study quantum mechanics? How does quantum mechanics get started? What is the relation between quantum physics with classical physics? Where is
From Quantum Mechanics to String Theory
 From Quantum Mechanics to String Theory Relativity (why it makes sense) Quantum mechanics: measurements and uncertainty Smashing things together: from Rutherford to the LHC Particle Interactions Quarks
From Quantum Mechanics to String Theory Relativity (why it makes sense) Quantum mechanics: measurements and uncertainty Smashing things together: from Rutherford to the LHC Particle Interactions Quarks
Dark Energy or Repulsive Gravity
 Dark Energy or Repulsive Gravity The leading theory to explain the accelerating expansion is the existence of a hypothetical repulsive force called dark energy. But in the new study, Massimo Villata, an
Dark Energy or Repulsive Gravity The leading theory to explain the accelerating expansion is the existence of a hypothetical repulsive force called dark energy. But in the new study, Massimo Villata, an
Decay rates and Cross section. Ashfaq Ahmad National Centre for Physics
 Decay rates and Cross section Ashfaq Ahmad National Centre for Physics 11/17/2014 Ashfaq Ahmad 2 Outlines Introduction Basics variables used in Exp. HEP Analysis Decay rates and Cross section calculations
Decay rates and Cross section Ashfaq Ahmad National Centre for Physics 11/17/2014 Ashfaq Ahmad 2 Outlines Introduction Basics variables used in Exp. HEP Analysis Decay rates and Cross section calculations
Lecture 3. Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams
 Lecture 3 Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams Natural Units & the Planck Scale Review of Relativistic Kinematics Cross-Sections, Matrix Elements & Phase Space Decay Rates, Lifetimes & Branching Fractions
Lecture 3 Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams Natural Units & the Planck Scale Review of Relativistic Kinematics Cross-Sections, Matrix Elements & Phase Space Decay Rates, Lifetimes & Branching Fractions
Discovery of New Ultra-High-Energy Neutrino
 Discovery of New Ultra-High-Energy Neutrino Evidence of a fourth ultra-high energy neutrino the highest-energy neutrino yet has been detected by the South Pole-based IceCube experiment, a project that
Discovery of New Ultra-High-Energy Neutrino Evidence of a fourth ultra-high energy neutrino the highest-energy neutrino yet has been detected by the South Pole-based IceCube experiment, a project that
Physics 116. Nov 22, Session 32 Models of atoms. R. J. Wilkes
 Physics 116 Session 32 Models of atoms Nov 22, 2011 Thomson Rutherford R. J. Wilkes Email: ph116@u.washington.edu Announcements Exam 3 next week (Tuesday, 11/29) Usual format and procedures I ll post example
Physics 116 Session 32 Models of atoms Nov 22, 2011 Thomson Rutherford R. J. Wilkes Email: ph116@u.washington.edu Announcements Exam 3 next week (Tuesday, 11/29) Usual format and procedures I ll post example
Discovery of the Positron
 Discovery of the Positron Michela Filaoro March 17, 2014 Abstract This paper presents with a study of cosmic-ray tracks the evidence of the existence of light positive particles, the positrons, confirming
Discovery of the Positron Michela Filaoro March 17, 2014 Abstract This paper presents with a study of cosmic-ray tracks the evidence of the existence of light positive particles, the positrons, confirming
OUTLINE. CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion
 Weak Interactions OUTLINE CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion CHARGED WEAK INTERACTIONS OF QUARKS - Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism - Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Weak Interactions OUTLINE CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion CHARGED WEAK INTERACTIONS OF QUARKS - Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism - Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Quantum Field Theory. Chapter Introduction. 8.2 The Many Particle State
 Chapter 8 Quantum Field Theory?? 8.1 Introduction We have studied the properties of photons primarily as single particles. It was Einstein s great discovery to realize that particulate basis of light.
Chapter 8 Quantum Field Theory?? 8.1 Introduction We have studied the properties of photons primarily as single particles. It was Einstein s great discovery to realize that particulate basis of light.
Particle Physics Lecture 1 : Introduction Fall 2015 Seon-Hee Seo
 Particle Physics Lecture 1 : Introduction Fall 2015 Seon-Hee Seo Particle Physics Fall 2015 1 Course Overview Lecture 1: Introduction, Decay Rates and Cross Sections Lecture 2: The Dirac Equation and Spin
Particle Physics Lecture 1 : Introduction Fall 2015 Seon-Hee Seo Particle Physics Fall 2015 1 Course Overview Lecture 1: Introduction, Decay Rates and Cross Sections Lecture 2: The Dirac Equation and Spin
Saturday Morning Physics -- Texas A&M University. What is Matter and what holds it together? Dr. Rainer J. Fries. January 27, 2007
 Saturday Morning Physics -- Texas A&M University Particles and Forces What is Matter and what holds it together? Dr. Rainer J. Fries January 27, 2007 Zooming in on the World around us Particles and Forces
Saturday Morning Physics -- Texas A&M University Particles and Forces What is Matter and what holds it together? Dr. Rainer J. Fries January 27, 2007 Zooming in on the World around us Particles and Forces
Saturday Morning Physics -- Texas A&M University Dr. Rainer J. Fries
 Saturday Morning Physics -- Texas A&M University Particles and Forces What is Matter and what holds it together? Dr. Rainer J. Fries January 27, 2007 Zooming in on the World around us Particles and Forces
Saturday Morning Physics -- Texas A&M University Particles and Forces What is Matter and what holds it together? Dr. Rainer J. Fries January 27, 2007 Zooming in on the World around us Particles and Forces
Particles and Interactions. Prof. Marina Cobal Corso Particelle ed interazioni fondamentali 2013/2014
 Particles and Interactions Prof. Marina Cobal Corso Particelle ed interazioni fondamentali 2013/2014 What is the world made of? In the ancient time: 4 elements 19 century atoms Beginning 20 th century
Particles and Interactions Prof. Marina Cobal Corso Particelle ed interazioni fondamentali 2013/2014 What is the world made of? In the ancient time: 4 elements 19 century atoms Beginning 20 th century
What is matter and how is it formed?
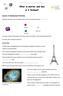 What is matter and how is it formed? Lesson 6: Subatomic Particles Subatomic particles refers to particles that are more "fundamental" than... Are these fundamental particles or are they made up of smaller,
What is matter and how is it formed? Lesson 6: Subatomic Particles Subatomic particles refers to particles that are more "fundamental" than... Are these fundamental particles or are they made up of smaller,
Lecture 26 Fundamentals of Physics Phys 120, Fall 2015 Quantum Fields
 Lecture 26 Fundamentals of Physics Phys 120, Fall 2015 Quantum Fields A. J. Wagner North Dakota State University, Fargo, ND 58102 Fargo, December 3, 2015 Overview Quantized Fields: the reason for particles
Lecture 26 Fundamentals of Physics Phys 120, Fall 2015 Quantum Fields A. J. Wagner North Dakota State University, Fargo, ND 58102 Fargo, December 3, 2015 Overview Quantized Fields: the reason for particles
Particle Physics. All science is either physics or stamp collecting and this from a 1908 Nobel laureate in Chemistry
 Particle Physics JJ Thompson discovered electrons in 1897 Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus in 1911 and the proton in 1919 (idea of gold foil expt) All science is either physics or stamp collecting
Particle Physics JJ Thompson discovered electrons in 1897 Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus in 1911 and the proton in 1919 (idea of gold foil expt) All science is either physics or stamp collecting
Lecture 3. lecture slides are at:
 Lecture 3 lecture slides are at: http://www.physics.smu.edu/ryszard/5380fa16/ Proton mass m p = 938.28 MeV/c 2 Electron mass m e = 0.511 MeV/c 2 Neutron mass m n = 939.56 MeV/c 2 Helium nucleus α: 2 protons+2
Lecture 3 lecture slides are at: http://www.physics.smu.edu/ryszard/5380fa16/ Proton mass m p = 938.28 MeV/c 2 Electron mass m e = 0.511 MeV/c 2 Neutron mass m n = 939.56 MeV/c 2 Helium nucleus α: 2 protons+2
Part A-type questions
 PHYS306: lecture 8 th February 008 Part A-type questions. You toss an apple horizontally at 8.7 m/s from a height of.6 m. Simultaneously, you drop a peach from the same height. How long does each take
PHYS306: lecture 8 th February 008 Part A-type questions. You toss an apple horizontally at 8.7 m/s from a height of.6 m. Simultaneously, you drop a peach from the same height. How long does each take
- ~200 times heavier than the e GeV µ travels on average. - does not interact strongly. - does emit bremsstrahlung in
 Muons M. Swartz 1 Muons: everything you ve ever wanted to know The muon was first observed in cosmic ray tracks in a cloud chamber by Carl Anderson and Seth Neddermeyer in 1937. It was eventually shown
Muons M. Swartz 1 Muons: everything you ve ever wanted to know The muon was first observed in cosmic ray tracks in a cloud chamber by Carl Anderson and Seth Neddermeyer in 1937. It was eventually shown
CHAPTER 3 The Experimental Basis of Quantum
 CHAPTER 3 The Experimental Basis of Quantum 3.1 Discovery of the X Ray and the Electron 3.2 Determination of Electron Charge 3.3 Line Spectra 3.4 Quantization 3.5 Blackbody Radiation 3.6 Photoelectric
CHAPTER 3 The Experimental Basis of Quantum 3.1 Discovery of the X Ray and the Electron 3.2 Determination of Electron Charge 3.3 Line Spectra 3.4 Quantization 3.5 Blackbody Radiation 3.6 Photoelectric
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Discovery and Properties of the electron
 Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom 27-1 Discovery and Properties of the electron Measure charge to mass ratio e/m (J. J. Thomson, 1897) When apply magnetic field only, the rays are
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom 27-1 Discovery and Properties of the electron Measure charge to mass ratio e/m (J. J. Thomson, 1897) When apply magnetic field only, the rays are
The Boundary between Classical and Quantum Mechanics
 The Boundary between Classical and Quantum Mechanics In the quantum world, physicists study the tiny particles that make up our classical world - neutrons, electrons, photons - either one at a time or
The Boundary between Classical and Quantum Mechanics In the quantum world, physicists study the tiny particles that make up our classical world - neutrons, electrons, photons - either one at a time or
Physics 4213/5213 Lecture 1
 August 28, 2002 1 INTRODUCTION 1 Introduction Physics 4213/5213 Lecture 1 There are four known forces: gravity, electricity and magnetism (E&M), the weak force, and the strong force. Each is responsible
August 28, 2002 1 INTRODUCTION 1 Introduction Physics 4213/5213 Lecture 1 There are four known forces: gravity, electricity and magnetism (E&M), the weak force, and the strong force. Each is responsible
Problems with Classical Physics. Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric Effect Compton Effect Bohr Model of Atom
 The Quantum Gang Problems with Classical Physics Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric Effect Compton Effect Bohr Model of Atom Why this shape? Why the drop? Blackbody Radiation A black body is an ideal system
The Quantum Gang Problems with Classical Physics Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric Effect Compton Effect Bohr Model of Atom Why this shape? Why the drop? Blackbody Radiation A black body is an ideal system
1. What does this poster contain?
 This poster presents the elementary constituents of matter (the particles) and their interactions, the latter having other particles as intermediaries. These elementary particles are point-like and have
This poster presents the elementary constituents of matter (the particles) and their interactions, the latter having other particles as intermediaries. These elementary particles are point-like and have
Introduction. Read: Ch 1 of M&S
 Introduction What questions does this field address? Want to know the basic law of nature. Can we unify all the forces with one equation or one theory? Read: Ch 1 of M&S K.K. Gan L1: Introduction 1 Particle
Introduction What questions does this field address? Want to know the basic law of nature. Can we unify all the forces with one equation or one theory? Read: Ch 1 of M&S K.K. Gan L1: Introduction 1 Particle
Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta. EECS Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku
 Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta EECS 598-002 Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku From classical to quantum theory In the beginning of the 20 th century, experiments
Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta EECS 598-002 Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku From classical to quantum theory In the beginning of the 20 th century, experiments
Chapter 39. Particles Behaving as Waves
 Chapter 39 Particles Behaving as Waves 39.1 Electron Waves Light has a dual nature. Light exhibits both wave and particle characteristics. Louis de Broglie postulated in 1924 that if nature is symmetric,
Chapter 39 Particles Behaving as Waves 39.1 Electron Waves Light has a dual nature. Light exhibits both wave and particle characteristics. Louis de Broglie postulated in 1924 that if nature is symmetric,
The Higgs - Theory. The Higgs. Theory. Arthur H. Compton Lecture th. Martin Bauer. Oct. 26 Arthur H. Compton Lectures Oct 26th 2013
 The Higgs - Theory The Higgs Martin Bauer Arthur H. Compton Lecture th Martin Oct. 26 2013Bauer Arthur H. Compton Lectures Oct 26th 2013 Theory Outline The Higgs: A new interaction How the Higgs field
The Higgs - Theory The Higgs Martin Bauer Arthur H. Compton Lecture th Martin Oct. 26 2013Bauer Arthur H. Compton Lectures Oct 26th 2013 Theory Outline The Higgs: A new interaction How the Higgs field
String Theory in the LHC Era
 String Theory in the LHC Era J Marsano (marsano@uchicago.edu) 1 String Theory in the LHC Era 1. Electromagnetism and Special Relativity 2. The Quantum World 3. Why do we need the Higgs? 4. The Standard
String Theory in the LHC Era J Marsano (marsano@uchicago.edu) 1 String Theory in the LHC Era 1. Electromagnetism and Special Relativity 2. The Quantum World 3. Why do we need the Higgs? 4. The Standard
Cosmology and particle physics
 Cosmology and particle physics Lecture notes Timm Wrase Lecture 5 The thermal universe - part I In the last lecture we have shown that our very early universe was in a very hot and dense state. During
Cosmology and particle physics Lecture notes Timm Wrase Lecture 5 The thermal universe - part I In the last lecture we have shown that our very early universe was in a very hot and dense state. During
Hand of Anna Röntgen. From Life magazine,6 April 1896
 FROM ELECTRONS TO QUARKS The development of Particle Physics QUARKNET 2001, FSU Laura Reina Outline ffl What is Particle Physics? ffl The origins of Particle Physics: the atom (p,e ), radioactivity, and
FROM ELECTRONS TO QUARKS The development of Particle Physics QUARKNET 2001, FSU Laura Reina Outline ffl What is Particle Physics? ffl The origins of Particle Physics: the atom (p,e ), radioactivity, and
NEUTRINOS. Concha Gonzalez-Garcia. San Feliu, June (Stony Brook-USA and IFIC-Valencia)
 NEUTRINOS (Stony Brook-USA and IFIC-Valencia San Feliu, June 2004 Plan of Lectures I. Standard Neutrino Properties and Mass Terms (Beyond Standard II. Neutrino Oscillations III. The Data and Its Interpretation
NEUTRINOS (Stony Brook-USA and IFIC-Valencia San Feliu, June 2004 Plan of Lectures I. Standard Neutrino Properties and Mass Terms (Beyond Standard II. Neutrino Oscillations III. The Data and Its Interpretation
The Development of Particle Physics. Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.:
 The Development of Particle Physics Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.: 0114 4531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk The structure of the nucleon Electron - nucleon elastic scattering Rutherford, Mott cross-sections
The Development of Particle Physics Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.: 0114 4531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk The structure of the nucleon Electron - nucleon elastic scattering Rutherford, Mott cross-sections
F. TASNÁDI LINKÖPING UNIVERSITY THEORETICAL PHYSICS NEUTRINO OSCILLATIONS & MASS
 F. TASNÁDI LINKÖPING UNIVERSITY THEORETICAL PHYSICS NEUTRINO OSCILLATIONS & MASS the fundamental discoveries in physics con4nues 1 CONGRATULATIONS - NOBEL PRIZE IN PHYSICS 2016 the secrets of exotic matter
F. TASNÁDI LINKÖPING UNIVERSITY THEORETICAL PHYSICS NEUTRINO OSCILLATIONS & MASS the fundamental discoveries in physics con4nues 1 CONGRATULATIONS - NOBEL PRIZE IN PHYSICS 2016 the secrets of exotic matter
Physics 107 Final Exam May 6, Your Name: 1. Questions
 Physics 107 Final Exam May 6, 1996 Your Name: 1. Questions 1. 9. 17. 5.. 10. 18. 6. 3. 11. 19. 7. 4. 1. 0. 8. 5. 13. 1. 9. 6. 14.. 30. 7. 15. 3. 8. 16. 4.. Problems 1. 4. 7. 10. 13.. 5. 8. 11. 14. 3. 6.
Physics 107 Final Exam May 6, 1996 Your Name: 1. Questions 1. 9. 17. 5.. 10. 18. 6. 3. 11. 19. 7. 4. 1. 0. 8. 5. 13. 1. 9. 6. 14.. 30. 7. 15. 3. 8. 16. 4.. Problems 1. 4. 7. 10. 13.. 5. 8. 11. 14. 3. 6.
Units and dimensions
 Particles and Fields Particles and Antiparticles Bosons and Fermions Interactions and cross sections The Standard Model Beyond the Standard Model Neutrinos and their oscillations Particle Hierarchy Everyday
Particles and Fields Particles and Antiparticles Bosons and Fermions Interactions and cross sections The Standard Model Beyond the Standard Model Neutrinos and their oscillations Particle Hierarchy Everyday
Introduction to Particle Physics. HST July 2016 Luis Alvarez Gaume 1
 Introduction to Particle Physics HST July 2016 Luis Alvarez Gaume 1 Basics Particle Physics describes the basic constituents of matter and their interactions It has a deep interplay with cosmology Modern
Introduction to Particle Physics HST July 2016 Luis Alvarez Gaume 1 Basics Particle Physics describes the basic constituents of matter and their interactions It has a deep interplay with cosmology Modern
COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Chiara Caprini (APC)
 COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Chiara Caprini (APC) the direct detection of GW by the LIGO interferometers has opened a new era in Astronomy - we now have a new messenger bringing complementary informations
COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Chiara Caprini (APC) the direct detection of GW by the LIGO interferometers has opened a new era in Astronomy - we now have a new messenger bringing complementary informations
Weak interactions. Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 Weak interactions As already discussed, weak interactions are responsible for many processes which involve the transformation of particles from one type to another. Weak interactions cause nuclear
Chapter 7 Weak interactions As already discussed, weak interactions are responsible for many processes which involve the transformation of particles from one type to another. Weak interactions cause nuclear
Some fundamental questions
 Some fundamental questions What is the standard model of elementary particles and their interactions? What is the origin of mass and electroweak symmetry breaking? What is the role of anti-matter in Nature?
Some fundamental questions What is the standard model of elementary particles and their interactions? What is the origin of mass and electroweak symmetry breaking? What is the role of anti-matter in Nature?
Physics Lecture 6
 Physics 3313 - Lecture 6 Monday February 8, 2010 Dr. Andrew Brandt 1. HW1 Due today HW2 weds 2/10 2. Electron+X-rays 3. Black body radiation 4. Compton Effect 5. Pair Production 2/8/10 3313 Andrew Brandt
Physics 3313 - Lecture 6 Monday February 8, 2010 Dr. Andrew Brandt 1. HW1 Due today HW2 weds 2/10 2. Electron+X-rays 3. Black body radiation 4. Compton Effect 5. Pair Production 2/8/10 3313 Andrew Brandt
Finish up our overview of small and large
 Finish up our overview of small and large Lecture 5 Limits of our knowledge Clicker practice quiz Some terminology... "Elementary particles" = objects that make up atoms (n,p,e) or are produced when atoms
Finish up our overview of small and large Lecture 5 Limits of our knowledge Clicker practice quiz Some terminology... "Elementary particles" = objects that make up atoms (n,p,e) or are produced when atoms
1 Introduction. 1.1 The Standard Model of particle physics The fundamental particles
 1 Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to provide a brief introduction to the Standard Model of particle physics. In particular, it gives an overview of the fundamental particles and the relationship
1 Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to provide a brief introduction to the Standard Model of particle physics. In particular, it gives an overview of the fundamental particles and the relationship
Neutron Decay Disagree
 Neutron Decay Disagree In fact, one of the biggest disagreements involves one of the most common particles in the Universe: the neutron. [4] The Weak Interaction transforms an electric charge in the diffraction
Neutron Decay Disagree In fact, one of the biggest disagreements involves one of the most common particles in the Universe: the neutron. [4] The Weak Interaction transforms an electric charge in the diffraction
Quantum Consciousness and Entanglement
 Quantum Consciousness and Entanglement The human body is a constant flux of thousands of chemical/biological interactions and processes connecting molecules, cells, organs, and fluids, throughout the brain,
Quantum Consciousness and Entanglement The human body is a constant flux of thousands of chemical/biological interactions and processes connecting molecules, cells, organs, and fluids, throughout the brain,
Complementi di Fisica Lectures 3, 4
 Complementi di Fisica Lectures 3, 4 Livio Lanceri Università di Trieste Trieste, 3/8-10-015 Course Outline - Reminder Quantum Mechanics: an introduction Waves as particles and particles as waves (the crisis
Complementi di Fisica Lectures 3, 4 Livio Lanceri Università di Trieste Trieste, 3/8-10-015 Course Outline - Reminder Quantum Mechanics: an introduction Waves as particles and particles as waves (the crisis
Quantum Mechanics. Physics April 2002 Lecture 9. Planck Bohr Schroedinger Heisenberg
 Quantum Mechanics Physics 102 18 April 2002 Lecture 9 Planck Bohr Schroedinger Heisenberg From: http://www.th.physik.uni-frankfurt.de/~jr/portraits.html 18 Apr 2002 Physics 102 Lecture 9 1 Blackbody radiation
Quantum Mechanics Physics 102 18 April 2002 Lecture 9 Planck Bohr Schroedinger Heisenberg From: http://www.th.physik.uni-frankfurt.de/~jr/portraits.html 18 Apr 2002 Physics 102 Lecture 9 1 Blackbody radiation
Solutions for Assignment of Week 06 Introduction to Astroparticle Physics
 s for Assignment of Week 06 Introduction to Astroparticle Physics Georg G. Raffelt Max-Planck-Institut für Physik (Werner-Heisenberg-Institut) Föhringer Ring 6, 80805 München Email: raffelt(at)mppmu.mpg.de
s for Assignment of Week 06 Introduction to Astroparticle Physics Georg G. Raffelt Max-Planck-Institut für Physik (Werner-Heisenberg-Institut) Föhringer Ring 6, 80805 München Email: raffelt(at)mppmu.mpg.de
