19. Genetic Drift. The biological context. There are four basic consequences of genetic drift:
|
|
|
- Clarence Hunter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 9. Genetic Drift Genetic drift is the alteration of gene frequencies due to sampling variation from one generation to the next. It operates to some degree in all finite populations, but can be significant as an evolutionary process in natural populations only when they are relatively small. The biological context There are four basic consequences of genetic drift: ) Random change: If the allele frequencies in a single small population are followed, they may be seen to change in an erratic manner from generation to generation, with no tendency to revert to their original values. 2) Differentiation among subpopulations: Genetic drift occurring independently in different subpopulations leads to genetic differentiation between them. Large populations in nature are seldom homogeneous because mating occurs more often between inhabitats of the same region; such subpopulations, if small, tend to differentiate by drift. Domesticated or laboratory populations are often subdivided (into herds or strains) and to become different over time. 3) Uniformity within subpopulations: Genetic variation within each subpopulation becomes progressively reduced, and individuals become more and more alike in genotype. This genetic uniformity is the reason for the widespread use of inbred strains of laboratory animals in many areas of biological research. 4) Decreased heterozygosity: Homozygotes increase in frequency at the expense of heterozygotes. This, coupled with the general tendency for deleterious alleles to be recessive, is the genetic basis for the loss of fertility and viability that almost always results from inbreeding. In theory, there are four situations in which genetic drift might play an effective role in the evolution of natural populations: ) Continuous drift: The population remains small in size, and sampling variation is effective in each generation. This is particularly likely to occur with endangered species.
2 9. Genetic drift 2 2) Intermittent drift: The population is occasionally reduced to a size sufficiently small to allow drift to operate. Reduction can be effective in one of two ways: a) Bottleneck effect: If mortality is random at the time of reduction in population size, the sample of survivors can have a different genetic composition, and reduced heterozygosity, due to chance alone. b) If the population remains small over two or more consecutive generations, the process of continuous drift is initiated. 3) Founder effect: New populations are often started by small numbers of migratory individuals, which carry only a fraction of the genetic variability of the parental population and thus differ randomly from it. Thus new populations tend to differ both from the parent population and from each other. 4) Wahlund effect: If a population is subdivided into small, effectively isolated demes, then genetic drift will be more effective than if the population were undergoing random mating. As a consequence, heterozygosity of the overall population is reduced relative to Hardy-Weinberg expectations. The quantitative model ) The probabilities of drawing various possible combinations of gametes (alleles) to form N progeny, based on the random selection of gametes from a parental gene pool having allele frequencies p and q (i.e., random mating), is given by the binomial distribution ( ) B(2 N, p) = p + q = = p q = C p q n n2 n n2 n n n = n= where n is the number of A alleles sampled, which varies from (the condition in which the progeny are fixed for A 2 ) to (the condition in which the progeny are fixed for A ), and n 2 is the n n2 number of A 2 allele sampled (n + n 2 = ). The term p q is the probability of combining n 2 N (2 N)! A alleles with n 2 A 2 alleles to form the progeny; the term = Cn = is the number of n n! n2! possible ways in which n A alleles and n 2 A 2 alleles can be combined to form the genotypes of the progeny. For example, the following sets of terms are the binomial expansions of the equation above. As above, N is the population size, and is the number of gametes sampled from the gene pool to form the offspring generation.
3 9. Genetic drift 3 N Binomial expansion 2 ( ) p+ q = pq + 2pq + pq = = p + 2pq+ q ( ) p+ q = pq + 4pq + 6pq + 4 pq + pq = = p + 4pq+ 6pq + 4pq + q ( ) p+ q = pq + 6pq + 5pq + 2pq = pq 6 pq pq = p + 6pq+ 5pq + 2pq + 5pq + 6pq + q ( ) p+ q = pq + 8pq + 28pq + 56pq + 7 pq = pq 28pq 8pq pq = p + 8pq+ 28pq + 56pq + 7 pq pq + 28pq + 8pq + q ( ) p+ q = p q + pq + 45pq + 2pq + 2pq pq = pq 2pq 45pq pq pq = p + pq+ 45pq + 2pq + 2pq pq pq + 2pq + 45pq + pq + q
4 9. Genetic drift 4 Context for the Model of Genetic Drift Model for analyzing the effects of random genetic drift on the differentiation of independent replicate subpopulations. Each of the subpopulations (vertical columns of boxes and arrows) founded from the initial large population is assumed to be genetically isolated from the others. Each subpopulation produces an infinite number of gametes, of which are chosen at random to form the next generation s breeding population. Random genetic drift results from sampling variation in this process. (From Hartl, 988).
5 9. Genetic drift 5 2) When a random sample of gametes is selected from the parental gene pool in accordance with the binomial probabilities, the allele frequencies of the sample are likely to be slightly different from those of the parents. This random change in allele frequencies from parents to offspring due solely to sampling variation is genetic drift. Although drift produces changes in allele frequencies, the subpopulation can be in Hardy-Weinberg-Castle equilibrium at each generation. 3) δq t = change in allele frequency, over t generations, due to genetic drift. This term is analogous to the q of previous deterministic models, but is a statistical rather than fixed value. It has an expected value (mean) and variance, but it s direction and magnitude can t be predicted in any particular case. 4) The expected net change of δq t (over numerous subpopulation replicates) is zero: E(δq t ) = 5) The expected variance in change (over numerous subpopulation replicates) in a single generation is 2 pq σ δ q =, where N is the subpopulation size (assumed to remain constant across generations). This value is the sampling variance (standard error of the mean) of the corresponding binomial distribution. 6) The expected variance in change (over numerous replicates) across t generations is 2 σ, ( ) t δ qt = pq. The form of this equation predicts that the variance due to drift: a) is large for small N, and small for large N (i.e., is inversely proportional to N ); b) increases with time, t ; c) is greatest for intermediate values of p and q (near.5), is smaller for very rare and very common alleles, and vanishes when one of the alleles becomes fixed. Note that, when t = [as in note (5), above], 2 σδ q, = pq ( ) = pq ( ) = pq + pq =
6 9. Genetic drift 6 7) The mean allele frequency among subpopulations, q, is the weighted mean allele frequency among the k subpopulations, weighted by subpopulation size, N i : q k = Nq. i i i= The variance in allele frequency among subpopulations is denoted heterozygotes in generation t is H = 2pq = 2pq σ. 2 t t t qt, 2 σ q. The expected number of 8) The probability of fixation or loss of an allele between one generation and the next is p + q (the two extreme terms of the binomial distribution). This implies that, on average, fixation and loss of alleles occur at a rate of roughly ¼ N per locus per generation. Thus the mean time to fixation or extinction of any given allele is approximately 4N generations (but this is a very rough approximation). N = [2, 5,, 5, 2, 25, ].9 Probability of fixation ( gen)
7 9. Genetic drift 7 9) The binomial distribution predicts the exact probabilities of forming specified combinations of genotypes, but becomes impractical to use for N > 2 or so. However, the central limit theorem of probability theory predicts that, as N becomes large, δq approaches a normal distribution having mean and standard deviation σ δ q. Thus, for larger population sizes, we can use normal distributions to provide approximate results. (However, the exact results are always provided by the binomial distribution, which are used in computer simulations for any value of N, no matter how large.)
8 9. Genetic drift 8 Computer simulations of genetic drift These examples portray the results of a stochastic computer model of genetic drift, as a function of population size and initial allele frequencies. In each case, replicates ( locus for populations, or loci for one population) were tracked independently for generations..9.8 N = p = N = p =. (q) (q) Generation Generation.9.8 N = 5 p = N = 5 p = Generation Generation.9.8 p = p = Generation Generation
9 9. Genetic drift 9 Binomial Distributions Centered on p = q =.5.5 N =.4.35 N = (p) (p).25 N = N = (p) (p) N = (p) (p)
10 9. Genetic drift Uncentered Binomial Distributions.3.25 N = 2 p =..2 N = 2 p = N = 2 p = N = 2 p = N = 2 p = N = 2 p =
11 9. Genetic drift Normal Approximations to the Binomial Distribution N = 5, p = N = 5, p = N = 5, p =
12 9. Genetic drift 2 Increase in Expected Variance due to Genetic Drift p =.3 t =.35 p =.3 t = 2 Frequency.4.3 Frequency Frequency p =.3 t = 3 Frequency p =.3 t = p =.3 t =.4 p =.3 t = 2 Frequency.5. Frequency
13 9. Genetic drift 3 The Standard Normal Distribution.4.35 Relative Frequency Standard Deviation Units % Relative Frequency %.5 95% 99% Standard Deviation Units
14 9. Genetic drift 4 One-tailed normal probabilities: proportion of area of the normal distribution that is equal to or more extreme than the specified z value. z <. <. <. <. <. <. <. <. <. <. 4. <. <. <. <. <. <. <. <. <. <.
8. Genetic Diversity
 8. Genetic Diversity Many ways to measure the diversity of a population: For any measure of diversity, we expect an estimate to be: when only one kind of object is present; low when >1 kind of objects
8. Genetic Diversity Many ways to measure the diversity of a population: For any measure of diversity, we expect an estimate to be: when only one kind of object is present; low when >1 kind of objects
Processes of Evolution
 15 Processes of Evolution Forces of Evolution Concept 15.4 Selection Can Be Stabilizing, Directional, or Disruptive Natural selection can act on quantitative traits in three ways: Stabilizing selection
15 Processes of Evolution Forces of Evolution Concept 15.4 Selection Can Be Stabilizing, Directional, or Disruptive Natural selection can act on quantitative traits in three ways: Stabilizing selection
LECTURE # How does one test whether a population is in the HW equilibrium? (i) try the following example: Genotype Observed AA 50 Aa 0 aa 50
 LECTURE #10 A. The Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium 1. From the definitions of p and q, and of p 2, 2pq, and q 2, an equilibrium is indicated (p + q) 2 = p 2 + 2pq + q 2 : if p and q remain constant, and if
LECTURE #10 A. The Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium 1. From the definitions of p and q, and of p 2, 2pq, and q 2, an equilibrium is indicated (p + q) 2 = p 2 + 2pq + q 2 : if p and q remain constant, and if
Life Cycles, Meiosis and Genetic Variability24/02/2015 2:26 PM
 Life Cycles, Meiosis and Genetic Variability iclicker: 1. A chromosome just before mitosis contains two double stranded DNA molecules. 2. This replicated chromosome contains DNA from only one of your parents
Life Cycles, Meiosis and Genetic Variability iclicker: 1. A chromosome just before mitosis contains two double stranded DNA molecules. 2. This replicated chromosome contains DNA from only one of your parents
Microevolution Changing Allele Frequencies
 Microevolution Changing Allele Frequencies Evolution Evolution is defined as a change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. Microevolution involves the
Microevolution Changing Allele Frequencies Evolution Evolution is defined as a change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. Microevolution involves the
Genetics and Natural Selection
 Genetics and Natural Selection Darwin did not have an understanding of the mechanisms of inheritance and thus did not understand how natural selection would alter the patterns of inheritance in a population.
Genetics and Natural Selection Darwin did not have an understanding of the mechanisms of inheritance and thus did not understand how natural selection would alter the patterns of inheritance in a population.
Outline of lectures 3-6
 GENOME 453 J. Felsenstein Evolutionary Genetics Autumn, 007 Population genetics Outline of lectures 3-6 1. We want to know what theory says about the reproduction of genotypes in a population. This results
GENOME 453 J. Felsenstein Evolutionary Genetics Autumn, 007 Population genetics Outline of lectures 3-6 1. We want to know what theory says about the reproduction of genotypes in a population. This results
Outline of lectures 3-6
 GENOME 453 J. Felsenstein Evolutionary Genetics Autumn, 009 Population genetics Outline of lectures 3-6 1. We want to know what theory says about the reproduction of genotypes in a population. This results
GENOME 453 J. Felsenstein Evolutionary Genetics Autumn, 009 Population genetics Outline of lectures 3-6 1. We want to know what theory says about the reproduction of genotypes in a population. This results
Breeding Values and Inbreeding. Breeding Values and Inbreeding
 Breeding Values and Inbreeding Genotypic Values For the bi-allelic single locus case, we previously defined the mean genotypic (or equivalently the mean phenotypic values) to be a if genotype is A 2 A
Breeding Values and Inbreeding Genotypic Values For the bi-allelic single locus case, we previously defined the mean genotypic (or equivalently the mean phenotypic values) to be a if genotype is A 2 A
Case Studies in Ecology and Evolution
 3 Non-random mating, Inbreeding and Population Structure. Jewelweed, Impatiens capensis, is a common woodland flower in the Eastern US. You may have seen the swollen seed pods that explosively pop when
3 Non-random mating, Inbreeding and Population Structure. Jewelweed, Impatiens capensis, is a common woodland flower in the Eastern US. You may have seen the swollen seed pods that explosively pop when
Population Genetics & Evolution
 The Theory of Evolution Mechanisms of Evolution Notes Pt. 4 Population Genetics & Evolution IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER: Populations, not individuals, evolve. Population = a group of individuals of the same
The Theory of Evolution Mechanisms of Evolution Notes Pt. 4 Population Genetics & Evolution IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER: Populations, not individuals, evolve. Population = a group of individuals of the same
Population genetics snippets for genepop
 Population genetics snippets for genepop Peter Beerli August 0, 205 Contents 0.Basics 0.2Exact test 2 0.Fixation indices 4 0.4Isolation by Distance 5 0.5Further Reading 8 0.6References 8 0.7Disclaimer
Population genetics snippets for genepop Peter Beerli August 0, 205 Contents 0.Basics 0.2Exact test 2 0.Fixation indices 4 0.4Isolation by Distance 5 0.5Further Reading 8 0.6References 8 0.7Disclaimer
- point mutations in most non-coding DNA sites likely are likely neutral in their phenotypic effects.
 January 29 th, 2010 Bioe 109 Winter 2010 Lecture 10 Microevolution 3 - random genetic drift - one of the most important shifts in evolutionary thinking over the past 30 years has been an appreciation of
January 29 th, 2010 Bioe 109 Winter 2010 Lecture 10 Microevolution 3 - random genetic drift - one of the most important shifts in evolutionary thinking over the past 30 years has been an appreciation of
Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Biology 5865 Conservation Biology. Problems of Small Populations Population Viability Analysis
 Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Biology 5865 Conservation Biology Problems of Small Populations Population Viability Analysis Minimum Viable Population (MVP) Schaffer (1981) MVP- A minimum viable population for
Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Biology 5865 Conservation Biology Problems of Small Populations Population Viability Analysis Minimum Viable Population (MVP) Schaffer (1981) MVP- A minimum viable population for
Question: If mating occurs at random in the population, what will the frequencies of A 1 and A 2 be in the next generation?
 October 12, 2009 Bioe 109 Fall 2009 Lecture 8 Microevolution 1 - selection The Hardy-Weinberg-Castle Equilibrium - consider a single locus with two alleles A 1 and A 2. - three genotypes are thus possible:
October 12, 2009 Bioe 109 Fall 2009 Lecture 8 Microevolution 1 - selection The Hardy-Weinberg-Castle Equilibrium - consider a single locus with two alleles A 1 and A 2. - three genotypes are thus possible:
Chapter 17: Population Genetics and Speciation
 Chapter 17: Population Genetics and Speciation Section 1: Genetic Variation Population Genetics: Normal Distribution: a line graph showing the general trends in a set of data of which most values are near
Chapter 17: Population Genetics and Speciation Section 1: Genetic Variation Population Genetics: Normal Distribution: a line graph showing the general trends in a set of data of which most values are near
Microevolution 2 mutation & migration
 Microevolution 2 mutation & migration Assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium 1. Mating is random 2. Population size is infinite (i.e., no genetic drift) 3. No migration 4. No mutation 5. No selection
Microevolution 2 mutation & migration Assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium 1. Mating is random 2. Population size is infinite (i.e., no genetic drift) 3. No migration 4. No mutation 5. No selection
Problems for 3505 (2011)
 Problems for 505 (2011) 1. In the simplex of genotype distributions x + y + z = 1, for two alleles, the Hardy- Weinberg distributions x = p 2, y = 2pq, z = q 2 (p + q = 1) are characterized by y 2 = 4xz.
Problems for 505 (2011) 1. In the simplex of genotype distributions x + y + z = 1, for two alleles, the Hardy- Weinberg distributions x = p 2, y = 2pq, z = q 2 (p + q = 1) are characterized by y 2 = 4xz.
The Wright-Fisher Model and Genetic Drift
 The Wright-Fisher Model and Genetic Drift January 22, 2015 1 1 Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Our goal is to understand the dynamics of allele and genotype frequencies in an infinite, randomlymating population
The Wright-Fisher Model and Genetic Drift January 22, 2015 1 1 Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Our goal is to understand the dynamics of allele and genotype frequencies in an infinite, randomlymating population
EXERCISES FOR CHAPTER 3. Exercise 3.2. Why is the random mating theorem so important?
 Statistical Genetics Agronomy 65 W. E. Nyquist March 004 EXERCISES FOR CHAPTER 3 Exercise 3.. a. Define random mating. b. Discuss what random mating as defined in (a) above means in a single infinite population
Statistical Genetics Agronomy 65 W. E. Nyquist March 004 EXERCISES FOR CHAPTER 3 Exercise 3.. a. Define random mating. b. Discuss what random mating as defined in (a) above means in a single infinite population
WHAT IS BIOLOGICAL DIVERSITY?
 WHAT IS BIOLOGICAL DIVERSITY? Biological diversity or biodiversity is the variety of life - the wealth of life forms found on earth. 9 WHAT IS BIOLOGICAL DIVERSITY? Wilcox s (1984) definition: Biological
WHAT IS BIOLOGICAL DIVERSITY? Biological diversity or biodiversity is the variety of life - the wealth of life forms found on earth. 9 WHAT IS BIOLOGICAL DIVERSITY? Wilcox s (1984) definition: Biological
Population Structure
 Ch 4: Population Subdivision Population Structure v most natural populations exist across a landscape (or seascape) that is more or less divided into areas of suitable habitat v to the extent that populations
Ch 4: Population Subdivision Population Structure v most natural populations exist across a landscape (or seascape) that is more or less divided into areas of suitable habitat v to the extent that populations
Mutation, Selection, Gene Flow, Genetic Drift, and Nonrandom Mating Results in Evolution
 Mutation, Selection, Gene Flow, Genetic Drift, and Nonrandom Mating Results in Evolution 15.2 Intro In biology, evolution refers specifically to changes in the genetic makeup of populations over time.
Mutation, Selection, Gene Flow, Genetic Drift, and Nonrandom Mating Results in Evolution 15.2 Intro In biology, evolution refers specifically to changes in the genetic makeup of populations over time.
URN MODELS: the Ewens Sampling Lemma
 Department of Computer Science Brown University, Providence sorin@cs.brown.edu October 3, 2014 1 2 3 4 Mutation Mutation: typical values for parameters Equilibrium Probability of fixation 5 6 Ewens Sampling
Department of Computer Science Brown University, Providence sorin@cs.brown.edu October 3, 2014 1 2 3 4 Mutation Mutation: typical values for parameters Equilibrium Probability of fixation 5 6 Ewens Sampling
Segregation versus mitotic recombination APPENDIX
 APPENDIX Waiting time until the first successful mutation The first time lag, T 1, is the waiting time until the first successful mutant appears, creating an Aa individual within a population composed
APPENDIX Waiting time until the first successful mutation The first time lag, T 1, is the waiting time until the first successful mutant appears, creating an Aa individual within a population composed
The theory of evolution continues to be refined as scientists learn new information.
 Section 3: The theory of evolution continues to be refined as scientists learn new information. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the conditions of the
Section 3: The theory of evolution continues to be refined as scientists learn new information. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the conditions of the
Evolutionary Theory. Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A.
 Evolutionary Theory Mathematical and Conceptual Foundations Sean H. Rice Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A. Contents Preface ix Introduction 1 CHAPTER 1 Selection on One
Evolutionary Theory Mathematical and Conceptual Foundations Sean H. Rice Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A. Contents Preface ix Introduction 1 CHAPTER 1 Selection on One
Quantitative Genetics I: Traits controlled my many loci. Quantitative Genetics: Traits controlled my many loci
 Quantitative Genetics: Traits controlled my many loci So far in our discussions, we have focused on understanding how selection works on a small number of loci (1 or 2). However in many cases, evolutionary
Quantitative Genetics: Traits controlled my many loci So far in our discussions, we have focused on understanding how selection works on a small number of loci (1 or 2). However in many cases, evolutionary
Big Idea #1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life
 BIG IDEA! Big Idea #1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life Key Terms for this section: emigration phenotype adaptation evolution phylogenetic tree adaptive radiation fertility
BIG IDEA! Big Idea #1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life Key Terms for this section: emigration phenotype adaptation evolution phylogenetic tree adaptive radiation fertility
Lecture 1 Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and key forces affecting gene frequency
 Lecture 1 Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and key forces affecting gene frequency Bruce Walsh lecture notes Introduction to Quantitative Genetics SISG, Seattle 16 18 July 2018 1 Outline Genetics of complex
Lecture 1 Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and key forces affecting gene frequency Bruce Walsh lecture notes Introduction to Quantitative Genetics SISG, Seattle 16 18 July 2018 1 Outline Genetics of complex
EVOLUTION UNIT. 3. Unlike his predecessors, Darwin proposed a mechanism by which evolution could occur called.
 EVOLUTION UNIT Name Read Chapters 1.3, 20, 21, 22, 24.1 and 35.9 and complete the following. Chapter 1.3 Review from The Science of Biology 1. Discuss the influences, experiences and observations that
EVOLUTION UNIT Name Read Chapters 1.3, 20, 21, 22, 24.1 and 35.9 and complete the following. Chapter 1.3 Review from The Science of Biology 1. Discuss the influences, experiences and observations that
Study of similarities and differences in body plans of major groups Puzzling patterns:
 Processes of Evolution Evolutionary Theories Widely used to interpret the past and present, and even to predict the future Reveal connections between the geological record, fossil record, and organismal
Processes of Evolution Evolutionary Theories Widely used to interpret the past and present, and even to predict the future Reveal connections between the geological record, fossil record, and organismal
Mechanisms of Evolution
 Mechanisms of Evolution 36-149 The Tree of Life Christopher R. Genovese Department of Statistics 132H Baker Hall x8-7836 http://www.stat.cmu.edu/ ~ genovese/. Plan 1. Two More Generations 2. The Hardy-Weinberg
Mechanisms of Evolution 36-149 The Tree of Life Christopher R. Genovese Department of Statistics 132H Baker Hall x8-7836 http://www.stat.cmu.edu/ ~ genovese/. Plan 1. Two More Generations 2. The Hardy-Weinberg
AEC 550 Conservation Genetics Lecture #2 Probability, Random mating, HW Expectations, & Genetic Diversity,
 AEC 550 Conservation Genetics Lecture #2 Probability, Random mating, HW Expectations, & Genetic Diversity, Today: Review Probability in Populatin Genetics Review basic statistics Population Definition
AEC 550 Conservation Genetics Lecture #2 Probability, Random mating, HW Expectations, & Genetic Diversity, Today: Review Probability in Populatin Genetics Review basic statistics Population Definition
Solutions to Even-Numbered Exercises to accompany An Introduction to Population Genetics: Theory and Applications Rasmus Nielsen Montgomery Slatkin
 Solutions to Even-Numbered Exercises to accompany An Introduction to Population Genetics: Theory and Applications Rasmus Nielsen Montgomery Slatkin CHAPTER 1 1.2 The expected homozygosity, given allele
Solutions to Even-Numbered Exercises to accompany An Introduction to Population Genetics: Theory and Applications Rasmus Nielsen Montgomery Slatkin CHAPTER 1 1.2 The expected homozygosity, given allele
Q1) Explain how background selection and genetic hitchhiking could explain the positive correlation between genetic diversity and recombination rate.
 OEB 242 Exam Practice Problems Answer Key Q1) Explain how background selection and genetic hitchhiking could explain the positive correlation between genetic diversity and recombination rate. First, recall
OEB 242 Exam Practice Problems Answer Key Q1) Explain how background selection and genetic hitchhiking could explain the positive correlation between genetic diversity and recombination rate. First, recall
Effective population size and patterns of molecular evolution and variation
 FunDamental concepts in genetics Effective population size and patterns of molecular evolution and variation Brian Charlesworth Abstract The effective size of a population,, determines the rate of change
FunDamental concepts in genetics Effective population size and patterns of molecular evolution and variation Brian Charlesworth Abstract The effective size of a population,, determines the rate of change
Outline of lectures 3-6
 GENOME 453 J. Felsenstein Evolutionary Genetics Autumn, 013 Population genetics Outline of lectures 3-6 1. We ant to kno hat theory says about the reproduction of genotypes in a population. This results
GENOME 453 J. Felsenstein Evolutionary Genetics Autumn, 013 Population genetics Outline of lectures 3-6 1. We ant to kno hat theory says about the reproduction of genotypes in a population. This results
Population Genetics 7: Genetic Drift
 Population Genetics 7: Genetic Drift Sampling error Assume a fair coin with p = ½: If you sample many times the most likely single outcome = ½ heads. The overall most likely outcome ½ heads n P = 2 k (
Population Genetics 7: Genetic Drift Sampling error Assume a fair coin with p = ½: If you sample many times the most likely single outcome = ½ heads. The overall most likely outcome ½ heads n P = 2 k (
overproduction variation adaptation Natural Selection speciation adaptation Natural Selection speciation
 Evolution Evolution Chapters 22-25 Changes in populations, species, or groups of species. Variances of the frequency of heritable traits that appear from one generation to the next. 2 Areas of Evolutionary
Evolution Evolution Chapters 22-25 Changes in populations, species, or groups of species. Variances of the frequency of heritable traits that appear from one generation to the next. 2 Areas of Evolutionary
UNIT V. Chapter 11 Evolution of Populations. Pre-AP Biology
 UNIT V Chapter 11 Evolution of Populations UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 11: The Evolution of Populations I. Genetic Variation Within Populations (11.1) A. Genetic variation in a population increases the chance
UNIT V Chapter 11 Evolution of Populations UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 11: The Evolution of Populations I. Genetic Variation Within Populations (11.1) A. Genetic variation in a population increases the chance
Population Genetics I. Bio
 Population Genetics I. Bio5488-2018 Don Conrad dconrad@genetics.wustl.edu Why study population genetics? Functional Inference Demographic inference: History of mankind is written in our DNA. We can learn
Population Genetics I. Bio5488-2018 Don Conrad dconrad@genetics.wustl.edu Why study population genetics? Functional Inference Demographic inference: History of mankind is written in our DNA. We can learn
Chapter 16. Table of Contents. Section 1 Genetic Equilibrium. Section 2 Disruption of Genetic Equilibrium. Section 3 Formation of Species
 Population Genetics and Speciation Table of Contents Section 1 Genetic Equilibrium Section 2 Disruption of Genetic Equilibrium Section 3 Formation of Species Section 1 Genetic Equilibrium Objectives Identify
Population Genetics and Speciation Table of Contents Section 1 Genetic Equilibrium Section 2 Disruption of Genetic Equilibrium Section 3 Formation of Species Section 1 Genetic Equilibrium Objectives Identify
Selection Page 1 sur 11. Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology SELECTION
 Selection Page 1 sur 11 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology SELECTION * I- Introduction II- Modeling and selective values III- Basic model IV- Equation of the recurrence of allele
Selection Page 1 sur 11 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology SELECTION * I- Introduction II- Modeling and selective values III- Basic model IV- Equation of the recurrence of allele
REVIEW 6: EVOLUTION. 1. Define evolution: Was not the first to think of evolution, but he did figure out how it works (mostly).
 Name: REVIEW 6: EVOLUTION 1. Define evolution: 2. Modern Theory of Evolution: a. Charles Darwin: Was not the first to think of evolution, but he did figure out how it works (mostly). However, Darwin didn
Name: REVIEW 6: EVOLUTION 1. Define evolution: 2. Modern Theory of Evolution: a. Charles Darwin: Was not the first to think of evolution, but he did figure out how it works (mostly). However, Darwin didn
The Genetics of Natural Selection
 The Genetics of Natural Selection Introduction So far in this course, we ve focused on describing the pattern of variation within and among populations. We ve talked about inbreeding, which causes genotype
The Genetics of Natural Selection Introduction So far in this course, we ve focused on describing the pattern of variation within and among populations. We ve talked about inbreeding, which causes genotype
Enduring Understanding: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution Pearson Education, Inc.
 Enduring Understanding: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution. Objective: You will be able to identify the key concepts of evolution theory Do Now: Read the enduring understanding
Enduring Understanding: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution. Objective: You will be able to identify the key concepts of evolution theory Do Now: Read the enduring understanding
NEUTRAL EVOLUTION IN ONE- AND TWO-LOCUS SYSTEMS
 æ 2 NEUTRAL EVOLUTION IN ONE- AND TWO-LOCUS SYSTEMS 19 May 2014 Variations neither useful nor injurious would not be affected by natural selection, and would be left either a fluctuating element, as perhaps
æ 2 NEUTRAL EVOLUTION IN ONE- AND TWO-LOCUS SYSTEMS 19 May 2014 Variations neither useful nor injurious would not be affected by natural selection, and would be left either a fluctuating element, as perhaps
Major questions of evolutionary genetics. Experimental tools of evolutionary genetics. Theoretical population genetics.
 Evolutionary Genetics (for Encyclopedia of Biodiversity) Sergey Gavrilets Departments of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and Mathematics, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996-6 USA Evolutionary
Evolutionary Genetics (for Encyclopedia of Biodiversity) Sergey Gavrilets Departments of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and Mathematics, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996-6 USA Evolutionary
5/31/2012. Speciation and macroevolution - Chapter
 Speciation and macroevolution - Chapter Objectives: - Review meiosis -Species -Repro. Isolating mechanisms - Speciation -Is evolution always slow -Extinction How Are Populations, Genes, And Evolution Related?
Speciation and macroevolution - Chapter Objectives: - Review meiosis -Species -Repro. Isolating mechanisms - Speciation -Is evolution always slow -Extinction How Are Populations, Genes, And Evolution Related?
Population Genetics. with implications for Linkage Disequilibrium. Chiara Sabatti, Human Genetics 6357a Gonda
 1 Population Genetics with implications for Linkage Disequilibrium Chiara Sabatti, Human Genetics 6357a Gonda csabatti@mednet.ucla.edu 2 Hardy-Weinberg Hypotheses: infinite populations; no inbreeding;
1 Population Genetics with implications for Linkage Disequilibrium Chiara Sabatti, Human Genetics 6357a Gonda csabatti@mednet.ucla.edu 2 Hardy-Weinberg Hypotheses: infinite populations; no inbreeding;
Inbreeding depression due to stabilizing selection on a quantitative character. Emmanuelle Porcher & Russell Lande
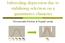 Inbreeding depression due to stabilizing selection on a quantitative character Emmanuelle Porcher & Russell Lande Inbreeding depression Reduction in fitness of inbred vs. outbred individuals Outcrossed
Inbreeding depression due to stabilizing selection on a quantitative character Emmanuelle Porcher & Russell Lande Inbreeding depression Reduction in fitness of inbred vs. outbred individuals Outcrossed
Appendix A Evolutionary and Genetics Principles
 Appendix A Evolutionary and Genetics Principles A.1 Genetics As a start, we need to distinguish between learning, which we take to mean behavioral adaptation by an individual, and evolution, which refers
Appendix A Evolutionary and Genetics Principles A.1 Genetics As a start, we need to distinguish between learning, which we take to mean behavioral adaptation by an individual, and evolution, which refers
Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution
 Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution Kimura Nature (968) 7:64-66 King and Jukes Science (969) 64:788-798 (Non-Darwinian Evolution) Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution Describes the source of variation
Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution Kimura Nature (968) 7:64-66 King and Jukes Science (969) 64:788-798 (Non-Darwinian Evolution) Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution Describes the source of variation
Evolution of Populations
 Evolution of Populations Gene Pools 1. All of the genes in a population - Contains 2 or more alleles (forms of a gene) for each trait 2. Relative frequencies - # of times an allele occurs in a gene pool
Evolution of Populations Gene Pools 1. All of the genes in a population - Contains 2 or more alleles (forms of a gene) for each trait 2. Relative frequencies - # of times an allele occurs in a gene pool
Biological Change Over Time. Lecture 12: Evolution. Microevolution. Microevolutionary Processes. Genotypes, Phenotypes and Environmental Effects
 Lecture 12: Evolution Biological Change Over Time Key terms: Reading: Ch16: Microevolution Ch17:Speciation Ch18:Macroevolution Microevolution Changes with in species Well defined mechanism Easily observed
Lecture 12: Evolution Biological Change Over Time Key terms: Reading: Ch16: Microevolution Ch17:Speciation Ch18:Macroevolution Microevolution Changes with in species Well defined mechanism Easily observed
List the five conditions that can disturb genetic equilibrium in a population.(10)
 List the five conditions that can disturb genetic equilibrium in a population.(10) The five conditions are non-random mating, small population size, immigration or emigration, mutations, and natural selection.
List the five conditions that can disturb genetic equilibrium in a population.(10) The five conditions are non-random mating, small population size, immigration or emigration, mutations, and natural selection.
NOTES CH 17 Evolution of. Populations
 NOTES CH 17 Evolution of Vocabulary Fitness Genetic Drift Punctuated Equilibrium Gene flow Adaptive radiation Divergent evolution Convergent evolution Gradualism Populations 17.1 Genes & Variation Darwin
NOTES CH 17 Evolution of Vocabulary Fitness Genetic Drift Punctuated Equilibrium Gene flow Adaptive radiation Divergent evolution Convergent evolution Gradualism Populations 17.1 Genes & Variation Darwin
Evolutionary Genetics Midterm 2008
 Student # Signature The Rules: (1) Before you start, make sure you ve got all six pages of the exam, and write your name legibly on each page. P1: /10 P2: /10 P3: /12 P4: /18 P5: /23 P6: /12 TOT: /85 (2)
Student # Signature The Rules: (1) Before you start, make sure you ve got all six pages of the exam, and write your name legibly on each page. P1: /10 P2: /10 P3: /12 P4: /18 P5: /23 P6: /12 TOT: /85 (2)
Week 7.2 Ch 4 Microevolutionary Proceses
 Week 7.2 Ch 4 Microevolutionary Proceses 1 Mendelian Traits vs Polygenic Traits Mendelian -discrete -single gene determines effect -rarely influenced by environment Polygenic: -continuous -multiple genes
Week 7.2 Ch 4 Microevolutionary Proceses 1 Mendelian Traits vs Polygenic Traits Mendelian -discrete -single gene determines effect -rarely influenced by environment Polygenic: -continuous -multiple genes
Mechanisms of Evolution Microevolution. Key Concepts. Population Genetics
 Mechanisms of Evolution Microevolution Population Genetics Key Concepts 23.1: Population genetics provides a foundation for studying evolution 23.2: Mutation and sexual recombination produce the variation
Mechanisms of Evolution Microevolution Population Genetics Key Concepts 23.1: Population genetics provides a foundation for studying evolution 23.2: Mutation and sexual recombination produce the variation
Natural Selection results in increase in one (or more) genotypes relative to other genotypes.
 Natural Selection results in increase in one (or more) genotypes relative to other genotypes. Fitness - The fitness of a genotype is the average per capita lifetime contribution of individuals of that
Natural Selection results in increase in one (or more) genotypes relative to other genotypes. Fitness - The fitness of a genotype is the average per capita lifetime contribution of individuals of that
Tutorial on Theoretical Population Genetics
 Tutorial on Theoretical Population Genetics Joe Felsenstein Department of Genome Sciences and Department of Biology University of Washington, Seattle Tutorial on Theoretical Population Genetics p.1/40
Tutorial on Theoretical Population Genetics Joe Felsenstein Department of Genome Sciences and Department of Biology University of Washington, Seattle Tutorial on Theoretical Population Genetics p.1/40
Lecture 2: Introduction to Quantitative Genetics
 Lecture 2: Introduction to Quantitative Genetics Bruce Walsh lecture notes Introduction to Quantitative Genetics SISG, Seattle 16 18 July 2018 1 Basic model of Quantitative Genetics Phenotypic value --
Lecture 2: Introduction to Quantitative Genetics Bruce Walsh lecture notes Introduction to Quantitative Genetics SISG, Seattle 16 18 July 2018 1 Basic model of Quantitative Genetics Phenotypic value --
Lecture 2. Basic Population and Quantitative Genetics
 Lecture Basic Population and Quantitative Genetics Bruce Walsh. Aug 003. Nordic Summer Course Allele and Genotype Frequencies The frequency p i for allele A i is just the frequency of A i A i homozygotes
Lecture Basic Population and Quantitative Genetics Bruce Walsh. Aug 003. Nordic Summer Course Allele and Genotype Frequencies The frequency p i for allele A i is just the frequency of A i A i homozygotes
Concepts of Evolution
 Concepts of Evolution Isn t Evolution Just A Theory? How does the scientific meaning of a term like theory differ from the way it is used in everyday life? Can the facts of science change over time? If
Concepts of Evolution Isn t Evolution Just A Theory? How does the scientific meaning of a term like theory differ from the way it is used in everyday life? Can the facts of science change over time? If
Lecture 1 Introduction to Quantitative Genetics
 Lecture Introduction to Quantitative Genetics Population Genetics Foundation Quantitative Genetics Quantitative Traits Continuous variation Varies by amount rather than kind Height, weight, IQ, etc What
Lecture Introduction to Quantitative Genetics Population Genetics Foundation Quantitative Genetics Quantitative Traits Continuous variation Varies by amount rather than kind Height, weight, IQ, etc What
Processes of Evolution
 Processes of Evolution Microevolution Processes of Microevolution How Species Arise Macroevolution Microevolution Population: localized group of individuals belonging to the same species with the potential
Processes of Evolution Microevolution Processes of Microevolution How Species Arise Macroevolution Microevolution Population: localized group of individuals belonging to the same species with the potential
It all depends on barriers that prevent members of two species from producing viable, fertile hybrids.
 Name: Date: Theory of Evolution Evolution: Change in a over a period of time Explains the great of organisms Major points of Origin of Species Descent with Modification o All organisms are related through
Name: Date: Theory of Evolution Evolution: Change in a over a period of time Explains the great of organisms Major points of Origin of Species Descent with Modification o All organisms are related through
Introduction to Natural Selection. Ryan Hernandez Tim O Connor
 Introduction to Natural Selection Ryan Hernandez Tim O Connor 1 Goals Learn about the population genetics of natural selection How to write a simple simulation with natural selection 2 Basic Biology genome
Introduction to Natural Selection Ryan Hernandez Tim O Connor 1 Goals Learn about the population genetics of natural selection How to write a simple simulation with natural selection 2 Basic Biology genome
Genetical theory of natural selection
 Reminders Genetical theory of natural selection Chapter 12 Natural selection evolution Natural selection evolution by natural selection Natural selection can have no effect unless phenotypes differ in
Reminders Genetical theory of natural selection Chapter 12 Natural selection evolution Natural selection evolution by natural selection Natural selection can have no effect unless phenotypes differ in
Darwinian Selection. Chapter 7 Selection I 12/5/14. v evolution vs. natural selection? v evolution. v natural selection
 Chapter 7 Selection I Selection in Haploids Selection in Diploids Mutation-Selection Balance Darwinian Selection v evolution vs. natural selection? v evolution ² descent with modification ² change in allele
Chapter 7 Selection I Selection in Haploids Selection in Diploids Mutation-Selection Balance Darwinian Selection v evolution vs. natural selection? v evolution ² descent with modification ² change in allele
Lecture 19. Long Term Selection: Topics Selection limits. Avoidance of inbreeding New Mutations
 Lecture 19 Long Term Selection: Topics Selection limits Avoidance of inbreeding New Mutations 1 Roberson (1960) Limits of Selection For a single gene selective advantage s, the chance of fixation is a
Lecture 19 Long Term Selection: Topics Selection limits Avoidance of inbreeding New Mutations 1 Roberson (1960) Limits of Selection For a single gene selective advantage s, the chance of fixation is a
Observation: we continue to observe large amounts of genetic variation in natural populations
 MUTATION AND GENETIC VARIATION Observation: we continue to observe large amounts of genetic variation in natural populations Problem: How does this variation arise and how is it maintained. Here, we look
MUTATION AND GENETIC VARIATION Observation: we continue to observe large amounts of genetic variation in natural populations Problem: How does this variation arise and how is it maintained. Here, we look
Microevolution. Chapter 17
 Microevolution Chapter 17 Selective Breeding & Evolution Evolution is genetic change in a line of descent through successive generations Selective breeding practices yield evidence that heritable changes
Microevolution Chapter 17 Selective Breeding & Evolution Evolution is genetic change in a line of descent through successive generations Selective breeding practices yield evidence that heritable changes
A. Correct! Genetically a female is XX, and has 22 pairs of autosomes.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 08: Meiosis and Genetic Variability Question No. 1 of 10 1. A human female has pairs of autosomes and her sex chromosomes are. Question #01 (A) 22, XX. (B) 23, X. (C) 23, XX.
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 08: Meiosis and Genetic Variability Question No. 1 of 10 1. A human female has pairs of autosomes and her sex chromosomes are. Question #01 (A) 22, XX. (B) 23, X. (C) 23, XX.
Natural Selection. DNA encodes information that interacts with the environment to influence phenotype
 Natural Selection DN encodes information that interacts with the environment to influence phenotype mong The Traits That Can Be Influenced By Genetically Determined Responses to the Environment re: 1.
Natural Selection DN encodes information that interacts with the environment to influence phenotype mong The Traits That Can Be Influenced By Genetically Determined Responses to the Environment re: 1.
Population Genetics: a tutorial
 : a tutorial Institute for Science and Technology Austria ThRaSh 2014 provides the basic mathematical foundation of evolutionary theory allows a better understanding of experiments allows the development
: a tutorial Institute for Science and Technology Austria ThRaSh 2014 provides the basic mathematical foundation of evolutionary theory allows a better understanding of experiments allows the development
Evolution AP Biology
 Darwin s Theory of Evolution How do biologists use evolutionary theory to develop better flu vaccines? Theory: Evolutionary Theory: Why do we need to understand the Theory of Evolution? Charles Darwin:
Darwin s Theory of Evolution How do biologists use evolutionary theory to develop better flu vaccines? Theory: Evolutionary Theory: Why do we need to understand the Theory of Evolution? Charles Darwin:
A consideration of the chi-square test of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in a non-multinomial situation
 Ann. Hum. Genet., Lond. (1975), 39, 141 Printed in Great Britain 141 A consideration of the chi-square test of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in a non-multinomial situation BY CHARLES F. SING AND EDWARD D.
Ann. Hum. Genet., Lond. (1975), 39, 141 Printed in Great Britain 141 A consideration of the chi-square test of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in a non-multinomial situation BY CHARLES F. SING AND EDWARD D.
F SR = (H R H S)/H R. Frequency of A Frequency of a Population Population
 Hierarchical structure, F-statistics, Wahlund effect, Inbreeding, Inbreeding coefficient Genetic difference: the difference of allele frequencies among the subpopulations Hierarchical population structure
Hierarchical structure, F-statistics, Wahlund effect, Inbreeding, Inbreeding coefficient Genetic difference: the difference of allele frequencies among the subpopulations Hierarchical population structure
Theory of Natural Selection
 5 The Theory of Natural Selection T his chapter introduces formal population genetic models. We first establish what the variables are that the models are concerned with, and the general structure of population
5 The Theory of Natural Selection T his chapter introduces formal population genetic models. We first establish what the variables are that the models are concerned with, and the general structure of population
Processes of Evolution
 15 Processes of Evolution Chapter 15 Processes of Evolution Key Concepts 15.1 Evolution Is Both Factual and the Basis of Broader Theory 15.2 Mutation, Selection, Gene Flow, Genetic Drift, and Nonrandom
15 Processes of Evolution Chapter 15 Processes of Evolution Key Concepts 15.1 Evolution Is Both Factual and the Basis of Broader Theory 15.2 Mutation, Selection, Gene Flow, Genetic Drift, and Nonrandom
Long-Term Response and Selection limits
 Long-Term Response and Selection limits Bruce Walsh lecture notes Uppsala EQG 2012 course version 5 Feb 2012 Detailed reading: online chapters 23, 24 Idealized Long-term Response in a Large Population
Long-Term Response and Selection limits Bruce Walsh lecture notes Uppsala EQG 2012 course version 5 Feb 2012 Detailed reading: online chapters 23, 24 Idealized Long-term Response in a Large Population
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Concepts of Evolution. Isn t Evolution Just A Theory? Evolution
 Slide 1 Concepts of Evolution Slide 2 Isn t Evolution Just A Theory? How does the scientific meaning of a term like theory differ from the way it is used in everyday life? Can the facts of science change
Slide 1 Concepts of Evolution Slide 2 Isn t Evolution Just A Theory? How does the scientific meaning of a term like theory differ from the way it is used in everyday life? Can the facts of science change
Q Expected Coverage Achievement Merit Excellence. Punnett square completed with correct gametes and F2.
 NCEA Level 2 Biology (91157) 2018 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2018 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of genetic variation and change (91157) Evidence Q Expected Coverage Achievement Merit Excellence
NCEA Level 2 Biology (91157) 2018 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2018 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of genetic variation and change (91157) Evidence Q Expected Coverage Achievement Merit Excellence
STABILIZING SELECTION ON HUMAN BIRTH WEIGHT
 STABILIZING SELECTION ON HUMAN BIRTH WEIGHT See Box 8.2 Mapping the Fitness Landscape in Z&E FROM: Cavalli-Sforza & Bodmer 1971 STABILIZING SELECTION ON THE GALL FLY, Eurosta solidaginis GALL DIAMETER
STABILIZING SELECTION ON HUMAN BIRTH WEIGHT See Box 8.2 Mapping the Fitness Landscape in Z&E FROM: Cavalli-Sforza & Bodmer 1971 STABILIZING SELECTION ON THE GALL FLY, Eurosta solidaginis GALL DIAMETER
Gene Flow, Genetic Drift Natural Selection
 Gene Flow, Genetic Drift Natural Selection Lecture 9 Spring 2013 Genetic drift Examples of genetic drift in nature? Bottleneck effect: an analogy ~ genetic drift > founder effect Ex. s Bottleneck effects
Gene Flow, Genetic Drift Natural Selection Lecture 9 Spring 2013 Genetic drift Examples of genetic drift in nature? Bottleneck effect: an analogy ~ genetic drift > founder effect Ex. s Bottleneck effects
Reproduction and Evolution Practice Exam
 Reproduction and Evolution Practice Exam Topics: Genetic concepts from the lecture notes including; o Mitosis and Meiosis, Homologous Chromosomes, Haploid vs Diploid cells Reproductive Strategies Heaviest
Reproduction and Evolution Practice Exam Topics: Genetic concepts from the lecture notes including; o Mitosis and Meiosis, Homologous Chromosomes, Haploid vs Diploid cells Reproductive Strategies Heaviest
STAT 536: Migration. Karin S. Dorman. October 3, Department of Statistics Iowa State University
 STAT 536: Migration Karin S. Dorman Department of Statistics Iowa State University October 3, 2006 Migration Introduction Migration is the movement of individuals between populations. Until now we have
STAT 536: Migration Karin S. Dorman Department of Statistics Iowa State University October 3, 2006 Migration Introduction Migration is the movement of individuals between populations. Until now we have
How robust are the predictions of the W-F Model?
 How robust are the predictions of the W-F Model? As simplistic as the Wright-Fisher model may be, it accurately describes the behavior of many other models incorporating additional complexity. Many population
How robust are the predictions of the W-F Model? As simplistic as the Wright-Fisher model may be, it accurately describes the behavior of many other models incorporating additional complexity. Many population
Notes on Population Genetics
 Notes on Population Genetics Graham Coop 1 1 Department of Evolution and Ecology & Center for Population Biology, University of California, Davis. To whom correspondence should be addressed: gmcoop@ucdavis.edu
Notes on Population Genetics Graham Coop 1 1 Department of Evolution and Ecology & Center for Population Biology, University of California, Davis. To whom correspondence should be addressed: gmcoop@ucdavis.edu
Gene Pool Recombination in Genetic Algorithms
 Gene Pool Recombination in Genetic Algorithms Heinz Mühlenbein GMD 53754 St. Augustin Germany muehlenbein@gmd.de Hans-Michael Voigt T.U. Berlin 13355 Berlin Germany voigt@fb10.tu-berlin.de Abstract: A
Gene Pool Recombination in Genetic Algorithms Heinz Mühlenbein GMD 53754 St. Augustin Germany muehlenbein@gmd.de Hans-Michael Voigt T.U. Berlin 13355 Berlin Germany voigt@fb10.tu-berlin.de Abstract: A
Lecture 13: Population Structure. October 8, 2012
 Lecture 13: Population Structure October 8, 2012 Last Time Effective population size calculations Historical importance of drift: shifting balance or noise? Population structure Today Course feedback The
Lecture 13: Population Structure October 8, 2012 Last Time Effective population size calculations Historical importance of drift: shifting balance or noise? Population structure Today Course feedback The
Monitoring Endangered Species Populations: Gene Dispersal Can Have Pronounced Effects on the Relationship between Census Size and Genetic Diversity
 American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2013, 4, 1932-1937 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2013.410238 Published Online October 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajps) Monitoring Endangered Species Populations:
American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2013, 4, 1932-1937 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2013.410238 Published Online October 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajps) Monitoring Endangered Species Populations:
CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS. Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection
 CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection 1. Genetic variation occurs within and between populations 2. Mutation and sexual recombination
CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection 1. Genetic variation occurs within and between populations 2. Mutation and sexual recombination
The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species Chapter 24 Both in space and time, we seem to be brought somewhere near to that great fact the mystery of mysteries-the first appearance of beings on Earth. Darwin from his diary
The Origin of Species Chapter 24 Both in space and time, we seem to be brought somewhere near to that great fact the mystery of mysteries-the first appearance of beings on Earth. Darwin from his diary
1 In evolutionary terms, the more closely related two different orgamisms are, the
 volution Review 1 In evolutionary terms, the more closely related two different orgamisms are, the more similar their habitats are. less similar their N sequences are. less likely they are to be related
volution Review 1 In evolutionary terms, the more closely related two different orgamisms are, the more similar their habitats are. less similar their N sequences are. less likely they are to be related
Evolutionary Forces. What changes populations (Ch. 17)
 Evolutionary Forces What changes populations (Ch. 17) Forces of evolutionary change Natural selection traits that improve survival or reproduction accumulate in the population ADAPTIVE change Genetic drift
Evolutionary Forces What changes populations (Ch. 17) Forces of evolutionary change Natural selection traits that improve survival or reproduction accumulate in the population ADAPTIVE change Genetic drift
Biology 110 Survey of Biology. Quizzam
 1. Mendel conducted his most memorable experiments on A) peas. B) roses. C) guinea pigs. D) fruit flies. E) clones. 2. Varieties of plants in which self-fertilization produces offspring that are identical
1. Mendel conducted his most memorable experiments on A) peas. B) roses. C) guinea pigs. D) fruit flies. E) clones. 2. Varieties of plants in which self-fertilization produces offspring that are identical
