SECTION - A. A current impulse, 5δ(t), is forced through a capacitor C. The voltage, Vc(t), across the capacitor is given by. 5 t C.
|
|
|
- Maximillian Harvey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SETION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..5) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is correct. Indicate the correct answer by darkening the appropriate bubble against the question number on the left hand side of the Objective esponse Sheet (OS). You may use the answer book provided for any rough work, if needed.. A current impulse, 5δ(t), is forced through a capacitor. The voltage, Vc(t), across the capacitor is given by 5t. 5u(t) - (c) 5 t (d) 5u ( t ) Fourier Series for the waveform, f(t) shown in Fig.. is f(t) sin (π t ) 9 sin (3π t ) 5 sin (5π t ) K π 8 sin (π t ) cos (3π t ) sin (5π t ) K 9 5 π (c) 8 cos (π t ) cos (3π t ) cos (5π t ) K 9 5 π (d) 8 cos (π t ) sin (3π t ) sin (5π t ) K 9 5 π The graph of an electrical network has N nodes and B branches. The number of links, L, with respect to the choice of a tree, is given by B N B N (c) N B (d) N B - Two in-phase, 5 Hz sinusoidal waveform of unit amplitude are fed into channel and channel respectively of an oscilloscope. Assuming that the voltage scale, time scale and other settings are exactly the same for both the channels, what would be observed if the oscilloscope is operated in X-Y mode? A circle of unit radius An ellipse (c) A parabola (d) A straight line inclined at 45 with respect to the x-axis
2 .5 r Given a vector field F, the divergence theorem states that r r r r r ur r ur F.dS =.FdV F.dS = FdV (c) s v s v r r F ds = s.6 r ur.fdv (d) v r r F ds = s r ur.fdv v If a 4V, 5 Hz, star connected, 3 phase squirrel cage induction motor is operated from a 4 V, 75 Hz supply, the torque that the motor can now provide while drawing rated current from the supply? reduces increases (c) remains the same.7 A dc series motor fed from rated supply voltage is overloaded and its magnetic circuit is saturated. The torque-speed characteristic of this motor will be approximately represented by which curve of Fig..7? Speed (d) increase or reduces depending upon the rotor resistance A urve A B urve B D (c) urve (d) urve D.8 Torque A kva, 3V/V, single phase, 5 Hz transformer having negligible winding resistance and leakage inductance is operating under saturation, while 5 V, 5 Hz sinusoidal supply is connected to the high voltage winding. A resistive load is connected to the low voltage winding which draws rated current. Which one of the following quantities will not be sinusoidal? Voltage induced across the low voltage winding ore flux (c) Load current (d) urrent drawn from the source.9 A 4V/V/V, 5 Hz three winding transformer is connected as shown in Fig..9. The reading of the voltmeter, V, will be V 4 V (c) 6 V (d) 8 V 4V 5 Hz ~ V 4::
3 . The frequency of the clock signal applied to the rising edge triggered D flip-flop shown in Fig.. is khz. The frequency of the signal available at Q is Q D FF khz.5 khz LK (c) khz Q (d) 5 khz. The forward resistance of the diode shown in Fig.. is 5Ω and the remaining parameters are same as those of an ideal diode. The dc component of the source current is ~ Vmsin(ωt) 45Ω ω=34 rad/s. Vm 5π Vm Vm (c) 5π π (d) Vm 5π The cut-in voltage of both Zener diode Dz and diode D shown in Fig.. is.7 V, while break down voltage of Dz is 3.3 V and reverse breakdown voltage of D is 5 V. the other parameters can be assumed to be the same as those of an ideal diode. The values of the peak output voltage (V) are kω DZ sin(ωt) ~ ω=34 rad/s I VO D 3.3 V in the positive half cycle and.4 V in the negative half cycle 4 V in the positive half cycle and 5 V in the negative half cycle (c) 3.3 V in both positive and negative half cycles (d) 4 V in both positive and negative half cycles.3 The line-to-line input voltage to the 3 phase, 5 Hz, ac circuit shown in Fig..3 is V rms. Assuming that the phase sequence is YB, the wattmeters would read. W W = 886 W and W = 886 W 5 6 Ω W = 5 W and W = 5 W (c) W = W and W = W (d) W = 5 W and W = 75 W 5 6 Ω Y B W 5 6 Ω
4 .4 The logic circuit used to generate the active low chip select (S) by an 885 microprocessor to address a peripheral is shown in Fig..4. The peripheral will respond to addresses in the range. E-EFFF A5 E-FFFE A4 (c) -FFFF (d) -FFF.5.6 A3 S A onsider a long, two-wire line composed of solid round conductors. The radius of both conductors is.5 cm and the distance between their centers is m. If this distance is doubled, then the inductance per unit length doubles halves (c) increases but does not double (d) decreases but does not halve onsider a power system with three identical generators. The transmission losses are negligible. One generator (G) has a speed governor which maintains its speed constant at the rated value, while the other generators (G and G3) have governors with a droop of 5%. If the load of the system is increased, then in steady state. generation of G and G3 is increased equally while generation of G is unchanged. generation of G alone is increased while generation of G and G3 is unchanged. (c) generation of G, G and G3 is increased equally. (d) generation of G, G and G3 is increased in the ratio.5:.5:.5..7 A long wire composed of a smooth round conductor runs above and parallel to the ground (assumed to be a large conducting plane). A high voltage exists between the conductor and the ground. The maximum electric stress occurs at the upper surface of the conductor the lower surface of the conductor (c) the ground surface (d) midway between the conductor and ground.8 onsider the problem of relay co-ordination for the distance relays and on adjacent lines of a transmission system (Fig..8). The Zone and Zone settings for both the relays are indicated on the diagram. Which of the following indicates the correct time setting for the Zone of relays and. TZ =.6s, TZ =.3s Zone () TZ =.3s, TZ =.6s (c) TZ =.3s, TZ =.3s (d) TZ =.s, TZ =.3s Zone () Zone () Zone ()
5 .9. Let s(t) be the step response of a linear system with zero initial conditions; then the response of this system to an input u(t) is t s ( t τ ) u (τ ) dτ t s ( t τ ) u (τ ) dτ dτ t (c) t d s ( t τ ) u (τ ) dτ t (d) s (t τ ) u (τ ) dτ.. Let Y(s) be the Laplace transformation of the function y(t), then the final value of the function is lim Y ( s ) s lim Y ( s ) (c) lim sy ( s ).. The determinant of the matrix 3 (d) lim sy ( s ) s s s is: (c) (d) 3.. The state transition matrix for the system X& = AX with initial state X() is ( si A) e At X ( ) (c) Laplace inverse of [ ( si A ) ] (d) Laplace inverse of [ ( si A ) X()].3. A six pulse thyristor rectifier bridge is connected to a balanced 5 Hz three phase ac source. Assuming that the dc output current of the rectifier is constant, the lowest frequency harmonic component in the ac source line current is Hz 5 Hz (c) 5 Hz (d) 3 Hz.4. What is the rms value of the voltage waveform shown in Fig..4? V θ π -V π/3 π V π V π/3 4π/3 5π/3 (c) V π (d) V
6 .5 A step down chopper is operated in the continuous conduction mode in steady state with a constant duty ratio D. If V is the magnitude of the dc output voltage V and if Vs is the magnitude of the dc input voltage, the ratio is given by Vs D - D (c) D (d) D D. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..5) of TWO marks each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is correct. Indicate the correct answer by darkening the appropriate bubble against the question number on the left hand side of the Objective esponse Sheet (OS). You may use the answer book provided for any rough work, if needed.. A two port network, shown in Fig.. is described by the following equations I = YE Y E I = YE Y E I I Ω E Ω E Ω The admittance parameters Y, Y, Y for the network shown are.5 mho, mho, mho and mho respectively mho, mho, mho and mho respectively (c).5 mho,.5 mho,.5 mho and mho respectively (d) mho, mho, mho and mho respectively In the circuit shown in Fig.., what value of will cause a unity power factor at the ac source? 68. µf 65 µf (c).68 µf 3V 5Hz ~ ZL=3 4 (d) 6.8 µf.3. A first order, low pass filter is given with = 5 Ω and = 5 µf. What is the frequency at which the gain of the voltage transfer function of the filter is.5? 4.9 khz.49 khz (c).46 khz (d) 4.6 khz
7 .4. A series -L- circuit has = 5Ω, L = µh and = µf. the lower half power frequency of the circuit is 3.55 khz (d).9 khz 4.77 Nm (c).45 Nm (d).5 Nm The rotor of a three phase, 5 kw, 4V, 5 Hz, slip ring induction motor is wound for 6 poles while its stator is wound for 4 poles. The approximate average no load steady state speed when this motor is connected to 4V, 5 Hz supply is 5 rpm.7. (c) 5.9 khz A V, rpm, A, separately excited dc motor has an armature resistance of Ω. ated dc voltage is applied to both the armature and field winding of the motor. If the armature drawn 5A from the source, the torque developed by the motor is 4.3 Nm khz 5 rpm (c) rpm (d) rpm The flux per pole in a synchronous motor with the field circuit ON and the stator disconnected from the supply is found to be 5 mwb. When the stator is connected to the rated supply with the field excitation unchanged, the flux per pole in the machine is found to be mwb while the motor is running on no load. Assuming no load losses to be zero, the no load current down by the motor from the supply lags the supply voltage leads the supply voltage (c) is in phase with the supply voltage (d) is zero An V pulse of µs duration is applied to the circuit shown in Fig..8. Assuming that the capacitor is completely discharged prior to applying the pulse, the peak value of the capacitor voltage is kω V 5.5 V (c) 6.3 V (d).96 V V kω.9. The output voltage (Vo) of the Schmitt trigger shown in Fig..9 swings between 5V and 5V. Assume that the operational amplifier is ideal. The output will change from 5V to 5V when the instantaneous value of the input sine wave is nf µs kω sin(ωt) - VO kω 5 V in the positive slope only 5 V in the negative slope only 3kΩ (c) 5 V in the positive and negative slopes (d) 3 V in the positive and negative slopes V
8 .. For the circuit shown in Fig.., the Boolean expression for the output Y in terms of inputs P, Q, and S is P Q Y S P Q S P Q S (c) ( P Q)( S ) (d) (P Q) ( S).. In the circuit shown in Fig.., it is found that the input ac voltage (v) and M current i are in phase. The coupling coefficient is K =, where M is the LL mutual inductance between the two coils. The value of K and the dot polarity of K the coil P-Q are K =.5 and dot at P P K =.5 and dot at P -jω (c) K =.5 and dot at Q Ω vi (d) K =.5 and dot at Q j8ω L - Q j8ω L.. onsider the circuit shown in Fig... If the frequency of the source is 5 Hz, then a value of t which results in a transient free response is ms 5Ω.78 ms (c).7 ms (d).9 ms.h t=t ~ sin(ωt).3. A three phase thyristor bridge rectifier is used in a HVD link. The firing angle α (as measured from the point of natural commutation) is constrained to lie between 5 and 3. If the dc side current and ac side voltage magnitudes are constant, which of the following statements is true (neglect harmonics in the ac side currents and commutation overlap in your analysis) eactive power absorbed by the rectifier is maximum when α = 5 eactive power absorbed by the rectifier is maximum when α = 3 (c) eactive power absorbed by the rectifier is maximum when α = 5 (d) eactive power absorbed by the rectifier is maximum when α =
9 .4. A power system consists of areas (Area and Area ) connected by a single tie line (Fig..4). It is required to carry out a load flow study on this system. While entering the network data, the tie-line data (connectivity and parameters) is inadvertently left out. If the load flow program is run with this incomplete data The load-flow will converge only if the slack bus is specified in Area The load-flow will converge only if the slack bus is specified in Area (c) The load-flow will converge if the slack bus is specified in either Area or Area (d) The load-flow will not converge if only one slack bus is specified..5. A transmission line has a total series reactance of. pu. eactive power compensation is applied at the midpoint of the line and it is controlled such that the midpoint voltage of the transmission line is always maintained at.98 pu. If voltage at both ends of the line are maintained at. pu, then the steady state power transfer limit of the transmission line is 9.8 pu 4.9 pu (c) 9.6 pu (d) 5 pu.6. A generator is connected to a transformer which feeds another transformer through a short feeder (see Fig..6). The zero sequence impedance values are expressed in pu on a common base and are indicated in Fig..6. the Thevenin equivalent zero sequence impedance at point B is X=.3 X=. X=.5 X=.7 ~ j.6.75 j. (c).75 j.5 (d).5 j For the system X& = X u, which of the following statements is true? 5 The system is controllable but unstable The system is uncontrollable but unstable (c) The system is controllable but stable (d) The system is uncontrollable but stable
10 .8. A unity feedback system has an open loop transfer function, G ( s ) = K s. The root locus plot is jω jω σ σ jω jω (c) (d) σ σ.9. The transfer function of the system described by d y dy du = u with u as input and y as output is ( s ) (s s ) ( s ) (s s ) (c) (s s (d) ) s (s s ).. For the system X& = X u; y = 4 X, with u as unit impulse and with 4 zero initial state, the output, y, becomes et 4 et (c) e4t.. The eigen values of the system represented by X& =,,,,,, (d) 4 e4t X are (c),,, - (d),,, L.. In the chopper circuit shown S in Fig.. the input dc il voltage has a constant value Vs. the output voltage Vo is V assumed ripple-free. The switch S is operated with a switching time period T and a duty ratio D. what is the value of D at the boundary of continuous discontinuous conduction of the inductor current il? V - and
11 D = Vs Vo D = L T (c) D = L T (d) D = T L.3. Fig..3 shows an inverter circuit with a dc source voltage Vs. The semiconductor switches of the inverter are operated in such a manner that the pole voltages v and v are as shown in Fig..3. What is the rms value of the pole-to-pole voltage v? Vsϕ π ϕ π Vs (c) Vs (d) Vs v Vs V θ π V - ϕ Vs π v θ Tφ Vs π π.4. In the circuit shown in Fig..4, the switch is closed at time t =. The steady state value of the voltage vc is t= mh Ω V V V - 5µF mh (c) 5 V (d).5 V Ω 5µF Vc -.5. In the single phase diode bridge rectifier shown in figure.5, the load resistor is = 5Ω. The source voltage is ν= sin(ωt), where ω=π 5 radians per second. The power dissipated in the load resistor is 3 π 4 π W W (c) 4 W (d) 8 W v ~
12 SETION B This section consists of TWENTY questions of FIVE marks each. ANY FIFTEEN out of them have to be answered. If more than fifteen questions are attempted, score off answers that are not to be evaluated. Otherwise only the first fifteen unscored answers will be considered. ur ˆz. An 3. The magnetic vector potential in a region is defined by A = e y sin ( x ).a infinitely long conductor, having ac ross section area, a = 5mm and carrying a dc current, I = 5A in they y direction, passes through this region as shown in Fig.P3. I y onductor x B I r r Determine the expression for B and force density f exerted on the conductor A constant current source is supplying A to a circuit shown in Fig.P4. the switch S, which is initially closed for a sufficiently long time, is suddenly opened. Obtain the differential equation governing the behaviour of the inductor current and hence obtain the complete time response of the inductor current. What is the energy stored in L, a long time after the switch is opened? i I A Ω il L S 5H An electrical network is fed by two ac sources, as shown Fig.P5. Given that Z = ( j)ω Z = ( j) Ω x and ZL = ( j)ω. Z Z Obtain the Thevenin equivalent circuit Z I V=3-45 ~ L L V=3 45 ~ (Thevenin voltage and impedance) across terminals x and y, and y determine the current IL through the load ZL
13 6. In the resistor network shown in Fig.P6, all resistor values are Ω. A current of A passes from terminal a to terminal b, as shown in the figure. alculate the voltage between terminals a and b. [Hint: You may exploit the symmetry of the circuit]. A b =Ω A 7. A 3V, 5 rpm. A separately excited dc motor has an armature resistance of.5ω. the motor is connected to 3V dc supply and rated dc voltage is applied to the field winding. It is driving a load whose torque speed characteristic is given by TL = 5 - ω, where ω is the rotational speed expressed in rad/sec and TL is the load torque in Nm. Find the steady state speed at which the motor will drive the load and the armature current drawn by it from the source. Neglect the rotational losses of the machine. 8. A single phase 63 kva, 5 Hz, 33V/4V distribution transformer is connected between two 5 Hz supply systems, A and B as shown in Fig.P8. the transformer has and 99 turns in the low and high voltage windings respectively. The magnetizing reactance of the transformer referred to the high voltage side is 5 Ω. The leakage reactance of the high and low voltage windings are.ω and.ω respectively. Neglect the winding resistance and core losses of the transformer. The Thevenin voltage of system A is 33V while that of system B is 4V. the short circuit reactance of systems A and B are.5ω and. Ω respectively. If no power is transferred between A and B, so that the two system voltages are in phase, find the magnetizing ampere turns of the transformer. A.5Ω 33V.Ω ~ 5Hz 9. B ~ 4V 5Hz A 44 V, 5 Hz, 6 pole and 96 rpm star connected induction machine has the following per phase parameters referred to the stator: s =.6Ω r =.3Ω Xs = Ω The magnetizing reactance is very high and is neglected. The machine is connected to the 44V, 5 Hz supply and a certain mechanical load is coupled to it. It is found that the magnitude of the stator current is equal to the rated current of the machine but the machine is running at a speed higher than its rated speed. Find the speed at which the machine is running. Also find the torque developed by the machine.
14 . A 45 V, pole, 3 phase, 5 Hz, star connected, non-salient pole synchronous motor has synchronous reactance of Ω per phase and negligible stator resistance. At a particular field excitation, it draws A at unity power factor from a 45 V, 3 phase, 5 Hz supply. The mechanical load on the motor is now increased till the stator current is equal to 5A. The field excitation remains unchanged. Determine: the per phase open circuit voltage Eo the developed power for the new operating condition and corresponding power factor.. For the circuit shown in Fig.P, IE = ma, β = 99 and VBE =.7 V. Determine the current through and. the output voltage Vo (c) the value of F 5V = kω F Vo = 7kΩ ma kω. Vy for the network shown in Fig.P. Determine the transfer function V x This network is used as a feedback circuit in an oscillator circuit shown in Fig.P to generate sinusoidal oscillations. Assuming that the operational amplifier is ideal, determine F for generating these oscillations. Also, determine the oscillation frequency if = kω and = pf. F kω VO VX VY
15 3. The ripple counter shown in Fig.P3 is made up negative edge triggered J-E flips flops. The signal levels at J and K inputs of all the flip-flops are maintained at logic. Assume that all outputs are cleared just prior to applying the clock signal. reate a table of Q,Q,Q and A in the format given below for successive input cycles of the clock LK. Determine the module number of the counter. (c) Modify the circuit of Fig.P3 to create a modulo-6 counter using the same components used in the figure. LK Q Q Q Format for : Q J J LK LK K L Q J LK Q LK K K L L A 4. A long lossless transmission line has a unity power factor (UPF) load at the receiving end and an ac voltage source at the sending end (Fig.P4). the parameters of the transmission line are as follows: haracteristic impedance Zc =4Ω, propagation constant β =.-3 rad/km, and length l = km. The equation relating sending and receiving end questions is Vs = Vr cos ( β l ) jzc sin ( β l ) I omplete the maximum power that can be transferred to the UPF load at the receiving end if Vs = 3kV. ~ VS Transmission Line I V UPF Load
16 5. Two transposed 3 phase lines run parallel to each other as shown in Fig.P5. the equation describing the voltage drop in both lines is given below. Va.5 V b.5 Vc.5 = j Va.4 V.4 b.4 Vc Ia.4 Ib.4 Ic.5 Ia.5 Ib.5 Ic ompute the self and mutual zero sequence impedances of this system i.e. compute Z, Z, Z in the following equations V = Z I Z I V = Z I Z I Where V, V, I, I are the zero sequence voltage drops and currents for the two lines respectively. 6. A synchronous generator is to be connected to an infinite bus through a transmission line of reactance X =. pu, as shown in Fig.P6. the generator data is as follows: x =.pu, E =. pu, H=5MJ/MVA, mechanical power Pm =. pu, ωb = π 5 rad/sec. All quantities are expressed on a common base. The generator is initially running on open circuit with the frequency of the open circuit voltage slightly higher than that of the infinite bus. If at the instant of dδ switch closure δ = and ω = = ωinit, compute the maximum value of ωinint so that the generator pulls into synchronism. Hint: Use the equation (H / ω B ) ω dω Pedδ = Pe x ~ 7. 5 Hz Infinite Bus x. E δ A single input single output system with y as output and u as input, is described dy dy du by y = 5 3u. For the above system find an input u(t), with zero initial condition, that produces the same output as with no input and with the initial conditions. ( ) = 4, y dy ( ) =.
17 8. Obtain a state variable representation of the system governed by the differential d y dy y = u ( t ) e, with the choice of state variables as equation dy y et. Also find x(t), given that u(t) is a unit step function and x = y, x = x () =. 9. The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback system is given by G (s) = (s α ) s ( s ) ( s ) Sketch the root locus as α varies from to. Find the angle and real axis intercept of the asymptotes, breakaway points and the imaginary axis crossing points, if any.. In Fig.P, the ideal switch S is switched on and off with a switching frequency f = khz. The switching time period is T = ton toff = µs. The circuit is operated in steady state at the boundary of continuous and discontinuous conduction, so that the inductor current i is as shown in Fig.P. Find The on-time ton of the switch. The value of the peak current IP. S V i µh - 5V ON IP i. OFF ON S t ton toff In the circuit shown in Fig.P, the source I is a dc current source. The switch S is operated with a time period T and a duty ratio D. You may assume that the capacitance has a finite value which is large enough so that the voltage. Vc has negligible ripple. alculate the following under steady state conditions, in terms of D, I and. The voltage Vc, with the polarity shown in Figure P. The average output voltage V, with the polarity shown. I S V Vo - S ON OFF DT T
18 . The semiconductor switch S in the circuit of Fig.P is operated at a frequency of khz and a duty ratio D =.5. The circuit operates in the steady state. alculate the power-transferred form the dc voltage source V to the dc voltage source V. V V 3V V µh S
EE Branch GATE Paper 2010
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Given ff(zz) = gg(zz) + h(zz), where ff, gg, h are complex valued functions of a complex variable zz. Which one of the following statements is TUE? (A) If ff(zz) is
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Given ff(zz) = gg(zz) + h(zz), where ff, gg, h are complex valued functions of a complex variable zz. Which one of the following statements is TUE? (A) If ff(zz) is
+ ( )= with initial condition
 Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering
 Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
Introduction to Synchronous. Machines. Kevin Gaughan
 Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
GATEFORUM- India s No.1 institute for GATE training 1
 EE-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. Given a vector field F = y xax yzay = x a z, the line integral F.dl evaluated along a segment on the x-axis from x= to x= is -.33 (B) 0.33 (D) 7 : (B) x 0.
EE-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. Given a vector field F = y xax yzay = x a z, the line integral F.dl evaluated along a segment on the x-axis from x= to x= is -.33 (B) 0.33 (D) 7 : (B) x 0.
3 d Calculate the product of the motor constant and the pole flux KΦ in this operating point. 2 e Calculate the torque.
 Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -1. Please read the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
 TELANGANA/ANDHRA PRADESH TRANSCO/GENCO/DISCUM Assistant Engineer Examination ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Previous Paper 7) AP TRANSCO - AP GENCO-AE QUESTION PAPER 1. In two wattmeter method of 3-phase power
TELANGANA/ANDHRA PRADESH TRANSCO/GENCO/DISCUM Assistant Engineer Examination ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Previous Paper 7) AP TRANSCO - AP GENCO-AE QUESTION PAPER 1. In two wattmeter method of 3-phase power
Power Electronics
 Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL
 Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator. The excitation
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator. The excitation
mywbut.com Lesson 16 Solution of Current in AC Parallel and Seriesparallel
 esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How to compute the total impedance/admittance in series/parallel circuits?. How
esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How to compute the total impedance/admittance in series/parallel circuits?. How
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Electric Machines
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
Conventional Paper I (a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials?
 Conventional Paper I-03.(a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials? (ii) Give one example each of a dielectric and a ferroelectric material
Conventional Paper I-03.(a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials? (ii) Give one example each of a dielectric and a ferroelectric material
LO 1: Three Phase Circuits
 Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis
 Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 79 CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase and three-phase self-excited induction generators has been presented
79 CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase and three-phase self-excited induction generators has been presented
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
EEE3405 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES 2 - TEST
 ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
An Introduction to Electrical Machines. P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy
 An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
Control of Wind Turbine Generators. James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University
 Control of Wind Turbine Generators James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University Review from Day 1 Review Last time, we started with basic concepts from physics such as
Control of Wind Turbine Generators James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University Review from Day 1 Review Last time, we started with basic concepts from physics such as
INDUCTION MOTOR MODEL AND PARAMETERS
 APPENDIX C INDUCTION MOTOR MODEL AND PARAMETERS C.1 Dynamic Model of the Induction Motor in Stationary Reference Frame A three phase induction machine can be represented by an equivalent two phase machine
APPENDIX C INDUCTION MOTOR MODEL AND PARAMETERS C.1 Dynamic Model of the Induction Motor in Stationary Reference Frame A three phase induction machine can be represented by an equivalent two phase machine
GATE-2015 ELECTRICAL ENGG 7th February 2015 Forenoon Session
 Page Section - I (General Aptitude) Q. Which one of the following combinations is incorrect? Acquiescence - Submission Wheedle - Roundabout Flippancy - Lightness Profligate - Extravagant Q. Didn t you
Page Section - I (General Aptitude) Q. Which one of the following combinations is incorrect? Acquiescence - Submission Wheedle - Roundabout Flippancy - Lightness Profligate - Extravagant Q. Didn t you
Module 4. Single-phase AC circuits. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 4 Single-phase circuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How
Module 4 Single-phase circuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits ersion EE T, Kharagpur n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
ONE MARK QUESTIONS. 1. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is
 ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is (a.) R L C (b.) R L C (c.) R L C (d.) R LC
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is (a.) R L C (b.) R L C (c.) R L C (d.) R LC
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY. 1. Understands the physical construction and characteristics of basic components.
 SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines. Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015
 ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015 1 Content (Materials are from Chapters 16-17) Synchronous Generators Synchronous Motors 2 Synchronous Generators
ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015 1 Content (Materials are from Chapters 16-17) Synchronous Generators Synchronous Motors 2 Synchronous Generators
Tutorial Sheet Fig. Q1
 Tutorial Sheet - 04 1. The magnetic circuit shown in Fig. Q1 has dimensions A c = A g = 9 cm 2, g = 0.050 cm, l c = 30 cm, and N = 500 turns. Assume the value of the relative permeability,µ r = 70,000
Tutorial Sheet - 04 1. The magnetic circuit shown in Fig. Q1 has dimensions A c = A g = 9 cm 2, g = 0.050 cm, l c = 30 cm, and N = 500 turns. Assume the value of the relative permeability,µ r = 70,000
SE]y[-2017(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
![SE]y[-2017(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. SE]y[-2017(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.](/thumbs/94/122291001.jpg) RoU No. 300218 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SE]y[-2017(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
RoU No. 300218 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SE]y[-2017(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 General Principles 2 Construction 3 Production of Rotating Field 4 Why Does the Rotor Rotate 5 The Slip and Rotor
Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 General Principles 2 Construction 3 Production of Rotating Field 4 Why Does the Rotor Rotate 5 The Slip and Rotor
Three Phase Circuits
 Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
Synchronous Machines
 Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
ECE 585 Power System Stability
 Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
12 Chapter Driven RLC Circuits
 hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
8 z 2, then the greatest value of z is. 2. The principal argument/amplitude of the complex number 1 2 i (C) (D) 3 (C)
 1. If z is a complex number and if 8 z 2, then the greatest value of z is z (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 4 2. The principal argument/amplitude of the complex number 1 2 i 1 3i is (A) 2 (B) 4 (C) (D) 3 4 3.
1. If z is a complex number and if 8 z 2, then the greatest value of z is z (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 4 2. The principal argument/amplitude of the complex number 1 2 i 1 3i is (A) 2 (B) 4 (C) (D) 3 4 3.
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]
![Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark] Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]](/thumbs/88/115570773.jpg) Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
ECE Branch GATE Paper The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2
 Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Solved Problems. Electric Circuits & Components. 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown.
 Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING
 INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
Impedance/Reactance Problems
 Impedance/Reactance Problems. Consider the circuit below. An AC sinusoidal voltage of amplitude V and frequency ω is applied to the three capacitors, each of the same capacitance C. What is the total reactance
Impedance/Reactance Problems. Consider the circuit below. An AC sinusoidal voltage of amplitude V and frequency ω is applied to the three capacitors, each of the same capacitance C. What is the total reactance
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012
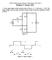 ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1
 Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA
 EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors)
 Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE
 Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
 Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
PROBLEMS TO BE SOLVED IN CLASSROOM
 PROLEMS TO E SOLVED IN LSSROOM Unit 0. Prerrequisites 0.1. Obtain a unit vector perpendicular to vectors 2i + 3j 6k and i + j k 0.2 a) Find the integral of vector v = 2xyi + 3j 2z k along the straight
PROLEMS TO E SOLVED IN LSSROOM Unit 0. Prerrequisites 0.1. Obtain a unit vector perpendicular to vectors 2i + 3j 6k and i + j k 0.2 a) Find the integral of vector v = 2xyi + 3j 2z k along the straight
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I)
 Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
AC Electric Machines. Objectives. Introduction. 1. To understand what the meant by the term ac circuit. 2. To understand how to analyze ac circuits.
 AC Electric Machines Objectives 1. To understand what the meant by the term ac circuit.. To understand how to analyze ac circuits. 3. To understand the basic construction and operation of an ac machine.
AC Electric Machines Objectives 1. To understand what the meant by the term ac circuit.. To understand how to analyze ac circuits. 3. To understand the basic construction and operation of an ac machine.
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits
 Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
3. (a) Figure 3(a) shows a Bridge T network used in control systems. The element values are clearly marked in the figure.
 I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
ECE3050 Assignment 7
 ECE3050 Assignment 7. Sketch and label the Bode magnitude and phase plots for the transfer functions given. Use loglog scales for the magnitude plots and linear-log scales for the phase plots. On the magnitude
ECE3050 Assignment 7. Sketch and label the Bode magnitude and phase plots for the transfer functions given. Use loglog scales for the magnitude plots and linear-log scales for the phase plots. On the magnitude
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
 CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2013 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY Copyright 2013 Caribbean Examinations Council
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2013 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY Copyright 2013 Caribbean Examinations Council
POWER SEMICONDUCTOR BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES
 POWER SEMICONDUCT BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES [Time: 3 Hrs] [Max. Marks: 80] Instructions: Solve any six questions from Q.No (1 or 2), Q.No (3 or 4), Q.No (5 or 6), Q.No (7 or 8), Q.No (9 or 10), Q.No (11 or
POWER SEMICONDUCT BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES [Time: 3 Hrs] [Max. Marks: 80] Instructions: Solve any six questions from Q.No (1 or 2), Q.No (3 or 4), Q.No (5 or 6), Q.No (7 or 8), Q.No (9 or 10), Q.No (11 or
Dynamics of the synchronous machine
 ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Dynamics of the synchronous machine Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 38 Time constants and
ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Dynamics of the synchronous machine Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 38 Time constants and
Conventional Paper-I Part A. 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy
 EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
POWER SYSTEM STABILITY
 LESSON SUMMARY-1:- POWER SYSTEM STABILITY 1. Introduction 2. Classification of Power System Stability 3. Dynamic Equation of Synchronous Machine Power system stability involves the study of the dynamics
LESSON SUMMARY-1:- POWER SYSTEM STABILITY 1. Introduction 2. Classification of Power System Stability 3. Dynamic Equation of Synchronous Machine Power system stability involves the study of the dynamics
CHAPTER 2 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS & FIELDS. In the circuit shown below, the current through the inductor is 2 A (B) (A) (C) (D) 0A
 CHAPTER ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS & FIELDS YEAR 0 ONE MARK MCQ. In the circuit shown below, the current through the inductor is (A) A (B) A + j + j MCQ. (C) A (D) 0A + j The impedance looking into nodes and
CHAPTER ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS & FIELDS YEAR 0 ONE MARK MCQ. In the circuit shown below, the current through the inductor is (A) A (B) A + j + j MCQ. (C) A (D) 0A + j The impedance looking into nodes and
Electrical Engineering Fundamentals for Non-Electrical Engineers
 Electrical Engineering Fundamentals for Non-Electrical Engineers by Brad Meyer, PE Contents Introduction... 3 Definitions... 3 Power Sources... 4 Series vs. Parallel... 9 Current Behavior at a Node...
Electrical Engineering Fundamentals for Non-Electrical Engineers by Brad Meyer, PE Contents Introduction... 3 Definitions... 3 Power Sources... 4 Series vs. Parallel... 9 Current Behavior at a Node...
Schedule. ECEN 301 Discussion #20 Exam 2 Review 1. Lab Due date. Title Chapters HW Due date. Date Day Class No. 10 Nov Mon 20 Exam Review.
 Schedule Date Day lass No. 0 Nov Mon 0 Exam Review Nov Tue Title hapters HW Due date Nov Wed Boolean Algebra 3. 3.3 ab Due date AB 7 Exam EXAM 3 Nov Thu 4 Nov Fri Recitation 5 Nov Sat 6 Nov Sun 7 Nov Mon
Schedule Date Day lass No. 0 Nov Mon 0 Exam Review Nov Tue Title hapters HW Due date Nov Wed Boolean Algebra 3. 3.3 ab Due date AB 7 Exam EXAM 3 Nov Thu 4 Nov Fri Recitation 5 Nov Sat 6 Nov Sun 7 Nov Mon
Equivalent Circuits with Multiple Damper Windings (e.g. Round rotor Machines)
 Equivalent Circuits with Multiple Damper Windings (e.g. Round rotor Machines) d axis: L fd L F - M R fd F L 1d L D - M R 1d D R fd R F e fd e F R 1d R D Subscript Notations: ( ) fd ~ field winding quantities
Equivalent Circuits with Multiple Damper Windings (e.g. Round rotor Machines) d axis: L fd L F - M R fd F L 1d L D - M R 1d D R fd R F e fd e F R 1d R D Subscript Notations: ( ) fd ~ field winding quantities
From now, we ignore the superbar - with variables in per unit. ψ ψ. l ad ad ad ψ. ψ ψ ψ
 From now, we ignore the superbar - with variables in per unit. ψ 0 L0 i0 ψ L + L L L i d l ad ad ad d ψ F Lad LF MR if = ψ D Lad MR LD id ψ q Ll + Laq L aq i q ψ Q Laq LQ iq 41 Equivalent Circuits for
From now, we ignore the superbar - with variables in per unit. ψ 0 L0 i0 ψ L + L L L i d l ad ad ad d ψ F Lad LF MR if = ψ D Lad MR LD id ψ q Ll + Laq L aq i q ψ Q Laq LQ iq 41 Equivalent Circuits for
Basic RL and RC Circuits R-L TRANSIENTS: STORAGE CYCLE. Engineering Collage Electrical Engineering Dep. Dr. Ibrahim Aljubouri
 st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Physics 240 Fall 2005: Exam #3 Solutions. Please print your name: Please list your discussion section number: Please list your discussion instructor:
 Physics 4 Fall 5: Exam #3 Solutions Please print your name: Please list your discussion section number: Please list your discussion instructor: Form #1 Instructions 1. Fill in your name above. This will
Physics 4 Fall 5: Exam #3 Solutions Please print your name: Please list your discussion section number: Please list your discussion instructor: Form #1 Instructions 1. Fill in your name above. This will
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 4 Single-phase A ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur esson 4 Solution of urrent in -- Series ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur In the last lesson, two points were described:. How to represent a sinusoidal
Module 4 Single-phase A ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur esson 4 Solution of urrent in -- Series ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur In the last lesson, two points were described:. How to represent a sinusoidal
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, pm, Room TBA
 EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03
![Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03](/thumbs/94/118747664.jpg) EE 4 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 016 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS NETWORK ANALYSIS Time: Three Hours Answer Question
EE 4 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 016 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS NETWORK ANALYSIS Time: Three Hours Answer Question
REACTANCE. By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013
 REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
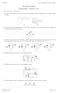 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
How an Induction Motor Works by Equations (and Physics)
 How an Induction Motor Works by Equations (and Physics) The magnetic field in the air gap from the voltage applied to the stator: The stator has three sets of windings that are aligned at 10 degrees to
How an Induction Motor Works by Equations (and Physics) The magnetic field in the air gap from the voltage applied to the stator: The stator has three sets of windings that are aligned at 10 degrees to
ALTERNATING CURRENT. with X C = 0.34 A. SET UP: The specified value is the root-mean-square current; I. EXECUTE: (a) V = (0.34 A) = 0.12 A.
 ATENATING UENT 3 3 IDENTIFY: i Icosωt and I I/ SET UP: The specified value is the root-mean-square current; I 34 A EXEUTE: (a) I 34 A (b) I I (34 A) 48 A (c) Since the current is positive half of the time
ATENATING UENT 3 3 IDENTIFY: i Icosωt and I I/ SET UP: The specified value is the root-mean-square current; I 34 A EXEUTE: (a) I 34 A (b) I I (34 A) 48 A (c) Since the current is positive half of the time
PHYS 241 EXAM #2 November 9, 2006
 1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
11. AC Circuit Power Analysis
 . AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
. AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines
 Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems Lesson 17_et332b.pptx 1 Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how synchronous machines
Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems Lesson 17_et332b.pptx 1 Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how synchronous machines
Page 2 GATE EE
 Page GATE EE 009 www.gatehelp.com SOL. Overall gain of the system is written as G = GG G 3 We know that for a quantity that is product of two or more quantities total percentage error is some of the percentage
Page GATE EE 009 www.gatehelp.com SOL. Overall gain of the system is written as G = GG G 3 We know that for a quantity that is product of two or more quantities total percentage error is some of the percentage
Conventional Paper I-2010
 Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor. The solution of this differential equation is
 RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam
 ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam December 12, 2013 Circle your division: Division 0101: Furgason (8:30 am) Division 0201: Bermel (9:30 am) Name (Last, First) Purdue ID # There are 18 multiple choice problems
ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam December 12, 2013 Circle your division: Division 0101: Furgason (8:30 am) Division 0201: Bermel (9:30 am) Name (Last, First) Purdue ID # There are 18 multiple choice problems
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Electric Power Engineering Department
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Electric Power Engineering Department EE471: Electrical Machines-II Tutorial # 2: 3-ph Induction Motor/Generator Question #1 A 100 hp, 60-Hz, three-phase
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Electric Power Engineering Department EE471: Electrical Machines-II Tutorial # 2: 3-ph Induction Motor/Generator Question #1 A 100 hp, 60-Hz, three-phase
CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 6 CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 5.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase SEIG has been discussed in the previous chapters. In this chapter,
6 CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 5.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase SEIG has been discussed in the previous chapters. In this chapter,
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous)
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Computer Methods in Power Systems Course Code : A60222
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Computer Methods in Power Systems Course Code : A60222
Single Phase Parallel AC Circuits
 Single Phase Parallel AC Circuits 1 Single Phase Parallel A.C. Circuits (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) n parallel a.c. circuits similar
Single Phase Parallel AC Circuits 1 Single Phase Parallel A.C. Circuits (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) n parallel a.c. circuits similar
Physics 240 Fall 2005: Exam #3. Please print your name: Please list your discussion section number: Please list your discussion instructor:
 Physics 240 Fall 2005: Exam #3 Please print your name: Please list your discussion section number: Please list your discussion instructor: Form #1 Instructions 1. Fill in your name above 2. This will be
Physics 240 Fall 2005: Exam #3 Please print your name: Please list your discussion section number: Please list your discussion instructor: Form #1 Instructions 1. Fill in your name above 2. This will be
GATE 2011 Electrical Engineering Set C
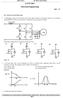 Electrical Engineering Set C Q. - Q.25 Carry One Mark each.. A three-phase current source inverter used for the speed control of an induction motor is to be realized using MOSFET switches as shown below.
Electrical Engineering Set C Q. - Q.25 Carry One Mark each.. A three-phase current source inverter used for the speed control of an induction motor is to be realized using MOSFET switches as shown below.
EE 212 PASSIVE AC CIRCUITS
 EE 212 PASSIVE AC CIRCUITS Condensed Text Prepared by: Rajesh Karki, Ph.D., P.Eng. Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of Saskatchewan About the EE 212 Condensed Text The major topics in the course
EE 212 PASSIVE AC CIRCUITS Condensed Text Prepared by: Rajesh Karki, Ph.D., P.Eng. Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of Saskatchewan About the EE 212 Condensed Text The major topics in the course
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Lecture 05 Power in AC circuit
 CA2627 Building Science Lecture 05 Power in AC circuit Instructor: Jiayu Chen Ph.D. Announcement 1. Makeup Midterm 2. Midterm grade Grade 25 20 15 10 5 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Grade Jiayu Chen, Ph.D. 2
CA2627 Building Science Lecture 05 Power in AC circuit Instructor: Jiayu Chen Ph.D. Announcement 1. Makeup Midterm 2. Midterm grade Grade 25 20 15 10 5 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Grade Jiayu Chen, Ph.D. 2
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.7 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 5, May-07 e-issn (O): 348-4470 p-issn (P): 348-6406 Mathematical modeling
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.7 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 5, May-07 e-issn (O): 348-4470 p-issn (P): 348-6406 Mathematical modeling
