Multinomial functional regression with application to lameness detection for horses
|
|
|
- Barry Sutton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Mathematical Sciences Multinomial functional regression with application to lameness detection for horses Helle Sørensen Joint with Seyed Nourollah Mousavi user! 2015, Ålborg
2 Background and aim for case study Data collected by veterinarian Maj Halling Thomsen and her colleaugues at University of Copenhagen. Problem: Difficult to detect lameness and identify the injured limb, especially for low-degree lameness Visual inspection and clinical examination is highly subjective Large variability in assessments from different veterinarians, and also between repeated assessments from the same vet Aim: Develop an objective method for lameness detection Slide 2/16
3 Detection of lameness: The movie Slide 3/16
4 85 data signals (after preprocessing) Acceleration LF RF NO Acceleration LH RH LF LH NO RF RH Each curve: Average vertical acceleration for one gait cycle First half: Stance on right-fore/left-hind diagonal Slide 4/16
5 Problem and approach Classification for functional data: Given a data signal, which group does it belong to? Our approach: Functional multinomial regression using wavelets and LASSO Idea: wavelets offer precise approximations with sparse representations; use LASSO to induce sparseness Extension of the work by Zhao, Ogden, Reiss (2012) Slide 5/16
6 Multinomial functional regression (MFR) Data: Covariate functions x i (t), categorical outcomes y i M Regression model Linear predictor for group m: η m (x) = α m + β m (t)x(t)dt Conditional probabilities: eη m(x) p m (x) = P(Y = m X = x) = l M e η l (x) Unknowns: Intercepts α m and coefficient functions β m (t) Classification of new curve, x 0 : Compute ˆη m (x 0 ) and ˆp m (x 0 ) for all groups, and assign x 0 to group with largest probability Slide 6/16
7 Estimation and computations Estimation approach Expand functions x i in a wavelet basis Use wavelet coefficients as covariates in ordinary multinomial regression with LASSO penalization Translate estimated regression coef s to coef. functions ˆβ m Tuning parameters are selected with cross validation: resolution level j 0 in wavelet basis and penalty parameter λ Computations fda package for preprocessing wavethresh package for wavelet computations glmnet package for penalized multinomial regression Slide 7/16
8 Cross validation results Mean cross validated deviance Left fore CVM j 0 =0 j 0 =1 j 0 =2 j 0 =3 j 0 =4 j 0 =5 j 0 =6 j 0 = j 0 =0 j 0 =1 j 0 =2 j 0 =3 j 0 = log(lambda) Tim Slide 8/16
9 Estimated coefficient functions: ˆβ m ˆβ no Left fore normal Right fore normal Left hind normal Right hind normal Slide 9/16
10 ... and 100 bootstrap samples Left fore normal Right fore normal Left hind normal Right hind normal Slide 10/16
11 Classification results Leave-one-out classification: Predicted group True group LF LH NO RF RH LF LH NO RF RH curves classified to correct group (80%); five more curves to correct diagonal; only one curve to wrong diagonal PC-LDA and method by Ferraty+Vieu (2003): 65% correct Simulation study with similar data: 89% correct classifications Slide 11/16
12 Discussion Estimated ˆβ m s satisfy, to some extend, natural symmetry restrictions. Possible to build in those restrictions explicitly. MFR performs at least as well as the other methods we have tested also in application from speech recognition Many possible variations which we didn t pursue Data come from only eight horses! Calls for random effect of horse at least for inference about coefficient functions. Thank you for your attention Questions and comments are most welcome: helle@math.ku.dk Slide 12/16
13 References Mousavi, S. N., and Sørensen, H. (2015). Multinomial functional regression with wavelets and LASSO penalization. Submitted. Zhao, Y., Ogden, R. T., and Reiss, P. T. (2012). Wavelet-based LASSO in functional linear regression. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 21: Friedman, J., Hastie, T., and Tibshirani, R. (2010). Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. Journal of statistical software, 33(1):1. Ferraty, F. and Vieu, P. (2003). Curves discrimination: a nonparametric functional approach. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 44: Slide 13/16
14 Simulation results Color Legend Test Data Twins Test Data 60 n=(20,20,20,20,20) n=(40,40,40,40,40) Misclassificaton rate(%) Dense Dense+Small noise Dense+Large noise Sparse Sparse+Small noise Sparse+Large noise Dense Dense+Small noise Dense+Large noise Sparse Sparse+Small noise Sparse+Large noise Slide 14/16
15 Probabilities for classification Correct group Correct diagonal, wrong group Remaining True status LF LH NO RF RH Maximum probability Slide 15/16
16 Estimated coefficient functions with symmetry restrictions Estimated deviation from NO group Estimated deviation from NO group LF LH RF RH LF LH RF RH Slide 16/16
Lecture 6: Methods for high-dimensional problems
 Lecture 6: Methods for high-dimensional problems Hector Corrada Bravo and Rafael A. Irizarry March, 2010 In this Section we will discuss methods where data lies on high-dimensional spaces. In particular,
Lecture 6: Methods for high-dimensional problems Hector Corrada Bravo and Rafael A. Irizarry March, 2010 In this Section we will discuss methods where data lies on high-dimensional spaces. In particular,
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDICES FOR WAVELET-DOMAIN REGRESSION AND PREDICTIVE INFERENCE IN PSYCHIATRIC NEUROIMAGING
 Submitted to the Annals of Applied Statistics SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDICES FOR WAVELET-DOMAIN REGRESSION AND PREDICTIVE INFERENCE IN PSYCHIATRIC NEUROIMAGING By Philip T. Reiss, Lan Huo, Yihong Zhao, Clare
Submitted to the Annals of Applied Statistics SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDICES FOR WAVELET-DOMAIN REGRESSION AND PREDICTIVE INFERENCE IN PSYCHIATRIC NEUROIMAGING By Philip T. Reiss, Lan Huo, Yihong Zhao, Clare
Fast Regularization Paths via Coordinate Descent
 August 2008 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Fast Regularization Paths via Coordinate Descent Trevor Hastie Stanford University joint work with Jerry Friedman and Rob Tibshirani. August 2008 Trevor
August 2008 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Fast Regularization Paths via Coordinate Descent Trevor Hastie Stanford University joint work with Jerry Friedman and Rob Tibshirani. August 2008 Trevor
A Blockwise Descent Algorithm for Group-penalized Multiresponse and Multinomial Regression
 A Blockwise Descent Algorithm for Group-penalized Multiresponse and Multinomial Regression Noah Simon Jerome Friedman Trevor Hastie November 5, 013 Abstract In this paper we purpose a blockwise descent
A Blockwise Descent Algorithm for Group-penalized Multiresponse and Multinomial Regression Noah Simon Jerome Friedman Trevor Hastie November 5, 013 Abstract In this paper we purpose a blockwise descent
ESL Chap3. Some extensions of lasso
 ESL Chap3 Some extensions of lasso 1 Outline Consistency of lasso for model selection Adaptive lasso Elastic net Group lasso 2 Consistency of lasso for model selection A number of authors have studied
ESL Chap3 Some extensions of lasso 1 Outline Consistency of lasso for model selection Adaptive lasso Elastic net Group lasso 2 Consistency of lasso for model selection A number of authors have studied
Graphical Model Selection
 May 6, 2013 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Graphical Model Selection Trevor Hastie Stanford University joint work with Jerome Friedman, Rob Tibshirani, Rahul Mazumder and Jason Lee May 6, 2013 Trevor
May 6, 2013 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Graphical Model Selection Trevor Hastie Stanford University joint work with Jerome Friedman, Rob Tibshirani, Rahul Mazumder and Jason Lee May 6, 2013 Trevor
Machine Learning for OR & FE
 Machine Learning for OR & FE Regression II: Regularization and Shrinkage Methods Martin Haugh Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University Email: martin.b.haugh@gmail.com
Machine Learning for OR & FE Regression II: Regularization and Shrinkage Methods Martin Haugh Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University Email: martin.b.haugh@gmail.com
Classification. Chapter Introduction. 6.2 The Bayes classifier
 Chapter 6 Classification 6.1 Introduction Often encountered in applications is the situation where the response variable Y takes values in a finite set of labels. For example, the response Y could encode
Chapter 6 Classification 6.1 Introduction Often encountered in applications is the situation where the response variable Y takes values in a finite set of labels. For example, the response Y could encode
Fast Regularization Paths via Coordinate Descent
 KDD August 2008 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Fast Regularization Paths via Coordinate Descent Trevor Hastie Stanford University joint work with Jerry Friedman and Rob Tibshirani. KDD August 2008
KDD August 2008 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Fast Regularization Paths via Coordinate Descent Trevor Hastie Stanford University joint work with Jerry Friedman and Rob Tibshirani. KDD August 2008
Proteomics and Variable Selection
 Proteomics and Variable Selection p. 1/55 Proteomics and Variable Selection Alex Lewin With thanks to Paul Kirk for some graphs Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Imperial
Proteomics and Variable Selection p. 1/55 Proteomics and Variable Selection Alex Lewin With thanks to Paul Kirk for some graphs Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Imperial
A Survey of L 1. Regression. Céline Cunen, 20/10/2014. Vidaurre, Bielza and Larranaga (2013)
 A Survey of L 1 Regression Vidaurre, Bielza and Larranaga (2013) Céline Cunen, 20/10/2014 Outline of article 1.Introduction 2.The Lasso for Linear Regression a) Notation and Main Concepts b) Statistical
A Survey of L 1 Regression Vidaurre, Bielza and Larranaga (2013) Céline Cunen, 20/10/2014 Outline of article 1.Introduction 2.The Lasso for Linear Regression a) Notation and Main Concepts b) Statistical
Data Mining and Data Warehousing. Henryk Maciejewski. Data Mining Predictive modelling: regression
 Data Mining and Data Warehousing Henryk Maciejewski Data Mining Predictive modelling: regression Algorithms for Predictive Modelling Contents Regression Classification Auxiliary topics: Estimation of prediction
Data Mining and Data Warehousing Henryk Maciejewski Data Mining Predictive modelling: regression Algorithms for Predictive Modelling Contents Regression Classification Auxiliary topics: Estimation of prediction
The lasso: some novel algorithms and applications
 1 The lasso: some novel algorithms and applications Newton Institute, June 25, 2008 Robert Tibshirani Stanford University Collaborations with Trevor Hastie, Jerome Friedman, Holger Hoefling, Gen Nowak,
1 The lasso: some novel algorithms and applications Newton Institute, June 25, 2008 Robert Tibshirani Stanford University Collaborations with Trevor Hastie, Jerome Friedman, Holger Hoefling, Gen Nowak,
MSA220/MVE440 Statistical Learning for Big Data
 MSA220/MVE440 Statistical Learning for Big Data Lecture 9-10 - High-dimensional regression Rebecka Jörnsten Mathematical Sciences University of Gothenburg and Chalmers University of Technology Recap from
MSA220/MVE440 Statistical Learning for Big Data Lecture 9-10 - High-dimensional regression Rebecka Jörnsten Mathematical Sciences University of Gothenburg and Chalmers University of Technology Recap from
Fast Regularization Paths via Coordinate Descent
 user! 2009 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Fast Regularization Paths via Coordinate Descent Trevor Hastie Stanford University joint work with Jerome Friedman and Rob Tibshirani. user! 2009 Trevor
user! 2009 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Fast Regularization Paths via Coordinate Descent Trevor Hastie Stanford University joint work with Jerome Friedman and Rob Tibshirani. user! 2009 Trevor
MSA220/MVE440 Statistical Learning for Big Data
 MSA220/MVE440 Statistical Learning for Big Data Lecture 7/8 - High-dimensional modeling part 1 Rebecka Jörnsten Mathematical Sciences University of Gothenburg and Chalmers University of Technology Classification
MSA220/MVE440 Statistical Learning for Big Data Lecture 7/8 - High-dimensional modeling part 1 Rebecka Jörnsten Mathematical Sciences University of Gothenburg and Chalmers University of Technology Classification
MS-C1620 Statistical inference
 MS-C1620 Statistical inference 10 Linear regression III Joni Virta Department of Mathematics and Systems Analysis School of Science Aalto University Academic year 2018 2019 Period III - IV 1 / 32 Contents
MS-C1620 Statistical inference 10 Linear regression III Joni Virta Department of Mathematics and Systems Analysis School of Science Aalto University Academic year 2018 2019 Period III - IV 1 / 32 Contents
A Significance Test for the Lasso
 A Significance Test for the Lasso Lockhart R, Taylor J, Tibshirani R, and Tibshirani R Ashley Petersen May 14, 2013 1 Last time Problem: Many clinical covariates which are important to a certain medical
A Significance Test for the Lasso Lockhart R, Taylor J, Tibshirani R, and Tibshirani R Ashley Petersen May 14, 2013 1 Last time Problem: Many clinical covariates which are important to a certain medical
Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso
 Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso ROBERT TIBSHIRANI, 1996 Presenter: Guiyun Feng April 27 () 1 / 20 Motivation Estimation in Linear Models: y = β T x + ɛ. data (x i, y i ), i = 1, 2,...,
Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso ROBERT TIBSHIRANI, 1996 Presenter: Guiyun Feng April 27 () 1 / 20 Motivation Estimation in Linear Models: y = β T x + ɛ. data (x i, y i ), i = 1, 2,...,
Permutation-invariant regularization of large covariance matrices. Liza Levina
 Liza Levina Permutation-invariant covariance regularization 1/42 Permutation-invariant regularization of large covariance matrices Liza Levina Department of Statistics University of Michigan Joint work
Liza Levina Permutation-invariant covariance regularization 1/42 Permutation-invariant regularization of large covariance matrices Liza Levina Department of Statistics University of Michigan Joint work
Other likelihoods. Patrick Breheny. April 25. Multinomial regression Robust regression Cox regression
 Other likelihoods Patrick Breheny April 25 Patrick Breheny High-Dimensional Data Analysis (BIOS 7600) 1/29 Introduction In principle, the idea of penalized regression can be extended to any sort of regression
Other likelihoods Patrick Breheny April 25 Patrick Breheny High-Dimensional Data Analysis (BIOS 7600) 1/29 Introduction In principle, the idea of penalized regression can be extended to any sort of regression
Prediction & Feature Selection in GLM
 Tarigan Statistical Consulting & Coaching statistical-coaching.ch Doctoral Program in Computer Science of the Universities of Fribourg, Geneva, Lausanne, Neuchâtel, Bern and the EPFL Hands-on Data Analysis
Tarigan Statistical Consulting & Coaching statistical-coaching.ch Doctoral Program in Computer Science of the Universities of Fribourg, Geneva, Lausanne, Neuchâtel, Bern and the EPFL Hands-on Data Analysis
Simultaneous Confidence Bands for the Coefficient Function in Functional Regression
 University of Haifa From the SelectedWorks of Philip T. Reiss August 7, 2008 Simultaneous Confidence Bands for the Coefficient Function in Functional Regression Philip T. Reiss, New York University Available
University of Haifa From the SelectedWorks of Philip T. Reiss August 7, 2008 Simultaneous Confidence Bands for the Coefficient Function in Functional Regression Philip T. Reiss, New York University Available
Variable Selection and Regularization
 Variable Selection and Regularization Sanford Weisberg October 15, 2012 Variable Selection In a regression problem with p predictors, we can reduce the dimension of the regression problem in two general
Variable Selection and Regularization Sanford Weisberg October 15, 2012 Variable Selection In a regression problem with p predictors, we can reduce the dimension of the regression problem in two general
Homework 1 Solutions Probability, Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE), Bayes Rule, knn
 Homework 1 Solutions Probability, Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE), Bayes Rule, knn CMU 10-701: Machine Learning (Fall 2016) https://piazza.com/class/is95mzbrvpn63d OUT: September 13th DUE: September
Homework 1 Solutions Probability, Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE), Bayes Rule, knn CMU 10-701: Machine Learning (Fall 2016) https://piazza.com/class/is95mzbrvpn63d OUT: September 13th DUE: September
Exploratory quantile regression with many covariates: An application to adverse birth outcomes
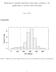 Exploratory quantile regression with many covariates: An application to adverse birth outcomes June 3, 2011 eappendix 30 Percent of Total 20 10 0 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Birth weights efigure 1: Histogram
Exploratory quantile regression with many covariates: An application to adverse birth outcomes June 3, 2011 eappendix 30 Percent of Total 20 10 0 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Birth weights efigure 1: Histogram
Building a Prognostic Biomarker
 Building a Prognostic Biomarker Noah Simon and Richard Simon July 2016 1 / 44 Prognostic Biomarker for a Continuous Measure On each of n patients measure y i - single continuous outcome (eg. blood pressure,
Building a Prognostic Biomarker Noah Simon and Richard Simon July 2016 1 / 44 Prognostic Biomarker for a Continuous Measure On each of n patients measure y i - single continuous outcome (eg. blood pressure,
Pathwise coordinate optimization
 Stanford University 1 Pathwise coordinate optimization Jerome Friedman, Trevor Hastie, Holger Hoefling, Robert Tibshirani Stanford University Acknowledgements: Thanks to Stephen Boyd, Michael Saunders,
Stanford University 1 Pathwise coordinate optimization Jerome Friedman, Trevor Hastie, Holger Hoefling, Robert Tibshirani Stanford University Acknowledgements: Thanks to Stephen Boyd, Michael Saunders,
Classification 1: Linear regression of indicators, linear discriminant analysis
 Classification 1: Linear regression of indicators, linear discriminant analysis Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: 36-462/36-662 April 2 2013 Optional reading: ISL 4.1, 4.2, 4.4, ESL 4.1 4.3 1 Classification
Classification 1: Linear regression of indicators, linear discriminant analysis Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: 36-462/36-662 April 2 2013 Optional reading: ISL 4.1, 4.2, 4.4, ESL 4.1 4.3 1 Classification
Variable Selection and Weighting by Nearest Neighbor Ensembles
 Variable Selection and Weighting by Nearest Neighbor Ensembles Jan Gertheiss (joint work with Gerhard Tutz) Department of Statistics University of Munich WNI 2008 Nearest Neighbor Methods Introduction
Variable Selection and Weighting by Nearest Neighbor Ensembles Jan Gertheiss (joint work with Gerhard Tutz) Department of Statistics University of Munich WNI 2008 Nearest Neighbor Methods Introduction
Classification. Classification is similar to regression in that the goal is to use covariates to predict on outcome.
 Classification Classification is similar to regression in that the goal is to use covariates to predict on outcome. We still have a vector of covariates X. However, the response is binary (or a few classes),
Classification Classification is similar to regression in that the goal is to use covariates to predict on outcome. We still have a vector of covariates X. However, the response is binary (or a few classes),
The lasso, persistence, and cross-validation
 The lasso, persistence, and cross-validation Daniel J. McDonald Department of Statistics Indiana University http://www.stat.cmu.edu/ danielmc Joint work with: Darren Homrighausen Colorado State University
The lasso, persistence, and cross-validation Daniel J. McDonald Department of Statistics Indiana University http://www.stat.cmu.edu/ danielmc Joint work with: Darren Homrighausen Colorado State University
Package Grace. R topics documented: April 9, Type Package
 Type Package Package Grace April 9, 2017 Title Graph-Constrained Estimation and Hypothesis Tests Version 0.5.3 Date 2017-4-8 Author Sen Zhao Maintainer Sen Zhao Description Use
Type Package Package Grace April 9, 2017 Title Graph-Constrained Estimation and Hypothesis Tests Version 0.5.3 Date 2017-4-8 Author Sen Zhao Maintainer Sen Zhao Description Use
Properties of optimizations used in penalized Gaussian likelihood inverse covariance matrix estimation
 Properties of optimizations used in penalized Gaussian likelihood inverse covariance matrix estimation Adam J. Rothman School of Statistics University of Minnesota October 8, 2014, joint work with Liliana
Properties of optimizations used in penalized Gaussian likelihood inverse covariance matrix estimation Adam J. Rothman School of Statistics University of Minnesota October 8, 2014, joint work with Liliana
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2012
 Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
Regularization and Variable Selection via the Elastic Net
 p. 1/1 Regularization and Variable Selection via the Elastic Net Hui Zou and Trevor Hastie Journal of Royal Statistical Society, B, 2005 Presenter: Minhua Chen, Nov. 07, 2008 p. 2/1 Agenda Introduction
p. 1/1 Regularization and Variable Selection via the Elastic Net Hui Zou and Trevor Hastie Journal of Royal Statistical Society, B, 2005 Presenter: Minhua Chen, Nov. 07, 2008 p. 2/1 Agenda Introduction
Gaussian Graphical Models and Graphical Lasso
 ELE 538B: Sparsity, Structure and Inference Gaussian Graphical Models and Graphical Lasso Yuxin Chen Princeton University, Spring 2017 Multivariate Gaussians Consider a random vector x N (0, Σ) with pdf
ELE 538B: Sparsity, Structure and Inference Gaussian Graphical Models and Graphical Lasso Yuxin Chen Princeton University, Spring 2017 Multivariate Gaussians Consider a random vector x N (0, Σ) with pdf
Variable Selection and Sensitivity Analysis via Dynamic Trees with an application to Computer Code Performance Tuning
 Variable Selection and Sensitivity Analysis via Dynamic Trees with an application to Computer Code Performance Tuning Robert B. Gramacy University of Chicago Booth School of Business faculty.chicagobooth.edu/robert.gramacy
Variable Selection and Sensitivity Analysis via Dynamic Trees with an application to Computer Code Performance Tuning Robert B. Gramacy University of Chicago Booth School of Business faculty.chicagobooth.edu/robert.gramacy
Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Hilary Term 2016
 Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Hilary Term 2016 Dino Sejdinovic Department of Statistics Oxford Slides and other materials available at: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdinov/sdmml Naïve Bayes
Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Hilary Term 2016 Dino Sejdinovic Department of Statistics Oxford Slides and other materials available at: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdinov/sdmml Naïve Bayes
COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning. James McInerney Adapted from slides by Nakul Verma
 COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning James McInerney Adapted from slides by Nakul Verma Announcements HW1: Please submit as a group Watch out for zero variance features (Q5) HW2 will be released
COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning James McInerney Adapted from slides by Nakul Verma Announcements HW1: Please submit as a group Watch out for zero variance features (Q5) HW2 will be released
Sufficient Dimension Reduction using Support Vector Machine and it s variants
 Sufficient Dimension Reduction using Support Vector Machine and it s variants Andreas Artemiou School of Mathematics, Cardiff University @AG DANK/BCS Meeting 2013 SDR PSVM Real Data Current Research and
Sufficient Dimension Reduction using Support Vector Machine and it s variants Andreas Artemiou School of Mathematics, Cardiff University @AG DANK/BCS Meeting 2013 SDR PSVM Real Data Current Research and
Recap from previous lecture
 Recap from previous lecture Learning is using past experience to improve future performance. Different types of learning: supervised unsupervised reinforcement active online... For a machine, experience
Recap from previous lecture Learning is using past experience to improve future performance. Different types of learning: supervised unsupervised reinforcement active online... For a machine, experience
Week 5: Classification
 Big Data BUS 41201 Week 5: Classification Veronika Ročková University of Chicago Booth School of Business http://faculty.chicagobooth.edu/veronika.rockova/ [5] Classification Parametric and non-parametric
Big Data BUS 41201 Week 5: Classification Veronika Ročková University of Chicago Booth School of Business http://faculty.chicagobooth.edu/veronika.rockova/ [5] Classification Parametric and non-parametric
Learning with Sparsity Constraints
 Stanford 2010 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Learning with Sparsity Constraints Trevor Hastie Stanford University recent joint work with Rahul Mazumder, Jerome Friedman and Rob Tibshirani earlier
Stanford 2010 Trevor Hastie, Stanford Statistics 1 Learning with Sparsity Constraints Trevor Hastie Stanford University recent joint work with Rahul Mazumder, Jerome Friedman and Rob Tibshirani earlier
LASSO-Type Penalization in the Framework of Generalized Additive Models for Location, Scale and Shape
 LASSO-Type Penalization in the Framework of Generalized Additive Models for Location, Scale and Shape Nikolaus Umlauf https://eeecon.uibk.ac.at/~umlauf/ Overview Joint work with Andreas Groll, Julien Hambuckers
LASSO-Type Penalization in the Framework of Generalized Additive Models for Location, Scale and Shape Nikolaus Umlauf https://eeecon.uibk.ac.at/~umlauf/ Overview Joint work with Andreas Groll, Julien Hambuckers
Applied Machine Learning Annalisa Marsico
 Applied Machine Learning Annalisa Marsico OWL RNA Bionformatics group Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Free University of Berlin 22 April, SoSe 2015 Goals Feature Selection rather than Feature
Applied Machine Learning Annalisa Marsico OWL RNA Bionformatics group Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Free University of Berlin 22 April, SoSe 2015 Goals Feature Selection rather than Feature
Model Selection, Estimation, and Bootstrap Smoothing. Bradley Efron Stanford University
 Model Selection, Estimation, and Bootstrap Smoothing Bradley Efron Stanford University Estimation After Model Selection Usually: (a) look at data (b) choose model (linear, quad, cubic...?) (c) fit estimates
Model Selection, Estimation, and Bootstrap Smoothing Bradley Efron Stanford University Estimation After Model Selection Usually: (a) look at data (b) choose model (linear, quad, cubic...?) (c) fit estimates
Chris Fraley and Daniel Percival. August 22, 2008, revised May 14, 2010
 Model-Averaged l 1 Regularization using Markov Chain Monte Carlo Model Composition Technical Report No. 541 Department of Statistics, University of Washington Chris Fraley and Daniel Percival August 22,
Model-Averaged l 1 Regularization using Markov Chain Monte Carlo Model Composition Technical Report No. 541 Department of Statistics, University of Washington Chris Fraley and Daniel Percival August 22,
Data Mining 2018 Logistic Regression Text Classification
 Data Mining 2018 Logistic Regression Text Classification Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Data Mining 1 / 50 Two types of approaches to classification In (probabilistic)
Data Mining 2018 Logistic Regression Text Classification Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Data Mining 1 / 50 Two types of approaches to classification In (probabilistic)
Lecture 3. Linear Regression II Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen
 Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 3 Linear Regression II 02.11.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de This Lecture: Advanced Machine Learning Regression
Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 3 Linear Regression II 02.11.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de This Lecture: Advanced Machine Learning Regression
JEROME H. FRIEDMAN Department of Statistics and Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University, Stanford, CA
 1 SEPARATING SIGNAL FROM BACKGROUND USING ENSEMBLES OF RULES JEROME H. FRIEDMAN Department of Statistics and Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305 E-mail: jhf@stanford.edu
1 SEPARATING SIGNAL FROM BACKGROUND USING ENSEMBLES OF RULES JEROME H. FRIEDMAN Department of Statistics and Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305 E-mail: jhf@stanford.edu
Some new ideas for post selection inference and model assessment
 Some new ideas for post selection inference and model assessment Robert Tibshirani, Stanford WHOA!! 2018 Thanks to Jon Taylor and Ryan Tibshirani for helpful feedback 1 / 23 Two topics 1. How to improve
Some new ideas for post selection inference and model assessment Robert Tibshirani, Stanford WHOA!! 2018 Thanks to Jon Taylor and Ryan Tibshirani for helpful feedback 1 / 23 Two topics 1. How to improve
Least Absolute Shrinkage is Equivalent to Quadratic Penalization
 Least Absolute Shrinkage is Equivalent to Quadratic Penalization Yves Grandvalet Heudiasyc, UMR CNRS 6599, Université de Technologie de Compiègne, BP 20.529, 60205 Compiègne Cedex, France Yves.Grandvalet@hds.utc.fr
Least Absolute Shrinkage is Equivalent to Quadratic Penalization Yves Grandvalet Heudiasyc, UMR CNRS 6599, Université de Technologie de Compiègne, BP 20.529, 60205 Compiègne Cedex, France Yves.Grandvalet@hds.utc.fr
Regularization in Cox Frailty Models
 Regularization in Cox Frailty Models Andreas Groll 1, Trevor Hastie 2, Gerhard Tutz 3 1 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität Munich, Department of Mathematics, Theresienstraße 39, 80333 Munich, Germany 2 University
Regularization in Cox Frailty Models Andreas Groll 1, Trevor Hastie 2, Gerhard Tutz 3 1 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität Munich, Department of Mathematics, Theresienstraße 39, 80333 Munich, Germany 2 University
Sparse regularization for functional logistic regression models
 Sparse regularization for functional logistic regression models Hidetoshi Matsui The Center for Data Science Education and Research, Shiga University 1-1-1 Banba, Hikone, Shiga, 5-85, Japan. hmatsui@biwako.shiga-u.ac.jp
Sparse regularization for functional logistic regression models Hidetoshi Matsui The Center for Data Science Education and Research, Shiga University 1-1-1 Banba, Hikone, Shiga, 5-85, Japan. hmatsui@biwako.shiga-u.ac.jp
Does Modeling Lead to More Accurate Classification?
 Does Modeling Lead to More Accurate Classification? A Comparison of the Efficiency of Classification Methods Yoonkyung Lee* Department of Statistics The Ohio State University *joint work with Rui Wang
Does Modeling Lead to More Accurate Classification? A Comparison of the Efficiency of Classification Methods Yoonkyung Lee* Department of Statistics The Ohio State University *joint work with Rui Wang
Lecture Notes 15 Prediction Chapters 13, 22, 20.4.
 Lecture Notes 15 Prediction Chapters 13, 22, 20.4. 1 Introduction Prediction is covered in detail in 36-707, 36-701, 36-715, 10/36-702. Here, we will just give an introduction. We observe training data
Lecture Notes 15 Prediction Chapters 13, 22, 20.4. 1 Introduction Prediction is covered in detail in 36-707, 36-701, 36-715, 10/36-702. Here, we will just give an introduction. We observe training data
Sparse regression. Optimization-Based Data Analysis. Carlos Fernandez-Granda
 Sparse regression Optimization-Based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_spring16 Carlos Fernandez-Granda 3/28/2016 Regression Least-squares regression Example: Global warming Logistic
Sparse regression Optimization-Based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_spring16 Carlos Fernandez-Granda 3/28/2016 Regression Least-squares regression Example: Global warming Logistic
Package covtest. R topics documented:
 Package covtest February 19, 2015 Title Computes covariance test for adaptive linear modelling Version 1.02 Depends lars,glmnet,glmpath (>= 0.97),MASS Author Richard Lockhart, Jon Taylor, Ryan Tibshirani,
Package covtest February 19, 2015 Title Computes covariance test for adaptive linear modelling Version 1.02 Depends lars,glmnet,glmpath (>= 0.97),MASS Author Richard Lockhart, Jon Taylor, Ryan Tibshirani,
STAT 535 Lecture 5 November, 2018 Brief overview of Model Selection and Regularization c Marina Meilă
 STAT 535 Lecture 5 November, 2018 Brief overview of Model Selection and Regularization c Marina Meilă mmp@stat.washington.edu Reading: Murphy: BIC, AIC 8.4.2 (pp 255), SRM 6.5 (pp 204) Hastie, Tibshirani
STAT 535 Lecture 5 November, 2018 Brief overview of Model Selection and Regularization c Marina Meilă mmp@stat.washington.edu Reading: Murphy: BIC, AIC 8.4.2 (pp 255), SRM 6.5 (pp 204) Hastie, Tibshirani
A Study of Relative Efficiency and Robustness of Classification Methods
 A Study of Relative Efficiency and Robustness of Classification Methods Yoonkyung Lee* Department of Statistics The Ohio State University *joint work with Rui Wang April 28, 2011 Department of Statistics
A Study of Relative Efficiency and Robustness of Classification Methods Yoonkyung Lee* Department of Statistics The Ohio State University *joint work with Rui Wang April 28, 2011 Department of Statistics
Accepted author version posted online: 28 Nov 2012.
 This article was downloaded by: [University of Minnesota Libraries, Twin Cities] On: 15 May 2013, At: 12:23 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954
This article was downloaded by: [University of Minnesota Libraries, Twin Cities] On: 15 May 2013, At: 12:23 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954
Classification using stochastic ensembles
 July 31, 2014 Topics Introduction Topics Classification Application and classfication Classification and Regression Trees Stochastic ensemble methods Our application: USAID Poverty Assessment Tools Topics
July 31, 2014 Topics Introduction Topics Classification Application and classfication Classification and Regression Trees Stochastic ensemble methods Our application: USAID Poverty Assessment Tools Topics
MSA200/TMS041 Multivariate Analysis
 MSA200/TMS041 Multivariate Analysis Lecture 8 Rebecka Jörnsten Mathematical Sciences University of Gothenburg and Chalmers University of Technology Back to Discriminant analysis As mentioned in the previous
MSA200/TMS041 Multivariate Analysis Lecture 8 Rebecka Jörnsten Mathematical Sciences University of Gothenburg and Chalmers University of Technology Back to Discriminant analysis As mentioned in the previous
Pre-Selection in Cluster Lasso Methods for Correlated Variable Selection in High-Dimensional Linear Models
 Pre-Selection in Cluster Lasso Methods for Correlated Variable Selection in High-Dimensional Linear Models Niharika Gauraha and Swapan Parui Indian Statistical Institute Abstract. We consider variable
Pre-Selection in Cluster Lasso Methods for Correlated Variable Selection in High-Dimensional Linear Models Niharika Gauraha and Swapan Parui Indian Statistical Institute Abstract. We consider variable
Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes. December 2, 2012
 Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 2, 2012 1 / 1 Neural networks Neural network Another classifier (or regression technique)
Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 2, 2012 1 / 1 Neural networks Neural network Another classifier (or regression technique)
Alternatives to Basis Expansions. Kernels in Density Estimation. Kernels and Bandwidth. Idea Behind Kernel Methods
 Alternatives to Basis Expansions Basis expansions require either choice of a discrete set of basis or choice of smoothing penalty and smoothing parameter Both of which impose prior beliefs on data. Alternatives
Alternatives to Basis Expansions Basis expansions require either choice of a discrete set of basis or choice of smoothing penalty and smoothing parameter Both of which impose prior beliefs on data. Alternatives
Statistical Consulting Topics Classification and Regression Trees (CART)
 Statistical Consulting Topics Classification and Regression Trees (CART) Suppose the main goal in a data analysis is the prediction of a categorical variable outcome. Such as in the examples below. Given
Statistical Consulting Topics Classification and Regression Trees (CART) Suppose the main goal in a data analysis is the prediction of a categorical variable outcome. Such as in the examples below. Given
A Robust Approach to Regularized Discriminant Analysis
 A Robust Approach to Regularized Discriminant Analysis Moritz Gschwandtner Department of Statistics and Probability Theory Vienna University of Technology, Austria Österreichische Statistiktage, Graz,
A Robust Approach to Regularized Discriminant Analysis Moritz Gschwandtner Department of Statistics and Probability Theory Vienna University of Technology, Austria Österreichische Statistiktage, Graz,
A Bias Correction for the Minimum Error Rate in Cross-validation
 A Bias Correction for the Minimum Error Rate in Cross-validation Ryan J. Tibshirani Robert Tibshirani Abstract Tuning parameters in supervised learning problems are often estimated by cross-validation.
A Bias Correction for the Minimum Error Rate in Cross-validation Ryan J. Tibshirani Robert Tibshirani Abstract Tuning parameters in supervised learning problems are often estimated by cross-validation.
Sparse statistical modelling
 Sparse statistical modelling Tom Bartlett Sparse statistical modelling Tom Bartlett 1 / 28 Introduction A sparse statistical model is one having only a small number of nonzero parameters or weights. [1]
Sparse statistical modelling Tom Bartlett Sparse statistical modelling Tom Bartlett 1 / 28 Introduction A sparse statistical model is one having only a small number of nonzero parameters or weights. [1]
LASSO Review, Fused LASSO, Parallel LASSO Solvers
 Case Study 3: fmri Prediction LASSO Review, Fused LASSO, Parallel LASSO Solvers Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade May 3, 2016 Sham Kakade 2016 1 Variable
Case Study 3: fmri Prediction LASSO Review, Fused LASSO, Parallel LASSO Solvers Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade May 3, 2016 Sham Kakade 2016 1 Variable
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Thomas G. Dietterich tgd@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Outline What is Machine Learning? Introduction to Supervised Learning: Linear Methods Overfitting, Regularization, and the
Introduction to Machine Learning Thomas G. Dietterich tgd@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Outline What is Machine Learning? Introduction to Supervised Learning: Linear Methods Overfitting, Regularization, and the
A simulation study of model fitting to high dimensional data using penalized logistic regression
 A simulation study of model fitting to high dimensional data using penalized logistic regression Ellinor Krona Kandidatuppsats i matematisk statistik Bachelor Thesis in Mathematical Statistics Kandidatuppsats
A simulation study of model fitting to high dimensional data using penalized logistic regression Ellinor Krona Kandidatuppsats i matematisk statistik Bachelor Thesis in Mathematical Statistics Kandidatuppsats
Functional Data Analysis & Variable Selection
 Auburn University Department of Mathematics and Statistics Universidad Nacional de Colombia Medellin, Colombia March 14, 2016 Functional Data Analysis Data Types Univariate - Contains numbers as its observations
Auburn University Department of Mathematics and Statistics Universidad Nacional de Colombia Medellin, Colombia March 14, 2016 Functional Data Analysis Data Types Univariate - Contains numbers as its observations
An Introduction to Graphical Lasso
 An Introduction to Graphical Lasso Bo Chang Graphical Models Reading Group May 15, 2015 Bo Chang (UBC) Graphical Lasso May 15, 2015 1 / 16 Undirected Graphical Models An undirected graph, each vertex represents
An Introduction to Graphical Lasso Bo Chang Graphical Models Reading Group May 15, 2015 Bo Chang (UBC) Graphical Lasso May 15, 2015 1 / 16 Undirected Graphical Models An undirected graph, each vertex represents
MS&E 226: Small Data
 MS&E 226: Small Data Lecture 9: Logistic regression (v2) Ramesh Johari ramesh.johari@stanford.edu 1 / 28 Regression methods for binary outcomes 2 / 28 Binary outcomes For the duration of this lecture suppose
MS&E 226: Small Data Lecture 9: Logistic regression (v2) Ramesh Johari ramesh.johari@stanford.edu 1 / 28 Regression methods for binary outcomes 2 / 28 Binary outcomes For the duration of this lecture suppose
Bi-level feature selection with applications to genetic association
 Bi-level feature selection with applications to genetic association studies October 15, 2008 Motivation In many applications, biological features possess a grouping structure Categorical variables may
Bi-level feature selection with applications to genetic association studies October 15, 2008 Motivation In many applications, biological features possess a grouping structure Categorical variables may
Lecture 14: Shrinkage
 Lecture 14: Shrinkage Reading: Section 6.2 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis October 27, 2017 1 / 19 Shrinkage methods The idea is to perform a linear regression, while regularizing or shrinking the
Lecture 14: Shrinkage Reading: Section 6.2 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis October 27, 2017 1 / 19 Shrinkage methods The idea is to perform a linear regression, while regularizing or shrinking the
arxiv: v3 [stat.ml] 14 Apr 2016
![arxiv: v3 [stat.ml] 14 Apr 2016 arxiv: v3 [stat.ml] 14 Apr 2016](/thumbs/72/67703342.jpg) arxiv:1307.0048v3 [stat.ml] 14 Apr 2016 Simple one-pass algorithm for penalized linear regression with cross-validation on MapReduce Kun Yang April 15, 2016 Abstract In this paper, we propose a one-pass
arxiv:1307.0048v3 [stat.ml] 14 Apr 2016 Simple one-pass algorithm for penalized linear regression with cross-validation on MapReduce Kun Yang April 15, 2016 Abstract In this paper, we propose a one-pass
Part I Week 7 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes
 Part I Week 7 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting December 2, 2012 1 / 1 2 / 1 Neural networks Artificial Neural networks: Networks
Part I Week 7 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting December 2, 2012 1 / 1 2 / 1 Neural networks Artificial Neural networks: Networks
Coordinate descent. Geoff Gordon & Ryan Tibshirani Optimization /
 Coordinate descent Geoff Gordon & Ryan Tibshirani Optimization 10-725 / 36-725 1 Adding to the toolbox, with stats and ML in mind We ve seen several general and useful minimization tools First-order methods
Coordinate descent Geoff Gordon & Ryan Tibshirani Optimization 10-725 / 36-725 1 Adding to the toolbox, with stats and ML in mind We ve seen several general and useful minimization tools First-order methods
Proximal Newton Method. Zico Kolter (notes by Ryan Tibshirani) Convex Optimization
 Proximal Newton Method Zico Kolter (notes by Ryan Tibshirani) Convex Optimization 10-725 Consider the problem Last time: quasi-newton methods min x f(x) with f convex, twice differentiable, dom(f) = R
Proximal Newton Method Zico Kolter (notes by Ryan Tibshirani) Convex Optimization 10-725 Consider the problem Last time: quasi-newton methods min x f(x) with f convex, twice differentiable, dom(f) = R
Saharon Rosset 1 and Ji Zhu 2
 Aust. N. Z. J. Stat. 46(3), 2004, 505 510 CORRECTED PROOF OF THE RESULT OF A PREDICTION ERROR PROPERTY OF THE LASSO ESTIMATOR AND ITS GENERALIZATION BY HUANG (2003) Saharon Rosset 1 and Ji Zhu 2 IBM T.J.
Aust. N. Z. J. Stat. 46(3), 2004, 505 510 CORRECTED PROOF OF THE RESULT OF A PREDICTION ERROR PROPERTY OF THE LASSO ESTIMATOR AND ITS GENERALIZATION BY HUANG (2003) Saharon Rosset 1 and Ji Zhu 2 IBM T.J.
MS&E 226: Small Data
 MS&E 226: Small Data Lecture 12: Logistic regression (v1) Ramesh Johari ramesh.johari@stanford.edu Fall 2015 1 / 30 Regression methods for binary outcomes 2 / 30 Binary outcomes For the duration of this
MS&E 226: Small Data Lecture 12: Logistic regression (v1) Ramesh Johari ramesh.johari@stanford.edu Fall 2015 1 / 30 Regression methods for binary outcomes 2 / 30 Binary outcomes For the duration of this
Sparse inverse covariance estimation with the lasso
 Sparse inverse covariance estimation with the lasso Jerome Friedman Trevor Hastie and Robert Tibshirani November 8, 2007 Abstract We consider the problem of estimating sparse graphs by a lasso penalty
Sparse inverse covariance estimation with the lasso Jerome Friedman Trevor Hastie and Robert Tibshirani November 8, 2007 Abstract We consider the problem of estimating sparse graphs by a lasso penalty
Categorical Predictor Variables
 Categorical Predictor Variables We often wish to use categorical (or qualitative) variables as covariates in a regression model. For binary variables (taking on only 2 values, e.g. sex), it is relatively
Categorical Predictor Variables We often wish to use categorical (or qualitative) variables as covariates in a regression model. For binary variables (taking on only 2 values, e.g. sex), it is relatively
Administration. Homework 1 on web page, due Feb 11 NSERC summer undergraduate award applications due Feb 5 Some helpful books
 STA 44/04 Jan 6, 00 / 5 Administration Homework on web page, due Feb NSERC summer undergraduate award applications due Feb 5 Some helpful books STA 44/04 Jan 6, 00... administration / 5 STA 44/04 Jan 6,
STA 44/04 Jan 6, 00 / 5 Administration Homework on web page, due Feb NSERC summer undergraduate award applications due Feb 5 Some helpful books STA 44/04 Jan 6, 00... administration / 5 STA 44/04 Jan 6,
A Modern Look at Classical Multivariate Techniques
 A Modern Look at Classical Multivariate Techniques Yoonkyung Lee Department of Statistics The Ohio State University March 16-20, 2015 The 13th School of Probability and Statistics CIMAT, Guanajuato, Mexico
A Modern Look at Classical Multivariate Techniques Yoonkyung Lee Department of Statistics The Ohio State University March 16-20, 2015 The 13th School of Probability and Statistics CIMAT, Guanajuato, Mexico
Chapter 3. Linear Models for Regression
 Chapter 3. Linear Models for Regression Wei Pan Division of Biostatistics, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455 Email: weip@biostat.umn.edu PubH 7475/8475 c Wei Pan Linear
Chapter 3. Linear Models for Regression Wei Pan Division of Biostatistics, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455 Email: weip@biostat.umn.edu PubH 7475/8475 c Wei Pan Linear
Lecture 17: October 27
 0-725/36-725: Convex Optimiation Fall 205 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Lecture 7: October 27 Scribes: Brandon Amos, Gines Hidalgo Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These
0-725/36-725: Convex Optimiation Fall 205 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Lecture 7: October 27 Scribes: Brandon Amos, Gines Hidalgo Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These
Importance Sampling: An Alternative View of Ensemble Learning. Jerome H. Friedman Bogdan Popescu Stanford University
 Importance Sampling: An Alternative View of Ensemble Learning Jerome H. Friedman Bogdan Popescu Stanford University 1 PREDICTIVE LEARNING Given data: {z i } N 1 = {y i, x i } N 1 q(z) y = output or response
Importance Sampling: An Alternative View of Ensemble Learning Jerome H. Friedman Bogdan Popescu Stanford University 1 PREDICTIVE LEARNING Given data: {z i } N 1 = {y i, x i } N 1 q(z) y = output or response
Statistical Inference
 Statistical Inference Liu Yang Florida State University October 27, 2016 Liu Yang, Libo Wang (Florida State University) Statistical Inference October 27, 2016 1 / 27 Outline The Bayesian Lasso Trevor Park
Statistical Inference Liu Yang Florida State University October 27, 2016 Liu Yang, Libo Wang (Florida State University) Statistical Inference October 27, 2016 1 / 27 Outline The Bayesian Lasso Trevor Park
Lecture 25: November 27
 10-725: Optimization Fall 2012 Lecture 25: November 27 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Scribes: Matt Wytock, Supreeth Achar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have
10-725: Optimization Fall 2012 Lecture 25: November 27 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Scribes: Matt Wytock, Supreeth Achar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have
The lasso: some novel algorithms and applications
 1 The lasso: some novel algorithms and applications Robert Tibshirani Stanford University ASA Bay Area chapter meeting Collaborations with Trevor Hastie, Jerome Friedman, Ryan Tibshirani, Daniela Witten,
1 The lasso: some novel algorithms and applications Robert Tibshirani Stanford University ASA Bay Area chapter meeting Collaborations with Trevor Hastie, Jerome Friedman, Ryan Tibshirani, Daniela Witten,
Independent Factor Discriminant Analysis
 Independent Factor Discriminant Analysis Angela Montanari, Daniela Giovanna Caló, and Cinzia Viroli Statistics Department University of Bologna, via Belle Arti 41, 40126, Bologna, Italy (e-mail: montanari@stat.unibo.it,
Independent Factor Discriminant Analysis Angela Montanari, Daniela Giovanna Caló, and Cinzia Viroli Statistics Department University of Bologna, via Belle Arti 41, 40126, Bologna, Italy (e-mail: montanari@stat.unibo.it,
Uncertainty quantification and visualization for functional random variables
 Uncertainty quantification and visualization for functional random variables MascotNum Workshop 2014 S. Nanty 1,3 C. Helbert 2 A. Marrel 1 N. Pérot 1 C. Prieur 3 1 CEA, DEN/DER/SESI/LSMR, F-13108, Saint-Paul-lez-Durance,
Uncertainty quantification and visualization for functional random variables MascotNum Workshop 2014 S. Nanty 1,3 C. Helbert 2 A. Marrel 1 N. Pérot 1 C. Prieur 3 1 CEA, DEN/DER/SESI/LSMR, F-13108, Saint-Paul-lez-Durance,
STA 450/4000 S: January
 STA 450/4000 S: January 6 005 Notes Friday tutorial on R programming reminder office hours on - F; -4 R The book Modern Applied Statistics with S by Venables and Ripley is very useful. Make sure you have
STA 450/4000 S: January 6 005 Notes Friday tutorial on R programming reminder office hours on - F; -4 R The book Modern Applied Statistics with S by Venables and Ripley is very useful. Make sure you have
Extensions to LDA and multinomial regression
 Extensions to LDA and multinomial regression Patrick Breheny September 22 Patrick Breheny BST 764: Applied Statistical Modeling 1/20 Introduction Quadratic discriminant analysis Fitting models Linear discriminant
Extensions to LDA and multinomial regression Patrick Breheny September 22 Patrick Breheny BST 764: Applied Statistical Modeling 1/20 Introduction Quadratic discriminant analysis Fitting models Linear discriminant
Lecture 10: Logistic Regression
 BIOINF 585: Machine Learning for Systems Biology & Clinical Informatics Lecture 10: Logistic Regression Jie Wang Department of Computational Medicine & Bioinformatics University of Michigan 1 Outline An
BIOINF 585: Machine Learning for Systems Biology & Clinical Informatics Lecture 10: Logistic Regression Jie Wang Department of Computational Medicine & Bioinformatics University of Michigan 1 Outline An
