BUSINESS MATHEMATICS XII - STANDARD MODEL QUESTION PAPER
|
|
|
- Basil Hancock
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BUSINESS MATHEMATICS XII - STANDARD MODEL QUESTION PAPER (ENGLISH VERSION) Time Allowed : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 00 Section - A Section A N.B. : (i) Answer all the 40 questions (ii) Each question carries one mark (iii) Choose and write the correct answer from the four choices given. 40 x ) The Adjoint of 0 is (a) 0 (b) - 0 (c) 0 1 (d) 0 ) If AB = BA = A I then the matrix B is (a) the inverse of A (b) the transpose of A (c) the Adjoint of A (d) A 3 1 3) If A = then A -1 A is 3 7 (a) 0 (b) A (c) I (d) A. 4) The rank of a non singular matrix of order n x n is (a) n (b) n (c) 0 (d) 1 a b 5) The relation R = a 0 1 is b 1 0 (a) Reflexive (b) Symmetric (c) Transititve (d) Reflexive and symmetric 6) Equation of the directrix of x = 4ay is (a) x + a = 0 (b) x - a = 0 (c) y + a = 0 (d) y - a = 0 7) The semi major and semi minor axes of x + y = 1 is 16 5 (a) (4, 5) (b) (8, 10) (c) (5, 4) (d) (10, 8) 8) The sum of focal distances of any point on the ellipse is equal to length of its (a) minor axis (b) semi minor axis (c) major axis (d) semi major axis 9) Eccentricity of the rectangular hyperbola is (a) (b) 1/ (c) (d) 1
2 10) For the cost function c = 10 e x, the marginal cost is (a) 10 (b) 15 e x (c) e 10 x (d) e 10 x 11) Given the demand equation p = -x + 10 ; (0 < x < 10) where p denotes the unit selling price and x denotes the number of units demanded of some product. Then the marginal revenue at x = 3 units is (a) Rs. 5 (b) Rs. 10 (c) Rs. 4 (d) Rs. 30 1) If the rate of change of y with respect to x is 6 and x is changing at 4 units/sec, then the rate of change of y per sec is (a) 4 units/sec (b) 10 units/sec (c) units/sec (d) units/sec 13) The slope of the tangent at (, 8) on the curve y = x 3 is (a) 3 (b) 1 (c) 6 (d) 8 14) The slope of the curve x = y - 6y at the point where it crosses the y axis is (a) 5 (b) -5 (c) (d) ) y = x 3 is always (a) An increasing function of x (b) Decreasing function of x (c) A constant function (d) None of these 16) If u = e x +y, then u is equal to x (a) y u (b) x u (c) xu (d) yu 17. If u = x y (x > 0) then u is equal to y a. x y log x b) log x c) y x log x d) log y x 18. The cost function y = 40-4x + x is minimum when a) x = b) x = - c) x = 4 d) x = -4 a -a 19. If f(x) is an odd function then f (x)dx is a) 1 b) a c) 0 d) a 0. The area bounded by the curve y = e x, the x - axis and the lines x = 0 and x = is a) e -1 b) e 7 +1 c) e d) e - 1. If the marginal cost function MC = - 4x, then the cost function is a) x-x +k b) -4x c) - 4 d) x-4x x 3. The order and degree of dy d 1+ y are dx = dx a) 3 and b) and 3 c) 3 and 3 d) and
3 3. The solutioin of x dy + y dx = 0 is a) x+y = c b) x +y = c c) xy = c d) y = cx dy 4. The integrating factor of + y = x 3 dx x a) log x b) e x c) 3 log (x ) d) x 5. The solutioin of d y - y = 0 is dx 6. E = a) (A + B)e x b) (Ax + B)e -x c) Ae x + B d) (A + Bx) e x a) 1 + b) 1 - c) + ) When h = 1 (x ) = a) x b) x-1 c) x+) 1 8. If a discrete random variable has the probability mass function is x then the value of k is p(x) k k 3k 5k a) 1 b) c) 3 d 4) The mean and variance of a binomial distribution are a) np, npq b) pq, npq c) np, npq d) np, nq 30) If X is a poission variate with P (X = 1) = P (X = ), the mean of the Poission variate is equal to (a) 1 (b) (c) - (d) 3 31) The normal distribution curve is (a) Bimodal (b) Unimodal (c) Skewed (d) none of these 3) The standard error of the sample mean is (a) Type I error (b) Type II error (c) Standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the mean (d) Variance of the sampling distribution of the mean 33) If a random sample of size 64 is taken from a population whose standard deviation is equal to 3, then the standard error of the mean is (a) 0.5 (b) (c) 4 (d) 3 e x 3
4 34) Probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true is (a) Type I error (b) Type II error (c) Sampling error (d) Standard error 35) The Z-value that is used to establish a 95% confidence interval for the estimation of a population parameter is (a) 1.8 (b) 1.65 (c)1.96 (d).58 36) A time series consists of (a) two components (b) three components (c) four components (d) none of these 37) Laspeyre s index formula uses the weights of the (a) base year quantities (b) current year quantities (c) average of the weights of number of years (d) none of these 38) Variation due to assignable causes in the product occur due to (a) faulty process (c) poor quality of raw material (b) carelessness of operators (d) all the above 39) Control charts in statistical quality consist of (a) three control lines (c) the level of process (b) upper and lower control limits (d) all the above 40) The range of correlation co-efficient is (a) 0 to (c) -1 to 1 (b) - 10 (d) none of these N.B. : Section - B (i) Answer any 10 questions out of 15 questions given (ii) Each question carries six marks 10 x 6 = Find the inverse of A = , if it exists Find the rank of the matrix Find the equation of the hyperbola whose eccentricity is 3, focus is (1, ) and the corresponding directrix is x + y = 1. 4
5 44. If y = 1 - x find Ey Obtain the values of η when x = 0 and x =. + 3x Ex x For the cost function y = 3x x , prove that the marginal cost falls continuously as the output x increases u u 46. If u = log x + y, show that + = 1 s x x x + y 47. The elasticity of demand with respect to price for a commodity is a constant and is equal to. Find the demand function and hence the total revenue function, given that when the price is 1, the demand is 4. dy 48. Solve dx + y cos x = sin x d 49. Solve y dy +4 +4y = 5 + e dx -x dx 50. Find the missing term from the following data. x : f(x) : Apply Lagrange s formula to find y when x = 5 given that x : y : A continuous random variable has the following p.d.f. f(x) = kx, 0<x<10 = 0 otherwise. Determine k- and evaluate (i) P (0. < x < 0.5) (ii) P(x < 3) 53. A random sample of marks in mathematics secured by 50 students out of 00 students showed a mean of 75 and a standard deviation of 10. Find the 95% confidence limits for the estimate of their mean marks. 54. Calculate the correlation co-efficient from the following data. x : y : Obtain the trend values by the method of Semi-Average Year Netprofit (Rs lakhs) 5
6 Section - C N.B. i) Answer any Ten Question out of 15 questions given ii) Each question carries 10 marks 56. Given a directed route G; 10 x 10 = 100 v 1 vv vv v vv3 Find the route matrix of G and using its powers, find whether G is strongly connected. 57. Suppose the inter-relationship between the production of two industries P and Q in a year (in lakhs of rupees) is User Producer Final Demand Total Output P Q P Q Find the outputs when the final demand changes to 1 for P and 18 for Q 58. Find the equation to the hyperbola which has the lines x + 4y - 5 = 0 and x - 3y + 1 = 0 for its asymptotes and which passes through the point (1, ). 59. Find the points on the curve y = (x-1) (x-) at which the tangent makes an angle 135 o with the positive direction of the x - axis. 60. Find EOQ for the data given below. Also verify that carrying costs is equal to ordering costs at EOQ. Item Monthly Ordering cost Carrying cost Requirements per order Per unit A 9000 Rs. 00 Rs The demand for a commodity X is q 1 = 15 - p - 3p Find the partial elasticities when 1 p 1 =3 and p = Evaluate π 3 π 6 dx 1 + tanx 6
7 63. The demand and supply functions under pure competition are p d = 16 - x and P s = x + 4. Find the consumers surplus and producers surplus at the market equilibrium price. 64. Suppose that the quantity demanded Q d = 4-4p - 4 dp + d p and quantity supplied dt dt Q s = p where p is the price. Find the equilibrium price for market clearance. 65. Fit a straight line to the following data: x : y : Find the mean and variance for the following probability distribution. f(x) = e-x, x >0 0, x <0 67. The diameter of shafts produced in a factory conforms to normal distribution. 31% of the shafts have a diameter less than 45mm. and 8% have more than 64mm. Find the mean and standard deviation of the diameter of shafts. Given: Z Area To test conjecture of the management that 60 percent employees favour a new bonus scheme, a sample of 150 employees was drawn and their opinioin was taken whether they favoured it or not. Only 55 employees out of 150 favoured the new bonus scheme. Test the conjecture at 1% level of significance. 69. Calculate Fisher s Ideal Index from the following data and show how it satisfies time reversal test and factor reversal test. Commodity Base year Current year (1997) (1998) Price Quantity Price Quantity A B C D E F
8 70. From the following data construct X and R chart and write your conclusion Sample no Sample no (Given for n = 3, A = 1.0, D 3 = 0, D 4 =.58) ******* 8
12 STD BUSINESS MATHEMATICS
 STD BUSINESS MATHEMATICS www.kalvisolai.com 0 MARK FAQ S: CHAPTER :. APPLICATION OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS. If A verify that AAdjA AdjA A AI. (M 0). Show that the equations y + z = 7, + y 5z =, + y
STD BUSINESS MATHEMATICS www.kalvisolai.com 0 MARK FAQ S: CHAPTER :. APPLICATION OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS. If A verify that AAdjA AdjA A AI. (M 0). Show that the equations y + z = 7, + y 5z =, + y
12 STD BUSINESS MATHEMATICS
 STD BUSINESS MATHEMATICS 6 MARK FAQ S: CHAPTER :. APPLICATION OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS. Given, A verify that A AdjA (J 7; O 7 ; O ). Find the inverse of, b a A and verify that I AA. (J 6). Verify A
STD BUSINESS MATHEMATICS 6 MARK FAQ S: CHAPTER :. APPLICATION OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS. Given, A verify that A AdjA (J 7; O 7 ; O ). Find the inverse of, b a A and verify that I AA. (J 6). Verify A
SLOW LEARNERS MATERIALS BUSINESS MATHEMATICS SIX MARKS QUESTIONS
 SLOW LEARNERS MATERIALS BUSINESS MATHEMATICS SIX MARKS QUESTIONS 1. Form the differential equation of the family of curves = + where a and b are parameters. 2. Find the differential equation by eliminating
SLOW LEARNERS MATERIALS BUSINESS MATHEMATICS SIX MARKS QUESTIONS 1. Form the differential equation of the family of curves = + where a and b are parameters. 2. Find the differential equation by eliminating
MATHEMATICS Code No. 13 INSTRUCTIONS
 DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO COMBINED COMPETITIVE (PRELIMINARY) EXAMINATION, 00 Serial No. MATHEMATICS Code No. A Time Allowed : Two Hours Maximum Marks : 00 INSTRUCTIONS.
DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO COMBINED COMPETITIVE (PRELIMINARY) EXAMINATION, 00 Serial No. MATHEMATICS Code No. A Time Allowed : Two Hours Maximum Marks : 00 INSTRUCTIONS.
Conic Sections. Geometry - Conics ~1~ NJCTL.org. Write the following equations in standard form.
 Conic Sections Midpoint and Distance Formula M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Conic Sections Midpoint and Distance Formula M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Quadratic function and equations Quadratic function/equations, supply, demand, market equilibrium
 Exercises 8 Quadratic function and equations Quadratic function/equations, supply, demand, market equilibrium Objectives - know and understand the relation between a quadratic function and a quadratic
Exercises 8 Quadratic function and equations Quadratic function/equations, supply, demand, market equilibrium Objectives - know and understand the relation between a quadratic function and a quadratic
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HOTEL MANAGEMENT, KOLKATA BUSINESS MATHEMATICS 3 rd Semester
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HOTEL MANAGEMENT, KOLKATA BUSINESS MATHEMATICS 3 rd Semester Choose (tick) the appropriate from the following options given below. 1. Find the number of subsets of a set {x : x is
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HOTEL MANAGEMENT, KOLKATA BUSINESS MATHEMATICS 3 rd Semester Choose (tick) the appropriate from the following options given below. 1. Find the number of subsets of a set {x : x is
1 Functions and Graphs
 1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions Cartesian Coordinate System A Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system is formed by the intersection of a horizontal real number line, usually called the x axis,
1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions Cartesian Coordinate System A Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system is formed by the intersection of a horizontal real number line, usually called the x axis,
Mathematics 2 for Business Schools Topic 7: Application of Integration to Economics. Building Competence. Crossing Borders.
 Mathematics 2 for Business Schools Topic 7: Application of Integration to Economics Building Competence. Crossing Borders. Spring Semester 2017 Learning objectives After finishing this section you should
Mathematics 2 for Business Schools Topic 7: Application of Integration to Economics Building Competence. Crossing Borders. Spring Semester 2017 Learning objectives After finishing this section you should
y mx 25m 25 4 circle. Then the perpendicular distance of tangent from the centre (0, 0) is the radius. Since tangent
 Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
QUESTION BANK ON. CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola)
 QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
MATHEMATICS. SECTION A (80 Marks) Find the number of ways in which 6 men and 5 women can dine at a round table if no two women are to sit together.
 MATHEMATICS (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MATHEMATICS (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
UNIVERSITY OF KWA-ZULU NATAL
 UNIVERSITY OF KWA-ZULU NATAL EXAMINATIONS: June 006 Solutions Subject, course and code: Mathematics 34 MATH34P Multiple Choice Answers. B. B 3. E 4. E 5. C 6. A 7. A 8. C 9. A 0. D. C. A 3. D 4. E 5. B
UNIVERSITY OF KWA-ZULU NATAL EXAMINATIONS: June 006 Solutions Subject, course and code: Mathematics 34 MATH34P Multiple Choice Answers. B. B 3. E 4. E 5. C 6. A 7. A 8. C 9. A 0. D. C. A 3. D 4. E 5. B
MAT1300 Final Review. Pieter Hofstra. December 4, 2009
 December 4, 2009 Sections from the book to study (8th Edition) Chapter 0: 0.1: Real line and Order 0.2: Absolute Value and Distance 0.3: Exponents and Radicals 0.4: Factoring Polynomials (you may omit
December 4, 2009 Sections from the book to study (8th Edition) Chapter 0: 0.1: Real line and Order 0.2: Absolute Value and Distance 0.3: Exponents and Radicals 0.4: Factoring Polynomials (you may omit
STATE COUNCIL OF EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH AND TRAINING TNCF DRAFT SYLLABUS
 STATE COUNCIL OF EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH AND TRAINING TNCF 2017 - DRAFT SYLLABUS Subject :Business Maths Class : XI Unit 1 : TOPIC Matrices and Determinants CONTENT Determinants - Minors; Cofactors; Evaluation
STATE COUNCIL OF EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH AND TRAINING TNCF 2017 - DRAFT SYLLABUS Subject :Business Maths Class : XI Unit 1 : TOPIC Matrices and Determinants CONTENT Determinants - Minors; Cofactors; Evaluation
3. A( 2,0) and B(6, -2), find M 4. A( 3, 7) and M(4,-3), find B. 5. M(4, -9) and B( -10, 11) find A 6. B(4, 8) and M(-2, 5), find A
 Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time is
 . If P(A) = x, P = 2x, P(A B) = 2, P ( A B) = 2 3, then the value of x is (A) 5 8 5 36 6 36 36 2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time
. If P(A) = x, P = 2x, P(A B) = 2, P ( A B) = 2 3, then the value of x is (A) 5 8 5 36 6 36 36 2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time
TARGET QUARTERLY MATHS MATERIAL
 Adyar Adambakkam Pallavaram Pammal Chromepet Now also at SELAIYUR TARGET QUARTERLY MATHS MATERIAL Achievement through HARDWORK Improvement through INNOVATION Target Centum Practising Package +2 GENERAL
Adyar Adambakkam Pallavaram Pammal Chromepet Now also at SELAIYUR TARGET QUARTERLY MATHS MATERIAL Achievement through HARDWORK Improvement through INNOVATION Target Centum Practising Package +2 GENERAL
Exam 4 SCORE. MA 114 Exam 4 Spring Section and/or TA:
 Exam 4 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may
Exam 4 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may
Chapter 4 Differentiation
 Chapter 4 Differentiation 08 Section 4. The derivative of a function Practice Problems (a) (b) (c) 3 8 3 ( ) 4 3 5 4 ( ) 5 3 3 0 0 49 ( ) 50 Using a calculator, the values of the cube function, correct
Chapter 4 Differentiation 08 Section 4. The derivative of a function Practice Problems (a) (b) (c) 3 8 3 ( ) 4 3 5 4 ( ) 5 3 3 0 0 49 ( ) 50 Using a calculator, the values of the cube function, correct
 Way to Success ⓬ MATHS PUBLIC EXAM SPECIAL GUIDE Prepared by Mr. K. Dinesh M.Sc., M.Phil., P.G.D.C.A., Ph.D., ------For subject related clarifications------ Mail us: dinesh.skksv9@gmail.com & ways00@gmail.com
Way to Success ⓬ MATHS PUBLIC EXAM SPECIAL GUIDE Prepared by Mr. K. Dinesh M.Sc., M.Phil., P.G.D.C.A., Ph.D., ------For subject related clarifications------ Mail us: dinesh.skksv9@gmail.com & ways00@gmail.com
MockTime.com. (b) 9/2 (c) 18 (d) 27
 212 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. Let X be any non-empty set containing n elements. Then what is the number of relations on X? 2 n 2 2n 2 2n n 2 2. Only 1 2 and 3 1 and 2 1 and 3 3. Consider the following
212 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. Let X be any non-empty set containing n elements. Then what is the number of relations on X? 2 n 2 2n 2 2n n 2 2. Only 1 2 and 3 1 and 2 1 and 3 3. Consider the following
Given the table of values, determine the equation
 3.1 Properties of Quadratic Functions Recall: Standard Form f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c Factored Form f(x) = a(x r)(x s) Vertex Form f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k Given the table of values, determine the equation x y 1
3.1 Properties of Quadratic Functions Recall: Standard Form f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c Factored Form f(x) = a(x r)(x s) Vertex Form f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k Given the table of values, determine the equation x y 1
Section 11.3 Rates of Change:
 Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7)
 Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Conic section. Ans: c. Ans: a. Ans: c. Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ. 1. A circle
 Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ Conic section 1. A circle gx fy c 0 is said to be imaginary circle if a) g + f = c b) g + f > c c) g + f < c d) g = f. If (1,-3) is the centre of the circle x y ax
Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ Conic section 1. A circle gx fy c 0 is said to be imaginary circle if a) g + f = c b) g + f > c c) g + f < c d) g = f. If (1,-3) is the centre of the circle x y ax
Centres at Pallavaram Opp. St. therasa s School Pammal Krishna Nagar Adyar Kasturiba Nagar Chrompet - Opp. MIT Selaiyur Near Camp Road Junction
 Adyar Adambakkam Pallavaram Pammal Chromepet Now also at SELAIYUR Day - wise Portions Day 1 : Day 2 : Day 3 : Matrices and Determinants, Complex Numbers and Vector Algebra Analytical Geometry, Discrete
Adyar Adambakkam Pallavaram Pammal Chromepet Now also at SELAIYUR Day - wise Portions Day 1 : Day 2 : Day 3 : Matrices and Determinants, Complex Numbers and Vector Algebra Analytical Geometry, Discrete
3. A( 2,0) and B(6, -2), find M 4. A( 3, 7) and M(4,-3), find B. 5. M(4, -9) and B( -10, 11) find A 6. B(4, 8) and M(-2, 5), find A
 Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M (3. 5, 3) (1.
Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M (3. 5, 3) (1.
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review
 Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review Dr. Garey Fox Professor and Buchanan Endowed Chair Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering October 16, 2014 Reference Material from FE Review Instructor
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review Dr. Garey Fox Professor and Buchanan Endowed Chair Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering October 16, 2014 Reference Material from FE Review Instructor
Circles. Example 2: Write an equation for a circle if the enpoints of a diameter are at ( 4,5) and (6, 3).
 Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
Math 110 Final Exam General Review. Edward Yu
 Math 110 Final Exam General Review Edward Yu Da Game Plan Solving Limits Regular limits Indeterminate Form Approach Infinities One sided limits/discontinuity Derivatives Power Rule Product/Quotient Rule
Math 110 Final Exam General Review Edward Yu Da Game Plan Solving Limits Regular limits Indeterminate Form Approach Infinities One sided limits/discontinuity Derivatives Power Rule Product/Quotient Rule
ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS FOR ECONOMICS
 ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS FOR ECONOMICS Catering the need of Second year B.A./B.Sc. Students of Economics (Major) Third Semester of Guwahati and other Indian Universities. 2nd Semester R.C. Joshi M.A., M.Phil.
ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS FOR ECONOMICS Catering the need of Second year B.A./B.Sc. Students of Economics (Major) Third Semester of Guwahati and other Indian Universities. 2nd Semester R.C. Joshi M.A., M.Phil.
MATHEMATICS & STATISTICS TOPIC : CORRELATION DURATION 3 HR MARKS 80. Q1. (A) Attempt ANY SIX OF THE FOLLOWING (12) dy = 18x x log7 dx 2 x x
 MATHEMATICS & STATISTICS MATRICES + FYJC FINAL EXAM 02 TOPIC : CORRELATION DURATION 3 HR MARKS 80 Q1. (A) Attempt ANY SIX OF THE FOLLOWING (12) 01. Differentiate the following function with respect to
MATHEMATICS & STATISTICS MATRICES + FYJC FINAL EXAM 02 TOPIC : CORRELATION DURATION 3 HR MARKS 80 Q1. (A) Attempt ANY SIX OF THE FOLLOWING (12) 01. Differentiate the following function with respect to
Section 11.7 The Chain Rule
 Section.7 The Chain Rule Composition of Functions There is another way of combining two functions to obtain a new function. For example, suppose that y = fu) = u and u = gx) = x 2 +. Since y is a function
Section.7 The Chain Rule Composition of Functions There is another way of combining two functions to obtain a new function. For example, suppose that y = fu) = u and u = gx) = x 2 +. Since y is a function
Multiple Choice Answers. MA 113 Calculus I Spring 2018 Exam 2 Tuesday, 6 March Question
 MA 113 Calculus I Spring 2018 Exam 2 Tuesday, 6 March 2018 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: This exam has 12 multiple choice questions (five points each) and 4 free response questions (ten
MA 113 Calculus I Spring 2018 Exam 2 Tuesday, 6 March 2018 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: This exam has 12 multiple choice questions (five points each) and 4 free response questions (ten
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION
 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION DEFINITION: If S is a sample space with a probability measure and x is a real valued function defined over the elements of S, then x is called a random variable. Types of Random
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION DEFINITION: If S is a sample space with a probability measure and x is a real valued function defined over the elements of S, then x is called a random variable. Types of Random
CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLES
 the Further Mathematics network www.fmnetwork.org.uk V 07 REVISION SHEET STATISTICS (AQA) CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLES The main ideas are: Properties of Continuous Random Variables Mean, Median and Mode
the Further Mathematics network www.fmnetwork.org.uk V 07 REVISION SHEET STATISTICS (AQA) CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLES The main ideas are: Properties of Continuous Random Variables Mean, Median and Mode
Study Guide - Part 2
 Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
(c) n (d) n 2. (a) (b) (c) (d) (a) Null set (b) {P} (c) {P, Q, R} (d) {Q, R} (a) 2k (b) 7 (c) 2 (d) K (a) 1 (b) 3 (c) 3xyz (d) 27xyz
 318 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. (1001)2 (101)2 (110)2 (100)2 2. z 1/z 2z z/2 3. The multiplication of the number (10101)2 by (1101)2 yields which one of the following? (100011001)2 (100010001)2 (110010011)2
318 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. (1001)2 (101)2 (110)2 (100)2 2. z 1/z 2z z/2 3. The multiplication of the number (10101)2 by (1101)2 yields which one of the following? (100011001)2 (100010001)2 (110010011)2
Centers at Malleshwaram Rajajinagar Yelahanka Mathikere
 1. x, y, z together start a business. If x invests 3 times as much as y invests and y invests two third of what z invests, then the ratio of capitals of x, y, z is : (a) 3 : 9 : 2 (b) 6 : 3 : 2 (c) 3 :
1. x, y, z together start a business. If x invests 3 times as much as y invests and y invests two third of what z invests, then the ratio of capitals of x, y, z is : (a) 3 : 9 : 2 (b) 6 : 3 : 2 (c) 3 :
SKILL BUILDER TEN. Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables. If x = 2 then y = = = 7 and (2, 7) is a solution.
 SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables. Break Even. Example. 240x x This is when total cost equals total revenue.
 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 1 Break Even This is when total cost equals total revenue C(x) = R(x) A company breaks even when the profit is zero P(x) = R(x) C(x) = 0 2 R x 565x C x 6000
Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 1 Break Even This is when total cost equals total revenue C(x) = R(x) A company breaks even when the profit is zero P(x) = R(x) C(x) = 0 2 R x 565x C x 6000
*** Sorry...no solutions will be posted*** University of Toronto at Scarborough Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences
 *** Sorry...no solutions will be posted*** University of Toronto at Scarborough Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences FINAL EXAMINATION MATA32F - Calculus for Management I Examiners: N. Cheng
*** Sorry...no solutions will be posted*** University of Toronto at Scarborough Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences FINAL EXAMINATION MATA32F - Calculus for Management I Examiners: N. Cheng
Functions. A function is a rule that gives exactly one output number to each input number.
 Functions A function is a rule that gives exactly one output number to each input number. Why it is important to us? The set of all input numbers to which the rule applies is called the domain of the function.
Functions A function is a rule that gives exactly one output number to each input number. Why it is important to us? The set of all input numbers to which the rule applies is called the domain of the function.
Mathematics for Economics ECON MA/MSSc in Economics-2017/2018. Dr. W. M. Semasinghe Senior Lecturer Department of Economics
 Mathematics for Economics ECON 53035 MA/MSSc in Economics-2017/2018 Dr. W. M. Semasinghe Senior Lecturer Department of Economics MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS LERNING OUTCOMES: By the end of this course unit
Mathematics for Economics ECON 53035 MA/MSSc in Economics-2017/2018 Dr. W. M. Semasinghe Senior Lecturer Department of Economics MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS LERNING OUTCOMES: By the end of this course unit
MA 162 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring Find the angle between the vectors v = 2i + 2j + k and w = 2i + 2j k. C.
 MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
JEE-ADVANCED MATHEMATICS. Paper-1. SECTION 1: (One or More Options Correct Type)
 JEE-ADVANCED MATHEMATICS Paper- SECTION : (One or More Options Correct Type) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONE OR
JEE-ADVANCED MATHEMATICS Paper- SECTION : (One or More Options Correct Type) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONE OR
Final Exam Review Part I: Unit IV Material
 Final Exam Review Part I: Unit IV Material Math114 Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky April 26, 2017 Math114 Lecture 37 1/ 11 Outline 1 Conic Sections Math114 Lecture 37 2/ 11 Outline 1
Final Exam Review Part I: Unit IV Material Math114 Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky April 26, 2017 Math114 Lecture 37 1/ 11 Outline 1 Conic Sections Math114 Lecture 37 2/ 11 Outline 1
Find the indicated derivative. 1) Find y(4) if y = 3 sin x. A) y(4) = 3 cos x B) y(4) = 3 sin x C) y(4) = - 3 cos x D) y(4) = - 3 sin x
 Assignment 5 Name Find the indicated derivative. ) Find y(4) if y = sin x. ) A) y(4) = cos x B) y(4) = sin x y(4) = - cos x y(4) = - sin x ) y = (csc x + cot x)(csc x - cot x) ) A) y = 0 B) y = y = - csc
Assignment 5 Name Find the indicated derivative. ) Find y(4) if y = sin x. ) A) y(4) = cos x B) y(4) = sin x y(4) = - cos x y(4) = - sin x ) y = (csc x + cot x)(csc x - cot x) ) A) y = 0 B) y = y = - csc
MATH150-E01 Test #2 Summer 2016 Show all work. Name 1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3).
 1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3). 2. Let the supply and demand functions for sugar be given by p = S(q) = 1.4q 0.6 and p = D(q) = 2q + 3.2 where p is the
1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3). 2. Let the supply and demand functions for sugar be given by p = S(q) = 1.4q 0.6 and p = D(q) = 2q + 3.2 where p is the
WINTER 16 EXAMINATION
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) WINTER 6 EXAMINATION Model wer ject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) WINTER 6 EXAMINATION Model wer ject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model
Formulas that must be memorized:
 Formulas that must be memorized: Position, Velocity, Acceleration Speed is increasing when v(t) and a(t) have the same signs. Speed is decreasing when v(t) and a(t) have different signs. Section I: Limits
Formulas that must be memorized: Position, Velocity, Acceleration Speed is increasing when v(t) and a(t) have the same signs. Speed is decreasing when v(t) and a(t) have different signs. Section I: Limits
( )( 2 ) n n! n! n! 1 1 = + + C = +
 Subject : Mathematics MARKING SCHEME (For Sample Question Paper) Class : Senior Secondary. ( )( )( 9 )( 9 ) L.H.S. ω ω ω. ω ω. ω ( ω)( ω )( ω)( ω ) [ ω ] ω ω ( )( ) ( ) 4 ω +ω +ω. [ 4 ] + + 49 R.H.S (Since
Subject : Mathematics MARKING SCHEME (For Sample Question Paper) Class : Senior Secondary. ( )( )( 9 )( 9 ) L.H.S. ω ω ω. ω ω. ω ( ω)( ω )( ω)( ω ) [ ω ] ω ω ( )( ) ( ) 4 ω +ω +ω. [ 4 ] + + 49 R.H.S (Since
PARABOLA. AIEEE Syllabus. Total No. of questions in Parabola are: Solved examples Level # Level # Level # Level # 4..
 PRBOL IEEE yllabus 1. Definition. Terms related to Parabola 3. tandard form of Equation of Parabola 4. Reduction to standard Equation 5. General Equation of a Parabola 6. Equation of Parabola when its
PRBOL IEEE yllabus 1. Definition. Terms related to Parabola 3. tandard form of Equation of Parabola 4. Reduction to standard Equation 5. General Equation of a Parabola 6. Equation of Parabola when its
2 Functions and Their
 CHAPTER Functions and Their Applications Chapter Outline Introduction The Concept of a Function Types of Functions Roots (Zeros) of a Function Some Useful Functions in Business and Economics Equilibrium
CHAPTER Functions and Their Applications Chapter Outline Introduction The Concept of a Function Types of Functions Roots (Zeros) of a Function Some Useful Functions in Business and Economics Equilibrium
2009 GCE A Level H1 Mathematics Solution
 2009 GCE A Level H1 Mathematics Solution 1) x + 2y = 3 x = 3 2y Substitute x = 3 2y into x 2 + xy = 2: (3 2y) 2 + (3 2y)y = 2 9 12y + 4y 2 + 3y 2y 2 = 2 2y 2 9y + 7 = 0 (2y 7)(y 1) = 0 y = 7 2, 1 x = 4,
2009 GCE A Level H1 Mathematics Solution 1) x + 2y = 3 x = 3 2y Substitute x = 3 2y into x 2 + xy = 2: (3 2y) 2 + (3 2y)y = 2 9 12y + 4y 2 + 3y 2y 2 = 2 2y 2 9y + 7 = 0 (2y 7)(y 1) = 0 y = 7 2, 1 x = 4,
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 2017 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 236 ELAC FALL 207 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) 27 p 3 27 p 3 ) 2) If 9 t 3 4t 9-2t = 3, find t. 2) Solve the equation.
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 207 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) 27 p 3 27 p 3 ) 2) If 9 t 3 4t 9-2t = 3, find t. 2) Solve the equation.
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems
 Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
2 = -30 or 20 Hence an output of 2000 will maximize profit.
 QUANTITATIVE TOOLS IN BUSINESS NOV. SOLUTION (a) (i) Marginal Cost MC = Q Q + Total Cost TC = ʃ Mc = ʃ (Q Q + ) = Q Q + Q + C Where C is the constant of integration (ie C is fixed cost in GHS ) When Q
QUANTITATIVE TOOLS IN BUSINESS NOV. SOLUTION (a) (i) Marginal Cost MC = Q Q + Total Cost TC = ʃ Mc = ʃ (Q Q + ) = Q Q + Q + C Where C is the constant of integration (ie C is fixed cost in GHS ) When Q
Final Exam Review. MATH Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri. Name:. Show all your work.
 MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri Dr. Kracht Name:. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. Final Exam Review Show all your work. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following
MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri Dr. Kracht Name:. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. Final Exam Review Show all your work. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following
TARGET : JEE 2013 SCORE. JEE (Advanced) Home Assignment # 03. Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad
 TARGT : J 01 SCOR J (Advanced) Home Assignment # 0 Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad J-Mathematics HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP 1. If x + y = 0 is a tangent at the vertex of a parabola and x + y 7 =
TARGT : J 01 SCOR J (Advanced) Home Assignment # 0 Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad J-Mathematics HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP 1. If x + y = 0 is a tangent at the vertex of a parabola and x + y 7 =
Tutorial letter 201/2/2018
 DSC1520/201/2/2018 Tutorial letter 201/2/2018 Quantitative Modelling 1 DSC1520 Semester 2 Department of Decision Sciences Solutions to Assignment 1 Bar code Dear Student This tutorial letter contains the
DSC1520/201/2/2018 Tutorial letter 201/2/2018 Quantitative Modelling 1 DSC1520 Semester 2 Department of Decision Sciences Solutions to Assignment 1 Bar code Dear Student This tutorial letter contains the
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
CALCULUS. Berkant Ustaoğlu CRYPTOLOUNGE.NET
 CALCULUS Berkant Ustaoğlu CRYPTOLOUNGE.NET Secant 1 Definition Let f be defined over an interval I containing u. If x u and x I then f (x) f (u) Q = x u is the difference quotient. Also if h 0, such that
CALCULUS Berkant Ustaoğlu CRYPTOLOUNGE.NET Secant 1 Definition Let f be defined over an interval I containing u. If x u and x I then f (x) f (u) Q = x u is the difference quotient. Also if h 0, such that
WBJEE Answer Keys by Aakash Institute, Kolkata Centre
 WBJEE - 08 Answer Keys by, Kolkata Centre MATHEMATICS Q.No. 0 A B C D 0 C D A B 0 B D A C 04 C B A B 05 C A C C 06 A C D C 07 B A C C 08 B *C,D C A 09 C D D B 0 D A C D B A B C C D A B B A A C 4 C C B
WBJEE - 08 Answer Keys by, Kolkata Centre MATHEMATICS Q.No. 0 A B C D 0 C D A B 0 B D A C 04 C B A B 05 C A C C 06 A C D C 07 B A C C 08 B *C,D C A 09 C D D B 0 D A C D B A B C C D A B B A A C 4 C C B
y = F (x) = x n + c dy/dx = F`(x) = f(x) = n x n-1 Given the derivative f(x), what is F(x)? (Integral, Anti-derivative or the Primitive function).
 Integration Course Manual Indefinite Integration 7.-7. Definite Integration 7.-7.4 Jacques ( rd Edition) Indefinite Integration 6. Definite Integration 6. y F (x) x n + c dy/dx F`(x) f(x) n x n- Given
Integration Course Manual Indefinite Integration 7.-7. Definite Integration 7.-7.4 Jacques ( rd Edition) Indefinite Integration 6. Definite Integration 6. y F (x) x n + c dy/dx F`(x) f(x) n x n- Given
S2 QUESTIONS TAKEN FROM JANUARY 2006, JANUARY 2007, JANUARY 2008, JANUARY 2009
 S2 QUESTIONS TAKEN FROM JANUARY 2006, JANUARY 2007, JANUARY 2008, JANUARY 2009 SECTION 1 The binomial and Poisson distributions. Students will be expected to use these distributions to model a real-world
S2 QUESTIONS TAKEN FROM JANUARY 2006, JANUARY 2007, JANUARY 2008, JANUARY 2009 SECTION 1 The binomial and Poisson distributions. Students will be expected to use these distributions to model a real-world
The questions listed below are drawn from midterm and final exams from the last few years at OSU. As the text book and structure of the class have
 The questions listed below are drawn from midterm and final eams from the last few years at OSU. As the tet book and structure of the class have recently changed, it made more sense to list the questions
The questions listed below are drawn from midterm and final eams from the last few years at OSU. As the tet book and structure of the class have recently changed, it made more sense to list the questions
ECONOMICS TRIPOS PART I. Friday 15 June to 12. Paper 3 QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN ECONOMICS
 ECONOMICS TRIPOS PART I Friday 15 June 2007 9 to 12 Paper 3 QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN ECONOMICS This exam comprises four sections. Sections A and B are on Mathematics; Sections C and D are on Statistics.
ECONOMICS TRIPOS PART I Friday 15 June 2007 9 to 12 Paper 3 QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN ECONOMICS This exam comprises four sections. Sections A and B are on Mathematics; Sections C and D are on Statistics.
Second Order Derivatives. Background to Topic 6 Maximisation and Minimisation
 Second Order Derivatives Course Manual Background to Topic 6 Maximisation and Minimisation Jacques (4 th Edition): Chapter 4.6 & 4.7 Y Y=a+bX a X Y= f (X) = a + bx First Derivative dy/dx = f = b constant
Second Order Derivatives Course Manual Background to Topic 6 Maximisation and Minimisation Jacques (4 th Edition): Chapter 4.6 & 4.7 Y Y=a+bX a X Y= f (X) = a + bx First Derivative dy/dx = f = b constant
This does not cover everything on the final. Look at the posted practice problems for other topics.
 Class 7: Review Problems for Final Exam 8.5 Spring 7 This does not cover everything on the final. Look at the posted practice problems for other topics. To save time in class: set up, but do not carry
Class 7: Review Problems for Final Exam 8.5 Spring 7 This does not cover everything on the final. Look at the posted practice problems for other topics. To save time in class: set up, but do not carry
Final Exam Study Guide
 Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam Coverage: Sections 10.1-10.2, 10.4-10.5, 10.7, 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.6, 13.1-13.2, 13.4-13.5, and 14.1 Sections/topics NOT on the exam: Sections 10.3 (Continuity, it definition
Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam Coverage: Sections 10.1-10.2, 10.4-10.5, 10.7, 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.6, 13.1-13.2, 13.4-13.5, and 14.1 Sections/topics NOT on the exam: Sections 10.3 (Continuity, it definition
3. Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve given by 3x y e x+y = 1 + ln x at (1, 1).
 1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
First Degree Programme in Mathematics. Semester 1 MM 1141 Methods of Mathematics
 UNIVERSITY OF KERALA First Degree Programme in Mathematics Model Question Paper Semester 1 MM 1141 Methods of Mathematics Time: Three hours Maximum marks : 80 Section I All the first ten questions are
UNIVERSITY OF KERALA First Degree Programme in Mathematics Model Question Paper Semester 1 MM 1141 Methods of Mathematics Time: Three hours Maximum marks : 80 Section I All the first ten questions are
Department of Agricultural Economics. PhD Qualifier Examination. May 2009
 Department of Agricultural Economics PhD Qualifier Examination May 009 Instructions: The exam consists of six questions. You must answer all questions. If you need an assumption to complete a question,
Department of Agricultural Economics PhD Qualifier Examination May 009 Instructions: The exam consists of six questions. You must answer all questions. If you need an assumption to complete a question,
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCE University of Toronto FINAL EXAMINATIONS, APRIL 2012 MAT 133Y1Y Calculus and Linear Algebra for Commerce
 FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCE University of Toronto FINAL EXAMINATIONS, APRIL 0 MAT 33YY Calculus and Linear Algebra for Commerce Duration: Examiners: 3 hours N. Francetic A. Igelfeld P. Kergin J. Tate LEAVE
FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCE University of Toronto FINAL EXAMINATIONS, APRIL 0 MAT 33YY Calculus and Linear Algebra for Commerce Duration: Examiners: 3 hours N. Francetic A. Igelfeld P. Kergin J. Tate LEAVE
SLIP TEST - 1 MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 7 & 8 XII STD MAX MARKS 50 TIME 1 HR 15 MINTS PART A
 SLIP TEST - MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 7 & 8 XII STD MAX MARKS 50 TIME HR 5 MINTS PART A [0] Answer all the questions Each question carries one mark. The area of the region bounded by the graph of y = sin x and
SLIP TEST - MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 7 & 8 XII STD MAX MARKS 50 TIME HR 5 MINTS PART A [0] Answer all the questions Each question carries one mark. The area of the region bounded by the graph of y = sin x and
DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO
 DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO T.B.C. : P-AQNA-L-ZNGU Serial No.- TEST BOOKLET MATHEMATICS Test Booklet Series Time Allowed : Two Hours and Thirty Minutes Maximum Marks : 00
DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO T.B.C. : P-AQNA-L-ZNGU Serial No.- TEST BOOKLET MATHEMATICS Test Booklet Series Time Allowed : Two Hours and Thirty Minutes Maximum Marks : 00
Finite Mathematics Chapter 1
 Finite Mathematics Chapter 1 Section 1.2 Straight Lines The equation of a horizontal line is of the form y # (namely b ), since m 0. The equation of a vertical line is of the form x # (namely the x -intercept
Finite Mathematics Chapter 1 Section 1.2 Straight Lines The equation of a horizontal line is of the form y # (namely b ), since m 0. The equation of a vertical line is of the form x # (namely the x -intercept
2012 HSC Mathematics Extension 2 Sample Answers
 01 HSC Mathematics Extension Sample Answers When examination committees develop questions for the examination, they may write sample answers or, in the case of some questions, answers could include. The
01 HSC Mathematics Extension Sample Answers When examination committees develop questions for the examination, they may write sample answers or, in the case of some questions, answers could include. The
SECTION 5.1: Polynomials
 1 SECTION 5.1: Polynomials Functions Definitions: Function, Independent Variable, Dependent Variable, Domain, and Range A function is a rule that assigns to each input value x exactly output value y =
1 SECTION 5.1: Polynomials Functions Definitions: Function, Independent Variable, Dependent Variable, Domain, and Range A function is a rule that assigns to each input value x exactly output value y =
Math 259 Winter Solutions to Homework # We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9.
 Math 59 Winter 9 Solutions to Homework Problems from Pages 5-5 (Section 9.) 18. We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9 r cos(θ) + r sin(θ) = 9 r (cos(θ) +
Math 59 Winter 9 Solutions to Homework Problems from Pages 5-5 (Section 9.) 18. We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9 r cos(θ) + r sin(θ) = 9 r (cos(θ) +
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 2010 SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
Lecture 17. Implicit differentiation. Making y the subject: If xy =1,y= x 1 & dy. changed to the subject of y. Note: Example 1.
 Implicit differentiation. Lecture 17 Making y the subject: If xy 1,y x 1 & dy dx x 2. But xy y 2 1 is harder to be changed to the subject of y. Note: d dx (f(y)) f (y) dy dx Example 1. Find dy dx given
Implicit differentiation. Lecture 17 Making y the subject: If xy 1,y x 1 & dy dx x 2. But xy y 2 1 is harder to be changed to the subject of y. Note: d dx (f(y)) f (y) dy dx Example 1. Find dy dx given
F. KEEP YOUR BUBBLE SHEET COVERED AT ALL TIMES.
 UF UNIVERSITY of Department of Mathematics FLORIDA MAC 2233 Exam 2A Spring 2017 A. Sign your bubble sheet on the back at the bottom in ink. B. In pencil, write and encode in the spaces indicated: 1) Name
UF UNIVERSITY of Department of Mathematics FLORIDA MAC 2233 Exam 2A Spring 2017 A. Sign your bubble sheet on the back at the bottom in ink. B. In pencil, write and encode in the spaces indicated: 1) Name
3.4 Conic sections. Such type of curves are called conics, because they arise from different slices through a cone
 3.4 Conic sections Next we consider the objects resulting from ax 2 + bxy + cy 2 + + ey + f = 0. Such type of curves are called conics, because they arise from different slices through a cone Circles belong
3.4 Conic sections Next we consider the objects resulting from ax 2 + bxy + cy 2 + + ey + f = 0. Such type of curves are called conics, because they arise from different slices through a cone Circles belong
MockTime.com. (b) (c) (d)
 373 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. If A, B and C are any three arbitrary events then which one of the following expressions shows that both A and B occur but not C? 2. Which one of the following is an
373 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. If A, B and C are any three arbitrary events then which one of the following expressions shows that both A and B occur but not C? 2. Which one of the following is an
2013 HSC Mathematics Extension 2 Marking Guidelines
 3 HSC Mathematics Extension Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer B A 3 D 4 A 5 B 6 D 7 C 8 C 9 B A 3 HSC Mathematics Extension Marking Guidelines Section II Question
3 HSC Mathematics Extension Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer B A 3 D 4 A 5 B 6 D 7 C 8 C 9 B A 3 HSC Mathematics Extension Marking Guidelines Section II Question
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions
 Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
Bivariate distributions
 Bivariate distributions 3 th October 017 lecture based on Hogg Tanis Zimmerman: Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.) Bivariate Distributions of the Discrete Type The Correlation Coefficient
Bivariate distributions 3 th October 017 lecture based on Hogg Tanis Zimmerman: Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.) Bivariate Distributions of the Discrete Type The Correlation Coefficient
M GENERAL MATHEMATICS -2- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel 1 Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester H
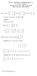 M - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 38-39 H 3 Q. Let A =, B = and C = 3 Compute (if possible) : A+B and BC A+B is impossible. ( ) BC = 3
M - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 38-39 H 3 Q. Let A =, B = and C = 3 Compute (if possible) : A+B and BC A+B is impossible. ( ) BC = 3
Tutorial 2: Comparative Statics
 Tutorial 2: Comparative Statics ECO42F 20 Derivatives and Rules of Differentiation For each of the functions below: (a) Find the difference quotient. (b) Find the derivative dx. (c) Find f (4) and f (3)..
Tutorial 2: Comparative Statics ECO42F 20 Derivatives and Rules of Differentiation For each of the functions below: (a) Find the difference quotient. (b) Find the derivative dx. (c) Find f (4) and f (3)..
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 2014: Lectures Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers. 24x + 72 (x 2 6x + 4) 4
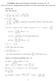 ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
Topic 2: Probability & Distributions. Road Map Probability & Distributions. ECO220Y5Y: Quantitative Methods in Economics. Dr.
 Topic 2: Probability & Distributions ECO220Y5Y: Quantitative Methods in Economics Dr. Nick Zammit University of Toronto Department of Economics Room KN3272 n.zammit utoronto.ca November 21, 2017 Dr. Nick
Topic 2: Probability & Distributions ECO220Y5Y: Quantitative Methods in Economics Dr. Nick Zammit University of Toronto Department of Economics Room KN3272 n.zammit utoronto.ca November 21, 2017 Dr. Nick
Functions, Graphs, Equations and Inequalities
 CAEM DPP Learning Outcomes per Module Module Functions, Graphs, Equations and Inequalities Learning Outcomes 1. Functions, inverse functions and composite functions 1.1. concepts of function, domain and
CAEM DPP Learning Outcomes per Module Module Functions, Graphs, Equations and Inequalities Learning Outcomes 1. Functions, inverse functions and composite functions 1.1. concepts of function, domain and
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCE University of Toronto FINAL EXAMINATIONS, APRIL 2016 MAT 133Y1Y Calculus and Linear Algebra for Commerce
 FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCE University of Toronto FINAL EXAMINATIONS, APRIL 206 MAT YY Calculus and Linear Algebra for Commerce Duration: Examiners: hours N. Hoell A. Igelfeld D. Reiss L. Shorser J. Tate
FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCE University of Toronto FINAL EXAMINATIONS, APRIL 206 MAT YY Calculus and Linear Algebra for Commerce Duration: Examiners: hours N. Hoell A. Igelfeld D. Reiss L. Shorser J. Tate
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 2017 TEST 3 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 6 ELAC FALL 7 TEST NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the integral using integration by parts. ) 9x ln x dx ) ) x 5 -
MATH 6 ELAC FALL 7 TEST NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the integral using integration by parts. ) 9x ln x dx ) ) x 5 -
