Problem 1: A simple 3-dof shear-building model has the following equation: =
|
|
|
- Archibald Cobb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MEEN 6 E: Normalization and Damped Response Fall 24 Problem : A simple -dof shear-building model has the following equation: m u k+ k2 k2 u p( t) m u k k k k + + u = p ( t) m u k k u p( t) where m = 4 lb-s 2 /in, m 2 = 2 lb-s 2 /in, m = 6 lb-s 2 /in, k = lb/in, k 2 = lb/in and k = 2 lb/in. he modal properties for this system are: = Φ λ = (a) Mass Orthonormalize the above mode Shapes and Find the corresponding frequencies in rad/sec. (b) If the system has initial conditions of: u ( t = ) = inches, u2 ( t = ) = -.5 inches and u ( t = ) = -.2 inches find the free-vibration response using modal superposition. Use the mode shapes from part (a). (c) In order to reduce the size of the problem, only mode shapes believed to contribute significantly to the response will be used. In this case, the response will be approximated by using only the first mode contribution. What is the resulting equation for the free-vibration response? (d) Compare the response found from parts (b) and (c). How accurate is the approximation? Problem 2: Now the system has % damping in the first mode, 5% damping in the second mode, and 2% damping in the third mode. (a) Find modal damping matrix with all the damping information given. Find the corresponding system damping matrix in the original coordinate system. (b) If the system has initial conditions of u ( t = ) =.5in, u ( t = ) =.75in, ( ) the free-vibration response using modal superposition 2 u t = = ; find (c) Now find the damping matrix using Rayleigh Damping and the damping given in the first and third modes only. What does the modal damping matrix look like? What happened to the damping in the second mode?
2 MEEN 6 E: Normalization and Damped Response Fall 24 Problem : phi = lambda = Part (a) Frequencies: omega = Scaling Constants: c = Mass-Orthonormalized Mode Shapes: Phi_star = For forces that can be described as proportional forces: P( t ) = s p ( t ) = M{ } u g ( t ) s Participaton Factors: the equation of motion for the i th mode due to base excitation can be written as: ({ φi} [ K]{ φi} ) ( φi s ) { q i} + q i = x g =Γ ixg φ M φ φ M φ ({ } [ ]{ }) { } { } { } i i { i} [ ]{ i} ( ) Where Γ i is the Seismic Participation Factor for the i th mode. his is a special parameter that: Implies the measure of the degree to which the i th mode participates in the response. Factor is NO independent on how the mode is normalized Factor also NO a DIREC measure of how mode contributes to the response. ake a look at participation factors calculated using both the original mode shapes (in problem statement) as well as the factors found using the mass-orthonormalized mode shapes found in part a. For the first mode, the equation when using the original mode shapes is:
3 MEEN 6 E: Normalization and Damped Response Fall 24 4 { } 2 ({ φi} { s} ) Γ = = = =.282 ({ φ} [ ]{ }) i M φ i { } Repeating for all modes, we get the following: Mode Symbol Original φ Orthonormalized φ Γ Γ Γ Strict Sum of Participation Factors Sum of Absolute Values Note that in one case the factors add up to one and in another they do not. ake a look at the ratio of contributions of each participation factor as a percent of the sum of the absolute values: Mode Symbol Original φ Orthonormalized φ Γ Γ Γ Notice that depending on your normalization, you would expect different modes to have the higher contributions to the seismic response. ypically, building codes will ask you to include modes to add up to at least 9% contribution. In this case, either method would result in using both modes and 2. Part (b) Inverse of Mass Orthonormalized Phi Matrix. iphi_star = Initial Conditions: Original Coordinate System Uo = Initial Conditions: Modal Coordinate System Qo =
4 MEEN 6 E: Normalization and Damped Response Fall 24 Response equations: Modal Coordinate System q(t) = cos(.277t) q2(t) = cos(.9464t) q(t) = -.64 cos(.648t) Response equations: Original Coordinate System u(t) = cos(.277t) +.75 cos(.9464t) cos(.648t) u2(t) = -.75 cos(.277t) cos(.9464t) cos(.648t) u(t) = cos(.277t) cos(.9464t) +.49 cos(.648t) Compare these equations with the resulting plots shown below. Response time histories are given in both Modal and Original Coordinate Systems Free Vibration: Modal Coordinates Modal Coordinate Modal Coordinate 2 Modal Coordinate Free Vibration: Original Coordinates Degree of Freedom Degree of Freedom 2 Degree of Freedom
5 MEEN 6 E: Normalization and Damped Response Fall 24 Part (c) Response Using Only Mode u(t) = cos(.277t) u2(t) = -.75 cos(.277t) u(t) = cos(.277t) 2 Free Vibration: Modal Coordinates Modal Coordinate Free Vibration Using Mode Only: Original Coordinates Degree of Freedom Degree of Freedom 2 Degree of Freedom You can clearly see that only frequency is present in the response of all degrees of freedom, and that comes from Mode.
6 MEEN 6 E: Normalization and Damped Response Fall 24 Part (d) Estimate the peak response of each dof using both ABSSUM and SRSS methods described in H2. Compare peak response from part (b) and part (c) Response Found Using All Modes: ABSSUM: Absolute Sum We assume the worst response in each mode all happen at the exact same time. So take a look at the response equations for each mode. he worst case happens when the COS term is equal to + or -. hen the resulting peak values (independent of sign) are given in the table below. Mode Response Equation Peak Value (Independ of Sign) q(t) = cos(.277t) q2(t) = cos(.9464t) 2.47 q(t) = -.64 cos(.648t).64 Looking at the response equation for Mode, we can clearly see the terms coming from each mode. u( t) = cos(.277 t) +.75 cos(.9464 t) cos(.648 t) Mode Contribution Mode 2 Contribution Mode Contribution Again, the worst case scenario would be for the COS terms to equal + or -. Imposing that condition and summing the absolute value of each modal term, we get: u ( t ) = =.454 Doing this for each degree of freedom, we can fill in the table with estimates of the peak value. SRSS: Square-Root of the Sum of the Squares his method is based on random vibration theory. While not guaranteed to be conservative, this method is generally conservative for systems with well spaced frequencies (which is the case for this example). o estimate the peak response, the worst case for each mode is squared, added together, and then we take the square root of the resulting sum. So for the first degree of freedom: ( ) ( ) ( ) u ( t ) = =.572 he results of the estimates using both methods are shown in the table below. he actual peak values are also given for comparison purposes. Degree of Freedom Actual Peak Value Using ABSSUM Using SRSS.652 inches.454 inches.572inches inches.45 inches.958 inches.2 inches.298 inches.88 inches
7 MEEN 6 E: Normalization and Damped Response Fall 24 Response Found Using Mode Only: Since only one mode is now used, the two modal combination strategies result in the same numerical answer for the peak estimates. Again, the peak values of the response for the actual system are given on this same table. Degree of Freedom Actual Peak Value Using ABSSUM Using SRSS.652 inches.227 inches.227 inches inches.75 inches.75 inches.2 inches.9674 inches.9674 inches In this case, using only mode does not result in good estimates of peak response. Problem 2: Part (a) Using Mass Orthonormalized Mode Shapes: Cm_Modal = C = Part (b) Initial conditions: Qo_b = Qdo = Damped Natural Frequencies: omega_d = Coeff. In Front of COS term: A_b = Coeff. In Front of SIN term: B_b =
8 MEEN 6 E: Normalization and Damped Response Fall 24 While explicit response equations are not provided, the resulting response is shown below Damped Free Vibration: Modal Coordinates Modal Coordinate Modal Coordinate 2 Modal Coordinate Damped Free Vibration: Original Coordinates Degree of Freedom Degree of Freedom 2 Degree of Freedom
9 MEEN 6 E: Normalization and Damped Response Fall 24 Part (c) Rayleigh Damping Recall that the coefficients for Rayleigh Damping can be found using the following: ω ω i i α ζ i 2 ω ω = j j α ζ j Substituting values from Modes and as required by the problem: α = α.2 α.48 = α.2 Now can substitute to solve for damping matrix in original coordinate system. m k+ k2 k2 C = α m2 α k2 k2 k k + + m k k Resulting in the following damping matrix: C = his matrix can now be converted to modal space. Since it is proportional to the mass and stiffness matrices, then the resulting matrix must also be diagonal: Cm = Note that this is NO the same modal damping matrix we had before. Knowing that the diagonal m elements must be: 2ζω i imi then we can determine the resulting damping ratios for all modes. In this example, we get zeta = We do get the exact damping ratios in modes and as specified. All other modes follow the trend described in the damping handout. As expected, the damping ratio for mode two is smaller than that of the two specified modes as it lies within the frequency range of the specified modes. his results in a MUCH smaller damping ratio than originally specified (5%).
Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance
 NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance Basic principles Ioannis N. Psycharis Lecture 3 MDOF systems Equation of motion M u + C u + K u = M r x g(t) where:
NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance Basic principles Ioannis N. Psycharis Lecture 3 MDOF systems Equation of motion M u + C u + K u = M r x g(t) where:
Seismic Analysis of Structures Prof. T.K. Datta Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Seismic Analysis of Structures Prof. T.K. Datta Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 20 Response Spectrum Method of Analysis In the last few lecture, we discussed
Seismic Analysis of Structures Prof. T.K. Datta Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 20 Response Spectrum Method of Analysis In the last few lecture, we discussed
3. Mathematical Properties of MDOF Systems
 3. Mathematical Properties of MDOF Systems 3.1 The Generalized Eigenvalue Problem Recall that the natural frequencies ω and modes a are found from [ - ω 2 M + K ] a = 0 or K a = ω 2 M a Where M and K are
3. Mathematical Properties of MDOF Systems 3.1 The Generalized Eigenvalue Problem Recall that the natural frequencies ω and modes a are found from [ - ω 2 M + K ] a = 0 or K a = ω 2 M a Where M and K are
FREE VIBRATION RESPONSE OF UNDAMPED SYSTEMS
 Lecture Notes: STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS / FALL 2011 / Page: 1 FREE VIBRATION RESPONSE OF UNDAMPED SYSTEMS : : 0, 0 As demonstrated previously, the above Equation of Motion (free-vibration equation) has a solution
Lecture Notes: STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS / FALL 2011 / Page: 1 FREE VIBRATION RESPONSE OF UNDAMPED SYSTEMS : : 0, 0 As demonstrated previously, the above Equation of Motion (free-vibration equation) has a solution
1. Multiple Degree-of-Freedom (MDOF) Systems: Introduction
 1. Multiple Degree-of-Freedom (MDOF) Systems: Introduction Lesson Objectives: 1) List examples of MDOF structural systems and state assumptions of the idealizations. 2) Formulate the equation of motion
1. Multiple Degree-of-Freedom (MDOF) Systems: Introduction Lesson Objectives: 1) List examples of MDOF structural systems and state assumptions of the idealizations. 2) Formulate the equation of motion
SHOCK RESPONSE OF MULTI-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEMS Revision F By Tom Irvine May 24, 2010
 SHOCK RESPONSE OF MULTI-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEMS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 4, 010 Introduction The primary purpose of this tutorial is to present the Modal Transient method
SHOCK RESPONSE OF MULTI-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEMS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 4, 010 Introduction The primary purpose of this tutorial is to present the Modal Transient method
Damping Matrix. Donkey2Ft
 1 Damping Matrix DonkeyFt Damping in a single-degree-of-freedom (SDOF) system is well studied. Whether the system is under-damped, over-damped, or critically damped is well known. For an under-damped system,
1 Damping Matrix DonkeyFt Damping in a single-degree-of-freedom (SDOF) system is well studied. Whether the system is under-damped, over-damped, or critically damped is well known. For an under-damped system,
Codal Provisions IS 1893 (Part 1) 2002
 Abstract Codal Provisions IS 1893 (Part 1) 00 Paresh V. Patel Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Nirma Institute of Technology, Ahmedabad 38481 In this article codal provisions of IS 1893
Abstract Codal Provisions IS 1893 (Part 1) 00 Paresh V. Patel Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Nirma Institute of Technology, Ahmedabad 38481 In this article codal provisions of IS 1893
Preliminary Examination - Dynamics
 Name: University of California, Berkeley Fall Semester, 2018 Problem 1 (30% weight) Preliminary Examination - Dynamics An undamped SDOF system with mass m and stiffness k is initially at rest and is then
Name: University of California, Berkeley Fall Semester, 2018 Problem 1 (30% weight) Preliminary Examination - Dynamics An undamped SDOF system with mass m and stiffness k is initially at rest and is then
NATURAL MODES OF VIBRATION OF BUILDING STRUCTURES CE 131 Matrix Structural Analysis Henri Gavin Fall, 2006
 NATURAL MODES OF VIBRATION OF BUILDING STRUCTURES CE 131 Matrix Structural Analysis Henri Gavin Fall, 006 1 Mass and Stiffness Matrices Consider a building frame modeled by a set of rigid, massive flos
NATURAL MODES OF VIBRATION OF BUILDING STRUCTURES CE 131 Matrix Structural Analysis Henri Gavin Fall, 006 1 Mass and Stiffness Matrices Consider a building frame modeled by a set of rigid, massive flos
Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 1 Lecture - 7 Duhamel's Integrals (Refer Slide Time: 00:14)
Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 1 Lecture - 7 Duhamel's Integrals (Refer Slide Time: 00:14)
2.710: Solutions to Home work 1
 .710: Solutions to Home work 1 Problem 1: Optics Buzzwords You will get full credit for this problem if your comments about the topic indicate a certain depth of understanding about what you have written
.710: Solutions to Home work 1 Problem 1: Optics Buzzwords You will get full credit for this problem if your comments about the topic indicate a certain depth of understanding about what you have written
Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 25 Continuous System In the last class, in this, we will
Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 25 Continuous System In the last class, in this, we will
AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS
 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS 1 / 50 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS Undamped Vibrations of n-dof Systems These slides are based on the recommended textbook: M. Géradin and D. Rixen, Mechanical Vibrations:
AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS 1 / 50 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS Undamped Vibrations of n-dof Systems These slides are based on the recommended textbook: M. Géradin and D. Rixen, Mechanical Vibrations:
Design of Earthquake-Resistant Structures
 NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS LABORATORY OF EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING Design of Earthquake-Resistant Structures Basic principles Ioannis N. Psycharis Basic considerations Design earthquake: small
NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS LABORATORY OF EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING Design of Earthquake-Resistant Structures Basic principles Ioannis N. Psycharis Basic considerations Design earthquake: small
Software Verification
 EXAMPLE 6-003 LINK GAP ELEMENT PROBLEM DESCRIPTION This example uses a single-bay, single-story rigid frame to test the gap link element. This link element carries compression loads only; it has zero stiffness
EXAMPLE 6-003 LINK GAP ELEMENT PROBLEM DESCRIPTION This example uses a single-bay, single-story rigid frame to test the gap link element. This link element carries compression loads only; it has zero stiffness
Introduction to structural dynamics
 Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
Identification Methods for Structural Systems. Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture March, 2016
 Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture 4-09. March, 2016 Fundamentals Overview Multiple DOF Systems State-space Formulation Eigenvalue Analysis The Mode Superposition Method The effect of Damping on Structural
Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture 4-09. March, 2016 Fundamentals Overview Multiple DOF Systems State-space Formulation Eigenvalue Analysis The Mode Superposition Method The effect of Damping on Structural
Damping Modelling and Identification Using Generalized Proportional Damping
 Damping Modelling and Identification Using Generalized Proportional Damping S Adhikari Department of Aerospace Engineering, University of Bristol, Bristol, U.K. Email: S.Adhikari@bristol.ac.uk Generalized
Damping Modelling and Identification Using Generalized Proportional Damping S Adhikari Department of Aerospace Engineering, University of Bristol, Bristol, U.K. Email: S.Adhikari@bristol.ac.uk Generalized
Multi Degrees of Freedom Systems
 Multi Degrees of Freedom Systems MDOF s http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano March 9, 07 Outline, a System
Multi Degrees of Freedom Systems MDOF s http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano March 9, 07 Outline, a System
Rayleigh s Classical Damping Revisited
 Rayleigh s Classical Damping Revisited S. Adhikari and A. Srikantha Phani Department of Aerospace Engineering, University of Bristol, Bristol, U.K. Email: S.Adhikari@bristol.ac.uk URL: http://www.aer.bris.ac.uk/contact/academic/adhikari/home.html
Rayleigh s Classical Damping Revisited S. Adhikari and A. Srikantha Phani Department of Aerospace Engineering, University of Bristol, Bristol, U.K. Email: S.Adhikari@bristol.ac.uk URL: http://www.aer.bris.ac.uk/contact/academic/adhikari/home.html
Reduction in number of dofs
 Reduction in number of dofs Reduction in the number of dof to represent a structure reduces the size of matrices and, hence, computational cost. Because a subset of the original dof represent the whole
Reduction in number of dofs Reduction in the number of dof to represent a structure reduces the size of matrices and, hence, computational cost. Because a subset of the original dof represent the whole
Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic. FEMAP & NX Nastran
 Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic FEMAP & NX Nastran Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. THE ACCELEROGRAM... 4 3. CREATING A RESPONSE SPECTRUM... 5 4. NX NASTRAN METHOD... 8 5. RESPONSE
Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic FEMAP & NX Nastran Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. THE ACCELEROGRAM... 4 3. CREATING A RESPONSE SPECTRUM... 5 4. NX NASTRAN METHOD... 8 5. RESPONSE
Modeling and Experimentation: Mass-Spring-Damper System Dynamics
 Modeling and Experimentation: Mass-Spring-Damper System Dynamics Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin July 20, 2014 Overview 1 This lab is meant to
Modeling and Experimentation: Mass-Spring-Damper System Dynamics Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin July 20, 2014 Overview 1 This lab is meant to
APPLICATION OF RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD TO PASSIVELY DAMPED DOME STRUCTURE WITH HIGH DAMPING AND HIGH FREQUENCY MODES
 3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 4 Paper No. 5 APPLICATION OF RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD TO PASSIVELY DAMPED DOME STRUCTURE WITH HIGH DAMPING AND HIGH FREQUENCY
3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 4 Paper No. 5 APPLICATION OF RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD TO PASSIVELY DAMPED DOME STRUCTURE WITH HIGH DAMPING AND HIGH FREQUENCY
ANALYSIS OF HIGHRISE BUILDING STRUCTURE WITH SETBACK SUBJECT TO EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTIONS
 ANALYSIS OF HIGHRISE BUILDING SRUCURE WIH SEBACK SUBJEC O EARHQUAKE GROUND MOIONS 157 Xiaojun ZHANG 1 And John L MEEK SUMMARY he earthquake response behaviour of unframed highrise buildings with setbacks
ANALYSIS OF HIGHRISE BUILDING SRUCURE WIH SEBACK SUBJEC O EARHQUAKE GROUND MOIONS 157 Xiaojun ZHANG 1 And John L MEEK SUMMARY he earthquake response behaviour of unframed highrise buildings with setbacks
Chapter 2: Rigid Bar Supported by Two Buckled Struts under Axial, Harmonic, Displacement Excitation..14
 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum
 STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum Overview of Structural Dynamics Structure Members, joints, strength, stiffness, ductility Structure
STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum Overview of Structural Dynamics Structure Members, joints, strength, stiffness, ductility Structure
Final Exam December 11, 2017
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are NOT allowed to use a calculator with communication capabilities during the exam. Usage
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are NOT allowed to use a calculator with communication capabilities during the exam. Usage
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber
 Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
Control of Earthquake Induced Vibrations in Asymmetric Buildings Using Passive Damping
 Control of Earthquake Induced Vibrations in Asymmetric Buildings Using Passive Damping Rakesh K. Goel, California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo Abstract This paper summarizes the results
Control of Earthquake Induced Vibrations in Asymmetric Buildings Using Passive Damping Rakesh K. Goel, California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo Abstract This paper summarizes the results
Dynamics of Structures
 Dynamics of Structures Elements of structural dynamics Roberto Tomasi 11.05.2017 Roberto Tomasi Dynamics of Structures 11.05.2017 1 / 22 Overview 1 SDOF system SDOF system Equation of motion Response spectrum
Dynamics of Structures Elements of structural dynamics Roberto Tomasi 11.05.2017 Roberto Tomasi Dynamics of Structures 11.05.2017 1 / 22 Overview 1 SDOF system SDOF system Equation of motion Response spectrum
Software Verification
 POGAM NAME: EVISION NO.: 0 EXAMPLE 6-005 LINK DAMPE ELEMENT UNDE HAMONIC LOADING POBLEM DESCIPTION In this single degree of freedom example a spring-mass-damper system is subjected to a harmonic load.
POGAM NAME: EVISION NO.: 0 EXAMPLE 6-005 LINK DAMPE ELEMENT UNDE HAMONIC LOADING POBLEM DESCIPTION In this single degree of freedom example a spring-mass-damper system is subjected to a harmonic load.
Part 6: Dynamic design analysis
 Part 6: Dynamic design analysis BuildSoft nv All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or manual, for any purpose, without written
Part 6: Dynamic design analysis BuildSoft nv All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or manual, for any purpose, without written
SEISMIC PROTECTIVE SYSTEMS: PASSIVE ENERGY DISSIPATION
 SEISMIC PROTECTIVE SYSTEMS: PASSIVE ENERGY DISSIPATION Presented & Developed by: Michael D. Symans, PhD Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Initially Developed by: Finley A. Charney, PE, PhD Virginia Polytechnic
SEISMIC PROTECTIVE SYSTEMS: PASSIVE ENERGY DISSIPATION Presented & Developed by: Michael D. Symans, PhD Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Initially Developed by: Finley A. Charney, PE, PhD Virginia Polytechnic
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping
 A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
APPROXIMATE DYNAMIC MODEL SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS FOR LARGE, COMPLEX SPACE STRUCTURES. Timothy S. West, Senior Engineer
 APPROXIMATE DYNAMIC MODEL SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS FOR LARGE, COMPLEX SPACE STRUCTURES Timothy S. West, Senior Engineer McDonnell Douglas Aerospace Space Station Division, Houston, Texas ABSTRACT During the
APPROXIMATE DYNAMIC MODEL SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS FOR LARGE, COMPLEX SPACE STRUCTURES Timothy S. West, Senior Engineer McDonnell Douglas Aerospace Space Station Division, Houston, Texas ABSTRACT During the
Prob. 1 SDOF Structure subjected to Ground Shaking
 Prob. 1 SDOF Structure subjected to Ground Shaking What is the maximum relative displacement and the amplitude of the total displacement of a SDOF structure subjected to ground shaking? magnitude of ground
Prob. 1 SDOF Structure subjected to Ground Shaking What is the maximum relative displacement and the amplitude of the total displacement of a SDOF structure subjected to ground shaking? magnitude of ground
Systems Analysis and Control
 Systems Analysis and Control Matthew M. Peet Arizona State University Lecture 21: Stability Margins and Closing the Loop Overview In this Lecture, you will learn: Closing the Loop Effect on Bode Plot Effect
Systems Analysis and Control Matthew M. Peet Arizona State University Lecture 21: Stability Margins and Closing the Loop Overview In this Lecture, you will learn: Closing the Loop Effect on Bode Plot Effect
SHAKING TABLE DEMONSTRATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF BASE-ISOLATED BUILDINGS ***** Instructor Manual *****
 SHAKING TABLE DEMONSTRATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF BASE-ISOLATED BUILDINGS ***** Instructor Manual ***** A PROJECT DEVELOPED FOR THE UNIVERSITY CONSORTIUM ON INSTRUCTIONAL SHAKE TABLES http://wusceel.cive.wustl.edu/ucist/
SHAKING TABLE DEMONSTRATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF BASE-ISOLATED BUILDINGS ***** Instructor Manual ***** A PROJECT DEVELOPED FOR THE UNIVERSITY CONSORTIUM ON INSTRUCTIONAL SHAKE TABLES http://wusceel.cive.wustl.edu/ucist/
Why You Can t Ignore Those Vibration Fixture Resonances Peter Avitabile, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts
 Why You Can t Ignore Those Vibration Fixture Resonances Peter Avitabile, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts SOUND AND VIBRATION March 1999 Vibration fixtures, at times, have resonant
Why You Can t Ignore Those Vibration Fixture Resonances Peter Avitabile, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts SOUND AND VIBRATION March 1999 Vibration fixtures, at times, have resonant
Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian
 Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: Mode-Superposition Method Mode-Superposition Method:
Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: Mode-Superposition Method Mode-Superposition Method:
Modal analysis of shear buildings
 Modal analysis of shear buildings A comprehensive modal analysis of an arbitrary multistory shear building having rigid beams and lumped masses at floor levels is obtained. Angular frequencies (rad/sec),
Modal analysis of shear buildings A comprehensive modal analysis of an arbitrary multistory shear building having rigid beams and lumped masses at floor levels is obtained. Angular frequencies (rad/sec),
Software Verification
 SAP000 EXAMPLE 6-00 LINK LINEAR LINK WITH RAMP LOADING PROBLEM DESCRIPTION In this example a ramp load is applied to an undamped single degree of freedom structure. The ramp loading has a finite rise time
SAP000 EXAMPLE 6-00 LINK LINEAR LINK WITH RAMP LOADING PROBLEM DESCRIPTION In this example a ramp load is applied to an undamped single degree of freedom structure. The ramp loading has a finite rise time
BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, Pilani Pilani Campus
 First Semester 2017-2018 Instruction Division Course Handout (Part II) Date: 02/08/2017 In addition to Part I (General Handout for all courses appended to the Time Table), this portion gives further specific
First Semester 2017-2018 Instruction Division Course Handout (Part II) Date: 02/08/2017 In addition to Part I (General Handout for all courses appended to the Time Table), this portion gives further specific
Chapter 7: Solving Structural Dynamic Problems Using DCALC By Karl Hanson, S.E., P.E.* September 2008
 Chapter 7: Solving Structural Dynamic Problems Using DCALC By Karl Hanson, S.E., P.E.* September 2008 7.1 Introduction: The last chapter presented the fundamental methods used in structural dynamics to
Chapter 7: Solving Structural Dynamic Problems Using DCALC By Karl Hanson, S.E., P.E.* September 2008 7.1 Introduction: The last chapter presented the fundamental methods used in structural dynamics to
Structural Matrices in MDOF Systems
 in MDOF Systems http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 9, 2016 Outline Additional Static Condensation
in MDOF Systems http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 9, 2016 Outline Additional Static Condensation
18. FAST NONLINEAR ANALYSIS. The Dynamic Analysis of a Structure with a Small Number of Nonlinear Elements is Almost as Fast as a Linear Analysis
 18. FAS NONLINEAR ANALYSIS he Dynamic Analysis of a Structure with a Small Number of Nonlinear Elements is Almost as Fast as a Linear Analysis 18.1 INRODUCION he response of real structures when subjected
18. FAS NONLINEAR ANALYSIS he Dynamic Analysis of a Structure with a Small Number of Nonlinear Elements is Almost as Fast as a Linear Analysis 18.1 INRODUCION he response of real structures when subjected
Structural health monitoring of offshore jacket platforms by inverse vibration problem. M. T. Nikoukalam On behalf of Kiarash M.
 Structural health monitoring of offshore jacket platforms by inverse vibration problem M. T. Nikoukalam On behalf of Kiarash M. Dolatshahi 1 Outline 1- Introduction 2- Motivation 3- Description of inverse
Structural health monitoring of offshore jacket platforms by inverse vibration problem M. T. Nikoukalam On behalf of Kiarash M. Dolatshahi 1 Outline 1- Introduction 2- Motivation 3- Description of inverse
Preliminary Examination in Dynamics
 Fall Semester 2017 Problem 1 The simple structure shown below weighs 1,000 kips and has a period of 1.25 sec. It has no viscous damping. It is subjected to the impulsive load shown in the figure. If the
Fall Semester 2017 Problem 1 The simple structure shown below weighs 1,000 kips and has a period of 1.25 sec. It has no viscous damping. It is subjected to the impulsive load shown in the figure. If the
a) Find the equation of motion of the system and write it in matrix form.
 .003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
Effects of Damping Ratio of Restoring force Device on Response of a Structure Resting on Sliding Supports with Restoring Force Device
 Effects of Damping Ratio of Restoring force Device on Response of a Structure Resting on Sliding Supports with Restoring Force Device A. Krishnamoorthy Professor, Department of Civil Engineering Manipal
Effects of Damping Ratio of Restoring force Device on Response of a Structure Resting on Sliding Supports with Restoring Force Device A. Krishnamoorthy Professor, Department of Civil Engineering Manipal
Outline. Structural Matrices. Giacomo Boffi. Introductory Remarks. Structural Matrices. Evaluation of Structural Matrices
 Outline in MDOF Systems Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Milano May 8, 014 Additional Today we will study the properties of structural matrices, that is the operators that
Outline in MDOF Systems Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Milano May 8, 014 Additional Today we will study the properties of structural matrices, that is the operators that
MODAL ANALYSIS OF PLANE FRAMES
 MODAL ANALYSIS OF PLANE FRAMES Mr. Mohammed Siraj Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Deogiri Institute of Engineering and Management Studies Aurangabad, M.S, India. ABSTRACT In the modal analysis
MODAL ANALYSIS OF PLANE FRAMES Mr. Mohammed Siraj Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Deogiri Institute of Engineering and Management Studies Aurangabad, M.S, India. ABSTRACT In the modal analysis
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES
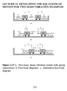 LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
Chapter 5 Design. D. J. Inman 1/51 Mechanical Engineering at Virginia Tech
 Chapter 5 Design Acceptable vibration levels (ISO) Vibration isolation Vibration absorbers Effects of damping in absorbers Optimization Viscoelastic damping treatments Critical Speeds Design for vibration
Chapter 5 Design Acceptable vibration levels (ISO) Vibration isolation Vibration absorbers Effects of damping in absorbers Optimization Viscoelastic damping treatments Critical Speeds Design for vibration
3. MDOF Systems: Modal Spectral Analysis
 3. MDOF Systems: Modal Spectral Analysis Lesson Objectives: 1) Construct response spectra for an arbitrarily varying excitation. 2) Compute the equivalent lateral force, base shear, and overturning moment
3. MDOF Systems: Modal Spectral Analysis Lesson Objectives: 1) Construct response spectra for an arbitrarily varying excitation. 2) Compute the equivalent lateral force, base shear, and overturning moment
CHAPTER 12 TIME DOMAIN: MODAL STATE SPACE FORM
 CHAPTER 1 TIME DOMAIN: MODAL STATE SPACE FORM 1.1 Introduction In Chapter 7 we derived the equations of motion in modal form for the system in Figure 1.1. In this chapter we will convert the modal form
CHAPTER 1 TIME DOMAIN: MODAL STATE SPACE FORM 1.1 Introduction In Chapter 7 we derived the equations of motion in modal form for the system in Figure 1.1. In this chapter we will convert the modal form
Structural Health Monitoring and Dynamic Identification of Structures: Applications
 Structural Health Monitoring and Dynamic Identification of Structures: Applications Computer Lab II, IMSS (017) Ground Work: Definition of the problem & System Modeling when we have full knowledge of the
Structural Health Monitoring and Dynamic Identification of Structures: Applications Computer Lab II, IMSS (017) Ground Work: Definition of the problem & System Modeling when we have full knowledge of the
 University of California at Berkeley Structural Engineering Mechanics & Materials Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Spring 2012 Student name : Doctoral Preliminary Examination in Dynamics
University of California at Berkeley Structural Engineering Mechanics & Materials Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Spring 2012 Student name : Doctoral Preliminary Examination in Dynamics
Alireza Mehdipanah BEHAVIOUR OF BUILDINGS FEATURING TRANSFER BEAMS IN THE REGIONS OF LOW TO MODERATE SEISMICITY
 BEHAVIOUR OF BUILDINGS FEATURING TRANSFER BEAMS IN THE REGIONS OF LOW TO MODERATE SEISMICITY Alireza Mehdipanah PhD Candidate at The University of Melbourne SUPERVISORS: A/PROF. NELSON LAM DR. ELISA LUMANTARNA
BEHAVIOUR OF BUILDINGS FEATURING TRANSFER BEAMS IN THE REGIONS OF LOW TO MODERATE SEISMICITY Alireza Mehdipanah PhD Candidate at The University of Melbourne SUPERVISORS: A/PROF. NELSON LAM DR. ELISA LUMANTARNA
EFFECTIVE MODAL MASS & MODAL PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F
 EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com March 9, 1 Introduction The effective modal mass provides a method for judging the significance of a vibration
EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com March 9, 1 Introduction The effective modal mass provides a method for judging the significance of a vibration
NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS
 NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS Nonlinear Structural Dynamics Using FE Methods emphasizes fundamental mechanics principles and outlines a modern approach to understanding structural dynamics.
NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS Nonlinear Structural Dynamics Using FE Methods emphasizes fundamental mechanics principles and outlines a modern approach to understanding structural dynamics.
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 5 Torsional Vibrations Lecture - 4 Transfer Matrix Approach
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 5 Torsional Vibrations Lecture - 4 Transfer Matrix Approach
on the figure. Someone has suggested that, in terms of the degrees of freedom x1 and M. Note that if you think the given 1.2
 1) A two-story building frame is shown below. The mass of the frame is assumed to be lumped at the floor levels and the floor slabs are considered rigid. The floor masses and the story stiffnesses are
1) A two-story building frame is shown below. The mass of the frame is assumed to be lumped at the floor levels and the floor slabs are considered rigid. The floor masses and the story stiffnesses are
Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser
 Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser What is a Modal Analysis? What answers do we get out of it? How is it useful? What does it not tell us? In this article, we ll discuss where a modal
Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser What is a Modal Analysis? What answers do we get out of it? How is it useful? What does it not tell us? In this article, we ll discuss where a modal
Dynamic Analysis Using Response Spectrum Seismic Loading
 Dynamic Analysis Using Response Spectrum Seismic Loading Paleti Teja M.Tech (Structural Engineering) Department of Civil Engineering Jogaiah Institute of Technology & Sciences College of Engineering Kalagampudi,
Dynamic Analysis Using Response Spectrum Seismic Loading Paleti Teja M.Tech (Structural Engineering) Department of Civil Engineering Jogaiah Institute of Technology & Sciences College of Engineering Kalagampudi,
Structural Damage Detection Using Time Windowing Technique from Measured Acceleration during Earthquake
 Structural Damage Detection Using Time Windowing Technique from Measured Acceleration during Earthquake Seung Keun Park and Hae Sung Lee ABSTRACT This paper presents a system identification (SI) scheme
Structural Damage Detection Using Time Windowing Technique from Measured Acceleration during Earthquake Seung Keun Park and Hae Sung Lee ABSTRACT This paper presents a system identification (SI) scheme
Software Verification
 EXAMPLE 6-6 LINK SUNY BUFFALO DAMPER WITH LINEAR VELOCITY EXPONENT PROBLEM DESCRIPTION This example comes from Section 5 of Scheller and Constantinou 1999 ( the SUNY Buffalo report ). It is a two-dimensional,
EXAMPLE 6-6 LINK SUNY BUFFALO DAMPER WITH LINEAR VELOCITY EXPONENT PROBLEM DESCRIPTION This example comes from Section 5 of Scheller and Constantinou 1999 ( the SUNY Buffalo report ). It is a two-dimensional,
DAMPING MODELLING AND IDENTIFICATION USING GENERALIZED PROPORTIONAL DAMPING
 DAMPING MODELLING AND IDENTIFICATION USING GENERALIZED PROPORTIONAL DAMPING S. Adhikari Department of Aerospace Engineering, University of Bristol, Queens Building, University Walk, Bristol BS8 1TR (U.K.)
DAMPING MODELLING AND IDENTIFICATION USING GENERALIZED PROPORTIONAL DAMPING S. Adhikari Department of Aerospace Engineering, University of Bristol, Queens Building, University Walk, Bristol BS8 1TR (U.K.)
Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi.
 Seismic Analysis of Structures by Dutta, Civil Department, II Delhi, New Delhi. Module Response Analysis for Specified Ground Motion Exercise Problems:.. Find the effective mass and stiffness of the structure
Seismic Analysis of Structures by Dutta, Civil Department, II Delhi, New Delhi. Module Response Analysis for Specified Ground Motion Exercise Problems:.. Find the effective mass and stiffness of the structure
Contents i. Contents
 Contents i Contents 7 SEISMIC LOADS Commentary 7. Estimation of Seismic Loads.............................. 7.. Seismic load and design earthquake motion.................. 4 7..2 Idealization of building
Contents i Contents 7 SEISMIC LOADS Commentary 7. Estimation of Seismic Loads.............................. 7.. Seismic load and design earthquake motion.................. 4 7..2 Idealization of building
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 2 Simpul Rotors Lecture - 2 Jeffcott Rotor Model In the
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 2 Simpul Rotors Lecture - 2 Jeffcott Rotor Model In the
Introduction to Vibration. Professor Mike Brennan
 Introduction to Vibration Professor Mie Brennan Introduction to Vibration Nature of vibration of mechanical systems Free and forced vibrations Frequency response functions Fundamentals For free vibration
Introduction to Vibration Professor Mie Brennan Introduction to Vibration Nature of vibration of mechanical systems Free and forced vibrations Frequency response functions Fundamentals For free vibration
MATH2351 Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations, Fall Hints to Week 07 Worksheet: Mechanical Vibrations
 MATH351 Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations, Fall 11-1 Hints to Week 7 Worksheet: Mechanical Vibrations 1. (Demonstration) ( 3.8, page 3, Q. 5) A mass weighing lb streches a spring by 6 in.
MATH351 Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations, Fall 11-1 Hints to Week 7 Worksheet: Mechanical Vibrations 1. (Demonstration) ( 3.8, page 3, Q. 5) A mass weighing lb streches a spring by 6 in.
Solutions for Homework #8. Landing gear
 Solutions or Homewor #8 PROBEM. (P. 9 on page 78 in the note) An airplane is modeled as a beam with masses as shown below: m m m m π [rad/sec] anding gear m m.5 Find the stiness and mass matrices. Find
Solutions or Homewor #8 PROBEM. (P. 9 on page 78 in the note) An airplane is modeled as a beam with masses as shown below: m m m m π [rad/sec] anding gear m m.5 Find the stiness and mass matrices. Find
MEEN 363. EXAMPLE of ANALYSIS (1 DOF) Luis San Andrés
 MEEN 363. EAMPLE of ANALYSIS (1 DOF) Luis San Anrés Objectives: a) To erive EOM for a 1-DOF (one egree of freeom) system b) To unerstan concept of static equilibrium c) To learn the correct usage of physical
MEEN 363. EAMPLE of ANALYSIS (1 DOF) Luis San Anrés Objectives: a) To erive EOM for a 1-DOF (one egree of freeom) system b) To unerstan concept of static equilibrium c) To learn the correct usage of physical
In-Structure Response Spectra Development Using Complex Frequency Analysis Method
 Transactions, SMiRT-22 In-Structure Response Spectra Development Using Complex Frequency Analysis Method Hadi Razavi 1,2, Ram Srinivasan 1 1 AREVA, Inc., Civil and Layout Department, Mountain View, CA
Transactions, SMiRT-22 In-Structure Response Spectra Development Using Complex Frequency Analysis Method Hadi Razavi 1,2, Ram Srinivasan 1 1 AREVA, Inc., Civil and Layout Department, Mountain View, CA
MEG6007: Advanced Dynamics -Principles and Computational Methods (Fall, 2017) Lecture DOF Modeling of Shock Absorbers. This lecture covers:
 MEG6007: Advanced Dynamics -Principles and Computational Methods (Fall, 207) Lecture 4. 2-DOF Modeling of Shock Absorbers This lecture covers: Revisit 2-DOF Spring-Mass System Understand the den Hartog
MEG6007: Advanced Dynamics -Principles and Computational Methods (Fall, 207) Lecture 4. 2-DOF Modeling of Shock Absorbers This lecture covers: Revisit 2-DOF Spring-Mass System Understand the den Hartog
Table of Contents. Preface... 13
 Table of Contents Preface... 13 Chapter 1. Vibrations of Continuous Elastic Solid Media... 17 1.1. Objective of the chapter... 17 1.2. Equations of motion and boundary conditions of continuous media...
Table of Contents Preface... 13 Chapter 1. Vibrations of Continuous Elastic Solid Media... 17 1.1. Objective of the chapter... 17 1.2. Equations of motion and boundary conditions of continuous media...
Modal Analysis Damped Systems
 Modal Analysis of MDOF Forced Damped Systems Lecture : MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF FORCED DAMPED SYSTEMS TABLE OF CONTENTS Page. Introduction..................... 3. What is Mechanical Damping?..............
Modal Analysis of MDOF Forced Damped Systems Lecture : MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF FORCED DAMPED SYSTEMS TABLE OF CONTENTS Page. Introduction..................... 3. What is Mechanical Damping?..............
RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOR ACCELERATION DEMAND
 RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOR ACCELERATION DEMAND Shahram Taghavi 1 and Eduardo Miranda 2 1 Senior catastrophe risk modeler, Risk Management Solutions, CA, USA 2 Associate Professor,
RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOR ACCELERATION DEMAND Shahram Taghavi 1 and Eduardo Miranda 2 1 Senior catastrophe risk modeler, Risk Management Solutions, CA, USA 2 Associate Professor,
Chapter 6: Fundamental Methods Used In Structural Dynamics By Karl Hanson, S.E., P.E.* April 2008
 Chapter 6: Fundamental Methods Used In Structural Dynamics By Karl Hanson, S.E., P.E.* April 2008 6.1 Introduction: Structural dynamics is a fascinating subject. After you get into it and understand it,
Chapter 6: Fundamental Methods Used In Structural Dynamics By Karl Hanson, S.E., P.E.* April 2008 6.1 Introduction: Structural dynamics is a fascinating subject. After you get into it and understand it,
7 SEISMIC LOADS. 7.1 Estimation of Seismic Loads. 7.2 Calculation of Seismic Loads
 1 7 SEISMIC LOADS 7.1 Estimation of Seismic Loads 7.1.1 Seismic load and design earthquake motion (1) For ordinary buildings, seismic load is evaluated using the acceleration response spectrum (see Sec.7.2)
1 7 SEISMIC LOADS 7.1 Estimation of Seismic Loads 7.1.1 Seismic load and design earthquake motion (1) For ordinary buildings, seismic load is evaluated using the acceleration response spectrum (see Sec.7.2)
822. Non-iterative mode shape expansion for threedimensional structures based on coordinate decomposition
 822. Non-iterative mode shape expansion for threedimensional structures based on coordinate decomposition Fushun Liu, Zhengshou Chen 2, Wei Li 3 Department of Ocean Engineering, Ocean University of China,
822. Non-iterative mode shape expansion for threedimensional structures based on coordinate decomposition Fushun Liu, Zhengshou Chen 2, Wei Li 3 Department of Ocean Engineering, Ocean University of China,
Structural System, Machines and Load Cases
 Machine-Induced Vibrations Machine-Induced Vibrations In the following example the dynamic excitation of two rotating machines is analyzed. A time history analysis in the add-on module RF-DYNAM Pro - Forced
Machine-Induced Vibrations Machine-Induced Vibrations In the following example the dynamic excitation of two rotating machines is analyzed. A time history analysis in the add-on module RF-DYNAM Pro - Forced
22.2. Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 22.2 Introduction Many applications of matrices in both engineering and science utilize eigenvalues and, sometimes, eigenvectors. Control theory, vibration
Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 22.2 Introduction Many applications of matrices in both engineering and science utilize eigenvalues and, sometimes, eigenvectors. Control theory, vibration
ANNEX A: ANALYSIS METHODOLOGIES
 ANNEX A: ANALYSIS METHODOLOGIES A.1 Introduction Before discussing supplemental damping devices, this annex provides a brief review of the seismic analysis methods used in the optimization algorithms considered
ANNEX A: ANALYSIS METHODOLOGIES A.1 Introduction Before discussing supplemental damping devices, this annex provides a brief review of the seismic analysis methods used in the optimization algorithms considered
ME scope Application Note 28
 App Note 8 www.vibetech.com 3/7/17 ME scope Application Note 8 Mathematics of a Mass-Spring-Damper System INTRODUCTION In this note, the capabilities of ME scope will be used to build a model of the mass-spring-damper
App Note 8 www.vibetech.com 3/7/17 ME scope Application Note 8 Mathematics of a Mass-Spring-Damper System INTRODUCTION In this note, the capabilities of ME scope will be used to build a model of the mass-spring-damper
Chapter 2 Basics of Vibration Dynamics
 Chapter 2 Basics of Vibration Dynamics Vibrations are mechanical oscillations about an equilibrium position. There are cases when vibrations are desirable, such as in certain types of machine tools or
Chapter 2 Basics of Vibration Dynamics Vibrations are mechanical oscillations about an equilibrium position. There are cases when vibrations are desirable, such as in certain types of machine tools or
Operating Deflection Shapes from Strain Measurement Data
 Operating Deflection Shapes from Strain Measurement Data Timothy G. Hunter, Ph.D., P.E. President Wolf Star Technologies, LLC 3321 N. Newhall St., Milwaukee, WI 53211 Abstract Strain gauges are often more
Operating Deflection Shapes from Strain Measurement Data Timothy G. Hunter, Ph.D., P.E. President Wolf Star Technologies, LLC 3321 N. Newhall St., Milwaukee, WI 53211 Abstract Strain gauges are often more
SPECIAL DYNAMIC SOIL- STRUCTURE ANALYSIS PROCEDURES DEMONSTATED FOR TWO TOWER-LIKE STRUCTURES
 2010/2 PAGES 1 8 RECEIVED 21. 9. 2009 ACCEPTED 20. 1. 2010 Y. KOLEKOVÁ, M. PETRONIJEVIĆ, G. SCHMID SPECIAL DYNAMIC SOIL- STRUCTURE ANALYSIS PROCEDURES DEMONSTATED FOR TWO TOWER-LIKE STRUCTURES ABSTRACT
2010/2 PAGES 1 8 RECEIVED 21. 9. 2009 ACCEPTED 20. 1. 2010 Y. KOLEKOVÁ, M. PETRONIJEVIĆ, G. SCHMID SPECIAL DYNAMIC SOIL- STRUCTURE ANALYSIS PROCEDURES DEMONSTATED FOR TWO TOWER-LIKE STRUCTURES ABSTRACT
Single-Degree-of-Freedom (SDOF) and Response Spectrum
 Single-Degree-of-Freedom (SDOF) and Response Spectrum Ahmed Elgamal 1 Dynamics of a Simple Structure The Single-Degree-Of-Freedom (SDOF) Equation References Dynamics of Structures, Anil K. Chopra, Prentice
Single-Degree-of-Freedom (SDOF) and Response Spectrum Ahmed Elgamal 1 Dynamics of a Simple Structure The Single-Degree-Of-Freedom (SDOF) Equation References Dynamics of Structures, Anil K. Chopra, Prentice
Advanced Vibrations. Elements of Analytical Dynamics. By: H. Ahmadian Lecture One
 Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
COMPARISON OF MODE SHAPE VECTORS IN OPERATIONAL MODAL ANALYSIS DEALING WITH CLOSELY SPACED MODES.
 IOMAC'5 6 th International Operational Modal Analysis Conference 5 May-4 Gijón - Spain COMPARISON OF MODE SHAPE VECTORS IN OPERATIONAL MODAL ANALYSIS DEALING WITH CLOSELY SPACED MODES. Olsen P., and Brincker
IOMAC'5 6 th International Operational Modal Analysis Conference 5 May-4 Gijón - Spain COMPARISON OF MODE SHAPE VECTORS IN OPERATIONAL MODAL ANALYSIS DEALING WITH CLOSELY SPACED MODES. Olsen P., and Brincker
Nonlinear Normal Modes of a Curved Beam and its Response to Random Loading
 Nonlinear Normal Modes of a Curved Beam and its Response to Random Loading Christopher I. VanDamme and Matthew S. Allen 2 Graduate Student; e-mail: cvandamme@wisc.edu 2 Associate Professor; e-mail: matt.allen@wisc.edu
Nonlinear Normal Modes of a Curved Beam and its Response to Random Loading Christopher I. VanDamme and Matthew S. Allen 2 Graduate Student; e-mail: cvandamme@wisc.edu 2 Associate Professor; e-mail: matt.allen@wisc.edu
SPACECRAFT EQUIPMENT VIBRATION QUALIFICATION TESTING APPLICABILITY AND ADVANTAGES OF NOTCHING
 SPACECRAFT EQUIPMENT VIBRATION QUALIFICATION TESTING APPLICABILITY AND ADVANTAGES OF NOTCHING Andrea Ceresetti Alenia Spazio S.p.A. - Technical Directorate Strada Antica di Collegno 53, 46 TORINO, Italy
SPACECRAFT EQUIPMENT VIBRATION QUALIFICATION TESTING APPLICABILITY AND ADVANTAGES OF NOTCHING Andrea Ceresetti Alenia Spazio S.p.A. - Technical Directorate Strada Antica di Collegno 53, 46 TORINO, Italy
Response Analysis for Multi Support Earthquake Excitation
 Chapter 5 Response Analysis for Multi Support Earthquake Excitation 5.1 Introduction It is very important to perform the dynamic analysis for the structure subjected to random/dynamic loadings. The dynamic
Chapter 5 Response Analysis for Multi Support Earthquake Excitation 5.1 Introduction It is very important to perform the dynamic analysis for the structure subjected to random/dynamic loadings. The dynamic
DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 41514
 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 454 PROJECT : Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Holistic Overview of the Project Steps & Their Conceptual Links
DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 454 PROJECT : Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Holistic Overview of the Project Steps & Their Conceptual Links
CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS. Base shear force in a linearly elastic system due to ground excitation is Vb
 CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS Base shear force in a linearl elastic sstem due to ground excitation is Vb = ( A/ g) w where A is the pseudo-acceleration corresponding to natural period
CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS Base shear force in a linearl elastic sstem due to ground excitation is Vb = ( A/ g) w where A is the pseudo-acceleration corresponding to natural period
