RVC-CAL dataflow implementations of MPEG AVC/H.264 CABAC decoding
|
|
|
- Merilyn McKinney
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RVC-CAL dataflow implementations of MPEG AVC/H.264 CABAC decoding Endri Bezati, Marco Mattavelli, Mickael Raulet To cite this version: Endri Bezati, Marco Mattavelli, Mickael Raulet. RVC-CAL dataflow implementations of MPEG AVC/H.264 CABAC decoding. Design and Architectures for Signal and Image Processing (DASIP), 2010 Conference on, 2010, United Kingdom. pp , 2010, < /DASIP >. <hal > HAL Id: hal Submitted on 11 Feb 2011 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access archive for the deposit and dissemination of scientific research documents, whether they are published or not. The documents may come from teaching and research institutions in France or abroad, or from public or private research centers. L archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des établissements d enseignement et de recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires publics ou privés.
2 RVC-CAL dataflow implementations of MPEG AVC/H.264 CABAC decoding Endri Bezati 1, Marco Mattavelli 1, Mickaël Raulet 2 Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, STI-SCI-MM 1 Institut National des Sciences Appliques de Rennes, IETR 2 ri.bezati@epfl.ch, marco.mattavelli@epfl.ch, mickael.raulet@insa-rennes.fr Abstract This paper presents the implementation of the CABAC entropy decoder in the RVC-CAL dataflow programming language. CABAC is the Context based Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding entropy decoder used in the AVC/H.264 main and high profile video standard. CABAC as an entropy decoding engine gives a better compression rate efficiency, but has a greater complexity compared to other entropy decoding engines. With the implementation of the CABAC entropy decoder in RVC-CAL, this paper is a proof that complex algorithms can be implemented in a high level design and that can be described in a data flow language as RVC- CAL is. Thought in this paper we are going to analyze two different methods of implementing the CABAC entropy decoder and propose a data flow model of the CABAC entropy decoder in RVC-CAL. 1. Introduction 1.1. RVC Standard The purpose of the MPEG RVC standard is to offer a more flexible use and faster path to innovation of MPEG standards in a way that is competitive in the current dynamic environment. This is meant to give MPEG standards an edge over its market competitors by substantially reducing the Time to Market (TTM). The RVC initiative exploits the reuse of obvious commonalities among different MPEG standards and their possible extensions using appropriate higher level formalisms. Thus the objective of the RVC standard is to describe current and future codecs in a way that makes such commonalities explicit, reducing the implementation burden for device vors. In order to achieve this objective, RVC suggests simplifying the specification of new coding tools by reusing components of previous standards instead of defining new ones. [1, 5] Figure 1. RVC Framework The MPEG-B standard defines the MPEG RVC framework and the RVC-CAL dataflow programming language. Also in the MPEG RVC framework the MPEG-C standard defines the library of the video coding tools (Video Tool Library or VTL). The Figure 1 describes how from an abstract decoder model using a Functional Unit (FU) network description a decoding solution can be achieved for a hardware or software implementation CAL Language CAL Actor Language is a language based on the Actor model of computation for data flow systems. It provides many natural concepts to facilitate modeling of those systems. An actor is a modular component that encapsulates its own state. Each actor interacts with each other through FIFO channels, see Figure 2. An actor in general contains global variables, state variables, global parameters, actions, procedures, functions and finite state machine to control the executions of actions. CAL enables concurrent development and has a strong encapsulation. CAL is used in a variety of applications and has been compiled to hardware and software implementations. The RVC-CAL language is a subset
3 of the CAL language the has been normalized by ISO/IEC as a part of the RVC standard. Although it has some restrictions in data types and feature that are in used in CAL [1,3]. Backs: Deping the target, ORCC offers a variety of back-s. Their purpose is to create target specific code. Each back will parse the hierarchical network from a top-level network and its child network. Also optionally it flattens the hierarchical network. ORCC for the moment offers a variety of backs. These back-s are C, C++, LLVM, VHDL and a partial support for the Xlim code generation. To generate a software decoding solution we used the C back of ORCC. The generated C code is ANSI-C compatible and it is portable to different platforms such as Windows, Linux, Mac OS X and others Entropy Encoding Figure 2. The CAL computing model 1.3. Open RVC-CAL Compiler In information theory an entropy encoding is a lossless data compression scheme that is indepent of the specific characteristics of the medium. In the AVC/H.264 three types of entropy encoding are used. Exp-Golomb for decoding the headers of the bitstream(video file). Furthermore the description of a macroblock and its quantized coefficients are encoded using the CAVLC or CABAC encoding. The Open RVC-CAL Compiler is a tool set which provides developers with a compiler infrastructure to generated source code in several languages from the RVC-CAL actors and XDF networks (a network of actors) [8] Figure 3. ORCC Framework Functional Unit (FU): is a video processing component or an actor in CAL language. The RVC framework provides a Video Tool Library which is consisted by a set of FUs that can be embedded by the client and combined for building the required decoder Front & IR : For a RVC-CAL dataflow program to be compiled, its compilation process its done in twosteps process. The fronted will parse all actors and it will translates them to an Intermediate Representation (IR) which is serialized to one file per actor in a JSONbased format (an XML file format). The IR is a data structure that is constructed from input data (the actor) to a program, and from which part or all of the output data of the program is constructed in turn. The next steps is to run a language target-specific back-. Figure 4. Entropy encoding as the final stage of compression 2. CABAC Entropy Decoder CABAC or Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding is an entropy decoder that gives better compression rates than the Baseline Profile CAVLC (Context Adaptive Variable Length Coding) entropy decoder. CABAC chooses a probability model for each syntax element, it adopts the estimated probability based on local statistics and it uses an arithmetic coder rather than variable-length coding (CAVLC). Though CAVLC is a lot more easy to implement and less power hungry, CAVLC gets the value directly by reading the bit-stream. However with CABAC the complexity is more important as there is a feedback loop between the context modeler and the arithmetic coder [2]. The H.264/AVC parser deping the context, demands the entropy decoding engine for the value of an Syntax Element (SE), see Figure 5. An SE is an element of data represented in the bit-stream, for example the Macro-block type Intra4x4, Intra16x16 or other.
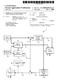
4 2.2. CABAC Variables In the H.264/AVC standard the prediction of the binary value is basically calculated by these variables. ctxidx, which indicates the context of the syntax element codirange and codioffset, corresponds to the status of the arithmetic decoding process Figure 5. An simple interpretation of the H.264/AVC parser Binarization Process Each SE has a particular binarization. four types of binarization are defined. In H.264/AVC Unary binarization, used for reference picture list reordering SE Truncate unary binarization, used for the Intra chroma prediction mode SE Concatenated unary/k-th order Exp-Golomb(UEKg) binarization, used mainly in the Residual block process and in the movement prediction for P and B slices Fixed Length binarization, used for flag types SE An example of the Fixed Length binarization process can be seen in the table below. The binidx, indicates the binary index of the binary string. For example this same binary strings indicates the values of the rem intra 4x4 pred mode and rem intra 8x8 pred mode SE from the H.264/AVC standard. Value of Syntax Element Bin String binidx Table 1. FL binarization with cmax = 7. pstateidx, corresponds to the probability state index valmps, corresponds to the value of the most probable symbol 2.3. CABAC Arithmetic coding engine After the binarization of an SE, each bin in the binarized string will be given an context (ctxidx) and then encoded using the CABAC arithmetic coding. The Context Arithmetic coding theory is based on the principle of recursive interval subdivision. Given a probability estimation p 0 and p 1 = 1 p 0 of the binary decision (0,1), codirange will be initially gives the code sub-interval, this range will be subdivided into two sub-intervals having the following range p 0 codirange and codirange p 0 codirange, respectively. Deping on the decision, the corresponding sub-interval is going to be chosen as the new code interval, and the binary code string pointing into that interval will represent the sequence of observed binary decisions. In the decoding decision procedure it is useful to distinguish between the most probable symbol (MPS) and the least probable symbol (LPS), it is better that the binary decisions have to be identified as either MPS or LPS, rather than 0 or 1. Given this terminology, each context is specified by the probability p of the LPS and the value of MPS (valmps), which is either 0 or 1. [7] 3. RVC-CAL CABAC Implementation The implementation of the RVC H.264/AVC parser FU in the current RVC-CAL AVC CBP (Constrained Base Profile) [4], [6] decoder is being used as a base for the CABAC entropy decoder. That means that each action used by the parser from the CAVLC is modified so that can support CABAC SE s extraction. The CABAC implementation is modelized by twelve untagged actions. These actions are not named in the source code because they are executed outside the FSM (Finite State Machine) of the parser FU. Here we give them names for clarity. We developed two methods to retrieve the Syntax Elements values from the AVC/H.264 parser Functional Unit. The first method is using a Look Up Table (LUT) for comparing the decode binary string given
5 by the CABAC procedure and the binarized Value of an Syntax Element. This method was later abandoned due to the complexity of the binarization LUT of the quantized coefficients (Macroblock residual values) and its slow double loop algorithm. Given the difficulty of the binarized residual values, we developed a new method, Bin By Bin, which is an adaptive decoding solution for each Syntax Element. Figure 6. RVC-CAL main CABAC parsing actions In the Figure 6 we represent the LUT and Bin by Bin method as CabacPasrsing, deping the method we want to use. CabacPasrsing is the main action and it controls the activation of the CABAC decoding actions. Deping the SE three actions are used to decode the binary value. These actions are DecodeDecision, DecodeByPass and DecodeTerminate. All three of them execute smaller actions to read the bitstream. Figure 7. The LUT Method needed to execute 255*(n bins) double loops. So to make the process more faster we created the Bin By Bin method. In this method each SE has a different de-binarization procedure. In this way the CABAC decoding is unique for each SE Look Up Table method After the CABAC arithmetic decoding the decoded bins have to be de-binarized so the value can we retrieved. A very simple way to get the decoding value from CABAC de-binarization is to use a Look Up Table. As Each SE has a specific binarization the idea was to create a look up-table for each SE and to stock the binarized values in a multi dimension table. Thus index of the table will be the decoded value and the rows of the table represents binarized bin string. With this method bits are recovered one by one and then are compared with the binarization table of the searched SE. As we mentioned before we abandoned this method, but all the SE expect the coeff abs level minus1 (quantized coefficients), ref lx and mvd lx (mouvement vectors) fully functional Bin by Bin method Using a LUT demands more memory and the compare algorithm could be much more time consuming. For example to decode the 255 residual value of the coeff abs level minus1 SE with LUT method, the algorithm Figure 8. The Bin By Bin Method The Figure 9 shows a part of the coeff abs level minus1 SE de-binarization process, this procedure is called as many times as the SE value is completely de-binarized. 4. Results 4.1. Conformance Sequences support The RVC-CAL CABAC implementation supports all the Syntax Element found in the AVC/H.264 standard except
6 procedure CoeffAbsParsing ( ) begin i f S t a r t P r e f i x then i f binvaldecoded = f a l s e then b i n I d x : = b i n I d x + 1 ; / / g i v e t h e c t x I d x ctxidxcoeffabslevel ( ) ; / / Get t h e b i n Value S t a r t D e c o d e D e c i s i o n := true ; C a b a c S t a r t P r o c e s s := f a l s e ; NextBitToDecode := f a l s e ; b i n I d x := 0 ;... i f binvaldecoded = true then / / I n c r e m e n t b i n I d x b i n I d x : = b i n I d x + 1 ; i f binval = 1 then CabacValue : = 1; e l s e CabacValue : = 1 ; / / F i n i s h i n g t h e P r e f i x f o r a 0 b i n V a l S t a r t P r e f i x := f a l s e ; numdecodabsleveleq1 := numdecodabsleveleq1 + 1 ; / / Stop cabac p r o c e s s and g i v e t h e v a l u e C a b a c S t a r t P r o c e s s := f a l s e ; FoundSE := true ;.... Figure 9. A part of the coeff abs level minus1 SE de-binarization procedure. the mb field decoding flag (which indicates if the macroblock is field coded). Also because the abstract decoder model used in this implementation is coming for the AVC CBP FU, it does not support the decoding of the BiPred slices. Thus our CABAC implementation supports all the encoded Macroblock SE except those coded in field order. The following Table 2 is a list of supported conformance AVC/H.264 sequences coded using the CABAC entropy encoding. Because of the AVC CBP FU the sequence marked as IPB are supported only by the AVC Parser FU, the decoding of those sequence is a work in progress of the AVC FRExt FU(Fidelity Range Extensions). Name Slice Type N. Frames Status CABA1 Sony D I 50 Passed CABA2 Sony E IP 300 Passed CABA3 Sony C IPB 300 Only Parser CABA3 TOSHIBA E IP 300 Passed CABA1 SVA B I 17 Passed CABA2 SVA B IP 17 Passed CABA3 SVA C IPB 33 Only Parser CANL1 TOSHIBA G I 300 Passed CANL1 Sony E I 17 Passed CANL2 Sony E IP 300 Passed CANL3 SVA C IPB 300 Only Parser CANL1 SVA B I 17 Passed CANL2 SVA B I 17 Passed CANL3 SVA B IP 17 Passed CANL4 SVA C IPB 33 Only Parser CAQP1 Sony B IP 50 Passed CACQP3 Sony D IPB 50 Only Parser Table 2. Conformance sequences supported by the Bin By Bin RVC-CAL implementation cally copy the of the Decode Decision flowchart. In addition the C code of the JM software contains pointers, the variables are not named exactly the same and in general the code readability is not as easy to read and analysable as the RVC-CAL code. Our full implementation of the CABAC in RVC-CAL contains less source code than the C implementation of the JM AVC decoder source code lines for the RVC-CAL and more than 3000 lines for the C code RVC-CAL CABAC versus JM CABAC implementation The RVC-CAL is by design ment to be a high level language. The Decode Decision process is used by almost all Syntax Element in the H.264/AVC standard. Here we compare the interpretation of the H.264/AVC Decode Decision flowchart(figure 10) with the RVC-CAL (Figure 11) and the C language used in the JM software Reference software of the H.264/AVC Standard (Figure 12). In term of source code we have exactly the same line of codes for this two different implementations but the difference is in the readability and the understanding of the source code. The RVC-CAL implementation is an identi- Figure 10. Decoding Decision flowchart in the H.264/AVC standard.
7 DecodeDecision : action guard S t a r t D e c o d e D e c i s i o n and b y p a s s F l a g = f a l s e and c t x I d x!= 276 and StartRenormD = f a l s e do qcodirangeidx := ( codirange >> 6 ) & 3 ; codirangelps : = rangetablps [ p S t a t e I d x [ c t x I d x ] ] [ qcodirangeidx ] ; codirange := codirange codirangelps ; i f c o d I O f f s e t >= codirange then binval := intxor ( valmps [ c t x I d x ] ) ; c o d I O f f s e t := c o d I O f f s e t codirange ; codirange := codirangelps ; i f p S t a t e I d x [ c t x I d x ] = 0 then valmps [ c t x I d x ] := 1 valmps [ c t x I d x ] ; p S t a t e I d x [ c t x I d x ] := t r a n s I d x L P S [ p S t a t e I d x [ c t x I d x ] ] ; e l s e binval := valmps [ c t x I d x ] ; p S t a t e I d x [ c t x I d x ] := transidxmps [ p S t a t e I d x [ c t x I d x ] ] ; / / Give t h e r i g h t t o compare i n CabacParsing binvaldecoded := true ; / / w r i t e t h e b i t i n t o t h e R e a d B i n S t r i n g Re ad B in St ri ng [ b i n I d x + 1] := binval ; i f codirange < 0 x0100 then StartRenormDRead := true ; e l s e C a b a c S t a r t P r o c e s s := true ; / / Do not c a l l again DecodeDecision S t a r t D e c o d e D e c i s i o n := f a l s e ; / / Do n o t g i v e t h e hand t o CabacParsing Figure 11. Decoding Decision action written in RVC-CAL. 5. To a data flow model The actual form of the AVC parser in RVC-CAL is sequential, as is supposed to be for a parser. As RVC-CAL is data flow based language, the idea here is to transform it s sequential form to a data flow one. Actually the challenge is how to pipeline a sequential parser. As a matter of fact the bitsream has a start up code when a new slice starts. We can store the whole bitstream for a slice to buffer and then analyzed it and dispatched it to where is necessary. Actually in this way we can separate the parser process in smaller actors and create a pipeline architecture. These actors are the BitstreamAnalyser, NAL, SPS, PPS, Slice- Header and EntropyDecoding. Appart EntropyDecoding all other actors are explicit, for a reconfigurable decoder is a necessity to separate the CAVLC and the CABAC entropy Decoding. So in the EntropyDecoding actor we will regroup SliceData, macroblock layer, mb pred, sub mb pred, residual and residual block [7]. The Figure 13 shows how unsigned i n t b i a r i d e c o d e s y m b o l ( D e c o d i n g E n v i r o n m e n t P t r dep, BiContextTypePtr b i c t ) { unsigned i n t b i t = b i c t >MPS; unsigned i n t v a l u e = &dep >Dvalue ; unsigned i n t r a n g e = &dep >Drange ; u i n t 1 6 s t a t e = &b i c t >s t a t e ; unsigned i n t rlps = r L P S t a b l e 6 4 x 4 [ s t a t e ] [ ( range >>6) & 0 x03 ] ; i n t D b i t s L e f t = &dep >D b i t s L e f t ; range = rlps ; i f ( v a l u e < ( r a n g e << D b i t s L e f t ) ) { / / MPS s t a t e = A C next s tate MPS 64 [ s t a t e ] ; / / n e x t s t a t e i f ( r a n g e >= QUARTER ){ return ( b i t ) ; } e l s e r a n g e <<= 1 ; ( D b i t s L e f t ) ; } e l s e { / / LPS i n t renorm = r e n o r m t a b l e 3 2 [ ( rlps>>3) & 0x1F ] ; v a l u e = ( r a n g e << dep >D b i t s L e f t ) ; range = ( rlps << renorm ) ; ( D b i t s L e f t ) = renorm ; b i t ˆ= 0 x01 ; i f (! ( s t a t e ) ) / / s w i t c h meaning o f MPS i f n e c e s s a r y b i c t >MPS ˆ= 0 x01 ; s t a t e = A C n e x t s t a t e L P S 6 4 [ s t a t e ] ; / / n e x t s t a t e } i f ( D b i t s L e f t > 0 ){ return ( b i t ) ; } e l s e { v a l u e <<= 1 6 ; value = getword ( dep ) ; ( D b i t s L e f t ) += 1 6 ; return ( b i t ) ; } } Figure 12. Decoding Decision action written in C from the JM. the sequential AVC/H.264 parser can be transformed to a dataflow model using RVC-CAL. Figure 13. A DataFlow model for the H.264/AVC Parser
8 6. Conclusions Implementing the basic CABAC process in RVC-CAL took one month and two months for making it possible to decode the I,P and B slices. Our implementation is supporting all the CABAC encoded Syntax Elements found in the AVC/H.264 standard except the Macroblock field flag. The software generated decoder by our RVC-CAL abstract description can successfully decode a big part of the AVC/H.264 conformance sequences. Using RVC-CAL to interpret the H.264/AVC standard is really easy and this cuts a lot the conception time and actual work compared to other languages. With RVC-CAL is not only possible to implement a type of algorithm in one way but you can implement it as sequential monolithic process, a monolithic dataflow model and to a networked data flow model. Thus implementing the AVC/H.264 Parser in a data flow model and it s entropy decoding engines (CAVLC and CABAC) will achieve higher performances than the actual monolithic data flow model. References [1] S. S. Bhattacharyya, J. Eker, J. W. Janneck, C. Lucarz, M. Mattavelli, and M. Raulet. Overview of the MPEG Reconfigurable Video Coding Framework. Springer journal of Signal Processing Systems. Special Issue on Reconfigurable Video Coding, [2] H. Eeckhaut, M. Christiaens, D. Stroobandt, and V. Nollet. Optimizing the critical loop in the H.264/AVC CABAC decoder. Field Programmable Technology, FPT IEEE International Conference, [3] J. Eker and J. Janneck. CAL Language Report. Technical Report ERL Technical Memo UCB/ERL M03/48, University of California at Berkeley, Dec [4] J. Gorin, M. Raulet, Y. Cheng, H. Lin, N. Siret, K. Sugimoto, and G. Lee. An RVC Dataflow Description of the AVC Constrained Baseline Profile Decoder. In Proceedings of ICIP 09, Nov [5] ISO/IEC FDIS MPEG systems technologies Part 4: Codec Configuration Representation, [6] J. W. Janneck, M. Mattavelli, M. Raulet, and M. Wipliez. Reconfigurable video coding: a stream programming approach to the specification of new video coding standards. In MMSys 10: Proceedings of the first annual ACM SIGMM conference on Multimedia systems, pages , New York, NY, USA, ACM. [7] I. JTC1/SC29/WG11 and I.-T. S. Q.6. Joint Draft ITU-T Rec. H.264 ISO/IEC / Amd.3 Scalable video coding, [8] M. Wipliez, G. Roquier, and J. Nezan. Software Code Generation for the RVC-CAL Language. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 2009.
Smart Bolometer: Toward Monolithic Bolometer with Smart Functions
 Smart Bolometer: Toward Monolithic Bolometer with Smart Functions Matthieu Denoual, Gilles Allègre, Patrick Attia, Olivier De Sagazan To cite this version: Matthieu Denoual, Gilles Allègre, Patrick Attia,
Smart Bolometer: Toward Monolithic Bolometer with Smart Functions Matthieu Denoual, Gilles Allègre, Patrick Attia, Olivier De Sagazan To cite this version: Matthieu Denoual, Gilles Allègre, Patrick Attia,
A new simple recursive algorithm for finding prime numbers using Rosser s theorem
 A new simple recursive algorithm for finding prime numbers using Rosser s theorem Rédoane Daoudi To cite this version: Rédoane Daoudi. A new simple recursive algorithm for finding prime numbers using Rosser
A new simple recursive algorithm for finding prime numbers using Rosser s theorem Rédoane Daoudi To cite this version: Rédoane Daoudi. A new simple recursive algorithm for finding prime numbers using Rosser
A Simple Proof of P versus NP
 A Simple Proof of P versus NP Frank Vega To cite this version: Frank Vega. A Simple Proof of P versus NP. 2016. HAL Id: hal-01281254 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01281254 Submitted
A Simple Proof of P versus NP Frank Vega To cite this version: Frank Vega. A Simple Proof of P versus NP. 2016. HAL Id: hal-01281254 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01281254 Submitted
Intra Prediction by a linear combination of Template Matching predictors
 Intra Prediction by a linear combination of Template Matching predictors Laurent Guillo, Tangi Poirier, Christine Guillemot To cite this version: Laurent Guillo, Tangi Poirier, Christine Guillemot. Intra
Intra Prediction by a linear combination of Template Matching predictors Laurent Guillo, Tangi Poirier, Christine Guillemot To cite this version: Laurent Guillo, Tangi Poirier, Christine Guillemot. Intra
Learning an Adaptive Dictionary Structure for Efficient Image Sparse Coding
 Learning an Adaptive Dictionary Structure for Efficient Image Sparse Coding Jérémy Aghaei Mazaheri, Christine Guillemot, Claude Labit To cite this version: Jérémy Aghaei Mazaheri, Christine Guillemot,
Learning an Adaptive Dictionary Structure for Efficient Image Sparse Coding Jérémy Aghaei Mazaheri, Christine Guillemot, Claude Labit To cite this version: Jérémy Aghaei Mazaheri, Christine Guillemot,
Computer Engineering Mekelweg 4, 2628 CD Delft The Netherlands MSc THESIS
 Computer Engineering Mekelweg 4, 2628 CD Delft The Netherlands http://ce.et.tudelft.nl/ 2010 MSc THESIS Analysis and Implementation of the H.264 CABAC entropy decoding engine Martinus Johannes Pieter Berkhoff
Computer Engineering Mekelweg 4, 2628 CD Delft The Netherlands http://ce.et.tudelft.nl/ 2010 MSc THESIS Analysis and Implementation of the H.264 CABAC entropy decoding engine Martinus Johannes Pieter Berkhoff
Methylation-associated PHOX2B gene silencing is a rare event in human neuroblastoma.
 Methylation-associated PHOX2B gene silencing is a rare event in human neuroblastoma. Loïc De Pontual, Delphine Trochet, Franck Bourdeaut, Sophie Thomas, Heather Etchevers, Agnes Chompret, Véronique Minard,
Methylation-associated PHOX2B gene silencing is a rare event in human neuroblastoma. Loïc De Pontual, Delphine Trochet, Franck Bourdeaut, Sophie Thomas, Heather Etchevers, Agnes Chompret, Véronique Minard,
On Newton-Raphson iteration for multiplicative inverses modulo prime powers
 On Newton-Raphson iteration for multiplicative inverses modulo prime powers Jean-Guillaume Dumas To cite this version: Jean-Guillaume Dumas. On Newton-Raphson iteration for multiplicative inverses modulo
On Newton-Raphson iteration for multiplicative inverses modulo prime powers Jean-Guillaume Dumas To cite this version: Jean-Guillaume Dumas. On Newton-Raphson iteration for multiplicative inverses modulo
Easter bracelets for years
 Easter bracelets for 5700000 years Denis Roegel To cite this version: Denis Roegel. Easter bracelets for 5700000 years. [Research Report] 2014. HAL Id: hal-01009457 https://hal.inria.fr/hal-01009457
Easter bracelets for 5700000 years Denis Roegel To cite this version: Denis Roegel. Easter bracelets for 5700000 years. [Research Report] 2014. HAL Id: hal-01009457 https://hal.inria.fr/hal-01009457
H.264/MPEG4 Part INTRODUCTION Terminology
 6 H.264/MPEG4 Part 10 6.1 INTRODUCTION The Moving Picture Experts Group and the Video Coding Experts Group (MPEG and VCEG) have developed a new standard that promises to outperform the earlier MPEG-4 and
6 H.264/MPEG4 Part 10 6.1 INTRODUCTION The Moving Picture Experts Group and the Video Coding Experts Group (MPEG and VCEG) have developed a new standard that promises to outperform the earlier MPEG-4 and
Vibro-acoustic simulation of a car window
 Vibro-acoustic simulation of a car window Christophe Barras To cite this version: Christophe Barras. Vibro-acoustic simulation of a car window. Société Française d Acoustique. Acoustics 12, Apr 12, Nantes,
Vibro-acoustic simulation of a car window Christophe Barras To cite this version: Christophe Barras. Vibro-acoustic simulation of a car window. Société Française d Acoustique. Acoustics 12, Apr 12, Nantes,
The magnetic field diffusion equation including dynamic, hysteresis: A linear formulation of the problem
 The magnetic field diffusion equation including dynamic, hysteresis: A linear formulation of the problem Marie-Ange Raulet, Benjamin Ducharne, Jean-Pierre Masson, G. Bayada To cite this version: Marie-Ange
The magnetic field diffusion equation including dynamic, hysteresis: A linear formulation of the problem Marie-Ange Raulet, Benjamin Ducharne, Jean-Pierre Masson, G. Bayada To cite this version: Marie-Ange
Exact Comparison of Quadratic Irrationals
 Exact Comparison of Quadratic Irrationals Phuc Ngo To cite this version: Phuc Ngo. Exact Comparison of Quadratic Irrationals. [Research Report] LIGM. 20. HAL Id: hal-0069762 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-0069762
Exact Comparison of Quadratic Irrationals Phuc Ngo To cite this version: Phuc Ngo. Exact Comparison of Quadratic Irrationals. [Research Report] LIGM. 20. HAL Id: hal-0069762 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-0069762
Can we reduce health inequalities? An analysis of the English strategy ( )
 Can we reduce health inequalities? An analysis of the English strategy (1997-2010) Johan P Mackenbach To cite this version: Johan P Mackenbach. Can we reduce health inequalities? An analysis of the English
Can we reduce health inequalities? An analysis of the English strategy (1997-2010) Johan P Mackenbach To cite this version: Johan P Mackenbach. Can we reduce health inequalities? An analysis of the English
How to make R, PostGIS and QGis cooperate for statistical modelling duties: a case study on hedonic regressions
 How to make R, PostGIS and QGis cooperate for statistical modelling duties: a case study on hedonic regressions Olivier Bonin To cite this version: Olivier Bonin. How to make R, PostGIS and QGis cooperate
How to make R, PostGIS and QGis cooperate for statistical modelling duties: a case study on hedonic regressions Olivier Bonin To cite this version: Olivier Bonin. How to make R, PostGIS and QGis cooperate
Full-order observers for linear systems with unknown inputs
 Full-order observers for linear systems with unknown inputs Mohamed Darouach, Michel Zasadzinski, Shi Jie Xu To cite this version: Mohamed Darouach, Michel Zasadzinski, Shi Jie Xu. Full-order observers
Full-order observers for linear systems with unknown inputs Mohamed Darouach, Michel Zasadzinski, Shi Jie Xu To cite this version: Mohamed Darouach, Michel Zasadzinski, Shi Jie Xu. Full-order observers
The Accelerated Euclidean Algorithm
 The Accelerated Euclidean Algorithm Sidi Mohamed Sedjelmaci To cite this version: Sidi Mohamed Sedjelmaci The Accelerated Euclidean Algorithm Laureano Gonzales-Vega and Thomas Recio Eds 2004, University
The Accelerated Euclidean Algorithm Sidi Mohamed Sedjelmaci To cite this version: Sidi Mohamed Sedjelmaci The Accelerated Euclidean Algorithm Laureano Gonzales-Vega and Thomas Recio Eds 2004, University
A non-commutative algorithm for multiplying (7 7) matrices using 250 multiplications
 A non-commutative algorithm for multiplying (7 7) matrices using 250 multiplications Alexandre Sedoglavic To cite this version: Alexandre Sedoglavic. A non-commutative algorithm for multiplying (7 7) matrices
A non-commutative algorithm for multiplying (7 7) matrices using 250 multiplications Alexandre Sedoglavic To cite this version: Alexandre Sedoglavic. A non-commutative algorithm for multiplying (7 7) matrices
3D-CE5.h: Merge candidate list for disparity compensated prediction
 3D-CE5.h: Merge candidate list for disparity compensated prediction Thomas Guionnet, Laurent Guillo, Guillemot Christine To cite this version: Thomas Guionnet, Laurent Guillo, Guillemot Christine. 3D-CE5.h:
3D-CE5.h: Merge candidate list for disparity compensated prediction Thomas Guionnet, Laurent Guillo, Guillemot Christine To cite this version: Thomas Guionnet, Laurent Guillo, Guillemot Christine. 3D-CE5.h:
Case report on the article Water nanoelectrolysis: A simple model, Journal of Applied Physics (2017) 122,
 Case report on the article Water nanoelectrolysis: A simple model, Journal of Applied Physics (2017) 122, 244902 Juan Olives, Zoubida Hammadi, Roger Morin, Laurent Lapena To cite this version: Juan Olives,
Case report on the article Water nanoelectrolysis: A simple model, Journal of Applied Physics (2017) 122, 244902 Juan Olives, Zoubida Hammadi, Roger Morin, Laurent Lapena To cite this version: Juan Olives,
Detailed Review of H.264/AVC
 Detailed Review of H.264/AVC, Ph.D.. abuhajar@digitavid.net (408) 506-2776 P.O. BOX:720998 San Jose, CA 95172 1 Outline Common Terminologies Color Space Macroblock and Slice Type Slice Block Diagram Intra-Prediction
Detailed Review of H.264/AVC, Ph.D.. abuhajar@digitavid.net (408) 506-2776 P.O. BOX:720998 San Jose, CA 95172 1 Outline Common Terminologies Color Space Macroblock and Slice Type Slice Block Diagram Intra-Prediction
On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian Block-Matrices
 On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices Antoine Mhanna To cite this version: Antoine Mhanna On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices 015 HAL Id: hal-0131860
On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices Antoine Mhanna To cite this version: Antoine Mhanna On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices 015 HAL Id: hal-0131860
Completeness of the Tree System for Propositional Classical Logic
 Completeness of the Tree System for Propositional Classical Logic Shahid Rahman To cite this version: Shahid Rahman. Completeness of the Tree System for Propositional Classical Logic. Licence. France.
Completeness of the Tree System for Propositional Classical Logic Shahid Rahman To cite this version: Shahid Rahman. Completeness of the Tree System for Propositional Classical Logic. Licence. France.
Dispersion relation results for VCS at JLab
 Dispersion relation results for VCS at JLab G. Laveissiere To cite this version: G. Laveissiere. Dispersion relation results for VCS at JLab. Compton Scattering from Low to High Momentum Transfer, Mar
Dispersion relation results for VCS at JLab G. Laveissiere To cite this version: G. Laveissiere. Dispersion relation results for VCS at JLab. Compton Scattering from Low to High Momentum Transfer, Mar
Evolution of the cooperation and consequences of a decrease in plant diversity on the root symbiont diversity
 Evolution of the cooperation and consequences of a decrease in plant diversity on the root symbiont diversity Marie Duhamel To cite this version: Marie Duhamel. Evolution of the cooperation and consequences
Evolution of the cooperation and consequences of a decrease in plant diversity on the root symbiont diversity Marie Duhamel To cite this version: Marie Duhamel. Evolution of the cooperation and consequences
Fast Computation of Moore-Penrose Inverse Matrices
 Fast Computation of Moore-Penrose Inverse Matrices Pierre Courrieu To cite this version: Pierre Courrieu. Fast Computation of Moore-Penrose Inverse Matrices. Neural Information Processing - Letters and
Fast Computation of Moore-Penrose Inverse Matrices Pierre Courrieu To cite this version: Pierre Courrieu. Fast Computation of Moore-Penrose Inverse Matrices. Neural Information Processing - Letters and
Passerelle entre les arts : la sculpture sonore
 Passerelle entre les arts : la sculpture sonore Anaïs Rolez To cite this version: Anaïs Rolez. Passerelle entre les arts : la sculpture sonore. Article destiné à l origine à la Revue de l Institut National
Passerelle entre les arts : la sculpture sonore Anaïs Rolez To cite this version: Anaïs Rolez. Passerelle entre les arts : la sculpture sonore. Article destiné à l origine à la Revue de l Institut National
AN IMPROVED CONTEXT ADAPTIVE BINARY ARITHMETIC CODER FOR THE H.264/AVC STANDARD
 4th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2006), Florence, Italy, September 4-8, 2006, copyright by EURASIP AN IMPROVED CONTEXT ADAPTIVE BINARY ARITHMETIC CODER FOR THE H.264/AVC STANDARD Simone
4th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2006), Florence, Italy, September 4-8, 2006, copyright by EURASIP AN IMPROVED CONTEXT ADAPTIVE BINARY ARITHMETIC CODER FOR THE H.264/AVC STANDARD Simone
A new approach of the concept of prime number
 A new approach of the concept of prime number Jamel Ghannouchi To cite this version: Jamel Ghannouchi. A new approach of the concept of prime number. 4 pages. 24. HAL Id: hal-3943 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-3943
A new approach of the concept of prime number Jamel Ghannouchi To cite this version: Jamel Ghannouchi. A new approach of the concept of prime number. 4 pages. 24. HAL Id: hal-3943 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-3943
Solving the neutron slowing down equation
 Solving the neutron slowing down equation Bertrand Mercier, Jinghan Peng To cite this version: Bertrand Mercier, Jinghan Peng. Solving the neutron slowing down equation. 2014. HAL Id: hal-01081772
Solving the neutron slowing down equation Bertrand Mercier, Jinghan Peng To cite this version: Bertrand Mercier, Jinghan Peng. Solving the neutron slowing down equation. 2014. HAL Id: hal-01081772
Analysis of Boyer and Moore s MJRTY algorithm
 Analysis of Boyer and Moore s MJRTY algorithm Laurent Alonso, Edward M. Reingold To cite this version: Laurent Alonso, Edward M. Reingold. Analysis of Boyer and Moore s MJRTY algorithm. Information Processing
Analysis of Boyer and Moore s MJRTY algorithm Laurent Alonso, Edward M. Reingold To cite this version: Laurent Alonso, Edward M. Reingold. Analysis of Boyer and Moore s MJRTY algorithm. Information Processing
Hardware Operator for Simultaneous Sine and Cosine Evaluation
 Hardware Operator for Simultaneous Sine and Cosine Evaluation Arnaud Tisserand To cite this version: Arnaud Tisserand. Hardware Operator for Simultaneous Sine and Cosine Evaluation. ICASSP 6: International
Hardware Operator for Simultaneous Sine and Cosine Evaluation Arnaud Tisserand To cite this version: Arnaud Tisserand. Hardware Operator for Simultaneous Sine and Cosine Evaluation. ICASSP 6: International
From Unstructured 3D Point Clouds to Structured Knowledge - A Semantics Approach
 From Unstructured 3D Point Clouds to Structured Knowledge - A Semantics Approach Christophe Cruz, Helmi Ben Hmida, Frank Boochs, Christophe Nicolle To cite this version: Christophe Cruz, Helmi Ben Hmida,
From Unstructured 3D Point Clouds to Structured Knowledge - A Semantics Approach Christophe Cruz, Helmi Ben Hmida, Frank Boochs, Christophe Nicolle To cite this version: Christophe Cruz, Helmi Ben Hmida,
Entropies and fractal dimensions
 Entropies and fractal dimensions Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. Entropies and fractal dimensions. Philica, Philica, 2016. HAL Id: hal-01377975
Entropies and fractal dimensions Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. Entropies and fractal dimensions. Philica, Philica, 2016. HAL Id: hal-01377975
Performance analysis of clouds with phase-type arrivals
 Performance analysis of clouds with phase-type arrivals Farah Ait Salaht, Hind Castel-Taleb To cite this version: Farah Ait Salaht, Hind Castel-Taleb. Performance analysis of clouds with phase-type arrivals.
Performance analysis of clouds with phase-type arrivals Farah Ait Salaht, Hind Castel-Taleb To cite this version: Farah Ait Salaht, Hind Castel-Taleb. Performance analysis of clouds with phase-type arrivals.
b-chromatic number of cacti
 b-chromatic number of cacti Victor Campos, Claudia Linhares Sales, Frédéric Maffray, Ana Silva To cite this version: Victor Campos, Claudia Linhares Sales, Frédéric Maffray, Ana Silva. b-chromatic number
b-chromatic number of cacti Victor Campos, Claudia Linhares Sales, Frédéric Maffray, Ana Silva To cite this version: Victor Campos, Claudia Linhares Sales, Frédéric Maffray, Ana Silva. b-chromatic number
Thomas Lugand. To cite this version: HAL Id: tel
 Contribution à la Modélisation et à l Optimisation de la Machine Asynchrone Double Alimentation pour des Applications Hydrauliques de Pompage Turbinage Thomas Lugand To cite this version: Thomas Lugand.
Contribution à la Modélisation et à l Optimisation de la Machine Asynchrone Double Alimentation pour des Applications Hydrauliques de Pompage Turbinage Thomas Lugand To cite this version: Thomas Lugand.
A non-linear simulator written in C for orbital spacecraft rendezvous applications.
 A non-linear simulator written in C for orbital spacecraft rendezvous applications. Paulo Ricardo Arantes Gilz To cite this version: Paulo Ricardo Arantes Gilz. A non-linear simulator written in C for
A non-linear simulator written in C for orbital spacecraft rendezvous applications. Paulo Ricardo Arantes Gilz To cite this version: Paulo Ricardo Arantes Gilz. A non-linear simulator written in C for
PRESSURE FLUCTUATION NUMERICAL SIMULATION IN A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP VOLUTE CASING
 PRESSURE FLUCTUATION NUMERICAL SIMULATION IN A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP VOLUTE CASING S. Timushev, B. Ovsyannikov To cite this version: S. Timushev, B. Ovsyannikov. PRESSURE FLUCTUATION NUMERICAL SIMULATION IN
PRESSURE FLUCTUATION NUMERICAL SIMULATION IN A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP VOLUTE CASING S. Timushev, B. Ovsyannikov To cite this version: S. Timushev, B. Ovsyannikov. PRESSURE FLUCTUATION NUMERICAL SIMULATION IN
Optical component modelling and circuit simulation using SERENADE suite
 Optical component modelling and circuit simulation using SERENADE suite Laurent Guilloton, Smail Tedjini, Tan-Phu Vuong To cite this version: Laurent Guilloton, Smail Tedjini, Tan-Phu Vuong. Optical component
Optical component modelling and circuit simulation using SERENADE suite Laurent Guilloton, Smail Tedjini, Tan-Phu Vuong To cite this version: Laurent Guilloton, Smail Tedjini, Tan-Phu Vuong. Optical component
A note on the computation of the fraction of smallest denominator in between two irreducible fractions
 A note on the computation of the fraction of smallest denominator in between two irreducible fractions Isabelle Sivignon To cite this version: Isabelle Sivignon. A note on the computation of the fraction
A note on the computation of the fraction of smallest denominator in between two irreducible fractions Isabelle Sivignon To cite this version: Isabelle Sivignon. A note on the computation of the fraction
L institution sportive : rêve et illusion
 L institution sportive : rêve et illusion Hafsi Bedhioufi, Sida Ayachi, Imen Ben Amar To cite this version: Hafsi Bedhioufi, Sida Ayachi, Imen Ben Amar. L institution sportive : rêve et illusion. Revue
L institution sportive : rêve et illusion Hafsi Bedhioufi, Sida Ayachi, Imen Ben Amar To cite this version: Hafsi Bedhioufi, Sida Ayachi, Imen Ben Amar. L institution sportive : rêve et illusion. Revue
Numerical Exploration of the Compacted Associated Stirling Numbers
 Numerical Exploration of the Compacted Associated Stirling Numbers Khaled Ben Letaïef To cite this version: Khaled Ben Letaïef. Numerical Exploration of the Compacted Associated Stirling Numbers. 2017.
Numerical Exploration of the Compacted Associated Stirling Numbers Khaled Ben Letaïef To cite this version: Khaled Ben Letaïef. Numerical Exploration of the Compacted Associated Stirling Numbers. 2017.
The Riemann Hypothesis Proof And The Quadrivium Theory
 The Riemann Hypothesis Proof And The Quadrivium Theory Thierno M. Sow To cite this version: Thierno M. Sow. The Riemann Hypothesis Proof And The Quadrivium Theory. 2017. HAL Id: hal-01513658 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01513658
The Riemann Hypothesis Proof And The Quadrivium Theory Thierno M. Sow To cite this version: Thierno M. Sow. The Riemann Hypothesis Proof And The Quadrivium Theory. 2017. HAL Id: hal-01513658 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01513658
Solving an integrated Job-Shop problem with human resource constraints
 Solving an integrated Job-Shop problem with human resource constraints Olivier Guyon, Pierre Lemaire, Eric Pinson, David Rivreau To cite this version: Olivier Guyon, Pierre Lemaire, Eric Pinson, David
Solving an integrated Job-Shop problem with human resource constraints Olivier Guyon, Pierre Lemaire, Eric Pinson, David Rivreau To cite this version: Olivier Guyon, Pierre Lemaire, Eric Pinson, David
Improving the Jet Reconstruction with the Particle Flow Method; an Introduction
 Improving the Jet Reconstruction with the Particle Flow Method; an Introduction Jean-Claude Brient To cite this version: Jean-Claude Brient. Improving the Jet Reconstruction with the Particle Flow Method;
Improving the Jet Reconstruction with the Particle Flow Method; an Introduction Jean-Claude Brient To cite this version: Jean-Claude Brient. Improving the Jet Reconstruction with the Particle Flow Method;
On sl3 KZ equations and W3 null-vector equations
 On sl3 KZ equations and W3 null-vector equations Sylvain Ribault To cite this version: Sylvain Ribault. On sl3 KZ equations and W3 null-vector equations. Conformal Field Theory, Integrable Models, and
On sl3 KZ equations and W3 null-vector equations Sylvain Ribault To cite this version: Sylvain Ribault. On sl3 KZ equations and W3 null-vector equations. Conformal Field Theory, Integrable Models, and
Quantum efficiency and metastable lifetime measurements in ruby ( Cr 3+ : Al2O3) via lock-in rate-window photothermal radiometry
 Quantum efficiency and metastable lifetime measurements in ruby ( Cr 3+ : Al2O3) via lock-in rate-window photothermal radiometry A. Mandelis, Z. Chen, R. Bleiss To cite this version: A. Mandelis, Z. Chen,
Quantum efficiency and metastable lifetime measurements in ruby ( Cr 3+ : Al2O3) via lock-in rate-window photothermal radiometry A. Mandelis, Z. Chen, R. Bleiss To cite this version: A. Mandelis, Z. Chen,
Soundness of the System of Semantic Trees for Classical Logic based on Fitting and Smullyan
 Soundness of the System of Semantic Trees for Classical Logic based on Fitting and Smullyan Shahid Rahman To cite this version: Shahid Rahman. Soundness of the System of Semantic Trees for Classical Logic
Soundness of the System of Semantic Trees for Classical Logic based on Fitting and Smullyan Shahid Rahman To cite this version: Shahid Rahman. Soundness of the System of Semantic Trees for Classical Logic
Trench IGBT failure mechanisms evolution with temperature and gate resistance under various short-circuit conditions
 Trench IGBT failure mechanisms evolution with temperature and gate resistance under various short-circuit conditions Adel Benmansour, Stephane Azzopardi, Jean-Christophe Martin, Eric Woirgard To cite this
Trench IGBT failure mechanisms evolution with temperature and gate resistance under various short-circuit conditions Adel Benmansour, Stephane Azzopardi, Jean-Christophe Martin, Eric Woirgard To cite this
Entropy Coders of the H.264/AVC Standard
 Signals and Communication Technology Entropy Coders of the H.264/AVC Standard Algorithms and VLSI Architectures Bearbeitet von Xiaohua Tian, Thinh M Le, Yong Lian 1st Edition. 2010. Buch. XXIV, 180 S.
Signals and Communication Technology Entropy Coders of the H.264/AVC Standard Algorithms and VLSI Architectures Bearbeitet von Xiaohua Tian, Thinh M Le, Yong Lian 1st Edition. 2010. Buch. XXIV, 180 S.
Computable priors sharpened into Occam s razors
 Computable priors sharpened into Occam s razors David R. Bickel To cite this version: David R. Bickel. Computable priors sharpened into Occam s razors. 2016. HAL Id: hal-01423673 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01423673v2
Computable priors sharpened into Occam s razors David R. Bickel To cite this version: David R. Bickel. Computable priors sharpened into Occam s razors. 2016. HAL Id: hal-01423673 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01423673v2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009.0245.349A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0245349 A1 Zhao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PARALLEL (21) Appl. No.:
US 2009.0245.349A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0245349 A1 Zhao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PARALLEL (21) Appl. No.:
On size, radius and minimum degree
 On size, radius and minimum degree Simon Mukwembi To cite this version: Simon Mukwembi. On size, radius and minimum degree. Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science, DMTCS, 2014, Vol. 16 no.
On size, radius and minimum degree Simon Mukwembi To cite this version: Simon Mukwembi. On size, radius and minimum degree. Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science, DMTCS, 2014, Vol. 16 no.
The Zenith Passage of the Sun in the Plan of Brasilia
 The Zenith Passage of the Sun in the Plan of Brasilia Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. The Zenith Passage of the Sun in the Plan of Brasilia. Philica, Philica,
The Zenith Passage of the Sun in the Plan of Brasilia Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. The Zenith Passage of the Sun in the Plan of Brasilia. Philica, Philica,
The Spatial Data Infrastructure for the Geological Reference of France
 The Spatial Data Infrastructure for the Geological Reference of France Marc Urvois, Thierry Baudin, Florence Cagnard, Philippe Calcagno, Nicolas Chauvin, Ulrich Clain, Santiago Gabillard, Sandrine Grataloup,
The Spatial Data Infrastructure for the Geological Reference of France Marc Urvois, Thierry Baudin, Florence Cagnard, Philippe Calcagno, Nicolas Chauvin, Ulrich Clain, Santiago Gabillard, Sandrine Grataloup,
Numerical Modeling of Eddy Current Nondestructive Evaluation of Ferromagnetic Tubes via an Integral. Equation Approach
 Numerical Modeling of Eddy Current Nondestructive Evaluation of Ferromagnetic Tubes via an Integral Equation Approach Anastassios Skarlatos, Grégoire Pichenot, Dominique Lesselier, Marc Lambert, Bernard
Numerical Modeling of Eddy Current Nondestructive Evaluation of Ferromagnetic Tubes via an Integral Equation Approach Anastassios Skarlatos, Grégoire Pichenot, Dominique Lesselier, Marc Lambert, Bernard
A Study of the Regular Pentagon with a Classic Geometric Approach
 A Study of the Regular Pentagon with a Classic Geometric Approach Amelia Carolina Sparavigna, Mauro Maria Baldi To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna, Mauro Maria Baldi. A Study of the Regular
A Study of the Regular Pentagon with a Classic Geometric Approach Amelia Carolina Sparavigna, Mauro Maria Baldi To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna, Mauro Maria Baldi. A Study of the Regular
Territorial Intelligence and Innovation for the Socio-Ecological Transition
 Territorial Intelligence and Innovation for the Socio-Ecological Transition Jean-Jacques Girardot, Evelyne Brunau To cite this version: Jean-Jacques Girardot, Evelyne Brunau. Territorial Intelligence and
Territorial Intelligence and Innovation for the Socio-Ecological Transition Jean-Jacques Girardot, Evelyne Brunau To cite this version: Jean-Jacques Girardot, Evelyne Brunau. Territorial Intelligence and
Lorentz force velocimetry using small-size permanent magnet systems and a multi-degree-of-freedom force/torque sensor
 Lorentz force velocimetry using small-size permanent magnet systems and a multi-degree-of-freedom force/torque sensor D Hernández, C Karcher To cite this version: D Hernández, C Karcher. Lorentz force
Lorentz force velocimetry using small-size permanent magnet systems and a multi-degree-of-freedom force/torque sensor D Hernández, C Karcher To cite this version: D Hernández, C Karcher. Lorentz force
Electromagnetic characterization of magnetic steel alloys with respect to the temperature
 Electromagnetic characterization of magnetic steel alloys with respect to the temperature B Paya, P Teixeira To cite this version: B Paya, P Teixeira. Electromagnetic characterization of magnetic steel
Electromagnetic characterization of magnetic steel alloys with respect to the temperature B Paya, P Teixeira To cite this version: B Paya, P Teixeira. Electromagnetic characterization of magnetic steel
Sparse multivariate factorization by mean of a few bivariate factorizations
 Sparse multivariate factorization by mean of a few bivariate factorizations Bernard Parisse To cite this version: Bernard Parisse. Sparse multivariate factorization by mean of a few bivariate factorizations.
Sparse multivariate factorization by mean of a few bivariate factorizations Bernard Parisse To cite this version: Bernard Parisse. Sparse multivariate factorization by mean of a few bivariate factorizations.
Control of an offshore wind turbine modeled as discrete system
 Control of an offshore wind turbine modeled as discrete system Pedro Guimarães, Suzana Ávila To cite this version: Pedro Guimarães, Suzana Ávila. Control of an offshore wind turbine modeled as discrete
Control of an offshore wind turbine modeled as discrete system Pedro Guimarães, Suzana Ávila To cite this version: Pedro Guimarães, Suzana Ávila. Control of an offshore wind turbine modeled as discrete
SOLAR RADIATION ESTIMATION AND PREDICTION USING MEASURED AND PREDICTED AEROSOL OPTICAL DEPTH
 SOLAR RADIATION ESTIMATION AND PREDICTION USING MEASURED AND PREDICTED AEROSOL OPTICAL DEPTH Carlos M. Fernández-Peruchena, Martín Gastón, Maria V Guisado, Ana Bernardos, Íñigo Pagola, Lourdes Ramírez
SOLAR RADIATION ESTIMATION AND PREDICTION USING MEASURED AND PREDICTED AEROSOL OPTICAL DEPTH Carlos M. Fernández-Peruchena, Martín Gastón, Maria V Guisado, Ana Bernardos, Íñigo Pagola, Lourdes Ramírez
On the longest path in a recursively partitionable graph
 On the longest path in a recursively partitionable graph Julien Bensmail To cite this version: Julien Bensmail. On the longest path in a recursively partitionable graph. 2012. HAL Id:
On the longest path in a recursively partitionable graph Julien Bensmail To cite this version: Julien Bensmail. On the longest path in a recursively partitionable graph. 2012. HAL Id:
Solution to Sylvester equation associated to linear descriptor systems
 Solution to Sylvester equation associated to linear descriptor systems Mohamed Darouach To cite this version: Mohamed Darouach. Solution to Sylvester equation associated to linear descriptor systems. Systems
Solution to Sylvester equation associated to linear descriptor systems Mohamed Darouach To cite this version: Mohamed Darouach. Solution to Sylvester equation associated to linear descriptor systems. Systems
Predicting the risk of non-compliance to EMC requirements during the life-cycle
 Predicting the risk of non-compliance to EMC requirements during the life-cycle Alexandre Boyer, He Huang, Sonia Ben Dhia To cite this version: Alexandre Boyer, He Huang, Sonia Ben Dhia. Predicting the
Predicting the risk of non-compliance to EMC requirements during the life-cycle Alexandre Boyer, He Huang, Sonia Ben Dhia To cite this version: Alexandre Boyer, He Huang, Sonia Ben Dhia. Predicting the
Voltage Stability of Multiple Distributed Generators in Distribution Networks
 oltage Stability of Multiple Distributed Generators in Distribution Networks Andi Wang, Chongxin Liu, Hervé Guéguen, Zhenquan Sun To cite this version: Andi Wang, Chongxin Liu, Hervé Guéguen, Zhenquan
oltage Stability of Multiple Distributed Generators in Distribution Networks Andi Wang, Chongxin Liu, Hervé Guéguen, Zhenquan Sun To cite this version: Andi Wang, Chongxin Liu, Hervé Guéguen, Zhenquan
Widely Linear Estimation with Complex Data
 Widely Linear Estimation with Complex Data Bernard Picinbono, Pascal Chevalier To cite this version: Bernard Picinbono, Pascal Chevalier. Widely Linear Estimation with Complex Data. IEEE Transactions on
Widely Linear Estimation with Complex Data Bernard Picinbono, Pascal Chevalier To cite this version: Bernard Picinbono, Pascal Chevalier. Widely Linear Estimation with Complex Data. IEEE Transactions on
Solubility prediction of weak electrolyte mixtures
 Solubility prediction of weak electrolyte mixtures Gilles Févotte, Xiang Zhang, Gang Qian, Xing-Gui Zhou, Wei-Kang Yuan To cite this version: Gilles Févotte, Xiang Zhang, Gang Qian, Xing-Gui Zhou, Wei-Kang
Solubility prediction of weak electrolyte mixtures Gilles Févotte, Xiang Zhang, Gang Qian, Xing-Gui Zhou, Wei-Kang Yuan To cite this version: Gilles Févotte, Xiang Zhang, Gang Qian, Xing-Gui Zhou, Wei-Kang
On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian Block-Matrices
 On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices Antoine Mhanna To cite this version: Antoine Mhanna On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices 016 HAL Id: hal-0131860
On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices Antoine Mhanna To cite this version: Antoine Mhanna On Symmetric Norm Inequalities And Hermitian lock-matrices 016 HAL Id: hal-0131860
Hook lengths and shifted parts of partitions
 Hook lengths and shifted parts of partitions Guo-Niu Han To cite this version: Guo-Niu Han Hook lengths and shifted parts of partitions The Ramanujan Journal, 009, 9 p HAL Id: hal-00395690
Hook lengths and shifted parts of partitions Guo-Niu Han To cite this version: Guo-Niu Han Hook lengths and shifted parts of partitions The Ramanujan Journal, 009, 9 p HAL Id: hal-00395690
Ultra low frequency pressure transducer calibration
 Ultra low frequency pressure transducer calibration A. Semenov To cite this version: A. Semenov. Ultra low frequency pressure transducer calibration. Journal de Physique IV Colloque, 1994, 04 (C5), pp.c7-251-c7-254.
Ultra low frequency pressure transducer calibration A. Semenov To cite this version: A. Semenov. Ultra low frequency pressure transducer calibration. Journal de Physique IV Colloque, 1994, 04 (C5), pp.c7-251-c7-254.
FORMAL TREATMENT OF RADIATION FIELD FLUCTUATIONS IN VACUUM
 FORMAL TREATMENT OF RADIATION FIELD FLUCTUATIONS IN VACUUM Frederic Schuller, Renaud Savalle, Michael Neumann-Spallart To cite this version: Frederic Schuller, Renaud Savalle, Michael Neumann-Spallart.
FORMAL TREATMENT OF RADIATION FIELD FLUCTUATIONS IN VACUUM Frederic Schuller, Renaud Savalle, Michael Neumann-Spallart To cite this version: Frederic Schuller, Renaud Savalle, Michael Neumann-Spallart.
Multiple sensor fault detection in heat exchanger system
 Multiple sensor fault detection in heat exchanger system Abdel Aïtouche, Didier Maquin, Frédéric Busson To cite this version: Abdel Aïtouche, Didier Maquin, Frédéric Busson. Multiple sensor fault detection
Multiple sensor fault detection in heat exchanger system Abdel Aïtouche, Didier Maquin, Frédéric Busson To cite this version: Abdel Aïtouche, Didier Maquin, Frédéric Busson. Multiple sensor fault detection
Some explanations about the IWLS algorithm to fit generalized linear models
 Some explanations about the IWLS algorithm to fit generalized linear models Christophe Dutang To cite this version: Christophe Dutang. Some explanations about the IWLS algorithm to fit generalized linear
Some explanations about the IWLS algorithm to fit generalized linear models Christophe Dutang To cite this version: Christophe Dutang. Some explanations about the IWLS algorithm to fit generalized linear
A non-commutative algorithm for multiplying (7 7) matrices using 250 multiplications
 A non-commutative algorithm for multiplying (7 7) matrices using 250 multiplications Alexandre Sedoglavic To cite this version: Alexandre Sedoglavic. A non-commutative algorithm for multiplying (7 7) matrices
A non-commutative algorithm for multiplying (7 7) matrices using 250 multiplications Alexandre Sedoglavic To cite this version: Alexandre Sedoglavic. A non-commutative algorithm for multiplying (7 7) matrices
Efficient Subquadratic Space Complexity Binary Polynomial Multipliers Based On Block Recombination
 Efficient Subquadratic Space Complexity Binary Polynomial Multipliers Based On Block Recombination Murat Cenk, Anwar Hasan, Christophe Negre To cite this version: Murat Cenk, Anwar Hasan, Christophe Negre.
Efficient Subquadratic Space Complexity Binary Polynomial Multipliers Based On Block Recombination Murat Cenk, Anwar Hasan, Christophe Negre To cite this version: Murat Cenk, Anwar Hasan, Christophe Negre.
New estimates for the div-curl-grad operators and elliptic problems with L1-data in the half-space
 New estimates for the div-curl-grad operators and elliptic problems with L1-data in the half-space Chérif Amrouche, Huy Hoang Nguyen To cite this version: Chérif Amrouche, Huy Hoang Nguyen. New estimates
New estimates for the div-curl-grad operators and elliptic problems with L1-data in the half-space Chérif Amrouche, Huy Hoang Nguyen To cite this version: Chérif Amrouche, Huy Hoang Nguyen. New estimates
Exogenous input estimation in Electronic Power Steering (EPS) systems
 Exogenous input estimation in Electronic Power Steering (EPS) systems Valentina Ciarla, Carlos Canudas de Wit, Franck Quaine, Violaine Cahouet To cite this version: Valentina Ciarla, Carlos Canudas de
Exogenous input estimation in Electronic Power Steering (EPS) systems Valentina Ciarla, Carlos Canudas de Wit, Franck Quaine, Violaine Cahouet To cite this version: Valentina Ciarla, Carlos Canudas de
A Slice Based 3-D Schur-Cohn Stability Criterion
 A Slice Based 3-D Schur-Cohn Stability Criterion Ioana Serban, Mohamed Najim To cite this version: Ioana Serban, Mohamed Najim. A Slice Based 3-D Schur-Cohn Stability Criterion. ICASSP 007, Apr 007, Honolulu,
A Slice Based 3-D Schur-Cohn Stability Criterion Ioana Serban, Mohamed Najim To cite this version: Ioana Serban, Mohamed Najim. A Slice Based 3-D Schur-Cohn Stability Criterion. ICASSP 007, Apr 007, Honolulu,
A CONDITION-BASED MAINTENANCE MODEL FOR AVAILABILITY OPTIMIZATION FOR STOCHASTIC DEGRADING SYSTEMS
 A CONDITION-BASED MAINTENANCE MODEL FOR AVAILABILITY OPTIMIZATION FOR STOCHASTIC DEGRADING SYSTEMS Abdelhakim Khatab, Daoud Ait-Kadi, Nidhal Rezg To cite this version: Abdelhakim Khatab, Daoud Ait-Kadi,
A CONDITION-BASED MAINTENANCE MODEL FOR AVAILABILITY OPTIMIZATION FOR STOCHASTIC DEGRADING SYSTEMS Abdelhakim Khatab, Daoud Ait-Kadi, Nidhal Rezg To cite this version: Abdelhakim Khatab, Daoud Ait-Kadi,
Factorisation of RSA-704 with CADO-NFS
 Factorisation of RSA-704 with CADO-NFS Shi Bai, Emmanuel Thomé, Paul Zimmermann To cite this version: Shi Bai, Emmanuel Thomé, Paul Zimmermann. Factorisation of RSA-704 with CADO-NFS. 2012. HAL Id: hal-00760322
Factorisation of RSA-704 with CADO-NFS Shi Bai, Emmanuel Thomé, Paul Zimmermann To cite this version: Shi Bai, Emmanuel Thomé, Paul Zimmermann. Factorisation of RSA-704 with CADO-NFS. 2012. HAL Id: hal-00760322
Some approaches to modeling of the effective properties for thermoelastic composites
 Some approaches to modeling of the ective properties for thermoelastic composites Anna Nasedkina Andrey Nasedkin Vladimir Remizov To cite this version: Anna Nasedkina Andrey Nasedkin Vladimir Remizov.
Some approaches to modeling of the ective properties for thermoelastic composites Anna Nasedkina Andrey Nasedkin Vladimir Remizov To cite this version: Anna Nasedkina Andrey Nasedkin Vladimir Remizov.
The Learner s Dictionary and the Sciences:
 The Learner s Dictionary and the Sciences: Geoffrey Williams To cite this version: Geoffrey Williams. The Learner s Dictionary and the Sciences:: Mismatch or no match?. Corpora, Language, Teaching, and
The Learner s Dictionary and the Sciences: Geoffrey Williams To cite this version: Geoffrey Williams. The Learner s Dictionary and the Sciences:: Mismatch or no match?. Corpora, Language, Teaching, and
h 8x8 chroma a b c d Boundary filtering: 16x16 luma H.264 / MPEG-4 Part 10 : Intra Prediction H.264 / MPEG-4 Part 10 White Paper Reconstruction Filter
 H.264 / MPEG-4 Part 10 White Paper Reconstruction Filter 1. Introduction The Joint Video Team (JVT) of ISO/IEC MPEG and ITU-T VCEG are finalising a new standard for the coding (compression) of natural
H.264 / MPEG-4 Part 10 White Paper Reconstruction Filter 1. Introduction The Joint Video Team (JVT) of ISO/IEC MPEG and ITU-T VCEG are finalising a new standard for the coding (compression) of natural
Diagnosability Analysis of Discrete Event Systems with Autonomous Components
 Diagnosability Analysis of Discrete Event Systems with Autonomous Components Lina Ye, Philippe Dague To cite this version: Lina Ye, Philippe Dague. Diagnosability Analysis of Discrete Event Systems with
Diagnosability Analysis of Discrete Event Systems with Autonomous Components Lina Ye, Philippe Dague To cite this version: Lina Ye, Philippe Dague. Diagnosability Analysis of Discrete Event Systems with
Nodal and divergence-conforming boundary-element methods applied to electromagnetic scattering problems
 Nodal and divergence-conforming boundary-element methods applied to electromagnetic scattering problems M. Afonso, Joao Vasconcelos, Renato Mesquita, Christian Vollaire, Laurent Nicolas To cite this version:
Nodal and divergence-conforming boundary-element methods applied to electromagnetic scattering problems M. Afonso, Joao Vasconcelos, Renato Mesquita, Christian Vollaire, Laurent Nicolas To cite this version:
Teaching Reitlinger Cycles To Improve Students Knowledge And Comprehension Of Thermodynamics
 Teaching Reitlinger Cycles To Improve Students Knowledge nd Comprehension Of Thermodynamics melia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: melia Carolina Sparavigna. Teaching Reitlinger Cycles To Improve
Teaching Reitlinger Cycles To Improve Students Knowledge nd Comprehension Of Thermodynamics melia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: melia Carolina Sparavigna. Teaching Reitlinger Cycles To Improve
On The Exact Solution of Newell-Whitehead-Segel Equation Using the Homotopy Perturbation Method
 On The Exact Solution of Newell-Whitehead-Segel Equation Using the Homotopy Perturbation Method S. Salman Nourazar, Mohsen Soori, Akbar Nazari-Golshan To cite this version: S. Salman Nourazar, Mohsen Soori,
On The Exact Solution of Newell-Whitehead-Segel Equation Using the Homotopy Perturbation Method S. Salman Nourazar, Mohsen Soori, Akbar Nazari-Golshan To cite this version: S. Salman Nourazar, Mohsen Soori,
Towards an active anechoic room
 Towards an active anechoic room Dominique Habault, Philippe Herzog, Emmanuel Friot, Cédric Pinhède To cite this version: Dominique Habault, Philippe Herzog, Emmanuel Friot, Cédric Pinhède. Towards an active
Towards an active anechoic room Dominique Habault, Philippe Herzog, Emmanuel Friot, Cédric Pinhède To cite this version: Dominique Habault, Philippe Herzog, Emmanuel Friot, Cédric Pinhède. Towards an active
Simulation and measurement of loudspeaker nonlinearity with a broad-band noise excitation
 Simulation and measurement of loudspeaker nonlinearity with a broad-band noise excitation Andrzej Dobrucki, Rafal Siczek To cite this version: Andrzej Dobrucki, Rafal Siczek. Simulation and measurement
Simulation and measurement of loudspeaker nonlinearity with a broad-band noise excitation Andrzej Dobrucki, Rafal Siczek To cite this version: Andrzej Dobrucki, Rafal Siczek. Simulation and measurement
Entropy-constrained quantization of exponentially damped sinusoids parameters
 Entropy-constrained quantization of exponentially damped sinusoids parameters Olivier Derrien, Roland Badeau, Gaël Richard To cite this version: Olivier Derrien, Roland Badeau, Gaël Richard. Entropy-constrained
Entropy-constrained quantization of exponentially damped sinusoids parameters Olivier Derrien, Roland Badeau, Gaël Richard To cite this version: Olivier Derrien, Roland Badeau, Gaël Richard. Entropy-constrained
Near-Earth Asteroids Orbit Propagation with Gaia Observations
 Near-Earth Asteroids Orbit Propagation with Gaia Observations David Bancelin, Daniel Hestroffer, William Thuillot To cite this version: David Bancelin, Daniel Hestroffer, William Thuillot. Near-Earth Asteroids
Near-Earth Asteroids Orbit Propagation with Gaia Observations David Bancelin, Daniel Hestroffer, William Thuillot To cite this version: David Bancelin, Daniel Hestroffer, William Thuillot. Near-Earth Asteroids
IMPROVEMENTS OF THE VARIABLE THERMAL RESISTANCE
 IMPROVEMENTS OF THE VARIABLE THERMAL RESISTANCE V. Szekely, S. Torok, E. Kollar To cite this version: V. Szekely, S. Torok, E. Kollar. IMPROVEMENTS OF THE VARIABLE THERMAL RESIS- TANCE. THERMINIC 2007,
IMPROVEMENTS OF THE VARIABLE THERMAL RESISTANCE V. Szekely, S. Torok, E. Kollar To cite this version: V. Szekely, S. Torok, E. Kollar. IMPROVEMENTS OF THE VARIABLE THERMAL RESIS- TANCE. THERMINIC 2007,
The FLRW cosmological model revisited: relation of the local time with th e local curvature and consequences on the Heisenberg uncertainty principle
 The FLRW cosmological model revisited: relation of the local time with th e local curvature and consequences on the Heisenberg uncertainty principle Nathalie Olivi-Tran, Paul M Gauthier To cite this version:
The FLRW cosmological model revisited: relation of the local time with th e local curvature and consequences on the Heisenberg uncertainty principle Nathalie Olivi-Tran, Paul M Gauthier To cite this version:
Sensitivity of hybrid filter banks A/D converters to analog realization errors and finite word length
 Sensitivity of hybrid filter banks A/D converters to analog realization errors and finite word length Tudor Petrescu, Jacques Oksman To cite this version: Tudor Petrescu, Jacques Oksman. Sensitivity of
Sensitivity of hybrid filter banks A/D converters to analog realization errors and finite word length Tudor Petrescu, Jacques Oksman To cite this version: Tudor Petrescu, Jacques Oksman. Sensitivity of
A Simple Model for Cavitation with Non-condensable Gases
 A Simple Model for Cavitation with Non-condensable Gases Mathieu Bachmann, Siegfried Müller, Philippe Helluy, Hélène Mathis To cite this version: Mathieu Bachmann, Siegfried Müller, Philippe Helluy, Hélène
A Simple Model for Cavitation with Non-condensable Gases Mathieu Bachmann, Siegfried Müller, Philippe Helluy, Hélène Mathis To cite this version: Mathieu Bachmann, Siegfried Müller, Philippe Helluy, Hélène
A Context free language associated with interval maps
 A Context free language associated with interval maps M Archana, V Kannan To cite this version: M Archana, V Kannan. A Context free language associated with interval maps. Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical
A Context free language associated with interval maps M Archana, V Kannan To cite this version: M Archana, V Kannan. A Context free language associated with interval maps. Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical
Eddy-Current Effects in Circuit Breakers During Arc Displacement Phase
 Eddy-Current Effects in Circuit Breakers During Arc Displacement Phase Olivier Chadebec, Gerard Meunier, V. Mazauric, Yann Le Floch, Patrice Labie To cite this version: Olivier Chadebec, Gerard Meunier,
Eddy-Current Effects in Circuit Breakers During Arc Displacement Phase Olivier Chadebec, Gerard Meunier, V. Mazauric, Yann Le Floch, Patrice Labie To cite this version: Olivier Chadebec, Gerard Meunier,
